QM353: Business Statistics. Chapter 2
|
|
|
- Ella Blake
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 QM353: Business Statistics Chapter 2 1. The administrator at Saint Frances Hospital is concerned about the amount of overtime the nursing staff is incurring and wonders whether so much overtime is really necessary. The hospital employs 60 nurses. Following is the number of hours of overtime reported by each nurse last week. These data are the population of interest. Using the random numbers table in Appendix A with a starting point in column (digit) 14 and row 10, select a random sample of 6 nurses. Go down the table from the starting point. Determine the mean hours of overtime for these 6 nurses and calculate the sampling error associated with this particular sample mean. 1
2 APPENDIX A : Random Numbers Table 2. SeaFair Fashions relies on its sales force of 220 to do an initial screening of all new fashions. The company is currently bringing out a new line of swimwear and has invited 40 salespeople to its Orlando home office. An issue of constant concern to the SeaFair sales office is the volume of orders generated by each salesperson. Last year, the overall company average was $417,330 with a standard deviation of $45,285. ( Hint: The finite population correction factor, Equation 7.5, is required.) a. Determine the probability the sample of 40 will have a sales average less than $400,000. b. What shape do you think the distribution of all possible sample means of 40 will have? Discuss. c. Determine the value of the standard deviation of the distribution of the sample mean of all possible samples of size 40. d. How would the answers to parts a, b, and c change if the home office brought 60 salespeople to Orlando? Provide the respective answers for this sample size. e. Each year SeaFair invites the sales personnel with sales above the 85th percentile to enjoy a complementary vacation in Hawaii. Determine the smallest average salary for the sales personnel that were in Hawaii last year. (Assume the distribution of sales was normally distributed last year.) 3. Airlines have recently toughened their standards for the weight of checked baggage, limiting the weight of a bag to 50 pounds on domestic U.S. flights. Heavier bags will be carried but at an additional fee. Suppose that one major airline has stated in an internal memo to employees that the mean weight for bags checked last year on the airline was 34.3 pounds with a standard 2
3 deviation of 5.7 pounds. Further, it stated that the distribution of weights was approximately normally distributed. This memo was leaked to a consumers group in Atlanta. This group had selected and weighed a random sample of 14 bags to be checked on a flight departing from Atlanta. The following data (pounds) were recorded: What is the probability that a sample mean as small or smaller than the one for this sample would occur if the airline s claims about the population of baggage weight is accurate? Comment on the results. 4. A random sample of size 100 is to be taken from a population that has a proportion equal to The sample proportion will be used to estimate the population proportion. a. Calculate the probability that the sample proportion will be within ±0.05 of the population proportion. b. Calculate the probability that the sample proportion will be within ±1 standard error of the population proportion. c. Calculate the probability that the sample proportion will be within ±0.10 of the population proportion. 5. A survey is conducted from a population of people of whom 40% have a college degree. The following sample data were recorded for a question asked of each person sampled, Do you have a college degree? a. Calculate the sample proportion of respondents who have a college degree. b. What is the probability of getting a sample proportion as extreme or more extreme than the one observed in part a if the population has 40% with college degrees? 6. According to the most recent Labor Department data, 10.5% of engineers (electrical, mechanical, civil, and industrial) were women. Suppose a random sample of 50 engineers is selected. a. How likely is it that the random sample of 50 engineers will contain 8 or more women in these positions? b. How likely is it that the random sample will contain fewer than 5 women in these positions? c. If the random sample included 200 engineers, how would this change your answer to part b? 3
4 7. Even before the record gas prices during the summer of 2008, an article written by Will Lester of the Associated Press reported on a poll in which 80% of those surveyed say that Americans who currently own a SUV (sport utility vehicle) should switch to a more fuel-efficient vehicle to ease America s dependency on foreign oil. This study was conducted by the Pew Research Center for the People & the Press. As a follow-up to this report, a consumer group conducted a study of SUV owners to estimate the mean mileage for their vehicles. A simple random sample of 91 SUV owners was selected, and the owners were asked to report their highway mileage. The following results were summarized from the sample data: Based on these sample data, compute and interpret a 90% confidence interval estimate for the mean highway mileage for SUVs. 8. According to USA Today, customers are not settling for automobiles straight off the production lines. As an example, those who purchase a $355,000 Rolls-Royce typically add $25,000 in accessories. One of the affordable automobiles to receive additions is BMW s Mini Cooper. A sample of 179 recent Mini purchasers yielded a sample mean of $5,000 above the $20,200 base sticker price. Suppose the cost of accessories purchased for all Mini Coopers has a standard deviation of $1,500. a. Calculate a 95% confidence interval for the average cost of accessories on Mini Coopers. b. Determine the margin of error in estimating the average cost of accessories on Mini Coopers. c. What sample size would be required to reduce the margin of error by 50%? 9. The concession managers for the Arkansas Travelers (a minor league baseball team located in Little Rock) are interested in estimating the average amount spent on food by fans attending the team s Friday night home games. Suppose a random sample of 36 receipts for food orders was taken from last year s receipts for Friday night home games with the following food expenditures recorded: a. Based on the sampled receipts, what is the best point estimate for the mean food expenditures for Friday night home games? b. Use the sample information to construct a 95% confidence interval estimate for the true mean expenditures for Friday night home games. c. Before the sample was taken, the food concessions manager stated that mean food expenditures were about $19.00 per order. Does his statement seem consistent with the results obtained in part b? 10. A survey of 499 women for the American Orthopedic Foot and Ankle Society revealed that 38% wear flats to work. 4
5 a. Use this sample information to develop a 99% confidence interval for the population proportion of women who wear flats to work. b. Suppose the society also wishes to estimate the proportion of women who wear athletic shoes to work with a margin of error of 0.01 with 95% confidence. Determine the sample size required. 11. Most major airlines allow passengers to carry two pieces of luggage (of a certain maximum size) onto the plane. However, their studies show that the more carry-on baggage passengers have, the longer it takes to unload and load passengers. One regional airline is considering changing its policy to allow only one carry-on per passenger. Before doing so, it decided to collect some data. Specifically, a random sample of 1,000 passengers was selected. The passengers were observed, and the number of bags carried on the plane was noted. Out of the 1,000 passengers, 345 had more than one bag. a. Based on this sample, develop and interpret a 95% confidence interval estimate for the proportion of the traveling population that would have been impacted had the one-bag limit been in effect. Discuss your result. b. The domestic version of Boeing s 747 has a capacity for 568 passengers. Determine an interval estimate of the number of passengers that you would expect to carry more than one piece of luggage on the plane. Assume the plane is at its passenger capacity. c. Suppose the airline also noted whether the passenger was male or female. Out of the 1,000 passengers observed, 690 were males. Of this group, 280 had more than one bag. Using this data, obtain and interpret a 95% confidence interval estimate for the proportion of male passengers in the population who would have been affected by the onebag limit. Discuss. d. Suppose the airline decides to conduct a survey of its customers to determine their opinion of the proposed onebag limit. The plan calls for a random sample of customers on different flights to be given a short written survey to complete during the flight. One key question on the survey will be: Do you approve of limiting the number of carryon bags to a maximum of one bag? Airline managers expect that only about 15% will say yes. Based on this assumption, what size sample should the airline take if it wants to develop a 95% confidence interval estimate for the population proportion who will say yes with a margin of error of ±0.02? 12. A report released by the College Board asserted the percentage of students who took and passed Advanced Placement (AP) courses in all subjects has increased in every state and the District of Columbia since Among public school students, 14.1% earned a passing grade on at least one AP exam, the report indicated. In an attempt to determine if the proportion of those passing the math and science AP exams is equal to the 14.1% success rate, a random sample of 300 students enrolled in AP math and science classes has been selected. a. If 35 of the students in the sample passed at least one AP math or science exam, calculate the proportion of those students who passed at least one AP math or science exam. Does this statistic indicate that the proportion of students who pass at least one AP math or science exam is less than that of those taking AP exams as a whole? Support your assertions. b. Calculate the probability that a sample proportion equal to or less than that calculated in part a would occur if the population proportion was actually Answer the question posed in part a using this probability. c. Calculate a 98% confidence interval for the proportion of those students who passed at least one AP math or science exam. Answer the question posed in part a using this confidence interval. Does this answer correspond to that of part b? Support your assertions. 5
University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics
 University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics Statistics 13 Instructor: Nicolas Christou The central limit theorem The distribution of the sample proportion The distribution of the sample
University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics Statistics 13 Instructor: Nicolas Christou The central limit theorem The distribution of the sample proportion The distribution of the sample
University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics. The central limit theorem The distribution of the sample mean
 University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics Statistics 12 Instructor: Nicolas Christou First: Population mean, µ: The central limit theorem The distribution of the sample mean Sample
University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics Statistics 12 Instructor: Nicolas Christou First: Population mean, µ: The central limit theorem The distribution of the sample mean Sample
Math 251, Test 2 Wednesday, May 19, 2004
 Math 251, Test 2 Wednesday, May 19, 2004 Name: Hints and Answers Instructions. Complete each of the following 9 problems. Please show all appropriate details in your solutions. Good Luck. 1. (15 pts) (a)
Math 251, Test 2 Wednesday, May 19, 2004 Name: Hints and Answers Instructions. Complete each of the following 9 problems. Please show all appropriate details in your solutions. Good Luck. 1. (15 pts) (a)
FINAL REVIEW W/ANSWERS
 FINAL REVIEW W/ANSWERS ( 03/15/08 - Sharon Coates) Concepts to review before answering the questions: A population consists of the entire group of people or objects of interest to an investigator, while
FINAL REVIEW W/ANSWERS ( 03/15/08 - Sharon Coates) Concepts to review before answering the questions: A population consists of the entire group of people or objects of interest to an investigator, while
Math 251: Practice Questions Hints and Answers. Review II. Questions from Chapters 4 6
 Math 251: Practice Questions Hints and Answers Review II. Questions from Chapters 4 6 II.A Probability II.A.1. The following is from a sample of 500 bikers who attended the annual rally in Sturgis South
Math 251: Practice Questions Hints and Answers Review II. Questions from Chapters 4 6 II.A Probability II.A.1. The following is from a sample of 500 bikers who attended the annual rally in Sturgis South
A probability distribution shows the possible outcomes of an experiment and the probability of each of these outcomes.
 Introduction In the previous chapter we discussed the basic concepts of probability and described how the rules of addition and multiplication were used to compute probabilities. In this chapter we expand
Introduction In the previous chapter we discussed the basic concepts of probability and described how the rules of addition and multiplication were used to compute probabilities. In this chapter we expand
Abraham Baldwin Agricultural College Math 2000 Practice Test 3
 Abraham Baldwin Agricultural College Math 000 Practice Test 3 To get credit you must show your work. If your answer involves using a formula, make sure you write down the formula! Also write down any expression
Abraham Baldwin Agricultural College Math 000 Practice Test 3 To get credit you must show your work. If your answer involves using a formula, make sure you write down the formula! Also write down any expression
Significance Test Review
 Significance Test Review 1) Kmart brand 60W light bulbs state on the package, Average life of 1000 hours. Let µ denote the true mean life of Kmart 60W light bulbs. People who purchase this brand would
Significance Test Review 1) Kmart brand 60W light bulbs state on the package, Average life of 1000 hours. Let µ denote the true mean life of Kmart 60W light bulbs. People who purchase this brand would
CHAPTER 2 Describing Data: Numerical
 CHAPTER Multiple-Choice Questions 1. A scatter plot can illustrate all of the following except: A) the median of each of the two variables B) the range of each of the two variables C) an indication of
CHAPTER Multiple-Choice Questions 1. A scatter plot can illustrate all of the following except: A) the median of each of the two variables B) the range of each of the two variables C) an indication of
Review Problems for MAT141 Final Exam
 Review Problems for MAT141 Final Exam The following problems will help you prepare for the final exam. Answers to all problems are at the end of the review packet. 1. Find the area and perimeter of the
Review Problems for MAT141 Final Exam The following problems will help you prepare for the final exam. Answers to all problems are at the end of the review packet. 1. Find the area and perimeter of the
Ch 8 One Population Confidence Intervals
 Ch 8 One Population Confidence Intervals Section A: Multiple Choice C 1. A single number used to estimate a population parameter is a. the confidence interval b. the population parameter c. a point estimate
Ch 8 One Population Confidence Intervals Section A: Multiple Choice C 1. A single number used to estimate a population parameter is a. the confidence interval b. the population parameter c. a point estimate
Discrete Probability Distributions
 Discrete Probability Distributions Chapter 6 Copyright 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. Learning
Discrete Probability Distributions Chapter 6 Copyright 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. Learning
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch. 9 Estimating the Value of a Parameter 9.1 Estimating a Population Proportion 1 Obtain a point estimate for the population proportion. 1) When 390 junior college students were surveyed,115 said that
Ch. 9 Estimating the Value of a Parameter 9.1 Estimating a Population Proportion 1 Obtain a point estimate for the population proportion. 1) When 390 junior college students were surveyed,115 said that
Name PID Section # (enrolled)
 STT 315 - Lecture 3 Instructor: Aylin ALIN 04/02/2014 Midterm # 2 A Name PID Section # (enrolled) * The exam is closed book and 80 minutes. * You may use a calculator and the formula sheet that you brought
STT 315 - Lecture 3 Instructor: Aylin ALIN 04/02/2014 Midterm # 2 A Name PID Section # (enrolled) * The exam is closed book and 80 minutes. * You may use a calculator and the formula sheet that you brought
I. Standard Error II. Standard Error III. Standard Error 2.54
 1) Original Population: Match the standard error (I, II, or III) with the correct sampling distribution (A, B, or C) and the correct sample size (1, 5, or 10) I. Standard Error 1.03 II. Standard Error
1) Original Population: Match the standard error (I, II, or III) with the correct sampling distribution (A, B, or C) and the correct sample size (1, 5, or 10) I. Standard Error 1.03 II. Standard Error
Exercises for Chapter (5)
 Exercises for Chapter (5) MULTILE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) 500 families were interviewed and the number of children per family was
Exercises for Chapter (5) MULTILE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) 500 families were interviewed and the number of children per family was
Edexcel past paper questions
 Edexcel past paper questions Statistics 1 Chapters 2-4 (Discrete) Statistics 1 Chapters 2-4 (Discrete) Page 1 Stem and leaf diagram Stem-and-leaf diagrams are used to represent data in its original form.
Edexcel past paper questions Statistics 1 Chapters 2-4 (Discrete) Statistics 1 Chapters 2-4 (Discrete) Page 1 Stem and leaf diagram Stem-and-leaf diagrams are used to represent data in its original form.
Lesson 3: Failing to Get Medical. Treatment the Right Way
 Lesson 3: Failing to Get Medical Treatment the Right Way Rule: The insurance company picks the medical provider. The injured worker can request a change in treatment. When you need a doctor, of course
Lesson 3: Failing to Get Medical Treatment the Right Way Rule: The insurance company picks the medical provider. The injured worker can request a change in treatment. When you need a doctor, of course
1. State Sales Tax. 2. Baggage Check
 1. State Sales Tax A survey asks a random sample of 1500 adults in Ohio if they support an increase in the state sales tax from 5% to 6% with the additional revenue going to education. If 40% of all adults
1. State Sales Tax A survey asks a random sample of 1500 adults in Ohio if they support an increase in the state sales tax from 5% to 6% with the additional revenue going to education. If 40% of all adults
d) Find the standard deviation of the random variable X.
 Q 1: The number of students using Math lab per day is found in the distribution below. x 6 8 10 12 14 P(x) 0.15 0.3 0.35 0.1 0.1 a) Find the mean for this probability distribution. b) Find the variance
Q 1: The number of students using Math lab per day is found in the distribution below. x 6 8 10 12 14 P(x) 0.15 0.3 0.35 0.1 0.1 a) Find the mean for this probability distribution. b) Find the variance
STA 103: Final Exam. Print clearly on this exam. Only correct solutions that can be read will be given credit.
 STA 103: Final Exam June 26, 2008 Name: } {{ } by writing my name i swear by the honor code Read all of the following information before starting the exam: Print clearly on this exam. Only correct solutions
STA 103: Final Exam June 26, 2008 Name: } {{ } by writing my name i swear by the honor code Read all of the following information before starting the exam: Print clearly on this exam. Only correct solutions
11.5: Normal Distributions
 11.5: Normal Distributions 11.5.1 Up to now, we ve dealt with discrete random variables, variables that take on only a finite (or countably infinite we didn t do these) number of values. A continuous random
11.5: Normal Distributions 11.5.1 Up to now, we ve dealt with discrete random variables, variables that take on only a finite (or countably infinite we didn t do these) number of values. A continuous random
AP Stats ~ Lesson 6B: Transforming and Combining Random variables
 AP Stats ~ Lesson 6B: Transforming and Combining Random variables OBJECTIVES: DESCRIBE the effects of transforming a random variable by adding or subtracting a constant and multiplying or dividing by a
AP Stats ~ Lesson 6B: Transforming and Combining Random variables OBJECTIVES: DESCRIBE the effects of transforming a random variable by adding or subtracting a constant and multiplying or dividing by a
Confidence Intervals: Review
 University of Utah February 28, 2018 1 2 Law of Large Numbers Draw your samples from any population with finite mean µ. Then LLN says Law of Large Numbers Draw your samples from any population with finite
University of Utah February 28, 2018 1 2 Law of Large Numbers Draw your samples from any population with finite mean µ. Then LLN says Law of Large Numbers Draw your samples from any population with finite
Please show work for all calculated answers. Show work in a neat and organized manner.
 Math 083 Review for Final Exam Name Please show work for all calculated answers. Show work in a neat and organized manner. 1) Using the frequency table for a monthly budget, find all of the relative frequencies
Math 083 Review for Final Exam Name Please show work for all calculated answers. Show work in a neat and organized manner. 1) Using the frequency table for a monthly budget, find all of the relative frequencies
Mathematical Concepts Joysheet 1 MAT 117, Spring 2011 D. Ivanšić. Name: Show all your work!
 Mathematical Concepts Joysheet 1 Use your calculator to compute each expression to 6 significant digits accuracy. Write down thesequence of keys youentered inorder to compute each expression. Donot roundnumbers
Mathematical Concepts Joysheet 1 Use your calculator to compute each expression to 6 significant digits accuracy. Write down thesequence of keys youentered inorder to compute each expression. Donot roundnumbers
b) What is a good approximation of S and why can you use it? d) What is the approximate probability exactly 38 plants sprout?
 Ex. 3: As a green thumb, you know that when you plant seeds, they are not guaranteed to sprout into plants. If each seed sprouts independently of one another, and each has a.68 probability of sprouting,
Ex. 3: As a green thumb, you know that when you plant seeds, they are not guaranteed to sprout into plants. If each seed sprouts independently of one another, and each has a.68 probability of sprouting,
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO SCARBOROUGH Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences. STAB22H3 Statistics I Duration: 1 hour and 45 minutes
 UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO SCARBOROUGH Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences STAB22H3 Statistics I Duration: 1 hour and 45 minutes Last Name: First Name: Student number: Aids allowed: - One handwritten
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO SCARBOROUGH Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences STAB22H3 Statistics I Duration: 1 hour and 45 minutes Last Name: First Name: Student number: Aids allowed: - One handwritten
Terms & Characteristics
 NORMAL CURVE Knowledge that a variable is distributed normally can be helpful in drawing inferences as to how frequently certain observations are likely to occur. NORMAL CURVE A Normal distribution: Distribution
NORMAL CURVE Knowledge that a variable is distributed normally can be helpful in drawing inferences as to how frequently certain observations are likely to occur. NORMAL CURVE A Normal distribution: Distribution
Name: Period: Date: 1. Suppose we are interested in the average weight of chickens in America.
 Name: Period: Date: Statistics Review MM4D1. Using simulation, students will develop the idea of the central limit theorem. MM4D2. Using student-generated data from random samples of at least 30 members,
Name: Period: Date: Statistics Review MM4D1. Using simulation, students will develop the idea of the central limit theorem. MM4D2. Using student-generated data from random samples of at least 30 members,
Discrete Probability Distributions
 Discrete Probability Distributions Chapter 6 McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2010 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. GOALS 6-2 1. Define the terms probability distribution and random variable.
Discrete Probability Distributions Chapter 6 McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2010 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. GOALS 6-2 1. Define the terms probability distribution and random variable.
Math 227 Practice Test 2 Sec Name
 Math 227 Practice Test 2 Sec 4.4-6.2 Name Find the indicated probability. ) A bin contains 64 light bulbs of which 0 are defective. If 5 light bulbs are randomly selected from the bin with replacement,
Math 227 Practice Test 2 Sec 4.4-6.2 Name Find the indicated probability. ) A bin contains 64 light bulbs of which 0 are defective. If 5 light bulbs are randomly selected from the bin with replacement,
Stat3011: Solution of Midterm Exam One
 1 Stat3011: Solution of Midterm Exam One Fall/2003, Tiefeng Jiang Name: Problem 1 (30 points). Choose one appropriate answer in each of the following questions. 1. (B ) The mean age of five people in a
1 Stat3011: Solution of Midterm Exam One Fall/2003, Tiefeng Jiang Name: Problem 1 (30 points). Choose one appropriate answer in each of the following questions. 1. (B ) The mean age of five people in a
3. Joyce needs to gather data that can be modeled with a linear function. Which situation would give Joyce the data she needs?
 Unit 6 Assessment: Linear Models and Tables Assessment 8 th Grade Math 1. Which equation describes the line through points A and B? A. x 3y = -5 B. x + 3y = -5 C. x + 3y = 7 D. 3x + y = 5 2. The table
Unit 6 Assessment: Linear Models and Tables Assessment 8 th Grade Math 1. Which equation describes the line through points A and B? A. x 3y = -5 B. x + 3y = -5 C. x + 3y = 7 D. 3x + y = 5 2. The table
Mutually Exclusive Events & Non-Mutually Exclusive Events. When two events A and B are mutually exclusive, the probability that A or B will occur is
 EVENTS & PROBABILITIES RULES PROBABILITY RULES Mutually Exclusive Events & Non-Mutually Exclusive Events Two events are mutually exclusive if they cannot occur at the same time (they have no outcomes in
EVENTS & PROBABILITIES RULES PROBABILITY RULES Mutually Exclusive Events & Non-Mutually Exclusive Events Two events are mutually exclusive if they cannot occur at the same time (they have no outcomes in
Chapter 5 The Standard Deviation as a Ruler and the Normal Model
 Chapter 5 The Standard Deviation as a Ruler and the Normal Model 55 Chapter 5 The Standard Deviation as a Ruler and the Normal Model 1. Stats test. Nicole scored 65 points on the test. That is one standard
Chapter 5 The Standard Deviation as a Ruler and the Normal Model 55 Chapter 5 The Standard Deviation as a Ruler and the Normal Model 1. Stats test. Nicole scored 65 points on the test. That is one standard
Business Statistics (BK/IBA) Tutorial 1 Exercises
 Business Statistics (BK/IBA) Tutorial 1 Exercises Instruction In a tutorial session of 2 hours, we will obviously not be able to discuss all questions. Therefore, the following procedure applies: we expect
Business Statistics (BK/IBA) Tutorial 1 Exercises Instruction In a tutorial session of 2 hours, we will obviously not be able to discuss all questions. Therefore, the following procedure applies: we expect
University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics. Normal distribution
 University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics Statistics 110A Instructor: Nicolas Christou Normal distribution The normal distribution is the most important distribution. It describes
University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics Statistics 110A Instructor: Nicolas Christou Normal distribution The normal distribution is the most important distribution. It describes
Chapter 15: Graphs, Charts, and Numbers Math 107
 Chapter 15: Graphs, Charts, and Numbers Math 107 Data Set & Data Point: Discrete v. Continuous: Frequency Table: Ex 1) Exam Scores Pictogram: Misleading Graphs: In reality, the data looks like this 45%
Chapter 15: Graphs, Charts, and Numbers Math 107 Data Set & Data Point: Discrete v. Continuous: Frequency Table: Ex 1) Exam Scores Pictogram: Misleading Graphs: In reality, the data looks like this 45%
Math 160 Professor Busken Chapter 5 Worksheets
 Math 160 Professor Busken Chapter 5 Worksheets Name: 1. Find the expected value. Suppose you play a Pick 4 Lotto where you pay 50 to select a sequence of four digits, such as 2118. If you select the same
Math 160 Professor Busken Chapter 5 Worksheets Name: 1. Find the expected value. Suppose you play a Pick 4 Lotto where you pay 50 to select a sequence of four digits, such as 2118. If you select the same
d) The sales manager wants to award the sales representatives who earn the commissions a bonus of $ He can award a bonus to 20 percent of the
 NORTON UNIVERSITY Department of Business Group: Bu2M1, M2, M5, M6 Semester 2, Academic Year 2013-2014 ASSIGNMENT Course Title: Business and Economics Statistics Lecturer: Mr. MONG Mara Deadline: June 14,
NORTON UNIVERSITY Department of Business Group: Bu2M1, M2, M5, M6 Semester 2, Academic Year 2013-2014 ASSIGNMENT Course Title: Business and Economics Statistics Lecturer: Mr. MONG Mara Deadline: June 14,
Math Take Home Quiz on Chapter 2
 Math 116 - Take Home Quiz on Chapter 2 Show the calculations that lead to the answer. Due date: Tuesday June 6th Name Time your class meets Provide an appropriate response. 1) A newspaper surveyed its
Math 116 - Take Home Quiz on Chapter 2 Show the calculations that lead to the answer. Due date: Tuesday June 6th Name Time your class meets Provide an appropriate response. 1) A newspaper surveyed its
Chapter 9 & 10. Multiple Choice.
 Chapter 9 & 10 Review Name Multiple Choice. 1. An agricultural researcher plants 25 plots with a new variety of corn. The average yield for these plots is X = 150 bushels per acre. Assume that the yield
Chapter 9 & 10 Review Name Multiple Choice. 1. An agricultural researcher plants 25 plots with a new variety of corn. The average yield for these plots is X = 150 bushels per acre. Assume that the yield
1. State whether the following groups are populations or samples. You are encouraged to justify your answers.
 MATH 2210 Exam 1 Review Solution Note: This review is NOT comprehensive, so do not limit your study to it. 1. State whether the following groups are populations or samples. You are encouraged to justify
MATH 2210 Exam 1 Review Solution Note: This review is NOT comprehensive, so do not limit your study to it. 1. State whether the following groups are populations or samples. You are encouraged to justify
Unit2: Probabilityanddistributions. 3. Normal and binomial distributions
 Announcements Unit2: Probabilityanddistributions 3. Normal and binomial distributions Sta 101 - Summer 2017 Duke University, Department of Statistical Science PS: Explain your reasoning + show your work
Announcements Unit2: Probabilityanddistributions 3. Normal and binomial distributions Sta 101 - Summer 2017 Duke University, Department of Statistical Science PS: Explain your reasoning + show your work
Activity #17b: Central Limit Theorem #2. 1) Explain the Central Limit Theorem in your own words.
 Activity #17b: Central Limit Theorem #2 1) Explain the Central Limit Theorem in your own words. Importance of the CLT: You can standardize and use normal distribution tables to calculate probabilities
Activity #17b: Central Limit Theorem #2 1) Explain the Central Limit Theorem in your own words. Importance of the CLT: You can standardize and use normal distribution tables to calculate probabilities
Normal distribution. We say that a random variable X follows the normal distribution if the probability density function of X is given by
 Normal distribution The normal distribution is the most important distribution. It describes well the distribution of random variables that arise in practice, such as the heights or weights of people,
Normal distribution The normal distribution is the most important distribution. It describes well the distribution of random variables that arise in practice, such as the heights or weights of people,
Test 6A AP Statistics Name:
 Test 6A AP Statistics Name: Part 1: Multiple Choice. Circle the letter corresponding to the best answer. 1. A marketing survey compiled data on the number of personal computers in households. If X = the
Test 6A AP Statistics Name: Part 1: Multiple Choice. Circle the letter corresponding to the best answer. 1. A marketing survey compiled data on the number of personal computers in households. If X = the
Name: Show all your work! Mathematical Concepts Joysheet 1 MAT 117, Spring 2012 D. Ivanšić
 Mathematical Concepts Joysheet 1 Use your calculator to compute each expression to 6 significant digits accuracy. Write down thesequence of keys youentered inorder to compute each expression. Donot roundnumbers
Mathematical Concepts Joysheet 1 Use your calculator to compute each expression to 6 significant digits accuracy. Write down thesequence of keys youentered inorder to compute each expression. Donot roundnumbers
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 First Name: Last Name: SID: Class Time: M Tu W Th math10 - HW3 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Continuous random variables are
First Name: Last Name: SID: Class Time: M Tu W Th math10 - HW3 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Continuous random variables are
8.1 Estimation of the Mean and Proportion
 8.1 Estimation of the Mean and Proportion Statistical inference enables us to make judgments about a population on the basis of sample information. The mean, standard deviation, and proportions of a population
8.1 Estimation of the Mean and Proportion Statistical inference enables us to make judgments about a population on the basis of sample information. The mean, standard deviation, and proportions of a population
STAT 1220 FALL 2010 Common Final Exam December 10, 2010
 STAT 1220 FALL 2010 Common Final Exam December 10, 2010 PLEASE PRINT THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION: Name: Instructor: Student ID #: Section/Time: THIS EXAM HAS TWO PARTS. PART I. Part I consists of 30 multiple
STAT 1220 FALL 2010 Common Final Exam December 10, 2010 PLEASE PRINT THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION: Name: Instructor: Student ID #: Section/Time: THIS EXAM HAS TWO PARTS. PART I. Part I consists of 30 multiple
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. State whether you think that the variables have strong positive correlation, weak positive correlation,
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. State whether you think that the variables have strong positive correlation, weak positive correlation,
Discrete Probability Distributions
 Discrete Probability Distributions Chapter 6 Learning Objectives Define terms random variable and probability distribution. Distinguish between discrete and continuous probability distributions. Calculate
Discrete Probability Distributions Chapter 6 Learning Objectives Define terms random variable and probability distribution. Distinguish between discrete and continuous probability distributions. Calculate
Chapter 3: Probability Distributions and Statistics
 Chapter 3: Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 3.-3.3 3. Random Variables and Histograms A is a rule that assigns precisely one real number to each outcome of an experiment. We usually denote
Chapter 3: Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 3.-3.3 3. Random Variables and Histograms A is a rule that assigns precisely one real number to each outcome of an experiment. We usually denote
Chapter 6: Random Variables
 Chapter 6: Random Variables Section 6. The Practice of Statistics, 4 th edition For AP* STARNES, YATES, MOORE Chapter 6 Random Variables 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables 6. 6.3 Binomial and
Chapter 6: Random Variables Section 6. The Practice of Statistics, 4 th edition For AP* STARNES, YATES, MOORE Chapter 6 Random Variables 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables 6. 6.3 Binomial and
LAMC Math 137 Test 3 Module 5 Yun 11/14/2014
 LAMC Math 137 Test 3 Module 5 Yun 11/14/2014 Last name First name You may use a calculator but not a cellphone, tablet or an ipod. Please clearly mark your choices on multiple choice questions and box
LAMC Math 137 Test 3 Module 5 Yun 11/14/2014 Last name First name You may use a calculator but not a cellphone, tablet or an ipod. Please clearly mark your choices on multiple choice questions and box
PRACTICE PROBLEMS CHAPTERS 14 & 15
 PRACTICE PROBLEMS CHAPTERS 14 & 15 Chapter 14 1. Sample spaces. For each of the following, list the sample space and tell whether you think the events are equally likely: a) Toss 2 coins; record the order
PRACTICE PROBLEMS CHAPTERS 14 & 15 Chapter 14 1. Sample spaces. For each of the following, list the sample space and tell whether you think the events are equally likely: a) Toss 2 coins; record the order
NOTES: Chapter 4 Describing Data
 NOTES: Chapter 4 Describing Data Intro to Statistics COLYER Spring 2017 Student Name: Page 2 Section 4.1 ~ What is Average? Objective: In this section you will understand the difference between the three
NOTES: Chapter 4 Describing Data Intro to Statistics COLYER Spring 2017 Student Name: Page 2 Section 4.1 ~ What is Average? Objective: In this section you will understand the difference between the three
Homework 1, Solutions Managerial Economics: Eco 685. a. To get the wage per hour, we can divide total wages by total hours hours = 50 $
 Homework 1, Solutions Managerial Economics: Eco 685 Question 1 a. To get the wage per hour, we can divide total wages by total hours. wage per hour = total wages total hours = $100,000 50 40 hours = 50
Homework 1, Solutions Managerial Economics: Eco 685 Question 1 a. To get the wage per hour, we can divide total wages by total hours. wage per hour = total wages total hours = $100,000 50 40 hours = 50
Math 235 Final Exam Practice test. Name
 Math 235 Final Exam Practice test Name Use the Gauss-Jordan method to solve the system of equations. 1) x + y + z = -1 x - y + 3z = -7 4x + y + z = -7 A) (-1, -2, 2) B) (-2, 2, -1) C)(-1, 2, -2) D) No
Math 235 Final Exam Practice test Name Use the Gauss-Jordan method to solve the system of equations. 1) x + y + z = -1 x - y + 3z = -7 4x + y + z = -7 A) (-1, -2, 2) B) (-2, 2, -1) C)(-1, 2, -2) D) No
4.1 Probability Distributions
 Probability and Statistics Mrs. Leahy Chapter 4: Discrete Probability Distribution ALWAYS KEEP IN MIND: The Probability of an event is ALWAYS between: and!!!! 4.1 Probability Distributions Random Variables
Probability and Statistics Mrs. Leahy Chapter 4: Discrete Probability Distribution ALWAYS KEEP IN MIND: The Probability of an event is ALWAYS between: and!!!! 4.1 Probability Distributions Random Variables
Mutually Exclusive Exhaustive Categories
 Activity 1 1.1 Mutually Exclusive Exhaustive Categories As a small group, write a question and 4 to 6 mutually exclusive answers that encompass all possible responses. Make sure that everyone who is asked
Activity 1 1.1 Mutually Exclusive Exhaustive Categories As a small group, write a question and 4 to 6 mutually exclusive answers that encompass all possible responses. Make sure that everyone who is asked
8.1 Binomial Distributions
 8.1 Binomial Distributions The Binomial Setting The 4 Conditions of a Binomial Setting: 1.Each observation falls into 1 of 2 categories ( success or fail ) 2 2.There is a fixed # n of observations. 3.All
8.1 Binomial Distributions The Binomial Setting The 4 Conditions of a Binomial Setting: 1.Each observation falls into 1 of 2 categories ( success or fail ) 2 2.There is a fixed # n of observations. 3.All
Putting Things Together Part 1
 Putting Things Together Part 1 These exercise blend ideas from various graphs (histograms and boxplots), differing shapes of distributions, and values summarizing the data. Data for 1, 5, and 6 are in
Putting Things Together Part 1 These exercise blend ideas from various graphs (histograms and boxplots), differing shapes of distributions, and values summarizing the data. Data for 1, 5, and 6 are in
Memorandum. Human Resources Division
 Memorandum Human Resources Division TO: FROM: RE: Vacellia Clark, Chief Examiner Civil Service Commission Human Resources Staff Establish a Passing Score for Animal Control Officer DATE: October 30, 2013
Memorandum Human Resources Division TO: FROM: RE: Vacellia Clark, Chief Examiner Civil Service Commission Human Resources Staff Establish a Passing Score for Animal Control Officer DATE: October 30, 2013
(c) The probability that a randomly selected driver having a California drivers license
 Statistics Test 2 Name: KEY 1 Classify each statement as an example of classical probability, empirical probability, or subjective probability (a An executive for the Krusty-O cereal factory makes an educated
Statistics Test 2 Name: KEY 1 Classify each statement as an example of classical probability, empirical probability, or subjective probability (a An executive for the Krusty-O cereal factory makes an educated
Confidence Intervals for the Mean. When σ is known
 Confidence Intervals for the Mean When σ is known Objective Find the confidence interval for the mean when s is known. Intro Suppose a college president wishes to estimate the average age of students attending
Confidence Intervals for the Mean When σ is known Objective Find the confidence interval for the mean when s is known. Intro Suppose a college president wishes to estimate the average age of students attending
STOR 155 Practice Midterm 1 Fall 2009
 STOR 155 Practice Midterm 1 Fall 2009 INSTRUCTIONS: BOTH THE EXAM AND THE BUBBLE SHEET WILL BE COLLECTED. YOU MUST PRINT YOUR NAME AND SIGN THE HONOR PLEDGE ON THE BUBBLE SHEET. YOU MUST BUBBLE-IN YOUR
STOR 155 Practice Midterm 1 Fall 2009 INSTRUCTIONS: BOTH THE EXAM AND THE BUBBLE SHEET WILL BE COLLECTED. YOU MUST PRINT YOUR NAME AND SIGN THE HONOR PLEDGE ON THE BUBBLE SHEET. YOU MUST BUBBLE-IN YOUR
Chapter 6 Test Practice Questions
 Probability and Statistics - Mrs. Leahy Name Chapter 6 Test Practice Questions Provide an appropriate response. 1) For a sample of 20 IQ scores the mean score is 105.8. The standard deviation,, is 15.
Probability and Statistics - Mrs. Leahy Name Chapter 6 Test Practice Questions Provide an appropriate response. 1) For a sample of 20 IQ scores the mean score is 105.8. The standard deviation,, is 15.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find a z-score satisfying the given condition. 1) 20.1% of the total area is to the right
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find a z-score satisfying the given condition. 1) 20.1% of the total area is to the right
DSST Introduction to Business Math
 DSST Introduction to Business Math Time 120 Minutes 100 Questions Each incomplete statement is followed by four suggested completions. Select the one that is best in each case. 1. Five years ago, the share
DSST Introduction to Business Math Time 120 Minutes 100 Questions Each incomplete statement is followed by four suggested completions. Select the one that is best in each case. 1. Five years ago, the share
Chapter Chapter 6. Modeling Random Events: The Normal and Binomial Models
 Chapter 6 107 Chapter 6 Modeling Random Events: The Normal and Binomial Models Chapter 6 108 Chapter 6 109 Table Number: Group Name: Group Members: Discrete Probability Distribution: Ichiro s Hit Parade
Chapter 6 107 Chapter 6 Modeling Random Events: The Normal and Binomial Models Chapter 6 108 Chapter 6 109 Table Number: Group Name: Group Members: Discrete Probability Distribution: Ichiro s Hit Parade
Problem max points points scored Total 120. Do all 6 problems.
 Solutions to (modified) practice exam 4 Statistics 224 Practice exam 4 FINAL Your Name Friday 12/21/07 Professor Michael Iltis (Lecture 2) Discussion section (circle yours) : section: 321 (3:30 pm M) 322
Solutions to (modified) practice exam 4 Statistics 224 Practice exam 4 FINAL Your Name Friday 12/21/07 Professor Michael Iltis (Lecture 2) Discussion section (circle yours) : section: 321 (3:30 pm M) 322
Problem Set 07 Discrete Random Variables
 Name Problem Set 07 Discrete Random Variables MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the mean of the random variable. 1) The random
Name Problem Set 07 Discrete Random Variables MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the mean of the random variable. 1) The random
6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables. 6.1A Discrete random Variables, Mean (Expected Value) of a Discrete Random Variable
 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables 6.1A Discrete random Variables, Mean (Expected Value) of a Discrete Random Variable Random variable Takes numerical values that describe the outcomes of some
6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables 6.1A Discrete random Variables, Mean (Expected Value) of a Discrete Random Variable Random variable Takes numerical values that describe the outcomes of some
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch. 8 Sampling Distributions 8.1 Distribution of the Sample Mean 1 Describe the distribution of the sample mean: normal population. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement
Ch. 8 Sampling Distributions 8.1 Distribution of the Sample Mean 1 Describe the distribution of the sample mean: normal population. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement
Section 8 TAX DEPRECIATION OF PASSENGER CARS AND OTHER VEHICLES
 Section 8 TAX DEPRECIATION OF PASSENGER CARS AND OTHER VEHICLES Introduction There are special dollar limits on annual depreciation that apply only to a passenger automobile, defined under tax law as any
Section 8 TAX DEPRECIATION OF PASSENGER CARS AND OTHER VEHICLES Introduction There are special dollar limits on annual depreciation that apply only to a passenger automobile, defined under tax law as any
Density curves. (James Madison University) February 4, / 20
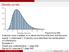 Density curves Figure 6.2 p 230. A density curve is always on or above the horizontal axis, and has area exactly 1 underneath it. A density curve describes the overall pattern of a distribution. Example
Density curves Figure 6.2 p 230. A density curve is always on or above the horizontal axis, and has area exactly 1 underneath it. A density curve describes the overall pattern of a distribution. Example
Key Concept. 155S6.6_3 Normal as Approximation to Binomial. March 02, 2011
 MAT 155 Statistical Analysis Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6 1 Review and Preview 6 2 The Standard Normal Distribution 6 3 Applications of Normal
MAT 155 Statistical Analysis Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6 1 Review and Preview 6 2 The Standard Normal Distribution 6 3 Applications of Normal
Name: Homework Assignment Six Due Friday, Feb. 27 th
 Name: Homework Assignment Six Due Friday, Feb. 27 th Suggest Reading: Chapter 5 Section 1 3, Chapter 6 Section 1- Section 2 1. List the probability model for the below situations. (Remember to list the
Name: Homework Assignment Six Due Friday, Feb. 27 th Suggest Reading: Chapter 5 Section 1 3, Chapter 6 Section 1- Section 2 1. List the probability model for the below situations. (Remember to list the
Honors Statistics. Daily Agenda
 Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM Daily Agenda 1. Review OTL C6#7 emphasis Normal Distributions Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 1. Multiple choice: Select the best answer for Exercises 65 and 66, which refer to the following
Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM Daily Agenda 1. Review OTL C6#7 emphasis Normal Distributions Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 1. Multiple choice: Select the best answer for Exercises 65 and 66, which refer to the following
STAT Chapter 6 The Standard Deviation (SD) as a Ruler and The Normal Model
 STAT 203 - Chapter 6 The Standard Deviation (SD) as a Ruler and The Normal Model In Chapter 5, we introduced a few measures of center and spread, and discussed how the mean and standard deviation are good
STAT 203 - Chapter 6 The Standard Deviation (SD) as a Ruler and The Normal Model In Chapter 5, we introduced a few measures of center and spread, and discussed how the mean and standard deviation are good
STAT Chapter 6 The Standard Deviation (SD) as a Ruler and The Normal Model
 STAT 203 - Chapter 6 The Standard Deviation (SD) as a Ruler and The Normal Model In Chapter 5, we introduced a few measures of center and spread, and discussed how the mean and standard deviation are good
STAT 203 - Chapter 6 The Standard Deviation (SD) as a Ruler and The Normal Model In Chapter 5, we introduced a few measures of center and spread, and discussed how the mean and standard deviation are good
Sampling Distributions Homework
 Name Sampling Distributions Homework Period Identify each boldface number as a parameter or a statistic and use the appropriate notation. 1. A carload lot of ball bearings has a mean diameter of 2.5003
Name Sampling Distributions Homework Period Identify each boldface number as a parameter or a statistic and use the appropriate notation. 1. A carload lot of ball bearings has a mean diameter of 2.5003
Maine Community College System Financial Procedures Manual. Payment of Travel Expenses
 Maine Community College System Financial Procedures Manual SUBJECT: GENERAL ACCOUNTING Page: 204 (Page 1 of 6) Effective: June 26, 2012 Section: 204 Payment of Travel Expenses 1. Purpose Payment of Travel
Maine Community College System Financial Procedures Manual SUBJECT: GENERAL ACCOUNTING Page: 204 (Page 1 of 6) Effective: June 26, 2012 Section: 204 Payment of Travel Expenses 1. Purpose Payment of Travel
4 4. Turn to Section 4 of your answer sheet to answer the questions in this section.
 Section 4 Math Test Calculator 45 MINUTES, 31 QUESTIONS Turn to Section 4 of your answer sheet to answer the questions in this section...directions.. Questions 1-27 ask you to solve a problem, select
Section 4 Math Test Calculator 45 MINUTES, 31 QUESTIONS Turn to Section 4 of your answer sheet to answer the questions in this section...directions.. Questions 1-27 ask you to solve a problem, select
Math 227 Elementary Statistics. Bluman 5 th edition
 Math 227 Elementary Statistics Bluman 5 th edition CHAPTER 6 The Normal Distribution 2 Objectives Identify distributions as symmetrical or skewed. Identify the properties of the normal distribution. Find
Math 227 Elementary Statistics Bluman 5 th edition CHAPTER 6 The Normal Distribution 2 Objectives Identify distributions as symmetrical or skewed. Identify the properties of the normal distribution. Find
STT 315 Practice Problems Chapter 3.7 and 4
 STT 315 Practice Problems Chapter 3.7 and 4 Answer the question True or False. 1) The number of children in a family can be modelled using a continuous random variable. 2) For any continuous probability
STT 315 Practice Problems Chapter 3.7 and 4 Answer the question True or False. 1) The number of children in a family can be modelled using a continuous random variable. 2) For any continuous probability
Probability Distributions. Chapter 6
 Probability Distributions Chapter 6 McGraw-Hill/Irwin The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 2008 GOALS Define the terms probability distribution and random variable. Distinguish between discrete and continuous
Probability Distributions Chapter 6 McGraw-Hill/Irwin The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 2008 GOALS Define the terms probability distribution and random variable. Distinguish between discrete and continuous
Record on a ScanTron, your choosen response for each question. You may write on this form. One page of notes and a calculator are allowed.
 Ch 16, 17 Math 240 Exam 4 v1 Good SAMPLE No Book, Yes 1 Page Notes, Yes Calculator, 120 Minutes Dressler Record on a ScanTron, your choosen response for each question. You may write on this form. One page
Ch 16, 17 Math 240 Exam 4 v1 Good SAMPLE No Book, Yes 1 Page Notes, Yes Calculator, 120 Minutes Dressler Record on a ScanTron, your choosen response for each question. You may write on this form. One page
Understanding what participants say and do uncovers opportunities to enhance plan design.
 line of Sight The Path Forward 2013: survey results THE IDEAL DC PLAN MAY BE CLOSER THAN YOU THINK Understanding what participants say and do uncovers opportunities to enhance plan design. During the last
line of Sight The Path Forward 2013: survey results THE IDEAL DC PLAN MAY BE CLOSER THAN YOU THINK Understanding what participants say and do uncovers opportunities to enhance plan design. During the last
Name PID Section # (enrolled)
 STT 315 - Lecture 3 Instructor: Aylin ALIN 02/19/2014 Midterm # 1 A Name PID Section # (enrolled) * The exam is closed book and 80 minutes. * You may use a calculator and the formula sheet that you brought
STT 315 - Lecture 3 Instructor: Aylin ALIN 02/19/2014 Midterm # 1 A Name PID Section # (enrolled) * The exam is closed book and 80 minutes. * You may use a calculator and the formula sheet that you brought
Both the quizzes and exams are closed book. However, For quizzes: Formulas will be provided with quiz papers if there is any need.
 Both the quizzes and exams are closed book. However, For quizzes: Formulas will be provided with quiz papers if there is any need. For exams (MD1, MD2, and Final): You may bring one 8.5 by 11 sheet of
Both the quizzes and exams are closed book. However, For quizzes: Formulas will be provided with quiz papers if there is any need. For exams (MD1, MD2, and Final): You may bring one 8.5 by 11 sheet of
22.2 Shape, Center, and Spread
 Name Class Date 22.2 Shape, Center, and Spread Essential Question: Which measures of center and spread are appropriate for a normal distribution, and which are appropriate for a skewed distribution? Eplore
Name Class Date 22.2 Shape, Center, and Spread Essential Question: Which measures of center and spread are appropriate for a normal distribution, and which are appropriate for a skewed distribution? Eplore
Guidelines for Arbitrator Reimbursement
 Guidelines for Arbitrator Reimbursement Revised January 2018 Thank you for agreeing to serve as an arbitrator for FINRA Office of Dispute Resolution. To better serve our users, we are continuing our efforts
Guidelines for Arbitrator Reimbursement Revised January 2018 Thank you for agreeing to serve as an arbitrator for FINRA Office of Dispute Resolution. To better serve our users, we are continuing our efforts
STAT 3090 Test 2 - Version B Fall Student s Printed Name: PLEASE READ DIRECTIONS!!!!
 Student s Printed Name: Instructor: XID: Section #: Read each question very carefully. You are permitted to use a calculator on all portions of this exam. You are NOT allowed to use any textbook, notes,
Student s Printed Name: Instructor: XID: Section #: Read each question very carefully. You are permitted to use a calculator on all portions of this exam. You are NOT allowed to use any textbook, notes,
Test # 3 Review Ch. 6 & 7.1 to 7.3 Math MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Test # 3 Review Ch. 6 & 7.1 to 7.3 Math 0306 Name Date: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Round your answer to the tenth of a percent.
Test # 3 Review Ch. 6 & 7.1 to 7.3 Math 0306 Name Date: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Round your answer to the tenth of a percent.
Instructor: A.E.Cary. Math 243 Exam 2
 Name: Instructor: A.E.Cary Instructions: Show all your work in a manner consistent with that demonstrated in class. Round your answers where appropriate. Use 3 decimal places when rounding answers. In
Name: Instructor: A.E.Cary Instructions: Show all your work in a manner consistent with that demonstrated in class. Round your answers where appropriate. Use 3 decimal places when rounding answers. In
The Standard Deviation as a Ruler and the Normal Model. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 The Standard Deviation as a Ruler and the Normal Mol Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. The trick in comparing very different-looking values is to use standard viations as our rulers. The standard
The Standard Deviation as a Ruler and the Normal Mol Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. The trick in comparing very different-looking values is to use standard viations as our rulers. The standard
