5.1 Mean, Median, & Mode
|
|
|
- Anissa Benson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 5.1 Mean, Median, & Mode definitions Mean: Median: Mode: Example 1 The Blue Jays score these amounts of runs in their last 9 games: 4, 7, 2, 4, 10, 5, 6, 7, 7 Find the mean, median, and mode: Example 2 Cheesy Burgers Restaurant gets the following reviews out of 10: 8, 6, 9, 7, 8, 4, 10, 7 Find the mean, median, and mode:
2 Example 3 For 30 randomly selected high school students, the following IQ frequency distribution was obtained. Determine the mean, median, and mode. Example 4 10 numbers have a mean of 37. If one number is removed, the mean is 38. What was the number that was removed? Example 5 The mean age of 4 people is The ages of three of the people are 20, 35, and 60. What is the age of the fourth person?
3 5.2 Standard Deviation definition What is standard deviation? How do you calculate standard deviation? Why is standard deviation useful in statistics? Example 1 Find the mean for each set of data. a) 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 b) 3, 5, 7, 9, 11 Analyzing the data, can you predict which set will have a larger standard deviation? How can you tell? Calculate the standard deviation for each:
4 Example 2 Calculate the standard deviation for the following sets of data: Daily Commute Time (mins) Number of Employees 0 to less than to less than to less than to less than to less than 50 2 Total 25 Daily Commute Time (mins) Number of Employees 0 to less than to less than to less than to less than to less than 50 1 Total 25 First, predict which table will have the higher standard deviation. Why? What would a standard deviation of zero signify? Example 3 - Without doing any calculations, what is the relationship between the standard deviation of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and the standard deviation of: a) 17, 19, 21, 23, 25 b) 100, 105, 110, 115, 120
5 5.3A The Normal Distribution Part 1 Data can be distributed in many ways. It can have many more smaller values than larger values, or visa versa. Or, it can be very jumbled up, some smaller values that are common, as well as larger values that are common: more smaller values more larger values jumbled However, there are many cases where data is symmetrical (or almost) around a central value, and this is called a normal distribution. Normal Distribution definition The Normal Distribution is a bell shaped curve used in statistical analysis to model the distribution of values in a data set. Examples of data that follow a normal distribution are: heights or weights of people or other species, sizes or weights of goods manufactured at a factory, marks on a test, length of time a battery lasts, milk produced by a cow in a day, etc. If data follows a normal distribution, it is easier to make predictions using the data. Most of the data points are in the middle. A small number of data points are on the edges. The Normal Distribution has the mean (µ) in the middle of the curve, & the shape of the curve is dependent on the standard deviation (σ) of the data set. Here are some characteristics of the Normal Distribution: - it is bell shaped and symmetric about the mean - the shape (tall & skinny OR short & wide) is due to the standard deviation - the enclosed area under is always equal to 1, which signifies the probability (100%) of a score falling within the bell curve. - the curve will never touch the x-axis; it extends to infinity in both directions
6 Example 1 What can you say about the mean (µ) for each normal distribution? What about their standard deviations (σ)? Example 2 What can you say about the mean for each normal distribution? What about their standard deviations? There are many different normal curves with different µ and σ. By transforming each raw score into a z-score, which is a measure of how many standard deviations the value is from the mean, you can get a sense of how far that raw score is from the mean compared to other raw scores. How to Calculate Z-Scores: Example 3 The test score mean was 76% with a standard deviation of 6%. If somebody scored 67% on their test, what is their z-score? What about 80%?
7 The Standard Normal Distribution: The value under each area in the curve represents the decimal value (multiply by 100 for percent) of the number of raw scores in that vicinity. Notice that the z-score is negative if smaller than the mean. It is good to know the standard deviation because we can say that any value is: likely to be within 1 standard deviation (68% chance), very likely to be within 2 standard deviations (95% chance), and almost certainly within 3 standard deviations (99.7% chance). Anything outside of this can be deemed an outlier. Example 4 Professor Hardmarker is marking a test and the following scores out of 60 result: 20, 15, 26, 32, 18, 28, 35, 14, 26, 22, 17. a) Any observations? b) Calculate the mean: c) Calculate the standard deviation: d) The test must have been really hard, so the Prof decides to only fail those who are more than one standard deviation below the average (he standardizes the exam). Use z-scores to find out how many people will fail:
8 5.3B The Normal Distribution Part 2 A standard normal distribution curve can also be used to estimate probabilities of many different possible results to a statistical study. We already know percentages for z-scores of 1, 2, and 3, as seen below: What is the percentage that a raw score has a z-score below 1? However, what, for instance, is the percentage chance of a raw score that has a z- score of below 1.5? We cannot tell using the graphic above. We can use a Standard Normal Distribution Table to find the answer. The table value always indicates the area or probability to the LEFT of the z-score. Example 1 Using last day s worksheet, let s answer #2e. The math exam had a mean of 62% with a standard deviation of 12. What percentage of students originally earned an A grade (86%)? Let s say the university wanted about 10% of the students to get an A in each course. Do you think the professor should standardize the scores (scale the test results)? If so, can you explain how the professor may go about this process (think about the area under the normal distribution and how this can help)? Example 2 If IQ scores are normally distributed with a mean of 100 and standard deviation of 15, determine: a) the z-score for 128 b) the probability that a randomly selected person has an IQ less than 128 c) the probability that a randomly selected person has an IQ more than 105
9 Example 3 Using the standard normal distribution table, find: a) the % that a z-score is below b) the % that a z-score is above c) the % that a z-score is below 1.75 d) the % that a z-score is above 3.31 e) the % that a z-score is between and 1.65 Example 4 The grade point average at Capital City High is 2.6, with a standard deviation of 0.5. If the top 15% of all students are eligible to attend Uvic, what is the minimum GPA needed to attend? Example 5 A manufacturer of cell phones indicated a mean of 26 months before there is a need of repairs, with a standard deviation of 6 months. What length of time for the warranty should the manufacturer set such that less than 10% of all cell phones will need repairs during the warranty period?
10 5.4 Confidence Interval for Means sample vs population Suppose you wanted to find out the average time that track athletes in Canada can run a 5K. How might you go about collecting the information necessary for this? Population: Sample: Therefore, in most cases where data is being collected, a sample is used rather than surveying the entire population (due to time, money, and convenience issues). If you survey a sample of the population to find out the average 5K time, how accurate will the sample mean (x ) be, meaning how close is it to the population mean (µ), the actual average time 5K time of all Canadian track athletes? What would you think the accuracy would depend on? Statisticians have developed a way to assess the accuracy of extrapolating a survey mean (x ) to a population mean (µ), by a method called Confidence Interval for Means. This is based on the premise that the sample data collection was random (to minimize any bias). For our example above, finding the average 5K time, let s say 200 athletes were randomly surveyed, and the sample mean x = 20 mins. Let s say a Confidence Interval for Mean analysis was done. The results would read something like this: The mean 5K time for track athletes in Canada is 20 mins, with results accurate to within 1.2 points, 19 times out of 20. So what does this mean? 1.2 points: 19 times out of 20: Overall Result:
11 Example 1 A survey was conducted to find the average height of teenagers in Victoria. 500 teens were sampled and the sample mean x = 165cm. A Confidence Interval for Mean analysis was run and the final results read like this: The average height of teenagers in Victoria is 165cm, with results accurate to 5 points, 19 times out of 20. Describe what this means: How is Confidence Interval for Means calculated? Most often, 19 times out of 20 is the standard for a survey, meaning surveyors want to state their results with 95% confidence. confidence. z-score for ( ): use the table to look up and you get 1.96 (and on the left end). µ The Confidence Interval should depend on the info above, but it should also depend on the standard deviation of the data (if the data is more spread out, there s a greater chance that the sample mean (x ) will differ from the population mean (µ). The standard deviation of the sample is symbolized by s. The standard deviation for the population (which is unknown) is symbolized by σ. It is widely accepted that as long as the sample size exceeds 30, s is close enough to σ to use in the calculation. The Confidence Interval also depends on the sample size. Asking Canadians should yield a more accurate x than asking 20 Canadians. Here is the formula for calculating a Confidence Interval for a Mean: For 95% confidence, = 1.96 Zα 2 s = standard deviation of sample σ = standard deviation of population (same as s if n > 30)
12 Example 2 A random sample of 64 teenagers in Victoria have a mean height, x = 160cm, with a standard deviation of 15. Find a 95% confidence interval for the mean of the population (µ). Example 3a A random sample of 1000 adult male Canadians were asked their weight, and x = 78kg, with a standard deviation of 15. Find a 90% confidence interval for µ. Example 3b Find a 95% confidence interval for µ.
Chapter Seven: Confidence Intervals and Sample Size
 Chapter Seven: Confidence Intervals and Sample Size A point estimate is: The best point estimate of the population mean µ is the sample mean X. Three Properties of a Good Estimator 1. Unbiased 2. Consistent
Chapter Seven: Confidence Intervals and Sample Size A point estimate is: The best point estimate of the population mean µ is the sample mean X. Three Properties of a Good Estimator 1. Unbiased 2. Consistent
The Normal Distribution
 5.1 Introduction to Normal Distributions and the Standard Normal Distribution Section Learning objectives: 1. How to interpret graphs of normal probability distributions 2. How to find areas under the
5.1 Introduction to Normal Distributions and the Standard Normal Distribution Section Learning objectives: 1. How to interpret graphs of normal probability distributions 2. How to find areas under the
Lecture 9. Probability Distributions. Outline. Outline
 Outline Lecture 9 Probability Distributions 6-1 Introduction 6- Probability Distributions 6-3 Mean, Variance, and Expectation 6-4 The Binomial Distribution Outline 7- Properties of the Normal Distribution
Outline Lecture 9 Probability Distributions 6-1 Introduction 6- Probability Distributions 6-3 Mean, Variance, and Expectation 6-4 The Binomial Distribution Outline 7- Properties of the Normal Distribution
What type of distribution is this? tml
 Warm Up Calculate the average Broncos score for the 2013 Season! 24, 27, 10, 10, 34, 37, 20, 51, 35, 31, 27, 28, 45, 33, 35, 52, 52, 37, 41, 49, 24, 26 What type of distribution is this? http://www.mathsisfun.com/data/quincunx.h
Warm Up Calculate the average Broncos score for the 2013 Season! 24, 27, 10, 10, 34, 37, 20, 51, 35, 31, 27, 28, 45, 33, 35, 52, 52, 37, 41, 49, 24, 26 What type of distribution is this? http://www.mathsisfun.com/data/quincunx.h
Expected Value of a Random Variable
 Knowledge Article: Probability and Statistics Expected Value of a Random Variable Expected Value of a Discrete Random Variable You're familiar with a simple mean, or average, of a set. The mean value of
Knowledge Article: Probability and Statistics Expected Value of a Random Variable Expected Value of a Discrete Random Variable You're familiar with a simple mean, or average, of a set. The mean value of
Lecture 9. Probability Distributions
 Lecture 9 Probability Distributions Outline 6-1 Introduction 6-2 Probability Distributions 6-3 Mean, Variance, and Expectation 6-4 The Binomial Distribution Outline 7-2 Properties of the Normal Distribution
Lecture 9 Probability Distributions Outline 6-1 Introduction 6-2 Probability Distributions 6-3 Mean, Variance, and Expectation 6-4 The Binomial Distribution Outline 7-2 Properties of the Normal Distribution
Determining Sample Size. Slide 1 ˆ ˆ. p q n E = z α / 2. (solve for n by algebra) n = E 2
 Determining Sample Size Slide 1 E = z α / 2 ˆ ˆ p q n (solve for n by algebra) n = ( zα α / 2) 2 p ˆ qˆ E 2 Sample Size for Estimating Proportion p When an estimate of ˆp is known: Slide 2 n = ˆ ˆ ( )
Determining Sample Size Slide 1 E = z α / 2 ˆ ˆ p q n (solve for n by algebra) n = ( zα α / 2) 2 p ˆ qˆ E 2 Sample Size for Estimating Proportion p When an estimate of ˆp is known: Slide 2 n = ˆ ˆ ( )
The Normal Probability Distribution
 1 The Normal Probability Distribution Key Definitions Probability Density Function: An equation used to compute probabilities for continuous random variables where the output value is greater than zero
1 The Normal Probability Distribution Key Definitions Probability Density Function: An equation used to compute probabilities for continuous random variables where the output value is greater than zero
Both the quizzes and exams are closed book. However, For quizzes: Formulas will be provided with quiz papers if there is any need.
 Both the quizzes and exams are closed book. However, For quizzes: Formulas will be provided with quiz papers if there is any need. For exams (MD1, MD2, and Final): You may bring one 8.5 by 11 sheet of
Both the quizzes and exams are closed book. However, For quizzes: Formulas will be provided with quiz papers if there is any need. For exams (MD1, MD2, and Final): You may bring one 8.5 by 11 sheet of
Math 227 Elementary Statistics. Bluman 5 th edition
 Math 227 Elementary Statistics Bluman 5 th edition CHAPTER 6 The Normal Distribution 2 Objectives Identify distributions as symmetrical or skewed. Identify the properties of the normal distribution. Find
Math 227 Elementary Statistics Bluman 5 th edition CHAPTER 6 The Normal Distribution 2 Objectives Identify distributions as symmetrical or skewed. Identify the properties of the normal distribution. Find
STAT:2010 Statistical Methods and Computing. Using density curves to describe the distribution of values of a quantitative
 STAT:10 Statistical Methods and Computing Normal Distributions Lecture 4 Feb. 6, 17 Kate Cowles 374 SH, 335-0727 kate-cowles@uiowa.edu 1 2 Using density curves to describe the distribution of values of
STAT:10 Statistical Methods and Computing Normal Distributions Lecture 4 Feb. 6, 17 Kate Cowles 374 SH, 335-0727 kate-cowles@uiowa.edu 1 2 Using density curves to describe the distribution of values of
Section 7.5 The Normal Distribution. Section 7.6 Application of the Normal Distribution
 Section 7.6 Application of the Normal Distribution A random variable that may take on infinitely many values is called a continuous random variable. A continuous probability distribution is defined by
Section 7.6 Application of the Normal Distribution A random variable that may take on infinitely many values is called a continuous random variable. A continuous probability distribution is defined by
Chapter 6. The Normal Probability Distributions
 Chapter 6 The Normal Probability Distributions 1 Chapter 6 Overview Introduction 6-1 Normal Probability Distributions 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution 6-3 Applications of the Normal Distribution 6-5
Chapter 6 The Normal Probability Distributions 1 Chapter 6 Overview Introduction 6-1 Normal Probability Distributions 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution 6-3 Applications of the Normal Distribution 6-5
Data that can be any numerical value are called continuous. These are usually things that are measured, such as height, length, time, speed, etc.
 Chapter 8 Measures of Center Data that can be any numerical value are called continuous. These are usually things that are measured, such as height, length, time, speed, etc. Data that can only be integer
Chapter 8 Measures of Center Data that can be any numerical value are called continuous. These are usually things that are measured, such as height, length, time, speed, etc. Data that can only be integer
Chapter 6: The Normal Distribution
 Chapter 6: The Normal Distribution Diana Pell Section 6.1: Normal Distributions Note: Recall that a continuous variable can assume all values between any two given values of the variables. Many continuous
Chapter 6: The Normal Distribution Diana Pell Section 6.1: Normal Distributions Note: Recall that a continuous variable can assume all values between any two given values of the variables. Many continuous
Chapter 6: The Normal Distribution
 Chapter 6: The Normal Distribution Diana Pell Section 6.1: Normal Distributions Note: Recall that a continuous variable can assume all values between any two given values of the variables. Many continuous
Chapter 6: The Normal Distribution Diana Pell Section 6.1: Normal Distributions Note: Recall that a continuous variable can assume all values between any two given values of the variables. Many continuous
Math 2311 Bekki George Office Hours: MW 11am to 12:45pm in 639 PGH Online Thursdays 4-5:30pm And by appointment
 Math 2311 Bekki George bekki@math.uh.edu Office Hours: MW 11am to 12:45pm in 639 PGH Online Thursdays 4-5:30pm And by appointment Class webpage: http://www.math.uh.edu/~bekki/math2311.html Math 2311 Class
Math 2311 Bekki George bekki@math.uh.edu Office Hours: MW 11am to 12:45pm in 639 PGH Online Thursdays 4-5:30pm And by appointment Class webpage: http://www.math.uh.edu/~bekki/math2311.html Math 2311 Class
Example - Let X be the number of boys in a 4 child family. Find the probability distribution table:
 Chapter7 Probability Distributions and Statistics Distributions of Random Variables tthe value of the result of the probability experiment is a RANDOM VARIABLE. Example - Let X be the number of boys in
Chapter7 Probability Distributions and Statistics Distributions of Random Variables tthe value of the result of the probability experiment is a RANDOM VARIABLE. Example - Let X be the number of boys in
Department of Quantitative Methods & Information Systems. Business Statistics. Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distribution QMIS 120. Dr.
 Department of Quantitative Methods & Information Systems Business Statistics Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distribution QMIS 120 Dr. Mohammad Zainal Chapter Goals After completing this chapter, you should
Department of Quantitative Methods & Information Systems Business Statistics Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distribution QMIS 120 Dr. Mohammad Zainal Chapter Goals After completing this chapter, you should
CH 5 Normal Probability Distributions Properties of the Normal Distribution
 Properties of the Normal Distribution Example A friend that is always late. Let X represent the amount of minutes that pass from the moment you are suppose to meet your friend until the moment your friend
Properties of the Normal Distribution Example A friend that is always late. Let X represent the amount of minutes that pass from the moment you are suppose to meet your friend until the moment your friend
NORMAL RANDOM VARIABLES (Normal or gaussian distribution)
 NORMAL RANDOM VARIABLES (Normal or gaussian distribution) Many variables, as pregnancy lengths, foot sizes etc.. exhibit a normal distribution. The shape of the distribution is a symmetric bell shape.
NORMAL RANDOM VARIABLES (Normal or gaussian distribution) Many variables, as pregnancy lengths, foot sizes etc.. exhibit a normal distribution. The shape of the distribution is a symmetric bell shape.
CHAPTER 6 Random Variables
 CHAPTER 6 Random Variables 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Discrete and Continuous Random
CHAPTER 6 Random Variables 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Discrete and Continuous Random
STAT Chapter 6 The Standard Deviation (SD) as a Ruler and The Normal Model
 STAT 203 - Chapter 6 The Standard Deviation (SD) as a Ruler and The Normal Model In Chapter 5, we introduced a few measures of center and spread, and discussed how the mean and standard deviation are good
STAT 203 - Chapter 6 The Standard Deviation (SD) as a Ruler and The Normal Model In Chapter 5, we introduced a few measures of center and spread, and discussed how the mean and standard deviation are good
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 First Name: Last Name: SID: Class Time: M Tu W Th math10 - HW5 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which choice is another term that
First Name: Last Name: SID: Class Time: M Tu W Th math10 - HW5 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which choice is another term that
AP Statistics Chapter 6 - Random Variables
 AP Statistics Chapter 6 - Random 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Objective: Recognize and define discrete random variables, and construct a probability distribution table and a probability histogram
AP Statistics Chapter 6 - Random 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Objective: Recognize and define discrete random variables, and construct a probability distribution table and a probability histogram
ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists
 ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists Session 7 The Normal Distribution Part 1 Lecturer: Dr. Bernardin Senadza, Dept. of Economics Contact Information: bsenadza@ug.edu.gh College of Education
ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists Session 7 The Normal Distribution Part 1 Lecturer: Dr. Bernardin Senadza, Dept. of Economics Contact Information: bsenadza@ug.edu.gh College of Education
Chapter Seven. The Normal Distribution
 Chapter Seven The Normal Distribution 7-1 Introduction Many continuous variables have distributions that are bellshaped and are called approximately normally distributed variables, such as the heights
Chapter Seven The Normal Distribution 7-1 Introduction Many continuous variables have distributions that are bellshaped and are called approximately normally distributed variables, such as the heights
Section Introduction to Normal Distributions
 Section 6.1-6.2 Introduction to Normal Distributions 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 of 105 Section 6.1-6.2 Objectives Interpret graphs of normal probability distributions Find areas
Section 6.1-6.2 Introduction to Normal Distributions 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 of 105 Section 6.1-6.2 Objectives Interpret graphs of normal probability distributions Find areas
Central Limit Theorem
 Central Limit Theorem Lots of Samples 1 Homework Read Sec 6-5. Discussion Question pg 329 Do Ex 6-5 8-15 2 Objective Use the Central Limit Theorem to solve problems involving sample means 3 Sample Means
Central Limit Theorem Lots of Samples 1 Homework Read Sec 6-5. Discussion Question pg 329 Do Ex 6-5 8-15 2 Objective Use the Central Limit Theorem to solve problems involving sample means 3 Sample Means
Unit 2: Statistics Probability
 Applied Math 30 3-1: Distributions Probability Distribution: - a table or a graph that displays the theoretical probability for each outcome of an experiment. - P (any particular outcome) is between 0
Applied Math 30 3-1: Distributions Probability Distribution: - a table or a graph that displays the theoretical probability for each outcome of an experiment. - P (any particular outcome) is between 0
Confidence Intervals for the Mean. When σ is known
 Confidence Intervals for the Mean When σ is known Objective Find the confidence interval for the mean when s is known. Intro Suppose a college president wishes to estimate the average age of students attending
Confidence Intervals for the Mean When σ is known Objective Find the confidence interval for the mean when s is known. Intro Suppose a college president wishes to estimate the average age of students attending
Example - Let X be the number of boys in a 4 child family. Find the probability distribution table:
 Chapter8 Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables tthe value of the result of the probability experiment is a RANDOM VARIABLE. Example - Let X be the number
Chapter8 Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables tthe value of the result of the probability experiment is a RANDOM VARIABLE. Example - Let X be the number
STAT Chapter 6 The Standard Deviation (SD) as a Ruler and The Normal Model
 STAT 203 - Chapter 6 The Standard Deviation (SD) as a Ruler and The Normal Model In Chapter 5, we introduced a few measures of center and spread, and discussed how the mean and standard deviation are good
STAT 203 - Chapter 6 The Standard Deviation (SD) as a Ruler and The Normal Model In Chapter 5, we introduced a few measures of center and spread, and discussed how the mean and standard deviation are good
2 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS
 Chapter 2 Descriptive Statistics 47 2 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Figure 2.1 When you have large amounts of data, you will need to organize it in a way that makes sense. These ballots from an election are rolled
Chapter 2 Descriptive Statistics 47 2 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Figure 2.1 When you have large amounts of data, you will need to organize it in a way that makes sense. These ballots from an election are rolled
The Normal Distribution
 Stat 6 Introduction to Business Statistics I Spring 009 Professor: Dr. Petrutza Caragea Section A Tuesdays and Thursdays 9:300:50 a.m. Chapter, Section.3 The Normal Distribution Density Curves So far we
Stat 6 Introduction to Business Statistics I Spring 009 Professor: Dr. Petrutza Caragea Section A Tuesdays and Thursdays 9:300:50 a.m. Chapter, Section.3 The Normal Distribution Density Curves So far we
Introduction to Statistics I
 Introduction to Statistics I Keio University, Faculty of Economics Continuous random variables Simon Clinet (Keio University) Intro to Stats November 1, 2018 1 / 18 Definition (Continuous random variable)
Introduction to Statistics I Keio University, Faculty of Economics Continuous random variables Simon Clinet (Keio University) Intro to Stats November 1, 2018 1 / 18 Definition (Continuous random variable)
The "bell-shaped" curve, or normal curve, is a probability distribution that describes many real-life situations.
 6.1 6.2 The Standard Normal Curve The "bell-shaped" curve, or normal curve, is a probability distribution that describes many real-life situations. Basic Properties 1. The total area under the curve is.
6.1 6.2 The Standard Normal Curve The "bell-shaped" curve, or normal curve, is a probability distribution that describes many real-life situations. Basic Properties 1. The total area under the curve is.
ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists 2016/2017
 ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists 2016/2017 Topic The Normal Distribution Lecturer: Dr. Bernardin Senadza, Dept. of Economics bsenadza@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and
ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists 2016/2017 Topic The Normal Distribution Lecturer: Dr. Bernardin Senadza, Dept. of Economics bsenadza@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and
Statistics vs. statistics
 Statistics vs. statistics Question: What is Statistics (with a capital S)? Definition: Statistics is the science of collecting, organizing, summarizing and interpreting data. Note: There are 2 main ways
Statistics vs. statistics Question: What is Statistics (with a capital S)? Definition: Statistics is the science of collecting, organizing, summarizing and interpreting data. Note: There are 2 main ways
Making Sense of Cents
 Name: Date: Making Sense of Cents Exploring the Central Limit Theorem Many of the variables that you have studied so far in this class have had a normal distribution. You have used a table of the normal
Name: Date: Making Sense of Cents Exploring the Central Limit Theorem Many of the variables that you have studied so far in this class have had a normal distribution. You have used a table of the normal
Since his score is positive, he s above average. Since his score is not close to zero, his score is unusual.
 Chapter 06: The Standard Deviation as a Ruler and the Normal Model This is the worst chapter title ever! This chapter is about the most important random variable distribution of them all the normal distribution.
Chapter 06: The Standard Deviation as a Ruler and the Normal Model This is the worst chapter title ever! This chapter is about the most important random variable distribution of them all the normal distribution.
Section Distributions of Random Variables
 Section 8.1 - Distributions of Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
Section 8.1 - Distributions of Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
22.2 Shape, Center, and Spread
 Name Class Date 22.2 Shape, Center, and Spread Essential Question: Which measures of center and spread are appropriate for a normal distribution, and which are appropriate for a skewed distribution? Eplore
Name Class Date 22.2 Shape, Center, and Spread Essential Question: Which measures of center and spread are appropriate for a normal distribution, and which are appropriate for a skewed distribution? Eplore
Continuous Probability Distributions
 Continuous Probability Distributions Chapter 7 Learning Objectives List the characteristics of the uniform distribution. Compute probabilities using the uniform distribution List the characteristics of
Continuous Probability Distributions Chapter 7 Learning Objectives List the characteristics of the uniform distribution. Compute probabilities using the uniform distribution List the characteristics of
Normal Probability Distributions
 Normal Probability Distributions Properties of Normal Distributions The most important probability distribution in statistics is the normal distribution. Normal curve A normal distribution is a continuous
Normal Probability Distributions Properties of Normal Distributions The most important probability distribution in statistics is the normal distribution. Normal curve A normal distribution is a continuous
A continuous random variable is one that can theoretically take on any value on some line interval. We use f ( x)
 Section 6-2 I. Continuous Probability Distributions A continuous random variable is one that can theoretically take on any value on some line interval. We use f ( x) to represent a probability density
Section 6-2 I. Continuous Probability Distributions A continuous random variable is one that can theoretically take on any value on some line interval. We use f ( x) to represent a probability density
DATA HANDLING Five-Number Summary
 DATA HANDLING Five-Number Summary The five-number summary consists of the minimum and maximum values, the median, and the upper and lower quartiles. The minimum and the maximum are the smallest and greatest
DATA HANDLING Five-Number Summary The five-number summary consists of the minimum and maximum values, the median, and the upper and lower quartiles. The minimum and the maximum are the smallest and greatest
These Statistics NOTES Belong to:
 These Statistics NOTES Belong to: Topic Notes Questions Date 1 2 3 4 5 6 REVIEW DO EVERY QUESTION IN YOUR PROVINCIAL EXAM BINDER Important Calculator Functions to know for this chapter Normal Distributions
These Statistics NOTES Belong to: Topic Notes Questions Date 1 2 3 4 5 6 REVIEW DO EVERY QUESTION IN YOUR PROVINCIAL EXAM BINDER Important Calculator Functions to know for this chapter Normal Distributions
Statistics 511 Supplemental Materials
 Gaussian (or Normal) Random Variable In this section we introduce the Gaussian Random Variable, which is more commonly referred to as the Normal Random Variable. This is a random variable that has a bellshaped
Gaussian (or Normal) Random Variable In this section we introduce the Gaussian Random Variable, which is more commonly referred to as the Normal Random Variable. This is a random variable that has a bellshaped
Measures of Variation. Section 2-5. Dotplots of Waiting Times. Waiting Times of Bank Customers at Different Banks in minutes. Bank of Providence
 Measures of Variation Section -5 1 Waiting Times of Bank Customers at Different Banks in minutes Jefferson Valley Bank 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 7.1 7.3 7.4 Bank of Providence 4. 5.4 5.8 6. 6.7 8.5 9.3 10.0 Mean
Measures of Variation Section -5 1 Waiting Times of Bank Customers at Different Banks in minutes Jefferson Valley Bank 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 7.1 7.3 7.4 Bank of Providence 4. 5.4 5.8 6. 6.7 8.5 9.3 10.0 Mean
If the distribution of a random variable x is approximately normal, then
 Confidence Intervals for the Mean (σ unknown) In many real life situations, the standard deviation is unknown. In order to construct a confidence interval for a random variable that is normally distributed
Confidence Intervals for the Mean (σ unknown) In many real life situations, the standard deviation is unknown. In order to construct a confidence interval for a random variable that is normally distributed
11.5: Normal Distributions
 11.5: Normal Distributions 11.5.1 Up to now, we ve dealt with discrete random variables, variables that take on only a finite (or countably infinite we didn t do these) number of values. A continuous random
11.5: Normal Distributions 11.5.1 Up to now, we ve dealt with discrete random variables, variables that take on only a finite (or countably infinite we didn t do these) number of values. A continuous random
Set up a normal distribution curve, to help estimate the percent of the band that, on average, practices a greater number of hours than Alexis.
 Section 5.5 Z-Scores Example 1 Alexis plays in her school jazz band. Band members practice an average of 16.5 h per week, with a standard deviation of 4.2 h. Alexis practices an average of 22 h per week.
Section 5.5 Z-Scores Example 1 Alexis plays in her school jazz band. Band members practice an average of 16.5 h per week, with a standard deviation of 4.2 h. Alexis practices an average of 22 h per week.
Math Tech IIII, May 7
 Math Tech IIII, May 7 The Normal Probability Models Book Sections: 5.1, 5.2, & 5.3 Essential Questions: How can I use the normal distribution to compute probability? Standards: S.ID.4 Properties of the
Math Tech IIII, May 7 The Normal Probability Models Book Sections: 5.1, 5.2, & 5.3 Essential Questions: How can I use the normal distribution to compute probability? Standards: S.ID.4 Properties of the
IOP 201-Q (Industrial Psychological Research) Tutorial 5
 IOP 201-Q (Industrial Psychological Research) Tutorial 5 TRUE/FALSE [1 point each] Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. To establish a cause-and-effect relation between two variables,
IOP 201-Q (Industrial Psychological Research) Tutorial 5 TRUE/FALSE [1 point each] Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. To establish a cause-and-effect relation between two variables,
Terms & Characteristics
 NORMAL CURVE Knowledge that a variable is distributed normally can be helpful in drawing inferences as to how frequently certain observations are likely to occur. NORMAL CURVE A Normal distribution: Distribution
NORMAL CURVE Knowledge that a variable is distributed normally can be helpful in drawing inferences as to how frequently certain observations are likely to occur. NORMAL CURVE A Normal distribution: Distribution
Density curves. (James Madison University) February 4, / 20
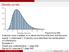 Density curves Figure 6.2 p 230. A density curve is always on or above the horizontal axis, and has area exactly 1 underneath it. A density curve describes the overall pattern of a distribution. Example
Density curves Figure 6.2 p 230. A density curve is always on or above the horizontal axis, and has area exactly 1 underneath it. A density curve describes the overall pattern of a distribution. Example
The Central Limit Theorem for Sums
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46997 1 The Central Limit Theorem for Sums OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Suppose X is a random
OpenStax-CNX module: m46997 1 The Central Limit Theorem for Sums OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Suppose X is a random
BIOL The Normal Distribution and the Central Limit Theorem
 BIOL 300 - The Normal Distribution and the Central Limit Theorem In the first week of the course, we introduced a few measures of center and spread, and discussed how the mean and standard deviation are
BIOL 300 - The Normal Distribution and the Central Limit Theorem In the first week of the course, we introduced a few measures of center and spread, and discussed how the mean and standard deviation are
2.) What is the set of outcomes that describes the event that at least one of the items selected is defective? {AD, DA, DD}
 Math 361 Practice Exam 2 (Use this information for questions 1 3) At the end of a production run manufacturing rubber gaskets, items are sampled at random and inspected to determine if the item is Acceptable
Math 361 Practice Exam 2 (Use this information for questions 1 3) At the end of a production run manufacturing rubber gaskets, items are sampled at random and inspected to determine if the item is Acceptable
Prob and Stats, Nov 7
 Prob and Stats, Nov 7 The Standard Normal Distribution Book Sections: 7.1, 7.2 Essential Questions: What is the standard normal distribution, how is it related to all other normal distributions, and how
Prob and Stats, Nov 7 The Standard Normal Distribution Book Sections: 7.1, 7.2 Essential Questions: What is the standard normal distribution, how is it related to all other normal distributions, and how
Statistical Methods in Practice STAT/MATH 3379
 Statistical Methods in Practice STAT/MATH 3379 Dr. A. B. W. Manage Associate Professor of Mathematics & Statistics Department of Mathematics & Statistics Sam Houston State University Overview 6.1 Discrete
Statistical Methods in Practice STAT/MATH 3379 Dr. A. B. W. Manage Associate Professor of Mathematics & Statistics Department of Mathematics & Statistics Sam Houston State University Overview 6.1 Discrete
6.1 Graphs of Normal Probability Distributions:
 6.1 Graphs of Normal Probability Distributions: Normal Distribution one of the most important examples of a continuous probability distribution, studied by Abraham de Moivre (1667 1754) and Carl Friedrich
6.1 Graphs of Normal Probability Distributions: Normal Distribution one of the most important examples of a continuous probability distribution, studied by Abraham de Moivre (1667 1754) and Carl Friedrich
Measures of Dispersion (Range, standard deviation, standard error) Introduction
 Measures of Dispersion (Range, standard deviation, standard error) Introduction We have already learnt that frequency distribution table gives a rough idea of the distribution of the variables in a sample
Measures of Dispersion (Range, standard deviation, standard error) Introduction We have already learnt that frequency distribution table gives a rough idea of the distribution of the variables in a sample
In a binomial experiment of n trials, where p = probability of success and q = probability of failure. mean variance standard deviation
 Name In a binomial experiment of n trials, where p = probability of success and q = probability of failure mean variance standard deviation µ = n p σ = n p q σ = n p q Notation X ~ B(n, p) The probability
Name In a binomial experiment of n trials, where p = probability of success and q = probability of failure mean variance standard deviation µ = n p σ = n p q σ = n p q Notation X ~ B(n, p) The probability
Applications of Data Dispersions
 1 Applications of Data Dispersions Key Definitions Standard Deviation: The standard deviation shows how far away each value is from the mean on average. Z-Scores: The distance between the mean and a given
1 Applications of Data Dispersions Key Definitions Standard Deviation: The standard deviation shows how far away each value is from the mean on average. Z-Scores: The distance between the mean and a given
AP * Statistics Review
 AP * Statistics Review Normal Models and Sampling Distributions Teacher Packet AP* is a trademark of the College Entrance Examination Board. The College Entrance Examination Board was not involved in the
AP * Statistics Review Normal Models and Sampling Distributions Teacher Packet AP* is a trademark of the College Entrance Examination Board. The College Entrance Examination Board was not involved in the
MAKING SENSE OF DATA Essentials series
 MAKING SENSE OF DATA Essentials series THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION Copyright by City of Bradford MDC Prerequisites Descriptive statistics Charts and graphs The normal distribution Surveys and sampling Correlation
MAKING SENSE OF DATA Essentials series THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION Copyright by City of Bradford MDC Prerequisites Descriptive statistics Charts and graphs The normal distribution Surveys and sampling Correlation
Module Tag PSY_P2_M 7. PAPER No.2: QUANTITATIVE METHODS MODULE No.7: NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
 Subject Paper No and Title Module No and Title Paper No.2: QUANTITATIVE METHODS Module No.7: NORMAL DISTRIBUTION Module Tag PSY_P2_M 7 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction 3. Properties
Subject Paper No and Title Module No and Title Paper No.2: QUANTITATIVE METHODS Module No.7: NORMAL DISTRIBUTION Module Tag PSY_P2_M 7 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction 3. Properties
What s Normal? Chapter 8. Hitting the Curve. In This Chapter
 Chapter 8 What s Normal? In This Chapter Meet the normal distribution Standard deviations and the normal distribution Excel s normal distribution-related functions A main job of statisticians is to estimate
Chapter 8 What s Normal? In This Chapter Meet the normal distribution Standard deviations and the normal distribution Excel s normal distribution-related functions A main job of statisticians is to estimate
Chapter 7. Sampling Distributions
 Chapter 7 Sampling Distributions Section 7.1 Sampling Distributions and the Central Limit Theorem Sampling Distributions Sampling distribution The probability distribution of a sample statistic. Formed
Chapter 7 Sampling Distributions Section 7.1 Sampling Distributions and the Central Limit Theorem Sampling Distributions Sampling distribution The probability distribution of a sample statistic. Formed
A probability distribution shows the possible outcomes of an experiment and the probability of each of these outcomes.
 Introduction In the previous chapter we discussed the basic concepts of probability and described how the rules of addition and multiplication were used to compute probabilities. In this chapter we expand
Introduction In the previous chapter we discussed the basic concepts of probability and described how the rules of addition and multiplication were used to compute probabilities. In this chapter we expand
Section Distributions of Random Variables
 Section 8.1 - Distributions of Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
Section 8.1 - Distributions of Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
STATS DOESN T SUCK! ~ CHAPTER 4
 CHAPTER 4 QUESTION 1 The Geometric Mean Suppose you make a 2-year investment of $5,000 and it grows by 100% to $10,000 during the first year. During the second year, however, the investment suffers a 50%
CHAPTER 4 QUESTION 1 The Geometric Mean Suppose you make a 2-year investment of $5,000 and it grows by 100% to $10,000 during the first year. During the second year, however, the investment suffers a 50%
Section Random Variables and Histograms
 Section 3.1 - Random Variables and Histograms Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
Section 3.1 - Random Variables and Histograms Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
Fall 2011 Exam Score: /75. Exam 3
 Math 12 Fall 2011 Name Exam Score: /75 Total Class Percent to Date Exam 3 For problems 1-10, circle the letter next to the response that best answers the question or completes the sentence. You do not
Math 12 Fall 2011 Name Exam Score: /75 Total Class Percent to Date Exam 3 For problems 1-10, circle the letter next to the response that best answers the question or completes the sentence. You do not
Continuous Distributions
 Quantitative Methods 2013 Continuous Distributions 1 The most important probability distribution in statistics is the normal distribution. Carl Friedrich Gauss (1777 1855) Normal curve A normal distribution
Quantitative Methods 2013 Continuous Distributions 1 The most important probability distribution in statistics is the normal distribution. Carl Friedrich Gauss (1777 1855) Normal curve A normal distribution
Math 140 Introductory Statistics. First midterm September
 Math 140 Introductory Statistics First midterm September 23 2010 Box Plots Graphical display of 5 number summary Q1, Q2 (median), Q3, max, min Outliers If a value is more than 1.5 times the IQR from the
Math 140 Introductory Statistics First midterm September 23 2010 Box Plots Graphical display of 5 number summary Q1, Q2 (median), Q3, max, min Outliers If a value is more than 1.5 times the IQR from the
Section 5.5 Z Scores soln.notebook. December 07, Section 5.5 Z Scores
 Section 5.5 Z Scores 1 Warm up/review: The Normal Distribution Curve Given that the average adult in North America has a mean mass of 72 kg, with a standard deviation of 14 kg. a) How many standard deviations
Section 5.5 Z Scores 1 Warm up/review: The Normal Distribution Curve Given that the average adult in North America has a mean mass of 72 kg, with a standard deviation of 14 kg. a) How many standard deviations
Honors Statistics. Daily Agenda
 Honors Statistics Daily Agenda 1. Review OTL C6#5 2. Quiz Section 6.1 A-Skip 35, 39, 40 Crickets The length in inches of a cricket chosen at random from a field is a random variable X with mean 1.2 inches
Honors Statistics Daily Agenda 1. Review OTL C6#5 2. Quiz Section 6.1 A-Skip 35, 39, 40 Crickets The length in inches of a cricket chosen at random from a field is a random variable X with mean 1.2 inches
Chapter 9 & 10. Multiple Choice.
 Chapter 9 & 10 Review Name Multiple Choice. 1. An agricultural researcher plants 25 plots with a new variety of corn. The average yield for these plots is X = 150 bushels per acre. Assume that the yield
Chapter 9 & 10 Review Name Multiple Choice. 1. An agricultural researcher plants 25 plots with a new variety of corn. The average yield for these plots is X = 150 bushels per acre. Assume that the yield
Continuous Probability Distributions & Normal Distribution
 Mathematical Methods Units 3/4 Student Learning Plan Continuous Probability Distributions & Normal Distribution 7 lessons Notes: Students need practice in recognising whether a problem involves a discrete
Mathematical Methods Units 3/4 Student Learning Plan Continuous Probability Distributions & Normal Distribution 7 lessons Notes: Students need practice in recognising whether a problem involves a discrete
When we look at a random variable, such as Y, one of the first things we want to know, is what is it s distribution?
 Distributions 1. What are distributions? When we look at a random variable, such as Y, one of the first things we want to know, is what is it s distribution? In other words, if we have a large number of
Distributions 1. What are distributions? When we look at a random variable, such as Y, one of the first things we want to know, is what is it s distribution? In other words, if we have a large number of
Key Objectives. Module 2: The Logic of Statistical Inference. Z-scores. SGSB Workshop: Using Statistical Data to Make Decisions
 SGSB Workshop: Using Statistical Data to Make Decisions Module 2: The Logic of Statistical Inference Dr. Tom Ilvento January 2006 Dr. Mugdim Pašić Key Objectives Understand the logic of statistical inference
SGSB Workshop: Using Statistical Data to Make Decisions Module 2: The Logic of Statistical Inference Dr. Tom Ilvento January 2006 Dr. Mugdim Pašić Key Objectives Understand the logic of statistical inference
Example. Chapter 8 Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables
 Chapter 8 Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables You are dealt a hand of 5 cards. Find the probability distribution table for the number of hearts. Graph
Chapter 8 Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables You are dealt a hand of 5 cards. Find the probability distribution table for the number of hearts. Graph
MATH FOR LIBERAL ARTS REVIEW 2
 MATH FOR LIBERAL ARTS REVIEW 2 Use the theoretical probability formula to solve the problem. Express the probability as a fraction reduced to lowest terms. 1) A die is rolled. The set of equally likely
MATH FOR LIBERAL ARTS REVIEW 2 Use the theoretical probability formula to solve the problem. Express the probability as a fraction reduced to lowest terms. 1) A die is rolled. The set of equally likely
Continuous Probability Distributions
 Continuous Probability Distributions Chapter 07 McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. LEARNING OBJECTIVES LO 7-1 List the characteristics of the uniform
Continuous Probability Distributions Chapter 07 McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. LEARNING OBJECTIVES LO 7-1 List the characteristics of the uniform
Section 7-2 Estimating a Population Proportion
 Section 7- Estimating a Population Proportion 1 Key Concept In this section we present methods for using a sample proportion to estimate the value of a population proportion. The sample proportion is the
Section 7- Estimating a Population Proportion 1 Key Concept In this section we present methods for using a sample proportion to estimate the value of a population proportion. The sample proportion is the
Discrete Probability Distribution
 1 Discrete Probability Distribution Key Definitions Discrete Random Variable: Has a countable number of values. This means that each data point is distinct and separate. Continuous Random Variable: Has
1 Discrete Probability Distribution Key Definitions Discrete Random Variable: Has a countable number of values. This means that each data point is distinct and separate. Continuous Random Variable: Has
A) The first quartile B) The Median C) The third quartile D) None of the previous. 2. [3] If P (A) =.8, P (B) =.7, and P (A B) =.
![A) The first quartile B) The Median C) The third quartile D) None of the previous. 2. [3] If P (A) =.8, P (B) =.7, and P (A B) =. A) The first quartile B) The Median C) The third quartile D) None of the previous. 2. [3] If P (A) =.8, P (B) =.7, and P (A B) =.](/thumbs/95/124846909.jpg) Review for stat2507 Final (December 2008) Part I: Multiple Choice questions (on 39%): Please circle only one choice. 1. [3] Which one of the following summary measures is affected most by outliers A) The
Review for stat2507 Final (December 2008) Part I: Multiple Choice questions (on 39%): Please circle only one choice. 1. [3] Which one of the following summary measures is affected most by outliers A) The
T.I.H.E. IT 233 Statistics and Probability: Sem. 1: 2013 ESTIMATION
 In Inferential Statistic, ESTIMATION (i) (ii) is called the True Population Mean and is called the True Population Proportion. You must also remember that are not the only population parameters. There
In Inferential Statistic, ESTIMATION (i) (ii) is called the True Population Mean and is called the True Population Proportion. You must also remember that are not the only population parameters. There
Chapter 6: Random Variables
 Chapter 6: Random Variables Section 6. The Practice of Statistics, 4 th edition For AP* STARNES, YATES, MOORE Chapter 6 Random Variables 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables 6. 6.3 Binomial and
Chapter 6: Random Variables Section 6. The Practice of Statistics, 4 th edition For AP* STARNES, YATES, MOORE Chapter 6 Random Variables 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables 6. 6.3 Binomial and
Chapter 7 Study Guide: The Central Limit Theorem
 Chapter 7 Study Guide: The Central Limit Theorem Introduction Why are we so concerned with means? Two reasons are that they give us a middle ground for comparison and they are easy to calculate. In this
Chapter 7 Study Guide: The Central Limit Theorem Introduction Why are we so concerned with means? Two reasons are that they give us a middle ground for comparison and they are easy to calculate. In this
Describing Data: One Quantitative Variable
 STAT 250 Dr. Kari Lock Morgan The Big Picture Describing Data: One Quantitative Variable Population Sampling SECTIONS 2.2, 2.3 One quantitative variable (2.2, 2.3) Statistical Inference Sample Descriptive
STAT 250 Dr. Kari Lock Morgan The Big Picture Describing Data: One Quantitative Variable Population Sampling SECTIONS 2.2, 2.3 One quantitative variable (2.2, 2.3) Statistical Inference Sample Descriptive
MAS1403. Quantitative Methods for Business Management. Semester 1, Module leader: Dr. David Walshaw
 MAS1403 Quantitative Methods for Business Management Semester 1, 2018 2019 Module leader: Dr. David Walshaw Additional lecturers: Dr. James Waldren and Dr. Stuart Hall Announcements: Written assignment
MAS1403 Quantitative Methods for Business Management Semester 1, 2018 2019 Module leader: Dr. David Walshaw Additional lecturers: Dr. James Waldren and Dr. Stuart Hall Announcements: Written assignment
Honors Statistics. 3. Review OTL C6#3. 4. Normal Curve Quiz. Chapter 6 Section 2 Day s Notes.notebook. May 02, 2016.
 Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM 3. Review OTL C6#3 4. Normal Curve Quiz Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 May 1-9:09 PM Apr 28-10:29 AM 2 27, 28, 29, 30 Nov 21-8:16 PM Working out Choose a person aged 19 to 25 years at
Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM 3. Review OTL C6#3 4. Normal Curve Quiz Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 May 1-9:09 PM Apr 28-10:29 AM 2 27, 28, 29, 30 Nov 21-8:16 PM Working out Choose a person aged 19 to 25 years at
Biostatistics and Design of Experiments Prof. Mukesh Doble Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Biostatistics and Design of Experiments Prof. Mukesh Doble Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 05 Normal Distribution So far we have looked at discrete distributions
Biostatistics and Design of Experiments Prof. Mukesh Doble Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 05 Normal Distribution So far we have looked at discrete distributions
WebAssign Math 3680 Homework 5 Devore Fall 2013 (Homework)
 WebAssign Math 3680 Homework 5 Devore Fall 2013 (Homework) Current Score : 135.45 / 129 Due : Friday, October 11 2013 11:59 PM CDT Mirka Martinez Applied Statistics, Math 3680-Fall 2013, section 2, Fall
WebAssign Math 3680 Homework 5 Devore Fall 2013 (Homework) Current Score : 135.45 / 129 Due : Friday, October 11 2013 11:59 PM CDT Mirka Martinez Applied Statistics, Math 3680-Fall 2013, section 2, Fall
Chapter 7 Sampling Distributions and Point Estimation of Parameters
 Chapter 7 Sampling Distributions and Point Estimation of Parameters Part 1: Sampling Distributions, the Central Limit Theorem, Point Estimation & Estimators Sections 7-1 to 7-2 1 / 25 Statistical Inferences
Chapter 7 Sampling Distributions and Point Estimation of Parameters Part 1: Sampling Distributions, the Central Limit Theorem, Point Estimation & Estimators Sections 7-1 to 7-2 1 / 25 Statistical Inferences
AP Stats Review. Mrs. Daniel Alonzo & Tracy Mourning Sr. High
 AP Stats Review Mrs. Daniel Alonzo & Tracy Mourning Sr. High sdaniel@dadeschools.net Agenda 1. AP Stats Exam Overview 2. AP FRQ Scoring & FRQ: 2016 #1 3. Distributions Review 4. FRQ: 2015 #6 5. Distribution
AP Stats Review Mrs. Daniel Alonzo & Tracy Mourning Sr. High sdaniel@dadeschools.net Agenda 1. AP Stats Exam Overview 2. AP FRQ Scoring & FRQ: 2016 #1 3. Distributions Review 4. FRQ: 2015 #6 5. Distribution
