Stat 333 Lab Assignment #2
|
|
|
- Douglas Burns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Stat 333 Lab Assignment #2 1. A consumer organization estimates that over a 1-year period 17% of cars will need to be repaired once, 7% will need repairs twice, and 4% will require three or more repairs. (a) What is the probability that a car chosen at random will need (1) no repairs? (.72) (2) No more than one repair? (.89) (3) Some repairs? (.28) (b) If you own two cars, what is the probability that (1) neither will need repair? (.5184) (2) Both will need repair? (.0784) 2. There s a meeting that is attended by 10 doctors and 5 psychologists. If a committee of 3 is selected at random, find the probability that at least 1 psychologist is selected for the committee. (.7363) 3. Does advertising influence buying? A random sample of 500 people were asked whether they bought a new product and whether they saw an advertisement for that product before the purchase. 280 in the sample did not purchase the product. 225 people did not see the advertisement for the product. 175 people saw the advertisement and purchased the product. One person is selected at random from the sample. (a) Find the probability that the person purchases the product (.44) (b) Find the probability that they did not see the advertisement and did not purchase the product. (.36) (c) Find the probability that they purchased the product or saw the advertisement. (.64) (d) Find the probability that given they saw the advertisement, they then purchase the product. (.6364) (e) Does advertisement affect the probability that a person buys the product? Explain using probability. Interpret results 4. A meeting is held with 10 individuals. If each person shakes hands with another person only once, how many handshakes occurred at the meeting? Note: you only shake hands with each person once. (45) 5. The failure rate of a heart attack alarm is For improved safety, a duplicate alarm is installed. If alarms work independently of one another, (a) What is the probability that a heart attack will not be signaled? ( ) (b) What is the probability that at least one of them does not detect a heart attack? ( ) 6. Police report that 78% of drives stopped on suspicion of drunk driving are given a breath test, 36% a blood test, and 22% both test. What is the probability that a randomly selected DWI suspect is given (a) a test? (.92) (b) A blood test or a breath test, but not both? (.7) (c) Neither? (.08) 7. You play tow games against the same opponent. The probability you win the first game is 0.4. If you win the first game, the probability you also win the second is 0.2. If you lose the first game, the probability that you win the second is 0.3 (a) Are the two games independent? Explain your answer using probabilities. (b) What s the probability you lose both games? (.42) (c) What s the probability you win both games? (.08) (d) Let the random variable X be the number of games you win. Find the probability distribution for X (e) What are the expected number and standard deviation for the number of games won? (µ =.66, σ =.62) 8. A consumer organization inspecting new wheelchairs, found that many had defects. While none had more than three defects, 7% had three, 11% two, and 21% one defect. Find the expected number of defects in a new wheelchair, and the standard deviation. (µ =.64, σ =.9330) Do more questions on probability and probability distributions from the text book for review.
2 2 Binomial Distribution 1. The probability that a person who undergoes a kidney operation will recover is 0.6. Find the probability that of 5 patients who undergo similar operations, (a) none will recover (b) one will recover (c) not more that one will recover (d) not more that two (e) at least 3 will recover MINITAB Instructions for Binomial From the MENU BAR select Calc>Probability Distributions>Binomial A dialog box will then appear. (i) If a single probability is needed as in part (a) and (b) of the example: Select Probability from the options listed (click on circle) In the box by Number of Trials, type 5 In Probability of Successes, type 0.6 In Input Constant, specify the x value from the question (0 for part (a), 1 for part (b)). Click OK or hit enter. (a) P(x=0)= (b) P(x=1) = (ii) When a sum of probabilities is involved, as in part (c), begin in the same way except this time select Cumulative Probabilities instead of Probability. In Input Constant, specify the x value from the question (1 for part (c), 2 for part (d)). Click OK or hit enter (c) P(x 1) = from MINITAB note: if you added by hand from above P(x 1) =P(x=0)+P(x=1) = = (d) P(x 2) = (iii) This method for (ii) could also be used for part (e), but the required probabilities would have to be expresses in terms of the cumulative probability and the complement. (e) P(x 3) = 1 P(x 2) Find the P(x 2) from the computer and then subtract this value from 1. P(x 2) = (from MINITAB) P(x 3) = 1 P(x 2) = = Assume that 13% of people are left-handed. If we select 5 people at random, find the probability of each outcome described below. (a) there are exactly 3 lefties in the group (.0179) (b) there are no more than 3 lefties in the group (.9987) (c) How many lefties do you expect? (µ =.65) (d) With what standard deviation? (σ =.7520) 3. A wildlife biologist examines frogs for a genetic trait he suspects may be linked to sensitivity to industrial toxins in the environment. Previous research had established that this trait is usually found in one of every 8 frogs. He collects and examines a dozen frogs. If the frequency of the trait has not changed, what s the probability he finds the trait in (a) none of the frogs? (b) at least 2 frogs? (c) 3 or 4 frogs? (d) No more than 4 frogs? (e) 6 frogs? If he actually observes 6 frogs with this trait, should he suspect that the frequency of the trait has changed? 4. About 8% of males are colorblind. A researcher needs some colorblind subjects for an experiment, and begins checking potential subject. If 100 men are randomly selected, (a) What s the probability that she won t find at least 6 that are colorblind? (0.1799) (b) Find the expected number and standard deviation for the number of colorblind men. (µ = 8, σ = )
3 3 MINITAB INSTRUCTIONS CALC Probability Distributions normal. Finding the area above and below a Z-value under the Standard Normal Curve For a given Z-value, you are required to find a probability. In the dialog box, which corresponds to the Normal distribution, you have three choices: Probability Cumulative probability Inverse cumulative probability Click Cumulative probability. This will calculate the cumulative probability associated with a specific Z- value (or the area under the Standard Normal Curve to the left of a specific Z-value.) The middle of the dialog box has 2 options: Mean Standard Deviation The default values for the Mean and Standard Deviation are 0 and 1, respectively. There is no need to change these values, so just leave these as is. In the bottom portion of the dialog box, select Input constant. It is in this box that you enter a specific Z- value. Once you have completed this, either press return or click on OK. In the upper portion of your screen, or the command module, MINITAB will return the area to the left of the Z-value you have entered. Note that when this routine is employed, the probability returned is ALWAYS THE AREA TO THE LEFT OF the Z-value entered above or P(Z<z) For practice, try question 1 using this routine. NOTE: Answers may vary due to rounding and whether or not you use the computer or tables. 1. Given that Z is a standard normal random variable, compute the following probabilities: (a) P(-0.72 Z 0) (.2642) (b) P(-0.35 Z 0.35) (.2736) (c) P(0.22 Z 1.87) (.3822) (d) P(Z -1.02) (.1539) (e) P(Z -0.88) (.8106) (f) P( Z 1.38) (.0838) (g) P(-0.34 Z 2.33) (.6232) Finding a Z-value for a given area (or probability under the Standard Normal Curve) For a given probability, you are required to find a Z-value that corresponds to this probability. This requires the use of the Inverse cumulative probability routine in the dialog box employed above. Click on the circle which corresponds to Inverse cumulative probability and just as was done previously, do not touch the box labeled Mean and Standard Deviation. This routine needs an area, and will subsequently find the Z-value which matches up with the area entered. Just as was done above, move your mouse down to the bottom portion of the dialog box and click on the circle which corresponds to Input constant. Previously you entered a Z-value here. But now you want to find a Z-value for a given area, or probability. So the number you will enter in the Input constant box is a probability, or an area to the left of the Z-value in question. Once you have entered the correct probability,
4 4 either press return or click on OK. MINITAB will return a Z-value in the command module on the upper portion of your screen. A good rule-of-thumb in these types of problems is to draw your standard normal curve and piece together the areas given. The Z-value will be given when you specify the area to the left of that value. Practice this routine on question Given that Z is a standard normal random variable, determine Zo if it is known that: (a) P(-Zo Z Zo) = 0.90 (1.645) (b) P(-Zo Z Zo) = 0.10 (.1257) (c) P( Z Zo) = 0.20 (.842) (d) P(-1.66 Z Zo) = 0.25 (-.529) (e) P( Z Zo) = 0.40 (-.253) (f) P(Zo Z 1.80) = 0.20 (.720) 3. Statistics from Cornell's Northeast Regional Climate Center indicate that Ithaca, NY, gets an average of 35.4" of rain each year, with a standard deviation of 4.2". Assume that a Normal Model applies (a) During what percentage of years does Ithaca get more than 40" of rain? (.1368) (b) Less than how much rain fall in the driest 20% of all years? (31.87 ) (c) A Cornell University student is in Ithaca for 4 years. What's the probability that those four years average less than 30" of rain? (.0051) 4. Carbon Monoxide (CO) emissions for a certain model of car vary with a mean 2.9gm/mi and standard deviation of 0.4 gm/mi. (a) Estimate the probability that a randomly chosen car of this model has CO emissions between 3.0 and 3.1 gm/mi. (b) A company has 80 of these cars in its fleet. (i) Estimate the probability that the mean CO emission of this fleet is between 3.0 and 3.1 gm/mi. (0.0127) (ii) There is only a 55% chance that the fleet's mean CO level is greater than what value? (2.89gm/mi) 5. Although most of us buy milk by the litre, farmers measure daily production in kilograms. Ayrshire cows average kg of mild a day, with a standard deviation of 2.73 kg (a) We select an Ayrshire at random. What's the probability that she averages more than kg of milk a day? (.3079) (b) A farmer has 20 of these cows. What's the probability that the average production for this small her exceed kg of mild a day? (.9320) 6. Assume that the duration of human pregnancies can be described by a normal model with a mean of 266 days and a standard deviation of 16 days. (a) What percentage of pregnancies should last between 270 and 280 days? (21.1%) (b) At least how many days should the longest 25 % of all pregnancies last? (276.8 days or more) (c) Suppose a certain obstetrician is currently providing prenatal care to 60 pregnant women. What's the probability that the mean duration of pregnancy for the women will be less than 260 days? (.0018) 7. A company has been production a 60 watt-bulb with a mean life of 750 hours and a standard deviation of 30 hours. An engineer developed a new process for production the bulb. It was believed that bulbs produced by the new process would show the same standard deviation but possibly a longer mean lifetime. Thirty-six bulbs produced by the new process were tested and showed a mean lifetime of 765 hours. (a) If the mean lifetime of bulbs produced by the new process were still 750 hours, find the probability of getting a value of the sample mean as large as or larger than 765. (.0013) (b) What conclusions might be drawn from the answer to part (a)?
5 5 Normal Approximation to the Binomial 1. A state wished to study the death rate from cancer in a Massachusetts town situated near a toxic waste dump. The death certificates of 200 randomly selected individuals in this town were examined, and it was found that 58 had died of cancer. It is known that 23% of all deaths in the state are due to cancer. (a) If the death rate from cancer in this town were the same for the state, find the probability that more than 57 out of 200 people in the town would die of cancer. (.0267) (b) What conclusions would you draw? 2. A hospital administrator claimed that an unusually large number of girls were born at the hospital in the preceding year. A check of the records showed that 120 girls and 75 boys had been born at the hospital the previous year. Do you think the administrator s claim is reasonable? Why? (.0008) 3. Suppose 65% of 45-year olds with a diagnosed illness die between the ages of 45 to 50. Assume that year-olds have the disease. (a) What is the probability that between 305 and 345 inclusive will die within the next 5 years? (.9454) (b) The 500 were given a new treatment, and 295 died instead of the expected 325. Do you think 65% is still a plausible percentage for a population receiving the treatment? (Hint: If 65% were still correct, how likely is it that fewer than 296 would die?) (.0028) 4. A diastolic blood pressure reading of less than 90 mm is considered normal. Assume that 2/3 of the participants in the Framingham Heart Study have diastolic blood pressure reading of less than 90 mm. In a random sample of 75 participants, what is the probability that 45 or more will have normal diastolic readings? (.9110)
Discrete Probability Distributions
 90 Discrete Probability Distributions Discrete Probability Distributions C H A P T E R 6 Section 6.2 4Example 2 (pg. 00) Constructing a Binomial Probability Distribution In this example, 6% of the human
90 Discrete Probability Distributions Discrete Probability Distributions C H A P T E R 6 Section 6.2 4Example 2 (pg. 00) Constructing a Binomial Probability Distribution In this example, 6% of the human
Problem Set 07 Discrete Random Variables
 Name Problem Set 07 Discrete Random Variables MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the mean of the random variable. 1) The random
Name Problem Set 07 Discrete Random Variables MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the mean of the random variable. 1) The random
Discrete Random Variables and Their Probability Distributions
 58 Chapter 5 Discrete Random Variables and Their Probability Distributions Discrete Random Variables and Their Probability Distributions Chapter 5 Section 5.6 Example 5-18, pg. 213 Calculating a Binomial
58 Chapter 5 Discrete Random Variables and Their Probability Distributions Discrete Random Variables and Their Probability Distributions Chapter 5 Section 5.6 Example 5-18, pg. 213 Calculating a Binomial
Lab#3 Probability
 36-220 Lab#3 Probability Week of September 19, 2005 Please write your name below, tear off this front page and give it to a teaching assistant as you leave the lab. It will be a record of your participation
36-220 Lab#3 Probability Week of September 19, 2005 Please write your name below, tear off this front page and give it to a teaching assistant as you leave the lab. It will be a record of your participation
5.2 Random Variables, Probability Histograms and Probability Distributions
 Chapter 5 5.2 Random Variables, Probability Histograms and Probability Distributions A random variable (r.v.) can be either continuous or discrete. It takes on the possible values of an experiment. It
Chapter 5 5.2 Random Variables, Probability Histograms and Probability Distributions A random variable (r.v.) can be either continuous or discrete. It takes on the possible values of an experiment. It
Example - Let X be the number of boys in a 4 child family. Find the probability distribution table:
 Chapter8 Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables tthe value of the result of the probability experiment is a RANDOM VARIABLE. Example - Let X be the number
Chapter8 Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables tthe value of the result of the probability experiment is a RANDOM VARIABLE. Example - Let X be the number
Chapter 4 Probability Distributions
 Slide 1 Chapter 4 Probability Distributions Slide 2 4-1 Overview 4-2 Random Variables 4-3 Binomial Probability Distributions 4-4 Mean, Variance, and Standard Deviation for the Binomial Distribution 4-5
Slide 1 Chapter 4 Probability Distributions Slide 2 4-1 Overview 4-2 Random Variables 4-3 Binomial Probability Distributions 4-4 Mean, Variance, and Standard Deviation for the Binomial Distribution 4-5
Overview. Definitions. Definitions. Graphs. Chapter 5 Probability Distributions. probability distributions
 Chapter 5 Probability Distributions 5-1 Overview 5-2 Random Variables 5-3 Binomial Probability Distributions 5-4 Mean, Variance, and Standard Deviation for the Binomial Distribution 5-5 The Poisson Distribution
Chapter 5 Probability Distributions 5-1 Overview 5-2 Random Variables 5-3 Binomial Probability Distributions 5-4 Mean, Variance, and Standard Deviation for the Binomial Distribution 5-5 The Poisson Distribution
Example - Let X be the number of boys in a 4 child family. Find the probability distribution table:
 Chapter7 Probability Distributions and Statistics Distributions of Random Variables tthe value of the result of the probability experiment is a RANDOM VARIABLE. Example - Let X be the number of boys in
Chapter7 Probability Distributions and Statistics Distributions of Random Variables tthe value of the result of the probability experiment is a RANDOM VARIABLE. Example - Let X be the number of boys in
Math Week in Review #10. Experiments with two outcomes ( success and failure ) are called Bernoulli or binomial trials.
 Math 141 Spring 2006 c Heather Ramsey Page 1 Section 8.4 - Binomial Distribution Math 141 - Week in Review #10 Experiments with two outcomes ( success and failure ) are called Bernoulli or binomial trials.
Math 141 Spring 2006 c Heather Ramsey Page 1 Section 8.4 - Binomial Distribution Math 141 - Week in Review #10 Experiments with two outcomes ( success and failure ) are called Bernoulli or binomial trials.
Math 160 Professor Busken Chapter 5 Worksheets
 Math 160 Professor Busken Chapter 5 Worksheets Name: 1. Find the expected value. Suppose you play a Pick 4 Lotto where you pay 50 to select a sequence of four digits, such as 2118. If you select the same
Math 160 Professor Busken Chapter 5 Worksheets Name: 1. Find the expected value. Suppose you play a Pick 4 Lotto where you pay 50 to select a sequence of four digits, such as 2118. If you select the same
Sampling Distributions For Counts and Proportions
 Sampling Distributions For Counts and Proportions IPS Chapter 5.1 2009 W. H. Freeman and Company Objectives (IPS Chapter 5.1) Sampling distributions for counts and proportions Binomial distributions for
Sampling Distributions For Counts and Proportions IPS Chapter 5.1 2009 W. H. Freeman and Company Objectives (IPS Chapter 5.1) Sampling distributions for counts and proportions Binomial distributions for
When the observations of a quantitative random variable can take on only a finite number of values, or a countable number of values.
 5.1 Introduction to Random Variables and Probability Distributions Statistical Experiment - any process by which an observation (or measurement) is obtained. Examples: 1) Counting the number of eggs in
5.1 Introduction to Random Variables and Probability Distributions Statistical Experiment - any process by which an observation (or measurement) is obtained. Examples: 1) Counting the number of eggs in
Binomial and Normal Distributions. Example: Determine whether the following experiments are binomial experiments. Explain.
 Binomial and Normal Distributions Objective 1: Determining if an Experiment is a Binomial Experiment For an experiment to be considered a binomial experiment, four things must hold: 1. The experiment is
Binomial and Normal Distributions Objective 1: Determining if an Experiment is a Binomial Experiment For an experiment to be considered a binomial experiment, four things must hold: 1. The experiment is
X P(X=x) E(X)= V(X)= S.D(X)= X P(X=x) E(X)= V(X)= S.D(X)=
 1. X 0 1 2 P(X=x) 0.2 0.4 0.4 E(X)= V(X)= S.D(X)= X 100 200 300 400 P(X=x) 0.1 0.2 0.5 0.2 E(X)= V(X)= S.D(X)= 2. A day trader buys an option on a stock that will return a $100 profit if the stock goes
1. X 0 1 2 P(X=x) 0.2 0.4 0.4 E(X)= V(X)= S.D(X)= X 100 200 300 400 P(X=x) 0.1 0.2 0.5 0.2 E(X)= V(X)= S.D(X)= 2. A day trader buys an option on a stock that will return a $100 profit if the stock goes
6.3: The Binomial Model
 6.3: The Binomial Model The Normal distribution is a good model for many situations involving a continuous random variable. For experiments involving a discrete random variable, where the outcome of the
6.3: The Binomial Model The Normal distribution is a good model for many situations involving a continuous random variable. For experiments involving a discrete random variable, where the outcome of the
EXERCISES FOR PRACTICE SESSION 2 OF STAT CAMP
 EXERCISES FOR PRACTICE SESSION 2 OF STAT CAMP Note 1: The exercises below that are referenced by chapter number are taken or modified from the following open-source online textbook that was adapted by
EXERCISES FOR PRACTICE SESSION 2 OF STAT CAMP Note 1: The exercises below that are referenced by chapter number are taken or modified from the following open-source online textbook that was adapted by
Overview. Definitions. Definitions. Graphs. Chapter 4 Probability Distributions. probability distributions
 Chapter 4 Probability Distributions 4-1 Overview 4-2 Random Variables 4-3 Binomial Probability Distributions 4-4 Mean, Variance, and Standard Deviation for the Binomial Distribution 4-5 The Poisson Distribution
Chapter 4 Probability Distributions 4-1 Overview 4-2 Random Variables 4-3 Binomial Probability Distributions 4-4 Mean, Variance, and Standard Deviation for the Binomial Distribution 4-5 The Poisson Distribution
Section Distributions of Random Variables
 Section 8.1 - Distributions of Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
Section 8.1 - Distributions of Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
GETTING STARTED. To OPEN MINITAB: Click Start>Programs>Minitab14>Minitab14 or Click Minitab 14 on your Desktop
 Minitab 14 1 GETTING STARTED To OPEN MINITAB: Click Start>Programs>Minitab14>Minitab14 or Click Minitab 14 on your Desktop The Minitab session will come up like this 2 To SAVE FILE 1. Click File>Save Project
Minitab 14 1 GETTING STARTED To OPEN MINITAB: Click Start>Programs>Minitab14>Minitab14 or Click Minitab 14 on your Desktop The Minitab session will come up like this 2 To SAVE FILE 1. Click File>Save Project
Chapter 4. Section 4.1 Objectives. Random Variables. Random Variables. Chapter 4: Probability Distributions
 Chapter 4: Probability s 4. Probability s 4. Binomial s Section 4. Objectives Distinguish between discrete random variables and continuous random variables Construct a discrete probability distribution
Chapter 4: Probability s 4. Probability s 4. Binomial s Section 4. Objectives Distinguish between discrete random variables and continuous random variables Construct a discrete probability distribution
Discrete Probability Distributions
 Page 1 of 6 Discrete Probability Distributions In order to study inferential statistics, we need to combine the concepts from descriptive statistics and probability. This combination makes up the basics
Page 1 of 6 Discrete Probability Distributions In order to study inferential statistics, we need to combine the concepts from descriptive statistics and probability. This combination makes up the basics
Discrete Probability Distributions
 Chapter 5 Discrete Probability Distributions Goal: To become familiar with how to use Excel 2007/2010 for binomial distributions. Instructions: Open Excel and click on the Stat button in the Quick Access
Chapter 5 Discrete Probability Distributions Goal: To become familiar with how to use Excel 2007/2010 for binomial distributions. Instructions: Open Excel and click on the Stat button in the Quick Access
Week 7. Texas A& M University. Department of Mathematics Texas A& M University, College Station Section 3.2, 3.3 and 3.4
 Week 7 Oğuz Gezmiş Texas A& M University Department of Mathematics Texas A& M University, College Station Section 3.2, 3.3 and 3.4 Oğuz Gezmiş (TAMU) Topics in Contemporary Mathematics II Week7 1 / 19
Week 7 Oğuz Gezmiş Texas A& M University Department of Mathematics Texas A& M University, College Station Section 3.2, 3.3 and 3.4 Oğuz Gezmiş (TAMU) Topics in Contemporary Mathematics II Week7 1 / 19
Sampling Distributions
 Section 8.1 119 Sampling Distributions Section 8.1 C H A P T E R 8 4Example 2 (pg. 378) Sampling Distribution of the Sample Mean The heights of 3-year-old girls are normally distributed with μ=38.72 and
Section 8.1 119 Sampling Distributions Section 8.1 C H A P T E R 8 4Example 2 (pg. 378) Sampling Distribution of the Sample Mean The heights of 3-year-old girls are normally distributed with μ=38.72 and
MATH 227 CP 6 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 MATH 227 CP 6 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Identify the given random variable as being discrete or continuous. 1) The number of phone
MATH 227 CP 6 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Identify the given random variable as being discrete or continuous. 1) The number of phone
PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS CHAPTER 4 NOTES DISCRETE PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS
 PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS CHAPTER 4 NOTES DISCRETE PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS I. INTRODUCTION TO RANDOM VARIABLES AND PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS A. Random Variables 1. A random variable x represents a value
PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS CHAPTER 4 NOTES DISCRETE PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS I. INTRODUCTION TO RANDOM VARIABLES AND PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS A. Random Variables 1. A random variable x represents a value
X P(X) (c) Express the event performing at least two tests in terms of X and find its probability.
 AP Stats ~ QUIZ 6 Name Period 1. The probability distribution below is for the random variable X = number of medical tests performed on a randomly selected outpatient at a certain hospital. X 0 1 2 3 4
AP Stats ~ QUIZ 6 Name Period 1. The probability distribution below is for the random variable X = number of medical tests performed on a randomly selected outpatient at a certain hospital. X 0 1 2 3 4
5.4 Normal Approximation of the Binomial Distribution
 5.4 Normal Approximation of the Binomial Distribution Bernoulli Trials have 3 properties: 1. Only two outcomes - PASS or FAIL 2. n identical trials Review from yesterday. 3. Trials are independent - probability
5.4 Normal Approximation of the Binomial Distribution Bernoulli Trials have 3 properties: 1. Only two outcomes - PASS or FAIL 2. n identical trials Review from yesterday. 3. Trials are independent - probability
Applied Mathematics 12 Extra Practice Exercises Chapter 3
 H E LP Applied Mathematics Extra Practice Exercises Chapter Tutorial., page 98. A bag contains 5 red balls, blue balls, and green balls. For each of the experiments described below, complete the given
H E LP Applied Mathematics Extra Practice Exercises Chapter Tutorial., page 98. A bag contains 5 red balls, blue balls, and green balls. For each of the experiments described below, complete the given
In a binomial experiment of n trials, where p = probability of success and q = probability of failure. mean variance standard deviation
 Name In a binomial experiment of n trials, where p = probability of success and q = probability of failure mean variance standard deviation µ = n p σ = n p q σ = n p q Notation X ~ B(n, p) The probability
Name In a binomial experiment of n trials, where p = probability of success and q = probability of failure mean variance standard deviation µ = n p σ = n p q σ = n p q Notation X ~ B(n, p) The probability
Session Window. Variable Name Row. Worksheet Window. Double click on MINITAB icon. You will see a split screen: Getting Started with MINITAB
 STARTING MINITAB: Double click on MINITAB icon. You will see a split screen: Session Window Worksheet Window Variable Name Row ACTIVE WINDOW = BLUE INACTIVE WINDOW = GRAY f(x) F(x) Getting Started with
STARTING MINITAB: Double click on MINITAB icon. You will see a split screen: Session Window Worksheet Window Variable Name Row ACTIVE WINDOW = BLUE INACTIVE WINDOW = GRAY f(x) F(x) Getting Started with
ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists 2016/2017
 ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists 2016/2017 Topic The Normal Distribution Lecturer: Dr. Bernardin Senadza, Dept. of Economics bsenadza@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and
ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists 2016/2017 Topic The Normal Distribution Lecturer: Dr. Bernardin Senadza, Dept. of Economics bsenadza@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and
Let X be the number that comes up on the next roll of the die.
 Chapter 6 - Discrete Probability Distributions 6.1 Random Variables Introduction If we roll a fair die, the possible outcomes are the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6, and each of these numbers has probability
Chapter 6 - Discrete Probability Distributions 6.1 Random Variables Introduction If we roll a fair die, the possible outcomes are the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6, and each of these numbers has probability
What is the probability of success? Failure? How could we do this simulation using a random number table?
 Probability Ch.4, sections 4.2 & 4.3 Binomial and Geometric Distributions Name: Date: Pd: 4.2. What is a binomial distribution? How do we find the probability of success? Suppose you have three daughters.
Probability Ch.4, sections 4.2 & 4.3 Binomial and Geometric Distributions Name: Date: Pd: 4.2. What is a binomial distribution? How do we find the probability of success? Suppose you have three daughters.
The Normal Probability Distribution
 102 The Normal Probability Distribution C H A P T E R 7 Section 7.2 4Example 1 (pg. 71) Finding Area Under a Normal Curve In this exercise, we will calculate the area to the left of 5 inches using a normal
102 The Normal Probability Distribution C H A P T E R 7 Section 7.2 4Example 1 (pg. 71) Finding Area Under a Normal Curve In this exercise, we will calculate the area to the left of 5 inches using a normal
Binomial Distributions
 Binomial Distributions (aka Bernouli s Trials) Chapter 8 Binomial Distribution an important class of probability distributions, which occur under the following Binomial Setting (1) There is a number n
Binomial Distributions (aka Bernouli s Trials) Chapter 8 Binomial Distribution an important class of probability distributions, which occur under the following Binomial Setting (1) There is a number n
Chapter 5 Probability Distributions. Section 5-2 Random Variables. Random Variable Probability Distribution. Discrete and Continuous Random Variables
 Chapter 5 Probability Distributions Section 5-2 Random Variables 5-2 Random Variables 5-3 Binomial Probability Distributions 5-4 Mean, Variance and Standard Deviation for the Binomial Distribution Random
Chapter 5 Probability Distributions Section 5-2 Random Variables 5-2 Random Variables 5-3 Binomial Probability Distributions 5-4 Mean, Variance and Standard Deviation for the Binomial Distribution Random
Exam II Math 1342 Capters 3-5 HCCS. Name
 Exam II Math 1342 Capters 3-5 HCCS Name Date Provide an appropriate response. 1) A single six-sided die is rolled. Find the probability of rolling a number less than 3. A) 0.5 B) 0.1 C) 0.25 D 0.333 1)
Exam II Math 1342 Capters 3-5 HCCS Name Date Provide an appropriate response. 1) A single six-sided die is rolled. Find the probability of rolling a number less than 3. A) 0.5 B) 0.1 C) 0.25 D 0.333 1)
Name Period AP Statistics Unit 5 Review
 Name Period AP Statistics Unit 5 Review Multiple Choice 1. Jay Olshansky from the University of Chicago was quoted in Chance News as arguing that for the average life expectancy to reach 100, 18% of people
Name Period AP Statistics Unit 5 Review Multiple Choice 1. Jay Olshansky from the University of Chicago was quoted in Chance News as arguing that for the average life expectancy to reach 100, 18% of people
Examples: Random Variables. Discrete and Continuous Random Variables. Probability Distributions
 Random Variables Examples: Random variable a variable (typically represented by x) that takes a numerical value by chance. Number of boys in a randomly selected family with three children. Possible values:
Random Variables Examples: Random variable a variable (typically represented by x) that takes a numerical value by chance. Number of boys in a randomly selected family with three children. Possible values:
Determine whether the given procedure results in a binomial distribution. If not, state the reason why.
 Math 5.3 Binomial Probability Distributions Name 1) Binomial Distrbution: Determine whether the given procedure results in a binomial distribution. If not, state the reason why. 2) Rolling a single die
Math 5.3 Binomial Probability Distributions Name 1) Binomial Distrbution: Determine whether the given procedure results in a binomial distribution. If not, state the reason why. 2) Rolling a single die
OCR Statistics 1. Discrete random variables. Section 2: The binomial and geometric distributions. When to use the binomial distribution
 Discrete random variables Section 2: The binomial and geometric distributions Notes and Examples These notes contain subsections on: When to use the binomial distribution Binomial coefficients Worked examples
Discrete random variables Section 2: The binomial and geometric distributions Notes and Examples These notes contain subsections on: When to use the binomial distribution Binomial coefficients Worked examples
TRUE-FALSE: Determine whether each of the following statements is true or false.
 Chapter 6 Test Review Name TRUE-FALSE: Determine whether each of the following statements is true or false. 1) A random variable is continuous when the set of possible values includes an entire interval
Chapter 6 Test Review Name TRUE-FALSE: Determine whether each of the following statements is true or false. 1) A random variable is continuous when the set of possible values includes an entire interval
ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists
 ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists Session 7 The Normal Distribution Part 1 Lecturer: Dr. Bernardin Senadza, Dept. of Economics Contact Information: bsenadza@ug.edu.gh College of Education
ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists Session 7 The Normal Distribution Part 1 Lecturer: Dr. Bernardin Senadza, Dept. of Economics Contact Information: bsenadza@ug.edu.gh College of Education
Bin(20,.5) and N(10,5) distributions
 STAT 600 Design of Experiments for Research Workers Lab 5 { Due Thursday, November 18 Example Weight Loss In a dietary study, 14 of 0 subjects lost weight. If weight is assumed to uctuate up or down by
STAT 600 Design of Experiments for Research Workers Lab 5 { Due Thursday, November 18 Example Weight Loss In a dietary study, 14 of 0 subjects lost weight. If weight is assumed to uctuate up or down by
MATH 446/546 Homework 1:
 MATH 446/546 Homework 1: Due September 28th, 216 Please answer the following questions. Students should type there work. 1. At time t, a company has I units of inventory in stock. Customers demand the
MATH 446/546 Homework 1: Due September 28th, 216 Please answer the following questions. Students should type there work. 1. At time t, a company has I units of inventory in stock. Customers demand the
Lecture 9. Probability Distributions. Outline. Outline
 Outline Lecture 9 Probability Distributions 6-1 Introduction 6- Probability Distributions 6-3 Mean, Variance, and Expectation 6-4 The Binomial Distribution Outline 7- Properties of the Normal Distribution
Outline Lecture 9 Probability Distributions 6-1 Introduction 6- Probability Distributions 6-3 Mean, Variance, and Expectation 6-4 The Binomial Distribution Outline 7- Properties of the Normal Distribution
Density curves. (James Madison University) February 4, / 20
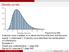 Density curves Figure 6.2 p 230. A density curve is always on or above the horizontal axis, and has area exactly 1 underneath it. A density curve describes the overall pattern of a distribution. Example
Density curves Figure 6.2 p 230. A density curve is always on or above the horizontal axis, and has area exactly 1 underneath it. A density curve describes the overall pattern of a distribution. Example
Chapter 5: Discrete Probability Distributions
 Chapter 5: Discrete Probability Distributions Section 5.1: Basics of Probability Distributions As a reminder, a variable or what will be called the random variable from now on, is represented by the letter
Chapter 5: Discrete Probability Distributions Section 5.1: Basics of Probability Distributions As a reminder, a variable or what will be called the random variable from now on, is represented by the letter
Statistics (This summary is for chapters 17, 28, 29 and section G of chapter 19)
 Statistics (This summary is for chapters 17, 28, 29 and section G of chapter 19) Mean, Median, Mode Mode: most common value Median: middle value (when the values are in order) Mean = total how many = x
Statistics (This summary is for chapters 17, 28, 29 and section G of chapter 19) Mean, Median, Mode Mode: most common value Median: middle value (when the values are in order) Mean = total how many = x
Section 7.5 The Normal Distribution. Section 7.6 Application of the Normal Distribution
 Section 7.6 Application of the Normal Distribution A random variable that may take on infinitely many values is called a continuous random variable. A continuous probability distribution is defined by
Section 7.6 Application of the Normal Distribution A random variable that may take on infinitely many values is called a continuous random variable. A continuous probability distribution is defined by
Section 8.4 The Binomial Distribution
 Section 8.4 The Binomial Distribution Binomial Experiment A binomial experiment has the following properties: 1. The number of trials in the experiment is fixed. 2. There are two outcomes of each trial:
Section 8.4 The Binomial Distribution Binomial Experiment A binomial experiment has the following properties: 1. The number of trials in the experiment is fixed. 2. There are two outcomes of each trial:
Statistics (This summary is for chapters 18, 29 and section H of chapter 19)
 Statistics (This summary is for chapters 18, 29 and section H of chapter 19) Mean, Median, Mode Mode: most common value Median: middle value (when the values are in order) Mean = total how many = x n =
Statistics (This summary is for chapters 18, 29 and section H of chapter 19) Mean, Median, Mode Mode: most common value Median: middle value (when the values are in order) Mean = total how many = x n =
Probability Notes: Binomial Probabilities
 Probability Notes: Binomial Probabilities A Binomial Probability is a type of discrete probability with only two outcomes (tea or coffee, win or lose, have disease or don t have disease). The category
Probability Notes: Binomial Probabilities A Binomial Probability is a type of discrete probability with only two outcomes (tea or coffee, win or lose, have disease or don t have disease). The category
Chapter 8 Solutions Page 1 of 15 CHAPTER 8 EXERCISE SOLUTIONS
 Chapter 8 Solutions Page of 5 8. a. Continuous. b. Discrete. c. Continuous. d. Discrete. e. Discrete. 8. a. Discrete. b. Continuous. c. Discrete. d. Discrete. CHAPTER 8 EXERCISE SOLUTIONS 8.3 a. 3/6 =
Chapter 8 Solutions Page of 5 8. a. Continuous. b. Discrete. c. Continuous. d. Discrete. e. Discrete. 8. a. Discrete. b. Continuous. c. Discrete. d. Discrete. CHAPTER 8 EXERCISE SOLUTIONS 8.3 a. 3/6 =
FINAL REVIEW W/ANSWERS
 FINAL REVIEW W/ANSWERS ( 03/15/08 - Sharon Coates) Concepts to review before answering the questions: A population consists of the entire group of people or objects of interest to an investigator, while
FINAL REVIEW W/ANSWERS ( 03/15/08 - Sharon Coates) Concepts to review before answering the questions: A population consists of the entire group of people or objects of interest to an investigator, while
d) Find the standard deviation of the random variable X.
 Q 1: The number of students using Math lab per day is found in the distribution below. x 6 8 10 12 14 P(x) 0.15 0.3 0.35 0.1 0.1 a) Find the mean for this probability distribution. b) Find the variance
Q 1: The number of students using Math lab per day is found in the distribution below. x 6 8 10 12 14 P(x) 0.15 0.3 0.35 0.1 0.1 a) Find the mean for this probability distribution. b) Find the variance
Lecture 9. Probability Distributions
 Lecture 9 Probability Distributions Outline 6-1 Introduction 6-2 Probability Distributions 6-3 Mean, Variance, and Expectation 6-4 The Binomial Distribution Outline 7-2 Properties of the Normal Distribution
Lecture 9 Probability Distributions Outline 6-1 Introduction 6-2 Probability Distributions 6-3 Mean, Variance, and Expectation 6-4 The Binomial Distribution Outline 7-2 Properties of the Normal Distribution
Revision Pack 4. Probability Distributions. Doublestruck & CIE - Licensed to Brillantmont International School 1
 S1 Revision Pack 4 Probability Distributions Doublestruck & CIE - Licensed to Brillantmont International School 1 1. Gohan throws a fair tetrahedral die with faces numbered 1, 2, 3, 4. If she throws an
S1 Revision Pack 4 Probability Distributions Doublestruck & CIE - Licensed to Brillantmont International School 1 1. Gohan throws a fair tetrahedral die with faces numbered 1, 2, 3, 4. If she throws an
Chapter 3: Probability Distributions and Statistics
 Chapter 3: Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 3.-3.3 3. Random Variables and Histograms A is a rule that assigns precisely one real number to each outcome of an experiment. We usually denote
Chapter 3: Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 3.-3.3 3. Random Variables and Histograms A is a rule that assigns precisely one real number to each outcome of an experiment. We usually denote
Example. Chapter 8 Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables
 Chapter 8 Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables You are dealt a hand of 5 cards. Find the probability distribution table for the number of hearts. Graph
Chapter 8 Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables You are dealt a hand of 5 cards. Find the probability distribution table for the number of hearts. Graph
Central Limit Theorem 11/08/2005
 Central Limit Theorem 11/08/2005 A More General Central Limit Theorem Theorem. Let X 1, X 2,..., X n,... be a sequence of independent discrete random variables, and let S n = X 1 + X 2 + + X n. For each
Central Limit Theorem 11/08/2005 A More General Central Limit Theorem Theorem. Let X 1, X 2,..., X n,... be a sequence of independent discrete random variables, and let S n = X 1 + X 2 + + X n. For each
Chapter 4 Discrete Random variables
 Chapter 4 Discrete Random variables A is a variable that assumes numerical values associated with the random outcomes of an experiment, where only one numerical value is assigned to each sample point.
Chapter 4 Discrete Random variables A is a variable that assumes numerical values associated with the random outcomes of an experiment, where only one numerical value is assigned to each sample point.
Section Distributions of Random Variables
 Section 8.1 - Distributions of Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
Section 8.1 - Distributions of Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
4.1 Probability Distributions
 Probability and Statistics Mrs. Leahy Chapter 4: Discrete Probability Distribution ALWAYS KEEP IN MIND: The Probability of an event is ALWAYS between: and!!!! 4.1 Probability Distributions Random Variables
Probability and Statistics Mrs. Leahy Chapter 4: Discrete Probability Distribution ALWAYS KEEP IN MIND: The Probability of an event is ALWAYS between: and!!!! 4.1 Probability Distributions Random Variables
Chapter 8: The Binomial and Geometric Distributions
 Chapter 8: The Binomial and Geometric Distributions 8.1 Binomial Distributions 8.2 Geometric Distributions 1 Let me begin with an example My best friends from Kent School had three daughters. What is the
Chapter 8: The Binomial and Geometric Distributions 8.1 Binomial Distributions 8.2 Geometric Distributions 1 Let me begin with an example My best friends from Kent School had three daughters. What is the
NORMAL RANDOM VARIABLES (Normal or gaussian distribution)
 NORMAL RANDOM VARIABLES (Normal or gaussian distribution) Many variables, as pregnancy lengths, foot sizes etc.. exhibit a normal distribution. The shape of the distribution is a symmetric bell shape.
NORMAL RANDOM VARIABLES (Normal or gaussian distribution) Many variables, as pregnancy lengths, foot sizes etc.. exhibit a normal distribution. The shape of the distribution is a symmetric bell shape.
The Binomial Distribution
 The Binomial Distribution Properties of a Binomial Experiment 1. It consists of a fixed number of observations called trials. 2. Each trial can result in one of only two mutually exclusive outcomes labeled
The Binomial Distribution Properties of a Binomial Experiment 1. It consists of a fixed number of observations called trials. 2. Each trial can result in one of only two mutually exclusive outcomes labeled
STOR 155 Introductory Statistics (Chap 5) Lecture 14: Sampling Distributions for Counts and Proportions
 The UNIVERSITY of NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL STOR 155 Introductory Statistics (Chap 5) Lecture 14: Sampling Distributions for Counts and Proportions 5/31/11 Lecture 14 1 Statistic & Its Sampling Distribution
The UNIVERSITY of NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL STOR 155 Introductory Statistics (Chap 5) Lecture 14: Sampling Distributions for Counts and Proportions 5/31/11 Lecture 14 1 Statistic & Its Sampling Distribution
Chapter 4 Discrete Random variables
 Chapter 4 Discrete Random variables A is a variable that assumes numerical values associated with the random outcomes of an experiment, where only one numerical value is assigned to each sample point.
Chapter 4 Discrete Random variables A is a variable that assumes numerical values associated with the random outcomes of an experiment, where only one numerical value is assigned to each sample point.
Chapter 6 Section Review day s.notebook. May 11, Honors Statistics. Aug 23-8:26 PM. 3. Review team test.
 Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM 3. Review team test Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Nov 27-10:28 PM 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 6.9 6.10 6.11 6.12 Nov 27-9:53 PM 2 May 8-7:44 PM May 1-9:09 PM 3 Dec 1-2:08 PM Sep
Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM 3. Review team test Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Nov 27-10:28 PM 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 6.9 6.10 6.11 6.12 Nov 27-9:53 PM 2 May 8-7:44 PM May 1-9:09 PM 3 Dec 1-2:08 PM Sep
PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS
 CHAPTER 3 PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Page Contents 3.1 Introduction to Probability Distributions 51 3.2 The Normal Distribution 56 3.3 The Binomial Distribution 60 3.4 The Poisson Distribution 64 Exercise
CHAPTER 3 PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Page Contents 3.1 Introduction to Probability Distributions 51 3.2 The Normal Distribution 56 3.3 The Binomial Distribution 60 3.4 The Poisson Distribution 64 Exercise
A.REPRESENTATION OF DATA
 A.REPRESENTATION OF DATA (a) GRAPHS : PART I Q: Why do we need a graph paper? Ans: You need graph paper to draw: (i) Histogram (ii) Cumulative Frequency Curve (iii) Frequency Polygon (iv) Box-and-Whisker
A.REPRESENTATION OF DATA (a) GRAPHS : PART I Q: Why do we need a graph paper? Ans: You need graph paper to draw: (i) Histogram (ii) Cumulative Frequency Curve (iii) Frequency Polygon (iv) Box-and-Whisker
Chapter 4 and Chapter 5 Test Review Worksheet
 Name: Date: Hour: Chapter 4 and Chapter 5 Test Review Worksheet You must shade all provided graphs, you must round all z-scores to 2 places after the decimal, you must round all probabilities to at least
Name: Date: Hour: Chapter 4 and Chapter 5 Test Review Worksheet You must shade all provided graphs, you must round all z-scores to 2 places after the decimal, you must round all probabilities to at least
Statistical Methods in Practice STAT/MATH 3379
 Statistical Methods in Practice STAT/MATH 3379 Dr. A. B. W. Manage Associate Professor of Mathematics & Statistics Department of Mathematics & Statistics Sam Houston State University Overview 6.1 Discrete
Statistical Methods in Practice STAT/MATH 3379 Dr. A. B. W. Manage Associate Professor of Mathematics & Statistics Department of Mathematics & Statistics Sam Houston State University Overview 6.1 Discrete
(# of die rolls that satisfy the criteria) (# of possible die rolls)
 BMI 713: Computational Statistics for Biomedical Sciences Assignment 2 1 Random variables and distributions 1. Assume that a die is fair, i.e. if the die is rolled once, the probability of getting each
BMI 713: Computational Statistics for Biomedical Sciences Assignment 2 1 Random variables and distributions 1. Assume that a die is fair, i.e. if the die is rolled once, the probability of getting each
Chapter 5. Discrete Probability Distributions. McGraw-Hill, Bluman, 7 th ed, Chapter 5 1
 Chapter 5 Discrete Probability Distributions McGraw-Hill, Bluman, 7 th ed, Chapter 5 1 Chapter 5 Overview Introduction 5-1 Probability Distributions 5-2 Mean, Variance, Standard Deviation, and Expectation
Chapter 5 Discrete Probability Distributions McGraw-Hill, Bluman, 7 th ed, Chapter 5 1 Chapter 5 Overview Introduction 5-1 Probability Distributions 5-2 Mean, Variance, Standard Deviation, and Expectation
1. Steve says I have two children, one of which is a boy. Given this information, what is the probability that Steve has two boys?
 Chapters 6 8 Review 1. Steve says I have two children, one of which is a boy. Given this information, what is the probability that Steve has two boys? (A) 1 (B) 3 1 (C) 3 (D) 4 1 (E) None of the above..
Chapters 6 8 Review 1. Steve says I have two children, one of which is a boy. Given this information, what is the probability that Steve has two boys? (A) 1 (B) 3 1 (C) 3 (D) 4 1 (E) None of the above..
 Homework Problems In each of the following situations, X is a count. Does X have a binomial distribution? Explain. 1. You observe the gender of the next 40 children born in a hospital. X is the number
Homework Problems In each of the following situations, X is a count. Does X have a binomial distribution? Explain. 1. You observe the gender of the next 40 children born in a hospital. X is the number
 Problem A Grade x P(x) To get "C" 1 or 2 must be 1 0.05469 B A 2 0.16410 3 0.27340 4 0.27340 5 0.16410 6 0.05470 7 0.00780 0.2188 0.5468 0.2266 Problem B Grade x P(x) To get "C" 1 or 2 must 1 0.31150 be
Problem A Grade x P(x) To get "C" 1 or 2 must be 1 0.05469 B A 2 0.16410 3 0.27340 4 0.27340 5 0.16410 6 0.05470 7 0.00780 0.2188 0.5468 0.2266 Problem B Grade x P(x) To get "C" 1 or 2 must 1 0.31150 be
the number of correct answers on question i. (Note that the only possible values of X i
 6851_ch08_137_153 16/9/02 19:48 Page 137 8 8.1 (a) No: There is no fixed n (i.e., there is no definite upper limit on the number of defects). (b) Yes: It is reasonable to believe that all responses are
6851_ch08_137_153 16/9/02 19:48 Page 137 8 8.1 (a) No: There is no fixed n (i.e., there is no definite upper limit on the number of defects). (b) Yes: It is reasonable to believe that all responses are
DO NOT POST THESE ANSWERS ONLINE BFW Publishers 2014
 Section 6.3 Check our Understanding, page 389: 1. Check the BINS: Binary? Success = get an ace. Failure = don t get an ace. Independent? Because you are replacing the card in the deck and shuffling each
Section 6.3 Check our Understanding, page 389: 1. Check the BINS: Binary? Success = get an ace. Failure = don t get an ace. Independent? Because you are replacing the card in the deck and shuffling each
Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables
 Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables Random Variable A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of a chance experiment. There are three types of random variables: 1. Finite
Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables Random Variable A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of a chance experiment. There are three types of random variables: 1. Finite
2017 Fall QMS102 Tip Sheet 2
 Chapter 5: Basic Probability 2017 Fall QMS102 Tip Sheet 2 (Covering Chapters 5 to 8) EVENTS -- Each possible outcome of a variable is an event, including 3 types. 1. Simple event = Described by a single
Chapter 5: Basic Probability 2017 Fall QMS102 Tip Sheet 2 (Covering Chapters 5 to 8) EVENTS -- Each possible outcome of a variable is an event, including 3 types. 1. Simple event = Described by a single
STAT Lab#5 Binomial Distribution & Midterm Review
 STAT 22000 Lab# Binomial Distribution & Midterm Review Binomial Distributions For X Bin(n, p), Assumptions: P (X = k) = n p k (1 p) n k k Only two possible outcomes The number of trials n must be fixed
STAT 22000 Lab# Binomial Distribution & Midterm Review Binomial Distributions For X Bin(n, p), Assumptions: P (X = k) = n p k (1 p) n k k Only two possible outcomes The number of trials n must be fixed
5.1 Personal Probability
 5. Probability Value Page 1 5.1 Personal Probability Although we think probability is something that is confined to math class, in the form of personal probability it is something we use to make decisions
5. Probability Value Page 1 5.1 Personal Probability Although we think probability is something that is confined to math class, in the form of personal probability it is something we use to make decisions
Chapter 8 Probability Models
 Chapter 8 Probability Models We ve already used the calculator to find probabilities based on normal models. There are many more models which are useful. This chapter explores three such models. Many types
Chapter 8 Probability Models We ve already used the calculator to find probabilities based on normal models. There are many more models which are useful. This chapter explores three such models. Many types
Honors Statistics. Daily Agenda
 Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM Daily Agenda 1. Review OTL C6#4 Chapter 6.2 rules for means and variances Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Nov 21-8:16 PM Working out Choose a person aged 19 to 25 years at random and
Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM Daily Agenda 1. Review OTL C6#4 Chapter 6.2 rules for means and variances Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Nov 21-8:16 PM Working out Choose a person aged 19 to 25 years at random and
5.4 Normal Approximation of the Binomial Distribution Lesson MDM4U Jensen
 5.4 Normal Approximation of the Binomial Distribution Lesson MDM4U Jensen Review From Yesterday Bernoulli Trials have 3 properties: 1. 2. 3. Binomial Probability Distribution In a binomial experiment with
5.4 Normal Approximation of the Binomial Distribution Lesson MDM4U Jensen Review From Yesterday Bernoulli Trials have 3 properties: 1. 2. 3. Binomial Probability Distribution In a binomial experiment with
MLLunsford 1. Activity: Central Limit Theorem Theory and Computations
 MLLunsford 1 Activity: Central Limit Theorem Theory and Computations Concepts: The Central Limit Theorem; computations using the Central Limit Theorem. Prerequisites: The student should be familiar with
MLLunsford 1 Activity: Central Limit Theorem Theory and Computations Concepts: The Central Limit Theorem; computations using the Central Limit Theorem. Prerequisites: The student should be familiar with
Section 8.4 The Binomial Distribution
 Section 84 The Binomial Distribution Binomial Experiment A binomial experiment has the following properties: 1 The number of trials in the experiment is fixed 2 There are two outcomes of each trial: success
Section 84 The Binomial Distribution Binomial Experiment A binomial experiment has the following properties: 1 The number of trials in the experiment is fixed 2 There are two outcomes of each trial: success
STT 315 Practice Problems Chapter 3.7 and 4
 STT 315 Practice Problems Chapter 3.7 and 4 Answer the question True or False. 1) The number of children in a family can be modelled using a continuous random variable. 2) For any continuous probability
STT 315 Practice Problems Chapter 3.7 and 4 Answer the question True or False. 1) The number of children in a family can be modelled using a continuous random variable. 2) For any continuous probability
Chapter 6. The Normal Probability Distributions
 Chapter 6 The Normal Probability Distributions 1 Chapter 6 Overview Introduction 6-1 Normal Probability Distributions 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution 6-3 Applications of the Normal Distribution 6-5
Chapter 6 The Normal Probability Distributions 1 Chapter 6 Overview Introduction 6-1 Normal Probability Distributions 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution 6-3 Applications of the Normal Distribution 6-5
Chapter 3 - Lecture 5 The Binomial Probability Distribution
 Chapter 3 - Lecture 5 The Binomial Probability October 12th, 2009 Experiment Examples Moments and moment generating function of a Binomial Random Variable Outline Experiment Examples A binomial experiment
Chapter 3 - Lecture 5 The Binomial Probability October 12th, 2009 Experiment Examples Moments and moment generating function of a Binomial Random Variable Outline Experiment Examples A binomial experiment
MATH 118 Class Notes For Chapter 5 By: Maan Omran
 MATH 118 Class Notes For Chapter 5 By: Maan Omran Section 5.1 Central Tendency Mode: the number or numbers that occur most often. Median: the number at the midpoint of a ranked data. Ex1: The test scores
MATH 118 Class Notes For Chapter 5 By: Maan Omran Section 5.1 Central Tendency Mode: the number or numbers that occur most often. Median: the number at the midpoint of a ranked data. Ex1: The test scores
Section Random Variables and Histograms
 Section 3.1 - Random Variables and Histograms Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
Section 3.1 - Random Variables and Histograms Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
Chapter 18 Sampling Distribution Models
 282 Part V From the Data at Hand to the World at Large 1. Send mone. Chapter 18 Sampling Distribution Models All of the histograms are centered around p = 005.. As n gets larger, the shape of the histograms
282 Part V From the Data at Hand to the World at Large 1. Send mone. Chapter 18 Sampling Distribution Models All of the histograms are centered around p = 005.. As n gets larger, the shape of the histograms
Normal Sampling and Modelling
 8.3 Normal Sampling and Modelling Many statistical studies take sample data from an underlying normal population. As you saw in the investigation on page 422, the distribution of the sample data reflects
8.3 Normal Sampling and Modelling Many statistical studies take sample data from an underlying normal population. As you saw in the investigation on page 422, the distribution of the sample data reflects
Lecture 3. Sampling distributions. Counts, Proportions, and sample mean.
 Lecture 3 Sampling distributions. Counts, Proportions, and sample mean. Statistical Inference: Uses data and summary statistics (mean, variances, proportions, slopes) to draw conclusions about a population
Lecture 3 Sampling distributions. Counts, Proportions, and sample mean. Statistical Inference: Uses data and summary statistics (mean, variances, proportions, slopes) to draw conclusions about a population
