Probability Distributions
|
|
|
- Brook Hunter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Economics 91 Spring 2010 Linus Yamane Pitzer College Probability Distributions 1. Assuming that the conditions of a Bernoulli process are met, determine the following: a. A test is administered 10 times and the probability of getting the correct answer is Use an appropriate formula to figure out the likelihood of getting precisely 9 correct answers. b. What is the probability of having exactly 3 boys in a family of 10 children (assuming that boys and girls are equally likely and different births are independent events.).3874, Small businesses are going bankrupt at a rate of 9.7 per month. What is the probability of at least 3 going bankrupt next month? of exactly 24 businesses going bankrupt?.9964, The length life of a computer component is an exponential random variable with a mean of 7 years. If the warranty period if 5 years, what proportion of the components can the manufacturer expect to replace under the warranty? What should the warranty period be if the manufacturer doesn't want to be bothered with having to replace more than 10 percent of the components?.510, College Board scores are normally distributed with standard deviation of 100 points for both left- and right-handed students. However, the mean math score for left-handed students is 525 whereas it is 500 for right-handed students. In the population as a whole, 10 percent of all students are left-handed. What proportion of right-handed students score over 700? What proportion of left-handed students score over 700? What fraction of students with math scores over 700 are left-handed?.0228,.0401, In the verbal ability scores on the GRE were approximately normally distributed with a mean of 480 and a standard deviation of 120. Approximately 35% of the students who took this test had scores below what value? Approximately 10% of the students had scores above what value? 433.8, The weight of medium-sized tomatoes selected at random from a bin at the local supermarket is a random variable with a mean μ = 10 ounces and a standard deviation σ = 2 ounces. Suppose we pick four tomatoes at random from the bin and put them in a bag. The weight of the bag is a random variable. What is the mean and the standard deviation of the weight of the bag? What is the probability that the bag will weigh less than 38 ounces? 40, 4, Suppose the heights of Americans, measured in inches, has a mean of 68 inches and a variance of 9. What would be the mean and variance of American heights if we measured them in centimeters? Remember that an inch is equal to 2.54 centimeters ,
2 8. Suppose that in the land of Sigma income Y has a mean of 200 and a standard deviation of 50 and that taxes T has a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 20. If the covariance of Y and T is 500, what is the standard deviation and variance of disposable income Yd = Y T? 43.59, The following table shows the joint distribution of two random variables X and Y. Y X a. What is the mean of X? mean of Y? b. What is the variance of X? variance of Y? c. What is the covariance of X and Y? d. What is the correlation coefficient? 0.7, 3.5, 0.21, 5.25, 0.55, A food processing company markets a successful line of canned soups. The firm knows the output of its can filling machine is normally distributed and can be programmed to any mean fill setting the company desires. The firm also knows the standard deviation of its production process is 0.05 ounces. What mean fill setting should the firm choose so that 95 percent of the cans its produces will contain at most 12 ounces of soup? Let F be a random variable measuring the Fahrenheit temperature in Nowhere, New Hampshire at noon during the month of March. Exhaustive National Weather Service records indicate that the mean and the variance of F are μ = 25 and The Celsius temperature is 5 given by C ( F 32). What is the mean and the standard deviation of the random variable C? , Grove stock has a mean rate of return of 5% and a variance of 64. Motley stock has a mean rate of return of 15% and a variance of 200. The correlation coefficient of the returns on Grove stock and Motley stock is Suppose we hold a portfolio which is 40% Grove stock and 60% Motley stock. What is the expected rate of return on the portfolio? What is the variance on the rate of return on the portfolio? 11%, Biologists and ecologists record the distribution of measurements made on animal species to help study the distribution and evolution of animals. The African finch Pyrenestes ostrinus is interesting because the distribution of its bill size has two peaks even though other body measurements follow normal distributions. For example, a study in Cameroon found that the wing length of male finches varies according to a normal distribution with a mean 61.2 mm and standard deviation 1.8 mm. a. What proportion of male finches have wings longer than 65 mm? b. What is the wing length that only 2% of male finches exceed? ,
3 14. An investor has $1,000 to invest and two investment opportunities, each requiring a minimum of $500. The profit per $100 from the first can be represented by a random variable X which is equal to $-5 with probability 0.40 and $20 with probability The profit per $100 from the second is given by the random variable Y which is equal to $0 with probability 0.60 and $25 with probability Both X and Y have an expected value of $10 and are independent. What is the variance in her profit if she invests $1,000 in the first investment? What is the variance in her profit if she invests $1,000 in the second investment? What is the variance in her profit if she invests $500 in the first and $500 in the second? 15. A market researcher conducts a survey to examine the effectiveness of advertising for a soft drink. She finds that 15% of people both saw the advertising and purchased the soft drink. Also, 45% of all people saw the advertising, and 20% of all people purchased the soft drink. Define a pair of random variables as follows: 1saw the advertising X 0 otherwise 1 purchased the soft drink Y 0 otherwise Find and interpret the covariance between X and Y. 16. a. Why is the Central Limit Theorem important? b. If X has a normal distribution with mean and variance 2 n, then what random variable has a N(0,1) distribution? c. If X is distributed N(0,1) and Y is distributed 2 n, then what random variable has a Student t distribution? How many degrees of freedom does it have? d. Why does X have a Student t distribution? S x n 17. Mensa is an organization whose members possess IQs in the top 2% of the population. To qualify, you must have an IQ greater than 133. If IQs are normally distributed with a mean of 100, what is the standard deviation and variance of IQs? 18. Suppose that your messages arrive randomly at an average rate of 4 per hour or 1 every 15 minutes. a. Using the poisson distribution, find the probability that exactly 2 messages will arrive during a specific 1 hour period. b. Using the exponential distribution, find the probability that the next message will not arrive within 30 minutes. 19. If you pay me $1, I will let you play the following gambling game. You drop your pencil point into the middle of a table of random numbers and look at the digit on which it lands. If it is a 7, you win $5. If it is a 1, you win $2.
4 Otherwise, you win nothing. Find the expected value of the amount you win in one play of this game. Explain in simple language what the expected value tells you about your winnings if you play the game many times. Is it your advantage to pay $1 to play? 20. Weights of newborn children in the United States vary according to the normal distribution with a mean 7.5 pounds and standard deviation of 1.25 pounds. The government classifies a newborn as having low birth weight if the weight is less than 5.5 pounds. a. What is the probability that a baby chosen at random weighs less than 5.5 pounds at birth? b. You choose 3 babies at random. What is the probability that their average birth weight is less than 5.5 pounds? 21. About 22% of the residents of California were born outside the United States. You choose a simple random sample of 1,000 California residents for a sample survey on immigration issues. You want to find the probability that 250 or more of the people in your sample were born outside the United States. What is this probability? 22. A community organization plans to ask 100 randomly selected individuals whether they favor a change in the zoning laws. You argue for a sample of 900 individuals instead of 100. You argue that the standard deviation of the proportion ˆ of the sample who say yes will be much smaller. How much smaller will it be? 23. The NASDAQ Composite Index describes the average price of common stock traded over the counter, that is, not on one of the stock exchanges. In 1991 the mean capitalization of the companies in the NASDAQ was $80 million and the median capitalization was $20 million. (A company s capitalization is the total market value of its stock.) Explain why the mean capitalization is much higher than the median. What does this tell you about the skewness of the distribution? 24. The length of human pregnancies from conception to birth varies according to a distribution that is approximately normal with a mean of 266 days and standard deviation of 16 days. a. What percent of pregnancies last less than 240 days (that s about 8 months)? b. What percent of pregnancies last between 240 and 270 days (roughly between 8 and 9 months)? c. How long do the longest 20% of pregnancies last? 25. The rate of return on stock indexes (which combine many individual stocks) is approximately normal. Since 1945, the Standard and Poor s 500 index has had a mean yearly return of about 12%, with a standard deviation of about 16.5%. Take this normal distribution to be the distribution of yearly returns over a long period. a. In what range do the middle 95% of all yearly returns lie? b. The market is down for the year if the return on the index is less than zero. In what percent of years is the market down? c. In what percent of years does the index gain 25% or more?
5 26. The Gallup Poll once found that about 15% of adults jog. Suppose that in fact the proportion of the adult population who job is p = What is the probability that the sample proportion of joggers in a simple random sample of size n = 200 lies between 14% and 17%? Use a normal approximation. 27. Suppose that 20 year old men have a life expectancy of 78 years with a standard deviation of 9 years. If an insurance company writes policies for 50 men, what is the probability that the average age of death for the policy holders will be less than 77 years? What if the company writes policies for 100 men? 28 Suppose we are concerned with the variability of the number of raisins in a box of raisin bran. Assume that the number of raisins is distributed normally. If a random sample of 16 boxes is taken, what is the probability that the sample variance will be more than twice the population variance? 29. Thelma and Louise play the following game: Thelma starts off with one cent and Louise with two cents. Thelma and Louise simultaneously flip one coin each. If both coins fall on the same side, Louise gives Thelma one cent. If the coins fall on different sides, Thelma gives Louise once cent. The game continues until either Thelma or Louise has all three coins. Write down the probability distribution of X where X is the number of flips required to end the game. 30. An investor is considering two mutual funds, the Slow and Steady (SS) Fund and the High Roller (HR) Fund. Based on past performance, the following probabilities are assigned to the possible percentage rates of return: SS Fund HR Fund return probability return probability Calculate the means and the standard deviations of these two funds. 31. The correlation coefficient between two random variables X and Y is = It is given that X = 1, 2 or 3 with equal probability and Y = -1, -2 or -3 with equal probability. Calculate the covariance of X and Y. 32. The accompanying table shows, for credit card holders with one to three credit cards, the joint probabilities for the number of cards owned (X) and the number of credit card purchases made in a week (Y). # of Cards # Purchases Y X
6 Are the number of cards owned and the number of purchases independent? Illustrate or explain why. 33. Let X be the number of between-meal snacks a student eats in a day and let Y be the number of exams she has the next day. Suppose the following is the joint probability distribution of X and Y. Y: exams X: snacks a. What is the expected value of X? of Y? b. What is the variance of X? of Y? c. What is the covariance of X and Y? d. What is the correlation coefficient? e. Are X and Y independent here? Why? f. Suppose we define a misery index Z = 3Y - 2X. What is the expected value of Z? What is the variance of Z? 34. For any two random variables X and Y, what is the relationship between the variance of (X- Y) and the variance of (Y-X)? Why would you expect this? 35. A medical clinic tests blood for a sexually transmitted disease, syphilis, which afflicts 1 out of every 100 persons. Up to now they have been testing each blood sample individually. But since each test is rather expensive, you have suggested that they pool about 50 blood samples together. If the pooled sample tests negative, then they can clear all 50 people with one test. If the pooled sample tests positive, then they have to test all 50 samples individually and run a total of 51 tests. a. What is the probability that all 50 people in a sample are healthy? b. What is the probability that at least one person in the sample has syphilis? c. What is the expected number of tests they will have to run? d. What is the variance of the number of tests they will have to run? 36. A college basketball player, who sinks 75% of his free throws, comes to the line to shoot a one and one (if the first shot is successful, he is allowed a second shot, but no second shot is take if the first is missed; one point is scored for each successful shot). Assume that the outcome of the second shot, if any, is independent of that of the first. Find the expected number of points resulting from the one and one. Compare this with the expected number of points from a twoshot foul, where a second shot is allowed irrespective of the outcome of the first. 37. Suppose that 80% of people actually pay their parking tickets, and that the parking tickets are for $30. If campus security issues 15 tickets, how much revenue can they expect to collect? 20 tickets? 25 tickets? What is the probability that they will generate $450 or more if they issue 15 tickets? 20 tickets? 25 tickets?
7 38. Records indicate that on average, 3.8 breakdowns per day occur on L.A. freeways during the morning rush hour. Assume that the distribution is Poisson. a. Find the probability that on any given day, there will be fewer than two breakdowns on the freeways during the morning rush hour. b. Find the probability that on any given day, there will be more than three breakdowns on the freeways during the morning rush hour. 39. Let the random variable Z follow a standard normal distribution with a mean 0 and variance 2 1. a. Find P(Z < 0.75) b. Find P(Z > -1.25) c. Find P(-0.33 < Z < 0.66) d. Find P(-0.80 < Z < -0.25) 40 An investment will be worth $1000, $2000, or $5000 at the end of the year. The probabilities of these values are 0.25, 0.60, and 0.15 respectively. Determine the mean and the variance of the value of this investment. 41.The Bates Motel has 5 rooms. Its experience has been that 20% of the people who make reservations never show up. How many no-shows can be expected if this motel accepts reservations for 5 rooms? for 8 rooms? for 10 rooms? What is the probability that there will not be enough rooms for those who do show up if this motel accepts reservations for 5 rooms? for 8 rooms? for 10 rooms? 42. The Beardstown Ladies wish to invest $1,000 in common stock. They are considering two stocks, Holden stock and Sanborn stock. They both have a normal distribution of returns, as follows: Holden stock N($1100, 1600) Sanborn stock N($1140, 2500). The Ladies only want to select one of the two stocks. Obviously Sanborn stock has a higher expected return, but it is also more risky in the sense that the variance of Sanborn s return is greater than that of Holden. The Beardstown Ladies want to choose the stock that has the smaller probability of returning less than $1000. Which stock should they choose? 43. A normal random variable has a standard deviation = 10. If there is a probability of that the random variable will take on a value less than 100, what is the probability that it will take on a value greater than 110? You should first find the mean of X. 44. A random variable has a 2 distribution with 8 degrees of freedom. What is the probability that the random variable will be between 13.4 and 17.5? Explain your work. 45. Assume W is a random variable with a t-distribution. Find the following probabilities. a. P[0 W 6.31] when W has 1 degree of freedom b. P[-2.02 W 3.36] when W has 5 degree of freedom c. P[-1.30 W 1.30] when W has 40 degrees of freedom d. P[-1.96 W 1.96] when W has degrees of freedom Make sure you show your work.
8 46. Let be distributed F(5,10) and let be distributed F(10,5). Which of the following probabilities is smaller, P[ 3.3 ] or P[ 3.3 ]? Explain. 47. An investment portfolio contains stocks from a large number of corporations. Over the past year 14% of the corporations had a rate of return over 20%, and 4.5% had a rate of return which was negative. Assuming that these rates of return have a normal distribution, what is the mean, variance, and standard deviation of these rates of return? 48. A professor sees students during regular office hours. The time spent with students follows an exponential distribution with a mean of 10 minutes. a. Find the probability that a given student spends less than 20 minutes with the professor. b. Find the probability that a given student spends between 10 and 15 minutes with the professor. 49. Harry and David only accept pears which weigh at least 12 ounces. Their pears have weights which are normally distributed with a mean of 15 ounces. If they reject 12% of their pears, what is the standard deviation and variance of the pear weights? 50. A use car dealer has numerous Toyota Corollas on the lot. The average age of the cars is 2.1 years with a variance of If she prices the used cars using the following formula, Price = 18,947 1,788Age What will be the average price of the cars and the variance of the price? 51. Suppose that X and Y have the following joint probability distribution. Y X What is the covariance of X and Y? What is the correlation coefficient of X and Y? Are X and Y independent here? Explain. 2 ( n 1) s 52. Why does 2 beginning with the definition of a similar. have a 2 n 1 distribution? Do not prove this. Just tell me a story 2 n distribution and how the above expression looks very 53. The Cincinnati Enquirer reported that the mean number of hours worked per week by those employed full-time is The article further indicated that about one third of those employed full-time work less than 40 hours per week. Assuming the number of hours worked is normally distributed, what is the standard deviation of the number of hours worked? 54. A true-false test consists of 50 questions. How many questions does a student have to get right to convince you that he is not merely guessing. Explain.
9 55. About 8% of males are colorblind. A researcher needs some colorblind subjects for an experiment, and begins checking potential subjects. a. on average, how many men should the researcher expect to check to find one who is colorblind? b. what s the probability that she won t find anyone colorblind among the first 4 men she checks? c. what s the probability that the first colorblind man found will be the sixth person checked? d. what s the probability that she finds someone who is colorblind before checking the tenth man? 56. Suppose that the amount of beer in a 12 ounce can has a normal distribution with a mean of 12 ounces and a standard deviation of 1.5 ounces. a. What is the probability that a randomly selected bottle of beer will contain more than 14.5 ounces of beer? b. What is the probability that a randomly selected bottle of beer will contain between 9 and 11 ounces of beer? 57. Suppose the weekly hours X of investment bankers is distributed as follows: X ~ N(90,144). The investment club interviews 25 investment bankers and asks them their hours last week. What is the probability that the sample s mean is greater than 91 but less than 93? 58. Suppose that X is a random variable distributed as follows: X N(150,625). A sample of 25 observations is taken. What is the probability that the sample's mean is greater than 140 but less than 147.5? 59. Suppose X is a random variable distributed as follows: X N(200,400). A sample is drawn from an infinite population, and the following probability concerning the sample mean holds: P( X ) 0.25 What is the sample size? 60. Suppose X N(, 2 ), where = 0 and 2 = 81. Calculate the probability P(X 3) if X is the average of a sample of size n and n is alternatively 9, 64, 81 and Suppose that the number of hours of sleep an American gets is a normally distributed random variable with mean = 8 hours. If for a random sample of size 25 Americans P( X 8.4) what is the variance of the number of hours of sleep an American gets? 62. The number of hours preschool children spend watching television every week is normally distributed with a standard deviation of 10 hours. A random sample of 4 children was taken in order to estimate the mean number of hours. What is the probability that the sample mean will exceed the population mean by more than 2 hours? What if we increase our sample to 8 children?
10 63. The number of students who actually come to lecture is normally distributed with a standard deviation of 3.6. A random sample of 4 lectures is taken. What is the probability that the sample variance is bigger than 30? 64. Suppose that the life expectancy of an 18-year-old woman is 80.3 years with a standard deviation of 7.5 years. If a life insurance company writes policies for year-old women, what is the probability that their average policy-holder will die before the age of 79.5 years? after the age of 81? 65. Suppose the number of quarts of ice cream consumed annually by an American has a standard deviation of 8 quarts. We select a random sample of 6 Americans in order to estimate the mean number of quarts consumed by all Americans. What is the probability that the sample mean will fall short of the population mean by more than 2 quarts? What if we increase our sample to 9 Americans? 66. Thanksgiving turkey weights are normally distributed with a mean of weight of 15.6 pounds and a standard deviation of 4 pounds. A random sample of 5 turkeys is taken. What is the probability that the sample variance is bigger than 25? 67. Bunge Inc claims that on average there is one defect per 200,000 feet of bunge cord, and the number of defects follows a Poisson distribution. You purchase 100,000 feet of bunge cord for your Bunge Jumping Club. a. Find the probability that your bunge cord has zero defects. b. Find the probability that your bunge cord has more than 2 defects. 68. Suppose the average age for a person getting married for the first time is 26 years, and that 15% of people get married before the age of 20. If the ages for first marriage are normally distributed, what is the standard deviation and variance of the ages for first marriage? 69. About 25% of the drivers who are members of the Teamsters Union earn over $18.68 an hour, and about 10% of these drivers earn less than $14.25 an hour. Assuming that these wages have a normal distribution, what is the mean, variance and standard deviation of these wages?
AP Statistics Section 6.1 Day 1 Multiple Choice Practice. a) a random variable. b) a parameter. c) biased. d) a random sample. e) a statistic.
 A Statistics Section 6.1 Day 1 ultiple Choice ractice Name: 1. A variable whose value is a numerical outcome of a random phenomenon is called a) a random variable. b) a parameter. c) biased. d) a random
A Statistics Section 6.1 Day 1 ultiple Choice ractice Name: 1. A variable whose value is a numerical outcome of a random phenomenon is called a) a random variable. b) a parameter. c) biased. d) a random
STT 315 Practice Problems Chapter 3.7 and 4
 STT 315 Practice Problems Chapter 3.7 and 4 Answer the question True or False. 1) The number of children in a family can be modelled using a continuous random variable. 2) For any continuous probability
STT 315 Practice Problems Chapter 3.7 and 4 Answer the question True or False. 1) The number of children in a family can be modelled using a continuous random variable. 2) For any continuous probability
X P(X=x) E(X)= V(X)= S.D(X)= X P(X=x) E(X)= V(X)= S.D(X)=
 1. X 0 1 2 P(X=x) 0.2 0.4 0.4 E(X)= V(X)= S.D(X)= X 100 200 300 400 P(X=x) 0.1 0.2 0.5 0.2 E(X)= V(X)= S.D(X)= 2. A day trader buys an option on a stock that will return a $100 profit if the stock goes
1. X 0 1 2 P(X=x) 0.2 0.4 0.4 E(X)= V(X)= S.D(X)= X 100 200 300 400 P(X=x) 0.1 0.2 0.5 0.2 E(X)= V(X)= S.D(X)= 2. A day trader buys an option on a stock that will return a $100 profit if the stock goes
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name The bar graph shows the number of tickets sold each week by the garden club for their annual flower show. ) During which week was the most number of tickets sold? ) A) Week B) Week C) Week 5
Exam Name The bar graph shows the number of tickets sold each week by the garden club for their annual flower show. ) During which week was the most number of tickets sold? ) A) Week B) Week C) Week 5
Exam II Math 1342 Capters 3-5 HCCS. Name
 Exam II Math 1342 Capters 3-5 HCCS Name Date Provide an appropriate response. 1) A single six-sided die is rolled. Find the probability of rolling a number less than 3. A) 0.5 B) 0.1 C) 0.25 D 0.333 1)
Exam II Math 1342 Capters 3-5 HCCS Name Date Provide an appropriate response. 1) A single six-sided die is rolled. Find the probability of rolling a number less than 3. A) 0.5 B) 0.1 C) 0.25 D 0.333 1)
and µ Asian male > " men
 A.P. Statistics Sampling Distributions and the Central Limit Theorem Definitions A parameter is a number that describes the population. A parameter always exists but in practice we rarely know its value
A.P. Statistics Sampling Distributions and the Central Limit Theorem Definitions A parameter is a number that describes the population. A parameter always exists but in practice we rarely know its value
Example. Chapter 8 Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables
 Chapter 8 Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables You are dealt a hand of 5 cards. Find the probability distribution table for the number of hearts. Graph
Chapter 8 Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables You are dealt a hand of 5 cards. Find the probability distribution table for the number of hearts. Graph
STUDY SET 1. Discrete Probability Distributions. x P(x) and x = 6.
 STUDY SET 1 Discrete Probability Distributions 1. Consider the following probability distribution function. Compute the mean and standard deviation of. x 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 P(x) 0.05 0.16 0.19 0.24 0.18 0.11
STUDY SET 1 Discrete Probability Distributions 1. Consider the following probability distribution function. Compute the mean and standard deviation of. x 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 P(x) 0.05 0.16 0.19 0.24 0.18 0.11
Name PID Section # (enrolled)
 STT 315 - Lecture 3 Instructor: Aylin ALIN 04/02/2014 Midterm # 2 A Name PID Section # (enrolled) * The exam is closed book and 80 minutes. * You may use a calculator and the formula sheet that you brought
STT 315 - Lecture 3 Instructor: Aylin ALIN 04/02/2014 Midterm # 2 A Name PID Section # (enrolled) * The exam is closed book and 80 minutes. * You may use a calculator and the formula sheet that you brought
Name Period AP Statistics Unit 5 Review
 Name Period AP Statistics Unit 5 Review Multiple Choice 1. Jay Olshansky from the University of Chicago was quoted in Chance News as arguing that for the average life expectancy to reach 100, 18% of people
Name Period AP Statistics Unit 5 Review Multiple Choice 1. Jay Olshansky from the University of Chicago was quoted in Chance News as arguing that for the average life expectancy to reach 100, 18% of people
PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS
 CHAPTER 3 PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Page Contents 3.1 Introduction to Probability Distributions 51 3.2 The Normal Distribution 56 3.3 The Binomial Distribution 60 3.4 The Poisson Distribution 64 Exercise
CHAPTER 3 PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Page Contents 3.1 Introduction to Probability Distributions 51 3.2 The Normal Distribution 56 3.3 The Binomial Distribution 60 3.4 The Poisson Distribution 64 Exercise
STAT 1220 FALL 2010 Common Final Exam December 10, 2010
 STAT 1220 FALL 2010 Common Final Exam December 10, 2010 PLEASE PRINT THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION: Name: Instructor: Student ID #: Section/Time: THIS EXAM HAS TWO PARTS. PART I. Part I consists of 30 multiple
STAT 1220 FALL 2010 Common Final Exam December 10, 2010 PLEASE PRINT THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION: Name: Instructor: Student ID #: Section/Time: THIS EXAM HAS TWO PARTS. PART I. Part I consists of 30 multiple
Example - Let X be the number of boys in a 4 child family. Find the probability distribution table:
 Chapter8 Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables tthe value of the result of the probability experiment is a RANDOM VARIABLE. Example - Let X be the number
Chapter8 Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables tthe value of the result of the probability experiment is a RANDOM VARIABLE. Example - Let X be the number
Example - Let X be the number of boys in a 4 child family. Find the probability distribution table:
 Chapter7 Probability Distributions and Statistics Distributions of Random Variables tthe value of the result of the probability experiment is a RANDOM VARIABLE. Example - Let X be the number of boys in
Chapter7 Probability Distributions and Statistics Distributions of Random Variables tthe value of the result of the probability experiment is a RANDOM VARIABLE. Example - Let X be the number of boys in
3. The n observations are independent. Knowing the result of one observation tells you nothing about the other observations.
 Binomial and Geometric Distributions - Terms and Formulas Binomial Experiments - experiments having all four conditions: 1. Each observation falls into one of two categories we call them success or failure.
Binomial and Geometric Distributions - Terms and Formulas Binomial Experiments - experiments having all four conditions: 1. Each observation falls into one of two categories we call them success or failure.
Chapter 8. Variables. Copyright 2004 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
 Chapter 8 Random Variables Copyright 2004 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. 8.1 What is a Random Variable? Random Variable: assigns a number to each outcome of a random circumstance, or,
Chapter 8 Random Variables Copyright 2004 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. 8.1 What is a Random Variable? Random Variable: assigns a number to each outcome of a random circumstance, or,
3. The n observations are independent. Knowing the result of one observation tells you nothing about the other observations.
 Binomial and Geometric Distributions - Terms and Formulas Binomial Experiments - experiments having all four conditions: 1. Each observation falls into one of two categories we call them success or failure.
Binomial and Geometric Distributions - Terms and Formulas Binomial Experiments - experiments having all four conditions: 1. Each observation falls into one of two categories we call them success or failure.
What is the probability of success? Failure? How could we do this simulation using a random number table?
 Probability Ch.4, sections 4.2 & 4.3 Binomial and Geometric Distributions Name: Date: Pd: 4.2. What is a binomial distribution? How do we find the probability of success? Suppose you have three daughters.
Probability Ch.4, sections 4.2 & 4.3 Binomial and Geometric Distributions Name: Date: Pd: 4.2. What is a binomial distribution? How do we find the probability of success? Suppose you have three daughters.
MATH CALCULUS & STATISTICS/BUSN - PRACTICE EXAM #2 - SUMMER DR. DAVID BRIDGE
 MATH 2053 - CALCULUS & STATISTICS/BUSN - PRACTICE EXAM #2 - SUMMER 2007 - DR. DAVID BRIDGE MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the
MATH 2053 - CALCULUS & STATISTICS/BUSN - PRACTICE EXAM #2 - SUMMER 2007 - DR. DAVID BRIDGE MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the
Density curves. (James Madison University) February 4, / 20
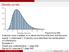 Density curves Figure 6.2 p 230. A density curve is always on or above the horizontal axis, and has area exactly 1 underneath it. A density curve describes the overall pattern of a distribution. Example
Density curves Figure 6.2 p 230. A density curve is always on or above the horizontal axis, and has area exactly 1 underneath it. A density curve describes the overall pattern of a distribution. Example
Normal distribution. We say that a random variable X follows the normal distribution if the probability density function of X is given by
 Normal distribution The normal distribution is the most important distribution. It describes well the distribution of random variables that arise in practice, such as the heights or weights of people,
Normal distribution The normal distribution is the most important distribution. It describes well the distribution of random variables that arise in practice, such as the heights or weights of people,
work to get full credit.
 Chapter 18 Review Name Date Period Write complete answers, using complete sentences where necessary.show your work to get full credit. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the
Chapter 18 Review Name Date Period Write complete answers, using complete sentences where necessary.show your work to get full credit. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the
Honors Statistics. 3. Review OTL C6#3. 4. Normal Curve Quiz. Chapter 6 Section 2 Day s Notes.notebook. May 02, 2016.
 Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM 3. Review OTL C6#3 4. Normal Curve Quiz Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 May 1-9:09 PM Apr 28-10:29 AM 2 27, 28, 29, 30 Nov 21-8:16 PM Working out Choose a person aged 19 to 25 years at
Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM 3. Review OTL C6#3 4. Normal Curve Quiz Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 May 1-9:09 PM Apr 28-10:29 AM 2 27, 28, 29, 30 Nov 21-8:16 PM Working out Choose a person aged 19 to 25 years at
Math Week in Review #10. Experiments with two outcomes ( success and failure ) are called Bernoulli or binomial trials.
 Math 141 Spring 2006 c Heather Ramsey Page 1 Section 8.4 - Binomial Distribution Math 141 - Week in Review #10 Experiments with two outcomes ( success and failure ) are called Bernoulli or binomial trials.
Math 141 Spring 2006 c Heather Ramsey Page 1 Section 8.4 - Binomial Distribution Math 141 - Week in Review #10 Experiments with two outcomes ( success and failure ) are called Bernoulli or binomial trials.
(j) Find the first quartile for a standard normal distribution.
 Examples for Chapter 5 Normal Probability Distributions Math 1040 1 Section 5.1 1. Heights of males at a certain university are approximately normal with a mean of 70.9 inches and a standard deviation
Examples for Chapter 5 Normal Probability Distributions Math 1040 1 Section 5.1 1. Heights of males at a certain university are approximately normal with a mean of 70.9 inches and a standard deviation
University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics. Normal distribution
 University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics Statistics 110A Instructor: Nicolas Christou Normal distribution The normal distribution is the most important distribution. It describes
University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics Statistics 110A Instructor: Nicolas Christou Normal distribution The normal distribution is the most important distribution. It describes
Math 227 (Statistics) Chapter 6 Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Math 227 (Statistics) Chapter 6 Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Using the following uniform density curve, answer the
Math 227 (Statistics) Chapter 6 Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Using the following uniform density curve, answer the
Honors Statistics. Daily Agenda
 Honors Statistics Daily Agenda 1. Review OTL C6#5 2. Quiz Section 6.1 A-Skip 35, 39, 40 Crickets The length in inches of a cricket chosen at random from a field is a random variable X with mean 1.2 inches
Honors Statistics Daily Agenda 1. Review OTL C6#5 2. Quiz Section 6.1 A-Skip 35, 39, 40 Crickets The length in inches of a cricket chosen at random from a field is a random variable X with mean 1.2 inches
Lecture 7 Random Variables
 Lecture 7 Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a variable whose value is a numerical outcome of a random phenomenon, so its values are determined by chance. We shall use letters such as X
Lecture 7 Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a variable whose value is a numerical outcome of a random phenomenon, so its values are determined by chance. We shall use letters such as X
Record on a ScanTron, your choosen response for each question. You may write on this form. One page of notes and a calculator are allowed.
 Ch 16, 17 Math 240 Exam 4 v1 Good SAMPLE No Book, Yes 1 Page Notes, Yes Calculator, 120 Minutes Dressler Record on a ScanTron, your choosen response for each question. You may write on this form. One page
Ch 16, 17 Math 240 Exam 4 v1 Good SAMPLE No Book, Yes 1 Page Notes, Yes Calculator, 120 Minutes Dressler Record on a ScanTron, your choosen response for each question. You may write on this form. One page
Section M Discrete Probability Distribution
 Section M Discrete Probability Distribution A random variable is a numerical measure of the outcome of a probability experiment, so its value is determined by chance. Random variables are typically denoted
Section M Discrete Probability Distribution A random variable is a numerical measure of the outcome of a probability experiment, so its value is determined by chance. Random variables are typically denoted
EDCC charges $50 per credit. Let T = tuition charge for a randomly-selected fulltime student. T = 50X. Tuit. T $600 $650 $700 $750 $800 $850 $900
 Chapter 7 Random Variables n 7.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables n 6.2 n Example: El Dorado Community College El Dorado Community College considers a student to be full-time if he or she is taking
Chapter 7 Random Variables n 7.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables n 6.2 n Example: El Dorado Community College El Dorado Community College considers a student to be full-time if he or she is taking
Chapter 4 and Chapter 5 Test Review Worksheet
 Name: Date: Hour: Chapter 4 and Chapter 5 Test Review Worksheet You must shade all provided graphs, you must round all z-scores to 2 places after the decimal, you must round all probabilities to at least
Name: Date: Hour: Chapter 4 and Chapter 5 Test Review Worksheet You must shade all provided graphs, you must round all z-scores to 2 places after the decimal, you must round all probabilities to at least
Binomial Random Variable - The count X of successes in a binomial setting
 6.3.1 Binomial Settings and Binomial Random Variables What do the following scenarios have in common? Toss a coin 5 times. Count the number of heads. Spin a roulette wheel 8 times. Record how many times
6.3.1 Binomial Settings and Binomial Random Variables What do the following scenarios have in common? Toss a coin 5 times. Count the number of heads. Spin a roulette wheel 8 times. Record how many times
Chapter 9 & 10. Multiple Choice.
 Chapter 9 & 10 Review Name Multiple Choice. 1. An agricultural researcher plants 25 plots with a new variety of corn. The average yield for these plots is X = 150 bushels per acre. Assume that the yield
Chapter 9 & 10 Review Name Multiple Choice. 1. An agricultural researcher plants 25 plots with a new variety of corn. The average yield for these plots is X = 150 bushels per acre. Assume that the yield
5.1 Personal Probability
 5. Probability Value Page 1 5.1 Personal Probability Although we think probability is something that is confined to math class, in the form of personal probability it is something we use to make decisions
5. Probability Value Page 1 5.1 Personal Probability Although we think probability is something that is confined to math class, in the form of personal probability it is something we use to make decisions
Section Distributions of Random Variables
 Section 8.1 - Distributions of Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
Section 8.1 - Distributions of Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
8.1 Binomial Distributions
 8.1 Binomial Distributions The Binomial Setting The 4 Conditions of a Binomial Setting: 1.Each observation falls into 1 of 2 categories ( success or fail ) 2 2.There is a fixed # n of observations. 3.All
8.1 Binomial Distributions The Binomial Setting The 4 Conditions of a Binomial Setting: 1.Each observation falls into 1 of 2 categories ( success or fail ) 2 2.There is a fixed # n of observations. 3.All
Chapter Six Probability Distributions
 6.1 Probability Distributions Discrete Random Variable Chapter Six Probability Distributions x P(x) 2 0.08 4 0.13 6 0.25 8 0.31 10 0.16 12 0.01 Practice. Construct a probability distribution for the number
6.1 Probability Distributions Discrete Random Variable Chapter Six Probability Distributions x P(x) 2 0.08 4 0.13 6 0.25 8 0.31 10 0.16 12 0.01 Practice. Construct a probability distribution for the number
Math 227 Practice Test 2 Sec Name
 Math 227 Practice Test 2 Sec 4.4-6.2 Name Find the indicated probability. ) A bin contains 64 light bulbs of which 0 are defective. If 5 light bulbs are randomly selected from the bin with replacement,
Math 227 Practice Test 2 Sec 4.4-6.2 Name Find the indicated probability. ) A bin contains 64 light bulbs of which 0 are defective. If 5 light bulbs are randomly selected from the bin with replacement,
Chapter 6 Section Review day s.notebook. May 11, Honors Statistics. Aug 23-8:26 PM. 3. Review team test.
 Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM 3. Review team test Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Nov 27-10:28 PM 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 6.9 6.10 6.11 6.12 Nov 27-9:53 PM 2 May 8-7:44 PM May 1-9:09 PM 3 Dec 1-2:08 PM Sep
Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM 3. Review team test Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Nov 27-10:28 PM 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 6.9 6.10 6.11 6.12 Nov 27-9:53 PM 2 May 8-7:44 PM May 1-9:09 PM 3 Dec 1-2:08 PM Sep
LECTURE 6 DISTRIBUTIONS
 LECTURE 6 DISTRIBUTIONS OVERVIEW Uniform Distribution Normal Distribution Random Variables Continuous Distributions MOST OF THE SLIDES ADOPTED FROM OPENINTRO STATS BOOK. NORMAL DISTRIBUTION Unimodal and
LECTURE 6 DISTRIBUTIONS OVERVIEW Uniform Distribution Normal Distribution Random Variables Continuous Distributions MOST OF THE SLIDES ADOPTED FROM OPENINTRO STATS BOOK. NORMAL DISTRIBUTION Unimodal and
Review Problems for MAT141 Final Exam
 Review Problems for MAT141 Final Exam The following problems will help you prepare for the final exam. Answers to all problems are at the end of the review packet. 1. Find the area and perimeter of the
Review Problems for MAT141 Final Exam The following problems will help you prepare for the final exam. Answers to all problems are at the end of the review packet. 1. Find the area and perimeter of the
Exercise Questions: Chapter What is wrong? Explain what is wrong in each of the following scenarios.
 5.9 What is wrong? Explain what is wrong in each of the following scenarios. (a) If you toss a fair coin three times and a head appears each time, then the next toss is more likely to be a tail than a
5.9 What is wrong? Explain what is wrong in each of the following scenarios. (a) If you toss a fair coin three times and a head appears each time, then the next toss is more likely to be a tail than a
Stat 201: Business Statistics I Additional Exercises on Chapter Chapter 3
 Stat 201: Business Statistics I Additional Exercises on Chapter Chapter 3 Student Name: Solve the problem. 1) A sociologist recently conducted a survey of senior citizens who have net worths too high to
Stat 201: Business Statistics I Additional Exercises on Chapter Chapter 3 Student Name: Solve the problem. 1) A sociologist recently conducted a survey of senior citizens who have net worths too high to
MATH 118 Class Notes For Chapter 5 By: Maan Omran
 MATH 118 Class Notes For Chapter 5 By: Maan Omran Section 5.1 Central Tendency Mode: the number or numbers that occur most often. Median: the number at the midpoint of a ranked data. Ex1: The test scores
MATH 118 Class Notes For Chapter 5 By: Maan Omran Section 5.1 Central Tendency Mode: the number or numbers that occur most often. Median: the number at the midpoint of a ranked data. Ex1: The test scores
In a binomial experiment of n trials, where p = probability of success and q = probability of failure. mean variance standard deviation
 Name In a binomial experiment of n trials, where p = probability of success and q = probability of failure mean variance standard deviation µ = n p σ = n p q σ = n p q Notation X ~ B(n, p) The probability
Name In a binomial experiment of n trials, where p = probability of success and q = probability of failure mean variance standard deviation µ = n p σ = n p q σ = n p q Notation X ~ B(n, p) The probability
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find a z-score satisfying the given condition. 1) 20.1% of the total area is to the right
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find a z-score satisfying the given condition. 1) 20.1% of the total area is to the right
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch. 8 Sampling Distributions 8.1 Distribution of the Sample Mean 1 Describe the distribution of the sample mean: normal population. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement
Ch. 8 Sampling Distributions 8.1 Distribution of the Sample Mean 1 Describe the distribution of the sample mean: normal population. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 First Name: Last Name: SID: Class Time: M Tu W Th math10 - HW3 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Continuous random variables are
First Name: Last Name: SID: Class Time: M Tu W Th math10 - HW3 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Continuous random variables are
Edexcel Statistics 1 Normal Distribution Edited by: K V Kumaran
 Edexcel Statistics 1 Normal Distribution Edited by: K V Kumaran kumarmaths.weebly.com 1 kumarmaths.weebly.com 2 kumarmaths.weebly.com 3 kumarmaths.weebly.com 4 kumarmaths.weebly.com 5 kumarmaths.weebly.com
Edexcel Statistics 1 Normal Distribution Edited by: K V Kumaran kumarmaths.weebly.com 1 kumarmaths.weebly.com 2 kumarmaths.weebly.com 3 kumarmaths.weebly.com 4 kumarmaths.weebly.com 5 kumarmaths.weebly.com
BIOL The Normal Distribution and the Central Limit Theorem
 BIOL 300 - The Normal Distribution and the Central Limit Theorem In the first week of the course, we introduced a few measures of center and spread, and discussed how the mean and standard deviation are
BIOL 300 - The Normal Distribution and the Central Limit Theorem In the first week of the course, we introduced a few measures of center and spread, and discussed how the mean and standard deviation are
The "bell-shaped" curve, or normal curve, is a probability distribution that describes many real-life situations.
 6.1 6.2 The Standard Normal Curve The "bell-shaped" curve, or normal curve, is a probability distribution that describes many real-life situations. Basic Properties 1. The total area under the curve is.
6.1 6.2 The Standard Normal Curve The "bell-shaped" curve, or normal curve, is a probability distribution that describes many real-life situations. Basic Properties 1. The total area under the curve is.
1. State Sales Tax. 2. Baggage Check
 1. State Sales Tax A survey asks a random sample of 1500 adults in Ohio if they support an increase in the state sales tax from 5% to 6% with the additional revenue going to education. If 40% of all adults
1. State Sales Tax A survey asks a random sample of 1500 adults in Ohio if they support an increase in the state sales tax from 5% to 6% with the additional revenue going to education. If 40% of all adults
ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists 2016/2017
 ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists 2016/2017 Topic The Normal Distribution Lecturer: Dr. Bernardin Senadza, Dept. of Economics bsenadza@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and
ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists 2016/2017 Topic The Normal Distribution Lecturer: Dr. Bernardin Senadza, Dept. of Economics bsenadza@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and
1. Steve says I have two children, one of which is a boy. Given this information, what is the probability that Steve has two boys?
 Chapters 6 8 Review 1. Steve says I have two children, one of which is a boy. Given this information, what is the probability that Steve has two boys? (A) 1 (B) 3 1 (C) 3 (D) 4 1 (E) None of the above..
Chapters 6 8 Review 1. Steve says I have two children, one of which is a boy. Given this information, what is the probability that Steve has two boys? (A) 1 (B) 3 1 (C) 3 (D) 4 1 (E) None of the above..
DO NOT POST THESE ANSWERS ONLINE BFW Publishers 2014
 Section 6.3 Check our Understanding, page 389: 1. Check the BINS: Binary? Success = get an ace. Failure = don t get an ace. Independent? Because you are replacing the card in the deck and shuffling each
Section 6.3 Check our Understanding, page 389: 1. Check the BINS: Binary? Success = get an ace. Failure = don t get an ace. Independent? Because you are replacing the card in the deck and shuffling each
Top Incorrect Problems
 What is the z-score for scores in the bottom 5%? a) -1.645 b) 1.645 c).4801 d) The score is not listed in the table. A professor grades 120 research papers and reports that the average score was an 80%.
What is the z-score for scores in the bottom 5%? a) -1.645 b) 1.645 c).4801 d) The score is not listed in the table. A professor grades 120 research papers and reports that the average score was an 80%.
Lecture 9. Probability Distributions. Outline. Outline
 Outline Lecture 9 Probability Distributions 6-1 Introduction 6- Probability Distributions 6-3 Mean, Variance, and Expectation 6-4 The Binomial Distribution Outline 7- Properties of the Normal Distribution
Outline Lecture 9 Probability Distributions 6-1 Introduction 6- Probability Distributions 6-3 Mean, Variance, and Expectation 6-4 The Binomial Distribution Outline 7- Properties of the Normal Distribution
2.) What is the set of outcomes that describes the event that at least one of the items selected is defective? {AD, DA, DD}
 Math 361 Practice Exam 2 (Use this information for questions 1 3) At the end of a production run manufacturing rubber gaskets, items are sampled at random and inspected to determine if the item is Acceptable
Math 361 Practice Exam 2 (Use this information for questions 1 3) At the end of a production run manufacturing rubber gaskets, items are sampled at random and inspected to determine if the item is Acceptable
Binomial formulas: The binomial coefficient is the number of ways of arranging k successes among n observations.
 Chapter 8 Notes Binomial and Geometric Distribution Often times we are interested in an event that has only two outcomes. For example, we may wish to know the outcome of a free throw shot (good or missed),
Chapter 8 Notes Binomial and Geometric Distribution Often times we are interested in an event that has only two outcomes. For example, we may wish to know the outcome of a free throw shot (good or missed),
Review for Final Exam Spring 2014 Jeremy Orloff and Jonathan Bloom
 Review for Final Exam 18.05 Spring 2014 Jeremy Orloff and Jonathan Bloom THANK YOU!!!! JON!! PETER!! RUTHI!! ERIKA!! ALL OF YOU!!!! Probability Counting Sets Inclusion-exclusion principle Rule of product
Review for Final Exam 18.05 Spring 2014 Jeremy Orloff and Jonathan Bloom THANK YOU!!!! JON!! PETER!! RUTHI!! ERIKA!! ALL OF YOU!!!! Probability Counting Sets Inclusion-exclusion principle Rule of product
STOR 155 Introductory Statistics (Chap 5) Lecture 14: Sampling Distributions for Counts and Proportions
 The UNIVERSITY of NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL STOR 155 Introductory Statistics (Chap 5) Lecture 14: Sampling Distributions for Counts and Proportions 5/31/11 Lecture 14 1 Statistic & Its Sampling Distribution
The UNIVERSITY of NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL STOR 155 Introductory Statistics (Chap 5) Lecture 14: Sampling Distributions for Counts and Proportions 5/31/11 Lecture 14 1 Statistic & Its Sampling Distribution
EXERCISES FOR PRACTICE SESSION 2 OF STAT CAMP
 EXERCISES FOR PRACTICE SESSION 2 OF STAT CAMP Note 1: The exercises below that are referenced by chapter number are taken or modified from the following open-source online textbook that was adapted by
EXERCISES FOR PRACTICE SESSION 2 OF STAT CAMP Note 1: The exercises below that are referenced by chapter number are taken or modified from the following open-source online textbook that was adapted by
Activity #17b: Central Limit Theorem #2. 1) Explain the Central Limit Theorem in your own words.
 Activity #17b: Central Limit Theorem #2 1) Explain the Central Limit Theorem in your own words. Importance of the CLT: You can standardize and use normal distribution tables to calculate probabilities
Activity #17b: Central Limit Theorem #2 1) Explain the Central Limit Theorem in your own words. Importance of the CLT: You can standardize and use normal distribution tables to calculate probabilities
Lecture 9. Probability Distributions
 Lecture 9 Probability Distributions Outline 6-1 Introduction 6-2 Probability Distributions 6-3 Mean, Variance, and Expectation 6-4 The Binomial Distribution Outline 7-2 Properties of the Normal Distribution
Lecture 9 Probability Distributions Outline 6-1 Introduction 6-2 Probability Distributions 6-3 Mean, Variance, and Expectation 6-4 The Binomial Distribution Outline 7-2 Properties of the Normal Distribution
Invitational Mathematics Competition. Statistics Individual Test
 Invitational Mathematics Competition Statistics Individual Test December 12, 2016 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. If you think that the correct answer is not present, then choose 'E' for none of the above. 1) What
Invitational Mathematics Competition Statistics Individual Test December 12, 2016 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. If you think that the correct answer is not present, then choose 'E' for none of the above. 1) What
Chapter 6: The Normal Distribution
 Chapter 6: The Normal Distribution Diana Pell Section 6.1: Normal Distributions Note: Recall that a continuous variable can assume all values between any two given values of the variables. Many continuous
Chapter 6: The Normal Distribution Diana Pell Section 6.1: Normal Distributions Note: Recall that a continuous variable can assume all values between any two given values of the variables. Many continuous
MATH 227 CP 6 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 MATH 227 CP 6 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Identify the given random variable as being discrete or continuous. 1) The number of phone
MATH 227 CP 6 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Identify the given random variable as being discrete or continuous. 1) The number of phone
 Homework Problems In each of the following situations, X is a count. Does X have a binomial distribution? Explain. 1. You observe the gender of the next 40 children born in a hospital. X is the number
Homework Problems In each of the following situations, X is a count. Does X have a binomial distribution? Explain. 1. You observe the gender of the next 40 children born in a hospital. X is the number
Chapter 6: Random Variables. Ch. 6-3: Binomial and Geometric Random Variables
 Chapter : Random Variables Ch. -3: Binomial and Geometric Random Variables X 0 2 3 4 5 7 8 9 0 0 P(X) 3???????? 4 4 When the same chance process is repeated several times, we are often interested in whether
Chapter : Random Variables Ch. -3: Binomial and Geometric Random Variables X 0 2 3 4 5 7 8 9 0 0 P(X) 3???????? 4 4 When the same chance process is repeated several times, we are often interested in whether
MATH1215: Mathematical Thinking Sec. 08 Spring Worksheet 9: Solution. x P(x)
 N. Name: MATH: Mathematical Thinking Sec. 08 Spring 0 Worksheet 9: Solution Problem Compute the expected value of this probability distribution: x 3 8 0 3 P(x) 0. 0.0 0.3 0. Clearly, a value is missing
N. Name: MATH: Mathematical Thinking Sec. 08 Spring 0 Worksheet 9: Solution Problem Compute the expected value of this probability distribution: x 3 8 0 3 P(x) 0. 0.0 0.3 0. Clearly, a value is missing
Sampling Distributions
 AP Statistics Ch. 7 Notes Sampling Distributions A major field of statistics is statistical inference, which is using information from a sample to draw conclusions about a wider population. Parameter:
AP Statistics Ch. 7 Notes Sampling Distributions A major field of statistics is statistical inference, which is using information from a sample to draw conclusions about a wider population. Parameter:
Chapter 7: Random Variables and Discrete Probability Distributions
 Chapter 7: Random Variables and Discrete Probability Distributions 7. Random Variables and Probability Distributions This section introduced the concept of a random variable, which assigns a numerical
Chapter 7: Random Variables and Discrete Probability Distributions 7. Random Variables and Probability Distributions This section introduced the concept of a random variable, which assigns a numerical
Problem Set 07 Discrete Random Variables
 Name Problem Set 07 Discrete Random Variables MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the mean of the random variable. 1) The random
Name Problem Set 07 Discrete Random Variables MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the mean of the random variable. 1) The random
Chapter 2. Section 2.1
 Chapter 2 Section 2.1 Check Your Understanding, page 89: 1. c 2. Her daughter weighs more than 87% of girls her age and she is taller than 67% of girls her age. 3. About 65% of calls lasted less than 30
Chapter 2 Section 2.1 Check Your Understanding, page 89: 1. c 2. Her daughter weighs more than 87% of girls her age and she is taller than 67% of girls her age. 3. About 65% of calls lasted less than 30
Honors Statistics. Daily Agenda
 Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM Daily Agenda 1. Review OTL C6#7 emphasis Normal Distributions Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 1. Multiple choice: Select the best answer for Exercises 65 and 66, which refer to the following
Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM Daily Agenda 1. Review OTL C6#7 emphasis Normal Distributions Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 1. Multiple choice: Select the best answer for Exercises 65 and 66, which refer to the following
Central Limit Theorem 11/08/2005
 Central Limit Theorem 11/08/2005 A More General Central Limit Theorem Theorem. Let X 1, X 2,..., X n,... be a sequence of independent discrete random variables, and let S n = X 1 + X 2 + + X n. For each
Central Limit Theorem 11/08/2005 A More General Central Limit Theorem Theorem. Let X 1, X 2,..., X n,... be a sequence of independent discrete random variables, and let S n = X 1 + X 2 + + X n. For each
AP Stats ~ Lesson 6B: Transforming and Combining Random variables
 AP Stats ~ Lesson 6B: Transforming and Combining Random variables OBJECTIVES: DESCRIBE the effects of transforming a random variable by adding or subtracting a constant and multiplying or dividing by a
AP Stats ~ Lesson 6B: Transforming and Combining Random variables OBJECTIVES: DESCRIBE the effects of transforming a random variable by adding or subtracting a constant and multiplying or dividing by a
Chapter 5. Sampling Distributions
 Lecture notes, Lang Wu, UBC 1 Chapter 5. Sampling Distributions 5.1. Introduction In statistical inference, we attempt to estimate an unknown population characteristic, such as the population mean, µ,
Lecture notes, Lang Wu, UBC 1 Chapter 5. Sampling Distributions 5.1. Introduction In statistical inference, we attempt to estimate an unknown population characteristic, such as the population mean, µ,
STAT Chapter 5: Continuous Distributions. Probability distributions are used a bit differently for continuous r.v. s than for discrete r.v. s.
 STAT 515 -- Chapter 5: Continuous Distributions Probability distributions are used a bit differently for continuous r.v. s than for discrete r.v. s. Continuous distributions typically are represented by
STAT 515 -- Chapter 5: Continuous Distributions Probability distributions are used a bit differently for continuous r.v. s than for discrete r.v. s. Continuous distributions typically are represented by
4.1 Probability Distributions
 Probability and Statistics Mrs. Leahy Chapter 4: Discrete Probability Distribution ALWAYS KEEP IN MIND: The Probability of an event is ALWAYS between: and!!!! 4.1 Probability Distributions Random Variables
Probability and Statistics Mrs. Leahy Chapter 4: Discrete Probability Distribution ALWAYS KEEP IN MIND: The Probability of an event is ALWAYS between: and!!!! 4.1 Probability Distributions Random Variables
STAT 201 Chapter 6. Distribution
 STAT 201 Chapter 6 Distribution 1 Random Variable We know variable Random Variable: a numerical measurement of the outcome of a random phenomena Capital letter refer to the random variable Lower case letters
STAT 201 Chapter 6 Distribution 1 Random Variable We know variable Random Variable: a numerical measurement of the outcome of a random phenomena Capital letter refer to the random variable Lower case letters
Survey Sampling, Fall, 2006, Columbia University Homework assignments (2 Sept 2006)
 Survey Sampling, Fall, 2006, Columbia University Homework assignments (2 Sept 2006) Assignment 1, due lecture 3 at the beginning of class 1. Lohr 1.1 2. Lohr 1.2 3. Lohr 1.3 4. Download data from the CBS
Survey Sampling, Fall, 2006, Columbia University Homework assignments (2 Sept 2006) Assignment 1, due lecture 3 at the beginning of class 1. Lohr 1.1 2. Lohr 1.2 3. Lohr 1.3 4. Download data from the CBS
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or Solve the problem. 1. Find forα=0.01. A. 1.96 B. 2.575 C. 1.645 D. 2.33 2.Whatistheconfidencelevelofthefolowingconfidenceintervalforμ?
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or Solve the problem. 1. Find forα=0.01. A. 1.96 B. 2.575 C. 1.645 D. 2.33 2.Whatistheconfidencelevelofthefolowingconfidenceintervalforμ?
Math 230 Exam 2 Name April 8, 1999
 Math 230 Exam 2 Name April 8, 1999 Instructions: Answer each question to the best of your ability. Most questions require that you give a concluding or summary statement. These statements should be complete
Math 230 Exam 2 Name April 8, 1999 Instructions: Answer each question to the best of your ability. Most questions require that you give a concluding or summary statement. These statements should be complete
STAT 3090 Test 2 - Version B Fall Student s Printed Name: PLEASE READ DIRECTIONS!!!!
 Student s Printed Name: Instructor: XID: Section #: Read each question very carefully. You are permitted to use a calculator on all portions of this exam. You are NOT allowed to use any textbook, notes,
Student s Printed Name: Instructor: XID: Section #: Read each question very carefully. You are permitted to use a calculator on all portions of this exam. You are NOT allowed to use any textbook, notes,
8.1 Estimation of the Mean and Proportion
 8.1 Estimation of the Mean and Proportion Statistical inference enables us to make judgments about a population on the basis of sample information. The mean, standard deviation, and proportions of a population
8.1 Estimation of the Mean and Proportion Statistical inference enables us to make judgments about a population on the basis of sample information. The mean, standard deviation, and proportions of a population
Probability and Probability Distributions Problems
 Probability and Probability Distributions Problems Q.1. Among male birds of a species, 20% have a particular gene. Among females of the species, 10% have the gene. The males comprise 40% of all the birds
Probability and Probability Distributions Problems Q.1. Among male birds of a species, 20% have a particular gene. Among females of the species, 10% have the gene. The males comprise 40% of all the birds
Please show work for all calculated answers. Show work in a neat and organized manner.
 Math 083 Review for Final Exam Name Please show work for all calculated answers. Show work in a neat and organized manner. 1) Using the frequency table for a monthly budget, find all of the relative frequencies
Math 083 Review for Final Exam Name Please show work for all calculated answers. Show work in a neat and organized manner. 1) Using the frequency table for a monthly budget, find all of the relative frequencies
Chapter 6: The Normal Distribution
 Chapter 6: The Normal Distribution Diana Pell Section 6.1: Normal Distributions Note: Recall that a continuous variable can assume all values between any two given values of the variables. Many continuous
Chapter 6: The Normal Distribution Diana Pell Section 6.1: Normal Distributions Note: Recall that a continuous variable can assume all values between any two given values of the variables. Many continuous
Math 160 Professor Busken Chapter 5 Worksheets
 Math 160 Professor Busken Chapter 5 Worksheets Name: 1. Find the expected value. Suppose you play a Pick 4 Lotto where you pay 50 to select a sequence of four digits, such as 2118. If you select the same
Math 160 Professor Busken Chapter 5 Worksheets Name: 1. Find the expected value. Suppose you play a Pick 4 Lotto where you pay 50 to select a sequence of four digits, such as 2118. If you select the same
Stat 333 Lab Assignment #2
 1 Stat 333 Lab Assignment #2 1. A consumer organization estimates that over a 1-year period 17% of cars will need to be repaired once, 7% will need repairs twice, and 4% will require three or more repairs.
1 Stat 333 Lab Assignment #2 1. A consumer organization estimates that over a 1-year period 17% of cars will need to be repaired once, 7% will need repairs twice, and 4% will require three or more repairs.
NORMAL RANDOM VARIABLES (Normal or gaussian distribution)
 NORMAL RANDOM VARIABLES (Normal or gaussian distribution) Many variables, as pregnancy lengths, foot sizes etc.. exhibit a normal distribution. The shape of the distribution is a symmetric bell shape.
NORMAL RANDOM VARIABLES (Normal or gaussian distribution) Many variables, as pregnancy lengths, foot sizes etc.. exhibit a normal distribution. The shape of the distribution is a symmetric bell shape.
FINAL REVIEW W/ANSWERS
 FINAL REVIEW W/ANSWERS ( 03/15/08 - Sharon Coates) Concepts to review before answering the questions: A population consists of the entire group of people or objects of interest to an investigator, while
FINAL REVIEW W/ANSWERS ( 03/15/08 - Sharon Coates) Concepts to review before answering the questions: A population consists of the entire group of people or objects of interest to an investigator, while
ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists
 ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists Session 7 The Normal Distribution Part 1 Lecturer: Dr. Bernardin Senadza, Dept. of Economics Contact Information: bsenadza@ug.edu.gh College of Education
ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists Session 7 The Normal Distribution Part 1 Lecturer: Dr. Bernardin Senadza, Dept. of Economics Contact Information: bsenadza@ug.edu.gh College of Education
Exercise Questions. Q7. The random variable X is known to be uniformly distributed between 10 and
 Exercise Questions This exercise set only covers some topics discussed after the midterm. It does not mean that the problems in the final will be similar to these. Neither solutions nor answers will be
Exercise Questions This exercise set only covers some topics discussed after the midterm. It does not mean that the problems in the final will be similar to these. Neither solutions nor answers will be
Chapter 4 Discrete Random variables
 Chapter 4 Discrete Random variables A is a variable that assumes numerical values associated with the random outcomes of an experiment, where only one numerical value is assigned to each sample point.
Chapter 4 Discrete Random variables A is a variable that assumes numerical values associated with the random outcomes of an experiment, where only one numerical value is assigned to each sample point.
STAT243 LS: Intro to Probability and Statistics Final Exam, Mar 20, 2017 KEY
 STAT243 LS: Intro to Probability and Statistics Final Exam, Mar 20, 2017 KEY This is a 110-min exam. Students may use a page of note (front and back), and a calculator, but nothing else is allowed. 1.
STAT243 LS: Intro to Probability and Statistics Final Exam, Mar 20, 2017 KEY This is a 110-min exam. Students may use a page of note (front and back), and a calculator, but nothing else is allowed. 1.
Stat 210 Exam Two. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Stat 210 Exam Two Read these directions carefully. Take your time and check your work. Many students do not take enough time on their tests. Each problem is worth four points. You may choose exactly question
Stat 210 Exam Two Read these directions carefully. Take your time and check your work. Many students do not take enough time on their tests. Each problem is worth four points. You may choose exactly question
