- International Scientific Journal about Simulation Volume: Issue: 2 Pages: ISSN
|
|
|
- Aubrey Lucas
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Received: 13 June 016 Accepted: 17 July 016 MONTE CARLO SIMULATION FOR ANOVA TU of Košice, Faculty SjF, Institute of Special Technical Sciences, Department of Applied Mathematics and Informatics, Letná 9, Košice, Keywords: One-way ANOVA, simulation, Monte Carlo method Abstract: The article we will present Monte Carlo simulation for assessing consequences of data n assumption. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) ) is used to determine whether there are any significant differences between the means of three or more independent (unrelated) groups. Fundamental assumption for ANOVA is that the independent variable is rmaly distributed and groups with equal variances. Monte Carlo simulation we observed Type I. error rate of analysis of variance. 1 Introduction Using quantitative mathematical or statistical model looking for the best optimal solution. In practice it is often unrealistic to find an optimal solution, for example, there are used the basic conditions of the methods. It is possible to use simulating models to solve these situations. Simulating real problems is one of the most frequently used approach that facilitates decision-making. The simulation model generally shows a system modeled using mathematical formulations and logical relationships. In the model we distinguish between a random input to control, that is transformed to output model. For the simulation experiment in the beginning you select controlled access and random (stochastic) inputs are randomly generated. Simulations are among the quantitative tools that can be used for decision support. Simulation of work with a particular model is an experiment with the model. It is a subset of simulation modeling allows broaden the scope of the investigation and of the specific model types. Monte Carlo simulation method is kwn that uses a large number of randomly generated samples from the probability distribution that is used for computer simulation solutions to various managerial problems from mathematics, physics, financing, design, sales, human resources, psychology and other [1], []. In statistical theory, we meet two basic types of methods: parametric and nparametric. Parametric methods (tests) are characterized in that they comply with certain assumptions. If you fulfill the requirements of the methods, such as processed data come from a rmal distribution, statistical methods offer an effective and valid estimates of the probability distribution of statistics [3]. When the theoretical assumptions do t examine data, then the validity of the statistics reliable estimates of the probability distribution is uncertain. In such situations, it is possible to use Monte Carlo simulations [4], [5]. This method favors empirical estimates statistics probability distribution file prior theoretical expectations on these figures. The essence of Monte Carlo method is that it generates numerous scenarios studied a random file. Using Monte Carlo simulation can demonstrate how to approach the theoretical results. In this paper, the Monte Carlo method applied to a situation where the assumptions are t met statistical methods, namely analysis of variance (ANOVA). Monte Carlo method comprises the following steps: Determine the objective of the simulation. Propose appropriate methods of Monte Carlo. On the basis of concrete statistics randomly generated data. Implement quantitative methods. Quantify the necessary statistics. Simulation contrary (eg. 100 to 1 000,000 times). Analysis of statistics found. Assess the results obtained by the methods of Monte Carlo. One-way ANOVA The One-way ANOVA (analysis of variance) is used to determine whether there are any significant differences between the means of three or more independent (unrelated) groups. The one-way ANOVA compares the means between the groups you are interested in and determines whether any of those means are significantly different from each other [6]. Specifically, it tests the null hypothesis (1): H 0 : µ 1 = µ = µ 3 = Lµ k (1) and then H 1 : n H 0 where µ - group mean and k - number of groups. If, however, the one-way ANOVA returns a significant result, we accept the alternative hypothesis (H 1 ), which is that there are at least two group means that are significantly different from each other. Its aim is to detect whether any differences between the means for these files are statistically significant or only incidental. Analysis of variance was trying to figure out which of quantitative or ~ 11 ~
2 qualitative factors significantly influence the monitored variables. The basic assumptions for the use of analysis of variance include: Independence of observations - the individual selections are independent of each other. Normality of sampling distribution - the samples come from a core set of rmal distribution. Homogeneity of variance (homoscedasticity) equal variances. Number of factors examined by analysis of variance divided on: One-way analysis of variance - if the observed effect of one factor. Multi-factorial analysis of variance - for the monitoring of the impact of several factors. According to distinguish the range of sample: Balanced model - if the coverage is the same sample. Unbalanced model- if different range of sample. Random selection of independence is considered logically and ensure the appropriate selection of files. To verify in practice the second and third condition. Whether the results are valid in ANOVA failing these checked by using the Monte Carlo simulation, in which will be monitored type I error by One-way ANOVA (p-value)..1 Various alternative for simulation by Monte Carlo methods Specifically, in this paper it is to test the hypothesis of conformity means of three groups: H 0 : µ 1 = µ = µ 3 = 100 Compared to the alternative hypothesis that the at least two diameters are equal. The simulation method Monte Carlo we will consider all alternatives that may arise, this means meeting respectively. failure to comply with terms and conditions of rmality data homogeneity of each group. Consider the following alternatives: (Table 1) The data come from a rmal distribution with means (averagea) µ = 10. The data come from the division that has skewness γ 3 =1.15 and kurtosis γ 4 =. Where equal variances we suppose 1 3 = σ = σ = σ 5. In case of different variances we suppose σ = 4, σ = 5, σ = Assume that the individual files have the same number of observations, for example, the twenty. Probability density graphs for all possible alternatives are on the Figure 1. Normal distribution is bell-shaped, which takes a maximum at x=µ. The hill is steepened when variances are smaller. The assumptions of rmality can be tested e.g. Shapiro-Wilk test. The Shapiro Wilk test utilizes the null hypothesis principle to check whether a sample x 1,..., x n came from a rmally distributed population. Result of test is p-value, if p <α (α = 0,05) and the null hypothesis is rejected on the significance level is Test results for the various alternatives are in Table. Alternatives C and D does t satisfy the condition of rmality. The equal of variances basic set can be determined by Bartlett's test, it's a universal test that can be used for assessing the homogeneity of variances, but is relatively weak and quite sensitive to the violation of rmality files, which can be a problem for files with a small number of observations. If the frequency of all choose the same used to test Cochrane test or Hartley test. The most commonly used test for homogeneity of variance test is Leveneov test, which we test the homogeneity of the various alternatives (Table 3). Alternatives B and D does t satisfy the condition of homoscedasticity. Table.1 Alternatives for One-way ANOVA - Monte Carlo simulation Alternatives Normal distribution Normality Homogeneity of variance A N (10,5) 1 N (10,5) N (10,5) 3 yes yes B N 1 (10, 4) N (10,5) N 3 (10,49) yes C N 1 ( µ,5) N ( µ,5) N 3 ( µ,5) γ =.15 γ yes D = N 1 ( µ,4) N (1 µ,5) N 3 ( µ,49) γ 3 = 1.15 γ 4 =. Generating random numbers Data should be generated for the Monte Carlo simulation. To create simulation models can also use MS Excel and its enhancements: Risk Risk Analyzer, Monte Carlo. In Microsoft Excel for generating random numbers, you can use the command RAND (), we get a random number with uniform distribution in the interval (0,1), or you can use the "Random Number Generation" the Data Analysis ToolPak on the Tools menu. We get a random number X~ N ( µ, σ ) with a given means and standard deviation. The program STATISTICA for generating random numbers, you can ~ 1 ~
3 use the "Rnd (x)", which generates a random number of interval (0, x), or the "RndNormal (x) ', which calculates. The number from a rmal distribution with a means 0 and standard deviation x. Example of generating random number is in Figure. A B D C Figure 1 The graph probability density of the alternatives Table Shapiro-Wilk test Alternatives SW-W Result p-value (Α=0.05) (Α=0.05) A H 0 accepted A H 0 accepted A H 0 accepted B H 0 accepted B H 0 accepted B H 0 accepted C H 0 rejected C H 0 rejected C H 0 accepted D H 0 accepted D H 0 rejected D H 0 rejected ~ 13 ~
4 Table 3 Levev test - testing homogeneity of variances Variable Levene Test of Homogeneity of Variances (levene) Marked effects are significant at p <.0500 SS df MS SS df MS F p Effect Effect Effect Error Error Error A , , B C D Since we need to generate value from N ( µ, σ ) a given means and standard deviation that can be generated directly using the "Random Number Generation" (MS Excel) and enter the parameters or to perform transformations (): Y = X *σ + µ, () where X ~ N (0,1) and Y ~ N ( µ, σ ), µ is the means value and is variance. In the case of data generation with determined skewness and kurtosis it is appropriate to use Fleishman's power of transformation methods. Fleishman's the squares polymial transformation (3) has the form: Y = a + b* X + c* X + d * X, (3) 3 where Y is the transformed variable with the desired skewness and kurtosis, and X ~ N (0,1) and a, b, c, d are the coefficients of which are, for some pairs of skewness and kurtosis tabulated, for example, we used the values of Table 4. ANOVA procedure was implemented for the various alternatives and tracks the probability of passing a null hypothesis. The group had of identical means and changed only valid or invalid assumptions about rmality and equal variances ANOVA. This means that the null hypothesis should t be rejected. Results simulations (p-value) are in Table 5 and Table 6. Figure Generating random number Table 4 Coeficients for Fleishmans transformation Skewness Kurtosis a b c d ~ 14 ~
5 Table 5 Results ANOVA p-value Sim. A B C D p-value p-value p-value p-value H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 accepted 0.30 H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 rejected H 0 accepted H 0 accepted 0.63 H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 rejected H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 rejected H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 accepted H 0 accepted Table 6 Outup of simulation method Monte Carlo for n=10 Normality Equal H 0 H 0 Var accepted rejected Freq. A yes yes % B yes % C yes 8 0% D % For each alternative. was found the percentage of rejection of the null hypothesis at a significance level of 5%, Tab.6. In the case of meeting the assumptions of rmality were refusals 10% of cases, even if the conditionality correlation variance. When rmality was t met we reject the null hypothesis twice if it was met assumption of conformity variances, it means that we have committed type I error in 0% of cases. The results of the simulation study for the 100 simulations are in Table 7, which indicates that the method is sensitive to ANOVA assumption of equal variances as the rmality of the data. Table 7 Outup of simulation method Monte Carlo for n=100 Equal H Normality 0 H 0 Freq. Var accepted rejected A yes yes % B yes % C yes 9 8 8% D % Conclusion The article is an example of Monte Carlo simulations for using ANOVA. It's proven to have the fulfillment of the assumptions of rmality of data and correlation scattering on ANOVA results. In the event of failure of assumptions it can be used to compare mean values more than two core set of n-parametric tests, example Kruskal-Wallis test. Ackwledgement This article was created by implementation of the grant project VEGA 1/0708/16 Development of a new research methods for simulation, assessment, evaluation and quantification of advanced methods of production. References [1] FLEISHMAN, A.I.: Functions for Simulating Data by Using Fleishman s Transformation, [Online], Available: 378_Appendix_D_Functions_for_Simulating_Data_ by_using_fleishmans_transformation.pdf [10 Apr 016], 016 [] KOČIŠKO,M.: Simulácia výrobných systémov, FVT TUKE, 016. (Original in Slovak) [3] MALINDŽÁK, D. et al.: Modelovanie a simulácia v logistike /teória modelovania a simulácie/. Košice: TU-BERG, p. 181, 009. (Original in Slovak) [4] TREBUŇA, P. et al: Modelovanie v priemyselm inžinierstve, TUKE, 015. (Original in Slovak) [5] STRAKA, M.: Diskrétna a spojitá simulácia v simulačm jazyku EXTEND, Košice, TU FBERG, Edičné stredisko/ams, [Online], Available: ad/simulation_scriptum_.pdf [10 Apr 016], 007. (Original in Slovak) [6] BOHÁCS, G., SEMRAU, K. F.: Automatic visual data collection in material flow systems and the application to simulation models, Logistics Journal, p. 1-7, 01. Review process Single-blind peer reviewed process by two reviewers. ~ 15 ~
XLSTAT TIP SHEET FOR BUSINESS STATISTICS CENGAGE LEARNING
 XLSTAT TIP SHEET FOR BUSINESS STATISTICS CENGAGE LEARNING INTRODUCTION XLSTAT makes accessible to anyone a powerful, complete and user-friendly data analysis and statistical solution. Accessibility to
XLSTAT TIP SHEET FOR BUSINESS STATISTICS CENGAGE LEARNING INTRODUCTION XLSTAT makes accessible to anyone a powerful, complete and user-friendly data analysis and statistical solution. Accessibility to
The Two-Sample Independent Sample t Test
 Department of Psychology and Human Development Vanderbilt University 1 Introduction 2 3 The General Formula The Equal-n Formula 4 5 6 Independence Normality Homogeneity of Variances 7 Non-Normality Unequal
Department of Psychology and Human Development Vanderbilt University 1 Introduction 2 3 The General Formula The Equal-n Formula 4 5 6 Independence Normality Homogeneity of Variances 7 Non-Normality Unequal
Simulating the Need of Working Capital for Decision Making in Investments
 INT J COMPUT COMMUN, ISSN 1841-9836 8(1):87-96, February, 2013. Simulating the Need of Working Capital for Decision Making in Investments M. Nagy, V. Burca, C. Butaci, G. Bologa Mariana Nagy Aurel Vlaicu
INT J COMPUT COMMUN, ISSN 1841-9836 8(1):87-96, February, 2013. Simulating the Need of Working Capital for Decision Making in Investments M. Nagy, V. Burca, C. Butaci, G. Bologa Mariana Nagy Aurel Vlaicu
Tests for Intraclass Correlation
 Chapter 810 Tests for Intraclass Correlation Introduction The intraclass correlation coefficient is often used as an index of reliability in a measurement study. In these studies, there are K observations
Chapter 810 Tests for Intraclass Correlation Introduction The intraclass correlation coefficient is often used as an index of reliability in a measurement study. In these studies, there are K observations
KARACHI UNIVERSITY BUSINESS SCHOOL UNIVERSITY OF KARACHI BS (BBA) VI
 88 P a g e B S ( B B A ) S y l l a b u s KARACHI UNIVERSITY BUSINESS SCHOOL UNIVERSITY OF KARACHI BS (BBA) VI Course Title : STATISTICS Course Number : BA(BS) 532 Credit Hours : 03 Course 1. Statistical
88 P a g e B S ( B B A ) S y l l a b u s KARACHI UNIVERSITY BUSINESS SCHOOL UNIVERSITY OF KARACHI BS (BBA) VI Course Title : STATISTICS Course Number : BA(BS) 532 Credit Hours : 03 Course 1. Statistical
Data Distributions and Normality
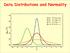 Data Distributions and Normality Definition (Non)Parametric Parametric statistics assume that data come from a normal distribution, and make inferences about parameters of that distribution. These statistical
Data Distributions and Normality Definition (Non)Parametric Parametric statistics assume that data come from a normal distribution, and make inferences about parameters of that distribution. These statistical
2018 AAPM: Normal and non normal distributions: Why understanding distributions are important when designing experiments and analyzing data
 Statistical Failings that Keep Us All in the Dark Normal and non normal distributions: Why understanding distributions are important when designing experiments and Conflict of Interest Disclosure I have
Statistical Failings that Keep Us All in the Dark Normal and non normal distributions: Why understanding distributions are important when designing experiments and Conflict of Interest Disclosure I have
The histogram should resemble the uniform density, the mean should be close to 0.5, and the standard deviation should be close to 1/ 12 =
 Chapter 19 Monte Carlo Valuation Question 19.1 The histogram should resemble the uniform density, the mean should be close to.5, and the standard deviation should be close to 1/ 1 =.887. Question 19. The
Chapter 19 Monte Carlo Valuation Question 19.1 The histogram should resemble the uniform density, the mean should be close to.5, and the standard deviation should be close to 1/ 1 =.887. Question 19. The
Chapter 7. Inferences about Population Variances
 Chapter 7. Inferences about Population Variances Introduction () The variability of a population s values is as important as the population mean. Hypothetical distribution of E. coli concentrations from
Chapter 7. Inferences about Population Variances Introduction () The variability of a population s values is as important as the population mean. Hypothetical distribution of E. coli concentrations from
Table of Contents. New to the Second Edition... Chapter 1: Introduction : Social Research...
 iii Table of Contents Preface... xiii Purpose... xiii Outline of Chapters... xiv New to the Second Edition... xvii Acknowledgements... xviii Chapter 1: Introduction... 1 1.1: Social Research... 1 Introduction...
iii Table of Contents Preface... xiii Purpose... xiii Outline of Chapters... xiv New to the Second Edition... xvii Acknowledgements... xviii Chapter 1: Introduction... 1 1.1: Social Research... 1 Introduction...
Key Objectives. Module 2: The Logic of Statistical Inference. Z-scores. SGSB Workshop: Using Statistical Data to Make Decisions
 SGSB Workshop: Using Statistical Data to Make Decisions Module 2: The Logic of Statistical Inference Dr. Tom Ilvento January 2006 Dr. Mugdim Pašić Key Objectives Understand the logic of statistical inference
SGSB Workshop: Using Statistical Data to Make Decisions Module 2: The Logic of Statistical Inference Dr. Tom Ilvento January 2006 Dr. Mugdim Pašić Key Objectives Understand the logic of statistical inference
Tests for One Variance
 Chapter 65 Introduction Occasionally, researchers are interested in the estimation of the variance (or standard deviation) rather than the mean. This module calculates the sample size and performs power
Chapter 65 Introduction Occasionally, researchers are interested in the estimation of the variance (or standard deviation) rather than the mean. This module calculates the sample size and performs power
Power of t-test for Simple Linear Regression Model with Non-normal Error Distribution: A Quantile Function Distribution Approach
 Available Online Publications J. Sci. Res. 4 (3), 609-622 (2012) JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH www.banglajol.info/index.php/jsr of t-test for Simple Linear Regression Model with Non-normal Error Distribution:
Available Online Publications J. Sci. Res. 4 (3), 609-622 (2012) JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH www.banglajol.info/index.php/jsr of t-test for Simple Linear Regression Model with Non-normal Error Distribution:
The Assumption(s) of Normality
 The Assumption(s) of Normality Copyright 2000, 2011, 2016, J. Toby Mordkoff This is very complicated, so I ll provide two versions. At a minimum, you should know the short one. It would be great if you
The Assumption(s) of Normality Copyright 2000, 2011, 2016, J. Toby Mordkoff This is very complicated, so I ll provide two versions. At a minimum, you should know the short one. It would be great if you
Review: Population, sample, and sampling distributions
 Review: Population, sample, and sampling distributions A population with mean µ and standard deviation σ For instance, µ = 0, σ = 1 0 1 Sample 1, N=30 Sample 2, N=30 Sample 100000000000 InterquartileRange
Review: Population, sample, and sampling distributions A population with mean µ and standard deviation σ For instance, µ = 0, σ = 1 0 1 Sample 1, N=30 Sample 2, N=30 Sample 100000000000 InterquartileRange
Mean GMM. Standard error
 Table 1 Simple Wavelet Analysis for stocks in the S&P 500 Index as of December 31 st 1998 ^ Shapiro- GMM Normality 6 0.9664 0.00281 11.36 4.14 55 7 0.9790 0.00300 56.58 31.69 45 8 0.9689 0.00319 403.49
Table 1 Simple Wavelet Analysis for stocks in the S&P 500 Index as of December 31 st 1998 ^ Shapiro- GMM Normality 6 0.9664 0.00281 11.36 4.14 55 7 0.9790 0.00300 56.58 31.69 45 8 0.9689 0.00319 403.49
AP Statistics Chapter 6 - Random Variables
 AP Statistics Chapter 6 - Random 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Objective: Recognize and define discrete random variables, and construct a probability distribution table and a probability histogram
AP Statistics Chapter 6 - Random 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Objective: Recognize and define discrete random variables, and construct a probability distribution table and a probability histogram
Asset Allocation Model with Tail Risk Parity
 Proceedings of the Asia Pacific Industrial Engineering & Management Systems Conference 2017 Asset Allocation Model with Tail Risk Parity Hirotaka Kato Graduate School of Science and Technology Keio University,
Proceedings of the Asia Pacific Industrial Engineering & Management Systems Conference 2017 Asset Allocation Model with Tail Risk Parity Hirotaka Kato Graduate School of Science and Technology Keio University,
PASS Sample Size Software
 Chapter 850 Introduction Cox proportional hazards regression models the relationship between the hazard function λ( t X ) time and k covariates using the following formula λ log λ ( t X ) ( t) 0 = β1 X1
Chapter 850 Introduction Cox proportional hazards regression models the relationship between the hazard function λ( t X ) time and k covariates using the following formula λ log λ ( t X ) ( t) 0 = β1 X1
Sample Size for Assessing Agreement between Two Methods of Measurement by Bland Altman Method
 Meng-Jie Lu 1 / Wei-Hua Zhong 1 / Yu-Xiu Liu 1 / Hua-Zhang Miao 1 / Yong-Chang Li 1 / Mu-Huo Ji 2 Sample Size for Assessing Agreement between Two Methods of Measurement by Bland Altman Method Abstract:
Meng-Jie Lu 1 / Wei-Hua Zhong 1 / Yu-Xiu Liu 1 / Hua-Zhang Miao 1 / Yong-Chang Li 1 / Mu-Huo Ji 2 Sample Size for Assessing Agreement between Two Methods of Measurement by Bland Altman Method Abstract:
Two-Sample T-Test for Non-Inferiority
 Chapter 198 Two-Sample T-Test for Non-Inferiority Introduction This procedure provides reports for making inference about the non-inferiority of a treatment mean compared to a control mean from data taken
Chapter 198 Two-Sample T-Test for Non-Inferiority Introduction This procedure provides reports for making inference about the non-inferiority of a treatment mean compared to a control mean from data taken
Week 1 Quantitative Analysis of Financial Markets Distributions B
 Week 1 Quantitative Analysis of Financial Markets Distributions B Christopher Ting http://www.mysmu.edu/faculty/christophert/ Christopher Ting : christopherting@smu.edu.sg : 6828 0364 : LKCSB 5036 October
Week 1 Quantitative Analysis of Financial Markets Distributions B Christopher Ting http://www.mysmu.edu/faculty/christophert/ Christopher Ting : christopherting@smu.edu.sg : 6828 0364 : LKCSB 5036 October
Non-Inferiority Tests for Two Means in a 2x2 Cross-Over Design using Differences
 Chapter 510 Non-Inferiority Tests for Two Means in a 2x2 Cross-Over Design using Differences Introduction This procedure computes power and sample size for non-inferiority tests in 2x2 cross-over designs
Chapter 510 Non-Inferiority Tests for Two Means in a 2x2 Cross-Over Design using Differences Introduction This procedure computes power and sample size for non-inferiority tests in 2x2 cross-over designs
A Skewed Truncated Cauchy Logistic. Distribution and its Moments
 International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 11, 2016, no. 20, 975-988 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/imf.2016.6791 A Skewed Truncated Cauchy Logistic Distribution and its Moments Zahra
International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 11, 2016, no. 20, 975-988 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/imf.2016.6791 A Skewed Truncated Cauchy Logistic Distribution and its Moments Zahra
On Some Test Statistics for Testing the Population Skewness and Kurtosis: An Empirical Study
 Florida International University FIU Digital Commons FIU Electronic Theses and Dissertations University Graduate School 8-26-2016 On Some Test Statistics for Testing the Population Skewness and Kurtosis:
Florida International University FIU Digital Commons FIU Electronic Theses and Dissertations University Graduate School 8-26-2016 On Some Test Statistics for Testing the Population Skewness and Kurtosis:
Some developments about a new nonparametric test based on Gini s mean difference
 Some developments about a new nonparametric test based on Gini s mean difference Claudio Giovanni Borroni and Manuela Cazzaro Dipartimento di Metodi Quantitativi per le Scienze Economiche ed Aziendali
Some developments about a new nonparametric test based on Gini s mean difference Claudio Giovanni Borroni and Manuela Cazzaro Dipartimento di Metodi Quantitativi per le Scienze Economiche ed Aziendali
Chapter 2 Uncertainty Analysis and Sampling Techniques
 Chapter 2 Uncertainty Analysis and Sampling Techniques The probabilistic or stochastic modeling (Fig. 2.) iterative loop in the stochastic optimization procedure (Fig..4 in Chap. ) involves:. Specifying
Chapter 2 Uncertainty Analysis and Sampling Techniques The probabilistic or stochastic modeling (Fig. 2.) iterative loop in the stochastic optimization procedure (Fig..4 in Chap. ) involves:. Specifying
Session 178 TS, Stats for Health Actuaries. Moderator: Ian G. Duncan, FSA, FCA, FCIA, FIA, MAAA. Presenter: Joan C. Barrett, FSA, MAAA
 Session 178 TS, Stats for Health Actuaries Moderator: Ian G. Duncan, FSA, FCA, FCIA, FIA, MAAA Presenter: Joan C. Barrett, FSA, MAAA Session 178 Statistics for Health Actuaries October 14, 2015 Presented
Session 178 TS, Stats for Health Actuaries Moderator: Ian G. Duncan, FSA, FCA, FCIA, FIA, MAAA Presenter: Joan C. Barrett, FSA, MAAA Session 178 Statistics for Health Actuaries October 14, 2015 Presented
A Study on the Risk Regulation of Financial Investment Market Based on Quantitative
 80 Journal of Advanced Statistics, Vol. 3, No. 4, December 2018 https://dx.doi.org/10.22606/jas.2018.34004 A Study on the Risk Regulation of Financial Investment Market Based on Quantitative Xinfeng Li
80 Journal of Advanced Statistics, Vol. 3, No. 4, December 2018 https://dx.doi.org/10.22606/jas.2018.34004 A Study on the Risk Regulation of Financial Investment Market Based on Quantitative Xinfeng Li
Two-Sample T-Test for Superiority by a Margin
 Chapter 219 Two-Sample T-Test for Superiority by a Margin Introduction This procedure provides reports for making inference about the superiority of a treatment mean compared to a control mean from data
Chapter 219 Two-Sample T-Test for Superiority by a Margin Introduction This procedure provides reports for making inference about the superiority of a treatment mean compared to a control mean from data
MODELLING OF INCOME AND WAGE DISTRIBUTION USING THE METHOD OF L-MOMENTS OF PARAMETER ESTIMATION
 International Days of Statistics and Economics, Prague, September -3, MODELLING OF INCOME AND WAGE DISTRIBUTION USING THE METHOD OF L-MOMENTS OF PARAMETER ESTIMATION Diana Bílková Abstract Using L-moments
International Days of Statistics and Economics, Prague, September -3, MODELLING OF INCOME AND WAGE DISTRIBUTION USING THE METHOD OF L-MOMENTS OF PARAMETER ESTIMATION Diana Bílková Abstract Using L-moments
Tests for Two ROC Curves
 Chapter 65 Tests for Two ROC Curves Introduction Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves are used to summarize the accuracy of diagnostic tests. The technique is used when a criterion variable is
Chapter 65 Tests for Two ROC Curves Introduction Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves are used to summarize the accuracy of diagnostic tests. The technique is used when a criterion variable is
Conover Test of Variances (Simulation)
 Chapter 561 Conover Test of Variances (Simulation) Introduction This procedure analyzes the power and significance level of the Conover homogeneity test. This test is used to test whether two or more population
Chapter 561 Conover Test of Variances (Simulation) Introduction This procedure analyzes the power and significance level of the Conover homogeneity test. This test is used to test whether two or more population
Tests for Two Means in a Multicenter Randomized Design
 Chapter 481 Tests for Two Means in a Multicenter Randomized Design Introduction In a multicenter design with a continuous outcome, a number of centers (e.g. hospitals or clinics) are selected at random
Chapter 481 Tests for Two Means in a Multicenter Randomized Design Introduction In a multicenter design with a continuous outcome, a number of centers (e.g. hospitals or clinics) are selected at random
SPSS t tests (and NP Equivalent)
 SPSS t tests (and NP Equivalent) Descriptive Statistics To get all the descriptive statistics you need: Analyze > Descriptive Statistics>Explore. Enter the IV into the Factor list and the DV into the Dependent
SPSS t tests (and NP Equivalent) Descriptive Statistics To get all the descriptive statistics you need: Analyze > Descriptive Statistics>Explore. Enter the IV into the Factor list and the DV into the Dependent
ANALYSIS OF THE GDP IN THE REPUBLIC OF MOLDOVA BASED ON MAJOR MACROECONOMIC INDICATORS. Ştefan Cristian CIUCU
 ANALYSIS OF THE GDP IN THE REPUBLIC OF MOLDOVA BASED ON MAJOR MACROECONOMIC INDICATORS Ştefan Cristian CIUCU Abstract The Republic of Moldova is listed by the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and by the
ANALYSIS OF THE GDP IN THE REPUBLIC OF MOLDOVA BASED ON MAJOR MACROECONOMIC INDICATORS Ştefan Cristian CIUCU Abstract The Republic of Moldova is listed by the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and by the
Tests for Two Variances
 Chapter 655 Tests for Two Variances Introduction Occasionally, researchers are interested in comparing the variances (or standard deviations) of two groups rather than their means. This module calculates
Chapter 655 Tests for Two Variances Introduction Occasionally, researchers are interested in comparing the variances (or standard deviations) of two groups rather than their means. This module calculates
Monte Carlo Simulation (General Simulation Models)
 Monte Carlo Simulation (General Simulation Models) Revised: 10/11/2017 Summary... 1 Example #1... 1 Example #2... 10 Summary Monte Carlo simulation is used to estimate the distribution of variables when
Monte Carlo Simulation (General Simulation Models) Revised: 10/11/2017 Summary... 1 Example #1... 1 Example #2... 10 Summary Monte Carlo simulation is used to estimate the distribution of variables when
Web Science & Technologies University of Koblenz Landau, Germany. Lecture Data Science. Statistics and Probabilities JProf. Dr.
 Web Science & Technologies University of Koblenz Landau, Germany Lecture Data Science Statistics and Probabilities JProf. Dr. Claudia Wagner Data Science Open Position @GESIS Student Assistant Job in Data
Web Science & Technologies University of Koblenz Landau, Germany Lecture Data Science Statistics and Probabilities JProf. Dr. Claudia Wagner Data Science Open Position @GESIS Student Assistant Job in Data
Parametric Statistics: Exploring Assumptions.
 Parametric Statistics: Exploring Assumptions http://www.pelagicos.net/classes_biometry_fa17.htm Reading - Field: Chapter 5 R Packages Used in This Chapter For this chapter, you will use the following packages:
Parametric Statistics: Exploring Assumptions http://www.pelagicos.net/classes_biometry_fa17.htm Reading - Field: Chapter 5 R Packages Used in This Chapter For this chapter, you will use the following packages:
The University of Chicago, Booth School of Business Business 41202, Spring Quarter 2009, Mr. Ruey S. Tsay. Solutions to Final Exam
 The University of Chicago, Booth School of Business Business 41202, Spring Quarter 2009, Mr. Ruey S. Tsay Solutions to Final Exam Problem A: (42 pts) Answer briefly the following questions. 1. Questions
The University of Chicago, Booth School of Business Business 41202, Spring Quarter 2009, Mr. Ruey S. Tsay Solutions to Final Exam Problem A: (42 pts) Answer briefly the following questions. 1. Questions
Normal Probability Distributions
 Normal Probability Distributions Properties of Normal Distributions The most important probability distribution in statistics is the normal distribution. Normal curve A normal distribution is a continuous
Normal Probability Distributions Properties of Normal Distributions The most important probability distribution in statistics is the normal distribution. Normal curve A normal distribution is a continuous
12. Conditional heteroscedastic models (ARCH) MA6622, Ernesto Mordecki, CityU, HK, 2006.
 12. Conditional heteroscedastic models (ARCH) MA6622, Ernesto Mordecki, CityU, HK, 2006. References for this Lecture: Robert F. Engle. Autoregressive Conditional Heteroscedasticity with Estimates of Variance
12. Conditional heteroscedastic models (ARCH) MA6622, Ernesto Mordecki, CityU, HK, 2006. References for this Lecture: Robert F. Engle. Autoregressive Conditional Heteroscedasticity with Estimates of Variance
ME3620. Theory of Engineering Experimentation. Spring Chapter III. Random Variables and Probability Distributions.
 ME3620 Theory of Engineering Experimentation Chapter III. Random Variables and Probability Distributions Chapter III 1 3.2 Random Variables In an experiment, a measurement is usually denoted by a variable
ME3620 Theory of Engineering Experimentation Chapter III. Random Variables and Probability Distributions Chapter III 1 3.2 Random Variables In an experiment, a measurement is usually denoted by a variable
ANALYSIS OF THE DISTRIBUTION OF INCOME IN RECENT YEARS IN THE CZECH REPUBLIC BY REGION
 International Days of Statistics and Economics, Prague, September -3, 11 ANALYSIS OF THE DISTRIBUTION OF INCOME IN RECENT YEARS IN THE CZECH REPUBLIC BY REGION Jana Langhamrová Diana Bílková Abstract This
International Days of Statistics and Economics, Prague, September -3, 11 ANALYSIS OF THE DISTRIBUTION OF INCOME IN RECENT YEARS IN THE CZECH REPUBLIC BY REGION Jana Langhamrová Diana Bílková Abstract This
Contents. An Overview of Statistical Applications CHAPTER 1. Contents (ix) Preface... (vii)
 Contents (ix) Contents Preface... (vii) CHAPTER 1 An Overview of Statistical Applications 1.1 Introduction... 1 1. Probability Functions and Statistics... 1..1 Discrete versus Continuous Functions... 1..
Contents (ix) Contents Preface... (vii) CHAPTER 1 An Overview of Statistical Applications 1.1 Introduction... 1 1. Probability Functions and Statistics... 1..1 Discrete versus Continuous Functions... 1..
Chapter 7 Sampling Distributions and Point Estimation of Parameters
 Chapter 7 Sampling Distributions and Point Estimation of Parameters Part 1: Sampling Distributions, the Central Limit Theorem, Point Estimation & Estimators Sections 7-1 to 7-2 1 / 25 Statistical Inferences
Chapter 7 Sampling Distributions and Point Estimation of Parameters Part 1: Sampling Distributions, the Central Limit Theorem, Point Estimation & Estimators Sections 7-1 to 7-2 1 / 25 Statistical Inferences
CHAPTER 6 DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION
 208 CHAPTER 6 DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION Sr. No. Content Page No. 6.1 Introduction 212 6.2 Reliability and Normality of Data 212 6.3 Descriptive Analysis 213 6.4 Cross Tabulation 218 6.5 Chi Square
208 CHAPTER 6 DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION Sr. No. Content Page No. 6.1 Introduction 212 6.2 Reliability and Normality of Data 212 6.3 Descriptive Analysis 213 6.4 Cross Tabulation 218 6.5 Chi Square
Diploma Part 2. Quantitative Methods. Examiner s Suggested Answers
 Diploma Part 2 Quantitative Methods Examiner s Suggested Answers Question 1 (a) The binomial distribution may be used in an experiment in which there are only two defined outcomes in any particular trial
Diploma Part 2 Quantitative Methods Examiner s Suggested Answers Question 1 (a) The binomial distribution may be used in an experiment in which there are only two defined outcomes in any particular trial
Random Variables and Probability Distributions
 Chapter 3 Random Variables and Probability Distributions Chapter Three Random Variables and Probability Distributions 3. Introduction An event is defined as the possible outcome of an experiment. In engineering
Chapter 3 Random Variables and Probability Distributions Chapter Three Random Variables and Probability Distributions 3. Introduction An event is defined as the possible outcome of an experiment. In engineering
Two Hours. Mathematical formula books and statistical tables are to be provided THE UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER. 22 January :00 16:00
 Two Hours MATH38191 Mathematical formula books and statistical tables are to be provided THE UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER STATISTICAL MODELLING IN FINANCE 22 January 2015 14:00 16:00 Answer ALL TWO questions
Two Hours MATH38191 Mathematical formula books and statistical tables are to be provided THE UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER STATISTICAL MODELLING IN FINANCE 22 January 2015 14:00 16:00 Answer ALL TWO questions
Market Risk Analysis Volume I
 Market Risk Analysis Volume I Quantitative Methods in Finance Carol Alexander John Wiley & Sons, Ltd List of Figures List of Tables List of Examples Foreword Preface to Volume I xiii xvi xvii xix xxiii
Market Risk Analysis Volume I Quantitative Methods in Finance Carol Alexander John Wiley & Sons, Ltd List of Figures List of Tables List of Examples Foreword Preface to Volume I xiii xvi xvii xix xxiii
Non-Inferiority Tests for the Ratio of Two Means in a 2x2 Cross-Over Design
 Chapter 515 Non-Inferiority Tests for the Ratio of Two Means in a x Cross-Over Design Introduction This procedure calculates power and sample size of statistical tests for non-inferiority tests from a
Chapter 515 Non-Inferiority Tests for the Ratio of Two Means in a x Cross-Over Design Introduction This procedure calculates power and sample size of statistical tests for non-inferiority tests from a
EX-POST VERIFICATION OF PREDICTION MODELS OF WAGE DISTRIBUTIONS
 EX-POST VERIFICATION OF PREDICTION MODELS OF WAGE DISTRIBUTIONS LUBOŠ MAREK, MICHAL VRABEC University of Economics, Prague, Faculty of Informatics and Statistics, Department of Statistics and Probability,
EX-POST VERIFICATION OF PREDICTION MODELS OF WAGE DISTRIBUTIONS LUBOŠ MAREK, MICHAL VRABEC University of Economics, Prague, Faculty of Informatics and Statistics, Department of Statistics and Probability,
INFORMATION EFFICIENCY HYPOTHESIS THE FINANCIAL VOLATILITY IN THE CZECH REPUBLIC CASE
 INFORMATION EFFICIENCY HYPOTHESIS THE FINANCIAL VOLATILITY IN THE CZECH REPUBLIC CASE Abstract Petr Makovský If there is any market which is said to be effective, this is the the FOREX market. Here we
INFORMATION EFFICIENCY HYPOTHESIS THE FINANCIAL VOLATILITY IN THE CZECH REPUBLIC CASE Abstract Petr Makovský If there is any market which is said to be effective, this is the the FOREX market. Here we
Calculating VaR. There are several approaches for calculating the Value at Risk figure. The most popular are the
 VaR Pro and Contra Pro: Easy to calculate and to understand. It is a common language of communication within the organizations as well as outside (e.g. regulators, auditors, shareholders). It is not really
VaR Pro and Contra Pro: Easy to calculate and to understand. It is a common language of communication within the organizations as well as outside (e.g. regulators, auditors, shareholders). It is not really
Application of value at risk on Moroccan exchange rates
 2018; 3(1): 118-125 ISSN: 2456-1452 Maths 2018; 3(1): 118-125 2018 Stats & Maths www.mathsjournal.com Received: 20-11-2017 Accepted: 22-12-2017 Karima Lamsaddak IbnTofail University, Faculty of Sciences,
2018; 3(1): 118-125 ISSN: 2456-1452 Maths 2018; 3(1): 118-125 2018 Stats & Maths www.mathsjournal.com Received: 20-11-2017 Accepted: 22-12-2017 Karima Lamsaddak IbnTofail University, Faculty of Sciences,
Where s the Beef Does the Mack Method produce an undernourished range of possible outcomes?
 Where s the Beef Does the Mack Method produce an undernourished range of possible outcomes? Daniel Murphy, FCAS, MAAA Trinostics LLC CLRS 2009 In the GIRO Working Party s simulation analysis, actual unpaid
Where s the Beef Does the Mack Method produce an undernourished range of possible outcomes? Daniel Murphy, FCAS, MAAA Trinostics LLC CLRS 2009 In the GIRO Working Party s simulation analysis, actual unpaid
As time goes by... On the performance of significance tests in reaction time experiments. Wolfgang Wiedermann & Bartosz Gula
 On the performance of significance tests in reaction time experiments Wolfgang Bartosz wolfgang.wiedermann@uni-klu.ac.at bartosz.gula@uni-klu.ac.at Department of Psychology University of Klagenfurt, Austria
On the performance of significance tests in reaction time experiments Wolfgang Bartosz wolfgang.wiedermann@uni-klu.ac.at bartosz.gula@uni-klu.ac.at Department of Psychology University of Klagenfurt, Austria
An approximate sampling distribution for the t-ratio. Caution: comparing population means when σ 1 σ 2.
 Stat 529 (Winter 2011) Non-pooled t procedures (The Welch test) Reading: Section 4.3.2 The sampling distribution of Y 1 Y 2. An approximate sampling distribution for the t-ratio. The Sri Lankan analysis.
Stat 529 (Winter 2011) Non-pooled t procedures (The Welch test) Reading: Section 4.3.2 The sampling distribution of Y 1 Y 2. An approximate sampling distribution for the t-ratio. The Sri Lankan analysis.
On Some Statistics for Testing the Skewness in a Population: An. Empirical Study
 Available at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 1932-9466 Vol. 12, Issue 2 (December 2017), pp. 726-752 Applications and Applied Mathematics: An International Journal (AAM) On Some Statistics
Available at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 1932-9466 Vol. 12, Issue 2 (December 2017), pp. 726-752 Applications and Applied Mathematics: An International Journal (AAM) On Some Statistics
Descriptive Analysis
 Descriptive Analysis HERTANTO WAHYU SUBAGIO Univariate Analysis Univariate analysis involves the examination across cases of one variable at a time. There are three major characteristics of a single variable
Descriptive Analysis HERTANTO WAHYU SUBAGIO Univariate Analysis Univariate analysis involves the examination across cases of one variable at a time. There are three major characteristics of a single variable
Tests for Paired Means using Effect Size
 Chapter 417 Tests for Paired Means using Effect Size Introduction This procedure provides sample size and power calculations for a one- or two-sided paired t-test when the effect size is specified rather
Chapter 417 Tests for Paired Means using Effect Size Introduction This procedure provides sample size and power calculations for a one- or two-sided paired t-test when the effect size is specified rather
Quantitative Methods for Economics, Finance and Management (A86050 F86050)
 Quantitative Methods for Economics, Finance and Management (A86050 F86050) Matteo Manera matteo.manera@unimib.it Marzio Galeotti marzio.galeotti@unimi.it 1 This material is taken and adapted from Guy Judge
Quantitative Methods for Economics, Finance and Management (A86050 F86050) Matteo Manera matteo.manera@unimib.it Marzio Galeotti marzio.galeotti@unimi.it 1 This material is taken and adapted from Guy Judge
THE USE OF THE LOGNORMAL DISTRIBUTION IN ANALYZING INCOMES
 International Days of tatistics and Economics Prague eptember -3 011 THE UE OF THE LOGNORMAL DITRIBUTION IN ANALYZING INCOME Jakub Nedvěd Abstract Object of this paper is to examine the possibility of
International Days of tatistics and Economics Prague eptember -3 011 THE UE OF THE LOGNORMAL DITRIBUTION IN ANALYZING INCOME Jakub Nedvěd Abstract Object of this paper is to examine the possibility of
Assicurazioni Generali: An Option Pricing Case with NAGARCH
 Assicurazioni Generali: An Option Pricing Case with NAGARCH Assicurazioni Generali: Business Snapshot Find our latest analyses and trade ideas on bsic.it Assicurazioni Generali SpA is an Italy-based insurance
Assicurazioni Generali: An Option Pricing Case with NAGARCH Assicurazioni Generali: Business Snapshot Find our latest analyses and trade ideas on bsic.it Assicurazioni Generali SpA is an Italy-based insurance
European Journal of Economic Studies, 2016, Vol.(17), Is. 3
 Copyright 2016 by Academic Publishing House Researcher Published in the Russian Federation European Journal of Economic Studies Has been issued since 2012. ISSN: 2304-9669 E-ISSN: 2305-6282 Vol. 17, Is.
Copyright 2016 by Academic Publishing House Researcher Published in the Russian Federation European Journal of Economic Studies Has been issued since 2012. ISSN: 2304-9669 E-ISSN: 2305-6282 Vol. 17, Is.
Section 3 describes the data for portfolio construction and alternative PD and correlation inputs.
 Evaluating economic capital models for credit risk is important for both financial institutions and regulators. However, a major impediment to model validation remains limited data in the time series due
Evaluating economic capital models for credit risk is important for both financial institutions and regulators. However, a major impediment to model validation remains limited data in the time series due
MEASURING PORTFOLIO RISKS USING CONDITIONAL COPULA-AR-GARCH MODEL
 MEASURING PORTFOLIO RISKS USING CONDITIONAL COPULA-AR-GARCH MODEL Isariya Suttakulpiboon MSc in Risk Management and Insurance Georgia State University, 30303 Atlanta, Georgia Email: suttakul.i@gmail.com,
MEASURING PORTFOLIO RISKS USING CONDITIONAL COPULA-AR-GARCH MODEL Isariya Suttakulpiboon MSc in Risk Management and Insurance Georgia State University, 30303 Atlanta, Georgia Email: suttakul.i@gmail.com,
A New Multivariate Kurtosis and Its Asymptotic Distribution
 A ew Multivariate Kurtosis and Its Asymptotic Distribution Chiaki Miyagawa 1 and Takashi Seo 1 Department of Mathematical Information Science, Graduate School of Science, Tokyo University of Science, Tokyo,
A ew Multivariate Kurtosis and Its Asymptotic Distribution Chiaki Miyagawa 1 and Takashi Seo 1 Department of Mathematical Information Science, Graduate School of Science, Tokyo University of Science, Tokyo,
Assessment on Credit Risk of Real Estate Based on Logistic Regression Model
 Assessment on Credit Risk of Real Estate Based on Logistic Regression Model Li Hongli 1, a, Song Liwei 2,b 1 Chongqing Engineering Polytechnic College, Chongqing400037, China 2 Division of Planning and
Assessment on Credit Risk of Real Estate Based on Logistic Regression Model Li Hongli 1, a, Song Liwei 2,b 1 Chongqing Engineering Polytechnic College, Chongqing400037, China 2 Division of Planning and
Subject CS1 Actuarial Statistics 1 Core Principles. Syllabus. for the 2019 exams. 1 June 2018
 ` Subject CS1 Actuarial Statistics 1 Core Principles Syllabus for the 2019 exams 1 June 2018 Copyright in this Core Reading is the property of the Institute and Faculty of Actuaries who are the sole distributors.
` Subject CS1 Actuarial Statistics 1 Core Principles Syllabus for the 2019 exams 1 June 2018 Copyright in this Core Reading is the property of the Institute and Faculty of Actuaries who are the sole distributors.
A STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF GDP AND FINAL CONSUMPTION USING SIMPLE LINEAR REGRESSION. THE CASE OF ROMANIA
 A STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF GDP AND FINAL CONSUMPTION USING SIMPLE LINEAR REGRESSION. THE CASE OF ROMANIA 990 200 Bălăcescu Aniela Lecturer PhD, Constantin Brancusi University of Targu Jiu, Faculty of Economics
A STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF GDP AND FINAL CONSUMPTION USING SIMPLE LINEAR REGRESSION. THE CASE OF ROMANIA 990 200 Bălăcescu Aniela Lecturer PhD, Constantin Brancusi University of Targu Jiu, Faculty of Economics
Experimental Design and Statistics - AGA47A
 Experimental Design and Statistics - AGA47A Czech University of Life Sciences in Prague Department of Genetics and Breeding Fall/Winter 2014/2015 Matúš Maciak (@ A 211) Office Hours: M 14:00 15:30 W 15:30
Experimental Design and Statistics - AGA47A Czech University of Life Sciences in Prague Department of Genetics and Breeding Fall/Winter 2014/2015 Matúš Maciak (@ A 211) Office Hours: M 14:00 15:30 W 15:30
Point-Biserial and Biserial Correlations
 Chapter 302 Point-Biserial and Biserial Correlations Introduction This procedure calculates estimates, confidence intervals, and hypothesis tests for both the point-biserial and the biserial correlations.
Chapter 302 Point-Biserial and Biserial Correlations Introduction This procedure calculates estimates, confidence intervals, and hypothesis tests for both the point-biserial and the biserial correlations.
UPDATED IAA EDUCATION SYLLABUS
 II. UPDATED IAA EDUCATION SYLLABUS A. Supporting Learning Areas 1. STATISTICS Aim: To enable students to apply core statistical techniques to actuarial applications in insurance, pensions and emerging
II. UPDATED IAA EDUCATION SYLLABUS A. Supporting Learning Areas 1. STATISTICS Aim: To enable students to apply core statistical techniques to actuarial applications in insurance, pensions and emerging
Quantile Regression due to Skewness. and Outliers
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 5, 2011, no. 39, 1947-1951 Quantile Regression due to Skewness and Outliers Neda Jalali and Manoochehr Babanezhad Department of Statistics Faculty of Sciences Golestan
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 5, 2011, no. 39, 1947-1951 Quantile Regression due to Skewness and Outliers Neda Jalali and Manoochehr Babanezhad Department of Statistics Faculty of Sciences Golestan
Robust Critical Values for the Jarque-bera Test for Normality
 Robust Critical Values for the Jarque-bera Test for Normality PANAGIOTIS MANTALOS Jönköping International Business School Jönköping University JIBS Working Papers No. 00-8 ROBUST CRITICAL VALUES FOR THE
Robust Critical Values for the Jarque-bera Test for Normality PANAGIOTIS MANTALOS Jönköping International Business School Jönköping University JIBS Working Papers No. 00-8 ROBUST CRITICAL VALUES FOR THE
Resampling techniques to determine direction of effects in linear regression models
 Resampling techniques to determine direction of effects in linear regression models Wolfgang Wiedermann, Michael Hagmann, Michael Kossmeier, & Alexander von Eye University of Vienna, Department of Psychology
Resampling techniques to determine direction of effects in linear regression models Wolfgang Wiedermann, Michael Hagmann, Michael Kossmeier, & Alexander von Eye University of Vienna, Department of Psychology
Descriptive Statistics in Analysis of Survey Data
 Descriptive Statistics in Analysis of Survey Data March 2013 Kenneth M Coleman Mohammad Nizamuddiin Khan Survey: Definition A survey is a systematic method for gathering information from (a sample of)
Descriptive Statistics in Analysis of Survey Data March 2013 Kenneth M Coleman Mohammad Nizamuddiin Khan Survey: Definition A survey is a systematic method for gathering information from (a sample of)
Linda Allen, Jacob Boudoukh and Anthony Saunders, Understanding Market, Credit and Operational Risk: The Value at Risk Approach
 P1.T4. Valuation & Risk Models Linda Allen, Jacob Boudoukh and Anthony Saunders, Understanding Market, Credit and Operational Risk: The Value at Risk Approach Bionic Turtle FRM Study Notes Reading 26 By
P1.T4. Valuation & Risk Models Linda Allen, Jacob Boudoukh and Anthony Saunders, Understanding Market, Credit and Operational Risk: The Value at Risk Approach Bionic Turtle FRM Study Notes Reading 26 By
MVE051/MSG Lecture 7
 MVE051/MSG810 2017 Lecture 7 Petter Mostad Chalmers November 20, 2017 The purpose of collecting and analyzing data Purpose: To build and select models for parts of the real world (which can be used for
MVE051/MSG810 2017 Lecture 7 Petter Mostad Chalmers November 20, 2017 The purpose of collecting and analyzing data Purpose: To build and select models for parts of the real world (which can be used for
CABARRUS COUNTY 2008 APPRAISAL MANUAL
 STATISTICS AND THE APPRAISAL PROCESS PREFACE Like many of the technical aspects of appraising, such as income valuation, you have to work with and use statistics before you can really begin to understand
STATISTICS AND THE APPRAISAL PROCESS PREFACE Like many of the technical aspects of appraising, such as income valuation, you have to work with and use statistics before you can really begin to understand
STA2601. Tutorial letter 105/2/2018. Applied Statistics II. Semester 2. Department of Statistics STA2601/105/2/2018 TRIAL EXAMINATION PAPER
 STA2601/105/2/2018 Tutorial letter 105/2/2018 Applied Statistics II STA2601 Semester 2 Department of Statistics TRIAL EXAMINATION PAPER Define tomorrow. university of south africa Dear Student Congratulations
STA2601/105/2/2018 Tutorial letter 105/2/2018 Applied Statistics II STA2601 Semester 2 Department of Statistics TRIAL EXAMINATION PAPER Define tomorrow. university of south africa Dear Student Congratulations
Week 2 Quantitative Analysis of Financial Markets Hypothesis Testing and Confidence Intervals
 Week 2 Quantitative Analysis of Financial Markets Hypothesis Testing and Confidence Intervals Christopher Ting http://www.mysmu.edu/faculty/christophert/ Christopher Ting : christopherting@smu.edu.sg :
Week 2 Quantitative Analysis of Financial Markets Hypothesis Testing and Confidence Intervals Christopher Ting http://www.mysmu.edu/faculty/christophert/ Christopher Ting : christopherting@smu.edu.sg :
**BEGINNING OF EXAMINATION** A random sample of five observations from a population is:
 **BEGINNING OF EXAMINATION** 1. You are given: (i) A random sample of five observations from a population is: 0.2 0.7 0.9 1.1 1.3 (ii) You use the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for testing the null hypothesis,
**BEGINNING OF EXAMINATION** 1. You are given: (i) A random sample of five observations from a population is: 0.2 0.7 0.9 1.1 1.3 (ii) You use the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for testing the null hypothesis,
LESSON 7 INTERVAL ESTIMATION SAMIE L.S. LY
 LESSON 7 INTERVAL ESTIMATION SAMIE L.S. LY 1 THIS WEEK S PLAN Part I: Theory + Practice ( Interval Estimation ) Part II: Theory + Practice ( Interval Estimation ) z-based Confidence Intervals for a Population
LESSON 7 INTERVAL ESTIMATION SAMIE L.S. LY 1 THIS WEEK S PLAN Part I: Theory + Practice ( Interval Estimation ) Part II: Theory + Practice ( Interval Estimation ) z-based Confidence Intervals for a Population
TABLE OF CONTENTS - VOLUME 2
 TABLE OF CONTENTS - VOLUME 2 CREDIBILITY SECTION 1 - LIMITED FLUCTUATION CREDIBILITY PROBLEM SET 1 SECTION 2 - BAYESIAN ESTIMATION, DISCRETE PRIOR PROBLEM SET 2 SECTION 3 - BAYESIAN CREDIBILITY, DISCRETE
TABLE OF CONTENTS - VOLUME 2 CREDIBILITY SECTION 1 - LIMITED FLUCTUATION CREDIBILITY PROBLEM SET 1 SECTION 2 - BAYESIAN ESTIMATION, DISCRETE PRIOR PROBLEM SET 2 SECTION 3 - BAYESIAN CREDIBILITY, DISCRETE
chapter 2-3 Normal Positive Skewness Negative Skewness
 chapter 2-3 Testing Normality Introduction In the previous chapters we discussed a variety of descriptive statistics which assume that the data are normally distributed. This chapter focuses upon testing
chapter 2-3 Testing Normality Introduction In the previous chapters we discussed a variety of descriptive statistics which assume that the data are normally distributed. This chapter focuses upon testing
Analysis of 2x2 Cross-Over Designs using T-Tests for Non-Inferiority
 Chapter 235 Analysis of 2x2 Cross-Over Designs using -ests for Non-Inferiority Introduction his procedure analyzes data from a two-treatment, two-period (2x2) cross-over design where the goal is to demonstrate
Chapter 235 Analysis of 2x2 Cross-Over Designs using -ests for Non-Inferiority Introduction his procedure analyzes data from a two-treatment, two-period (2x2) cross-over design where the goal is to demonstrate
A Statistical Analysis to Predict Financial Distress
 J. Service Science & Management, 010, 3, 309-335 doi:10.436/jssm.010.33038 Published Online September 010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jssm) 309 Nicolas Emanuel Monti, Roberto Mariano Garcia Department
J. Service Science & Management, 010, 3, 309-335 doi:10.436/jssm.010.33038 Published Online September 010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jssm) 309 Nicolas Emanuel Monti, Roberto Mariano Garcia Department
Financial Returns. Dakota Wixom Quantitative Analyst QuantCourse.com INTRO TO PORTFOLIO RISK MANAGEMENT IN PYTHON
 INTRO TO PORTFOLIO RISK MANAGEMENT IN PYTHON Financial Returns Dakota Wixom Quantitative Analyst QuantCourse.com Course Overview Learn how to analyze investment return distributions, build portfolios and
INTRO TO PORTFOLIO RISK MANAGEMENT IN PYTHON Financial Returns Dakota Wixom Quantitative Analyst QuantCourse.com Course Overview Learn how to analyze investment return distributions, build portfolios and
Determining Sample Size. Slide 1 ˆ ˆ. p q n E = z α / 2. (solve for n by algebra) n = E 2
 Determining Sample Size Slide 1 E = z α / 2 ˆ ˆ p q n (solve for n by algebra) n = ( zα α / 2) 2 p ˆ qˆ E 2 Sample Size for Estimating Proportion p When an estimate of ˆp is known: Slide 2 n = ˆ ˆ ( )
Determining Sample Size Slide 1 E = z α / 2 ˆ ˆ p q n (solve for n by algebra) n = ( zα α / 2) 2 p ˆ qˆ E 2 Sample Size for Estimating Proportion p When an estimate of ˆp is known: Slide 2 n = ˆ ˆ ( )
A Study on Optimal Limit Order Strategy using Multi-Period Stochastic Programming considering Nonexecution Risk
 Proceedings of the Asia Pacific Industrial Engineering & Management Systems Conference 2018 A Study on Optimal Limit Order Strategy using Multi-Period Stochastic Programming considering Nonexecution Ris
Proceedings of the Asia Pacific Industrial Engineering & Management Systems Conference 2018 A Study on Optimal Limit Order Strategy using Multi-Period Stochastic Programming considering Nonexecution Ris
Statistics 431 Spring 2007 P. Shaman. Preliminaries
 Statistics 4 Spring 007 P. Shaman The Binomial Distribution Preliminaries A binomial experiment is defined by the following conditions: A sequence of n trials is conducted, with each trial having two possible
Statistics 4 Spring 007 P. Shaman The Binomial Distribution Preliminaries A binomial experiment is defined by the following conditions: A sequence of n trials is conducted, with each trial having two possible
Independent-Samples t Test
 Chapter 14 Aplia week 8 (Two independent samples) Testing hypotheses about means of two populations naturally occurring populations introverts vs. extroverts neuroticism experimentally defined (random
Chapter 14 Aplia week 8 (Two independent samples) Testing hypotheses about means of two populations naturally occurring populations introverts vs. extroverts neuroticism experimentally defined (random
Mixed Models Tests for the Slope Difference in a 3-Level Hierarchical Design with Random Slopes (Level-3 Randomization)
 Chapter 375 Mixed Models Tests for the Slope Difference in a 3-Level Hierarchical Design with Random Slopes (Level-3 Randomization) Introduction This procedure calculates power and sample size for a three-level
Chapter 375 Mixed Models Tests for the Slope Difference in a 3-Level Hierarchical Design with Random Slopes (Level-3 Randomization) Introduction This procedure calculates power and sample size for a three-level
The Great Moderation Flattens Fat Tails: Disappearing Leptokurtosis
 The Great Moderation Flattens Fat Tails: Disappearing Leptokurtosis WenShwo Fang Department of Economics Feng Chia University 100 WenHwa Road, Taichung, TAIWAN Stephen M. Miller* College of Business University
The Great Moderation Flattens Fat Tails: Disappearing Leptokurtosis WenShwo Fang Department of Economics Feng Chia University 100 WenHwa Road, Taichung, TAIWAN Stephen M. Miller* College of Business University
Equivalence Tests for the Ratio of Two Means in a Higher- Order Cross-Over Design
 Chapter 545 Equivalence Tests for the Ratio of Two Means in a Higher- Order Cross-Over Design Introduction This procedure calculates power and sample size of statistical tests of equivalence of two means
Chapter 545 Equivalence Tests for the Ratio of Two Means in a Higher- Order Cross-Over Design Introduction This procedure calculates power and sample size of statistical tests of equivalence of two means
Break-even analysis under randomness with heavy-tailed distribution
 Break-even analysis under randomness with heavy-tailed distribution Aleš KRESTA a* Karolina LISZTWANOVÁ a a Department of Finance, Faculty of Economics, VŠB TU Ostrava, Sokolská tř. 33, 70 00, Ostrava,
Break-even analysis under randomness with heavy-tailed distribution Aleš KRESTA a* Karolina LISZTWANOVÁ a a Department of Finance, Faculty of Economics, VŠB TU Ostrava, Sokolská tř. 33, 70 00, Ostrava,
