Honors Statistics. Daily Agenda
|
|
|
- Lewis Watkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM Daily Agenda 1. Review OTL C6#7 emphasis Normal Distributions Aug 23-8:31 PM 1
2 1. Multiple choice: Select the best answer for Exercises 65 and 66, which refer to the following setting. The number of calories in a 1-ounce serving of a certain breakfast cereal is a random variable with mean 110 and standard deviation 10. The number of calories in a cup of whole milk is a random variable with mean 140 and standard deviation 12. For breakfast, you eat 1 ounce of the cereal with 1/2 cup of whole milk. Let T be the random variable that represents the total number of calories in this breakfast. The mean of T is (a) 110 (b) 140 (c) 180 (d) 195 (e) 250 Dec 7-3:48 PM 2. Multiple choice: Select the best answer for Exercises 65 and 66, which refer to the following setting. The number of calories in a 1-ounce serving of a certain breakfast cereal is a random variable with mean 110 and standard deviation 10. The number of calories in a cup of whole milk is a random variable with mean 140 and standard deviation 12. For breakfast, you eat 1 ounce of the cereal with 1/2 cup of whole milk. Let T be the random variable that represents the total number of calories in this breakfast. The standard deviation of T is (a) 22. (b) 16. (c) (d) (e) 4. Dec 7-3:48 PM 2
3 3. T6.5. A certain vending machine offers 20-ounce bottles of soda for $1.50. The number of bottles X bought from the machine on any day is a random variable with mean 50 and standard deviation 15. Let the random variable Y equal the total revenue from this machine on a given day. Assume that the machine works properly and that no sodas are stolen from the machine. What are the mean and standard deviation of Y? > (a)µ Y = $1.50, σ Y = $22.50 > (b)µ Y = $1.50, σ Y = $33.75 > (c)µ Y = $75, σ Y = $18.37 > (d)µ Y = $75, σ Y = $22.50 > (e)µ Y = $75, σ Y = $33.75 Dec 9-9:49 PM 4. T6.4. Suppose a student is randomly selected from your school. Which of the following pairs of random variables are most likely independent? > (a)x = student s height; Y = student s weight > (b)x = student s IQ; Y = student s GPA > (c)x = student s PSAT Math score; Y = student s PSAT Verbal score > (d)x = average amount of homework the student does per night; Y = student s GPA > (e)x = average amount of homework the student does per night; Y = student s height Dec 9-9:48 PM 3
4 Nov 21-8:16 PM Rainy days Imagine that we randomly select a day from the past 10 years. Let X be the recorded rainfall on this date at the airport in Orlando, Florida, and Y be the recorded rainfall on this date at Disney World just outside Orlando. Suppose that you know the means µ X and µ Y and the variances and of both variables. (a) Is it reasonable to take the mean of the total rainfall X+ Y to be µ X + µ Y? Explain your answer. It is reasonable to take the mean of the total rainfall because the rainfall two cities that are close in location does not depend on independence. You can always combine means of data sets. (b) Is it reasonable to take the variance of the total rainfall to be Explain your answer. It is NOT reasonable to take the variance of the total rainfall because the rainfall of two closely located cities will NOT be independent. Dec 6-11:13 PM 4
5 Get on the boat! Refer to Exercise 41. Find the expected value and standard deviation of the total amount of profit made on two randomly selected days. Show your work. Big assumption... two randomly selected days are INDEPENDENT so... go ahead and calculate! Remember... µ Y = $ = $-0.65 σ Y = $6.45 Use the formula T = Y 1 + Y 2 µ T = $ $-0.65 = $-1.30 Remember you can never add STANDARD DEVIATIONS. σ Y = $6.45 so σ 2 Y = (6.45) 2 = σ 2 T = σ 2 Y1 + σ 2 Y2 σ 2 T = = σ T = = $9.12 Dec 6-11:13 PM Essay errors Typographical and spelling errors can be either nonword errors or word errors. A nonword error is not a real word, as when the is typed as teh. A word error is a real word, but not the right word, as when lose is typed as loose. When students are asked to write a 250-word essay (without spell-checking), The number of nonword errors X in a randomly selected essay has the following probability distribution: The number of word errors Y has this probability distribution: Assume that X and Y are independent. An English professor deducts 3 points from a student s essay score for each nonword error and 2 points for each word error. Find the mean and standard deviation of the total score deductions for a randomly selected essay. Show your work. Use Formula D = 3(X) + 2(Y) D = deductions, X = "non-word error" and Y = word error µ D = 3(2.1) + 2(1.0) = 8.3 points deducted The expected number of points deducted on two randomly selected essays is 8.3 points. If many, many essays are randomly selected, this is the average amount of point deductions on two essays. (In the long run!!) Remember you can never add STANDARD DEVIATIONS. σ X = so σ 2 X = (1.136) 2 = σ Y = 1.0 so σ 2 Y = (1.0) 2 = 1.0 σ 2 D = (3) 2 σ 2 X + (2) 2 σ 2 Y = 9(1.136) 2 + 4(1.0) 2 = σ D = = points The standard deviation of the mean is 3.95 points. The deductions on the 2 essays will typically differ from the mean of 8.3 by 3.95 points. Dec 6-11:14 PM 5
6 = = -1.1 The expected difference in number of points (for word vs. non-word errors) deducted on a randomly selected essay is -1.1 points. If many, many essays are randomly selected, -1.1 points is the average amount of difference between word vs non-word errors point (In the long run!!)... Fewer word errors than non-word errors σ 2 D = σ 2 Y + σ 2 X σ 2 D = (1.136) 2 + (1) 2 = σ D = = 1.51 If one essay is randomly selected the difference in error types (word vs. non-word errors) will typically differ from the mean of -1.1 points by 1.51 points The results in the yellow triangle make up the event a randomly selected student makes more word errors than non-word errors. P( (Y-X) > 0) = = 0.15 Dec 6-11:14 PM The Survey of Study Habits and Attitudes (SSHA) is a psychological test that measures academic motivation and study habits. The distribution of SSHA scores among the women at a college has mean 120 and standard deviation 28, and the distribution of scores among male students has mean 105 and standard deviation 35. You select a single male student and a single female student at random and give them the SSHA test. Find the mean and standard deviation of the difference (female minus male) between their scores. Interpret each value in context. Use Formula D = X - Y = = 15 points The expected number of points a randomly selected female outscores a randomly selected male on the SSHA test is 15 points. If many, many essays are randomly selected, 15 points is the average amount of points a female outscores a male in the SSHA (In the long run!!) 2009 = The standard deviation of the mean is points. The amount of points in which the female outscores the males will typically differ from the mean of 15 by points. From the information given, can you find the probability that the woman chosen scores higher than the man? If so, find this probability. If not, explain why you cannot. If we new the shape of the distribution (specifically if it was normally distributed) then we could answer the question. Currently we do not have enough information. Dec 6-11:14 PM 6
7 Essay scores Refer to Exercise 51. Find the mean and standard deviation of the difference in score deductions (nonword word) for a randomly selected essay. Show your work. Use Formula D = 3(X) - 2(Y) D = deductions, X = "non-word error" and Y = word error µ D = 3(2.1) - 2(1.0) = 4.3 points deducted If many, many essays are randomly selected, the expected difference in score deduction will average 4.3 points. Remember you can never Remember you can never subtract VARIANCES. = so = (1.136) = = 1.0 so = (1.0) = 9(1.136) = = = points The standard deviation of the mean is 3.95 points. The deductions on a randomly selected essay will typically differfrom the mean of 8.3 by 3.95 points. Jan 27-1:35 PM Exercises 57 and 58 refer to the following setting. In Exercises 14 and 18 of Section 6.1,we examined the probability distribution of the random variable X = the amount a life insurance company earns on a randomly chosen 5-year term life policy. Calculations reveal that µ X = $ and σ X = $ Life insurance The risk of insuring one person s life is reduced if we insure many people. Suppose that we insure two 21-year-old males, and that their ages at death are independent. If X1 and X2 are the insurer s income from the two insurance policies, the insurer s average income W on the two policies is Find the mean and standard deviation of W. (You see that the mean income is the same as for a single policy but the standard deviation is less.) µ W = $ $ = $ Remember you can never add STANDARD DEVIATIONS. σ X = $ so σ 2 x = ( ) 2 = σ 2 W = σ 2 X1 + σ 2 X2 σ 2 W = ( ) 2 + ( ) σ 2 W = σ W = = $ Nov 30-7:46 PM 7
8 Life insurance If four 21-year-old men are insured, the insurer s average income is where X i is the income from insuring one man. Assuming that the amount of income earned on individual policies is independent, find the mean and standard deviation of V. (If you compare with the results of Exercise 57, you should see that averaging over more insured individuals reduces risk.) µ V = $ $ = $ Remember you can never add STANDARD DEVIATIONS. σ X = $ so σ 2 x = ( ) 2 = σ 2 V = σ 2 X1 + σ 2 X2 + σ 2 X3 + σ 2 X4 4 2 σ 2 V = ( ) 2 + ( ) 2 + ( ) 2 + ( ) 2 σ 2 V = σ V = = $ Dec 6-11:13 PM = 7 pounds = so σ = pounds = 0.12 = 21.6 pounds Jan 22-7:07 PM 8
9 or σ 2 B = σ M = (0.15)2 (50) 2 = σ B = ~ 7.5 dollars Jan 22-7:07 PM Nov 30-7:23 PM 9
10 Nov 30-7:23 PM Dec 1-2:08 PM 10
11 Sep 26-6:57 PM Sep 26-6:58 PM 11
12 Dec 9-9:54 AM Dec 11-7:07 PM 12
13 Dec 11-7:05 PM May 4-9:19 AM 13
14 (done in class) Nov 21-8:16 PM 14
Honors Statistics. 3. Review OTL C6#6. emphasis Normal Distributions. Chapter 6 Section 2 Day s.notebook. May 05, 2016.
 Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM 3. Review OTL C6#6 emphasis Normal Distributions Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Nov 21-8:16 PM Rainy days Imagine that we randomly select a day from the past 10 years. Let X be the recorded
Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM 3. Review OTL C6#6 emphasis Normal Distributions Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Nov 21-8:16 PM Rainy days Imagine that we randomly select a day from the past 10 years. Let X be the recorded
Chapter 6 Section Review day s.notebook. May 11, Honors Statistics. Aug 23-8:26 PM. 3. Review team test.
 Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM 3. Review team test Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Nov 27-10:28 PM 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 6.9 6.10 6.11 6.12 Nov 27-9:53 PM 2 May 8-7:44 PM May 1-9:09 PM 3 Dec 1-2:08 PM Sep
Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM 3. Review team test Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Nov 27-10:28 PM 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 6.9 6.10 6.11 6.12 Nov 27-9:53 PM 2 May 8-7:44 PM May 1-9:09 PM 3 Dec 1-2:08 PM Sep
Honors Statistics. 3. Review OTL C6#3. 4. Normal Curve Quiz. Chapter 6 Section 2 Day s Notes.notebook. May 02, 2016.
 Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM 3. Review OTL C6#3 4. Normal Curve Quiz Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 May 1-9:09 PM Apr 28-10:29 AM 2 27, 28, 29, 30 Nov 21-8:16 PM Working out Choose a person aged 19 to 25 years at
Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM 3. Review OTL C6#3 4. Normal Curve Quiz Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 May 1-9:09 PM Apr 28-10:29 AM 2 27, 28, 29, 30 Nov 21-8:16 PM Working out Choose a person aged 19 to 25 years at
Test 7A AP Statistics Name: Directions: Work on these sheets.
 Test 7A AP Statistics Name: Directions: Work on these sheets. Part 1: Multiple Choice. Circle the letter corresponding to the best answer. 1. Suppose X is a random variable with mean µ. Suppose we observe
Test 7A AP Statistics Name: Directions: Work on these sheets. Part 1: Multiple Choice. Circle the letter corresponding to the best answer. 1. Suppose X is a random variable with mean µ. Suppose we observe
Honors Statistics. Daily Agenda
 Honors Statistics Daily Agenda 1. Review OTL C6#5 2. Quiz Section 6.1 A-Skip 35, 39, 40 Crickets The length in inches of a cricket chosen at random from a field is a random variable X with mean 1.2 inches
Honors Statistics Daily Agenda 1. Review OTL C6#5 2. Quiz Section 6.1 A-Skip 35, 39, 40 Crickets The length in inches of a cricket chosen at random from a field is a random variable X with mean 1.2 inches
Chapter 6 Section 1 Day s.notebook. April 29, Honors Statistics. Aug 23-8:26 PM. 3. Review OTL C6#2. Aug 23-8:31 PM
 Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM 3. Review OTL C6#2 Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Apr 27-9:20 AM Jan 18-2:13 PM 2 Nov 27-10:28 PM 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 6.9 6.10 6.11 6.12 Nov 27-9:53 PM 3 Ask about 1 and
Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM 3. Review OTL C6#2 Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Apr 27-9:20 AM Jan 18-2:13 PM 2 Nov 27-10:28 PM 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 6.9 6.10 6.11 6.12 Nov 27-9:53 PM 3 Ask about 1 and
Honors Statistics. Daily Agenda
 Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM Daily Agenda 1. Review OTL C6#4 Chapter 6.2 rules for means and variances Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Nov 21-8:16 PM Working out Choose a person aged 19 to 25 years at random and
Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM Daily Agenda 1. Review OTL C6#4 Chapter 6.2 rules for means and variances Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Nov 21-8:16 PM Working out Choose a person aged 19 to 25 years at random and
AP Stats ~ Lesson 6B: Transforming and Combining Random variables
 AP Stats ~ Lesson 6B: Transforming and Combining Random variables OBJECTIVES: DESCRIBE the effects of transforming a random variable by adding or subtracting a constant and multiplying or dividing by a
AP Stats ~ Lesson 6B: Transforming and Combining Random variables OBJECTIVES: DESCRIBE the effects of transforming a random variable by adding or subtracting a constant and multiplying or dividing by a
Chapter 6: Random Variables
 Chapter 6: Random Variables Section 6. The Practice of Statistics, 4 th edition For AP* STARNES, YATES, MOORE Chapter 6 Random Variables 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables 6. 6.3 Binomial and
Chapter 6: Random Variables Section 6. The Practice of Statistics, 4 th edition For AP* STARNES, YATES, MOORE Chapter 6 Random Variables 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables 6. 6.3 Binomial and
NORMAL RANDOM VARIABLES (Normal or gaussian distribution)
 NORMAL RANDOM VARIABLES (Normal or gaussian distribution) Many variables, as pregnancy lengths, foot sizes etc.. exhibit a normal distribution. The shape of the distribution is a symmetric bell shape.
NORMAL RANDOM VARIABLES (Normal or gaussian distribution) Many variables, as pregnancy lengths, foot sizes etc.. exhibit a normal distribution. The shape of the distribution is a symmetric bell shape.
Homework: Due Wed, Nov 3 rd Chapter 8, # 48a, 55c and 56 (count as 1), 67a
 Homework: Due Wed, Nov 3 rd Chapter 8, # 48a, 55c and 56 (count as 1), 67a Announcements: There are some office hour changes for Nov 5, 8, 9 on website Week 5 quiz begins after class today and ends at
Homework: Due Wed, Nov 3 rd Chapter 8, # 48a, 55c and 56 (count as 1), 67a Announcements: There are some office hour changes for Nov 5, 8, 9 on website Week 5 quiz begins after class today and ends at
Homework: Due Wed, Feb 20 th. Chapter 8, # 60a + 62a (count together as 1), 74, 82
 Announcements: Week 5 quiz begins at 4pm today and ends at 3pm on Wed If you take more than 20 minutes to complete your quiz, you will only receive partial credit. (It doesn t cut you off.) Today: Sections
Announcements: Week 5 quiz begins at 4pm today and ends at 3pm on Wed If you take more than 20 minutes to complete your quiz, you will only receive partial credit. (It doesn t cut you off.) Today: Sections
*****CENTRAL LIMIT THEOREM (CLT)*****
 Sampling Distributions and CLT Day 5 *****CENTRAL LIMIT THEOREM (CLT)***** (One of the MOST important theorems in Statistics - KNOW AND UNDERSTAND THIS!!!!!!) Draw an SRS of size n from ANY population
Sampling Distributions and CLT Day 5 *****CENTRAL LIMIT THEOREM (CLT)***** (One of the MOST important theorems in Statistics - KNOW AND UNDERSTAND THIS!!!!!!) Draw an SRS of size n from ANY population
Normal distribution. We say that a random variable X follows the normal distribution if the probability density function of X is given by
 Normal distribution The normal distribution is the most important distribution. It describes well the distribution of random variables that arise in practice, such as the heights or weights of people,
Normal distribution The normal distribution is the most important distribution. It describes well the distribution of random variables that arise in practice, such as the heights or weights of people,
I. Standard Error II. Standard Error III. Standard Error 2.54
 1) Original Population: Match the standard error (I, II, or III) with the correct sampling distribution (A, B, or C) and the correct sample size (1, 5, or 10) I. Standard Error 1.03 II. Standard Error
1) Original Population: Match the standard error (I, II, or III) with the correct sampling distribution (A, B, or C) and the correct sample size (1, 5, or 10) I. Standard Error 1.03 II. Standard Error
AP * Statistics Review
 AP * Statistics Review Normal Models and Sampling Distributions Teacher Packet AP* is a trademark of the College Entrance Examination Board. The College Entrance Examination Board was not involved in the
AP * Statistics Review Normal Models and Sampling Distributions Teacher Packet AP* is a trademark of the College Entrance Examination Board. The College Entrance Examination Board was not involved in the
Section 6.5. The Central Limit Theorem
 Section 6.5 The Central Limit Theorem Idea Will allow us to combine the theory from 6.4 (sampling distribution idea) with our central limit theorem and that will allow us the do hypothesis testing in the
Section 6.5 The Central Limit Theorem Idea Will allow us to combine the theory from 6.4 (sampling distribution idea) with our central limit theorem and that will allow us the do hypothesis testing in the
and µ Asian male > " men
 A.P. Statistics Sampling Distributions and the Central Limit Theorem Definitions A parameter is a number that describes the population. A parameter always exists but in practice we rarely know its value
A.P. Statistics Sampling Distributions and the Central Limit Theorem Definitions A parameter is a number that describes the population. A parameter always exists but in practice we rarely know its value
MATH 118 Class Notes For Chapter 5 By: Maan Omran
 MATH 118 Class Notes For Chapter 5 By: Maan Omran Section 5.1 Central Tendency Mode: the number or numbers that occur most often. Median: the number at the midpoint of a ranked data. Ex1: The test scores
MATH 118 Class Notes For Chapter 5 By: Maan Omran Section 5.1 Central Tendency Mode: the number or numbers that occur most often. Median: the number at the midpoint of a ranked data. Ex1: The test scores
PRINTABLE VERSION. Quiz 6. Suppose that x is normally distributed with a mean of 20 and a standard deviation of 3. What is P(16.91 x 24.59)?
 PRINTABLE VERSION Quiz 6 Question 1 Suppose that x is normally distributed with a mean of 20 and a standard deviation of 3. What is P(16.91 x 24.59)? a) 0.348 b) 0.438 c) 0.353 d) 0.437 e) 0.785 Question
PRINTABLE VERSION Quiz 6 Question 1 Suppose that x is normally distributed with a mean of 20 and a standard deviation of 3. What is P(16.91 x 24.59)? a) 0.348 b) 0.438 c) 0.353 d) 0.437 e) 0.785 Question
EDCC charges $50 per credit. Let T = tuition charge for a randomly-selected fulltime student. T = 50X. Tuit. T $600 $650 $700 $750 $800 $850 $900
 Chapter 7 Random Variables n 7.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables n 6.2 n Example: El Dorado Community College El Dorado Community College considers a student to be full-time if he or she is taking
Chapter 7 Random Variables n 7.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables n 6.2 n Example: El Dorado Community College El Dorado Community College considers a student to be full-time if he or she is taking
Section 6.2 Transforming and Combining Random Variables. Linear Transformations
 Section 6.2 Transforming and Combining Random Variables Linear Transformations In Section 6.1, we learned that the mean and standard deviation give us important information about a random variable. In
Section 6.2 Transforming and Combining Random Variables Linear Transformations In Section 6.1, we learned that the mean and standard deviation give us important information about a random variable. In
Central Limit Theorem
 Central Limit Theorem Lots of Samples 1 Homework Read Sec 6-5. Discussion Question pg 329 Do Ex 6-5 8-15 2 Objective Use the Central Limit Theorem to solve problems involving sample means 3 Sample Means
Central Limit Theorem Lots of Samples 1 Homework Read Sec 6-5. Discussion Question pg 329 Do Ex 6-5 8-15 2 Objective Use the Central Limit Theorem to solve problems involving sample means 3 Sample Means
University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics. Normal distribution
 University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics Statistics 110A Instructor: Nicolas Christou Normal distribution The normal distribution is the most important distribution. It describes
University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics Statistics 110A Instructor: Nicolas Christou Normal distribution The normal distribution is the most important distribution. It describes
5.1 Mean, Median, & Mode
 5.1 Mean, Median, & Mode definitions Mean: Median: Mode: Example 1 The Blue Jays score these amounts of runs in their last 9 games: 4, 7, 2, 4, 10, 5, 6, 7, 7 Find the mean, median, and mode: Example 2
5.1 Mean, Median, & Mode definitions Mean: Median: Mode: Example 1 The Blue Jays score these amounts of runs in their last 9 games: 4, 7, 2, 4, 10, 5, 6, 7, 7 Find the mean, median, and mode: Example 2
Example - Let X be the number of boys in a 4 child family. Find the probability distribution table:
 Chapter8 Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables tthe value of the result of the probability experiment is a RANDOM VARIABLE. Example - Let X be the number
Chapter8 Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables tthe value of the result of the probability experiment is a RANDOM VARIABLE. Example - Let X be the number
Chapter 6. The Normal Probability Distributions
 Chapter 6 The Normal Probability Distributions 1 Chapter 6 Overview Introduction 6-1 Normal Probability Distributions 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution 6-3 Applications of the Normal Distribution 6-5
Chapter 6 The Normal Probability Distributions 1 Chapter 6 Overview Introduction 6-1 Normal Probability Distributions 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution 6-3 Applications of the Normal Distribution 6-5
CHAPTER 6 Random Variables
 CHAPTER 6 Random Variables 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Discrete and Continuous Random
CHAPTER 6 Random Variables 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Discrete and Continuous Random
Section 7.4 Transforming and Combining Random Variables (DAY 1)
 Section 7.4 Learning Objectives (DAY 1) After this section, you should be able to DESCRIBE the effect of performing a linear transformation on a random variable (DAY 1) COMBINE random variables and CALCULATE
Section 7.4 Learning Objectives (DAY 1) After this section, you should be able to DESCRIBE the effect of performing a linear transformation on a random variable (DAY 1) COMBINE random variables and CALCULATE
1. State Sales Tax. 2. Baggage Check
 1. State Sales Tax A survey asks a random sample of 1500 adults in Ohio if they support an increase in the state sales tax from 5% to 6% with the additional revenue going to education. If 40% of all adults
1. State Sales Tax A survey asks a random sample of 1500 adults in Ohio if they support an increase in the state sales tax from 5% to 6% with the additional revenue going to education. If 40% of all adults
Chapter Six Probability Distributions
 6.1 Probability Distributions Discrete Random Variable Chapter Six Probability Distributions x P(x) 2 0.08 4 0.13 6 0.25 8 0.31 10 0.16 12 0.01 Practice. Construct a probability distribution for the number
6.1 Probability Distributions Discrete Random Variable Chapter Six Probability Distributions x P(x) 2 0.08 4 0.13 6 0.25 8 0.31 10 0.16 12 0.01 Practice. Construct a probability distribution for the number
(j) Find the first quartile for a standard normal distribution.
 Examples for Chapter 5 Normal Probability Distributions Math 1040 1 Section 5.1 1. Heights of males at a certain university are approximately normal with a mean of 70.9 inches and a standard deviation
Examples for Chapter 5 Normal Probability Distributions Math 1040 1 Section 5.1 1. Heights of males at a certain university are approximately normal with a mean of 70.9 inches and a standard deviation
ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists 2016/2017
 ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists 2016/2017 Topic The Normal Distribution Lecturer: Dr. Bernardin Senadza, Dept. of Economics bsenadza@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and
ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists 2016/2017 Topic The Normal Distribution Lecturer: Dr. Bernardin Senadza, Dept. of Economics bsenadza@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and
Chapter 6: Random Variables
 Chapter 6: Random Variables Section 6.2 The Practice of Statistics, 4 th edition For AP* STARNES, YATES, MOORE Chapter 6 Random Variables 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables 6.2 6.3 Binomial and
Chapter 6: Random Variables Section 6.2 The Practice of Statistics, 4 th edition For AP* STARNES, YATES, MOORE Chapter 6 Random Variables 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables 6.2 6.3 Binomial and
Chapter 6: Random Variables
 Chapter 6: Random Variables Section 6.2 The Practice of Statistics, 4 th edition For AP* STARNES, YATES, MOORE Chapter 6 Random Variables 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables 6.2 6.3 Binomial and
Chapter 6: Random Variables Section 6.2 The Practice of Statistics, 4 th edition For AP* STARNES, YATES, MOORE Chapter 6 Random Variables 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables 6.2 6.3 Binomial and
Introduction to Business Statistics QM 120 Chapter 6
 DEPARTMENT OF QUANTITATIVE METHODS & INFORMATION SYSTEMS Introduction to Business Statistics QM 120 Chapter 6 Spring 2008 Chapter 6: Continuous Probability Distribution 2 When a RV x is discrete, we can
DEPARTMENT OF QUANTITATIVE METHODS & INFORMATION SYSTEMS Introduction to Business Statistics QM 120 Chapter 6 Spring 2008 Chapter 6: Continuous Probability Distribution 2 When a RV x is discrete, we can
Uniform Probability Distribution. Continuous Random Variables &
 Continuous Random Variables & What is a Random Variable? It is a quantity whose values are real numbers and are determined by the number of desired outcomes of an experiment. Is there any special Random
Continuous Random Variables & What is a Random Variable? It is a quantity whose values are real numbers and are determined by the number of desired outcomes of an experiment. Is there any special Random
ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists
 ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists Session 7 The Normal Distribution Part 1 Lecturer: Dr. Bernardin Senadza, Dept. of Economics Contact Information: bsenadza@ug.edu.gh College of Education
ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists Session 7 The Normal Distribution Part 1 Lecturer: Dr. Bernardin Senadza, Dept. of Economics Contact Information: bsenadza@ug.edu.gh College of Education
STAT:2010 Statistical Methods and Computing. Using density curves to describe the distribution of values of a quantitative
 STAT:10 Statistical Methods and Computing Normal Distributions Lecture 4 Feb. 6, 17 Kate Cowles 374 SH, 335-0727 kate-cowles@uiowa.edu 1 2 Using density curves to describe the distribution of values of
STAT:10 Statistical Methods and Computing Normal Distributions Lecture 4 Feb. 6, 17 Kate Cowles 374 SH, 335-0727 kate-cowles@uiowa.edu 1 2 Using density curves to describe the distribution of values of
Exam II Math 1342 Capters 3-5 HCCS. Name
 Exam II Math 1342 Capters 3-5 HCCS Name Date Provide an appropriate response. 1) A single six-sided die is rolled. Find the probability of rolling a number less than 3. A) 0.5 B) 0.1 C) 0.25 D 0.333 1)
Exam II Math 1342 Capters 3-5 HCCS Name Date Provide an appropriate response. 1) A single six-sided die is rolled. Find the probability of rolling a number less than 3. A) 0.5 B) 0.1 C) 0.25 D 0.333 1)
Chapter 9 & 10. Multiple Choice.
 Chapter 9 & 10 Review Name Multiple Choice. 1. An agricultural researcher plants 25 plots with a new variety of corn. The average yield for these plots is X = 150 bushels per acre. Assume that the yield
Chapter 9 & 10 Review Name Multiple Choice. 1. An agricultural researcher plants 25 plots with a new variety of corn. The average yield for these plots is X = 150 bushels per acre. Assume that the yield
Example. Chapter 8 Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables
 Chapter 8 Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables You are dealt a hand of 5 cards. Find the probability distribution table for the number of hearts. Graph
Chapter 8 Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables You are dealt a hand of 5 cards. Find the probability distribution table for the number of hearts. Graph
Normal Distribution: Introduction
 Connexions module: m16979 1 Normal Distribution: Introduction Susan Dean Barbara Illowsky, Ph.D. This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
Connexions module: m16979 1 Normal Distribution: Introduction Susan Dean Barbara Illowsky, Ph.D. This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
Test 6A AP Statistics Name:
 Test 6A AP Statistics Name: Part 1: Multiple Choice. Circle the letter corresponding to the best answer. 1. A marketing survey compiled data on the number of personal computers in households. If X = the
Test 6A AP Statistics Name: Part 1: Multiple Choice. Circle the letter corresponding to the best answer. 1. A marketing survey compiled data on the number of personal computers in households. If X = the
AMS7: WEEK 4. CLASS 3
 AMS7: WEEK 4. CLASS 3 Sampling distributions and estimators. Central Limit Theorem Normal Approximation to the Binomial Distribution Friday April 24th, 2015 Sampling distributions and estimators REMEMBER:
AMS7: WEEK 4. CLASS 3 Sampling distributions and estimators. Central Limit Theorem Normal Approximation to the Binomial Distribution Friday April 24th, 2015 Sampling distributions and estimators REMEMBER:
MATH 264 Problem Homework I
 MATH Problem Homework I Due to December 9, 00@:0 PROBLEMS & SOLUTIONS. A student answers a multiple-choice examination question that offers four possible answers. Suppose that the probability that the
MATH Problem Homework I Due to December 9, 00@:0 PROBLEMS & SOLUTIONS. A student answers a multiple-choice examination question that offers four possible answers. Suppose that the probability that the
Version A. Problem 1. Let X be the continuous random variable defined by the following pdf: 1 x/2 when 0 x 2, f(x) = 0 otherwise.
 Math 224 Q Exam 3A Fall 217 Tues Dec 12 Version A Problem 1. Let X be the continuous random variable defined by the following pdf: { 1 x/2 when x 2, f(x) otherwise. (a) Compute the mean µ E[X]. E[X] x
Math 224 Q Exam 3A Fall 217 Tues Dec 12 Version A Problem 1. Let X be the continuous random variable defined by the following pdf: { 1 x/2 when x 2, f(x) otherwise. (a) Compute the mean µ E[X]. E[X] x
Example - Let X be the number of boys in a 4 child family. Find the probability distribution table:
 Chapter7 Probability Distributions and Statistics Distributions of Random Variables tthe value of the result of the probability experiment is a RANDOM VARIABLE. Example - Let X be the number of boys in
Chapter7 Probability Distributions and Statistics Distributions of Random Variables tthe value of the result of the probability experiment is a RANDOM VARIABLE. Example - Let X be the number of boys in
CHAPTER 6 Random Variables
 CHAPTER 6 Random Variables 6.2 Transforming and Combining Random Variables The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers 6.2 Reading Quiz (T or F)
CHAPTER 6 Random Variables 6.2 Transforming and Combining Random Variables The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers 6.2 Reading Quiz (T or F)
The Central Limit Theorem. Sec. 8.2: The Random Variable. it s Distribution. it s Distribution
 The Central Limit Theorem Sec. 8.1: The Random Variable it s Distribution Sec. 8.2: The Random Variable it s Distribution X p and and How Should You Think of a Random Variable? Imagine a bag with numbers
The Central Limit Theorem Sec. 8.1: The Random Variable it s Distribution Sec. 8.2: The Random Variable it s Distribution X p and and How Should You Think of a Random Variable? Imagine a bag with numbers
Chapter 3. Lecture 3 Sections
 Chapter 3 Lecture 3 Sections 3.4 3.5 Measure of Position We would like to compare values from different data sets. We will introduce a z score or standard score. This measures how many standard deviation
Chapter 3 Lecture 3 Sections 3.4 3.5 Measure of Position We would like to compare values from different data sets. We will introduce a z score or standard score. This measures how many standard deviation
work to get full credit.
 Chapter 18 Review Name Date Period Write complete answers, using complete sentences where necessary.show your work to get full credit. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the
Chapter 18 Review Name Date Period Write complete answers, using complete sentences where necessary.show your work to get full credit. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the
Previously, when making inferences about the population mean, μ, we were assuming the following simple conditions:
 Chapter 17 Inference about a Population Mean Conditions for inference Previously, when making inferences about the population mean, μ, we were assuming the following simple conditions: (1) Our data (observations)
Chapter 17 Inference about a Population Mean Conditions for inference Previously, when making inferences about the population mean, μ, we were assuming the following simple conditions: (1) Our data (observations)
SECTION 6.2 (DAY 1) TRANSFORMING RANDOM VARIABLES NOVEMBER 16 TH, 2017
 SECTION 6.2 (DAY 1) TRANSFORMING RANDOM VARIABLES NOVEMBER 16 TH, 2017 TODAY S OBJECTIVES Describe the effects of transforming a random variable by: adding or subtracting a constant multiplying or dividing
SECTION 6.2 (DAY 1) TRANSFORMING RANDOM VARIABLES NOVEMBER 16 TH, 2017 TODAY S OBJECTIVES Describe the effects of transforming a random variable by: adding or subtracting a constant multiplying or dividing
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch. 8 Sampling Distributions 8.1 Distribution of the Sample Mean 1 Describe the distribution of the sample mean: normal population. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement
Ch. 8 Sampling Distributions 8.1 Distribution of the Sample Mean 1 Describe the distribution of the sample mean: normal population. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement
8.1 Estimation of the Mean and Proportion
 8.1 Estimation of the Mean and Proportion Statistical inference enables us to make judgments about a population on the basis of sample information. The mean, standard deviation, and proportions of a population
8.1 Estimation of the Mean and Proportion Statistical inference enables us to make judgments about a population on the basis of sample information. The mean, standard deviation, and proportions of a population
CHAPTER 6 Random Variables
 CHAPTER 6 Random Variables 6.2 Transforming and Combining Random Variables The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Transforming and Combining
CHAPTER 6 Random Variables 6.2 Transforming and Combining Random Variables The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Transforming and Combining
Unit 04 Review. Probability Rules
 Unit 04 Review Probability Rules A sample space contains all the possible outcomes observed in a trial of an experiment, a survey, or some random phenomenon. The sum of the probabilities for all possible
Unit 04 Review Probability Rules A sample space contains all the possible outcomes observed in a trial of an experiment, a survey, or some random phenomenon. The sum of the probabilities for all possible
No, because np = 100(0.02) = 2. The value of np must be greater than or equal to 5 to use the normal approximation.
 1) If n 100 and p 0.02 in a binomial experiment, does this satisfy the rule for a normal approximation? Why or why not? No, because np 100(0.02) 2. The value of np must be greater than or equal to 5 to
1) If n 100 and p 0.02 in a binomial experiment, does this satisfy the rule for a normal approximation? Why or why not? No, because np 100(0.02) 2. The value of np must be greater than or equal to 5 to
AP Statistics Section 6.1 Day 1 Multiple Choice Practice. a) a random variable. b) a parameter. c) biased. d) a random sample. e) a statistic.
 A Statistics Section 6.1 Day 1 ultiple Choice ractice Name: 1. A variable whose value is a numerical outcome of a random phenomenon is called a) a random variable. b) a parameter. c) biased. d) a random
A Statistics Section 6.1 Day 1 ultiple Choice ractice Name: 1. A variable whose value is a numerical outcome of a random phenomenon is called a) a random variable. b) a parameter. c) biased. d) a random
6.1 Discrete & Continuous Random Variables. Nov 4 6:53 PM. Objectives
 6.1 Discrete & Continuous Random Variables examples vocab Objectives Today we will... - Compute probabilities using the probability distribution of a discrete random variable. - Calculate and interpret
6.1 Discrete & Continuous Random Variables examples vocab Objectives Today we will... - Compute probabilities using the probability distribution of a discrete random variable. - Calculate and interpret
Honors Statistics. Aug 23-8:26 PM. 1. Collect folders and materials. 2. Continue Binomial Probability. 3. Review OTL C6#11 homework
 Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM 1. Collect folders and materials 2. Continue Binomial Probability 3. Review OTL C6#11 homework 4. Binomial mean and standard deviation 5. Past Homework discussion 6. Return
Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM 1. Collect folders and materials 2. Continue Binomial Probability 3. Review OTL C6#11 homework 4. Binomial mean and standard deviation 5. Past Homework discussion 6. Return
Chapter 5 Student Lecture Notes 5-1. Department of Quantitative Methods & Information Systems. Business Statistics
 Chapter 5 Student Lecture Notes 5-1 Department of Quantitative Methods & Information Systems Business Statistics Chapter 5 Discrete Probability Distributions QMIS 120 Dr. Mohammad Zainal Chapter Goals
Chapter 5 Student Lecture Notes 5-1 Department of Quantitative Methods & Information Systems Business Statistics Chapter 5 Discrete Probability Distributions QMIS 120 Dr. Mohammad Zainal Chapter Goals
Lecture 37 Sections 11.1, 11.2, Mon, Mar 31, Hampden-Sydney College. Independent Samples: Comparing Means. Robb T. Koether.
 : : Lecture 37 Sections 11.1, 11.2, 11.4 Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Mar 31, 2008 Outline : 1 2 3 4 5 : When two samples are taken from two different populations, they may be taken independently or not
: : Lecture 37 Sections 11.1, 11.2, 11.4 Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Mar 31, 2008 Outline : 1 2 3 4 5 : When two samples are taken from two different populations, they may be taken independently or not
Exercise Questions. Q7. The random variable X is known to be uniformly distributed between 10 and
 Exercise Questions This exercise set only covers some topics discussed after the midterm. It does not mean that the problems in the final will be similar to these. Neither solutions nor answers will be
Exercise Questions This exercise set only covers some topics discussed after the midterm. It does not mean that the problems in the final will be similar to these. Neither solutions nor answers will be
Problem Set 08 Sampling Distribution of Sample Mean
 Problem Set 08 Sampling Distribution of Sample Mean MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the requested probability. 1) The table reports
Problem Set 08 Sampling Distribution of Sample Mean MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the requested probability. 1) The table reports
Chapter 7: Sampling Distributions Chapter 7: Sampling Distributions
 Chapter 7: Sampling Distributions Objectives: Students will: Define a sampling distribution. Contrast bias and variability. Describe the sampling distribution of a proportion (shape, center, and spread).
Chapter 7: Sampling Distributions Objectives: Students will: Define a sampling distribution. Contrast bias and variability. Describe the sampling distribution of a proportion (shape, center, and spread).
Density curves. (James Madison University) February 4, / 20
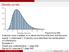 Density curves Figure 6.2 p 230. A density curve is always on or above the horizontal axis, and has area exactly 1 underneath it. A density curve describes the overall pattern of a distribution. Example
Density curves Figure 6.2 p 230. A density curve is always on or above the horizontal axis, and has area exactly 1 underneath it. A density curve describes the overall pattern of a distribution. Example
* Point estimate for P is: x n
 Estimation and Confidence Interval Estimation and Confidence Interval: Single Mean: To find the confidence intervals for a single mean: 1- X ± ( Z 1 σ n σ known S - X ± (t 1,n 1 n σ unknown Estimation
Estimation and Confidence Interval Estimation and Confidence Interval: Single Mean: To find the confidence intervals for a single mean: 1- X ± ( Z 1 σ n σ known S - X ± (t 1,n 1 n σ unknown Estimation
Lecture 6: Normal distribution
 Lecture 6: Normal distribution Statistics 101 Mine Çetinkaya-Rundel February 2, 2012 Announcements Announcements HW 1 due now. Due: OQ 2 by Monday morning 8am. Statistics 101 (Mine Çetinkaya-Rundel) L6:
Lecture 6: Normal distribution Statistics 101 Mine Çetinkaya-Rundel February 2, 2012 Announcements Announcements HW 1 due now. Due: OQ 2 by Monday morning 8am. Statistics 101 (Mine Çetinkaya-Rundel) L6:
L04: Homework Answer Key
 L04: Homework Answer Key Instructions: You are encouraged to collaborate with other students on the homework, but it is important that you do your own work. Before working with someone else on the assignment,
L04: Homework Answer Key Instructions: You are encouraged to collaborate with other students on the homework, but it is important that you do your own work. Before working with someone else on the assignment,
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name The bar graph shows the number of tickets sold each week by the garden club for their annual flower show. ) During which week was the most number of tickets sold? ) A) Week B) Week C) Week 5
Exam Name The bar graph shows the number of tickets sold each week by the garden club for their annual flower show. ) During which week was the most number of tickets sold? ) A) Week B) Week C) Week 5
Determining Sample Size. Slide 1 ˆ ˆ. p q n E = z α / 2. (solve for n by algebra) n = E 2
 Determining Sample Size Slide 1 E = z α / 2 ˆ ˆ p q n (solve for n by algebra) n = ( zα α / 2) 2 p ˆ qˆ E 2 Sample Size for Estimating Proportion p When an estimate of ˆp is known: Slide 2 n = ˆ ˆ ( )
Determining Sample Size Slide 1 E = z α / 2 ˆ ˆ p q n (solve for n by algebra) n = ( zα α / 2) 2 p ˆ qˆ E 2 Sample Size for Estimating Proportion p When an estimate of ˆp is known: Slide 2 n = ˆ ˆ ( )
Lecture 7 Random Variables
 Lecture 7 Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a variable whose value is a numerical outcome of a random phenomenon, so its values are determined by chance. We shall use letters such as X
Lecture 7 Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a variable whose value is a numerical outcome of a random phenomenon, so its values are determined by chance. We shall use letters such as X
Probability: Week 4. Kwonsang Lee. University of Pennsylvania February 13, 2015
 Probability: Week 4 Kwonsang Lee University of Pennsylvania kwonlee@wharton.upenn.edu February 13, 2015 Kwonsang Lee STAT111 February 13, 2015 1 / 21 Probability Sample space S: the set of all possible
Probability: Week 4 Kwonsang Lee University of Pennsylvania kwonlee@wharton.upenn.edu February 13, 2015 Kwonsang Lee STAT111 February 13, 2015 1 / 21 Probability Sample space S: the set of all possible
(c) The probability that a randomly selected driver having a California drivers license
 Statistics Test 2 Name: KEY 1 Classify each statement as an example of classical probability, empirical probability, or subjective probability (a An executive for the Krusty-O cereal factory makes an educated
Statistics Test 2 Name: KEY 1 Classify each statement as an example of classical probability, empirical probability, or subjective probability (a An executive for the Krusty-O cereal factory makes an educated
Using the Central Limit
 Using the Central Limit Theorem By: OpenStaxCollege It is important for you to understand when to use the central limit theorem. If you are being asked to find the probability of the mean, use the clt
Using the Central Limit Theorem By: OpenStaxCollege It is important for you to understand when to use the central limit theorem. If you are being asked to find the probability of the mean, use the clt
Cover Page Homework #8
 MODESTO JUNIOR COLLEGE Department of Mathematics MATH 134 Fall 2011 Problem 11.6 Cover Page Homework #8 (a) What does the population distribution describe? (b) What does the sampling distribution of x
MODESTO JUNIOR COLLEGE Department of Mathematics MATH 134 Fall 2011 Problem 11.6 Cover Page Homework #8 (a) What does the population distribution describe? (b) What does the sampling distribution of x
Honors Statistics. Daily Agenda
 Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM Daily Agenda Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Write a program to generate random numbers. I've decided to give them free will. A Skip 4, 12, 16 Apr 25-10:55 AM Toss 4 times Suppose you
Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM Daily Agenda Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Write a program to generate random numbers. I've decided to give them free will. A Skip 4, 12, 16 Apr 25-10:55 AM Toss 4 times Suppose you
MTH 245: Mathematics for Management, Life, and Social Sciences
 1/14 MTH 245: Mathematics for Management, Life, and Social Sciences Section 7.6 Section 7.6: The Normal Distribution. 2/14 The Normal Distribution. Figure: Abraham DeMoivre Section 7.6: The Normal Distribution.
1/14 MTH 245: Mathematics for Management, Life, and Social Sciences Section 7.6 Section 7.6: The Normal Distribution. 2/14 The Normal Distribution. Figure: Abraham DeMoivre Section 7.6: The Normal Distribution.
. 13. The maximum error (margin of error) of the estimate for μ (based on known σ) is:
 Statistics Sample Exam 3 Solution Chapters 6 & 7: Normal Probability Distributions & Estimates 1. What percent of normally distributed data value lie within 2 standard deviations to either side of the
Statistics Sample Exam 3 Solution Chapters 6 & 7: Normal Probability Distributions & Estimates 1. What percent of normally distributed data value lie within 2 standard deviations to either side of the
STAT 1220 FALL 2010 Common Final Exam December 10, 2010
 STAT 1220 FALL 2010 Common Final Exam December 10, 2010 PLEASE PRINT THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION: Name: Instructor: Student ID #: Section/Time: THIS EXAM HAS TWO PARTS. PART I. Part I consists of 30 multiple
STAT 1220 FALL 2010 Common Final Exam December 10, 2010 PLEASE PRINT THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION: Name: Instructor: Student ID #: Section/Time: THIS EXAM HAS TWO PARTS. PART I. Part I consists of 30 multiple
FORMULA FOR STANDARD DEVIATION:
 Chapter 5 Review: Statistics Textbook p.210-282 Summary: p.238-239, p.278-279 Practice Questions p.240, p.280-282 Z- Score Table p.592 Key Concepts: Central Tendency, Standard Deviation, Graphing, Normal
Chapter 5 Review: Statistics Textbook p.210-282 Summary: p.238-239, p.278-279 Practice Questions p.240, p.280-282 Z- Score Table p.592 Key Concepts: Central Tendency, Standard Deviation, Graphing, Normal
Chapter 7 Study Guide: The Central Limit Theorem
 Chapter 7 Study Guide: The Central Limit Theorem Introduction Why are we so concerned with means? Two reasons are that they give us a middle ground for comparison and they are easy to calculate. In this
Chapter 7 Study Guide: The Central Limit Theorem Introduction Why are we so concerned with means? Two reasons are that they give us a middle ground for comparison and they are easy to calculate. In this
1 Sampling Distributions
 1 Sampling Distributions 1.1 Statistics and Sampling Distributions When a random sample is selected the numerical descriptive measures calculated from such a sample are called statistics. These statistics
1 Sampling Distributions 1.1 Statistics and Sampling Distributions When a random sample is selected the numerical descriptive measures calculated from such a sample are called statistics. These statistics
MA131 Lecture 8.2. The normal distribution curve can be considered as a probability distribution curve for normally distributed variables.
 Normal distribution curve as probability distribution curve The normal distribution curve can be considered as a probability distribution curve for normally distributed variables. The area under the normal
Normal distribution curve as probability distribution curve The normal distribution curve can be considered as a probability distribution curve for normally distributed variables. The area under the normal
Chapter 3 - Lecture 3 Expected Values of Discrete Random Va
 Chapter 3 - Lecture 3 Expected Values of Discrete Random Variables October 5th, 2009 Properties of expected value Standard deviation Shortcut formula Properties of the variance Properties of expected value
Chapter 3 - Lecture 3 Expected Values of Discrete Random Variables October 5th, 2009 Properties of expected value Standard deviation Shortcut formula Properties of the variance Properties of expected value
Examples of continuous probability distributions: The normal and standard normal
 Examples of continuous probability distributions: The normal and standard normal The Normal Distribution f(x) Changing μ shifts the distribution left or right. Changing σ increases or decreases the spread.
Examples of continuous probability distributions: The normal and standard normal The Normal Distribution f(x) Changing μ shifts the distribution left or right. Changing σ increases or decreases the spread.
Business Statistics. Chapter 5 Discrete Probability Distributions QMIS 120. Dr. Mohammad Zainal
 Department of Quantitative Methods & Information Systems Business Statistics Chapter 5 Discrete Probability Distributions QMIS 120 Dr. Mohammad Zainal Chapter Goals After completing this chapter, you should
Department of Quantitative Methods & Information Systems Business Statistics Chapter 5 Discrete Probability Distributions QMIS 120 Dr. Mohammad Zainal Chapter Goals After completing this chapter, you should
The Uniform Distribution
 The Uniform Distribution EXAMPLE 1 The previous problem is an example of the uniform probability distribution. Illustrate the uniform distribution. The data that follows are 55 smiling times, in seconds,
The Uniform Distribution EXAMPLE 1 The previous problem is an example of the uniform probability distribution. Illustrate the uniform distribution. The data that follows are 55 smiling times, in seconds,
Chapter 7 Sampling Distributions and Point Estimation of Parameters
 Chapter 7 Sampling Distributions and Point Estimation of Parameters Part 1: Sampling Distributions, the Central Limit Theorem, Point Estimation & Estimators Sections 7-1 to 7-2 1 / 25 Statistical Inferences
Chapter 7 Sampling Distributions and Point Estimation of Parameters Part 1: Sampling Distributions, the Central Limit Theorem, Point Estimation & Estimators Sections 7-1 to 7-2 1 / 25 Statistical Inferences
Name PID Section # (enrolled)
 STT 315 - Lecture 3 Instructor: Aylin ALIN 04/02/2014 Midterm # 2 A Name PID Section # (enrolled) * The exam is closed book and 80 minutes. * You may use a calculator and the formula sheet that you brought
STT 315 - Lecture 3 Instructor: Aylin ALIN 04/02/2014 Midterm # 2 A Name PID Section # (enrolled) * The exam is closed book and 80 minutes. * You may use a calculator and the formula sheet that you brought
Class 12. Daniel B. Rowe, Ph.D. Department of Mathematics, Statistics, and Computer Science. Marquette University MATH 1700
 Class 12 Daniel B. Rowe, Ph.D. Department of Mathematics, Statistics, and Computer Science Copyright 2017 by D.B. Rowe 1 Agenda: Recap Chapter 6.1-6.2 Lecture Chapter 6.3-6.5 Problem Solving Session. 2
Class 12 Daniel B. Rowe, Ph.D. Department of Mathematics, Statistics, and Computer Science Copyright 2017 by D.B. Rowe 1 Agenda: Recap Chapter 6.1-6.2 Lecture Chapter 6.3-6.5 Problem Solving Session. 2
Statistics for Business and Economics: Random Variables:Continuous
 Statistics for Business and Economics: Random Variables:Continuous STT 315: Section 107 Acknowledgement: I d like to thank Dr. Ashoke Sinha for allowing me to use and edit the slides. Murray Bourne (interactive
Statistics for Business and Economics: Random Variables:Continuous STT 315: Section 107 Acknowledgement: I d like to thank Dr. Ashoke Sinha for allowing me to use and edit the slides. Murray Bourne (interactive
The Central Limit Theorem for Sums
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46997 1 The Central Limit Theorem for Sums OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Suppose X is a random
OpenStax-CNX module: m46997 1 The Central Limit Theorem for Sums OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Suppose X is a random
Confidence Intervals for the Mean. When σ is known
 Confidence Intervals for the Mean When σ is known Objective Find the confidence interval for the mean when s is known. Intro Suppose a college president wishes to estimate the average age of students attending
Confidence Intervals for the Mean When σ is known Objective Find the confidence interval for the mean when s is known. Intro Suppose a college president wishes to estimate the average age of students attending
Math 227 Practice Test 2 Sec Name
 Math 227 Practice Test 2 Sec 4.4-6.2 Name Find the indicated probability. ) A bin contains 64 light bulbs of which 0 are defective. If 5 light bulbs are randomly selected from the bin with replacement,
Math 227 Practice Test 2 Sec 4.4-6.2 Name Find the indicated probability. ) A bin contains 64 light bulbs of which 0 are defective. If 5 light bulbs are randomly selected from the bin with replacement,
Part 1 In which we meet the law of averages. The Law of Averages. The Expected Value & The Standard Error. Where Are We Going?
 1 The Law of Averages The Expected Value & The Standard Error Where Are We Going? Sums of random numbers The law of averages Box models for generating random numbers Sums of draws: the Expected Value Standard
1 The Law of Averages The Expected Value & The Standard Error Where Are We Going? Sums of random numbers The law of averages Box models for generating random numbers Sums of draws: the Expected Value Standard
Statistics 511 Supplemental Materials
 Gaussian (or Normal) Random Variable In this section we introduce the Gaussian Random Variable, which is more commonly referred to as the Normal Random Variable. This is a random variable that has a bellshaped
Gaussian (or Normal) Random Variable In this section we introduce the Gaussian Random Variable, which is more commonly referred to as the Normal Random Variable. This is a random variable that has a bellshaped
2.) What is the set of outcomes that describes the event that at least one of the items selected is defective? {AD, DA, DD}
 Math 361 Practice Exam 2 (Use this information for questions 1 3) At the end of a production run manufacturing rubber gaskets, items are sampled at random and inspected to determine if the item is Acceptable
Math 361 Practice Exam 2 (Use this information for questions 1 3) At the end of a production run manufacturing rubber gaskets, items are sampled at random and inspected to determine if the item is Acceptable
