Extrinsic and Intrinsic Motivations for Tax Compliance: Evidence from a Field Experiment in Germany
|
|
|
- Grace Blair
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Extrinsic and Intrinsic Motivations for Tax Compliance: Evidence from a Field Experiment in Germany Nadja Dwenger (MPI) Henrik Kleven (LSE) Imran Rasul (UCL) Johannes Rincke (Erlangen-Nuremberg) October 2014
2 A Tax Compliance Puzzle? Gap between theory and evidence: Theory predicts low compliance under low audit probabilities or penalties (Becker-Allingham-Sandmo) Evidence shows high compliance in modern tax systems despite low audit probabilities and penalties Closing the gap: Third-party information creates large detection probabilities Misperception of enforcement parameters Intrinsic or social motivations
3 Extrinsic and Intrinsic Motivations Extrinsic motivation (pecuniary): Deterrence and tax policy Intrinsic motivation (non-pecuniary): Duty,guilt,shame,socialnorms,reciprocity,etc. Studying intrinsic motives is difficult: measurement, variation We consider a setting in which we can identify extrinsically and intrinsically motivated individuals We vary deterrence and rewards/recognition in a field experiment
4 Local Church Tax in Germany: Key features Feature 1: tax and charity Legal obligation to pay for church members Overpayments are encouraged and represent donations Feature2: truetaxbaseisobservable True tax base for church = reported taxable income to government Distinguish evaders, compliers & donors Feature 3: zero deterrence in the baseline Church never cross-checks reports against income tax returns Baseline compliance = intrinsic motivation
5 Local Church Tax in Germany: Identifying Motivation Baseline behavior (p = 0) reveals motivation: Baseline compliers & donors: intrinsically motivated Baseline evaders: extrinsically motivated Compliance type is very persistent prior to experiment: We define types based simply on one pre-treatment year Each type could be subject to misperception (p 0): Estimate misperception via (randomized) communication of =0 Separate misperception from motivation
6 Outline 1. Conceptual framework: warm-glow model of tax compliance 2. Context, design and data 3. Empirical findings (a) Baseline compliance under zero deterrence: Amount of intrinsic motivation; duty to comply (b) Randomized field experiment: Simplification; misperception; deterrence; rewards 4. Conclusion
7 Outline 1. Conceptual framework: warm-glow model of tax compliance 2. Context, design and data 3. Empirical findings (a) Baseline compliance under zero deterrence: Amount of intrinsic motivation; duty to comply (b) Randomized field experiment: Simplification; misperception; deterrence; rewards 4. Conclusion
8 Local Church Tax in Germany Legal tax obligation for church members above 18 years of age Membership by baptism; possible to quit church 60% of the population are members Two tiers of church taxes: federal state, church district Our focus: Local church tax for Protestant church in a large metro area of Bavaria Legal tax obligation determined by a progressive schedule Payments above legal tax obligation defined as donations Concern with external validity: stakes are small
9 Local Church Tax in Germany: Tax Schedule
10 Experimental Design Manipulations of the official tax notification from the church tax authority Randomly assignment to treatment letters: Tax simplification Zero deterrence (misperception) Positive Deterrence (audit probabilities) Compliance rewards (social and monetary rewards) Randomization successful across all letter groups All treatments were truthfully implemented
11 Data Linked administrative panel data : Church District tax records State personal income tax records About 40,000 individuals per year with information on actual church taxes paid, true church taxes owed, and personal characteristics Individual records of tax compliance for up to 4 years pre-treatment
12 Outline 1. Conceptual framework: warm-glow model of tax compliance 2. Context, design and data 3. Empirical findings (a) Baseline compliance under zero deterrence: Amount of intrinsic motivation; duty to comply (b) Randomized field experiment: Simplification; misperception; deterrence; rewards 4. Conclusion
13 Compliance Under Zero Deterrence [Distributions of Payment Made and Payment Owed] (Control Group)
14 Finding 1: Intrinsic Motivation is Substantial (or Not) Under zero deterrence, predicted compliance is zero absent intrinsic motivation But a significant fraction of individuals comply: 20% of individuals make payment true taxes owed 80% of individuals make payment true taxes owed (and most of them pay zero) Implications for the compliance puzzle debate: The Becker-Allingham-Sandmo model is 20% wrong, 80% right
15 Bunching at Exact Compliance under Zero Deterrence [Distribution of payment made payment owed] (Control Group)
16 Finding 2: Bunching at Exact Compliance Sharp bunching at exact compliance under zero deterrence: No pecuniary discontinuity at exact compliance under zero deterrence Discontinuity in intrinsic motivation at exact compliance Two possible explanations (labels): 1. Duty to comply with the letter of the law 2. Attention/focal point effects (We provide a test suggesting against the latter)
17 Outline 1. Conceptual framework: warm-glow model of tax compliance 2. Context, design and data 3. Empirical findings (a) Baseline compliance under zero deterrence: Amount of intrinsic motivation; duty to comply (b) Randomized field experiment: Simplification; misperception; deterrence; rewards 4. Conclusion
18 Tax Simplification [Heterogeneity Across Compliance Types] (Simplification vs Control) Full Sample Baseline Evaders Baseline Donors (Extrinsically Motivated) (Intrinsically Motivated) Probability of Evading Evasion Rate Probability of Evading Evasion Rate Probability of Donating Increased Donation Rate Tax Simplification -2.45** -3.17*** -2.66*** -3.36*** (0.971) (0.910) (0.747) (0.732) (6.97) (27.88) Outcome in comparison group (control group) 79.29% 76.35% 94.98% 92.35% 62.34% 9.09% Number of Observations
19 Tax Simplification [Distributional Effects on Baseline Evaders] (Simplification vs Control)
20 Correcting Misperception [Heterogeneity Across Compliance Types] (Zero Audit Probability vs Simplification) Full Sample Baseline Evaders Baseline Donors (Extrinsically Motivated) (Intrinsically Motivated) Probability of Evading Evasion Rate Probability of Evading Evasion Rate Probability of Donating Increased Donation Rate Correcting Misperception ** 1.41* (0.889) (0.857) (0.715) (0.720) (5.78) (37.38) Outcome in comparison group (simplification group) 77.30% 73.37% 92.35% 88.69% 61.63% 5.71% Number of Observations
21 Correcting Misperception [Distributional Effects on Baseline Evaders] (Zero Audit Probability vs Simplification)
22 Finding 3: Simplification Matters, Misperception Less So Tax simplification: Baseline evaders: strong positive effect on compliance Baseline donors: no significant effect Correcting misperception of audit probability: Baseline evaders: weak negative effect on compliance Baseline donors: no significant effect
23 Outline 1. Conceptual framework: warm-glow model of tax compliance 2. Context, design and data 3. Empirical findings (a) Baseline compliance under zero deterrence: Amount of intrinsic motivation; duty to comply (b) Randomized field experiment: Simplification; misperception; deterrence; rewards 4. Conclusion
24 Positive Audit Probability [Heterogeneity Across Compliance Types] (Positive Audit Probability vs Zero Audit Probability) Full Sample Baseline Evaders Baseline Donors (Extrinsically Motivated) (Intrinsically Motivated) Probability of Evading Evasion Rate Probability of Evading Evasion Rate Probability of Donating Increased Donation Rate Deterrence -3.13*** -2.80*** -3.12*** -2.81*** 7.07* (0.660) (0.627) (0.536) (0.534) (4.22) (22.20) Outcome in comparison group (zero audit prob group) 78.04% 74.52% 93.80% 90.43% 61.72% 8.16% Number of Observations
25 Positive Audit Probability [Distributional Effects on Baseline Evaders] (Positive Audit Probability vs Zero Audit Probability)
26 Perceived Penalty? Audit results suggest a perceived penalty of being caught evading But we can provide direct evidence using a bunching approach: Asymmetric treatment of evaders (expected penalty = )and donors (zero penalty) Penalty kink under 0 iff perceived penalty is positive There is already bunching under =0( duty-to-comply ), so we consider Change in bunching when moving from =0to 0
27 Perceived Penalty [Change in Bunching at Exact Compliance] (Positive Audit Probability vs Simplification)
28 Finding 4: Deterrence Works on the Extrinsically Motivated, Not on the Intrinsically Motivated Baseline evaders: compliance increases with deterrence Significant increases for uniform audit probabilities of 10%, 20%, 50% Stronger effects for notched audit probability Significant responses to perceived penalty Baseline donors: weak effect of deterrence No effect on donation amount, weak effect on probability of donating Hence there is no extrinsic-intrinsic crowd-out
29 Outline 1. Conceptual framework: warm-glow model of tax compliance 2. Context, design and data 3. Empirical findings (a) Baseline compliance under zero deterrence: Amount of intrinsic motivation; duty to comply (b) Randomized field experiment: Simplification; misperception; deterrence; rewards 4. Conclusion
30 Compliance Rewards [Heterogeneity Across Compliance Types] (Social/Monetary Rewards vs Simplification) Full Sample Baseline Evaders (Extrinsically Motivated) Baseline Donors (Intrinsically Motivated) Probability of Evading Evasion Rate Probability of Evading Evasion Rate Probability of Donating Increased Donation Rate Compliance Rewards * 1.20* ** (0.821) (0.789) (0.664) (0.666) (4.95) (32.80) Outcome in comparison group (simplification group) 77.30% 73.37% 92.35% 88.69% 61.63% 5.71% Number of Observations
31 Compliance Rewards [Distributional Effects on Baseline Evaders] (Social/Monetary Rewards vs Simplification)
32 Finding 5: Recognition Works on the Intrinsically Motivated, Not on the Extrinsically Motivated Compliance rewards create opposite effects on the two types: Baseline donors increase donations Baseline evaders further reduce compliance Average effect is strongly attenuated Interpretation: Rewarding compliers (rather than punishing evaders) highlights voluntary contribution aspect and downplays mandatory tax aspect
33 Conclusions Some of the first evidence on intrinsically motivated tax compliance Direct evidence on intrinsic motivation from a zero deterrence baseline: Becker-Allingham-Sandmo model is 20% wrong, 80% right Study interaction between individual motivation and policy First integrated treatment of tax compliance and charitable giving Imperfectly enforced tax systems have an element of voluntary giving External validity issues are addressed in the paper: Smallness of tax; zero enforcement signal; donation substitution
Economic and Social Incentives for Tax Compliance: Evidence from a Field Experiment in Germany
 Economic and Social Incentives for Tax Compliance: Evidence from a Field Experiment in Germany Nadja Dwenger (MPI) Henrik Kleven (LSE) Imran Rasul (UCL) Johannes Rincke (Univ. of Erlangen-Nuremberg) July
Economic and Social Incentives for Tax Compliance: Evidence from a Field Experiment in Germany Nadja Dwenger (MPI) Henrik Kleven (LSE) Imran Rasul (UCL) Johannes Rincke (Univ. of Erlangen-Nuremberg) July
Extrinsic and Intrinsic Motivations for Tax Compliance: Evidence from a Field Experiment in Germany
 Extrinsic and Intrinsic Motivations for Tax Compliance: Evidence from a Field Experiment in Germany By Nadja Dwenger, Henrik Kleven, Imran Rasul, and Johannes Rincke We study extrinsic and intrinsic motivations
Extrinsic and Intrinsic Motivations for Tax Compliance: Evidence from a Field Experiment in Germany By Nadja Dwenger, Henrik Kleven, Imran Rasul, and Johannes Rincke We study extrinsic and intrinsic motivations
Extrinsic and Intrinsic Motivations for Tax Compliance: Evidence from a Field Experiment in Germany
 Extrinsic and Intrinsic Motivations for Tax Compliance: Evidence from a Field Experiment in Germany Nadja Dwenger, Henrik Kleven, Imran Rasul, Johannes Rincke May 2014 Abstract We study extrinsic and intrinsic
Extrinsic and Intrinsic Motivations for Tax Compliance: Evidence from a Field Experiment in Germany Nadja Dwenger, Henrik Kleven, Imran Rasul, Johannes Rincke May 2014 Abstract We study extrinsic and intrinsic
econstor Make Your Publications Visible.
 econstor Make Your Publications Visible. A Service of Wirtschaft Centre zbwleibniz-informationszentrum Economics Dwenger, Nadja; Kleven, Henrik; Rasul, Imran; Rincke, Johannes Conference Paper Extrinsic
econstor Make Your Publications Visible. A Service of Wirtschaft Centre zbwleibniz-informationszentrum Economics Dwenger, Nadja; Kleven, Henrik; Rasul, Imran; Rincke, Johannes Conference Paper Extrinsic
Who Pays Maine Use Tax?
 Who Pays Maine Use Tax? David Gunter Maine Revenue Services Disclaimer: This presentation does not represent the views of Maine Revenue Services or the state of Maine. Maine use tax background 5% rate
Who Pays Maine Use Tax? David Gunter Maine Revenue Services Disclaimer: This presentation does not represent the views of Maine Revenue Services or the state of Maine. Maine use tax background 5% rate
Do Taxes Crowd Out Intrinsic Motivation? Field-Experimental Evidence from Germany
 Do Taxes Crowd Out Intrinsic Motivation? Field-Experimental Evidence from Germany Pierre C. Boyer, Nadja Dwenger, Johannes Rincke July 30, 2015 Abstract This paper studies how imposing norms on contribution
Do Taxes Crowd Out Intrinsic Motivation? Field-Experimental Evidence from Germany Pierre C. Boyer, Nadja Dwenger, Johannes Rincke July 30, 2015 Abstract This paper studies how imposing norms on contribution
Taxation and Development
 Taxation and Development Henrik Kleven London School of Economics January 2017 1 / 51 What Separates PF-Devo From PF? PF-Devo is more than just studying taxation in developing countries Focus on tax enforcement
Taxation and Development Henrik Kleven London School of Economics January 2017 1 / 51 What Separates PF-Devo From PF? PF-Devo is more than just studying taxation in developing countries Focus on tax enforcement
Behavioural insights and tax compliance: Evidence from large-scale field experiments in Belgium
 Behavioural insights and tax compliance: Evidence from large-scale field experiments in Belgium Clement Imbert (Warwick) with Jan-Emmanuel De Neve (Oxford), Maarten Luts (FOD Finance), Johannes Spinnewijn
Behavioural insights and tax compliance: Evidence from large-scale field experiments in Belgium Clement Imbert (Warwick) with Jan-Emmanuel De Neve (Oxford), Maarten Luts (FOD Finance), Johannes Spinnewijn
Tax Gap Map Tax Year 2006 ($ billions)
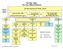 Tax Gap Map Tax Year 2006 ($ billions) Total Tax Liability $2,660 Gross Tax Gap: $450 (Voluntary Compliance Rate = 83.1%) Tax Paid Voluntarily & Timely: $2,210 Enforced & Other Late Payments of Tax $65
Tax Gap Map Tax Year 2006 ($ billions) Total Tax Liability $2,660 Gross Tax Gap: $450 (Voluntary Compliance Rate = 83.1%) Tax Paid Voluntarily & Timely: $2,210 Enforced & Other Late Payments of Tax $65
Tax Compliance by Trust and Power of Authorities Stephan Muehlbacher a ; Erich Kirchler a a
 This article was downloaded by: [Muehlbacher, Stephan] On: 15 December 010 Access details: Access Details: [subscription number 931135118] Publisher Routledge Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales
This article was downloaded by: [Muehlbacher, Stephan] On: 15 December 010 Access details: Access Details: [subscription number 931135118] Publisher Routledge Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales
Increasing tax compliance auditing, appeals to tax morale, or both? A lab experiment.
 Increasing tax compliance auditing, appeals to tax morale, or both? A lab experiment. Kristina M. Bott Norwegian School of Economics May 17, 2016 Abstract In a novel public good game design, this paper
Increasing tax compliance auditing, appeals to tax morale, or both? A lab experiment. Kristina M. Bott Norwegian School of Economics May 17, 2016 Abstract In a novel public good game design, this paper
Tax Morale. Erzo F.P. Luttmer and Monica Singhal
 Tax Morale Erzo F.P. Luttmer and Monica Singhal Erzo F.P. Luttmer is Professor of Economics, Dartmouth College, Hanover, New Hampshire. Monica Singhal is Associate Professor of Public Policy, Harvard Kennedy
Tax Morale Erzo F.P. Luttmer and Monica Singhal Erzo F.P. Luttmer is Professor of Economics, Dartmouth College, Hanover, New Hampshire. Monica Singhal is Associate Professor of Public Policy, Harvard Kennedy
Online Appendix. income and saving-consumption preferences in the context of dividend and interest income).
 Online Appendix 1 Bunching A classical model predicts bunching at tax kinks when the budget set is convex, because individuals above the tax kink wish to decrease their income as the tax rate above the
Online Appendix 1 Bunching A classical model predicts bunching at tax kinks when the budget set is convex, because individuals above the tax kink wish to decrease their income as the tax rate above the
Tax Notches in Pakistan: Tax Evasion, Real Responses, and Income Shifting
 Tax Notches in Pakistan: Tax Evasion, Real Responses, and Income Shifting Henrik Jacobsen Kleven, London School of Economics Mazhar Waseem, London School of Economics May 2011 Abstract Using administrative
Tax Notches in Pakistan: Tax Evasion, Real Responses, and Income Shifting Henrik Jacobsen Kleven, London School of Economics Mazhar Waseem, London School of Economics May 2011 Abstract Using administrative
University of Mannheim
 Threshold Events and Identication: A Study of Cash Shortfalls Bakke and Whited, published in the Journal of Finance in June 2012 Introduction The paper combines three objectives 1 Provide general guidelines
Threshold Events and Identication: A Study of Cash Shortfalls Bakke and Whited, published in the Journal of Finance in June 2012 Introduction The paper combines three objectives 1 Provide general guidelines
Strictness of Tax Compliance Norms: A Factorial Survey on the Acceptance of Inheritance Tax Evasion in Germany
 Strictness of Tax Compliance Norms: A Factorial Survey on the Acceptance of Inheritance Tax Evasion in Germany Martin Abraham, Kerstin Lorek, Friedemann Richter, Matthias Wrede Rational Choice Sociology
Strictness of Tax Compliance Norms: A Factorial Survey on the Acceptance of Inheritance Tax Evasion in Germany Martin Abraham, Kerstin Lorek, Friedemann Richter, Matthias Wrede Rational Choice Sociology
Are the Neighbors Cheating? Evidence from a Social Norm Experiment on Property Taxes in Peru. Job Market Paper
 Are the Neighbors Cheating? Evidence from a Social Norm Experiment on Property Taxes in Peru Job Market Paper Lucia Del Carpio November 12, 2013 Abstract I study the role of norms on tax compliance through
Are the Neighbors Cheating? Evidence from a Social Norm Experiment on Property Taxes in Peru Job Market Paper Lucia Del Carpio November 12, 2013 Abstract I study the role of norms on tax compliance through
how can we explain the observed historical and comparative development of tax structures? A rapid survey about State s capacity to raise taxes
 how can we explain the observed historical and comparative development of tax structures? A rapid survey about State s capacity to raise taxes Besley, Persson (2007a), The origin of state capacity: property
how can we explain the observed historical and comparative development of tax structures? A rapid survey about State s capacity to raise taxes Besley, Persson (2007a), The origin of state capacity: property
Who is audited? Experimental study on rule-based tax auditing schemes
 Social Design Engineering Series SDES-2015-21 Who is audited? Experimental study on rule-based tax auditing schemes Yoshio Kamijo Kochi University of Technology Research Center for Social Design Engineering,
Social Design Engineering Series SDES-2015-21 Who is audited? Experimental study on rule-based tax auditing schemes Yoshio Kamijo Kochi University of Technology Research Center for Social Design Engineering,
Evidence from a tax audit experiment in Denmark. Claus Thustrup Kreiner University of Copenhagen, CESifo, CEPR, Danish Economic Council.
 What makes tax payers comply? Evidence from a tax audit experiment in Denmark Claus Thustrup Kreiner University of Copenhagen, CESifo, CEPR, Danish Economic Council ECFIN Workshop November 2011 Overview
What makes tax payers comply? Evidence from a tax audit experiment in Denmark Claus Thustrup Kreiner University of Copenhagen, CESifo, CEPR, Danish Economic Council ECFIN Workshop November 2011 Overview
The Price of Warm Glow
 DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 7445 The Price of Warm Glow Andrew Lilley Robert Slonim June 2013 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit Institute for the Study of Labor The Price of Warm Glow Andrew
DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 7445 The Price of Warm Glow Andrew Lilley Robert Slonim June 2013 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit Institute for the Study of Labor The Price of Warm Glow Andrew
Using Differences in Knowledge Across Neighborhoods to Uncover the Impacts of the EITC on Earnings
 Using Differences in Knowledge Across Neighborhoods to Uncover the Impacts of the EITC on Earnings Raj Chetty, Harvard and NBER John N. Friedman, Harvard and NBER Emmanuel Saez, UC Berkeley and NBER April
Using Differences in Knowledge Across Neighborhoods to Uncover the Impacts of the EITC on Earnings Raj Chetty, Harvard and NBER John N. Friedman, Harvard and NBER Emmanuel Saez, UC Berkeley and NBER April
Nudging Businesses to Pay Their Taxes: Does the Timing of Reminder Letters Matter?
 Nudging Businesses to Pay Their Taxes: Does the Timing of Reminder Letters Matter? Christian Gillitzer School of Economics, University of Sydney Mathias Sinning ANU Crawford School of Public Policy, RWI,
Nudging Businesses to Pay Their Taxes: Does the Timing of Reminder Letters Matter? Christian Gillitzer School of Economics, University of Sydney Mathias Sinning ANU Crawford School of Public Policy, RWI,
The Effect of Audit Regimes on Applications for Long-Term Care
 CHAPTER 4 The Effect of Audit Regimes on Applications for Long-Term Care 4.1 Introduction In the provision of long-term care a trade-off has to be made between providing services quickly when needed and
CHAPTER 4 The Effect of Audit Regimes on Applications for Long-Term Care 4.1 Introduction In the provision of long-term care a trade-off has to be made between providing services quickly when needed and
Learning Dynamics in Tax Bunching at the Kink: Evidence from Ecuador
 Learning Dynamics in Tax Bunching at the Kink: Evidence from Ecuador Albrecht Bohne Jan Sebastian Nimczik University of Mannheim UNU-WIDER Public Economics for Development July 2017 Albrecht Bohne (U Mannheim)
Learning Dynamics in Tax Bunching at the Kink: Evidence from Ecuador Albrecht Bohne Jan Sebastian Nimczik University of Mannheim UNU-WIDER Public Economics for Development July 2017 Albrecht Bohne (U Mannheim)
WORKING PAPER SERIES
 March 2010 No.3 The Price Elasticity of Charitable Giving: Does the Form of Tax Relief Matter? Prof Kimberley Scharf (Warwick) and Dr Sarah Smith (Bristol) WORKING PAPER SERIES Centre for Competitive Advantage
March 2010 No.3 The Price Elasticity of Charitable Giving: Does the Form of Tax Relief Matter? Prof Kimberley Scharf (Warwick) and Dr Sarah Smith (Bristol) WORKING PAPER SERIES Centre for Competitive Advantage
Unwilling or Unable to Cheat? Evidence from a Randomized Tax Audit Experiment in Denmark
 Unwilling or Unable to Cheat? Evidence from a Randomized Tax Audit Experiment in Denmark Henrik J. Kleven, London School of Economics Martin B. Knudsen, Danish Inland Revenue (SKAT) Claus T. Kreiner, University
Unwilling or Unable to Cheat? Evidence from a Randomized Tax Audit Experiment in Denmark Henrik J. Kleven, London School of Economics Martin B. Knudsen, Danish Inland Revenue (SKAT) Claus T. Kreiner, University
ECON 4624 Income taxation 1/24
 ECON 4624 Income taxation 1/24 Why is it important? An important source of revenue in most countries (60-70%) Affect labour and capital (savings) supply and overall economic activity how much depend on
ECON 4624 Income taxation 1/24 Why is it important? An important source of revenue in most countries (60-70%) Affect labour and capital (savings) supply and overall economic activity how much depend on
THEORIES OF TAX EVASION AND THE HIDDEN ECONOMY
 THEORIES OF TAX EVASION AND THE HIDDEN ECONOMY Nordic Workshop on Tax Evasion AGNAR SANDMO Norwegian School of Economics (NHH) TAX EVASION: AN OVERVIEW Point of departure: The expected utility theory of
THEORIES OF TAX EVASION AND THE HIDDEN ECONOMY Nordic Workshop on Tax Evasion AGNAR SANDMO Norwegian School of Economics (NHH) TAX EVASION: AN OVERVIEW Point of departure: The expected utility theory of
The Minnesota Income Tax Compliance Experiment: Replication of the Social Norms Experiment
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive The Minnesota Income Tax Compliance Experiment: Replication of the Social Norms Experiment Stephen Coleman Metropolitan State University November 2007 Online at http://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/5820/
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive The Minnesota Income Tax Compliance Experiment: Replication of the Social Norms Experiment Stephen Coleman Metropolitan State University November 2007 Online at http://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/5820/
Online Appendix for The Importance of Being. Marginal: Gender Differences in Generosity
 Online Appendix for The Importance of Being Marginal: Gender Differences in Generosity Stefano DellaVigna, John List, Ulrike Malmendier, Gautam Rao January 14, 2013 This appendix describes the structural
Online Appendix for The Importance of Being Marginal: Gender Differences in Generosity Stefano DellaVigna, John List, Ulrike Malmendier, Gautam Rao January 14, 2013 This appendix describes the structural
The Intergenerational Causal Effect of Tax Evasion: Evidence from the Commuter Tax Allowance in Austria
 The Intergenerational Causal Effect of Tax Evasion: Evidence from the Commuter Tax Allowance in Austria Wolfgang Frimmel a,b, Martin Halla a,b,c,d, Jörg Paetzold e a Johannes Kepler University Linz b Christian
The Intergenerational Causal Effect of Tax Evasion: Evidence from the Commuter Tax Allowance in Austria Wolfgang Frimmel a,b, Martin Halla a,b,c,d, Jörg Paetzold e a Johannes Kepler University Linz b Christian
Evidence of the Invisible: Toward a Credibility Revolution in the Empirical Analysis of Tax Evasion and the Informal Economy
 International Tax and Public Finance manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Evidence of the Invisible: Toward a Credibility Revolution in the Empirical Analysis of Tax Evasion and the Informal
International Tax and Public Finance manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Evidence of the Invisible: Toward a Credibility Revolution in the Empirical Analysis of Tax Evasion and the Informal
Altruism. Voluntary contributions to public goods in large economies (Corrected after the lecture) Readings
 Altruism Voluntary contributions to public goods in large economies (Corrected 08.11.11 after the lecture) Readings Nyborg, K. and M. Rege, 2003: Does Public Policy Crowd Out Private Contributions to Public
Altruism Voluntary contributions to public goods in large economies (Corrected 08.11.11 after the lecture) Readings Nyborg, K. and M. Rege, 2003: Does Public Policy Crowd Out Private Contributions to Public
Empirical Household Finance. Theresa Kuchler (NYU Stern)
 Empirical Household Finance Theresa Kuchler (NYU Stern) Overview Three classes: 1. Questions and topics on household finance 2. Recent work: Online data sources 3. Recent work: Administrative data sources
Empirical Household Finance Theresa Kuchler (NYU Stern) Overview Three classes: 1. Questions and topics on household finance 2. Recent work: Online data sources 3. Recent work: Administrative data sources
Online Appendix A: Verification of Employer Responses
 Online Appendix for: Do Employer Pension Contributions Reflect Employee Preferences? Evidence from a Retirement Savings Reform in Denmark, by Itzik Fadlon, Jessica Laird, and Torben Heien Nielsen Online
Online Appendix for: Do Employer Pension Contributions Reflect Employee Preferences? Evidence from a Retirement Savings Reform in Denmark, by Itzik Fadlon, Jessica Laird, and Torben Heien Nielsen Online
Adjustment Costs, Firm Responses, and Labor Supply Elasticities: Evidence from Danish Tax Records
 Adjustment Costs, Firm Responses, and Labor Supply Elasticities: Evidence from Danish Tax Records Raj Chetty, Harvard University and NBER John N. Friedman, Harvard University and NBER Tore Olsen, Harvard
Adjustment Costs, Firm Responses, and Labor Supply Elasticities: Evidence from Danish Tax Records Raj Chetty, Harvard University and NBER John N. Friedman, Harvard University and NBER Tore Olsen, Harvard
THE EFFECTS OF IRS AUDITS ON EITC CLAIMANTS. Jason DeBacker, Bradley T. Heim, Anh Tran, and Alexander Yuskavage
 THE EFFECTS OF IRS AUDITS ON EITC CLAIMANTS Jason DeBacker, Bradley T. Heim, Anh Tran, and Alexander Yuskavage The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) devotes substantial resources to audit tax returns of Earned
THE EFFECTS OF IRS AUDITS ON EITC CLAIMANTS Jason DeBacker, Bradley T. Heim, Anh Tran, and Alexander Yuskavage The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) devotes substantial resources to audit tax returns of Earned
Empirical Approaches in Public Finance. Hilary Hoynes EC230. Outline of Lecture:
 Lecture: Empirical Approaches in Public Finance Hilary Hoynes hwhoynes@ucdavis.edu EC230 Outline of Lecture: 1. Statement of canonical problem a. Challenges for causal identification 2. Non-experimental
Lecture: Empirical Approaches in Public Finance Hilary Hoynes hwhoynes@ucdavis.edu EC230 Outline of Lecture: 1. Statement of canonical problem a. Challenges for causal identification 2. Non-experimental
Public Goods Provision with Rent-Extracting Administrators
 Supplementary Online Appendix to Public Goods Provision with Rent-Extracting Administrators Tobias Cagala, Ulrich Glogowsky, Veronika Grimm, Johannes Rincke November 27, 2017 Cagala: Deutsche Bundesbank
Supplementary Online Appendix to Public Goods Provision with Rent-Extracting Administrators Tobias Cagala, Ulrich Glogowsky, Veronika Grimm, Johannes Rincke November 27, 2017 Cagala: Deutsche Bundesbank
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES IMPORTING CORRUPTION CULTURE FROM OVERSEAS: EVIDENCE FROM CORPORATE TAX EVASION IN THE UNITED STATES
 NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES IMPORTING CORRUPTION CULTURE FROM OVERSEAS: EVIDENCE FROM CORPORATE TAX EVASION IN THE UNITED STATES Jason M. DeBacker Bradley T. Heim Anh Tran Working Paper 17770 http://www.nber.org/papers/w17770
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES IMPORTING CORRUPTION CULTURE FROM OVERSEAS: EVIDENCE FROM CORPORATE TAX EVASION IN THE UNITED STATES Jason M. DeBacker Bradley T. Heim Anh Tran Working Paper 17770 http://www.nber.org/papers/w17770
Public Goods Provision: Lotteries, Provision Point Mechanisms and Voluntary Contribution Schemes
 Public Goods Provision: Lotteries, Provision Point Mechanisms and Voluntary Contribution Schemes Srajal Nayak EC 426 - Public Economics March 19, 2018 rajal Nayak (EC 426 - Public Economics) Public Goods
Public Goods Provision: Lotteries, Provision Point Mechanisms and Voluntary Contribution Schemes Srajal Nayak EC 426 - Public Economics March 19, 2018 rajal Nayak (EC 426 - Public Economics) Public Goods
Empirical Methods for Corporate Finance. Regression Discontinuity Design
 Empirical Methods for Corporate Finance Regression Discontinuity Design Basic Idea of RDD Observations (e.g. firms, individuals, ) are treated based on cutoff rules that are known ex ante For instance,
Empirical Methods for Corporate Finance Regression Discontinuity Design Basic Idea of RDD Observations (e.g. firms, individuals, ) are treated based on cutoff rules that are known ex ante For instance,
Tax Credits Response to Tax Enforcement: Evidence from a Quasi-Experiment in Chile. January 2012
 Tax Credits Response to Tax Enforcement: Evidence from a Quasi-Experiment in Chile Claudio A. Agostini * Claudia Martínez A. Universidad Adolfo Ibañez Universidad de Chile January 2012 Abstract Diesel
Tax Credits Response to Tax Enforcement: Evidence from a Quasi-Experiment in Chile Claudio A. Agostini * Claudia Martínez A. Universidad Adolfo Ibañez Universidad de Chile January 2012 Abstract Diesel
The Effect of Taxpayer Service Provision on Tax Compliance for Large Taxpayers in Jamaica. Oronde Small. Andrew Young School of Policy Studies
 The Effect of Taxpayer Service Provision on Tax Compliance for Large Taxpayers in Jamaica Oronde Small Andrew Young School of Policy Studies Georgia State University Draft: November 1, 2016 Abstract This
The Effect of Taxpayer Service Provision on Tax Compliance for Large Taxpayers in Jamaica Oronde Small Andrew Young School of Policy Studies Georgia State University Draft: November 1, 2016 Abstract This
Bakke & Whited [JF 2012] Threshold Events and Identification: A Study of Cash Shortfalls Discussion by Fabian Brunner & Nicolas Boob
![Bakke & Whited [JF 2012] Threshold Events and Identification: A Study of Cash Shortfalls Discussion by Fabian Brunner & Nicolas Boob Bakke & Whited [JF 2012] Threshold Events and Identification: A Study of Cash Shortfalls Discussion by Fabian Brunner & Nicolas Boob](/thumbs/85/92264989.jpg) Bakke & Whited [JF 2012] Threshold Events and Identification: A Study of Cash Shortfalls Discussion by Background and Motivation Rauh (2006): Financial constraints and real investment Endogeneity: Investment
Bakke & Whited [JF 2012] Threshold Events and Identification: A Study of Cash Shortfalls Discussion by Background and Motivation Rauh (2006): Financial constraints and real investment Endogeneity: Investment
Effectiveness of the Cutoff Audit Rule and Inequality of Income
 α Effectiveness of the Cutoff Audit Rule and Inequality of Income by PISSAS DIMITRIOS a and KOTSIOS STELIOS b Department of Economics, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Athens, Greece. email:
α Effectiveness of the Cutoff Audit Rule and Inequality of Income by PISSAS DIMITRIOS a and KOTSIOS STELIOS b Department of Economics, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Athens, Greece. email:
Less Cheating? The Effects of Prefilled Forms on Compliance Behavior
 Arbeitskreis Quantitative Steuerlehre Quantitative Research in Taxation Discussion Papers Martin Fochmann, Nadja Müller, Michael Overesch Less Cheating? The Effects of Prefilled Forms on Compliance Behavior
Arbeitskreis Quantitative Steuerlehre Quantitative Research in Taxation Discussion Papers Martin Fochmann, Nadja Müller, Michael Overesch Less Cheating? The Effects of Prefilled Forms on Compliance Behavior
The Value of Unemployment Insurance
 The Value of Unemployment Insurance Camille Landais (LSE) and Johannes Spinnewijn (LSE) September, 2018 Landais & Spinnewijn (LSE) Value of UI September, 2018 1 / 27 Motivation: Value of Insurance Key
The Value of Unemployment Insurance Camille Landais (LSE) and Johannes Spinnewijn (LSE) September, 2018 Landais & Spinnewijn (LSE) Value of UI September, 2018 1 / 27 Motivation: Value of Insurance Key
Taxation and Development from the WIDER Perspective
 Taxation and Development from the WIDER Perspective Jukka Pirttilä (UNU-WIDER) UNU-WIDER 30th Anniversary Conference 1 / 29 Outline Introduction Modern public economics approach to tax analysis Taxes in
Taxation and Development from the WIDER Perspective Jukka Pirttilä (UNU-WIDER) UNU-WIDER 30th Anniversary Conference 1 / 29 Outline Introduction Modern public economics approach to tax analysis Taxes in
Charitable Giving & Taxes
 Charitable Giving & Taxes 2 nd Annual St. Lawrence County Non-Profit Conference October 10, 2018 Presented By: Angela M. Gray, CPA Canton Office One Main Street, Canton, NY Phone: 315.386.2925 www.graycpas.com
Charitable Giving & Taxes 2 nd Annual St. Lawrence County Non-Profit Conference October 10, 2018 Presented By: Angela M. Gray, CPA Canton Office One Main Street, Canton, NY Phone: 315.386.2925 www.graycpas.com
An Allingham-Sandmo Tax Compliance Model with Imperfect Enforcement
 An Allingham-Sandmo Tax Compliance Model with Imperfect Enforcement Norman Gemmell WORKING PAPER 09/2016 November 2016 Working Papers in Public Finance Chair in Public Finance Victoria Business School
An Allingham-Sandmo Tax Compliance Model with Imperfect Enforcement Norman Gemmell WORKING PAPER 09/2016 November 2016 Working Papers in Public Finance Chair in Public Finance Victoria Business School
Active vs. Passive Decisions and Crowd-out in Retirement Savings Accounts: Evidence from Denmark
 Active vs. Passive Decisions and Crowd-out in Retirement Savings Accounts: Evidence from Denmark Raj Chetty, Harvard and NBER John N. Friedman, Harvard and NBER Soren Leth Petersen, Univ. of Copenhagen
Active vs. Passive Decisions and Crowd-out in Retirement Savings Accounts: Evidence from Denmark Raj Chetty, Harvard and NBER John N. Friedman, Harvard and NBER Soren Leth Petersen, Univ. of Copenhagen
Econ 230B Graduate Public Economics. Tax evasion. Gabriel Zucman
 Econ 230B Graduate Public Economics Tax evasion Gabriel Zucman zucman@berkeley.edu 1 Roadmap 1. The size of tax evasion 2. Why do people evade? 3. The supply side of evasion services 2 1 The size of tax
Econ 230B Graduate Public Economics Tax evasion Gabriel Zucman zucman@berkeley.edu 1 Roadmap 1. The size of tax evasion 2. Why do people evade? 3. The supply side of evasion services 2 1 The size of tax
The dynamic effects of tax audits
 The dynamic effects of tax audits IFS Working Paper W17/24 Arun Advani William Elming Jonathan Shaw The Dynamic Effects of Tax Audits Arun Advani William Elming Jonathan Shaw October 24, 2017 Abstract
The dynamic effects of tax audits IFS Working Paper W17/24 Arun Advani William Elming Jonathan Shaw The Dynamic Effects of Tax Audits Arun Advani William Elming Jonathan Shaw October 24, 2017 Abstract
LANGUAGE TRENDS IN PUBLIC ECONOMICS
 LANGUAGE TRENDS IN PUBLIC ECONOMICS Henrik Jacobsen Kleven Princeton University July 2018 What Are We Talking About In Public Economics? Understanding new directions in research based on word and language
LANGUAGE TRENDS IN PUBLIC ECONOMICS Henrik Jacobsen Kleven Princeton University July 2018 What Are We Talking About In Public Economics? Understanding new directions in research based on word and language
1. Introduction. 1.1 Motivation and scope
 1. Introduction 1.1 Motivation and scope IASB standardsetting International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are on the way to become the globally predominating accounting regime. Today, more than
1. Introduction 1.1 Motivation and scope IASB standardsetting International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are on the way to become the globally predominating accounting regime. Today, more than
Social networks and tax avoidance: Evidence from a well-defined Norwegian tax shelter
 Social networks and tax avoidance: Evidence from a well-defined Norwegian tax shelter Annette Alstadsæter, Wojciech Kopczuk, and Kjetil Telle October 16, 2018 We are grateful to Jim Hines, Henrik Kleven,
Social networks and tax avoidance: Evidence from a well-defined Norwegian tax shelter Annette Alstadsæter, Wojciech Kopczuk, and Kjetil Telle October 16, 2018 We are grateful to Jim Hines, Henrik Kleven,
Managers Green Investment and Related Disclosures Decisions. Patrick R. Martin. Donald V. Moser
 Managers Green Investment and Related Disclosures Decisions Patrick R. Martin Donald V. Moser Katz Graduate School of Business University of Pittsburgh December 21, 2011 We thank Jake Birnberg, Willie
Managers Green Investment and Related Disclosures Decisions Patrick R. Martin Donald V. Moser Katz Graduate School of Business University of Pittsburgh December 21, 2011 We thank Jake Birnberg, Willie
ONLINE APPENDIX (NOT FOR PUBLICATION) Appendix A: Appendix Figures and Tables
 ONLINE APPENDIX (NOT FOR PUBLICATION) Appendix A: Appendix Figures and Tables 34 Figure A.1: First Page of the Standard Layout 35 Figure A.2: Second Page of the Credit Card Statement 36 Figure A.3: First
ONLINE APPENDIX (NOT FOR PUBLICATION) Appendix A: Appendix Figures and Tables 34 Figure A.1: First Page of the Standard Layout 35 Figure A.2: Second Page of the Credit Card Statement 36 Figure A.3: First
Investment Decisions and Negative Interest Rates
 Investment Decisions and Negative Interest Rates No. 16-23 Anat Bracha Abstract: While the current European Central Bank deposit rate and 2-year German government bond yields are negative, the U.S. 2-year
Investment Decisions and Negative Interest Rates No. 16-23 Anat Bracha Abstract: While the current European Central Bank deposit rate and 2-year German government bond yields are negative, the U.S. 2-year
Reciprocal citizen Cuts in public spending reduce voluntary contributions in a field. experiment
 Reciprocal citizen Cuts in public spending reduce voluntary contributions in a field experiment Andries Richter, Environmental Economics and Natural Resources group, Wageningen University, andries.richter@wur.nl
Reciprocal citizen Cuts in public spending reduce voluntary contributions in a field experiment Andries Richter, Environmental Economics and Natural Resources group, Wageningen University, andries.richter@wur.nl
Self-Government and Public Goods: An Experiment
 Self-Government and Public Goods: An Experiment Kenju Kamei and Louis Putterman Brown University Jean-Robert Tyran* University of Copenhagen * No blame for this draft. Centralized vs. Decentralized Sanctions
Self-Government and Public Goods: An Experiment Kenju Kamei and Louis Putterman Brown University Jean-Robert Tyran* University of Copenhagen * No blame for this draft. Centralized vs. Decentralized Sanctions
The Intergenerational Causal Effect of Tax Evasion: Evidence from a Commuter Tax Allowance in Austria
 The Intergenerational Causal Effect of Tax Evasion: Evidence from a Commuter Tax Allowance in Austria Wolfgang Frimmel a,b, Martin Halla b,c,d, Jörg Paetzold e a Johannes Kepler University Linz b Christian
The Intergenerational Causal Effect of Tax Evasion: Evidence from a Commuter Tax Allowance in Austria Wolfgang Frimmel a,b, Martin Halla b,c,d, Jörg Paetzold e a Johannes Kepler University Linz b Christian
The Effects of Penalty Information on Tax Compliance: Evidence from a New Zealand Field Experiment. Norman Gemmell and Marisa Ratto.
 The Effects of Penalty Information on Tax Compliance: Evidence from a New Zealand Field Experiment by Norman Gemmell and Marisa Ratto January 2017 ABSTRACT The standard Allingham-Sandmo-Yitzhaki (ASY)
The Effects of Penalty Information on Tax Compliance: Evidence from a New Zealand Field Experiment by Norman Gemmell and Marisa Ratto January 2017 ABSTRACT The standard Allingham-Sandmo-Yitzhaki (ASY)
Taxation of Earnings and the Impact on Labor Supply and Human Capital. Discussion by Henrik Kleven (LSE)
 Taxation of Earnings and the Impact on Labor Supply and Human Capital Discussion by Henrik Kleven (LSE) The Empirical Foundations of Supply Side Economics The Becker Friedman Institute, September 2013
Taxation of Earnings and the Impact on Labor Supply and Human Capital Discussion by Henrik Kleven (LSE) The Empirical Foundations of Supply Side Economics The Becker Friedman Institute, September 2013
When Interest Rates Go Up, What Will This Mean For the Mortgage Market and the Wider Economy?
 SIEPR policy brief Stanford University October 2015 Stanford Institute for Economic Policy Research on the web: http://siepr.stanford.edu When Interest Rates Go Up, What Will This Mean For the Mortgage
SIEPR policy brief Stanford University October 2015 Stanford Institute for Economic Policy Research on the web: http://siepr.stanford.edu When Interest Rates Go Up, What Will This Mean For the Mortgage
Cooperation and Rent Extraction in Repeated Interaction
 Supplementary Online Appendix to Cooperation and Rent Extraction in Repeated Interaction Tobias Cagala, Ulrich Glogowsky, Veronika Grimm, Johannes Rincke July 29, 2016 Cagala: University of Erlangen-Nuremberg
Supplementary Online Appendix to Cooperation and Rent Extraction in Repeated Interaction Tobias Cagala, Ulrich Glogowsky, Veronika Grimm, Johannes Rincke July 29, 2016 Cagala: University of Erlangen-Nuremberg
Key words : Tax Evasion; Conspicuous Consumption; Signal Auditing JEL Classification: H26
 TAX EVASION, CONSPICUOUS CONSUMPTION, AND SIGNAL AUDITING by Yossi Tubul* Bar-Ilan University, Israel A B S T R A C T The vast economic literature on income tax evasion has almost entirely ignored an important
TAX EVASION, CONSPICUOUS CONSUMPTION, AND SIGNAL AUDITING by Yossi Tubul* Bar-Ilan University, Israel A B S T R A C T The vast economic literature on income tax evasion has almost entirely ignored an important
Aggressive Corporate Tax Behavior versus Decreasing Probability of Fiscal Control (Preliminary and incomplete)
 Aggressive Corporate Tax Behavior versus Decreasing Probability of Fiscal Control (Preliminary and incomplete) Cristian M. Litan Sorina C. Vâju October 29, 2007 Abstract We provide a model of strategic
Aggressive Corporate Tax Behavior versus Decreasing Probability of Fiscal Control (Preliminary and incomplete) Cristian M. Litan Sorina C. Vâju October 29, 2007 Abstract We provide a model of strategic
OPINIONS ON THE ETHICS OF TAX EVASION: A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF UTAH AND NEW JERSEY
 OPINIONS ON THE ETHICS OF TAX EVASION: A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF UTAH AND NEW JERSEY Robert W. McGee, Florida International University, 3000 NE 151 st Street, North Miami, FL 33181, bob414@hotmail.com, (305)
OPINIONS ON THE ETHICS OF TAX EVASION: A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF UTAH AND NEW JERSEY Robert W. McGee, Florida International University, 3000 NE 151 st Street, North Miami, FL 33181, bob414@hotmail.com, (305)
Aggressive Corporate Tax Behavior versus Decreasing Probability of Fiscal Control
 Aggressive Corporate Tax Behavior versus Decreasing Probability of Fiscal Control Cristian M. Litan Sorina C. Vâju February 6, 2008 Abstract We provide a model of strategic interaction between the Internal
Aggressive Corporate Tax Behavior versus Decreasing Probability of Fiscal Control Cristian M. Litan Sorina C. Vâju February 6, 2008 Abstract We provide a model of strategic interaction between the Internal
Economic Policy Analysis: Lecture 4
 Economic Policy Analysis: Lecture 4 Local Public Finance Camille Landais Stanford University February 10, 2010 Outline Background The Tiebout Conjecture Optimal Federalism Figure 1: Local vs Federal Spending
Economic Policy Analysis: Lecture 4 Local Public Finance Camille Landais Stanford University February 10, 2010 Outline Background The Tiebout Conjecture Optimal Federalism Figure 1: Local vs Federal Spending
Unemployment, tax evasion and the slippery slope framework
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Unemployment, tax evasion and the slippery slope framework Gaetano Lisi CreaM Economic Centre (University of Cassino) 18. March 2012 Online at https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/37433/
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Unemployment, tax evasion and the slippery slope framework Gaetano Lisi CreaM Economic Centre (University of Cassino) 18. March 2012 Online at https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/37433/
Appendices: Not for Publication
 Appendices: Not for Publication A Mathematical Appendix A.1 Theoretical Model We develop a model that generates testable implications on how agents view donations of time and money. Following Duncan (1999),
Appendices: Not for Publication A Mathematical Appendix A.1 Theoretical Model We develop a model that generates testable implications on how agents view donations of time and money. Following Duncan (1999),
Julio Videras Department of Economics Hamilton College
 LUCK AND GIVING Julio Videras Department of Economics Hamilton College Abstract: This paper finds that individuals who consider themselves lucky in finances donate more than individuals who do not consider
LUCK AND GIVING Julio Videras Department of Economics Hamilton College Abstract: This paper finds that individuals who consider themselves lucky in finances donate more than individuals who do not consider
Inflation Expectations and Behavior: Do Survey Respondents Act on their Beliefs? October Wilbert van der Klaauw
 Inflation Expectations and Behavior: Do Survey Respondents Act on their Beliefs? October 16 2014 Wilbert van der Klaauw The views presented here are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect those
Inflation Expectations and Behavior: Do Survey Respondents Act on their Beliefs? October 16 2014 Wilbert van der Klaauw The views presented here are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect those
Econ 2230: Public Economics. Lecture 21: Subsidizing giving
 Econ 2230: Public Economics Lecture 21: Subsidizing giving Subsidizing charitable giving 1. Tax subsidy a) Characterizing the US deduction for charitable donations b) Optimal subsidy c) Intended and unintended
Econ 2230: Public Economics Lecture 21: Subsidizing giving Subsidizing charitable giving 1. Tax subsidy a) Characterizing the US deduction for charitable donations b) Optimal subsidy c) Intended and unintended
LABOR SUPPLY RESPONSES TO TAXES AND TRANSFERS: PART I (BASIC APPROACHES) Henrik Jacobsen Kleven London School of Economics
 LABOR SUPPLY RESPONSES TO TAXES AND TRANSFERS: PART I (BASIC APPROACHES) Henrik Jacobsen Kleven London School of Economics Lecture Notes for MSc Public Finance (EC426): Lent 2013 AGENDA Efficiency cost
LABOR SUPPLY RESPONSES TO TAXES AND TRANSFERS: PART I (BASIC APPROACHES) Henrik Jacobsen Kleven London School of Economics Lecture Notes for MSc Public Finance (EC426): Lent 2013 AGENDA Efficiency cost
Taking, Giving, and Impure Altruism in Dictator Games
 Taking, Giving, and Impure Altruism in Dictator Games Oleg Korenok, Edward L. Millner *, and Laura Razzolini Department of Economics Virginia Commonwealth University 301 West Main Street Richmond, VA 23284-4000
Taking, Giving, and Impure Altruism in Dictator Games Oleg Korenok, Edward L. Millner *, and Laura Razzolini Department of Economics Virginia Commonwealth University 301 West Main Street Richmond, VA 23284-4000
VAT Remittance Responsibility, Firm Compliance, and Production
 VAT Remittance Responsibility, Firm Compliance, and Production Evidence from a Withholding Reform in Senegal Bassirou Sarr - Paris School of Economics (PSE) WIDER Development Conference Public Economics
VAT Remittance Responsibility, Firm Compliance, and Production Evidence from a Withholding Reform in Senegal Bassirou Sarr - Paris School of Economics (PSE) WIDER Development Conference Public Economics
Julia Bredtmann RWI, and IZA, Germany. Cons. Pros. Keywords: private philanthropy, time and money donations, government spending, crowding out
 Julia Bredtmann RWI, and IZA, Germany Does government spending crowd out voluntary labor and donations? There is little evidence that government spending crowds out private charitable donations of time
Julia Bredtmann RWI, and IZA, Germany Does government spending crowd out voluntary labor and donations? There is little evidence that government spending crowds out private charitable donations of time
The Effect of Pension Subsidies on Retirement Timing of Older Women: Evidence from a Regression Kink Design
 The Effect of Pension Subsidies on Retirement Timing of Older Women: Evidence from a Regression Kink Design Han Ye University of Mannheim 20th Annual Joint Meeting of the Retirement Research Consortium
The Effect of Pension Subsidies on Retirement Timing of Older Women: Evidence from a Regression Kink Design Han Ye University of Mannheim 20th Annual Joint Meeting of the Retirement Research Consortium
TAXES, TRANSFERS, AND LABOR SUPPLY. Henrik Jacobsen Kleven London School of Economics. Lecture Notes for PhD Public Finance (EC426): Lent Term 2012
 TAXES, TRANSFERS, AND LABOR SUPPLY Henrik Jacobsen Kleven London School of Economics Lecture Notes for PhD Public Finance (EC426): Lent Term 2012 AGENDA Why care about labor supply responses to taxes and
TAXES, TRANSFERS, AND LABOR SUPPLY Henrik Jacobsen Kleven London School of Economics Lecture Notes for PhD Public Finance (EC426): Lent Term 2012 AGENDA Why care about labor supply responses to taxes and
Best practices. Chapter V
 103 Chapter V Best practices This chapter describes best practices for tobacco tax policy, emphasizing the public health impact of tobacco taxes while also recognizing the importance of the revenues generated
103 Chapter V Best practices This chapter describes best practices for tobacco tax policy, emphasizing the public health impact of tobacco taxes while also recognizing the importance of the revenues generated
0. Finish the Auberbach/Obsfeld model (last lecture s slides, 13 March, pp. 13 )
 Monetary Policy, 16/3 2017 Henrik Jensen Department of Economics University of Copenhagen 0. Finish the Auberbach/Obsfeld model (last lecture s slides, 13 March, pp. 13 ) 1. Money in the short run: Incomplete
Monetary Policy, 16/3 2017 Henrik Jensen Department of Economics University of Copenhagen 0. Finish the Auberbach/Obsfeld model (last lecture s slides, 13 March, pp. 13 ) 1. Money in the short run: Incomplete
The Elasticity of Corporate Taxable Income - Evidence from South Africa
 The Elasticity of Corporate Taxable Income - Evidence from South Africa Collen Lediga a, Nadine Riedel a,b,, Kristina Strohmaier c a University of Bochum b CESifo Munich c University of Tübingen Abstract
The Elasticity of Corporate Taxable Income - Evidence from South Africa Collen Lediga a, Nadine Riedel a,b,, Kristina Strohmaier c a University of Bochum b CESifo Munich c University of Tübingen Abstract
Collaboration between The Norwegian Tax Administration and academia - to the benefit of both
 Collaboration between The Norwegian Tax Administration and academia - to the benefit of both - Research and raised awareness on tax issues and increased compliance Barcelona 23.October 2017 Outline The
Collaboration between The Norwegian Tax Administration and academia - to the benefit of both - Research and raised awareness on tax issues and increased compliance Barcelona 23.October 2017 Outline The
USING NOTCHES TO UNCOVER OPTIMIZATION FRICTIONS AND STRUCTURAL ELASTICITIES: THEORY AND EVIDENCE FROM PAKISTAN HENRIK J. KLEVEN AND MAZHAR WASEEM
 USING NOTCHES TO UNCOVER OPTIMIZATION FRICTIONS AND STRUCTURAL ELASTICITIES: THEORY AND EVIDENCE FROM PAKISTAN HENRIK J. KLEVEN AND MAZHAR WASEEM DECEMBER 2012 Abstract We develop a framework for non-parametrically
USING NOTCHES TO UNCOVER OPTIMIZATION FRICTIONS AND STRUCTURAL ELASTICITIES: THEORY AND EVIDENCE FROM PAKISTAN HENRIK J. KLEVEN AND MAZHAR WASEEM DECEMBER 2012 Abstract We develop a framework for non-parametrically
How can we assess the policy effectiveness of randomized control trials when people don t comply?
 Zahra Siddique University of Reading, UK, and IZA, Germany Randomized control trials in an imperfect world How can we assess the policy effectiveness of randomized control trials when people don t comply?
Zahra Siddique University of Reading, UK, and IZA, Germany Randomized control trials in an imperfect world How can we assess the policy effectiveness of randomized control trials when people don t comply?
The investment effect of taxation: evidence from a corporate tax kink WP 13/17. November Working paper series 2013
 The investment effect of taxation: evidence from a corporate tax kink November 2013 WP 13/17 Anne Brockmeyer London School of Economics Working paper series 2013 The paper is circulated for discussion
The investment effect of taxation: evidence from a corporate tax kink November 2013 WP 13/17 Anne Brockmeyer London School of Economics Working paper series 2013 The paper is circulated for discussion
A theoretical examination of tax evasion among the self-employed
 Theoretical and Applied Economics FFet al Volume XXIII (2016), No. 1(606), Spring, pp. 119-128 A theoretical examination of tax evasion among the self-employed Dennis BARBER III Armstrong State University,
Theoretical and Applied Economics FFet al Volume XXIII (2016), No. 1(606), Spring, pp. 119-128 A theoretical examination of tax evasion among the self-employed Dennis BARBER III Armstrong State University,
Unwilling, unable or unaware? The role of different behavioral factors in responding to tax incentives
 Unwilling, unable or unaware? The role of different behavioral factors in responding to tax incentives Tuomas Kosonen Tuomas Matikka VATT Tax Systems Conference (Oxford) 10.10.2014 Tuomas Matikka (VATT)
Unwilling, unable or unaware? The role of different behavioral factors in responding to tax incentives Tuomas Kosonen Tuomas Matikka VATT Tax Systems Conference (Oxford) 10.10.2014 Tuomas Matikka (VATT)
Evaluating Monitoring Unemployed Workers Using Experiment. Controlled Social Experiment. Gerard J. van den Berg
 Evaluating the Monitoring of Unemployed Workers Using a Controlled Social Experiment (Alexander von Humboldt Professor, Mannheim) AIM: study effects of C&M on individual outcomes: exit rate to work, outcomes
Evaluating the Monitoring of Unemployed Workers Using a Controlled Social Experiment (Alexander von Humboldt Professor, Mannheim) AIM: study effects of C&M on individual outcomes: exit rate to work, outcomes
230B: Public Economics Tax Enforcement
 230B: Public Economics Tax Enforcement Emmanuel Saez Berkeley 1 Tax Enforcement Problem Most models of optimal taxation (income or commodity) assume away enforcement issues. In practice: 1) Enforcement
230B: Public Economics Tax Enforcement Emmanuel Saez Berkeley 1 Tax Enforcement Problem Most models of optimal taxation (income or commodity) assume away enforcement issues. In practice: 1) Enforcement
Association of Accounting Technicians response to HMRC s technical consultation Tackling disguised remuneration
 Association of Accounting Technicians response to HMRC s technical consultation Tackling disguised remuneration 1 Association of Accounting Technicians response to HMTC s technical consultation Tackling
Association of Accounting Technicians response to HMRC s technical consultation Tackling disguised remuneration 1 Association of Accounting Technicians response to HMTC s technical consultation Tackling
The Balance-Matching Heuristic *
 How Do Americans Repay Their Debt? The Balance-Matching Heuristic * John Gathergood Neale Mahoney Neil Stewart Jörg Weber February 6, 2019 Abstract In Gathergood et al. (forthcoming), we studied credit
How Do Americans Repay Their Debt? The Balance-Matching Heuristic * John Gathergood Neale Mahoney Neil Stewart Jörg Weber February 6, 2019 Abstract In Gathergood et al. (forthcoming), we studied credit
Taxable Income Elasticities. 131 Undergraduate Public Economics Emmanuel Saez UC Berkeley
 Taxable Income Elasticities 131 Undergraduate Public Economics Emmanuel Saez UC Berkeley 1 TAXABLE INCOME ELASTICITIES Modern public finance literature focuses on taxable income elasticities instead of
Taxable Income Elasticities 131 Undergraduate Public Economics Emmanuel Saez UC Berkeley 1 TAXABLE INCOME ELASTICITIES Modern public finance literature focuses on taxable income elasticities instead of
The Impact of State and Local Government Spending on Charitable Giving in the United States. Lynn Vandendriessche
 The Impact of State and Local Government Spending on Charitable Giving in the United States Lynn Vandendriessche Professor Peter Arcidiacono, Faculty Advisor Professor Michelle Connolly, Faculty Advisor
The Impact of State and Local Government Spending on Charitable Giving in the United States Lynn Vandendriessche Professor Peter Arcidiacono, Faculty Advisor Professor Michelle Connolly, Faculty Advisor
Parallel Accommodating Conduct: Evaluating the Performance of the CPPI Index
 Parallel Accommodating Conduct: Evaluating the Performance of the CPPI Index Marc Ivaldi Vicente Lagos Preliminary version, please do not quote without permission Abstract The Coordinate Price Pressure
Parallel Accommodating Conduct: Evaluating the Performance of the CPPI Index Marc Ivaldi Vicente Lagos Preliminary version, please do not quote without permission Abstract The Coordinate Price Pressure
