Insights. NAIC s ORSA. A Broader Approach to Regulation. NAIC S ORSA Part of a Global Shift to Regulatory Modernization
|
|
|
- Wilfred Lawrence
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Insights June 2011 NAIC s ORSA A Broader Approach to Regulation Broad regulatory changes are on the horizon for U.S. insurers. The National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC s) Solvency Modernization Initiative (SMI) has increased the regulatory focus on insurer risk and capital management. One proposed component of the SMI the Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) will require U.S. insurers to make a self-assessment of the capital available to support their business risks. ORSA will require insurer management teams to be much more deliberate and explicit in how they identify, measure and manage enterprise risks. The good news is that insurers have been investing in enterprise risk management (ERM) for several years. Insurers should expect that their ERM activities will provide a strong foundation for the development of ORSA procedures. That said, ORSA development will require management teams to invest additional time and money enhancing their enterprise risk, capital management and governance processes. NAIC S ORSA Part of a Global Shift to Regulatory Modernization The NAIC recently released a draft proposal for the creation of a U.S. ORSA process. The proposal requires insurers to complete an ORSA annually for each statutory entity, as well as at the insurance group level, and submit the results to state regulators. The results should demonstrate that each entity s capital both regulatory and economic is suffi cient to cover the risks inherent in the entity s business plan. Regulators will use this information to better understand the prospective risks to each insurer s plan and judge the adequacy of capital for the risks identifi ed. The ORSA proposal represents a broader and more prospective approach to U.S. insurance regulation. Historically, insurers managed to the highest and most demanding regulatory bar, which was typically set by rating agencies such as A.M. Best and Standard & Poor s (S&P), often viewed as de facto regulators. The NAIC s capital requirements were typically less than those of the rating agencies, using risk-based capital (RBC) formulas to assess insurer solvency. RBC has served the NAIC well for almost 20 years, but it is being eclipsed by more dynamic, forward-looking and comprehensive regulatory approaches. Solvency II, the regulatory regime that is being implemented in Europe, is the most prominent example of such an approach. It uses a three-pillared approach: quantitative capital (Pillar 1), governance and risk management (Pillar 2), and disclosure and transparency requirements (Pillar 3). As currently planned, all European Union-domiciled insurers will be subject to Solvency II requirements by January 2013 and will face an ORSA requirement under Pillar 2. Other jurisdictions, including Bermuda, Switzerland and Japan, are implementing similar changes to ensure regulatory equivalence with Solvency II. Further, the International Association of Insurance Supervisors (IAIS), consisting of insurance regulators from 190 jurisdictions around the world, has identifi ed a set of principle-based regulatory practices, which include enterprise risk and capital management and ORSA, as global best practices. The NAIC is moving in a similar direction. Its evolving SMI seeks to enhance the regulatory review of capital requirements, governance and risk management, group supervision, statutory accounting and fi nancial reporting, and reinsurance. As part of the SMI, the ORSA proposal outlines the NAIC s proposed approach to reviewing each insurer s governance and risk management framework. The good news is that insurers have been investing in enterprise risk management (ERM) for several years. Insurers should expect that their ERM activities will provide a strong foundation for the development of ORSA procedures.
2 Towers Watson believes that the SMI, including the adoption of ORSA, will accelerate over the coming years for several reasons. First, the NAIC recognizes that its existing tools are limited to assessing retrospective risks to insurer solvency. Work on SMI will address this limitation by examining global regulatory practices and identifying more powerful and prospective regulatory tools to strengthen the NAIC s toolbox. ORSA is one of these tools: It examines the risks associated with future business plans, rather than evaluating only risk associated with past performance (as RBC does). Clearly, ORSA will supplement the existing RBC review and provide regulators with a more dynamic view of each company s risk profi le. Regulators will be able to key in on each insurer s top risks and more effi ciently allocate resources to the most critical areas for regulatory review. Presumably, the SMI and the ORSA requirements will complement other forward-looking regulatory tools being implemented by the NAIC, including the newly implemented risk-focused exam and Form F enterprise risk reporting requirement of the Insurance Company System Regulatory Act. In addition to strengthening tools at home, the NAIC must ensure that the U.S. regulatory framework is deemed equivalent under Solvency II in Europe. Equivalence is important to the competitiveness of U.S. insurers doing business in the Europe Economic Area (EEA), particularly to ensure that capital add-ons or collateralization are not imposed as a result of being domiciled and regulated by a non-eea equivalent regulator. Switzerland and Bermuda are the fi rst two countries to be tested for full equivalency with Solvency II. Japan will be tested specifi cally for reinsurance equivalence. The U.S. was noticeably absent from this list. The NAIC s SMI and ORSA will aid in any future Solvency II equivalency reviews. Understanding ORSA The proposed ORSA requires an insurer to internally assess the suffi ciency of its capital to back the risks inherent in its business plan. It is a self graded exam, with the following key questions: What is our strategy? What level of risk are we willing to assume in pursuit of this strategy? What are the key risks that could hinder our ability to achieve our strategy? How much capital do we need to cover those key risks? What risks individually or collectively would subject us to losses that exceed our tolerance levels? What risk scenarios would cause us to fail or stop operating as a going concern? The proposed ORSA requires the insurer to demonstrate qualitatively and quantitatively its process for identifying, measuring, monitoring and managing all reasonably foreseeable and relevant material risks to the business strategy. A robust ORSA addresses current and prospective risks in fi ve key categories: underwriting, credit, market, operational and liquidity (Figure 1). It also identifi es and measures the risks associated with being a member of a larger insurance or non-insurance group. While at its core ORSA is a process, ensuring adequate documentation and reporting of ORSA is integral to its successful use by management and, from the NAIC s perspective, for regulatory supervision. The NAIC suggests that each insurer develop a formal risk policy as part of its ORSA. The policy would document the risk management approach and contain three distinct sections. Figure 1. How the ORSA fits within risk management Stress and scenario testing Link to business strategy Risk appetite Risk culture Monitoring and reporting Identify and assess risks Risk measurement 2 towerswatson.com
3 Section 1: Description of Risk Management Policy Under the proposal, Section 1 of ORSA details the amount of risk an insurer is willing to take to achieve its mission in the marketplace. It requires insurers to explicitly sketch out a three- to fi ve-year business plan and identify risks that could inhibit that plan. As part of this process, the NAIC proposal suggests that the insurer detail the following elements in Section 1: A list of all relevant and material risk categories Details on how risk categories are managed and monitored on a day-to-day basis Risk tolerance statements, including the link between risk tolerance and required economic and regulatory capital An investment policy that addresses credit, market, liquidity and counterparty risk An underwriting policy with a demonstrated link to product design and pricing Claim underwriting and processing policies showing how coverage terms are defi ned Anti-fraud policies in place to detect fraudulent claims Asset/liability management (ALM) activities with a demonstrated link to product development, pricing and investment management Any retention or conservation policies such as multiple-coverage discounts, extra interest credits or other policyholder options Description of any reinsurance counterparty credit risk measures Policies to identify, measure, manage and control risks associated with group membership Although many companies already have components of ORSA in place, we believe one of the major challenges will be joining these processes in a coherent manner. For example, companies typically establish risk identifi cation, measurement and reporting processes, but often these are not aligned. They will need to be part of ORSA development and refl ect use by multiple, geographically diverse stakeholders. It is therefore essential that the process is well understood and that communication between linked elements is clear, effi cient and timely. Finally, risk management policies and procedures will need to be clearly defi ned, documented, tested and updated on a regular basis. Section 2: Quantitative Measurement of Risk Exposure in Normal and Stressed Environments Section 2 of the proposed ORSA is designed to explain how the insurer quantifies the risks identified in Section 1 under normal and stressed scenarios. It suggests that the insurer document its measurement methodology for each key risk category, including credit, market, liquidity, cash-flow mismatch, underwriting, claims, expenses and operational risks associated with group membership. Additionally, the insurer should list each of the key assumptions that underlie these risk calculations. The NAIC states that quantitative risk measurement should incorporate a range of outcomes and use risk measurement techniques that are appropriate to the nature, scale and complexity of the risks. These statements are purposely open-ended and deliberately nonprescriptive. They allow the insurer to tailor its approach both scenarios considered and measurement methodologies used based on the unique risks in its business plan. So the ORSA approach will vary depending on the nature, complexity and scale of the risks inherent in the business. The NAIC has not provided explicit guidance on proportionality, the use of risk measuring tools that fit a firm s risk profile, or its expectations for different types or sizes of companies. Risk culture can be defined as the norms and traditions of behavior of individuals and of groups within an organization that determine the way in which they identify, understand, discuss and act on the risks the organization confronts and takes. towerswatson.com 3
4 That said, the NAIC s proposal does provide a generic matrix that shows how an insurer might list risk measurements for each key risk category. The matrix displays each risk category, shows the notional amount of exposure for each, and the expected payment amount required over a oneyear time horizon for both normal and stressed scenarios. In addition, the NAIC suggests that the insurer calculate a reverse stress test for each risk that will identify the level of stress that would cause the insurer to fail using its current level of economic capital. Towers Watson notes that a large portion of the U.S. insurance industry will benefit from investing time and money in quantitative risk modeling tools to meet the NAIC s suggested requirements. There is some debate over whether companies need to develop sophisticated measurement tools to satisfy the ORSA requirement. A proportional approach recommended in IAIS core principles suggests that the insurer employ methods that are appropriate for the fi rm s risk profi le. These methods may range from simple stress and scenario tests to economic capital modeling that vary in sophistication. In reality, the measurement methodology and projection capability is likely to be developed iteratively. The focus should be on building a measurement methodology consistent with the fi rm s culture and that is well understood by the insurer s management team. Towers Watson notes that a large portion of the U.S. insurance industry will benefi t from investing time and money in quantitative risk modeling tools to meet the NAIC s suggested requirements. A 2010 survey conducted by Towers Watson fi nds that only 49% of U.S. insurers have built and implemented economic capital models. While economic capital is not necessary for all risk calculations, we suggest that it is the most appropriate tool for measuring the risks inherent in an insurer s business plan and determining an appropriate level of capital to support such risks. Section 3: Prospective Solvency Assessment Section 3 of the proposed ORSA represents the integration of the fi rm s qualitative risk policies (Section 1) and quantitative measurement methodologies (Section 2). It should demonstrate how the policies and measurements, in combination, result in economic and regulatory capital that fully supports the risks inherent in a three-to-fi ve year business plan. Insurers with capital shortages measured by risk identifi ed must demonstrate how they will modify their three-to-fi ve year business plan to ensure adequate fi nancial capital. The link between business strategy and required capital is a key element of ORSA. For many companies, this link should build on existing capital management and budgeting processes. Typically, new business sales are examined under base, optimistic and pessimistic scenarios. As part of the business planning process, companies need to understand how these scenarios affect risk and associated capital requirements. For example, scenarios may help management decide if there is suffi cient capital to support organic growth under optimistic sales plans. Organizations contemplating major strategic acquisitions or divestments will need to look at the impact on their risk profi le and decide if the board s agreed appetite and tolerances are honored. Similarly, product pricing, design, risk transfer and ALM processes will need to be reviewed regularly to ensure consistency with risk appetite and capital constraints. Ultimately, the state regulator should be able to review all three sections of the insurer s risk policy and understand the link between risk policies, measurements, capital allocation and day-today operational decisions. This concept, known more commonly as the use test, has proved to be a challenge to demonstrate. In fact, a survey conducted by Towers Watson in 2010 found that only a small minority of European insurers feel that their internal risk models would meet the use test requirements under Solvency II. Numbers in the U.S. would likely be comparable or even lower given that the European industry has been working on these issues for a longer period. To foster use, an effective risk management policy must be technically sound and an effective communication tool. We feel there should be focus on developing a slim-line report for an organization s executive management team effectively a high- 4 towerswatson.com
5 level explanation of how risk is managed within the business. This report could follow a cascade structure and link to other significant documentation requirements that exist around public and supervisory reporting, internal models and internal requirements. The depth and breadth of ORSA documentation is likely to exceed most companies current output. Organizations of all sizes (especially groups) will be challenged because they have not typically been required to document risk identifi cation, measurement and management policies in such unifi ed and clear terms. ORSA Only a Starting Point The NAIC s ORSA proposal is the starting point for its approach to reviewing insurer governance and risk management practices. The proposal will be shaped over the next several years. It will incorporate industry feedback, new IAIS pronouncements, guidance from other regulatory jurisdictions (the European Insurance and Occupational Pensions Authority, the Bermuda Monetary Authority and the Offi ce of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions in Canada) and industry expertise offered by actuaries, accountants and risk managers. Towers Watson maintains that the NAIC s ORSA proposal needs to address several key elements before being fi nalized. These include: Confidentiality. How will the NAIC ensure that an insurer s highly proprietary strategy and risk management information remain safe and secure? Consistency. How will the NAIC guarantee that ORSA reviews are consistent across states (particularly for groups that maintain statutory entities in multiple states i.e., most of the industry)? Group versus statutory entity. How will the NAIC reconcile statutory and group-level ORSAs that are conducted in different states? Size threshold. Will ORSA apply uniformly across the industry? Or will there be tiered requirements based on company size and a phased rollout schedule? Group Solvency Issues (EX) Working Group (GSIWG) Timeline for ORSA Discussions June July August October November Extent to which current U.S. reporting requirements can meet any of the ORSA expectations ORSA proposal paragraphs 1 10 Introduction Solvency regime requirements Background Implementation authority Purpose ORSA proposal paragraphs U.S. ORSA requirements Section 1 Description of the Risk Management Policy ORSA proposal paragraphs Section 2 Quantitative Measurements of Risk Exposure in Normal and Stressed Environments ORSA proposal paragraphs Section 3 Prospective Solvency Assessment Other topics for discussion and follow-up on previous sections GSIWG National Meeting Review newly revised draft of ORSA proposal Revised Group Capital Assessment proposal GSIWG Public Hearing on ORSA Final edits before adoption SMI Task Force Receive and discuss proposal towerswatson.com 5
6 Role of board versus management. Will the NAIC change its ORSA wording to clarify that the board remains responsible for oversight, while management is responsible for ORSA execution? Regulatory input. What degree of input will state regulators have in company scenario testing and model calibration? Regulatory capital. Will ORSA be linked to a standard regulatory capital formula such as RBC? Will RBC change to refl ect more dynamic measurement approaches? Will the NAIC allow for the use of internal capital models in determining regulatory capital positions? A Road Map for Success Many companies will face considerable internal challenges for dedicated management time and buy-in to the new metrics and changes in processes that underlie ORSA. Success will depend on an early start and senior executives engagement in how ORSA can add value to business development. The sooner that the new approach filters into daily internal risk governance and risk reporting, the better the chance for a high level of engagement, a prerequisite for better embedding of risk management. We also recommend that insurers clearly defi ne roles and responsibilities for executing the ORSA action plan. Within the organization, ORSA will be a joint effort with some expected responsibilities from various stakeholders (Figure 2). Figure 2. Expected responsibilities from stakeholders Stakeholder Board/executive Risk management function Actuarial function/finance Strategy/treasury function External organizations/ internal audit Selected responsibilities Setting the overall business strategy and direction Setting risk appetite for the organization Engendering a positive risk culture, including incentive systems Appropriate governance, committee structure and escalation procedures such that risks are monitored and managed Agreeing to a business plan for the organization Engaging in stress tests, reverse stress tests and emerging risks Signing off various deliverables, including ORSA policy, ORSA report and other associated policies Producing the ORSA report slim-line document suitable for executives and board Translating risk appetite into more granular tolerance and risk limits Working with stakeholders to develop appropriate risk reporting templates Setting risk policies consistent with risk appetite Ensuring consistency among risk identification, measurement and reporting Managing scenario testing and reverse stress testing with input from other stakeholders Measuring and monitoring risk culture within the organization Documenting the process Working with stakeholders to develop appropriate risk reporting templates Developing tools to ensure appropriate risk measurement and monitoring including, where necessary, lite models such as replicating portfolios and curve fi tting Carrying out fi nancial projections to better understand the risk drivers during the business planning horizon Carrying out stress and scenario analysis Investigating risk/reward optimization Setting business and contingency plans Providing input on strategic direction Providing input on capital structure, including: Dividend plans Issuing/retiring of existing capital instruments Fungibility and transferability constraints Providing challenge, benchmarking and independent review Ensuring that there is an appropriate control framework in place for the process to be sufficiently robust Providing quality assurance 6 towerswatson.com
7 Companies should consider the following steps to successful ORSA compliance: Perform an ORSA gap analysis. Develop an ORSA policy. Develop the ORSA template as a slim-line document covering risk management for senior management. Refresh risk appetite within the organization. Translate risk appetite into more granular tolerances and limits for business use. Measure and benchmark the risk culture and degree of embedding within the organization. Ensure consistency among risk identifi cation, measurement and reporting exercises. Develop a pro forma risk dashboard for continuous solvency monitoring and management information. Develop internal stress and scenario tests (and reverse stress tests) at both the solo and group levels. Review mandates and delegation of authority for various risk committees within the organization. Link risk information into existing ALM, strategic decisions, pricing, product design and risk transfer strategy. Europe Preparing for ORSA As part of the pending Solvency II regulatory framework in Europe, European companies will also be required to perform an ORSA. While there are many similarities between the proposed ORSA for U.S. insurers developed by the NAIC and Solvency II s ORSA for European insurers, they are not identical. A copy of Towers Watson s Insights article on the ORSA requirements under Solvency II can be obtained from: towerswatson.com/united-kingdom/newsletters/solvency-ii/4254 A copy of the proposed NAIC ORSA may be obtained here: naic.org/documents/committees_ex_isftf_exposures_orsa.pdf Towers Watson will compare the two ORSAs in a subsequent article. Conduct board education and wider training regarding ORSA. Link existing documentation to support ORSA. Longer term, we expect ORSA will be a foundational element of the NAIC s Solvency Modernization Initiative. The signifi cant overlap between ORSA and ERM creates an opportunity for companies to embrace ORSA to gain business benefi ts from substantial investment in the new NAIC requirements. Companies need to be developing their ORSA approach now to ensure they realize these benefi ts. towerswatson.com 7
8 About the Authors Joseph Lebens is a director at Towers Watson who specializes in enterprise risk management issues and leads the company s economic capital initiative in North America for property & casualty insurers. For more information, please contact: joe.lebens@towerswatson.com Mark Scanlon is a senior consultant with Towers Watson who specializes in enterprise risk management issues and leads the company s economic capital initiative in North America for life insurers. For more information, please contact: mark.scanlon@towerswatson.com Anthony Shapella is a consultant with Towers Watson and specializes in strategic and competitive analysis, reinsurance market research, fi nancial statement analysis, and credit rating agency and enterprise risk management consulting. For more information, please contact: anthony.shapella@towerswatson.com About Towers Watson Towers Watson is a leading global professional services company that helps organizations improve performance through effective people, risk and financial management. With 14,000 associates around the world, we offer solutions in the areas of employee benefits, talent management, rewards, and risk and capital management. Copyright 2011 Towers Watson. All rights reserved. TW-NA towerswatson.com
INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF INSURANCE SUPERVISORS
 Guidance Paper No. 2.2.x INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF INSURANCE SUPERVISORS GUIDANCE PAPER ON ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT FOR CAPITAL ADEQUACY AND SOLVENCY PURPOSES DRAFT, MARCH 2008 This document was prepared
Guidance Paper No. 2.2.x INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF INSURANCE SUPERVISORS GUIDANCE PAPER ON ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT FOR CAPITAL ADEQUACY AND SOLVENCY PURPOSES DRAFT, MARCH 2008 This document was prepared
NAIC OWN RISK AND SOLVENCY ASSESSMENT (ORSA) GUIDANCE MANUAL
 NAIC OWN RISK AND SOLVENCY ASSESSMENT (ORSA) GUIDANCE MANUAL Created by the NAIC Group Solvency Issues Working Group Of the Solvency Modernization Initiatives (EX) Task Force 2011 National Association
NAIC OWN RISK AND SOLVENCY ASSESSMENT (ORSA) GUIDANCE MANUAL Created by the NAIC Group Solvency Issues Working Group Of the Solvency Modernization Initiatives (EX) Task Force 2011 National Association
GUIDELINE ON ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT
 GUIDELINE ON ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT Insurance Authority Table of Contents Page 1. Introduction 1 2. Application 2 3. Overview of Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Framework and 4 General Requirements
GUIDELINE ON ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT Insurance Authority Table of Contents Page 1. Introduction 1 2. Application 2 3. Overview of Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Framework and 4 General Requirements
INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF INSURANCE SUPERVISORS
 Guidance Paper No. 2.2.6 INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF INSURANCE SUPERVISORS GUIDANCE PAPER ON ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT FOR CAPITAL ADEQUACY AND SOLVENCY PURPOSES OCTOBER 2007 This document was prepared
Guidance Paper No. 2.2.6 INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF INSURANCE SUPERVISORS GUIDANCE PAPER ON ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT FOR CAPITAL ADEQUACY AND SOLVENCY PURPOSES OCTOBER 2007 This document was prepared
Solvency II Insights for North American Insurers. CAS Centennial Meeting Damon Paisley Bill VonSeggern November 10, 2014
 Solvency II Insights for North American Insurers CAS Centennial Meeting Damon Paisley Bill VonSeggern November 10, 2014 Agenda 1 Introduction to Solvency II 2 Pillar I 3 Pillar II and Governance 4 North
Solvency II Insights for North American Insurers CAS Centennial Meeting Damon Paisley Bill VonSeggern November 10, 2014 Agenda 1 Introduction to Solvency II 2 Pillar I 3 Pillar II and Governance 4 North
Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA)
 Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Presentations to OCCA (Nov. 19, 2014) and AAIARD (Nov. 21, 2014) Jacqueline Friedland, FCIA, FCAS, FSA, MAAA Chief Actuary, RSA Canada Presentation Outline What
Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Presentations to OCCA (Nov. 19, 2014) and AAIARD (Nov. 21, 2014) Jacqueline Friedland, FCIA, FCAS, FSA, MAAA Chief Actuary, RSA Canada Presentation Outline What
Actuaries Club of the Southwest
 www.pwc.com Actuaries Club of the Southwest 3-2-1-ORSA Drivers of Enterprise Risk Management ( ERM ) Fed 1. Rating Agencies AM Best SRQ ERM Questions & S&P ERM Level III Reviews FASB/IASB 2. IAIS ICP 16
www.pwc.com Actuaries Club of the Southwest 3-2-1-ORSA Drivers of Enterprise Risk Management ( ERM ) Fed 1. Rating Agencies AM Best SRQ ERM Questions & S&P ERM Level III Reviews FASB/IASB 2. IAIS ICP 16
Mondrian Investment Partners Limited Fifth Floor, 10 Gresham Street, London EC2V 7JD Authorised and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority
 Mondrian Investment Partners Limited Fifth Floor, 10 Gresham Street, London EC2V 7JD Authorised and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority M O N D R I A N I N V E S T M E N T P A R T N E R S L I
Mondrian Investment Partners Limited Fifth Floor, 10 Gresham Street, London EC2V 7JD Authorised and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority M O N D R I A N I N V E S T M E N T P A R T N E R S L I
ERM Implementation and the Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA)
 ERM Implementation and the Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Kevin Olberding June 2013 1 Agenda ERM IMPLEMENTATION AND THE OWN RISK AND SOLVENCY ASSESSMENT (ORSA) Evolution of Enterprise Risk Management
ERM Implementation and the Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Kevin Olberding June 2013 1 Agenda ERM IMPLEMENTATION AND THE OWN RISK AND SOLVENCY ASSESSMENT (ORSA) Evolution of Enterprise Risk Management
Own Risk Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Linking Risk Management, Capital Management and Strategic Planning
 Own Risk Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Linking Risk Management, Capital Management and Strategic Planning Moderator: David Holland, Risk Director, Ally Insurance SPEAKERS Mary-ellen Coggins, Managing Director,
Own Risk Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Linking Risk Management, Capital Management and Strategic Planning Moderator: David Holland, Risk Director, Ally Insurance SPEAKERS Mary-ellen Coggins, Managing Director,
Keeping Pace With Solvency II
 Keeping Pace With Solvency II Challenges and Opportunities Facing Insurers By Gerard L Aimable, Colin Murray and Naren Persad Scheduled for 2013, Solvency II will introduce a risk-based regulatory framework
Keeping Pace With Solvency II Challenges and Opportunities Facing Insurers By Gerard L Aimable, Colin Murray and Naren Persad Scheduled for 2013, Solvency II will introduce a risk-based regulatory framework
Property & Casualty Insurance CFO Survey. The Current Market. Property Significantly harder. Somewhat harder. About the same.
 Insights March 2 Property & Casualty Insurance CFO Survey Trends in Reinsurance and Alternative Forms of Capital As the market for insurance-linked securities and other alternative forms of capital has
Insights March 2 Property & Casualty Insurance CFO Survey Trends in Reinsurance and Alternative Forms of Capital As the market for insurance-linked securities and other alternative forms of capital has
ERM and the new world of insurance regulation. Where insurers should focus now to find business value
 ERM and the new world of insurance regulation Where insurers should focus now to find business value Enterprise risk management is a common denominator Reform efforts have much in common, including enhanced
ERM and the new world of insurance regulation Where insurers should focus now to find business value Enterprise risk management is a common denominator Reform efforts have much in common, including enhanced
INSURANCE CORE PRINCIPLES, STANDARDS, GUIDANCE AND ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY
 INSURANCE CORE PRINCIPLES, STANDARDS, GUIDANCE AND ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY Revised ICP 8 and the additional ComFrame material in ICP 8 for public consultation (redline version) This public consultation
INSURANCE CORE PRINCIPLES, STANDARDS, GUIDANCE AND ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY Revised ICP 8 and the additional ComFrame material in ICP 8 for public consultation (redline version) This public consultation
Solvency II Detailed guidance notes for dry run process. March 2010
 Solvency II Detailed guidance notes for dry run process March 2010 Introduction The successful implementation of Solvency II at Lloyd s is critical to maintain the competitive position and capital advantages
Solvency II Detailed guidance notes for dry run process March 2010 Introduction The successful implementation of Solvency II at Lloyd s is critical to maintain the competitive position and capital advantages
ORSA An International Development
 ORSA An International Development 25.02.14 Agenda What is an ORSA? Global reach Comparison of requirements Common challenges Potential solutions Origin of ORSA FSA ICAS Solvency II IAIS ICP16 What is an
ORSA An International Development 25.02.14 Agenda What is an ORSA? Global reach Comparison of requirements Common challenges Potential solutions Origin of ORSA FSA ICAS Solvency II IAIS ICP16 What is an
NAIC OWN RISK AND SOLVENCY ASSESSMENT (ORSA) GUIDANCE MANUAL
 NAIC OWN RISK AND SOLVENCY ASSESSMENT (ORSA) GUIDANCE MANUAL As of December 2017 The NAIC is the authoritative source for insurance industry information. Our expert solutions support the efforts of regulators,
NAIC OWN RISK AND SOLVENCY ASSESSMENT (ORSA) GUIDANCE MANUAL As of December 2017 The NAIC is the authoritative source for insurance industry information. Our expert solutions support the efforts of regulators,
Southeastern Actuaries Conference 2012 Annual Meeting. Jeffrey S. Schlinsog, CFA, FSA, MAAA
 www.pwc.com November 15, 2012 ERM Topics Southeastern Actuaries Conference 2012 Annual Meeting Jeffrey S. Schlinsog, CFA, FSA, MAAA ERM Topics 1. The development and implementation of the ORSA 2. The contents
www.pwc.com November 15, 2012 ERM Topics Southeastern Actuaries Conference 2012 Annual Meeting Jeffrey S. Schlinsog, CFA, FSA, MAAA ERM Topics 1. The development and implementation of the ORSA 2. The contents
ORSA An international requirement
 Prepared by: Padraic O'Malley, Principal, Dublin Eamonn Phelan, Principal, Dublin December 2013 ORSA An international requirement Title Author a [Footer - regular] Month YYYY Title Author b [Footer - regular]
Prepared by: Padraic O'Malley, Principal, Dublin Eamonn Phelan, Principal, Dublin December 2013 ORSA An international requirement Title Author a [Footer - regular] Month YYYY Title Author b [Footer - regular]
Pillar 2 for Insurer s:
 Pillar 2 for Insurer s: Greater requirements, enhanced value? September 2018 Order of events Presenters: 1. Pillar 2 in context 2. Redefining the standard for Enterprise Risk Management Michael van Vuuren
Pillar 2 for Insurer s: Greater requirements, enhanced value? September 2018 Order of events Presenters: 1. Pillar 2 in context 2. Redefining the standard for Enterprise Risk Management Michael van Vuuren
ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT, INTERNAL MODELS AND OPERATIONAL RISK FOR LIFE INSURERS DISCUSSION PAPER DP14-09
 ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT, INTERNAL MODELS AND FOR LIFE INSURERS DISCUSSION PAPER DP14-09 This paper is issued by the Insurance and Pensions Authority ( the IPA ), the regulatory authority responsible
ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT, INTERNAL MODELS AND FOR LIFE INSURERS DISCUSSION PAPER DP14-09 This paper is issued by the Insurance and Pensions Authority ( the IPA ), the regulatory authority responsible
Solvency Assessment and Management: Pillar 2 - Sub Committee ORSA and Use Test Task Group Discussion Document 35 (v 3) Use Test
 Solvency Assessment and Management: Pillar 2 - Sub Committee ORSA and Use Test Task Group Discussion Document 35 (v 3) Use Test EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 1. INTRODUCTION AND PURPOSE The purpose of this document
Solvency Assessment and Management: Pillar 2 - Sub Committee ORSA and Use Test Task Group Discussion Document 35 (v 3) Use Test EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 1. INTRODUCTION AND PURPOSE The purpose of this document
BERMUDA INSURANCE (GROUP SUPERVISION) RULES 2011 BR 76 / 2011
 QUO FA T A F U E R N T BERMUDA INSURANCE (GROUP SUPERVISION) RULES 2011 BR 76 / 2011 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Citation and commencement PART 1 GROUP RESPONSIBILITIES
QUO FA T A F U E R N T BERMUDA INSURANCE (GROUP SUPERVISION) RULES 2011 BR 76 / 2011 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Citation and commencement PART 1 GROUP RESPONSIBILITIES
ORSA reports: gaps and opportunities
 ORSA reports: gaps and opportunities Market benchmarking of ORSA reports for Singapore general insurers Industry-wide Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) 1 2 Contents 1 Executive summary 2 Our assessment
ORSA reports: gaps and opportunities Market benchmarking of ORSA reports for Singapore general insurers Industry-wide Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) 1 2 Contents 1 Executive summary 2 Our assessment
Solvency Assessment and Management: Steering Committee Position Paper 34 1 (v 5) Own Risk and Solvency Assessment
 Solvency Assessment and Management: Steering Committee Position Paper 34 1 (v 5) Own Risk and Solvency Assessment EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 1. INTRODUCTION AND PURPOSE The purpose of this document is to present
Solvency Assessment and Management: Steering Committee Position Paper 34 1 (v 5) Own Risk and Solvency Assessment EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 1. INTRODUCTION AND PURPOSE The purpose of this document is to present
Guideline. Own Risk and Solvency Assessment. Category: Sound Business and Financial Practices. No: E-19 Date: November 2015
 Guideline Subject: Category: Sound Business and Financial Practices No: E-19 Date: November 2015 This guideline sets out OSFI s expectations with respect to the Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA)
Guideline Subject: Category: Sound Business and Financial Practices No: E-19 Date: November 2015 This guideline sets out OSFI s expectations with respect to the Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA)
Enterprise Risk Management
 Enterprise Risk Management Southeastern Actuaries Conference Rebecca Scotchie June 2011 ERM is 2 1 Agenda What is ERM? Why is risk management important? ERM maturity model/evolution of ERM ERM Framework
Enterprise Risk Management Southeastern Actuaries Conference Rebecca Scotchie June 2011 ERM is 2 1 Agenda What is ERM? Why is risk management important? ERM maturity model/evolution of ERM ERM Framework
OIC & ORSA. Thanita Anusonadisai Director of Capital and Solvency Standard Department Office of Insurance Commission, Thailand
 OIC & ORSA Thanita Anusonadisai Director of Capital and Solvency Standard Department Office of Insurance Commission, Thailand Agenda http://www.oic.or.th Changes in insurance regulatory approach Update
OIC & ORSA Thanita Anusonadisai Director of Capital and Solvency Standard Department Office of Insurance Commission, Thailand Agenda http://www.oic.or.th Changes in insurance regulatory approach Update
A.M. Best s New Risk Management Standards
 A.M. Best s New Risk Management Standards Stephanie Guethlein McElroy, A.M. Best Manager, Rating Criteria and Rating Relations Hubert Mueller, Towers Perrin, Principal March 24, 2008 Introduction A.M.
A.M. Best s New Risk Management Standards Stephanie Guethlein McElroy, A.M. Best Manager, Rating Criteria and Rating Relations Hubert Mueller, Towers Perrin, Principal March 24, 2008 Introduction A.M.
Regulation and risk The strategic response to insurance regulatory developments Alex Thomson, May 2013
 Regulation and risk The strategic response to insurance regulatory developments Alex Thomson, May 2013!@# Agenda 1. Strategic priorities and regulation 2. Global insurance regulatory developments 3. East
Regulation and risk The strategic response to insurance regulatory developments Alex Thomson, May 2013!@# Agenda 1. Strategic priorities and regulation 2. Global insurance regulatory developments 3. East
A. General comments. October 27, 2012
 AEGON N.V./Transamerica comments on Comparing Certain Aspects of the Insurance Supervisory and Regulatory Regimes in the European Union and the United States October 27, 2012 AEGON appreciates the opportunity
AEGON N.V./Transamerica comments on Comparing Certain Aspects of the Insurance Supervisory and Regulatory Regimes in the European Union and the United States October 27, 2012 AEGON appreciates the opportunity
INTERNAL CAPITAL ADEQUACY ASSESSMENT PROCESS GUIDELINE. Nepal Rastra Bank Bank Supervision Department. August 2012 (updated July 2013)
 INTERNAL CAPITAL ADEQUACY ASSESSMENT PROCESS GUIDELINE Nepal Rastra Bank Bank Supervision Department August 2012 (updated July 2013) Table of Contents Page No. 1. Introduction 1 2. Internal Capital Adequacy
INTERNAL CAPITAL ADEQUACY ASSESSMENT PROCESS GUIDELINE Nepal Rastra Bank Bank Supervision Department August 2012 (updated July 2013) Table of Contents Page No. 1. Introduction 1 2. Internal Capital Adequacy
Re: Consultation Paper on Commercial Insurer s Solvency Self Assessment ( CISSA CP )
 December 8, 2010 Dear Insurers, Re: Consultation Paper on Commercial Insurer s Solvency Self Assessment ( CISSA CP ) The Bermuda Monetary Authority ( the Authority ) wishes to thank the stakeholders for
December 8, 2010 Dear Insurers, Re: Consultation Paper on Commercial Insurer s Solvency Self Assessment ( CISSA CP ) The Bermuda Monetary Authority ( the Authority ) wishes to thank the stakeholders for
Draft Guideline. Corporate Governance. Category: Sound Business and Financial Practices. I. Purpose and Scope of the Guideline. Date: November 2017
 Draft Guideline Subject: Category: Sound Business and Financial Practices Date: November 2017 I. Purpose and Scope of the Guideline This guideline communicates OSFI s expectations with respect to corporate
Draft Guideline Subject: Category: Sound Business and Financial Practices Date: November 2017 I. Purpose and Scope of the Guideline This guideline communicates OSFI s expectations with respect to corporate
Solvency II implications for Asian life insurers
 Solvency II implications for Asian life insurers 1 2 Solvency II implications for Asian life insurers Solvency II implications for Asian life insurers 1. Introduction Solvency II is the new insurance supervision
Solvency II implications for Asian life insurers 1 2 Solvency II implications for Asian life insurers Solvency II implications for Asian life insurers 1. Introduction Solvency II is the new insurance supervision
IAIS: Enterprise Risk Management for Capital Adequacy & Solvency Purposes. George Brady. IAIS Deputy Secretary General
 IAIS: Enterprise Risk Management for Capital Adequacy & Solvency Purposes George Brady IAIS Deputy Secretary General Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2. Governance and an Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)
IAIS: Enterprise Risk Management for Capital Adequacy & Solvency Purposes George Brady IAIS Deputy Secretary General Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2. Governance and an Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)
SOLVENCY AND FINANCIAL CONDITION REPORT EUROLIFE LTD
 SOLVENCY AND FINANCIAL CONDITION REPORT EUROLIFE LTD FOR THE YEAR ENDING 31 DECEMBER 2016 1 Table of Contents 1.Executive Summary... 5 1.1 Overview... 5 1.2 Business and performance... 5 1.3 System of
SOLVENCY AND FINANCIAL CONDITION REPORT EUROLIFE LTD FOR THE YEAR ENDING 31 DECEMBER 2016 1 Table of Contents 1.Executive Summary... 5 1.1 Overview... 5 1.2 Business and performance... 5 1.3 System of
Solvency II Update. Latest developments and industry challenges (Session 10) Réjean Besner
 Solvency II Update Latest developments and industry challenges (Session 10) Canadian Institute of Actuaries - Annual Meeting, 29 June 2011 Réjean Besner Content Solvency II framework Solvency II equivalence
Solvency II Update Latest developments and industry challenges (Session 10) Canadian Institute of Actuaries - Annual Meeting, 29 June 2011 Réjean Besner Content Solvency II framework Solvency II equivalence
GUIDANCE NOTE ASSET MANAGEMENT BY AUTHORIZED INSURERS
 GN13 GUIDANCE NOTE ON ASSET MANAGEMENT BY AUTHORIZED INSURERS Office of the Commissioner of Insurance June 2004 GN13 Guidance Note on Asset Management By Authorized Insurers Table of Contents Page Preamble...
GN13 GUIDANCE NOTE ON ASSET MANAGEMENT BY AUTHORIZED INSURERS Office of the Commissioner of Insurance June 2004 GN13 Guidance Note on Asset Management By Authorized Insurers Table of Contents Page Preamble...
The ORSA opportunity:
 The ORSA opportunity: Compliance and business value 12 March 2014 Today s agenda Background and regulatory update ORSA overview Industry perspectives Achieving long-term business value Page 2 Today s agenda
The ORSA opportunity: Compliance and business value 12 March 2014 Today s agenda Background and regulatory update ORSA overview Industry perspectives Achieving long-term business value Page 2 Today s agenda
ERM/ORSA Training Thai General Insurance Association (TGIA)
 ERM/ORSA Training Thai General Insurance Association (TGIA) 10 October 2017 Agenda Time Topics 8.30-9.00 Registration ORSA for Non-life Insurance Top 10 global business risk in 2017 Weakness and past failures
ERM/ORSA Training Thai General Insurance Association (TGIA) 10 October 2017 Agenda Time Topics 8.30-9.00 Registration ORSA for Non-life Insurance Top 10 global business risk in 2017 Weakness and past failures
Actuaries and the Regulatory Environment. Role of the Actuary in the Solvency II framework
 Actuaries and the Regulatory Environment Role of the Actuary in the Solvency II framework IAA Fund Southeast Europe Actuarial Seminar, Zagreb, 3 October 2011 1 Solvency II primary objectives fundamental
Actuaries and the Regulatory Environment Role of the Actuary in the Solvency II framework IAA Fund Southeast Europe Actuarial Seminar, Zagreb, 3 October 2011 1 Solvency II primary objectives fundamental
International Regulatory Developments
 International Regulatory Developments An Introduction to Solvency II Simone Brathwaite, FSA, FCIA, CERA Principal Oliver Wyman December 2, 2010 Many bodies driving global regulatory change A simplification
International Regulatory Developments An Introduction to Solvency II Simone Brathwaite, FSA, FCIA, CERA Principal Oliver Wyman December 2, 2010 Many bodies driving global regulatory change A simplification
Risk Appetite for Life Offices IFoA working party
 Risk Appetite for Life Offices IFoA working party Gautam Kakar, Chairman 30 October 2015 Members of Working Party: Gautam Kakar Lana Nguyen Shayanthan Pathmanathan Rod Bryn-Hussey Fabio Schiaffini Crystal
Risk Appetite for Life Offices IFoA working party Gautam Kakar, Chairman 30 October 2015 Members of Working Party: Gautam Kakar Lana Nguyen Shayanthan Pathmanathan Rod Bryn-Hussey Fabio Schiaffini Crystal
INSURANCE REGULATION OMNIBUS CONSULTATION A CONSULTATION PAPER ON REVISION OF THE RULES AND GUIDANCE FOR LICENSED INSURERS
 INSURANCE REGULATION OMNIBUS CONSULTATION A CONSULTATION PAPER ON REVISION OF THE RULES AND GUIDANCE FOR LICENSED INSURERS Issued 17 April 2018 This Consultation Paper makes proposals in respect of the
INSURANCE REGULATION OMNIBUS CONSULTATION A CONSULTATION PAPER ON REVISION OF THE RULES AND GUIDANCE FOR LICENSED INSURERS Issued 17 April 2018 This Consultation Paper makes proposals in respect of the
Statement of Investment Principles
 Statement of Investment Principles July 2009 Contents Introduction 1 Governance of the Pension Protection Fund 2 Strategic management of the Fund s assets 3 Risk measurement and management 4 Investment
Statement of Investment Principles July 2009 Contents Introduction 1 Governance of the Pension Protection Fund 2 Strategic management of the Fund s assets 3 Risk measurement and management 4 Investment
2014 Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Feedback Pilot Project Observations of the Group Solvency Issues (E) Working Group
 2014 Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Feedback Pilot Project Observations of the Group Solvency Issues (E) Working Group During October 2014 through June 2015, a third ORSA Feedback Pilot Project
2014 Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Feedback Pilot Project Observations of the Group Solvency Issues (E) Working Group During October 2014 through June 2015, a third ORSA Feedback Pilot Project
Risk Appetite Survey Current state of the Insurance Industry
 Risk Appetite Survey Current state of the Insurance Industry Deloitte Belgium and The Netherlands Financial Services Industry The survey was conducted during July 2013 till December 2013 Introduction The
Risk Appetite Survey Current state of the Insurance Industry Deloitte Belgium and The Netherlands Financial Services Industry The survey was conducted during July 2013 till December 2013 Introduction The
Applying a holistic approach to RIC tax administration
 Applying a holistic approach to RIC tax administration Integrating people, processes and technology to administer compliance in a complex and evolving investment environment As investment companies incorporate
Applying a holistic approach to RIC tax administration Integrating people, processes and technology to administer compliance in a complex and evolving investment environment As investment companies incorporate
SOLVENCY AND FINANCIAL CONDITION REPORT EUROLIFE LTD
 SOLVENCY AND FINANCIAL CONDITION REPORT EUROLIFE LTD FOR THE YEAR ENDING 31 DECEMBER 2017 1 Table of Contents 1. Executive Summary... 5 1.1 Overview... 5 1.2 Business and performance... 5 1.3 System of
SOLVENCY AND FINANCIAL CONDITION REPORT EUROLIFE LTD FOR THE YEAR ENDING 31 DECEMBER 2017 1 Table of Contents 1. Executive Summary... 5 1.1 Overview... 5 1.2 Business and performance... 5 1.3 System of
Measuring Policyholder Behavior in Variable Annuity Contracts
 Insights September 2010 Measuring Policyholder Behavior in Variable Annuity Contracts Is Predictive Modeling the Answer? by David J. Weinsier and Guillaume Briere-Giroux Life insurers that write variable
Insights September 2010 Measuring Policyholder Behavior in Variable Annuity Contracts Is Predictive Modeling the Answer? by David J. Weinsier and Guillaume Briere-Giroux Life insurers that write variable
The Solvency II project and the work of CEIOPS
 Thomas Steffen CEIOPS Chairman Budapest, 16 May 07 The Solvency II project and the work of CEIOPS Outline Reasons for a change in the insurance EU regulatory framework The Solvency II project Drivers Process
Thomas Steffen CEIOPS Chairman Budapest, 16 May 07 The Solvency II project and the work of CEIOPS Outline Reasons for a change in the insurance EU regulatory framework The Solvency II project Drivers Process
MAS consults on Enterprise Risk Management ( ERM )
 www.pwc.com/sg MAS consults on Enterprise Risk Management ( ERM ) for insurers Following the MAS consultation paper on RBC 2 in August 2012, the expected consultation paper on ERM has now been published
www.pwc.com/sg MAS consults on Enterprise Risk Management ( ERM ) for insurers Following the MAS consultation paper on RBC 2 in August 2012, the expected consultation paper on ERM has now been published
ORSA is a central part of Solvency II and
 13th Global Conference of Actuaries 2011 Emerging Risks Daring Solutions From quantification to management: Solvencyy II Own Risk and Solvencyy Assessment James Creedon Director, Towers Watson Hong Kong
13th Global Conference of Actuaries 2011 Emerging Risks Daring Solutions From quantification to management: Solvencyy II Own Risk and Solvencyy Assessment James Creedon Director, Towers Watson Hong Kong
Critical Reflection of Two State-of-the-Art Risk Management Frameworks (SRM004)
 Critical Reflection of Two State-of-the-Art Risk Management Frameworks (SRM004) Speakers: Dr. Kathrin Anne Meier, Chief Risk Officer, Allianz Global Corporate & Specialty John Adams, VP Global ERM, PepsiCo
Critical Reflection of Two State-of-the-Art Risk Management Frameworks (SRM004) Speakers: Dr. Kathrin Anne Meier, Chief Risk Officer, Allianz Global Corporate & Specialty John Adams, VP Global ERM, PepsiCo
American Academy of Actuaries Webinar: The Practice of ERM in the Insurance Industry. Enterprise Risk Management Committee November 19, 2013
 American Academy of Actuaries Webinar: The Practice of ERM in the Insurance Industry Enterprise Risk Management Committee November 19, 2013 All Rights Reserved. 1 Presenters Bruce Jones, MAAA, FCAS, CERA
American Academy of Actuaries Webinar: The Practice of ERM in the Insurance Industry Enterprise Risk Management Committee November 19, 2013 All Rights Reserved. 1 Presenters Bruce Jones, MAAA, FCAS, CERA
Solvency II: Implementation Challenges & Experiences Learned
 Solvency II: Implementation Challenges & Experiences Learned Appointed Actuary Symposium Actuarial Society of Hong Kong (ASHK) Jonathan Zhao - Actuarial Services Practice Leader, Asia Pacific 3 November
Solvency II: Implementation Challenges & Experiences Learned Appointed Actuary Symposium Actuarial Society of Hong Kong (ASHK) Jonathan Zhao - Actuarial Services Practice Leader, Asia Pacific 3 November
Exploring the New Era of ORSA Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)/ Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Committee
 Exploring the New Era of ORSA Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)/ Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Committee Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. Presenters Tricia
Exploring the New Era of ORSA Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)/ Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Committee Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. Presenters Tricia
Corporate Governance of Federally-Regulated Financial Institutions
 Draft Guideline Subject: -Regulated Financial Institutions Category: Sound Business and Financial Practices Date: I. Purpose and Scope of the Guideline The purpose of this guideline is to set OSFI s expectations
Draft Guideline Subject: -Regulated Financial Institutions Category: Sound Business and Financial Practices Date: I. Purpose and Scope of the Guideline The purpose of this guideline is to set OSFI s expectations
SMI. Capital Requirements. Governance & Risk Management. Group Supervision. Statutory Accounting & Financial Reporting.
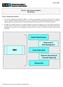 Solvency Modernization Initiative ROADMAP Solvency Modernization Initiative 1. The Solvency Modernization Initiative (SMI) is a critical self-examination to update the United States insurance solvency
Solvency Modernization Initiative ROADMAP Solvency Modernization Initiative 1. The Solvency Modernization Initiative (SMI) is a critical self-examination to update the United States insurance solvency
Developments & Insights in Singapore RBC 2 and Overview of ORSA across Regions
 Developments & Insights in Singapore RBC 2 and Overview of ORSA across Regions 1 Agenda RBC 2 Developments in Singapore Comparison of ORSA Across Jurisdictions RBC2 Developments in Singapore In 2004, the
Developments & Insights in Singapore RBC 2 and Overview of ORSA across Regions 1 Agenda RBC 2 Developments in Singapore Comparison of ORSA Across Jurisdictions RBC2 Developments in Singapore In 2004, the
INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF INSURANCE SUPERVISORS
 INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF INSURANCE SUPERVISORS ISSUES PAPER ON GROUP-WIDE SOLVENCY ASSESSMENT AND SUPERVISION 5 MARCH 2009 This document was prepared jointly by the Solvency and Actuarial Issues Subcommittee
INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF INSURANCE SUPERVISORS ISSUES PAPER ON GROUP-WIDE SOLVENCY ASSESSMENT AND SUPERVISION 5 MARCH 2009 This document was prepared jointly by the Solvency and Actuarial Issues Subcommittee
Solvency Assessment and Management: Stress Testing Task Group Discussion Document 96 (v 3) General Stress Testing Guidance for Insurance Companies
 Solvency Assessment and Management: Stress Testing Task Group Discussion Document 96 (v 3) General Stress Testing Guidance for Insurance Companies 1 INTRODUCTION AND PURPOSE The business of insurance is
Solvency Assessment and Management: Stress Testing Task Group Discussion Document 96 (v 3) General Stress Testing Guidance for Insurance Companies 1 INTRODUCTION AND PURPOSE The business of insurance is
EIOPA Proposal for Guidelines on the preparation for Solvency II. October Milliman Solvency II Update
 EIOPA Proposal for Guidelines on the preparation for Solvency II October 2013 EIOPA s final guidelines for the preparation of Solvency II look set to require firms and supervisors to put in place elements
EIOPA Proposal for Guidelines on the preparation for Solvency II October 2013 EIOPA s final guidelines for the preparation of Solvency II look set to require firms and supervisors to put in place elements
Gregg Clifton. CFO Aurigen Reinsurance
 Gregg Clifton CFO Aurigen Reinsurance Regulatory Capital When it comes to regulatory capital, is there a discernable clicking sound of a ratchet? More onerous Canadian capital requirements and the inherent
Gregg Clifton CFO Aurigen Reinsurance Regulatory Capital When it comes to regulatory capital, is there a discernable clicking sound of a ratchet? More onerous Canadian capital requirements and the inherent
Guidance on the Actuarial Function MARCH 2018
 Guidance on the Actuarial Function MARCH 2018 Disclaimer No responsibility or liability is accepted by the Society of Lloyd s, the Council, or any Committee of Board constituted by the Society of Lloyd
Guidance on the Actuarial Function MARCH 2018 Disclaimer No responsibility or liability is accepted by the Society of Lloyd s, the Council, or any Committee of Board constituted by the Society of Lloyd
CONSULTATION PAPER ON A RISK- BASED CAPITAL FRAMEWORK FOR THE INSURANCE INDUSTRY IN HONG KONG
 CONSULTATION PAPER ON A RISK- BASED CAPITAL FRAMEWORK FOR THE INSURANCE INDUSTRY IN HONG KONG On 16 September 2014, the Office of the Commissioner of Insurance ("OCI") announced the publication by the
CONSULTATION PAPER ON A RISK- BASED CAPITAL FRAMEWORK FOR THE INSURANCE INDUSTRY IN HONG KONG On 16 September 2014, the Office of the Commissioner of Insurance ("OCI") announced the publication by the
From: Director Christina Urias, Chair of the Solvency Modernization Initiative (EX) Task Force
 June 7, 2010 To: Lou Felice, Chair of the Capital Adequacy (E) Task Force From: Director Christina Urias, Chair of the Solvency Modernization Initiative (EX) Task Force Subject: SMI's RBC Proposals Dear
June 7, 2010 To: Lou Felice, Chair of the Capital Adequacy (E) Task Force From: Director Christina Urias, Chair of the Solvency Modernization Initiative (EX) Task Force Subject: SMI's RBC Proposals Dear
Guidance paper on the use of internal models for risk and capital management purposes by insurers
 Guidance paper on the use of internal models for risk and capital management purposes by insurers October 1, 2008 Stuart Wason Chair, IAA Solvency Sub-Committee Agenda Introduction Global need for guidance
Guidance paper on the use of internal models for risk and capital management purposes by insurers October 1, 2008 Stuart Wason Chair, IAA Solvency Sub-Committee Agenda Introduction Global need for guidance
ECONOMIC CAPITAL MODELING CARe Seminar JUNE 2016
 ECONOMIC CAPITAL MODELING CARe Seminar JUNE 2016 Boston Catherine Eska The Hanover Insurance Group Paul Silberbush Guy Carpenter & Co. Ronald Wilkins - PartnerRe Economic Capital Modeling Safe Harbor Notice
ECONOMIC CAPITAL MODELING CARe Seminar JUNE 2016 Boston Catherine Eska The Hanover Insurance Group Paul Silberbush Guy Carpenter & Co. Ronald Wilkins - PartnerRe Economic Capital Modeling Safe Harbor Notice
Guidance on the Actuarial Function April 2016
 Guidance on the Actuarial Function April 2016 Disclaimer No responsibility or liability is accepted by the Society of Lloyd s, the Council, or any Committee of Board constituted by the Society of Lloyd
Guidance on the Actuarial Function April 2016 Disclaimer No responsibility or liability is accepted by the Society of Lloyd s, the Council, or any Committee of Board constituted by the Society of Lloyd
Frequently Asked Questions for The global risk-based Insurance Capital Standard (ICS) Updated 21 July 2017
 Updated 21 July 2017 Frequently Asked Questions for The global risk-based Insurance Capital Standard (ICS) Updated 21 July 2017 Questions 1. What is the risk-based global insurance capital standard (ICS)?...
Updated 21 July 2017 Frequently Asked Questions for The global risk-based Insurance Capital Standard (ICS) Updated 21 July 2017 Questions 1. What is the risk-based global insurance capital standard (ICS)?...
I want to build up my wealth for a promising future
 life protection & savings I want to build up my wealth for a promising future wealth advance savings plan Table of Contents What are your dreams and life goals? 1 Realise your dreams with Wealth Advance
life protection & savings I want to build up my wealth for a promising future wealth advance savings plan Table of Contents What are your dreams and life goals? 1 Realise your dreams with Wealth Advance
1. INTRODUCTION AND PURPOSE
 Solvency Assessment and Management: Pillar I - Sub Committee Capital Requirements Task Group Discussion Document 61 (v 1) SCR standard formula: Operational Risk EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 1. INTRODUCTION AND PURPOSE
Solvency Assessment and Management: Pillar I - Sub Committee Capital Requirements Task Group Discussion Document 61 (v 1) SCR standard formula: Operational Risk EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 1. INTRODUCTION AND PURPOSE
REQUEST TO EIOPA FOR TECHNICAL ADVICE ON THE REVIEW OF THE SOLVENCY II DIRECTIVE (DIRECTIVE 2009/138/EC)
 Ref. Ares(2019)782244-11/02/2019 REQUEST TO EIOPA FOR TECHNICAL ADVICE ON THE REVIEW OF THE SOLVENCY II DIRECTIVE (DIRECTIVE 2009/138/EC) With this mandate to EIOPA, the Commission seeks EIOPA's Technical
Ref. Ares(2019)782244-11/02/2019 REQUEST TO EIOPA FOR TECHNICAL ADVICE ON THE REVIEW OF THE SOLVENCY II DIRECTIVE (DIRECTIVE 2009/138/EC) With this mandate to EIOPA, the Commission seeks EIOPA's Technical
Academy Presentation to NAIC ORSA Implementation (E) Subgroup
 Academy Presentation to NAIC ORSA Implementation (E) Subgroup Tricia Matson, MAAA, FSA Chairperson, Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) and Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Committee August 10, 2016
Academy Presentation to NAIC ORSA Implementation (E) Subgroup Tricia Matson, MAAA, FSA Chairperson, Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) and Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Committee August 10, 2016
BERGRIVIER MUNICIPALITY. Risk Management Risk Appetite Framework
 BERGRIVIER MUNICIPALITY Risk Management Risk Appetite Framework APRIL 2018 1 Document review and approval Revision history Version Author Date reviewed 1 2 3 4 5 This document has been reviewed by Version
BERGRIVIER MUNICIPALITY Risk Management Risk Appetite Framework APRIL 2018 1 Document review and approval Revision history Version Author Date reviewed 1 2 3 4 5 This document has been reviewed by Version
Guidance Note System of Governance - Insurance Transition to Governance Requirements established under the Solvency II Directive
 Guidance Note Transition to Governance Requirements established under the Solvency II Directive Issued : 31 December 2013 Table of Contents 1.Introduction... 4 2. Detailed Guidelines... 4 General governance
Guidance Note Transition to Governance Requirements established under the Solvency II Directive Issued : 31 December 2013 Table of Contents 1.Introduction... 4 2. Detailed Guidelines... 4 General governance
Consultation paper on CEBS s Guidelines on Liquidity Cost Benefit Allocation
 10 March 2010 Consultation paper on CEBS s Guidelines on Liquidity Cost Benefit Allocation (CP 36) Table of contents 1. Introduction 2 2. Main objectives.. 3 3. Contents.. 3 4. The guidelines. 5 Annex
10 March 2010 Consultation paper on CEBS s Guidelines on Liquidity Cost Benefit Allocation (CP 36) Table of contents 1. Introduction 2 2. Main objectives.. 3 3. Contents.. 3 4. The guidelines. 5 Annex
International Insurance Regulation 101: International Association of Insurance Supervisors
 The Academy Capitol Forum: Meet the Experts International Insurance Regulation 101: International Association of Insurance Supervisors George Brady, Deputy Secretary General, IAIS Moderator: Jeffrey S.
The Academy Capitol Forum: Meet the Experts International Insurance Regulation 101: International Association of Insurance Supervisors George Brady, Deputy Secretary General, IAIS Moderator: Jeffrey S.
Increased Corporate Governance Requirements for Insurers
 Increased Corporate Governance Requirements for Insurers 0 INCREASED CORPORATE GOVERNANCE REQUIREMENTS FOR INSURERS Introduction On 17 December 2009, the definitive text of the Solvency II Directive (2009/138/EC)
Increased Corporate Governance Requirements for Insurers 0 INCREASED CORPORATE GOVERNANCE REQUIREMENTS FOR INSURERS Introduction On 17 December 2009, the definitive text of the Solvency II Directive (2009/138/EC)
Consultation Paper on the draft proposal for Guidelines on reporting and public disclosure
 EIOPA-CP-14/047 27 November 2014 Consultation Paper on the draft proposal for Guidelines on reporting and public disclosure EIOPA Westhafen Tower, Westhafenplatz 1-60327 Frankfurt Germany - Tel. + 49 69-951119-20;
EIOPA-CP-14/047 27 November 2014 Consultation Paper on the draft proposal for Guidelines on reporting and public disclosure EIOPA Westhafen Tower, Westhafenplatz 1-60327 Frankfurt Germany - Tel. + 49 69-951119-20;
ERM and ORSA Assuring a Necessary Level of Risk Control
 ERM and ORSA Assuring a Necessary Level of Risk Control Dave Ingram, MAAA, FSA, CERA, FRM, PRM Chair of IAA Enterprise & Financial Risk Committee Executive Vice President, Willis Re September, 2012 1 DISCLAIMER
ERM and ORSA Assuring a Necessary Level of Risk Control Dave Ingram, MAAA, FSA, CERA, FRM, PRM Chair of IAA Enterprise & Financial Risk Committee Executive Vice President, Willis Re September, 2012 1 DISCLAIMER
EIOPA's Supervisory Statement. Solvency II: Solvency and Financial Condition Report
 EIOPA-BoS/17-310 18 December 2017 EIOPA's Supervisory Statement Solvency II: Solvency and Financial Condition Report EIOPA Westhafen Tower, Westhafenplatz 1-60327 Frankfurt Germany - Tel. + 49 69-951119-20;
EIOPA-BoS/17-310 18 December 2017 EIOPA's Supervisory Statement Solvency II: Solvency and Financial Condition Report EIOPA Westhafen Tower, Westhafenplatz 1-60327 Frankfurt Germany - Tel. + 49 69-951119-20;
ERM and Reserve Risk
 ERM and Reserve Risk Alietia Caughron, PhD CNA Insurance Casualty Actuarial Society s 2014 Centennial Celebration and Annual Meeting New York City, NY November 11, 2014 Disclaimer The purpose of this presentation
ERM and Reserve Risk Alietia Caughron, PhD CNA Insurance Casualty Actuarial Society s 2014 Centennial Celebration and Annual Meeting New York City, NY November 11, 2014 Disclaimer The purpose of this presentation
Stress Tests From stressful times to business as usual an updated point of view
 Stress Tests From stressful times to business as usual an updated point of view Informational presentation for our clients May 2009 1 Point of view From stressful times to business as usual Stress test
Stress Tests From stressful times to business as usual an updated point of view Informational presentation for our clients May 2009 1 Point of view From stressful times to business as usual Stress test
FIL Life Insurance (Ireland) DAC. Solvency and Financial Condition Report as at 30 June 2016
 FIL Life Insurance (Ireland) DAC Solvency and Financial Condition Report as at 30 June 2016 1 Contents INTRODUCTION... 5 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 6 A.1 Business... 8 A.2 Underwriting Performance... 9 A.3 Investment
FIL Life Insurance (Ireland) DAC Solvency and Financial Condition Report as at 30 June 2016 1 Contents INTRODUCTION... 5 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 6 A.1 Business... 8 A.2 Underwriting Performance... 9 A.3 Investment
EIOPA-CP-13/ March Cover note for the Consultation on Guidelines on preparing for Solvency II
 EIOPA-CP-13/015 27 March 2013 Cover note for the Consultation on Guidelines on preparing for Solvency II EIOPA Westhafen Tower, Westhafenplatz 1-60327 Frankfurt Germany - Tel. + 49 69-951119-20; Fax. +
EIOPA-CP-13/015 27 March 2013 Cover note for the Consultation on Guidelines on preparing for Solvency II EIOPA Westhafen Tower, Westhafenplatz 1-60327 Frankfurt Germany - Tel. + 49 69-951119-20; Fax. +
Final Report. Guidelines on the management of interest rate risk arising from non-trading book activities EBA/GL/2018/02.
 EBA/GL/2018/02 19 July 2018 Final Report Guidelines on the management of interest rate risk arising from non-trading book activities Contents 1. Executive summary 3 2. Background and rationale 5 3. Guidelines
EBA/GL/2018/02 19 July 2018 Final Report Guidelines on the management of interest rate risk arising from non-trading book activities Contents 1. Executive summary 3 2. Background and rationale 5 3. Guidelines
Session 5: Evolution of ORSA in the US. Moderator: Michael Anthony McComis Jr. MAAA,FCAS
 Session 5: Evolution of ORSA in the US Moderator: Michael Anthony McComis Jr. MAAA,FCAS Presenters: S Douglas Caldwell FSA,MAAA,CERA Chad R Runchey FSA,MAAA Elisabetta Russo MAAA SOA Antitrust Disclaimer
Session 5: Evolution of ORSA in the US Moderator: Michael Anthony McComis Jr. MAAA,FCAS Presenters: S Douglas Caldwell FSA,MAAA,CERA Chad R Runchey FSA,MAAA Elisabetta Russo MAAA SOA Antitrust Disclaimer
Forsikringsselskabet Privatsikring A/S. Solvency and Financial Condition Report
 Forsikringsselskabet Privatsikring A/S Solvency and Financial Condition Report 2017 Introduction... 3 Summary... 4 A. Business and Performance... 6 A.1 Business... 6 A.2 Underwriting Performance... 9 A.3
Forsikringsselskabet Privatsikring A/S Solvency and Financial Condition Report 2017 Introduction... 3 Summary... 4 A. Business and Performance... 6 A.1 Business... 6 A.2 Underwriting Performance... 9 A.3
Prudential Standard GOI 3 Risk Management and Internal Controls for Insurers
 Prudential Standard GOI 3 Risk Management and Internal Controls for Insurers Objectives and Key Requirements of this Prudential Standard Effective risk management is fundamental to the prudent management
Prudential Standard GOI 3 Risk Management and Internal Controls for Insurers Objectives and Key Requirements of this Prudential Standard Effective risk management is fundamental to the prudent management
WHITE PAPER. Solvency II Compliance and beyond: Title The essential steps for insurance firms
 WHITE PAPER Solvency II Compliance and beyond: Title The essential steps for insurance firms ii Contents Introduction... 1 Step 1 Data Management... 1 Step 2 Risk Calculations... 3 Solvency Capital Requirement
WHITE PAPER Solvency II Compliance and beyond: Title The essential steps for insurance firms ii Contents Introduction... 1 Step 1 Data Management... 1 Step 2 Risk Calculations... 3 Solvency Capital Requirement
Defining the Internal Model for Risk & Capital Management under the Solvency II Directive
 14 Defining the Internal Model for Risk & Capital Management under the Solvency II Directive Mark Dougherty is an international Senior Corporate Governance and Risk Management professional and Chartered
14 Defining the Internal Model for Risk & Capital Management under the Solvency II Directive Mark Dougherty is an international Senior Corporate Governance and Risk Management professional and Chartered
BERMUDA MONETARY AUTHORITY
 BERMUDA MONETARY AUTHORITY CONSULTATION PAPER ON COMMERCIAL INSURER S SOLVENCY SELF ASSESSMENT JUNE 2010 TABLE OF CONTENTS 0. INTRODUCTION 2 1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 3 2. BACKGROUND 6 3. INTERNATIONAL DEVELOPMENTS
BERMUDA MONETARY AUTHORITY CONSULTATION PAPER ON COMMERCIAL INSURER S SOLVENCY SELF ASSESSMENT JUNE 2010 TABLE OF CONTENTS 0. INTRODUCTION 2 1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 3 2. BACKGROUND 6 3. INTERNATIONAL DEVELOPMENTS
The Society of Actuaries in Ireland. Actuarial Standard of Practice INS-1, Actuarial Function Report
 The Society of Actuaries in Ireland Actuarial Standard of Practice INS-1, Actuarial Function Report Classification Mandatory MEMBERS ARE REMINDED THAT THEY MUST ALWAYS COMPLY WITH THE CODE OF PROFESSIONAL
The Society of Actuaries in Ireland Actuarial Standard of Practice INS-1, Actuarial Function Report Classification Mandatory MEMBERS ARE REMINDED THAT THEY MUST ALWAYS COMPLY WITH THE CODE OF PROFESSIONAL
Cover Note Authorisation and supervision of branches of thirdcountry insurance undertakings by the Central Bank of Ireland
 Cover Note Authorisation and supervision of branches of thirdcountry insurance undertakings by the Central Bank of Ireland Consultation Paper 115 November 2017 [Type here] Consultation on the Authorisation
Cover Note Authorisation and supervision of branches of thirdcountry insurance undertakings by the Central Bank of Ireland Consultation Paper 115 November 2017 [Type here] Consultation on the Authorisation
Overview of Results of ERM 1 Assessment based on ORSA 2 Reports and ERM Hearings
 Overview of Results of ERM 1 Assessment based on ORSA 2 Reports and ERM Hearings 1. Background Based on the equation below, assuming that the amount of capital is constant, insurance companies can improve
Overview of Results of ERM 1 Assessment based on ORSA 2 Reports and ERM Hearings 1. Background Based on the equation below, assuming that the amount of capital is constant, insurance companies can improve
PILLAR III DISCLOSURES
 PILLAR III DISCLOSURES 2014 PILLAR III Disclosures - 2014 Page 1 of 21 TABLE OF CONTENT 1 SCOPE OF APPLICATION... 4 1.1 PILLAR I MINIMUM CAPITAL REQUIREMENTS... 4 1.2 PILLAR II INTERNAL CAPITAL ADEQUACY
PILLAR III DISCLOSURES 2014 PILLAR III Disclosures - 2014 Page 1 of 21 TABLE OF CONTENT 1 SCOPE OF APPLICATION... 4 1.1 PILLAR I MINIMUM CAPITAL REQUIREMENTS... 4 1.2 PILLAR II INTERNAL CAPITAL ADEQUACY
Insurance Summit Mr Raymond Tam Executive Director (Policy and Development) Insurance Authority 21 September 2017
 Insurance Summit 2017 Mr Raymond Tam Executive Director (Policy and Development) Insurance Authority 21 September 2017 Priority of Policy Initiatives Development of risk-based capital regime Facilitation
Insurance Summit 2017 Mr Raymond Tam Executive Director (Policy and Development) Insurance Authority 21 September 2017 Priority of Policy Initiatives Development of risk-based capital regime Facilitation
