u w 1.5 < 0 These two results imply that the utility function is concave.
|
|
|
- Roberta Long
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A person with initial wealth of Rs.1000 has a 20% possibility of getting in a mischance. On the off chance that he gets in a mishap, he will lose Rs.800, abandoning him with Rs.200; on the off chance that he doesn't, he doesn't loses anything. He maximizes expected utility, and his VNM utility function is u(w) = w. Answer questions 1 to 8 based on the data provided. 1. What is the u (w), i.e., the second derivative of this person s utility function? A) The individual is risk-seeker B) The individual is risk-neutral C) The individual is risk-averse D) Cannot be determined from the given data (Ans.: C) Explanation: Notice that u(w) = w can be written as u(w) = w 0.5. Therefore, u (w) = 0.5 w 0.5 > 0 u (w) = w 1.5 < 0 These two results imply that the utility function is concave. 2. What is the expected amount of money he will lose? A) Rs. 800 B) Rs. 200 C) Rs. 160 D) Rs. 0 (Ans.: C) The expected amount of money he will lose is = (0.2)(Rs.800) + (0.8)(Rs.0) = Rs.160: 3. What is his expected wealth? A) Rs B) Rs. 200 C) Rs. 840 D) Rs. 600 (Ans.: C) His expected wealth is: (0.2)(Rs.200) + (0.8)(Rs.1000) = $ What is his expected utility? A) B) C) D) 20.14
2 (Ans.: A) Explanation: Expected Utility = 0.2 u(rs. 200) u(rs. 1000) = = What is his certainty equivalent wealth, i.e., the certain wealth level that gives him an indistinguishable expected utility from his indeterminate circumstance? A) Rs B) Rs C) Rs D) Rs (Ans.: D) Explanation: u(w) = w = w w = = What is the maximum amount he would pay for full insurance, i.e. what is the greatest premium he would pay an insurance agency to cover the majority of his misfortunes? A) Rs B) Rs C) Rs.0.18 D) Rs (Ans.: B) Explanation: The maximum amount he would pay for full insurance is his initial wealth minus his sure thing equivalent wealth, i.e.: Rs.1000 Rs = Rs The story here is basically this: He starts out with base wealth of Rs If he pays Rs to the insurance company in exchange for them covering his loses in case of an accident, his wealth (regardless of whether or not an accident occurs) will always be Rs.1000-Rs = Rs From this we know that he is indifferent between having certain wealth of Rs and facing the uncertain situation he started out with: both give him an expected utility of So, if he pays Rs for full insurance, he ends up with the same expected utility that he started out with. 7. What is his risk premium, i.e., the amount more than his expected loss is he willing to pay for full protection? A) Rs
3 B) Rs C) Rs.0 D) Rs (Ans.: B) Explanation: He s willing to pay a maximum of Rs for full insurance, and his expected loss is Rs.160. So his risk premium is Rs Rs.160 = Rs What can you conclude about the behaviour of the person if the insurance can be purchased for Rs.150? A) Will purchase the insurance. B) Will not purchase the insurance. C) Will change his utility function according to the price of the insurance. D) There is not enough information given in the question to determine an answer. (Ans.: A) Explanation: If he can get full insurance for one Rupee less (i.e., for Rs.207), buying the insurance will increase his expected utility, so he will want to buy the insurance. If he can only get insurance by paying one Rupee more (i.e., for Rs.209), buying the insurance will decrease his expected utility, so he will refuse to buy the insurance.
4 Answer Questions 9 and 10 based on the data provided. If you are given the following utility function U(W) = e aw + b W + c; (a > 0, b 0 and c 0), then: 9. What can you conclude about the Absolute Risk Aversion properties of the Utility Function? A) As the amount of wealth (W) increases the amount held in risky assets decreases. B) As the amount of wealth (W) increases the amount held in risky assets also increases C) As the amount of wealth (W) decreases the amount held in risky assets remains same D) None of the above (Ans.: B) 10. What can you conclude about the Relative Risk Aversion properties of the Utility Function? A) As the amount of wealth (W) increases the % held in risky assets also increases. B) As the amount of wealth (W) increases the % held in risky assets decreases. C) As the amount of wealth (W) increases the % held in risky assets remains same. D) None of the above (Ans.: A) Explanation: U(W) = e aw + b W + c; (a > 0, b 0 and c 0). We are required to find the properties of this utility function: U (W) = ae aw + b and U (W) = a 2 e aw. As U (W) > 0 and U (W) > 0, hence the utility function has the two fundamental property of (i) non-satiation and (ii) risk averseness. Now let us find absolute risk aversion and relative risk aversion properties of this particular utility function: i. A(W) = U (W) U (W) = a2 e aw ae aw +b. Therefore A (W) < 0, which implies decreasing absolute ii. risk aversion property, i.e., as the amount of wealth (W) increases the amount held in risky assets also increases R(W) = W U (W) = W a2 e aw. Therefore U (W) ae aw +b R (W) < 0, decreasing relative risk aversion property, i.e., as the amount of wealth (W) increases the % held in risky assets also increases
5 11. A new project has begun. The project charter has been written and the project manager has been assigned. The project manager is preparing the work breakdown structure for the project. The WBS is typically used for: A) Explaining the scope of the project relevant to the client B) The basis for organizing and defining the total scope of the project C) Showing the resource conflicts that exist in the project D) The logical relationship between tasks in the project (Ans.: B) Explanation: The work breakdown structure approach allows us to visually see the work that is needed in order to complete a project. The bottom line is by using a work breakdown structure it reduces the number of surprises and improves the ability to better estimate future projects. The work breakdown structure can be used to effectively decompose the project scope, to improve estimating, to better control the project execution and to more accurately verify project completion. In addition, using a work breakdown structure approach summarizes project information to improve the opportunity for use of historical information, which, can aid in both speed and accuracy of future projects. The work breakdown structure is a repeatable process that can be used as a template for future projects.
6 12. In a very large project having a budget of $5 million and a project team of over one hundred people, the project manager constructs a work breakdown structure. The project manager will do the WBS to the detail level of which of the following? A. Task B. Activity C. WBS element D. Work package (Ans.: D) Explanation: The following guidelines should be considered when creating a work breakdown structure: The top level represents the final deliverable or project Sub-deliverables contain work packages that are assigned to a organization s department or unit All elements of the work breakdown structure don t need to be defined to the same level The work package defines the work, duration, and costs for the tasks required to produce the sub-deliverable Work packages should not exceed 10 days of duration Work packages should be independent of other work packages in the work breakdown structure Work packages are unique and should not be duplicated across the work breakdown structure
7 13. The highest element in the hierarchical breakdown of the WBS is: A) A work package B) Sub deliverables C) A cost account D) The final deliverable of the project (Ans.: D) Explanation: Please refer the Explanation of Question No. 12
8 14. All of the following are usually included in a work package except: A) The time needed to complete the work B) A single person who is responsible for its completion C) All the costs for the work package D) All of these are included in a work package (Ans.: D) Explanation: Please refer the Explanation of Question No. 12
9 15. The final step in the creation of a Work Breakdown Structure is to: A) Code the WBS for tracking B) Assign the cost account to a manager C) Assign the work package to a manager D) Develop the responsibility matrix (Ans.: A) Explanation: Please refer the Explanation of Question No. 12
10 16. A project manager has been asked by the client to meet the promise date of the project. The project manager analyzes the schedule before promising a date to the customer. The project manager uses the program evaluation and review technique to evaluate the project schedule. She decides that based on the PERT calculations she can promise a delivery date of June 30. The expected value of the project completion date is May 30. If the project manager is willing to accept a 5% probability that the project will be delivered later than June 30, what is the standard deviation of the duration of the activities on the critical path? Assume a five-day workweek. A. Ten days B. Fifteen days C. One-half month D. One month (Ans.: C) Explanation: Rule for normal distribution, 1σ implies 68% 2σ implies 95% 3σ implies 99.7% In the question it is given that 30 June date represents 95% confidence, which is approximately 2 standard deviations (2σ) and therefore 1 SD or σ is half the difference between 30 May and 30 June. Let x = SD or σ since 2x = 1 month therefore x = 0.5 month So the answer is half month.
11 17. Which one of the following is captured in the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)? A) The life cycle phases. B) The logical order of tasks. C) The scope of the project. D) Project costs. (Ans.: C) Explanation: Please read Explanation for Question no. 11.
12 18. You are the project manager for a high visibility project. The margin on this project is low, and it is extremely important that the cost estimates for the work on the project be accurate. While reviewing the cost estimates for this project you notice that one of the cost estimates for an element in the WBS is 10% higher than two previous projects for very similar work. What should you do? A) Accept the estimate because you trust all of the people on your project team, and they are responsible for estimates B) Reduce the estimate and add the additional budget to the management reserve C) Ask the person responsible for the estimate to explain the difference and bring supporting information to you D) Reduce the estimate and add the additional budget to the contingency reserve (Ans.: C) Explanation: The responsible team member must be asked to justify the estimate with regard to historical information he used.
13 19. Which of the following is true? A. The critical path is the path through the network that has the highest total duration B. The critical path is the path with the least amount of free float C. The critical path is the list of activities that have zero float D. The critical path is the list of activities that have critical risks associated with them (Ans.: C) Explanation: Critical path activities are the project tasks that must start and finish on time to ensure that the project ends on schedule. A delay in any critical path activity will delay completion of the project, unless the project plan can be adjusted so that successor tasks finish more quickly than planned.
14 20. A task was scheduled to use two persons, full time, and take two weeks to complete. Instead, the project manager was only able to assign one person to this task. At the end of two weeks, the person assigned to the task was 75% complete. What is the cost performance index? A B. 1.5 C D. 0.5 (Ans.: B) Explanation: 2 persons X 2 weeks =100 %work. 1 person working for 2 weeks can only complete 50% work...but actual complete is 75%. So, CPI = 75/50 = 1.5
15 21. The main difference between the two types diagramming methods (ADM, arrow diagramming method, and PDM, precedence diagramming method) of the critical path method (CPM) of scheduling is: A. Placement of the activity on the logic diagram line B. Arrow diagramming method (ADM) is a deterministic method, whereas the precedence diagramming method (PDM) is a probabilistic method C. Precedence diagramming method (PDM) is a deterministic method, whereas the arrow diagramming method (ADM) is a probabilistic method D. Precedence diagramming method (PDM) is a more accurate method (Ans.: A) Explanation: The precedence diagram method (PDM) is a tool for scheduling activities in a project plan. It is a method of constructing a project schedule network diagram that uses boxes, referred to as nodes, to represent activities and connects them with arrows that show the dependencies. It is also called the activity-on-node (AON) method. Arrow diagramming method (ADM) is a network diagramming technique in which activities are represented by arrows. ADM is also known as the activity-on-arrow (AOA) method.
16 22. A risk has four possible outcomes. Given the following information, what is the expected value of this risk? Probability Result of Risk , , , ,500 A. -$20,000 B. -$14,500 C. $7,000 D. -$7,500 (Ans.: D) Explanation: Expected Value = (0.4 X 10,000) + (0.3 X 7,500) + (0.2 X 5,000) + (0.1 X 2.500) = 7,500
17 23. The method used to collect information to use through all phases of the project life cycle is called: A) Responsibility matrix B) Organization breakdown structure C) Work breakdown structure D) Priority matrix (Ans.: C) Explanation: Please read Explanation for Question no. 11.
18 24. A project manager is looking at the risk associated with the project schedule. Realizing that if the risks occur the project will be delivered to the stakeholders late, the project manager decides to consider the risk and promise delivery later than the most likely project completion date. He then takes the time between the promise date and the most likely completion date and distributes it among the activities of the project schedule. This creates float in the schedule. This process is called: A. Schedule delay B. Critical chain scheduling C. Buffering D. Contingency scheduling (Ans.: C) Explanation: The Critical Chain/Buffer Management (CC/BM) approach aims at the construction of latest start schedules where the project activities use aggressive time estimates and puts a clear focus on the determination of a realistic project deadline. In order to keep the probability high that the project deadline will be met, the CC/BM approach protects the project duration and the critical chain of the project using various buffers.
19 25. Refer to the table. What is the critical path? A. Start A B C I Finish B. Start A B H I Finish C. Start D E H I Finish D. Start F G I Finish (Ans.: D) Explanation: Start-A-B-C-I-Finish = 11 units Start-A-B-H-I-Finish = 12 units Start-D-E-H-I-Finish = 12 units Start-F-G-I-Finish = 16 units The critical path is the longest one, in this case, Start-F-G-I-Finish
Project Management Professional (PMP) Exam Prep Course 06 - Project Time Management
 Project Management Professional (PMP) Exam Prep Course 06 - Project Time Management Slide 1 Looking Glass Development, LLC (303) 663-5402 / (888) 338-7447 4610 S. Ulster St. #150 Denver, CO 80237 information@lookingglassdev.com
Project Management Professional (PMP) Exam Prep Course 06 - Project Time Management Slide 1 Looking Glass Development, LLC (303) 663-5402 / (888) 338-7447 4610 S. Ulster St. #150 Denver, CO 80237 information@lookingglassdev.com
SCHEDULE CREATION AND ANALYSIS. 1 Powered by POeT Solvers Limited
 SCHEDULE CREATION AND ANALYSIS 1 www.pmtutor.org Powered by POeT Solvers Limited While building the project schedule, we need to consider all risk factors, assumptions and constraints imposed on the project
SCHEDULE CREATION AND ANALYSIS 1 www.pmtutor.org Powered by POeT Solvers Limited While building the project schedule, we need to consider all risk factors, assumptions and constraints imposed on the project
GPE engineering project management. Project Management in an Engineering Context
 GPE engineering project management Project Management in an Engineering Context Network diagrams in context PM SOW CHARTER SCOPE DEFINITION WBS circulation, negotiation, translation WBS WP à activities
GPE engineering project management Project Management in an Engineering Context Network diagrams in context PM SOW CHARTER SCOPE DEFINITION WBS circulation, negotiation, translation WBS WP à activities
International Project Management. prof.dr MILOŠ D. MILOVANČEVIĆ
 International Project Management prof.dr MILOŠ D. MILOVANČEVIĆ Project time management Project cost management Time in project management process Time is a valuable resource. It is also the scarcest. Time
International Project Management prof.dr MILOŠ D. MILOVANČEVIĆ Project time management Project cost management Time in project management process Time is a valuable resource. It is also the scarcest. Time
Real-World Project Management. Chapter 15
 Real-World Project Chapter 15 Characteristics of Project Unique one-time focus Difficulties arise from originality Subject to uncertainties Unexplained or unplanned events often arise, affecting resources,
Real-World Project Chapter 15 Characteristics of Project Unique one-time focus Difficulties arise from originality Subject to uncertainties Unexplained or unplanned events often arise, affecting resources,
Textbook: pp Chapter 11: Project Management
 1 Textbook: pp. 405-444 Chapter 11: Project Management 2 Learning Objectives After completing this chapter, students will be able to: Understand how to plan, monitor, and control projects with the use
1 Textbook: pp. 405-444 Chapter 11: Project Management 2 Learning Objectives After completing this chapter, students will be able to: Understand how to plan, monitor, and control projects with the use
The Project Times and Costs
 The Project Times and Costs Not to underestimate the estimate Chapter 5 Defining the Project Step 1: Defining the Scope Step 2: Establishing Priorities Step 3: Creating the Work Breakdown Structure Step
The Project Times and Costs Not to underestimate the estimate Chapter 5 Defining the Project Step 1: Defining the Scope Step 2: Establishing Priorities Step 3: Creating the Work Breakdown Structure Step
A convenient analytical and visual technique of PERT and CPM prove extremely valuable in assisting the managers in managing the projects.
 Introduction Any project involves planning, scheduling and controlling a number of interrelated activities with use of limited resources, namely, men, machines, materials, money and time. The projects
Introduction Any project involves planning, scheduling and controlling a number of interrelated activities with use of limited resources, namely, men, machines, materials, money and time. The projects
Project Management Techniques (PMT)
 Project Management Techniques (PMT) Critical Path Method (CPM) and Project Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) are 2 main basic techniques used in project management. Example: Construction of a house.
Project Management Techniques (PMT) Critical Path Method (CPM) and Project Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) are 2 main basic techniques used in project management. Example: Construction of a house.
PROJECT MANAGEMENT COURSE 5: PROJECT TIME MANAGEMENT. G.N. Sandhy Widyasthana
 PROJECT MANAGEMENT COURSE 5: PROJECT TIME MANAGEMENT G.N. Sandhy Widyasthana widyasthana@gmail.com 022 70702020 081 225 702020 1 2 3 Process of identifying the specific actions to be performed to produce
PROJECT MANAGEMENT COURSE 5: PROJECT TIME MANAGEMENT G.N. Sandhy Widyasthana widyasthana@gmail.com 022 70702020 081 225 702020 1 2 3 Process of identifying the specific actions to be performed to produce
Project planning and creating a WBS
 37E01500 Project Management and Consulting Practice Project planning and creating a WBS Matti Rossi Lecture 3, Tue 28.2.2017 Learning objectives Describe the project time management planning tasks, and
37E01500 Project Management and Consulting Practice Project planning and creating a WBS Matti Rossi Lecture 3, Tue 28.2.2017 Learning objectives Describe the project time management planning tasks, and
Project Planning. Identifying the Work to Be Done. Gantt Chart. A Gantt Chart. Given: Activity Sequencing Network Diagrams
 Project Planning Identifying the Work to Be Done Activity Sequencing Network Diagrams Given: Statement of work written description of goals work & time frame of project Work Breakdown Structure Be able
Project Planning Identifying the Work to Be Done Activity Sequencing Network Diagrams Given: Statement of work written description of goals work & time frame of project Work Breakdown Structure Be able
Introduction. Introduction. Six Steps of PERT/CPM. Six Steps of PERT/CPM LEARNING OBJECTIVES
 Valua%on and pricing (November 5, 2013) LEARNING OBJECTIVES Lecture 12 Project Management Olivier J. de Jong, LL.M., MM., MBA, CFD, CFFA, AA www.olivierdejong.com 1. Understand how to plan, monitor, and
Valua%on and pricing (November 5, 2013) LEARNING OBJECTIVES Lecture 12 Project Management Olivier J. de Jong, LL.M., MM., MBA, CFD, CFFA, AA www.olivierdejong.com 1. Understand how to plan, monitor, and
Project Management Chapter 13
 Lecture 12 Project Management Chapter 13 Introduction n Managing large-scale, complicated projects effectively is a difficult problem and the stakes are high. n The first step in planning and scheduling
Lecture 12 Project Management Chapter 13 Introduction n Managing large-scale, complicated projects effectively is a difficult problem and the stakes are high. n The first step in planning and scheduling
Project Planning. Planning is an important step in project execution. Planning means:
 Project Planning Planning is an important step in project execution. Planning means: Thinking through future project actions Seeking and mentally inspecting the long path from the start to the finish Achieving
Project Planning Planning is an important step in project execution. Planning means: Thinking through future project actions Seeking and mentally inspecting the long path from the start to the finish Achieving
MS Project 2007 Page 1 of 18
 MS Project 2007 Page 1 of 18 PROJECT MANAGEMENT (PM):- There are powerful environment forces contributed to the rapid expansion of the projects and project management approaches to the business problems
MS Project 2007 Page 1 of 18 PROJECT MANAGEMENT (PM):- There are powerful environment forces contributed to the rapid expansion of the projects and project management approaches to the business problems
Appendix B: Glossary of Project Management Terms
 Appendix B: Glossary of Project Management Terms Assumption - There may be external circumstances or events that must occur for the project to be successful (or that should happen to increase your chances
Appendix B: Glossary of Project Management Terms Assumption - There may be external circumstances or events that must occur for the project to be successful (or that should happen to increase your chances
1. A is a decision support tool that uses a tree-like graph or model of decisions and their possible consequences, including chance event outcomes,
 1. A is a decision support tool that uses a tree-like graph or model of decisions and their possible consequences, including chance event outcomes, resource costs, and utility. A) Decision tree B) Graphs
1. A is a decision support tool that uses a tree-like graph or model of decisions and their possible consequences, including chance event outcomes, resource costs, and utility. A) Decision tree B) Graphs
CHAPTER 5 STOCHASTIC SCHEDULING
 CHPTER STOCHSTIC SCHEDULING In some situations, estimating activity duration becomes a difficult task due to ambiguity inherited in and the risks associated with some work. In such cases, the duration
CHPTER STOCHSTIC SCHEDULING In some situations, estimating activity duration becomes a difficult task due to ambiguity inherited in and the risks associated with some work. In such cases, the duration
UNIT-II Project Organization and Scheduling Project Element
 UNIT-II Project Organization and Scheduling Project Element Five Key Elements are Unique. Projects are unique, one-of-a-kind, never been done before. Start and Stop Date. Projects must have a definite
UNIT-II Project Organization and Scheduling Project Element Five Key Elements are Unique. Projects are unique, one-of-a-kind, never been done before. Start and Stop Date. Projects must have a definite
Introduction to Project Management. Modeling after NYS ITS
 Introduction to Project Management Modeling after NYS ITS What is Project Management? Project management is the application of knowledge, skills, tools and techniques to project activities to meet project
Introduction to Project Management Modeling after NYS ITS What is Project Management? Project management is the application of knowledge, skills, tools and techniques to project activities to meet project
Unit 3 Research Project. Eddie S. Jackson. Kaplan University. IT511: Information Systems Project Management
 Running head: UNIT 3 RESEARCH PROJECT 1 Unit 3 Research Project Eddie S. Jackson Kaplan University IT511: Information Systems Project Management 04/06/2014 UNIT 3 RESEARCH PROJECT 2 Unit 3 Research Project
Running head: UNIT 3 RESEARCH PROJECT 1 Unit 3 Research Project Eddie S. Jackson Kaplan University IT511: Information Systems Project Management 04/06/2014 UNIT 3 RESEARCH PROJECT 2 Unit 3 Research Project
Project Management -- Developing the Project Plan
 Project Management -- Developing the Project Plan Dr. Tai-Yue Wang Department of Industrial and Information Management National Cheng Kung University Tainan, TAIWAN, ROC 1 Where We Are Now 6 2 Developing
Project Management -- Developing the Project Plan Dr. Tai-Yue Wang Department of Industrial and Information Management National Cheng Kung University Tainan, TAIWAN, ROC 1 Where We Are Now 6 2 Developing
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Index
 Index Note to the reader: Throughout this index boldfaced page numbers indicate primary discussions of a topic. Italicized page numbers indicate illustrations. A A+ certification, 28 acceptance criteria
Index Note to the reader: Throughout this index boldfaced page numbers indicate primary discussions of a topic. Italicized page numbers indicate illustrations. A A+ certification, 28 acceptance criteria
Unit 4.3: Uncertainty
 Unit 4.: Uncertainty Michael Malcolm June 8, 20 Up until now, we have been considering consumer choice problems where the consumer chooses over outcomes that are known. However, many choices in economics
Unit 4.: Uncertainty Michael Malcolm June 8, 20 Up until now, we have been considering consumer choice problems where the consumer chooses over outcomes that are known. However, many choices in economics
IT Certification Exams Provider! Weofferfreeupdateserviceforoneyear! h ps://
 IT Certification Exams Provider! Weofferfreeupdateserviceforoneyear! h ps://www.certqueen.com Exam: PMI-002 Title : Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM) Certification Version : DEMO 1 / 7 1.A
IT Certification Exams Provider! Weofferfreeupdateserviceforoneyear! h ps://www.certqueen.com Exam: PMI-002 Title : Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM) Certification Version : DEMO 1 / 7 1.A
Project Planning. Jesper Larsen. Department of Management Engineering Technical University of Denmark
 Project Planning jesla@man.dtu.dk Department of Management Engineering Technical University of Denmark 1 Project Management Project Management is a set of techniques that helps management manage large-scale
Project Planning jesla@man.dtu.dk Department of Management Engineering Technical University of Denmark 1 Project Management Project Management is a set of techniques that helps management manage large-scale
Risk Video #1. Video 1 Recap
 Risk Video #1 Video 1 Recap 1 Risk Video #2 Video 2 Recap 2 Risk Video #3 Risk Risk Management Process Uncertain or chance events that planning can not overcome or control. Risk Management A proactive
Risk Video #1 Video 1 Recap 1 Risk Video #2 Video 2 Recap 2 Risk Video #3 Risk Risk Management Process Uncertain or chance events that planning can not overcome or control. Risk Management A proactive
PROJECT MANAGEMENT CPM & PERT TECHNIQUES
 PROJECT MANAGEMENT CPM & PERT TECHNIQUES FLOW OF PRESENTATION INTRODUCTION NETWORK PLANNING ESTIMATING TIME CPM PERT Project Management Project A project is an interrelated set of activities that has a
PROJECT MANAGEMENT CPM & PERT TECHNIQUES FLOW OF PRESENTATION INTRODUCTION NETWORK PLANNING ESTIMATING TIME CPM PERT Project Management Project A project is an interrelated set of activities that has a
Haeryip Sihombing 1. Risk. Risk Management
 Project Management Managing Risk 7 Haeryip Sihombing Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka (UTeM) BMFP 4542 1 2 Risk Management Process The Risk Event Graph Risk Uncertain or chance events that planning
Project Management Managing Risk 7 Haeryip Sihombing Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka (UTeM) BMFP 4542 1 2 Risk Management Process The Risk Event Graph Risk Uncertain or chance events that planning
Investment and Portfolio Management. Lecture 1: Managed funds fall into a number of categories that pool investors funds
 Lecture 1: Managed funds fall into a number of categories that pool investors funds Types of managed funds: Unit trusts Investors funds are pooled, usually into specific types of assets Investors are assigned
Lecture 1: Managed funds fall into a number of categories that pool investors funds Types of managed funds: Unit trusts Investors funds are pooled, usually into specific types of assets Investors are assigned
Program Evaluation and Review Techniques (PERT) Critical Path Method (CPM):
 Program Evaluation and Review Techniques (PERT) Critical Path Method (CPM): A Rough Guide by Andrew Scouller PROJECT MANAGEMENT Project Managers can use project management software to keep track of the
Program Evaluation and Review Techniques (PERT) Critical Path Method (CPM): A Rough Guide by Andrew Scouller PROJECT MANAGEMENT Project Managers can use project management software to keep track of the
For the PMP Exam using PMBOK Guide 5 th Edition. PMI, PMP, PMBOK Guide are registered trade marks of Project Management Institute, Inc.
 For the PMP Exam using PMBOK Guide 5 th Edition PMI, PMP, PMBOK Guide are registered trade marks of Project Management Institute, Inc. 1 Contacts Name: Khaled El-Nakib, MSc, PMP, PMI-RMP URL: http://www.khaledelnakib.com
For the PMP Exam using PMBOK Guide 5 th Edition PMI, PMP, PMBOK Guide are registered trade marks of Project Management Institute, Inc. 1 Contacts Name: Khaled El-Nakib, MSc, PMP, PMI-RMP URL: http://www.khaledelnakib.com
1 of 14 4/27/2009 7:45 AM
 1 of 14 4/27/2009 7:45 AM Chapter 7 - Network Models in Project Management INTRODUCTION Most realistic projects that organizations like Microsoft, General Motors, or the U.S. Defense Department undertake
1 of 14 4/27/2009 7:45 AM Chapter 7 - Network Models in Project Management INTRODUCTION Most realistic projects that organizations like Microsoft, General Motors, or the U.S. Defense Department undertake
Programme Evaluation and Review Techniques (PERT) And Critical Path Method (CPM) By K.K. Bandyopadhyay. August 2001
 Programme Evaluation and Review Techniques (PERT) And Critical Path Method (CPM) By K.K. Bandyopadhyay August 2001 Participatory Research In Asia Introduction Programme Evaluation and Review Technique
Programme Evaluation and Review Techniques (PERT) And Critical Path Method (CPM) By K.K. Bandyopadhyay August 2001 Participatory Research In Asia Introduction Programme Evaluation and Review Technique
ETSF01: Software Engineering Process Economy and Quality
 ETSF01: Software Engineering Process Economy and Quality Dietmar Pfahl Lund University 1. Identify project objectives 0.Select project 2. Identify project infrastructure Project planning steps Review Lower
ETSF01: Software Engineering Process Economy and Quality Dietmar Pfahl Lund University 1. Identify project objectives 0.Select project 2. Identify project infrastructure Project planning steps Review Lower
Expected value is basically the average payoff from some sort of lottery, gamble or other situation with a randomly determined outcome.
 Economics 352: Intermediate Microeconomics Notes and Sample Questions Chapter 18: Uncertainty and Risk Aversion Expected Value The chapter starts out by explaining what expected value is and how to calculate
Economics 352: Intermediate Microeconomics Notes and Sample Questions Chapter 18: Uncertainty and Risk Aversion Expected Value The chapter starts out by explaining what expected value is and how to calculate
CHAPTER 6 CRASHING STOCHASTIC PERT NETWORKS WITH RESOURCE CONSTRAINED PROJECT SCHEDULING PROBLEM
 CHAPTER 6 CRASHING STOCHASTIC PERT NETWORKS WITH RESOURCE CONSTRAINED PROJECT SCHEDULING PROBLEM 6.1 Introduction Project Management is the process of planning, controlling and monitoring the activities
CHAPTER 6 CRASHING STOCHASTIC PERT NETWORKS WITH RESOURCE CONSTRAINED PROJECT SCHEDULING PROBLEM 6.1 Introduction Project Management is the process of planning, controlling and monitoring the activities
INSE 6230: Assignment 1 - Winter (0% of final grade) 1. The table below provides information about a short IT project.
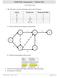 INSE 6230: Assignment - Winter 208 (0% of final grade). The table below provides information about a short IT project. Activity Predecessors Duration (Months) A - 2 B - 3 C A 4 D A, B 2 E D 2 F B, C, E
INSE 6230: Assignment - Winter 208 (0% of final grade). The table below provides information about a short IT project. Activity Predecessors Duration (Months) A - 2 B - 3 C A 4 D A, B 2 E D 2 F B, C, E
Project Management. Managing Risk. Clifford F. Gray Eric W. Larson Third Edition. Chapter 7
 Project Management THE MANAGERIAL PROCESS Clifford F. Gray Eric W. Larson Third Edition Chapter 7 Managing Risk Copyright 2006 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. PowerPoint Presentation by
Project Management THE MANAGERIAL PROCESS Clifford F. Gray Eric W. Larson Third Edition Chapter 7 Managing Risk Copyright 2006 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. PowerPoint Presentation by
PMI PMI-SP. PMI Scheduling Professional. Download Full Version :
 PMI PMI-SP PMI Scheduling Professional Download Full Version : http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/pmi-sp QUESTION: 311 A company hires a scheduler for one of its projects. What skills should he
PMI PMI-SP PMI Scheduling Professional Download Full Version : http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/pmi-sp QUESTION: 311 A company hires a scheduler for one of its projects. What skills should he
Utility and Choice Under Uncertainty
 Introduction to Microeconomics Utility and Choice Under Uncertainty The Five Axioms of Choice Under Uncertainty We can use the axioms of preference to show how preferences can be mapped into measurable
Introduction to Microeconomics Utility and Choice Under Uncertainty The Five Axioms of Choice Under Uncertainty We can use the axioms of preference to show how preferences can be mapped into measurable
Plan Implementation. Pushpa Lal Shakya
 Plan Implementation Pushpa Lal Shakya Outline of Presentation 1. Plan Implementation: Meaning 2. Use of MTEF in Plan Implementation 3. Plan implementation Process and Implementation Modalities 4. Application
Plan Implementation Pushpa Lal Shakya Outline of Presentation 1. Plan Implementation: Meaning 2. Use of MTEF in Plan Implementation 3. Plan implementation Process and Implementation Modalities 4. Application
Earned Value Management. Danielle Kellogg. Hodges University
 Earned Value Management 1 EARNED VALUE MANAGEMENT Earned Value Management Danielle Kellogg Hodges University Earned Value Management 2 Abstract Earned Value Management has been used with enterprise-level
Earned Value Management 1 EARNED VALUE MANAGEMENT Earned Value Management Danielle Kellogg Hodges University Earned Value Management 2 Abstract Earned Value Management has been used with enterprise-level
PMP Exam Preparation Course. Madras Management Training W.L.L All Rights Reserved
 Project Cost Management 1 Project Cost Management Processes 1. Estimate Costs 2. Determine Budget 3. Control Costs In some projects, especially with smaller scope, cost estimation and cost budgeting are
Project Cost Management 1 Project Cost Management Processes 1. Estimate Costs 2. Determine Budget 3. Control Costs In some projects, especially with smaller scope, cost estimation and cost budgeting are
Pass PMP in 21 Days - ITTO Toolbox PROCESS MAP
 PROCESS MAP 1 IntEgratIon Pass PMP in 21 Days - ITTO Toolbox InItIatIng PlannIng ExEcutIng MonItorIng & controlling closing Develop Project Charter Develop Project Management Plan Direct & Manage Project
PROCESS MAP 1 IntEgratIon Pass PMP in 21 Days - ITTO Toolbox InItIatIng PlannIng ExEcutIng MonItorIng & controlling closing Develop Project Charter Develop Project Management Plan Direct & Manage Project
Exam Questions PMI-SP
 Exam Questions PMI-SP PMI Scheduling Professional Practice Test https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/pmi-sp/ 1.CORRECT TEXT Fill in the blank with the appropriate word. When activities are logically linked,
Exam Questions PMI-SP PMI Scheduling Professional Practice Test https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/pmi-sp/ 1.CORRECT TEXT Fill in the blank with the appropriate word. When activities are logically linked,
// Measuring Risk Exposure through Risk Range Certainty (RRC) Overcoming the Shortcomings of Schedule Confidence Levels
 // Measuring Risk Exposure through Risk Range Certainty (RRC) Overcoming the Shortcomings of Schedule Confidence Levels Dr. Dan Patterson, PMP CEO & President, Acumen October 2009 www.projectacumen.com
// Measuring Risk Exposure through Risk Range Certainty (RRC) Overcoming the Shortcomings of Schedule Confidence Levels Dr. Dan Patterson, PMP CEO & President, Acumen October 2009 www.projectacumen.com
Management Management
 Project Management Management Management in all business and organizational activities is the act of getting people together to accomplish desired goals and objectives using available resources efficiently
Project Management Management Management in all business and organizational activities is the act of getting people together to accomplish desired goals and objectives using available resources efficiently
Project Risk Management
 Project Risk Management Introduction Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 PMP Exam Preparation Project Integration Management Project Scope Management Project Time Management Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Project Cost Management
Project Risk Management Introduction Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 PMP Exam Preparation Project Integration Management Project Scope Management Project Time Management Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Project Cost Management
Making sense of Schedule Risk Analysis
 Making sense of Schedule Risk Analysis John Owen Barbecana Inc. Version 2 December 19, 2014 John Owen - jowen@barbecana.com 2 5 Years managing project controls software in the Oil and Gas industry 28 years
Making sense of Schedule Risk Analysis John Owen Barbecana Inc. Version 2 December 19, 2014 John Owen - jowen@barbecana.com 2 5 Years managing project controls software in the Oil and Gas industry 28 years
INSE 6230 Total Quality Project Management Winter 2018 Quiz I. Max : 70 points. This is a closed book exam. Answer all the questions in the booklet.
 . Surname, given names: Student Number: INSE 6230 Total Quality Project Management Winter 2018 Quiz I. Max : 70 points This is a closed book exam. Answer all the questions in the booklet. Ensure that your
. Surname, given names: Student Number: INSE 6230 Total Quality Project Management Winter 2018 Quiz I. Max : 70 points This is a closed book exam. Answer all the questions in the booklet. Ensure that your
PASS4TEST. IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way! We offer free update service for one year
 PASS4TEST IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way! \ We offer free update service for one year Exam : PMI-SP Title : PMI Scheduling Professional Vendors : PMI Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid PMI-SP
PASS4TEST IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way! \ We offer free update service for one year Exam : PMI-SP Title : PMI Scheduling Professional Vendors : PMI Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid PMI-SP
Step 1: Confirm Implementation Factors and Consolidated Gaps
 Architecture Roadmap is one of the TOGAF deliverables you can create with the TOGAF software. The Architecture Roadmap lists individual increments of change and lays them out on a timeline to show progression
Architecture Roadmap is one of the TOGAF deliverables you can create with the TOGAF software. The Architecture Roadmap lists individual increments of change and lays them out on a timeline to show progression
Full Monte. Looking at your project through rose-colored glasses? Let s get real.
 Realistic plans for project success. Looking at your project through rose-colored glasses? Let s get real. Full Monte Cost and schedule risk analysis add-in for Microsoft Project that graphically displays
Realistic plans for project success. Looking at your project through rose-colored glasses? Let s get real. Full Monte Cost and schedule risk analysis add-in for Microsoft Project that graphically displays
70-632_formatted. Number: Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 1.0
 70-632_formatted Number: 000-000 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 1.0 http://www.gratisexam.com/ Microsoft EXAM 70-632 TS:Microsoft Office Project 2007. Managing Projects Total Questions:
70-632_formatted Number: 000-000 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 1.0 http://www.gratisexam.com/ Microsoft EXAM 70-632 TS:Microsoft Office Project 2007. Managing Projects Total Questions:
Characterization of the Optimum
 ECO 317 Economics of Uncertainty Fall Term 2009 Notes for lectures 5. Portfolio Allocation with One Riskless, One Risky Asset Characterization of the Optimum Consider a risk-averse, expected-utility-maximizing
ECO 317 Economics of Uncertainty Fall Term 2009 Notes for lectures 5. Portfolio Allocation with One Riskless, One Risky Asset Characterization of the Optimum Consider a risk-averse, expected-utility-maximizing
06IP/IM74 OPERATIONS RESEARCH
 06IP/IM74 OPERATIONS RESEARCH UNIT - 6: PROJECT MANAGEMENT USING NETWORK ANALYSIS (By Dr.G.N.MOHAN BABU, Prof & HOD (I&P Engg), MCE, Hassan 573 021) LEARNING OBJECTIVES OF THE MODULE: By the end of this
06IP/IM74 OPERATIONS RESEARCH UNIT - 6: PROJECT MANAGEMENT USING NETWORK ANALYSIS (By Dr.G.N.MOHAN BABU, Prof & HOD (I&P Engg), MCE, Hassan 573 021) LEARNING OBJECTIVES OF THE MODULE: By the end of this
Optimization Prof. A. Goswami Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur. Lecture - 18 PERT
 Optimization Prof. A. Goswami Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 18 PERT (Refer Slide Time: 00:56) In the last class we completed the C P M critical path analysis
Optimization Prof. A. Goswami Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 18 PERT (Refer Slide Time: 00:56) In the last class we completed the C P M critical path analysis
PROJECT MANAGEMENT. Trying to manage a project without project management is like trying to play a football game without a game plan
 PROJECT MANAGEMENT Trying to manage a project without project management is like trying to play a football game without a game plan K. Tate (Past Board Member, PMI). Brad Fink 28 February 2013 Executive
PROJECT MANAGEMENT Trying to manage a project without project management is like trying to play a football game without a game plan K. Tate (Past Board Member, PMI). Brad Fink 28 February 2013 Executive
Choice under Uncertainty
 Chapter 7 Choice under Uncertainty 1. Expected Utility Theory. 2. Risk Aversion. 3. Applications: demand for insurance, portfolio choice 4. Violations of Expected Utility Theory. 7.1 Expected Utility Theory
Chapter 7 Choice under Uncertainty 1. Expected Utility Theory. 2. Risk Aversion. 3. Applications: demand for insurance, portfolio choice 4. Violations of Expected Utility Theory. 7.1 Expected Utility Theory
UNIT 5 PROJECT ANALYSIS PERT/CPM MODULE - 2
 UNIT 5 PROJECT ANALYSIS MODULE - 2 UNIT 5 PROJECT ANALYSIS Structure 5.0 Introduction 5.1 Unit Objectives 5.2 Definitions of Project and Project Management 5.3 Characteristics of a Project 5.4 Life Cycle
UNIT 5 PROJECT ANALYSIS MODULE - 2 UNIT 5 PROJECT ANALYSIS Structure 5.0 Introduction 5.1 Unit Objectives 5.2 Definitions of Project and Project Management 5.3 Characteristics of a Project 5.4 Life Cycle
SECTION ARCHITECTURAL AND ENGINEERING CPM SCHEDULES
 SECTION 01 32 16.01 ARCHITECTURAL AND ENGINEERING CPM SCHEDULES PART 1- GENERAL 1.1 DESCRIPTION: The Architect/Engineer of Record (A/E) shall develop a Critical Path Method (CPM Schedule) plan and schedule
SECTION 01 32 16.01 ARCHITECTURAL AND ENGINEERING CPM SCHEDULES PART 1- GENERAL 1.1 DESCRIPTION: The Architect/Engineer of Record (A/E) shall develop a Critical Path Method (CPM Schedule) plan and schedule
What do Coin Tosses and Decision Making under Uncertainty, have in common?
 What do Coin Tosses and Decision Making under Uncertainty, have in common? J. Rene van Dorp (GW) Presentation EMSE 1001 October 27, 2017 Presented by: J. Rene van Dorp 10/26/2017 1 About René van Dorp
What do Coin Tosses and Decision Making under Uncertainty, have in common? J. Rene van Dorp (GW) Presentation EMSE 1001 October 27, 2017 Presented by: J. Rene van Dorp 10/26/2017 1 About René van Dorp
05/05/2011. Degree of Risk. Degree of Risk. BUSA 4800/4810 May 5, Uncertainty
 BUSA 4800/4810 May 5, 2011 Uncertainty We must believe in luck. For how else can we explain the success of those we don t like? Jean Cocteau Degree of Risk We incorporate risk and uncertainty into our
BUSA 4800/4810 May 5, 2011 Uncertainty We must believe in luck. For how else can we explain the success of those we don t like? Jean Cocteau Degree of Risk We incorporate risk and uncertainty into our
Vendor: PMI. Exam Code: CA Exam Name: Certified Associate in Project Management. Version: Demo
 Vendor: PMI Exam Code: CA0-001 Exam Name: Certified Associate in Project Management Version: Demo QUESTION: 1 On what is project baseline development established? A. Approved product requirements B. Estimated
Vendor: PMI Exam Code: CA0-001 Exam Name: Certified Associate in Project Management Version: Demo QUESTION: 1 On what is project baseline development established? A. Approved product requirements B. Estimated
Expected utility theory; Expected Utility Theory; risk aversion and utility functions
 ; Expected Utility Theory; risk aversion and utility functions Prof. Massimo Guidolin Portfolio Management Spring 2016 Outline and objectives Utility functions The expected utility theorem and the axioms
; Expected Utility Theory; risk aversion and utility functions Prof. Massimo Guidolin Portfolio Management Spring 2016 Outline and objectives Utility functions The expected utility theorem and the axioms
Quality Project Management
 Quality Project Management By James N. Salapatas, PE, PMP www.suncam.com Copyright 2014 James N. Salapatas Page 1 of 44 Table of Contents Title Page LIST OF CHARTS 2 LIST OF FIGURES 3 ABOUT THE COURSE
Quality Project Management By James N. Salapatas, PE, PMP www.suncam.com Copyright 2014 James N. Salapatas Page 1 of 44 Table of Contents Title Page LIST OF CHARTS 2 LIST OF FIGURES 3 ABOUT THE COURSE
Project Theft Management,
 Project Theft Management, by applying best practises of Project Risk Management Philip Rosslee, BEng. PrEng. MBA PMP PMO Projects South Africa PMO Projects Group www.pmo-projects.co.za philip.rosslee@pmo-projects.com
Project Theft Management, by applying best practises of Project Risk Management Philip Rosslee, BEng. PrEng. MBA PMP PMO Projects South Africa PMO Projects Group www.pmo-projects.co.za philip.rosslee@pmo-projects.com
Making Hard Decision. ENCE 627 Decision Analysis for Engineering. Identify the decision situation and understand objectives. Identify alternatives
 CHAPTER Duxbury Thomson Learning Making Hard Decision Third Edition RISK ATTITUDES A. J. Clark School of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 13 FALL 2003 By Dr. Ibrahim. Assakkaf
CHAPTER Duxbury Thomson Learning Making Hard Decision Third Edition RISK ATTITUDES A. J. Clark School of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 13 FALL 2003 By Dr. Ibrahim. Assakkaf
Project Management with Brief Information regarding CPM and PERT Methods
 99 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC & ENGINEERING RESEARCH, VOLUME 9, ISSUE, JULY-8 Project Management with Brief Information regarding CPM and PERT Methods Rohan Agarwal Guide: Sheetal Patel Abstract
99 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC & ENGINEERING RESEARCH, VOLUME 9, ISSUE, JULY-8 Project Management with Brief Information regarding CPM and PERT Methods Rohan Agarwal Guide: Sheetal Patel Abstract
Chapter 5: Estimating Project Times and Costs 4KF3
 Lecture Notes Importance of Estimates Support good decisions Schedule work o Make sure your team members can take on added work of project Determine length of project and costs o Projects can be cancelled
Lecture Notes Importance of Estimates Support good decisions Schedule work o Make sure your team members can take on added work of project Determine length of project and costs o Projects can be cancelled
IP-CIS : CIS Project Management
 Meltem Özturan www.mis.boun.edu.tr/ozturan/mis301 1 Project Management Tools and Techniques (PMTT) Feasibility Analysis Organizational Breakdown Structure Work Breakdown Structure Scheduling Earned Value
Meltem Özturan www.mis.boun.edu.tr/ozturan/mis301 1 Project Management Tools and Techniques (PMTT) Feasibility Analysis Organizational Breakdown Structure Work Breakdown Structure Scheduling Earned Value
CHAPTER 9: PROJECT MANAGEMENT
 CHAPTER 9: PROJECT MANAGEMENT The aim is to coordinate and plan a single job consisting lots of tasks between which precedence relationships exist Project planning Most popular planning tools are utilized
CHAPTER 9: PROJECT MANAGEMENT The aim is to coordinate and plan a single job consisting lots of tasks between which precedence relationships exist Project planning Most popular planning tools are utilized
Unit 9: Risk Management (PMBOK Guide, Chapter 11)
 (PMBOK Guide, Chapter 11) Some exam takers may be unfamiliar with the basic concepts of probability, expected monetary value, and decision trees. This unit will review all these concepts so that you should
(PMBOK Guide, Chapter 11) Some exam takers may be unfamiliar with the basic concepts of probability, expected monetary value, and decision trees. This unit will review all these concepts so that you should
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK VI SEMESTER CE6005 CONSTRUCTION PLANNING AND SCHEDULING Regulation 2013 Academic Year 2017
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK VI SEMESTER CE6005 CONSTRUCTION PLANNING AND SCHEDULING Regulation 2013 Academic Year 2017
POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA
 POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF MANAGEMENT PROJECT MANAGEMENT BACHELOR OF BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION 07BBMA SUBJECT CODE: PRM422S DATE: DURATION: MARKS: EXAMINERS: MODERATOR:
POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF MANAGEMENT PROJECT MANAGEMENT BACHELOR OF BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION 07BBMA SUBJECT CODE: PRM422S DATE: DURATION: MARKS: EXAMINERS: MODERATOR:
6/7/2018. Overview PERT / CPM PERT/CPM. Project Scheduling PERT/CPM PERT/CPM
 /7/018 PERT / CPM BSAD 0 Dave Novak Summer 018 Overview Introduce PERT/CPM Discuss what a critical path is Discuss critical path algorithm Example Source: Anderson et al., 01 Quantitative Methods for Business
/7/018 PERT / CPM BSAD 0 Dave Novak Summer 018 Overview Introduce PERT/CPM Discuss what a critical path is Discuss critical path algorithm Example Source: Anderson et al., 01 Quantitative Methods for Business
Project Management. Chapter 2. Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
 Project Management Chapter 2 02-0 1 What is a Project? Project An interrelated set of activities with a definite starting and ending point, which results in a unique outcome for a specific allocation of
Project Management Chapter 2 02-0 1 What is a Project? Project An interrelated set of activities with a definite starting and ending point, which results in a unique outcome for a specific allocation of
Appendix A Decision Support Analysis
 Field Manual 100-11 Appendix A Decision Support Analysis Section I: Introduction structure development, and facilities. Modern quantitative methods can greatly facilitate this Complex decisions associated
Field Manual 100-11 Appendix A Decision Support Analysis Section I: Introduction structure development, and facilities. Modern quantitative methods can greatly facilitate this Complex decisions associated
SWEN 256 Software Process & Project Management
 SWEN 256 Software Process & Project Management Plan: Identify activities. No specific start and end dates. Estimating: Determining the size & duration of activities. Schedule: Adds specific start and end
SWEN 256 Software Process & Project Management Plan: Identify activities. No specific start and end dates. Estimating: Determining the size & duration of activities. Schedule: Adds specific start and end
Project Risk Analysis and Management Exercises (Part II, Chapters 6, 7)
 Project Risk Analysis and Management Exercises (Part II, Chapters 6, 7) Chapter II.6 Exercise 1 For the decision tree in Figure 1, assume Chance Events E and F are independent. a) Draw the appropriate
Project Risk Analysis and Management Exercises (Part II, Chapters 6, 7) Chapter II.6 Exercise 1 For the decision tree in Figure 1, assume Chance Events E and F are independent. a) Draw the appropriate
Outline. Global Company Profile: Bechtel Group. The Importance of Project Management Project Planning Project Scheduling Project Controlling
 Project Management Outline Global Company Profile: Bechtel Group The Importance of Project Management Project Planning Project Scheduling Project Controlling Outline - Continued Project Management Techniques:
Project Management Outline Global Company Profile: Bechtel Group The Importance of Project Management Project Planning Project Scheduling Project Controlling Outline - Continued Project Management Techniques:
4. (10 pts) Portfolios A and B lie on the capital allocation line shown below. What is the risk-free rate X?
 First Midterm Exam Fall 017 Econ 180-367 Closed Book. Formula Sheet Provided. Calculators OK. Time Allowed: 1 Hour 15 minutes All Questions Carry Equal Marks 1. (15 pts). Investors can choose to purchase
First Midterm Exam Fall 017 Econ 180-367 Closed Book. Formula Sheet Provided. Calculators OK. Time Allowed: 1 Hour 15 minutes All Questions Carry Equal Marks 1. (15 pts). Investors can choose to purchase
After complete studying this chapter, You should be able to
 Chapter 10 Project Management Ch10: What Is Project Management? After complete studying this chapter, You should be able to Define key terms like Project, Project Management, Discuss the main characteristics
Chapter 10 Project Management Ch10: What Is Project Management? After complete studying this chapter, You should be able to Define key terms like Project, Project Management, Discuss the main characteristics
Chapter 2 The PERT/CPM Technique
 Chapter The PERT/CPM Technique Abstract Completing a project on time and within budget is not an easy task. The project scheduling phase plays a central role in predicting both the time and cost aspects
Chapter The PERT/CPM Technique Abstract Completing a project on time and within budget is not an easy task. The project scheduling phase plays a central role in predicting both the time and cost aspects
Decision Analysis under Uncertainty. Christopher Grigoriou Executive MBA/HEC Lausanne
 Decision Analysis under Uncertainty Christopher Grigoriou Executive MBA/HEC Lausanne 2007-2008 2008 Introduction Examples of decision making under uncertainty in the business world; => Trade-off between
Decision Analysis under Uncertainty Christopher Grigoriou Executive MBA/HEC Lausanne 2007-2008 2008 Introduction Examples of decision making under uncertainty in the business world; => Trade-off between
Project Management Fundamentals
 Project Management Fundamentals Course No: B04-003 Credit: 4 PDH Najib Gerges, Ph.D., P.E. Continuing Education and Development, Inc. 9 Greyridge Farm Court Stony Point, NY 10980 P: (877) 322-5800 F: (877)
Project Management Fundamentals Course No: B04-003 Credit: 4 PDH Najib Gerges, Ph.D., P.E. Continuing Education and Development, Inc. 9 Greyridge Farm Court Stony Point, NY 10980 P: (877) 322-5800 F: (877)
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING. MSc CIVIL ENGINEERING MSc CONSTRUCTION PROJECT MANAGEMENT SEMESTER ONE EXAMINATION 2017/2018
 ENG026 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING MSc CIVIL ENGINEERING MSc CONSTRUCTION PROJECT MANAGEMENT SEMESTER ONE EXAMINATION 2017/2018 PROJECT MANAGEMENT MODULE NO: CPM7002 Date: 15 January 2018
ENG026 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING MSc CIVIL ENGINEERING MSc CONSTRUCTION PROJECT MANAGEMENT SEMESTER ONE EXAMINATION 2017/2018 PROJECT MANAGEMENT MODULE NO: CPM7002 Date: 15 January 2018
Managing Project Risk DHY
 Managing Project Risk DHY01 0407 Copyright ESI International April 2007 All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or
Managing Project Risk DHY01 0407 Copyright ESI International April 2007 All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or
Answers to chapter 3 review questions
 Answers to chapter 3 review questions 3.1 Explain why the indifference curves in a probability triangle diagram are straight lines if preferences satisfy expected utility theory. The expected utility of
Answers to chapter 3 review questions 3.1 Explain why the indifference curves in a probability triangle diagram are straight lines if preferences satisfy expected utility theory. The expected utility of
Uncertainty. Contingent consumption Subjective probability. Utility functions. BEE2017 Microeconomics
 Uncertainty BEE217 Microeconomics Uncertainty: The share prices of Amazon and the difficulty of investment decisions Contingent consumption 1. What consumption or wealth will you get in each possible outcome
Uncertainty BEE217 Microeconomics Uncertainty: The share prices of Amazon and the difficulty of investment decisions Contingent consumption 1. What consumption or wealth will you get in each possible outcome
Chapter16Project Management and. Scheduling Project management
 Chapter6Project Management and Scheduling Figure 6. On completion of this chapter, you should be able to identify key components of projects and the issues associated with them, and you should be able
Chapter6Project Management and Scheduling Figure 6. On completion of this chapter, you should be able to identify key components of projects and the issues associated with them, and you should be able
Choose between the four lotteries with unknown probabilities on the branches: uncertainty
 R.E.Marks 2000 Lecture 8-1 2.11 Utility Choose between the four lotteries with unknown probabilities on the branches: uncertainty A B C D $25 $150 $600 $80 $90 $98 $ 20 $0 $100$1000 $105$ 100 R.E.Marks
R.E.Marks 2000 Lecture 8-1 2.11 Utility Choose between the four lotteries with unknown probabilities on the branches: uncertainty A B C D $25 $150 $600 $80 $90 $98 $ 20 $0 $100$1000 $105$ 100 R.E.Marks
Learning Objectives = = where X i is the i t h outcome of a decision, p i is the probability of the i t h
 Learning Objectives After reading Chapter 15 and working the problems for Chapter 15 in the textbook and in this Workbook, you should be able to: Distinguish between decision making under uncertainty and
Learning Objectives After reading Chapter 15 and working the problems for Chapter 15 in the textbook and in this Workbook, you should be able to: Distinguish between decision making under uncertainty and
Project Risk Evaluation and Management Exercises (Part II, Chapters 4, 5, 6 and 7)
 Project Risk Evaluation and Management Exercises (Part II, Chapters 4, 5, 6 and 7) Chapter II.4 Exercise 1 Explain in your own words the role that data can play in the development of models of uncertainty
Project Risk Evaluation and Management Exercises (Part II, Chapters 4, 5, 6 and 7) Chapter II.4 Exercise 1 Explain in your own words the role that data can play in the development of models of uncertainty
The purpose of this paper is to briefly review some key tools used in the. The Basics of Performance Reporting An Investor s Guide
 Briefing The Basics of Performance Reporting An Investor s Guide Performance reporting is a critical part of any investment program. Accurate, timely information can help investors better evaluate the
Briefing The Basics of Performance Reporting An Investor s Guide Performance reporting is a critical part of any investment program. Accurate, timely information can help investors better evaluate the
SCHOOL OF ACCOUNTING AND BUSINESS BSc. (APPLIED ACCOUNTING) GENERAL / SPECIAL DEGREE PROGRAMME END SEMESTER EXAMINATION JULY 2016
 All Rights Reserved No. of Pages - 10 No of Questions - 06 SCHOOL OF ACCOUNTING AND BUSINESS BSc. (APPLIED ACCOUNTING) GENERAL / SPECIAL DEGREE PROGRAMME END SEMESTER EXAMINATION JULY 2016 MGT 30725 Project
All Rights Reserved No. of Pages - 10 No of Questions - 06 SCHOOL OF ACCOUNTING AND BUSINESS BSc. (APPLIED ACCOUNTING) GENERAL / SPECIAL DEGREE PROGRAMME END SEMESTER EXAMINATION JULY 2016 MGT 30725 Project
Review Session. Prof. Manuela Pedio Theory of Finance
 Review Session Prof. Manuela Pedio 20135 Theory of Finance 12 October 2018 Three most common utility functions (1/3) We typically assume that investors are non satiated (they always prefer more to less)
Review Session Prof. Manuela Pedio 20135 Theory of Finance 12 October 2018 Three most common utility functions (1/3) We typically assume that investors are non satiated (they always prefer more to less)
Mohammed Rafiuddin CEO and General Manager, BIOSI Biohazards Solutions Innovators
 Mohammed Rafiuddin CEO and General Manager, BIOSI Biohazards Solutions Innovators Profile of Mohammed Rafiuddin Mohammed is an active member of AACE International since 2006 with 30 years of experience
Mohammed Rafiuddin CEO and General Manager, BIOSI Biohazards Solutions Innovators Profile of Mohammed Rafiuddin Mohammed is an active member of AACE International since 2006 with 30 years of experience
