Comments by: Sebnem Kalemli-Ozcan Associate Professor of Economics University of Houston and NBER. August 2007
|
|
|
- Ashley Barker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Capital Flows and Asset Prices by Kosuke Aoki, Gianluca Benigno, and Nobuhiro Kiyotaki Comments by: Sebnem Kalemli-Ozcan Associate Professor of Economics University of Houston and NBER August 2007 This paper by Aoki, Benigno, and Kiyotaki (ABK) provides a useful sequel to their influential 2006 paper. Both papers rest on the observation that upon capital account liberalization countries experience large swings both in the value of fixed assets and in the available amounts of foreign and domestic credits. The authors argue that although these changes are observed both by industrial and emerging market countries they are ignored by the standard models. In particular, the authors would like to know how does the adjustment to capital account liberalization depend on the degree of development of domestic financial institutions and why the economies with underdeveloped financial systems are more vulnerable to these foreign and domestic credit shocks? To answer these questions, they develop a model of small open economy, where it is difficult to enforce debtors to repay their debt unless it is secured by a collateral. The fixed asset (land) acts as collateral and the borrower s credit limit is affected by the price of the fixed asset and vice versa. The interaction between credit limits and the asset prices turns out to be a propagation mechanism, which may generate large swings in aggregate economics activities. The main result of both ABK (2006) and ABK (2007) is as follows. Capital account liberalization cause temporary recessions, but liberalization can also enhance long-run total factor productivity (TFP). The focus of the current paper is on the dynamics of asset prices which leads to different short run dynamics in TFP depending on the interaction between the value of the fixed assets, the credit limits and the degree of the development of the domestic financial system. 1
2 I like this paper. I think linking capital account liberalization to the quality of the domestic financial markets and to broader institutional framework is the right way to proceed theoretically, given the evidence. There is an extensive empirical literature, which finds no effect of capital account liberalization on growth. 1 Some papers within this literature show that if there is any beneficial effect of foreign investment on growth it must be operating through the quality of domestic financial institutions. 2 Hence to incorporate the role of financial markets in the analysis of the effects of capital account liberalization is essential. Another paper with a similar focus to the current paper is Mendoza (2006). The main difference between the two papers is that ABK allows for endogeneity in aggregate productivity based on differential effect of domestic financial development as opposed to exogenous productivity shocks in Mendoza (2006). My main comments will be about the specific mechanisms and the results of the model that are hard to justify given the data. In the model there are two types of entrepreneurs: high productivity and low productivity. It is optimal for low types to lend funds to high types. Upon liberalization outside source of funds become available and low types keep lending to high types. The assumption that liberalization only brings additional source of funding is definitely not true in the data and becomes problematic in this entrepreneurial setup. Upon liberalization one form of financing will involve foreign direct investment (FDI). In fact FDI is a much bigger source of external finance for emerging market countries than private equity and private debt, which is what the authors are focusing on. 3 FDI not only provides direct capital financing but also creates positive externalities via the adoption of foreign technology and know-how. The adoption process operates through licensing agreements, imitation, employee training, the introduction of new processes, and products by foreign firms, and the creation of linkages between foreign and domestic firms. Recent empirical literature finds evidence of such externalities and knowledge spillovers. 4 1 See the recent review by Kose, Prasad, Rogoff, and Wei (2006). 2 See Alfaro, Chanda, Kalemli-Ozcan, Sayek (2004), and Durham (2004). 3 See Alfaro, Kalemli-Ozcan, and Volosovych (2007a). 4 See Javorcik (2004), and Kugler (2006). The authors assume that productivity of each 2
3 agent is positively correlated so high and low types stay like that. It is not clear why low types can not benefit from knowledge spillovers and learn? The model does not allow the real life situation, where low skilled workers are employed by the foreign company, they learn and they start up a business. I understand that the authors focus is on the change in TFP via the change in the resource allocation between high and low productivity producers even if the productivity of each producer stays constant. I think this is a simplifying assumption with not so simple repercussions. If shifting people from workers to entrepreneurs was allowed in the model, this will raises wages, pushing down investment demand and lowering threshold at which unproductive entrepreneurs leave labor market, raising TFP at lower levels of financial development. This will alter the key results of the paper. Another real life benefit of capital account liberalization is the improvement in domestic financial markets through numerous channels. 5 In the model, financial market development is represented by a single given parameter θ. In addition, since threshold level of financial market development is decreasing in the share of land, only in the range of θ < θ liberalization affects TFP. The authors try to deal with this indirectly by increasing θ exogenously, however in my view, the two-way relationship between capital account liberalization and financial development is too important and should not be only investigated exogenously by numerically changing the parameter θ, especially given this rich framework of ABK model. The main results of the paper also do not seem to be fitting the facts. To start with, it is not very clear which stylized facts the model is trying to match? Is this a model for industrial countries or emerging markets? Are the authors focusing on debt or equity liberalization? The authors claim they focus on private debt and private equity and ignore FDI and sovereign debt. This is a fine assumption but the paper reads as more of a debt story. More importantly we know that there is a big difference in terms of volatility and crisis when one considers debt vs equity liberalization since debt is intermediated through banks with little oversight, as argued by Henry (2006). Besides, Durdu, Mendoza, Terrones (2007) show that there is no evidence of systematic increases in volatility for Sudden Stop economies in the era 5 See Galindo, Schantarelli, and Reis (2007) for evidence on one such channel, i.e., allocative efficiency. 3
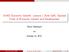
4 Figure 1: Interest Rates and Financial Development 10 GEO Lending Rates, % VUT NOR DEUSA SLE DZA NGA EST TZA LBY MWI KOR LTU WSM ETH FJI CYP GNQ IDN HND GBR UKR BRB BHR FIN CHE CHL SWZ LAO BEL KEN BHS CAN LBR SWE AUS PER 3 2 JAM Private Credit to GDP, % of financial globalization. One of the key results of the paper, which is countries with poor financial system receive inflows, does not hold in the data as shown by Alfaro, Kalemli-Ozcan, Volosovych (2007b). More generally this paper cannot fully explain the direction or the size of a country s capital flows under credit frictions as argued by the authors since they not only ignore the other determinants of capital flows but also they abstract from FDI and sovereign debt, the two most important components of capital flows. The model predicts a U-shaped relationship between financial development and interest rates. Do we have solid evidence of this? A first look at the data shows that there is no relation between interest rates and financial development, proxied by the ratio of private credit to GDP (see figure 1). 4
5 Even we assume that the U-shape exists what distinguishes this theory from others? It is hard to test this theory even at the firm level since there are two critical issues that one must deal with: First, value of collateral is not observable due to the lack of active secondary markets for collateralizable assets, such as plants and machineries, and second, collateral is endogenous to investment. When firms invest they need to purchase machines and build plants, which expands their collateralizable assets. To sum up, I think the authors developed a very rich model and I enjoyed reading it and learned a lot. However due to the limited empirical validity of the assumptions of the model, an important policy question remains unanswered: What is the relative welfare gain from domestic financial improvement versus capital account liberalization? It seems like the model predicts that welfare improves more with further financial development, a powerful result that not only needs to be confirmed in the data, but also needs to be based on empirically sound assumptions. 5
6 References Alfaro, L., A. Chanda, S. Kalemli-Ozcan, and S. Sayek, FDI and Economic Growth, The Role of Local Financial Markets, Journal of International Economics 64, Alfaro, L., S. Kalemli-Ozcan, and V. Volosovych, 2007a. Capital Flows in a Globalized World: The Role of Policies and Institutions, in S. Edwards, editor, Capital Controls and Capital Flows in Emerging Economies: Policies, Practices and Consequences. Alfaro, L., S. Kalemli-Ozcan, and V. Volosovych, 2007b. Why does not Capital Flow to Rich Countries? An Empirical Investigation, Review of Economics and Statistics, forthcoming. Aoki, K., G. Benigno, and N. Kiyotaki, Adjusting to Capital Account Liberalization, mimeo. Durdu, B., E. Mendoza, M. Terrones, Precautionary Demand for Foreign Assets in Sudden Stop Economies: An Assessment of the New Mercantilism, NBER Working Paper Durham, K. B., Absorptive Capacity and the Effects of Foreign Direct Investment and Equity Foreign Portfolio Investment on Economic Growth, European Economic Review 48, Galindo, A., F. Schiantarelli, and A. Weiss, Does Financial Liberalization Improve the Allocation of Investment? Micro-evidence from Developing Countries, Journal of Development Economics, 83. Henry, P. B., Capital Account Liberalization: Theory, Evidence, and Speculation, NBER Working Paper Javorcik, B. S., Does Foreign Direct Investment Increase the Productivity of Domestic Firms? In Search of Spillovers Through Backward Linkages, American Economic Review 94,
7 Kose, A., E. Prasad, K. Rogoff, and S. Wei, Financial Globalization: A Reappraisal, mimeo. Mendoza, E., Endogenous Sudden Stops in a Business Cycle Model with Collateral Constraints: A Fisherian Deflation of Tobin s Q, NBER Working Paper
Patterns of International Capital Flows and Their Implications for Developing Countries 1
 Patterns of International Capital Flows and Their Implications for Developing Countries 1 Mika Nieminen (University of Jyväskylä) 2018 Nordic Conference on Development Economics June 11, 2018 Helsinki
Patterns of International Capital Flows and Their Implications for Developing Countries 1 Mika Nieminen (University of Jyväskylä) 2018 Nordic Conference on Development Economics June 11, 2018 Helsinki
Financial Globalization. Bilò Valentina. Maran Elena
 Financial Globalization Bilò Valentina Maran Elena Three types of international transactions Goods and services Goods and services Assets Assets The Ricardian model of comparative advantage A country has
Financial Globalization Bilò Valentina Maran Elena Three types of international transactions Goods and services Goods and services Assets Assets The Ricardian model of comparative advantage A country has
Capital Flows and Asset Prices. Kosuke Aoki, Gianluca Benigno and Nobuhiro Kiyotaki
 Capital Flows and Asset Prices Kosuke Aoki, Gianluca Benigno and Nobuhiro Kiyotaki 1 Introduction After liberalizing international transaction of nancial assets, many countries experience large swings
Capital Flows and Asset Prices Kosuke Aoki, Gianluca Benigno and Nobuhiro Kiyotaki 1 Introduction After liberalizing international transaction of nancial assets, many countries experience large swings
Does Encourage Inward FDI Always Be a Dominant Strategy for Domestic Government? A Theoretical Analysis of Vertically Differentiated Industry
 Lin, Journal of International and Global Economic Studies, 7(2), December 2014, 17-31 17 Does Encourage Inward FDI Always Be a Dominant Strategy for Domestic Government? A Theoretical Analysis of Vertically
Lin, Journal of International and Global Economic Studies, 7(2), December 2014, 17-31 17 Does Encourage Inward FDI Always Be a Dominant Strategy for Domestic Government? A Theoretical Analysis of Vertically
University of Pennsylvania & NBER. This paper reflects only the authors views, and not those of the IMF
 An Anatomy of Credit Booms and their Demise Enrique G. Mendoza University of Pennsylvania & NBER Marco E. Terrones IMF This paper reflects only the authors views, and not those of the IMF Motivation and
An Anatomy of Credit Booms and their Demise Enrique G. Mendoza University of Pennsylvania & NBER Marco E. Terrones IMF This paper reflects only the authors views, and not those of the IMF Motivation and
Capital Flows and Asset Prices
 Capital Flows and Asset Prices Kosuke Aoki, Gianluca Benigno and Nobuhiro Kiyotaki August, 2007 Abstract After liberalizing international transaction of nancial assets, many countries experience large
Capital Flows and Asset Prices Kosuke Aoki, Gianluca Benigno and Nobuhiro Kiyotaki August, 2007 Abstract After liberalizing international transaction of nancial assets, many countries experience large
Business cycle fluctuations Part II
 Understanding the World Economy Master in Economics and Business Business cycle fluctuations Part II Lecture 7 Nicolas Coeurdacier nicolas.coeurdacier@sciencespo.fr Lecture 7: Business cycle fluctuations
Understanding the World Economy Master in Economics and Business Business cycle fluctuations Part II Lecture 7 Nicolas Coeurdacier nicolas.coeurdacier@sciencespo.fr Lecture 7: Business cycle fluctuations
Foreign Capital and Economic Growth
 Foreign Capital and Economic Growth Arvind Subramanian (Eswar Prasad and Raghuram Rajan) Western Hemisphere Department Workshop November 17, 2006 *This presentation reflects the views of the authors only
Foreign Capital and Economic Growth Arvind Subramanian (Eswar Prasad and Raghuram Rajan) Western Hemisphere Department Workshop November 17, 2006 *This presentation reflects the views of the authors only
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES GLOBAL SAVINGS AND GLOBAL INVESTMENT: THE TRANSMISSION OF IDENTIFIED FISCAL SHOCKS. James Feyrer Jay C.
 NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES GLOBAL SAVINGS AND GLOBAL INVESTMENT: THE TRANSMISSION OF IDENTIFIED FISCAL SHOCKS James Feyrer Jay C. Shambaugh Working Paper 15113 http://www.nber.org/papers/w15113 NATIONAL
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES GLOBAL SAVINGS AND GLOBAL INVESTMENT: THE TRANSMISSION OF IDENTIFIED FISCAL SHOCKS James Feyrer Jay C. Shambaugh Working Paper 15113 http://www.nber.org/papers/w15113 NATIONAL
Capital Flows to Developing Countries: the Allocation Puzzle. Discussion by Fabio Ghironi 2007 ASSA Annual Meetings Chicago, January 5-7, 2007
 Capital Flows to Developing Countries: the Allocation Puzzle Pierre-Olivier Gourinchas and Olivier Jeanne Discussion by Fabio Ghironi 2007 ASSA Annual Meetings Chicago, January 5-7, 2007 Introduction This
Capital Flows to Developing Countries: the Allocation Puzzle Pierre-Olivier Gourinchas and Olivier Jeanne Discussion by Fabio Ghironi 2007 ASSA Annual Meetings Chicago, January 5-7, 2007 Introduction This
Comment on: Capital Controls and Monetary Policy Autonomy in a Small Open Economy by J. Scott Davis and Ignacio Presno
 Comment on: Capital Controls and Monetary Policy Autonomy in a Small Open Economy by J. Scott Davis and Ignacio Presno Fabrizio Perri Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis and CEPR fperri@umn.edu December
Comment on: Capital Controls and Monetary Policy Autonomy in a Small Open Economy by J. Scott Davis and Ignacio Presno Fabrizio Perri Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis and CEPR fperri@umn.edu December
A Solution to Two Paradoxes of International Capital Flows. Jiandong Ju and Shang-Jin Wei. Discussion by Fabio Ghironi
 A Solution to Two Paradoxes of International Capital Flows Jiandong Ju and Shang-Jin Wei Discussion by Fabio Ghironi NBER Summer Institute International Finance and Macroeconomics Program July 10-14, 2006
A Solution to Two Paradoxes of International Capital Flows Jiandong Ju and Shang-Jin Wei Discussion by Fabio Ghironi NBER Summer Institute International Finance and Macroeconomics Program July 10-14, 2006
ECON 385. Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory II. Solow Model With Technological Progress and Data. Instructor: Dmytro Hryshko
 ECON 385. Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory II. Solow Model With Technological Progress and Data Instructor: Dmytro Hryshko 1 / 35 Examples of technological progress 1970: 50,000 computers in the world;
ECON 385. Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory II. Solow Model With Technological Progress and Data Instructor: Dmytro Hryshko 1 / 35 Examples of technological progress 1970: 50,000 computers in the world;
Overborrowing, Financial Crises and Macro-prudential Policy
 Overborrowing, Financial Crises and Macro-prudential Policy Javier Bianchi University of Wisconsin Enrique G. Mendoza University of Maryland & NBER The case for macro-prudential policies Credit booms are
Overborrowing, Financial Crises and Macro-prudential Policy Javier Bianchi University of Wisconsin Enrique G. Mendoza University of Maryland & NBER The case for macro-prudential policies Credit booms are
Sudden Stops and Output Drops
 Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis Research Department Staff Report 353 January 2005 Sudden Stops and Output Drops V. V. Chari University of Minnesota and Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis Patrick J.
Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis Research Department Staff Report 353 January 2005 Sudden Stops and Output Drops V. V. Chari University of Minnesota and Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis Patrick J.
Sudden Stops and Output Drops
 NEW PERSPECTIVES ON REPUTATION AND DEBT Sudden Stops and Output Drops By V. V. CHARI, PATRICK J. KEHOE, AND ELLEN R. MCGRATTAN* Discussants: Andrew Atkeson, University of California; Olivier Jeanne, International
NEW PERSPECTIVES ON REPUTATION AND DEBT Sudden Stops and Output Drops By V. V. CHARI, PATRICK J. KEHOE, AND ELLEN R. MCGRATTAN* Discussants: Andrew Atkeson, University of California; Olivier Jeanne, International
Monetary Policy and Financial System During Demographic Change:
 Monetary Policy and Financial System During Demographic Change: Three questions Gauti B. Eggertsson Brown University 1. Can demographic change account for worldwide decline in interest rate? 2. What is
Monetary Policy and Financial System During Demographic Change: Three questions Gauti B. Eggertsson Brown University 1. Can demographic change account for worldwide decline in interest rate? 2. What is
Leverage Across Firms, Banks and Countries
 Şebnem Kalemli-Özcan, Bent E. Sørensen and Sevcan Yeşiltaş University of Houston and NBER, University of Houston and CEPR, and Johns Hopkins University Dallas Fed Conference on Financial Frictions and
Şebnem Kalemli-Özcan, Bent E. Sørensen and Sevcan Yeşiltaş University of Houston and NBER, University of Houston and CEPR, and Johns Hopkins University Dallas Fed Conference on Financial Frictions and
Quantitative Significance of Collateral Constraints as an Amplification Mechanism
 RIETI Discussion Paper Series 09-E-05 Quantitative Significance of Collateral Constraints as an Amplification Mechanism INABA Masaru The Canon Institute for Global Studies KOBAYASHI Keiichiro RIETI The
RIETI Discussion Paper Series 09-E-05 Quantitative Significance of Collateral Constraints as an Amplification Mechanism INABA Masaru The Canon Institute for Global Studies KOBAYASHI Keiichiro RIETI The
Transition to FDI Openness
 Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis Research Department Transition to FDI Openness Ellen R. McGrattan Working Paper 671 April 2009 ABSTRACT Empirical studies quantifying the benefits of increased foreign
Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis Research Department Transition to FDI Openness Ellen R. McGrattan Working Paper 671 April 2009 ABSTRACT Empirical studies quantifying the benefits of increased foreign
Online Appendix for Explaining Educational Attainment across Countries and over Time
 Online Appendix for Explaining Educational Attainment across Countries and over Time Diego Restuccia University of Toronto Guillaume Vandenbroucke University of Southern California March 2014 Contents
Online Appendix for Explaining Educational Attainment across Countries and over Time Diego Restuccia University of Toronto Guillaume Vandenbroucke University of Southern California March 2014 Contents
Business Cycles and Macroeconomic Policy in Emerging Market Economies
 Business Cycles and Macroeconomic Policy in Emerging Market Economies Project Leader Valery Charnavoki, Assistant Professor, New Economic School https://sites.google.com/site/charnavoki/ This research
Business Cycles and Macroeconomic Policy in Emerging Market Economies Project Leader Valery Charnavoki, Assistant Professor, New Economic School https://sites.google.com/site/charnavoki/ This research
IS FINANCIAL REPRESSION REALLY BAD? Eun Young OH Durham Univeristy 17 Sidegate, Durham, United Kingdom
 IS FINANCIAL REPRESSION REALLY BAD? Eun Young OH Durham Univeristy 17 Sidegate, Durham, United Kingdom E-mail: e.y.oh@durham.ac.uk Abstract This paper examines the relationship between reserve requirements,
IS FINANCIAL REPRESSION REALLY BAD? Eun Young OH Durham Univeristy 17 Sidegate, Durham, United Kingdom E-mail: e.y.oh@durham.ac.uk Abstract This paper examines the relationship between reserve requirements,
International Spillovers and Local Credit Cycles
 International Spillovers and Local Credit Cycles Yusuf Soner Baskaya Julian di Giovanni Şebnem Kalemli-Özcan Mehmet Fatih Ulu Comments by Sole Martinez Peria Macro-Financial Division IMF Prepared for the
International Spillovers and Local Credit Cycles Yusuf Soner Baskaya Julian di Giovanni Şebnem Kalemli-Özcan Mehmet Fatih Ulu Comments by Sole Martinez Peria Macro-Financial Division IMF Prepared for the
Foreign Direct Investment, Productivity, and Financial. Development: An Empirical Analysis of Complementarities and. Channels
 Foreign Direct Investment, Productivity, and Financial Development: An Empirical Analysis of Complementarities and Channels Laura Alfaro Harvard Business School and NBER Sebnem Kalemli-Ozcan University
Foreign Direct Investment, Productivity, and Financial Development: An Empirical Analysis of Complementarities and Channels Laura Alfaro Harvard Business School and NBER Sebnem Kalemli-Ozcan University
CAN FDI CONTRIBUTE TO INCLUSIVE GROWTH: ROLE OF INVESTMENT FACILITATION
 CAN FDI CONTRIBUTE TO INCLUSIVE GROWTH: ROLE OF INVESTMENT FACILITATION Iza Lejarraga Head of Unit, Investment Policy Linkages OECD Investment Division FIFD Workshop on Investment Facilitation for Development
CAN FDI CONTRIBUTE TO INCLUSIVE GROWTH: ROLE OF INVESTMENT FACILITATION Iza Lejarraga Head of Unit, Investment Policy Linkages OECD Investment Division FIFD Workshop on Investment Facilitation for Development
Financial Cycles and Credit Growth Across Countries
 Financial Cycles and Credit Growth Across Countries By Nuno Coimbra and Helene Rey Credit growth is an ubiquitous variable in the literature on crises and financial stability. Crises tend to be credit
Financial Cycles and Credit Growth Across Countries By Nuno Coimbra and Helene Rey Credit growth is an ubiquitous variable in the literature on crises and financial stability. Crises tend to be credit
Booms and Banking Crises
 Booms and Banking Crises F. Boissay, F. Collard and F. Smets Macro Financial Modeling Conference Boston, 12 October 2013 MFM October 2013 Conference 1 / Disclaimer The views expressed in this presentation
Booms and Banking Crises F. Boissay, F. Collard and F. Smets Macro Financial Modeling Conference Boston, 12 October 2013 MFM October 2013 Conference 1 / Disclaimer The views expressed in this presentation
Credit Supply, Household Debt, and Business Cycles
 Credit Supply, Household Debt, and Business Cycles Amir Sufi University of Chicago Booth School of Business; NBER; co-director of IGM February 2017 Big Picture Questions What is the source of macroeconomic
Credit Supply, Household Debt, and Business Cycles Amir Sufi University of Chicago Booth School of Business; NBER; co-director of IGM February 2017 Big Picture Questions What is the source of macroeconomic
Introduction: macroeconomic implications of capital flows in a global economy
 Journal of Economic Theory 119 (2004) 1 5 www.elsevier.com/locate/jet Editorial Introduction: macroeconomic implications of capital flows in a global economy Abstract The papers in this volume address
Journal of Economic Theory 119 (2004) 1 5 www.elsevier.com/locate/jet Editorial Introduction: macroeconomic implications of capital flows in a global economy Abstract The papers in this volume address
Banks and Liquidity Crises in Emerging Market Economies
 Banks and Liquidity Crises in Emerging Market Economies Tarishi Matsuoka Tokyo Metropolitan University May, 2015 Tarishi Matsuoka (TMU) Banking Crises in Emerging Market Economies May, 2015 1 / 47 Introduction
Banks and Liquidity Crises in Emerging Market Economies Tarishi Matsuoka Tokyo Metropolitan University May, 2015 Tarishi Matsuoka (TMU) Banking Crises in Emerging Market Economies May, 2015 1 / 47 Introduction
Informal Sector and Economic Growth: The Supply of Credit Channel
 Informal Sector and Economic Growth: The Supply of Credit Channel Baptiste Massenot Stéphane Straub September 2011 Abstract A standard view holds that removing barriers to entry and improving judicial
Informal Sector and Economic Growth: The Supply of Credit Channel Baptiste Massenot Stéphane Straub September 2011 Abstract A standard view holds that removing barriers to entry and improving judicial
Comment on Aoki, Benigno and Kiyotaki, Monetary and Financial Policies in Emerging Markets
 Comment on Aoki, Benigno and Kiyotaki, Monetary and Financial Policies in Emerging Markets Lawrence Christiano Department of Economics, Northwestern University Model Small open economy faces downward-sloped
Comment on Aoki, Benigno and Kiyotaki, Monetary and Financial Policies in Emerging Markets Lawrence Christiano Department of Economics, Northwestern University Model Small open economy faces downward-sloped
José Darío Uribe E. Governor central bank of colombia October 13, 2011
 Capital Flows, Policy Challenges and Policy Options José Darío Uribe E. Governor central bank of colombia October 13, 2011 Outline Review the fluctuations of macroeconomic aggregates along the cycles of
Capital Flows, Policy Challenges and Policy Options José Darío Uribe E. Governor central bank of colombia October 13, 2011 Outline Review the fluctuations of macroeconomic aggregates along the cycles of
Estimating Macroeconomic Models of Financial Crises: An Endogenous Regime-Switching Approach
 Estimating Macroeconomic Models of Financial Crises: An Endogenous Regime-Switching Approach Gianluca Benigno 1 Andrew Foerster 2 Christopher Otrok 3 Alessandro Rebucci 4 1 London School of Economics and
Estimating Macroeconomic Models of Financial Crises: An Endogenous Regime-Switching Approach Gianluca Benigno 1 Andrew Foerster 2 Christopher Otrok 3 Alessandro Rebucci 4 1 London School of Economics and
FDI and economic growth: new evidence on the role of financial markets
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive FDI and economic growth: new evidence on the role of financial markets W.N.W. Azman-Saini and Siong Hook Law and Abdul Halim Ahmad Universiti Putra Malaysia, Universiti
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive FDI and economic growth: new evidence on the role of financial markets W.N.W. Azman-Saini and Siong Hook Law and Abdul Halim Ahmad Universiti Putra Malaysia, Universiti
Economic Growth: Lecture 1 (first half), Stylized Facts of Economic Growth and Development
 14.452 Economic Growth: Lecture 1 (first half), Stylized Facts of Economic Growth and Development Daron Acemoglu MIT October 24, 2012. Daron Acemoglu (MIT) Economic Growth Lecture 1 October 24, 2012. 1
14.452 Economic Growth: Lecture 1 (first half), Stylized Facts of Economic Growth and Development Daron Acemoglu MIT October 24, 2012. Daron Acemoglu (MIT) Economic Growth Lecture 1 October 24, 2012. 1
Chapter 6. Macroeconomic Data. Zekarias M. Hussein and Angel H. Aguiar Uses of Macroeconomic Data
 Chapter 6 Macroeconomic Data Zekarias M. Hussein and Angel H. Aguiar This chapter provides an overview of the macroeconomic features of the 8 Data Base. We will first present how the macroeconomic data
Chapter 6 Macroeconomic Data Zekarias M. Hussein and Angel H. Aguiar This chapter provides an overview of the macroeconomic features of the 8 Data Base. We will first present how the macroeconomic data
Reforms in a Debt Overhang
 Structural Javier Andrés, Óscar Arce and Carlos Thomas 3 National Bank of Belgium, June 8 4 Universidad de Valencia, Banco de España Banco de España 3 Banco de España National Bank of Belgium, June 8 4
Structural Javier Andrés, Óscar Arce and Carlos Thomas 3 National Bank of Belgium, June 8 4 Universidad de Valencia, Banco de España Banco de España 3 Banco de España National Bank of Belgium, June 8 4
Is Full Employment Sustainable?
 Is Full Employment Sustainable? Antonio Fatas INSEAD Very preliminary. This version: March 11, 2019 Introduction The US economy started its current expansion phase in June 2009. This means that, as of
Is Full Employment Sustainable? Antonio Fatas INSEAD Very preliminary. This version: March 11, 2019 Introduction The US economy started its current expansion phase in June 2009. This means that, as of
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES INTRINSIC OPENNESS AND ENDOGENOUS INSTITUTIONAL QUALITY. Yang Jiao Shang-Jin Wei
 NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES INTRINSIC OPENNESS AND ENDOGENOUS INSTITUTIONAL QUALITY Yang Jiao Shang-Jin Wei Working Paper 24052 http://www.nber.org/papers/w24052 NATIONAL BUREAU OF ECONOMIC RESEARCH 1050
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES INTRINSIC OPENNESS AND ENDOGENOUS INSTITUTIONAL QUALITY Yang Jiao Shang-Jin Wei Working Paper 24052 http://www.nber.org/papers/w24052 NATIONAL BUREAU OF ECONOMIC RESEARCH 1050
Globalization and crises
 Globalization and crises Luis Servén The World Bank Kuala Lumpur, November 2016 1 Plan Stylized facts 1. Financial globalization 2. Currency crises 3. Bubbles 4. Sovereign debt and default 5. Financial
Globalization and crises Luis Servén The World Bank Kuala Lumpur, November 2016 1 Plan Stylized facts 1. Financial globalization 2. Currency crises 3. Bubbles 4. Sovereign debt and default 5. Financial
Fiscal Policy and Economic Growth
 Fiscal Policy and Economic Growth Vitor Gaspar Director, Fiscal Affairs Department International Monetary Fund Peterson Institute for International Economics June 3, 15 Background The study draws on an
Fiscal Policy and Economic Growth Vitor Gaspar Director, Fiscal Affairs Department International Monetary Fund Peterson Institute for International Economics June 3, 15 Background The study draws on an
Financial Integration within EU Countries: The Role of Institutions, Confidence and Trust
 Financial Integration within EU Countries: The Role of Institutions, Confidence and Trust Comments by Enrique G. Mendoza, University of Maryland and NBER. October 3, 2007 This paper undertakes an empirical
Financial Integration within EU Countries: The Role of Institutions, Confidence and Trust Comments by Enrique G. Mendoza, University of Maryland and NBER. October 3, 2007 This paper undertakes an empirical
Exchange Rate Adjustment in Financial Crises
 Exchange Rate Adjustment in Financial Crises Michael B. Devereux 1 Changhua Yu 2 1 University of British Columbia 2 Peking University Swiss National Bank June 2016 Motivation: Two-fold Crises in Emerging
Exchange Rate Adjustment in Financial Crises Michael B. Devereux 1 Changhua Yu 2 1 University of British Columbia 2 Peking University Swiss National Bank June 2016 Motivation: Two-fold Crises in Emerging
The Long and Short of Empirical Evidence on the Impact of NAFTA on Canada. Eugene Beaulieu Yang Song Mustafa Zamen
 The Long and Short of Empirical Evidence on the Impact of NAFTA on Canada Eugene Beaulieu Yang Song Mustafa Zamen Overview Evolution of the debate and evidence The pre-nafta world: little white lies and
The Long and Short of Empirical Evidence on the Impact of NAFTA on Canada Eugene Beaulieu Yang Song Mustafa Zamen Overview Evolution of the debate and evidence The pre-nafta world: little white lies and
Innovations in Macroeconomics
 Paul JJ. Welfens Innovations in Macroeconomics Third Edition 4y Springer Contents A. Globalization, Specialization and Innovation Dynamics 1 A. 1 Introduction 1 A.2 Approaches in Modern Macroeconomics
Paul JJ. Welfens Innovations in Macroeconomics Third Edition 4y Springer Contents A. Globalization, Specialization and Innovation Dynamics 1 A. 1 Introduction 1 A.2 Approaches in Modern Macroeconomics
Hours Worked Across the World: Facts and Driving Forces
 : Facts and Driving Forces Goethe University Frankfurt Anglo-German Foundation Annual Lecture April 18, 2018 1 Hours worked worldwide 1 Hours worked worldwide 2 Hours worked in Europe and the US - Decomposition
: Facts and Driving Forces Goethe University Frankfurt Anglo-German Foundation Annual Lecture April 18, 2018 1 Hours worked worldwide 1 Hours worked worldwide 2 Hours worked in Europe and the US - Decomposition
International Capital Allocation, Sovereign Borrowing, and Growth
 International Capital Allocation, Sovereign Borrowing, and Growth Laura Alfaro Harvard Business School and NBER Vadym Volosovych Erasmus University Rotterdam Sebnem Kalemli-Ozcan University of Houston
International Capital Allocation, Sovereign Borrowing, and Growth Laura Alfaro Harvard Business School and NBER Vadym Volosovych Erasmus University Rotterdam Sebnem Kalemli-Ozcan University of Houston
Optimal Debt and Profitability in the Tradeoff Theory
 Optimal Debt and Profitability in the Tradeoff Theory Andrew B. Abel discussion by Toni Whited Tepper-LAEF Conference This paper presents a tradeoff model in which leverage is negatively related to profits!
Optimal Debt and Profitability in the Tradeoff Theory Andrew B. Abel discussion by Toni Whited Tepper-LAEF Conference This paper presents a tradeoff model in which leverage is negatively related to profits!
FISHERIAN MODELS OF FINANCIAL CRISES IN MACROEONOMICS. Enrique G. Mendoza University of Pennsylvania & NBER
 FISHERIAN MODELS OF FINANCIAL CRISES IN MACROEONOMICS Enrique G. Mendoza University of Pennsylvania & NBER A writer s perspective debt happens as a result of actions occurring over time. Therefore, any
FISHERIAN MODELS OF FINANCIAL CRISES IN MACROEONOMICS Enrique G. Mendoza University of Pennsylvania & NBER A writer s perspective debt happens as a result of actions occurring over time. Therefore, any
Precautionary Demand for Foreign Assets in Sudden Stop Economies: An Assessment of the New Mercantilism
 Precautionary Demand for Foreign Assets in Sudden Stop Economies: An Assessment of the New Mercantilism Ceyhun Bora Durdu Enrique G. Mendoza Marco E. Terrones Board of Governors of the University of Maryland
Precautionary Demand for Foreign Assets in Sudden Stop Economies: An Assessment of the New Mercantilism Ceyhun Bora Durdu Enrique G. Mendoza Marco E. Terrones Board of Governors of the University of Maryland
Lecture 17 Foreign Financing
 Introduction Lecture 17 Foreign Financing Develo ping economies financial linkages with the global economy have risen significantly in recent decades. theoretical models identify channels through which
Introduction Lecture 17 Foreign Financing Develo ping economies financial linkages with the global economy have risen significantly in recent decades. theoretical models identify channels through which
Trade led Growth in Times of Crisis Asia Pacific Trade Economists Conference 2 3 November 2009, Bangkok. Session 12
 Trade led Growth in Times of Crisis Asia Pacific Trade Economists Conference 2 3 November 2009, Bangkok Session 12 Factors Contributing to Export Performance in the Aftermath of Global Economic Crisis
Trade led Growth in Times of Crisis Asia Pacific Trade Economists Conference 2 3 November 2009, Bangkok Session 12 Factors Contributing to Export Performance in the Aftermath of Global Economic Crisis
The Public Debt Crisis of the United States
 The Public Debt Crisis of the United States Enrique G. Mendoza University of Pennsylvania, NBER & PIER Seminario sobre Sostenibilidad de la Deuda Pública: AIReF September 5, 2017 Madrid, Spain What debt
The Public Debt Crisis of the United States Enrique G. Mendoza University of Pennsylvania, NBER & PIER Seminario sobre Sostenibilidad de la Deuda Pública: AIReF September 5, 2017 Madrid, Spain What debt
Comments on Jeffrey Frankel, Commodity Prices and Monetary Policy by Lars Svensson
 Comments on Jeffrey Frankel, Commodity Prices and Monetary Policy by Lars Svensson www.princeton.edu/svensson/ This paper makes two main points. The first point is empirical: Commodity prices are decreasing
Comments on Jeffrey Frankel, Commodity Prices and Monetary Policy by Lars Svensson www.princeton.edu/svensson/ This paper makes two main points. The first point is empirical: Commodity prices are decreasing
Global Pricing of Risk and Stabilization Policies
 Global Pricing of Risk and Stabilization Policies Tobias Adrian Daniel Stackman Erik Vogt Federal Reserve Bank of New York The views expressed here are the authors and are not necessarily representative
Global Pricing of Risk and Stabilization Policies Tobias Adrian Daniel Stackman Erik Vogt Federal Reserve Bank of New York The views expressed here are the authors and are not necessarily representative
Investment and Financing Policies of Nepalese Enterprises
 Investment and Financing Policies of Nepalese Enterprises Kapil Deb Subedi 1 Abstract Firm financing and investment policies are central to the study of corporate finance. In imperfect capital market,
Investment and Financing Policies of Nepalese Enterprises Kapil Deb Subedi 1 Abstract Firm financing and investment policies are central to the study of corporate finance. In imperfect capital market,
Spillovers, Capital Flows and Prudential Regulation in Small Open Economies
 Spillovers, Capital Flows and Prudential Regulation in Small Open Economies Paul Castillo, César Carrera, Marco Ortiz & Hugo Vega Presented by: Hugo Vega BIS CCA Research Network Conference Incorporating
Spillovers, Capital Flows and Prudential Regulation in Small Open Economies Paul Castillo, César Carrera, Marco Ortiz & Hugo Vega Presented by: Hugo Vega BIS CCA Research Network Conference Incorporating
FDI with Reverse Imports and Hollowing Out
 FDI with Reverse Imports and Hollowing Out Kiyoshi Matsubara August 2005 Abstract This article addresses the decision of plant location by a home firm and its impact on the home economy, especially through
FDI with Reverse Imports and Hollowing Out Kiyoshi Matsubara August 2005 Abstract This article addresses the decision of plant location by a home firm and its impact on the home economy, especially through
International Financial Integration and Entrepreneurship
 International Financial Integration and Entrepreneurship Laura Alfaro and Andrew Charlton Discussion by Jean Imbs IMF 7 th Jacques Polak Conference 9-10 November 2006 The views expressed in this paper
International Financial Integration and Entrepreneurship Laura Alfaro and Andrew Charlton Discussion by Jean Imbs IMF 7 th Jacques Polak Conference 9-10 November 2006 The views expressed in this paper
2. Preceded (followed) by expansions (contractions) in domestic. 3. Capital, labor account for small fraction of output drop,
 Mendoza (AER) Sudden Stop facts 1. Large, abrupt reversals in capital flows 2. Preceded (followed) by expansions (contractions) in domestic production, absorption, asset prices, credit & leverage 3. Capital,
Mendoza (AER) Sudden Stop facts 1. Large, abrupt reversals in capital flows 2. Preceded (followed) by expansions (contractions) in domestic production, absorption, asset prices, credit & leverage 3. Capital,
Foreign Currency Debt, Financial Crises and Economic Growth : A Long-Run Exploration
 Foreign Currency Debt, Financial Crises and Economic Growth : A Long-Run Exploration Michael D. Bordo Rutgers University and NBER Christopher M. Meissner UC Davis and NBER GEMLOC Conference, World Bank,
Foreign Currency Debt, Financial Crises and Economic Growth : A Long-Run Exploration Michael D. Bordo Rutgers University and NBER Christopher M. Meissner UC Davis and NBER GEMLOC Conference, World Bank,
Financial Integration and Macroeconomic Volatility
 IMF Staff Papers Vol. 50, Special Issue 2003 International Monetary Fund Financial Integration and Macroeconomic Volatility M. AYHAN KOSE, ESWAR S. PRASAD, and MARCO E. TERRONES * This paper examines the
IMF Staff Papers Vol. 50, Special Issue 2003 International Monetary Fund Financial Integration and Macroeconomic Volatility M. AYHAN KOSE, ESWAR S. PRASAD, and MARCO E. TERRONES * This paper examines the
Costs of Business Cycles Empirical Evidence
 Costs of Business Cycles Empirical Evidence Petr Sedláček Bonn University Summer Term 2014 1 / 48 Background and some empirical evidence Seminal contribution by, Lucas (2003) Empirical evidence on the
Costs of Business Cycles Empirical Evidence Petr Sedláček Bonn University Summer Term 2014 1 / 48 Background and some empirical evidence Seminal contribution by, Lucas (2003) Empirical evidence on the
Productivity adjustment in ICP
 3rd Meeting of the PPP Compilation and Computation Task Force September 27 28, 2018 World Bank, 1818 H St. NW, Washington, DC MC 10-100 Productivity adjustment in ICP Robert Inklaar Productivity adjustment
3rd Meeting of the PPP Compilation and Computation Task Force September 27 28, 2018 World Bank, 1818 H St. NW, Washington, DC MC 10-100 Productivity adjustment in ICP Robert Inklaar Productivity adjustment
Automatic Stabilization and Labor Supply
 Automatic Stabilization and Labor Supply Mathias Dolls (ZEW Mannheim) Clemens Fuest (ifo Institut) Andreas Peichl (ZEW Mannheim) Christian Wittneben (ZEW Mannheim) Very preliminary draft. Please do not
Automatic Stabilization and Labor Supply Mathias Dolls (ZEW Mannheim) Clemens Fuest (ifo Institut) Andreas Peichl (ZEW Mannheim) Christian Wittneben (ZEW Mannheim) Very preliminary draft. Please do not
The International Transmission of Credit Bubbles: Theory and Policy
 The International Transmission of Credit Bubbles: Theory and Policy Alberto Martin and Jaume Ventura CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE March 14, 2015 Martin and Ventura (CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE) BIS Research
The International Transmission of Credit Bubbles: Theory and Policy Alberto Martin and Jaume Ventura CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE March 14, 2015 Martin and Ventura (CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE) BIS Research
Aggregation with a double non-convex labor supply decision: indivisible private- and public-sector hours
 Ekonomia nr 47/2016 123 Ekonomia. Rynek, gospodarka, społeczeństwo 47(2016), s. 123 133 DOI: 10.17451/eko/47/2016/233 ISSN: 0137-3056 www.ekonomia.wne.uw.edu.pl Aggregation with a double non-convex labor
Ekonomia nr 47/2016 123 Ekonomia. Rynek, gospodarka, społeczeństwo 47(2016), s. 123 133 DOI: 10.17451/eko/47/2016/233 ISSN: 0137-3056 www.ekonomia.wne.uw.edu.pl Aggregation with a double non-convex labor
CREI Lectures 2010 Differences in Technology Across Space and Time
 CREI Lectures 2010 Differences in Technology Across Space and Time Francesco Caselli Barcelona, June 16-18 1 / 77 General Introduction 2 / 77 Adam Smith would be surprised 3 / 77 Adam Smith would be surprised
CREI Lectures 2010 Differences in Technology Across Space and Time Francesco Caselli Barcelona, June 16-18 1 / 77 General Introduction 2 / 77 Adam Smith would be surprised 3 / 77 Adam Smith would be surprised
1 Business-Cycle Facts Around the World 1
 Contents Preface xvii 1 Business-Cycle Facts Around the World 1 1.1 Measuring Business Cycles 1 1.2 Business-Cycle Facts Around the World 4 1.3 Business Cycles in Poor, Emerging, and Rich Countries 7 1.4
Contents Preface xvii 1 Business-Cycle Facts Around the World 1 1.1 Measuring Business Cycles 1 1.2 Business-Cycle Facts Around the World 4 1.3 Business Cycles in Poor, Emerging, and Rich Countries 7 1.4
Financial integration: Patterns, effects and challenges.
 Financial integration: Patterns, effects and challenges. Viktoria Hnatkovska UBC and Wharton School BREAD-IGC-ISI Summer School, Delhi July 23 2012 Introduction New Delhi, March 2012: Mr Kaushik Basu,
Financial integration: Patterns, effects and challenges. Viktoria Hnatkovska UBC and Wharton School BREAD-IGC-ISI Summer School, Delhi July 23 2012 Introduction New Delhi, March 2012: Mr Kaushik Basu,
Productivity and income differences in the 20 th century
 Productivity and income differences in the 20 th century Robert Inklaar and Daniel Gallardo Albarrán (University of Groningen) World KLEMS Conference, June 4 5 2018 Development accounting What can account
Productivity and income differences in the 20 th century Robert Inklaar and Daniel Gallardo Albarrán (University of Groningen) World KLEMS Conference, June 4 5 2018 Development accounting What can account
Mthuli Ncube Professor of Public Policy, Blavatnik School of Government, University of Oxford
 Global Growth and Financial Spillovers and the South African Macro-economy Mthuli Ncube Professor of Public Policy, Blavatnik School of Government, University of Oxford Nombulelo Gumata Economist, South
Global Growth and Financial Spillovers and the South African Macro-economy Mthuli Ncube Professor of Public Policy, Blavatnik School of Government, University of Oxford Nombulelo Gumata Economist, South
the Federal Reserve to carry out exceptional policies for over seven year in order to alleviate its effects.
 The Great Recession and Financial Shocks 1 Zhen Huo New York University José-Víctor Ríos-Rull University of Pennsylvania University College London Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis CAERP, CEPR, NBER
The Great Recession and Financial Shocks 1 Zhen Huo New York University José-Víctor Ríos-Rull University of Pennsylvania University College London Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis CAERP, CEPR, NBER
The impact of foreign direct investment in the Western Balkans
 The impact of foreign direct investment in the Western Balkans Dr. Alma Zisi University "Aleksander Moisiu",Durrës, Square No. 1, Currila, Durrës, Albania Dr. Armela Anamali University "Aleksander Moisiu",Durrës,
The impact of foreign direct investment in the Western Balkans Dr. Alma Zisi University "Aleksander Moisiu",Durrës, Square No. 1, Currila, Durrës, Albania Dr. Armela Anamali University "Aleksander Moisiu",Durrës,
International Trade in Goods and Assets. 1. The economic activity of a small, open economy can affect the world prices.
 Chapter 13 International Trade in Goods and Assets Overview In order to understand the role of international trade, this chapter presents three models of a small, open economy where domestic economic actors
Chapter 13 International Trade in Goods and Assets Overview In order to understand the role of international trade, this chapter presents three models of a small, open economy where domestic economic actors
Private Leverage and Sovereign Default
 Private Leverage and Sovereign Default Cristina Arellano Yan Bai Luigi Bocola FRB Minneapolis University of Rochester Northwestern University Economic Policy and Financial Frictions November 2015 1 / 37
Private Leverage and Sovereign Default Cristina Arellano Yan Bai Luigi Bocola FRB Minneapolis University of Rochester Northwestern University Economic Policy and Financial Frictions November 2015 1 / 37
II. Major Engines of Sustained Economic Growth
 Opening Speech by Toshihiko Fukui, Governor of the Bank of Japan I. Introduction Good morning, ladies and gentlemen. I am very pleased to address the 11th international conference hosted by the Institute
Opening Speech by Toshihiko Fukui, Governor of the Bank of Japan I. Introduction Good morning, ladies and gentlemen. I am very pleased to address the 11th international conference hosted by the Institute
Cross-border Financial Risk Sharing in the Euro Area
 Philipp Hartmann European Central Bank Cross-border Financial Risk Sharing in the Euro Area Luxembourg 17 November 2016 European Investment Bank Annual Economics Conference on Financing Productivity Growth
Philipp Hartmann European Central Bank Cross-border Financial Risk Sharing in the Euro Area Luxembourg 17 November 2016 European Investment Bank Annual Economics Conference on Financing Productivity Growth
Overborrowing, Financial Crises and Macro-prudential Policy. Macro Financial Modelling Meeting, Chicago May 2-3, 2013
 Overborrowing, Financial Crises and Macro-prudential Policy Javier Bianchi University of Wisconsin & NBER Enrique G. Mendoza Universtiy of Pennsylvania & NBER Macro Financial Modelling Meeting, Chicago
Overborrowing, Financial Crises and Macro-prudential Policy Javier Bianchi University of Wisconsin & NBER Enrique G. Mendoza Universtiy of Pennsylvania & NBER Macro Financial Modelling Meeting, Chicago
Spillovers: The Role of Prudential Regulation and Monetary Policy in Small Open Economies
 Spillovers: The Role of Prudential Regulation and Monetary Policy in Small Open Economies Paul Castillo, César Carrera, Marco Ortiz & Hugo Vega Presented by: Marco Ortiz Closing Conference of the BIS CCA
Spillovers: The Role of Prudential Regulation and Monetary Policy in Small Open Economies Paul Castillo, César Carrera, Marco Ortiz & Hugo Vega Presented by: Marco Ortiz Closing Conference of the BIS CCA
Collateralized capital and news-driven cycles. Abstract
 Collateralized capital and news-driven cycles Keiichiro Kobayashi Research Institute of Economy, Trade, and Industry Kengo Nutahara Graduate School of Economics, University of Tokyo, and the JSPS Research
Collateralized capital and news-driven cycles Keiichiro Kobayashi Research Institute of Economy, Trade, and Industry Kengo Nutahara Graduate School of Economics, University of Tokyo, and the JSPS Research
Global Liquidity, House Prices, and the Macroeconomy: Evidence from Advanced and Emerging Economies
 Global Liquidity, House Prices, and the Macroeconomy: Evidence from Advanced and Emerging Economies By Ambrogio Cesa-Bianchi, Luis Felipe Cespedes, Alessandro Rebucci Bank of Canada and European Central
Global Liquidity, House Prices, and the Macroeconomy: Evidence from Advanced and Emerging Economies By Ambrogio Cesa-Bianchi, Luis Felipe Cespedes, Alessandro Rebucci Bank of Canada and European Central
Exorbitant Privilege and Exorbitant Duty P.O. Gourinchas, H. Rey, N. Govillot Comments
 Exorbitant Privilege and Exorbitant Duty P.O. Gourinchas, H. Rey, N. Govillot Comments Banco de España - Banco Mundial - CREI Financial Globalization: Shifting Balances Banco de España, Madrid July 1-2,
Exorbitant Privilege and Exorbitant Duty P.O. Gourinchas, H. Rey, N. Govillot Comments Banco de España - Banco Mundial - CREI Financial Globalization: Shifting Balances Banco de España, Madrid July 1-2,
What Happens During Recessions, Crunches and Busts?
 What Happens During Recessions, Crunches and Busts? Stijn Claessens, M. Ayhan Kose and Marco E. Terrones Financial Studies Division, Research Department International Monetary Fund Presentation at the
What Happens During Recessions, Crunches and Busts? Stijn Claessens, M. Ayhan Kose and Marco E. Terrones Financial Studies Division, Research Department International Monetary Fund Presentation at the
The instability of money demand
 Liverpool Economic Insights 2019/1 The instability of money demand Aleksander Berentsen, Samuel Huber and Alessandro Marchesiani University of Liverpool Management School Subject Group Economics 2 LEI
Liverpool Economic Insights 2019/1 The instability of money demand Aleksander Berentsen, Samuel Huber and Alessandro Marchesiani University of Liverpool Management School Subject Group Economics 2 LEI
Market Reforms in the Time of Imbalance: Online Appendix
 Market Reforms in the Time of Imbalance: Online Appendix Matteo Cacciatore HEC Montréal Romain Duval International Monetary Fund Giuseppe Fiori North Carolina State University Fabio Ghironi University
Market Reforms in the Time of Imbalance: Online Appendix Matteo Cacciatore HEC Montréal Romain Duval International Monetary Fund Giuseppe Fiori North Carolina State University Fabio Ghironi University
Financial Inclusion, Education & the Arab World
 Financial Inclusion, Education & the Arab World Nadine Chehade nchehade@worldbank.org October 2016 Framing the discussions Why is financial inclusion important? Where does / will the Arab world stand?
Financial Inclusion, Education & the Arab World Nadine Chehade nchehade@worldbank.org October 2016 Framing the discussions Why is financial inclusion important? Where does / will the Arab world stand?
A PVAR Approach to the Modeling of FDI and Spill Overs Effects in Africa
 International Journal of Business and Economics, 2014, Vol. 13, No. 2, 181-185 A PVAR Approach to the Modeling of FDI and Spill Overs Effects in Africa Sheereen Fauzel Boopen Seetanah R. V. Sannassee 1.
International Journal of Business and Economics, 2014, Vol. 13, No. 2, 181-185 A PVAR Approach to the Modeling of FDI and Spill Overs Effects in Africa Sheereen Fauzel Boopen Seetanah R. V. Sannassee 1.
Enrique Martínez-García. University of Texas at Austin and Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas
 Discussion: International Recessions, by Fabrizio Perri (University of Minnesota and FRB of Minneapolis) and Vincenzo Quadrini (University of Southern California) Enrique Martínez-García University of
Discussion: International Recessions, by Fabrizio Perri (University of Minnesota and FRB of Minneapolis) and Vincenzo Quadrini (University of Southern California) Enrique Martínez-García University of
Capital Flows and Spillovers
 CHAPTER 2 Capital Flows and Spillovers Şebnem Kalemli-Özcan Introduction Do gross capital flows import global shocks to emerging markets? If so, what are the output spillovers from such shocks to emerging
CHAPTER 2 Capital Flows and Spillovers Şebnem Kalemli-Özcan Introduction Do gross capital flows import global shocks to emerging markets? If so, what are the output spillovers from such shocks to emerging
Why doesn t Capital Flow from Rich to Poor Countries? An Empirical Investigation
 Why doesn t Capital Flow from Rich to Poor Countries? An Empirical Investigation Laura Alfaro Harvard Business School Sebnem Kalemli-Ozcan University of Houston December 2003 Vadym Volosovych University
Why doesn t Capital Flow from Rich to Poor Countries? An Empirical Investigation Laura Alfaro Harvard Business School Sebnem Kalemli-Ozcan University of Houston December 2003 Vadym Volosovych University
External Financing and the Role of Financial Frictions over the Business Cycle: Measurement and Theory. November 7, 2014
 External Financing and the Role of Financial Frictions over the Business Cycle: Measurement and Theory Ali Shourideh Wharton Ariel Zetlin-Jones CMU - Tepper November 7, 2014 Introduction Question: How
External Financing and the Role of Financial Frictions over the Business Cycle: Measurement and Theory Ali Shourideh Wharton Ariel Zetlin-Jones CMU - Tepper November 7, 2014 Introduction Question: How
Fiscal Policy and Macro-systemic Risks
 Fiscal Policy and Macro-systemic Risks Vitor Gaspar Director, Fiscal Affairs Department International Monetary Fund Integrated Macro-Financial Modeling for Robust Policy Design MACFINROBODS Paris, June
Fiscal Policy and Macro-systemic Risks Vitor Gaspar Director, Fiscal Affairs Department International Monetary Fund Integrated Macro-Financial Modeling for Robust Policy Design MACFINROBODS Paris, June
The Role of Financial Markets and Innovation in Productivity and Growth in Europe
 The Role of Financial Markets and Innovation in Productivity and Growth in Europe Philipp Hartmann, Florian Heider, Elias Papaioannou, Marco Lo Duca European Central Bank Disclaimer: This paper is based
The Role of Financial Markets and Innovation in Productivity and Growth in Europe Philipp Hartmann, Florian Heider, Elias Papaioannou, Marco Lo Duca European Central Bank Disclaimer: This paper is based
A Utility Function Explanation of the Empirical Behavior of Income Relative to International Reserves for Selected Economies
 Journal of Business & Economic Policy Vol. 5, No. 4, December 2018 doi:10.30845/jbep.v5n4p5 A Utility Function Explanation of the Empirical Behavior of Income Relative to International Reserves for Selected
Journal of Business & Economic Policy Vol. 5, No. 4, December 2018 doi:10.30845/jbep.v5n4p5 A Utility Function Explanation of the Empirical Behavior of Income Relative to International Reserves for Selected
Identifying the exchange-rate balance sheet effect over firms
 Identifying the exchange-rate balance sheet effect over firms CÉSAR CARRERA Banco Central de Reserva del Perú Abstract: This version: May 2014 I use firm-level data on investment and evaluate the balance
Identifying the exchange-rate balance sheet effect over firms CÉSAR CARRERA Banco Central de Reserva del Perú Abstract: This version: May 2014 I use firm-level data on investment and evaluate the balance
Collateralized capital and News-driven cycles
 RIETI Discussion Paper Series 07-E-062 Collateralized capital and News-driven cycles KOBAYASHI Keiichiro RIETI NUTAHARA Kengo the University of Tokyo / JSPS The Research Institute of Economy, Trade and
RIETI Discussion Paper Series 07-E-062 Collateralized capital and News-driven cycles KOBAYASHI Keiichiro RIETI NUTAHARA Kengo the University of Tokyo / JSPS The Research Institute of Economy, Trade and
Introduction The Story of Macroeconomics. September 2011
 Introduction The Story of Macroeconomics September 2011 Keynes General Theory (1936) regards volatile expectations as the main source of economic fluctuations. animal spirits (shifts in expectations) econ
Introduction The Story of Macroeconomics September 2011 Keynes General Theory (1936) regards volatile expectations as the main source of economic fluctuations. animal spirits (shifts in expectations) econ
