Americans AV Preferences: Dynamic Ride-Sharing, Privacy & Long-Distance Mode Choices. Dr. Kara Kockelman & Krishna Murthy Gurumurthy
|
|
|
- Morgan Higgins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Americans AV Preferences: Dynamic Ride-Sharing, Privacy & Long-Distance Mode Choices Dr. Kara Kockelman & Krishna Murthy Gurumurthy
2 Survey Stats. 2,588 Americans answered 70-questions. 1,258 responses from Texas. Each response weighted to match U.S. demographics. Weighted summary: Wtd. Sample Demographics Mean SD Min Max Age (in yrs) 46.0 yrs Gender (Male) 48.6 % Employed Full-Time 37.6 % Bachelor s Degree Holder 17.6 % U.S. License Holder 89.8 % % 0 1 Driving Disability 7.9 % HH Size 2.33 persons HH Annual Income $70.3k $47.2k $5k $250k # Workers in HH 1.15 workers # Children in HH 0.54 children # Vehicles in HH 1.75 vehicles
3 Screening Q s
4 Ride-sharing & WTP Only 63% Americans & 55% Texans may be willing to share their ride with no travel delays (for a 5-mile trip) during the day. These % s dropped to 25% & 30% for 15-minute travel delays & <10% for 30-minute or higher delays. National average of WTP was 74 per trip-mile for all respondents willing to share rides irrespective of travel delays. Very few Americans willing to share rides at night (<5%). But those willing to share show long duration: 40 min (day & night). Another 8% want to opt in if the stranger in the shared ride is prechecked for a criminal record. Location broadcasting services seem to encourage up to 15% more Americans to share their ride.
5 Crash Scenario & Responsibility AVs inevitably crash into a group of pedestrians AVs inevitably crash into other vehicles on the road Who is responsible for all damages in an unavoidable crash involving an AV? Crash Ethics Most preferred outcome/choice AVs must not change course, no matter what, & must crash into whoever is ahead. (54.2%, 47.6%) Crash must occur without any biases on vehicle-type, value or insurance. (38.4%, 38.9%) AV manufacturer should take responsibility. (60.9%, 59.7%) Next preferred outcome/choice The crash must should occur without any biases or preferences on age, race & gender of individuals in the group of pedestrians. (24.8%, 26.4%) AVs must not change course, no matter what, & must crash into the first vehicle it encounters. (31.8%, 31.8%) Programmer who built the AV s algorithm. (23.2%, 23.2%) (U.S. %, Texas %)
6 Privacy Concerns & Long-distance (LD) Impacts 89% respondents have at least some privacy concerns. Americans (~60%) are WTPay ~$1 per trip to anonymize their location while using AVs & SAVs. Comfortable with location data being used for Managing traffic & forecasting travel conditions (53.5%), Policing activities (53.7%), & Community surveillance (46.8%). Uncomfortable with location data used for directed advertising (60.4%). >80% of Americans prefer to use own household vehicle for a nonbusiness trip < 500 miles. Introduction of AVs & SAVs drops this use to 40%. AVs & SAVs enjoy a combined mode-share of 50% for business trips under 500 miles.
7 WTP for Dynamic Ride-Sharing: Model Estimation % Respondents not WTP to share rides was high: 47% (even if only 5 min added) Cragg s Hurdle (2-stage) model: Selection variable captures binary willingness to share ride. Exponential regression estimates the $ WTP. Heteroscedasticity was allowed as function of age. Binary Selection Model (WTP > $0 or Not) Independent Variables Coefficients T-stat Constant Time added to the shared ride (in minutes) Worker present in the household? Age (in years) Have U.S. driver s license? HH s income between $75k & $125k? Has attended some college? Population density (per square mile) -0.3E Employment density (per square mile) 0.5E Exponential Regression Model Independent Variables Coefficients T-stat Constant Age (in years) Has attended some college? Functional Variables for Hetroscedasticity Age (in years): Exponential model Fit statistics Pseudo R-square # Observations & # Respondents 12,940 (2,588)
8 Practical Impacts in WTP for DRS Practical significance obtained by studying % change in WTP values after changing X values of an average American. If age increases, 26% less WTP for DRS may be observed. Lack of driver s license associated with 38% higher WTP. 1 std. dev. higher jobs density comes with 21% rise in WTP. Higher household income comes with rise in WTP. Independent Variables Worker present in the household? Age of respondent (in years) Have U.S. driver s license? Household income between $75k & $125k? Has attended some college? Population density (per sq mile) Employment density (per sq mile) % Change in WTP Y +19.6% N -7.8% +1SD -26.9% -1SD +18.1% Y -4.7% N +38.2% Y +26.1% N -6.6% Y +6.7% N -10.0% +1SD -19.5% -1SD +10.5% +1SD +21.6% -1SD -5.9%
9 WTP for Anonymization of Trip Ends: Model Estimation Cragg s Hurdle (two-part) model Heteroscedasticity as function of age. Many variables significant. Men less willing to anonymize trip ends, on average. Older people typ. willing to pay less. Privacy concerns increase WTP. Binary Selection Model (WTP > $0 or Not) Independent Variables Ceof. T-stat Constant Concerned Exponential about privacy? Regression Model Independent No disability? Variables Coef T-stat Constant Household owns 1 vehicle? Age of respondent (in years) 2 vehicles? -0.4E Have U.S. driver s license? 3 vehicles? Caucasian? 4+ vehicles? Household Household has 2 or size less equal children? to 2? Household income: < $20,000 equal to 3? < $30,000 equal to 4+? Household < workers $40,000 equal to 1? < $50,000 equal to 2? < $60,000 equal to 3? < $75,000 equal to ? < $100, Age of respondent < $125,000 (in years) Is Male? < $150, Household < income: $200,000 < $20, > $200,000 < $30, Population density (per square < $40,000 mile) -0.2E < $50, Employment density (per square < $60, E mile) < $75, Variables with Heteroscedasticity < $100, Age of respondent (in years): < $125, E Exponential model < $150, Fit statistics < $200, Pseudo R-square > $200,
10 Practical Effects in WTP to Anonymize Obtained by studying % change in values by changing 1 attribute of an avg. person. All % changes in WTP negative. Lack of HH vehicle reduces WTP (-56%). Old people less willing to pay (-56%). Negative sensitivities for all predictors. Lack of WTPay in the future to anonymize trip ends. Independent Variables % Change % Change in WTP in Independent Variables HH Income: < $20,000 WTP -21.0% Y: -35.1% No disability? < $30, % N: -13.1% < $40, % HH owns 0 vehicles? -55.6% < $50, % 1 vehicle? -33.1% < 2 $60,000 vehicles? -30.5% -42.3% < 3 $75,000 vehicles? -32.0% -28.6% < 4+ $100,000 vehicles? -30.9% -32.3% HH size equal < $125,000 to 1? -36.2% -35.3% equal to 2? -30.3% < $150, % equal to 3? -26.5% < $200, % equal to 4+? -40.2% HH workers > $200,000 equal to 0? -29.7% -26.2% Have U.S. driver s equal to 1? Y: -34.0% -32.8% license? equal to 2? N: -33.3% -39.1% equal to 3? Y: -47.0% -35.2% Caucasian? equal to 4+? N: -48.5% -31.3% Age of respondent (in +1SD: -55.6% +1SD: -36.5% Pop. years) density (per sq. mi) -1SD: -15.0% -1SD: Y: -40.0% -30.0% Is Male? Employment density (per +1SD: N: -27.4% -29.5% sq. mi) -1SD: -34.4%
11 Long-Distance (LD) Mode Choice Practical impact studied using multinomial logit. SAVs focused on business trips (+67% share). HHs with more Workers prefer private AVs (+50%). Non-owners of cars prefer SAV for LD Trip (+43%). Independent Variables Change in Mode Share AVs SAVs Airplane Trip Type Personal? +3.8% -25.0% -7.2% Business? -22.2% +67.4% +11.9% Recreation? -5.0% -16.4% +1.4% Distance: miles +19.5% +24.5% -38.7% > 500 miles -18.6% -22.6% +37.3% HH owns 0 vehicles? +43.6% -10.4% -18.8% 1 vehicle? +2.1% -31.0% +12.2% 2 vehicles? -15.4% +1.8% +4.8% 3 vehicles? +14.3% +51.7% -18.3% 4+ vehicles? +22.6% +51.8% -37.6% HH size equal to 1? -8.9% +8.4% +11.7% equal to 2? +33.4% +22.2% -27.2% equal to 3? -14.9% -13.8% +14.1% equal to 4+? -22.7% -20.2% +10.6% HH workers equal to 0? +0.6% +33.7% +9.0% equal to 1? +6.2% -11.9% -17.9% equal to 2? -10.8% +11.7% +14.8% equal to 3? +2.0% -37.3% -12.8% equal to 4+? +50.3% -44.9% -6.8% Age of respondent (in years) Have U.S. driver s license? +1SD: -10.5% -11.8% -8.0% -1SD: +9.5% -8.0% +4.6% Y: -5.5% -3.5% -0.2% N: +57.9% +50.7% -7.4%
12 LD Mode Choice (2) Middle-class households strongly prefer SAVs - with 196% higher mode share! Children increase household use of AVs 83% & lower airplane use 39%. Those in wealthy HHs may continue to fly (+44%). Singles may not own AVs (with 40% lower probability for LD trips). Independent Variables % Change in Mode Share AVs SAVs Airplane Caucasian? Y: +5.9% -22.5% -8.8% N: -6.3% +32.3% +14.0% No child in HH -17.7% -23.6% +19.8% Children in the HH: 1 child? +23.7% +65.7% -39.4% 2 children? +64.1% +23.5% -43.5% 3 children? +84.0% +38.4% -39.4% 4+ children? -31.9% +36.7% -14.4% HH Income < $20, % -53.1% -29.4% < $30, % +56.7% -55.0% < $40, % +45.4% -32.7% < $50, % -32.0% +6.7% < $60, % % -44.6% < $75, % -77.6% +6.7% < $100, % +44.5% +17.4% < $125, % +6.8% +30.0% < $150, % -51.5% +45.2% < $200, % -76.2% +43.5% > $200, % -61.9% +44.3% Has attended some college? Y: -3.1% +13.5% +7.8% N: +9.9% -27.2% -16.7% Currently working? Y: +54.9% +13.3% -8.2% N: -8.9% -8.1% +0.6% Single? Y: -40.3% -7.5% +21.7% N: +22.0% -0.5% -16.2% Pop. density (per sq. mi) +1SD: -5.4% +20.6% +10.1% -1SD: +1.3% -7.3% -5.0% Employment density (per sq. mil +1SD: -1.8% -15.7% -9.4% -1SD: -0.5% +9.1% +2.1%
13 Key Results Current U.S. perceptions of ride-sharing in an automated future are cautious. Ride-sharing expected to increase, with Millennials opting in, alongside their anticipated income increases. Privacy is a concern now (WTPay ~$1 to anonymize each trip). But, in the future, anonymization may not be necessary. Most long-distance business trips may be made in SAVs. Flying may still be favored by older people & families with no children. Evolving perceptions warrant continuing survey effort.
14 Thank you! Questions & Suggestions?
ARE WE READY TO EMBRACE CONNECTED AND SELF-DRIVING VEHICLES? A CASE STUDY OF TEXANS
 ARE WE READY TO EMBRACE CONNECTED AND SELF-DRIVING VEHICLES? A CASE STUDY OF TEXANS Prateek Bansal Graduate Research Assistant Department of Civil, Architectural and Environmental Engineering The University
ARE WE READY TO EMBRACE CONNECTED AND SELF-DRIVING VEHICLES? A CASE STUDY OF TEXANS Prateek Bansal Graduate Research Assistant Department of Civil, Architectural and Environmental Engineering The University
Automobile Ownership Model
 Automobile Ownership Model Prepared by: The National Center for Smart Growth Research and Education at the University of Maryland* Cinzia Cirillo, PhD, March 2010 *The views expressed do not necessarily
Automobile Ownership Model Prepared by: The National Center for Smart Growth Research and Education at the University of Maryland* Cinzia Cirillo, PhD, March 2010 *The views expressed do not necessarily
PROPOSED SHOPPING CENTER
 PROPOSED SHOPPING CENTER Southeast Corner I-95 & Highway 192 Melbourne, Florida In a 5 Mile Radius 80,862 Population 32,408 Households $61K Avg HH Income SOONER INVESTMENT Commercial & Investment Real
PROPOSED SHOPPING CENTER Southeast Corner I-95 & Highway 192 Melbourne, Florida In a 5 Mile Radius 80,862 Population 32,408 Households $61K Avg HH Income SOONER INVESTMENT Commercial & Investment Real
Making Transportation Sustainable: Insights from Germany
 Making Transportation Sustainable: Insights from Germany Dr. Ralph Buehler, Assistant Professor in urban affairs and planning at the School of Public and International Affairs, Virginia Tech, Alexandria,
Making Transportation Sustainable: Insights from Germany Dr. Ralph Buehler, Assistant Professor in urban affairs and planning at the School of Public and International Affairs, Virginia Tech, Alexandria,
Willingness to Pay for Green Electricity in Tianjin, China: Based on Contingent Valuation Method
 Willingness to Pay for Green Electricity in Tianjin, China: Based on Contingent Valuation Method Li-Qiu Liu College of Management and Economics, Tianjin University the 40 th June 20, 2017, IAEE, Singapore
Willingness to Pay for Green Electricity in Tianjin, China: Based on Contingent Valuation Method Li-Qiu Liu College of Management and Economics, Tianjin University the 40 th June 20, 2017, IAEE, Singapore
The Trails. 1,500 sf Space Available. In a 3 Mile Radius 69,985 Population 25,450 Households $78,216 Avg HH Inc. 1,500 sf Corner Space
 1,500 sf Space Available The Trails Edmond Rd (2nd St) & Santa Fe Ave ~ Edmond, Oklahoma Current Tenancy: Edmond YMCA Spinal Wellness Clinic Lemongrass Thai Cuisine Kumon Learning Center Katie s Family
1,500 sf Space Available The Trails Edmond Rd (2nd St) & Santa Fe Ave ~ Edmond, Oklahoma Current Tenancy: Edmond YMCA Spinal Wellness Clinic Lemongrass Thai Cuisine Kumon Learning Center Katie s Family
Econometric Methods for Valuation Analysis
 Econometric Methods for Valuation Analysis Margarita Genius Dept of Economics M. Genius (Univ. of Crete) Econometric Methods for Valuation Analysis Cagliari, 2017 1 / 25 Outline We will consider econometric
Econometric Methods for Valuation Analysis Margarita Genius Dept of Economics M. Genius (Univ. of Crete) Econometric Methods for Valuation Analysis Cagliari, 2017 1 / 25 Outline We will consider econometric
Segmentation Survey. Results of Quantitative Research
 Segmentation Survey Results of Quantitative Research August 2016 1 Methodology KRC Research conducted a 20-minute online survey of 1,000 adults age 25 and over who are not unemployed or retired. The survey
Segmentation Survey Results of Quantitative Research August 2016 1 Methodology KRC Research conducted a 20-minute online survey of 1,000 adults age 25 and over who are not unemployed or retired. The survey
Understanding Changes in Youth Mobility
 Understanding Changes in Youth Mobility TECHNICAL APPENDICES TO THE FINAL DELIVERABLE Prepared for NCHRP 08-36 Task 132 Transportation Research Board of The National Academies 1 Table of Contents: The
Understanding Changes in Youth Mobility TECHNICAL APPENDICES TO THE FINAL DELIVERABLE Prepared for NCHRP 08-36 Task 132 Transportation Research Board of The National Academies 1 Table of Contents: The
Analysis of Long-Distance Travel Behavior of the Elderly and Low Income
 PAPER Analysis of Long-Distance Travel Behavior of the Elderly and Low Income NEVINE LABIB GEORGGI Center for Urban Transportation Research University of South Florida RAM M. PENDYALA Department of Civil
PAPER Analysis of Long-Distance Travel Behavior of the Elderly and Low Income NEVINE LABIB GEORGGI Center for Urban Transportation Research University of South Florida RAM M. PENDYALA Department of Civil
Satisfaction with getting to work 57% 14% 13% 9% Total distance travelled. miles per week
 Page/... Headlines All Organisations Travel to Work Survey March 0 Number of respondents Main modes of travel (%) % Satisfaction with getting to work % % % Satisfaction with getting % % (driver with others/
Page/... Headlines All Organisations Travel to Work Survey March 0 Number of respondents Main modes of travel (%) % Satisfaction with getting to work % % % Satisfaction with getting % % (driver with others/
ECON Introductory Econometrics. Seminar 4. Stock and Watson Chapter 8
 ECON4150 - Introductory Econometrics Seminar 4 Stock and Watson Chapter 8 empirical exercise E8.2: Data 2 In this exercise we use the data set CPS12.dta Each month the Bureau of Labor Statistics in the
ECON4150 - Introductory Econometrics Seminar 4 Stock and Watson Chapter 8 empirical exercise E8.2: Data 2 In this exercise we use the data set CPS12.dta Each month the Bureau of Labor Statistics in the
Transport Data Analysis and Modeling Methodologies
 Transport Data Analysis and Modeling Methodologies Lab Session #14 (Discrete Data Latent Class Logit Analysis based on Example 13.1) In Example 13.1, you were given 151 observations of a travel survey
Transport Data Analysis and Modeling Methodologies Lab Session #14 (Discrete Data Latent Class Logit Analysis based on Example 13.1) In Example 13.1, you were given 151 observations of a travel survey
What is spatial transferability?
 Improving the spatial transferability of travel demand forecasting models: An empirical assessment of the impact of incorporatingattitudeson model transferability 1 Divyakant Tahlyan, Parvathy Vinod Sheela,
Improving the spatial transferability of travel demand forecasting models: An empirical assessment of the impact of incorporatingattitudeson model transferability 1 Divyakant Tahlyan, Parvathy Vinod Sheela,
Sport England: Understanding variations in sports participation between local authorities
 Sport England: Understanding variations in sports participation between local authorities August 2010 1 Background & Objectives 2009 The Futures Company Background Sport England is focused on the creation
Sport England: Understanding variations in sports participation between local authorities August 2010 1 Background & Objectives 2009 The Futures Company Background Sport England is focused on the creation
TEMPE CROSSING II - RETAIL PAD
 Excellent infill pad opportunity in dynamic retail corridor, 1 mi. East of I-10 Fully finished pad. Over $250,000 worth of site work already completed. Buildable up to 8,500 square feet. Excellent parking!
Excellent infill pad opportunity in dynamic retail corridor, 1 mi. East of I-10 Fully finished pad. Over $250,000 worth of site work already completed. Buildable up to 8,500 square feet. Excellent parking!
MATH 217 Test 2 Version A
 MATH 217 Test 2 Version A Name: KEY Sec Number: Answer all questions to the best of your ability. Note you should show as much work as is possible. For questions answered using Excel be sure to include
MATH 217 Test 2 Version A Name: KEY Sec Number: Answer all questions to the best of your ability. Note you should show as much work as is possible. For questions answered using Excel be sure to include
Tax Progressivity in Australia:
 Tax Progressivity in Australia: Facts, Measurements and Estimates (In Progress) Chung Tran Australian National University Nabeeh Zakariyya Australian National University Australian-Korean Tax and Welfare
Tax Progressivity in Australia: Facts, Measurements and Estimates (In Progress) Chung Tran Australian National University Nabeeh Zakariyya Australian National University Australian-Korean Tax and Welfare
COMMUNITY ADVANTAGE PANEL SURVEY: DATA COLLECTION UPDATE AND ANALYSIS OF PANEL ATTRITION
 COMMUNITY ADVANTAGE PANEL SURVEY: DATA COLLECTION UPDATE AND ANALYSIS OF PANEL ATTRITION Technical Report: March 2011 By Sarah Riley HongYu Ru Mark Lindblad Roberto Quercia Center for Community Capital
COMMUNITY ADVANTAGE PANEL SURVEY: DATA COLLECTION UPDATE AND ANALYSIS OF PANEL ATTRITION Technical Report: March 2011 By Sarah Riley HongYu Ru Mark Lindblad Roberto Quercia Center for Community Capital
Renters Report Future Home Buying Optimism, While Family Financial Assistance Is Most Available to Populations with Higher Homeownership Rates
 Renters Report Future Home Buying Optimism, While Family Financial Assistance Is Most Available to Populations with Higher Homeownership Rates National Housing Survey Topic Analysis Q3 2016 Published on
Renters Report Future Home Buying Optimism, While Family Financial Assistance Is Most Available to Populations with Higher Homeownership Rates National Housing Survey Topic Analysis Q3 2016 Published on
Exiting Poverty: Does Sex Matter?
 Exiting Poverty: Does Sex Matter? LORI CURTIS AND KATE RYBCZYNSKI DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO CRDCN WEBINAR MARCH 8, 2016 Motivation Women face higher risk of long term poverty.(finnie
Exiting Poverty: Does Sex Matter? LORI CURTIS AND KATE RYBCZYNSKI DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO CRDCN WEBINAR MARCH 8, 2016 Motivation Women face higher risk of long term poverty.(finnie
Valuing Environmental Impacts: Practical Guidelines for the Use of Value Transfer in Policy and Project Appraisal
 Valuing Environmental Impacts: Practical Guidelines for the Use of Value Transfer in Policy and Project Appraisal Annex 3 Glossary of Econometric Terminology Submitted to Department for Environment, Food
Valuing Environmental Impacts: Practical Guidelines for the Use of Value Transfer in Policy and Project Appraisal Annex 3 Glossary of Econometric Terminology Submitted to Department for Environment, Food
Choices for retirement income products and financial advice: Appendices
 Choices for retirement income products and financial advice: Appendices The role of the Financial Services Compensation Scheme Prepared for the Financial Services Compensation Scheme 18 January 2018 www.oxera.com
Choices for retirement income products and financial advice: Appendices The role of the Financial Services Compensation Scheme Prepared for the Financial Services Compensation Scheme 18 January 2018 www.oxera.com
COMMUNITY ADVANTAGE PANEL SURVEY: DATA COLLECTION UPDATE AND ANALYSIS OF PANEL ATTRITION
 COMMUNITY ADVANTAGE PANEL SURVEY: DATA COLLECTION UPDATE AND ANALYSIS OF PANEL ATTRITION Technical Report: February 2013 By Sarah Riley Qing Feng Mark Lindblad Roberto Quercia Center for Community Capital
COMMUNITY ADVANTAGE PANEL SURVEY: DATA COLLECTION UPDATE AND ANALYSIS OF PANEL ATTRITION Technical Report: February 2013 By Sarah Riley Qing Feng Mark Lindblad Roberto Quercia Center for Community Capital
Fall 2010 Fall 2011 Fall 2012 Fall 2013 Fall 2014 Fall 2015
 Employee Headcount by Employee Classification Group, s - 2010 through 2015 800 700 Number of Employees 600 500 400 300 200 100 0 Fall 2010 Fall 2011 Fall 2012 Fall 2013 Fall 2014 Fall 2015 Number of Employees
Employee Headcount by Employee Classification Group, s - 2010 through 2015 800 700 Number of Employees 600 500 400 300 200 100 0 Fall 2010 Fall 2011 Fall 2012 Fall 2013 Fall 2014 Fall 2015 Number of Employees
Transportation Research Board NHTS for Transportation Decision Making Washington D.C. June 6, 2011
 Transportation Research Board NHTS for Transportation Decision Making Washington D.C. June 6, 2011 To identify new or emerging travel behaviors, technologies and perspectives that may affect future travel
Transportation Research Board NHTS for Transportation Decision Making Washington D.C. June 6, 2011 To identify new or emerging travel behaviors, technologies and perspectives that may affect future travel
Supporting Information: Preferences for International Redistribution: The Divide over the Eurozone Bailouts
 Supporting Information: Preferences for International Redistribution: The Divide over the Eurozone Bailouts Michael M. Bechtel University of St.Gallen Jens Hainmueller Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Supporting Information: Preferences for International Redistribution: The Divide over the Eurozone Bailouts Michael M. Bechtel University of St.Gallen Jens Hainmueller Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Labor Supply and Taxation in Europe
 Labor Supply and Taxation in Europe Fabrizio Colonna - Banca d Italia Stefania Marcassa - Paris School of Economics November 16, 2010 Motivation Observe differences in Female Labor Force Participation
Labor Supply and Taxation in Europe Fabrizio Colonna - Banca d Italia Stefania Marcassa - Paris School of Economics November 16, 2010 Motivation Observe differences in Female Labor Force Participation
Estimating Consumer Price Inflation by Household
 Estimating Consumer Price Inflation by Household Jess Diamond Hitotsubashi University Kota Watanabe Meiji University Tsutomu Watanabe University of Tokyo Aim Of The Study Seek to shed light on 2 issues:
Estimating Consumer Price Inflation by Household Jess Diamond Hitotsubashi University Kota Watanabe Meiji University Tsutomu Watanabe University of Tokyo Aim Of The Study Seek to shed light on 2 issues:
Ram M. Pendyala and Karthik C. Konduri School of Sustainable Engineering and the Built Environment Arizona State University, Tempe
 Ram M. Pendyala and Karthik C. Konduri School of Sustainable Engineering and the Built Environment Arizona State University, Tempe Using Census Data for Transportation Applications Conference, Irvine,
Ram M. Pendyala and Karthik C. Konduri School of Sustainable Engineering and the Built Environment Arizona State University, Tempe Using Census Data for Transportation Applications Conference, Irvine,
COMMUNITY ADVANTAGE PANEL SURVEY: DATA COLLECTION UPDATE AND ANALYSIS OF PANEL ATTRITION
 COMMUNITY ADVANTAGE PANEL SURVEY: DATA COLLECTION UPDATE AND ANALYSIS OF PANEL ATTRITION Technical Report: February 2012 By Sarah Riley HongYu Ru Mark Lindblad Roberto Quercia Center for Community Capital
COMMUNITY ADVANTAGE PANEL SURVEY: DATA COLLECTION UPDATE AND ANALYSIS OF PANEL ATTRITION Technical Report: February 2012 By Sarah Riley HongYu Ru Mark Lindblad Roberto Quercia Center for Community Capital
Final Exam, section 1. Thursday, May hour, 30 minutes
 San Francisco State University Michael Bar ECON 312 Spring 2018 Final Exam, section 1 Thursday, May 17 1 hour, 30 minutes Name: Instructions 1. This is closed book, closed notes exam. 2. You can use one
San Francisco State University Michael Bar ECON 312 Spring 2018 Final Exam, section 1 Thursday, May 17 1 hour, 30 minutes Name: Instructions 1. This is closed book, closed notes exam. 2. You can use one
Final Exam, section 1. Tuesday, December hour, 30 minutes
 San Francisco State University Michael Bar ECON 312 Fall 2018 Final Exam, section 1 Tuesday, December 18 1 hour, 30 minutes Name: Instructions 1. This is closed book, closed notes exam. 2. You can use
San Francisco State University Michael Bar ECON 312 Fall 2018 Final Exam, section 1 Tuesday, December 18 1 hour, 30 minutes Name: Instructions 1. This is closed book, closed notes exam. 2. You can use
An overview of the financial profile fact finder
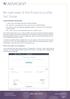 An overview of the financial profile fact finder Functions addressed in this document: A step-by-step walk through of the financial profile fact finder. How data entry is presented to the client within
An overview of the financial profile fact finder Functions addressed in this document: A step-by-step walk through of the financial profile fact finder. How data entry is presented to the client within
Supporting Information for:
 Supporting Information for: Can Political Participation Prevent Crime? Results from a Field Experiment about Citizenship, Participation, and Criminality This appendix contains the following material: Supplemental
Supporting Information for: Can Political Participation Prevent Crime? Results from a Field Experiment about Citizenship, Participation, and Criminality This appendix contains the following material: Supplemental
TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH BOARD. Changes in Demographics and Markets for Public Transportation. Wednesday, November 28, :00-3:30 PM ET
 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH BOARD Changes in Demographics and Markets for Public Transportation Wednesday, November 28, 2018 2:00-3:30 PM ET Purpose Discuss TCRP Report 201. Learning Objectives At the end
TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH BOARD Changes in Demographics and Markets for Public Transportation Wednesday, November 28, 2018 2:00-3:30 PM ET Purpose Discuss TCRP Report 201. Learning Objectives At the end
Are Old Age Workers Out of Luck? An Empirical Study of the U.S. Labor Market. Keith Brian Kline II Sreenath Majumder, PhD March 16, 2015
 Are Old Age Workers Out of Luck? An Empirical Study of the U.S. Labor Market Keith Brian Kline II Sreenath Majumder, PhD March 16, 2015 Are Old Age Workers Out of Luck? An Empirical Study of the U.S. Labor
Are Old Age Workers Out of Luck? An Empirical Study of the U.S. Labor Market Keith Brian Kline II Sreenath Majumder, PhD March 16, 2015 Are Old Age Workers Out of Luck? An Empirical Study of the U.S. Labor
THE CHORE WARS Household Bargaining and Leisure Time
 THE CHORE WARS Household Bargaining and Leisure Time Leora Friedberg University of Virginia and NBER Anthony Webb Center for Retirement Research, Boston College Motivation Can time use of spouses be explained
THE CHORE WARS Household Bargaining and Leisure Time Leora Friedberg University of Virginia and NBER Anthony Webb Center for Retirement Research, Boston College Motivation Can time use of spouses be explained
Chapter 10 Equity and Environmental Justice
 Chapter 10 Equity and Environmental Justice Introduction An important consideration for the 2040 Transportation Policy Plan is its impact on all populations in the Minneapolis-Saint Paul region, particularly
Chapter 10 Equity and Environmental Justice Introduction An important consideration for the 2040 Transportation Policy Plan is its impact on all populations in the Minneapolis-Saint Paul region, particularly
For Lease. Free-standing Retail / Office Building 1304 Saratoga Avenue San Jose, CA
 For Lease Free-standing Retail / Office Building 1304 Saratoga Avenue San Jose, CA 95117 Description Approximately 4,500 sf plus mezzanine Outstanding identity and visibility In neighborhood shopping center
For Lease Free-standing Retail / Office Building 1304 Saratoga Avenue San Jose, CA 95117 Description Approximately 4,500 sf plus mezzanine Outstanding identity and visibility In neighborhood shopping center
Modeling of Shopping Participation and Duration of Workers in Calicut
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Scienc es 104 ( 2013 ) 543 552 2 nd Conference of Transportation Research Group of India (2nd CTRG) Modeling of
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Scienc es 104 ( 2013 ) 543 552 2 nd Conference of Transportation Research Group of India (2nd CTRG) Modeling of
Nonlinear Econometric Analysis (ECO 722) Answers to Homework 4
 Nonlinear Econometric Analysis (ECO 722) Answers to Homework 4 1 Greene and Hensher (1997) report estimates of a model of travel mode choice for travel between Sydney and Melbourne, Australia The dataset
Nonlinear Econometric Analysis (ECO 722) Answers to Homework 4 1 Greene and Hensher (1997) report estimates of a model of travel mode choice for travel between Sydney and Melbourne, Australia The dataset
Allison notes there are two conditions for using fixed effects methods.
 Panel Data 3: Conditional Logit/ Fixed Effects Logit Models Richard Williams, University of Notre Dame, http://www3.nd.edu/~rwilliam/ Last revised April 2, 2017 These notes borrow very heavily, sometimes
Panel Data 3: Conditional Logit/ Fixed Effects Logit Models Richard Williams, University of Notre Dame, http://www3.nd.edu/~rwilliam/ Last revised April 2, 2017 These notes borrow very heavily, sometimes
Changes in Economic Mobility
 December 11 Changes in Economic Mobility Lin Xia SM 222 Prof. Shulamit Kahn Xia 2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Over years, income inequality has been one of the most continuously controversial topics. Most recent
December 11 Changes in Economic Mobility Lin Xia SM 222 Prof. Shulamit Kahn Xia 2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Over years, income inequality has been one of the most continuously controversial topics. Most recent
Exiting poverty : Does gender matter?
 CRDCN Webinar Series Exiting poverty : Does gender matter? with Lori J. Curtis and Kathleen Rybczynski March 8, 2016 1 The Canadian Research Data Centre Network 1) Improve access to Statistics Canada detailed
CRDCN Webinar Series Exiting poverty : Does gender matter? with Lori J. Curtis and Kathleen Rybczynski March 8, 2016 1 The Canadian Research Data Centre Network 1) Improve access to Statistics Canada detailed
PASS Sample Size Software
 Chapter 850 Introduction Cox proportional hazards regression models the relationship between the hazard function λ( t X ) time and k covariates using the following formula λ log λ ( t X ) ( t) 0 = β1 X1
Chapter 850 Introduction Cox proportional hazards regression models the relationship between the hazard function λ( t X ) time and k covariates using the following formula λ log λ ( t X ) ( t) 0 = β1 X1
Supplement to: Martin, Isaac W., and Jennifer M. Nations Taxation and Citizen Voice in School District Parcel Tax Elections.
 Supplement to: Martin, Isaac W., and Jennifer M. Nations. 2018. Taxation and Citizen Voice in School District Parcel Tax Elections. Sociological Science 5: 653-668. S1 Appendix to in School District Parcel
Supplement to: Martin, Isaac W., and Jennifer M. Nations. 2018. Taxation and Citizen Voice in School District Parcel Tax Elections. Sociological Science 5: 653-668. S1 Appendix to in School District Parcel
NEIGHBORHOOD REPORT. Kendall, Florida. Presented by Lynda Fernandez
 NEIGHBORHOOD REPORT, Florida Presented by Lynda Fernandez , Florida Neighborhood: Housing Stats and Charts Miami-Dade County Florida USA Median Estimated Home Value $187K $291K $222K $222K Estimated Home
NEIGHBORHOOD REPORT, Florida Presented by Lynda Fernandez , Florida Neighborhood: Housing Stats and Charts Miami-Dade County Florida USA Median Estimated Home Value $187K $291K $222K $222K Estimated Home
P = The model satisfied the Luce s axiom of independence of irrelevant alternatives (IIA) which can be stated as
 1.4 Multinomial logit model The multinomial logit model calculates the probability of choosing mode. The multinomial logit model is of the following form and the probability of using mode I, p is given
1.4 Multinomial logit model The multinomial logit model calculates the probability of choosing mode. The multinomial logit model is of the following form and the probability of using mode I, p is given
Financial Risk Tolerance and the influence of Socio-demographic Characteristics of Retail Investors
 Financial Risk Tolerance and the influence of Socio-demographic Characteristics of Retail Investors * Ms. R. Suyam Praba Abstract Risk is inevitable in human life. Every investor takes considerable amount
Financial Risk Tolerance and the influence of Socio-demographic Characteristics of Retail Investors * Ms. R. Suyam Praba Abstract Risk is inevitable in human life. Every investor takes considerable amount
Transportation Theory and Applications
 Fall 2017 - MTAT.08.043 Transportation Theory and Applications Lecture III: Trip Generation Modelling A. Hadachi Definitions Trip or Journey: is a one-way movement from origin to destination. Home-based
Fall 2017 - MTAT.08.043 Transportation Theory and Applications Lecture III: Trip Generation Modelling A. Hadachi Definitions Trip or Journey: is a one-way movement from origin to destination. Home-based
Final Exam - section 1. Thursday, December hours, 30 minutes
 Econometrics, ECON312 San Francisco State University Michael Bar Fall 2013 Final Exam - section 1 Thursday, December 19 1 hours, 30 minutes Name: Instructions 1. This is closed book, closed notes exam.
Econometrics, ECON312 San Francisco State University Michael Bar Fall 2013 Final Exam - section 1 Thursday, December 19 1 hours, 30 minutes Name: Instructions 1. This is closed book, closed notes exam.
The Role of Exponential-Growth Bias and Present Bias in Retirment Saving Decisions
 The Role of Exponential-Growth Bias and Present Bias in Retirment Saving Decisions Gopi Shah Goda Stanford University & NBER Matthew Levy London School of Economics Colleen Flaherty Manchester University
The Role of Exponential-Growth Bias and Present Bias in Retirment Saving Decisions Gopi Shah Goda Stanford University & NBER Matthew Levy London School of Economics Colleen Flaherty Manchester University
An Examination of the Impact of the Texas Methodist Foundation Clergy Development Program. on the United Methodist Church in Texas
 An Examination of the Impact of the Texas Methodist Foundation Clergy Development Program on the United Methodist Church in Texas The Texas Methodist Foundation completed its first, two-year Clergy Development
An Examination of the Impact of the Texas Methodist Foundation Clergy Development Program on the United Methodist Church in Texas The Texas Methodist Foundation completed its first, two-year Clergy Development
99TH AVENUE AND GLENDALE AVENUE
 N ATHAN & A SSOCIATES, I NC. 7600 East Doubletree Ranch Road Suite #150 Scottsdale Arizona 85258 Phone: 480.367.0700 Fax: 480.367.8341 www.nathanandassociatesinc.com 99TH AVENUE AND GLENDALE AVENUE S URROUNDING
N ATHAN & A SSOCIATES, I NC. 7600 East Doubletree Ranch Road Suite #150 Scottsdale Arizona 85258 Phone: 480.367.0700 Fax: 480.367.8341 www.nathanandassociatesinc.com 99TH AVENUE AND GLENDALE AVENUE S URROUNDING
Logit with multiple alternatives
 Logit with multiple alternatives Matthieu de Lapparent matthieu.delapparent@epfl.ch Transport and Mobility Laboratory, School of Architecture, Civil and Environmental Engineering, Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale
Logit with multiple alternatives Matthieu de Lapparent matthieu.delapparent@epfl.ch Transport and Mobility Laboratory, School of Architecture, Civil and Environmental Engineering, Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale
What is the Level of Volatility in Instantaneous Driving Decisions?
 Transportation for Livability by Integrating Vehicles, Drivers and the Environment: What is the Level of Volatility in Instantaneous Driving Decisions? Asad Khattak, Ph.D. Beaman Professor of CEE, University
Transportation for Livability by Integrating Vehicles, Drivers and the Environment: What is the Level of Volatility in Instantaneous Driving Decisions? Asad Khattak, Ph.D. Beaman Professor of CEE, University
Ethnicity (optional) Hispanic Not Hispanic. Full-time at home parent Student Unemployed
 LIVE ON Organ Donation, Inc. (LIVE ON) provides financial assistance to living organ donors and their recipients in the form of grants to defray non-medical unavoidable costs that arise during the living
LIVE ON Organ Donation, Inc. (LIVE ON) provides financial assistance to living organ donors and their recipients in the form of grants to defray non-medical unavoidable costs that arise during the living
Risk Tolerance Profile of Cash-Value Life Insurance Owners
 Risk Tolerance Profile of Cash-Value Life Insurance Owners Abed Rabbani, University of Missouri 1 Zheying Yao, University of Missouri 2 Abstract Life insurance, a risk management tool, generally provides
Risk Tolerance Profile of Cash-Value Life Insurance Owners Abed Rabbani, University of Missouri 1 Zheying Yao, University of Missouri 2 Abstract Life insurance, a risk management tool, generally provides
Beliefs in Technology and Support for Environmental Taxes: An Empirical Investigation
 Beliefs in Technology and Support for Environmental Taxes: An Empirical Investigation Estefania Santacreu-Vasut and Jose Vives-Rego ESSEC Business School and THEMA France; Universitat de Barcelona 29/01/2015
Beliefs in Technology and Support for Environmental Taxes: An Empirical Investigation Estefania Santacreu-Vasut and Jose Vives-Rego ESSEC Business School and THEMA France; Universitat de Barcelona 29/01/2015
Violence, Non-violence, and the Effects of International Human Rights Law. Supplemental Information
 Violence, Non-violence, and the Effects of International Human Rights Law Supplemental Information Yonatan Lupu Department of Political Science, George Washington University Monroe Hall, Room 417, 2115
Violence, Non-violence, and the Effects of International Human Rights Law Supplemental Information Yonatan Lupu Department of Political Science, George Washington University Monroe Hall, Room 417, 2115
Appendix 18f: Fineline Social Tariff Research
 Appendix 18f: Fineline Social Tariff Research fineline market research Bridging the gap between you and your customers Social Tariffs Research Research Findings Contents Background & objectives Methodology
Appendix 18f: Fineline Social Tariff Research fineline market research Bridging the gap between you and your customers Social Tariffs Research Research Findings Contents Background & objectives Methodology
Itasca County Wellness Court Evaluation
 Itasca County A U G U S T 2 0 1 5 Prepared by: Laura Schauben 451 Lexington Parkway North Saint Paul, Minnesota 55104 651-280-2700 www.wilderresearch.org Wilder Research Information. Insight. Impact. Contents
Itasca County A U G U S T 2 0 1 5 Prepared by: Laura Schauben 451 Lexington Parkway North Saint Paul, Minnesota 55104 651-280-2700 www.wilderresearch.org Wilder Research Information. Insight. Impact. Contents
Table 4. Probit model of union membership. Probit coefficients are presented below. Data from March 2008 Current Population Survey.
 1. Using a probit model and data from the 2008 March Current Population Survey, I estimated a probit model of the determinants of pension coverage. Three specifications were estimated. The first included
1. Using a probit model and data from the 2008 March Current Population Survey, I estimated a probit model of the determinants of pension coverage. Three specifications were estimated. The first included
Puget Sound 4K Model Version Draft Model Documentation
 Puget Sound 4K Model Version 4.0.3 Draft Model Documentation Prepared by: Puget Sound Regional Council Staff June 2015 1 Table of Contents Trip Generation 9 1.0 Introduction 9 Changes made with Puget Sound
Puget Sound 4K Model Version 4.0.3 Draft Model Documentation Prepared by: Puget Sound Regional Council Staff June 2015 1 Table of Contents Trip Generation 9 1.0 Introduction 9 Changes made with Puget Sound
Labor Force Participation and the Wage Gap Detailed Notes and Code Econometrics 113 Spring 2014
 Labor Force Participation and the Wage Gap Detailed Notes and Code Econometrics 113 Spring 2014 In class, Lecture 11, we used a new dataset to examine labor force participation and wages across groups.
Labor Force Participation and the Wage Gap Detailed Notes and Code Econometrics 113 Spring 2014 In class, Lecture 11, we used a new dataset to examine labor force participation and wages across groups.
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 602894 Central Cities (CC) 227,818 Outside Central Cities 375,076 Percent of Entire MSA 37.79% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 602894 Central Cities (CC) 227,818 Outside Central Cities 375,076 Percent of Entire MSA 37.79% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1187941 Central Cities (CC) 511,843 Outside Central Cities 676,098 Percent of Entire MSA 43.09% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1187941 Central Cities (CC) 511,843 Outside Central Cities 676,098 Percent of Entire MSA 43.09% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 661645 Central Cities (CC) 247,057 Outside Central Cities 414,588 Percent of Entire MSA 37.34% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 661645 Central Cities (CC) 247,057 Outside Central Cities 414,588 Percent of Entire MSA 37.34% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 583845 Central Cities (CC) 316,649 Outside Central Cities 267,196 Percent of Entire MSA 54.24% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 583845 Central Cities (CC) 316,649 Outside Central Cities 267,196 Percent of Entire MSA 54.24% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1251509 Central Cities (CC) 540,423 Outside Central Cities 711,086 Percent of Entire MSA 43.18% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1251509 Central Cities (CC) 540,423 Outside Central Cities 711,086 Percent of Entire MSA 43.18% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1135614 Central Cities (CC) 677,766 Outside Central Cities 457,848 Percent of Entire MSA 59.68% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1135614 Central Cities (CC) 677,766 Outside Central Cities 457,848 Percent of Entire MSA 59.68% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 591932 Central Cities (CC) 260,970 Outside Central Cities 330,962 Percent of Entire MSA 44.09% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 591932 Central Cities (CC) 260,970 Outside Central Cities 330,962 Percent of Entire MSA 44.09% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1100491 Central Cities (CC) 735,617 Outside Central Cities 364,874 Percent of Entire MSA 66.84% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1100491 Central Cities (CC) 735,617 Outside Central Cities 364,874 Percent of Entire MSA 66.84% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 540258 Central Cities (CC) 198,915 Outside Central Cities 341,343 Percent of Entire MSA 36.82% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 540258 Central Cities (CC) 198,915 Outside Central Cities 341,343 Percent of Entire MSA 36.82% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1249763 Central Cities (CC) 691,295 Outside Central Cities 558,468 Percent of Entire MSA 55.31% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1249763 Central Cities (CC) 691,295 Outside Central Cities 558,468 Percent of Entire MSA 55.31% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1088514 Central Cities (CC) 272,953 Outside Central Cities 815,561 Percent of Entire MSA 25.08% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1088514 Central Cities (CC) 272,953 Outside Central Cities 815,561 Percent of Entire MSA 25.08% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 922516 Central Cities (CC) 470,859 Outside Central Cities 451,657 Percent of Entire MSA 51.04% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 922516 Central Cities (CC) 470,859 Outside Central Cities 451,657 Percent of Entire MSA 51.04% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 687249 Central Cities (CC) 198,500 Outside Central Cities 488,749 Percent of Entire MSA 28.88% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 687249 Central Cities (CC) 198,500 Outside Central Cities 488,749 Percent of Entire MSA 28.88% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 542149 Central Cities (CC) 181870 Outside Central Cities 360279 Percent of Entire MSA 33.55% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 542149 Central Cities (CC) 181870 Outside Central Cities 360279 Percent of Entire MSA 33.55% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1025598 Central Cities (CC) 293,834 Outside Central Cities 731,764 Percent of Entire MSA 28.65% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1025598 Central Cities (CC) 293,834 Outside Central Cities 731,764 Percent of Entire MSA 28.65% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 875583 Central Cities (CC) 232,835 Outside Central Cities 642,748 Percent of Entire MSA 26.59% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 875583 Central Cities (CC) 232,835 Outside Central Cities 642,748 Percent of Entire MSA 26.59% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 716998 Central Cities (CC) 448,275 Outside Central Cities 268,723 Percent of Entire MSA 62.52% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 716998 Central Cities (CC) 448,275 Outside Central Cities 268,723 Percent of Entire MSA 62.52% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1333914 Central Cities (CC) 284,943 Outside Central Cities 1,048,971 Percent of Entire MSA 21.36% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1333914 Central Cities (CC) 284,943 Outside Central Cities 1,048,971 Percent of Entire MSA 21.36% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 712738 Central Cities (CC) 448,607 Outside Central Cities 264,131 Percent of Entire MSA 62.94% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 712738 Central Cities (CC) 448,607 Outside Central Cities 264,131 Percent of Entire MSA 62.94% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean. Population Entire MSA
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1169641 Central Cities (CC) 0 Outside Central Cities 1,169,641 Percent of Entire MSA 0% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999 to
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1169641 Central Cities (CC) 0 Outside Central Cities 1,169,641 Percent of Entire MSA 0% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999 to
Millennial Money Mindset Report
 Millennial Money Mindset Report 2017 In Partnership with: Data Analysis support by Executive Summary 2017 Millennial Money Mindset Report Previous studies have shown that the expectations of Millennials
Millennial Money Mindset Report 2017 In Partnership with: Data Analysis support by Executive Summary 2017 Millennial Money Mindset Report Previous studies have shown that the expectations of Millennials
Appendix C: Econometric Analyses of IFC and World Bank SME Lending Projects: Drivers of Successful Development Outcomes
 Appendix C: Econometric Analyses of IFC and World Bank SME Lending Projects: Drivers of Successful Development Outcomes IFC Investments RESEARCH QUESTIONS Do project characteristics matter in the development
Appendix C: Econometric Analyses of IFC and World Bank SME Lending Projects: Drivers of Successful Development Outcomes IFC Investments RESEARCH QUESTIONS Do project characteristics matter in the development
Recreational marijuana and collision claim frequencies
 Highway Loss Data Institute Bulletin Vol. 34, No. 14 : April 2017 Recreational marijuana and collision claim frequencies Summary Colorado was the first state to legalize recreational marijuana for adults
Highway Loss Data Institute Bulletin Vol. 34, No. 14 : April 2017 Recreational marijuana and collision claim frequencies Summary Colorado was the first state to legalize recreational marijuana for adults
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 3251876 Central Cities (CC) 2,078,750 Outside Central Cities 1,173,126 Percent of Entire MSA 63.92% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 3251876 Central Cities (CC) 2,078,750 Outside Central Cities 1,173,126 Percent of Entire MSA 63.92% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1592383 Central Cities (CC) 1,181,140 Outside Central Cities 411,243 Percent of Entire MSA 74.17% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1592383 Central Cities (CC) 1,181,140 Outside Central Cities 411,243 Percent of Entire MSA 74.17% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1776062 Central Cities (CC) 716,793 Outside Central Cities 1,059,269 Percent of Entire MSA 40.36% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1776062 Central Cities (CC) 716,793 Outside Central Cities 1,059,269 Percent of Entire MSA 40.36% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 4112198 Central Cities (CC) 416,474 Outside Central Cities 3,695,724 Percent of Entire MSA 10.13% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 4112198 Central Cities (CC) 416,474 Outside Central Cities 3,695,724 Percent of Entire MSA 10.13% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 9519338 Central Cities (CC) 4408996 Outside Central Cities 5110342 Percent of Entire MSA 46.32% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 9519338 Central Cities (CC) 4408996 Outside Central Cities 5110342 Percent of Entire MSA 46.32% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1623018 Central Cities (CC) 152397 Outside Central Cities 1470621 Percent of Entire MSA 9.39% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1623018 Central Cities (CC) 152397 Outside Central Cities 1470621 Percent of Entire MSA 9.39% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1731183 Central Cities (CC) 776733 Outside Central Cities 954450 Percent of Entire MSA 44.87% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1731183 Central Cities (CC) 776733 Outside Central Cities 954450 Percent of Entire MSA 44.87% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 2968806 Central Cities (CC) 669,769 Outside Central Cities 2,299,037 Percent of Entire MSA 22.56% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 2968806 Central Cities (CC) 669,769 Outside Central Cities 2,299,037 Percent of Entire MSA 22.56% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 2846289 Central Cities (CC) 809063 Outside Central Cities 2037226 Percent of Entire MSA 28.43% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 2846289 Central Cities (CC) 809063 Outside Central Cities 2037226 Percent of Entire MSA 28.43% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 4441551 Central Cities (CC) 1147720 Outside Central Cities 3293831 Percent of Entire MSA 25.84% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 4441551 Central Cities (CC) 1147720 Outside Central Cities 3293831 Percent of Entire MSA 25.84% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from
SDs from Regional Peer Group Mean. SDs from Size Peer Group Mean
 Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1500741 Central Cities (CC) 661799 Outside Central Cities 838942 Percent of Entire MSA 44.1% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
Family: Population Demographics Population Entire MSA 1500741 Central Cities (CC) 661799 Outside Central Cities 838942 Percent of Entire MSA 44.1% Population in CC Percent Change in Population from 1999
