Exploring the New Era of ORSA Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)/ Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Committee
|
|
|
- Mitchell Rice
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Exploring the New Era of ORSA Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)/ Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Committee Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved.
2 Presenters Tricia Matson, MAAA, FSA Chairperson, ERM/ORSA Committee Chairperson, Actuarial Standards Board Bill Wilkins, MAAA, FCAS Member, ERM/ORSA Committee Mike Celichowski, MAAA, FSA Member, ERM/ORSA Committee Special acknowledgements to Matt Covalle and Seong-Min Eom who helped develop this presentation. Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 2
3 Agenda Definition of ERM and ORSA Evolution Two primary goals Evolution of ORSA Iterative nature of ERM Risk culture and governance Risk governance structures ERM policies and procedures The Basics of ERM Risk identification and evaluation Models and tools (including economic capital) Monitoring and mitigating risks Trends for the future Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 3
4 Agenda ERM Standard/ Regulations US ORSA - summary report Process implementation Solvency II Regulatory comparisons on ORSA Relevant ASOPs Q and A Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 4
5 ERM: Two Primary Goals Identify, assess, and quantify risks And their correlations and dependencies from all sources within an organization Ensure implementation of risk treatment strategies That leverage risk knowledge to achieve appropriate risk and return tradeoffs in line with organization s values and goals ORSA is essentially an ERM process (i.e., the insurer s own assessment of risk and solvency) Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 5
6 ORSA Evolution Part of early Solvency II guidance, included as part of Pillar 2 Risk Governance Designed as an evaluation of an organization s own view of its capital position, as compared to the regulatory capital requirements ( Pillar 1 ) Further defined with the advent of Insurance Core Principle 16 (ICP 16), which created a global standard for insurer reporting on ERM Solvency II equivalence and ICP 16 both were drivers of the Solvency Modernization Initiative (SMI) work on U.S. ORSA requirements ORSA is now a common element of most international capital and risk structures in some form Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 6
7 Overall Timeline of ORSA SII* level 2 ORSA guidance approved; SII delayed to 2014 Global Milestones ICP 16 adopted SII level 3 ORSA guidance approved FLAOR** guidance released Regional Pilots FLAOR in force Full SII ORSA in force?? US Milestones Consultation paper released ORSA guidance manual adopted Pilot 1 Pilot 2 Pilot 3 ORSA proposal released Model Act adopted U.S. ORSA in force * Solvency II **Forward looking assessment of own risks Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 7
8 Global Standard: ICP 16 The ORSA should: Include all reasonably foreseeable and relevant material risks Be proportionate to the nature, scale, and complexity of the business Include insurer's own assessment of quality and adequacy of capital resources in determining economic capital and in demonstrating that regulatory capital requirements are met Be undertaken on a regular basis as well as after significant changes in risk profile Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 8
9 Global Standard: ICP 16 As part of the ORSA, the insurer should: Undertake periodic, forward-looking continuity analyses Be able to demonstrate the ability to manage risks over the longer term under a range of plausible adverse scenarios Apply reverse stress testing to identify scenarios that would be likely to cause business failure Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 9
10 Global Standard: ICP 16 ICP (Page 29): While an insurer may itself decide to hold additional capital or reduce its risks as a direct result of its continuity analysis as well as taking other management actions, the analysis should not of itself be used as a basis for increasing current regulatory capital requirements/solvency control levels. The responsibility for the ORSA lies with the board and senior management Effectiveness of the ORSA should be assured through an independent review Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 10
11 Iterative Nature of ERM Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 11
12 Role of the Actuary in ERM & ORSA Actuaries have long been recognized for their important and unique professional role in contributing to insurer solvency While current guidance on ORSA does not prescribe a specific actuarial role, actuaries will likely be involved in ORSA because of their: Education-Competency in specialized aspects of insurance, investments, and accounting Experience-Variety of practice areas and scenario planning Standards of actuarial professionalism-protect both the public interest and the integrity of professional work Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 12
13 Risk culture encompasses: Risk Culture Risk-based decisions Broad risk management competency everyone is responsible Questioning, challenging, and engaged management Clearly defined risk roles and responsibilities Engaged CRO and/or ERM team Risk management leaders undertaking coordinated efforts Common risk language Proper calibration to the complexity and sophistication of the underlying business Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 13
14 Governance and Policies/Procedures Effective risk governance should consider: Well-defined risk appetite, tolerances, and limits Escalation procedures if limits are approached or breached Portfolio assessment of assets and liabilities Effective assessment of results and feedback Management communication of risk metrics and responses Risk mitigation supported by cost benefit analysis Business continuity for extreme events Efficient and effective use of capital in reinsurance and capital markets Performance measurements based on risk adjusted returns Effective controls without impeding the ability to operate Risk event planning (e.g., cybersecurity breach and operational risks) Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 14
15 Risk Governance Structures Business and Product Resources Required at All Levels Risks Functions Committees Board of Directors & Executive / Management Committee Operating Committee Regulatory Review Investment Risk Corporate Leadership Rating Agency Review Investment Committee Analytics Operational Risk Underwriting Human Resources Committee Asset Liability Management Insurance Risk Risk Committee Pricing Reserving/ Experience Studies Strategic Risk Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 15
16 Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. ERM Basics
17 To Manage Risk, You Must First Identify It Define the concept of risks for an organization and establish the risk assessment environment Do not determine solely by recent experience or external (rating agency or regulator) considerations How various risks interrelate under range of different conditions (economic, financial, marketplace) is key Identify risk categories to be used and associated subrisks in order to manage risks at granular level Actuarial resources are well suited to play a role in risk identification process Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 17
18 Characteristics of Effective Risk Comprehensive Inclusive Efficient Consistent Focused Identification Process Risk assessments are done on both a regularly scheduled basis as well as whenever material changes to organization occur Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 18
19 Common Risk Categories Efficiency, ease of communication, and development of a consistent risk language are established through the use of standard risk categories. These generally include: Investment Risk Insurance Risk Operational Risk Strategic Risk Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 19
20 Holistic and Flexible Approach Required For ERM to be effective: Risks cannot be examined solely on standalone bases Impacts of activities on the full portfolio of the organization must be reviewed Risk metrics and methodologies must be well defined Both internal and external drivers of risk must be recognized, as well as changes to the organization s risk profile The view of risk needs to evolve over time as the organizational ability to absorb and manage risks change Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 20
21 Establishing a Risk Appetite Tolerance Enterprise Strategy Tolerance 1 Tolerance 2 Tolerance 4 Limit Risk Appetite Early Warning Tolerance % 10% 12% 3 etc 4 Current Exposure Risk appetite is the amount of specific risk and aggregate risk that an organization chooses to take during a defined time period in pursuit of its objectives Risk tolerance is the aggregate risk-taking capacity of an organization Risk limit is a threshold used to monitor the actual risk exposure of a specific risk or activity unit of the organization to ensure that the level of actual risk remains within the risk tolerance Source: American Academy of Actuaries Insurance Enterprise Risk Management Practices Practice Note July Source: Risk & Regulatory Consulting, LLC, May 2014 Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 21
22 Risk Appetite Example Strategy Setting and Business Planning Strategic objective: stay financially strong and provide value to shareholders 3-year financial plan for 8% growth target Risk Appetite and Tolerance Definition Financial strength component of risk appetite defined based on RBC ratio Risk tolerance is a minimum 300% RBC ratio Scenario Definition and Limit Setting Limit: maintain RBC ratio of at least 300% (325% early warning signal) 3 stress scenarios defined Analyze, Communicate, and Manage Scenario RBC Ratio Year 1 RBC Ratio Year 3 Baseline 400% 400% Severe recession 345% 315% Reputational Event 385% 395% Sharp rise in rates 345% 360% Based on breach of early warning, mitigation plans involve curtailing growth in capital intensive business Source: Risk & Regulatory Consulting, LLC, May 2014 Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 22
23 Emerging Risk Process Beyond a regular process to identify and manage ongoing risks, organizations must uncover and assess potential emerging risks in real time Requires a strong internal communication network and self-reflection Environmental scans also required for changes to external environment Industry conferences, journals, committee service Periodic interface with industry experts Review of general demographic and sociographic trends Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 23
24 Next Step Requires Proper Tools Once risks have been identified, you need tools to evaluate the potential impact to the organization Can be done on both qualitative and quantitative basis Quantitative methods used include: Stress tests and reverse stress tests Stochastic models Reference to standard measures Qualitative reviews vary by organization and risk Emerging risks need to be monitored, managed, or mitigated Actuarial models and resources can play a crucial role in the aggregation of risk measures for use in calibration against the various metrics Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 24
25 Risk Quantification ERM should provide specific criteria for assessing the likelihood, severity, and velocity of risks Sample Likelihood Scale In addition, the time Somewhat Highly period of the Unlikely Likely Likely Likely assessment should be defined (i.e., % 15-30% 30%-50% >50% year, 2 years, etc.) Sample Severity Scale Impact on: Immaterial Moderate Threatening Severe Capital <250M M 500M-1B >1B Earnings <10% drop 10-20% drop Liquidity <20% outflow increase Source: Risk & Regulatory Consulting, LLC, May % outflow increase Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved % drop >40% drop 40-60% outflow increase >60% outflow increase
26 Risk Assessment Results Heatmaps are often used to show prioritization by frequency, severity, and speed of onset (velocity) Heatmap Scenario Assessment Examples Source: Risk & Regulatory Consulting, LLC, May 2014 Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 26
27 Stress and Scenario Testing Examples of actuarial scenarios currently being evaluated as part of ORSA include: Business Scenario Definition Use of Results P&C P&C Cat Risk: Hurricane Reserve increases vs. cat losses Specific level of hurricane occurs in multiple cities in the same time period (e.g., 1 year) 1 in 3 insolvencies arise from reserve issues Assess impact on capital, liquidity, and ratings to determine whether still within defined risk tolerance (and if not, determine necessary immediate mitigating actions) Understand level of exposure over time to influence strategic decisions on business mix, growth plans, and potential mitigation strategies Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 27
28 Stress and Scenario Testing Examples of actuarial scenarios currently being evaluated as part of ORSA include: Business Scenario Definition Use of Results Health Health Life Regulatory Change Risk: ACA Regulatory Change Risk: ACA Market Risk: Low Interest Rates Anti-selection under new ACA requirements increases morbidity/claims by 10% 30% increase and decrease in membership driven by ACA requirements Interest rates drop 50% and stay at that level for 10 years before a gradual recovery Assess impact on capital, liquidity, and ratings to determine whether still within defined risk tolerance (and if not, determine necessary immediate mitigating actions) Understand level of exposure over time to influence strategic decisions on business mix, growth plans, and potential mitigation strategies Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 28
29 Reverse Stress Testing Identify the scenario that causes a breach in limit Typically stresses a single variable at a time (i.e., equity levels, interest rates, hurricane, climate change, etc.) Demonstrate how protected the business is in a crisis Helpful to calibrate the resulting level of stress if feasible Examples: RBC ratio falls below the risk tolerance with a drop in equities that is 20% worse than 2008 financial crisis GAAP earnings loss falls below the risk tolerance with a hurricane that is 1.5 times the magnitude of Sandy in the Northeast corridor Reputational damage falls below the risk tolerance with a customer data breach equal to Target, Home Depot, etc. Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 29
30 Fit for Purpose Risk Models Reproducible and adaptable to new risks Proper trade-off between precision and simplicity Complexity proportionate to materiality Understanding of data input limitations Dependencies and interactions among risks properly captured Independently validated for integrity, particularly when subjective assumptions required Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 30
31 Control Strategies for Risk Models Data reconciliation Peer reviews Reasonability checks Affirmations Supporting documentation Independent validation Controls over IT environment and systems used Model risk management as emerging actuarial discipline Back-testing as a validator Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 31
32 Economic Capital Models One of primary tools used in assessing risk to an organization is an economic capital (EC) model EC is a measure of the capital an organization requires to survive or meet a business objective over a given timeframe at a selected confidence level Aligns with, and helps flesh out, the risk profile of the organization Scope, complexity, and use of such models varies widely A strong model provides key metrics for capital and risk decisions across the organization Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 32
33 Uses of EC Models Assessing capital adequacy Determining appropriate risk treatment strategies Analyzing financial performance Pricing Developing business strategies Determining relative risk and reward Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 33
34 Internal Models A variety of internal models may be used for components of ERM Key considerations include: Link to strategy and risk appetite Data source Reconciliations Use of results in strategic decision making Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 34
35 Internal Models Strategic Objectives, Risk Appetite, Risk Tolerance Data Sources Asset data Policy data Market data Data load Approach & Assumptions Data Capture and Staging Data storage Transformation Stress Testing Risk Modeling ERM-Owned Models Risk Appetite Economic Capital Model Governance Framework Risk Monitoring & Management Risk reporting Risk mitigation Strategic decisions Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 35
36 Internal Models In light of the complexity of these models, a critical component of ERM processes is the existence of an appropriate model governance framework Actuaries are increasingly focused in the areas of model governance and model validation Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 36
37 Model Validation Core Principle* Build for intended purpose Model validation is independent Establish model validation owner Appropriate model governance Consider proportionality Validate model components Address validation limitations Document the validation Considerations While the idea of a single model is nice in theory, it often fails in practice Many ERM models are designed for full enterprise use, and therefore may be less granular than other company models A separate functional area charged with validation Creates accountability Should have authority to communicate and remediate Defined policies that cover roles, responsibilities, and minimum requirements Critical for validation to provide sufficient benefits for the cost Data, methods, assumptions, calculations, and outputs Including plans to address in the future Can be used to improve and focus future validations *8 core principles identified in the North American CRO Council s paper Model Validation Principles Applied to Risk and Capital Models in the Insurance Industry Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 37
38 Modeling ASOP Comprehensive standard that applies to the design, selection, build, modification, development, use, review, and evaluation of models Model: A representation of relationships among variables using statistical, financial, economic, mathematical, or scientific concepts and equations Extent of requirements dependent on the extent of reliance upon and financial effect of the model General requirements include understanding/assessment of fit for purpose, appropriateness of model inputs, model validation, governance and controls, documentation, and reliance Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 38
39 Key Risk Metrics Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 39
40 Risk Mitigation Insurance/reinsurance Hedging Capital market products Awareness campaigns, educational programs, and loss control measures Change in governance or process controls Change in business mix or target markets De-risk products or reduce risk exposure Actuarial skills are essential to set and implement risk transfer programs and should be utilized in the process Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 40
41 Trends and Improvements Improved linkage to overall strategies and decision making Increased cascading of risk to individual business units Increased use of multiple risk lenses and metrics Increased consistency across insurance industry Separation of duties into three lines of defense Improved infrastructure and documentation Increased regulatory scrutiny Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 41
42 ERM Standards and Regulations Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved.
43 ORSA Summary Report Section 1 Description of the Insurer s Risk Management Framework Risk culture and governance Risk identification and prioritization Risk appetite, tolerance, and limits Risk management and controls Risk reporting and communication Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 43
44 ORSA Summary Report Section 2 Insurer s Assessment of Risk Exposure Primary risk assessment in normal and stressed environments Risks exposures measured in quantitative and qualitative method Descriptions and explanations of the identified risks, assessment method, key assumptions, risk-mitigation activities, and stress scenario outcomes Impact of risks on balance sheet, financial statements, and cash flows Stress impact on risk capital, available capital, and required capital Model validation and model calibration factors for risk assessments Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 44
45 ORSA Summary Report Section 3 Group Risk Capital and Prospective Solvency Assessment Definition of solvency and accounting or valuation regime Business included and aggregation and diversification Time horizon Risks modeled and quantification method Risk capital metric Defined security standard Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 45
46 Roles and Responsibilities In ORSA Process Implementation Actuarial Risk Management Underwriting Finance Develop actuarial models and methodologies, maintain and update assumptions Perform risk assessment calculations and longterm projections Provide quantitative and qualitative assessments of impacts of actions on risks Assist with the development of the ERM framework, risk appetite, risk tolerance, and risk limits Analyze the risk profile of the insurer, and cooperate with all the other areas to oversee the risk management processes and controls Have ownership in underwriting risk management and provide underwriting risk input into ORSA process and report Assess future underwriting decisions Produce external financial reports Incorporate projections of the future capital management information within the business plan Coordinate with other areas to consolidate financial data Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 46
47 Roles and Responsibilities In ORSA Process Implementation Internal Audit Information Technology Compliance Investment Provide an independent oversight of the ORSA process Enhance systems to efficiently produce accurate information Assist in the development and file of the ORSA Summary Report Provide a mechanism to identify changing regulations and evolve ORSA guidance Manage ORSA compliance risks Provide investment data and projections Manage ALM under both normal and stress conditions Develop risk mitigation strategies Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 47
48 What are companies doing now in response to the NAIC ORSA? Review the effectiveness of the current corporate ERM program, including risk governance Identify gaps between the current company practice and the ORSA requirements Analyze the materiality of the identified risks, prioritize key risks, and evaluate aggregate risk across the group Develop and enhance aggregate group level capital model and stress/scenario testing framework Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 48
49 Company Response to NAIC ORSA Develop process to perform forward looking assessments of risk and solvency over the planning horizon Integrate ERM into the group strategic planning process Develop a mock ORSA Summary Report Industry have provided feedback on the pilots: elated_docs_pilot_feedback.pdf Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 49
50 Draft NAIC Guidance for Regulators Risk-Focused Surveillance Working Group released detailed guidance on use of ORSA in financial analysis and exams in March 2014 Since then, three exposure periods have been completed. Principle goals of ORSA are: To foster an effective level of ERM at all insurers To provide a group-level perspective on risk and capital, as a supplement to the existing legal entity view To allow the regulator to obtain a high level understanding of the insurer s ORSA and to assist the commissioner in determining the scope, depth, and minimum timing of risk-focused analysis and examination procedures Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 50
51 Draft NAIC Guidance for Regulators Summarizes the guidance as well as the RIMS ERM maturity model to provide education to the user on what to expect from good ERM Failure to demonstrate sufficient ERM is likely to result in increased supervision, up to and including a hazardous financial condition determination ERM assessed on a 1-5 scale Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 51
52 Draft NAIC Guidance for Regulators RIMS risk maturity as described in the guidance. Additional details are provided for each section and subsection of the ORSA report Non-Existent No identification, monitoring, or management Ad-Hoc No developed or documented standard processes; relies on individual efforts. Initial Processes in place, but not operating consistently and effectively. Certain risks defined and managed in silos. Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 52 Repeatable Processes in place; designed and operated in a timely, consistent, sustained way. Actions taken to address issues for high priority risks. Managed Activities coordinated across business areas; tools and processes activities used. Enterprisewide identification, monitoring, management, and reporting in place. Leading Tools embedded in strategic planning, capital allocation, etc and used in daily decision making. Limits in place to identify breaches and require corrective action by Board and management.
53 Assessing Solvency Per the NAIC ORSA Guidance Manual, assessment of group solvency should describe approach used, methods, assumptions. Examples from the guidance include: Considerations Description of Methods/Assumptions Examples Definition of Solvency Accounting/Valuatio n Regime Business Included How solvency is defined (capital and liquidity) Underlying accounting/valuation basis Subset of business included in capital analysis Cash flow basis, balance sheet basis GAAP, Stat, market consistent, IFRS, rating agency In-force as of a specific date, new business included Time Horizon Horizon over which risks are modeled 1 year, multi-year, lifetime, runoff Risks Modeled Which risks included, are all relevant and material ones in? Credit, market, insurance, liquidity, operational Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 53
54 Assessing Solvency Per the NAIC ORSA Guidance Manual, assessment of group solvency should describe approach used, methods, assumptions. Examples from the guidance include: Considerations Quantification Method Risk Capital Metric Defined Security Standard Aggregation/ Diversification Description of Methods/Assumptions Examples How risk exposure is quantified Measurement metric for determining needed capital Standard used to determine risk capital, including link to strategy Method of aggregation and group diversification benefits considered/calculated Stresses, stochastic, factor-based VaR, TVaR, P(ruin), P(ruin) given capital available AA solvency, percentile confidence, percent of RBC Correlation matrix, dependency structure, full/part/no diversification Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 54
55 Assessing Solvency Sample of the type of information that may be included in Section 3 of the ORSA, assuming the insurer has a prospective view on economic solvency Current and 2 Year Prospective Solvency Required risk capital: Operational Expense Behavior Morbidity Longevity Mortality Currency Market Credit Sample Commentary: International operations sold in late 2014, eliminating currency risk Planning entry into disability income in 2015, which will create exposure to morbidity risk but also drive diversification benefits 0 Regulatory Economic Regulatory Economic Regulatory Economic Available regulatory capital Available economic capital Source: Risk & Regulatory Consulting, LLC, May 2014 Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 55
56 Relevant ASOPs* ASOP No. 1 Introductory Actuarial Standard of Practice ASOP No. 7 Analysis of Life, Health, or Property/Casualty Insurer Cash Flows ASOP No. 10 Methods and Assumptions for Use in Life Insurance Company Financial Statements Prepared in Accordance with U.S. GAAP ASOP No. 11 Financial Statement Treatment of Reinsurance Transactions Involving Life or Health Insurance * These are suggested ASOPs only. It is the responsibility of the actuary to determine which ASOPs apply to their work. Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 56
57 Relevant ASOPs ASOP No. 12 Risk Classification (for All Practice Areas) ASOP No. 18 Long-Term Care Insurance ASOP No. 19 Appraisals of Casualty, Health, and Life Insurance Businesses ASOP No. 20 Discounting of Property/Casualty Unpaid Claim Estimates * These are suggested ASOPs only. It is the responsibility of the actuary to determine which ASOPs apply to their work. Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 57
58 Relevant ASOPs ASOP No. 21 Responding to or Assisting Auditors or Examiners in Connection with Financial Statements for All Practice Areas ASOP No. 22 Statements of Opinion Based on Asset Adequacy Analysis by Actuaries for Life or Health Insurers ASOP No. 23 Data Quality ASOP No. 25 Credibility Procedures * These are suggested ASOPs only. It is the responsibility of the actuary to determine which ASOPs apply to their work. Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 58
59 Relevant ASOPs ASOP No. 38 Catastrophe Modeling (for All Practice Areas) revision pending ASOP No. 41 Actuarial Communications ASOP No. 43 Property/Casualty Unpaid Claim Estimates ASOP No. 46 Risk Evaluation in Enterprise Risk Management ASOP No. 47 Risk Treatment in Enterprise Risk Management * These are suggested ASOPs only. It is the responsibility of the actuary to determine which ASOPs apply to their work. Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 59
60 Summary ERM and ORSA are used to: Identify, assess, and quantify risks Ensure implementation of risk treatment strategies Actuaries are likely to be involved in the ORSA because of their specific education, experience, and standards When working on ERM and ORSA, it is important to understand an insurer s risk culture, governance structure, and policies/procedures Risks are both numerous and complex. They must be identified as part of ERM Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 60
61 Summary The proper tools are needed to evaluate risk within ERM Actuarial models and resources, including the ASOPs, can play a crucial role in the aggregation of risk measures Options for risk mitigation should be suggested as part of this process ERM standards and regulations, including the ORSA report, are critical to managing, evaluating, and mitigating insurer risks Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 61
62 Copyright 2015 by the American Academy of Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. Questions?
American Academy of Actuaries Webinar: The Practice of ERM in the Insurance Industry. Enterprise Risk Management Committee November 19, 2013
 American Academy of Actuaries Webinar: The Practice of ERM in the Insurance Industry Enterprise Risk Management Committee November 19, 2013 All Rights Reserved. 1 Presenters Bruce Jones, MAAA, FCAS, CERA
American Academy of Actuaries Webinar: The Practice of ERM in the Insurance Industry Enterprise Risk Management Committee November 19, 2013 All Rights Reserved. 1 Presenters Bruce Jones, MAAA, FCAS, CERA
NAIC OWN RISK AND SOLVENCY ASSESSMENT (ORSA) GUIDANCE MANUAL
 NAIC OWN RISK AND SOLVENCY ASSESSMENT (ORSA) GUIDANCE MANUAL Created by the NAIC Group Solvency Issues Working Group Of the Solvency Modernization Initiatives (EX) Task Force 2011 National Association
NAIC OWN RISK AND SOLVENCY ASSESSMENT (ORSA) GUIDANCE MANUAL Created by the NAIC Group Solvency Issues Working Group Of the Solvency Modernization Initiatives (EX) Task Force 2011 National Association
ERM and Reserve Risk
 ERM and Reserve Risk Alietia Caughron, PhD CNA Insurance Casualty Actuarial Society s 2014 Centennial Celebration and Annual Meeting New York City, NY November 11, 2014 Disclaimer The purpose of this presentation
ERM and Reserve Risk Alietia Caughron, PhD CNA Insurance Casualty Actuarial Society s 2014 Centennial Celebration and Annual Meeting New York City, NY November 11, 2014 Disclaimer The purpose of this presentation
Academy Presentation to NAIC ORSA Implementation (E) Subgroup
 Academy Presentation to NAIC ORSA Implementation (E) Subgroup Tricia Matson, MAAA, FSA Chairperson, Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) and Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Committee August 10, 2016
Academy Presentation to NAIC ORSA Implementation (E) Subgroup Tricia Matson, MAAA, FSA Chairperson, Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) and Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Committee August 10, 2016
Re: Comments on ORSA Guidance in the Financial Analysis and Financial Condition Examiners Handbooks
 May 16, 2014 Mr. Jim Hattaway, Co-Chair Mr. Doug Slape, Co-Chair Risk-Focused Surveillance (E) Working Group National Association of Insurance Commissioners Via email: c/o Becky Meyer (bmeyer@naic.org)
May 16, 2014 Mr. Jim Hattaway, Co-Chair Mr. Doug Slape, Co-Chair Risk-Focused Surveillance (E) Working Group National Association of Insurance Commissioners Via email: c/o Becky Meyer (bmeyer@naic.org)
Own Risk Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Linking Risk Management, Capital Management and Strategic Planning
 Own Risk Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Linking Risk Management, Capital Management and Strategic Planning Moderator: David Holland, Risk Director, Ally Insurance SPEAKERS Mary-ellen Coggins, Managing Director,
Own Risk Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Linking Risk Management, Capital Management and Strategic Planning Moderator: David Holland, Risk Director, Ally Insurance SPEAKERS Mary-ellen Coggins, Managing Director,
Southeastern Actuaries Conference 2012 Annual Meeting. Jeffrey S. Schlinsog, CFA, FSA, MAAA
 www.pwc.com November 15, 2012 ERM Topics Southeastern Actuaries Conference 2012 Annual Meeting Jeffrey S. Schlinsog, CFA, FSA, MAAA ERM Topics 1. The development and implementation of the ORSA 2. The contents
www.pwc.com November 15, 2012 ERM Topics Southeastern Actuaries Conference 2012 Annual Meeting Jeffrey S. Schlinsog, CFA, FSA, MAAA ERM Topics 1. The development and implementation of the ORSA 2. The contents
INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF INSURANCE SUPERVISORS
 Guidance Paper No. 2.2.x INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF INSURANCE SUPERVISORS GUIDANCE PAPER ON ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT FOR CAPITAL ADEQUACY AND SOLVENCY PURPOSES DRAFT, MARCH 2008 This document was prepared
Guidance Paper No. 2.2.x INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF INSURANCE SUPERVISORS GUIDANCE PAPER ON ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT FOR CAPITAL ADEQUACY AND SOLVENCY PURPOSES DRAFT, MARCH 2008 This document was prepared
Enterprise Risk Management
 Enterprise Risk Management Southeastern Actuaries Conference Rebecca Scotchie June 2011 ERM is 2 1 Agenda What is ERM? Why is risk management important? ERM maturity model/evolution of ERM ERM Framework
Enterprise Risk Management Southeastern Actuaries Conference Rebecca Scotchie June 2011 ERM is 2 1 Agenda What is ERM? Why is risk management important? ERM maturity model/evolution of ERM ERM Framework
NAIC OWN RISK AND SOLVENCY ASSESSMENT (ORSA) GUIDANCE MANUAL
 NAIC OWN RISK AND SOLVENCY ASSESSMENT (ORSA) GUIDANCE MANUAL As of December 2017 The NAIC is the authoritative source for insurance industry information. Our expert solutions support the efforts of regulators,
NAIC OWN RISK AND SOLVENCY ASSESSMENT (ORSA) GUIDANCE MANUAL As of December 2017 The NAIC is the authoritative source for insurance industry information. Our expert solutions support the efforts of regulators,
Solvency II Insights for North American Insurers. CAS Centennial Meeting Damon Paisley Bill VonSeggern November 10, 2014
 Solvency II Insights for North American Insurers CAS Centennial Meeting Damon Paisley Bill VonSeggern November 10, 2014 Agenda 1 Introduction to Solvency II 2 Pillar I 3 Pillar II and Governance 4 North
Solvency II Insights for North American Insurers CAS Centennial Meeting Damon Paisley Bill VonSeggern November 10, 2014 Agenda 1 Introduction to Solvency II 2 Pillar I 3 Pillar II and Governance 4 North
RED 2.1 & 4.2: Quantifying Risk Exposure for ORSA. Moderator: Presenters: Lesley R. Bosniack, CERA, FCAS, MAAA
 RED 2.1 & 4.2: Quantifying Risk Exposure for ORSA Moderator: Lesley R. Bosniack, CERA, FCAS, MAAA Presenters: Lesley R. Bosniack, CERA, FCAS, MAAA William Robert Wilkins, ASA, CERA, FCAS, MAAA SOA Antitrust
RED 2.1 & 4.2: Quantifying Risk Exposure for ORSA Moderator: Lesley R. Bosniack, CERA, FCAS, MAAA Presenters: Lesley R. Bosniack, CERA, FCAS, MAAA William Robert Wilkins, ASA, CERA, FCAS, MAAA SOA Antitrust
2014 Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Feedback Pilot Project Observations of the Group Solvency Issues (E) Working Group
 2014 Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Feedback Pilot Project Observations of the Group Solvency Issues (E) Working Group During October 2014 through June 2015, a third ORSA Feedback Pilot Project
2014 Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Feedback Pilot Project Observations of the Group Solvency Issues (E) Working Group During October 2014 through June 2015, a third ORSA Feedback Pilot Project
A.M. Best s New Risk Management Standards
 A.M. Best s New Risk Management Standards Stephanie Guethlein McElroy, A.M. Best Manager, Rating Criteria and Rating Relations Hubert Mueller, Towers Perrin, Principal March 24, 2008 Introduction A.M.
A.M. Best s New Risk Management Standards Stephanie Guethlein McElroy, A.M. Best Manager, Rating Criteria and Rating Relations Hubert Mueller, Towers Perrin, Principal March 24, 2008 Introduction A.M.
The ORSA opportunity:
 The ORSA opportunity: Compliance and business value 12 March 2014 Today s agenda Background and regulatory update ORSA overview Industry perspectives Achieving long-term business value Page 2 Today s agenda
The ORSA opportunity: Compliance and business value 12 March 2014 Today s agenda Background and regulatory update ORSA overview Industry perspectives Achieving long-term business value Page 2 Today s agenda
Actuaries Club of the Southwest
 www.pwc.com Actuaries Club of the Southwest 3-2-1-ORSA Drivers of Enterprise Risk Management ( ERM ) Fed 1. Rating Agencies AM Best SRQ ERM Questions & S&P ERM Level III Reviews FASB/IASB 2. IAIS ICP 16
www.pwc.com Actuaries Club of the Southwest 3-2-1-ORSA Drivers of Enterprise Risk Management ( ERM ) Fed 1. Rating Agencies AM Best SRQ ERM Questions & S&P ERM Level III Reviews FASB/IASB 2. IAIS ICP 16
INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF INSURANCE SUPERVISORS
 Guidance Paper No. 2.2.6 INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF INSURANCE SUPERVISORS GUIDANCE PAPER ON ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT FOR CAPITAL ADEQUACY AND SOLVENCY PURPOSES OCTOBER 2007 This document was prepared
Guidance Paper No. 2.2.6 INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF INSURANCE SUPERVISORS GUIDANCE PAPER ON ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT FOR CAPITAL ADEQUACY AND SOLVENCY PURPOSES OCTOBER 2007 This document was prepared
SOLVENCY II INSIGHTS FOR NORTH AMERICAN INSURERS. CAS Centennial Meeting Melissa Salton November 10, 2014
 SOLVENCY II INSIGHTS FOR NORTH AMERICAN INSURERS CAS Centennial Meeting Melissa Salton 609-243-4424 November 10, 2014 Risk Management Components at MRG provides a framework for all US entities Disclosure
SOLVENCY II INSIGHTS FOR NORTH AMERICAN INSURERS CAS Centennial Meeting Melissa Salton 609-243-4424 November 10, 2014 Risk Management Components at MRG provides a framework for all US entities Disclosure
US Life Insurer Stress Testing
 US Life Insurer Stress Testing Presentation to the Office of Financial Research June 12, 2015 Nancy Bennett, MAAA, FSA, CERA John MacBain, MAAA, FSA Tom Campbell, MAAA, FSA, CERA May not be reproduced
US Life Insurer Stress Testing Presentation to the Office of Financial Research June 12, 2015 Nancy Bennett, MAAA, FSA, CERA John MacBain, MAAA, FSA Tom Campbell, MAAA, FSA, CERA May not be reproduced
ERM and ORSA Assuring a Necessary Level of Risk Control
 ERM and ORSA Assuring a Necessary Level of Risk Control Dave Ingram, MAAA, FSA, CERA, FRM, PRM Chair of IAA Enterprise & Financial Risk Committee Executive Vice President, Willis Re September, 2012 1 DISCLAIMER
ERM and ORSA Assuring a Necessary Level of Risk Control Dave Ingram, MAAA, FSA, CERA, FRM, PRM Chair of IAA Enterprise & Financial Risk Committee Executive Vice President, Willis Re September, 2012 1 DISCLAIMER
ERM/ORSA Training Thai General Insurance Association (TGIA)
 ERM/ORSA Training Thai General Insurance Association (TGIA) 10 October 2017 Agenda Time Topics 8.30-9.00 Registration ORSA for Non-life Insurance Top 10 global business risk in 2017 Weakness and past failures
ERM/ORSA Training Thai General Insurance Association (TGIA) 10 October 2017 Agenda Time Topics 8.30-9.00 Registration ORSA for Non-life Insurance Top 10 global business risk in 2017 Weakness and past failures
ERM Implementation and the Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA)
 ERM Implementation and the Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Kevin Olberding June 2013 1 Agenda ERM IMPLEMENTATION AND THE OWN RISK AND SOLVENCY ASSESSMENT (ORSA) Evolution of Enterprise Risk Management
ERM Implementation and the Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Kevin Olberding June 2013 1 Agenda ERM IMPLEMENTATION AND THE OWN RISK AND SOLVENCY ASSESSMENT (ORSA) Evolution of Enterprise Risk Management
Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA)
 Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Presentations to OCCA (Nov. 19, 2014) and AAIARD (Nov. 21, 2014) Jacqueline Friedland, FCIA, FCAS, FSA, MAAA Chief Actuary, RSA Canada Presentation Outline What
Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) Presentations to OCCA (Nov. 19, 2014) and AAIARD (Nov. 21, 2014) Jacqueline Friedland, FCIA, FCAS, FSA, MAAA Chief Actuary, RSA Canada Presentation Outline What
GUIDELINE ON ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT
 GUIDELINE ON ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT Insurance Authority Table of Contents Page 1. Introduction 1 2. Application 2 3. Overview of Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Framework and 4 General Requirements
GUIDELINE ON ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT Insurance Authority Table of Contents Page 1. Introduction 1 2. Application 2 3. Overview of Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Framework and 4 General Requirements
Session 5: Evolution of ORSA in the US. Moderator: Michael Anthony McComis Jr. MAAA,FCAS
 Session 5: Evolution of ORSA in the US Moderator: Michael Anthony McComis Jr. MAAA,FCAS Presenters: S Douglas Caldwell FSA,MAAA,CERA Chad R Runchey FSA,MAAA Elisabetta Russo MAAA SOA Antitrust Disclaimer
Session 5: Evolution of ORSA in the US Moderator: Michael Anthony McComis Jr. MAAA,FCAS Presenters: S Douglas Caldwell FSA,MAAA,CERA Chad R Runchey FSA,MAAA Elisabetta Russo MAAA SOA Antitrust Disclaimer
Sections of the ORSA Report
 Lessons Learned From Orsa Reviews Impact on Risk Focused Examination NAIC Insurance Summit INS Companies Joe Fritsch, Director INS Companies Don Carbone, Exam Manager INS Companies Sections of the ORSA
Lessons Learned From Orsa Reviews Impact on Risk Focused Examination NAIC Insurance Summit INS Companies Joe Fritsch, Director INS Companies Don Carbone, Exam Manager INS Companies Sections of the ORSA
ORSA An International Development
 ORSA An International Development 25.02.14 Agenda What is an ORSA? Global reach Comparison of requirements Common challenges Potential solutions Origin of ORSA FSA ICAS Solvency II IAIS ICP16 What is an
ORSA An International Development 25.02.14 Agenda What is an ORSA? Global reach Comparison of requirements Common challenges Potential solutions Origin of ORSA FSA ICAS Solvency II IAIS ICP16 What is an
Global Enterprise Risk Management in Insurance
 Global Enterprise Risk Management in Insurance Caroline Bennet National Leader, Deloitte Actuaries & Consultants Australia Meeting the Challenges of Change 14 th Global Conference of Actuaries 19 th 21
Global Enterprise Risk Management in Insurance Caroline Bennet National Leader, Deloitte Actuaries & Consultants Australia Meeting the Challenges of Change 14 th Global Conference of Actuaries 19 th 21
Guideline. Own Risk and Solvency Assessment. Category: Sound Business and Financial Practices. No: E-19 Date: November 2015
 Guideline Subject: Category: Sound Business and Financial Practices No: E-19 Date: November 2015 This guideline sets out OSFI s expectations with respect to the Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA)
Guideline Subject: Category: Sound Business and Financial Practices No: E-19 Date: November 2015 This guideline sets out OSFI s expectations with respect to the Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA)
Risk Appetite for Life Offices IFoA working party
 Risk Appetite for Life Offices IFoA working party Gautam Kakar, Chairman 30 October 2015 Members of Working Party: Gautam Kakar Lana Nguyen Shayanthan Pathmanathan Rod Bryn-Hussey Fabio Schiaffini Crystal
Risk Appetite for Life Offices IFoA working party Gautam Kakar, Chairman 30 October 2015 Members of Working Party: Gautam Kakar Lana Nguyen Shayanthan Pathmanathan Rod Bryn-Hussey Fabio Schiaffini Crystal
IAIS: Enterprise Risk Management for Capital Adequacy & Solvency Purposes. George Brady. IAIS Deputy Secretary General
 IAIS: Enterprise Risk Management for Capital Adequacy & Solvency Purposes George Brady IAIS Deputy Secretary General Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2. Governance and an Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)
IAIS: Enterprise Risk Management for Capital Adequacy & Solvency Purposes George Brady IAIS Deputy Secretary General Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2. Governance and an Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)
New Actuarial Standards of Practice No. 46 Risk Evaluation in ERM No. 47 Risk Treatment in ERM
 New Actuarial Standards of Practice No. 46 Risk Evaluation in ERM No. 47 Risk Treatment in ERM August 1, 2013 1 Professional Disclaimer Any opinions expressed within this presentation are the presenter
New Actuarial Standards of Practice No. 46 Risk Evaluation in ERM No. 47 Risk Treatment in ERM August 1, 2013 1 Professional Disclaimer Any opinions expressed within this presentation are the presenter
Statement of Guidance for Licensees seeking approval to use an Internal Capital Model ( ICM ) to calculate the Prescribed Capital Requirement ( PCR )
 MAY 2016 Statement of Guidance for Licensees seeking approval to use an Internal Capital Model ( ICM ) to calculate the Prescribed Capital Requirement ( PCR ) 1 Table of Contents 1 STATEMENT OF OBJECTIVES...
MAY 2016 Statement of Guidance for Licensees seeking approval to use an Internal Capital Model ( ICM ) to calculate the Prescribed Capital Requirement ( PCR ) 1 Table of Contents 1 STATEMENT OF OBJECTIVES...
The Rating Agency View of Capital Modelling. Simon Harris Team Managing Director European Insurance
 The Rating Agency View of Capital Modelling Simon Harris Team Managing Director European Insurance September 2007 Agenda The importance of risk and capitalisation in the rating process Moody s approach
The Rating Agency View of Capital Modelling Simon Harris Team Managing Director European Insurance September 2007 Agenda The importance of risk and capitalisation in the rating process Moody s approach
ERM in the U.S. life and annuity industry
 Milliman Research Report Prepared by: Anna Berezovskaya, FSA, MAAA Tony Dardis, FSA, MAAA, CERA, CFA June 016 01 Survey - Summary report Milliman For a copy of the full report, please contact the authors.
Milliman Research Report Prepared by: Anna Berezovskaya, FSA, MAAA Tony Dardis, FSA, MAAA, CERA, CFA June 016 01 Survey - Summary report Milliman For a copy of the full report, please contact the authors.
Critical Reflection of Two State-of-the-Art Risk Management Frameworks (SRM004)
 Critical Reflection of Two State-of-the-Art Risk Management Frameworks (SRM004) Speakers: Dr. Kathrin Anne Meier, Chief Risk Officer, Allianz Global Corporate & Specialty John Adams, VP Global ERM, PepsiCo
Critical Reflection of Two State-of-the-Art Risk Management Frameworks (SRM004) Speakers: Dr. Kathrin Anne Meier, Chief Risk Officer, Allianz Global Corporate & Specialty John Adams, VP Global ERM, PepsiCo
May 2015 DISCUSSION DRAFT For Illustrative Purposes Only Content NOT Reviewed or Approved by the Actuarial Standards Board DISCUSSION DRAFT
 DISCUSSION DRAFT Capital Adequacy Assessment for Insurers Developed by the Enterprise Risk Management Committee of the Actuarial Standards Board TABLE OF CONTENTS Transmittal Memorandum iv STANDARD OF
DISCUSSION DRAFT Capital Adequacy Assessment for Insurers Developed by the Enterprise Risk Management Committee of the Actuarial Standards Board TABLE OF CONTENTS Transmittal Memorandum iv STANDARD OF
WHITE PAPER. Solvency II Compliance and beyond: Title The essential steps for insurance firms
 WHITE PAPER Solvency II Compliance and beyond: Title The essential steps for insurance firms ii Contents Introduction... 1 Step 1 Data Management... 1 Step 2 Risk Calculations... 3 Solvency Capital Requirement
WHITE PAPER Solvency II Compliance and beyond: Title The essential steps for insurance firms ii Contents Introduction... 1 Step 1 Data Management... 1 Step 2 Risk Calculations... 3 Solvency Capital Requirement
Article from: Risks & Rewards. August 2014 Issue 64
 Article from: Risks & Rewards August 2014 Issue 64 ALM TRANSFORMATION By Eric L. Clapprood, Jeffrey R. Lortie and Kathryn M. Nelson In a world of uncertainty, there are consistently two sure things consultants
Article from: Risks & Rewards August 2014 Issue 64 ALM TRANSFORMATION By Eric L. Clapprood, Jeffrey R. Lortie and Kathryn M. Nelson In a world of uncertainty, there are consistently two sure things consultants
Does the ORSA add value? Challenges and initial achievements. Lukas Ziewer Risk Management Perspectives, 18/11/2014
 Does the ORSA add value? Challenges and initial achievements Lukas Ziewer Risk Management Perspectives, 18/11/2014 My three wishes for a prudential regime 1. Capital as a single currency for risk as a
Does the ORSA add value? Challenges and initial achievements Lukas Ziewer Risk Management Perspectives, 18/11/2014 My three wishes for a prudential regime 1. Capital as a single currency for risk as a
ECONOMIC CAPITAL MODELING CARe Seminar JUNE 2016
 ECONOMIC CAPITAL MODELING CARe Seminar JUNE 2016 Boston Catherine Eska The Hanover Insurance Group Paul Silberbush Guy Carpenter & Co. Ronald Wilkins - PartnerRe Economic Capital Modeling Safe Harbor Notice
ECONOMIC CAPITAL MODELING CARe Seminar JUNE 2016 Boston Catherine Eska The Hanover Insurance Group Paul Silberbush Guy Carpenter & Co. Ronald Wilkins - PartnerRe Economic Capital Modeling Safe Harbor Notice
International Insurance Regulation 101: International Association of Insurance Supervisors
 The Academy Capitol Forum: Meet the Experts International Insurance Regulation 101: International Association of Insurance Supervisors George Brady, Deputy Secretary General, IAIS Moderator: Jeffrey S.
The Academy Capitol Forum: Meet the Experts International Insurance Regulation 101: International Association of Insurance Supervisors George Brady, Deputy Secretary General, IAIS Moderator: Jeffrey S.
Preparing for an Own Risk & Solvency Assessment
 www.pwc.com Preparing for an Own Risk & Solvency Assessment March 2013 Brian Paton Director, Insurance Risk and Capital Practice brian.paton@us.pwc.com Contents 1. ORSA challenges 2. ORSA readiness and
www.pwc.com Preparing for an Own Risk & Solvency Assessment March 2013 Brian Paton Director, Insurance Risk and Capital Practice brian.paton@us.pwc.com Contents 1. ORSA challenges 2. ORSA readiness and
OWN RISK AND SOLVENCY ASSESSMENT. ERM Seminar Compliance All Dealing from the same deck now
 OWN RISK AND SOLVENCY ASSESSMENT ERM Seminar - 2014 Compliance All Dealing from the same deck now Own and Solvency Assessment! Originated in the UK about 10 years ago Now a global insurance regulatory
OWN RISK AND SOLVENCY ASSESSMENT ERM Seminar - 2014 Compliance All Dealing from the same deck now Own and Solvency Assessment! Originated in the UK about 10 years ago Now a global insurance regulatory
January 30, Dear Mr. Seeley:
 January 30, 2014 Alan Seeley Chair, SMI RBC Subgroup National Association of Insurance Commissioners 2301 McGee Street, Suite 800 Kansas City, MO 64108-2662 Dear Mr. Seeley: The American Academy of Actuaries
January 30, 2014 Alan Seeley Chair, SMI RBC Subgroup National Association of Insurance Commissioners 2301 McGee Street, Suite 800 Kansas City, MO 64108-2662 Dear Mr. Seeley: The American Academy of Actuaries
Economic Capital: Recent Market Trends and Best Practices for Implementation
 1 Economic Capital: Recent Market Trends and Best Practices for Implementation 7-11 September 2009 Hubert Mueller 2 Overview Recent Market Trends Implementation Issues Economic Capital (EC) Aggregation
1 Economic Capital: Recent Market Trends and Best Practices for Implementation 7-11 September 2009 Hubert Mueller 2 Overview Recent Market Trends Implementation Issues Economic Capital (EC) Aggregation
Insights. NAIC s ORSA. A Broader Approach to Regulation. NAIC S ORSA Part of a Global Shift to Regulatory Modernization
 Insights June 2011 NAIC s ORSA A Broader Approach to Regulation Broad regulatory changes are on the horizon for U.S. insurers. The National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC s) Solvency Modernization
Insights June 2011 NAIC s ORSA A Broader Approach to Regulation Broad regulatory changes are on the horizon for U.S. insurers. The National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC s) Solvency Modernization
MEMORANDUM. To: From: Metrolinx Board of Directors Robert Siddall Chief Financial Officer Date: September 14, 2017 ERM Policy and Framework
 MEMORANDUM To: From: Metrolinx Board of Directors Robert Siddall Chief Financial Officer Date: September 14, 2017 Re: ERM Policy and Framework Executive Summary Attached are the draft Enterprise Risk Management
MEMORANDUM To: From: Metrolinx Board of Directors Robert Siddall Chief Financial Officer Date: September 14, 2017 Re: ERM Policy and Framework Executive Summary Attached are the draft Enterprise Risk Management
The Components of a Sound Emerging Risk Management Framework
 North American CRO Council The Components of a Sound Emerging Risk Management Framework December 6, 2012 2012 North American CRO Council Incorporated chairperson@crocouncil.org North American CRO Council
North American CRO Council The Components of a Sound Emerging Risk Management Framework December 6, 2012 2012 North American CRO Council Incorporated chairperson@crocouncil.org North American CRO Council
Certified Enterprise Risk Professional (CERP) Test Content Outline
 Certified Enterprise Risk Professional (CERP) Test Content Outline SECTION 1: RISK GOVERNANCE Domain 1: Board and Senior Management Oversight (8%) Task 1: Provide relevant, timely, and accurate information
Certified Enterprise Risk Professional (CERP) Test Content Outline SECTION 1: RISK GOVERNANCE Domain 1: Board and Senior Management Oversight (8%) Task 1: Provide relevant, timely, and accurate information
ORSA An international requirement
 Prepared by: Padraic O'Malley, Principal, Dublin Eamonn Phelan, Principal, Dublin December 2013 ORSA An international requirement Title Author a [Footer - regular] Month YYYY Title Author b [Footer - regular]
Prepared by: Padraic O'Malley, Principal, Dublin Eamonn Phelan, Principal, Dublin December 2013 ORSA An international requirement Title Author a [Footer - regular] Month YYYY Title Author b [Footer - regular]
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)
 Southeastern Actuaries Conference Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) November 16, 2007 ING. Your future. Made easier. Agenda ERM Are you doing it? Definition of ERM What is it? Industry Overview What is
Southeastern Actuaries Conference Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) November 16, 2007 ING. Your future. Made easier. Agenda ERM Are you doing it? Definition of ERM What is it? Industry Overview What is
Pillar 2 for Insurer s:
 Pillar 2 for Insurer s: Greater requirements, enhanced value? September 2018 Order of events Presenters: 1. Pillar 2 in context 2. Redefining the standard for Enterprise Risk Management Michael van Vuuren
Pillar 2 for Insurer s: Greater requirements, enhanced value? September 2018 Order of events Presenters: 1. Pillar 2 in context 2. Redefining the standard for Enterprise Risk Management Michael van Vuuren
DEVELOPING A GROUP CAPITAL CALCULATION
 Bill Schwegler, Senior Actuary, AEGON DEVELOPING A GROUP CAPITAL CALCULATION Presentation to NAIC s Group Solvency Issues Working Group March 25, 2011 Economic capital models: critical decisions 1. Definition
Bill Schwegler, Senior Actuary, AEGON DEVELOPING A GROUP CAPITAL CALCULATION Presentation to NAIC s Group Solvency Issues Working Group March 25, 2011 Economic capital models: critical decisions 1. Definition
A (personal) view. Philip Whittingham, European Chief Enterprise Risk Officer. 22 March 2010
 The role of the risk profession in a Solvency II world A (personal) view Philip Whittingham, European Chief Enterprise Risk Officer XL Group plc 22 March 2010 Session Aims Successful Solvency II implementation
The role of the risk profession in a Solvency II world A (personal) view Philip Whittingham, European Chief Enterprise Risk Officer XL Group plc 22 March 2010 Session Aims Successful Solvency II implementation
BERMUDA INSURANCE (GROUP SUPERVISION) RULES 2011 BR 76 / 2011
 QUO FA T A F U E R N T BERMUDA INSURANCE (GROUP SUPERVISION) RULES 2011 BR 76 / 2011 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Citation and commencement PART 1 GROUP RESPONSIBILITIES
QUO FA T A F U E R N T BERMUDA INSURANCE (GROUP SUPERVISION) RULES 2011 BR 76 / 2011 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Citation and commencement PART 1 GROUP RESPONSIBILITIES
INSURANCE CORE PRINCIPLES, STANDARDS, GUIDANCE AND ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY
 INSURANCE CORE PRINCIPLES, STANDARDS, GUIDANCE AND ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY Revised ICP 8 and the additional ComFrame material in ICP 8 for public consultation (redline version) This public consultation
INSURANCE CORE PRINCIPLES, STANDARDS, GUIDANCE AND ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY Revised ICP 8 and the additional ComFrame material in ICP 8 for public consultation (redline version) This public consultation
Applying COSO s Enterprise Risk Management Integrated Framework. September 29, 2004
 Applying COSO s Enterprise Risk Management Integrated Framework September 29, 2004 Today s organizations are concerned about: Risk Management Governance Control Assurance (and Consulting) ERM Defined:
Applying COSO s Enterprise Risk Management Integrated Framework September 29, 2004 Today s organizations are concerned about: Risk Management Governance Control Assurance (and Consulting) ERM Defined:
Credit risk management. Why it matters and how insurers can enhance their capabilities
 Credit risk management Why it matters and how insurers can enhance their capabilities As enterprise risk management has moved up the strategic agenda for insurance executives in the years since the global
Credit risk management Why it matters and how insurers can enhance their capabilities As enterprise risk management has moved up the strategic agenda for insurance executives in the years since the global
The Role of Finance and Accounting as Critical Players in ERM and ORSA
 The Role of Finance and Accounting as Critical Players in ERM and ORSA Session Number 404 Jim Stangroom Baker Tilly John Romano Baker Tilly John Holdorf NYCM Insurance Amy Purdy Godleski Columbian Financial
The Role of Finance and Accounting as Critical Players in ERM and ORSA Session Number 404 Jim Stangroom Baker Tilly John Romano Baker Tilly John Holdorf NYCM Insurance Amy Purdy Godleski Columbian Financial
P/C Risk-Based Capital: State and International Solvency Regulation
 P/C Risk-Based Capital: State and International Solvency Regulation May 31, 2011 Presented by the Property and Casualty Risk-Based Capital Committee 1 Presenters Moderator and speaker: Alex Krutov, FCAS,
P/C Risk-Based Capital: State and International Solvency Regulation May 31, 2011 Presented by the Property and Casualty Risk-Based Capital Committee 1 Presenters Moderator and speaker: Alex Krutov, FCAS,
An Introduction to Solvency II
 An Introduction to Solvency II Peter Withey KPMG Agenda 1. Background to Solvency II 2. Pillar 1: Quantitative Pillar Basic building blocks Assets Technical Reserves Solvency Capital Requirement Internal
An Introduction to Solvency II Peter Withey KPMG Agenda 1. Background to Solvency II 2. Pillar 1: Quantitative Pillar Basic building blocks Assets Technical Reserves Solvency Capital Requirement Internal
Prudential Standard GOI 3 Risk Management and Internal Controls for Insurers
 Prudential Standard GOI 3 Risk Management and Internal Controls for Insurers Objectives and Key Requirements of this Prudential Standard Effective risk management is fundamental to the prudent management
Prudential Standard GOI 3 Risk Management and Internal Controls for Insurers Objectives and Key Requirements of this Prudential Standard Effective risk management is fundamental to the prudent management
ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT, INTERNAL MODELS AND OPERATIONAL RISK FOR LIFE INSURERS DISCUSSION PAPER DP14-09
 ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT, INTERNAL MODELS AND FOR LIFE INSURERS DISCUSSION PAPER DP14-09 This paper is issued by the Insurance and Pensions Authority ( the IPA ), the regulatory authority responsible
ENTERPRISE RISK MANAGEMENT, INTERNAL MODELS AND FOR LIFE INSURERS DISCUSSION PAPER DP14-09 This paper is issued by the Insurance and Pensions Authority ( the IPA ), the regulatory authority responsible
Enterprise Risk Management How much risk do you want to take? Mark Lim Risk Consulting and Software Towers Watson
 Enterprise Risk Management How much risk do you want to take? Mark Lim Risk Consulting and Software Towers Watson 1 Agenda 1 Introduction 2 Developing an ERM framework 3 Defining and integrating Risk Appetite
Enterprise Risk Management How much risk do you want to take? Mark Lim Risk Consulting and Software Towers Watson 1 Agenda 1 Introduction 2 Developing an ERM framework 3 Defining and integrating Risk Appetite
ERM in the Rating Process: A Practical Perspective
 ERM in the Rating Process: A Practical Perspective Jeffrey Mango, Group Vice President, A.M. Best Michelle Baurkot, Assistant Vice President, A.M. Best Tom Zitelli, Managing Senior Financial Analyst, A.M.
ERM in the Rating Process: A Practical Perspective Jeffrey Mango, Group Vice President, A.M. Best Michelle Baurkot, Assistant Vice President, A.M. Best Tom Zitelli, Managing Senior Financial Analyst, A.M.
U.S. Senate Committee on Banking, Housing, and Urban Affairs Subcommittee on Financial Institutions and Consumer Protection
 U.S. Senate Committee on Banking, Housing, and Urban Affairs Subcommittee on Financial Institutions and Consumer Protection Hearing on Finding the Right Capital Regulation for Insurers Submitted Testimony
U.S. Senate Committee on Banking, Housing, and Urban Affairs Subcommittee on Financial Institutions and Consumer Protection Hearing on Finding the Right Capital Regulation for Insurers Submitted Testimony
SMI. Capital Requirements. Governance & Risk Management. Group Supervision. Statutory Accounting & Financial Reporting.
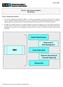 Solvency Modernization Initiative ROADMAP Solvency Modernization Initiative 1. The Solvency Modernization Initiative (SMI) is a critical self-examination to update the United States insurance solvency
Solvency Modernization Initiative ROADMAP Solvency Modernization Initiative 1. The Solvency Modernization Initiative (SMI) is a critical self-examination to update the United States insurance solvency
DRAFT 3/18/14 Financial Analysis Handbook 2014 Annual/2015 Quarterly
 ORSA Summary Report The NAIC Risk Management and Own Risk and Solvency Assessment Model Act (Model #505) requires all insurers with direct written premium and unaffiliated assumed premium of $500 million
ORSA Summary Report The NAIC Risk Management and Own Risk and Solvency Assessment Model Act (Model #505) requires all insurers with direct written premium and unaffiliated assumed premium of $500 million
Role of the Systemic Risk Regulator
 A Public Policy White Paper Role of the Systemic Risk Regulator May 2010 American Academy of Actuaries Financial Regulatory Reform Task Force A PUBLIC POLICY WHITE PAPER Role of the Systemic Risk Regulator
A Public Policy White Paper Role of the Systemic Risk Regulator May 2010 American Academy of Actuaries Financial Regulatory Reform Task Force A PUBLIC POLICY WHITE PAPER Role of the Systemic Risk Regulator
Applying COSO s Enterprise Risk Management Integrated Framework
 Applying COSO s Enterprise Risk Management Integrated Framework COSO COSO stands for the Committee Of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. The sponsoring organizations are: Institute of
Applying COSO s Enterprise Risk Management Integrated Framework COSO COSO stands for the Committee Of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. The sponsoring organizations are: Institute of
Solvency Assessment and Management: Stress Testing Task Group Discussion Document 96 (v 3) General Stress Testing Guidance for Insurance Companies
 Solvency Assessment and Management: Stress Testing Task Group Discussion Document 96 (v 3) General Stress Testing Guidance for Insurance Companies 1 INTRODUCTION AND PURPOSE The business of insurance is
Solvency Assessment and Management: Stress Testing Task Group Discussion Document 96 (v 3) General Stress Testing Guidance for Insurance Companies 1 INTRODUCTION AND PURPOSE The business of insurance is
From: Director Christina Urias, Chair of the Solvency Modernization Initiative (EX) Task Force
 June 7, 2010 To: Lou Felice, Chair of the Capital Adequacy (E) Task Force From: Director Christina Urias, Chair of the Solvency Modernization Initiative (EX) Task Force Subject: SMI's RBC Proposals Dear
June 7, 2010 To: Lou Felice, Chair of the Capital Adequacy (E) Task Force From: Director Christina Urias, Chair of the Solvency Modernization Initiative (EX) Task Force Subject: SMI's RBC Proposals Dear
CEIOPS-DOC-61/10 January Former Consultation Paper 65
 CEIOPS-DOC-61/10 January 2010 CEIOPS Advice for Level 2 Implementing Measures on Solvency II: Partial internal models Former Consultation Paper 65 CEIOPS e.v. Westhafenplatz 1-60327 Frankfurt Germany Tel.
CEIOPS-DOC-61/10 January 2010 CEIOPS Advice for Level 2 Implementing Measures on Solvency II: Partial internal models Former Consultation Paper 65 CEIOPS e.v. Westhafenplatz 1-60327 Frankfurt Germany Tel.
Quantifying Risk Exposures for Own Risk and Solvency Assessment Reports
 A P U B L I C P O L I C Y P R A C T I C E N O T E Quantifying Risk Exposures for Own Risk and Solvency Assessment Reports June 2016 Developed by the Risk Exposures Subgroup of the ERM/ORSA Committee of
A P U B L I C P O L I C Y P R A C T I C E N O T E Quantifying Risk Exposures for Own Risk and Solvency Assessment Reports June 2016 Developed by the Risk Exposures Subgroup of the ERM/ORSA Committee of
RESERVE BANK OF MALAWI
 RESERVE BANK OF MALAWI GUIDELINES ON INTERNAL CAPITAL ADEQUACY ASSESSMENT PROCESS (ICAAP) Bank Supervision Department March 2013 Table of Contents 1.0 INTRODUCTION... 2 2.0 MANDATE... 2 3.0 RATIONALE...
RESERVE BANK OF MALAWI GUIDELINES ON INTERNAL CAPITAL ADEQUACY ASSESSMENT PROCESS (ICAAP) Bank Supervision Department March 2013 Table of Contents 1.0 INTRODUCTION... 2 2.0 MANDATE... 2 3.0 RATIONALE...
CONSULTATION PAPER ON A RISK- BASED CAPITAL FRAMEWORK FOR THE INSURANCE INDUSTRY IN HONG KONG
 CONSULTATION PAPER ON A RISK- BASED CAPITAL FRAMEWORK FOR THE INSURANCE INDUSTRY IN HONG KONG On 16 September 2014, the Office of the Commissioner of Insurance ("OCI") announced the publication by the
CONSULTATION PAPER ON A RISK- BASED CAPITAL FRAMEWORK FOR THE INSURANCE INDUSTRY IN HONG KONG On 16 September 2014, the Office of the Commissioner of Insurance ("OCI") announced the publication by the
Re: Proposed Actuarial Standard of Practice, Capital Adequacy Assessment for Insurers, Second Exposure Draft
 March 1, 2018 Actuarial Standards Board (ASB) 1850 M Street NW, Suite 300 Washington, DC 20036 Via email to: comments@actuary.org Re: Proposed Actuarial Standard of Practice, Capital Adequacy Assessment
March 1, 2018 Actuarial Standards Board (ASB) 1850 M Street NW, Suite 300 Washington, DC 20036 Via email to: comments@actuary.org Re: Proposed Actuarial Standard of Practice, Capital Adequacy Assessment
Preparing for the New ERM and Solvency Regulatory Requirements
 OWN RISK AND SOLVENCY ASSESSMENT Preparing for the New ERM and Solvency Regulatory Requirements A White Paper from Willis Re Analytics Insurance solvency regulation is moving into new territory. Insurer
OWN RISK AND SOLVENCY ASSESSMENT Preparing for the New ERM and Solvency Regulatory Requirements A White Paper from Willis Re Analytics Insurance solvency regulation is moving into new territory. Insurer
Stochastic Analysis Of Long Term Multiple-Decrement Contracts
 Stochastic Analysis Of Long Term Multiple-Decrement Contracts Matthew Clark, FSA, MAAA and Chad Runchey, FSA, MAAA Ernst & Young LLP January 2008 Table of Contents Executive Summary...3 Introduction...6
Stochastic Analysis Of Long Term Multiple-Decrement Contracts Matthew Clark, FSA, MAAA and Chad Runchey, FSA, MAAA Ernst & Young LLP January 2008 Table of Contents Executive Summary...3 Introduction...6
Defining the Internal Model for Risk & Capital Management under the Solvency II Directive
 14 Defining the Internal Model for Risk & Capital Management under the Solvency II Directive Mark Dougherty is an international Senior Corporate Governance and Risk Management professional and Chartered
14 Defining the Internal Model for Risk & Capital Management under the Solvency II Directive Mark Dougherty is an international Senior Corporate Governance and Risk Management professional and Chartered
What Is Enterprise Risk Management?
 What Is Enterprise Risk Management? April 24, 2006 Marty Przygoda AVP, Enterprise Risk Management 2002 Allstate Insurance Company Before we start talking about ERM, it might be helpful to know who we are...
What Is Enterprise Risk Management? April 24, 2006 Marty Przygoda AVP, Enterprise Risk Management 2002 Allstate Insurance Company Before we start talking about ERM, it might be helpful to know who we are...
How to review an ORSA
 How to review an ORSA Patrick Kelliher FIA CERA, Actuarial and Risk Consulting Network Ltd. Done properly, the Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) can be a key tool for insurers to understand the evolution
How to review an ORSA Patrick Kelliher FIA CERA, Actuarial and Risk Consulting Network Ltd. Done properly, the Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) can be a key tool for insurers to understand the evolution
Risk Appetite. What is risk appetite?
 Risk Appetite Presented by Mike Claffey 30 March 2011 What is risk appetite? Risk appetite is the degree of risk that an organisation is willing to accept in order to achieve its objectives, both in terms
Risk Appetite Presented by Mike Claffey 30 March 2011 What is risk appetite? Risk appetite is the degree of risk that an organisation is willing to accept in order to achieve its objectives, both in terms
Enterprise Risk Management Economic Capital Modleing and the Financial Crisis
 Risk Management and The Crisis Enterprise Risk Management Economic Capital Modleing and the Financial Crisis What worked and what did not Insurance Industry Continues to Respond to Risk Dynamics Risk Sources
Risk Management and The Crisis Enterprise Risk Management Economic Capital Modleing and the Financial Crisis What worked and what did not Insurance Industry Continues to Respond to Risk Dynamics Risk Sources
Insurance Summit Mr Raymond Tam Executive Director (Policy and Development) Insurance Authority 21 September 2017
 Insurance Summit 2017 Mr Raymond Tam Executive Director (Policy and Development) Insurance Authority 21 September 2017 Priority of Policy Initiatives Development of risk-based capital regime Facilitation
Insurance Summit 2017 Mr Raymond Tam Executive Director (Policy and Development) Insurance Authority 21 September 2017 Priority of Policy Initiatives Development of risk-based capital regime Facilitation
ERM, the New Regulatory Requirements and Quantitative Analyses
 ERM, the New Regulatory Requirements and Quantitative Analyses Presenters Lisa Cosentino, Managing Director, SMART DEVINE Kim Piersol, Consulting Actuary, Huggins Actuarial Services, Inc. 2 Objectives
ERM, the New Regulatory Requirements and Quantitative Analyses Presenters Lisa Cosentino, Managing Director, SMART DEVINE Kim Piersol, Consulting Actuary, Huggins Actuarial Services, Inc. 2 Objectives
Overview and context
 Michael Eves Overview and context Why Are We Talking About This Now? One facet of a long-term reaction to the financial crisis by many stakeholders: Increasing knowledge of models Decreasing confidence
Michael Eves Overview and context Why Are We Talking About This Now? One facet of a long-term reaction to the financial crisis by many stakeholders: Increasing knowledge of models Decreasing confidence
Embedding Stress Testing as Part of an Integrated Risk Management Framework
 Life conference and exhibition 2011 Alastair Clarkson and David Hare Embedding Stress Testing as Part of an Integrated Risk Management Framework 20-22 November 2011 2010 The Actuarial Profession www.actuaries.org.uk
Life conference and exhibition 2011 Alastair Clarkson and David Hare Embedding Stress Testing as Part of an Integrated Risk Management Framework 20-22 November 2011 2010 The Actuarial Profession www.actuaries.org.uk
CAPITAL MANAGEMENT GUIDELINE
 CAPITAL MANAGEMENT GUIDELINE May 2015 Capital Management Guideline 1 Preambule TABLE OF CONTENTS Preamble... 3 Scope... 4 Coming into effect and updating... 5 Introduction... 6 1. Capital management...
CAPITAL MANAGEMENT GUIDELINE May 2015 Capital Management Guideline 1 Preambule TABLE OF CONTENTS Preamble... 3 Scope... 4 Coming into effect and updating... 5 Introduction... 6 1. Capital management...
ORSA reports: gaps and opportunities
 ORSA reports: gaps and opportunities Market benchmarking of ORSA reports for Singapore general insurers Industry-wide Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) 1 2 Contents 1 Executive summary 2 Our assessment
ORSA reports: gaps and opportunities Market benchmarking of ORSA reports for Singapore general insurers Industry-wide Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (ORSA) 1 2 Contents 1 Executive summary 2 Our assessment
Keeping Pace With Solvency II
 Keeping Pace With Solvency II Challenges and Opportunities Facing Insurers By Gerard L Aimable, Colin Murray and Naren Persad Scheduled for 2013, Solvency II will introduce a risk-based regulatory framework
Keeping Pace With Solvency II Challenges and Opportunities Facing Insurers By Gerard L Aimable, Colin Murray and Naren Persad Scheduled for 2013, Solvency II will introduce a risk-based regulatory framework
LEGAL & GENERAL GROUP PLC risk management supplement
 LEGAL & GENERAL GROUP PLC 2017 risk management supplement Supplement contents Within this supplement we set out descriptions of the risks we face, how our risk management framework operates, as well as
LEGAL & GENERAL GROUP PLC 2017 risk management supplement Supplement contents Within this supplement we set out descriptions of the risks we face, how our risk management framework operates, as well as
Risk Appetite Survey Current state of the Insurance Industry
 Risk Appetite Survey Current state of the Insurance Industry Deloitte Belgium and The Netherlands Financial Services Industry The survey was conducted during July 2013 till December 2013 Introduction The
Risk Appetite Survey Current state of the Insurance Industry Deloitte Belgium and The Netherlands Financial Services Industry The survey was conducted during July 2013 till December 2013 Introduction The
Pricing of Life Insurance and Annuity Products
 Actuarial Standard of Practice No. 54 Pricing of Life Insurance and Annuity Products Developed by the Life Insurance and Annuity Pricing Task Force of the Life Committee of the Actuarial Standards Board
Actuarial Standard of Practice No. 54 Pricing of Life Insurance and Annuity Products Developed by the Life Insurance and Annuity Pricing Task Force of the Life Committee of the Actuarial Standards Board
Enterprise Risk Management
 Enterprise Risk Management Its implications, benefits and process by Janice Englesbe, CFA, and Abbe Bensimon, FCAS, MAAA, Gen Re Capital Consultants A Berkshire Hathaway Company The 2005 hurricane season
Enterprise Risk Management Its implications, benefits and process by Janice Englesbe, CFA, and Abbe Bensimon, FCAS, MAAA, Gen Re Capital Consultants A Berkshire Hathaway Company The 2005 hurricane season
ORSA for Captives. Vermont Captive Insurance Association 2013 Annual Conference. Moderator: Sandy Bigglestone, Director of Captive Insurance, VT DFR
 ORSA for Captives Vermont Captive Insurance Association 2013 Annual Conference Moderator: Sandy Bigglestone, Director of Captive Insurance, VT DFR Panelist: Joelle Hren, VP, American Excess Insurance Exchange
ORSA for Captives Vermont Captive Insurance Association 2013 Annual Conference Moderator: Sandy Bigglestone, Director of Captive Insurance, VT DFR Panelist: Joelle Hren, VP, American Excess Insurance Exchange
Economic Capital in a Canadian Context
 Economic Capital in a Canadian Context ERM Seminar May 2005 Topics 1. Rationale for Economic Capital 2. Canadian Regulatory Context 3. Economic Capital Principles 4. Economic Capital Issues 5. Economic
Economic Capital in a Canadian Context ERM Seminar May 2005 Topics 1. Rationale for Economic Capital 2. Canadian Regulatory Context 3. Economic Capital Principles 4. Economic Capital Issues 5. Economic
Guidance paper on the use of internal models for risk and capital management purposes by insurers
 Guidance paper on the use of internal models for risk and capital management purposes by insurers October 1, 2008 Stuart Wason Chair, IAA Solvency Sub-Committee Agenda Introduction Global need for guidance
Guidance paper on the use of internal models for risk and capital management purposes by insurers October 1, 2008 Stuart Wason Chair, IAA Solvency Sub-Committee Agenda Introduction Global need for guidance
Solvency II Detailed guidance notes for dry run process. March 2010
 Solvency II Detailed guidance notes for dry run process March 2010 Introduction The successful implementation of Solvency II at Lloyd s is critical to maintain the competitive position and capital advantages
Solvency II Detailed guidance notes for dry run process March 2010 Introduction The successful implementation of Solvency II at Lloyd s is critical to maintain the competitive position and capital advantages
