Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz. Holt Algebra McDougal 1 Algebra 1
|
|
|
- Myron Potter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1-4 Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Holt Algebra McDougal 1 Algebra 1
2 Warm Up Evaluate each expression ( 2) ( 5 + 7) (7 5) 18 Simplify each expression c + c 11c b + 3.8b 12b m + 2(2m 7) 9m x (2x + 5) 4x 5
3 Objective Solve equations in one variable that contain more than one operation.
4 Alex Notice belongs that this to equation a music club. contains In this multiplication club, students can and buy addition. a student Equations discount that card contain for $ more than This one card operation allows require them to more buy than CDs one for $3.95 step to each. solve. After one Identify year, the Alex operations has spent in $ the equation and the order in which they are applied to the variable. To find the number of CDs c that Alex bought, you Then use inverse operations and work backward to can solve an equation. undo them one at a time. Cost per CD Total cost Cost of discount card
5 Operations in the Equation 1. First c is multiplied by To Solve 1. Subtract from both sides of the equation. 2. Then is added. 2. Then divide both sides by 3.95.
6 Example 1A: Solving Two-Step Equations Solve 18 = 4a = 4a = 4a 8 = 4a = a First a is multiplied by 4. Then 10 is added. Work backward: Subtract 10 from both sides. Since a is multiplied by 4, divide both sides by 4 to undo the multiplication.
7 Example 1B: Solving Two-Step Equations Solve 5t 2 = 32. 5t 2 = t = 30 5t = t = 6 First t is multiplied by 5. Then 2 is subtracted. Work backward: Add 2 to both sides. Since t is multiplied by 5, divide both sides by 5 to undo the multiplication.
8 Check it Out! Example 1a Solve 4 + 7x = x = x = 7 7x = x = 1 First x is multiplied by 7. Then 4 is added. Work backward: Add 4 to both sides. Since x is multiplied by 7, divide both sides by 7 to undo the multiplication.
9 Check it Out! Example 1b Solve 1.5 = 1.2y = 1.2y = 1.2y 7.2 = 1.2y = y First y is multiplied by 1.2. Then 5.7 is subtracted. Work backward: Add 5.7 to both sides. Since y is multiplied by 1.2, divide both sides by 1.2 to undo the multiplication.
10 Check it Out! Example 1c Solve. 2 2 First n is divided by 7. Then 2 is added. Work backward: Subtract 2 from both sides. n = 0 Since n is divided by 7, multiply both sides by 7 to undo the division.
11 Example 2A: Solving Two-Step Equations That Contain Fractions Solve. Method 1 Use fraction operations. 3 Since is subtracted from, add to both sides to undo the subtraction. y 3 Since y is divided by 8, multiply both sides by 8 to undo the division.
12 Example 2A Continued Solve. Method 1 Use fraction operations. Simplify.
13 Example 2A Continued Solve. Method 2 Multiply by the LCD to clear the fractions. Multiply both sides by 24, the LCD of the fractions. Distribute 24 on the left side. 3y 18 = y = 32 Simplify. Since 18 is subtracted from 3y, add 18 to both sides to undo the subtraction.
14 Example 2A Continued Solve. Method 2 Multiply by the LCD to clear the fractions. 3y = 32 Since y is multiplied by 3, divide both sides by 3 to undo the 3 3 multiplication.
15 Example 2B: Solving Two-Step Equations That Contain Fractions Solve. Method 1 Use fraction operations. Since 3 is added to 2 r, subtract 4 from both sides to undo the addition The reciprocal of is. Since r is multiplied by 3 by , multiply both sides
16 Example 2B Continued Solve. Method 1 Use fraction operations.
17 Example 2B Continued Solve. Method 2 Multiply by the LCD to clear the fractions. Multiply both sides by 12, the LCD of the fractions. Distribute 12 on the left side. 8r + 9 = r = 2 Simplify. Since 9 is added to 8r, subtract 9 from both sides to undo the addition.
18 Example 2B Continued Solve. Method 2 Multiply by the LCD to clear the fractions. 8r = Since r is multiplied by 8, divide both sides by 8 to undo the multiplication.
19 Check It Out! Example 2a Solve. Method 2 Multiply by the LCD to clear the fractions. Multiply both sides by 10, the LCD of the fractions. Distribute 10 on the left side. 4x 5 = x = 55 Simplify. Since 5 is subtracted from 4x, add 5 to both sides to undo the subtraction.
20 Check It Out! Example 2a Solve. Method 2 Multiply by the LCD to clear the fractions. 4x = Simplify. Since 4 is multiplied by x, divide both sides by 4 to undo the multiplication.
21 Check It Out! Example 2b Solve. Method 2 Multiply by the LCD to clear the fractions. Multiply both sides by 8, the LCD of the fractions. Distribute 8 on the left side. 6u + 4 = u = 3 Simplify. Since 4 is added to 6u, subtract 4 from both sides to undo the addition.
22 Check It Out! Example 2b Continued Solve. Method 2 Multiply by the LCD to clear the fractions u = 3 Since u is multiplied by 6, divide both sides by 6 to undo the multiplication.
23 Check It Out! Example 2c Solve. Method 1 Use fraction operations. 1 Since is subtracted from, add to both sides to undo the subtraction. n 1 Simplify.
24 Check It Out! Example 2c Continued Solve. Method 1 Use fraction operations. n = 15 Since n is divided by 5, multiply both sides by 5 to undo the division.
25 Equations that are more complicated may have to be simplified before they can be solved. You may have to use the Distributive Property or combine like terms before you begin using inverse operations.
26 Example 3A: Simplifying Before Solving Equations Solve 8x 21 5x = 15. 8x 21 5x = 15 8x 5x 21 = 15 Use the Commutative Property of Addition. 3x 21 = 15 Combine like terms Since 21 is subtracted from 3x, add 21 3x = 6 to both sides to undo the subtraction. x = 2 Since x is multiplied by 3, divide both sides by 3 to undo the multiplication.
27 Example 3B: Simplifying Before Solving Equations Solve 10y (4y + 8) = 20 10y + ( 1)(4y + 8) = 20 10y + ( 1)(4y) + ( 1)( 8) = 20 10y 4y 8 = 20 6y 8 = y = 12 6y = y = 2 Write subtraction as addition of the opposite. Distribute 1 on the left side. Simplify. Combine like terms. Since 8 is subtracted from 6y, add 8 to both sides to undo the subtraction. Since y is multiplied by 6, divide both sides by 6 to undo the multiplication.
28 Solve 2a + 3 8a = 8. Check It Out! Example 3a 2a + 3 8a = 8 2a 8a + 3 = 8 Use the Commutative Property of Addition. 6a + 3 = 8 Combine like terms a = 5 Since 3 is added to 6a, subtract 3 from both sides to undo the addition. Since a is multiplied by 6, divide both sides by 6 to undo the multiplication.
29 Solve 2(3 d) = 4 Check It Out! Example 3b 2(3 d) = 4 ( 2)(3) + ( 2)( d) = 4 Distribute 2 on the left side d = d = d = 10 d = 5 Simplify. Add 6 to both sides. 2d = 10 Since d is multiplied by 2, 2 2 divide both sides by 2 to undo the multiplication.
30 Solve 4(x 2) + 2x = 40 Check It Out! Example 3c 4(x 2) + 2x = 40 (4)(x) + (4)( 2) + 2x = 40 4x 8 + 2x = 40 4x + 2x 8 = 40 6x 8 = x = 48 6x = x = 8 Distribute 4 on the left side. Simplify. Commutative Property of Addition. Combine like terms. Since 8 is subtracted from 6x, add 8 to both sides to undo the subtraction. Since x is multiplied by 6, divide both sides by 6 to undo the multiplication.
31 Example 4: Application Jan joined the dining club at the local café for a fee of $ Being a member entitles her to save $2.50 every time she buys lunch. So far, Jan calculates that she has saved a total of $12.55 by joining the club. Write and solve an equation to find how many time Jan has eaten lunch at the café.
32 Example 4: Application Continued 1 Understand the Problem The answer will be the number of times Jan has eaten lunch at the café. List the important information: Jan paid a $29.95 dining club fee. Jan saves $2.50 on every lunch meal. After one year, Jan has saved $12.55.
33 Example 4: Application Continued 2 Make a Plan Let m represent the number of meals that Jan has paid for at the café. That means that Jan has saved $2.50m. However, Jan must also add the amount she spent to join the dining club. total amount saved amount saved on each meal = dining club fee = 2.50m 29.95
34 3 Example 4: Application Continued Solve = 2.50m = 2.50m = 2.50m = m Since is subtracted from 2.50m, add to both sides to undo the subtraction. Since m is multiplied by 2.50, divide both sides by 2.50 to undo the multiplication.
35 Example 4: Application Continued 4 Look Back Check that the answer is reasonable. Jan saves $2.50 every time she buys lunch, so if she has lunch 17 times at the café, the amount saved is 17(2.50) = Subtract the cost of the dining club fee, which is about $30. So the total saved is about $12.50, which is close to the amount given in the problem, $12.55.
36 Check It Out! Example 4 Sara paid $15.95 to become a member at a gym. She then paid a monthly membership fee. Her total cost for 12 months was $ How much was the monthly fee?
37 Check It Out! Example 4 Continued 1 Understand the Problem The answer will the monthly membership fee. List the important information: Sara paid $15.95 to become a gym member. Sara pays a monthly membership fee. Her total cost for 12 months was $
38 Check It Out! Example 4 Continued 2 Make a Plan Let m represent the monthly membership fee that Sara must pay. That means that Sara must pay 12m. However, Sara must also add the amount she spent to become a gym member. total cost monthly = + fee initial membership = 12m
39 3 Check It Out! Example 4 Continued Solve = 12m = 12m 720 = 12m = m Since is added to 12m, subtract from both sides to undo the addition. Since m is multiplied by 12, divide both sides by 12 to undo the multiplication.
40 4 Check It Out! Example 4 Continued Look Back Check that the answer is reasonable. Sara pays $60 a month, so after 12 months Sara has paid 12(60) = 720. Add the cost of the initial membership fee, which is about $16. So the total paid is about $736, which is close to the amount given in the problem, $
41 Example 5A: Solving Equations to Find an Indicated Value If 4a = 5, find the value of a 1. Step 1 Find the value of a. 4a = a = 4.8 a = 1.2 Step 2 Find the value of a 1. Since 0.2 is added to 4a, subtract 0.2 from both sides to undo the addition. Since a is multiplied by 4, divide both sides by 4 to undo the multiplication To find the value of a 1, substitute 1.2 for a. 0.2 Simplify.
42 Example 5B: Solving Equations to Find an Indicated Value If 3d (9 2d) = 51, find the value of 3d. Step 1 Find the value of d. 3d (9 2d) = 51 3d 9 + 2d = 51 5d 9 = d = 60 d = 12 Since 9 is subtracted from 5d, add 9 to both sides to undo the subtraction. Since d is multiplied by 5, divide both sides by 5 to undo the multiplication.
43 Example 5B Continued If 3d (9 2d) = 51, find the value of 3d. Step 2 Find the value of 3d. d = 12 3(12) To find the value of 3d, substitute 12 for d. 36 Simplify.
44 Solve each equation. 1. 4y + 8 = 2 Lesson Quiz: Part y y = (x 9) = x (12 x) =
45 Lesson Quiz: Part 2 7. If 3b (6 b) = 22, find the value of 7b. 8. Josie bought 4 cases of sports drinks for an upcoming meet. After talking to her coach, she bought 3 more cases and spent an additional $6.95 on other items. Her receipts totaled $ Write and solve an equation to find how much each case of sports drinks cost. 4c + 3c = 74.15; $
Name For those going into. Algebra 1 Honors. School years that begin with an ODD year: do the odds
 Name For those going into LESSON 2.1 Study Guide For use with pages 64 70 Algebra 1 Honors GOAL: Graph and compare positive and negative numbers Date Natural numbers are the numbers 1,2,3, Natural numbers
Name For those going into LESSON 2.1 Study Guide For use with pages 64 70 Algebra 1 Honors GOAL: Graph and compare positive and negative numbers Date Natural numbers are the numbers 1,2,3, Natural numbers
8-6 Applications of Percents
 Learn to find commission, sales tax, and withholding tax. commission commission rate sales tax withholding tax Vocabulary Real estate agents often work for commission. A commission is a fee paid to a person
Learn to find commission, sales tax, and withholding tax. commission commission rate sales tax withholding tax Vocabulary Real estate agents often work for commission. A commission is a fee paid to a person
(x + 2)(x + 3) + (x + 2)(x + 3) 5(x + 3) (x + 2)(x + 3) + x(x + 2) 5x + 15 (x + 2)(x + 3) + x 2 + 2x. 5x x 2 + 2x. x 2 + 7x + 15 x 2 + 5x + 6
 Which is correct? Alex s add the numerators and the denominators way 5 x + 2 + x Morgan s find a common denominator way 5 x + 2 + x 5 x + 2 + x I added the numerator plus the numerator and the denominator
Which is correct? Alex s add the numerators and the denominators way 5 x + 2 + x Morgan s find a common denominator way 5 x + 2 + x 5 x + 2 + x I added the numerator plus the numerator and the denominator
Adding and Subtracting Fractions
 Adding and Subtracting Fractions Adding Fractions with Like Denominators In order to add fractions the denominators must be the same If the denominators of the fractions are the same we follow these two
Adding and Subtracting Fractions Adding Fractions with Like Denominators In order to add fractions the denominators must be the same If the denominators of the fractions are the same we follow these two
Here are the steps required for Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions:
 Here are the steps required for Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions: Step 1: Factor the denominator of each fraction to help find the LCD. Step 3: Find the new numerator for each fraction. To find
Here are the steps required for Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions: Step 1: Factor the denominator of each fraction to help find the LCD. Step 3: Find the new numerator for each fraction. To find
CSM Day 1. Your Name. Partner s Name
 CSM Day Your Name Partner s Name You will study students solutions to algebra equations. You should:. Describe each student s solution to your partner and finish labeling their steps. 2. Talk about the
CSM Day Your Name Partner s Name You will study students solutions to algebra equations. You should:. Describe each student s solution to your partner and finish labeling their steps. 2. Talk about the
Chapter 7 BUILD YOUR VOCABULARY
 C H A P T E R 7 BUILD YOUR VOCABULARY This is an alphabetical list of new vocabulary terms you will learn in Chapter 7. As you complete the study notes for the chapter, you will see Build Your Vocabulary
C H A P T E R 7 BUILD YOUR VOCABULARY This is an alphabetical list of new vocabulary terms you will learn in Chapter 7. As you complete the study notes for the chapter, you will see Build Your Vocabulary
11-3. IWBAT solve equations with variables on both sides of the equal sign.
 IWBAT solve equations with variables on both sides of the equal sign. WRITE: Some problems produce equations that have variables on both sides of the equal sign. Solving an equation with variables on both
IWBAT solve equations with variables on both sides of the equal sign. WRITE: Some problems produce equations that have variables on both sides of the equal sign. Solving an equation with variables on both
Warm up. Seek and Solve!!!
 Warm up Seek and Solve!!! Seek and Solve Answers: 0 2 DNE 3 Investigation # 1 Use the graph of y = 2 below to find the following limits: 1. lim x 2 2 = 3 2. lim x 0 2 = 3 3 3. lim x 3 2 = 3 Basic Limit
Warm up Seek and Solve!!! Seek and Solve Answers: 0 2 DNE 3 Investigation # 1 Use the graph of y = 2 below to find the following limits: 1. lim x 2 2 = 3 2. lim x 0 2 = 3 3 3. lim x 3 2 = 3 Basic Limit
2-4 Completing the Square
 2-4 Completing the Square Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 2 Warm Up Write each expression as a trinomial. 1. (x 5) 2 x 2 10x + 25 2. (3x + 5) 2 9x 2 + 30x + 25 Factor each expression. 3.
2-4 Completing the Square Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 2 Warm Up Write each expression as a trinomial. 1. (x 5) 2 x 2 10x + 25 2. (3x + 5) 2 9x 2 + 30x + 25 Factor each expression. 3.
Solve Problems with Percents
 Domain 1 Lesson 2 Solve Problems with Percents Common Core Standard: 7.RP.3 Getting the Idea Percents are used for many things, such as the sale price of an item, the sales tax you pay on an item, and
Domain 1 Lesson 2 Solve Problems with Percents Common Core Standard: 7.RP.3 Getting the Idea Percents are used for many things, such as the sale price of an item, the sales tax you pay on an item, and
Arithmetic. Mathematics Help Sheet. The University of Sydney Business School
 Arithmetic Mathematics Help Sheet The University of Sydney Business School Common Arithmetic Symbols is not equal to is approximately equal to is identically equal to infinity, which is a non-finite number
Arithmetic Mathematics Help Sheet The University of Sydney Business School Common Arithmetic Symbols is not equal to is approximately equal to is identically equal to infinity, which is a non-finite number
Real Estate Expenses. Example 1. Example 2. To calculate the initial expenses of buying a home
 Real Estate Expenses To calculate the initial expenses of buying a home One of the largest investments most people ever make is the purchase of a home. The major initial expense in that purchase is the
Real Estate Expenses To calculate the initial expenses of buying a home One of the largest investments most people ever make is the purchase of a home. The major initial expense in that purchase is the
MFM1P Foundations of Mathematics Unit 1 Lesson 3
 Integers Lesson 3 Lesson Three Concepts Overall Expectations Solve problems involving proportional reasoning. Specific Expectations Simplify numerical expressions involving integers and rational numbers
Integers Lesson 3 Lesson Three Concepts Overall Expectations Solve problems involving proportional reasoning. Specific Expectations Simplify numerical expressions involving integers and rational numbers
16 If Rodney spins the spinner 32 times, how many times should he get silver? ( 2 Points)
 ACL_Quiz 0: CPM_Chapter _End_ *. Rodney and his friend Tom designed a spinner for a game, but Tom didn t come back from winter break, and now Rodney needs to make the spinner so he can turn it in. All
ACL_Quiz 0: CPM_Chapter _End_ *. Rodney and his friend Tom designed a spinner for a game, but Tom didn t come back from winter break, and now Rodney needs to make the spinner so he can turn it in. All
Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions
 Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions To add or subtract rational expressions, follow procedures similar to those used in adding and subtracting rational numbers. 4 () 4(3) 10 1 3 3() (3) 1 1 1 All
Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions To add or subtract rational expressions, follow procedures similar to those used in adding and subtracting rational numbers. 4 () 4(3) 10 1 3 3() (3) 1 1 1 All
Lesson 3 The Percent Proportion
 Lesson 3 The Percent Proportion A percent proportion compares part of a quantity to a whole quantity for one ratio and lists the percent as a number over 100 for the other ratio. is(part) of(whole) = %
Lesson 3 The Percent Proportion A percent proportion compares part of a quantity to a whole quantity for one ratio and lists the percent as a number over 100 for the other ratio. is(part) of(whole) = %
Name Date Class. 2. p = $600, r = 4%, t = 3 years. 4. I = $270, r = 5%, t = 3 years. 6. I = $108, p = $900, t = 3 years
 Practice A Find each missing value. The first one is done for you. 1. p = $1,000, r = 5%, t = 2 years I = $1,000 0.05 2 I = $100 3. I = $330, r = 3%, t = 1 year = p p = 5. I = $600, p = $2,500, t = 4 years
Practice A Find each missing value. The first one is done for you. 1. p = $1,000, r = 5%, t = 2 years I = $1,000 0.05 2 I = $100 3. I = $330, r = 3%, t = 1 year = p p = 5. I = $600, p = $2,500, t = 4 years
HFCC Math Lab Intermediate Algebra - 8 ADDITION AND SUBTRATION OF RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS
 HFCC Math Lab Intermediate Algebra - 8 ADDITION AND SUBTRATION OF RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS Adding or subtracting two rational expressions require the rational expressions to have the same denominator. Example
HFCC Math Lab Intermediate Algebra - 8 ADDITION AND SUBTRATION OF RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS Adding or subtracting two rational expressions require the rational expressions to have the same denominator. Example
6th Grade Mathematics. STAAR Study Guide. This Study Guide belongs to:
 This Study Guide belongs to: TABLE OF CONTENTS Absolute Value & Opposite of a Number Page 7 Additive & Multiplicative Relationships Page 3 Area & Volume (Rec, Parallelogram) Page 1 Area & Volume (Trapezoid
This Study Guide belongs to: TABLE OF CONTENTS Absolute Value & Opposite of a Number Page 7 Additive & Multiplicative Relationships Page 3 Area & Volume (Rec, Parallelogram) Page 1 Area & Volume (Trapezoid
MSM Course 1 Flashcards. Associative Property. base (in numeration) Commutative Property. Distributive Property. Chapter 1 (p.
 1 Chapter 1 (p. 26, 1-5) Associative Property Associative Property: The property that states that for three or more numbers, their sum or product is always the same, regardless of their grouping. 2 3 8
1 Chapter 1 (p. 26, 1-5) Associative Property Associative Property: The property that states that for three or more numbers, their sum or product is always the same, regardless of their grouping. 2 3 8
Grade 8 Exponents and Powers
 ID : ae-8-exponents-and-powers [] Grade 8 Exponents and Powers For more such worksheets visit wwwedugaincom Answer the questions ()? (2) Simplify (a -2 + b -2 ) - (3) Simplify 32-3/5 (4) Find value of
ID : ae-8-exponents-and-powers [] Grade 8 Exponents and Powers For more such worksheets visit wwwedugaincom Answer the questions ()? (2) Simplify (a -2 + b -2 ) - (3) Simplify 32-3/5 (4) Find value of
Section 9.1 Solving Linear Inequalities
 Section 9.1 Solving Linear Inequalities We know that a linear equation in x can be expressed as ax + b = 0. A linear inequality in x can be written in one of the following forms: ax + b < 0, ax + b 0,
Section 9.1 Solving Linear Inequalities We know that a linear equation in x can be expressed as ax + b = 0. A linear inequality in x can be written in one of the following forms: ax + b < 0, ax + b 0,
Section 6.4 Adding & Subtracting Like Fractions
 Section 6.4 Adding & Subtracting Like Fractions ADDING ALGEBRAIC FRACTIONS As you now know, a rational expression is an algebraic fraction in which the numerator and denominator are both polynomials. Just
Section 6.4 Adding & Subtracting Like Fractions ADDING ALGEBRAIC FRACTIONS As you now know, a rational expression is an algebraic fraction in which the numerator and denominator are both polynomials. Just
Equations and Inequalities Test
 1. An equation is modeled. What value of x makes the equation true? A. 1 B. 7 C. -5 D. -1 2. Which situation is best represented by the following equation? 45w + 123.95 = 753.95 A. Ben paid $753.95 to
1. An equation is modeled. What value of x makes the equation true? A. 1 B. 7 C. -5 D. -1 2. Which situation is best represented by the following equation? 45w + 123.95 = 753.95 A. Ben paid $753.95 to
7th Grade Math Chapter 6 Percents
 7th Grade Math Chapter 6 Percents Name: Period: Common Core State Standards CC.7.EE.2 - Understand that rewriting an expression in different forms in a problem context can shed light on the problem and
7th Grade Math Chapter 6 Percents Name: Period: Common Core State Standards CC.7.EE.2 - Understand that rewriting an expression in different forms in a problem context can shed light on the problem and
2. Solve the following inequality and graph your solution on a number line. Show all your work.
 1. Solve the following inequality and graph your solution on a number line. Show all your work. 2. Solve the following inequality and graph your solution on a number line. Show all your work. 12 3x 4
1. Solve the following inequality and graph your solution on a number line. Show all your work. 2. Solve the following inequality and graph your solution on a number line. Show all your work. 12 3x 4
TOPIC SKILLS R A G. Expand Double Brackets Including brackets with 3 terms. Squaring Brackets (x + 8) 2. Amber/Red Go to. Page 8-10.
 TOPIC SKILLS R A G Amber/Red Go to Expand Double Brackets Including brackets with 3 terms (x + 2)(x + 3) = x 2 + 2x + 3x + 6 = x 2 + 5x + 6 Page 8-10 (x + 2)(x 6) = x 2 + 2x 6x 12 = x 2 4x 12 (2x 8)(3x
TOPIC SKILLS R A G Amber/Red Go to Expand Double Brackets Including brackets with 3 terms (x + 2)(x + 3) = x 2 + 2x + 3x + 6 = x 2 + 5x + 6 Page 8-10 (x + 2)(x 6) = x 2 + 2x 6x 12 = x 2 4x 12 (2x 8)(3x
Operations with Whole Numbers and Exponents. 30A Positive exponents Let s apply the product and quotient rules for exponents to solve a few examples.
 Lesson 30 Operations with Whole Numbers and Exponents Review: Lesson 3, rules for Lesson 7 applied to numbers. Lessons 30-33 will be related to operations with numbers and numerical bases. Then, in Lessons
Lesson 30 Operations with Whole Numbers and Exponents Review: Lesson 3, rules for Lesson 7 applied to numbers. Lessons 30-33 will be related to operations with numbers and numerical bases. Then, in Lessons
3.4.1 Convert Percents, Decimals, and Fractions
 3.4.1 Convert Percents, Decimals, and Fractions Learning Objective(s) 1 Describe the meaning of percent. 2 Represent a number as a decimal, percent, and fraction. Introduction Three common formats for
3.4.1 Convert Percents, Decimals, and Fractions Learning Objective(s) 1 Describe the meaning of percent. 2 Represent a number as a decimal, percent, and fraction. Introduction Three common formats for
Algebra II Quiz: Lessons 7.1 through 7.4 Review
 Class: Date: Algebra II Quiz: Lessons 7.1 through 7.4 Review Graph: 1. f( x) = 4 x 1 2. Graph the function: f( x) = 3 x 2 a. b. 3 c. d. 3. Find the y-intercept of the equation. y = 3 7 x a. 4 b. 21 c.
Class: Date: Algebra II Quiz: Lessons 7.1 through 7.4 Review Graph: 1. f( x) = 4 x 1 2. Graph the function: f( x) = 3 x 2 a. b. 3 c. d. 3. Find the y-intercept of the equation. y = 3 7 x a. 4 b. 21 c.
Algebra 2: Lesson 11-9 Calculating Monthly Payments. Learning Goal: 1) How do we determine a monthly payment for a loan using any given formula?
 NAME: DATE: Algebra 2: Lesson 11-9 Calculating Monthly Payments Learning Goal: 1) How do we determine a monthly payment for a loan using any given formula? Warm Up: Ready? Scenerio. You are 25 years old
NAME: DATE: Algebra 2: Lesson 11-9 Calculating Monthly Payments Learning Goal: 1) How do we determine a monthly payment for a loan using any given formula? Warm Up: Ready? Scenerio. You are 25 years old
FRACTIONS. If you eat 9/12 from one candy bar and eat 4/12 from the other candy bar, how much did you eat altogether?
 Brain Pop Add & Subtract Fractions: Like Denominators Title: Add and Subtract Fractions (Like Denominators) Time: minutes Grade: th Mathematics Objective: SWBAT NJCCCS:. Warm Up Cake Warm Up You are having
Brain Pop Add & Subtract Fractions: Like Denominators Title: Add and Subtract Fractions (Like Denominators) Time: minutes Grade: th Mathematics Objective: SWBAT NJCCCS:. Warm Up Cake Warm Up You are having
Unit 3: Writing Equations Chapter Review
 Unit 3: Writing Equations Chapter Review Part 1: Writing Equations in Slope Intercept Form. (Lesson 1) 1. Write an equation that represents the line on the graph. 2. Write an equation that has a slope
Unit 3: Writing Equations Chapter Review Part 1: Writing Equations in Slope Intercept Form. (Lesson 1) 1. Write an equation that represents the line on the graph. 2. Write an equation that has a slope
Math League SCASD. Meet #2. Self-study Packet
 Math League SCASD Meet #2 Self-study Packet Problem Categories for this Meet: 1. Mystery: Problem solving 2. Geometry: Angle measures in plane figures including supplements and complements 3. Number Theory:
Math League SCASD Meet #2 Self-study Packet Problem Categories for this Meet: 1. Mystery: Problem solving 2. Geometry: Angle measures in plane figures including supplements and complements 3. Number Theory:
Lesson 7.1 Assignment
 Lesson 7.1 Assignment Name Date Picture This Picture Algebra 1. The Sharks Aquatic Club recently held a fundraiser to raise money for a local charity. The swimmers received money for each lap that they
Lesson 7.1 Assignment Name Date Picture This Picture Algebra 1. The Sharks Aquatic Club recently held a fundraiser to raise money for a local charity. The swimmers received money for each lap that they
Adding & Subtracting Percents
 Ch. 5 PERCENTS Percents can be defined in terms of a ratio or in terms of a fraction. Percent as a fraction a percent is a special fraction whose denominator is. Percent as a ratio a comparison between
Ch. 5 PERCENTS Percents can be defined in terms of a ratio or in terms of a fraction. Percent as a fraction a percent is a special fraction whose denominator is. Percent as a ratio a comparison between
Applications of Exponential Functions Group Activity 7 Business Project Week #10
 Applications of Exponential Functions Group Activity 7 Business Project Week #10 In the last activity we looked at exponential functions. This week we will look at exponential functions as related to interest
Applications of Exponential Functions Group Activity 7 Business Project Week #10 In the last activity we looked at exponential functions. This week we will look at exponential functions as related to interest
Lesson Exponential Models & Logarithms
 SACWAY STUDENT HANDOUT SACWAY BRAINSTORMING ALGEBRA & STATISTICS STUDENT NAME DATE INTRODUCTION Compound Interest When you invest money in a fixed- rate interest earning account, you receive interest at
SACWAY STUDENT HANDOUT SACWAY BRAINSTORMING ALGEBRA & STATISTICS STUDENT NAME DATE INTRODUCTION Compound Interest When you invest money in a fixed- rate interest earning account, you receive interest at
Pre-Algebra, Unit 7: Percents Notes
 Pre-Algebra, Unit 7: Percents Notes Percents are special fractions whose denominators are 100. The number in front of the percent symbol (%) is the numerator. The denominator is not written, but understood
Pre-Algebra, Unit 7: Percents Notes Percents are special fractions whose denominators are 100. The number in front of the percent symbol (%) is the numerator. The denominator is not written, but understood
1. FRACTIONAL AND DECIMAL EQUIVALENTS OF PERCENTS
 Percent 7. FRACTIONAL AND DECIMAL EQUIVALENTS OF PERCENTS Percent means out of 00. If you understand this concept, it then becomes very easy to change a percent to an equivalent decimal or fraction. %
Percent 7. FRACTIONAL AND DECIMAL EQUIVALENTS OF PERCENTS Percent means out of 00. If you understand this concept, it then becomes very easy to change a percent to an equivalent decimal or fraction. %
REVIEW PROBLEMS FOR NUMERICAL SKILLS ASSESSMENT TEST-Rev 1 (Note: No calculators are allowed at the time of the test.)
 - - REVIEW PROBLEMS FOR NUMERICAL SKILLS ASSESSMENT TEST-Rev (Note: No calculators are allowed at the time of the test.). 9 + 67 =. 97 7 =. 7 X 6 =. 6 7 =. = 6. 6 7 7. Anne saves $7 every month out of
- - REVIEW PROBLEMS FOR NUMERICAL SKILLS ASSESSMENT TEST-Rev (Note: No calculators are allowed at the time of the test.). 9 + 67 =. 97 7 =. 7 X 6 =. 6 7 =. = 6. 6 7 7. Anne saves $7 every month out of
2.01 Products of Polynomials
 2.01 Products of Polynomials Recall from previous lessons that when algebraic expressions are added (or subtracted) they are called terms, while expressions that are multiplied are called factors. An algebraic
2.01 Products of Polynomials Recall from previous lessons that when algebraic expressions are added (or subtracted) they are called terms, while expressions that are multiplied are called factors. An algebraic
7-4. Compound Interest. Vocabulary. Interest Compounded Annually. Lesson. Mental Math
 Lesson 7-4 Compound Interest BIG IDEA If money grows at a constant interest rate r in a single time period, then after n time periods the value of the original investment has been multiplied by (1 + r)
Lesson 7-4 Compound Interest BIG IDEA If money grows at a constant interest rate r in a single time period, then after n time periods the value of the original investment has been multiplied by (1 + r)
Analyzing Financial Performance Reports
 Analyzing Financial Performance Reports Calculating Variances Effective systems identify variances down to the lowest level of management. Variances are hierarchical. As shown in Exhibit 10.2, they begin
Analyzing Financial Performance Reports Calculating Variances Effective systems identify variances down to the lowest level of management. Variances are hierarchical. As shown in Exhibit 10.2, they begin
100 = % = 25. a = p w. part of the whole. Finding a Part of a Number. What number is 24% of 50? So, 12 is 24% of 50. Reasonable?
 12.1 Lesson Key Vocabulary percent A percent is a ratio whose denominator is 100. Here are two examples. 4 4% = 100 = 0.04 25% = 25 100 = 0.25 The Percent Equation Words To represent a is p percent of
12.1 Lesson Key Vocabulary percent A percent is a ratio whose denominator is 100. Here are two examples. 4 4% = 100 = 0.04 25% = 25 100 = 0.25 The Percent Equation Words To represent a is p percent of
CHAPTER 7: RELATING FRACTIONS, DECIMALS, AND PERCENTS
 CHAPTER 7: RELATING FRACTIONS, DECIMALS, AND PERCENTS 7. CONVERTING FRACTIONS TO DECIMALS P. -3 7. CONVERTING DECIMALS TO FRACTIONS P. 4-5 7.3 CONVERTING DECIMALS AND PERCENTS P. 6-7 7.4 CONVERSIONS REVIEW
CHAPTER 7: RELATING FRACTIONS, DECIMALS, AND PERCENTS 7. CONVERTING FRACTIONS TO DECIMALS P. -3 7. CONVERTING DECIMALS TO FRACTIONS P. 4-5 7.3 CONVERTING DECIMALS AND PERCENTS P. 6-7 7.4 CONVERSIONS REVIEW
SV151, Principles of Economics K. Christ 6 9 February 2012
 SV151, Principles of Economics K. Christ 6 9 February 2012 SV151, Principles of Economics K. Christ 9 February 2012 Key terms / chapter 21: Medium of exchange Unit of account Store of value Liquidity Commodity
SV151, Principles of Economics K. Christ 6 9 February 2012 SV151, Principles of Economics K. Christ 9 February 2012 Key terms / chapter 21: Medium of exchange Unit of account Store of value Liquidity Commodity
6 th Math Common Assessment Unit #3B PART ONE: Expressions and Equations Form A (6.9A, 6.9B, 6.9C, 6.10A, 6.10B)
 6 th Math Common Assessment Unit #3B PART ONE: Expressions and Equations Form A (6.9A, 6.9B, 6.9C, 6.10A, 6.10B) Name: 1. (6.9A) Eric is trying to earn enough money to rent a house on the beach for the
6 th Math Common Assessment Unit #3B PART ONE: Expressions and Equations Form A (6.9A, 6.9B, 6.9C, 6.10A, 6.10B) Name: 1. (6.9A) Eric is trying to earn enough money to rent a house on the beach for the
Lesson 4: Real World Problems Using Inequalities
 Lesson 4: Real World Problems Using Inequalities Key Words in Real World Problems that Involve Inequalities Example 1 Keith must rent a truck for the day to clean up the house and yard. Home Store Plus
Lesson 4: Real World Problems Using Inequalities Key Words in Real World Problems that Involve Inequalities Example 1 Keith must rent a truck for the day to clean up the house and yard. Home Store Plus
How can you use what you know about adding integers to add rational numbers? ACTIVITY: Adding Rational Numbers
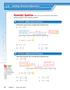 . How can you use what you know about adding integers to add rational numbers? ACTIVITY: Work with a partner. Use a number line to find the sum. a.. +.) Start at 0. Move. units to the right. Add... Then
. How can you use what you know about adding integers to add rational numbers? ACTIVITY: Work with a partner. Use a number line to find the sum. a.. +.) Start at 0. Move. units to the right. Add... Then
T Find the amount of interest earned.
 LESSON 4-14 California Standards Gr. 6 NS 1.4: Calculate given percentages of quantities and solve problems involving discounts at sales, interest earned, and tips. Gr. 7 NS 1.7: Solve problems that involve
LESSON 4-14 California Standards Gr. 6 NS 1.4: Calculate given percentages of quantities and solve problems involving discounts at sales, interest earned, and tips. Gr. 7 NS 1.7: Solve problems that involve
r 1. Discuss the meaning of compounding using the formula A= A0 1+
 Money and the Exponential Function Goals: x 1. Write and graph exponential functions of the form f ( x) = a b (3.15) 2. Use exponential equations to solve problems. Solve by graphing, substitution. (3.17)
Money and the Exponential Function Goals: x 1. Write and graph exponential functions of the form f ( x) = a b (3.15) 2. Use exponential equations to solve problems. Solve by graphing, substitution. (3.17)
Mathematics Success Grade 8
 Mathematics Success Grade 8 T379 [OBJECTIVE] The student will derive the equation of a line and use this form to identify the slope and y-intercept of an equation. [PREREQUISITE SKILLS] Slope [MATERIALS]
Mathematics Success Grade 8 T379 [OBJECTIVE] The student will derive the equation of a line and use this form to identify the slope and y-intercept of an equation. [PREREQUISITE SKILLS] Slope [MATERIALS]
troduction to Algebra
 Chapter Six Percent Percents, Decimals, and Fractions Understanding Percent The word percent comes from the Latin phrase per centum,, which means per 100. Percent means per one hundred. The % symbol is
Chapter Six Percent Percents, Decimals, and Fractions Understanding Percent The word percent comes from the Latin phrase per centum,, which means per 100. Percent means per one hundred. The % symbol is
Unit Review Return to Table of Contents
 Slide 1 / 65 Unit Review Return to Table of Contents Slide 2 / 65 1 3x and -2x A B Are Like Terms Are Unlike Terms Slide 3 / 65 2 5a and 5b A B Are Like Terms Are Unlike Terms Slide 4 / 65 3 4y and 5xy
Slide 1 / 65 Unit Review Return to Table of Contents Slide 2 / 65 1 3x and -2x A B Are Like Terms Are Unlike Terms Slide 3 / 65 2 5a and 5b A B Are Like Terms Are Unlike Terms Slide 4 / 65 3 4y and 5xy
This is Appendix B: Extensions of the Aggregate Expenditures Model, appendix 2 from the book Economics Principles (index.html) (v. 2.0).
 This is Appendix B: Extensions of the Aggregate Expenditures Model, appendix 2 from the book Economics Principles (index.html) (v. 2.0). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
This is Appendix B: Extensions of the Aggregate Expenditures Model, appendix 2 from the book Economics Principles (index.html) (v. 2.0). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
Trimester 2 Final Practice CC 7 Date Period. Unit Rates (7.RP.1)
 Trimester 2 Final Practice Name CC 7 Date Period Unit Rates (7.RP.1) 1. This diagram shows how much apple juice is mixed with carrot juice for a recipe. How many cups of apple juice are used for 1 cup
Trimester 2 Final Practice Name CC 7 Date Period Unit Rates (7.RP.1) 1. This diagram shows how much apple juice is mixed with carrot juice for a recipe. How many cups of apple juice are used for 1 cup
MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
 MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS A1.1.1.1.1 1. An expression is shown below. 629542 2 Ï } 51x Which value of x makes the expression equivalent to 10 Ï } 51? A. 5 B. 25 * C. 50 D. 100 A student could determine
MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS A1.1.1.1.1 1. An expression is shown below. 629542 2 Ï } 51x Which value of x makes the expression equivalent to 10 Ï } 51? A. 5 B. 25 * C. 50 D. 100 A student could determine
10% is 8, and 1% is 0.8. ACTIVITY: Finding 10% of a Number. a. How did Newton know that 10% of 80 is 8? = 10 =
 5.6 Solving Percent Problems percent of a number? How can you use mental math to find the I have a secret way for finding 2% of 80. 0% is 8, and % is 0.8. So, 2% is 8 + 8 + 0.8 = 6.8. ACTIVITY: Finding
5.6 Solving Percent Problems percent of a number? How can you use mental math to find the I have a secret way for finding 2% of 80. 0% is 8, and % is 0.8. So, 2% is 8 + 8 + 0.8 = 6.8. ACTIVITY: Finding
Expressions and Equations Post Assessment
 Name Expressions and Equations Post Assessment Class Date Multiple-Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Bubble in the answer for each question
Name Expressions and Equations Post Assessment Class Date Multiple-Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Bubble in the answer for each question
Sriramanujan1729.weebly.com
 1 Sriramanujan1729.weebly.com Ratio Ratios are used to compare quantities. To compare two quantities, the units of the quantities must be the same. Or A Ratio is an ordered comparison of two quantities.
1 Sriramanujan1729.weebly.com Ratio Ratios are used to compare quantities. To compare two quantities, the units of the quantities must be the same. Or A Ratio is an ordered comparison of two quantities.
Unit 8 Notes: Solving Quadratics by Factoring Alg 1
 Unit 8 Notes: Solving Quadratics by Factoring Alg 1 Name Period Day Date Assignment (Due the next class meeting) Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Monday Tuesday
Unit 8 Notes: Solving Quadratics by Factoring Alg 1 Name Period Day Date Assignment (Due the next class meeting) Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Monday Tuesday
Algebra Success. [MULTIPLE REPRESENTATIONS] SOLVE, Verbal Description, Algebraic Formula, Concrete Representation, Pictorial Representation
![Algebra Success. [MULTIPLE REPRESENTATIONS] SOLVE, Verbal Description, Algebraic Formula, Concrete Representation, Pictorial Representation Algebra Success. [MULTIPLE REPRESENTATIONS] SOLVE, Verbal Description, Algebraic Formula, Concrete Representation, Pictorial Representation](/thumbs/93/112561762.jpg) T755 [OBJECTIVE] The student will learn how to multiply polynomials. [MATERIALS] Student pages S289 S297 Transparencies T765, T767, T769, T771, T773, T775 [ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS] 1. When multiplying polynomials,
T755 [OBJECTIVE] The student will learn how to multiply polynomials. [MATERIALS] Student pages S289 S297 Transparencies T765, T767, T769, T771, T773, T775 [ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS] 1. When multiplying polynomials,
Park Forest Math Team. Meet #2. Self-study Packet
 Park Forest Math Team Meet #2 Self-study Packet Problem Categories for this Meet: 1. Mystery: Problem solving 2. Geometry: Angle measures in plane figures including supplements and complements 3. Number
Park Forest Math Team Meet #2 Self-study Packet Problem Categories for this Meet: 1. Mystery: Problem solving 2. Geometry: Angle measures in plane figures including supplements and complements 3. Number
5.6 Special Products of Polynomials
 5.6 Special Products of Polynomials Learning Objectives Find the square of a binomial Find the product of binomials using sum and difference formula Solve problems using special products of polynomials
5.6 Special Products of Polynomials Learning Objectives Find the square of a binomial Find the product of binomials using sum and difference formula Solve problems using special products of polynomials
7-5 Factoring Special Products
 7-5 Factoring Special Products Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 1 Warm Up Determine whether the following are perfect squares. If so, find the square root. 1. 64 yes; 8 2. 36 3. 45 no 4.
7-5 Factoring Special Products Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 1 Warm Up Determine whether the following are perfect squares. If so, find the square root. 1. 64 yes; 8 2. 36 3. 45 no 4.
b. $52.50; Sample explanation: $63 120% 100% 11. (See Figure 1) 12. (See Figure 2) Selling Price
 Applications 1. 0.07 $6.00 = $.. 0.06 $6.80 = $.77 (rounded value). 0.0 $.90 = $1.1 (rounded value) 4. 0.04 $49.99 = $10.00 (rounded value). 0.08 $9.9 = $.40 (rounded value) 6. All five strategies are
Applications 1. 0.07 $6.00 = $.. 0.06 $6.80 = $.77 (rounded value). 0.0 $.90 = $1.1 (rounded value) 4. 0.04 $49.99 = $10.00 (rounded value). 0.08 $9.9 = $.40 (rounded value) 6. All five strategies are
Criteria A: Knowledge and Understanding Percent. 23 = x
 Name: Criteria A: Knowledge and Understanding Percent The student consistently solves simple, complex, and challenging problems correctly. Day/Block: 7-8 5-6 3-4 1-2 The student generally The student sometimes
Name: Criteria A: Knowledge and Understanding Percent The student consistently solves simple, complex, and challenging problems correctly. Day/Block: 7-8 5-6 3-4 1-2 The student generally The student sometimes
Chapter 10. Rational Numbers
 Chapter 0 Rational Numbers The Histor of Chess 0. Rational Epressions 0. Multipling Rational Epressions 0.3 Dividing Rational Epressions 0. Dividing Polnomials 0.5 Addition and Subtraction of Rational
Chapter 0 Rational Numbers The Histor of Chess 0. Rational Epressions 0. Multipling Rational Epressions 0.3 Dividing Rational Epressions 0. Dividing Polnomials 0.5 Addition and Subtraction of Rational
MATH 008 LECTURE NOTES Dr JASON SAMUELS. Ch1 Whole Numbers $55. Solution: =81+495= = 36$
 MATH 008 LECTURE NOTES Dr JASON SAMUELS Ch1 Whole Numbers $55 Solution: 81+9 55=81+495=576 576-540 = 36$ This alternate way to multiply is called the lattice method, because the boxes make a lattice. The
MATH 008 LECTURE NOTES Dr JASON SAMUELS Ch1 Whole Numbers $55 Solution: 81+9 55=81+495=576 576-540 = 36$ This alternate way to multiply is called the lattice method, because the boxes make a lattice. The
6.1 Introduction to Percents and Conversions to Fractions and Decimals
 CHAPTER 6: PERCENTS CHAPTER 6 CONTENTS 6.1 Introduction to Percents 6.2 Solve Percent Problems 6.3 Application Problems 6.4 Financial Literacy 6.5 Circle Graphs 6.1 Introduction to Percents and Conversions
CHAPTER 6: PERCENTS CHAPTER 6 CONTENTS 6.1 Introduction to Percents 6.2 Solve Percent Problems 6.3 Application Problems 6.4 Financial Literacy 6.5 Circle Graphs 6.1 Introduction to Percents and Conversions
Book 14: Budgeting Recreation
 Math 21 Recreation and Wellness Book 14: Budgeting Recreation Name: Start Date: Completion Date: Year Overview: Earning and Spending Money Home Travel Recreation and Wellness 1. Budget 2. Personal Banking
Math 21 Recreation and Wellness Book 14: Budgeting Recreation Name: Start Date: Completion Date: Year Overview: Earning and Spending Money Home Travel Recreation and Wellness 1. Budget 2. Personal Banking
Module 6 Percent % Section 6.1 Understanding Percent. 1 of MAT001 MODULE 6 PERCENT. Denominators of 100
 Module 6 Percent % Section 6.1 Understanding Percent CQ-6-01. Write 0.19% 19% 1900% 0.0019% 19 as a percent. P. 1 of 54 P. 4 of 54 Denominators of The word percent means per hundred. A percent is another
Module 6 Percent % Section 6.1 Understanding Percent CQ-6-01. Write 0.19% 19% 1900% 0.0019% 19 as a percent. P. 1 of 54 P. 4 of 54 Denominators of The word percent means per hundred. A percent is another
A reciprocal is a fraction that is written upside down. The numerator becomes the denominator and the denominator becomes the numerator.
 Dividing Fractions Reciprocals A reciprocal is a fraction that is written upside down. The numerator becomes the denominator and the denominator becomes the numerator. Check out the reciprocals below.
Dividing Fractions Reciprocals A reciprocal is a fraction that is written upside down. The numerator becomes the denominator and the denominator becomes the numerator. Check out the reciprocals below.
EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS
 EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS 7.. 7..6 In these sections, students generalize what they have learned about geometric sequences to investigate exponential functions. Students study exponential functions of the
EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS 7.. 7..6 In these sections, students generalize what they have learned about geometric sequences to investigate exponential functions. Students study exponential functions of the
Graphing Equations Chapter Test Review
 Graphing Equations Chapter Test Review Part 1: Calculate the slope of the following lines: (Lesson 3) Unit 2: Graphing Equations 2. Find the slope of a line that has a 3. Find the slope of the line that
Graphing Equations Chapter Test Review Part 1: Calculate the slope of the following lines: (Lesson 3) Unit 2: Graphing Equations 2. Find the slope of a line that has a 3. Find the slope of the line that
How can the strategy make a table help you organize and keep track of your bank account balance?
 ? Name 1.8 PROBLEM SOLVING Add and Subtract Money Essential Question How can the strategy make a table help you organize and keep track of your bank account balance? Number and Operations 5.3.K Also 5.10.D
? Name 1.8 PROBLEM SOLVING Add and Subtract Money Essential Question How can the strategy make a table help you organize and keep track of your bank account balance? Number and Operations 5.3.K Also 5.10.D
Math 7 NOTES Part B: Percent
 Math 7 NOTES Part B: Percent Prep for 7.RP.A.3 Percents are special fractions whose denominators are 00. The number in front of the percent symbol (%) is the numerator. The denominator is not written,
Math 7 NOTES Part B: Percent Prep for 7.RP.A.3 Percents are special fractions whose denominators are 00. The number in front of the percent symbol (%) is the numerator. The denominator is not written,
Lesson 18: Writing, Evaluating, and Finding Equivalent Expressions with Rational Numbers
 Writing, Evaluating, and Finding Equivalent Expressions with Rational Numbers Student Outcomes Students create equivalent forms of expressions in order to see structure, reveal characteristics, and make
Writing, Evaluating, and Finding Equivalent Expressions with Rational Numbers Student Outcomes Students create equivalent forms of expressions in order to see structure, reveal characteristics, and make
Chapter 5: Finance. Section 5.1: Basic Budgeting. Chapter 5: Finance
 Chapter 5: Finance Most adults have to deal with the financial topics in this chapter regardless of their job or income. Understanding these topics helps us to make wise decisions in our private lives
Chapter 5: Finance Most adults have to deal with the financial topics in this chapter regardless of their job or income. Understanding these topics helps us to make wise decisions in our private lives
9 months 1 year = 0.75 years 1 12 months
 Free Pre-Algebra Lesson 4 page 1 Lesson 4 Ierest The financial world is in large part based on loaning and borrowing money at ierest. A credit union is a good example of how this works on a small scale.
Free Pre-Algebra Lesson 4 page 1 Lesson 4 Ierest The financial world is in large part based on loaning and borrowing money at ierest. A credit union is a good example of how this works on a small scale.
ACCUPLACER Elementary Algebra Assessment Preparation Guide
 ACCUPLACER Elementary Algebra Assessment Preparation Guide Please note that the guide is for reference only and that it does not represent an exact match with the assessment content. The Assessment Centre
ACCUPLACER Elementary Algebra Assessment Preparation Guide Please note that the guide is for reference only and that it does not represent an exact match with the assessment content. The Assessment Centre
Name (s) Class Date ERROR ANALYSIS WORD PROBLEMS
 7 th Grade Common Core Name (s) Class Date ERROR ANALYSIS EXPRESSIONS WORD PROBLEMS Includes: * Evaluating Expressions * Writing Expressions * Sequences * Simplifying Expressions * Adding & Subtracting
7 th Grade Common Core Name (s) Class Date ERROR ANALYSIS EXPRESSIONS WORD PROBLEMS Includes: * Evaluating Expressions * Writing Expressions * Sequences * Simplifying Expressions * Adding & Subtracting
Section 6.3 Multiplying & Dividing Rational Expressions
 Section 6.3 Multiplying & Dividing Rational Expressions MULTIPLYING FRACTIONS In arithmetic, we can multiply fractions by multiplying the numerators separately from the denominators. For example, multiply
Section 6.3 Multiplying & Dividing Rational Expressions MULTIPLYING FRACTIONS In arithmetic, we can multiply fractions by multiplying the numerators separately from the denominators. For example, multiply
Algebra Success. LESSON 14: Discovering y = mx + b
 T282 Algebra Success [OBJECTIVE] The student will determine the slope and y-intercept of a line by examining the equation for the line written in slope-intercept form. [MATERIALS] Student pages S7 S Transparencies
T282 Algebra Success [OBJECTIVE] The student will determine the slope and y-intercept of a line by examining the equation for the line written in slope-intercept form. [MATERIALS] Student pages S7 S Transparencies
Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions
 COMMON CORE 4 Locker LESSON 9. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions Name Class Date 9. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions Essential Question: How can you multiply and divide rational
COMMON CORE 4 Locker LESSON 9. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions Name Class Date 9. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions Essential Question: How can you multiply and divide rational
UNIT 5 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Lesson 2: Creating and Solving Quadratic Equations in One Variable Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: multiplying polynomials working with complex numbers Introduction 2 b 2 A trinomial of the form x + bx + that can be written as
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: multiplying polynomials working with complex numbers Introduction 2 b 2 A trinomial of the form x + bx + that can be written as
Unit 9 Notes: Polynomials and Factoring. Unit 9 Calendar: Polynomials and Factoring. Day Date Assignment (Due the next class meeting) Monday Wednesday
 Name Period Unit 9 Calendar: Polynomials and Factoring Day Date Assignment (Due the next class meeting) Monday Wednesday 2/26/18 (A) 2/28/18 (B) 9.1 Worksheet Adding, Subtracting Polynomials, Multiplying
Name Period Unit 9 Calendar: Polynomials and Factoring Day Date Assignment (Due the next class meeting) Monday Wednesday 2/26/18 (A) 2/28/18 (B) 9.1 Worksheet Adding, Subtracting Polynomials, Multiplying
Practice Test - Chapter 4
 Use the Distributive Property to write each expression as an equivalent algebraic expression. 1. 6(s + 10) 2. 9(a 4) 3. 5(3 b) 4. 11(m + 7) 5. ENTERTAINMENT Suppose you pay $15 per hour to go horseback
Use the Distributive Property to write each expression as an equivalent algebraic expression. 1. 6(s + 10) 2. 9(a 4) 3. 5(3 b) 4. 11(m + 7) 5. ENTERTAINMENT Suppose you pay $15 per hour to go horseback
Lesson Multi-Step Inequalities with Distributive Property
 Lesson: Lesson 6..6 Multi-Step Inequalities with Distributive Property 6..6 (Day ) - Supplement Multi-Step Inequalities with Distributive Property Teacher Lesson Plan CC Standards 7.EE.4b Use variables
Lesson: Lesson 6..6 Multi-Step Inequalities with Distributive Property 6..6 (Day ) - Supplement Multi-Step Inequalities with Distributive Property Teacher Lesson Plan CC Standards 7.EE.4b Use variables
SOLVING EQUATIONS ENGAGE NY PINK PACKET PAGE 18
 SOLVING EQUATIONS ENGAGE NY PINK PACKET PAGE 18 INEQUALITIES SPRINT #2 You will have 3 minutes to complete as many problems as possible. As soon as the bomb goes off, submit!!! Winner= Person with the
SOLVING EQUATIONS ENGAGE NY PINK PACKET PAGE 18 INEQUALITIES SPRINT #2 You will have 3 minutes to complete as many problems as possible. As soon as the bomb goes off, submit!!! Winner= Person with the
1. Use order of operations and the mathematical properties of numbers to simplify these numbers =
 Name: Date: Graded Assignment Unit 4 Assignment Answer each unit review question. When you are done, give your assignment to your teacher according to his or her directions. Each problem is worth point.
Name: Date: Graded Assignment Unit 4 Assignment Answer each unit review question. When you are done, give your assignment to your teacher according to his or her directions. Each problem is worth point.
Summer Math Packet for Entering Algebra 1 Honors Baker High School
 Summer Math Packet for Entering Algebra 1 Honors Baker High School *You should be fluent in operations with fractions involved (multiplying, dividing, adding, and subtracting). *You should know all of
Summer Math Packet for Entering Algebra 1 Honors Baker High School *You should be fluent in operations with fractions involved (multiplying, dividing, adding, and subtracting). *You should know all of
Instructor: Imelda Valencia Course: 6th Grade Sy
 Student: Date: Instructor: Imelda Valencia Course: 6th Grade Sy 207 208 Assignment: Summer Homework for incoming 6th Graders SY 207 208 *. Fill in the blank to make a true statement. A 3 in the place has
Student: Date: Instructor: Imelda Valencia Course: 6th Grade Sy 207 208 Assignment: Summer Homework for incoming 6th Graders SY 207 208 *. Fill in the blank to make a true statement. A 3 in the place has
D This process could be written backwards and still be a true equation. = A D + B D C D
 Section 4 2: Dividing Polynomials Dividing Polynomials if the denominator is a monomial. We add and subtract fractions with a common denominator using the following rule. If there is a common denominator
Section 4 2: Dividing Polynomials Dividing Polynomials if the denominator is a monomial. We add and subtract fractions with a common denominator using the following rule. If there is a common denominator
5.2 Partial Variation
 5.2 Partial Variation Definition: A relationship between two variables in which the dependent variable is the sum of a number and a constant multiple of the independent variable. Notice: If we take the
5.2 Partial Variation Definition: A relationship between two variables in which the dependent variable is the sum of a number and a constant multiple of the independent variable. Notice: If we take the
Pauline is considering becoming a member of a CD club, which offers discounts on CDs. There is a membership fee of 100 but then each CD is only 10.
 Problem 1 (20 points) Pauline loves music. Her income is 300. Let x1 denote the quantity of CDs she buys and x2 the quantity of other goods. She has a positive marginal utility for CDs and other goods
Problem 1 (20 points) Pauline loves music. Her income is 300. Let x1 denote the quantity of CDs she buys and x2 the quantity of other goods. She has a positive marginal utility for CDs and other goods
Tuberculosis Tuesday, January 15 Whooping Cough Wednesday, January 16
 Tuberculosis Tuesday, January 15 Whooping Cough Wednesday, January 16 Learning target: I can explain the multiplier effect, marginal propensity to consume (MPC) and marginal propensity to save (MPS). I
Tuberculosis Tuesday, January 15 Whooping Cough Wednesday, January 16 Learning target: I can explain the multiplier effect, marginal propensity to consume (MPC) and marginal propensity to save (MPS). I
Commutative Property of Addition a + b = b + a Multiplication a b = b a
 1 Properties: Commutative Property of Addition a + b = b + a Multiplication a b = b a 1 Which property is illustrated in each of the equations below? A. Associative Property of Addition (a + b) + c = a
1 Properties: Commutative Property of Addition a + b = b + a Multiplication a b = b a 1 Which property is illustrated in each of the equations below? A. Associative Property of Addition (a + b) + c = a
