Math 230 Exam 2 Name April 8, 1999
|
|
|
- Mariah Porter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Math 230 Exam 2 Name April 8, 1999 Instructions: Answer each question to the best of your ability. Most questions require that you give a concluding or summary statement. These statements should be complete sentences. Good Luck!!! 1. (3.4) You are on the staff of a member of Congress who is considering a bill that would provide government-sponsored insurance for nursing home care. You report that 1128 letters have been received on the issue, of which 871 oppose the legislation. I m surprised that most of my constituents oppose the bill. I thought it would be quite popular, says the congresswoman. Are you convinced that a majority of the voters oppose the bill? How would you explain the statistical issue to the congresswoman? 2. Just before a presidential election, a national opinion polling firm increases the size of its weekly sample from the usual 1500 people to 4000 people. a) Does the larger random sample reduce bias of the poll result? Explain! b) Does it improve the precision of the result? Explain!
2 3. (3.39) Fizz Laboratories, a pharmaceutical company, has developed a new pain-relief medication. Sixty patients suffering from arthritis and needing pain relief are available. Each patient will be treated and asked an hour later, About what percentage of pain relief did you experience? (a) Why should Fizz not simply administer the new drug and record the patients responses? (b) Outline the design of an experiment to compare the drug s effectiveness with that of aspirin and of a placebo. (c) Should patients be told which drug they are receiving? How would this knowledge probably affect their reactions? (d) If patients are not told which treatment they are receiving, the experiment is single-blind. Should this experiment be double-blind also? Explain! (e) Choosing the most effect size of the treatment groups requires more statistical expertise. We will learn more about this aspect of design is later chapters. Explain in plain language the advantage of using larger groups of subjects.
3 4. (4.9) The Internal Revenue Service plans to examine an SRS of individual federal income tax returns from each state. One variable of interest is the proportion of returns claiming itemized deductions. The total number of tax returns in a state varies from almost 14 million in California to fewer than 210,000 in Wyoming. (a) Will the sampling variability of the sample proportion change from state to state if an SRS of 2000 tax returns is selected in each state? Explain your answer. (b) Will the sampling variability of the sample proportion change from state to state if an SRS of 1% of all tax returns is selected in each state? Explain your answer. 5. (4.13) If you draw an M&M candy at random from a bag of candies, the candy you draw will have one of six colors (before the new blue was added). The probability of drawing each color depends on the proportion of each color among all candies made. The table below give the probabilities that a random chosen M&M has each color. Color Brown Re d Yellow Green Orange Tan Pr obability ? a) What must be the probability of drawing a tan candy? b) What is the probability that the candy drawn is any of red, yellow, or orange?
4 6. To predict the inventory required for a particular type of CD player, a stereo dealer analyzed the weekly number of sales over a long period of time. The appropriate probability distribution of the number, X, of sales per week is shown in the table. (Use the accompanying Minitab) x P(X = x) a) Find the expected number, µ, of sales per week. b) Find σ 2 and σ. MTB > print c1 c2 x (c1) p(x) (c2) MTB > let c3=c1*c2 MTB > sum c3 k1 Sum of C3 = MTB > let c4=(c1-k1)**2 MTB > sum c4 k2 Sum of C4 = MTB > let k3=sqrt(k2) MTB > print k1 k2 k3 Data Display K K K
5 7. An opinion poll asks an simple random sample of 1500 adults, Do you happen to jog? Suppose (as is approximately correct) that the population proportion who jog is p = In a large number of samples, the proportion ˆ p who answer Yes will be approximately normally distributed with mean 0.15 and standard deviation Carefully sketch this normal curve and use it (and Table A) to answer these questions: a) What percent of many samples will have a sample proportion who jog that is 0.15 or less? b) What is the probability that ˆ p will take a value between and 0.159? c) What is the probability that ˆ p does not lie between and 0.159? d) What is the probability that ˆ p would be greater than 0.159?
6 8. The systolic blood pressure of a random sample of 100 female students has sample mean x = If the standard deviation of blood pressure for the entire population of females students is assumed to be 20, a) find a 90% confidence interval for the mean blood pressure in the population. Assume that a 90% confidence interval for the mean blood pressure in the population has been calculated based on a known population standard deviation of 20. State whether the following would increase or decrease the width of the confidence interval. Briefly state why. b) The confidence level is changed to 95%. c) The population standard deviation is found to be 15 rather than 20. d) A sample of only 50 female students is measured. 9. Short Answer or Multiple Choice a) A new teaching method is tried on a large class. At the end of the course, a final is given. The average score is 73 out of 100 and only 3% of the class failed. Does this show the new method was successful? Explain. b) In October, 1976, a nationwide vaccination program was started against swine flu. The first shots were given to the group most at risk - the elderly and infirm. During the first week of the program, 24,000 persons aged 65 and over were given shots, and three of these persons died. As a result, eight states suspended the vaccination program. What would a statistician (you) say?
7 c). If X 1, X 2,L, X 16 is a random sample from a normal distribution with mean 18 and standard deviation 64, then X will have a) What distribution? b) What mean? c) What standard deviation? d). You notice that your car seems to run better when you use Brand A of gasoline than when you use Brand B. Can you conclude that Brand A is better than Brand B for you Car? a) Yes. This is a simple random sample. b) No. The evidence is anecdotal. c) Yes. This is a comparative experiment. d) No. The two brands are the same. e) None of the above. e). A new headache remedy is given to a group of 25 patients who suffer severe headaches. Of these, 20 report that the remedy is very helpful in treating their headaches. From this information you conclude a) the remedy is effective for the treatment of headaches. b) nothing, because the sample size is too small. c) nothing, because there is no control group for comparison. d) the new treatment is better than aspirin. e) none of the above. f). A randomly selected student is asked to respond yes, no, or maybe to the question: "Do you intend to vote in the next presidential election?" The sample space is {yes, no, maybe}. Which of the following represent a legitimate assignment of probabilities for this sample space? a).4,.4,.2 b).4,.6,.4 c).3,.3,.3 d).5,.7, -.2 e) none of the above. g). You want to compute a 95% confidence interval for a population mean. Assume that the population standard deviation is known to be 10 and the sample size is 50. The value of z * to be used in this calculation is a) b) c) 1.96 d).8289 e).8352
PRINTABLE VERSION. Quiz 10
 PRINTABLE VERSION Quiz 10 Question 1 The z-score associated with the 97.5 percent confidence interval is a) 2.160 b) 1.900 c) 2.241 d) 2.744 e) 1.960 Question 2 What will reduce the width of a confidence
PRINTABLE VERSION Quiz 10 Question 1 The z-score associated with the 97.5 percent confidence interval is a) 2.160 b) 1.900 c) 2.241 d) 2.744 e) 1.960 Question 2 What will reduce the width of a confidence
Section 5.5 Z Scores soln.notebook. December 07, Section 5.5 Z Scores
 Section 5.5 Z Scores 1 Warm up/review: The Normal Distribution Curve Given that the average adult in North America has a mean mass of 72 kg, with a standard deviation of 14 kg. a) How many standard deviations
Section 5.5 Z Scores 1 Warm up/review: The Normal Distribution Curve Given that the average adult in North America has a mean mass of 72 kg, with a standard deviation of 14 kg. a) How many standard deviations
AP Statistics Review Ch. 6
 AP Statistics Review Ch. 6 Name 1. Which of the following data sets is not continuous? a. The gallons of gasoline in a car. b. The time it takes to commute in a car. c. Number of goals scored by a hockey
AP Statistics Review Ch. 6 Name 1. Which of the following data sets is not continuous? a. The gallons of gasoline in a car. b. The time it takes to commute in a car. c. Number of goals scored by a hockey
Math 14, Homework 6.2 p. 337 # 3, 4, 9, 10, 15, 18, 19, 21, 22 Name
 Name 3. Population in U.S. Jails The average daily jail population in the United States is 706,242. If the distribution is normal and the standard deviation is 52,145, find the probability that on a randomly
Name 3. Population in U.S. Jails The average daily jail population in the United States is 706,242. If the distribution is normal and the standard deviation is 52,145, find the probability that on a randomly
Significance Test Review
 Significance Test Review 1) Kmart brand 60W light bulbs state on the package, Average life of 1000 hours. Let µ denote the true mean life of Kmart 60W light bulbs. People who purchase this brand would
Significance Test Review 1) Kmart brand 60W light bulbs state on the package, Average life of 1000 hours. Let µ denote the true mean life of Kmart 60W light bulbs. People who purchase this brand would
Chapter 7: Sampling Distributions Chapter 7: Sampling Distributions
 Chapter 7: Sampling Distributions Objectives: Students will: Define a sampling distribution. Contrast bias and variability. Describe the sampling distribution of a proportion (shape, center, and spread).
Chapter 7: Sampling Distributions Objectives: Students will: Define a sampling distribution. Contrast bias and variability. Describe the sampling distribution of a proportion (shape, center, and spread).
Part 1 In which we meet the law of averages. The Law of Averages. The Expected Value & The Standard Error. Where Are We Going?
 1 The Law of Averages The Expected Value & The Standard Error Where Are We Going? Sums of random numbers The law of averages Box models for generating random numbers Sums of draws: the Expected Value Standard
1 The Law of Averages The Expected Value & The Standard Error Where Are We Going? Sums of random numbers The law of averages Box models for generating random numbers Sums of draws: the Expected Value Standard
Estimation. Focus Points 10/11/2011. Estimating p in the Binomial Distribution. Section 7.3
 Estimation 7 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Section 7.3 Estimating p in the Binomial Distribution Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Focus Points Compute the maximal length
Estimation 7 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Section 7.3 Estimating p in the Binomial Distribution Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Focus Points Compute the maximal length
Name Period AP Statistics Unit 5 Review
 Name Period AP Statistics Unit 5 Review Multiple Choice 1. Jay Olshansky from the University of Chicago was quoted in Chance News as arguing that for the average life expectancy to reach 100, 18% of people
Name Period AP Statistics Unit 5 Review Multiple Choice 1. Jay Olshansky from the University of Chicago was quoted in Chance News as arguing that for the average life expectancy to reach 100, 18% of people
I. Standard Error II. Standard Error III. Standard Error 2.54
 1) Original Population: Match the standard error (I, II, or III) with the correct sampling distribution (A, B, or C) and the correct sample size (1, 5, or 10) I. Standard Error 1.03 II. Standard Error
1) Original Population: Match the standard error (I, II, or III) with the correct sampling distribution (A, B, or C) and the correct sample size (1, 5, or 10) I. Standard Error 1.03 II. Standard Error
Exam II Math 1342 Capters 3-5 HCCS. Name
 Exam II Math 1342 Capters 3-5 HCCS Name Date Provide an appropriate response. 1) A single six-sided die is rolled. Find the probability of rolling a number less than 3. A) 0.5 B) 0.1 C) 0.25 D 0.333 1)
Exam II Math 1342 Capters 3-5 HCCS Name Date Provide an appropriate response. 1) A single six-sided die is rolled. Find the probability of rolling a number less than 3. A) 0.5 B) 0.1 C) 0.25 D 0.333 1)
(c) The probability that a randomly selected driver having a California drivers license
 Statistics Test 2 Name: KEY 1 Classify each statement as an example of classical probability, empirical probability, or subjective probability (a An executive for the Krusty-O cereal factory makes an educated
Statistics Test 2 Name: KEY 1 Classify each statement as an example of classical probability, empirical probability, or subjective probability (a An executive for the Krusty-O cereal factory makes an educated
Central Limit Theorem
 Central Limit Theorem Lots of Samples 1 Homework Read Sec 6-5. Discussion Question pg 329 Do Ex 6-5 8-15 2 Objective Use the Central Limit Theorem to solve problems involving sample means 3 Sample Means
Central Limit Theorem Lots of Samples 1 Homework Read Sec 6-5. Discussion Question pg 329 Do Ex 6-5 8-15 2 Objective Use the Central Limit Theorem to solve problems involving sample means 3 Sample Means
d) Find the standard deviation of the random variable X.
 Q 1: The number of students using Math lab per day is found in the distribution below. x 6 8 10 12 14 P(x) 0.15 0.3 0.35 0.1 0.1 a) Find the mean for this probability distribution. b) Find the variance
Q 1: The number of students using Math lab per day is found in the distribution below. x 6 8 10 12 14 P(x) 0.15 0.3 0.35 0.1 0.1 a) Find the mean for this probability distribution. b) Find the variance
Solutions for practice questions: Chapter 15, Probability Distributions If you find any errors, please let me know at
 Solutions for practice questions: Chapter 15, Probability Distributions If you find any errors, please let me know at mailto:msfrisbie@pfrisbie.com. 1. Let X represent the savings of a resident; X ~ N(3000,
Solutions for practice questions: Chapter 15, Probability Distributions If you find any errors, please let me know at mailto:msfrisbie@pfrisbie.com. 1. Let X represent the savings of a resident; X ~ N(3000,
4.1 Probability Distributions
 Probability and Statistics Mrs. Leahy Chapter 4: Discrete Probability Distribution ALWAYS KEEP IN MIND: The Probability of an event is ALWAYS between: and!!!! 4.1 Probability Distributions Random Variables
Probability and Statistics Mrs. Leahy Chapter 4: Discrete Probability Distribution ALWAYS KEEP IN MIND: The Probability of an event is ALWAYS between: and!!!! 4.1 Probability Distributions Random Variables
8.1 Binomial Distributions
 8.1 Binomial Distributions The Binomial Setting The 4 Conditions of a Binomial Setting: 1.Each observation falls into 1 of 2 categories ( success or fail ) 2 2.There is a fixed # n of observations. 3.All
8.1 Binomial Distributions The Binomial Setting The 4 Conditions of a Binomial Setting: 1.Each observation falls into 1 of 2 categories ( success or fail ) 2 2.There is a fixed # n of observations. 3.All
Binomial Random Variable - The count X of successes in a binomial setting
 6.3.1 Binomial Settings and Binomial Random Variables What do the following scenarios have in common? Toss a coin 5 times. Count the number of heads. Spin a roulette wheel 8 times. Record how many times
6.3.1 Binomial Settings and Binomial Random Variables What do the following scenarios have in common? Toss a coin 5 times. Count the number of heads. Spin a roulette wheel 8 times. Record how many times
Distribution of the Sample Mean
 Distribution of the Sample Mean MATH 130, Elements of Statistics I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Experiment (1 of 3) Suppose we have the following population : 4 8 1 2 3 4 9 1
Distribution of the Sample Mean MATH 130, Elements of Statistics I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Experiment (1 of 3) Suppose we have the following population : 4 8 1 2 3 4 9 1
Math 251, Test 2 Wednesday, May 19, 2004
 Math 251, Test 2 Wednesday, May 19, 2004 Name: Hints and Answers Instructions. Complete each of the following 9 problems. Please show all appropriate details in your solutions. Good Luck. 1. (15 pts) (a)
Math 251, Test 2 Wednesday, May 19, 2004 Name: Hints and Answers Instructions. Complete each of the following 9 problems. Please show all appropriate details in your solutions. Good Luck. 1. (15 pts) (a)
Contents. The Binomial Distribution. The Binomial Distribution The Normal Approximation to the Binomial Left hander example
 Contents The Binomial Distribution The Normal Approximation to the Binomial Left hander example The Binomial Distribution When you flip a coin there are only two possible outcomes - heads or tails. This
Contents The Binomial Distribution The Normal Approximation to the Binomial Left hander example The Binomial Distribution When you flip a coin there are only two possible outcomes - heads or tails. This
. 13. The maximum error (margin of error) of the estimate for μ (based on known σ) is:
 Statistics Sample Exam 3 Solution Chapters 6 & 7: Normal Probability Distributions & Estimates 1. What percent of normally distributed data value lie within 2 standard deviations to either side of the
Statistics Sample Exam 3 Solution Chapters 6 & 7: Normal Probability Distributions & Estimates 1. What percent of normally distributed data value lie within 2 standard deviations to either side of the
Math 227 Practice Test 2 Sec Name
 Math 227 Practice Test 2 Sec 4.4-6.2 Name Find the indicated probability. ) A bin contains 64 light bulbs of which 0 are defective. If 5 light bulbs are randomly selected from the bin with replacement,
Math 227 Practice Test 2 Sec 4.4-6.2 Name Find the indicated probability. ) A bin contains 64 light bulbs of which 0 are defective. If 5 light bulbs are randomly selected from the bin with replacement,
Problem Set 07 Discrete Random Variables
 Name Problem Set 07 Discrete Random Variables MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the mean of the random variable. 1) The random
Name Problem Set 07 Discrete Random Variables MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the mean of the random variable. 1) The random
Using the Central Limit
 Using the Central Limit Theorem By: OpenStaxCollege It is important for you to understand when to use the central limit theorem. If you are being asked to find the probability of the mean, use the clt
Using the Central Limit Theorem By: OpenStaxCollege It is important for you to understand when to use the central limit theorem. If you are being asked to find the probability of the mean, use the clt
Previously, when making inferences about the population mean, μ, we were assuming the following simple conditions:
 Chapter 17 Inference about a Population Mean Conditions for inference Previously, when making inferences about the population mean, μ, we were assuming the following simple conditions: (1) Our data (observations)
Chapter 17 Inference about a Population Mean Conditions for inference Previously, when making inferences about the population mean, μ, we were assuming the following simple conditions: (1) Our data (observations)
Chapter 9 & 10. Multiple Choice.
 Chapter 9 & 10 Review Name Multiple Choice. 1. An agricultural researcher plants 25 plots with a new variety of corn. The average yield for these plots is X = 150 bushels per acre. Assume that the yield
Chapter 9 & 10 Review Name Multiple Choice. 1. An agricultural researcher plants 25 plots with a new variety of corn. The average yield for these plots is X = 150 bushels per acre. Assume that the yield
Name: Period: Date: 1. Suppose we are interested in the average weight of chickens in America.
 Name: Period: Date: Statistics Review MM4D1. Using simulation, students will develop the idea of the central limit theorem. MM4D2. Using student-generated data from random samples of at least 30 members,
Name: Period: Date: Statistics Review MM4D1. Using simulation, students will develop the idea of the central limit theorem. MM4D2. Using student-generated data from random samples of at least 30 members,
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Midterm Review Name 1) As part of an economics class project, students were asked to randomly select 500 New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) stocks from the Wall Street Journal. As part of the project, students
Midterm Review Name 1) As part of an economics class project, students were asked to randomly select 500 New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) stocks from the Wall Street Journal. As part of the project, students
Chapter 4. Section 4.1 Objectives. Random Variables. Random Variables. Chapter 4: Probability Distributions
 Chapter 4: Probability s 4. Probability s 4. Binomial s Section 4. Objectives Distinguish between discrete random variables and continuous random variables Construct a discrete probability distribution
Chapter 4: Probability s 4. Probability s 4. Binomial s Section 4. Objectives Distinguish between discrete random variables and continuous random variables Construct a discrete probability distribution
Chapter 6 Section Review day s.notebook. May 11, Honors Statistics. Aug 23-8:26 PM. 3. Review team test.
 Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM 3. Review team test Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Nov 27-10:28 PM 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 6.9 6.10 6.11 6.12 Nov 27-9:53 PM 2 May 8-7:44 PM May 1-9:09 PM 3 Dec 1-2:08 PM Sep
Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM 3. Review team test Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Nov 27-10:28 PM 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 6.9 6.10 6.11 6.12 Nov 27-9:53 PM 2 May 8-7:44 PM May 1-9:09 PM 3 Dec 1-2:08 PM Sep
Final/Exam #3 Form B - Statistics 211 (Fall 1999)
 Final/Exam #3 Form B - Statistics 211 (Fall 1999) This test consists of nine numbered pages. Make sure you have all 9 pages. It is your responsibility to inform me if a page is missing!!! You have at least
Final/Exam #3 Form B - Statistics 211 (Fall 1999) This test consists of nine numbered pages. Make sure you have all 9 pages. It is your responsibility to inform me if a page is missing!!! You have at least
1. State whether the following groups are populations or samples. You are encouraged to justify your answers.
 MATH 2210 Exam 1 Review Solution Note: This review is NOT comprehensive, so do not limit your study to it. 1. State whether the following groups are populations or samples. You are encouraged to justify
MATH 2210 Exam 1 Review Solution Note: This review is NOT comprehensive, so do not limit your study to it. 1. State whether the following groups are populations or samples. You are encouraged to justify
Chapter 6: Random Variables. Ch. 6-3: Binomial and Geometric Random Variables
 Chapter : Random Variables Ch. -3: Binomial and Geometric Random Variables X 0 2 3 4 5 7 8 9 0 0 P(X) 3???????? 4 4 When the same chance process is repeated several times, we are often interested in whether
Chapter : Random Variables Ch. -3: Binomial and Geometric Random Variables X 0 2 3 4 5 7 8 9 0 0 P(X) 3???????? 4 4 When the same chance process is repeated several times, we are often interested in whether
Instructor: A.E.Cary. Math 243 Exam 2
 Name: Instructor: A.E.Cary Instructions: Show all your work in a manner consistent with that demonstrated in class. Round your answers where appropriate. Use 3 decimal places when rounding answers. In
Name: Instructor: A.E.Cary Instructions: Show all your work in a manner consistent with that demonstrated in class. Round your answers where appropriate. Use 3 decimal places when rounding answers. In
FINAL REVIEW W/ANSWERS
 FINAL REVIEW W/ANSWERS ( 03/15/08 - Sharon Coates) Concepts to review before answering the questions: A population consists of the entire group of people or objects of interest to an investigator, while
FINAL REVIEW W/ANSWERS ( 03/15/08 - Sharon Coates) Concepts to review before answering the questions: A population consists of the entire group of people or objects of interest to an investigator, while
Math 251: Practice Questions Hints and Answers. Review II. Questions from Chapters 4 6
 Math 251: Practice Questions Hints and Answers Review II. Questions from Chapters 4 6 II.A Probability II.A.1. The following is from a sample of 500 bikers who attended the annual rally in Sturgis South
Math 251: Practice Questions Hints and Answers Review II. Questions from Chapters 4 6 II.A Probability II.A.1. The following is from a sample of 500 bikers who attended the annual rally in Sturgis South
STAT 3090 Test 2 - Version B Fall Student s Printed Name: PLEASE READ DIRECTIONS!!!!
 Student s Printed Name: Instructor: XID: Section #: Read each question very carefully. You are permitted to use a calculator on all portions of this exam. You are NOT allowed to use any textbook, notes,
Student s Printed Name: Instructor: XID: Section #: Read each question very carefully. You are permitted to use a calculator on all portions of this exam. You are NOT allowed to use any textbook, notes,
Fall 2011 Exam Score: /75. Exam 3
 Math 12 Fall 2011 Name Exam Score: /75 Total Class Percent to Date Exam 3 For problems 1-10, circle the letter next to the response that best answers the question or completes the sentence. You do not
Math 12 Fall 2011 Name Exam Score: /75 Total Class Percent to Date Exam 3 For problems 1-10, circle the letter next to the response that best answers the question or completes the sentence. You do not
Set up a normal distribution curve, to help estimate the percent of the band that, on average, practices a greater number of hours than Alexis.
 Section 5.5 Z-Scores Example 1 Alexis plays in her school jazz band. Band members practice an average of 16.5 h per week, with a standard deviation of 4.2 h. Alexis practices an average of 22 h per week.
Section 5.5 Z-Scores Example 1 Alexis plays in her school jazz band. Band members practice an average of 16.5 h per week, with a standard deviation of 4.2 h. Alexis practices an average of 22 h per week.
Applied Mathematics 12 Extra Practice Exercises Chapter 3
 H E LP Applied Mathematics Extra Practice Exercises Chapter Tutorial., page 98. A bag contains 5 red balls, blue balls, and green balls. For each of the experiments described below, complete the given
H E LP Applied Mathematics Extra Practice Exercises Chapter Tutorial., page 98. A bag contains 5 red balls, blue balls, and green balls. For each of the experiments described below, complete the given
Chapter Six Probability Distributions
 6.1 Probability Distributions Discrete Random Variable Chapter Six Probability Distributions x P(x) 2 0.08 4 0.13 6 0.25 8 0.31 10 0.16 12 0.01 Practice. Construct a probability distribution for the number
6.1 Probability Distributions Discrete Random Variable Chapter Six Probability Distributions x P(x) 2 0.08 4 0.13 6 0.25 8 0.31 10 0.16 12 0.01 Practice. Construct a probability distribution for the number
Math : Spring 2008
 Math 1070-2: Spring 2008 Lecture 7 Davar Khoshnevisan Department of Mathematics University of Utah http://www.math.utah.edu/ davar February 27, 2008 An example A WHO study of health: In Canada, the systolic
Math 1070-2: Spring 2008 Lecture 7 Davar Khoshnevisan Department of Mathematics University of Utah http://www.math.utah.edu/ davar February 27, 2008 An example A WHO study of health: In Canada, the systolic
Sampling Distributions
 AP Statistics Ch. 7 Notes Sampling Distributions A major field of statistics is statistical inference, which is using information from a sample to draw conclusions about a wider population. Parameter:
AP Statistics Ch. 7 Notes Sampling Distributions A major field of statistics is statistical inference, which is using information from a sample to draw conclusions about a wider population. Parameter:
CHAPTER 5 Sampling Distributions
 CHAPTER 5 Sampling Distributions 5.1 The possible values of p^ are 0, 1/3, 2/3, and 1. These correspond to getting 0 persons with lung cancer, 1 with lung cancer, 2 with lung cancer, and all 3 with lung
CHAPTER 5 Sampling Distributions 5.1 The possible values of p^ are 0, 1/3, 2/3, and 1. These correspond to getting 0 persons with lung cancer, 1 with lung cancer, 2 with lung cancer, and all 3 with lung
Math 227 Elementary Statistics. Bluman 5 th edition
 Math 227 Elementary Statistics Bluman 5 th edition CHAPTER 6 The Normal Distribution 2 Objectives Identify distributions as symmetrical or skewed. Identify the properties of the normal distribution. Find
Math 227 Elementary Statistics Bluman 5 th edition CHAPTER 6 The Normal Distribution 2 Objectives Identify distributions as symmetrical or skewed. Identify the properties of the normal distribution. Find
MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES AND STATISTICS (252 BE)
 MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES AND STATISTICS (252 BE) Normal and Binomial Distribution Applied to Construction Management Sampling and Confidence Intervals Sr Tan Liat Choon Email: tanliatchoon@gmail.com Mobile:
MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES AND STATISTICS (252 BE) Normal and Binomial Distribution Applied to Construction Management Sampling and Confidence Intervals Sr Tan Liat Choon Email: tanliatchoon@gmail.com Mobile:
MATH 446/546 Homework 1:
 MATH 446/546 Homework 1: Due September 28th, 216 Please answer the following questions. Students should type there work. 1. At time t, a company has I units of inventory in stock. Customers demand the
MATH 446/546 Homework 1: Due September 28th, 216 Please answer the following questions. Students should type there work. 1. At time t, a company has I units of inventory in stock. Customers demand the
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Chapter 6 Exam A Name The given values are discrete. Use the continuity correction and describe the region of the normal distribution that corresponds to the indicated probability. 1) The probability of
Chapter 6 Exam A Name The given values are discrete. Use the continuity correction and describe the region of the normal distribution that corresponds to the indicated probability. 1) The probability of
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Use the Central Limit Theorem to find the indicated probability. The sample size is n,
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Use the Central Limit Theorem to find the indicated probability. The sample size is n,
Math 140 Introductory Statistics
 Math 140 Introductory Statistics Let s make our own sampling! If we use a random sample (a survey) or if we randomly assign treatments to subjects (an experiment) we can come up with proper, unbiased conclusions
Math 140 Introductory Statistics Let s make our own sampling! If we use a random sample (a survey) or if we randomly assign treatments to subjects (an experiment) we can come up with proper, unbiased conclusions
STAT Chapter 7: Confidence Intervals
 STAT 515 -- Chapter 7: Confidence Intervals With a point estimate, we used a single number to estimate a parameter. We can also use a set of numbers to serve as reasonable estimates for the parameter.
STAT 515 -- Chapter 7: Confidence Intervals With a point estimate, we used a single number to estimate a parameter. We can also use a set of numbers to serve as reasonable estimates for the parameter.
Record on a ScanTron, your choosen response for each question. You may write on this form. One page of notes and a calculator are allowed.
 Ch 16, 17 Math 240 Exam 4 v1 Good SAMPLE No Book, Yes 1 Page Notes, Yes Calculator, 120 Minutes Dressler Record on a ScanTron, your choosen response for each question. You may write on this form. One page
Ch 16, 17 Math 240 Exam 4 v1 Good SAMPLE No Book, Yes 1 Page Notes, Yes Calculator, 120 Minutes Dressler Record on a ScanTron, your choosen response for each question. You may write on this form. One page
Section Random Variables and Histograms
 Section 3.1 - Random Variables and Histograms Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
Section 3.1 - Random Variables and Histograms Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
Chapter 7. Confidence Intervals and Sample Sizes. Definition. Definition. Definition. Definition. Confidence Interval : CI. Point Estimate.
 Chapter 7 Confidence Intervals and Sample Sizes 7. Estimating a Proportion p 7.3 Estimating a Mean µ (σ known) 7.4 Estimating a Mean µ (σ unknown) 7.5 Estimating a Standard Deviation σ In a recent poll,
Chapter 7 Confidence Intervals and Sample Sizes 7. Estimating a Proportion p 7.3 Estimating a Mean µ (σ known) 7.4 Estimating a Mean µ (σ unknown) 7.5 Estimating a Standard Deviation σ In a recent poll,
3/28/18. Estimation. Focus Points. Focus Points. Estimating p in the Binomial Distribution. Estimating p in the Binomial Distribution. Section 7.
 Which side of a cheetah has the most spots? Estimation The outside. 7 Section 7.3 Estimating p in the Binomial Distribution Boy, I m tired. I ve been up since the quack of dawn. Focus Points Compute the
Which side of a cheetah has the most spots? Estimation The outside. 7 Section 7.3 Estimating p in the Binomial Distribution Boy, I m tired. I ve been up since the quack of dawn. Focus Points Compute the
Chapter 6 Test Practice Questions
 Probability and Statistics - Mrs. Leahy Name Chapter 6 Test Practice Questions Provide an appropriate response. 1) For a sample of 20 IQ scores the mean score is 105.8. The standard deviation,, is 15.
Probability and Statistics - Mrs. Leahy Name Chapter 6 Test Practice Questions Provide an appropriate response. 1) For a sample of 20 IQ scores the mean score is 105.8. The standard deviation,, is 15.
1. State Sales Tax. 2. Baggage Check
 1. State Sales Tax A survey asks a random sample of 1500 adults in Ohio if they support an increase in the state sales tax from 5% to 6% with the additional revenue going to education. If 40% of all adults
1. State Sales Tax A survey asks a random sample of 1500 adults in Ohio if they support an increase in the state sales tax from 5% to 6% with the additional revenue going to education. If 40% of all adults
CHAPTER 6 Random Variables
 CHAPTER 6 Random Variables 6.3 Binomial and Geometric Random Variables The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Binomial and Geometric Random
CHAPTER 6 Random Variables 6.3 Binomial and Geometric Random Variables The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Binomial and Geometric Random
BIOL The Normal Distribution and the Central Limit Theorem
 BIOL 300 - The Normal Distribution and the Central Limit Theorem In the first week of the course, we introduced a few measures of center and spread, and discussed how the mean and standard deviation are
BIOL 300 - The Normal Distribution and the Central Limit Theorem In the first week of the course, we introduced a few measures of center and spread, and discussed how the mean and standard deviation are
Lecture 7 Random Variables
 Lecture 7 Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a variable whose value is a numerical outcome of a random phenomenon, so its values are determined by chance. We shall use letters such as X
Lecture 7 Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a variable whose value is a numerical outcome of a random phenomenon, so its values are determined by chance. We shall use letters such as X
MATHEMATICS FRIDAY 23 MAY 2008 ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE 4732/01. Probability & Statistics 1. Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
 ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE 4732/01 MATHEMATICS Probability & Statistics 1 FRIDAY 23 MAY 2008 Additional materials (enclosed): Additional materials (required): Answer Booklet (8 pages) List of Formulae (MF1)
ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE 4732/01 MATHEMATICS Probability & Statistics 1 FRIDAY 23 MAY 2008 Additional materials (enclosed): Additional materials (required): Answer Booklet (8 pages) List of Formulae (MF1)
Chapter Chapter 6. Modeling Random Events: The Normal and Binomial Models
 Chapter 6 107 Chapter 6 Modeling Random Events: The Normal and Binomial Models Chapter 6 108 Chapter 6 109 Table Number: Group Name: Group Members: Discrete Probability Distribution: Ichiro s Hit Parade
Chapter 6 107 Chapter 6 Modeling Random Events: The Normal and Binomial Models Chapter 6 108 Chapter 6 109 Table Number: Group Name: Group Members: Discrete Probability Distribution: Ichiro s Hit Parade
Math 160 Professor Busken Chapter 5 Worksheets
 Math 160 Professor Busken Chapter 5 Worksheets Name: 1. Find the expected value. Suppose you play a Pick 4 Lotto where you pay 50 to select a sequence of four digits, such as 2118. If you select the same
Math 160 Professor Busken Chapter 5 Worksheets Name: 1. Find the expected value. Suppose you play a Pick 4 Lotto where you pay 50 to select a sequence of four digits, such as 2118. If you select the same
Section 6.3 Binomial and Geometric Random Variables
 Section 6.3 Binomial and Geometric Random Variables Mrs. Daniel AP Stats Binomial Settings A binomial setting arises when we perform several independent trials of the same chance process and record the
Section 6.3 Binomial and Geometric Random Variables Mrs. Daniel AP Stats Binomial Settings A binomial setting arises when we perform several independent trials of the same chance process and record the
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch. 8 Sampling Distributions 8.1 Distribution of the Sample Mean 1 Describe the distribution of the sample mean: normal population. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement
Ch. 8 Sampling Distributions 8.1 Distribution of the Sample Mean 1 Describe the distribution of the sample mean: normal population. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement
Introduction to Statistics I
 Introduction to Statistics I Keio University, Faculty of Economics Continuous random variables Simon Clinet (Keio University) Intro to Stats November 1, 2018 1 / 18 Definition (Continuous random variable)
Introduction to Statistics I Keio University, Faculty of Economics Continuous random variables Simon Clinet (Keio University) Intro to Stats November 1, 2018 1 / 18 Definition (Continuous random variable)
(j) Find the first quartile for a standard normal distribution.
 Examples for Chapter 5 Normal Probability Distributions Math 1040 1 Section 5.1 1. Heights of males at a certain university are approximately normal with a mean of 70.9 inches and a standard deviation
Examples for Chapter 5 Normal Probability Distributions Math 1040 1 Section 5.1 1. Heights of males at a certain university are approximately normal with a mean of 70.9 inches and a standard deviation
The Central Limit Theorem (Solutions) COR1-GB.1305 Statistics and Data Analysis
 The Central Limit Theorem (Solutions) COR1-GB1305 Statistics and Data Analysis 1 You draw a random sample of size n = 64 from a population with mean µ = 50 and standard deviation σ = 16 From this, you
The Central Limit Theorem (Solutions) COR1-GB1305 Statistics and Data Analysis 1 You draw a random sample of size n = 64 from a population with mean µ = 50 and standard deviation σ = 16 From this, you
2.) What is the set of outcomes that describes the event that at least one of the items selected is defective? {AD, DA, DD}
 Math 361 Practice Exam 2 (Use this information for questions 1 3) At the end of a production run manufacturing rubber gaskets, items are sampled at random and inspected to determine if the item is Acceptable
Math 361 Practice Exam 2 (Use this information for questions 1 3) At the end of a production run manufacturing rubber gaskets, items are sampled at random and inspected to determine if the item is Acceptable
Density curves. (James Madison University) February 4, / 20
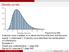 Density curves Figure 6.2 p 230. A density curve is always on or above the horizontal axis, and has area exactly 1 underneath it. A density curve describes the overall pattern of a distribution. Example
Density curves Figure 6.2 p 230. A density curve is always on or above the horizontal axis, and has area exactly 1 underneath it. A density curve describes the overall pattern of a distribution. Example
Sampling Distributions For Counts and Proportions
 Sampling Distributions For Counts and Proportions IPS Chapter 5.1 2009 W. H. Freeman and Company Objectives (IPS Chapter 5.1) Sampling distributions for counts and proportions Binomial distributions for
Sampling Distributions For Counts and Proportions IPS Chapter 5.1 2009 W. H. Freeman and Company Objectives (IPS Chapter 5.1) Sampling distributions for counts and proportions Binomial distributions for
Math 1070 Sample Exam 2 Spring 2015
 University of Connecticut Department of Mathematics Math 1070 Sample Exam 2 Spring 2015 Name: Instructor Name: Section: Exam 2 will cover Sections 4.6-4.7, 5.3-5.4, 6.1-6.4, and F.1-F.4. This sample exam
University of Connecticut Department of Mathematics Math 1070 Sample Exam 2 Spring 2015 Name: Instructor Name: Section: Exam 2 will cover Sections 4.6-4.7, 5.3-5.4, 6.1-6.4, and F.1-F.4. This sample exam
The "bell-shaped" curve, or normal curve, is a probability distribution that describes many real-life situations.
 6.1 6.2 The Standard Normal Curve The "bell-shaped" curve, or normal curve, is a probability distribution that describes many real-life situations. Basic Properties 1. The total area under the curve is.
6.1 6.2 The Standard Normal Curve The "bell-shaped" curve, or normal curve, is a probability distribution that describes many real-life situations. Basic Properties 1. The total area under the curve is.
Final Exam Practice Set, STT 315, Section 106
 Final Exam Practice Set, STT 315, Section 106 Options in BOLD are correct choices.: Question 1. Refer following sentences: I. If you flip a FAIR coin many, many times; the proportion of heads will be approximately
Final Exam Practice Set, STT 315, Section 106 Options in BOLD are correct choices.: Question 1. Refer following sentences: I. If you flip a FAIR coin many, many times; the proportion of heads will be approximately
Normal distribution. We say that a random variable X follows the normal distribution if the probability density function of X is given by
 Normal distribution The normal distribution is the most important distribution. It describes well the distribution of random variables that arise in practice, such as the heights or weights of people,
Normal distribution The normal distribution is the most important distribution. It describes well the distribution of random variables that arise in practice, such as the heights or weights of people,
Section Distributions of Random Variables
 Section 8.1 - Distributions of Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
Section 8.1 - Distributions of Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
5.1 Mean, Median, & Mode
 5.1 Mean, Median, & Mode definitions Mean: Median: Mode: Example 1 The Blue Jays score these amounts of runs in their last 9 games: 4, 7, 2, 4, 10, 5, 6, 7, 7 Find the mean, median, and mode: Example 2
5.1 Mean, Median, & Mode definitions Mean: Median: Mode: Example 1 The Blue Jays score these amounts of runs in their last 9 games: 4, 7, 2, 4, 10, 5, 6, 7, 7 Find the mean, median, and mode: Example 2
MATH 227 CP 6 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 MATH 227 CP 6 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Identify the given random variable as being discrete or continuous. 1) The number of phone
MATH 227 CP 6 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Identify the given random variable as being discrete or continuous. 1) The number of phone
AMS7: WEEK 4. CLASS 3
 AMS7: WEEK 4. CLASS 3 Sampling distributions and estimators. Central Limit Theorem Normal Approximation to the Binomial Distribution Friday April 24th, 2015 Sampling distributions and estimators REMEMBER:
AMS7: WEEK 4. CLASS 3 Sampling distributions and estimators. Central Limit Theorem Normal Approximation to the Binomial Distribution Friday April 24th, 2015 Sampling distributions and estimators REMEMBER:
Math 2311 Bekki George Office Hours: MW 11am to 12:45pm in 639 PGH Online Thursdays 4-5:30pm And by appointment
 Math 2311 Bekki George bekki@math.uh.edu Office Hours: MW 11am to 12:45pm in 639 PGH Online Thursdays 4-5:30pm And by appointment Class webpage: http://www.math.uh.edu/~bekki/math2311.html Math 2311 Class
Math 2311 Bekki George bekki@math.uh.edu Office Hours: MW 11am to 12:45pm in 639 PGH Online Thursdays 4-5:30pm And by appointment Class webpage: http://www.math.uh.edu/~bekki/math2311.html Math 2311 Class
Section 7.5 The Normal Distribution. Section 7.6 Application of the Normal Distribution
 Section 7.6 Application of the Normal Distribution A random variable that may take on infinitely many values is called a continuous random variable. A continuous probability distribution is defined by
Section 7.6 Application of the Normal Distribution A random variable that may take on infinitely many values is called a continuous random variable. A continuous probability distribution is defined by
Honors Statistics. Daily Agenda
 Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM Daily Agenda Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Write a program to generate random numbers. I've decided to give them free will. A Skip 4, 12, 16 Apr 25-10:55 AM Toss 4 times Suppose you
Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM Daily Agenda Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Write a program to generate random numbers. I've decided to give them free will. A Skip 4, 12, 16 Apr 25-10:55 AM Toss 4 times Suppose you
Lesson 9: Comparing Estimated Probabilities to Probabilities Predicted by a Model
 Lesson 9: Comparing Estimated Probabilities to Probabilities Predicted by a Student Outcomes Students compare estimated probabilities to those predicted by a probability model. Classwork This lesson continues
Lesson 9: Comparing Estimated Probabilities to Probabilities Predicted by a Student Outcomes Students compare estimated probabilities to those predicted by a probability model. Classwork This lesson continues
Data Analysis and Statistical Methods Statistics 651
 Review of previous lecture: Why confidence intervals? Data Analysis and Statistical Methods Statistics 651 http://www.stat.tamu.edu/~suhasini/teaching.html Suhasini Subba Rao Suppose you want to know the
Review of previous lecture: Why confidence intervals? Data Analysis and Statistical Methods Statistics 651 http://www.stat.tamu.edu/~suhasini/teaching.html Suhasini Subba Rao Suppose you want to know the
Chapter 8. Variables. Copyright 2004 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
 Chapter 8 Random Variables Copyright 2004 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. 8.1 What is a Random Variable? Random Variable: assigns a number to each outcome of a random circumstance, or,
Chapter 8 Random Variables Copyright 2004 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. 8.1 What is a Random Variable? Random Variable: assigns a number to each outcome of a random circumstance, or,
Engineering Statistics ECIV 2305
 Engineering Statistics ECIV 2305 Section 5.3 Approximating Distributions with the Normal Distribution Introduction A very useful property of the normal distribution is that it provides good approximations
Engineering Statistics ECIV 2305 Section 5.3 Approximating Distributions with the Normal Distribution Introduction A very useful property of the normal distribution is that it provides good approximations
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name The bar graph shows the number of tickets sold each week by the garden club for their annual flower show. ) During which week was the most number of tickets sold? ) A) Week B) Week C) Week 5
Exam Name The bar graph shows the number of tickets sold each week by the garden club for their annual flower show. ) During which week was the most number of tickets sold? ) A) Week B) Week C) Week 5
Section 5 3 The Mean and Standard Deviation of a Binomial Distribution!
 Section 5 3 The Mean and Standard Deviation of a Binomial Distribution! Previous sections required that you to find the Mean and Standard Deviation of a Binomial Distribution by using the values from a
Section 5 3 The Mean and Standard Deviation of a Binomial Distribution! Previous sections required that you to find the Mean and Standard Deviation of a Binomial Distribution by using the values from a
Name PID Section # (enrolled)
 STT 315 - Lecture 3 Instructor: Aylin ALIN 04/02/2014 Midterm # 2 A Name PID Section # (enrolled) * The exam is closed book and 80 minutes. * You may use a calculator and the formula sheet that you brought
STT 315 - Lecture 3 Instructor: Aylin ALIN 04/02/2014 Midterm # 2 A Name PID Section # (enrolled) * The exam is closed book and 80 minutes. * You may use a calculator and the formula sheet that you brought
Exercises for Chapter (5)
 Exercises for Chapter (5) MULTILE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) 500 families were interviewed and the number of children per family was
Exercises for Chapter (5) MULTILE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) 500 families were interviewed and the number of children per family was
Determine whether the given events are disjoint. 1) Drawing a face card from a deck of cards and drawing a deuce A) Yes B) No
 Assignment 8.-8.6 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine whether the given events are disjoint. 1) Drawing a face card from
Assignment 8.-8.6 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine whether the given events are disjoint. 1) Drawing a face card from
Example - Let X be the number of boys in a 4 child family. Find the probability distribution table:
 Chapter7 Probability Distributions and Statistics Distributions of Random Variables tthe value of the result of the probability experiment is a RANDOM VARIABLE. Example - Let X be the number of boys in
Chapter7 Probability Distributions and Statistics Distributions of Random Variables tthe value of the result of the probability experiment is a RANDOM VARIABLE. Example - Let X be the number of boys in
Chapter 6 Section 1 Day s.notebook. April 29, Honors Statistics. Aug 23-8:26 PM. 3. Review OTL C6#2. Aug 23-8:31 PM
 Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM 3. Review OTL C6#2 Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Apr 27-9:20 AM Jan 18-2:13 PM 2 Nov 27-10:28 PM 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 6.9 6.10 6.11 6.12 Nov 27-9:53 PM 3 Ask about 1 and
Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM 3. Review OTL C6#2 Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Apr 27-9:20 AM Jan 18-2:13 PM 2 Nov 27-10:28 PM 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 6.9 6.10 6.11 6.12 Nov 27-9:53 PM 3 Ask about 1 and
Confidence Intervals: Review
 University of Utah February 28, 2018 1 2 Law of Large Numbers Draw your samples from any population with finite mean µ. Then LLN says Law of Large Numbers Draw your samples from any population with finite
University of Utah February 28, 2018 1 2 Law of Large Numbers Draw your samples from any population with finite mean µ. Then LLN says Law of Large Numbers Draw your samples from any population with finite
Honors Statistics. Aug 23-8:26 PM. 1. Collect folders and materials. 2. Continue Binomial Probability. 3. Review OTL C6#11 homework
 Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM 1. Collect folders and materials 2. Continue Binomial Probability 3. Review OTL C6#11 homework 4. Binomial mean and standard deviation 5. Past Homework discussion 6. Return
Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM 1. Collect folders and materials 2. Continue Binomial Probability 3. Review OTL C6#11 homework 4. Binomial mean and standard deviation 5. Past Homework discussion 6. Return
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A population has a standard deviation σ = 20.2. How large a sample must be drawn so that
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A population has a standard deviation σ = 20.2. How large a sample must be drawn so that
Example 1: Find the equation of the line containing points (1,2) and (2,3).
 Example 1: Find the equation of the line containing points (1,2) and (2,3). Example 2: The Ace Company installed a new machine in one of its factories at a cost of $20,000. The machine is depreciated linearly
Example 1: Find the equation of the line containing points (1,2) and (2,3). Example 2: The Ace Company installed a new machine in one of its factories at a cost of $20,000. The machine is depreciated linearly
Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel 7 th Edition
 Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel 7 th Edition Chapter 7 Sampling Distributions Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel 7e Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Chap 7-1 Learning Objectives
Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel 7 th Edition Chapter 7 Sampling Distributions Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel 7e Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Chap 7-1 Learning Objectives
Chapter 8 Estimation
 Chapter 8 Estimation There are two important forms of statistical inference: estimation (Confidence Intervals) Hypothesis Testing Statistical Inference drawing conclusions about populations based on samples
Chapter 8 Estimation There are two important forms of statistical inference: estimation (Confidence Intervals) Hypothesis Testing Statistical Inference drawing conclusions about populations based on samples
