CONSENSUS FORECAST. Euro area April Contributors
|
|
|
- Shanon Flowers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CONSENSUS FORECAST April 5 SUMMARY CALENDAR 5 EURO AREA 7 GERMANY FRANCE ITALY 57 SPAIN 69 AUSTRIA 8 BELGIUM 88 ESTONIA 96 FINLAND GREECE IRELAND LATVIA 9 LITHUANIA 5 NETHERLANDS PORTUGAL 9 SLOVAKIA 57 SLOVENIA 6 CYPRUS 69 LUXEMBOURG 7 MALTA 75 NOTES 78 PUBLICATION DATE March 5 FORECASTS COLLECTED March - March 5 INFORMATION AVAILABLE Up to and including March 5 NEXT EDITION 5 May 5 Contributors ARNE POHLMAN Chief Economist ARMANDO CICCARELLI Head of Research RICARDO ACEVES Senior Economist RICARD TORNÉ Senior Economist OLGA COSCODAN Economist CARL KELLY Economist TERESA KERSTING Economist DIRINA MANÇELLARI Economist ANGELA BOUZANIS Economist CECILIA SIMKIEVICH Economist ROBERT HILL Economist ERIC DENIS Economist MIRIAM DOWD Editor
2 Summary April 5 Summary Regional outlook improves REAL SECTOR Greece submits list of reforms, agreement with European leaders pending Euro Area Economic Growth Change in GDP forecasts..6 Greece s relationship with the rest of the Eurozone deteriorated in recent days at a time when the country is running out of cash. On 7 March, Greece submitted a list of reforms, which the Eurogroup is expected to evaluate this week. Although the Greek government conceded to retain an unpopular property tax in the plan and to increase the value-added tax for Greek islands, the list failed to include reforms to labor laws and the pension system. It remains to be seen whether an agreement regarding the set of reforms will be sufficient for Athens to unlock much-needed external financing, or whether the Greek government will have to implement further reforms and push legislation through parliament. If European leaders merely seeing the set of reforms provided by the Greek government proves to be sufficient, this would represent a major concession for Greece. Conversely, if detailed reforms are not agreed upon soon, the political stalemate will be prolonged, capital controls are likely to be imposed in Greece, and the Greek government will go into arrears on its obligations to the IMF and the ECB in the coming months. Under this scenario, Greece would likely enter back into recession and the primary budget would return to deficit, which would put pressure on the SYRIZAled government to shift its economic policy. - - Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 Note: GDP, real annual variation in %, Q - Q Note: GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months...8 Against this backdrop of uncertainty, Greek households and businesses pulled EUR 7.6 billion out of their bank accounts in February, driving deposit levels down to EUR.5 billion (February : EUR 6.5 billion), which is the lowest level since March 5. Although the withdrawals were smaller to those in January (EUR. billion), the nearly EUR billion extracted from bank accounts in the first two months of the year reflects the serious risk that Greece could reach a full-scale bank run before the Greek government comes to an agreement with Eurozone leaders to extend its EUR billion bailout to June. Despite the headwinds that Greece s latest cash crisis has caused, more signs have emerged that the Eurozone economy is strengthening. Detailed data show that the region s GDP improved in the fourth quarter of. Although the improvement in Q was marginal relative to the growth rate registered in the previous quarter, recent data provide further evidence that the bloc s economy is gaining momentum at the outset of 5. The composite PMI a closely-watched leading indicator rose to the highest level in nearly four years in March and confidence regarding improving economic prospects in the Eurozone FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
3 Summary April 5 strengthened further in the same month. Moreover, the recent slide of the euro should provide support for European export-oriented manufacturers, while borrowers will benefit from the ECB s ultraloose monetary policy. Change in GDP Growth Forecasts 5 6 Spain Spain Ireland Netherlands Finland France Netherlands Belgium Italy Belgium Ireland Italy Finland France Austria Austria Note: Change between April 5 and March 5 in percentage points. Source: FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast.. OUTLOOK Outlook improves on start of QE program and more upbeat economic data The European Central Bank (ECB) began its bond-buying program also known as quantitative easing (QE) in the secondary market on 9 March. The program that the ECB launched on January is expected to revive the economy and lift inflation. Although analysts remain cautious regarding whether the QE program will effectively fuel economic growth in the common currency area, the current slide of the euro against the U.S. dollar, lower oil prices and easing fiscal austerity will support growth in the Eurozone. The FocusEconomics panel is becoming more optimistic regarding the outlook for the Eurozone economy. Analysts polled this month raised their 5 GDP growth forecasts again, this time by. percentage points over the previous month, and they now see the regional economy expanding.%. April s result mainly reflects rising optimism regarding the ECB QE program as well as an improvement in recent economic data. At a country level, the improving economic outlook for the region reflects upward revisions for 6 of the 9 economies surveyed, including key players such as France,, and Spain. The forecasts for 7 economies were left unchanged, while projections for the remaining 6 economies were cut. Forecasters also raised their 6 regional GDP growth forecast this month to.7% from the.6% that was expected last month. Cyprus and Finland are expected to be the weakest links in 5, with a projected expansion of.% and.5%, respectively. At the other end of the range, Ireland is expected to be the strongest performer with.6% growth, followed by Malta with a.8% increase. Looking at the region s major economies, Spain continues to outperform its European peers with an expected GDP growth of.%, followed by Europe s powerhouse with a.8% expansion. Meanwhile, panelists raised France s growth prospects in April to.%, while Italy s projection was left unchanged at last month s.5%. - Greece Economic Growth -8 Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 Note: GDP, real annual variation in %, Q - Q 6. Change in GDP forecasts 5 6 Note: GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 5 GREECE Government presents list of reforms, but the country s future is still uncertain The Greek economy grew in for the first time in six years, largely on the back of a recovery in private consumption and the external sector. However, Greece s future is shrouded in uncertainty. The country is at the brink of bankruptcy and desperately needs additional financing from its European lenders. On 7 March, Prime Minister Alexis Tspiras presented Greece s newest reform plan, which includes previously-discussed measures to reduce corruption and tax evasion. Tsipras also conceded to retain an unpopular property tax and increase the value added tax for Greek islands, although the proposal did not touch on reforms to the pension system or labor laws. Further discussions with troika FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
4 Summary April 5 representatives are slated for this week, but at this point it is unlikely the latest plan will be enough to cement a deal and allow Greece to receive bailout extension funding. Looking forward, Greece s outlook is deteriorating rapidly. The government s funding gap is weighing heavily on the forecast and political tensions are rising in the country. Further, large downside risks of another election or even a grexit from the Eurozone still loom. FocusEconomics Consensus panelists expect the economy to expand.9% in 5, which is down.7 percentage points from last month s forecast. For 6, the panel sees the economy growing.%. (see details on page ) Economic Growth - Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 Note: GDP, real annual variation in %, Q - Q 6. Change in GDP forecasts 5 6 Note: GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months GERMANY Economic activity remains strong at the outset of the year, prospects are bright ended on a very strong note. Private consumption was the main anchor of growth in, helped by the significant decline in the global oil price. Data for Q are somewhat mixed, but suggest overall that remains on a solid growth track. Industrial production growth moderated and exports shrank in January, but business sentiment and the composite PMI improved again in March and the consumer confidence indicator reached an over-thirteen-year high in April. Finance Minister Wolfgang Schäuble presented amendments to this year s budget, the draft 6 budget and fiscal plans up to 9 on 8 March. The key policy measure is an increase in public investment mainly in infrastructure which amounts to EUR.5 billion until 8, although the government remains committed to its goal of achieving a balanced budget through 9. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists revised up s economic outlook for a third straight month on expectations that a strong labor market, lower oil prices and a weak euro will boost growth. The panel expects the economy to expand.8% in 5, which is up. percentage points from last month s projection. For 6, the panel foresees growth of.9%. (see details on page ) France Economic Growth - Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 Note: GDP, real annual variation in %, Q - Q 6. Change in GDP forecasts 5 6 Note: GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months FRANCE Recent data signal improving economic conditions; Sarkozy s UMP scores key result in local elections Following the anemic growth recorded in the final quarter of, recent economic indicators signal that the economy is gradually shifting into higher gear. Industrial production expanded for a second consecutive month in January and the March Composite PMI suggests that French business activity is expanding. In addition, March sentiment surveys showed that businesses and consumers are perceiving a mild economic recovery. On the political front, the right-wing National Front (FN) made limited gains in the second-round local elections held on 9 March. Conversely, former president Nicolas Sarkozy s Union for a Popular Movement (UMP) and its allies scored a key victory, garnering over twothirds of the departments. Although voter turnout was low, the election result represents the current electoral mood as the popularity of the Socialist Party, and particularly that of President François Hollande, is at a record low. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
5 Summary April 5 The French economy is going to benefit from a stimulatory monetary policy, low oil prices and a less restrictive fiscal policy. In addition, the weaker euro is likely to boost exports to countries outside the Eurozone. FocusEconomics panelists raised their growth forecasts by. percentage points over the previous month and now expect the French economy to expand.% in 5. For 6, panelists expect economic growth to accelerate to.%. (see details on page ) - Italy Economic Growth - Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 Note: GDP, real annual variation in %, Q - Q 6. Change in GDP forecasts 5 6 Note: GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months ITALY Improving economic situation and stable political conditions support implementation of reform agenda According to more detailed data released on 5 March, the Italian economy recorded flat growth in the final quarter of last year, which marks an improvement after several quarters of contractions. A gradual rebound in economic indicators in recent months and a relatively stable political situation suggest that the government is in a good position to start implementing muchneeded structural reforms this year. One major change has already been implemented in the banking sector. In an attempt to improve governance and increase the efficiency of the banking system, on March, the parliament approved a reform to convert the country s ten largest cooperative banks into joint stock companies. The move is expected to speed up board decision making processes and lead to increased mergers, as it puts an end to ownership limits and dismantles the previous voting system of one-head, one-vote which used to allow minority shareholders to block unwanted changes. The Italian economy is expected to expand for the first time in four years in 5. FocusEconomics panelists expect the Italian economy to expand.5% this year, which is unchanged from last month s forecast. For 6, the panel sees economic growth picking up to.%. (see details on page 57) Spain Economic Growth -. Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 Note: GDP, real annual variation in %, Q - Q 6. Change in GDP forecasts 5 6 Note: GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months SPAIN Domestic demand fuels economic recovery in, but risks to the outlook persist The Spanish economy expanded for the first time in five years last year, driven mainly by a recovery in domestic demand. Renewed consumer confidence and an improving labor market are expected to carry s momentum into this year. In addition, low energy prices should boost private consumption and the country s current account. However, some risks to Spain s outlook still remain. The country is facing multiple elections in 5, and general elections are due before year-end. On March, the Spanish Socialist Workers Party (PSOE), led by Susana Díaz, was reelected in Andalucía s regional vote. While the outcome was rather unsurprising, the result signaled a potential change in Spain s political landscape as the traditionally-dominant PSOE and the People s Party (PP) lost 8% of the vote to emerging parties. Growth prospects for the Spanish economy continue to improve. FocusEconomics panelists raised their forecast for the third month in a row and see GDP expanding.% in 5, which is up. percentage points from last month s forecast. For 6, the panel sees the economy also growing.%. (see details on page 69) FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 5
6 Summary April 5 INFLATION February records third consecutive month with inflation in negative territory, QE aimed at lifting inflation going forward More complete data confirmed that inflation in the Eurozone remained in negative territory in February. Harmonized consumer prices declined.% over the same month last year, which followed the.6% decrease registered in January. The result sparked fears that the Eurozone could fall into a sustained period of declining prices. Nonetheless, the ECB s QE program is designed to inject EUR. trillion to the financial system to increase lending, support economic growth and lift inflation going forward. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists left their 5 inflation forecasts unchanged over the previous month and project zero inflation. For 6, inflation is expected to increase and average.%. Ricardo Aceves Senior Economist FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 6
7 Summary April 5 Quarterly Data Economic Growth and Inflation Q - Q 6 Gross domestic product 5 6 yoy var. in % Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain GDP, yoy var. in % Inflation, yoy var. of quarterly avg. CPI in % France Italy Netherlands Spain - France Italy Netherlands Spain - Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 - Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 Inflation, yoy var. of 5 6 quarterly avg. CPI in % Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 7
8 Summary April 5 Gross Domestic Product, annual variation in % Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Ireland Malta Lithuania Slovakia Latvia Spain Luxembourg Estonia Slovenia Portugal Netherlands Belgium France Greece Austria Finland Italy Cyprus Notes and sources GDP Growth, 5 Note: Gross domestic product, real annual variation in %. Sources: National statistical institutes and Eurostat Austria 8, 8,65 9,,,,6, Belgium 5, 5,96 6,7 7,7 8,5 9,5,8 Cyprus,55 9,6 9,587 9,87,77,87,5 Estonia,96,8,85 5,87 6, 7,6 8,8 Finland 7, 7,5 7,5 8,9 9,8,75,85 France,,57,78, 5,56 6,7 7,7,88 5,9 6,66 7,97 9,85,68,95 Greece 6,9 6, 6,6 6,67 7,9 7,875 8,69 Ireland 6,598 8,587 9,78,,88,58 6,8 Italy 6,96 6,96 6,98 7, 7,88 8,76 9, Latvia,7,8,,95,77,77 5,768 Lithuania,777,76,765,6, 5,7 6,5 Luxembourg 8,7 85,6 87,7 89, 9,6 9,7 95,98 Malta 7,98 8,865 9,57,5,8,869,6 Netherlands 8,6 8,89 9,89,5,7,67,6 Portugal 6,6 6,9 6,76 7,5 7,69 8, 8,79 Slovakia,6,885,86,95 5,668 6, 7,8 Slovenia 7,55 8,65 8,9 9,8 9,8,68,6 Spain,5,759,,6,9 5,88 6,77 9,88,5,6,,,,6 5, France Italy Spain Netherlands GDP per capita, EUR Ireland Netherlands Austria Finland Belgium France Italy Spain Cyprus Malta Slovenia Portugal Greece Estonia Slovakia Lithuania Latvia Notes and sources GDP per capita, 5, 7,5 5,,5,, 5 6 Note: GDP per capita in current EUR. Chart excludes Luxembourg due to methodological inconsistencies. Sources: National statistical institutes, central banks and Eurostat. 5,, 5,, France Italy Spain Netherlands FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 8
9 Private Consumption, annual variation in % Summary Private Consumption Growth, 5 April Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Lithuania Estonia Latvia Spain Slovakia Malta Ireland Luxembourg Portugal France Belgium Greece Slovenia Netherlands Austria Italy Finland Cyprus Notes and sources - Note: Private consumption, real annual variation in %. Sources: National statistical institutes and Eurostat Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain France Italy Spain Netherlands Investment, annual variation in % Ireland Lithuania Spain Malta Slovakia Netherlands Luxembourg Slovenia Portugal Latvia Estonia Belgium Greece Austria Cyprus Italy Finland France Notes and sources Investment Growth, Note: Gross fixed investment, real annual variation in %. Sources: National statistical institutes and Eurostat France Italy Spain Netherlands FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 9
10 Summary April 5 Exports of Goods and Services, annual variation in % Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Slovakia Ireland Latvia Slovenia Portugal Spain Greece France Luxembourg Italy Netherlands Malta Belgium Finland Austria Cyprus Lithuania Estonia Notes and sources Exports Growth, Note: Exports of good and services, real annual variation in %. Sources: National statistical institutes and Eurostat Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain France Italy Spain Netherlands Imports of Goods and Services, annual variation in % Latvia Slovenia Ireland Slovakia Spain Portugal Greece Luxembourg France Malta Netherlands Belgium Italy Austria Finland Lithuania Cyprus Estonia Notes and sources Imports Growth, Note: Imports of good and services, real annual variation in %. Sources: National statistical institutes and Eurostat France Italy Spain Netherlands FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
11 Summary April 5 Industrial Production, annual variation in % Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Industrial Production Growth, 5 Ireland Slovakia Estonia Slovenia Lithuania Latvia Spain Portugal Finland Austria Belgium Netherlands France Italy Greece - 6 Notes and sources Note: Industrial production, real annual variation in %. Sources: National statistical institutes and Eurostat Unemployment, % of active population Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain France Italy Spain Netherlands Greece Spain Cyprus Portugal Italy Slovakia France Lithuania Ireland Latvia Slovenia Finland Belgium Netherlands Estonia Luxembourg Malta Austria Notes and sources Unemployment, Note: Average unemployment rate for the year. Sources: National statistical institutes and Eurostat. 5 5 France Italy Spain Netherlands FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
12 Summary April 5 Fiscal Balance, % of GDP Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Luxembourg Estonia Latvia Lithuania Greece Austria Netherlands Malta Finland Slovakia Belgium Ireland Italy Portugal Cyprus Slovenia France Spain Notes and sources Fiscal Balance, Note: Fiscal balance as % of GDP. Source: Eurostat Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain France Italy Spain Netherlands 5 6 Public Debt, % of GDP Greece Italy Portugal Cyprus Ireland Belgium Spain France Austria Slovenia Netherlands Malta Finland Slovakia Lithuania Latvia Luxembourg Estonia Notes and sources Note: Public debt as % of GDP. Source: Eurostat. Public Debt, France Italy Spain Netherlands FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
13 Summary April 5 Inflation, annual average variation of consumer prices in % Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Luxembourg Malta Austria Estonia Lithuania Latvia Slovenia Finland Slovakia Cyprus France Belgium Ireland Portugal Italy Netherlands Spain Greece Notes and sources Inflation, Note: Annual average variation of consumer prices in %. refers to national consumer price indices (CPI). All other countries are based on harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP). Sources: National statistical institutes, central banks and Eurostat Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain France Italy Spain Netherlands 5 6 -Year Bond Yield, % Greece Portugal Spain Italy Ireland Belgium France Finland Netherlands Austria Notes and sources -Year Bond Yield, Note: -year bond yield in %, end of period. Sources: National central banks and European Central Bank (ECB). France Italy Spain Netherlands FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
14 Summary April 5 Current Account Balance, % of GDP Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Netherlands Ireland Slovenia Luxembourg Slovakia Italy Malta Austria Greece Portugal Belgium Spain Cyprus Lithuania Finland France Estonia Latvia Notes and sources Current Account Balance, Note: Current account balance as % of GDP. Sources: National statistical institutes and Eurostat. - France Italy Spain Netherlands FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
15 Calendar April 5 Economic Release Calendar Date Country Event March February Unemployment March March Consumer Prices (*) March Ireland Q National Accounts March Italy March Consumer Prices (*) March Spain January Balance of Payments March Spain February Retail Sales April Greece April Markit Manufacturing PMI (*) April Ireland March Investec Manufacturing PMI April Italy March Markit/ADACI Manufacturing PMI April Netherlands March NEVI Manufacturing PMI April Spain March Markit Manufacturing PMI April Ireland March Investec Services PMI 7 April Cyprus March Consumer Prices 7 April Spain March Markit Services PMI 8 April Ireland March Consumer Confidence (**) 9 April February Industrial Production 9 April February Merchandise Trade 9 April Greece February Industrial Production April Finland February Industrial Production April France February Industrial Production April Ireland February Industrial Production (**) April Spain February Industrial Production April Italy February Industrial Production April February Industrial Production April Italy March Consumer Prices April Spain March Consumer Prices 5 April Central Bank Meeting 5 April Finland February Balance of Payments 5 April Finland February Trend Indicator of Output 5 April France March Consumer Prices 7 April March Consumer Prices 7 April Austria March Consumer Prices April Cyprus January Industrial Production April Portugal April Leading Indicators April Portugal March Industrial Production April Netherlands April Consumer Confidence April April Markit Composite PMI (*) April France April Markit Composite PMI (*) April France April Business Confidence April April Markit Composite PMI (*) April May Consumer Confidence April Austria February Industrial Production April Belgium April Leading Indicators (*) April Belgium February Industrial Production April April Business Confidence April Netherlands April Business Confidence (*) Preliminary estimate. (**) Approximate date. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 5
16 April 5 Economic Release Calendar Date Country Event 8 April France April Consumer Confidence 9 April April Economic Sentiment 9 April Austria April Consumer Confidence 9 April Austria March Unemployment 9 April Austria April Bank Austria Manufacturing PMI 9 April Belgium April Consumer Prices 9 April Belgium Q National Accounts 9 April April Consumer Prices (*) 9 April Italy April Consumer Confidence 9 April Italy April Business Confidence 9 April Spain March Retail Sales April March Unemployment April April Consumer Prices (*) April Austria Q 5 National Accounts (*) April Italy April Consumer Prices (*) April Spain February Balance of Payments April Spain February Housing Permits April Spain Q 5 National Accounts (*) May Greece May Markit Manufacturing PMI (*) May Ireland April Investec Manufacturing PMI May Italy April Markit/ADACI Manufacturing PMI May Netherlands April NEVI Manufacturing PMI May Spain April Markit Manufacturing PMI (*) Preliminary estimate. (**) Approximate date. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 6
17 April 5 LONG-TERM TRENDS -year averages Population (million): GDP (EUR bn): 9,85,6,68 GDP per capita (EUR): 9,7,797, GDP growth (%):...6 Fiscal Balance (% of GDP): Public Debt (% of GDP): Inflation (%):..5.6 Current Account (% of GDP):..5. Outlook improves The Eurozone economy improved in the fourth quarter of. Although growth picked up just slightly over the third quarter, recent data provide further evidence that the bloc s economy is gaining momentum at the outset of 5. The composite PMI a closely-watched leading indicator rose to a nearly-four-year high in March and economic sentiment improved in the same month. Businesses and consumers are more upbeat as the euro s slide supports export-oriented manufacturers and borrowers are benefitting from the European Central Bank s ultra-loose monetary policy. Growth prospects for the Eurozone economy in 5 improved this month, reflecting tailwinds from low oil prices, a weak euro, easing fiscal austerity and stronger signals from the latest leading indicators. The FocusEconomics panel raised the 5 growth forecast from the.% expected last month to.%. For 6, forecasters see the bloc s economy picking up pace and expanding.7%. Consumer prices fell.% year-on-year in February (January: -.6% yearon-year), which marked the third straight month of declining prices. On 9 March, the European Central Bank (ECB) began its bond-buying program, which is designed to pump over EUR trillion into the financial system to kick-start lending and push inflation. FocusEconomics panelists see zero inflation in 5, which is unchanged from last month s forecast. For 6, the panel foresees inflation rising to.%. Ricardo Aceves Senior Economist REAL SECTOR More complete data show mild GDP acceleration in Q The Eurozone economy grew a seasonally-adjusted.% in Q, according to preliminary data released by Eurostat on 6 March. The reading came in slightly above the.% rise observed in Q and was in line with market expectations. On an annual basis, GDP growth rose from.8% in Q to.9% in Q. Gross Domestic Product variation in %.. Quarter-on-quarter s.a. (left scale) Year-on-year (right scale).5. % % The mild acceleration in Q reflected an improvement in the external sector and a stronger growth in fixed investment. Exports of goods and service services increased.8% in Q over the previous quarter, which followed the.5% expansion observed in Q. Imports grew.% in Q, which came in below the.7% expansion witnessed in Q. As exports expanded faster than imports, the external sector s net contribution to overall economic growth was. percentage points in Q, which improved over a flat reading in Q Q Q Q Q Q On the domestic front, private consumption grew.% in Q (Q: +.5% quarter-on-quarter) and government spending expanded.%, mirroring an increase of the same magnitude in Q. Meanwhile, fixed investment swung from a flat reading in Q to a.% expansion in Q. Note: Quarter-on-quarter changes of seasonally-adjusted GDP and year-on-year variarion in %. Source: Eurostat and FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. In, the Eurozone economy expanded.9%, recovering from the.% contraction registered in. The European Commission expects the Eurozone economy to increase.% in 5. In 6, the Commission sees FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 7
18 April 5 economic growth picking up to.9%. Meanwhile, in its March review of the economy, the European Central Bank (ECB) raised its 5 GDP growth forecasts for the bloc s economy and now expects it to expand.5% (previous estimate: +.%). For 6, the ECB also raised its projection and now sees economic growth rising to.9%, which is up its previous.5% estimate. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect the economy to expand.% in 5, which is up. percentage points from last month s forecast. For 6, panelists expect the economy to expand.7%. Purchasing Managers Index Mar- Sep- Mar- Sep- Mar-5 Note: Markit Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) Composite Output. A reading above 5 indicates an expansion in business activity while a value below 5 points to a contraction. Source: Markit. REAL SECTOR Eurozone PMI climbs to highest level in nearly four years The flash estimate of the Markit Eurozone PMI Composite Output Index came in at 5. in March. The reading was above the revised 5. recorded in February (previously reported: 5.5) and smashed the 5.6 that the markets had expected. March s result represented the fourth consecutive increase in the gauge, which also climbed to its highest level in nearly four years, rising further above the 5-threshold that separates expansion from contraction in business activity in the common currency area. The strong reading was driven by notable rises in the manufacturing and services sectors, particularly the services sector, which also picked up to the highest level in almost four years. According to Markit, the acceleration in business activity was propelled by faster growth in new orders and a stronger increase in both in business activity and manufacturing output. Meanwhile, employment rose over the previous month and was more noticeable in the manufacturing sector. Markit concluded that the strong improvement observed in the March PMI provides, welcome news to a region awaiting signs that the ECB s quantitative easing is stimulating the real economy. Markit added the economy looks to have expanded by.% in the first quarter, buoyed by a.% expansion in and signs of a long-awaited recovery in France. At a country level, s composite PMI rose in March to the highest point in eight months. Meanwhile, France s composite PMI continued to signal an expansion in business activity for the second month in a row, although the pace of growth moderated over the previous month. Excluding and France, the composite PMI for all the other countries in the region rose to the highest level since July. Industrial Production variation in %.. %...5 %. REAL SECTOR Industrial production in common currency area contracts mildly In January, industrial production fell a seasonally-adjusted.% over the previous month. The reading contrasted both the revised.% rise observed in December (previously reported:.% month-on-month) and market expectations that had industrial output rising.%. -. Month-on-month s.a. (left scale) Annual average (right scale) Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan-5 Note: Month-on-month var. of seasonally-adjusted industrial production and annual average growth rate in %. Source: Eurostat. -.5 The mild contraction observed in January reflected a contraction in the three Baltic economies (Estonia: -.5% mom, Latvia: -.% mom, Lithuania: -.% mom). regional worst performers were Finland (-.5% mom) and Luxembourg (-.8% mom). On the other side of the spectrum, Malta (+6.% mom) and the Netherlands (+.% mom) registered better results. Regarding the four major economies in the Eurozone, in France industrial production increased.% in January, while in industrial output growth was flat. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 8
19 April 5 In Spain, industrial production expanded.% over the previous month, while in Italy it contracted.7%. On an annual basis, industrial production accelerated from a revised.6% increase in December (previously reported: -.% year-on-year) to a.% expansion in January. The reading represented the fastest year-on-year increase in six months. The trend remains subdued, with annual average growth in industrial production inching down from.7% in December to.6% in January. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists see industrial production expanding.5% in 5, which is up. percentage points from last month s forecast. For 6, panelists see industrial production growing.%. Economic Sentiment March 5 Malta Slovenia Spain Italy Lithuania Netherlands Portugal Cyprus Slovakia Belgium France Greece Estonia Austria Finland Luxembourg 8 9 Note: The Economic Sentiment Indicator (ESI) is based on surveys addressed to the manufacturing, services, retail trade and construction sectors, as well as to consumers. Values above indicate an above-average economic sentiment, whereas values below indicate a below-average position. Source: European Commission. OUTLOOK Economic sentiment hits highest level since July The Economic Sentiment Index (ESI) elaborated by the European Commission rose from a revised. points in February (previously reported:. points) to.9 points in March. The reading, which was on par with market expectations, represented the highest level since July and continued to hover above the -point long-term average. March s improvement was broad based, with consumer sentiment, industry and services showing the largest gains. At a country level, high economic sentiment was registered in Malta and Slovenia and Lithuania. At the other side of the spectrum, Austria, Finland and Luxembourg were the worst performers. Among the four largest economies, all countries registered higher sentiment. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists see private consumption growing.5% in 5, which is up. percentage points from last month s projection. For 6, panelists see consumption expanding.%. Panelists expect investment to grow.% in 5, which is up. percentage points from last month s forecast. In 6, panelists see investment increasing.6%. Inflation variation in %.. MONETARY SECTOR More complete data confirm third consecutive annual fall in consumer prices More complete data published by Eurostat on 7 March showed that the harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) in February jumped.6% over the previous month, which contrasted the.6% drop recorded in January. In annual terms, harmonized consumer prices fell.% in February, which confirmed the preliminary estimate and marked a third consecutive month in negative territory, sparking fears that the could fall into a sustained period of falling prices.. %. -. Month-on-month (left scale) Year-on-year (right scale) Feb- Aug- Feb- Aug- Feb-5 Note: Year-on-year and monthly variation of harmonized consumer price index (HICP) in %. Source: Eurostat..6 %.8. More complete data also showed that of the 9 Eurozone economies posted annual inflation rates equal to or below the regional average. Greece (-.9%), Lithuania (-.5%), and Spain (-.%) recorded the lowest annual inflation rates. At the other end of the spectrum, Malta (+.6%) and Austria (+.5%) showed the highest year-on-year increases in harmonized consumer prices. Among the remaining major economies in the Eurozone, in consumer prices fell.% annually in February and in France prices dropped.% over the same month last year. In Italy, harmonized inflation rose a mild.% in February. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast participants see zero inflation in 5, which is unchanged from last month s forecast. For 6, panelists expect inflation to average.%. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 9
20 April 5 MONETARY SECTOR ECB leaves key rates unchanged, begins purchase of euro-denominated public sector securities The European Central Bank (ECB) decided to leave the main refinancing rate unchanged at the record low of.5% at its 5 March monetary policy meeting held in Nicosia. The ECB also kept the deposit rate the rate banks receive for parking funds at the ECB at minus.% and left the marginal lending rate at.%. Market analysts had anticipated the Bank s decision to maintain the rates unchanged. The Bank s decision came amid an improving outlook for the Eurozone economy as growth momentum is continuing to strengthen. Nonetheless, the Bank recognized that downward risks to the outlook persist, although they have diminished following the Bank s recent monetary policy decisions and partially as a result of the fall in oil prices. In fact, the Central Bank raised its growth forecasts for the bloc s economy for both 5 and 6. On the inflation side, the Bank stated that the fall in consumer prices in February, which marked the third consecutive month of decline, was mainly due to the impact of the sharp drop in global oil prices. The Bank recognized, however, that it expects inflation to remain low or negative in the coming months, while it foresees it starting to rise gradually at the end of 5. ECB Refinancing Rate in %.. %.. -. Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan-5 Note: ECB Refinancing Rate in %. Source: European Central Bank (ECB). Marginal Lending Rate Main Refinancing Rate Deposit Rate Regarding the quantitative easing (QE) program that the ECB launched on January, the Bank began the purchase of euro-denominated public sector securities in the secondary market on 9 March. The ECB had set a target for its monthly purchases at EUR 6 billion per month; considering that the pace of asset-backed securities (ABS) and covered bond purchases has been around EUR billion per month since the programs started, this means that additional purchases of sovereign bonds will be set at around EUR 5 billion per month. The ECB set end-september 6 as the deadline for the end of the purchase program and emphasized that it is open-ended in nature as the Bank will continue purchasing assets until it sees, a sustained adjustment in the path of inflation which is consistent with our aim of achieving inflation rates below, but close to, % over the medium term. ECB President Mario Draghi underlined that at the current stage, monetary authorities are not willing to enter into any discussion regarding if or when the pace of purchases may be adjusted, tapered or stop. Skepticism persists among many analysts regarding the pace of adjustment of the QE program and its impact on the Eurozone economy. According to Nick Matthews, Senior European Economist at Nomura: Given the current improvement in the data it is difficult to disagree with the ECB s baseline in the short-term. But at this stage we do not have the conviction that core inflation will pick up as strongly as the ECB staff project over time for us to be confident that the staff projections will be realised and the Governing Council will be in a position to stop purchases in September 6. We therefore continue to believe it is more likely than not that the ECB will be forced to continue its asset purchases beyond September 6. It also remains to be seen whether the QE program will help to revive the Eurozone economy, as skepticism persists as to whether this controversial measure will help to revive the economy and lift inflation. The ECB s QE is an aggressive and bold program that demonstrates European monetary authorities commitment to fighting deflation. Whether or not it is effective FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
21 April 5 remains to be seen given that QE has not helped the subdued inflation situation in other countries like the U.K. and Japan. Within this setting, all FocusEconomics panelists expect the ECB to maintain the policy rate unchanged at the current record-low of.5% over the course of the next two years. MONETARY SECTOR Euro almost touches parity with dollar, recent gains seem short lived Like many major currencies, the euro dropped to multi-year lows against the U.S. dollar in the first days of March. The euro had experienced a strengthening trend between the second half of and the first half of, but this trend has reversed in the last six months. Starting in H, the euro began experiencing sharp, almost uninterrupted drops against the greenback, hitting multi-year lows in the first days of March. In fact, on March, the euro traded at.5 EUR per USD, having weakened 7.7% over the same day the previous month and losing nearly a quarter of its value against the U.S. dollar in annual terms. This broke the psychological barrier of. EUR per USD as the euro hit the lowest level since. Exchange Rate USD per EUR Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan-5 Note: Daily spot of U.S. dollar (USD) against euro (EUR). Source: Thomson Reuters. A variety of domestic and external factors have exerted pressure on the single currency. Among these factors are the European Central Bank s extension of its asset purchase program also known as quantitative easing (QE) as well as expectations of an increase in U.S. interest rates this year and a decline in global oil prices. On the political front, the weakening of the euro has been aggravated by disagreement between the new Greek government, which is led by the anti-austerity SYRIZA party, and European leaders regarding Greece s reform plans and whether the bailout program will keep Athens from running out of cash. However, the euro did gain some of the ground it had lost against the greenback in recent days, which mainly resulted from recent disappointing data on the U.S. economy and the Federal Reserve s meeting in which Chair Janet Yellen made a subtle modification to the Fed s guidance. Another factor contributing to the euro s rally against the U.S. dollar is the notable improvement observed in economic indicators for the Eurozone. However, despite the euro s recent uptick, further weakening is expected to continue as Mark Cliffe, Global Head of Financial Markets at ING Bank, points out: In FX markets, the much anticipated divergence in transatlantic monetary policy is delivering a sharper-than-expected adjustment in the EUR/USD exchange rate. We had thought that parity would not be seen until year end, but aggressive EUR hedging from the buy side and still the prospect of higher US market interest rates over coming months means that we our [sic] bringing forward our parity forecast to June. Should the depreciation of the euro continue this year, this will translate into an economic boost for export-oriented European manufacturers and ultimately for the whole economy in the Eurozone. Forecasters polled by FocusEconomics expect that the euro will trade at. EUR per USD at the end of 5. At the end of 6, the euro is expected to trade at.7 EUR per USD. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
22 Economic Indicators - 9 April 5 Annual Data Real Sector Population (million) GDP per capita (EUR) 8,777 9,6 9,667 9,88,5,6,,,,6 GDP (EUR bn) 9,5 9,768 9,8 9,896,75,,5,89,6,5 Economic Growth (Nominal GDP, ann. var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Domestic Demand (annual variation in %) Private Consumption (annual var. in %) Government Consumption (annual var. in %) Fixed Investment (annual variation in %) Exports (G&S, annual variation in %) Imports (G&S, annual variation in %) Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Unemployment (% of active population, aop) Fiscal Balance (% of GDP) Public Debt (% of GDP) Monetary and Financial Sector Money (annual variation of M in %) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, eop) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) Inflation (PPI, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Yr Bond Yield (weighted Euro avg. %, eop) Stock Market (Eurostoxx 5, var. in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, aop) External Sector Current Account Balance (% of GDP) Current Account Balance (EUR bn) Trade Balance (EUR bn) Quarterly Data Q Q Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, s.a. qoq var. in %) Private Consumption (s.a. qoq var. in %) Fixed Investment (s.a. qoq variation in %) Exports (G&S, s.a. qoq variation in %) Imports (G&S, s.a. qoq variation in %) Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Unemployment (% of active population, aop) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, aop) Monthly Data Jun- Jul- Aug- Sep- Oct- Nov- Dec- Jan-5 Feb-5 Mar-5 Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Industrial Production (s.a. mom var. in %) Unemployment (% of active population) Econ. Sent. Indicator (-point threshold) Markit Composite PMI (5-threshold) Inflation (HICP, mom variation in %) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
23 Real Sector Gross Domestic Product April 5 Real GDP -9 var. in % 6 - G7-6 World 5 5 GDP 5 evolution of forecasts Maximum Consensus Minimum 5 GDP 5 Panelist Distribution 8% 6% % % % Real GDP Q -Q 6 var. in % - G7 - Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 GDP 6 evolution of forecasts Maximum Consensus Minimum - < >. Real GDP growth in % Individual Forecasts 5 6 Allianz.5.6 Banco BPI..7 Bankia.5.8 BBVA Research.. Berenberg..9 Berliner Sparkasse.. BNP Paribas..8 Citigroup Global Mkts.5. Coe-Rexecode.6.7 Commerzbank.. Credit Agricole..5 Credit Suisse.5. DekaBank.5.7 Deutsche Bank..6 DIW Berlin.. DNB.. DZ Bank..5 EIU..5 Eurobank. - Goldman Sachs.5.7 Gruppo MPS..5 Holding Monex..5 Ifo Institut.9 - ING..7 Instituto Flores de Lemus..8 Intesa Sanpaolo..6 JPMorgan.7.5 Julius Baer.5.8 KBC.6.8 Kiel Institute..7 La Caixa.5.8 Lloyds TSB..9 NIBC Bank.. Nomura.. Nordea..6 Novo Banco..7 Oxford Economics.6.8 Raiffeisen Research..9 Sal. Oppenheim..6 Scotiabank..6 Société Générale..5 Standard Chartered.5. UBS.6. Unicredit..8 Summary Minimum.9. Maximum.7.5 Median..7 Consensus..7 History days ago..6 6 days ago..5 9 days ago..5 Additional Forecasts European Commission (Feb. 5)..9 ECB (Mar. 5).5.9 IMF (Jan. 5).. Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from Eurostat. Forecasts are based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. GDP, real annual variation in %. Quarterly GDP (seasonally adjusted), year-on-year variation in %. GDP, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. GDP, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 5 GDP, panelist distribution of 5 forecasts. Concentration of panelists in forecast interval in %. Higher columns with darker colors represent a larger number of panelists. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
24 Real Sector Additional forecasts April 5 Consumption and Investment Consumption Investment variation in % variation in % Individual Forecasts Allianz Banco BPI Bankia BBVA Research Berenberg.5... Berliner Sparkasse BNP Paribas.8... Citigroup Global Mkts Coe-Rexecode Commerzbank Credit Agricole...7. Credit Suisse DekaBank....6 Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DNB DZ Bank.... EIU Eurobank Goldman Sachs Gruppo MPS Holding Monex....7 Ifo Institut ING Instituto Flores de Lemus....9 Intesa Sanpaolo....7 JPMorgan Julius Baer KBC Kiel Institute La Caixa Lloyds TSB NIBC Bank Nomura..9.. Nordea Novo Banco Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research Sal. Oppenheim.5... Scotiabank Société Générale.6... Standard Chartered UBS Unicredit Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Consumption variation in % G Consumption evolution of fcst Investment variation in % G Investment evol. of forecasts Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from Eurostat. Forecasts are based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 6 Private consumption, annual variation in %. 7 Private consumption, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 8 Gross fixed investment, annual variation in %. 9 Gross fixed investment, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
25 Real Sector Additional forecasts April 5 Exports and Imports Exports Imports variation in % variation in % Individual Forecasts Allianz...6. Banco BPI Bankia BBVA Research Berenberg Berliner Sparkasse BNP Paribas Citigroup Global Mkts Coe-Rexecode Commerzbank Credit Agricole Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DNB DZ Bank EIU Eurobank Goldman Sachs Gruppo MPS Holding Monex Ifo Institut ING Instituto Flores de Lemus Intesa Sanpaolo....5 JPMorgan Julius Baer KBC Kiel Institute La Caixa Lloyds TSB NIBC Bank Nomura.9... Nordea Novo Banco Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research Sal. Oppenheim Scotiabank Société Générale...9. Standard Chartered UBS....9 Unicredit Summary Minimum.... Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Exports variation in % G Exports evolution of fcst Imports variation in % G Imports evol. of forecasts 6 5 Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from Eurostat. Forecasts are based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. Real exports of goods and services, annual variation in %. Exports, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Real imports of goods and services, annual variation in %. Imports, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 5 6 FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 5
26 Real Sector Additional forecasts April 5 Industry and Unemployment Industry Unemployment variation in % % of active pop. Individual Forecasts Allianz Banco BPI Bankia BBVA Research Berenberg...9. Berliner Sparkasse....5 BNP Paribas Citigroup Global Mkts Coe-Rexecode Commerzbank Credit Agricole Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DNB DZ Bank EIU Eurobank Goldman Sachs Gruppo MPS Holding Monex Ifo Institut ING Instituto Flores de Lemus Intesa Sanpaolo....8 JPMorgan Julius Baer KBC Kiel Institute La Caixa Lloyds TSB NIBC Bank Nomura Nordea Novo Banco Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research Sal. Oppenheim Scotiabank Société Générale Standard Chartered UBS Unicredit Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago....9 Industry variation in % - G Industry evolution of fcst Unemployment % of active pop. G Unemployment evol. of forecasts Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from Eurostat. Forecasts are based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. Industrial production, annual variation in %. 5 Industrial production, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 6 Unemployment, % of active population. 7 Unemployment, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months...5 FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 6
27 Real Sector Additional forecasts April 5 Fiscal Balance and Public Debt Fiscal Balance Public Debt % of GDP % of GDP Individual Forecasts Allianz Banco BPI Bankia BBVA Research Berenberg Berliner Sparkasse BNP Paribas Citigroup Global Mkts Coe-Rexecode Commerzbank Credit Agricole Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DNB DZ Bank EIU Eurobank Goldman Sachs Gruppo MPS Holding Monex Ifo Institut ING Instituto Flores de Lemus Intesa Sanpaolo JPMorgan Julius Baer KBC Kiel Institute La Caixa Lloyds TSB NIBC Bank Nomura Nordea Novo Banco Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research Sal. Oppenheim Scotiabank Société Générale Standard Chartered UBS Unicredit Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Fiscal Balance % of GDP G Fiscal Balance evolution of fcst Public Debt % of GDP G Public Debt evolution of fcst Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from Eurostat. Forecasts are based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 8 Fiscal balance as % of GDP. 9 Fiscal balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Public debt as % of GDP. Public debt as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 9 9 FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 7
28 Monetary Sector Inflation April 5 Inflation - 9 in % Inflation 5 evolution of fcst G7-5 5 Maximum Consensus Minimum - 6 Inflation 5 Panelist Distribution 5% % % % % % Inflation Q -Q 6 in % 5 Inflation 6 evolution of fcst < >.8 Notes and sources G7 - Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 Maximum Consensus Minimum - Inflation annual variation of consumer price index in % Individual Forecasts 5 6 Allianz -.. Banco BPI..5 Bankia..7 BBVA Research.. Berenberg.. Berliner Sparkasse -..6 BNP Paribas.. Citigroup Global Mkts..5 Coe-Rexecode.. Commerzbank -.. Credit Agricole.. Credit Suisse.. DekaBank.. Deutsche Bank.. DIW Berlin.. DNB..8 DZ Bank -..9 EIU -..8 Eurobank -. - Goldman Sachs.. Gruppo MPS.. Holding Monex Ifo Institut - - ING..5 Instituto Flores de Lemus.. Intesa Sanpaolo - - JPMorgan. - Julius Baer..6 KBC.. Kiel Institute.. La Caixa..6 Lloyds TSB -.. NIBC Bank -.. Nomura..7 Nordea.. Novo Banco.. Oxford Economics -.. Raiffeisen Research.. Sal. Oppenheim.. Scotiabank.. Société Générale.. Standard Chartered..7 UBS..5 Unicredit -.. Summary Minimum Maximum..7 Median.. Consensus.. History days ago.. 6 days ago.. 9 days ago.6. Additional Forecasts European Commission (Feb. 5) -.. ECB (Mar. 5)..5 IMF (Oct. ).9. Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All monetary sector data are from Eurostat. Forecasts are based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. Inflation, annual average variation of harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) in %. Inflation, annual variation of quarterly average harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) in %. Inflation, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. 5 Inflation, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 6 Inflation, panelist distribution of 5 forecasts. Concentration of panelists in forecast interval in %. Higher columns with darker colors represent a larger number of panelists. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 8
29 Monetary Sector Interest Rates April 5 ECB Refinancing Rate and -Month EURIBOR Refinancing Rate -Month EURIBOR in % in % Individual Forecasts Allianz Banco BPI Bankia BBVA Research Berenberg Berliner Sparkasse BNP Paribas Citigroup Global Mkts Coe-Rexecode Commerzbank Credit Agricole Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DNB DZ Bank EIU Eurobank Goldman Sachs Gruppo MPS Holding Monex Ifo Institut ING Instituto Flores de Lemus Intesa Sanpaolo JPMorgan Julius Baer KBC Kiel Institute La Caixa Lloyds TSB NIBC Bank Nomura Nordea Novo Banco Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research Sal. Oppenheim Scotiabank Société Générale Standard Chartered UBS Unicredit Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Policy Rate in % 8 United States Japan Policy Rate evolution of fcst Benchmark Rate in % 8 United States Japan Benchmark Rate evolution of fcst Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All monetary sector data are from the European Central Bank (ECB), the Federal Reserve Board (Fed) and the Bank of Japan (BoJ). Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 7 Refinancing rate in % (eop). 8 Refinancing rate, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 9 -month EURIBOR in % (eop). -month EURIBOR, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months...5. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 9
30 Monetary Sector Exchange rate April 5 Exchange Rate USD per EUR USD per EUR 5 evol. of fcst.6... Maximum Consensus Minimum.8 5 USD per EUR 5 Panelist Distribution 6% % % % Exchange Rate USD per EUR USD per EUR 6 evol. of fcst < > Q Q Q Q 5 Q Maximum Consensus Minimum.8 Exchange Rate USD per EUR Individual Forecasts 5 6 Allianz - - Banco BPI - - Bankia.. BBVA Research.5. Berenberg - - Berliner Sparkasse - - BNP Paribas - - Citigroup Global Mkts.9 - Coe-Rexecode..9 Commerzbank. - Credit Agricole.5. Credit Suisse. - DekaBank.. Deutsche Bank. - DIW Berlin - - DNB - - DZ Bank - - EIU..6 Eurobank - - Goldman Sachs - - Gruppo MPS - - Holding Monex.9.5 Ifo Institut - - ING.95.9 Instituto Flores de Lemus - - Intesa Sanpaolo - - JPMorgan.5 - Julius Baer - - KBC.95 - Kiel Institute.. La Caixa..6 Lloyds TSB.7.5 NIBC Bank..5 Nomura.5.5 Nordea.5. Novo Banco..9 Oxford Economics.. Raiffeisen Research.9. Sal. Oppenheim - - Scotiabank.5. Société Générale.. Standard Chartered..5 UBS.5. Unicredit.8.6 Summary Minimum.9.9 Maximum.5. Median.5.8 Consensus..7 History days ago.. 6 days ago.. 9 days ago.8.5 Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All monetary sector data are from European Central Bank (ECB). Forecasts are based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. Exchange rate, USD per EUR (eop). Quarterly exchange rate, USD per EUR (eop). Exchange rate, evolution of 5 forecast during the last 8 months. Exchange rate, evolution of 6 forecast during the last 8 months. 5 Exchange rate, panelist distribution of 5 forecasts. Concentration of panelists in forecast interval in %. Higher columns with darker colors represent a larger number of panelists. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
31 External Sector Current Account Balance April 5 6 Current Account % of GDP Current Account 5 evol. of fcst Current Account 5 Panelist Distribution 6% % % % G7 Maximum Consensus Minimum 7 Curr Account Q -Q 6 % of GDP 9 Current Account 6 evol. of fcst Maximum Consensus Minimum < >.5 Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 Current Account Balance % of GDP Individual Forecasts 5 6 Allianz.6. Banco BPI - - Bankia - - BBVA Research.7.7 Berenberg.6.6 Berliner Sparkasse.. BNP Paribas.8.9 Citigroup Global Mkts.. Coe-Rexecode.7.9 Commerzbank..9 Credit Agricole.. Credit Suisse - - DekaBank.5.6 Deutsche Bank.. DIW Berlin - - DNB - - DZ Bank.6.7 EIU.. Eurobank.5 - Goldman Sachs - - Gruppo MPS.6 - Holding Monex - - Ifo Institut.7 - ING - - Instituto Flores de Lemus - - Intesa Sanpaolo.7.5 JPMorgan - - Julius Baer - - KBC - - Kiel Institute.5.6 La Caixa - - Lloyds TSB - - NIBC Bank - - Nomura.9. Nordea.9.7 Novo Banco.5.5 Oxford Economics.7. Raiffeisen Research.. Sal. Oppenheim - - Scotiabank.5. Société Générale.7.8 Standard Chartered..9 UBS.. Unicredit..9 Summary Minimum..9 Maximum.. Median.6.6 Consensus.7.6 History days ago days ago days ago.5.5 Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All external sector data are from Eurostat. Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 6 Current account balance as % of GDP. 7 -quarter moving average of current account balance as % of GDP. 8 Current account balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. 9 Current account balance as % of GDP, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Current account balance as % of GDP, panelist distribution of 5 forecasts. Concentration of panelists in forecast interval in %. Higher columns with darker colors represent a larger number of panelists. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
32 April 5 LONG-TERM TRENDS -year averages Population (million): GDP (EUR bn):,75,985,99 GDP per capita (EUR):,8 6,8,687 GDP growth (%):..8.6 Fiscal Balance (% of GDP): -... Public Debt (% of GDP): Inflation (%):.9.9. Current Account (% of GDP): Outlook improves ended on a very strong note. Private consumption was the main anchor of growth in, helped by the significant decline in the global oil price. Data for Q are somewhat mixed, but suggest overall that remains on a solid growth track. Industrial production growth moderated and exports shrank in January, but business sentiment and the composite PMI improved again in March and the consumer confidence indicator reached an over-thirteen-year high in April. Finance Minister Wolfgang Schäuble presented amendments to this year s budget, the draft 6 budget and fiscal plans up to 9 on 8 March. The key policy measure is an increase in public investment mainly in infrastructure which amounts to EUR.5 billion until 8, although the government remains committed to its goal of achieving a balanced budget through 9. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists revised up s economic outlook for a third straight month on expectations that a strong labor market, lower oil prices and a weak euro will boost growth. The panel expects the economy to expand.8% in 5, which is up. percentage points from last month s projection. For 6, the panel foresees growth of.9%. Inflation stood at.% in March (February: +.% year-on-year), recording a second consecutive increase. Panelists see inflation averaging.% in 5 before rising to.6% in 6. Teresa Kersting Economist Purchasing Managers Index 6 REAL SECTOR Flash PMI rises to eight-month high in March Markit s composite Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) in March rose to the highest level since July, increasing from February s 5.8 to 55.. As a result, the composite PMI the result of a survey of over, manufacturing and service businesses based in moved a bit further above the 5-threshold, where it has remained since April Mar- Sep- Mar- Sep- Mar-5 Note: Markit Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) Composite Output. A reading above 5 indicates an expansion in business activity while a value below 5 points to a contraction. Source: Markit. March s improvement reflects increases in both the services and the manufacturing segment. According to Markit, March s print largely reflects faster growth of output, new orders, new export business and investment. In addition, private sector employment and work outstanding both increased and business expectations at service providers remained positive. In March, input costs rose for the first time in four months, resulting from the weaker euro and the introduction of the national minimum wage in January, and companies increased output charges. Markit commented on the result, stating that, [i]t looks like the German economy is entering the economic fast lane again, with survey data suggesting that we should expect another quarter of solid GDP growth. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
33 April 5 FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect fixed investment to expand.% in 5, which is up. percentage points from last month s forecast. For 6, panelists expect fixed investment to grow.6%. The government expects the economy to expand.5% in 5. The Central Bank foresees economic growth of.% for 5 and of.6% for 6. FocusEconomics Consensus forecast panelists expect economic activity to expand.8% in 5, which is up. percentage points from last month s forecast. For 6, the panel forecasts GDP growth of.9%. Industrial Production variation in %.. %. 6.. %. REAL SECTOR Industrial production growth inches down in January In January, industrial production grew a seasonally-adjusted.6% over the previous month, coming in below December s.% increase. The reading exceeded market expectations of a.5% increase slightly and represented the fifth consecutive expansion. January s print mainly reflected that increases in the production of capital goods and construction more than compensated for contractions in the production of intermediate and consumer goods Month-on-month s.a. (left scale) Year-on-year (right scale) Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan-5 Note: Month-on-month changes of seasonally-adjusted industrial production and annual growth rate in %. Source: Federal Statistical Office and FocusEconomics calculations.. -. Compared to the same month of the previous year, industrial production rose.9%, which followed December s.5% growth. Nevertheless, the overall trend deteriorated as annual average growth in industrial production edged down from December s.5% to a -month low of.% in January. Forecasters polled by FocusEconomics expect that industrial production will expand.% in 5, which is up. percentage points from last month s forecast. For 6, the panel sees industrial production increasing.%. GfK Consumer Climate 8 6 Apr- Oct- Apr- Oct- Apr- Oct- Apr-5 Note: GfK Consumer Climate Index. Source: The GfK Group. OUTLOOK Consumer confidence reaches over -year high The mood among German consumers improved for a sixth consecutive month. The forward-looking consumer confidence indicator published by the GfK increased from 9.7 points in March to. points for April, coming in above the 9.8 points that markets had expected. Consumer confidence has not been this high since October. According to GfK, [t]he tug of war in Europe over the future of Greece is currently having no impact whatsoever on the consumer mood of Germans. Consumers consider the German economy to be on clear upward trend based on a weak euro, which is boosting exports, and lower energy costs. In addition to the overall consumer confidence indicator, which estimates consumer confidence in the coming month, the GfK elaborates on three sub-indicators, which refer to the previous month. In March, households expectations for the overall economy recorded a fourth consecutive notable increase. GfK pointed out that, [t]he low interest rate policy of the European Central Bank (ECB) has placed the euro under great pressure of devaluation. This has therefore significantly improved the competitiveness of German exports outside the eurozone. In addition, the effect of exceedingly low energy costs for households and companies is similar to a mini economic stimulus program. In addition, consumers willingness to buy rose for a sixth straight month, reaching the highest level since December 6, and households income expectations recorded a third consecutive improvement. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect private consumption to expand.% in 5, which is up. percentage points from last month s estimate. For 6, panelists see private consumption growing.5%. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
34 April 5 Ifo Business Climate 5 5 Mar- Sep- Mar- Sep- Mar- Sep- Mar-5 Note: Ifo Business Climate Index, =. Source: Ifo Business Survey. OUTLOOK Business confidence rises to eight-month high in March The business confidence index, elaborated by the Ifo Institute, advanced from 6.8 in February to 7.9 in March and came in above market expectations of an increase to 7.. Following the declines recorded between May and October of, the index improved in March for a fifth consecutive month and continued to recover some of the lost ground. Now the index sits at the highest level in eight months. According to the Institute, March s print reflects that firms were more positive regarding both their current economic situations and future business development than in the previous month. Business climate rose in the manufacturing, wholesaling and retailing sectors but worsened in construction. Overall, the Ifo Institute commented that the reading suggests that, [t]he German economy continues to expand. Inflation Consumer Price Index MONETARY SECTOR Inflation rises in March Consumer prices in March rose.5% over the previous month, according to preliminary data released by the Federal Statistics Office (Destatis) on March. The result followed February s.% increase...5 %...5 %. In annual terms, consumer prices rose.% in March, coming in above February s mild.% increase, and marking the highest print in four months. Nevertheless, annual average inflation inched down from February s.7% to.6% in March, the lowest reading since June Month-on-month (left scale) Year-on-year (right scale) Mar- Sep- Mar- Sep- Mar-5 Note: Month-on-month and annual consumer price index variation in %. Source: Federal Statistical Office and FocusEconomics calculations..5. Meanwhile, harmonized consumer prices rose.% in annual terms, contrasting February s.% decrease. Annual average HICP inflation moderated from.6% in February to.5% in March. The Central Bank expects inflation of.% in 5, before increasing to.8% in 6. FocusEconomics panelists expect inflation to average.% in 5, which is down. percentage points from the previous month s forecast. For 6, panelists expect inflation to increase to.6%. EXTERNAL SECTOR Trade surplus narrows on shrinking exports The seasonally- and calendar-adjusted trade surplus decreased from December s EUR.5 billion record-high to EUR 9.7 billion in January. Merchandise Trade Trade balance (EUR bn, left scale) Exports (yoy, right scale) Imports (yoy, right scale) The trade surplus in January narrowed over the previous month as exports contracted at a faster pace than imports. Exports shrank a seasonally-adjusted.% over the previous month, contrasting December s.8% increase. Meanwhile, imports fell.% in January, coming in above December s.7% decline Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan-5 Note: -month sum of trade balance in EUR billion and annual variation of the -month sum of exports and imports in %. Source: Federal Statistical Office and FocusEconomics calculations. % Compared to the same month last year, exports fell.6% (December: +.% year-on-year). Imports contracted.% annually in January, contrasting December s.% rise. The -month sum of exports to January grew.5% over the same period last year and the trade surplus totaled EUR.9 billion, reaching yet another all-time record high. The Federation of German Wholesale, Foreign Trade and Services (BGA) noted in a recent statement that the print reflects a disappointing start to this year, as rising exports to the U.S. and China did not compensate for lower demand from BRIC countries and economic weakness in the. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
35 April 5 Economic Indicators - 9 Annual Data Real Sector Population (million) GDP per capita (EUR),,55,7,88 5,9 6,66 7,97 9,85,68,95 GDP (EUR bn),57,695,75,8,98,97,75,86,99, Economic Growth (Nom. GDP, ann. var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Domestic Demand (annual variation in %) Private Consumption (annual var. in %) Government Consumption (ann. var. in %) Fixed Investment (annual variation in %) Exports (G&S, annual variation in %) Imports (G&S, annual variation in %) Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Retail Sales (annual variation in %) Unemployment (% of active population, aop) Fiscal Balance (% of GDP) Public Debt (% of GDP) Monetary and Financial Sector Inflation (CPI, annual variation in %, eop) Inflation (CPI, annual variation in %, aop) Inflation (PPI, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Year Bond Yield (%, eop) Stock Market (variation of DAX in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, aop) External Sector Current Account Balance (% of GDP) Current Account Balance (EUR bn) Trade Balance (EUR bn) Quarterly Data Q Q Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, s.a. qoq var. in %) Private Consumption (s.a. qoq var. in %) Fixed Investment (s.a. qoq variation in %) Exports (G&S, s.a. qoq variation in %) Imports (G&S, s.a. qoq variation in %) Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Unemployment (% of active population, aop) Inflation (CPI, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Year Bond Yield (%, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Current Account Balance (% of GDP) Current Account Balance (EUR bn) Monthly Data Jul- Aug- Sep- Oct- Nov- Dec- Jan-5 Feb-5 Mar-5 Apr-5 Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Industrial Production (s.a. mom var. in %) Retail Sales (annual variation in %) Unemployment (% of active population) GfK Consumer Climate Ifo Business Climate (=) Markit Composite PMI (5-threshold) Inflation (CPI, mom variation in %) Inflation (CPI, annual variation in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Exports (s.a. mom variation in %) Imports (s.a. mom variation in %) FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 5
36 Real Sector Gross Domestic Product April 5 Real GDP -9 var. in % Real GDP Q -Q 6 var. in % 6. G G7 World Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 GDP 5 evolution of forecasts GDP 6 evolution of forecasts Maximum Consensus Minimum Maximum Consensus Minimum 5 GDP 5 Panelist Distribution 5% % % % % % < >.8 Real GDP growth in % Individual Forecasts 5 6 Allianz..7 BBVA Research.. Berenberg.8. Berliner Sparkasse.7.6 BNP Paribas.. Citigroup Global Mkts.9. Commerzbank.8.8 Credit Agricole..5 Credit Suisse.8. DekaBank.. Deutsche Bank..7 DIW Berlin..9 DZ Bank.8.6 EIU.8.7 Frontier Strategy Group..7 Goldman Sachs.7.9 HWWI.9.7 Ifo Institut.5 - ING.8. Intesa Sanpaolo..9 JPMorgan.. Julius Baer..8 Kiel Institute.8. Lloyds TSB.8. Nomura.7.5 Nordea.7.6 Oxford Economics.. Raiffeisen Research.6. RWI..9 Sal. Oppenheim.8.6 Scotiabank.5.8 UBS.. Unicredit.. Summary Minimum..5 Maximum.. Median.8.9 Consensus.8.9 History days ago days ago..8 9 days ago..8 Additional Forecasts Central Bank (Dec. )..6 IMF (Jan. 5)..5 European Comission (Feb. 5).5. Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the Federal Statistical Office (Destatis, Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland). Forecasts are based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. GDP, annual variation in %. Quarterly GDP (seasonally adjusted), quarter-on-quarter variation in %. GDP, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. GDP, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 5 GDP, panelist distribution of 5 forecasts. Concentration of panelists in forecast interval in %. Higher columns with darker colors represent a larger number of panelists. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 6
37 Real Sector Additional forecasts April 5 Consumption and Investment Consumption Investment variation in % variation in % Individual Forecasts Allianz BBVA Research Berenberg Berliner Sparkasse BNP Paribas Citigroup Global Mkts...8. Commerzbank Credit Agricole Credit Suisse..9.. DekaBank....8 Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DZ Bank EIU Frontier Strategy Group Goldman Sachs HWWI Ifo Institut ING Intesa Sanpaolo...7. JPMorgan Julius Baer Kiel Institute Lloyds TSB Nomura Nordea Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research RWI Sal. Oppenheim Scotiabank UBS Unicredit Summary Minimum Maximum Median....5 Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Consumption variation in % G Consumption evolution of fcst Investment variation in % - G Investment evol. of forecasts 5 Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the Federal Statistical Office (Destatis, Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland). Forecasts are based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 6 Private consumption, annual variation in %. 7 Private consumption, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 8 Gross fixed investment, annual variation in %. 9 Gross fixed investment, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 5 6 FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 7
38 Real Sector Additional forecasts April 5 Exports and Imports Exports Imports variation in % variation in % Individual Forecasts Allianz BBVA Research Berenberg Berliner Sparkasse BNP Paribas Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Credit Agricole Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DZ Bank EIU Frontier Strategy Group Goldman Sachs HWWI Ifo Institut ING Intesa Sanpaolo JPMorgan Julius Baer Kiel Institute Lloyds TSB Nomura Nordea Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research RWI Sal. Oppenheim Scotiabank UBS Unicredit Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Exports variation in % - G7-5 5 Exports evolution of fcst Imports variation in % - G7-5 5 Imports evol. of forecasts Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the Federal Statistical Office (Destatis, Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland). Forecasts are based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. Real exports of goods and services, annual variation in %. Exports, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Real imports of goods and services, annual variation in %. Imports, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 8
39 Real Sector Additional forecasts April 5 Industry and Unemployment Industry Unemployment variation in % % of active pop. Individual Forecasts Allianz BBVA Research Berenberg Berliner Sparkasse BNP Paribas Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Credit Agricole Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DZ Bank EIU Frontier Strategy Group Goldman Sachs HWWI Ifo Institut ING Intesa Sanpaolo JPMorgan Julius Baer Kiel Institute Lloyds TSB Nomura Nordea Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research RWI Sal. Oppenheim Scotiabank UBS Unicredit Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Industry variation in % - G Industry evol. of forecasts Unemployment % of active pop. 8 6 G Unemployment evol. of forecasts Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the Federal Statistical Office (Destatis, Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland) and the Federal Labour Office (BA, Bundesagentur für Arbeit). See below for details. Forecasts are based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. Industrial production, annual variation in %. Source: Destatis. 5 Industrial production, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 6 Unemployment, % of active population. Source: BA. 7 Unemployment, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 9
40 Real Sector Additional forecasts April 5 Fiscal Balance and Public Debt Fiscal Balance Public Debt % of GDP % of GDP Individual Forecasts Allianz BBVA Research Berenberg Berliner Sparkasse BNP Paribas Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Credit Agricole Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DZ Bank EIU Frontier Strategy Group Goldman Sachs HWWI Ifo Institut ING Intesa Sanpaolo JPMorgan Julius Baer Kiel Institute Lloyds TSB Nomura Nordea Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research RWI Sal. Oppenheim Scotiabank UBS Unicredit Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Fiscal Balance % of GDP 5 G Fiscal Balance evol. of forecasts Public Debt % of GDP 5 G Public Debt evol. of forecasts Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from Eurostat. Forecasts are based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 8 General government balance as % of GDP. 9 General government balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Public debt as % of GDP. Public debt as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
41 Monetary Sector Inflation and -Year Bond Yield April 5 Inflation and -Year Bond Yield Prices (CPI) -Year Bond variation in % Yield in % Individual Forecasts Allianz BBVA Research Berenberg Berliner Sparkasse BNP Paribas Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Credit Agricole Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DZ Bank EIU Frontier Strategy Group Goldman Sachs HWWI Ifo Institut ING Intesa Sanpaolo JPMorgan Julius Baer Kiel Institute Lloyds TSB Nomura Nordea Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research..6.. RWI..5.. Sal. Oppenheim Scotiabank UBS...9. Unicredit Summary Minimum.... Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Inflation - 9 in % G7-5 5 Inflation evol. of forecasts year Bond Yield -9 8 France Italy year Bond Yield evol. of forecasts..5. Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All monetary sector data are from Federal Statistical Office (Destatis, Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland), the German Central Bank (BBK, Deutsche Bundesbank) and the European Central Bank (ECB). See below for details. Forecasts are based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. Inflation, annual average variation of consumer price index (CPI) in %. Source: Destatis. Inflation, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. -year benchmark bond yield (eop). Source: BBK, ECB. 5 -year benchmark bond yield, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
42 External Sector Current Account Balance April 5 6 Current Account % of GDP Current Account 5 evol. of fcst Maximum Consensus Minimum Current Account 5 Panelist Distribution 6% % % G7 7 Curr Account Q - Q 6 % of GDP Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 9 Current Account 6 evol. of fcst Maximum Consensus Minimum Current Account Balance % of GDP Individual Forecasts 5 6 Allianz BBVA Research Berenberg Berliner Sparkasse BNP Paribas Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Credit Agricole - - Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DZ Bank EIU Frontier Strategy Group - - Goldman Sachs - - HWWI Ifo Institut 7. - ING - - Intesa Sanpaolo JPMorgan - - Julius Baer - - Kiel Institute Lloyds TSB - - Nomura - - Nordea Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research RWI Sal. Oppenheim - - Scotiabank UBS Unicredit Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago % < >. Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All external sector data are from the German Central Bank (BBK, Deutsche Bundesbank). Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 6 Current account balance as % of GDP. 7 -quarter moving average of current account balance as % of GDP. 8 Current account balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. 9 Current account balance as % of GDP, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Current account balance as % of GDP, panelist distribution of 5 forecasts. Concentration of panelists in forecast interval in %. Higher columns with darker colors represent a larger number of panelists. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
43 FOCUSECONOMICS Fact Sheet April 5 General Data Official name: Federal Republic of Capital: Berlin (5.m) cities: Düsseldorf (7.8m) Frankfurt am Main (.7m) Area (km): 57, Population (million, est.): 8.9 Population density (per km, ): 7 Population growth rate (%, est.): -. Life expectancy (years, est.): 8. Illiteracy rate (%, ):. Language: German Measures: Metric system Time: GMT+ in the Region Population %-share in G7 France 8.5% United Kingdom 8.6% Canada.7% Italy 8.% Japan 6.9%.8% United States.% France 8.% United Kingdom 8.% Japan.% GDP %-share in G7 Italy 6.% Canada 5.%.9% United States 8.8% Economic Infrastructure Telecommunication () Telephones - main lines (per inhabitants): 58.9 Telephones - mobile cellular (per inhabit.): 9 Internet Users (per inhabitants): 8. Broadband Subscriptions (per inhabitants):.6 Energy () Primary Energy Production (trillion Btu):,8 Primary Energy Consumption (trillion Btu):,66 Electricity Generation (billion kw-h): 585 Electricity Consumption (billion kw-h): 5 Oil Supply (thousand bpd): 6 Oil Consumption (thousand bpd):,89 CO Emmissions (million metric tons): 788 Economic Structure 8 6 GDP by Sector share in % GDP by Expenditure share in % Agriculture Manufacturing Industry Services Net Exports Investment Government Consumption Private Consumption Transportation () Airports: 59 Railways (km):,98 Roadways (km): 65, Waterways (km): 7,67 Chief Ports: Hamburg, Bremerhaven, Kiel Trade Structure Primary markets share in % Political Data Chancellor: Angela Merkel Last elections: September Next elections: September 7 Central Bank Governor: Jens Weidmann Long-term Foreign Currency Ratings Agency Rating Outlook Moody s: Aaa Stable S&P: AAA Stable Fitch Ratings: AAA Stable 8.% China 5.% Asia ex-japan 5.% Netherlands U.K. 6.9% 7.% U.S.A. 6.% Exports France.% EU- 7.%.5% China 6.7% Primary products share in % Belgium 6.% Imports France 7.5% EU- 7.8% Netherlands.% Strengths Government debt and deficit below average Innovation, research and development Important role of export-oriented SME's (Mittelstand). Weaknesses Ageing population Large and powerful labor unions Persistent backwardness of eastern federal states. Food 5.5% Exports Manufact. Products 8.8%.6% Mineral Fuels.% Food 7.5% Imports.7% Manufact. Products 66.6% FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
44 France April 5 France France LONG-TERM TRENDS -year averages Population (million): GDP (EUR bn):,88,78,57 GDP per capita (EUR):,95,896 6,86 GDP growth (%): Fiscal Balance (% of GDP): Public Debt (% of GDP): Inflation (%):.8.6. Current Account (% of GDP): Outlook improves Following the anemic growth recorded in the final quarter of, recent economic indicators signal that the economy is gradually shifting into higher gear. Industrial production expanded for a second consecutive month in January and the March Composite PMI suggests that French business activity is expanding. In addition, March sentiment surveys showed that businesses and consumers are perceiving a mild economic recovery. On the political front, the right-wing National Front (FN) made limited gains in the second-round local elections held on 9 March. Conversely, former president Nicolas Sarkozy s Union for a Popular Movement (UMP) and its allies scored a key victory, garnering over two-thirds of the departments. Although voter turnout was low, the election result represents the current electoral mood as the popularity of the Socialist Party, and particularly that of President François Hollande, is at a record low. The French economy is going to benefit from a stimulatory monetary policy, low oil prices and a less restrictive fiscal policy. In addition, the weaker euro is likely to boost exports to countries outside the Eurozone. FocusEconomics panelists raised their growth forecasts by. percentage points over the previous month and now expect the French economy to expand.% in 5. For 6, panelists expect economic growth to accelerate to.%. Ricardo Aceves Senior Economist Gross Domestic Product variation in %. Quarter-on-quarter s.a. (left scale) Year-on-year (right scale). In February, the annual fall in consumer prices moderated compared to the previous month but inflation is likely to start rising in the coming months. Panelists foresee HICP inflation averaging.% in 5 and.% in 6. REAL SECTOR French GDP growth slows in Q More complete data released by the statistical office (INSEE) confirmed that the French economy decelerated in the last quarter of. In Q, GDP increased a seasonally-adjusted.% over the previous quarter, which came in below the.% rise seen in Q and was on par with market expectations. Yea-on-year, GDP decelerated from a.% increase in Q to.% expansion in Q. In, the French economy increased.%, which matched the growth rate seen in...5 % %.. The fourth quarter s deceleration was the result of slower growth in domestic demand. Private consumption grew.% in Q, below the.% rise in Q. Government spending increased.5% in Q, a tad below the.6% expansion in Q. Meanwhile, gross fixed investment continued to contract in Q, although at a slower pace than in Q (Q: -.5% quarter-on-quarter; Q: -.6% qoq). -. Q Q Q Q Q 5 Note: Quarter-on-quarter changes of seasonally-adjusted GDP and year-on-year variation in %. Source: National Institute of Statistics and Economic Studies (INSEE) and FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. -.5 On a positive note, the external sector improved in the last quarter of as exports of goods and services expanded a robust.5% over the previous quarter (Q: +.% qoq), while imports increased.7% (Q: +.7% qoq). As a result, the external sector s net contribution to overall economic growth swung from minus. percentage points in Q to plus. percentage points in Q. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
45 France April 5 The government expects the economy to increase.% in 5. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect the economy to grow.% in 5, which is up. percentage points from last month s forecast. For 6, panelists see economic growth at.%. Purchasing Managers Index Mar- Sep- Mar- Sep- Mar-5 Note: Markit Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) Composite Output. A reading above 5 indicates an expansion in business activity while a value below 5 points to a contraction. Source: Markit. REAL SECTOR Composite PMI moderates in March, still signals expansion in business activity The composite Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) elaborated by Markit moderated in March, inching down from February s three-and-half year high 5. to 5.7 in March. With March s result, the composite PMI remained for the second consecutive month above the 5-threshold that indicates expansion in business activity, after the indicator had remained in contractionary territory over the last nine months. According to Markit, the rate of growth eased since February and was modest overall. As in previous surveys, business activity growth in services offset a decrease in activity in the manufacturing sector. Growth in services was solid, although slower than in the previous month. In the manufacturing sector, business activity registered a similar drop as in February. Markit reported that new businesses rose for the fourth consecutive month in March and the growth pace was the fastest since August. Conversely, new export orders in the manufacturing sector continued to contract in March. Meanwhile, employment rose for the first time in 7 months, but the increase was only marginal over the previous month. Markit concluded that, March s PMI data show a further tentative expansion of output in France s private sector economy. [ ] However, the divergence in sector performance continued, with the service sector again shouldering the burden of expansion amid ongoing contraction in manufacturing. Industrial Production variation in %. Month-on-month s.a. (left scale) Year-on-year (right scale). REAL SECTOR Industrial production expands for second consecutive month In January, industrial production expanded a seasonally-adjusted.% over the previous month, which came in below the revised.% expansion tallied in December (previously reported: +.5% month-on-month). The print, which overshot the.% contraction the markets had expected, reflected a deterioration in both manufacturing and construction.. %.. % -. In annual terms, industrial output swung from a.% contraction in December to a.6% increase in January, which marked the first expansion in industrial output since November Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan-5 Note: Month-on-month changes of seasonally-adjusted industrial production and annual growth rate in %. Source: National Institute of Statistics and Economic Studies (INSEE) and FocusEconomics calculations. The trend appeared to have stabilized. The annual average variation in industrial production remained unchanged at December s minus.% in January. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect industrial production to increase.7% in 5, which is down. percentage points from last month s forecast. For 6, the panel expects industrial output to expand.9%. OUTLOOK Confidence among French firms wanes somewhat in March The monthly business sentiment index published by the National Statistical Institute (INSEE) inched down from February s points to 99 points in March. The reading also fell short of the points the markets had expected. The FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 5
46 France April 5 Business Sentiment 5 indicator has been below the long-term -point average the benchmark measure the INSEE uses to distinguish between improving and worsening business expectations in nine of the last months Mar- Sep- Mar- Sep- Mar- Sep- Mar-5 Note: Value of monthly business sentiment indicator index; long-term avg. at. Source: National Institute of Statistics and Economic Studies (INSEE). March s mild drop reflected that businesses were less optimistic regarding their own production expectations. Respondents to the March survey also signaled more pessimism regarding their own business activity compared to a year ago. Conversely, firms assessment regarding general production expectations improved over the previous month along with businesses opinions about global order books. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists see fixed investment decreasing.% in 5, which is down. percentage points over the previous month s estimate. For 6, the panel sees investment expanding.%. Consumer Confidence 95 OUTLOOK Confidence among consumers rises to highest level in over four years The consumer confidence indicator elaborated by the National Statistics Institute (INSEE) rose from February s 9 points to 9 points in March and matched market expectations. The result marked the highest level since November. Despite the increase, the index is still below its long-term average of Mar- Sep- Mar- Sep- Mar- Sep- Mar-5 Note: Value of monthly consumer confidence index; long-term average at. Source: National Institute of Statistics and Economic Studies (INSEE). According to INSEE, March s result reflected consumers more optimistic opinions regarding both their current living standards as well as their future living standards. In addition, households responded that they were more optimistic regarding their current and future savings capacity. This month s survey also showed consumers more optimistic assessment regarding employment prospects and households intentions to buy big ticket items in the next months improved over the previous month. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect private consumption to increase.% in 5, which is up. percentage points over last month s forecast. The panel expects private consumption to accelerate to a.% rise in 6. Inflation Consumer Price Index. Month-on-month (left scale).5 % Year-on-year (right scale).5. % MONETARY SECTOR Annual fall in consumer prices moderates in February In February, consumer prices jumped.7% over the previous month. The increase contrasted the.% drop observed in January, which had represented the fastest monthly drop in several years and slightly overshot the.6% increase the markets has expected. According to the national statistical institute (INSEE), higher prices for manufactured products are due to the end of the seasonal sales as well as winter services tariffs related to the holidays Feb- Aug- Feb- Aug- Feb-5 Note: Year-on-year and month-on-month variation of consumer price index in %. Source: National Institute of Statistics and Economic Studies (INSEE)..5. Despite the monthly increase, consumer prices fell.% in February over the same month last year, which followed the.% drop observed in January. Core consumer prices, which do not consider volatile categories such as fresh food and energy prices nor regulated prices rose.% over the previous month, which was up from the flat reading observed in January. Annual core inflation inched down from.% in January to.% in February. Harmonized consumer prices (based on the harmonized index of consumer prices, HICP) rose.7% over the previous month (January: -.% month-onmonth). Harmonized consumer prices fell.% annually in February as well. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 6
47 France April 5 Annual average HICP inflation inched down from.5% in January to.% in February. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect HICP inflation to average.% in 5, which is unchanged from last month s forecast. For 6, panelists project that inflation will accelerate to.%. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 7
48 France April 5 Economic Indicators - 9 Annual Data Real Sector Population (million) GDP per capita (EUR),8,6,98,,57,78, 5,56 6,7 7,7 GDP (EUR bn),997,58,9,5,,68,,86,56,9 Economic Growth (Nominal GDP, ann. var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Domestic Demand (annual variation in %) Private Consumption (annual var. in %) Government Consumption (ann. var. in %) Fixed Investment (annual variation in %) Exports (G&S, annual variation in %) Imports (G&S, annual variation in %) Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Retail Sales (annual variation in %) Unemployment (% of active population, aop) Fiscal Balance (% of GDP) Public Debt (% of GDP) Monetary and Financial Sector Inflation (Core, annual variation in %, aop) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, eop) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) Inflation (PPI, annual variation in %, eop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Year Bond Yield (%, eop) Stock Market (variation of CAC in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, aop) External Sector Current Account Balance (% of GDP) Current Account Balance (EUR bn) Trade Balance (EUR bn) Quarterly Data Q Q Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, s.a. qoq var. in %) Unemployment (% of active population, aop) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Year Bond Yield (%, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Monthly Data Jun- Jul- Aug- Sep- Oct- Nov- Dec- Jan-5 Feb-5 Mar-5 Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Industrial Production (s.a. mom var. in %) Unemployment (eop, % of active population) Markit Composite PMI (5-threshold) Consumer Conf. (long-term avg. ) Business Sentiment (long-term avg. ) Inflation (CPI, mom variation in %) Inflation (CPI, annual variation in %) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 8
49 Real Sector Gross Domestic Product France April 5 Real GDP -9 var. in % GDP 5 evolution of forecasts 6 - France G7 - World 5 5 5% % % % % Maximum Consensus Minimum 5 GDP 5 Panelist Distribution Real GDP Q -Q 6 var. in %..5. France G7 -.5 Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 GDP 6 evolution of forecasts Maximum Consensus Minimum.5 Real GDP growth in % Individual Forecasts 5 6 Asterès. - BBVA Research..8 Berenberg.8. BNP Paribas.9.5 Citigroup Global Mkts..8 Coe-Rexecode..6 Commerzbank.9.9 Credit Agricole.9. Credit Suisse..9 DekaBank.. Deutsche Bank..6 DIW Berlin.7. DZ Bank.. EIU.9. Frontier Strategy Group.7. Goldman Sachs..7 ING..6 Intesa Sanpaolo.7. JPMorgan.. Julius Baer.8.9 Lloyds TSB..7 Nomura.9.8 Nordea.9. OFCE. - Oxford Economics..7 Raiffeisen Research.7.5 Scotiabank.8. Société Générale.8. UBS..5 Unicredit.9.5 Xerfi..8 Summary Minimum.7.8 Maximum.. Median..5 Consensus.. History days ago.9. 6 days ago.9. 9 days ago.9. Additional Forecasts European Commission (Feb. 5)..8 IMF (Jan. 5).9. % < >.7 Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the National Statistical Institute (INSEE, Institut national de la statistique et des études économiques). Forecasts are based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. GDP, annual variation in %. Quarterly GDP (seasonally adjusted), quarter-on-quarter variation in %. GDP, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. GDP, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 5 GDP, panelist distribution of 5 forecasts. Concentration of panelists in forecast interval in %. Higher columns with darker colors represent a larger number of panelists. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 9
50 Real Sector Additional forecasts France April 5 Consumption and Investment Consumption Investment variation in % variation in % Individual Forecasts Asterès BBVA Research... - Berenberg BNP Paribas Citigroup Global Mkts Coe-Rexecode Commerzbank Credit Agricole Credit Suisse.... DekaBank Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DZ Bank EIU...5. Frontier Strategy Group Goldman Sachs ING.5... Intesa Sanpaolo..7.. JPMorgan Julius Baer Lloyds TSB Nomura Nordea OFCE Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research Scotiabank Société Générale UBS Unicredit Xerfi Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Consumption variation in % France G Consumption evolution of fcst Investment variation in % - France G Investment evol. of forecasts Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the National Statistical Institute (INSEE, Institut national de la statistique et des études économiques). Forecasts are based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 6 Private consumption, annual variation in %. 7 Private consumption, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 8 Gross fixed investment, annual variation in %. 9 Gross fixed investment, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 5
51 Real Sector Additional forecasts France April 5 Exports and Imports Exports Imports variation in % variation in % Individual Forecasts Asterès BBVA Research Berenberg BNP Paribas Citigroup Global Mkts Coe-Rexecode Commerzbank Credit Agricole...9. Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DZ Bank EIU Frontier Strategy Group Goldman Sachs ING Intesa Sanpaolo JPMorgan Julius Baer Lloyds TSB Nomura Nordea OFCE Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research Scotiabank Société Générale UBS Unicredit Xerfi Summary Minimum..5.. Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Exports variation in % - France G7-5 5 Exports evolution of fcst Imports variation in % - France G7-5 5 Imports evol. of forecasts..5 Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the National Statistical Institute (INSEE, Institut national de la statistique et des études économiques). Forecasts are based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. Real exports of goods and services, annual variation in %. Exports, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Real imports of goods and services, annual variation in %. Imports, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 5
52 Real Sector Additional forecasts France April 5 Industry and Unemployment Industry Unemployment variation in % % of active pop. Individual Forecasts Asterès BBVA Research Berenberg BNP Paribas Citigroup Global Mkts Coe-Rexecode Commerzbank Credit Agricole Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DZ Bank EIU Frontier Strategy Group Goldman Sachs ING Intesa Sanpaolo JPMorgan Julius Baer Lloyds TSB Nomura Nordea OFCE Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research Scotiabank Société Générale UBS Unicredit Xerfi Summary Minimum Maximum Median.9... Consensus History days ago days ago days ago.... Industry variation in % France G Industry evol. of forecasts Unemployment % of active pop. France G Unemployment evol. of forecasts..5. Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the National Statistical Institute (INSEE, Institut national de la statistique et des études économiques). Forecasts are based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. Industrial production, annual variation in %. 5 Industrial production, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 6 Unemployment, % of active population. 7 Unemployment, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 5
53 Real Sector Additional forecasts France April 5 Fiscal Balance and Public Debt Fiscal Balance Public Debt % of GDP % of GDP Individual Forecasts Asterès BBVA Research Berenberg BNP Paribas Citigroup Global Mkts Coe-Rexecode Commerzbank Credit Agricole Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DZ Bank EIU Frontier Strategy Group Goldman Sachs ING Intesa Sanpaolo JPMorgan Julius Baer Lloyds TSB Nomura Nordea OFCE Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research Scotiabank Société Générale UBS Unicredit Xerfi Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Fiscal Balance % of GDP France G Fiscal Balance evol. of forecasts Public Debt % of GDP 8 6 France G7 5 5 Public Debt evol. of forecasts Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from Eurostat. Forecasts are based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 8 General government balance as % of GDP. 9 General government balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Public debt as % of GDP. Public debt as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 5
54 Monetary Sector Inflation and -Year Bond Yield France April 5 Inflation and -Year Bond Yield Prices (HICP) -Year Bond variation in % Yield in % Individual Forecasts Asterès BBVA Research Berenberg BNP Paribas Citigroup Global Mkts Coe-Rexecode Commerzbank Credit Agricole Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DZ Bank EIU Frontier Strategy Group Goldman Sachs ING Intesa Sanpaolo JPMorgan Julius Baer Lloyds TSB Nomura Nordea OFCE Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research Scotiabank Société Générale...5. UBS..6.. Unicredit Xerfi Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Inflation - 9 in % G year Bond Yield France Inflation evol. of forecasts France Italy year Bond Yield evol. of forecasts Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All monetary sector data are from the Bank of France (BdF, Banque de France), the European Central Bank (ECB) and the National Statistical Institute (INSEE, Institut national de la statistique et des études économiques). See below for details. Forecasts are based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. Inflation, annual average variation of harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) in %. Source: INSEE. Inflation, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. -year benchmark bond yield (eop). Source: ECB, BdF. 5 -year benchmark bond yield, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 5 6 FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 5
55 External Sector Current Account Balance France April 5 6 Current Account % of GDP - - G Current Account 5 evol. of fcst Current Account 5 Panelist Distribution 5% % % % France Maximum Consensus Minimum 7 Curr Account Q -Q 6 % of GDP 9 Current Account 6 evol. of fcst Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 - Maximum Consensus Minimum - Current Account Balance % of GDP Individual Forecasts 5 6 Asterès - - BBVA Research Berenberg BNP Paribas Citigroup Global Mkts -.. Coe-Rexecode Commerzbank - - Credit Agricole Credit Suisse DekaBank - - Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin - - DZ Bank EIU Frontier Strategy Group - - Goldman Sachs ING Intesa Sanpaolo JPMorgan - - Julius Baer - - Lloyds TSB - - Nomura - - Nordea OFCE -. - Oxford Economics - - Raiffeisen Research - - Scotiabank Société Générale UBS Unicredit Xerfi Summary Minimum Maximum -.. Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago % % < >. Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All external sector data are from the Bank of France (BdF, Banque de France). Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 6 Current account balance as % of GDP. 7 -quarter moving average of current account balance as % of GDP. 8 Current account balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. 9 Current account balance as % of GDP, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Current account balance as % of GDP, panelist distribution of 5 forecasts. Concentration of panelists in forecast interval in %. Higher columns with darker colors represent a larger number of panelists. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 55
56 FOCUSECONOMICS Fact Sheet France April 5 General Data Official name: French Republic Capital: Paris (.6m) cities: Marseille (. m) Lyon (.5m) Area (km): 6,8 Population (million, est.): 6. Population density (per km, ): 99 Population growth rate (%, est.):.5 Life expectancy (years, est.): 8.7 Illiteracy rate (%, ): <. Language: French Measures: Metric system Time: GMT+ France in the Region Population %-share in G7 Canada Italy.7% 8.% United Kingdom 8.6%.8% Japan 6.9% France 8.5% United States.% United Kingdom 8.%.8% GDP %-share in G7 Japan.% Italy Canada 6.% 5.% France 8.% United States 9.% Economic Infrastructure Telecommunication () Telephones - main lines (per inhabitants): 6.8 Telephones - mobile cellular (per inhabit.): 98 Internet Users (per inhabitants): 8.9 Broadband Subscriptions (per inhabitants): 8.8 Energy () Primary Energy Production (trillion Btu): 5,76 Primary Energy Consumption (trillion Btu):,69 Electricity Generation (billion kw-h): 5 Electricity Consumption (billion kw-h): 5 Oil Supply (thousand bpd): 7. Oil Consumption (thousand bpd):,77 CO Emmissions (million metric tons): 65 Economic Structure 8 6 GDP by Sector share in % GDP by Expenditure share in % Agriculture Manufacturing Industry Services Net Exports Investment Government Consumption Private Consumption Transportation () Airports: 6 Railways (km): 9,6 Roadways (km):,8,6 Waterways (km): 8,5 Chief Ports: Le Havre, Dunkirk, Marseille Trade Structure - Primary markets share in % Political Data President: François Hollande Last elections: April Next elections: June 7 Central Bank Governor: Christian Noyer.9% U.S.A. 5.7% Exports EU- 7.6%.% Imports EU- 7.7% Long-term Foreign Currency Ratings Agency Rating Outlook Moody s: Aa Negative S&P: AA Negative Fitch Ratings: AA Stable Asia ex- Japan.% Belgium 7.5% Italy 7.5% 6.7% Asia ex- Japan 8.6% Italy 7.7% Primary products share in % Belgium.% 9.5%. Strengths Weaknesses Committed to fiscal consolidation Subdued growth outlook Moderate household debt Large public debt Tourist attractiveness High structural unemployment Important exporter of commercial Loss of competitiveness in services and merchandise goods exporting sector Food.8% Exports.% Manufact. Products 76.9% Mineral Fuels 6.9% Food 8.6%.% Imports Manufact. Products 7.5% FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 56
57 Italy April 5 Italy Italy LONG-TERM TRENDS -year averages Population (million): GDP (EUR bn):,6,6,77 GDP per capita (EUR): 7,55 7,6 8,87 GDP growth (%): -... Fiscal Balance (% of GDP): Public Debt (% of GDP): 7 Inflation (%):.5.. Current Account (% of GDP): Outlook stable According to more detailed data released on 5 March, the Italian economy recorded flat growth in the final quarter of last year, which marks an improvement after several quarters of contractions. A gradual rebound in economic indicators in recent months and a relatively stable political situation suggest that the government is in a good position to start implementing much-needed structural reforms this year. One major change has already been implemented in the banking sector. In an attempt to improve governance and increase the efficiency of the banking system, on March, the parliament approved a reform to convert the country s ten largest cooperative banks into joint stock companies. The move is expected to speed up board decision making processes and lead to increased mergers, as it puts an end to ownership limits and dismantles the previous voting system of one-head, one-vote which used to allow minority shareholders to block unwanted changes. The Italian economy is expected to expand for the first time in four years in 5. FocusEconomics panelists expect the Italian economy to expand.5% this year, which is unchanged from last month s forecast. For 6, the panel sees economic growth picking up to.%. The decline in consumer prices eased from a record-low.6% in January to.% in February. Panelists project an average inflation of.% for this year, while they expect inflation to rise to.9% in 6. Cecilia Simkievich Economist Gross Domestic Product variation in % Quarter-on-quarter s.a. (left scale) Year-on-year (right scale) % % -. Q Q Q Q Q 5 Note: Quarter-on-quarter changes of seasonally-adjusted GDP and year-on-year variation in %. Source: National Statistical Institute (Istat) and FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast REAL SECTOR Economy posts flat growth in Q; GDP contracts in full year In Q, GDP recorded flat growth over the previous quarter in seasonallyand working-day adjusted terms, according to more detailed data released by the National Statistics Office (ISTAT) on 5 March. The reading matched the preliminary estimate and came in slightly above the.% decrease observed in the third quarter. Q s result reflected an improvement both in domestic demand and in exports. Growth in private consumption inched down from.% in Q to.% in Q, while government consumption ticked up from a.% increase to a.% rise. In addition, fixed investment swung from a.% contraction in Q to a mild.% expansion in Q. On the external side of the economy, growth in exports accelerated from.% in Q to.6% in Q, while imports slowed from a.7% rise to a.% increase. As a result, the external sector s net contribution to overall growth improved from minus. percentage points in Q to plus. percentage points in Q. In annual terms, the economy contracted.5% in Q, which matched Q s result but was slightly below the preliminary estimate of a.% decrease. In the full year, the economy contracted.%, which represented an improvement compared to the.7% contraction registered in. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 57
58 Italy April 5 The Bank of Italy expects the economy to expand.% in 5 and.% in 6. FocusEconomics panelists see the economy expanding.5% in 5, which is unchanged from last month s forecast. For 6, panelists expect the economy to expand.%. Industrial Production variation in %. Month-on-month s.a. (left scale) Year-on-year (right scale). % %. -5. REAL SECTOR Industrial production contracts in January In January, industrial output fell a seasonally-adjusted.7% over the previous month, which contrasted the.% increase tallied in December. January s result marked the lowest reading in four months and undershot market expectations of a.% rise. The result was driven by a significant contraction in manufacturing production, which had posted a mild expansion in December. Conversely, electricity, gas, steam and air conditioning, as well as mining and quarrying, recorded stronger increases in January compared to the previous month Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan-5 Note: Month-on-month changes of seasonally-adjusted industrial production and annual growth rate in %. Source: National Statistical Institute (Istat) and FocusEconomics calculations. On an annual basis, industrial output dropped a working-day adjusted.% in January, which contrasted the.% increase observed in the previous month and marked a three-month low. As a result, annual average growth in industrial output declined from minus.7% in December to minus.% in January. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect industrial production to expand.% in 5, which is up. percentage points from last month s forecast. For 6, panelists expect industrial output to expand.5%. Business Confidence OUTLOOK Business confidence jumps up in March The National Institute of Statistics (Istat) composite business confidence indicator (IESE, Istat Economic Sentiment Indicator), which covers the manufacturing, construction, service and retail sectors, shot up from 97.5 points in February to. points in March Mar- Sep- Mar- Sep- Mar- Sep- Mar-5 March s increase resulted from an improvement in all of the sectors that comprise the index. Services posted the highest increase, jumping from. points in February to 8. in March. Construction posted the second largest improvement, increasing from 8.5 points in February to 6. points in March. Finally, manufacturing output rose from February s.5 points to.7 points. Note: Value of monthly business confidence index. Source: National Statistical Institute (Istat). FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists see fixed investment posting flat growth in 5, which is up. percentage points from the previous month s estimate. For 6, the panel expects fixed investment increasing.9%. Consumer Confidence 9 8 Mar- Sep- Mar- Sep- Mar- Sep- Mar-5 Note: Value of monthly consumer confidence index. Source: National Statistical Institute (Istat). OUTLOOK Consumer confidence improves in March The National Institute of Statistics (Istat) consumer confidence index jumped up from 7.7 points in February to.9 points in March. The result was in line with market expectations. March s strong increase reflected an improvement in all of the subcomponents that comprise the index. Consumers expectations regarding the country s general economic situation improved notably. In addition, households were more upbeat regarding both their current and prospective personal economic situations. Consumer sentiment regarding employment perspectives also improved compared to the previous month, suggesting that the economy is continuing along a good path during the first months of 5. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 58
59 Italy April 5 Panelists expect private consumption to expand.6% in 5, which is unchanged from last month s forecast. For 6, panelists see private consumption growing.8%. Inflation Consumer Price Index.5 Month-on-month (left scale) Year-on-year (right scale). %... %. MONETARY SECTOR Fall in consumer prices eases in February Consumer prices rose.% in February over the previous month, which contrasted the.% drop tallied in January and overshot the.% rise that the markets had expected. According to the National Statistics Institute (Instat), February s increase mainly reflected higher prices for food and beverages, tobacco, and, to a lesser extent, transportation services. In annual terms, consumer prices dropped.% in February, which was slightly above the flash estimate of a.% drop, and marked a significant improvement compared to the record-low.6% fall tallied in January Feb- Aug- Feb- Aug- Feb-5 Note: Year-on-year and month-on-month var. of consumer price index in %. Source: National Statistical Institute (Istat).. Core consumer prices, which exclude more volatile categories such as unprocessed food and energy, increased.% over the previous month in February. The print contrasted the.% decline recorded in January. Annual core inflation rose from January s.% to.6% in February. Finally, annual harmonized consumer prices swung from a.5% decline in January to a.% rise in February, which marked the highest reading in three months. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect inflation to average.% in 5, which is up. percentage points from the previous month s projection. For 6, panelists expect inflation to average.9%. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 59
60 Italy April 5 Economic Indicators - 9 Annual Data Real Sector Population (million) GDP per capita (EUR) 7,6 7,65 7,89 6,96 6,96 6,98 7, 7,88 8,76 9, GDP (EUR bn),6,69,65,69,67,65,658,69,76,78 Economic Growth (Nominal GDP, ann. var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Domestic Demand (annual variation in %) Private Consumption (annual var. in %) Government Consumption (annual var. in %) Fixed Investment (annual variation in %) Exports (G&S, annual variation in %) Imports (G&S, annual variation in %) Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Retail Sales (annual variation in %) Unemployment (% of active population, aop) Fiscal Balance (% of GDP) Public Debt (% of GDP) Monetary and Financial Sector Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, eop) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) Inflation (PPI, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Benchmark BTP -Year Yield (%, eop) Stock Market (var. of FTSE MIB in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, aop) External Sector Current Account Balance (% of GDP) Current Account Balance (EUR bn) Trade Balance (EUR bn) Quarterly Data Q Q Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, s.a. qoq var. in %) Unemployment (% of active population) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Benchmark BTP -Year Yield (%, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Monthly Data Jun- Jul- Aug- Sep- Oct- Nov- Dec- Jan-5 Feb-5 Mar-5 Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Industrial Production (s.a. mom var. in %) Markit/ADACI Manufacturing PMI (5-threshold) Retail Sales (annual variation in %) Consumer Confidence Index Economic Sentiment Indicator Inflation (CPI, mom variation in %) Inflation (CPI, annual variation in %) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 6
61 Real Sector Gross Domestic Product Italy April 5 Real GDP -9 var. in % 6 - Italy G7 World GDP 5 evolution of forecasts Maximum Consensus Minimum - 5 GDP 5 Panelist Distribution 6% % % Real GDP Q -Q 6 var. in %. Italy G Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 GDP 6 evolution of forecasts Maximum Consensus Minimum - Real GDP growth in % Individual Forecasts 5 6 BBVA Research.6. Berenberg.. BNP Paribas.5. CER.9. Citigroup Global Mkts.8. Commerzbank..5 Confindustria.5. Credit Agricole.. Credit Suisse.7.6 DekaBank.5. Deutsche Bank.6. DIW Berlin..5 DZ Bank.7. EIU.5.9 Frontier Strategy Group..5 Goldman Sachs..9 Gruppo MPS..9 ING.7. Intesa Sanpaolo.. JPMorgan.6. Julius Baer.. Lloyds TSB.6. Nomura.. Nordea.5. Oxford Economics.. Prometeia.7. Raiffeisen Research.. ref..7. Scotiabank..9 UBS.7. Unicredit.6. Summary Minimum.. Maximum.9.6 Median.5. Consensus.5. History days ago.5. 6 days ago.. 9 days ago..9 Additional Forecasts European Commission (Feb. 5).6. IMF (Jan. 5)..8 Central Bank (Jan. 5).. % < >.7 Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the National Statistical Institute (Istat, Istituto Nazionale di Statistica). Forecasts are based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. GDP, annual variation in %. Quarterly GDP (seasonally adjusted), quarter-on-quarter variation in %. GDP, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. GDP, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 5 GDP, panelist distribution of 5 forecasts. Concentration of panelists in forecast interval in %. Higher columns with darker colors represent a larger number of panelists. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 6
62 Real Sector Additional forecasts Italy April 5 Consumption and Investment Consumption Investment variation in % variation in % Individual Forecasts BBVA Research Berenberg BNP Paribas CER Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Confindustria Credit Agricole Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DZ Bank.8... EIU Frontier Strategy Group Goldman Sachs Gruppo MPS ING Intesa Sanpaolo JPMorgan Julius Baer Lloyds TSB Nomura Nordea Oxford Economics Prometeia Raiffeisen Research ref Scotiabank UBS Unicredit Summary Minimum Maximum.... Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Consumption variation in % - - Italy G Consumption evolution of fcst Investment variation in % - Italy G Investment evol. of forecasts Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the National Statistical Institute (Istat, Istituto Nazionale di Statistica). Forecasts are based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 6 Private consumption, annual variation in %. 7 Private consumption, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 8 Gross fixed investment, annual variation in %. 9 Gross fixed investment, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 6
63 Real Sector Additional forecasts Italy April 5 Exports and Imports Exports Imports variation in % variation in % Individual Forecasts BBVA Research Berenberg BNP Paribas CER Citigroup Global Mkts...9. Commerzbank Confindustria.5... Credit Agricole Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DZ Bank EIU Frontier Strategy Group.7... Goldman Sachs Gruppo MPS ING Intesa Sanpaolo...5. JPMorgan Julius Baer Lloyds TSB Nomura..8.. Nordea Oxford Economics Prometeia Raiffeisen Research ref Scotiabank UBS.8... Unicredit Summary Minimum.5... Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Exports variation in % Italy G Exports evolution of fcst Imports variation in % - Italy G7-5 5 Imports evol. of forecasts..5 Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the National Statistical Institute (Istat, Istituto Nazionale di Statistica). Forecasts are based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. Real exports of goods and services, annual variation in %. Exports, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Real imports of goods and services, annual variation in %. Imports, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 6
64 Real Sector Additional forecasts Italy April 5 Industry and Unemployment Industry Unemployment variation in % % of active pop. Individual Forecasts BBVA Research Berenberg BNP Paribas CER Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Confindustria Credit Agricole Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DZ Bank EIU Frontier Strategy Group Goldman Sachs Gruppo MPS ING Intesa Sanpaolo....5 JPMorgan Julius Baer Lloyds TSB Nomura Nordea Oxford Economics Prometeia Raiffeisen Research ref Scotiabank UBS Unicredit Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Industry variation in % - Italy G Industry evol. of forecasts Unemployment % of active pop. 5 Italy G Unemployment evol. of forecasts..5. Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the National Statistical Institute (Istat, Istituto Nazionale di Statistica). Forecasts are based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. Industrial production, annual variation in %. 5 Industrial production, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 6 Unemployment, % of active population. 7 Unemployment, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 6
65 Real Sector Additional forecasts Italy April 5 Fiscal Balance and Public Debt Fiscal Balance Public Debt % of GDP % of GDP Individual Forecasts BBVA Research Berenberg BNP Paribas CER Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Confindustria Credit Agricole Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DZ Bank EIU Frontier Strategy Group Goldman Sachs Gruppo MPS ING Intesa Sanpaolo JPMorgan Julius Baer Lloyds TSB Nomura Nordea Oxford Economics Prometeia Raiffeisen Research ref Scotiabank UBS Unicredit Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Fiscal Balance % of GDP Italy G Fiscal Balance evol. of forecasts Public Debt % of GDP 5 Italy G Public Debt evol. of forecasts Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from Eurostat. Forecasts are based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 8 General government balance as % of GDP. 9 General government balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Public debt as % of GDP. Public debt as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 65
66 Monetary Sector Inflation and -Year Bond Yield Italy April 5 Inflation and -Year Bond Yield Prices (HICP) -Year Bond variation in % Yield in % Individual Forecasts BBVA Research Berenberg BNP Paribas CER Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Confindustria Credit Agricole Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DZ Bank EIU Frontier Strategy Group Goldman Sachs Gruppo MPS....8 ING...5. Intesa Sanpaolo....9 JPMorgan Julius Baer Lloyds TSB Nomura Nordea Oxford Economics Prometeia Raiffeisen Research... - ref Scotiabank UBS Unicredit Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Inflation - 9 in % Italy G7-5 5 Inflation evol. of forecasts year Bond Yield Italy France year Bond Yield evol. of forecasts 5 Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All monetary sector data are from National Statistical Institute (Istat, Istituto Nazionale di Statistica), Bank of Italy (BdI) and the European Central Bank (ECB). See below for details. Forecasts are based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. Inflation, annual average variation of harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) in %. Source: Istat. Inflation, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. -year benchmark bond yield (eop). Source: BdI, ECB. 5 -year benchmark bond yield, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 5 6 FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 66
67 External Sector Current Account Balance Italy April 5 6 Current Account % of GDP 7 Curr Account Q -Q 6 % of GDP Italy G Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 8 Current Account 5 evol. of fcst 9 Current Account 6 evol. of fcst Maximum Maximum Consensus Consensus Minimum Minimum - - Current Account 5 Panelist Distribution % % % Current Account Balance % of GDP Individual Forecasts 5 6 BBVA Research..9 Berenberg..5 BNP Paribas.. CER..5 Citigroup Global Mkts.9. Commerzbank - - Confindustria.6.9 Credit Agricole - - Credit Suisse.6.6 DekaBank.8.8 Deutsche Bank.5.7 DIW Berlin - - DZ Bank..6 EIU.. Frontier Strategy Group - - Goldman Sachs.9. Gruppo MPS.7 - ING - - Intesa Sanpaolo..5 JPMorgan - - Julius Baer - - Lloyds TSB - - Nomura - - Nordea.6.6 Oxford Economics.. Prometeia.7.5 Raiffeisen Research.. ref. - - Scotiabank.5.5 UBS - - Unicredit.. Summary Minimum.. Maximum..5 Median.. Consensus.. History days ago.. 6 days ago days ago.6.7 % % < >.8 Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All external sector data are from the Bank of Italy (BdI). Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 6 Current account balance as % of GDP. 7 -quarter moving average of current account balance as % of GDP. 8 Current account balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. 9 Current account balance as % of GDP, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Current account balance as % of GDP, panelist distribution of 5 forecasts. Concentration of panelists in forecast interval in %. Higher columns with darker colors represent a larger number of panelists. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 67
68 FOCUSECONOMICS Fact Sheet Italy April 5 General Data Official name: Italian Republic Capital: Rome (.m) cities: Milan (8.m) Naples (.m) Area (km):, Population (million, est.): 6. Population density (per km, ): 99 Population growth rate (%, est.):. Life expectancy (years, est.): 8. Illiteracy rate (%, ):. Language: Italian Measures: Metric system Time: GMT+ Italy in the Region Population %-share in G7 United Kingdom 8.6%.8% Canada France.7% 8.5% Japan 6.9% Italy 8.% United States.%.9% GDP %-share in G7 Canada France 5.% 8.% United Kingdom 8.% Japan.% Italy 6.% United States 8.8% Economic Infrastructure Telecommunication () Telephones - main lines (per inhabitants):. Telephones - mobile cellular (per inhabit.): 59 Internet Users (per inhabitants): 58.5 Broadband Subscriptions (per inhabitants):. Energy () Primary Energy Production (trillion Btu):, Primary Energy Consumption (trillion Btu): 7,7 Electricity Generation (billion kw-h): 8 Electricity Consumption (billion kw-h): Oil Supply (thousand bpd): 55 Oil Consumption (thousand bpd):,7 CO Emmissions (million metric tons): 86 Economic Structure 8 6 GDP by Sector share in % GDP by Expenditure share in % Agriculture Manufacturing Industry Services Net Exports Investment Government Consumption Private Consumption Transportation () Airports: 9 Railways (km):,55 Roadways (km): 87,7 Waterways (km):, Chief Ports: Genoa, Gioia Tauro, La Spezia Trade Structure - Primary markets share in % Political Data Prime Minister: Matteo Renzi Last elections: -5 February Next elections: 8 Central Bank Governor: Ignazio Visco Long-term Foreign Currency Ratings Agency Rating Outlook Moody s: Baa Stable S&P: BBB- Stable Fitch Ratings: BBB+ Stable Asia ex- Japan 7.9%.% France.% Exports U.S.A. 6.6% Switzerland 5.8%.8% EU- 7.% 5.8% Primary products share in % Imports China 7.% France Netherlands 9.% 5.8% EU % 5.6% Strengths Low household indebtness Tourist attractiveness Relevance of Italian brands in highly profitable product niches x Weaknesses Strong shadow and criminal economy Large public debt Persistent divergence between North and South Food 7.9% Manufact. Products 8.6% 9.5% Exports Mineral Fuels 8.8% Food 9.6% 8.% Imports Manufact. Products 6.% FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 68
69 Spain April 5 Spain Spain LONG-TERM TRENDS -year averages Population (million): GDP (EUR bn):,6,8,9 GDP per capita (EUR):,69,5 5,8 GDP growth (%): -... Fiscal Balance (% of GDP): Public Debt (% of GDP): Inflation (%):... Current Account (% of GDP): Outlook improves The Spanish economy expanded for the first time in five years last year, driven mainly by a recovery in domestic demand. Renewed consumer confidence and an improving labor market are expected to carry s momentum into this year. In addition, low energy prices should boost private consumption and the country s current account. However, some risks to Spain s outlook still remain. The country is facing multiple elections in 5, and general elections are due before year-end. On March, the Spanish Socialist Workers Party (PSOE), led by Susana Díaz, was re-elected in Andalucía s regional vote. While the outcome was rather unsurprising, the result signaled a potential change in Spain s political landscape as the traditionally-dominant PSOE and the People s Party (PP) lost 8% of the vote to emerging parties. Growth prospects for the Spanish economy continue to improve. FocusEconomics panelists raised their forecast for the third month in a row and see GDP expanding.% in 5, which is up. percentage points from last month s forecast. For 6, the panel sees the economy also growing.%. Harmonized consumer prices fell.7% in March in annual terms (February: -.% year-on-year), marking the ninth consecutive month of decline. Panelists foresee harmonized consumer prices falling.5% in 5, which is unchanged from last month s estimate. In 6, the panel foresees harmonized inflation of.%. Angela Bouzanis Economist Industrial Production variation in % 5.. % -5. Year-on-year Annual average -. Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan-5 Note: Year-on-year and annual average variation of working-day adjusted industrial production index. Source: National Statistical Institute (INE) and FocusEconomics calculations. REAL SECTOR Industrial production rises in January In January, industrial production rose.% over the same month of the previous year in working-day adjusted terms, which was above the revised zero growth tallied in December (previously reported: -.9% year-on-year). The print mainly reflected a rebound in energy production and an increase in the production of capital and intermediate goods, which was partly offset by sharp contraction in the production of consumer goods. Annual average variation of industrial production inched down from December s.% to.% in January, thereby reaching the lowest print in seven months. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists see industrial production expanding.9% in 5, which is down. percentage points from last month s forecast. For 6, the panel sees industrial output growth at.9%. The Central Bank expects the economy to expand.8% in 5 and.7% in 6, while the government expects the economy to grow.% in 5. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect GDP to expand.% in 5, which is up. percentage points from last month s forecast. In 6, panelists expect the economy to also increase.%. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 69
70 Spain April 5 Retail Sales variation in % 6.. % -6. Year-on-year Annual average -. Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan-5 Note: Year-on-year and annual average variation of retail sales. Source: National Statistical Institute (INE) and FocusEconomics calculations. REAL SECTOR Retail sales moderate in January In January, retail sales rose.% over the same month last year, which was below December s 5.% increase. December s print had marked the highest rate since March 7. The result was mainly a moderation in the sales of household goods and of food at general shops. On a working-day adjusted basis, retail sales expanded.% over the same month last year in January (December: +6.5% yoy). Annual average growth in retail sales increased from the previous month s.9% to.% in January, which marked the highest level since February 8. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists see private consumption expanding.7% in 5, which is up. percentage points from last month s forecast. For 6, the panel sees private consumption growth at.%. Housing Permits 6,,, Monthly permits (left scale) -month sum (right scale), 5,, REAL SECTOR Housing permits hit six-month high in January In January, the Spanish Board of Architects (Colegio de Arquitectos Tecnicos) granted,66 new construction permits, according to data published by the Ministry of Public Works (Ministerio de Fomento). The figure was well above the,866 permits approved in December and marked the most permits granted since July. On an annual basis, permits expanded a strong 9.%. The print contrasted the 5.% drop recorded in the previous month and represented the largest increase since September 6. 5, Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan-5 Note: Monthly construction permits and three-month sum in thousands. Source: Ministry of Public Works and Spanish Board of Architects. As a result of the monthly figure, the moving three-month sum of permits totaled 7,8 in January, which represented a.9% decrease over the same period last year. The figure followed the.% contraction tallied in December. The current number of permits represents a mere fraction of the 68,66 permits that were granted during the July September 6 peak. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 7
71 Spain April 5 Economic Indicators - 9 Annual Data Real Sector Population (million) GDP per capita (EUR),,5,56,5,759,,6,9 5,88 6,77 GDP (EUR bn),8,75,55,9,58,78,,5,89, Economic Growth (Nominal GDP, ann. var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Domestic Demand (annual variation in %) Private Consumption (annual var. in %) Government Consumption (ann. var. in %) Fixed Investment (annual variation in %) Exports (G&S, annual variation in %) Imports (G&S, annual variation in %) Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Retail Sales (annual variation in %) Housing Permits (thousands) Home Prices (annual variation in %) Unemployment (% of active population, aop) Fiscal Balance (% of GDP) Public Debt (% of GDP) Monetary and Financial Sector Inflation (Core, annual variation in %, aop) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, eop) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) Producer Prices (annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Year Bond Yield (%, eop) Stock Market (variation of IBEX 5 in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, aop) External Sector Current Account Balance (% of GDP) Current Account Balance (EUR bn) Trade Balance (EUR bn) Quarterly Data Q Q Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, s.a. qoq var. in %) Housing Permits (thousands) Home Prices (annual variation in %) Unemployment (% of active population, aop) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Year Bond Yield (%, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Current Account Balance (% of GDP) Current Account Balance (EUR bn) Monthly Data Jun- Jul- Aug- Sep- Oct- Nov- Dec- Jan-5 Feb-5 Mar-5 Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Retail Sales (annual variation in %) Housing Permits (thousands) Markit PMI Composite (5-threshold) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Current Account Balance (EUR bn) FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 7
72 Real Sector Gross Domestic Product Spain April 5 Real GDP -9 var. in % GDP 5 evolution of forecasts 6 - Spain World % % % % Maximum Consensus Minimum 5 GDP 5 Panelist Distribution Real GDP Q -Q 6 var. in % - Spain World - Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 GDP 6 evolution of forecasts Maximum Consensus Minimum Real GDP growth in % Individual Forecasts 5 6 Banco BPI.. Bankia.7.6 BBVA Research.7.7 Berenberg.. BNP Paribas.9.8 CEPREDE.. Citigroup Global Mkts.5.5 Commerzbank.. Credit Agricole.7.9 Credit Suisse.5.5 DekaBank.. Deutsche Bank.5. DIW Berlin.. DZ Bank.. EIU.5. Frontier Strategy Group.6.6 FUNCAS..8 Goldman Sachs.. ING.5. Instituto Flores de Lemus.7.5 JPMorgan.8. La Caixa.5. Lloyds TSB.. Nomura.. Nordea.. Oxford Economics.5.5 Raiffeisen Research.. Santander.6.6 Scotiabank.. UBS.. Unicredit.. Summary Minimum.6. Maximum.. Median.. Consensus.. History days ago.. 6 days ago.. 9 days ago.8. Additional Forecasts IMF (Jan. 5)..8 European Commission (Feb. 5)..5 Central Bank (Mar. 5).8.7 % < >. Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the National Statistical Institute (INE, Instituto Nacional de Estadistica). Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. GDP, annual variation in %. Quarterly GDP (seasonally adjusted), year-on-year variation in %. GDP, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. GDP, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 5 GDP, panelist distribution of 5 forecasts. Concentration of panelists in forecast interval in %. Higher columns with darker colors represent a larger number of panelists. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 7
73 Real Sector Additional forecasts Spain April 5 Consumption and Investment Consumption Investment variation in % variation in % Individual Forecasts Banco BPI Bankia BBVA Research Berenberg BNP Paribas CEPREDE Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Credit Agricole Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DZ Bank....9 EIU...5. Frontier Strategy Group FUNCAS Goldman Sachs ING....5 Instituto Flores de Lemus..8.. JPMorgan La Caixa Lloyds TSB Nomura Nordea Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research Santander Scotiabank UBS Unicredit Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus.7... History days ago days ago days ago Consumption variation in % 6 - Spain Consumption evolution of fcst Investment variation in % - Spain Investment evol. of forecasts 5 Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the National Statistical Institute (INE, Instituto Nacional de Estadistica). Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 6 Private consumption, annual variation in %. 7 Private consumption, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 8 Gross fixed investment, annual variation in %. 9 Gross fixed investment, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 5 6 FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 7
74 Real Sector Additional forecasts Spain April 5 Exports and Imports Exports Imports variation in % variation in % Individual Forecasts Banco BPI Bankia BBVA Research Berenberg BNP Paribas CEPREDE Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Credit Agricole Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DZ Bank EIU Frontier Strategy Group FUNCAS Goldman Sachs ING Instituto Flores de Lemus JPMorgan La Caixa Lloyds TSB Nomura Nordea Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research Santander Scotiabank UBS Unicredit Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Exports variation in % - Spain Exports evolution of fcst Imports variation in % - Spain Imports evol. of forecasts Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the National Statistical Institute (INE, Instituto Nacional de Estadistica). Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. Real exports of goods and services, annual variation in %. Exports, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Real imports of goods and services, annual variation in %. Imports, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 7
75 Real Sector Additional forecasts Spain April 5 Industry and Unemployment Industry Unemployment variation in % % of active pop. Individual Forecasts Banco BPI Bankia BBVA Research Berenberg.7... BNP Paribas CEPREDE Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Credit Agricole Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DZ Bank EIU...9. Frontier Strategy Group..8.. FUNCAS Goldman Sachs ING Instituto Flores de Lemus JPMorgan La Caixa Lloyds TSB Nomura Nordea Oxford Economics....9 Raiffeisen Research Santander Scotiabank UBS Unicredit Summary Minimum Maximum....6 Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Industry variation in % - Spain Industry evol. of forecasts Unemployment % of active pop. Spain Unemployment evol. of forecasts Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the National Statistical Institute (INE, Instituto Nacional de Estadistica). Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. Industrial production, annual variation in %. 5 Industrial production, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 6 Unemployment, % of active population. 7 Unemployment, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 75
76 Real Sector Additional forecasts Spain April 5 Fiscal Balance and Public Debt Fiscal Balance Public Debt % of GDP % of GDP Individual Forecasts Banco BPI Bankia BBVA Research Berenberg BNP Paribas CEPREDE Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Credit Agricole Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DZ Bank EIU Frontier Strategy Group FUNCAS Goldman Sachs ING Instituto Flores de Lemus JPMorgan La Caixa Lloyds TSB Nomura Nordea Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research Santander Scotiabank UBS Unicredit Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Fiscal Balance % of GDP Spain Fiscal Balance evol. of forecasts Public Debt % of GDP Spain Public Debt evol. of forecasts Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from Eurostat. Forecasts are based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 8 General government balance as % of GDP. 9 General government balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Public debt as % of GDP. Public debt as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 76
77 Monetary Sector Inflation and -Year Bond Yield Spain April 5 Inflation and -Year Bond Yield Prices (HICP) -Year Bond variation in % Yield in % Individual Forecasts Banco BPI Bankia BBVA Research Berenberg BNP Paribas CEPREDE Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Credit Agricole Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DZ Bank EIU Frontier Strategy Group FUNCAS Goldman Sachs ING Instituto Flores de Lemus JPMorgan La Caixa Lloyds TSB Nomura Nordea Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research Santander Scotiabank UBS Unicredit Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Inflation - 9 in % year Bond Yield Spain Inflation evol. of forecasts Spain year Bond Yield evol. of forecasts 6 5 Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All monetary and external sector data are from the National Statistical Institute (INE, Instituto Nacional de Estadistica), the Bank of Spain (BdE, Banco de España) and the European Central Bank (ECB). See below for details. Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. Inflation, annual average variation of harmonized index of consumer price index (HICP) in %. Source: INE. Inflation, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. -year benchmark bond yield (eop). Source: BdE, ECB. 5 -year benchmark bond yield, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 5 6 FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 77
78 External Sector Current Account Balance Spain April 5 6 Current Account % of GDP 7 Curr Account Q -Q 6 % of GDP Spain Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 8 Current Account 5 evol. of fcst 9 Current Account 6 evol. of fcst 6 6 Maximum Maximum Consensus Consensus Minimum Minimum - - Current Account 5 Panelist Distribution % % % Current Account Balance % of GDP Individual Forecasts 5 6 Banco BPI - - Bankia.8.7 BBVA Research.9. Berenberg.. BNP Paribas - - CEPREDE.5. Citigroup Global Mkts.. Commerzbank - - Credit Agricole.5.5 Credit Suisse.. DekaBank.7.9 Deutsche Bank.7.5 DIW Berlin - - DZ Bank.. EIU. -. Frontier Strategy Group - - FUNCAS.8.5 Goldman Sachs.. ING - - Instituto Flores de Lemus - - JPMorgan - - La Caixa.6.6 Lloyds TSB - - Nomura - - Nordea.6.5 Oxford Economics.. Raiffeisen Research. -. Santander.8. Scotiabank.6.5 UBS.. Unicredit.5.8 Summary Minimum. -. Maximum.. Median.5.5 Consensus.5. History days ago days ago days ago.6.5 % % < >.6 Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All external sector data are from the Bank of Spain (BdE, Banco de España). Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 6 Current account balance as % of GDP. 7 -quarter moving average of current account balance as % of GDP. 8 Current account balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. 9 Current account balance as % of GDP, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Current account balance as % of GDP, panelist distribution of 5 forecasts. Concentration of panelists in forecast interval in %. Higher columns with darker colors represent a larger number of panelists. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 78
79 FOCUSECONOMICS Spain April 5 Fact Sheet General Data Official name: Kingdom of Spain Capital: Madrid (6.m) cities: Barcelona (5.m) Valencia (.5m) Area (km): 55,7 Population (million, est.): 6.5 Population density (per km, ): 9. Population growth rate (%, est.):.8 Life expectancy (years, est.): 8.5 Illiteracy rate (%, ):. Language: Spanish, Catalan, Galician and Basque Measures: Metric system Time: GMT to GMT+ Spain in the Region Population %-share in Netherlands 5.% Italy 8.% 9.% France 9.% Spain.%.% GDP %-share in Netherlands 6.% Italy 5.6% 9.% France.7% Spain.% 8.% Economic Infrastructure Telecommunication () Telephones - main lines (per inhabitants):.7 Telephones - mobile cellular (per inhabit.): 7 Internet Users (per inhabitants): 7.6 Broadband Subscriptions (per inhabitants): 5.6 Energy () Primary Energy Production (trillion Btu):,57 Primary Energy Consumption (trillion Btu): 6,9 Electricity Generation (billion kw-h): 8 Electricity Consumption (billion kw-h): Oil Supply (thousand bpd): 9. Oil Consumption (thousand bpd):, CO Emmissions (million metric tons): Economic Structure 8 6 GDP by Sector share in % GDP by Expenditure share in % Agriculture Industry Services Net Exports Investment Government Consumption Private Consumption Transportation () Airports: 5 Railways (km): 5,9 Roadways (km): 68,75 Waterways (km):, Chief Ports: Barcelona, Valencia, Algeciras Trade Structure - Primary markets share in % Political Data President: Mariano Rajoy Brey Last elections: November Next elections: Before December 5 Central Bank Governor: Luis María Linde de Castro 8.% Exports EU- 7.% France 6.7% 7.% Imports EU- 7 9.%.9% Long-term Foreign Currency Ratings Agency Rating Outlook Moody s: Baa Positive S&P: BBB Stable Fitch Ratings: BBB+ Stable LatAm 5.% Italy 7.6%.9% LatAm 7.6% Primary products share in % China 5.6% Italy 6.7% France.5% Strengths Highly developed infrastructure Tourist potential Close ties with Latin America Ongoing external rebalancing process Weaknesses Large fiscal deficit and public debt High structural unemployment High levels of household debt Excess of unsold and unfinished housing stock Mineral Fuels 6.5% Food 5.% 8.% Exports Manufact. Products 7.% Mineral Fuels.5% Food.7% 5.9% Imports Manufact. Products 6.9% FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 79
80 Austria April 5 Austria Austria LONG-TERM TRENDS -year averages Population (million): GDP (EUR bn): GDP per capita (EUR): 7,8 9,9,66 GDP growth (%):..9.5 Fiscal Balance (% of GDP): Public Debt (% of GDP): Inflation (%):.7.. Current Account (% of GDP):... Outlook moderates The Austrian economy barely grew in, and recent economic data show that the weakness carried over into the first months of 5. In an attempt to boost economic growth, the government announced a tax reform aimed at stimulating private consumption on March. The new tax package consists of a EUR 5 billion cut in payroll taxes for those in low and middle income brackets. The government plans to finance the reform by fighting tax evasion, saving on administrative costs and raising existing tax rates on dividends. However, no new taxes on wealth or inheritances for high-income households will be introduced. The Austrian economy is expected to expand at a moderate rate this year. The recently-announced tax reform, coupled with low energy prices, is expected to support private consumption going forward. However, FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists revised downward their GDP growth forecasts by. percentage points this month, and see the economy increasing.8% in 5. For 6, the panel sees economic growth picking up to.5%. In February, HICP inflation remained stable at January s.5%, which had marked an over-five-year low. Panelists expect that HICP inflation will average.9% this year. For 6, the panel sees inflation rising to.6%. Cecilia Simkievich Economist Purchasing Managers Index Mar- Sep- Mar- Sep- Mar-5 Note: Bank Austria Manufacturing Purchasing Managers Index (PMI). A reading above 5 indicates an expansion in business activity while a value below 5 points to a contraction. Source: Bank Austria and Markit. REAL SECTOR PMI falls to four-month low in March The manufacturing Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) elaborated by Bank Austria fell from 8.7 in February to 7.7 in March, marking a four-month low. As a result, the index is further below the 5 threshold that indicates a contraction in business activity in the manufacturing sector, where it has been hovering since September of last year. According to Bank Austria, the deterioration observed in March was driven by sharp declines in both output and new orders. The fall in production was the second strongest decline in two years, while the drop in new orders was broadbased. As a result of the decreases in new orders and output, firms continued to reduce their workforce numbers. March s rate of decline in employment was the strongest in 5 thus far. Regarding prices, the Bank pointed out that, Austrian manufacturers reported a much weaker decline in input costs than in the previous month in March. The milder drop in costs was attributed by panel members to increased import prices resulting from a weak euro. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect gross fixed investment to expand.9% in 5, which is down. percentage points from last month s forecast. In 6, the panel sees investment growth accelerating to.5%. The Central Bank expects the economy to increase.7% in 5. For 6, the Bank sees economic growth picking up to.6%. FocusEconomics panelists project the economy to grow.8% in 5, which is down. percentage FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 8
81 Austria April 5 points from last month s estimate. For 6, panelists expect the economy to grow.5%. Industrial Production variation in %. Month-on-month (left scale) Year-on-year (right scale). % 8.. % REAL SECTOR Growth in industrial production eases in January In January, industrial output rose a seasonally-adjusted.% over the previous month. The result came in below December s.5% increase, although it markedly overshot the flat readings posted in both October and November of last year. January s increase was mainly the result of a strong rebound in the production of electricity and gas and in mining and quarrying. Conversely, the manufacturing and water supply categories deteriorated Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan-5 Note: Year-on-year changes and annual average variation of industrial production index in %. Source: Statistics Austria (STAT) and FocusEconomics calculations.. Compared to the same month of the previous year, industrial production contracted a working-day adjusted.% in January, which was up from the.5% fall observed in December and marked the highest result in seven months. Despite January s slight improvement, annual average growth in industrial production fell from minus.% in December to minus.7% in January. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect industrial production to rise.5% this year, which is unchanged from last month s forecast. For 6, participants expect industrial output to pick up to.5%. Consumer Confidence OUTLOOK Consumer confidence hits an eight-month-high in March The consumer confidence index elaborated by Fessel-GfK rose from February s minus points to minus points in March, marking the highest print in eight months. Nevertheless, the index continues to hover below the -point threshold, which indicates that pessimists outnumber optimists. - - Mar- Sep- Mar- Sep- Mar- Sep- Mar-5 Note: Fessel-GfK Consumer Confidence Index. The -point threshold separates optimistic from pessimistic sentiment. Source: The Fessel-GfK Institute. March s improvement mainly reflected consumers more optimistic assessments regarding both the current and prospective macroeconomic situation of the country. Households views regarding current and future major purchases also improved notably compared to the previous month. Conversely, inflation and unemployment expectations deteriorated compared to February. FocusEconomics panelists expect private consumption to expand.7% in 5, which is down. percentage points from last month s forecast. For 6, panelists see private consumption rising.%. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 8
82 Economic Indicators - 9 Austria April Real Sector Population (million) GDP per capita (EUR) 5,75 6,656 7,69 8, 8,65 9,,,,6, GDP (EUR bn) Economic Growth (Nominal GDP, ann. var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Domestic Demand (annual variation in %) Private Consumption (annual var. in %) Government Consumption (ann. var. in %) Fixed Investment (annual variation in %) Exports (G&S, annual variation in %) Imports (G&S, annual variation in %) Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Unemployment (% of active population, aop) Fiscal Balance (% of GDP) Public Debt (% of GDP) Monetary and Financial Sector Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, eop) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Year Bond Yield (%, eop) Stock Market (variation of ATX in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, aop) External Sector Current Account Balance (% of GDP) Current Account Balance (EUR bn) Trade Balance (EUR bn) Quarterly Data Q Q Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, s.a. qoq var. in %) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Year Bond Yield (%, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Monthly Data Jun- Jul- Aug- Sep- Oct- Nov- Dec- Jan-5 Feb-5 Mar-5 Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Industrial Production (s.a. mom var. in %) Unemployment (% of active population) Consumer Confidence Index Bank Austria Manufacturing PMI (5-threshold) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 8
83 Real Sector Gross Domestic Product Austria April 5 Real GDP -9 var. in % Real GDP Q -Q 6 var. in % Real GDP growth in % 6 - Austria World GDP 5 evolution of forecasts Maximum Consensus Minimum. Austria World - Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 GDP 6 evolution of forecasts.5 Maximum Consensus. Minimum Individual Forecasts 5 6 Commerzbank.8. Credit Suisse..8 DekaBank.5. Deutsche Bank..8 DZ Bank..6 EIU.6. IHS.8.6 Nomura.7. Oxford Economics.8.7 Raiffeisen Research.7.8 UBS.8.5 Unicredit.9.5 WIFO.5. Summary Minimum.5. Maximum..8 Median.8.5 Consensus.8.5 History days ago..6 6 days ago..6 9 days ago..6 Additional Forecasts Central Bank (Dec. ).7.6 IMF (Oct. ).9.7 European Commission (Feb. 5) Consumption variation in % 6 Consumption evolution of fcst.5.. Austria Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the Austrian Institute of Economic Research (WIFO). Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. GDP, annual variation in %. Quarterly GDP (seasonally adjusted), year-on-year variation in %. GDP, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. GDP, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 5 Private consumption, annual variation in %. 6 Private consumption, change in 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 7 Gross fixed capital formation, annual variation in %. 8 Real exports of goods and services, annual variation in %. 9 Real imports of goods and services, annual variation in %. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 8
84 Real Sector Additional forecasts Austria April 5 Consumption Investment Exports Imports variation in % variation in % variation in % variation in % Individual Forecasts Commerzbank Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DZ Bank EIU IHS Nomura Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research UBS Unicredit WIFO Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Investment variation in % 8 Exports variation in % 9 Imports variation in % Austria Austria Austria Investment evol. of forecasts Exports evol. of forecasts 6 Imports evol. of forecasts FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 8
85 Real Sector Additional forecasts Austria April 5 Unemployment % of active pop. 5 Austria Fiscal Balance % of GDP - - Unemployment, Fiscal Balance and Public Debt Unemployment Fiscal Balance Public Debt % of active pop. % of GDP % of GDP Individual Forecasts Commerzbank Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DZ Bank EIU IHS Nomura Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research UBS Unicredit WIFO Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Austria Fiscal Balance evolution of fcst Public Debt % of GDP 9 Austria Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the Austrian National Bank (OeNB, Oesterreichische Nationalbank) and Eurostat. See below for details. Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. Gross fixed investment, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Exports, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Imports, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Unemployment, % of active population. Source: OeNB. General government balance as % of GDP. Source: Eurostat. 5 General government balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 6 Public debt as % of GDP. Source: Eurostat. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 85
86 Austria April 5 Monetary and External Sector Inflation and Current Account Balance 7 Inflation - 9 in % 8 Inflation Q -Q 6 in % Consumer Prices and Current Account Balance Austria Inflation 5 evolution of fcst Maximum Consensus Minimum Austria - Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 Inflation 6 evolution of fcst Maximum Consensus Minimum Prices (HICP) var. in % Current Acct % of GDP Individual Forecasts Commerzbank Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DZ Bank EIU IHS Nomura Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research UBS Unicredit WIFO..5.. Summary Minimum Maximum.6... Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago..7.. Additional Forecasts Central Bank (Dec. ) IMF (Oct. ) Euro. Comm. (Feb. 5) Current Account % of GDP Current Account evol. of fcst 6 Austria Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All monetary and external sector data are from the Austrian National Bank (OeNB, Oesterreichische Nationalbank). Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 7 Inflation, annual average variation of harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) in %. 8 Inflation, annual variation of quarterly average harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) in %. 9 Inflation, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. Inflation, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Current account balance as % of GDP. Current account balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 86
87 FOCUSECONOMICS Fact Sheet Austria April 5 General Data Official name: Federal Republic of Austria Capital: Vienna (.m) cities: Linz (.6m) Graz (.m) Area (km): 8,87 Population (million, est.): 8.5 Population density (per km, ): Population growth rate (%, est.):. Life expectancy (years, est.): 79.9 Illiteracy rate (%, ):. Language: German Measures: Metric system Time: GMT+ Austria in the Region Population %-share in Spain.%.% Italy 8.% Austria.6%.5% France 9.% GDP %-share in Spain.% Italy 7.% 5.6% Austria.5% France.5%.% Economic Infrastructure Telecommunication () Telephones - main lines (per inhabitants): 9. Telephones - mobile cellular (per inhabit.): 56 Internet Users (per inhabitants): 8.6 Broadband Subscriptions (per inhabitants): 6. Energy () Primary Energy Production (trillion Btu): 597 Primary Energy Consumption (trillion Btu):,9 Electricity Generation (billion kw-h): 6.9 Electricity Consumption (billion kw-h): 6. Oil Supply (thousand bpd): 9.5 Oil Consumption (thousand bpd): 6 CO Emmissions (million metric tons): 66.7 Economic Structure 8 6 GDP by Sector share in % GDP by Expenditure share in % Agriculture Manufacturing Industry Services Net Exports Investment Government Consumption Private Consumption Transportation () Airports: 5 Railways (km): 6,99 Roadways (km):,58 Waterways (km): 58 Chief Ports: Vienna, Krems, Linz Trade Structure Primary markets share in % Political Data Chancellor: Werner Faymann Last elections: 9 September Next elections: September 7 Central Bank Governor: Ewald Nowotny Asia ex- Japan 5.5% Italy 6.9%.% Exports EU- 7.% Asia ex- Japan 5.% Italy 6.6%.% Switzerland 5.% Imports EU- 7 9.% Long-term Foreign Currency Ratings Agency Rating Outlook Moody s: Aaa Stable S&P: AA+ Stable Fitch Ratings: AA+ Stable.% Primary products share in %.% Strengths Manufacturing competitiveness and high labor productivity Low household debt Low unemployment Weaknesses Dependance on and Central European economies Population challenges Banking sector vulnerable to Central and Eastern European economies. Food 7.% Exports Manufact. Products 8.%.5% Ores & Metals 5.% Mineral Fuels.% Food 7.%.6% Imports Manufact. Products 7.% FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 87
88 Belgium April 5 Belgium Belgium Outlook stable After two years of muted growth, Belgium s economy strengthened in, recording the strongest expansion since. Recent data suggest that growth will continue to pick up pace this year, albeit modestly. Industrial production expanded in January and business confidence rose for the second straight month in March. However, unemployment remains relatively high and consumer sentiment deteriorated in March. LONG-TERM TRENDS -year averages Population (million):...5 GDP (EUR bn): 88 5 GDP per capita (EUR):,98 6,7 9,7 GDP growth (%):.7..8 Fiscal Balance (% of GDP): Public Debt (% of GDP): Inflation (%):..7.6 Current Account (% of GDP):...5 Looking forward, low oil prices should boost private consumption. However, fiscal consolidation and subdued levels of external demand will weigh on the pace of growth. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists see GDP growing.% in 5, which is unchanged from last month s forecast. For 6, panelists expect GDP to expand.6%. Harmonized consumer prices fell.% in February over the same month of the previous year (January: -.6% year-on-year). Inflationary pressures are expected to remain subdued due to the drop in energy prices and muted wage growth. Panelists expect HICP inflation to average.% in 5, which is down. percentage points from last month s forecast. For 6, the panel sees inflation at.%. Angela Bouzanis Economist Industrial Production variation in %.. % % Month-on-month Year-on-year Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan-5 Note: Year-on-year changes and annual average variation of industrial production index in %. Source: Statistics Belgium and FocusEconomics calculations REAL SECTOR Industrial production expands in January In January, industrial production rose a seasonally-adjusted.9% over the previous month. The reading contrasted the notable.8% contraction registered in December. January s result reflected a broad-based improvement across industries. In year-on-year terms, industrial production fell.%, which marked a deterioration over December s.7% contraction. As a result of this deceleration, annual average growth in industrial output ticked down from.8% in December to.% in January. The Federal Planning Bureau (FPB) expects the economy to increase.% in 5. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect the economy to expand.% in 5, which is unchanged over the previous month s Consensus. For 6, the panel expects economic growth to pick up to.6%. OUTLOOK Business confidence improves, while consumer confidence worsens in March The business confidence index elaborated by the National Bank of Belgium (NBB) improved from February s minus 8. points to minus 6. points in March. The reading came in above the minus 7.5 points that the markets had expected and marked a four-month high. According to the NBB, the result was due to a broad-based improvement in confidence. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 88
89 Belgium April 5 Leading indicators FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect fixed investment to expand.7% in 5, which is down. percentage points from last month s projection. For 6, the panel sees fixed investment growing at.7%. - - Business confidence Consumer confidence - Mar- Sep- Mar- Sep- Mar- Sep- Mar-5 Note: Business and consumer confidence indicators. Source: National Bank of Belgium (NBB). The consumer confidence index elaborated by the NBB fell for the first time in four months from minus 5. points in February to minus 6. points in March. According to the NBB, consumers have become more pessimistic regarding the future economic situation in Belgium. In addition, the Bank pointed out that, the fear of a rise in unemployment has grown somewhat for the first time in six months. However, expectations regarding households saving capacity improvement for the fourth month in a row. FocusEconomics panelists expect private consumption to grow.% in 5, which is unchanged from last month s estimate. For 6, the panel expects private consumption to grow.%. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 89
90 Economic Indicators - 9 Belgium April 5 Annual Data Real Sector Population (million) GDP per capita (EUR),7,5,995 5, 5,96 6,7 7,7 8,5 9,5,8 GDP (EUR bn) Economic Growth (Nominal GDP, ann. var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Domestic Demand (annual variation in %) Private Consumption (annual var. in %) Government Consumption (ann. var. in %) Fixed Investment (annual variation in %) Exports (G&S, annual variation in %) Imports (G&S, annual variation in %) Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Unemployment (% of active population, aop) Fiscal Balance (% of GDP) Public Debt (% of GDP) Monetary and Financial Sector Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, eop) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Year Bond Yield (%, eop) Stock Market (variation of BEL in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, aop) External Sector Current Account Balance (% of GDP) Current Account Balance (EUR bn) Trade Balance (EUR bn) Quarterly Data Q Q Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, s.a. qoq var. in %) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Year Bond Yield (%, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Monthly Data Jun- Jul- Aug- Sep- Oct- Nov- Dec- Jan-5 Feb-5 Mar-5 Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Industrial Production (s.a. mom var. in %) Unemployment (% of active population) Consumer Confidence Index Business Confidence Index Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 9
91 Real Sector Gross Domestic Product Belgium April 5 Real GDP -9 var. in % Real GDP Q -Q 6 var. in % Real GDP growth in % 6 - Belgium -6 World 5 5 GDP 5 evolution of forecasts Maximum Consensus Minimum. Belgium World - Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 GDP 6 evolution of forecasts.5..5 Maximum Consensus Minimum. Individual Forecasts 5 6 BNP Paribas Fortis..7 Citigroup Global Mkts..8 Commerzbank..5 Credit Suisse..8 DekaBank..5 Deutsche Bank..6 DZ Bank..5 EIU..6 ING..6 KBC..7 Nomura.. Oxford Economics..6 Raiffeisen Research.. UBS.. Summary Minimum.. Maximum.. Median..6 Consensus..6 History days ago..6 6 days ago..6 9 days ago..6 Additional Forecasts Federal Planning Bureau (Feb. 5). - IMF (Oct. )..5 European Commission (Feb. 5).. 5 Consumption variation in % 6 Consumption evolution of fcst Belgium Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the National Bank of Belgium (NBB, Nationale Bank van Belgie). Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. GDP, annual variation in %. Quarterly GDP (seasonally adjusted), year-on-year variation in %. GDP, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. GDP, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 5 Private consumption, annual variation in %. 6 Private consumption, change in 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 7 Gross fixed capital formation, annual variation in %. 8 Real exports of goods and services, annual variation in %. 9 Real imports of goods and services, annual variation in %. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 9
92 Real Sector Additional forecasts Belgium April 5 Consumption Investment Exports Imports variation in % variation in % variation in % variation in % Individual Forecasts BNP Paribas Fortis Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DZ Bank EIU ING KBC Nomura Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research UBS Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Investment variation in % 8 Exports variation in % 9 Imports variation in % Belgium Belgium Belgium Investment evol. of forecasts Exports evol. of forecasts Imports evol. of forecasts FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 9
93 Real Sector Additional forecasts Belgium April 5 Unemployment % of active pop. Belgium Fiscal Balance % of GDP - - Unemployment, Fiscal Balance and Public Debt Unemployment Fiscal Balance Public Debt % of active pop. % of GDP % of GDP Individual Forecasts BNP Paribas Fortis Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DZ Bank EIU ING KBC Nomura Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research UBS Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Belgium Fiscal Balance evolution of fcst Public Debt % of GDP Belgium Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the National Bank of Belgium (NBB, Nationale Bank van Belgie) and Eurostat. See below for details. Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. Gross fixed investment, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Exports, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Imports, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Unemployment, % of active population. Source: NBB. General government balance as % of GDP. Source: Eurostat. 5 General government balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 6 Public debt as % of GDP. Source: Eurostat. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 9
94 Belgium April 5 Monetary and External Sector Inflation and Current Account Balance 7 Inflation - 9 in % 8 Inflation Q -Q 6 in % Consumer Prices and Current Account Balance 6 Belgium Inflation 5 evolution of fcst Maximum Consensus Minimum - Belgium - Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 Inflation 6 evolution of fcst Maximum Consensus Minimum.5 Prices (HICP) var. in % Current Acct % of GDP Individual Forecasts BNP Paribas Fortis Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Credit Suisse...6. DekaBank Deutsche Bank DZ Bank EIU ING KBC.... Nomura Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research UBS Summary Minimum Maximum.7... Median...8. Consensus.... History days ago days ago days ago Additional Forecasts FPB (March 5) IMF (Oct. ) Euro. Comm. (Feb. 5) Current Account % of GDP Current Account evol. of fcst 6 Belgium Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All monetary and external sector data are from the National Bank of Belgium (NBB, Nationale Bank van Belgie) and Statistics Belgium (SB). See below for details. Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 7 Inflation, annual average variation of harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) in %. Source: SB. 8 Inflation, annual variation of quarterly average harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) in %. Source: SB. 9 Inflation, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. Inflation, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Current account balance as % of GDP. Source: NBB. Current account balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 9
95 FOCUSECONOMICS Fact Sheet Belgium April 5 General Data Official name: Kingdom of Belgium Capital: Brussels (.6m) cities: Antwerp (.m) Liege (.6m) Area (km):,58 Population (million, est.):. Population density (per km, ): 67 Population growth rate (%, est.):. Life expectancy (years, est.): 79.7 Illiteracy rate (%, ):. Language: Dutch, French, German Measures: Metric system Time: GMT+ Belgium in the Region Population %-share in Spain.%.6% Italy 8.% Belgium.%.5% France 9.% GDP %-share in Spain.% Italy 7.%.% France.6% Belgium.%.7% Economic Infrastructure Telecommunication () Telephones - main lines (per inhabitants):. Telephones - mobile cellular (per inhabit.): Internet Users (per inhabitants): 8. Broadband Subscriptions (per inhabitants):. Energy () Primary Energy Production (trillion Btu): 98 Primary Energy Consumption (trillion Btu):,59 Electricity Generation (billion kw-h): 76. Electricity Consumption (billion kw-h): 8.9 Oil Supply (thousand bpd):.5 Oil Consumption (thousand bpd): 66 CO Emmissions (million metric tons): 9 Economic Structure 8 6 GDP by Sector share in % GDP by Expenditure share in % Agriculture Manufacturing Industry Services Net Exports Investment Government Consumption Private Consumption Transportation () Airports: Railways (km):, Roadways (km): 5, Waterways (km):, Chief Ports: Antwerp, Zeebruge Trade Structure Primary markets share in % Political Data Prime Minister: Charles Michel Last elections: 5 May Next elections: May 9 Central Bank Governor: Luc Coene Long-term Foreign Currency Ratings Asia ex- Japan 6.6%.% Netherlands.9% U.S.A. 5.% Exports France 6.% EU- 7 8.% 8.% Asia ex- Japan 8.9%.% France.6%.% U.S.A. 6.% Imports EU- 7 7.% Netherlands.8% Agency Rating Outlook Moody s: Aa Stable S&P: AA Stable Fitch Ratings: AA Negative Primary products share in % Strengths Presence of European institutions and international organizations Qualified labor force External net creditor position Weaknesses Political tensions between Flanders and Wallonia Government debt above Euro area average Vulnerable banking system Mineral Fuels.% Food 9.% 7.% Exports Manufact. Products 7.5% Mineral Fuels 5.8% Food 8.5% 6.8% Imports Manufact. Products 68.8% FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 95
96 Estonia April 5 Estonia Estonia LONG-TERM TRENDS -year averages Population (million):... GDP (EUR bn): GDP per capita (EUR):,8,89 7, GDP growth (%):.8..5 Fiscal Balance (% of GDP):. -.. Public Debt (% of GDP): Inflation (%):...5 Current Account (% of GDP): Outlook moderates The Estonian economy closed in good shape, expanding at a slightly faster pace than in the previous year. According to a flash estimate released on February, the economy accelerated in the final quarter of last year, underpinned by strong growth in the manufacturing sector, particularly in electronics and wood products. Meanwhile, in the political arena, Estonia s ruling liberal Reform Party won parliamentary elections on March. Prime Minister Taavi Roivas Reform party beat pro-russophone Centre Party in a close vote and now must look for alliances in order to reach majority in parliament. Estonia is expected to post healthy growth this year, although geopolitical tensions between the European Union and Russia will continue to create uncertainty in various sectors of the economy. Domestic demand will continue to be the main driver of the economy this year, supported by increased wages and historically low energy prices. FocusEconomics panelists see GDP expanding.% in 5, which is down. percentage points from last month s forecast. The panel expects GDP growth to accelerate to.8% in 6. Harmonized consumer prices declined.5% annually in January, hitting a five-year-low (December: +.% year-on-year). FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect HICP inflation to pick up both this year and the next, averaging.8% in 5 and.9% in 6. Cecilia Simkievich Economist Parliamentary Elections Results Free Party 8.7% IRL.7% SDE 5.% EKRE 8.%.7% Note: Percentage of votes. Source: Estonian National Electoral Committee. Reform Party 7.8% Centre Party.8% POLITICS Estonia s ruling liberal Reform Party wins parliamentary election in close vote Estonia s ruling center-right Reform Party won the March parliamentary election, beating the pro-russophone Centre Party in a close contest that was mainly centered on national security issues amid the Russia-Ukraine ongoing conflict. While the Reform Party garnered the most seats, it fell short of absolute majority in the -seat Riigikogu (parliament). Prime Minister Taavi Roivas ruling Reform Party received 7.8% of the votes, which was slightly down from the result achieved in the elections that were held in. The result was high enough to beat opposition pro-russophone Centre Party, which obtained.8%. The Social Democrat Party (SDE) came in third with 5.%, followed by the conservative Pro Patria-Res Publica Union (IRL), which received just.7%. Two new smaller parties made their way into the Parliament for the first time. The Free Party got 8.7% of the votes and the anti-immigration Conservative People s Party (EKRE) received 8.%. Prime Minister Roivas now faces a more difficult scenario in which to form a coalition as parliament has fragmented into six parties rather than the previous election s four parties. Roivas has already ruled out a coalition with the pro-russophone Centre Party, which is not a surprise considering that FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 96
97 Estonia April 5 his party has a pro-nato foreign policy and is openly against Russia s role in Ukraine. While the Social Democrat Party is most likely to remain a member of the ruling coalition, Roivas will need to look for other alliances if he aims to have majority in parliament. It is still unclear what parties will comprise the government coalition. Gross Domestic Product variation in % 8 % REAL SECTOR GDP accelerates in the final quarter of ; ends on a high note According to the flash estimate released by Statistics Estonia (SE) on February, the Estonian economy expanded.7% over the same quarter of the previous year in Q. The result marked an acceleration from the.% tallied in Q. According to SE, the expansion in Q was mainly driven by growth in the manufacturing sector, particularly in electronics and wood products. In addition to manufacturing, the other main contributors to growth were energy and trade activities. Exports also improved markedly in Q, increasing a solid 8.% (Q: +6.6% year-on-year). Q Q Q Q Q 5 Note: Year-on-year changes of GDP in %. Source: Statistics Estonia and FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. In seasonally- and working-day adjusted terms, GDP increased.% quarteron-quarter in Q, which was notably above the mild.% expansion tallied in the third quarter. In the full year, GDP expanded.8%, which represented a slight improvement compared to the.6% increase registered in. More detailed data for national accounts will be released on March. The Central Bank expects GDP growth to reach.% in 5 and.% in 6. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast participants see the economy growing.% in 5, which is down. percentage points from last month s estimate. In 6, economic growth is expected to accelerate to.8%. Industrial Production variation in % Year-on-year 8 % Annual average REAL SECTOR Growth in industrial production slows in January after December s peak In January, industrial production increased a working-day adjusted.8% over the same month of the previous year, which came in well below the 7.9% rise tallied in December and marked the lowest reading in three months. According to Statistics Estonia, January s mild expansion reflected improvements in the production of electronics, wood, metal products and furniture. Conversely, the food industry, chemicals and motor vehicles recorded contractions compared to the same month of the previous year Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan-5 Note: Year-on-year changes and annual average growth of industrial production index in %. Source: Statistics Estonia and FocusEconomics calculations. A month-on-month assessment shows that industrial output decreased.5% in seasonally- and working-day-adjusted terms in January, which followed the.7% drop observed in December. As a result of the slight improvement, the overall trend continued to improve in January, with annual average growth in industrial production rising to.5% from December s.%. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect industrial production to expand.% in 5, which is up.6 percentage points from the previous month s projection. In 6, the panel expects industrial production to increase.8%. MONETARY SECTOR Consumer prices decline again in February Consumer prices increased.6% over the previous month in February, which contrasted the.% drop tallied in January and marked a nearly-two-year high. According to Statistics Estonia, the result mainly reflected increases in alcoholic beverages, clothing and transport. Conversely, prices for housing FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 97
98 Estonia April 5 Inflation Consumer Price Index.8 6. and for recreation and culture recorded lower prices compared to the previous month.. %. -. Month-on-month (left scale). %.. Consumer prices decreased.8% compared to the same month last year in February, which was a less pronounced decline than the.% drop tallied in the previous month. Meanwhile, annual HICP inflation swung from a.% rise in December to a.5% fall in January (the last month for which data are available). As a result of the marked drop in prices, annual average HICP inflation ticked down from December s.5% to.% in January. Year-on-year (right scale) Feb- Aug- Feb- Aug- Feb-5 Note: Year-on-year and month-on-month variation of consumer price index in %. Source: Statistics Estonia. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect harmonized inflation to average.8% in 5, which is down.8 percentage points from last month s forecast. In 6, the panel expects average inflation to accelerate to.9%. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 98
99 Economic Indicators - 9 Estonia April 5 Annual Data Real Sector Population (million) GDP per capita (USD),67 7,7 7, 8,85 9,7 5,96 6,69 8,5,7,96 GDP (USD bn) GDP per capita (EUR),5,,,96,8,85 5,87 6, 7,6 8,8 GDP (EUR bn) Economic Growth (Nom. GDP, ann. var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Private Consumption (annual var. in %) Government Consumption (ann. var. in %) Fixed Investment (annual var. in %) Industrial Production (annual var. in %) Retail Sales (annual variation in %) Unemployment (% of active population, aop) Fiscal Balance (% of GDP) Public Debt (% of GDP) Monetary and Financial Sector Money (annual variation of M in %) Inflation (CPI, annual variation in %, eop) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) Inflation (PPI, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, aop) External Sector Current Account Balance (% of GDP) Current Account Balance (EUR bn) Merchandise Trade Balance (EUR bn) Merchandise Exports (EUR bn) Merchandise Imports (EUR bn) Merchandise Exports (annual variation in %) Merchandise Imports (annual variation in %) External Debt (EUR bn) External Debt (% of GDP) Quarterly Data Q Q Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, s.a. qoq variation in %) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Monthly Data May- Jun- Jul- Aug- Sep- Oct- Nov- Dec- Jan-5 Feb-5 Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Inflation (CPI, mom variation in %) Inflation (CPI, annual variation in %) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 99
100 Real Sector Gross Domestic Product and Fiscal Balance Estonia April 5 Real GDP -9 var. in % Real GDP Q -Q 6 var. in % Economic Growth and Fiscal Balance Estonia Eastern Europe World GDP 5 evolution of forecasts 6 Maximum Consensus Minimum Oct Jan Apr Jul Oct Jan 6 Estonia Eastern Europe - World Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 GDP 6 evolution of forecasts 5 Maximum Consensus Minimum Oct Jan Apr Jul Oct Jan Real GDP Fiscal Balance variation in % % of GDP Individual Forecasts Capital Economics Danske Bank DekaBank DNB EIU..8.. JPMorgan Nordea Oxford Economics SEB Swedbank WIIW Summary Minimum Maximum.... Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Additional Forecasts Central Bank (Dec. ) IMF (Oct. ) Euro. Comm. (Feb. 5) Unemployment % of active pop. 6 Fiscal Balance % of GDP Estonia Eastern Europe Estonia Eastern Europe Unemployment evolution of fcst Oct Jan Apr Jul Oct Jan 8 Fiscal Balance evolution of fcst Oct Jan Apr Jul Oct Jan Notes and sources General: Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the Statistics Estonia (SE) and Eurostat. Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. GDP, annual variation in %. Source: SE. Quarterly GDP (not seasonally-adjusted), year-on-year variation in %. Source: SE. GDP, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. GDP, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 5 Unemployment, % of active population. Source: SE. 6 Balance of non-financial public sector as % of GDP. Source: Eurostat. 7 Unemployment, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 8 Balance of non-financial public sector as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
101 Estonia April 5 Monetary and External Sector Inflation and Current Account Balance 9 Inflation -9 in % 5 Estonia Eastern Europe Inflation 5 evolution of fcst 5 Maximum Consensus Minimum Inflation Q -Q 6 in % Inflation and Current Account Balance Inflation 6 evolution of fcst 5 Estonia Eastern Europe -5 Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 Maximum Consensus Minimum Prices (HICP) Current Account variation in % % of GDP Individual Forecasts Capital Economics Danske Bank DekaBank DNB EIU JPMorgan Nordea Oxford Economics SEB Swedbank WIIW Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Additional Forecasts Central Bank (Dec. ) IMF (Oct. ) Euro. Comm. (Feb. 5)..6 - Oct Jan Apr Jul Oct Jan Oct Jan Apr Jul Oct Jan Current Account % of GDP Current Account evol. of fcst Estonia Eastern Europe Oct Jan Apr Jul Oct Jan Notes and sources General: Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All monetary and external sector data are from the Statistics Estonia (SE) and the Bank of Estonia (EP, Eesti Pank). See below for details. Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 9 Inflation, annual average variation of harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) in % Source: SE. Inflation, annual variation of quarterly average harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) in %. Source: SE. Inflation, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. Inflation, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Current account balance as % of GDP. Source: EP. Current account balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
102 Fact Sheet Estonia April 5 General Data Official name: Republic of Estonia Capital: Tallinn (.5m) Area (km): 5,8 Population (million, est.):. Population density (per km, ): 9.5 Population growth rate (%, est.): -.7 Life expectancy (years, est.): 7. Illiteracy rate (%, ):. Language: Estonian, Russian Measures: Metric system Time: GMT+ Estonia in the Region Population %-share in Baltics Latvia.% Estonia.% GDP %-share in Baltics Latvia.% Estonia.% Lithuania 6.8% Lithuania 5.6% Economic Infrastructure Telecommunication () Telephones - main lines (per inhabitants):. Telephones - mobile cellular (per inhabit.): 6 Internet Users (per inhabitants): 8. Broadband Subscriptions (per inhabitants): 6.5 Energy () Primary Energy Production (trillion Btu): Primary Energy Consumption (trillion Btu): 9 Electricity Generation (billion kw-h):. Electricity Consumption (billion kw-h): 8. Oil Supply (thousand bpd):. Oil Consumption (thousand bpd): 8.6 CO Emmissions (million metric tons): 5.7 Economic Structure 8 6 GDP by Sector share in % GDP by Expenditure share in % Agriculture Manufacturing Industry Services Net Exports Investment Government Consumption Private Consumption Transportation () Airports: 8 Railways (km):,96 Roadways (km): 58, Waterways (km): 5 Chief Ports: Tallinn, Kunda, Pärnu Trade Structure - Primary markets share in % Political Data Prime Minister: Taavi Roivas Last elections: March 5 Next elections: 9 Central Bank President: Ardo Hansson Latvia 9.%.% Exports Russia.7% EU- 7.9% Asia ex- Japan 5.5% Sweden.8%.% Imports EU- 7 7.% Long-term Foreign Currency Ratings Finland 5.% Sweden 6.8%.% Finland 5.% Agency Rating Outlook Moody s: A Stable S&P: AA- Stable Fitch Ratings: A+ Stable Primary products share in % Strengths Commitment to prudent fiscal policy Widespread English proficiency High per capita income Weaknesses Small domestic market High external debt Ageing population Mineral Fuels 6.% Food 9.% Exports.5% Mineral Fuels 7.% Food.% 9.% Imports Manufact. Products 6.% Manufact. Products 6.5% FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
103 Finland April 5 Finland Finland LONG-TERM TRENDS -year averages Population (million): GDP (EUR bn): 7 7 GDP per capita (EUR): 6,96 7,76,76 GDP growth (%): Fiscal Balance (% of GDP): Public Debt (% of GDP): Inflation (%): Current Account (% of GDP): Outlook deteriorates Economic growth is expected to rebound this year, thereby putting an end to three consecutive years of declining output. Although household consumption remains subdued, the weakening of the euro coupled with the fall in oil prices is supporting growth. Despite the recovery expected for 5, Fitch Ratings changed Finland s credit outlook from stable to negative on March, but affirmed the country s rating at AAA. The agency cited the structural decline in the electronics and paper sectors, which have been key drivers in the past. This, combined with an ageing population, has led to a sharp decline in productivity growth and in economic growth estimates. In addition, Finland is suffering from a sharp fall in exports to Russia, the country s third-largest trading partner. In the political arena, the opposition Centre Party of Finland is leading the polls in advance of the 9 April general elections. Although Finland s economic outlook is clouded by ongoing domestic difficulties, the pick-up in economic growth in the Eurozone and the decline in oil prices are expected to foster growth this year. FocusEconomics panelists expect the recovery to be mild in 5 with GDP projected to expand.5%, which is down. percentage points from last month s projection. In 6, panelists see the economy growing.%. Harmonized consumer prices decreased.% in February (January: -.% year-on-year). The decline in oil prices and subdued economic growth are keeping inflationary pressures at bay. Panelists expect inflation to average.% in 5, which is down. percentage points from last month s estimate. Next year, the panel sees inflation at.%. Ricard Torné Senior Economist Monthly GDP variation in %.. % -. Year-on-year w.d.a. Annual average -. Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan-5 Note: Year-on-year and annual average variation of working-day adjusted Trend Indicator of Output (TIO) in %. Source: Statistics Finland and FocusEconomics calculations. REAL SECTOR Economic activity rebounds at the outset of the year In January, economic activity rose a working-day adjusted.7% over the same month last year, according to the monthly Trend Indicator of Output. The reading contrasted the revised.% drop recorded in December (previously reported: -.% year-on-year) and marked the largest increase in three months. January s expansion reflected a healthy increase in services, while growth in both the primary and secondary sectors was flat. On a monthly basis, economic output expanded.5% in seasonally- and working-day adjusted terms in January, coming in well above December s.8% contraction and marking the largest increase in months. Annual average growth in economic activity stabilized at December s.% in January. The Central Bank expects the economy to contract.% in 5 and to expand.% in 6. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists are more optimistic than the Central Bank s forecast and expect the economy to expand.5% in 5, which is down. percentage points from last month s projection. For 6, the panel sees GDP expanding.%. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
104 Finland April 5 Current Account Balance EUR billion EXTERNAL SECTOR Current account records largest deficit in six months in January The current account posted a EUR 5 million deficit in January. Although the print represented a slight improvement compared to the EUR 75 million shortfall recorded in the same month last year, it marked the largest deficit in six months. The trade balance registered a deficit of EUR million in January, contrasting the EUR million surplus recorded in December. Exports contracted at the fastest pace since August, falling.% over the same month last year (December: +.6% year-on-year). Imports followed suit and declined.% annually in January (December: -6.9% yoy), which represented the largest drop since October 9. Monthly current account balance (left scale) -month current account balance (right scale) Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan-5 Note: Monthly and -month current account balance in EUR billion. Source: Bank of Finland (BoF) and FocusEconomics calculations. In the months up to January, the current account balance recorded a EUR.6 billion deficit. The print was up from the EUR.8 billion shortfall recorded in the months up to the previous month and represented the smallest deficit in months. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect the current account deficit to reach.% of GDP in 5. For 6, the panel expects the current account deficit to be at.7% of GDP. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
105 Economic Indicators - 9 Finland April 5 Annual Data Real Sector Population (million) GDP per capita (EUR),96 6,65 6,99 7, 7,5 7,5 8,9 9,8,75,85 GDP (EUR bn) Economic Growth (Nom. GDP, ann. var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Domestic Demand (annual variation in %) Private Consumption (annual var. in %) Government Consumption (annual var. in %) Fixed Investment (annual variation in %) Exports (G&S, annual variation in %) Imports (G&S, annual variation in %) Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Unemployment (% of active population, aop) Fiscal Balance (% of GDP) Public Debt (% of GDP) Monetary and Financial Sector Inflation (CPI, annual variation in %, aop) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) Inflation (PPI, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Year Bond Yield (%, eop) Stock Market (var. of OMXH5 in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, aop) External Sector Current Account Balance (% of GDP) Current Account Balance (EUR bn) Trade Balance (EUR bn) Quarterly Data Q Q Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, s.a. qoq var. in %) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Monthly Data Jun- Jul- Aug- Sep- Oct- Nov- Dec- Jan-5 Feb-5 Mar-5 Trend Indicator of Output (annual var. in %) Trend Indicator of Output (s.a. mom var. in %) Industrial Production (annual var. in %) Unemployment (% of active population) Cons. Confidence Index (-threshold) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Current Account Balance (EUR bn) FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 5
106 Real Sector Gross Domestic Product Finland April 5 Real GDP -9 var. in % Real GDP Q - Q 6 var. in % Real GDP growth in % 5-5 Finland World GDP 5 evolution of forecasts Maximum Consensus Minimum - - Finland World - Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 GDP 6 evolution of forecasts Maximum Consensus Minimum Individual Forecasts 5 6 Aktia Bank.. Commerzbank.7.8 Credit Suisse.8.5 Danske Bank.5.5 DekaBank.. Deutsche Bank.8. DZ Bank.6.5 EIU.. ETLA Research Institute.6.8 Handelsbanken.5.5 Nordea..5 OP-Pohjola Group..7 Oxford Economics.. Raiffeisen Research.5.8 SEB.. Swedbank..8 UBS.8. Summary Minimum..8 Maximum..8 Median.5. Consensus.5. History days ago.6. 6 days ago.6. 9 days ago.7. Additional Forecasts Central Bank (Dec. ) -.. IMF (Oct. ).9.6 Euro. Comm. (Feb. 5).8. 5 Consumption variation in % 6 6 Consumption evolution of fcst Finland Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from Statistics Finland (SF). Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. GDP, annual variation in %. Quarterly GDP (seasonally-adjusted), year-on-year variation in %. GDP, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. GDP, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 5 Private consumption, annual variation in %. 6 Private consumption, change in 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 7 Gross fixed capital formation, annual variation in %. 8 Real exports of goods and services, annual variation in %. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 6
107 Real Sector Additional forecasts Finland April 5 Consumption Investment Exports Imports variation in % variation in % variation in % variation in % Individual Forecasts Aktia Bank Commerzbank Credit Suisse Danske Bank DekaBank Deutsche Bank DZ Bank EIU ETLA Research Institute Handelsbanken Nordea OP-Pohjola Group Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research SEB Swedbank UBS Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Investment variation in % 8 Exports variation in % 9 Imports variation in % - - Finland Finland Finland Investment evol. of forecasts Exports evol. of forecasts Imports evol. of forecasts FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 7
108 Real Sector Additional forecasts Finland April 5 Unemployment % of active pop. Finland Fiscal Balance % of GDP Finland Unemployment, Fiscal Balance and Public Debt Unemployment Fiscal Balance Public Debt % of active pop. % of GDP % of GDP Individual Forecasts Aktia Bank Commerzbank Credit Suisse Danske Bank DekaBank Deutsche Bank DZ Bank EIU ETLA Research Institute Handelsbanken Nordea OP-Pohjola Group Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research SEB Swedbank UBS Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Fiscal Balance evolution of fcst Public Debt % of GDP Finland 9 Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from Statistics Finland (SF) and Eurostat. See below for details. Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 9 Real imports of goods and services, annual variation in %. Source: SF. Gross fixed investment, evolution of 5 and forecasts during the last 8 months. Exports, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Imports, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Unemployment, % of active population. Source: SF. General government balance as % of GDP. Source: Eurostat. 5 General government balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and forecasts during the last 8 months. 6 Public debt as % of GDP. Source: Eurostat. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 8
109 Finland April 5 Monetary and External Sector Inflation and Current Account Balance 7 Inflation - 9 in % 8 Inflation Q - Q 6 in % Consumer Prices and Current Account Balance Inflation 5 evolution of fcst Finland Maximum Consensus Minimum - Finland - Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 Inflation 6 evolution of fcst Maximum Consensus Minimum Prices (HICP) Current Acct var. in % % of GDP Individual Forecasts Aktia Bank Commerzbank Credit Suisse Danske Bank DekaBank Deutsche Bank DZ Bank EIU ETLA Research Institute Handelsbanken Nordea OP-Pohjola Group Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research SEB Swedbank UBS Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Additional Forecasts Central Bank (Dec. ) IMF (Oct. ) Euro. Comm. (Feb. 5) Current Account % of GDP Current Account evol. of fcst 9 6 Finland Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All monetary and external sector data are from Statistics Finland (SF) and the Bank of Finland (BoF). See below for details. Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 7 Inflation, annual average variation of harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) in %. Source: SF. 8 Inflation, annual variation of quarterly average harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) in %. Source: SF. 9 Inflation, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. Inflation, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Current account balance as % of GDP. Source: BoF. Current account balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 9
110 FOCUSECONOMICS Finland April 5 Fact Sheet General Data Official name: Republic of Finland Capital: Helsinki (.5m) cities: Tampere (.5 m) Turku (.5 m) Area (km): 8,5 Population (million, est.): 5.5 Population density (per km, ): 6 Population growth rate (%, est.):. Life expectancy (years, est.): 79.7 Illiteracy rate (%, ):. Language: Finnish and Swedish Measures: Metric system Time: GMT+ Finland in the Region Population %-share in Spain.%.7% Italy 8.% Finland.6%.% France 9.% GDP %-share in Spain.%.5% Italy 5.6% Finland.% France.7% 8.% Economic Infrastructure Telecommunication () Telephones - main lines (per inhabitants):.9 Telephones - mobile cellular (per inhabit.): 7 Internet Users (per inhabitants): 9.5 Broadband Subscriptions (per inhabitants):.9 Energy () Primary Energy Production (trillion Btu): 9 Primary Energy Consumption (trillion Btu):, Electricity Generation (billion kw-h): 67.5 Electricity Consumption (billion kw-h): 8. Oil Supply (thousand bpd):.5 Oil Consumption (thousand bpd): 98 CO Emmissions (million metric tons): 6.8 Economic Structure 8 6 GDP by Sector share in % GDP by Expenditure share in % Agriculture Manufacturing Industry Services Net Exports Investment Government Consumption Private Consumption Transportation () Airports: 8 Railways (km): 5,9 Roadways (km): 78, Waterways (km): 8, Chief Ports: Helsinki, Kotka, Naantali Trade Structure Primary markets share in % Political Data Prime Minister: Alexander Stubb Last elections: 7 April Next elections: April 5 Central Bank Governor: Erkki Liikanen Long-term Foreign Currency Ratings Agency Rating Outlook Moody s: Aaa Stable S&P: AA+ Stable Fitch Ratings: AAA Negative Asia ex- Japan.%.7% Netherlands 6.% 9.% Russia 9.9% Exports Sweden.% U.S.A. 6.% EU- 7.% Asia ex- Japan 6.9% Netherlands 8.%.9% Primary products share in %.% Imports Sweden.8% Russia 7.7% EU- 7 6.% Strengths High competitiveness Technology infrastructure Highly industrialized economy Commitment to medium-term fiscal stability. Weaknesses Ageing population Small open economy sensitive to external demand shocks Highly dependant on energy imports Agric. Raw Mat. Mineral 6.%.8% Fuels 9.7% Ores & Metals 5.% Exports Manufact. Products 7.% Ores & Metals 7.8% Mineral Fuels.7% Imports.6% Manufact. Products 58.9% FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
111 Greece April 5 Greece Greece LONG-TERM TRENDS -year averages Population (million):... GDP (EUR bn): GDP per capita (EUR): 7,5 6,7 7,895 GDP growth (%): Fiscal Balance (% of GDP): Public Debt (% of GDP): Inflation (%): Current Account (% of GDP): Outlook deteriorates The Greek economy grew in for the first time in six years, largely on the back of a recovery in private consumption and the external sector. However, Greece s future is shrouded in uncertainty. The country is at the brink of bankruptcy and desperately needs additional financing from its European lenders. On 7 March, Prime Minister Alexis Tspiras presented Greece s newest reform plan, which includes previously-discussed measures to reduce corruption and tax evasion. Tsipras also conceded to retain an unpopular property tax and increase the value added tax for Greek islands, although the proposal did not touch on reforms to the pension system or labor laws. Further discussions with troika representatives are slated for this week, but at this point it is unlikely the latest plan will be enough to cement a deal and allow Greece to receive bailout extension funding. Looking forward, Greece s outlook is deteriorating rapidly. The government s funding gap is weighing heavily on the forecast and political tensions are rising in the country. Further, large downside risks of another election or even a grexit from the Eurozone still loom. FocusEconomics Consensus panelists expect the economy to expand.9% in 5, which is down.7 percentage points from last month s forecast. For 6, the panel sees the economy growing.%. In February, harmonized consumer prices fell.9% over the same month of the previous year (January: -.8% year-on-year). Panelists expect consumer prices to fall.% in 5. For 6, the panel sees consumer prices rising.5%. Angela Bouzanis Economist POLITICS Greece presents new reform plan in hopes of securing desperately-needed cash On 7 March, Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras presented Greece s newest reform plan to Eurozone leaders and the IMF in an effort to unlock desperatelyneeded funds and avoid bankruptcy. The new economic plan follows tense negotiations over Greece s future in earlier weeks and includes previouslydiscussed measures to crack down on corruption and tax evasion as well as honoring the privatization sales that have already been completed. In the latest version of the plan, which was debated with troika representatives and creditors over the weekend, Tsipras also conceded to retain an unpopular property tax in the plan and increase the value-added tax for Greek islands. The Greek government says its plan will help raise EUR billion of revenue and generate a.5% primary budget surplus this year. However, the proposal did not touch on reforms to the pension system or labor laws, two areas which Eurozone leaders insist must be overhauled. A four-month extension of Greece s EUR billion bailout program was approved by Eurozone finance ministers on February, although no new funds have yet been dispersed. Eurozone leaders have stipulated that Greece will have to outline a comprehensive reform plan and fulfill the conditions to receive the extension FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
112 Greece April 5 funds. Further talks are planned for this week, but it is not clear if the latest proposal will be enough to seal a deal nor is it known when new funds might be released. Industrial Production variation in % 5 % -5 Year-on-year Annual average - Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan-5 Note: Year-on-year changes and annual average variation of industrial production index in %. Source: Hellenic Statistical Authority (EL.STAT.) and FocusEconomics calculations. Tsipras move comes amidst increasing uncertainty over Greece s future. The country s finances have depleted and Greece has a number of payments due in the upcoming weeks, including a EUR 67 million loan repayment to the IMF on 9 April and EUR 6.7 billion due for maturing bonds in July and August. On 5 March, the European Central Bank (ECB) raised the amount that Greek banks can borrow from EUR 69.8 billion to EUR 7. billion extending a small lifeline to the country s finances. However, the European Financial Stability Facility denied Greece s appeal for cash on the same day, and Eurozone leaders have reiterated that Greece must commit to reform to earn funds. Moreover, Tsipras faces a tough road ahead even if Greece does receive additional funding. Tsipras campaigned on an anti-austerity platform and his coalition government has had to compromise on some key campaign pledges in the reform plan. Hard left-wing members of the coalition have criticized the government s actions and there is a risk of political gridlock or snap elections if they oppose Tsipras policies. Looking forward, Greece s outlook is deteriorating. The government must walk a tight-rope between balancing anti-austerity campaign promises and satisfying creditors demands for reform. On the extreme side, the possibility of another snap election or even a grexit from the Eurozone still pose a large downside risk. Against this backdrop, FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists revised their projections for 5 downward this month. Panelists foresee a.9% expansion, which is down.7 percentage points from last month s forecast. For 6, the panel expects growth to pick up to.%. REAL SECTOR Industrial production swings back to expansion In January, industrial production expanded a working-day adjusted.% compared to the same month of the previous year, which contrasted the revised.% contraction tallied in December (previously reported: -.8%). January s gain reflected an improvement in all of the sub-components that comprise the index. Labour Market Change in unemployed (mom, left scale) Unemployment rate (right scale) 9 8 Industrial output declined.7% over the previous month in seasonally-adjusted terms in January, which was below the.7% fall in December. January s result marked a five-month low. Annual average variation in industrial production increased from minus. in December to minus.9 in January. - % 7 6 FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists see industrial production falling.% in 5, which is down. percentage points from last month s forecast. In 6, the panel sees industrial production increasing.%. - 5 Dec- Jun- Dec- Jun- Dec- Note: Month-on month variation of unemployed people in thousands and unemployment rate in %. Source: Hellenic Statistical Authority (EL.STAT.). REAL SECTOR Unemployment rate rises in December The number of unemployed fell by in December, according to the Hellenic Statistical Authority (EL.STAT.). December s fall marked a smaller drop over November s, decrease. The unemployment rate inched up from 5.9% in November to 6.% in December. The reading was below that of the same month of the previous year (December : 7.%). Despite the improvements registered in recent months, Greece s unemployment rate is still well above the Eurozone average. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
113 Greece April 5 FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect unemployment to average 5.5% in 5, which is up. percentage points from last month s forecast. For 6, the panel expects the unemployment rate to average.9%. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
114 Economic Indicators - 9 Greece April 5 Annual Data Real Sector Population (million) GDP per capita (EUR),6 8,678 7,59 6,9 6, 6,6 6,67 7,9 7,875 8,69 GDP (EUR bn) Economic Growth (Nominal GDP, ann. var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Domestic Demand (annual variation in %) Private Consumption (annual var. in %) Government Consumption (ann. var. in %) Fixed Investment (annual variation in %) Exports (G&S, annual variation in %) Imports (G&S, annual variation in %) Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Unemployment (% of active population, aop) Fiscal Balance (% of GDP) Public Debt (% of GDP) Monetary and Financial Sector Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, eop) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) Inflation (PPI, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Year Bond Yield (%, eop) Stock Market (var. of ASE in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, aop) External Sector Current Account Balance (% of GDP) Current Account Balance (EUR bn) Trade Balance (EUR bn) Quarterly Data Q Q Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Monthly Data May- Jun- Jul- Aug- Sep- Oct- Nov- Dec- Jan-5 Feb-5 Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Markit Manufacturing PMI (5-threshold) Unemployment (% of active population) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
115 Real Sector Gross Domestic Product Greece April 5 Real GDP - 9 var. in % Real GDP Q -Q 6 var. in % Real GDP growth in % 5-5 Greece World GDP 5 evolution of forecasts Maximum Consensus Minimum - 5 Consumption variation in % 5-5 Greece World - Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 GDP 6 evolution of forecasts Maximum Consensus Minimum 6 Consumption evolution of fcst Individual Forecasts 5 6 Citigroup Global Mkts -..5 Commerzbank..5 Credit Suisse.8.9 DekaBank.5. Deutsche Bank.8. DZ Bank -.. EIU.5. Eurobank.9.8 Frontier Strategy Group.. ING.. National Bank of Greece.. Nomura..7 Oxford Economics.. Piraeus Bank.8 - UBS.5.5 Unicredit.8.5 Summary Minimum -.. Maximum.9. Median.8.5 Consensus.9. History days ago days ago days ago..5 Additional Forecasts IMF (Oct. ).9.7 European Commission (Feb. 5) Greece Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the Hellenic Statistical Authority (EL.STAT.) and Eurostat. See below for details. Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. GDP, annual variation in %. Source: Eurostat and EL.STAT. Quarterly GDP (non seasonally adjusted), year-on-year variation in %. Source: Eurostat and EL.STAT. GDP, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. GDP, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 5 Private consumption, annual variation in %. Source: Eurostat and EL.STAT. 6 Private consumption, change in 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 7 Gross fixed capital formation, annual variation in %. Source: Eurostat and EL.STAT. 8 Real exports of goods and services, annual variation in %. Source: Eurostat and EL.STAT. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 5
116 Real Sector Additional forecasts Greece April 5 Consumption Investment Exports Imports variation in % variation in % variation in % variation in % Individual Forecasts Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DZ Bank EIU Eurobank Frontier Strategy Group ING National Bank of Greece Nomura Oxford Economics Piraeus Bank UBS Unicredit Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Investment variation in % 8 Exports variation in % 9 Imports variation in % 5-5 Greece Greece Greece Investment evol. of forecasts Exports evol. of forecasts Imports evol. of forecasts FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 6
117 Real Sector Additional forecasts Greece April 5 Unemployment % of active pop. Greece Fiscal Balance % of GDP Greece Unemployment, Fiscal Balance and Public Debt Unemployment Fiscal Balance Public Debt % of active pop. % of GDP % of GDP Individual Forecasts Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DZ Bank EIU Eurobank Frontier Strategy Group ING National Bank of Greece Nomura Oxford Economics Piraeus Bank UBS Unicredit Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Fiscal Balance evolution of fcst Public Debt % of GDP Greece Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the Hellenic Statistical Authority (EL.STAT.) and Eurostat. See below for details. Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 9 Real imports of goods and services, annual variation in %. Source: EL.STAT. Gross fixed investment, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Exports, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Imports, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Unemployment, % of active population. Source: EL.STAT. General government fiscal balance as % of GDP. Source: Eurostat. 5 General government fiscal balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 6 Public debt as % of GDP. Source: Eurostat. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 7
118 Greece April 5 Monetary and External Sector Inflation and Current Account Balance 7 Inflation - 9 in % 8 Inflation Q -Q 6 in % Consumer Prices and Current Account Balance Inflation 5 evolution of fcst - 6 Greece Maximum Consensus Minimum -. Greece Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 Inflation 6 evolution of fcst Maximum Consensus Minimum - - Prices (HICP) Current Acct var. in % % of GDP Individual Forecasts Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DZ Bank EIU Eurobank Frontier Strategy Group ING National Bank of Greece Nomura Oxford Economics Piraeus Bank UBS Unicredit Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Additional Forecasts IMF (Oct. ) Euro. Comm. (Feb. 5) Current Account % of GDP Current Account evol. of fcst 5 Greece Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All monetary and external sector data are from the Hellenic Statistical Authority (EL.STAT.) and the Bank of Greece (BoG). See below for details. Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 7 Inflation, annual average variation of harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) in %. Source: EL.STAT. 8 Inflation, annual variation of quarterly average harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) in %. Source: EL.STAT. 9 Inflation, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. Inflation, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Current account balance as % of GDP. Source: BoG. Current account balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 8
119 FOCUSECONOMICS Greece April 5 Fact Sheet General Data Official name: Hellenic Republic Capital: Athens (.m) cities: Thessaloniki (.m) Area (km):,957 Population (million, est.):. Population density (per km, ): 8.7 Population growth rate (%, est.):. Life expectancy (years, est.): 8. Illiteracy rate (%, ):.7 Language: Greek Measures: Metric system Time: GMT+ Greece in the Region Population %-share in Spain.%.% Italy 8.% Greece.%.% France 9.% GDP %-share in Spain.%.7% Italy 5.6% Greece.7% France.7% 8.% Economic Infrastructure Telecommunication () Telephones - main lines (per inhabitants): 7.9 Telephones - mobile cellular (per inhabit.): 7 Internet Users (per inhabitants): 59.9 Broadband Subscriptions (per inhabitants): 6. Energy () Primary Energy Production (trillion Btu): 8 Primary Energy Consumption (trillion Btu):,5 Electricity Generation (billion kw-h): 57.6 Electricity Consumption (billion kw-h): 57.7 Oil Supply (thousand bpd): 7.5 Oil Consumption (thousand bpd): 6 CO Emmissions (million metric tons): 87.6 Economic Structure 8 6 GDP by Sector share in % GDP by Expenditure share in % Agriculture Industry Services Net Exports Investment Government Consumption Private Consumption Transportation () Airports: 77 Railways (km):,58 Roadways (km): 6,96 Waterways (km): 6 Chief Ports: Piraeus, Thessaloniki Trade Structure - Primary markets share in % Political Data Prime Minister: Alexis Tsipras Last elections: 5 January 5 Next elections: February 9 Central Bank Governor: Yannis Stournaras.% Exports Turkey.9% EU- 7 9.%.5% Imports Russia.% EU % Long-term Foreign Currency Ratings Agency Rating Outlook Moody s: Caa RUR S&P: B- Negative Fitch Ratings: B Negative Asia ex- 6.5% Japan Bulgaria 5.5% 5.8% Italy 7.8% Asia ex- Japan.% Primary products share in % Italy 8.% 9.5% Strengths Leading ship owner Tourist potential Ongoing external rebalancing process Weaknesses Large public debt High structural unemployment High levels of household debt Widespread tax evasion Mineral Fuels 6.8% Food 9.9%.9% Exports Ores & Metals 8.% Manufact. Products.% Mineral Fuels 9.8% Imports 7.% Manufact. Products 5.8% FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 9
120 Ireland April 5 Ireland Ireland LONG-TERM TRENDS -year averages Population (million): GDP (EUR bn): 7 9 GDP per capita (EUR): 7, 9,897,57 GDP growth (%):.9.. Fiscal Balance (% of GDP): Public Debt (% of GDP): Inflation (%):..6.5 Current Account (% of GDP): Outlook stable Ireland was the European Union s fastest growing economy last year, expanding at a post-recession high of.8%. However, last year s recovery might be less dynamic than suggested by this fast expansion. Last year s performance was partly driven by companies that are based in Ireland to take advantage of its favorable tax system and who record financial transactions offshore. Nevertheless, the fact that private consumption finally picked up in indicates that the recovery has broadened. More recent indicators generally suggest that the economy is on a solid growth track: the services PMI and consumer confidence both remained high in February, despite having moderated. In the political arena, growing weariness with austerity policies has been reflected in rising support for the left-wing opposition Sinn Fein party and ongoing protests against new water fees. Ireland s growth prospects remain positive on expectations of solid growth in private consumption and investment. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect the economy to grow.6% in 5, which is unchanged from last month s forecast. The panel also forecasts an expansion of.6% in 6. Teresa Kersting Economist Gross Domestic Product variation in %. 9. In February, harmonized consumer prices fell.% in annual terms, matching January s print, which had marked the largest decline since November. Panelists expect HICP inflation to average.% in 5 and see it picking up to.% in 6. REAL SECTOR Economic growth slows in Q; full-year GDP records largest expansion in seven years According to preliminary data, in Q, the economy increased a mild.% over the previous quarter in seasonally-adjusted terms, which followed the.% expansion observed in Q and marked the worst print since Q. The result, which fell short of the.% growth expected by the market, was driven by a worse performance of the external sector.. % %. -. Quarter-on-quarter s.a. (left scale) Year-on-year (right scale) -. Q Q Q Q Q 5 Note: Quarter-on-quarter changes of seasonally-adjusted GDP and year-on-year variation in %. Source: Central Statistics Office Ireland (CSO) and FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast Domestic demand sped up from a.9% increase in Q to a.5% expansion in Q. Private consumption grew.% (Q: +.% quarter-on-quarter), and government spending advanced from Q s.7% decline to a milder.% contraction in Q. Conversely, fixed investment slowed from a.% increase in Q to a weaker.7% rise in Q. On the external side of the economy, exports decelerated from a.% rise in Q to a.% increase in Q, which marked the weakest growth since Q. At the same time, imports recorded a 5.% expansion (Q: +.% qoq). As a result, the external sector s net contribution to GDP growth deteriorated from minus. percentage points in Q to minus.7 percentage points in Q. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
121 Ireland April 5 On an annual basis, GDP grew.% in Q, mirroring Q s reading. In the full year, the economy expanded.8%, which marked a notable improvement over s.% expansion and was the largest gain since 7. According to its Q Quarterly Bulletin, the Central Bank expects GDP to grow.7% in 5 and.8% in 6. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect the economy to grow.6% in 5, which is unchanged from last month s forecast. For 6, the panel also sees economic growth of.6%. Services Purchasing Managers Index REAL SECTOR Services PMI moderates but remains high in February The Investec Services Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) inched down from January s 6.5 to 6. in February. Even though this marks the lowest level in seven months, the index remains quite high. The index has been above the 6. mark since March, well above the 5-threshold that indicates expansion in the services sector. February s moderation mainly reflected that the rate of growth in new export orders and outstanding business slowed. Conversely, business sentiment improved and growth in new business continued to strengthen. Moreover, employment grew yet again. Input and output prices both rose in February. 5 Feb- Aug- Feb- Aug- Feb-5 Note: Investec Services PMI. Readings above 5 indicate an expansion in the services sector while readings below 5 indicate a contraction. Source: Investec and Markit. According to the survey report, the result suggests that, [n]otwithstanding the softening of a number of the indices within the PMI survey, Irish services firms remain upbeat about their future prospects, with the forward looking Confidence index improving to a three month high in February. Once again it stands close to the year high that was posted in February, with threefifths of panellists expecting to see an increase in activity over the coming year and fewer than one in twenty expecting to see a decrease. Industrial Production variation in % 5 5 % Year-on-year Annual average -5 Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan-5 Note: Year-on-year and annual average variation in %. Source: Central Statistics Office Ireland (CSO) and FocusEconomics calculations. REAL SECTOR Industrial production continues to moderate in January In January, industrial production tallied a seasonally- and working-day adjusted.6% expansion over the same month last year, which was down from the.6% increase tallied in December. The print represented the lowest gain since June of last year and a third consecutive moderation. According to the Central Statistics Office (CSO), the slowdown reflects a slower production in the traditional sector. Conversely, production in the modern sector, which includes pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and high-tech, picked up compared to December. The extraordinary gains that were recorded in October and November in October an over-decade-high expansion was tallied had partly been due to a positive base effect resulting from the expiration of several patents in. Industrial production contracted.% over the previous month in seasonallyadjusted terms in January, marking an improvement over the.9% decrease tallied in December. Meanwhile, annual average growth in industrial production inched up from.% in December to.% in January. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect industrial production to expand 5.6% in 5, which is up.6 percentage points from last month s forecast. For 6, the panel sees industrial production rising also.%. OUTLOOK Consumer confidence edges down from almost nine-year high in February The KBC Bank Ireland/ESRI Consumer Sentiment Index decreased from. points in January, which had marked the highest level since February 6, to 96. points in February. February s result reflects moderations in FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
122 Ireland April 5 Consumer Confidence 8 6 Feb- Aug- Feb- Aug- Feb- Aug- Feb-5 Note: The KBC Bank Ireland/ESRI Consumer Sentiment Index. Source: The Economic and Social Research Institute (ESRI). both consumers perceptions of the current economic environment and their outlook for the Irish economy. The deterioration was broad-based, with most subcategories performing worse over the previous month. Particularly, compared to the previous month, consumers were less positive about their personal financial situations in the past and the next months, the general economic outlook and major purchases. Conversely, they assessed the outlook for unemployment more positively than in January. According to the survey report, [t]he pullback in consumer sentiment in February [ ] is disappointing but not entirely unexpected. Most Irish consumers are not experiencing a straight line recovery where each month sees a clear and progressive improvement in their personal circumstances. In addition, the broader global outlook remains quite uncertain and through the survey period renewed concerns about Greece would have been a forceful reminder of downside risks to macroeconomic prospects. So, while our sense is that the underlying trend in Irish consumer sentiment remains solidly positive, the monthly index is likely to continue to make progress by taking two steps forward followed by one back. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect private consumption to expand.% in 5, which is up. percentage points from last month s forecast. For 6, the panel sees private consumption increasing.%. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
123 Economic Indicators - 9 Ireland April 5 Annual Data Real Sector Population (million) GDP per capita (EUR) 6,8 7,86 7,678 6,598 8,587 9,78,,88,58 6,8 GDP (EUR bn) Economic Growth (Nominal GDP, ann. var. in % Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Domestic Demand (annual variation in %) Private Consumption (annual var. in %) Government Consumption (ann. var. in %) Fixed Investment (annual variation in %) Exports (G&S, annual variation in %) Imports (G&S, annual variation in %) Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Unemployment (% of active population, aop) Fiscal Balance (% of GDP) Public Debt (% of GDP) Monetary and Financial Sector Inflation (Core, annual variation in %, aop) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, eop) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) Inflation (WPI, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Year Bond Yield (%, eop) Stock Market (var. of ISEQ in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, aop) External Sector Current Account Balance (% of GDP) Current Account Balance (EUR bn) Trade Balance (EUR bn) Quarterly Data Q Q Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, s.a. qoq var. in %) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Year Bond Yield (%, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Monthly Data May- Jun- Jul- Aug- Sep- Oct- Nov- Dec- Jan-5 Feb-5 Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Unemployment (% of active population) Consumer Confidence Index Investec Manufacturing PMI (5-threshold) Investec Services PMI (5-threshold) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
124 Real Sector Gross Domestic Product Ireland April 5 Real GDP -9 var. in % Real GDP Q -Q 6 var. in % Real GDP growth in % 5-5 Ireland World GDP 5 evolution of forecasts 6 Maximum Consensus Minimum 5 Consumption variation in % 9 6 Ireland World - Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 GDP 6 evolution of forecasts 9 6 Maximum Consensus Minimum 6 Consumption evolution of fcst Individual Forecasts 5 6 AIB Global Treasury.. Bank of Ireland..8 Citigroup Global Mkts. 5. Commerzbank.5.5 Credit Suisse..8 Dan McLaughlin.. Davy.7. DekaBank.. Deutsche Bank.7.5 DZ Bank..5 EIU.5.9 ESRI..7 Goodbody Stockbrokers..8 IBEC.8 - Investec Ireland.7.5 Nomura..8 Oxford Economics..9 Raiffeisen Research.9.5 UBS.5.6 Summary Minimum..8 Maximum.8 5. Median.5.5 Consensus.6.6 History days ago.6. 6 days ago days ago.6. Additional Forecasts Central Bank (Feb. 5).7.8 IMF (Oct. )..5 European Commission (Feb. 5) Ireland Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the Central Statistics Office Ireland (CSO). Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. GDP, annual variation in %. Quarterly GDP (non seasonally adjusted), year-on-year variation in %. GDP, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. GDP, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 5 Private consumption, annual variation in %. 6 Private consumption, change in 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 7 Gross fixed capital formation, annual variation in %. 8 Real exports of goods and services, annual variation in %. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
125 Real Sector Additional forecasts Ireland April 5 Consumption Investment Exports Imports variation in % variation in % variation in % variation in % Individual Forecasts AIB Global Treasury Bank of Ireland Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Credit Suisse Dan McLaughlin Davy DekaBank Deutsche Bank DZ Bank EIU ESRI Goodbody Stockbrokers IBEC Investec Ireland Nomura Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research UBS Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Investment variation in % 8 Exports variation in % 9 Imports variation in % - - Ireland Ireland Ireland Investment evol. of forecasts Exports evol. of forecasts Imports evol. of forecasts FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 5
126 Real Sector Additional forecasts Ireland April 5 Unemployment % of active pop. 8 Ireland Fiscal Balance % of GDP Ireland Unemployment, Fiscal Balance and Public Debt Unemployment Fiscal Balance Public Debt % of active pop. % of GDP % of GDP Individual Forecasts AIB Global Treasury Bank of Ireland Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Credit Suisse Dan McLaughlin Davy DekaBank Deutsche Bank DZ Bank EIU ESRI Goodbody Stockbrokers IBEC Investec Ireland Nomura Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research UBS Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Fiscal Balance evolution of fcst Public Debt % of GDP 5 Ireland Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the Central Statistics Office Ireland (CSO) and Eurostat. See below for details. Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 9 Real imports of goods and services, annual variation in %. Source: CSO. Gross fixed investment, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Exports, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Imports, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Unemployment, % of active population. Source: CSO. General government balance as % of GDP. Source: Eurostat. 5 General government balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 6 Public debt as % of GDP. Source: Eurostat. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 6
127 Ireland April 5 Monetary and External Sector Inflation and Current Account Balance 7 Inflation - 9 in % 8 Inflation Q -Q 6 in % Consumer Prices and Current Account Balance 6 Ireland Inflation 5 evolution of fcst Maximum Consensus Minimum - Current Account % of GDP 8 Ireland Ireland - Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 Inflation 6 evolution of fcst Maximum Consensus Minimum Current Account evol. of fcst 7 6 Prices (HICP) Current Acct var. in % % of GDP Individual Forecasts AIB Global Treasury Bank of Ireland Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Credit Suisse Dan McLaughlin Davy DekaBank Deutsche Bank DZ Bank EIU ESRI Goodbody Stockbrokers IBEC Investec Ireland.5... Nomura Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research UBS Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Additional Forecasts Central Bank (Feb. 5) IMF (Oct. ) Euro. Comm. (Feb. 5) Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All monetary and external sector data are from the Central Statistics Office Ireland (CSO). Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 7 Inflation, annual average variation of harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) in %. 8 Inflation, annual variation of quarterly average harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) in %. 9 Inflation, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. Inflation, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Current account balance as % of GDP. Current account balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 7
128 FOCUSECONOMICS Fact Sheet Ireland April 5 General Data Official name: Ireland Capital: Dublin (.7m) cities: Cork (.6m) Area (km): 7,7 Population (million, est.):.8 Population density (per km, ): 68. Population growth rate (%, est.):. Life expectancy (years, est.): 8.6 Illiteracy rate (%, ):. Language: English, Irish Measures: Metric system Time: GMT Ireland in the Region Population %-share in Spain.%.9% Italy 8.% Ireland.%.% France 9.% GDP %-share in Spain.%.7% Italy 5.6% Ireland.8% France.7% 8.% Economic Infrastructure Telecommunication () Telephones - main lines (per inhabitants):. Telephones - mobile cellular (per inhabit.): Internet Users (per inhabitants): 78. Broadband Subscriptions (per inhabitants):. Energy () Primary Energy Production (trillion Btu): 6. Primary Energy Consumption (trillion Btu): 58 Electricity Generation (billion kw-h): 5.9 Electricity Consumption (billion kw-h):. Oil Supply (thousand bpd):.7 Oil Consumption (thousand bpd): 6 CO Emmissions (million metric tons): 5.5 Economic Structure 8 6 GDP by Sector share in % GDP by Expenditure share in % Agriculture Industry Services Net Exports Investment Government Consumption Private Consumption Transportation () Airports: Railways (km):,7 Roadways (km): 96,6 Waterways (km): 956 Chief Ports: Dublin, Cork, Shannon Trade Structure Primary markets share in % Political Data Prime Minister: Enda Kenny Last elections: 5 February Next elections: April 6 Central Bank Governor: Patrick Honohan 8.% Belgium 5.7%.% Exports U.S.A. 8.% Switzerland 5.8% EU- 7.5% Asia ex- Japan 6.9% Netherlands 5.6% 7.6%.% Imports U.S.A..% EU- 7.7% Long-term Foreign Currency Ratings U.K. 7.% U.K. 9.8% Agency Rating Outlook Moody s: Baa Stable S&P: A Stable Fitch Ratings: A- Stable Primary products share in % Strengths Low corporate tax rate attracts inward investment High competitiveness One of the highest GDP per capita levels in the EU Weaknesses Troubled property market Large public debt Small open economy sensitive to external demand shocks. Food 9.8% 5.% Exports Manufact. Products 85.% Mineral Fuels.6% Food.8% 7.6% Imports Manufact. Products 66.% FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 8
129 Latvia April 5 Latvia Latvia LONG-TERM TRENDS -year averages Population (million):... GDP (EUR bn): GDP per capita (EUR):,65,,756 GDP growth (%):.7.7. Fiscal Balance (% of GDP): Public Debt (% of GDP): Inflation (%):...5 Current Account (% of GDP): Outlook deteriorates A full breakdown of fourth quarter GDP data showed that the economy was more resilient than suggested by the preliminary estimate. However, with a.% expansion recorded for the full year, the economy expanded at a much slower pace than in. Exports weakened throughout due to geopolitical tensions between Russia and Europe. Conversely, domestic demand held up relatively well. The first indicators for 5 show that economic activity started on a negative note: Industrial production contracted.5% annually in January, which followed the.6% contraction observed in December. The reading marked the fastest contraction in a year. Latvia s economic prospects are gradually deteriorating. Although expectations of low oil prices, together with an accommodative monetary policy are expected to support domestic demand, tensions between the EU and Russia will continue to create uncertainty in various fronts of the economy. FocusEconomics panelists estimate that GDP will grow.5% in 5, which is down. percentage points from last month s estimate. Panelists expect that GDP growth will increase to.% in 6. Inflation declined sharply toward the end of last year and Latvia is now on the brink of deflation. In January, harmonized consumer prices registered their first year-on-year decrease in over a year due to low oil prices. Although the weaker euro is offsetting lower energy prices, economists reduced Latvia s inflation forecasts by.7 percentage points over the previous month and now expect HICP inflation to average.6% this year. In 6, the panel sees inflation rising to an average of.9%. Ricardo Aceves Senior Economist Gross Domestic Product variation in % 8 6 % Q Q Q Q Q 5 Note: Year-on-year changes of GDP in %. Source: Central Statistics Bureau and FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. REAL SECTOR Economic growth moderates less than previously estimated According to revised data published by the National Statistics Office, GDP increased.% over the same quarter of the previous year. The reading represented a mild deceleration compared to the.% expansion registered in the third quarter, but was revised up from the.9% rise registered in a preliminary estimate. A detraction from net exports to overall economic growth was the main driver behind Q s slowdown. Exports of goods and services increased.% yearon-year in Q, which came in above the.% rise observed in Q. Imports swung from a.7% contraction in Q to a.% expansion in Q. As imports growth outpaced that of exports, the net contribution from the external sector to overall economic growth deteriorated and fell from plus.7 percentage points in Q to minus. percentage points in Q. Domestic demand, on the other hand, improved in Q. Private consumption increased.% in Q, which was slightly above the.% rise in Q. Government consumption accelerated the pace from a.% increase in Q FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 9
130 Latvia April 5 to a.% expansion in Q. Gross fixed investment rebounded and expanded.% in Q, which contrasted the.7% contraction observed in Q. A sequential comparison showed a brighter picture for the Latvian economy than the deceleration suggested by the annual data. GDP increased a seasonally-adjusted.6% in Q over the previous quarter, which came in above the.5% expansion observed in Q. Q s result was revised up from a previous estimate that had GDP rising.%. The economy increased.% in the full year, which marked a deceleration compared to the.% expansion in. The Central Bank expects the economy to expand.7% this year. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect the economy to grow.5% in 5, which is down. percentage points from last month s projection. For 6, panelists expect the economy to expand.%. Industrial Production variation in % Year-on-year 5 % Annual average REAL SECTOR Industrial production drops to one-year low In January, industrial production contracted.5% over the same month last year. The reading followed the.6% drop observed in December and represented the fastest contraction since January. January s deterioration was solely the result of a massive contraction in electricity production and gas supply, which plummeted 9% annually. That said, manufacturing output and mining and quarrying rebounded in January. A month-on-month comparison confirms the deterioration suggested by the annual data. Industrial production fell a seasonally-adjusted.% over the previous month, which contrasted the.% increase observed in December. -5 Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan-5 Note: Year-on-year changes and annual average variation of industrial production index in %. Source: Central Statistics Bureau and FocusEconomics calculations. Meanwhile, the annual average variation in Industrial production in January was unchanged at December s minus.9%. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect industrial production to expand.% in 5, which is down. percentage points over the previous month s projection. For 6, the panel expects growth in industrial output to pick up to.5%. Inflation Consumer Price Index..5 %. -.5 Month-on-month (left scale) Year-on-year (right scale) Feb- Aug- Feb- Aug- Feb-5 Note: Month-on-month and year-on-year variations of consumer price index in %. Source: Central Statistics Bureau..5. %.5. MONETARY SECTOR Latvia registers second annual drop in consumer prices in February In February, consumer prices rose.% over the previous month, which came in above the.% increase tallied in January. February s increase was the result of higher prices for food and non-alcoholic beverages as well as for transport. Consumer prices fell.% over the same month last year in February, which followed the.% drop observed in January. The reading marked the second annual decline in consumer prices since December. Meanwhile, annual HICP consumer prices based on the harmonized index of consumer prices fell.% annually in January, which is the last month for which data are available. The reading contrasted the.% increase tallied in December. Annual average HICP inflation inched down from.7% in December to.6% in January. The Central Bank expects HICP inflation to average.% in 5. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect HICP inflation to average.6% in 5, which is down.7 percentage points from last month s projection. For 6, the panel expects inflation to average.9%. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
131 Economic Indicators 9-9 Latvia April 5 Annual Data Real Sector Population (million) GDP per capita (USD),,68,77 5,76 5,77,6,65 5, 6,95 8,7 GDP (USD bn) GDP per capita (EUR) 8,565 9,78,779,7,8,,95,77,77 5,768 GDP (EUR bn) Economic Growth (Nom. GDP, ann. var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Private Consumption (annual var. in %) Government Consumption (ann. var. in %) Fixed Investment (annual var. in %) Industrial Production (annual var. in %) Retail Sales (annual var. in %) Unemployment (% of active population, aop) Fiscal Balance (% of GDP) Public Debt (% of GDP) Monetary and Financial Sector Money (annual var. of M in %) Inflation (CPI, annual variation in %, eop) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) Inflation (PPI, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Year Bond Yield (%, eop) Stock Market (variation of OMXR in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, aop) External Sector Current Account Balance (% of GDP) Current Account Balance (EUR bn) Merchandise Trade Balance (EUR bn) Merchandise Exports (EUR bn) Merchandise Imports (EUR bn) Merchandise Exports (annual variation in %) Merchandise Imports (annual variation in %) External Debt (EUR bn) External Debt (% of GDP) Quarterly Data Q Q Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, qoq variation in %) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Monthly Data May- Jun- Jul- Aug- Sep- Oct- Nov- Dec- Jan-5 Feb-5 Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Inflation (CPI, mom variation in %) Inflation (CPI, annual variation in %) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
132 Real Sector Gross Domestic Product and Fiscal Balance Latvia April 5 Real GDP -9 var. in % Real GDP Q -Q 6 var. in % Economic Growth and Fiscal Balance - Latvia Eastern Europe - World 5 5 GDP 5 evolution of forecasts 6 5 Maximum Consensus Minimum Oct Jan Apr Jul Oct Jan 9 6 Latvia Eastern Europe World - Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 GDP 6 evolution of forecasts 6 5 Maximum Consensus Minimum Oct Jan Apr Jul Oct Jan Real GDP Fiscal Balance variation in % % of GDP Individual Forecasts Capital Economics Citadele Danske Bank DekaBank DNB EIU JPMorgan Nordea Oxford Economics SEB Swedbank WIIW Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Additional Forecasts Cen. Bank (Dec. ) Euro. Comm. (Feb. 5) IMF (Oct. ) Unemployment % of active pop. 6 Fiscal Balance % of GDP 5 Latvia Latvia Eastern Europe Eastern Europe Unemployment evolution of fcst 8 Fiscal Balance evolution of fcst Notes and sources General: Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the Central Statistical Bureau (CSB) and Eurostat. See below for details. Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast Oct Jan Apr Jul Oct Jan Oct Jan Apr Jul Oct Jan GDP, annual variation in %. Source: CSB. Quarterly GDP (non-seasonally adjusted), year-on-year variation in %. Source: CSB. GDP, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. GDP, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 5 Unemployment, % of active population. Source: CSB. 6 Balance of non-financial public sector as % of GDP. Source: Eurostat. 7 Unemployment, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 8 Balance of non-financial public sector as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
133 Latvia April 5 Monetary and External Sector Inflation and Current Account Balance 9 Inflation - 9 In % Inflation Q -Q 6 In % Inflation and Current Account Balance Inflation 5 evolution of fcst Latvia Eastern Europe Maximum Consensus Minimum - Oct Jan Apr Jul Oct Jan 5 Latvia Eastern Europe -5 Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 Inflation 6 evolution of fcst 5 Maximum Consensus Minimum Oct Jan Apr Jul Oct Jan HICP Current Account variation in % % of GDP Individual Forecasts Capital Economics Citadele Danske Bank DekaBank DNB EIU JPMorgan Nordea Oxford Economics SEB Swedbank WIIW Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Additional Forecasts Cen. Bank (Dec. ) Euro. Comm. (Feb. 5) IMF (Oct. ) Current Account % of GDP Current Account evol. of fcst Latvia Eastern Europe Oct Jan Apr Jul Oct Jan Notes and sources General: Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All monetary and externa sector data are from the Central Statistical Bureau (CSB) and the Bank of Latvia (BoL, Latvijas Banka). See below for details. Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 9 Inflation, annual average variation of harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) in %. Source: CSB. Inflation, annual variation of quarterly average harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) in %. Source: CSB. Inflation, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. Inflation, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Current account balance as % of GDP. Source: BoL. Current account balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
134 FOCUSECONOMICS Fact Sheet Latvia April 5 General Data Official name: Republic of Latvia Capital: Riga (.m) Area (km): 6,589 Population (million, est.):. Population density (per km, ):.5 Population growth rate (%, est.): -.6 Life expectancy (years, est.): 7. Illiteracy rate (%, ):. Language: Latvian, Russian Measures: Metric system Time: GMT+ Latvia in the Region Population %-share in Baltics Estonia.% Latvia.% GDP %-share in Baltics Estonia.% Latvia.% Lithuania 6.8% Lithuania 5.6% Economic Infrastructure Telecommunication () Telephones - main lines (per inhabitants):. Telephones - mobile cellular (per inhabit.): 7 Internet Users (per inhabitants): 75. Broadband Subscriptions (per inhabitants):.7 Energy () Primary Energy Production (trillion Btu): 9. Primary Energy Consumption (trillion Btu): 69 Electricity Generation (billion kw-h): 6. Electricity Consumption (billion kw-h): 7. Oil Consumption (thousand bpd):. CO Emmissions (million metric tons): 7.9 Economic Structure 8 6 GDP by Sector share in % GDP by Expenditure share in % Agriculture Manufacturing Industry Services Net Exports Investment Government Consumption Private Consumption Transportation () Airports: Railways (km):,9 Roadways (km): 7, Waterways (km): Chief Ports: Riga, Ventspils Trade Structure - Primary markets share in % Political Data Prime Minister: Laimdota Straujuma Last elections: October Next elections: October 8 Central Bank President: Ilmars Rimsevics Long-term Foreign Currency Ratings Agency Rating Outlook Moody s: A Stable S&P: A- Stable Fitch Ratings: A- Stable 7.5%.% Estonia.% Exports Lithuania.8% Russia 8.% EU- 7.% Poland 8.%.6% 9.8% Primary products share in % Lithuania 9.% Russia 9.% Imports EU- 7.% Strengths Strategic location between Russia and European Union EU membership provides support against financial crisis Weaknesses Strong dependency on energy supply from Russia High private debt Small domestic market Agric. Raw Mat..% Mineral Fuels 7.% Food 6.9% 9.% Exports Manufact. Products 56.% Mineral Fuels 6.% Food.8% Imports.7% Manufact. Products 57.% FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
135 Lithuania April 5 Lithuania Lithuania LONG-TERM TRENDS -year averages Population (million):..9.9 GDP (EUR bn): GDP per capita (EUR):,75,8 5,65 GDP growth (%):...9 Fiscal Balance (% of GDP): Public Debt (% of GDP): Inflation (%):.8.8. Current Account (% of GDP): External Debt (% of GDP): Outlook moderates The economy continued to slow down in the fourth quarter of, expanding.% in annual terms, which was the smallest gain in two and a half years. The external sector s subdued performance was mainly behind the slowdown, reflecting economic struggles in Russia Lithuania s main exports destination outside the European Union. Moreover, industrial production expanded at the slowest rate in five months in January. On 7 February, liquefied natural gas importer Litgas signed a preliminary agreement to buy gas from an U.S. supplier in a move aimed to reduce the country s strong dependence on Russian gas deliveries. Lithuania s growth prospects moderates slightly as subdued growth in the along with ongoing geopolitical tensions and economic weakness in Russia pose downside risks. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists see the economy growing.7% in 5, which is down. percentage points from last month s forecast. For 6, the panel expects the economy to expand.%. In January, harmonized consumer prices registered the steepest drop since February, falling.% in annual terms (December: -.% yearon-year). January s decline reflected dropping prices for several items, including transport and communications. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast participants expect HICP inflation to average.7% in 5 and.6% in 6. Teresa Kersting Economist Gross Domestic Product variation in % 8 6 % Q Q Q Q Q 5 Note: Year-on-year changes of GDP in %. Source: Statistics Lithuania and FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. REAL SECTOR Economic growth slows in Q to over two-year low In Q, GDP grew.% over the same period of the previous year, according to revised data published on 7 February. The result met the flash estimate, but was down from the.7% expansion recorded in the third quarter and marked the slowest growth since Q. The weaker performance of the external sector was mainly behind the slowdown. In the full year, GDP grew.9%, which was down from s.% increase. On the domestic side, private consumption growth picked up from.% in Q to 6.% in Q. Government consumption increased.% over the same period of the previous year (Q: +.% year-on-year). Fixed investment edged down to a.% increase in Q (Q: +.8% yoy). On the external side, exports of goods and services slowed from a 6.% expansion in the third quarter to a.% increase in the fourth. Simultaneously, imports growth accelerated from Q s.6% increase to a 9.% expansion. As exports slowed down while imports picked up, the external sector s net contribution to overall economic growth deteriorated from plus. percentage points in the third quarter to minus.9 percentage points in the fourth. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 5
136 Lithuania April 5 A quarter-on-quarter analysis does not corroborate the deceleration suggested by annual figures; GDP expanded a seasonally- and working-day adjusted.6% in Q over the previous quarter, which was a tad above.5% increase registered in the third quarter. The Central Bank expects GDP to grow.% in 5. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists see the economy growing.7% in 5, which is down. percentage points from last month s estimate. In 6, the panel expects GDP to expand.%. Industrial Production variation in % % - Year-on-year Annual average - Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan-5 Note: Year-on-year changes and annual average growth of industrial production index in %. Source: Statistics Lithuania and FocusEconomics calculations. REAL SECTOR Industrial production decelerates in January In January, industrial production expanded.% over the same month of last year, which was below the.8% increase recorded in December and marked the lowest print in five months. The moderation reflects that large contractions in several sectors, including mining and quarrying as well as electricity, gas and steam, more than offset a mild pick-up in manufacturing. On a sequential basis, industrial production decreased.% over the previous month in seasonally-adjusted terms, coming in above the.8% fall recorded in December. Annual average growth in industrial production improved from.% in December to.8% in January. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect industrial production to increase.% year, which is down. percentage points over last month s estimate. The panel expects industrial production to accelerate to a.5% expansion in 6. Inflation Consumer Price Index.. MONETARY SECTOR Consumer prices register largest drop in years In February, consumer prices decreased.% over the previous month, which was up from the.% decrease registered in January. According to the statistical institute, the result was mainly driven by lower prices for foodstuff, fuel and clothing.. % -. Month-on-month (left scale) Year-on-year (right scale) Feb- Aug- Feb- Aug- Feb-5 Note: Year-on-year and month-on-month variation of consumer price index in %. Source: Statistics Lithuania and FocusEconomics calculations.. %. In annual terms, consumer prices fell.8%, which followed January s.5% drop and represented the largest decrease since February. Meanwhile, harmonized consumer prices (based on the harmonized index of consumer prices) fell.% in January, which is the last month for which data are available, coming in further below December s.% decline. Annual average HICP inflation inched down from December s.% to.% in January. The Central Bank expects HICP inflation to average.% in 5. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect harmonized inflation to average.7% in 5, which is down. percentage points from last month s estimate. In 6, the panel sees inflation at.6%. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 6
137 Economic Indicators - 9 Lithuania April 5 Annual Data Real Sector Population (million) GDP per capita (USD),88,99,9 5,579 6,,7,9 5,75 7,55 9, GDP (USD bn) GDP per capita (EUR) 9,,,5,777,76,765,6, 5,7 6,5 GDP (EUR bn) Economic Growth (Nom. GDP, ann. var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Total Consumption (annual var. in %) Private Consumption (annual var. in %) Government Consumption (ann. var. in %) Fixed Investment (annual var. in %) Industrial Production (annual var. in %) Retail Sales (annual variation in %) Unemployment (aop, % of active population) Fiscal Balance (% of GDP) Public Debt (% of GDP) Monetary and Financial Sector Money (annual variation of M in %) Inflation (CPI, annual variation in %, eop) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) Inflation (PPI, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Year Bond Yield (%, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, aop) External Sector Current Account Balance (% of GDP) Current Account Balance (EUR bn) Merchandise Trade Balance (EUR bn) Merchandise Exports (EUR bn) Merchandise Imports (EUR bn) Merchandise Exports (annual var. in %) Merchandise Imports (annual var. in %) External Debt (EUR bn) External Debt (% of GDP) Quarterly Data Q Q Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, qoq variation in %) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Monthly Data May- Jun- Jul- Aug- Sep- Oct- Nov- Dec- Jan-5 Feb-5 Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Inflation (CPI, mom variation in %) Inflation (CPI, annual variation in %) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 7
138 Real Sector Gross Domestic Product and Fiscal Balance Lithuania April 5 Real GDP -9 var. in % - Lithuania Eastern Europe World GDP 5 evolution of forecasts 6 5 Maximum Consensus Minimum Oct Jan Apr Jul Oct Jan Real GDP Q -Q 6 var. in % Economic Growth and Fiscal Balance 6 Lithuania Eastern Europe World - Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 GDP 6 evolution of forecasts 5 Maximum Consensus Minimum Oct Jan Apr Jul Oct Jan Real GDP Fiscal Balance variation in % % of GDP Individual Forecasts Capital Economics Danske Bank DNB EIU JPMorgan Nordea Oxford Economics SEB Swedbank WIIW Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Additional Forecasts Central Bank (Dec. ) IMF (Oct. ) Eur. Comm. (Feb. 5) Unemployment % of active pop. 6 Fiscal Balance % of GDP 5 5 Lithuania Eastern Europe 5-5 Lithuania Eastern Europe Unemployment evolution of fcst Oct Jan Apr Jul Oct Jan 8 Fiscal Balance evolution of fcst Oct Jan Apr Jul Oct Jan Notes and sources General: Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from Statistics Lithuania (SL, Statistikos Departementas) and Eurostat. Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. GDP, annual variation in %. Source: SL. Quarterly GDP (not seasonally adjusted), year-on-year variation in %. Source: SL. GDP, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. GDP, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 5 Unemployment, % of active population. Source: SL. 6 Balance of non-financial public sector as % of GDP. Source: Eurostat. 7 Unemployment, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 8 Balance of non-financial public sector as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 8
139 Lithuania April 5 Monetary and External Sector Inflation and Current Account Balance 9 Inflation - 9 in % Inflation 5 evolution of fcst Lithuania Eastern Europe Maximum Consensus Minimum Oct Jan Apr Jul Oct Jan Inflation Q -Q 6 in % Inflation and Current Account Balance 8 6 Lithuania Eastern Europe Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 Inflation 6 evolution of fcst Maximum Consensus Minimum Oct Jan Apr Jul Oct Jan HICP Current Account variation in % % of GDP Individual Forecasts Capital Economics Danske Bank DNB EIU JPMorgan.... Nordea Oxford Economics SEB Swedbank WIIW Summary Minimum Maximum.5... Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Additional Forecasts Central Bank (Dec. ) IMF (Oct. ) Eur. Comm. (Feb. 5) Current Account % of GDP Current Account evol. of fcst Lithuania Eastern Europe Oct Jan Apr Jul Oct Jan Notes and sources General: Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All monetary and external sector data are from Statistics Lithuania (SL, Statistikos Departementas) and the Bank of Lithuania (LB, Lietuvos Bankas). See below for details. Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 9 Inflation, annual average variation of harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) in % Source: SL. Inflation, annual variation of quarterly average harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) in %. Source: SL. Inflation, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. Inflation, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Current account balance as % of GDP. Source: LB. Current account balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 9
140 Fact Sheet Lithuania April 5 General Data Official name: Republic of Lithuania Capital: Vilnius (.8m) cities: Kaunas (.6m) Area (km): 65, Population (million, est.):. Population density (per km, ): 5. Population growth rate (%, est.): -. Life expectancy (years, est.): 76. Illiteracy rate (%, ):. Language: Lithuanian, Russian and Polish Measures: Metric system Time: GMT+ Lithuania in the Region Population %-share in Baltics Estonia.% Latvia.% Lithuania 6.8% GDP %-share in Baltics Estonia.% Latvia 9.8% Lithuania 5.8% Economic Infrastructure Telecommunication () Telephones - main lines (per inhabitants):.7 Telephones - mobile cellular (per inhabit.): 5 Internet Users (per inhabitants): 68.5 Broadband Subscriptions (per inhabitants):. Energy () Primary Energy Production (trillion Btu): 6. Primary Energy Consumption (trillion Btu): 8 Electricity Generation (billion kw-h):.9 Electricity Consumption (billion kw-h): 9.7 Oil Supply (thousand bpd): 9. Oil Consumption (thousand bpd): 7.7 CO Emmissions (million metric tons): 6.7 Economic Structure 8 6 GDP by Sector share in % GDP by Expenditure share in % Agriculture Manufacturing Industry Services Net Exports Investment Government Consumption Private Consumption Transportation () Airports: 6 Railways (km):,767 Roadways (km): 8,66 Waterways (km): Chief Ports: Klaipeda Trade Structure - Primary markets share in % Political Data Prime Minister: Algirdas Butkevičius Last elections: October Next elections: 6 Central Bank President: Vitas Vasiliauskas Long-term Foreign Currency Ratings Agency Rating Outlook Moody s: Baa Positive S&P: A- Stable Fitch Ratings: A- Stable Estonia 7.8% 6.% 7.9% Exports Latvia.% Russia 9.% EU- 7 8.% Latvia 6.% Poland 9.9%.% 6.% Primary products share in % Imports EU- 7 6.% Russia.6% Strengths Open economic structure EU membership guarantees stable legal system Adoption of the euro as official currency in January 5 Weaknesses Small domestic market Sizeable external imbalances Limited fiscal discipline. Mineral Fuels.5% Food 6.9% 5.6% Exports Manufact. Products 5.% Mineral Fuels.% Food.% 6.% Imports Manufact. Products 9.% FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
141 Netherlands April 5 Netherlands Netherlands LONG-TERM TRENDS -year averages Population (million): GDP (EUR bn): GDP per capita (EUR): 8,8 9,59,7 GDP growth (%): Fiscal Balance (% of GDP): Public Debt (% of GDP): Inflation (%): Current Account (% of GDP): Outlook improves Following two years in recession, the Dutch economy returned to modest growth last year. While exports made the largest contribution to the expansion, fixed investment rebounded and private consumption posted the first mild gain in three years, showing that the recovery is broadening. Consumer confidence turned positive for the first time since 7 and business confidence continued to be robust in March, suggesting that the domestic economy will continue to gain momentum going forward. In the political arena, results from the 8 March provincial elections, which indirectly determine the composition of the upper house of the Parliament, show that the center-right government coalition will lose one-third of its seats in the Senate in May. As a consequence, the government will have to rely more on support from other parties and the implementation of reforms should become even more difficult. FocusEconomics panelists assessment of the Netherlands economic prospects is now more positive on expectations that solid exports and increasing consumption will sustain growth. Panelists see GDP expanding.5% in 5, which is up. percentage points from last month s projection. For 6, they expect the economy to expand.6%. In February, harmonized consumer prices fell.5% annually, which was slightly up from January s historical sharp decline of.7%. Panelists expect harmonized consumer prices to be flat in 5, which is unchanged from last month s estimate. For 6, the panel sees inflation averaging.%. Teresa Kersting Economist Gross Domestic Product variation in % Quarter-on-quarter s.a. (left scale) Year-on-year (right scale) % % -. Q Q Q Q Q 5 Note: Quarter-on-quarter changes of seasonally adjusted GDP and year-on-year variation in %. Source: Statistics Netherlands (CBS) and FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast REAL SECTOR Economy picks up in Q; returns to full-year economic growth in In the fourth quarter of, GDP increased.8% in seasonally-adjusted terms over the previous quarter, according to more detailed data released by Statistics Netherlands on 6 March. The reading came in above both the preliminary estimate and market expectations of a.5% increase. Moreover, the reading marked an improvement compared to the.% expansion recorded in Q and the largest expansion since Q. According to Statistics Netherlands, Q s acceleration resulted from stronger fixed investment, private consumption, and a better performance of the external sector. Private consumption grew.6% over the previous quarter, which came in above the.% increase observed in Q. Government consumption deteriorated from Q s.% contraction to a.6% decline in Q. On the other hand, fixed investment growth sped up from a.% rise in Q to a 5.% expansion, thus recording the fastest growth rhythm since Q. On the external front, growth in exports of goods and services fell from.9% in Q to.5% in Q. Imports of goods and services also decelerated, growing.7% in Q (Q: +.6% quarter-on-quarter). As a result, the external FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
142 Netherlands April 5 sector s net contribution to overall economic growth advanced from minus. percentage points in Q to minus. percentage points in Q. The economy grew.% in the fourth quarter over the same quarter of the previous year, which was up from Q s.% expansion. In the full year, the economy expanded.9%, which contrasted s.7% contraction and marked the first year of growth following two years of shrinking GDP. The Central Bank expects GDP to expand.7% in 5 and sees growth picking up to.8% in 6. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists see GDP growing.5% in 5, which is up. percentage points from last month s projection. For 6, the panel expects the economy to expand.6%. Consumer Confidence Mar- Sep- Mar- Sep- Mar- Sep- Mar-5 Note: Value of consumer confidence indicator index. The -point threshold separates optimistic from pessimistic sentiment. Source: Statistics Netherlands (CBS). OUTLOOK Consumer confidence jumps to positive territory for first time in over seven years The seasonally-adjusted consumer confidence indicator produced by the Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS) swung from February s minus 7. points to plus. points in March. As a result, for the first time since August 7, the index jumped above the -point threshold, which indicates that optimists outnumber pessimists. Consumer confidence in March increased mainly as households assessed the general economic climate much more positively than in the previous month. According to the CBS, this improvement is, probably due to the positive news about the economy and the labour market in the past month. In addition, consumers willingness to buy was slightly less negative than in February. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists see private consumption expanding.% in 5, which is up. percentage points from last month s estimate. In 6, the panel expects private consumption to also grow.%. Business Confidence 5 OUTLOOK Business confidence moderates again but remains in positive territory in March The producer confidence indicator, which measures Dutch manufacturers sentiment, declined from. points in February to a six-month low of. points in March, according to the Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS). This marks the third drop after three consecutive increases. However, the index still remains above the -point threshold that separates optimistic from pessimistic sentiment Mar- Sep- Mar- Sep- Mar- Sep- Mar-5 Note: Value of producer confidence indicator index. The -point threshold separates optimistic from pessimistic sentiment. Source: Statistics Netherlands (CBS). According to the CBS, March s slight deterioration resulted from the fact that producers were more negative about their future output. Conversely, manufacturers assessed their order books and their stocks of finished products more positively than in the previous month. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists see fixed investment rising.5% in 5, which is down. percentage points from the previous month s estimate. For 6, the panel expects fixed investment to increase.9%. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
143 Economic Indicators - 9 Netherlands April 5 Annual Data Real Sector Population (million) GDP per capita (EUR) 8,8 8,55 8,8 8,6 8,89 9,89,5,7,67,6 GDP (EUR bn) Economic Growth (Nom. GDP, ann. var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Domestic Demand (annual variation in %) Private Consumption (annual var. in %) Government Consumption (ann. var. in %) Fixed Investment (annual variation in %) Exports (G&S, annual variation in %) Imports (G&S, annual variation in %) Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Unemployment (% of active population, aop) Fiscal Balance (% of GDP) Public Debt (% of GDP) Monetary and Financial Sector Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, eop) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) Inflation (PPI, annual variation in %, eop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Year Bond Yield (%, eop) Stock Market (var. of AEX in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, aop) External Sector Current Account Balance (% of GDP) Current Account Balance (EUR bn) Trade Balance (EUR bn) Quarterly Data Q Q Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, s.a. qoq var. in %) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Year Bond Yield (%, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Monthly Data Jun- Jul- Aug- Sep- Oct- Nov- Dec- Jan-5 Feb-5 Mar-5 Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Unemployment (% of active population) Consumer Confidence Index Business Confidence Index NEVI Manufacturing PMI (5-threshold) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Exports (annual variation in %) FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
144 Real Sector Gross Domestic Product Netherlands April 5 Real GDP -9 var. in % Real GDP Q -Q 6 var. in % Real GDP growth in % 6 - Netherlands World GDP 5 evolution of forecasts Maximum Consensus Minimum Netherlands World - Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 GDP 6 evolution of forecasts Maximum Consensus Minimum - Individual Forecasts 5 6 ABN AMRO Bank.6. Citigroup Global Mkts..9 Commerzbank.5.6 Credit Suisse.7. DekaBank.6.7 Deutsche Bank.7. DIW Berlin.8.8 DZ Bank.5.5 EIU.9. ING.6.8 NIBC Bank.8. Nomura.. Oxford Economics.. Rabobank.7.8 Raiffeisen Research.5. UBS.8. Summary Minimum.9. Maximum.8. Median.6.8 Consensus.5.6 History days ago..5 6 days ago..5 9 days ago..5 Additional Forecasts Central Bank (Mar. 5).7.8 Euro. Comm. (Feb. 5)..7 IMF (Oct. )..6 5 Consumption variation in % 6 Consumption evolution of fcst 6 Netherlands Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from Statistics Netherlands (CBS, Centraal Bureau voor de Statistiek). See below for details. Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. GDP, annual variation in %. Quarterly GDP, year-on-year variation in %. GDP, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. GDP, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 5 Private consumption, annual variation in %. 6 Private consumption, change in 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 7 Gross fixed capital formation, annual variation in %. 8 Real exports of goods and services, annual variation in %. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast
145 Real Sector Additional forecasts Netherlands April 5 Consumption Investment Exports Imports variation in % variation in % variation in % variation in % Individual Forecasts ABN AMRO Bank Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DZ Bank EIU ING NIBC Bank Nomura Oxford Economics Rabobank Raiffeisen Research UBS Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Investment variation in % 8 Exports variation in % 9 Imports variation in % Netherlands Netherlands Netherlands Investment evol. of forecasts Exports evol. of forecasts Imports evol. of forecasts FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 5
146 Real Sector Additional forecasts Netherlands April 5 Unemployment % of active pop. Netherlands Fiscal Balance % of GDP - -6 Netherlands Unemployment, Fiscal Balance and Public Debt Unemployment Fiscal Balance Public Debt % of active pop. % of GDP % of GDP Individual Forecasts ABN AMRO Bank Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DIW Berlin DZ Bank EIU ING NIBC Bank Nomura Oxford Economics Rabobank Raiffeisen Research UBS Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Fiscal Balance evolution of fcst Public Debt % of GDP Netherlands Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from Statistics Netherlands (CBS, Centraal Bureau voor de Statistiek) and Eurostat. See below for details. Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 9 Real imports of goods and services, annual variation in %. Source: CBS. Gross fixed investment, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Exports, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Imports, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Unemployment, % of active population. Source: CBS. General government balance as % of GDP. Source: Eurostat. 5 General government balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 6 Public debt as % of GDP. Source: Eurostat. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 6
147 Netherlands April 5 Monetary and External Sector Inflation and Current Account Balance 7 Inflation - 9 in % 8 Inflation Q -Q 6 in % Consumer Prices and Current Account Balance 6 Netherlands Inflation 5 evolution of fcst Maximum Consensus Minimum - Current Account % of GDP Netherlands - Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 Inflation 6 evolution of fcst Maximum Consensus Minimum Current Account evol. of fcst Prices (HICP) var. in % Current Acct % of GDP Individual Forecasts ABN AMRO Bank Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank....5 DIW Berlin DZ Bank EIU ING NIBC Bank Nomura Oxford Economics Rabobank Raiffeisen Research UBS Summary Minimum Maximum Median.... Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Additional Forecasts Central Bank (Mar. 5) Euro. Comm. (Feb. 5) IMF (Oct. ) Netherlands Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All monetary and external sector data are from Statistics Netherlands (CBS, Centraal Bureau voor de Statistiek), the Central Bank (DNB, De Nederlandsche Bank). See below for details. Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 7 Inflation, annual average variation of harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) in %. Source: CBS. 8 Inflation, annual variation of quarterly average harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) in %. Source: CBS. 9 Inflation, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. Inflation, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Current account balance as % of GDP. Source: DNB. Current account balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 7
148 FOCUSECONOMICS Fact Sheet Netherlands April 5 General Data Official name: Kingdom of the Netherlands Capital: Amsterdam (.7m) cities: Rotterdam (.8m) Area (km):,5 Population (million, est.): 6.9 Population density (per km, ): 6 Population growth rate (%, est.):. Life expectancy (years, est.): 8. Illiteracy rate (%, ):. Language: Dutch Measures: Metric system Time: GMT+ Netherlands in the Region Population %-share in Spain.% 9.% Italy 8.% Netherlands 5.% France 9.%.% GDP %-share in Spain.% 9.% Italy 5.6% France.7% Netherlands 6.% 8.% Economic Infrastructure Telecommunication () Telephones - main lines (per inhabitants):.5 Telephones - mobile cellular (per inhabit.): Internet Users (per inhabitants): 9. Broadband Subscriptions (per inhabitants):. Energy () Primary Energy Production (trillion Btu):,755 Primary Energy Consumption (trillion Btu):,5 Electricity Generation (billion kw-h): 95 Electricity Consumption (billion kw-h): 7 Oil Supply (thousand bpd): Oil Consumption (thousand bpd):, CO Emmissions (million metric tons): Economic Structure 8 6 GDP by Sector share in % GDP by Expenditure share in % Agriculture Manufacturing Industry Services Net Exports Investment Government Consumption Private Consumption Transportation () Airports: 9 Railways (km):, Roadways (km): 9,95 Waterways (km): 6,7 Chief Ports: Amsterdam, Rotterdam Trade Structure Primary markets share in % Political Data Prime Minister: Mark Rutte Last elections: September Next elections: March 7 Central Bank Governor: Klaas Knot Long-term Foreign Currency Ratings Agency Rating Outlook Moody s: Aaa Stable S&P: AA+ Stable Fitch Ratings: AAA Stable.% France 8.8% Exports Belgium.7% EU- 7.5% 6.6% China.%.% Asia ex-japan 6.9% U.K. 6.7% Primary products share in % Imports Russia 6.% U.S.A. 6.% Belgium 8.% EU %.8% Strengths Diversified exports One of the highest GDP per capita levels in the EU Public debt under control Weaknesses Collapsed property market Large household debt Economy dependent on European neighbors Banking sector under strain Mineral Fuels.5% Food.7% Exports.% Manufact. Products 59.6% Mineral Fuels 9.% Food.%.% Imports Manufact. Products 58.9% FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 8
149 Portugal April 5 Portugal Portugal LONG-TERM TRENDS -year averages Population (million): GDP (EUR bn): GDP per capita (EUR): 6, 6,8 8,5 GDP growth (%): Fiscal Balance (% of GDP): Public Debt (% of GDP): Inflation (%):... Current Account (% of GDP): Outlook improves Last year, Portugal exited its EUR 78 billion bailout program and the economy expanded for the first time since. Moreover, the government announced a plan in February to make an early repayment of a portion of the bailout loan, reflecting its renewed fiscal soundness. In spite of these notable achievements, the center-right coalition government s popularity is still at low levels due to four years of painful austerity measures that were determined by the terms of the bailout program. The country faces general elections in the final quarter of this year, and recent polls suggest that it will be a close call between the government coalition and the Socialist Party. The evolution of the economy will be crucial, with a continued economic rebound likely tipping the balance in favor of the current governing coalition. The Portuguese economy is expected to accelerate this year, mainly underpinned by stronger export growth. FocusEconomics panelists expect GDP to expand.6% in 5, which is up. percentage points from last month s forecast. For 6, the panel foresees the economy growing.7%. Harmonized consumer prices dropped.% in February, easing from the.% decline recorded in the previous month. FocusEconomics panelists see harmonized inflation averaging.% in 5 and.% in 6. Cecilia Simkievich Economist Industrial Production variation in % 8.. %. -. Year-on-Year Annual average REAL SECTOR Drop in industrial production slightly less pronounced in February In February, industrial production declined.% over the same month of last year, which marked a slight improvement compared to the revised.% fall tallied in January (previously reported: -.% year-on-year). According to Statistics Portugal (INE), February s less pronounced decrease in industrial output was the result of a strong rebound in the electricity, gas and water sector as well as a sharp increase in mining. The electricity sector swung from a 7.% fall in January to a healthy.8% rise in February. The mining sector accelerated from January s.% increase to a strong.7% rise in February, marking the highest reading since October. Manufacturing was the only sector that deteriorated compared to the previous month s result, contracting.% in February (January: -.% yoy). -8. Feb- Aug- Feb- Aug- Feb-5 Note: Year-on-year changes and annual average growth of industrial production index in %. Source: Statistics Portugal (INE) and FocusEconomics calculations. Compared to the previous month, industrial output fell a seasonally-adjusted.5% in February. The result contrasted the.6% rise tallied in January. Annual average growth continued to worsen in February, falling to.% from January s.6% increase. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect industrial production to rise.6% in 5, which is down.5 percentage points from last month s forecast. For 6, participants expect industrial output to expand.%. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 9
150 Portugal April 5 The Bank of Portugal expects the economy to expand.7% in 5 and.9% in 6. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect that GDP will expand.6% in 5, which is up. percentage points from last month s projection. For 6, the panel expects economic growth to accelerate to.7%. Leading Indicators Consumer Confidence (left scale) Economic Climate (right scale) OUTLOOK Consumer confidence and economic climate improve in March The consumer confidence index rose from minus 9. points in February to minus 7.5 points in March, marking the highest reading since April and prolonging the upward trend that has been observed since the beginning of. According to the Statistical Institute, the rise in consumer confidence reflected improvements in all the sub-components that comprise the index. Consumers were particularly more optimistic regarding their opportunities to purchase durable goods and the evolution of their own financial situations in the last months. Households expectations regarding the outlook of the country s economic situation also improved markedly compared to the previous month Mar- Sep- Mar- Sep- Mar- Sep- Mar-5 Note: Consumer Confidence and Economic Climate indicators. Source: Statistics Portugal (INE). FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect private consumption to expand.7% in 5, which is down. percentage points from last month s estimate. For 6, the panel expects private consumption to also increase.6%. The economic climate indicator remained in optimistic territory and inched up from. in February to.6 in March, which marked the highest print in six months. Panelists expect fixed investment to increase.8% in 5, which is down. percentage points from last month s estimate. The panel sees fixed investment expanding.% in 6. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 5
151 Economic Indicators - 9 Portugal April 5 Annual Data Real Sector Population (million) GDP per capita (EUR) 6,95 6,585 5,98 6,6 6,9 6,76 7,5 7,69 8, 8,79 GDP (EUR bn) Economic Growth (Nominal GDP, ann. var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Domestic Demand (annual variation in %) Private Consumption (annual var. in %) Government Consumption (ann. var. in %) Fixed Investment (annual variation in %) Exports (G&S, annual variation in %) Imports (G&S, annual variation in %) Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Unemployment (% of active population, aop) Fiscal Balance (% of GDP) Public Debt (% of GDP) Monetary and Financial Sector Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, eop) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) Inflation (PPI, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Year Bond Yield (%, eop) PSI- (var. in %, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, aop) External Sector Current Account Balance (% of GDP) Current Account Balance (EUR bn) Trade Balance (EUR bn) Quarterly Data Q Q Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, s.a. qoq var. in %) Unemployment (% of active population, aop) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Year Bond Yield (%, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Monthly Data Jun- Jul- Aug- Sep- Oct- Nov- Dec- Jan-5 Feb-5 Mar-5 Retail Sales (annual variation in %) Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Consumer Confidence Index Economic Climate Index Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 5
152 Real Sector Gross Domestic Product Portugal April 5 Real GDP -9 var. in % Real GDP Q -Q 6 var. in % Real GDP growth in % 6 - Portugal World GDP 5 evolution of forecasts Maximum Consensus Minimum - 5 Consumption variation in % Portugal World -6 Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 GDP 6 evolution of forecasts Maximum Consensus Minimum - 6 Consumption evolution of fcst. Individual Forecasts 5 6 Banco BPI.5.7 BBVA Research.5.8 Berenberg.7. Citigroup Global Mkts.9. Commerzbank.5. Credit Agricole..5 Credit Suisse.5.9 DekaBank.6.5 Deutsche Bank.6.6 DZ Bank.7.8 EIU.5.5 Nomura..5 Novo Banco..5 Oxford Economics.7. Raiffeisen Research.7. UBS.6.9 Unicredit.8.7 Univ. Católica Portuguesa.9.8 Summary Minimum.. Maximum.9. Median.6.7 Consensus.6.7 History days ago days ago days ago..7 Additional Forecasts Euro. Comm. (Feb. 5).6.7 IMF (Oct. ).5.7 Central Bank (Mar. 5) Portugal Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from Statistics Portugal (INE, Instituto Nacional de Estatistica). Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. GDP, annual variation in %. Quarterly GDP (seasonally adjusted), year-on-year variation in %. GDP, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. GDP, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 5 Private consumption, annual variation in %. 6 Private consumption, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 7 Gross fixed capital formation, annual variation in %. 8 Real exports of goods and services, annual variation in %. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 5
153 Real Sector Additional forecasts Portugal April 5 Consumption Investment Exports Imports variation in % variation in % variation in % variation in % Individual Forecasts Banco BPI BBVA Research Berenberg Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Credit Agricole Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DZ Bank EIU Nomura Novo Banco Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research UBS Unicredit Univ. Católica Portuguesa Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Investment variation in % 8 Exports variation in % 9 Imports variation in % - Portugal Portugal Portugal Investment evol. of forecasts Exports evol. of forecasts 5.5 Imports evol. of forecasts FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 5
154 Real Sector Additional forecasts Portugal April 5 Unemployment % of active pop. Portugal Fiscal Balance % of GDP - -8 Portugal Unemployment, Fiscal Balance and Public Debt Unemployment % of active pop. Fiscal Balance % of GDP Public Debt % of GDP Individual Forecasts Banco BPI BBVA Research Berenberg Citigroup Global Mkts Commerzbank Credit Agricole Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank DZ Bank EIU Nomura Novo Banco Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research UBS Unicredit Univ. Católica Portuguesa Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Fiscal Balance evolution of fcst Public Debt % of GDP Portugal Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from Statistics Portugal (INE, Instituto Nacional de Estatistica) and Eurostat. See below for details. Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 9 Real imports of goods and services, annual variation in %. Source: INE. Gross fixed investment, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Exports, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Imports, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Unemployment, % of active population. Source: INE. General government balance as % of GDP. Source: Eurostat. 5 General government balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 5
155 Portugal April 5 Monetary and External Sector Inflation and Current Account Balance 7 Inflation - 9 in % 8 Inflation Q -Q 6 in % Consumer Prices and Current Account Balance Inflation 5 evolution of fcst - 6 Portugal Maximum Consensus Minimum - Current Account % of GDP Portugal - Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 Inflation 6 evolution of fcst Maximum Consensus Minimum - Current Account evol. of fcst Prices (HICP) var. in % Current Acct % of GDP Individual Forecasts Banco BPI.... BBVA Research Berenberg Citigroup Global Mkts.... Commerzbank Credit Agricole Credit Suisse DekaBank Deutsche Bank....7 DZ Bank EIU..9.. Nomura Novo Banco Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research UBS.... Unicredit..8.. Univ. Católica Portuguesa.7... Summary Minimum Maximum Median.... Consensus.... History days ago days ago days ago Additional Forecasts Euro. Comm. (Feb. 5) IMF (Oct. ) Central Bank (Mar. 5).. 5 Portugal Notes and sources Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All monetary and external sector data are from Statistics Portugal (INE), Eurostat and the Bank of Portugal (BP). See below for details. Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. 6 Public debt as % of GDP. Source: Eurostat. 7 Inflation, annual average variation of harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) in %. Source: INE. 8 Inflation, annual variation of quarterly average harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) in %. Source: INE. 9 Inflation, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. Inflation, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. Current account balance as % of GDP. Source: BP. Current account balance as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 55
156 FOCUSECONOMICS Portugal April 5 Fact Sheet General Data Official name: Portuguese Republic Capital: Lisbon (.8m) cities: Porto (.m) Area (km): 9,9 Population (million, est.):.5 Population density (per km, ): Population growth rate (%, est.):. Life expectancy (years, est.): 79. Illiteracy rate (%, ):.6 Language: Portuguese and Mirandese Measures: Metric system Time: GMT Portugal in the Region Population %-share in Spain.%.% Italy 8.% Portugal.%.% France 9.% GDP %-share in Spain.%.8% Italy 5.6% Portugal.7% France.7% 8.% Economic Infrastructure Telecommunication () Telephones - main lines (per inhabitants):.7 Telephones - mobile cellular (per inhabit.): Internet Users (per inhabitants): 6. Broadband Subscriptions (per inhabitants):.8 Energy () Primary Energy Production (trillion Btu): 8 Primary Energy Consumption (trillion Btu): 978 Electricity Generation (billion kw-h):. Electricity Consumption (billion kw-h): 6.6 Oil Supply (thousand bpd): 5. Oil Consumption (thousand bpd): 7 CO Emmissions (million metric tons): 5. Economic Structure 8 6 GDP by Sector share in % GDP by Expenditure share in % Agriculture Manufacturing Industry Services Net Exports Investment Government Consumption Private Consumption Transportation () Airports: 6 Railways (km):,9 Roadways (km): 8,9 Waterways (km): Chief Ports: Leixoes, Lisbon, Setubal Trade Structure - Primary markets share in % Political Data Prime Minister: Pedro Passos Coelho Last elections: 5 June Next elections: October 5 Central Bank Governor: Carlos da Silva Costa Long-term Foreign Currency Ratings Agency Rating Outlook Moody s: Ba Stable S&P: BB Stable Fitch Ratings: BB+ Positive 5.% France.9% Exports.5% EU- 7 8.% Spain.7%.% France 6.6% Primary products share in % Imports.5% EU % Spain.% Strengths Highly developed logistics and communications infrastructure Attractive tourist destination Strong commitment to economic reforms Weaknesses Large fiscal deficit and public debt Limited size of manufacturing industry High exposure of banks to sovereign risk Mineral Fuels 7.% Food.% 6.9% Exports Manufact. Products 7.6% Mineral Fuels 7.5% Imports Manufact. Products 6.% 9.% FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 56
157 Slovakia April 5 Slovakia Slovakia Outlook stable LONG-TERM TRENDS -year averages Population (million): GDP (EUR bn): GDP per capita (EUR):,,69 6, GDP growth (%):...8 Fiscal Balance (% of GDP): Public Debt (% of GDP): Inflation (%):.5.7. Current Account (% of GDP):...9 The Slovakian economy picked up in, after a mild expansion in the previous year. Domestic demand was the main driver of growth last year, with private consumption and fixed investment posting strong results. In fact, private consumption grew for the first time in four years, underpinned by increased household income, improving labor market conditions and a rise in consumer sentiment. Investment swung from a sharp contraction in to a notable expansion in, mainly supported by investment in equipment. Growth momentum is expected to have carried over into 5, as suggested by improved consumer expectations and record-high business confidence in February. Consumer spending is likely to be the main factor driving economic growth this year, supported by continued improvement in the labor market and increased real household income due to low energy prices. Stronger exports derived from a weakened euro are also expected to contribute to growth. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecasts panelists expect GDP to expand.6% in 5, which is unchanged from last month s forecast. For 6, the panel sees economic growth picking up to.%. Harmonized consumer prices declined.5% annually in January, which represented a multi-year low (December: -.% year-on-year). The FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panel expects HICP inflation to average.% this year before rising to.7% in 6. Cecilia Simkievich Economist Gross Domestic Product variation in %.... %. Q Q Q Q Q 5 Note: Year-on-year changes of GDP in %. Source: Statistical Office of the Slovak Republic (SOSR) and FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. REAL SECTOR Economic growth stable in Q; GDP accelerates in full year In the fourth quarter, GDP grew.% over the same period of the previous year, according to official data released by the Statistical Office of the Slovak Republic (SOSR) on 6 March. The print matched both the preliminary estimate and the expansion registered in Q. On a sequential basis, the economy grew a seasonally-adjusted.6% in Q, which mirrored Q s result. Q s expansion mainly reflected that an acceleration in domestic demand was partially offset by a slowdown in exports. Domestic demand increased.7% over the same quarter of the previous year, which was up from the.% rise tallied in Q. Private consumption and government spending were the main factors behind the pick-up in domestic demand. Private consumption accelerated from a.6% rise in Q to a.% increase in Q. Government consumption rose.%, which marked an improvement from the.% increase in Q. Conversely, investment slowed from a 7.7% expansion to a 6.8% rise. On the external front, exports decelerated from Q s.6% growth to a mild.% increase in Q. Imports contracted.% in the final quarter of the year, which contrasted the.7% increase tallied in Q. Since imports fell faster than FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 57
158 Slovakia April 5 exports, the external sector s net contribution to overall economic growth rose from a flat reading in Q to plus.5 percentage points in Q. In the full year, GDP expanded.%, which marked a notable improvement over the.% expansion registered in. The National Bank of Slovakia (NBS) projects that GDP will grow.9% in 5 and.6% in 6. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast panelists expect GDP growth to reach.6% in 5, which is unchanged from last month s forecast. For 6, the panel projects that economic growth will accelerate to.%. Inflation Consumer Price Index. Month-on-month (left scale) Year-on-year (right scale).8.. MONETARY SECTOR Consumer prices drop into negative territory in January In January, consumer prices fell.% over the previous month, which came in above the.% decline tallied in December. January s reading mainly reflected lower prices for transport, as well as for clothing and footwear, and housing. Conversely, food and non-alcoholic beverages, as along with alcoholic beverages and tobacco recorded higher prices than in the previous month.. % Jan- Jul- Jan- Jul- Jan-5 Note: Month-on-month and year-on-year variation of consumer price index in %. Source: Statistical Office of the Slovak Republic (SOSR).. %. Consumer prices declined.% in January compared to the same month of last year, which contrasted the.% increase observed in December and marked the lowest reading since December 9. Meanwhile, the harmonized index of consumer prices fell.5% in annual terms in January, which was down from the.% decrease tallied in December and marked a multi-yearlow. The National Bank of Slovakia (NBS) expects HICP inflation to be flat in 5 and pick up to.% in 6. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast participants expect HICP inflation to average.% in 5, which is down. percentage points from last month s forecast. In 6, the panel expects HICP inflation to increase to.7%. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 58
159 Economic Indicators - 9 Slovakia April 5 Annual Data Real Sector Population (million) GDP per capita (USD) 6, 8,5 7,7 8,6 8,8 5,67 5,785 7,6 8,97,69 GDP (USD bn) GDP per capita (EUR),95,,58,6,885,86,95 5,668 6, 7,8 GDP (EUR bn) Economic Growth (Nominal GDP, ann. var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Private Consumption (annual var. in %) Government Consumption (ann. var. in %) Fixed Investment (annual var. in %) Industrial Production (annual var. in %) Retail Sales (annual variation in %) Unemployment (% of active population, aop) Fiscal Balance (% of GDP) Public Debt (% of GDP) Monetary and Financial Sector Money (annual variation of M in %, eop) Inflation (CPI, annual variation in %, eop) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) Inflation (PPI, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, aop) External Sector Current Account Balance (% of GDP) Current Account Balance (EUR bn) Merchandise Trade Balance (EUR bn) Merchandise Exports (EUR bn) Merchandise Imports (EUR bn) Merchandise Exports (annual variation in %) Merchandise Imports (annual variation in %) External Debt (EUR bn) External Debt (% of GDP) Quarterly Data Q Q Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 5 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Q 6 Economic Growth (GDP, annual var. in %) Economic Growth (GDP, s.a. qoq var. in %) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %, aop) ECB Refinancing Rate (%, eop) Month EURIBOR (%, eop) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) Monthly Data May- Jun- Jul- Aug- Sep- Oct- Nov- Dec- Jan-5 Feb-5 Industrial Production (annual variation in %) Unemployment (% of active population) Inflation (CPI, mom variation in %) Inflation (CPI, annual variation in %) Inflation (HICP, annual variation in %) Exchange Rate (USD per EUR, eop) FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 59
160 Real Sector Gross Domestic Product and Fiscal Balance Slovakia April 5 Real GDP - 9 var. in % Real GDP Q -Q 6 var. in % Economic Growth and Fiscal Balance Slovakia Eastern Europe World GDP 5 evolution of forecasts Maximum Consensus Minimum Oct Jan Apr Jul Oct Jan Slovakia Eastern Europe World - Q Q Q Q 5 Q 6 GDP 6 evolution of forecasts Maximum Consensus Minimum. Oct Jan Apr Jul Oct Jan Real GDP Fiscal Balance variation in % % of GDP Individual Forecasts Capital Economics Citigroup Global Mkts CSOB DekaBank EIU Erste Bank Experian Frontier Strategy Group Komerční Banka OTP Bank Oxford Economics Raiffeisen Research UniCredit VÚB Banka WIIW Summary Minimum Maximum Median Consensus History days ago days ago days ago Additional Forecasts Central Bank (Jan. 5) Euro. Comm. (Feb. 5) IMF (Oct. ) Unemployment % of active pop. 6 Fiscal Balance % of GDP 5 Slovakia Eastern Europe Slovakia Eastern Europe Unemployment evolution of fcst Oct Jan Apr Jul Oct Jan 8 Fiscal Balance evolution of fcst Oct Jan Apr Jul Oct Jan Notes and sources General: Long-term chart period from to 9 unless otherwise stated. All real sector data are from the Statistical Office of the Slovak Republic (SOSR, Statisticky urad Slovenskej republiky). Forecasts based on FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast. GDP, annual variation in %. Quarterly GDP (not seasonally adjusted), year-on-year variation in %. GDP, evolution of 5 forecasts during the last 8 months. GDP, evolution of 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 5 Unemployment, % of active population. 6 Balance of non-financial public sector as % of GDP. 7 Unemployment, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. 8 Balance of non-financial public sector as % of GDP, evolution of 5 and 6 forecasts during the last 8 months. FocusEconomics Consensus Forecast 6
Eurozone. Economic Watch FEBRUARY 2017
 Eurozone Economic Watch FEBRUARY 2017 EUROZONE WATCH FEBRUARY 2017 Eurozone: A slight upward revision to our GDP growth projections The recovery proceeded at a steady and solid pace in, resulting in an
Eurozone Economic Watch FEBRUARY 2017 EUROZONE WATCH FEBRUARY 2017 Eurozone: A slight upward revision to our GDP growth projections The recovery proceeded at a steady and solid pace in, resulting in an
Main Economic & Financial Indicators Eurozone
 Main Economic & Financial Indicators Eurozone 7 MAY 2015 AKIKO DARVELL ASSOCIATE ECONOMIST ECONOMIC RESEARCH OFFICE (LONDON) T +44(0)2075771591 E akiko.darvell@uk.mufg.jp The Bank of TokyoMitsubishi UFJ,
Main Economic & Financial Indicators Eurozone 7 MAY 2015 AKIKO DARVELL ASSOCIATE ECONOMIST ECONOMIC RESEARCH OFFICE (LONDON) T +44(0)2075771591 E akiko.darvell@uk.mufg.jp The Bank of TokyoMitsubishi UFJ,
Main Economic & Financial Indicators Eurozone
 Main Economic & Financial Indicators Eurozone 30 MARCH 2015 AKIKO DARVELL ASSOCIATE ECONOMIST ECONOMIC RESEARCH OFFICE (LONDON) T +44(0)2075771591 E akiko.darvell@uk.mufg.jp The Bank of TokyoMitsubishi
Main Economic & Financial Indicators Eurozone 30 MARCH 2015 AKIKO DARVELL ASSOCIATE ECONOMIST ECONOMIC RESEARCH OFFICE (LONDON) T +44(0)2075771591 E akiko.darvell@uk.mufg.jp The Bank of TokyoMitsubishi
Eurozone Economic Watch Higher growth forecasts for January 2018
 Eurozone Economic Watch Higher growth forecasts for 2018-19 January 2018 Eurozone Economic Watch January 2018 Eurozone: Higher growth forecasts for 2018-19 Our MICA-BBVA model estimates a broadly stable
Eurozone Economic Watch Higher growth forecasts for 2018-19 January 2018 Eurozone Economic Watch January 2018 Eurozone: Higher growth forecasts for 2018-19 Our MICA-BBVA model estimates a broadly stable
Main Economic & Financial Indicators Eurozone
 Main Economic & Financial Indicators Eurozone 03 NOVEMBER 2015 AKIKO DARVELL ASSOCIATE ECONOMIST ECONOMIC RESEARCH OFFICE (LONDON) T +44-(0)20-7577-1591 E akiko.darvell@uk.mufg.jp The Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi
Main Economic & Financial Indicators Eurozone 03 NOVEMBER 2015 AKIKO DARVELL ASSOCIATE ECONOMIST ECONOMIC RESEARCH OFFICE (LONDON) T +44-(0)20-7577-1591 E akiko.darvell@uk.mufg.jp The Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi
Main Economic & Financial Indicators Eurozone
 Main Economic & Financial Indicators Eurozone 4 MARCH 2015 AKIKO DARVELL ASSOCIATE ECONOMIST ECONOMIC RESEARCH OFFICE (LONDON) T +44(0)2075771591 E akiko.darvell@uk.mufg.jp The Bank of TokyoMitsubishi
Main Economic & Financial Indicators Eurozone 4 MARCH 2015 AKIKO DARVELL ASSOCIATE ECONOMIST ECONOMIC RESEARCH OFFICE (LONDON) T +44(0)2075771591 E akiko.darvell@uk.mufg.jp The Bank of TokyoMitsubishi
Eurozone Economic Watch. November 2017
 Eurozone Economic Watch November 2017 Eurozone: improved outlook, still subdued inflation Our MICA-BBVA model for growth estimates for the moment a quarterly GDP figure of around -0.7% in, after % QoQ
Eurozone Economic Watch November 2017 Eurozone: improved outlook, still subdued inflation Our MICA-BBVA model for growth estimates for the moment a quarterly GDP figure of around -0.7% in, after % QoQ
Main Economic & Financial Indicators Eurozone
 Main Economic & Financial Indicators Eurozone 24 DECEMBER 2015 AKIKO DARVELL ASSOCIATE ECONOMIST ECONOMIC RESEARCH OFFICE (LONDON) T +44-(0)20-7577-1591 E akiko.darvell@uk.mufg.jp The Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi
Main Economic & Financial Indicators Eurozone 24 DECEMBER 2015 AKIKO DARVELL ASSOCIATE ECONOMIST ECONOMIC RESEARCH OFFICE (LONDON) T +44-(0)20-7577-1591 E akiko.darvell@uk.mufg.jp The Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi
Main Economic & Financial Indicators Eurozone
 Main Economic & Financial Indicators Eurozone 28 JANUARY 2016 AKIKO DARVELL ASSOCIATE ECONOMIST ECONOMIC RESEARCH OFFICE (LONDON) T +44(0)2075771591 E akiko.darvell@uk.mufg.jp The Bank of TokyoMitsubishi
Main Economic & Financial Indicators Eurozone 28 JANUARY 2016 AKIKO DARVELL ASSOCIATE ECONOMIST ECONOMIC RESEARCH OFFICE (LONDON) T +44(0)2075771591 E akiko.darvell@uk.mufg.jp The Bank of TokyoMitsubishi
Main Economic & Financial Indicators Eurozone
 Main Economic & Financial Indicators Eurozone 30 NOVEMBER 2015 AKIKO DARVELL ASSOCIATE ECONOMIST ECONOMIC RESEARCH OFFICE (LONDON) T +44(0)2075771591 E akiko.darvell@uk.mufg.jp The Bank of TokyoMitsubishi
Main Economic & Financial Indicators Eurozone 30 NOVEMBER 2015 AKIKO DARVELL ASSOCIATE ECONOMIST ECONOMIC RESEARCH OFFICE (LONDON) T +44(0)2075771591 E akiko.darvell@uk.mufg.jp The Bank of TokyoMitsubishi
Fixed Income. EURO SOVEREIGN OUTLOOK SIX PRINCIPAL INFLUENCES TO CONSIDER IN 2016.
 PRICE POINT February 2016 Timely intelligence and analysis for our clients. Fixed Income. EURO SOVEREIGN OUTLOOK SIX PRINCIPAL INFLUENCES TO CONSIDER IN 2016. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Kenneth Orchard Portfolio
PRICE POINT February 2016 Timely intelligence and analysis for our clients. Fixed Income. EURO SOVEREIGN OUTLOOK SIX PRINCIPAL INFLUENCES TO CONSIDER IN 2016. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Kenneth Orchard Portfolio
Eurozone. EY Eurozone Forecast September 2013
 Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast September 213 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for Greece Rising
Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast September 213 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for Greece Rising
Short-term indicators and Updated Forecasts. Eurozone NOVEMBER 2016
 Short-term indicators and Updated Forecasts Eurozone NOVEMBER 2016 EUROZONE WATCH NOVEMBER 2016 Key messages: resilience and unchanged projections The moderate pace of economic growth continued in the
Short-term indicators and Updated Forecasts Eurozone NOVEMBER 2016 EUROZONE WATCH NOVEMBER 2016 Key messages: resilience and unchanged projections The moderate pace of economic growth continued in the
Eurozone. EY Eurozone Forecast September 2014
 Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast September 2014 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for
Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast September 2014 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for
Eurozone Economic Watch. July 2018
 Eurozone Economic Watch July 2018 Eurozone: A shift to more moderate growth with increased downward risks BBVA Research - Eurozone Economic Watch July 2018 / 2 Hard data improved in May but failed to recover
Eurozone Economic Watch July 2018 Eurozone: A shift to more moderate growth with increased downward risks BBVA Research - Eurozone Economic Watch July 2018 / 2 Hard data improved in May but failed to recover
Eurozone. EY Eurozone Forecast June 2014
 Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast June 214 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for Slovenia
Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast June 214 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for Slovenia
Eurozone Economic Watch. April 2018
 Eurozone Economic Watch April 2018 Eurozone: solid growth and broadly unchanged projections, with protectionist risks BBVA Research - Eurozone Economic Watch / 2 Confidence has weakened in 1Q18 since the
Eurozone Economic Watch April 2018 Eurozone: solid growth and broadly unchanged projections, with protectionist risks BBVA Research - Eurozone Economic Watch / 2 Confidence has weakened in 1Q18 since the
Eurozone. EY Eurozone Forecast December 2013
 Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast December 213 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for Germany Strong
Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast December 213 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for Germany Strong
EUROZONE ECONOMIC WATCH JANUARY 2017
 EUROZONE ECONOMIC WATCH JANUARY 2017 Key messages: some changes for the better Improving confidence in across the board shows the resilience of the eurozone to the various potentially disturbing political
EUROZONE ECONOMIC WATCH JANUARY 2017 Key messages: some changes for the better Improving confidence in across the board shows the resilience of the eurozone to the various potentially disturbing political
Eurozone Economic Watch. May 2018
 Eurozone Economic Watch May 2018 BBVA Research - Eurozone Economic Watch / 2 Eurozone: more moderate growth with higher uncertainty The eurozone GDP growth slowed in more than expected. Beyond temporary
Eurozone Economic Watch May 2018 BBVA Research - Eurozone Economic Watch / 2 Eurozone: more moderate growth with higher uncertainty The eurozone GDP growth slowed in more than expected. Beyond temporary
The European Economy. Simon Barry Chief Economist Republic of Ireland. December 2012
 The European Economy Simon Barry Chief Economist Republic of Ireland December 212 Euro area economy now back in recession as GDP contracts in 3 of the past 4 quarters Euro Area Real GDP Growth, % 1.5 1..5.
The European Economy Simon Barry Chief Economist Republic of Ireland December 212 Euro area economy now back in recession as GDP contracts in 3 of the past 4 quarters Euro Area Real GDP Growth, % 1.5 1..5.
Eurozone. EY Eurozone Forecast September 2013
 Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast September 213 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for Germany
Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast September 213 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for Germany
Eurozone. EY Eurozone Forecast June 2014
 Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast June 2014 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for exits bailout,
Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast June 2014 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for exits bailout,
Eurozone Economic Watch. March 2018
 Eurozone Economic Watch March 20 Eurozone Economic Watch March 20 Eurozone: The moderation of confidence continues We expect GDP growth to remain steady early this year supported mostly by strong global
Eurozone Economic Watch March 20 Eurozone Economic Watch March 20 Eurozone: The moderation of confidence continues We expect GDP growth to remain steady early this year supported mostly by strong global
Eurozone Ernst & Young Eurozone Forecast Spring edition March 2013
 Eurozone Ernst & Young Eurozone Forecast Spring edition March 2013 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain
Eurozone Ernst & Young Eurozone Forecast Spring edition March 2013 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain
The real change in private inventories added 0.22 percentage points to the second quarter GDP growth, after subtracting 0.65% in the first quarter.
 QIRGRETA Monthly Macroeconomic Commentary United States The U.S. economy bounced back in the second quarter of 2007, growing at the fastest pace in more than a year. According the final estimates released
QIRGRETA Monthly Macroeconomic Commentary United States The U.S. economy bounced back in the second quarter of 2007, growing at the fastest pace in more than a year. According the final estimates released
Eurozone. EY Eurozone Forecast March 2015
 Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast March 2015 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for Modest
Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast March 2015 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for Modest
Eurozone Economic Watch. February 2018
 Eurozone Economic Watch February 2018 Eurozone: Strong growth continues in 1Q18, but confidence seems to peak GDP growth moderated slightly in, but there was an upward revision to previous quarters. Available
Eurozone Economic Watch February 2018 Eurozone: Strong growth continues in 1Q18, but confidence seems to peak GDP growth moderated slightly in, but there was an upward revision to previous quarters. Available
Eurozone. EY Eurozone Forecast March 2015
 Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast March 2015 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook
Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast March 2015 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook
Eurozone. EY Eurozone Forecast March 2014
 Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast March 2014 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for Germany
Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast March 2014 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for Germany
Eurozone Ernst & Young Eurozone Forecast Spring edition March 2012
 Eurozone Ernst & Young Eurozone Forecast Spring edition March 2012 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain
Eurozone Ernst & Young Eurozone Forecast Spring edition March 2012 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain
The real change in private inventories added 0.15 percentage points to the second quarter GDP growth, after subtracting 0.65% in the first quarter.
 QIRGRETA Monthly Macroeconomic Commentary United States The U.S. economy rebounded in the second quarter of 2007, growing at an annual rate of 3.4% Q/Q (+1.8% Y/Y), according to the GDP advance estimates
QIRGRETA Monthly Macroeconomic Commentary United States The U.S. economy rebounded in the second quarter of 2007, growing at an annual rate of 3.4% Q/Q (+1.8% Y/Y), according to the GDP advance estimates
Main Economic & Financial Indicators Eurozone
 Main Economic & Financial Indicators Eurozone 13 JULY 2015 AKIKO DARVELL ASSOCIATE ECONOMIST ECONOMIC RESEARCH OFFICE (LONDON) T +44(0)2075771591 E akiko.darvell@uk.mufg.jp The Bank of TokyoMitsubishi
Main Economic & Financial Indicators Eurozone 13 JULY 2015 AKIKO DARVELL ASSOCIATE ECONOMIST ECONOMIC RESEARCH OFFICE (LONDON) T +44(0)2075771591 E akiko.darvell@uk.mufg.jp The Bank of TokyoMitsubishi
Eurozone. EY Eurozone Forecast September 2014
 Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast September 2014 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for
Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast September 2014 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for
CONSENSUS FORECAST. Greece April Contributors GREECE 2 CALENDAR 11 NOTES 13
 CONSENSUS FORECAST April 215 GREECE 2 CALENDAR 11 NOTES 13 PUBLICATION DATE 31 March 215 FORECASTS COLLECTED 24 March - 3 March 215 INFORMATION AVAILABLE Up to and including 3 March 215 NEXT EDITION 5
CONSENSUS FORECAST April 215 GREECE 2 CALENDAR 11 NOTES 13 PUBLICATION DATE 31 March 215 FORECASTS COLLECTED 24 March - 3 March 215 INFORMATION AVAILABLE Up to and including 3 March 215 NEXT EDITION 5
Europe Outlook. Third Quarter 2015
 Europe Outlook Third Quarter 2015 Main messages 1 2 3 4 5 Moderation of global growth and slowdown in emerging economies, with downside risks The recovery continues in the eurozone, but still marked by
Europe Outlook Third Quarter 2015 Main messages 1 2 3 4 5 Moderation of global growth and slowdown in emerging economies, with downside risks The recovery continues in the eurozone, but still marked by
Eurozone Economic Watch
 BBVA Research Eurozone Economic Watch November 2018 / 1 Eurozone Economic Watch November 2018 Eurozone: Growth to recover in 4Q18, but concerns about the slowdown next year are growing Eurozone GDP growth
BBVA Research Eurozone Economic Watch November 2018 / 1 Eurozone Economic Watch November 2018 Eurozone: Growth to recover in 4Q18, but concerns about the slowdown next year are growing Eurozone GDP growth
Insolvency forecasts. Economic Research August 2017
 Insolvency forecasts Economic Research August 2017 Summary We present our new insolvency forecasting model which offers a broader scope of macroeconomic developments to better predict insolvency developments.
Insolvency forecasts Economic Research August 2017 Summary We present our new insolvency forecasting model which offers a broader scope of macroeconomic developments to better predict insolvency developments.
Zenith Monthly Economic Report October 2011
 Zenith Monthly Economic Report October 211 ECONOMIC STATISTICS SUMMARY Cash Rate Inflation Rate (%) Unemployment Rate (%) GDP Annual Growth (%) Country Latest Last Change Latest Change Latest Change Past
Zenith Monthly Economic Report October 211 ECONOMIC STATISTICS SUMMARY Cash Rate Inflation Rate (%) Unemployment Rate (%) GDP Annual Growth (%) Country Latest Last Change Latest Change Latest Change Past
Eurozone. EY Eurozone Forecast March 2015
 Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast March 2015 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook
Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast March 2015 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook
Global PMI. Global economic growth kicks higher at start of fourth quarter but outlook darkens. November 14 th 2016
 Global PMI Global economic growth kicks higher at start of fourth quarter but outlook darkens November 14 th 2016 2 Global PMI at 11-month high in October Global economic growth kicked higher at the start
Global PMI Global economic growth kicks higher at start of fourth quarter but outlook darkens November 14 th 2016 2 Global PMI at 11-month high in October Global economic growth kicked higher at the start
Previsions Macroeconòmiques. Macroeconomic scenario for the Catalan economy 2017 and June 2017
 PM Previsions Macroeconòmiques Macroeconomic scenario for the Catalan economy 2017 and 2018 June 2017 Previsions macroeconòmiques Macroeconomic scenario for the Catalan economy June 2017 ISSN: 2013-2182
PM Previsions Macroeconòmiques Macroeconomic scenario for the Catalan economy 2017 and 2018 June 2017 Previsions macroeconòmiques Macroeconomic scenario for the Catalan economy June 2017 ISSN: 2013-2182
Eurozone. EY Eurozone Forecast June 2014
 Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast June 2014 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for Finland
Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast June 2014 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for Finland
Eurozone. EY Eurozone Forecast September 2014
 Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast September 214 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for Cyprus
Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast September 214 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for Cyprus
Eurozone. EY Eurozone Forecast September 2013
 Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast September 2013 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for Ireland
Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast September 2013 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for Ireland
B-GUIDE: Economic Outlook
 Aug-12 Apr-13 Dec-13 Aug-14 Apr-15 Dec-15 Aug-16 Apr-17 Jul-15 Nov-15 Mar-16 Jul-16 Nov-16 Mar-17 Jul-17 Quarterly Economic Outlook: Quarter 4 2017 4 January 2018 B-GUIDE: Economic Outlook The economy
Aug-12 Apr-13 Dec-13 Aug-14 Apr-15 Dec-15 Aug-16 Apr-17 Jul-15 Nov-15 Mar-16 Jul-16 Nov-16 Mar-17 Jul-17 Quarterly Economic Outlook: Quarter 4 2017 4 January 2018 B-GUIDE: Economic Outlook The economy
Editor: Felix Ewert. The Week Ahead Key Events Mar 2018
 Editor: Felix Ewert The Week Ahead Key Events 12 18 Mar 2018 Monday 12, 08.00 SWE: Unemployment, registered (Feb) SEB Cons. Prev. Open 3.9 --- 4.0 Open, seas. adj. 3.8 --- 3.8 Total seas. adj. 7.1 ---
Editor: Felix Ewert The Week Ahead Key Events 12 18 Mar 2018 Monday 12, 08.00 SWE: Unemployment, registered (Feb) SEB Cons. Prev. Open 3.9 --- 4.0 Open, seas. adj. 3.8 --- 3.8 Total seas. adj. 7.1 ---
Ranking Country Page. Category 1: Countries with positive CEP Default Index and positive NTE. 1 Estonia 1. 2 Luxembourg 2.
 Overview: Single Results of Euro Countries Ranking Country Page Category 1: Countries with positive CEP Default Index and positive NTE 1 Estonia 1 2 Luxembourg 2 3 Germany 3 4 Netherlands 4 5 Austria 5
Overview: Single Results of Euro Countries Ranking Country Page Category 1: Countries with positive CEP Default Index and positive NTE 1 Estonia 1 2 Luxembourg 2 3 Germany 3 4 Netherlands 4 5 Austria 5
SEE macroeconomic outlook Recovery gains traction, fiscal discipline improving. Alen Kovac, Chief Economist EBC May 2016 Ljubljana
 SEE macroeconomic outlook Recovery gains traction, fiscal discipline improving Alen Kovac, Chief Economist EBC May 216 Ljubljana Real economy highlights Recent GDP track record reveals more favorable footprint
SEE macroeconomic outlook Recovery gains traction, fiscal discipline improving Alen Kovac, Chief Economist EBC May 216 Ljubljana Real economy highlights Recent GDP track record reveals more favorable footprint
Eurozone Economic Watch
 BBVA Research - Global Economic Watch December 2018 / 1 Eurozone Economic Watch December 2018 Eurozone GDP growth still slows gradually, but high uncertainty could take its toll GDP growth could grow by
BBVA Research - Global Economic Watch December 2018 / 1 Eurozone Economic Watch December 2018 Eurozone GDP growth still slows gradually, but high uncertainty could take its toll GDP growth could grow by
CONSENSUS FORECAST. Portugal April Contributors PORTUGAL 2 CALENDAR 10 NOTES 12
 CONSENSUS FORECAST PORTUGAL 2 CALENDAR 10 NOTES 12 PUBLICATION DATE 31 March 2015 FORECASTS COLLECTED 24 March - 30 March 2015 INFORMATION AVAILABLE Up to and including 30 March 2015 NEXT EDITION 5 May
CONSENSUS FORECAST PORTUGAL 2 CALENDAR 10 NOTES 12 PUBLICATION DATE 31 March 2015 FORECASTS COLLECTED 24 March - 30 March 2015 INFORMATION AVAILABLE Up to and including 30 March 2015 NEXT EDITION 5 May
LKP SECURITIES LIMITED 13th Floor Raheja Center, Free Press Marg, Nariman Point, Mumbai
 Free Press Marg, Nariman Point, Mumbai-400021 Item Open High Low Close % Cng Net Cng Trend Market Update Gold $ Silver $ LME Alum. LME Copper LME Lead LME Nickel LME Zinc Crude $ Nat. Gas $ Precious Metals
Free Press Marg, Nariman Point, Mumbai-400021 Item Open High Low Close % Cng Net Cng Trend Market Update Gold $ Silver $ LME Alum. LME Copper LME Lead LME Nickel LME Zinc Crude $ Nat. Gas $ Precious Metals
OVERVIEW. The EU recovery is firming. Table 1: Overview - the winter 2014 forecast Real GDP. Unemployment rate. Inflation. Winter 2014 Winter 2014
 OVERVIEW The EU recovery is firming Europe's economic recovery, which began in the second quarter of 2013, is expected to continue spreading across countries and gaining strength while at the same time
OVERVIEW The EU recovery is firming Europe's economic recovery, which began in the second quarter of 2013, is expected to continue spreading across countries and gaining strength while at the same time
Eurozone. EY Eurozone Forecast September 2014
 Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast September 214 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for Slovenia
Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast September 214 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for Slovenia
Eurozone. EY Eurozone Forecast March 2015
 Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast March 2015 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for
Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast March 2015 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for
2016 Economic Outlook for Ireland & Eurozone IFP Launch
 2016 Economic Outlook for Ireland & Eurozone IFP Launch December 3 rd 2015 Jim Power Global Background US & UK growing at reasonable pace Euro Zone growing well below potential Emerging markets in some
2016 Economic Outlook for Ireland & Eurozone IFP Launch December 3 rd 2015 Jim Power Global Background US & UK growing at reasonable pace Euro Zone growing well below potential Emerging markets in some
CALENDAR 14 UNITED STATES
 CONSENSUS FORECAST Major Economies SUMMARY CALENDAR 1 UNITED STATES 16 CANADA 1 JAPAN UNITED KINGDOM 59 EURO AREA 7 FRANCE 89 GERMANY 1 ITALY 11 NOTES 16 PUBLICATION DATE 1 March 15 FORECASTS COLLECTED
CONSENSUS FORECAST Major Economies SUMMARY CALENDAR 1 UNITED STATES 16 CANADA 1 JAPAN UNITED KINGDOM 59 EURO AREA 7 FRANCE 89 GERMANY 1 ITALY 11 NOTES 16 PUBLICATION DATE 1 March 15 FORECASTS COLLECTED
Eurozone. EY Eurozone Forecast March 2014
 Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast March 214 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for Estonia
Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast March 214 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for Estonia
Italy s Eurozone Trap
 Italy s Eurozone Trap Ashoka Mody Based on EuroTragedy: A Drama in Nine Acts, New York: Oxford University Press, June 2018. Italy needed and needs the crutch of a depreciating currency to offset its abysmal
Italy s Eurozone Trap Ashoka Mody Based on EuroTragedy: A Drama in Nine Acts, New York: Oxford University Press, June 2018. Italy needed and needs the crutch of a depreciating currency to offset its abysmal
THE EU S ECONOMIC RECOVERY PICKS UP MOMENTUM
 THE EU S ECONOMIC RECOVERY PICKS UP MOMENTUM ECONOMIC SITUATION The EU economy saw a pick-up in growth momentum at the beginning of this year, boosted by strong business and consumer confidence. Output
THE EU S ECONOMIC RECOVERY PICKS UP MOMENTUM ECONOMIC SITUATION The EU economy saw a pick-up in growth momentum at the beginning of this year, boosted by strong business and consumer confidence. Output
Zenith Monthly Economic Report December 2011
 Zenith Monthly Economic Report December 211 ECONOMIC STATISTICS SUMMARY Cash Rate Inflation Rate (%) Unemployment Rate (%) GDP Annual Growth (%) Country Latest Last Change Latest Change Latest Change Past
Zenith Monthly Economic Report December 211 ECONOMIC STATISTICS SUMMARY Cash Rate Inflation Rate (%) Unemployment Rate (%) GDP Annual Growth (%) Country Latest Last Change Latest Change Latest Change Past
Financial Market Outlook: Further Stock Gain on Faster GDP Rebound and Earnings Recovery. Year-end Target Raised
 For Market Commentary Interviews Contact: Lisa Villareal, 973-367-2503/lisa.villareal@prudential.com Financial Market Outlook & Strategy: FurtherStock Gains Likely, Year-end Target Raised. Bond Under Pressure
For Market Commentary Interviews Contact: Lisa Villareal, 973-367-2503/lisa.villareal@prudential.com Financial Market Outlook & Strategy: FurtherStock Gains Likely, Year-end Target Raised. Bond Under Pressure
Economic ProjEctions for
 Economic Projections for 2016-2018 ECONOMIC PROJECTIONS FOR 2016-2018 Outlook for the Maltese economy 1 Economic growth is expected to ease Following three years of strong expansion, the Bank s latest
Economic Projections for 2016-2018 ECONOMIC PROJECTIONS FOR 2016-2018 Outlook for the Maltese economy 1 Economic growth is expected to ease Following three years of strong expansion, the Bank s latest
NBS MoNthly BulletiN NoveMBer 2016
 Published by: Národná banka Slovenska Address: Národná banka Slovenska Imricha Karvaša 1, 813 5 Bratislava Slovakia Contact: +1//5787 1 http://www.nbs.sk Discussed by the Bank Board on November. All rights
Published by: Národná banka Slovenska Address: Národná banka Slovenska Imricha Karvaša 1, 813 5 Bratislava Slovakia Contact: +1//5787 1 http://www.nbs.sk Discussed by the Bank Board on November. All rights
The Cyprus Economy: from Recovery to Sustainable Growth. Vincenzo Guzzo Resident Representative in Cyprus
 The Economy: from Recovery to Sustainable Growth Vincenzo Guzzo Resident Representative in Growth momentum remains strong 18 : Real GDP ( billion) 1 Deviation from Pre-Crisis Level and Trend (Percent)
The Economy: from Recovery to Sustainable Growth Vincenzo Guzzo Resident Representative in Growth momentum remains strong 18 : Real GDP ( billion) 1 Deviation from Pre-Crisis Level and Trend (Percent)
DEVELOPMENTS IN THE COST COMPETITIVENESS OF THE EUROPEAN UNION, THE UNITED STATES AND JAPAN MAIN FEATURES
 DEVELOPMENTS IN THE COST COMPETITIVENESS OF THE EUROPEAN UNION, THE UNITED STATES AND JAPAN MAIN FEATURES The euro against major international currencies: During the second quarter of 2000, the US dollar,
DEVELOPMENTS IN THE COST COMPETITIVENESS OF THE EUROPEAN UNION, THE UNITED STATES AND JAPAN MAIN FEATURES The euro against major international currencies: During the second quarter of 2000, the US dollar,
CONSENSUS FORECAST. Eastern Europe April Contributors
 CONSENSUS FORECAST April 1 SUMMARY CALENDAR 1 BULGARIA 17 CROATIA CZECH REP. 9 ESTONIA HUNGARY LATVIA 6 LITHUANIA 71 POLAND 77 ROMANIA 9 RUSSIA 11 SLOVAKIA 119 SLOVENIA 1 TURKEY 11 UKRAINE 17 NOTES 16
CONSENSUS FORECAST April 1 SUMMARY CALENDAR 1 BULGARIA 17 CROATIA CZECH REP. 9 ESTONIA HUNGARY LATVIA 6 LITHUANIA 71 POLAND 77 ROMANIA 9 RUSSIA 11 SLOVAKIA 119 SLOVENIA 1 TURKEY 11 UKRAINE 17 NOTES 16
Second JCER-OMFIF seminar
 Second JCER-OMFIF seminar State of play of ECB monetary policy The problems of shared sovereignty David Marsh, Managing Director, OMFIF Tokyo, 22 November 217 The ECB s QE next steps Buoyant euro area
Second JCER-OMFIF seminar State of play of ECB monetary policy The problems of shared sovereignty David Marsh, Managing Director, OMFIF Tokyo, 22 November 217 The ECB s QE next steps Buoyant euro area
Economic activity gathers pace
 Produced by the Economic Research Unit October 2014 A quarterly analysis of trends in the Irish economy Economic activity gathers pace Positive data flow Recovery broadening out GDP growth revised up to
Produced by the Economic Research Unit October 2014 A quarterly analysis of trends in the Irish economy Economic activity gathers pace Positive data flow Recovery broadening out GDP growth revised up to
CECIMO Statistical Toolbox
 European Association of the Machine Tool Industries where manufacturing begins Inside this edition... 0 Executive Summary 1 Machine Tool Orders 1.1 Orders per Country 1.2 Peter Meier s Forecast CECIMO
European Association of the Machine Tool Industries where manufacturing begins Inside this edition... 0 Executive Summary 1 Machine Tool Orders 1.1 Orders per Country 1.2 Peter Meier s Forecast CECIMO
Markit Global Business Outlook
 News Release Markit Global Business Outlook EMBARGOED UNTIL: 00:01, 16 March 2015 Global business confidence and hiring intentions slip to post-crisis low Expectations regarding activity and employment
News Release Markit Global Business Outlook EMBARGOED UNTIL: 00:01, 16 March 2015 Global business confidence and hiring intentions slip to post-crisis low Expectations regarding activity and employment
The Prospects Service
 The Prospects Service LEADING ECONOMIC ANALYSIS, FORECASTS AND DATA Global Prospects, September 2017 Toplines The combination of rising consumer confidence, low borrowing costs and declining unemployment
The Prospects Service LEADING ECONOMIC ANALYSIS, FORECASTS AND DATA Global Prospects, September 2017 Toplines The combination of rising consumer confidence, low borrowing costs and declining unemployment
Editor: Felix Ewert. The Week Ahead Key Events 29 Jan 4 Feb, 2018
 Editor: Felix Ewert The Week Ahead Key Events 29 Jan 4 Feb, 2018 Tuesday 30, 08.00 NOR: Retail sales (Dec) % mom/yoy SEB Cons. Prev. Retail sales exc. autos -0.5/4.5-0.7/--- 2.1/3.5 Retail sales surged
Editor: Felix Ewert The Week Ahead Key Events 29 Jan 4 Feb, 2018 Tuesday 30, 08.00 NOR: Retail sales (Dec) % mom/yoy SEB Cons. Prev. Retail sales exc. autos -0.5/4.5-0.7/--- 2.1/3.5 Retail sales surged
March 2005 Euro-zone external trade surplus 4.2 bn euro 6.5 bn euro deficit for EU25
 STAT/05/67 24 May 2005 March 2005 Euro-zone external trade surplus 4.2 6.5 deficit for EU25 The first estimate for euro-zone 1 trade with the rest of the world in March 2005 was a 4.2 billion euro surplus,
STAT/05/67 24 May 2005 March 2005 Euro-zone external trade surplus 4.2 6.5 deficit for EU25 The first estimate for euro-zone 1 trade with the rest of the world in March 2005 was a 4.2 billion euro surplus,
Economic Indicators. Roland Berger Institute
 Economic Indicators Roland Berger Institute October 2017 Overview Key points Economic Indicators A publication, compiled by the Roland Berger Institute, that provides you with the most important macroeconomic
Economic Indicators Roland Berger Institute October 2017 Overview Key points Economic Indicators A publication, compiled by the Roland Berger Institute, that provides you with the most important macroeconomic
Euro-QE at the end of the road for now
 Germany France Italy Agencies Spain Netherlands Belgium Austria Portugal Finland Ireland Slovakia Slovenia Lux Latvia Lithuania Malta 7.8 2.6 2.1 3.21 1.17 Trend Macrolytics, LLC Donald Luskin, Chief Investment
Germany France Italy Agencies Spain Netherlands Belgium Austria Portugal Finland Ireland Slovakia Slovenia Lux Latvia Lithuania Malta 7.8 2.6 2.1 3.21 1.17 Trend Macrolytics, LLC Donald Luskin, Chief Investment
Global PMI. Solid Q2 growth masks widening growth differentials. July 7 th IHS Markit. All Rights Reserved.
 Global PMI Solid Q2 growth masks widening growth differentials July 7 th 2017 2 Widening developed and emerging world growth trends The global economy enjoyed further steady growth in June, according to
Global PMI Solid Q2 growth masks widening growth differentials July 7 th 2017 2 Widening developed and emerging world growth trends The global economy enjoyed further steady growth in June, according to
ILO World of Work Report 2013: EU Snapshot
 Greece Spain Ireland Poland Belgium Portugal Eurozone France Slovenia EU-27 Cyprus Denmark Netherlands Italy Bulgaria Slovakia Romania Lithuania Latvia Czech Republic Estonia Finland United Kingdom Sweden
Greece Spain Ireland Poland Belgium Portugal Eurozone France Slovenia EU-27 Cyprus Denmark Netherlands Italy Bulgaria Slovakia Romania Lithuania Latvia Czech Republic Estonia Finland United Kingdom Sweden
Explore the themes and thinking behind our decisions.
 ASSET ALLOCATION COMMITTEE VIEWPOINTS First Quarter 2017 These views are informed by a subjective assessment of the relative attractiveness of asset classes and subclasses over a 6- to 18-month horizon.
ASSET ALLOCATION COMMITTEE VIEWPOINTS First Quarter 2017 These views are informed by a subjective assessment of the relative attractiveness of asset classes and subclasses over a 6- to 18-month horizon.
The Week Ahead Key Events 4 10 Jan, 2016
 Editor: Carl Hammer The Week Ahead Key Events 4 10 Jan, 2016 Editor: Benjamin Dousa Monday 4, 08.30 SWE: PMI manufacturing (Dec) Index SEB Cons. Prev PMI 55.0 --- 54.9 Manufacturing confidence according
Editor: Carl Hammer The Week Ahead Key Events 4 10 Jan, 2016 Editor: Benjamin Dousa Monday 4, 08.30 SWE: PMI manufacturing (Dec) Index SEB Cons. Prev PMI 55.0 --- 54.9 Manufacturing confidence according
Global PMI. Global economy buoyed by rising US strength. June 12 th IHS Markit. All Rights Reserved.
 Global PMI Global economy buoyed by rising US strength June 12 th 2018 2 Global PMI rises but also brings signs of slower future growth At 54.0 in May, the headline JPMorgan Global Composite PMI, compiled
Global PMI Global economy buoyed by rising US strength June 12 th 2018 2 Global PMI rises but also brings signs of slower future growth At 54.0 in May, the headline JPMorgan Global Composite PMI, compiled
Austria s economy set to grow by close to 3% in 2018
 Austria s economy set to grow by close to 3% in 218 Gerhard Fenz, Friedrich Fritzer, Fabio Rumler, Martin Schneider 1 Economic growth in Austria peaked at the end of 217. The first half of 218 saw a gradual
Austria s economy set to grow by close to 3% in 218 Gerhard Fenz, Friedrich Fritzer, Fabio Rumler, Martin Schneider 1 Economic growth in Austria peaked at the end of 217. The first half of 218 saw a gradual
Inflation projection of Narodowy Bank Polski based on the NECMOD model
 Economic Institute Inflation projection of Narodowy Bank Polski based on the NECMOD model Warsaw / 9 March Inflation projection of the NBP based on the NECMOD model Outline: Introduction Changes between
Economic Institute Inflation projection of Narodowy Bank Polski based on the NECMOD model Warsaw / 9 March Inflation projection of the NBP based on the NECMOD model Outline: Introduction Changes between
Global FX 3 Jan 2012
 Global FX Jan The euro area s sovereign debt crisis has been dominating trading in financial markets over the past year and the currency market was no exception. The region s debt problems spread from
Global FX Jan The euro area s sovereign debt crisis has been dominating trading in financial markets over the past year and the currency market was no exception. The region s debt problems spread from
News Release. IHS Markit Flash Eurozone PMI. Eurozone growth slips to one-and-a-half year low in May
 IHS Markit Flash Eurozone PMI Purchasing Managers Index MARKET SENSITIVE INFORMATION EMBARGOED UNTIL 1000 (CEST) / 0800 (UTC) May 23 Eurozone growth slips to one-and-a-half year low in May Key findings:
IHS Markit Flash Eurozone PMI Purchasing Managers Index MARKET SENSITIVE INFORMATION EMBARGOED UNTIL 1000 (CEST) / 0800 (UTC) May 23 Eurozone growth slips to one-and-a-half year low in May Key findings:
74 ECB THE 2012 MACROECONOMIC IMBALANCE PROCEDURE
 Box 7 THE 2012 MACROECONOMIC IMBALANCE PROCEDURE This year s European Semester (i.e. the framework for EU policy coordination introduced in 2011) includes, for the first time, the implementation of the
Box 7 THE 2012 MACROECONOMIC IMBALANCE PROCEDURE This year s European Semester (i.e. the framework for EU policy coordination introduced in 2011) includes, for the first time, the implementation of the
: Monetary Economics and the European Union. Lecture 8. Instructor: Prof Robert Hill. The Costs and Benefits of Monetary Union II
 320.326: Monetary Economics and the European Union Lecture 8 Instructor: Prof Robert Hill The Costs and Benefits of Monetary Union II De Grauwe Chapters 3, 4, 5 1 1. Countries in Trouble in the Eurozone
320.326: Monetary Economics and the European Union Lecture 8 Instructor: Prof Robert Hill The Costs and Benefits of Monetary Union II De Grauwe Chapters 3, 4, 5 1 1. Countries in Trouble in the Eurozone
Eurozone. EY Eurozone Forecast September 2014
 Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast September 2014 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Luxembourg Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for Stronger
Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast September 2014 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Luxembourg Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for Stronger
Prudential International Investments Advisers, LLC. Global Investment Strategy June 2009
 Prudential International Investments Advisers, LLC. Global Investment Strategy June 2009 By John Praveen, Chief Investment Strategist For Market Commentary Interviews Contact: Lisa Villareal, 973-367-2503/lisa.villareal@prudential.com
Prudential International Investments Advisers, LLC. Global Investment Strategy June 2009 By John Praveen, Chief Investment Strategist For Market Commentary Interviews Contact: Lisa Villareal, 973-367-2503/lisa.villareal@prudential.com
PERSPECTIVES. By Ruth Lea, Economic Adviser to the Arbuthnot Banking Group
 PERSPECTIVES By Ruth Lea, Economic Adviser to the Arbuthnot Banking Group Increasing concerns about global economic growth, especially in the Eurozone Ruth Lea Economic Adviser Arbuthnot Banking Group
PERSPECTIVES By Ruth Lea, Economic Adviser to the Arbuthnot Banking Group Increasing concerns about global economic growth, especially in the Eurozone Ruth Lea Economic Adviser Arbuthnot Banking Group
KEY INDICATORS FOR THE EURO AREA
 #### This update: () 9-Mar-1 16 17 Next update: -May-1 - Directorate A - Policy, strategy and communication 9-17 1-17 11-17 1-17 1-1 -1 LTA (1) 16 17 17Q 17Q3 17Q 1Q1 Sep-17 Oct-17 Nov-17 Dec-17 Jan-1
#### This update: () 9-Mar-1 16 17 Next update: -May-1 - Directorate A - Policy, strategy and communication 9-17 1-17 11-17 1-17 1-1 -1 LTA (1) 16 17 17Q 17Q3 17Q 1Q1 Sep-17 Oct-17 Nov-17 Dec-17 Jan-1
remain the same until the end of 2018.
 We predict that the European interest rate will remain the same until the end of 2018. Throughout the past three years the interest rate has remained low. In 2017 and 2016 it has been 0.00% and in 2015
We predict that the European interest rate will remain the same until the end of 2018. Throughout the past three years the interest rate has remained low. In 2017 and 2016 it has been 0.00% and in 2015
Editor: Thomas Nilsson. The Week Ahead Key Events 31 Jul 6 Aug, 2017
 Editor: Thomas Nilsson The Week Ahead Key Events 31 Jul 6 Aug, 2017 European Sovereign Rating Reviews Recent rating reviews Friday, 21 July 2017 Agency previous new action Greece S&P B- / Stable B- /
Editor: Thomas Nilsson The Week Ahead Key Events 31 Jul 6 Aug, 2017 European Sovereign Rating Reviews Recent rating reviews Friday, 21 July 2017 Agency previous new action Greece S&P B- / Stable B- /
MonitorING Turkey ING BANK A.Ş. Further fiscal support in the Medium Term Plan. Emerging Markets 4 October 2017
 q ING BANK A.Ş. ECONOMIC RESEARCH GROUP MonitorING Turkey October 17 Emerging Markets October 17 USD/TRY MonitorING Turkey Further fiscal support in the Medium Term Plan In 17, accelerated spending and
q ING BANK A.Ş. ECONOMIC RESEARCH GROUP MonitorING Turkey October 17 Emerging Markets October 17 USD/TRY MonitorING Turkey Further fiscal support in the Medium Term Plan In 17, accelerated spending and
Eurozone Ernst & Young Eurozone Forecast June 2013
 Eurozone Ernst & Young Eurozone Forecast June 2013 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Ernst & Young
Eurozone Ernst & Young Eurozone Forecast June 2013 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Ernst & Young
Global PMI. Global economy grows at fastest rate for over two years, inflationary pressures rise. September 8 th 2017
 Global PMI Global economy grows at fastest rate for over two years, inflationary pressures rise September 8 th 2017 2 Global PMI records fastest growth for over two years Global economic growth rose to
Global PMI Global economy grows at fastest rate for over two years, inflationary pressures rise September 8 th 2017 2 Global PMI records fastest growth for over two years Global economic growth rose to
Economic and Portfolio Outlook 4th Quarter 2014 (Released October 2014)
 Economic and Portfolio Outlook 4th Quarter 2014 (Released October 2014) Our economic outlook for the fourth quarter of 2014 for the U.S. is continued slow growth. We stated in our 3 rd quarter Economic
Economic and Portfolio Outlook 4th Quarter 2014 (Released October 2014) Our economic outlook for the fourth quarter of 2014 for the U.S. is continued slow growth. We stated in our 3 rd quarter Economic
NBS MoNthly BulletiN february 2017
 Published by: Národná banka Slovenska Address: Národná banka Slovenska Imricha Karvaša 1, 813 5 Bratislava Slovakia Contact: +41//5787 146 http://www.nbs.sk All rights reserved. Reproduction for educational
Published by: Národná banka Slovenska Address: Národná banka Slovenska Imricha Karvaša 1, 813 5 Bratislava Slovakia Contact: +41//5787 146 http://www.nbs.sk All rights reserved. Reproduction for educational
Euro-QE at the end of the road for now
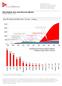 Germany France Italy Agencies Spain Netherlands Belgium Austria Portugal Finland Ireland Slovakia Slovenia Lux Latvia Lithuania Malta 7.9 2.6 2.1 3.16 1.15 Trend Macrolytics, LLC Donald Luskin, Chief Investment
Germany France Italy Agencies Spain Netherlands Belgium Austria Portugal Finland Ireland Slovakia Slovenia Lux Latvia Lithuania Malta 7.9 2.6 2.1 3.16 1.15 Trend Macrolytics, LLC Donald Luskin, Chief Investment
Forecast for Eurozone. (Annual percentage changes unless specified)
 4 Mar Country Economic Forecast Eurozone Highlights Research Recent data have presented conflicting signs on the likely path of Eurozone GDP growth in the early stages of. We have left our forecast for
4 Mar Country Economic Forecast Eurozone Highlights Research Recent data have presented conflicting signs on the likely path of Eurozone GDP growth in the early stages of. We have left our forecast for
