Binomial and Normal Distributions. Example: Determine whether the following experiments are binomial experiments. Explain.
|
|
|
- Stuart Carroll
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Binomial and Normal Distributions Objective 1: Determining if an Experiment is a Binomial Experiment For an experiment to be considered a binomial experiment, four things must hold: 1. The experiment is performed for a fixed number of trials. (We let n denote the number of trials.) 2. The trials are independent. 3. For each trial, there are only two mutually exclusive outcomes (success and failure). 4. The probability of success is the same for each trial. (We let p denote the probability of success.) Example: Determine whether the following experiments are binomial experiments. Explain. (a) According to a recent study, 33% of Americans, 23 years or older, have been arrested. A random sample of 500 Americans, 23 years or older, are asked whether or not they have been arrested. (b) Mary is at the fair, playing pop the balloon with 6 darts. There are 20 balloons total, 15 which say LOSE and 5 which say WIN. (c) Bob flips a coin until the coin lands on heads. 1
2 Objective 2: Calculating Probabilities for a Binomial Distribution You can use this table to help you calculate probabilities for binomial distributions. Phrase Math Symbol Calculator Example exactly, equals, is P(X = x) binompdf(n, p, x) exactly 5 P X = 5 = binompdf n, p, 5 between a and b, inclusive P(a X b) binompdf n, p, a + + binompdf n, p, b OR binomcdf n, p, b binomcdf(n, p, a 1) between 6 and 8, inclusive P 6 X 8 = binompdf n, p, 6 + binompdf n, p, 7 + binompdf(n, p, 8) OR between 5 and 12, inclusive P 5 X 12 = binomcdf n, p, 12 binomcdf n, p, 4 no more than, at most P(X x) binomcdf(n, p, x) no more than 5 P X 5 = binomcdf(n, p, 5) fewer than, less than P(X < x) binomcdf(n, p, x 1) fewer than 5 P X < 5 = binomcdf(n, p, 4) at least, no less than P(X x) 1 binomcdf(n, p, x 1) at least 7 P X 7 = 1 binomcdf(n, p, 6) more than, greater than P(X > x) 1 binomcdf(n, p, x) more than 7 P X > 7 = 1 binomcdf(n, p, 7) n = number of trials p = probability of success x = number of success To get to either binompdf or binomcdf in your calculator, press find either binompdf or binomcdf. and scroll up until you 2
3 Example: A study was done which stated that 41% of Americans only have a cell-phone in their house (no landline). What is the probability that in a random sample of 50 American households, that exactly 20 only have a cell-phone? TI-83 Screen TI-84 Screen binompdf(50,0.41, 20) Example: According to a recent article, 38% of buses in Chicago arrive on time. A random sample of 30 Chicago buses is taken. (a) In a random sample of 30 Chicago buses, what is the probability that less than 10 arrive on time? (b) In a random sample of 30 Chicago buses, what is the probability that exactly 17 arrive on time? 3
4 (c) In a random sample of 30 Chicago buses, what is the probability that at least 12 arrive on time? (d) In a random sample of 30 Chicago buses, what is the probability that between 5 and 7, inclusive, arrive on time? P between 5 and 7, inclusive = P between 5 and 7, inclusive = 4
5 Objective 3: Finding Probabilities, Percents, or Proportions Using Normalcdf Procedure: To find a probability, percent, or proportion for a normal distribution Step 1: Draw the normal curve (optional). Step 2: Calculate any z-scores using the formula z =!!!!. Step 3: Find the probability using normalcdf and entering in the lower bound and upper bound. (To get to normalcdf in your calculator press and select normalcdf.) If you have a TI-84, the following menu will appear. You will type your lower bound under lower and the upper bound under upper. Keep the mean, μ, at 0 and the standard deviation, σ, at 1. Example: The weight of an American male is normally distributed with a mean of 199 pounds and a standard deviation of 15 pounds. (a) What is the probability that a randomly selected American male will weigh less than 215 pounds? 5
6 Example (continued): The weight of an American male is normally distributed with a mean of 199 pounds and a standard deviation of 15 pounds. (b) What percent of American males weigh more than 185 pounds? (c) What proportion of American males weigh between 150 and 175 pounds? 6
7 Objective 4: Finding the Value of a Normal Random Variable Using InvNorm Procedure: To find a probability, percent, or proportion for a normal distribution Step 1: Draw the normal curve (optional). Step 2: Find any z-scores by using invnorm and entering in the area to the LEFT of the value you are trying to find. (To get to invnorm in your calculator press and select invnorm.) If you have a TI-84, the following menu will appear. You will type in the area to the left under area and keep the mean, μ, at 0 and the standard deviation, σ, at 1. Step 3: Find the value of your random variable, x, by using the formula x = μ + zσ. Example: The weight of an American male is normally distributed with a mean of 199 pounds and a standard deviation of 15 pounds. (a) Determine the 75 th percentile for the weight of American males. (b) Determine the weights that make up the middle 80% of weights for American males. 7
5.1 Sampling Distributions for Counts and Proportions. Ulrich Hoensch MAT210 Rocky Mountain College Billings, MT 59102
 5.1 Sampling Distributions for Counts and Proportions Ulrich Hoensch MAT210 Rocky Mountain College Billings, MT 59102 Sampling and Population Distributions Example: Count of People with Bachelor s Degrees
5.1 Sampling Distributions for Counts and Proportions Ulrich Hoensch MAT210 Rocky Mountain College Billings, MT 59102 Sampling and Population Distributions Example: Count of People with Bachelor s Degrees
Section 8.4 The Binomial Distribution
 Section 8.4 The Binomial Distribution Binomial Experiment A binomial experiment has the following properties: 1. The number of trials in the experiment is fixed. 2. There are two outcomes of each trial:
Section 8.4 The Binomial Distribution Binomial Experiment A binomial experiment has the following properties: 1. The number of trials in the experiment is fixed. 2. There are two outcomes of each trial:
Discrete Random Variables and Their Probability Distributions
 Chapter 5 Discrete Random Variables and Their Probability Distributions Mean and Standard Deviation of a Discrete Random Variable Computing the mean and standard deviation of a discrete random variable
Chapter 5 Discrete Random Variables and Their Probability Distributions Mean and Standard Deviation of a Discrete Random Variable Computing the mean and standard deviation of a discrete random variable
The Binomial and Geometric Distributions. Chapter 8
 The Binomial and Geometric Distributions Chapter 8 8.1 The Binomial Distribution A binomial experiment is statistical experiment that has the following properties: The experiment consists of n repeated
The Binomial and Geometric Distributions Chapter 8 8.1 The Binomial Distribution A binomial experiment is statistical experiment that has the following properties: The experiment consists of n repeated
CH 5 Normal Probability Distributions Properties of the Normal Distribution
 Properties of the Normal Distribution Example A friend that is always late. Let X represent the amount of minutes that pass from the moment you are suppose to meet your friend until the moment your friend
Properties of the Normal Distribution Example A friend that is always late. Let X represent the amount of minutes that pass from the moment you are suppose to meet your friend until the moment your friend
Chapter 5 Probability Distributions. Section 5-2 Random Variables. Random Variable Probability Distribution. Discrete and Continuous Random Variables
 Chapter 5 Probability Distributions Section 5-2 Random Variables 5-2 Random Variables 5-3 Binomial Probability Distributions 5-4 Mean, Variance and Standard Deviation for the Binomial Distribution Random
Chapter 5 Probability Distributions Section 5-2 Random Variables 5-2 Random Variables 5-3 Binomial Probability Distributions 5-4 Mean, Variance and Standard Deviation for the Binomial Distribution Random
AP Statistics Ch 8 The Binomial and Geometric Distributions
 Ch 8.1 The Binomial Distributions The Binomial Setting A situation where these four conditions are satisfied is called a binomial setting. 1. Each observation falls into one of just two categories, which
Ch 8.1 The Binomial Distributions The Binomial Setting A situation where these four conditions are satisfied is called a binomial setting. 1. Each observation falls into one of just two categories, which
Week 7. Texas A& M University. Department of Mathematics Texas A& M University, College Station Section 3.2, 3.3 and 3.4
 Week 7 Oğuz Gezmiş Texas A& M University Department of Mathematics Texas A& M University, College Station Section 3.2, 3.3 and 3.4 Oğuz Gezmiş (TAMU) Topics in Contemporary Mathematics II Week7 1 / 19
Week 7 Oğuz Gezmiş Texas A& M University Department of Mathematics Texas A& M University, College Station Section 3.2, 3.3 and 3.4 Oğuz Gezmiş (TAMU) Topics in Contemporary Mathematics II Week7 1 / 19
Chapter 6: Discrete Probability Distributions
 120C-Choi-Spring-2019 1 Chapter 6: Discrete Probability Distributions Section 6.1: Discrete Random Variables... p. 2 Section 6.2: The Binomial Probability Distribution... p. 10 The notes are based on Statistics:
120C-Choi-Spring-2019 1 Chapter 6: Discrete Probability Distributions Section 6.1: Discrete Random Variables... p. 2 Section 6.2: The Binomial Probability Distribution... p. 10 The notes are based on Statistics:
Chapter 6: Random Variables. Ch. 6-3: Binomial and Geometric Random Variables
 Chapter : Random Variables Ch. -3: Binomial and Geometric Random Variables X 0 2 3 4 5 7 8 9 0 0 P(X) 3???????? 4 4 When the same chance process is repeated several times, we are often interested in whether
Chapter : Random Variables Ch. -3: Binomial and Geometric Random Variables X 0 2 3 4 5 7 8 9 0 0 P(X) 3???????? 4 4 When the same chance process is repeated several times, we are often interested in whether
Statistics (This summary is for chapters 18, 29 and section H of chapter 19)
 Statistics (This summary is for chapters 18, 29 and section H of chapter 19) Mean, Median, Mode Mode: most common value Median: middle value (when the values are in order) Mean = total how many = x n =
Statistics (This summary is for chapters 18, 29 and section H of chapter 19) Mean, Median, Mode Mode: most common value Median: middle value (when the values are in order) Mean = total how many = x n =
Chapter 8. Binomial and Geometric Distributions
 Chapter 8 Binomial and Geometric Distributions Lesson 8-1, Part 1 Binomial Distribution What is a Binomial Distribution? Specific type of discrete probability distribution The outcomes belong to two categories
Chapter 8 Binomial and Geometric Distributions Lesson 8-1, Part 1 Binomial Distribution What is a Binomial Distribution? Specific type of discrete probability distribution The outcomes belong to two categories
Section Random Variables
 Section 6.2 - Random Variables According to the Bureau of the Census, the latest family data pertaining to family size for a small midwestern town, Nomore, is shown in Table 6.. If a family from this town
Section 6.2 - Random Variables According to the Bureau of the Census, the latest family data pertaining to family size for a small midwestern town, Nomore, is shown in Table 6.. If a family from this town
Chapter 7 1. Random Variables
 Chapter 7 1 Random Variables random variable numerical variable whose value depends on the outcome of a chance experiment - discrete if its possible values are isolated points on a number line - continuous
Chapter 7 1 Random Variables random variable numerical variable whose value depends on the outcome of a chance experiment - discrete if its possible values are isolated points on a number line - continuous
Using the Central Limit Theorem It is important for you to understand when to use the CLT. If you are being asked to find the probability of the
 Using the Central Limit Theorem It is important for you to understand when to use the CLT. If you are being asked to find the probability of the mean, use the CLT for the mean. If you are being asked to
Using the Central Limit Theorem It is important for you to understand when to use the CLT. If you are being asked to find the probability of the mean, use the CLT for the mean. If you are being asked to
Chapter 4 and 5 Note Guide: Probability Distributions
 Chapter 4 and 5 Note Guide: Probability Distributions Probability Distributions for a Discrete Random Variable A discrete probability distribution function has two characteristics: Each probability is
Chapter 4 and 5 Note Guide: Probability Distributions Probability Distributions for a Discrete Random Variable A discrete probability distribution function has two characteristics: Each probability is
The Normal Probability Distribution
 102 The Normal Probability Distribution C H A P T E R 7 Section 7.2 4Example 1 (pg. 71) Finding Area Under a Normal Curve In this exercise, we will calculate the area to the left of 5 inches using a normal
102 The Normal Probability Distribution C H A P T E R 7 Section 7.2 4Example 1 (pg. 71) Finding Area Under a Normal Curve In this exercise, we will calculate the area to the left of 5 inches using a normal
Discrete Probability Distributions
 Page 1 of 6 Discrete Probability Distributions In order to study inferential statistics, we need to combine the concepts from descriptive statistics and probability. This combination makes up the basics
Page 1 of 6 Discrete Probability Distributions In order to study inferential statistics, we need to combine the concepts from descriptive statistics and probability. This combination makes up the basics
Statistics (This summary is for chapters 17, 28, 29 and section G of chapter 19)
 Statistics (This summary is for chapters 17, 28, 29 and section G of chapter 19) Mean, Median, Mode Mode: most common value Median: middle value (when the values are in order) Mean = total how many = x
Statistics (This summary is for chapters 17, 28, 29 and section G of chapter 19) Mean, Median, Mode Mode: most common value Median: middle value (when the values are in order) Mean = total how many = x
Binomial Distributions
 Binomial Distributions Conditions for a Binomial Distribution: [Memorize this!] There are n trials or repetitions There are 2 outcomes for each trial, S or F The P(Success), P, for each trial is constant.
Binomial Distributions Conditions for a Binomial Distribution: [Memorize this!] There are n trials or repetitions There are 2 outcomes for each trial, S or F The P(Success), P, for each trial is constant.
Data that can be any numerical value are called continuous. These are usually things that are measured, such as height, length, time, speed, etc.
 Chapter 8 Measures of Center Data that can be any numerical value are called continuous. These are usually things that are measured, such as height, length, time, speed, etc. Data that can only be integer
Chapter 8 Measures of Center Data that can be any numerical value are called continuous. These are usually things that are measured, such as height, length, time, speed, etc. Data that can only be integer
Section 8.4 The Binomial Distribution
 Section 84 The Binomial Distribution Binomial Experiment A binomial experiment has the following properties: 1 The number of trials in the experiment is fixed 2 There are two outcomes of each trial: success
Section 84 The Binomial Distribution Binomial Experiment A binomial experiment has the following properties: 1 The number of trials in the experiment is fixed 2 There are two outcomes of each trial: success
Chapter 8: The Binomial and Geometric Distributions
 Chapter 8: The Binomial and Geometric Distributions 8.1 Binomial Distributions 8.2 Geometric Distributions 1 Let me begin with an example My best friends from Kent School had three daughters. What is the
Chapter 8: The Binomial and Geometric Distributions 8.1 Binomial Distributions 8.2 Geometric Distributions 1 Let me begin with an example My best friends from Kent School had three daughters. What is the
5.2 Random Variables, Probability Histograms and Probability Distributions
 Chapter 5 5.2 Random Variables, Probability Histograms and Probability Distributions A random variable (r.v.) can be either continuous or discrete. It takes on the possible values of an experiment. It
Chapter 5 5.2 Random Variables, Probability Histograms and Probability Distributions A random variable (r.v.) can be either continuous or discrete. It takes on the possible values of an experiment. It
Statistics TI-83 Usage Handout
 Statistics TI-83 Usage Handout This handout includes instructions for performing several different functions on a TI-83 calculator for use in Statistics. The Contents table below lists the topics covered
Statistics TI-83 Usage Handout This handout includes instructions for performing several different functions on a TI-83 calculator for use in Statistics. The Contents table below lists the topics covered
Continuous Random Variables and the Normal Distribution
 Chapter 6 Continuous Random Variables and the Normal Distribution Continuous random variables are used to approximate probabilities where there are many possible outcomes or an infinite number of possible
Chapter 6 Continuous Random Variables and the Normal Distribution Continuous random variables are used to approximate probabilities where there are many possible outcomes or an infinite number of possible
As you draw random samples of size n, as n increases, the sample means tend to be normally distributed.
 The Central Limit Theorem The central limit theorem (clt for short) is one of the most powerful and useful ideas in all of statistics. The clt says that if we collect samples of size n with a "large enough
The Central Limit Theorem The central limit theorem (clt for short) is one of the most powerful and useful ideas in all of statistics. The clt says that if we collect samples of size n with a "large enough
The Binomial Distribution
 MATH 382 The Binomial Distribution Dr. Neal, WKU Suppose there is a fixed probability p of having an occurrence (or success ) on any single attempt, and a sequence of n independent attempts is made. Then
MATH 382 The Binomial Distribution Dr. Neal, WKU Suppose there is a fixed probability p of having an occurrence (or success ) on any single attempt, and a sequence of n independent attempts is made. Then
Normal Probability Distributions
 C H A P T E R Normal Probability Distributions 5 Section 5.2 Example 3 (pg. 248) Normal Probabilities Assume triglyceride levels of the population of the United States are normally distributed with a mean
C H A P T E R Normal Probability Distributions 5 Section 5.2 Example 3 (pg. 248) Normal Probabilities Assume triglyceride levels of the population of the United States are normally distributed with a mean
The instructions on this page also work for the TI-83 Plus and the TI-83 Plus Silver Edition.
 The instructions on this page also work for the TI-83 Plus and the TI-83 Plus Silver Edition. The position of the graphically represented keys can be found by moving your mouse on top of the graphic. Turn
The instructions on this page also work for the TI-83 Plus and the TI-83 Plus Silver Edition. The position of the graphically represented keys can be found by moving your mouse on top of the graphic. Turn
Unit 2: Statistics Probability
 Applied Math 30 3-1: Distributions Probability Distribution: - a table or a graph that displays the theoretical probability for each outcome of an experiment. - P (any particular outcome) is between 0
Applied Math 30 3-1: Distributions Probability Distribution: - a table or a graph that displays the theoretical probability for each outcome of an experiment. - P (any particular outcome) is between 0
The Binomial Probability Distribution
 The Binomial Probability Distribution MATH 130, Elements of Statistics I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2017 Objectives After this lesson we will be able to: determine whether a probability
The Binomial Probability Distribution MATH 130, Elements of Statistics I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2017 Objectives After this lesson we will be able to: determine whether a probability
Density curves. (James Madison University) February 4, / 20
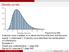 Density curves Figure 6.2 p 230. A density curve is always on or above the horizontal axis, and has area exactly 1 underneath it. A density curve describes the overall pattern of a distribution. Example
Density curves Figure 6.2 p 230. A density curve is always on or above the horizontal axis, and has area exactly 1 underneath it. A density curve describes the overall pattern of a distribution. Example
Math Week in Review #10. Experiments with two outcomes ( success and failure ) are called Bernoulli or binomial trials.
 Math 141 Spring 2006 c Heather Ramsey Page 1 Section 8.4 - Binomial Distribution Math 141 - Week in Review #10 Experiments with two outcomes ( success and failure ) are called Bernoulli or binomial trials.
Math 141 Spring 2006 c Heather Ramsey Page 1 Section 8.4 - Binomial Distribution Math 141 - Week in Review #10 Experiments with two outcomes ( success and failure ) are called Bernoulli or binomial trials.
Binomial formulas: The binomial coefficient is the number of ways of arranging k successes among n observations.
 Chapter 8 Notes Binomial and Geometric Distribution Often times we are interested in an event that has only two outcomes. For example, we may wish to know the outcome of a free throw shot (good or missed),
Chapter 8 Notes Binomial and Geometric Distribution Often times we are interested in an event that has only two outcomes. For example, we may wish to know the outcome of a free throw shot (good or missed),
The Normal Probability Distribution
 1 The Normal Probability Distribution Key Definitions Probability Density Function: An equation used to compute probabilities for continuous random variables where the output value is greater than zero
1 The Normal Probability Distribution Key Definitions Probability Density Function: An equation used to compute probabilities for continuous random variables where the output value is greater than zero
Section Distributions of Random Variables
 Section 8.1 - Distributions of Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
Section 8.1 - Distributions of Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
30 Wyner Statistics Fall 2013
 30 Wyner Statistics Fall 2013 CHAPTER FIVE: DISCRETE PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Summary, Terms, and Objectives A probability distribution shows the likelihood of each possible outcome. This chapter deals
30 Wyner Statistics Fall 2013 CHAPTER FIVE: DISCRETE PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Summary, Terms, and Objectives A probability distribution shows the likelihood of each possible outcome. This chapter deals
1. Find the area under the standard normal distribution curve for each. (a) Between z = 0.19 and z = 1.23.
 Statistics Test 3 Name: KEY 1 Find the area under the standard normal distribution curve for each a Between = 019 and = 123 normalcdf 019, 123 = 04660 b To the left of = 156 normalcdf 100, 156 = 00594
Statistics Test 3 Name: KEY 1 Find the area under the standard normal distribution curve for each a Between = 019 and = 123 normalcdf 019, 123 = 04660 b To the left of = 156 normalcdf 100, 156 = 00594
PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS. Chapter 6
 PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Chapter 6 6.1 Summarize Possible Outcomes and their Probabilities Random Variable Random variable is numerical outcome of random phenomenon www.physics.umd.edu 3 Random Variable
PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Chapter 6 6.1 Summarize Possible Outcomes and their Probabilities Random Variable Random variable is numerical outcome of random phenomenon www.physics.umd.edu 3 Random Variable
Section 8.4 The Binomial Distribution. (a) Rolling a fair die 20 times and observing how many heads appear. s
 Section 8.4 The Binomial Distribution Binomial Experiment A binomial experiment has the following properties: 1. The number of trials in the experiment is fixed. 2. There are two outcomes of each trial:
Section 8.4 The Binomial Distribution Binomial Experiment A binomial experiment has the following properties: 1. The number of trials in the experiment is fixed. 2. There are two outcomes of each trial:
AP Stats Review. Mrs. Daniel Alonzo & Tracy Mourning Sr. High
 AP Stats Review Mrs. Daniel Alonzo & Tracy Mourning Sr. High sdaniel@dadeschools.net Agenda 1. AP Stats Exam Overview 2. AP FRQ Scoring & FRQ: 2016 #1 3. Distributions Review 4. FRQ: 2015 #6 5. Distribution
AP Stats Review Mrs. Daniel Alonzo & Tracy Mourning Sr. High sdaniel@dadeschools.net Agenda 1. AP Stats Exam Overview 2. AP FRQ Scoring & FRQ: 2016 #1 3. Distributions Review 4. FRQ: 2015 #6 5. Distribution
The Binomial Distribution
 The Binomial Distribution Properties of a Binomial Experiment 1. It consists of a fixed number of observations called trials. 2. Each trial can result in one of only two mutually exclusive outcomes labeled
The Binomial Distribution Properties of a Binomial Experiment 1. It consists of a fixed number of observations called trials. 2. Each trial can result in one of only two mutually exclusive outcomes labeled
No, because np = 100(0.02) = 2. The value of np must be greater than or equal to 5 to use the normal approximation.
 1) If n 100 and p 0.02 in a binomial experiment, does this satisfy the rule for a normal approximation? Why or why not? No, because np 100(0.02) 2. The value of np must be greater than or equal to 5 to
1) If n 100 and p 0.02 in a binomial experiment, does this satisfy the rule for a normal approximation? Why or why not? No, because np 100(0.02) 2. The value of np must be greater than or equal to 5 to
7. For the table that follows, answer the following questions: x y 1-1/4 2-1/2 3-3/4 4
 7. For the table that follows, answer the following questions: x y 1-1/4 2-1/2 3-3/4 4 - Would the correlation between x and y in the table above be positive or negative? The correlation is negative. -
7. For the table that follows, answer the following questions: x y 1-1/4 2-1/2 3-3/4 4 - Would the correlation between x and y in the table above be positive or negative? The correlation is negative. -
Chapter 8 Homework Solutions Compiled by Joe Kahlig. speed(x) freq 25 x < x < x < x < x < x < 55 5
 H homework problems, C-copyright Joe Kahlig Chapter Solutions, Page Chapter Homework Solutions Compiled by Joe Kahlig. (a) finite discrete (b) infinite discrete (c) continuous (d) finite discrete (e) continuous.
H homework problems, C-copyright Joe Kahlig Chapter Solutions, Page Chapter Homework Solutions Compiled by Joe Kahlig. (a) finite discrete (b) infinite discrete (c) continuous (d) finite discrete (e) continuous.
Chapter 8 Probability Models
 Chapter 8 Probability Models We ve already used the calculator to find probabilities based on normal models. There are many more models which are useful. This chapter explores three such models. Many types
Chapter 8 Probability Models We ve already used the calculator to find probabilities based on normal models. There are many more models which are useful. This chapter explores three such models. Many types
5.4 Normal Approximation of the Binomial Distribution
 5.4 Normal Approximation of the Binomial Distribution Bernoulli Trials have 3 properties: 1. Only two outcomes - PASS or FAIL 2. n identical trials Review from yesterday. 3. Trials are independent - probability
5.4 Normal Approximation of the Binomial Distribution Bernoulli Trials have 3 properties: 1. Only two outcomes - PASS or FAIL 2. n identical trials Review from yesterday. 3. Trials are independent - probability
Statistics for Business and Economics: Random Variables:Continuous
 Statistics for Business and Economics: Random Variables:Continuous STT 315: Section 107 Acknowledgement: I d like to thank Dr. Ashoke Sinha for allowing me to use and edit the slides. Murray Bourne (interactive
Statistics for Business and Economics: Random Variables:Continuous STT 315: Section 107 Acknowledgement: I d like to thank Dr. Ashoke Sinha for allowing me to use and edit the slides. Murray Bourne (interactive
STATISTICAL DISTRIBUTIONS AND THE CALCULATOR
 STATISTICAL DISTRIBUTIONS AND THE CALCULATOR 1. Basic data sets a. Measures of Center - Mean ( ): average of all values. Characteristic: non-resistant is affected by skew and outliers. - Median: Either
STATISTICAL DISTRIBUTIONS AND THE CALCULATOR 1. Basic data sets a. Measures of Center - Mean ( ): average of all values. Characteristic: non-resistant is affected by skew and outliers. - Median: Either
1 / * / * / * / * / * The mean winnings are $1.80
 DISCRETE vs. CONTINUOUS BASIC DEFINITION Continuous = things you measure Discrete = things you count OFFICIAL DEFINITION Continuous data can take on any value including fractions and decimals You can zoom
DISCRETE vs. CONTINUOUS BASIC DEFINITION Continuous = things you measure Discrete = things you count OFFICIAL DEFINITION Continuous data can take on any value including fractions and decimals You can zoom
X P(X) (c) Express the event performing at least two tests in terms of X and find its probability.
 AP Stats ~ QUIZ 6 Name Period 1. The probability distribution below is for the random variable X = number of medical tests performed on a randomly selected outpatient at a certain hospital. X 0 1 2 3 4
AP Stats ~ QUIZ 6 Name Period 1. The probability distribution below is for the random variable X = number of medical tests performed on a randomly selected outpatient at a certain hospital. X 0 1 2 3 4
Math 166: Topics in Contemporary Mathematics II
 Math 166: Topics in Contemporary Mathematics II Ruomeng Lan Texas A&M University October 15, 2014 Ruomeng Lan (TAMU) Math 166 October 15, 2014 1 / 12 Mean, Median and Mode Definition: 1. The average or
Math 166: Topics in Contemporary Mathematics II Ruomeng Lan Texas A&M University October 15, 2014 Ruomeng Lan (TAMU) Math 166 October 15, 2014 1 / 12 Mean, Median and Mode Definition: 1. The average or
MATH 118 Class Notes For Chapter 5 By: Maan Omran
 MATH 118 Class Notes For Chapter 5 By: Maan Omran Section 5.1 Central Tendency Mode: the number or numbers that occur most often. Median: the number at the midpoint of a ranked data. Ex1: The test scores
MATH 118 Class Notes For Chapter 5 By: Maan Omran Section 5.1 Central Tendency Mode: the number or numbers that occur most often. Median: the number at the midpoint of a ranked data. Ex1: The test scores
Examples: Random Variables. Discrete and Continuous Random Variables. Probability Distributions
 Random Variables Examples: Random variable a variable (typically represented by x) that takes a numerical value by chance. Number of boys in a randomly selected family with three children. Possible values:
Random Variables Examples: Random variable a variable (typically represented by x) that takes a numerical value by chance. Number of boys in a randomly selected family with three children. Possible values:
Abraham Baldwin Agricultural College Math 2000 Practice Test 3
 Abraham Baldwin Agricultural College Math 000 Practice Test 3 To get credit you must show your work. If your answer involves using a formula, make sure you write down the formula! Also write down any expression
Abraham Baldwin Agricultural College Math 000 Practice Test 3 To get credit you must show your work. If your answer involves using a formula, make sure you write down the formula! Also write down any expression
ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists 2016/2017
 ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists 2016/2017 Topic The Normal Distribution Lecturer: Dr. Bernardin Senadza, Dept. of Economics bsenadza@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and
ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists 2016/2017 Topic The Normal Distribution Lecturer: Dr. Bernardin Senadza, Dept. of Economics bsenadza@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and
Chapter 8. Variables. Copyright 2004 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
 Chapter 8 Random Variables Copyright 2004 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. 8.1 What is a Random Variable? Random Variable: assigns a number to each outcome of a random circumstance, or,
Chapter 8 Random Variables Copyright 2004 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. 8.1 What is a Random Variable? Random Variable: assigns a number to each outcome of a random circumstance, or,
These Statistics NOTES Belong to:
 These Statistics NOTES Belong to: Topic Notes Questions Date 1 2 3 4 5 6 REVIEW DO EVERY QUESTION IN YOUR PROVINCIAL EXAM BINDER Important Calculator Functions to know for this chapter Normal Distributions
These Statistics NOTES Belong to: Topic Notes Questions Date 1 2 3 4 5 6 REVIEW DO EVERY QUESTION IN YOUR PROVINCIAL EXAM BINDER Important Calculator Functions to know for this chapter Normal Distributions
Chapter 6 Probability
 Chapter 6 Probability Learning Objectives 1. Simulate simple experiments and compute empirical probabilities. 2. Compute both theoretical and empirical probabilities. 3. Apply the rules of probability
Chapter 6 Probability Learning Objectives 1. Simulate simple experiments and compute empirical probabilities. 2. Compute both theoretical and empirical probabilities. 3. Apply the rules of probability
5.4 Normal Approximation of the Binomial Distribution Lesson MDM4U Jensen
 5.4 Normal Approximation of the Binomial Distribution Lesson MDM4U Jensen Review From Yesterday Bernoulli Trials have 3 properties: 1. 2. 3. Binomial Probability Distribution In a binomial experiment with
5.4 Normal Approximation of the Binomial Distribution Lesson MDM4U Jensen Review From Yesterday Bernoulli Trials have 3 properties: 1. 2. 3. Binomial Probability Distribution In a binomial experiment with
Overview. Definitions. Definitions. Graphs. Chapter 5 Probability Distributions. probability distributions
 Chapter 5 Probability Distributions 5-1 Overview 5-2 Random Variables 5-3 Binomial Probability Distributions 5-4 Mean, Variance, and Standard Deviation for the Binomial Distribution 5-5 The Poisson Distribution
Chapter 5 Probability Distributions 5-1 Overview 5-2 Random Variables 5-3 Binomial Probability Distributions 5-4 Mean, Variance, and Standard Deviation for the Binomial Distribution 5-5 The Poisson Distribution
Homework: Due Wed, Nov 3 rd Chapter 8, # 48a, 55c and 56 (count as 1), 67a
 Homework: Due Wed, Nov 3 rd Chapter 8, # 48a, 55c and 56 (count as 1), 67a Announcements: There are some office hour changes for Nov 5, 8, 9 on website Week 5 quiz begins after class today and ends at
Homework: Due Wed, Nov 3 rd Chapter 8, # 48a, 55c and 56 (count as 1), 67a Announcements: There are some office hour changes for Nov 5, 8, 9 on website Week 5 quiz begins after class today and ends at
Probability is the tool used for anticipating what the distribution of data should look like under a given model.
 AP Statistics NAME: Exam Review: Strand 3: Anticipating Patterns Date: Block: III. Anticipating Patterns: Exploring random phenomena using probability and simulation (20%-30%) Probability is the tool used
AP Statistics NAME: Exam Review: Strand 3: Anticipating Patterns Date: Block: III. Anticipating Patterns: Exploring random phenomena using probability and simulation (20%-30%) Probability is the tool used
MA : Introductory Probability
 MA 320-001: Introductory Probability David Murrugarra Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky http://www.math.uky.edu/~dmu228/ma320/ Spring 2017 David Murrugarra (University of Kentucky) MA 320:
MA 320-001: Introductory Probability David Murrugarra Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky http://www.math.uky.edu/~dmu228/ma320/ Spring 2017 David Murrugarra (University of Kentucky) MA 320:
2.) What is the set of outcomes that describes the event that at least one of the items selected is defective? {AD, DA, DD}
 Math 361 Practice Exam 2 (Use this information for questions 1 3) At the end of a production run manufacturing rubber gaskets, items are sampled at random and inspected to determine if the item is Acceptable
Math 361 Practice Exam 2 (Use this information for questions 1 3) At the end of a production run manufacturing rubber gaskets, items are sampled at random and inspected to determine if the item is Acceptable
Chapter Five. The Binomial Distribution and Related Topics
 Chapter Five The Binomial Distribution and Related Topics Section 2 Binomial Probabilities Essential Question What are the three methods for solving binomial probability questions? Explain each of the
Chapter Five The Binomial Distribution and Related Topics Section 2 Binomial Probabilities Essential Question What are the three methods for solving binomial probability questions? Explain each of the
PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS CHAPTER 4 NOTES DISCRETE PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS
 PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS CHAPTER 4 NOTES DISCRETE PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS I. INTRODUCTION TO RANDOM VARIABLES AND PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS A. Random Variables 1. A random variable x represents a value
PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS CHAPTER 4 NOTES DISCRETE PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS I. INTRODUCTION TO RANDOM VARIABLES AND PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS A. Random Variables 1. A random variable x represents a value
Discrete Probability Distribution
 1 Discrete Probability Distribution Key Definitions Discrete Random Variable: Has a countable number of values. This means that each data point is distinct and separate. Continuous Random Variable: Has
1 Discrete Probability Distribution Key Definitions Discrete Random Variable: Has a countable number of values. This means that each data point is distinct and separate. Continuous Random Variable: Has
Binomial Distributions
 Binomial Distributions A binomial experiment is a probability experiment that satisfies these conditions. 1. The experiment has a fixed number of trials, where each trial is independent of the other trials.
Binomial Distributions A binomial experiment is a probability experiment that satisfies these conditions. 1. The experiment has a fixed number of trials, where each trial is independent of the other trials.
MTH 245: Mathematics for Management, Life, and Social Sciences
 1/14 MTH 245: Mathematics for Management, Life, and Social Sciences Section 7.6 Section 7.6: The Normal Distribution. 2/14 The Normal Distribution. Figure: Abraham DeMoivre Section 7.6: The Normal Distribution.
1/14 MTH 245: Mathematics for Management, Life, and Social Sciences Section 7.6 Section 7.6: The Normal Distribution. 2/14 The Normal Distribution. Figure: Abraham DeMoivre Section 7.6: The Normal Distribution.
Section 7.5 The Normal Distribution. Section 7.6 Application of the Normal Distribution
 Section 7.6 Application of the Normal Distribution A random variable that may take on infinitely many values is called a continuous random variable. A continuous probability distribution is defined by
Section 7.6 Application of the Normal Distribution A random variable that may take on infinitely many values is called a continuous random variable. A continuous probability distribution is defined by
Chapter 6. The Normal Probability Distributions
 Chapter 6 The Normal Probability Distributions 1 Chapter 6 Overview Introduction 6-1 Normal Probability Distributions 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution 6-3 Applications of the Normal Distribution 6-5
Chapter 6 The Normal Probability Distributions 1 Chapter 6 Overview Introduction 6-1 Normal Probability Distributions 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution 6-3 Applications of the Normal Distribution 6-5
Chapter 14 - Random Variables
 Chapter 14 - Random Variables October 29, 2014 There are many scenarios where probabilities are used to determine risk factors. Examples include Insurance, Casino, Lottery, Business, Medical, and other
Chapter 14 - Random Variables October 29, 2014 There are many scenarios where probabilities are used to determine risk factors. Examples include Insurance, Casino, Lottery, Business, Medical, and other
MidTerm 1) Find the following (round off to one decimal place):
 MidTerm 1) 68 49 21 55 57 61 70 42 59 50 66 99 Find the following (round off to one decimal place): Mean = 58:083, round off to 58.1 Median = 58 Range = max min = 99 21 = 78 St. Deviation = s = 8:535,
MidTerm 1) 68 49 21 55 57 61 70 42 59 50 66 99 Find the following (round off to one decimal place): Mean = 58:083, round off to 58.1 Median = 58 Range = max min = 99 21 = 78 St. Deviation = s = 8:535,
7 THE CENTRAL LIMIT THEOREM
 CHAPTER 7 THE CENTRAL LIMIT THEOREM 373 7 THE CENTRAL LIMIT THEOREM Figure 7.1 If you want to figure out the distribution of the change people carry in their pockets, using the central limit theorem and
CHAPTER 7 THE CENTRAL LIMIT THEOREM 373 7 THE CENTRAL LIMIT THEOREM Figure 7.1 If you want to figure out the distribution of the change people carry in their pockets, using the central limit theorem and
Section 6.5. The Central Limit Theorem
 Section 6.5 The Central Limit Theorem Idea Will allow us to combine the theory from 6.4 (sampling distribution idea) with our central limit theorem and that will allow us the do hypothesis testing in the
Section 6.5 The Central Limit Theorem Idea Will allow us to combine the theory from 6.4 (sampling distribution idea) with our central limit theorem and that will allow us the do hypothesis testing in the
11.5: Normal Distributions
 11.5: Normal Distributions 11.5.1 Up to now, we ve dealt with discrete random variables, variables that take on only a finite (or countably infinite we didn t do these) number of values. A continuous random
11.5: Normal Distributions 11.5.1 Up to now, we ve dealt with discrete random variables, variables that take on only a finite (or countably infinite we didn t do these) number of values. A continuous random
1. Steve says I have two children, one of which is a boy. Given this information, what is the probability that Steve has two boys?
 Chapters 6 8 Review 1. Steve says I have two children, one of which is a boy. Given this information, what is the probability that Steve has two boys? (A) 1 (B) 3 1 (C) 3 (D) 4 1 (E) None of the above..
Chapters 6 8 Review 1. Steve says I have two children, one of which is a boy. Given this information, what is the probability that Steve has two boys? (A) 1 (B) 3 1 (C) 3 (D) 4 1 (E) None of the above..
Section 3.4 The Normal Distribution
 Section 3.4 The Normal Distribution Properties of the Normal Distribution Curve 1. We denote the normal random variable with X = x. 2. The curve has a peak at x = µ. 3. The curve is symmetric about the
Section 3.4 The Normal Distribution Properties of the Normal Distribution Curve 1. We denote the normal random variable with X = x. 2. The curve has a peak at x = µ. 3. The curve is symmetric about the
Example - Let X be the number of boys in a 4 child family. Find the probability distribution table:
 Chapter8 Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables tthe value of the result of the probability experiment is a RANDOM VARIABLE. Example - Let X be the number
Chapter8 Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables tthe value of the result of the probability experiment is a RANDOM VARIABLE. Example - Let X be the number
3.2 Binomial and Hypergeometric Probabilities
 3.2 Binomial and Hypergeometric Probabilities Ulrich Hoensch Wednesday, January 23, 2013 Example An urn contains ten balls, exactly seven of which are red. Suppose five balls are drawn at random and with
3.2 Binomial and Hypergeometric Probabilities Ulrich Hoensch Wednesday, January 23, 2013 Example An urn contains ten balls, exactly seven of which are red. Suppose five balls are drawn at random and with
MATH 264 Problem Homework I
 MATH Problem Homework I Due to December 9, 00@:0 PROBLEMS & SOLUTIONS. A student answers a multiple-choice examination question that offers four possible answers. Suppose that the probability that the
MATH Problem Homework I Due to December 9, 00@:0 PROBLEMS & SOLUTIONS. A student answers a multiple-choice examination question that offers four possible answers. Suppose that the probability that the
AP Stats. Review. Mrs. Daniel Alonzo & Tracy Mourning Sr. High
 AP Stats Review Mrs. Daniel Alonzo & Tracy Mourning Sr. High sdaniel@dadeschools.net Agenda 1. AP Stats Exam Overview 2. AP FRQ Scoring & FRQ: 2016 #1 3. Distributions Review 4. FRQ: 2015 #6 5. Distribution
AP Stats Review Mrs. Daniel Alonzo & Tracy Mourning Sr. High sdaniel@dadeschools.net Agenda 1. AP Stats Exam Overview 2. AP FRQ Scoring & FRQ: 2016 #1 3. Distributions Review 4. FRQ: 2015 #6 5. Distribution
Normal distribution. We say that a random variable X follows the normal distribution if the probability density function of X is given by
 Normal distribution The normal distribution is the most important distribution. It describes well the distribution of random variables that arise in practice, such as the heights or weights of people,
Normal distribution The normal distribution is the most important distribution. It describes well the distribution of random variables that arise in practice, such as the heights or weights of people,
Probability Distributions. Definitions Discrete vs. Continuous Mean and Standard Deviation TI 83/84 Calculator Binomial Distribution
 Probability Distributions Definitions Discrete vs. Continuous Mean and Standard Deviation TI 83/84 Calculator Binomial Distribution Definitions Random Variable: a variable that has a single numerical value
Probability Distributions Definitions Discrete vs. Continuous Mean and Standard Deviation TI 83/84 Calculator Binomial Distribution Definitions Random Variable: a variable that has a single numerical value
6.1 Discrete & Continuous Random Variables. Nov 4 6:53 PM. Objectives
 6.1 Discrete & Continuous Random Variables examples vocab Objectives Today we will... - Compute probabilities using the probability distribution of a discrete random variable. - Calculate and interpret
6.1 Discrete & Continuous Random Variables examples vocab Objectives Today we will... - Compute probabilities using the probability distribution of a discrete random variable. - Calculate and interpret
Lecture 9. Probability Distributions. Outline. Outline
 Outline Lecture 9 Probability Distributions 6-1 Introduction 6- Probability Distributions 6-3 Mean, Variance, and Expectation 6-4 The Binomial Distribution Outline 7- Properties of the Normal Distribution
Outline Lecture 9 Probability Distributions 6-1 Introduction 6- Probability Distributions 6-3 Mean, Variance, and Expectation 6-4 The Binomial Distribution Outline 7- Properties of the Normal Distribution
Version A. Problem 1. Let X be the continuous random variable defined by the following pdf: 1 x/2 when 0 x 2, f(x) = 0 otherwise.
 Math 224 Q Exam 3A Fall 217 Tues Dec 12 Version A Problem 1. Let X be the continuous random variable defined by the following pdf: { 1 x/2 when x 2, f(x) otherwise. (a) Compute the mean µ E[X]. E[X] x
Math 224 Q Exam 3A Fall 217 Tues Dec 12 Version A Problem 1. Let X be the continuous random variable defined by the following pdf: { 1 x/2 when x 2, f(x) otherwise. (a) Compute the mean µ E[X]. E[X] x
CHAPTER 4 DISCRETE PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS
 CHAPTER 4 DISCRETE PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS A random variable is the description of the outcome of an experiment in words. The verbal description of a random variable tells you how to find or calculate
CHAPTER 4 DISCRETE PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS A random variable is the description of the outcome of an experiment in words. The verbal description of a random variable tells you how to find or calculate
Chpt The Binomial Distribution
 Chpt 5 5-4 The Binomial Distribution 1 /36 Chpt 5-4 Chpt 5 Homework p262 Applying the Concepts Exercises p263 1-11, 14-18, 23, 24, 26 2 /36 Objective Chpt 5 Find the exact probability for x successes in
Chpt 5 5-4 The Binomial Distribution 1 /36 Chpt 5-4 Chpt 5 Homework p262 Applying the Concepts Exercises p263 1-11, 14-18, 23, 24, 26 2 /36 Objective Chpt 5 Find the exact probability for x successes in
Lecture 9. Probability Distributions
 Lecture 9 Probability Distributions Outline 6-1 Introduction 6-2 Probability Distributions 6-3 Mean, Variance, and Expectation 6-4 The Binomial Distribution Outline 7-2 Properties of the Normal Distribution
Lecture 9 Probability Distributions Outline 6-1 Introduction 6-2 Probability Distributions 6-3 Mean, Variance, and Expectation 6-4 The Binomial Distribution Outline 7-2 Properties of the Normal Distribution
Lecture Slides. Elementary Statistics Tenth Edition. by Mario F. Triola. and the Triola Statistics Series. Slide 1
 Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Tenth Edition and the Triola Statistics Series by Mario F. Triola Slide 1 Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Overview 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution
Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Tenth Edition and the Triola Statistics Series by Mario F. Triola Slide 1 Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Overview 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution
Binomial Distributions
 Binomial Distributions (aka Bernouli s Trials) Chapter 8 Binomial Distribution an important class of probability distributions, which occur under the following Binomial Setting (1) There is a number n
Binomial Distributions (aka Bernouli s Trials) Chapter 8 Binomial Distribution an important class of probability distributions, which occur under the following Binomial Setting (1) There is a number n
Chapter Six Probability Distributions
 6.1 Probability Distributions Discrete Random Variable Chapter Six Probability Distributions x P(x) 2 0.08 4 0.13 6 0.25 8 0.31 10 0.16 12 0.01 Practice. Construct a probability distribution for the number
6.1 Probability Distributions Discrete Random Variable Chapter Six Probability Distributions x P(x) 2 0.08 4 0.13 6 0.25 8 0.31 10 0.16 12 0.01 Practice. Construct a probability distribution for the number
The Central Limit Theorem for Sums
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46997 1 The Central Limit Theorem for Sums OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Suppose X is a random
OpenStax-CNX module: m46997 1 The Central Limit Theorem for Sums OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Suppose X is a random
Math Tech IIII, May 7
 Math Tech IIII, May 7 The Normal Probability Models Book Sections: 5.1, 5.2, & 5.3 Essential Questions: How can I use the normal distribution to compute probability? Standards: S.ID.4 Properties of the
Math Tech IIII, May 7 The Normal Probability Models Book Sections: 5.1, 5.2, & 5.3 Essential Questions: How can I use the normal distribution to compute probability? Standards: S.ID.4 Properties of the
Chapter 3: Probability Distributions and Statistics
 Chapter 3: Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 3.-3.3 3. Random Variables and Histograms A is a rule that assigns precisely one real number to each outcome of an experiment. We usually denote
Chapter 3: Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 3.-3.3 3. Random Variables and Histograms A is a rule that assigns precisely one real number to each outcome of an experiment. We usually denote
Math 243 Section 4.3 The Binomial Distribution
 Math 243 Section 4.3 The Binomial Distribution Overview Notation for the mean, standard deviation and variance The Binomial Model Bernoulli Trials Notation for the mean, standard deviation and variance
Math 243 Section 4.3 The Binomial Distribution Overview Notation for the mean, standard deviation and variance The Binomial Model Bernoulli Trials Notation for the mean, standard deviation and variance
The normal distribution is a theoretical model derived mathematically and not empirically.
 Sociology 541 The Normal Distribution Probability and An Introduction to Inferential Statistics Normal Approximation The normal distribution is a theoretical model derived mathematically and not empirically.
Sociology 541 The Normal Distribution Probability and An Introduction to Inferential Statistics Normal Approximation The normal distribution is a theoretical model derived mathematically and not empirically.
