M G T 2251 Management Science. Exam 3
|
|
|
- Amberly Perkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 M G T 2251 Management Science Exam 3 Professor Chang November 8, 2012 Your Name (Print): ID#: Read each question carefully before you answer. Work at a steady pace, and you should have ample time to finish. Good Luck!!! My signature certifies that I have taken this exam in accordance with the Georgia Tech honor Code. Signature Page 1 of 17
2 1. Keith Littlefield is a racecar driver on the NASCAR circuit. He has promised to participate in the Pocono 300, to be held 15 weeks from now. In order to be competitive, Keith feels he must completely modify his racecar. The following table summarizes the normal and crash costs and completion times (in weeks) of the rebuilding project activities. The predecessors of each activity are also shown in the table. Activity Normal Crash Normal Crash Immediate Name time time cost cost predecessor A 8 3 $4800 $ B C,E C A D G E A F C,D G A The AON project network with normal times is drawn below. Page 2 of 17
3 (a). Use the normal time to perform the critical path analysis, i.e., perform the forward pass and backward pass to find the earliest start time (ES), earliest finish time (EF), latest start time (LS), latest finish time (LF), and slack time for each activity. Write the ES/EF/LS/LF on the above AON diagram and write the slack times in the table below. (10 points) Activity Slack Time A 0 B 4 C 4 D 0 E 4 F 0 G 0 (b). Based on (a), determine the critical path and find the total project completion time. (3 points) CP: A-G-D-F Total project completion time = 28 weeks (c). Draw the Gantt chart using the earliest times from (a)? (5 points) Page 3 of 17
4 (d). If the project due date is set at 15 weeks, how many weeks is the project overdue based on the above critical path analysis? If each week delay will be penalized at $500, what is the total project cost (including normal costs and penalty costs) if the above normal times are adopted to execute the project? (3 points) Page 4 of 17
5 The project will be late by 13 weeks. Total project costs = $ (13) = $ (e). If the project is overdue and Keith is looking to speed up the project by crashing some activity times, which activity times need to be crashed first? How much extra cost per week is needed if this activity is crashed? (2 points) Crash activity A first. Extra cost per week = $ Fifty-eight days ago a nervous Board of Directors of Igloo Foods, owners of the Igloo Frozen Yogurt chain, watched as the company began a program to test market its product in London, England. The target opening date for the first store was four months (122 days) from the inception of the project. If the store proves successful, Igloo plans to open up at least two dozen Igloo Frozen Yogurt stores across Great Britain and the European continent. This is the first such venture for Igloo Foods outside of the United States. The project consists of the 18 work packages (i.e., activities) summarized in the table, together with budget information and time estimates in days. Work Package Immediate Optimistic Most Pessimistic Budget Predecessor Time Likely Time A. Select vice president for Europe $ 0 B. Select menu consultant $ 2,000 C. Choose district for shop A $ 0 D. Make exact site selection C $ 15,000 E. Negotiate lease D $ 4,000 F. Design store layout A $ 40,000 G. Construct store E, F $260,000 H. Develop recipes B $ 15,000 I. Test recipes H $ 10,000 J. Purchase equipment F, I $150,000 K. Design Accessories F, I $ 15,000 L. Purchase supplies K $100,000 M. Develop training program J, K $ 18,000 N. Train employees M $ 7,000 O. Select advertising agency A $ 12,000 P. Develop marketing program D, O $ 90,000 Q. Purchase advertising space P $ 80,000 R. Install signs G, Q $ 26,000 A PERT/CPM analysis based on the three-time estimate approach was used to generate a schedule of work packages for the project. The following template shows the initial analysis of the critical path. It shows there is 30.55% to finish the project in 122 days. Page 5 of 17
6 (a). Using the information in the above table, what is the chance to finish the project in ( ) 130 days? (3 points) P(X 130)=P(Z ( )/ )=P(Z 0.31)= (b). Using the information in the above table, what is the chance to finish the project over (>) 135 days? (3 points) P(X>135)=P(Z>( )/ )=P(Z>0.81)= =0.209 (c). Using the information in the above table, if the company is to be 99% sure to finish the project, what is the target due date (D) should be? (3 points) P(X D)=0.99, Z=2.33 D= * =149.9 days or to set the deadline at 150 days. Now, 58 days into the project, the Board of Directors has received the following project status report. The activity completion and value analysis is provided in the following progress report table. However, the detail actual cost (expenditure) for each work package is not available but the total expenditure is estimated at $255,000. Date: Day 58 Actual Total Expenditure (Cost) to Date: $255,000 Progress Report Page 6 of 17
7 (d). Based on the above progress report, what is the total value of the project at day 58? Is the project actual cost at day 58 under run or overrun and by how much? (3 points) The total value of the project = $206,250. It is less than the actual expenditure $255,000. Therefore, it is overrun By 255, ,250=$48,750. At day 58 (i.e., 64 days away from the target 122 days), based on the above project status report, the new critical path analysis is shown below. The chance to meet the deadline at 122 days is Page 7 of 17
8 (e). Based on the above revised critical path analysis at day 58, the chance to meet the deadline by 122 days (64 days away) is The Igloo management decides to delay the opening day by 35 days, which extends the deadline to be 99 days from day 58. How much will this improve the chance to finish the project with the new deadline as compared to the old deadline? (The new mean and standard deviation are shown on the above table.) (3 points) P(X<=99)=P(Z<=(99-84)/ )=P(Z<=2.34)= This increases the chance of meeting deadline by = %. 3. The following table shows the activity information for the Southwestern University Stadium Construction Project. T A B L E Southwestern University Stadium Project. TIME ESTIMATES (DAYS) ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION PREDECESSORS OPTIMISTIC MOST LIKELY PESSIMISTIC A B C D Bonding, insurance, tax structuring Foundation concrete footings for boxes Upgrading skyboxes, stadium seating Upgrading walkways, stairwells, elevators A A C Page 8 of 17
9 E Interior wiring, lathes B F Inspection approvals E G Plumbing D, E H Painting G I Hardware/air conditioning/ H metal workings J Tile/carpeting/windows H K Inspection J L Final detail work/ cleanup I, K (a). Draw the project network in AON format. Do not write the activity times. (5 points) AON network for the project: (b). What is the average time and standard deviation time for activity A? (3 points) Average time for activity A = (20+(4)*30+40)/6=30 Standard deviation time for activity A = (40-20)/6= Southern Homes is a home builder located in a suburb of Atlanta. The company must decide whether to leave its model homes unfurnished, furnish them with minimal accessories, or completely furnish them using a custom decorator. The new-home market is generally quite profitable, but Southern is suffering cash flow problems. The following table gives the profit per lot for Southern Homes based on how Southern furnishes its model homes and the overall demand for housing in Atlanta market. Model Home Housing Market in Atlanta Furnishing Alternative Weak Moderate Strong Very Strong Unfurnished -$1,500 $1,000 $2,000 $3,000 Minimal Accessories -$4,000 $500 $3,500 $6,000 Custom Decorated -$7,000 $1,500 $2,500 $9,500 (a). What is the best decision if Southern management is very optimistic and aggressive (i.e., uses the maximax criterion)? What is the decision payoff value? (3 points) Best Decision by Maximax: Custom Decorated. Page 9 of 17
10 Decision Payoff = $9,500. (b). What is the best decision if Southern management is very conservative and pessimistic (i.e., uses the maximin criterion)? What is the decision payoff value? (3 points) Best Decision by Maximin: Unfurnished model homes. Decision Payoff = -$1,500. (c). Fill in the regret values for Southern management in the following table. (5 points) Model Home Furnishing Alternative Unfurnished Minimal Accessories Custom Decorated Housing Market in Atlanta Weak Moderate Strong Very Strong Model Home Housing Market in Atlanta Furnishing Alternative Weak Moderate Strong Very Strong Unfurnished $0 $500 $1,500 $6,500 Minimal Accessories $2,500 $1,000 $0 $3,500 Custom Decorated $5,500 $0 $1,000 $0 (d). What is the best decision if Southern management maximum regret (i.e., uses the minimax regret criterion)? What is the decision regret value? (3 points) Best Decision by Minimax regret: Minimal Accessories. Decision Regret = $3,500. (e). Based on past experience, suppose Southern management believes that the following probabilities hold for the housing market in Atlanta: P(Weak) = 0.20 P(Moderate) = 0.40 P(Strong) = 0.30 P(Very Strong) = 0.10 The following payoff table has the probabilities of market situations. Model Home Housing Market in Atlanta Furnishing Alternative Weak Moderate Strong Very Strong Unfurnished -$1,500 $1,000 $2,000 $3,000 Minimal Accessories -$4,000 $500 $3,500 $6,000 Custom Decorated -$7,000 $1,500 $2,500 $9,500 Probability Page 10 of 17
11 What is the best decision if Southern management uses the expected money value criterion? What is the expected payoff value (expected money value, EMV)? (5 points) EMV(Unfurnished)=.2(-1,500)+.4(1,000)+.3(2,000)+.1(3,000)=$1,000 EMV(Minimal Accessories)=.2(-4,000)+.4(500)+.3(3500)+.1(6000)=$1,050 EMV(Custom Decorated)=.2(-7000)+.4(1500)+.3(2500)+.1(9500)=$900 Best Decision by Expected Value: Minimal Accessories. Best EMV = $1,050. (f). If someone has a crystal ball which tells the housing market is going to be strong for sure, what is the value of this perfect information? (3 points) Payoff (Strong)= $3, 500 with Model homes furnished with minimal accessories. VPI(Strong)= =$2450. (g). Based on the probabilities given above, what is the expected value of perfect information (EVPI) about the housing market if it is available? (5 points) EVwPI=.2(-1500)+.4(1500)+.3(3500)+.1(9500)=$2300 EVPI=EVwPI- Best EMV = =$1, Pickens Exploration Company has been offered a lease to drill for oil on a particular piece of property. While oil has been found on nearby land, there are no assurances that Pickens will be successful in finding oil. The company feels that it will strike a major find, an average find, or a dry hole. A major find can be sold to an oil company for $6 million, while an average find will only bring in $2 million (also will be sold to an oil company). A dry hole will cost the company $80,000 to cap (definitely no one will buy it). The cost of the lease is $400,000 plus 20% of the revenue if the oil well is sold to an oil company. Pickens estimates that it can drill a well at a cost of $160,000. Without based on historical evidence that there is a 5% chance that the well will be a major find, a 45% chance that it will be an average find, and a 50% chance that it will be a dry hole. In order to get a better estimate of the probability of finding oil in the well, the geologist is contemplating performing either a geologic or a seismic test. A geologic test will cost $20,000. From the past experience, if the test predicts oil, the geologist believes that the following conditional probabilities hold: P(test predicts oil/major find) =.75 P(test predicts oil/average find) =.50 P(test predicts oil/dry hole) =.20 Instead of the geologic test, the firm can perform the more detailed seismic test, which costs $50,000. From the past experience, if this test predicts oil, the geologist believes that the following conditional probabilities hold: Page 11 of 17
12 P(test predicts oil/major find) =.90 P(test predicts oil/average find) =.60 P(test predicts oil/dry hole) =.10 Pickens can do the testing prior to deciding whether or not to procure the lease and drill. If Pickens gets a prediction of oil from either the geologic or seismic tests, it can sell a half-interest in the well to a Dallas investor for $800,000. In this case Pickens will be responsible for any and all losses on the well should it lose money, but will split profits on the well equally with the investor. To help making the decision, the company computes the payoffs before any test for the results of major find, average find, and dry hole. Payoff: MF = 6* =4.24M; AF = 2* =1.04M; DH = = -0.64M (all in millions) After the geologic test, if the test predicts oil, the payoffs for selling half-interest to the Dallas investor and not selling for the results of major find, average find, and dry hole are computed below. Payoffs with selling ½ interest: Payoffs with not selling ½ interest: MF=( )/2+0.8=2.91M; AF=( )/2+0.8=1.31; DH= = 0.14M MF= =4.22M; AF= =1.02; DH= = -0.66M After the geologic test, if the test predicts no oil, the payoffs for the results of major find, average find, and dry hole are computed below. Payoffs: MF= =4.22M; AF= =1.02; DH= = -0.66M After the seismic test, if the test predicts oil, the payoffs for selling half-interest to the Dallas investor and not selling for the results of major find, average find, and dry hole are computed below. Payoffs with selling ½ interest: Payoffs with not selling ½ interest: MF=( )/2+0.8=2.895M; AF=( )/2+0.8=1.295; DH= = 0.11M MF= =4.19M; AF= =0.99; DH= = -0.69M Page 12 of 17
13 After the seismic test, if the test predicts no oil, the payoffs for the results of major find, average find, and dry hole are computed below. Payoffs: MF= =4.19M; AF= =0.99; DH= = -0.69M With the help of a convenient Excel template, the posterior (revised) probability analysis for the geologic test is shown in the following table. (PO: predict oil; PNO: predict no oil) State of nature(sn) P(SN) P(I/SN) P(I,SN) P(SN/I) PO PNO PO PNO PO PNO MF (major find) AF (average find) DH (dry hole) P(I)= Similarly with the help of the Excel template, the posterior (revised) probability analysis for the seismic test is shown in the following table. State of nature(sn) P(SN) P(I/SN) P(I,SN) P(SN/I) PO PNO PO PNO PO PNO MF (major find) AF (average find) DH (dry hole) P(I)= (a). From the above revised probability tables, what is the probability of an average finding if the geologic test predicts no oil, i.e., P(average find/test predicts no oil)? What is the probability of a major finding if the seismic test predicts oil, i.e., P(major find/test predicts oil)? (2 points) P(AF/PNO)=0.353; P(MF/PO)=0.123 (b). The following decision tree represents the complete decision situation. The payoffs and the related probabilities are included. Perform the decision tree analysis. That is to complete the computation of the expected values for all chance nodes and the choice of the best decisions for all decision nodes. (15 points) Page 13 of 17
14 Page 14 of 17
15 (c). What optimal decision(s) and sequence should Pickens take and what is the expected payoff? (4 points) Do Seismic Test, if test predicts oil then sell half the interest and drill; if test predicts no oil then do not drill. The final and overall expected payoff = EV (ST)= 0.453M (d). What is the value of the geologic test? (3 points) EVSI(GT)= = 0.097M (e). What is the value of the seismic test? (3 points) EVSI(ST)= = 0.143M Page 15 of 17
16 Areas of the Standard Normal Distribution 0 z An entry in the table is the proportion under the entire curve which is between Z = 0 and a positive value of z. Areas for negative values of z are obtained by symmetry. z Page 16 of 17
17 Page 17 of 17
Chapter 13 Decision Analysis
 Problem Formulation Chapter 13 Decision Analysis Decision Making without Probabilities Decision Making with Probabilities Risk Analysis and Sensitivity Analysis Decision Analysis with Sample Information
Problem Formulation Chapter 13 Decision Analysis Decision Making without Probabilities Decision Making with Probabilities Risk Analysis and Sensitivity Analysis Decision Analysis with Sample Information
Textbook: pp Chapter 11: Project Management
 1 Textbook: pp. 405-444 Chapter 11: Project Management 2 Learning Objectives After completing this chapter, students will be able to: Understand how to plan, monitor, and control projects with the use
1 Textbook: pp. 405-444 Chapter 11: Project Management 2 Learning Objectives After completing this chapter, students will be able to: Understand how to plan, monitor, and control projects with the use
Project Management Chapter 13
 Lecture 12 Project Management Chapter 13 Introduction n Managing large-scale, complicated projects effectively is a difficult problem and the stakes are high. n The first step in planning and scheduling
Lecture 12 Project Management Chapter 13 Introduction n Managing large-scale, complicated projects effectively is a difficult problem and the stakes are high. n The first step in planning and scheduling
Introduction. Introduction. Six Steps of PERT/CPM. Six Steps of PERT/CPM LEARNING OBJECTIVES
 Valua%on and pricing (November 5, 2013) LEARNING OBJECTIVES Lecture 12 Project Management Olivier J. de Jong, LL.M., MM., MBA, CFD, CFFA, AA www.olivierdejong.com 1. Understand how to plan, monitor, and
Valua%on and pricing (November 5, 2013) LEARNING OBJECTIVES Lecture 12 Project Management Olivier J. de Jong, LL.M., MM., MBA, CFD, CFFA, AA www.olivierdejong.com 1. Understand how to plan, monitor, and
Module 15 July 28, 2014
 Module 15 July 28, 2014 General Approach to Decision Making Many Uses: Capacity Planning Product/Service Design Equipment Selection Location Planning Others Typically Used for Decisions Characterized by
Module 15 July 28, 2014 General Approach to Decision Making Many Uses: Capacity Planning Product/Service Design Equipment Selection Location Planning Others Typically Used for Decisions Characterized by
Project Planning. Identifying the Work to Be Done. Gantt Chart. A Gantt Chart. Given: Activity Sequencing Network Diagrams
 Project Planning Identifying the Work to Be Done Activity Sequencing Network Diagrams Given: Statement of work written description of goals work & time frame of project Work Breakdown Structure Be able
Project Planning Identifying the Work to Be Done Activity Sequencing Network Diagrams Given: Statement of work written description of goals work & time frame of project Work Breakdown Structure Be able
Chapter 18 Student Lecture Notes 18-1
 Chapter 18 Student Lecture Notes 18-1 Business Statistics: A Decision-Making Approach 6 th Edition Chapter 18 Introduction to Decision Analysis 5 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Chap 18-1 Chapter Goals After completing
Chapter 18 Student Lecture Notes 18-1 Business Statistics: A Decision-Making Approach 6 th Edition Chapter 18 Introduction to Decision Analysis 5 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Chap 18-1 Chapter Goals After completing
MBF1413 Quantitative Methods
 MBF1413 Quantitative Methods Prepared by Dr Khairul Anuar 4: Decision Analysis Part 1 www.notes638.wordpress.com 1. Problem Formulation a. Influence Diagrams b. Payoffs c. Decision Trees Content 2. Decision
MBF1413 Quantitative Methods Prepared by Dr Khairul Anuar 4: Decision Analysis Part 1 www.notes638.wordpress.com 1. Problem Formulation a. Influence Diagrams b. Payoffs c. Decision Trees Content 2. Decision
Project Management. Chapter 2. Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
 Project Management Chapter 2 02-0 1 What is a Project? Project An interrelated set of activities with a definite starting and ending point, which results in a unique outcome for a specific allocation of
Project Management Chapter 2 02-0 1 What is a Project? Project An interrelated set of activities with a definite starting and ending point, which results in a unique outcome for a specific allocation of
Objective of Decision Analysis. Determine an optimal decision under uncertain future events
 Decision Analysis Objective of Decision Analysis Determine an optimal decision under uncertain future events Formulation of Decision Problem Clear statement of the problem Identify: The decision alternatives
Decision Analysis Objective of Decision Analysis Determine an optimal decision under uncertain future events Formulation of Decision Problem Clear statement of the problem Identify: The decision alternatives
UNIT 5 DECISION MAKING
 UNIT 5 DECISION MAKING This unit: UNDER UNCERTAINTY Discusses the techniques to deal with uncertainties 1 INTRODUCTION Few decisions in construction industry are made with certainty. Need to look at: The
UNIT 5 DECISION MAKING This unit: UNDER UNCERTAINTY Discusses the techniques to deal with uncertainties 1 INTRODUCTION Few decisions in construction industry are made with certainty. Need to look at: The
Agenda. Lecture 2. Decision Analysis. Key Characteristics. Terminology. Structuring Decision Problems
 Agenda Lecture 2 Theory >Introduction to Making > Making Without Probabilities > Making With Probabilities >Expected Value of Perfect Information >Next Class 1 2 Analysis >Techniques used to make decisions
Agenda Lecture 2 Theory >Introduction to Making > Making Without Probabilities > Making With Probabilities >Expected Value of Perfect Information >Next Class 1 2 Analysis >Techniques used to make decisions
Project Planning. Jesper Larsen. Department of Management Engineering Technical University of Denmark
 Project Planning jesla@man.dtu.dk Department of Management Engineering Technical University of Denmark 1 Project Management Project Management is a set of techniques that helps management manage large-scale
Project Planning jesla@man.dtu.dk Department of Management Engineering Technical University of Denmark 1 Project Management Project Management is a set of techniques that helps management manage large-scale
Decision Analysis. Chapter Topics
 Decision Analysis Chapter Topics Components of Decision Making Decision Making without Probabilities Decision Making with Probabilities Decision Analysis with Additional Information Utility Decision Analysis
Decision Analysis Chapter Topics Components of Decision Making Decision Making without Probabilities Decision Making with Probabilities Decision Analysis with Additional Information Utility Decision Analysis
CHAPTER 5. Project Scheduling Models
 CHAPTER 5 Project Scheduling Models 1 5.1 Introduction A project is a collection of tasks that must be completed in minimum time or at minimal cost. Objectives of Project Scheduling Completing the project
CHAPTER 5 Project Scheduling Models 1 5.1 Introduction A project is a collection of tasks that must be completed in minimum time or at minimal cost. Objectives of Project Scheduling Completing the project
Decision Analysis. Chapter 12. Chapter Topics. Decision Analysis Components of Decision Making. Decision Analysis Overview
 Chapter Topics Components of Decision Making with Additional Information Chapter 12 Utility 12-1 12-2 Overview Components of Decision Making A state of nature is an actual event that may occur in the future.
Chapter Topics Components of Decision Making with Additional Information Chapter 12 Utility 12-1 12-2 Overview Components of Decision Making A state of nature is an actual event that may occur in the future.
1 of 14 4/27/2009 7:45 AM
 1 of 14 4/27/2009 7:45 AM Chapter 7 - Network Models in Project Management INTRODUCTION Most realistic projects that organizations like Microsoft, General Motors, or the U.S. Defense Department undertake
1 of 14 4/27/2009 7:45 AM Chapter 7 - Network Models in Project Management INTRODUCTION Most realistic projects that organizations like Microsoft, General Motors, or the U.S. Defense Department undertake
A B C D E F 1 PAYOFF TABLE 2. States of Nature
 Chapter Decision Analysis Problem Formulation Decision Making without Probabilities Decision Making with Probabilities Risk Analysis and Sensitivity Analysis Decision Analysis with Sample Information Computing
Chapter Decision Analysis Problem Formulation Decision Making without Probabilities Decision Making with Probabilities Risk Analysis and Sensitivity Analysis Decision Analysis with Sample Information Computing
- Economic Climate Country Decline Stable Improve South Korea Philippines Mexico
 1) Micro-comp is a Toronto based manufacturer of personal computers. It is planning to build a new manufacturing and distribution facility in South Korea, Philippines, or Mexico. The profit (in $ millions)
1) Micro-comp is a Toronto based manufacturer of personal computers. It is planning to build a new manufacturing and distribution facility in South Korea, Philippines, or Mexico. The profit (in $ millions)
CHAPTER 9: PROJECT MANAGEMENT
 CHAPTER 9: PROJECT MANAGEMENT The aim is to coordinate and plan a single job consisting lots of tasks between which precedence relationships exist Project planning Most popular planning tools are utilized
CHAPTER 9: PROJECT MANAGEMENT The aim is to coordinate and plan a single job consisting lots of tasks between which precedence relationships exist Project planning Most popular planning tools are utilized
56:171 Operations Research Midterm Examination Solutions PART ONE
 56:171 Operations Research Midterm Examination Solutions Fall 1997 Answer both questions of Part One, and 4 (out of 5) problems from Part Two. Possible Part One: 1. True/False 15 2. Sensitivity analysis
56:171 Operations Research Midterm Examination Solutions Fall 1997 Answer both questions of Part One, and 4 (out of 5) problems from Part Two. Possible Part One: 1. True/False 15 2. Sensitivity analysis
Decision Analysis. Chapter Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
 Decision Analysis Chapter 12 12-1 Chapter Topics Components of Decision Making Decision Making without Probabilities Decision Making with Probabilities Decision Analysis with Additional Information Utility
Decision Analysis Chapter 12 12-1 Chapter Topics Components of Decision Making Decision Making without Probabilities Decision Making with Probabilities Decision Analysis with Additional Information Utility
Decision Analysis CHAPTER LEARNING OBJECTIVES CHAPTER OUTLINE. After completing this chapter, students will be able to:
 CHAPTER 3 Decision Analysis LEARNING OBJECTIVES After completing this chapter, students will be able to: 1. List the steps of the decision-making process. 2. Describe the types of decision-making environments.
CHAPTER 3 Decision Analysis LEARNING OBJECTIVES After completing this chapter, students will be able to: 1. List the steps of the decision-making process. 2. Describe the types of decision-making environments.
A convenient analytical and visual technique of PERT and CPM prove extremely valuable in assisting the managers in managing the projects.
 Introduction Any project involves planning, scheduling and controlling a number of interrelated activities with use of limited resources, namely, men, machines, materials, money and time. The projects
Introduction Any project involves planning, scheduling and controlling a number of interrelated activities with use of limited resources, namely, men, machines, materials, money and time. The projects
SCHEDULE CREATION AND ANALYSIS. 1 Powered by POeT Solvers Limited
 SCHEDULE CREATION AND ANALYSIS 1 www.pmtutor.org Powered by POeT Solvers Limited While building the project schedule, we need to consider all risk factors, assumptions and constraints imposed on the project
SCHEDULE CREATION AND ANALYSIS 1 www.pmtutor.org Powered by POeT Solvers Limited While building the project schedule, we need to consider all risk factors, assumptions and constraints imposed on the project
Causes of Poor Decisions
 Lecture 7: Decision Analysis Decision process Decision tree analysis The Decision Process Specify objectives and the criteria for making a choice Develop alternatives Analyze and compare alternatives Select
Lecture 7: Decision Analysis Decision process Decision tree analysis The Decision Process Specify objectives and the criteria for making a choice Develop alternatives Analyze and compare alternatives Select
INSE 6230: Assignment 1 - Winter (0% of final grade) 1. The table below provides information about a short IT project.
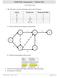 INSE 6230: Assignment - Winter 208 (0% of final grade). The table below provides information about a short IT project. Activity Predecessors Duration (Months) A - 2 B - 3 C A 4 D A, B 2 E D 2 F B, C, E
INSE 6230: Assignment - Winter 208 (0% of final grade). The table below provides information about a short IT project. Activity Predecessors Duration (Months) A - 2 B - 3 C A 4 D A, B 2 E D 2 F B, C, E
SCHOOL OF BUSINESS, ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT. BF360 Operations Research
 SCHOOL OF BUSINESS, ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT BF360 Operations Research Unit 5 Moses Mwale e-mail: moses.mwale@ictar.ac.zm BF360 Operations Research Contents Unit 5: Decision Analysis 3 5.1 Components
SCHOOL OF BUSINESS, ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT BF360 Operations Research Unit 5 Moses Mwale e-mail: moses.mwale@ictar.ac.zm BF360 Operations Research Contents Unit 5: Decision Analysis 3 5.1 Components
Probabilistic Completion Time in Project Scheduling Min Khee Chin 1, Sie Long Kek 2, Sy Yi Sim 3, Ta Wee Seow 4
 Probabilistic Completion Time in Project Scheduling Min Khee Chin 1, Sie Long Kek 2, Sy Yi Sim 3, Ta Wee Seow 4 1 Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia 2 Center
Probabilistic Completion Time in Project Scheduling Min Khee Chin 1, Sie Long Kek 2, Sy Yi Sim 3, Ta Wee Seow 4 1 Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia 2 Center
Decision Making Models
 Decision Making Models Prof. Yongwon Seo (seoyw@cau.ac.kr) College of Business Administration, CAU Decision Theory Decision theory problems are characterized by the following: A list of alternatives. A
Decision Making Models Prof. Yongwon Seo (seoyw@cau.ac.kr) College of Business Administration, CAU Decision Theory Decision theory problems are characterized by the following: A list of alternatives. A
Chapter 3. Decision Analysis. Learning Objectives
 Chapter 3 Decision Analysis To accompany Quantitative Analysis for Management, Eleventh Edition, by Render, Stair, and Hanna Power Point slides created by Brian Peterson Learning Objectives After completing
Chapter 3 Decision Analysis To accompany Quantitative Analysis for Management, Eleventh Edition, by Render, Stair, and Hanna Power Point slides created by Brian Peterson Learning Objectives After completing
Decision Making. DKSharma
 Decision Making DKSharma Decision making Learning Objectives: To make the students understand the concepts of Decision making Decision making environment; Decision making under certainty; Decision making
Decision Making DKSharma Decision making Learning Objectives: To make the students understand the concepts of Decision making Decision making environment; Decision making under certainty; Decision making
MBF1413 Quantitative Methods
 MBF1413 Quantitative Methods Prepared by Dr Khairul Anuar 5: Decision Analysis Part II www.notes638.wordpress.com Content 4. Risk Analysis and Sensitivity Analysis a. Risk Analysis b. b. Sensitivity Analysis
MBF1413 Quantitative Methods Prepared by Dr Khairul Anuar 5: Decision Analysis Part II www.notes638.wordpress.com Content 4. Risk Analysis and Sensitivity Analysis a. Risk Analysis b. b. Sensitivity Analysis
Teori Pengambilan Keputusan. Week 12 Project Management
 Teori Pengambilan Keputusan Week 1 Project Management Project Management Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) Critical Path Method (CPM) PERT and CPM Network techniques Developed in 195 s CPM
Teori Pengambilan Keputusan Week 1 Project Management Project Management Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) Critical Path Method (CPM) PERT and CPM Network techniques Developed in 195 s CPM
Dr. Abdallah Abdallah Fall Term 2014
 Quantitative Analysis Dr. Abdallah Abdallah Fall Term 2014 1 Decision analysis Fundamentals of decision theory models Ch. 3 2 Decision theory Decision theory is an analytic and systemic way to tackle problems
Quantitative Analysis Dr. Abdallah Abdallah Fall Term 2014 1 Decision analysis Fundamentals of decision theory models Ch. 3 2 Decision theory Decision theory is an analytic and systemic way to tackle problems
56:171 Operations Research Midterm Examination Solutions PART ONE
 56:171 Operations Research Midterm Examination Solutions Fall 1997 Write your name on the first page, and initial the other pages. Answer both questions of Part One, and 4 (out of 5) problems from Part
56:171 Operations Research Midterm Examination Solutions Fall 1997 Write your name on the first page, and initial the other pages. Answer both questions of Part One, and 4 (out of 5) problems from Part
INSE 6230 Total Quality Project Management Winter 2018 Quiz I. Max : 70 points. This is a closed book exam. Answer all the questions in the booklet.
 . Surname, given names: Student Number: INSE 6230 Total Quality Project Management Winter 2018 Quiz I. Max : 70 points This is a closed book exam. Answer all the questions in the booklet. Ensure that your
. Surname, given names: Student Number: INSE 6230 Total Quality Project Management Winter 2018 Quiz I. Max : 70 points This is a closed book exam. Answer all the questions in the booklet. Ensure that your
Full file at CHAPTER 3 Decision Analysis
 CHAPTER 3 Decision Analysis TRUE/FALSE 3.1 Expected Monetary Value (EMV) is the average or expected monetary outcome of a decision if it can be repeated a large number of times. 3.2 Expected Monetary Value
CHAPTER 3 Decision Analysis TRUE/FALSE 3.1 Expected Monetary Value (EMV) is the average or expected monetary outcome of a decision if it can be repeated a large number of times. 3.2 Expected Monetary Value
UNIT-II Project Organization and Scheduling Project Element
 UNIT-II Project Organization and Scheduling Project Element Five Key Elements are Unique. Projects are unique, one-of-a-kind, never been done before. Start and Stop Date. Projects must have a definite
UNIT-II Project Organization and Scheduling Project Element Five Key Elements are Unique. Projects are unique, one-of-a-kind, never been done before. Start and Stop Date. Projects must have a definite
DECISION ANALYSIS. Decision often must be made in uncertain environments. Examples:
 DECISION ANALYSIS Introduction Decision often must be made in uncertain environments. Examples: Manufacturer introducing a new product in the marketplace. Government contractor bidding on a new contract.
DECISION ANALYSIS Introduction Decision often must be made in uncertain environments. Examples: Manufacturer introducing a new product in the marketplace. Government contractor bidding on a new contract.
The Course So Far. Decision Making in Deterministic Domains. Decision Making in Uncertain Domains. Next: Decision Making in Uncertain Domains
 The Course So Far Decision Making in Deterministic Domains search planning Decision Making in Uncertain Domains Uncertainty: adversarial Minimax Next: Decision Making in Uncertain Domains Uncertainty:
The Course So Far Decision Making in Deterministic Domains search planning Decision Making in Uncertain Domains Uncertainty: adversarial Minimax Next: Decision Making in Uncertain Domains Uncertainty:
Optimization Prof. A. Goswami Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur. Lecture - 18 PERT
 Optimization Prof. A. Goswami Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 18 PERT (Refer Slide Time: 00:56) In the last class we completed the C P M critical path analysis
Optimization Prof. A. Goswami Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 18 PERT (Refer Slide Time: 00:56) In the last class we completed the C P M critical path analysis
DECISION ANALYSIS. (Hillier & Lieberman Introduction to Operations Research, 8 th edition)
 DECISION ANALYSIS (Hillier & Lieberman Introduction to Operations Research, 8 th edition) Introduction Decision often must be made in uncertain environments Examples: Manufacturer introducing a new product
DECISION ANALYSIS (Hillier & Lieberman Introduction to Operations Research, 8 th edition) Introduction Decision often must be made in uncertain environments Examples: Manufacturer introducing a new product
PROJECT MANAGEMENT. Trying to manage a project without project management is like trying to play a football game without a game plan
 PROJECT MANAGEMENT Trying to manage a project without project management is like trying to play a football game without a game plan K. Tate (Past Board Member, PMI). Brad Fink 28 February 2013 Executive
PROJECT MANAGEMENT Trying to manage a project without project management is like trying to play a football game without a game plan K. Tate (Past Board Member, PMI). Brad Fink 28 February 2013 Executive
Decision Making. D.K.Sharma
 Decision Making D.K.Sharma 1 Decision making Learning Objectives: To make the students understand the concepts of Decision making Decision making environment; Decision making under certainty; Decision
Decision Making D.K.Sharma 1 Decision making Learning Objectives: To make the students understand the concepts of Decision making Decision making environment; Decision making under certainty; Decision
Chapter 4: Decision Analysis Suggested Solutions
 Chapter 4: Decision Analysis Suggested Solutions Fall 2010 Que 1a. 250 25 75 b. Decision Maximum Minimum Profit Profit 250 25 75 Optimistic approach: select Conservative approach: select Regret or opportunity
Chapter 4: Decision Analysis Suggested Solutions Fall 2010 Que 1a. 250 25 75 b. Decision Maximum Minimum Profit Profit 250 25 75 Optimistic approach: select Conservative approach: select Regret or opportunity
Chapter 12. Decision Analysis
 Page 1 of 80 Chapter 12. Decision Analysis [Page 514] [Page 515] In the previous chapters dealing with linear programming, models were formulated and solved in order to aid the manager in making a decision.
Page 1 of 80 Chapter 12. Decision Analysis [Page 514] [Page 515] In the previous chapters dealing with linear programming, models were formulated and solved in order to aid the manager in making a decision.
Introduction LEARNING OBJECTIVES. The Six Steps in Decision Making. Thompson Lumber Company. Thompson Lumber Company
 Valua%on and pricing (November 5, 2013) Lecture 4 Decision making (part 1) Olivier J. de Jong, LL.M., MM., MBA, CFD, CFFA, AA www.olivierdejong.com LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. List the steps of the decision-making
Valua%on and pricing (November 5, 2013) Lecture 4 Decision making (part 1) Olivier J. de Jong, LL.M., MM., MBA, CFD, CFFA, AA www.olivierdejong.com LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. List the steps of the decision-making
Outline. Global Company Profile: Bechtel Group. The Importance of Project Management Project Planning Project Scheduling Project Controlling
 Project Management Outline Global Company Profile: Bechtel Group The Importance of Project Management Project Planning Project Scheduling Project Controlling Outline - Continued Project Management Techniques:
Project Management Outline Global Company Profile: Bechtel Group The Importance of Project Management Project Planning Project Scheduling Project Controlling Outline - Continued Project Management Techniques:
Final: Total 200 points (3-hour exam)
 Final: Total 200 points (3-hour exam) [Engineering Economics] IRR Calculation [15 points] One alternative for improving a company s operations is to do nothing for the next 2 years and then spend $10,000
Final: Total 200 points (3-hour exam) [Engineering Economics] IRR Calculation [15 points] One alternative for improving a company s operations is to do nothing for the next 2 years and then spend $10,000
19 Decision Making. Expected Monetary Value Expected Opportunity Loss Return-to-Risk Ratio Decision Making with Sample Information
 19 Decision Making USING STATISTICS @ The Reliable Fund 19.1 Payoff Tables and Decision Trees 19.2 Criteria for Decision Making Maximax Payoff Maximin Payoff Expected Monetary Value Expected Opportunity
19 Decision Making USING STATISTICS @ The Reliable Fund 19.1 Payoff Tables and Decision Trees 19.2 Criteria for Decision Making Maximax Payoff Maximin Payoff Expected Monetary Value Expected Opportunity
Project Management -- Developing the Project Plan
 Project Management -- Developing the Project Plan Dr. Tai-Yue Wang Department of Industrial and Information Management National Cheng Kung University Tainan, TAIWAN, ROC 1 Where We Are Now 6 2 Developing
Project Management -- Developing the Project Plan Dr. Tai-Yue Wang Department of Industrial and Information Management National Cheng Kung University Tainan, TAIWAN, ROC 1 Where We Are Now 6 2 Developing
Decision Analysis REVISED TEACHING SUGGESTIONS ALTERNATIVE EXAMPLES
 M03_REND6289_0_IM_C03.QXD 5/7/08 3:48 PM Page 7 3 C H A P T E R Decision Analysis TEACHING SUGGESTIONS Teaching Suggestion 3.: Using the Steps of the Decision-Making Process. The six steps used in decision
M03_REND6289_0_IM_C03.QXD 5/7/08 3:48 PM Page 7 3 C H A P T E R Decision Analysis TEACHING SUGGESTIONS Teaching Suggestion 3.: Using the Steps of the Decision-Making Process. The six steps used in decision
The Course So Far. Atomic agent: uninformed, informed, local Specific KR languages
 The Course So Far Traditional AI: Deterministic single agent domains Atomic agent: uninformed, informed, local Specific KR languages Constraint Satisfaction Logic and Satisfiability STRIPS for Classical
The Course So Far Traditional AI: Deterministic single agent domains Atomic agent: uninformed, informed, local Specific KR languages Constraint Satisfaction Logic and Satisfiability STRIPS for Classical
PROJECT MANAGEMENT COURSE 5: PROJECT TIME MANAGEMENT. G.N. Sandhy Widyasthana
 PROJECT MANAGEMENT COURSE 5: PROJECT TIME MANAGEMENT G.N. Sandhy Widyasthana widyasthana@gmail.com 022 70702020 081 225 702020 1 2 3 Process of identifying the specific actions to be performed to produce
PROJECT MANAGEMENT COURSE 5: PROJECT TIME MANAGEMENT G.N. Sandhy Widyasthana widyasthana@gmail.com 022 70702020 081 225 702020 1 2 3 Process of identifying the specific actions to be performed to produce
36106 Managerial Decision Modeling Decision Analysis in Excel
 36106 Managerial Decision Modeling Decision Analysis in Excel Kipp Martin University of Chicago Booth School of Business October 19, 2017 Reading and Excel Files Reading: Powell and Baker: Sections 13.1,
36106 Managerial Decision Modeling Decision Analysis in Excel Kipp Martin University of Chicago Booth School of Business October 19, 2017 Reading and Excel Files Reading: Powell and Baker: Sections 13.1,
Decision Making Supplement A
 Decision Making Supplement A Break-Even Analysis Break-even analysis is used to compare processes by finding the volume at which two different processes have equal total costs. Break-even point is the
Decision Making Supplement A Break-Even Analysis Break-even analysis is used to compare processes by finding the volume at which two different processes have equal total costs. Break-even point is the
Learning Objectives = = where X i is the i t h outcome of a decision, p i is the probability of the i t h
 Learning Objectives After reading Chapter 15 and working the problems for Chapter 15 in the textbook and in this Workbook, you should be able to: Distinguish between decision making under uncertainty and
Learning Objectives After reading Chapter 15 and working the problems for Chapter 15 in the textbook and in this Workbook, you should be able to: Distinguish between decision making under uncertainty and
A Taxonomy of Decision Models
 Decision Trees and Influence Diagrams Prof. Carlos Bana e Costa Lecture topics: Decision trees and influence diagrams Value of information and control A case study: Drilling for oil References: Clemen,
Decision Trees and Influence Diagrams Prof. Carlos Bana e Costa Lecture topics: Decision trees and influence diagrams Value of information and control A case study: Drilling for oil References: Clemen,
Decision Analysis under Uncertainty. Christopher Grigoriou Executive MBA/HEC Lausanne
 Decision Analysis under Uncertainty Christopher Grigoriou Executive MBA/HEC Lausanne 2007-2008 2008 Introduction Examples of decision making under uncertainty in the business world; => Trade-off between
Decision Analysis under Uncertainty Christopher Grigoriou Executive MBA/HEC Lausanne 2007-2008 2008 Introduction Examples of decision making under uncertainty in the business world; => Trade-off between
Project Management Fundamentals
 Project Management Fundamentals Course No: B04-003 Credit: 4 PDH Najib Gerges, Ph.D., P.E. Continuing Education and Development, Inc. 9 Greyridge Farm Court Stony Point, NY 10980 P: (877) 322-5800 F: (877)
Project Management Fundamentals Course No: B04-003 Credit: 4 PDH Najib Gerges, Ph.D., P.E. Continuing Education and Development, Inc. 9 Greyridge Farm Court Stony Point, NY 10980 P: (877) 322-5800 F: (877)
Project Risk Evaluation and Management Exercises (Part II, Chapters 4, 5, 6 and 7)
 Project Risk Evaluation and Management Exercises (Part II, Chapters 4, 5, 6 and 7) Chapter II.4 Exercise 1 Explain in your own words the role that data can play in the development of models of uncertainty
Project Risk Evaluation and Management Exercises (Part II, Chapters 4, 5, 6 and 7) Chapter II.4 Exercise 1 Explain in your own words the role that data can play in the development of models of uncertainty
Decision making under uncertainty
 Decision making under uncertainty 1 Outline 1. Components of decision making 2. Criteria for decision making 3. Utility theory 4. Decision trees 5. Posterior probabilities using Bayes rule 6. The Monty
Decision making under uncertainty 1 Outline 1. Components of decision making 2. Criteria for decision making 3. Utility theory 4. Decision trees 5. Posterior probabilities using Bayes rule 6. The Monty
Allocate and Level Project Resources
 Allocate and Level Project Resources Resource Allocation: Defined Resource Allocation is the scheduling of activities and the resources required by those activities while taking into consideration both
Allocate and Level Project Resources Resource Allocation: Defined Resource Allocation is the scheduling of activities and the resources required by those activities while taking into consideration both
Real-World Project Management. Chapter 15
 Real-World Project Chapter 15 Characteristics of Project Unique one-time focus Difficulties arise from originality Subject to uncertainties Unexplained or unplanned events often arise, affecting resources,
Real-World Project Chapter 15 Characteristics of Project Unique one-time focus Difficulties arise from originality Subject to uncertainties Unexplained or unplanned events often arise, affecting resources,
POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA
 POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF MANAGEMENT PROJECT MANAGEMENT BACHELOR OF BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION 07BBMA SUBJECT CODE: PRM422S DATE: DURATION: MARKS: EXAMINERS: MODERATOR:
POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF MANAGEMENT PROJECT MANAGEMENT BACHELOR OF BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION 07BBMA SUBJECT CODE: PRM422S DATE: DURATION: MARKS: EXAMINERS: MODERATOR:
Textbook: pp Chapter 3: Decision Analysis
 1 Textbook: pp. 81-128 Chapter 3: Decision Analysis 2 Learning Objectives After completing this chapter, students will be able to: List the steps of the decision-making process. Describe the types of decision-making
1 Textbook: pp. 81-128 Chapter 3: Decision Analysis 2 Learning Objectives After completing this chapter, students will be able to: List the steps of the decision-making process. Describe the types of decision-making
56:171 Operations Research Midterm Examination October 28, 1997 PART ONE
 56:171 Operations Research Midterm Examination October 28, 1997 Write your name on the first page, and initial the other pages. Answer both questions of Part One, and 4 (out of 5) problems from Part Two.
56:171 Operations Research Midterm Examination October 28, 1997 Write your name on the first page, and initial the other pages. Answer both questions of Part One, and 4 (out of 5) problems from Part Two.
Construction Management
 Construction Management 1. Which one of the following represents an activity A. excavation for foundation B. curing of concrete C. setting of question paper D. preparation of breakfast 2. Pick up the incorrect
Construction Management 1. Which one of the following represents an activity A. excavation for foundation B. curing of concrete C. setting of question paper D. preparation of breakfast 2. Pick up the incorrect
DECISION ANALYSIS: INTRODUCTION. Métodos Cuantitativos M. En C. Eduardo Bustos Farias 1
 DECISION ANALYSIS: INTRODUCTION Cuantitativos M. En C. Eduardo Bustos Farias 1 Agenda Decision analysis in general Structuring decision problems Decision making under uncertainty - without probability
DECISION ANALYSIS: INTRODUCTION Cuantitativos M. En C. Eduardo Bustos Farias 1 Agenda Decision analysis in general Structuring decision problems Decision making under uncertainty - without probability
Chapter 2 supplement. Decision Analysis
 Chapter 2 supplement At the operational level hundreds of decisions are made in order to achieve local outcomes that contribute to the achievement of the company's overall strategic goal. These local outcomes
Chapter 2 supplement At the operational level hundreds of decisions are made in order to achieve local outcomes that contribute to the achievement of the company's overall strategic goal. These local outcomes
DECISION MAKING. Decision making under conditions of uncertainty
 DECISION MAKING Decision making under conditions of uncertainty Set of States of nature: S 1,..., S j,..., S n Set of decision alternatives: d 1,...,d i,...,d m The outcome of the decision C ij depends
DECISION MAKING Decision making under conditions of uncertainty Set of States of nature: S 1,..., S j,..., S n Set of decision alternatives: d 1,...,d i,...,d m The outcome of the decision C ij depends
Lecture 5: Project Management
 Lecture 5: Management organization structure ritical path method (PM) Time/cost tradeoff PM with three activity it time estimates t Readings: hapter 10 Management series of related jobs usually directed
Lecture 5: Management organization structure ritical path method (PM) Time/cost tradeoff PM with three activity it time estimates t Readings: hapter 10 Management series of related jobs usually directed
After complete studying this chapter, You should be able to
 Chapter 10 Project Management Ch10: What Is Project Management? After complete studying this chapter, You should be able to Define key terms like Project, Project Management, Discuss the main characteristics
Chapter 10 Project Management Ch10: What Is Project Management? After complete studying this chapter, You should be able to Define key terms like Project, Project Management, Discuss the main characteristics
MODULE: INTRODUCTION TO PROJECT MANAGEMENT / PROJECT MANAGEMENT
 Programme BA (Hons) Fashion and Textiles (Top-Up) BA (Hons) Graphic Design with Animation (Top-Up) BA (Hons) Interior Design Cohort FDI- BFT(TP)/14B/PT FDI- BGDA(TP)/14B/PT FDI-BAID/13B/FT Examinations
Programme BA (Hons) Fashion and Textiles (Top-Up) BA (Hons) Graphic Design with Animation (Top-Up) BA (Hons) Interior Design Cohort FDI- BFT(TP)/14B/PT FDI- BGDA(TP)/14B/PT FDI-BAID/13B/FT Examinations
Chapter 11: PERT for Project Planning and Scheduling
 Chapter 11: PERT for Project Planning and Scheduling PERT, the Project Evaluation and Review Technique, is a network-based aid for planning and scheduling the many interrelated tasks in a large and complex
Chapter 11: PERT for Project Planning and Scheduling PERT, the Project Evaluation and Review Technique, is a network-based aid for planning and scheduling the many interrelated tasks in a large and complex
6/7/2018. Overview PERT / CPM PERT/CPM. Project Scheduling PERT/CPM PERT/CPM
 /7/018 PERT / CPM BSAD 0 Dave Novak Summer 018 Overview Introduce PERT/CPM Discuss what a critical path is Discuss critical path algorithm Example Source: Anderson et al., 01 Quantitative Methods for Business
/7/018 PERT / CPM BSAD 0 Dave Novak Summer 018 Overview Introduce PERT/CPM Discuss what a critical path is Discuss critical path algorithm Example Source: Anderson et al., 01 Quantitative Methods for Business
Decision Theory Using Probabilities, MV, EMV, EVPI and Other Techniques
 1 Decision Theory Using Probabilities, MV, EMV, EVPI and Other Techniques Thompson Lumber is looking at marketing a new product storage sheds. Mr. Thompson has identified three decision options (alternatives)
1 Decision Theory Using Probabilities, MV, EMV, EVPI and Other Techniques Thompson Lumber is looking at marketing a new product storage sheds. Mr. Thompson has identified three decision options (alternatives)
Decision Making. BUS 735: Business Decision Making and Research. Learn how to conduct regression analysis with a dummy independent variable.
 Making BUS 735: Business Making and Research 1 Goals of this section Specific goals: Learn how to conduct regression analysis with a dummy independent variable. Learning objectives: LO5: Be able to use
Making BUS 735: Business Making and Research 1 Goals of this section Specific goals: Learn how to conduct regression analysis with a dummy independent variable. Learning objectives: LO5: Be able to use
Project Management. Project Mangement. ( Notes ) For Private Circulation Only. Prof. : A.A. Attarwala.
 Project Mangement ( Notes ) For Private Circulation Only. Prof. : A.A. Attarwala. Page 1 of 380 26/4/2008 Syllabus 1. Total Project Management Concept, relationship with other function and other organizations,
Project Mangement ( Notes ) For Private Circulation Only. Prof. : A.A. Attarwala. Page 1 of 380 26/4/2008 Syllabus 1. Total Project Management Concept, relationship with other function and other organizations,
Project Risk Analysis and Management Exercises (Part II, Chapters 6, 7)
 Project Risk Analysis and Management Exercises (Part II, Chapters 6, 7) Chapter II.6 Exercise 1 For the decision tree in Figure 1, assume Chance Events E and F are independent. a) Draw the appropriate
Project Risk Analysis and Management Exercises (Part II, Chapters 6, 7) Chapter II.6 Exercise 1 For the decision tree in Figure 1, assume Chance Events E and F are independent. a) Draw the appropriate
Project Management Professional (PMP) Exam Prep Course 06 - Project Time Management
 Project Management Professional (PMP) Exam Prep Course 06 - Project Time Management Slide 1 Looking Glass Development, LLC (303) 663-5402 / (888) 338-7447 4610 S. Ulster St. #150 Denver, CO 80237 information@lookingglassdev.com
Project Management Professional (PMP) Exam Prep Course 06 - Project Time Management Slide 1 Looking Glass Development, LLC (303) 663-5402 / (888) 338-7447 4610 S. Ulster St. #150 Denver, CO 80237 information@lookingglassdev.com
IX. Decision Theory. A. Basic Definitions
 IX. Decision Theory Techniques used to find optimal solutions in situations where a decision maker is faced with several alternatives (Actions) and an uncertain or risk-filled future (Events or States
IX. Decision Theory Techniques used to find optimal solutions in situations where a decision maker is faced with several alternatives (Actions) and an uncertain or risk-filled future (Events or States
BSc (Hons) Software Engineering BSc (Hons) Computer Science with Network Security
 BSc (Hons) Software Engineering BSc (Hons) Computer Science with Network Security Cohorts BCNS/ 06 / Full Time & BSE/ 06 / Full Time Resit Examinations for 2008-2009 / Semester 1 Examinations for 2008-2009
BSc (Hons) Software Engineering BSc (Hons) Computer Science with Network Security Cohorts BCNS/ 06 / Full Time & BSE/ 06 / Full Time Resit Examinations for 2008-2009 / Semester 1 Examinations for 2008-2009
ESD.71 Engineering Systems Analysis for Design
 ESD.71 Engineering Systems Analysis for Design Assignment 4 Solution November 18, 2003 15.1 Money Bags Call Bag A the bag with $640 and Bag B the one with $280. Also, denote the probabilities: P (A) =
ESD.71 Engineering Systems Analysis for Design Assignment 4 Solution November 18, 2003 15.1 Money Bags Call Bag A the bag with $640 and Bag B the one with $280. Also, denote the probabilities: P (A) =
PROJECT MANAGEMENT CPM & PERT TECHNIQUES
 PROJECT MANAGEMENT CPM & PERT TECHNIQUES FLOW OF PRESENTATION INTRODUCTION NETWORK PLANNING ESTIMATING TIME CPM PERT Project Management Project A project is an interrelated set of activities that has a
PROJECT MANAGEMENT CPM & PERT TECHNIQUES FLOW OF PRESENTATION INTRODUCTION NETWORK PLANNING ESTIMATING TIME CPM PERT Project Management Project A project is an interrelated set of activities that has a
Lecture 3 Project Scheduling
 B10 Lecture Project Scheduling Omar El-Anwar, PhD, PMP Network alculations The purpose of conducting network calculations is to know more about the scheduling of activities: When will each activity start?
B10 Lecture Project Scheduling Omar El-Anwar, PhD, PMP Network alculations The purpose of conducting network calculations is to know more about the scheduling of activities: When will each activity start?
EXERCISE Draw the network diagram. a. Activity Name A B C D E F G H
 XRIS. What do you mean by network analysis? xplain with counter examples.. What are the basic differences between PM and PRT analysis of project work?. State the rule of constructing the network diagram..
XRIS. What do you mean by network analysis? xplain with counter examples.. What are the basic differences between PM and PRT analysis of project work?. State the rule of constructing the network diagram..
Subject : Computer Science. Paper: Machine Learning. Module: Decision Theory and Bayesian Decision Theory. Module No: CS/ML/10.
 e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Paper: Machine Learning Module: Decision Theory and Bayesian Decision Theory Module No: CS/ML/0 Quadrant I e-text Welcome to the e-pg Pathshala Lecture Series
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Paper: Machine Learning Module: Decision Theory and Bayesian Decision Theory Module No: CS/ML/0 Quadrant I e-text Welcome to the e-pg Pathshala Lecture Series
Decision Analysis Models
 Decision Analysis Models 1 Outline Decision Analysis Models Decision Making Under Ignorance and Risk Expected Value of Perfect Information Decision Trees Incorporating New Information Expected Value of
Decision Analysis Models 1 Outline Decision Analysis Models Decision Making Under Ignorance and Risk Expected Value of Perfect Information Decision Trees Incorporating New Information Expected Value of
CHAPTER 4 MANAGING STRATEGIC CAPACITY 1
 CHAPTER 4 MANAGING STRATEGIC CAPACITY 1 Using Decision Trees to Evaluate Capacity Alternatives A convenient way to lay out the steps of a capacity problem is through the use of decision trees. The tree
CHAPTER 4 MANAGING STRATEGIC CAPACITY 1 Using Decision Trees to Evaluate Capacity Alternatives A convenient way to lay out the steps of a capacity problem is through the use of decision trees. The tree
CISC 322 Software Architecture
 CISC 22 Software Architecture Project Scheduling (PERT/CPM) Ahmed E. Hassan (Edited For Course Presentation, 206) Project A project is a temporary endeavour undertaken to create a "unique" product or service
CISC 22 Software Architecture Project Scheduling (PERT/CPM) Ahmed E. Hassan (Edited For Course Presentation, 206) Project A project is a temporary endeavour undertaken to create a "unique" product or service
TIm 206 Lecture notes Decision Analysis
 TIm 206 Lecture notes Decision Analysis Instructor: Kevin Ross 2005 Scribes: Geoff Ryder, Chris George, Lewis N 2010 Scribe: Aaron Michelony 1 Decision Analysis: A Framework for Rational Decision- Making
TIm 206 Lecture notes Decision Analysis Instructor: Kevin Ross 2005 Scribes: Geoff Ryder, Chris George, Lewis N 2010 Scribe: Aaron Michelony 1 Decision Analysis: A Framework for Rational Decision- Making
Handling Uncertainty. Ender Ozcan given by Peter Blanchfield
 Handling Uncertainty Ender Ozcan given by Peter Blanchfield Objectives Be able to construct a payoff table to represent a decision problem. Be able to apply the maximin and maximax criteria to the table.
Handling Uncertainty Ender Ozcan given by Peter Blanchfield Objectives Be able to construct a payoff table to represent a decision problem. Be able to apply the maximin and maximax criteria to the table.
stake and attain maximum profitability. Therefore, it s judicious to employ the best practices in
 1 2 Success or failure of any undertaking mainly lies with the decisions made in every step of the undertaking. When it comes to business the main goal would be to maximize shareholders stake and attain
1 2 Success or failure of any undertaking mainly lies with the decisions made in every step of the undertaking. When it comes to business the main goal would be to maximize shareholders stake and attain
1.The 6 steps of the decision process are:
 1.The 6 steps of the decision process are: a. Clearly define the problem Discussion and the factors that Questions influence it. b. Develop specific and measurable objectives. c. Develop a model. d. Evaluate
1.The 6 steps of the decision process are: a. Clearly define the problem Discussion and the factors that Questions influence it. b. Develop specific and measurable objectives. c. Develop a model. d. Evaluate
Next Year s Demand -Alternatives- Low High Do nothing Expand Subcontract 40 70
 Lesson 04 Decision Making Solutions Solved Problem #1: see text book Solved Problem #2: see textbook Solved Problem #3: see textbook Solved Problem #6: (costs) see textbook #1: A small building contractor
Lesson 04 Decision Making Solutions Solved Problem #1: see text book Solved Problem #2: see textbook Solved Problem #3: see textbook Solved Problem #6: (costs) see textbook #1: A small building contractor
Decision Making. BUS 735: Business Decision Making and Research. exercises. Assess what we have learned. 2 Decision Making Without Probabilities
 Making BUS 735: Business Making and Research 1 1.1 Goals and Agenda Goals and Agenda Learning Objective Learn how to make decisions with uncertainty, without using probabilities. Practice what we learn.
Making BUS 735: Business Making and Research 1 1.1 Goals and Agenda Goals and Agenda Learning Objective Learn how to make decisions with uncertainty, without using probabilities. Practice what we learn.
INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF JAPAN Public Management and Policy Analysis Program Graduate School of International Relations
 Hun Myoung Park (5/2/2018) Decision Analysis: 1 INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF JAPAN Public Management and Policy Analysis Program Graduate School of International Relations DCC5350/ADC5005 (2 Credits) Public
Hun Myoung Park (5/2/2018) Decision Analysis: 1 INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF JAPAN Public Management and Policy Analysis Program Graduate School of International Relations DCC5350/ADC5005 (2 Credits) Public
University of Windsor Faculty of Business Administration Winter 2001 Mid Term Examination: units.
 Time: 1 hour 20 minutes University of Winsor Faculty of Business Aministration Winter 2001 Mi Term Examination: 73-320 Instructors: Dr. Y. Aneja NAME: LAST (PLEASE PRINT) FIRST Stuent ID Number: Signature:
Time: 1 hour 20 minutes University of Winsor Faculty of Business Aministration Winter 2001 Mi Term Examination: 73-320 Instructors: Dr. Y. Aneja NAME: LAST (PLEASE PRINT) FIRST Stuent ID Number: Signature:
