Continuous Random Variables and the Normal Distribution
|
|
|
- Charlene Hunter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 6 Continuous Random Variables and the Normal Distribution Continuous random variables are used to approximate probabilities where there are many possible outcomes or an infinite number of possible outcomes on a given trial. One of the most well-known continuous distributions used to approximate probabilities is the normal distribution. Traditionally, normal distribution probabilities were obtained using a normal distribution table. These tables are being replaced with calculators such as the TI-84 Plus. The calculator reduces the time needed to perform the calculations and reduces the rounding errors that occur because of the brevity of the tables in elementary statistics textbooks. Normal Distribution Randomly Generating a Number From a Normal Distribution Just as the TI-84 has a built-in function to generate random real numbers from a Binomial distribution, it also has a built-in function to generate random real numbers from a specific normal distribution with a mean µ and standard deviation σ. The random real numbers represent x values. The general syntax is randnorm(µ, σ, n), where n is the number of random real numbers. To generate 30 numbers from a normal distribution with a mean of 45 and a standard deviation of 8 and store them in L 2 : Press. Select 6:randNorm( from the PRB menu. Type 45, 8, 30). Press. Type L 2 and press.
2 Generate 200 numbers from a normal distribution with µ = 100 and σ = 15 and store them in L 3. Generate a histogram of the 200 numbers in L 3 and observe that the histogram is beginning to look like a normal distribution. Experiment with generating a larger number of data values. Computing Normal Distribution Probabilities The computation commands for normal distributions are normalpdf(, normalcdf(, and invnorm(. All three commands can be found by pressing ( ) and selecting the DISTR menu. Computing Cumulative Normal Probabilities The normalcdf( function stands for normal cumulative density function and gives the probability of getting an x value that falls within an interval of values from the normal distribution. There are three different scenarios: Finding the probability that a number will fall between two values under a normal distribution. Finding the probability that a number will fall to the left of a value under a normal distribution. Finding the probability that a number will fall to the right of a value under a normal distribution. The syntax for the normalcdf( function is normalcdf(a, b, µ, σ), where a is the lower bound of the interval, b is the upper bound of the interval, µ is the mean, and σ is the standard deviation. Finding the Area Between Two Values To find the area between two numbers a and b under the standard normal curve, use the normalcdf( function. Find the probability of getting a value between 1.04 and 1.82 under the standard normal curve. P(1.04 < z < 1.82) = Select normalcdf( from the DISTR menu. Enter 1.04 at the lower: prompt. Enter 1.82 at the upper: prompt. 2
3 Find the probability of getting a value between 10 and 13 under the Normal curve with a mean of 10 and a standard deviation of 2. P(10 < x < 13) = Find the probability of getting a value between 2 and 12 under the Normal curve with a mean of 10 and a standard deviation of 2. Finding the Area to the Left of a Value To find the area to the left of b under a normal curve, use the normalcdf( function. The lower bound should be negative infinity (- ). The problem is that the TI-84 calculator does not have a built-in key for negative infinity (- ). Thus, the value -1E99 is used, which represents a negative number that lies far to the left on the number line. The letter E stands for scientific notation and it is located above the comma key (press ). Find the probability of getting a value less than 0 under the Standard Normal curve. P(z < 0) = 0.5. Select normalcdf( from the DISTR menu. Enter -1E99 at the lower: prompt. Enter 0 at the upper: prompt. Find the probability of getting a value less than under the normal curve with mean 25 and standard deviation 6. The probability is Finding the Area to the Right of a Value To find the area to right of a under the normal curve, use the normalcdf( function. The upper bound should be positive infinity (+ ). Since the TI-84 calculator does not have a built-in key for negative infinity (+ ), use the value 1E99, which represents a positive number that lies far to the right on the number line. The letter E stands for scientific notation and it is located above the comma key (press ). 3
4 Find the probability of getting a value greater than under the standard normal curve. P(z > -1.08) = Select normalcdf( from the DISTR menu. Enter -1E99 at the lower: prompt. Enter 0 at the upper: prompt. Find the probability of getting a value greater than 15.3 under the Normal curve with mean 12 and standard deviation 4. P(z > 15.3) = Inverse Normal Distribution Probabilities There are times in statistics when we have a probability from a normal distribution and need a relevant z-score or raw score. Such computations are called inverse normal probability calculations and can be performed using tables of normal probabilities, but the work is tedious. The TI-84 Plus calculator has a function, invnorm(, that performs these calculations. Suppose we are looking for a number k from a standard normal distribution such that P(z < k) = In other words, what number cuts off an area of to its left in a standard normal distribution? P(z < ) = Select invnorm( from the DISTR menu. Enter at the area: prompt. The invnorm( function always performs calculations based on an area to the left of a number. If you are given an area to the right of a number, find the complementary area on the left by subtracting from 1. 4
5 Find the number x with an area of 0.65 to its right from a normal distribution with a mean of 10 and a standard deviation of 4. That is, find a value x from a normal distribution with the given mean and standard deviation such that P(x < k) = P(x < ) = Graph the Normal Probability Density Function The function normalpdf( stands for normal probability density function and does not actually generate a probability, since it applies to a single x value in a continuous distribution and that probability is always zero. Instead, the output is the height of the normal distribution above the horizontal axis (the y- coordinate of the graph). The main use of this command is to draw the normal curve. The syntax for the function is normalpdf(x, μ, σ), where μ is the mean and σ is the standard deviation. The following sequence of commands will draw the standard normal curve (μ =0 and σ = 1). Press. (Do NOT forget this step!) To view this graph in the proper window, press Select 1: normalpdf( from the DISTR menu. Press at the area: prompt.. and select 9:ZoomStat. You can trace the curve by pressing. This command may be used to draw any normal distribution curve with any mean and standard deviation. 5
6 Shade the Normal Probability Density Function When calculating the probability of an area under a normal curve, it is often helpful to shade the area. The syntax for the TI-84 Plus command to do this is ShadeNorm(a, b, µ, σ). Example Press to view the DRAW menu. Select 1: ShadeNorm( from the DRAW menu. Enter 1.04 at the lower: prompt. Enter 1.82 at the upper: prompt. Highlight Draw and press. Example Suppose you wish to shade the area under the standard normal curve that corresponds to 1.04 < z < Begin by turning off all other functions ( ) and statistical plots ( ). Press and adjust the settings to view the standard normal curve, as shown to the left. Find the probability of getting a value greater than 15.3 under the Normal curve with mean 12 and standard deviation 4. Press and adjust the settings as shown to the right. P(x > 15.3) = Notice that the area of the shaded region is also shown on the graph and it is the same value previously calculated from the normalcdf( command. Thus, the ShadeNorm( is an alternative command for normalcdf(, with the added benefit of the shading the area of interest. Optimal window settings are Xmin = μ 3σ, Xmax = μ + 3σ, Xscl = σ, Ymin = -0.2/σ, and Ymax = 0.5/σ. Choose any value you wish for Yscl. 6
The Normal Probability Distribution
 102 The Normal Probability Distribution C H A P T E R 7 Section 7.2 4Example 1 (pg. 71) Finding Area Under a Normal Curve In this exercise, we will calculate the area to the left of 5 inches using a normal
102 The Normal Probability Distribution C H A P T E R 7 Section 7.2 4Example 1 (pg. 71) Finding Area Under a Normal Curve In this exercise, we will calculate the area to the left of 5 inches using a normal
Normal Probability Distributions
 C H A P T E R Normal Probability Distributions 5 Section 5.2 Example 3 (pg. 248) Normal Probabilities Assume triglyceride levels of the population of the United States are normally distributed with a mean
C H A P T E R Normal Probability Distributions 5 Section 5.2 Example 3 (pg. 248) Normal Probabilities Assume triglyceride levels of the population of the United States are normally distributed with a mean
3. Continuous Probability Distributions
 3.1 Continuous probability distributions 3. Continuous Probability Distributions K The normal probability distribution A continuous random variable X is said to have a normal distribution if it has a probability
3.1 Continuous probability distributions 3. Continuous Probability Distributions K The normal probability distribution A continuous random variable X is said to have a normal distribution if it has a probability
Using the TI-83 Statistical Features
 Entering data (working with lists) Consider the following small data sets: Using the TI-83 Statistical Features Data Set 1: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} Data Set 2: {2, 3, 4, 4, 6} Press STAT to access the statistics
Entering data (working with lists) Consider the following small data sets: Using the TI-83 Statistical Features Data Set 1: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} Data Set 2: {2, 3, 4, 4, 6} Press STAT to access the statistics
Week 7. Texas A& M University. Department of Mathematics Texas A& M University, College Station Section 3.2, 3.3 and 3.4
 Week 7 Oğuz Gezmiş Texas A& M University Department of Mathematics Texas A& M University, College Station Section 3.2, 3.3 and 3.4 Oğuz Gezmiş (TAMU) Topics in Contemporary Mathematics II Week7 1 / 19
Week 7 Oğuz Gezmiş Texas A& M University Department of Mathematics Texas A& M University, College Station Section 3.2, 3.3 and 3.4 Oğuz Gezmiş (TAMU) Topics in Contemporary Mathematics II Week7 1 / 19
Unit 2: Statistics Probability
 Applied Math 30 3-1: Distributions Probability Distribution: - a table or a graph that displays the theoretical probability for each outcome of an experiment. - P (any particular outcome) is between 0
Applied Math 30 3-1: Distributions Probability Distribution: - a table or a graph that displays the theoretical probability for each outcome of an experiment. - P (any particular outcome) is between 0
Statistics (This summary is for chapters 18, 29 and section H of chapter 19)
 Statistics (This summary is for chapters 18, 29 and section H of chapter 19) Mean, Median, Mode Mode: most common value Median: middle value (when the values are in order) Mean = total how many = x n =
Statistics (This summary is for chapters 18, 29 and section H of chapter 19) Mean, Median, Mode Mode: most common value Median: middle value (when the values are in order) Mean = total how many = x n =
Chapter 7 1. Random Variables
 Chapter 7 1 Random Variables random variable numerical variable whose value depends on the outcome of a chance experiment - discrete if its possible values are isolated points on a number line - continuous
Chapter 7 1 Random Variables random variable numerical variable whose value depends on the outcome of a chance experiment - discrete if its possible values are isolated points on a number line - continuous
Statistics TI-83 Usage Handout
 Statistics TI-83 Usage Handout This handout includes instructions for performing several different functions on a TI-83 calculator for use in Statistics. The Contents table below lists the topics covered
Statistics TI-83 Usage Handout This handout includes instructions for performing several different functions on a TI-83 calculator for use in Statistics. The Contents table below lists the topics covered
Section 15.0: The Normal Distribution
 Section 15.0: The Normal Distribution The Normal distribution is the most widely recognized of all probability distributions. It is a continuous distribution, which means its graph has no gaps. The shape
Section 15.0: The Normal Distribution The Normal distribution is the most widely recognized of all probability distributions. It is a continuous distribution, which means its graph has no gaps. The shape
Section 7.5 The Normal Distribution. Section 7.6 Application of the Normal Distribution
 Section 7.6 Application of the Normal Distribution A random variable that may take on infinitely many values is called a continuous random variable. A continuous probability distribution is defined by
Section 7.6 Application of the Normal Distribution A random variable that may take on infinitely many values is called a continuous random variable. A continuous probability distribution is defined by
As you draw random samples of size n, as n increases, the sample means tend to be normally distributed.
 The Central Limit Theorem The central limit theorem (clt for short) is one of the most powerful and useful ideas in all of statistics. The clt says that if we collect samples of size n with a "large enough
The Central Limit Theorem The central limit theorem (clt for short) is one of the most powerful and useful ideas in all of statistics. The clt says that if we collect samples of size n with a "large enough
Statistics (This summary is for chapters 17, 28, 29 and section G of chapter 19)
 Statistics (This summary is for chapters 17, 28, 29 and section G of chapter 19) Mean, Median, Mode Mode: most common value Median: middle value (when the values are in order) Mean = total how many = x
Statistics (This summary is for chapters 17, 28, 29 and section G of chapter 19) Mean, Median, Mode Mode: most common value Median: middle value (when the values are in order) Mean = total how many = x
The Normal Distribution
 5.1 Introduction to Normal Distributions and the Standard Normal Distribution Section Learning objectives: 1. How to interpret graphs of normal probability distributions 2. How to find areas under the
5.1 Introduction to Normal Distributions and the Standard Normal Distribution Section Learning objectives: 1. How to interpret graphs of normal probability distributions 2. How to find areas under the
Binomial and Normal Distributions. Example: Determine whether the following experiments are binomial experiments. Explain.
 Binomial and Normal Distributions Objective 1: Determining if an Experiment is a Binomial Experiment For an experiment to be considered a binomial experiment, four things must hold: 1. The experiment is
Binomial and Normal Distributions Objective 1: Determining if an Experiment is a Binomial Experiment For an experiment to be considered a binomial experiment, four things must hold: 1. The experiment is
CH 5 Normal Probability Distributions Properties of the Normal Distribution
 Properties of the Normal Distribution Example A friend that is always late. Let X represent the amount of minutes that pass from the moment you are suppose to meet your friend until the moment your friend
Properties of the Normal Distribution Example A friend that is always late. Let X represent the amount of minutes that pass from the moment you are suppose to meet your friend until the moment your friend
No, because np = 100(0.02) = 2. The value of np must be greater than or equal to 5 to use the normal approximation.
 1) If n 100 and p 0.02 in a binomial experiment, does this satisfy the rule for a normal approximation? Why or why not? No, because np 100(0.02) 2. The value of np must be greater than or equal to 5 to
1) If n 100 and p 0.02 in a binomial experiment, does this satisfy the rule for a normal approximation? Why or why not? No, because np 100(0.02) 2. The value of np must be greater than or equal to 5 to
Discrete Random Variables and Their Probability Distributions
 Chapter 5 Discrete Random Variables and Their Probability Distributions Mean and Standard Deviation of a Discrete Random Variable Computing the mean and standard deviation of a discrete random variable
Chapter 5 Discrete Random Variables and Their Probability Distributions Mean and Standard Deviation of a Discrete Random Variable Computing the mean and standard deviation of a discrete random variable
Lecture Slides. Elementary Statistics Tenth Edition. by Mario F. Triola. and the Triola Statistics Series. Slide 1
 Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Tenth Edition and the Triola Statistics Series by Mario F. Triola Slide 1 Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Overview 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution
Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Tenth Edition and the Triola Statistics Series by Mario F. Triola Slide 1 Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Overview 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution
Chapter 6: Continuous Probability Distributions
 Chapter 6: Continuous Probability Distributions Chapter 5 dealt with probability distributions arising from discrete random variables. Mostly that chapter focused on the binomial experiment. There are
Chapter 6: Continuous Probability Distributions Chapter 5 dealt with probability distributions arising from discrete random variables. Mostly that chapter focused on the binomial experiment. There are
Name: Class: Date: A2R 3.4 Problem Set - Major Characteristics of Polynomial Graphs
 Name: Class: Date: A2R 3.4 Problem Set - Major Characteristics of Polynomial Graphs Use the coordinate plane to sketch a graph with the given characteristics. If the graph is not possible to sketch, explain
Name: Class: Date: A2R 3.4 Problem Set - Major Characteristics of Polynomial Graphs Use the coordinate plane to sketch a graph with the given characteristics. If the graph is not possible to sketch, explain
Shifting and rescaling data distributions
 Shifting and rescaling data distributions It is useful to consider the effect of systematic alterations of all the values in a data set. The simplest such systematic effect is a shift by a fixed constant.
Shifting and rescaling data distributions It is useful to consider the effect of systematic alterations of all the values in a data set. The simplest such systematic effect is a shift by a fixed constant.
ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists
 ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists Session 7 The Normal Distribution Part 1 Lecturer: Dr. Bernardin Senadza, Dept. of Economics Contact Information: bsenadza@ug.edu.gh College of Education
ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists Session 7 The Normal Distribution Part 1 Lecturer: Dr. Bernardin Senadza, Dept. of Economics Contact Information: bsenadza@ug.edu.gh College of Education
Chapter 8 Probability Models
 Chapter 8 Probability Models We ve already used the calculator to find probabilities based on normal models. There are many more models which are useful. This chapter explores three such models. Many types
Chapter 8 Probability Models We ve already used the calculator to find probabilities based on normal models. There are many more models which are useful. This chapter explores three such models. Many types
Section 3.4 The Normal Distribution
 Section 3.4 The Normal Distribution Properties of the Normal Distribution Curve 1. We denote the normal random variable with X = x. 2. The curve has a peak at x = µ. 3. The curve is symmetric about the
Section 3.4 The Normal Distribution Properties of the Normal Distribution Curve 1. We denote the normal random variable with X = x. 2. The curve has a peak at x = µ. 3. The curve is symmetric about the
5-1 pg ,4,5, EOO,39,47,50,53, pg ,5,9,13,17,19,21,22,25,30,31,32, pg.269 1,29,13,16,17,19,20,25,26,28,31,33,38
 5-1 pg. 242 3,4,5, 17-37 EOO,39,47,50,53,56 5-2 pg. 249 9,10,13,14,17,18 5-3 pg. 257 1,5,9,13,17,19,21,22,25,30,31,32,34 5-4 pg.269 1,29,13,16,17,19,20,25,26,28,31,33,38 5-5 pg. 281 5-14,16,19,21,22,25,26,30
5-1 pg. 242 3,4,5, 17-37 EOO,39,47,50,53,56 5-2 pg. 249 9,10,13,14,17,18 5-3 pg. 257 1,5,9,13,17,19,21,22,25,30,31,32,34 5-4 pg.269 1,29,13,16,17,19,20,25,26,28,31,33,38 5-5 pg. 281 5-14,16,19,21,22,25,26,30
ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists 2016/2017
 ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists 2016/2017 Topic The Normal Distribution Lecturer: Dr. Bernardin Senadza, Dept. of Economics bsenadza@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and
ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists 2016/2017 Topic The Normal Distribution Lecturer: Dr. Bernardin Senadza, Dept. of Economics bsenadza@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and
Statistics for Business and Economics: Random Variables:Continuous
 Statistics for Business and Economics: Random Variables:Continuous STT 315: Section 107 Acknowledgement: I d like to thank Dr. Ashoke Sinha for allowing me to use and edit the slides. Murray Bourne (interactive
Statistics for Business and Economics: Random Variables:Continuous STT 315: Section 107 Acknowledgement: I d like to thank Dr. Ashoke Sinha for allowing me to use and edit the slides. Murray Bourne (interactive
The instructions on this page also work for the TI-83 Plus and the TI-83 Plus Silver Edition.
 The instructions on this page also work for the TI-83 Plus and the TI-83 Plus Silver Edition. The position of the graphically represented keys can be found by moving your mouse on top of the graphic. Turn
The instructions on this page also work for the TI-83 Plus and the TI-83 Plus Silver Edition. The position of the graphically represented keys can be found by moving your mouse on top of the graphic. Turn
Graphing a Binomial Probability Distribution Histogram
 Chapter 6 8A: Using a Normal Distribution to Approximate a Binomial Probability Distribution Graphing a Binomial Probability Distribution Histogram Lower and Upper Class Boundaries are used to graph the
Chapter 6 8A: Using a Normal Distribution to Approximate a Binomial Probability Distribution Graphing a Binomial Probability Distribution Histogram Lower and Upper Class Boundaries are used to graph the
Chapter 5 Normal Probability Distributions
 Chapter 5 Normal Probability Distributions Section 5-1 Introduction to Normal Distributions and the Standard Normal Distribution A The normal distribution is the most important of the continuous probability
Chapter 5 Normal Probability Distributions Section 5-1 Introduction to Normal Distributions and the Standard Normal Distribution A The normal distribution is the most important of the continuous probability
Statistical Methods in Practice STAT/MATH 3379
 Statistical Methods in Practice STAT/MATH 3379 Dr. A. B. W. Manage Associate Professor of Mathematics & Statistics Department of Mathematics & Statistics Sam Houston State University Overview 6.1 Discrete
Statistical Methods in Practice STAT/MATH 3379 Dr. A. B. W. Manage Associate Professor of Mathematics & Statistics Department of Mathematics & Statistics Sam Houston State University Overview 6.1 Discrete
STAT Chapter 5: Continuous Distributions. Probability distributions are used a bit differently for continuous r.v. s than for discrete r.v. s.
 STAT 515 -- Chapter 5: Continuous Distributions Probability distributions are used a bit differently for continuous r.v. s than for discrete r.v. s. Continuous distributions typically are represented by
STAT 515 -- Chapter 5: Continuous Distributions Probability distributions are used a bit differently for continuous r.v. s than for discrete r.v. s. Continuous distributions typically are represented by
Section Introduction to Normal Distributions
 Section 6.1-6.2 Introduction to Normal Distributions 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 of 105 Section 6.1-6.2 Objectives Interpret graphs of normal probability distributions Find areas
Section 6.1-6.2 Introduction to Normal Distributions 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 of 105 Section 6.1-6.2 Objectives Interpret graphs of normal probability distributions Find areas
Graphing Calculator Appendix
 Appendix GC GC-1 This appendix contains some keystroke suggestions for many graphing calculator operations that are featured in this text. The keystrokes are for the TI-83/ TI-83 Plus calculators. The
Appendix GC GC-1 This appendix contains some keystroke suggestions for many graphing calculator operations that are featured in this text. The keystrokes are for the TI-83/ TI-83 Plus calculators. The
Binomial Probabilities The actual probability that P ( X k ) the formula n P X k p p. = for any k in the range {0, 1, 2,, n} is given by. n n!
 Introduction We are often more interested in experiments in which there are two outcomes of interest (success/failure, make/miss, yes/no, etc.). In this chapter we study two types of probability distributions
Introduction We are often more interested in experiments in which there are two outcomes of interest (success/failure, make/miss, yes/no, etc.). In this chapter we study two types of probability distributions
Manual for the TI-83, TI-84, and TI-89 Calculators
 Manual for the TI-83, TI-84, and TI-89 Calculators to accompany Mendenhall/Beaver/Beaver s Introduction to Probability and Statistics, 13 th edition James B. Davis Contents Chapter 1 Introduction...4 Chapter
Manual for the TI-83, TI-84, and TI-89 Calculators to accompany Mendenhall/Beaver/Beaver s Introduction to Probability and Statistics, 13 th edition James B. Davis Contents Chapter 1 Introduction...4 Chapter
Estimation of the Mean and Proportion
 Chapter 8 Estimation of the Mean and Proportion In statistics, we collect samples to know more about a population. If the sample is representative of the population, the sample mean or proportion should
Chapter 8 Estimation of the Mean and Proportion In statistics, we collect samples to know more about a population. If the sample is representative of the population, the sample mean or proportion should
Making Sense of Cents
 Name: Date: Making Sense of Cents Exploring the Central Limit Theorem Many of the variables that you have studied so far in this class have had a normal distribution. You have used a table of the normal
Name: Date: Making Sense of Cents Exploring the Central Limit Theorem Many of the variables that you have studied so far in this class have had a normal distribution. You have used a table of the normal
PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS. Chapter 6
 PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Chapter 6 6.1 Summarize Possible Outcomes and their Probabilities Random Variable Random variable is numerical outcome of random phenomenon www.physics.umd.edu 3 Random Variable
PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Chapter 6 6.1 Summarize Possible Outcomes and their Probabilities Random Variable Random variable is numerical outcome of random phenomenon www.physics.umd.edu 3 Random Variable
The Normal Probability Distribution
 1 The Normal Probability Distribution Key Definitions Probability Density Function: An equation used to compute probabilities for continuous random variables where the output value is greater than zero
1 The Normal Probability Distribution Key Definitions Probability Density Function: An equation used to compute probabilities for continuous random variables where the output value is greater than zero
5.4 Normal Approximation of the Binomial Distribution Lesson MDM4U Jensen
 5.4 Normal Approximation of the Binomial Distribution Lesson MDM4U Jensen Review From Yesterday Bernoulli Trials have 3 properties: 1. 2. 3. Binomial Probability Distribution In a binomial experiment with
5.4 Normal Approximation of the Binomial Distribution Lesson MDM4U Jensen Review From Yesterday Bernoulli Trials have 3 properties: 1. 2. 3. Binomial Probability Distribution In a binomial experiment with
Homework: Due Wed, Nov 3 rd Chapter 8, # 48a, 55c and 56 (count as 1), 67a
 Homework: Due Wed, Nov 3 rd Chapter 8, # 48a, 55c and 56 (count as 1), 67a Announcements: There are some office hour changes for Nov 5, 8, 9 on website Week 5 quiz begins after class today and ends at
Homework: Due Wed, Nov 3 rd Chapter 8, # 48a, 55c and 56 (count as 1), 67a Announcements: There are some office hour changes for Nov 5, 8, 9 on website Week 5 quiz begins after class today and ends at
5.4 Normal Approximation of the Binomial Distribution
 5.4 Normal Approximation of the Binomial Distribution Bernoulli Trials have 3 properties: 1. Only two outcomes - PASS or FAIL 2. n identical trials Review from yesterday. 3. Trials are independent - probability
5.4 Normal Approximation of the Binomial Distribution Bernoulli Trials have 3 properties: 1. Only two outcomes - PASS or FAIL 2. n identical trials Review from yesterday. 3. Trials are independent - probability
Density curves. (James Madison University) February 4, / 20
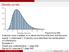 Density curves Figure 6.2 p 230. A density curve is always on or above the horizontal axis, and has area exactly 1 underneath it. A density curve describes the overall pattern of a distribution. Example
Density curves Figure 6.2 p 230. A density curve is always on or above the horizontal axis, and has area exactly 1 underneath it. A density curve describes the overall pattern of a distribution. Example
Analyzing Accumulated Change: More Applications of Integrals & 7.1 Differences of Accumulated Changes
 Chapter 7 Analyzing Accumulated Change: More Applications of Integrals & 7.1 Differences of Accumulated Changes This chapter helps you effectively use your calculatorõs numerical integrator with various
Chapter 7 Analyzing Accumulated Change: More Applications of Integrals & 7.1 Differences of Accumulated Changes This chapter helps you effectively use your calculatorõs numerical integrator with various
Section Distributions of Random Variables
 Section 8.1 - Distributions of Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
Section 8.1 - Distributions of Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
Overview. Definitions. Definitions. Graphs. Chapter 5 Probability Distributions. probability distributions
 Chapter 5 Probability Distributions 5-1 Overview 5-2 Random Variables 5-3 Binomial Probability Distributions 5-4 Mean, Variance, and Standard Deviation for the Binomial Distribution 5-5 The Poisson Distribution
Chapter 5 Probability Distributions 5-1 Overview 5-2 Random Variables 5-3 Binomial Probability Distributions 5-4 Mean, Variance, and Standard Deviation for the Binomial Distribution 5-5 The Poisson Distribution
Data that can be any numerical value are called continuous. These are usually things that are measured, such as height, length, time, speed, etc.
 Chapter 8 Measures of Center Data that can be any numerical value are called continuous. These are usually things that are measured, such as height, length, time, speed, etc. Data that can only be integer
Chapter 8 Measures of Center Data that can be any numerical value are called continuous. These are usually things that are measured, such as height, length, time, speed, etc. Data that can only be integer
Statistics for Business and Economics
 Statistics for Business and Economics Chapter 5 Continuous Random Variables and Probability Distributions Ch. 5-1 Probability Distributions Probability Distributions Ch. 4 Discrete Continuous Ch. 5 Probability
Statistics for Business and Economics Chapter 5 Continuous Random Variables and Probability Distributions Ch. 5-1 Probability Distributions Probability Distributions Ch. 4 Discrete Continuous Ch. 5 Probability
Chapter 4 Random Variables & Probability. Chapter 4.5, 6, 8 Probability Distributions for Continuous Random Variables
 Chapter 4.5, 6, 8 Probability for Continuous Random Variables Discrete vs. continuous random variables Examples of continuous distributions o Uniform o Exponential o Normal Recall: A random variable =
Chapter 4.5, 6, 8 Probability for Continuous Random Variables Discrete vs. continuous random variables Examples of continuous distributions o Uniform o Exponential o Normal Recall: A random variable =
4: Probability. What is probability? Random variables (RVs)
 4: Probability b binomial µ expected value [parameter] n number of trials [parameter] N normal p probability of success [parameter] pdf probability density function pmf probability mass function RV random
4: Probability b binomial µ expected value [parameter] n number of trials [parameter] N normal p probability of success [parameter] pdf probability density function pmf probability mass function RV random
GETTING STARTED. To OPEN MINITAB: Click Start>Programs>Minitab14>Minitab14 or Click Minitab 14 on your Desktop
 Minitab 14 1 GETTING STARTED To OPEN MINITAB: Click Start>Programs>Minitab14>Minitab14 or Click Minitab 14 on your Desktop The Minitab session will come up like this 2 To SAVE FILE 1. Click File>Save Project
Minitab 14 1 GETTING STARTED To OPEN MINITAB: Click Start>Programs>Minitab14>Minitab14 or Click Minitab 14 on your Desktop The Minitab session will come up like this 2 To SAVE FILE 1. Click File>Save Project
STATISTICAL DISTRIBUTIONS AND THE CALCULATOR
 STATISTICAL DISTRIBUTIONS AND THE CALCULATOR 1. Basic data sets a. Measures of Center - Mean ( ): average of all values. Characteristic: non-resistant is affected by skew and outliers. - Median: Either
STATISTICAL DISTRIBUTIONS AND THE CALCULATOR 1. Basic data sets a. Measures of Center - Mean ( ): average of all values. Characteristic: non-resistant is affected by skew and outliers. - Median: Either
5.1 Sampling Distributions for Counts and Proportions. Ulrich Hoensch MAT210 Rocky Mountain College Billings, MT 59102
 5.1 Sampling Distributions for Counts and Proportions Ulrich Hoensch MAT210 Rocky Mountain College Billings, MT 59102 Sampling and Population Distributions Example: Count of People with Bachelor s Degrees
5.1 Sampling Distributions for Counts and Proportions Ulrich Hoensch MAT210 Rocky Mountain College Billings, MT 59102 Sampling and Population Distributions Example: Count of People with Bachelor s Degrees
3500. What types of numbers do not make sense for x? What types of numbers do not make sense for y? Graph y = 250 x+
 Name Date TI-84+ GC 19 Choosing an Appropriate Window for Applications Objective: Choose appropriate window for applications Example 1: A small company makes a toy. The price of one toy x (in dollars)
Name Date TI-84+ GC 19 Choosing an Appropriate Window for Applications Objective: Choose appropriate window for applications Example 1: A small company makes a toy. The price of one toy x (in dollars)
BARUCH COLLEGE MATH 2205 SPRING MANUAL FOR THE UNIFORM FINAL EXAMINATION Joseph Collison, Warren Gordon, Walter Wang, April Allen Materowski
 BARUCH COLLEGE MATH 05 SPRING 006 MANUAL FOR THE UNIFORM FINAL EXAMINATION Joseph Collison, Warren Gordon, Walter Wang, April Allen Materowski The final examination for Math 05 will consist of two parts.
BARUCH COLLEGE MATH 05 SPRING 006 MANUAL FOR THE UNIFORM FINAL EXAMINATION Joseph Collison, Warren Gordon, Walter Wang, April Allen Materowski The final examination for Math 05 will consist of two parts.
Section 3.5a Applying the Normal Distribution MDM4U Jensen
 Section 3.5a Applying the Normal Distribution MDM4U Jensen Part 1: Normal Distribution Video While watching the video, answer the following questions 1. What is another name for the Empirical rule? The
Section 3.5a Applying the Normal Distribution MDM4U Jensen Part 1: Normal Distribution Video While watching the video, answer the following questions 1. What is another name for the Empirical rule? The
The Binomial and Geometric Distributions. Chapter 8
 The Binomial and Geometric Distributions Chapter 8 8.1 The Binomial Distribution A binomial experiment is statistical experiment that has the following properties: The experiment consists of n repeated
The Binomial and Geometric Distributions Chapter 8 8.1 The Binomial Distribution A binomial experiment is statistical experiment that has the following properties: The experiment consists of n repeated
11.5: Normal Distributions
 11.5: Normal Distributions 11.5.1 Up to now, we ve dealt with discrete random variables, variables that take on only a finite (or countably infinite we didn t do these) number of values. A continuous random
11.5: Normal Distributions 11.5.1 Up to now, we ve dealt with discrete random variables, variables that take on only a finite (or countably infinite we didn t do these) number of values. A continuous random
Confidence Intervals and Sample Size
 Confidence Intervals and Sample Size Chapter 6 shows us how we can use the Central Limit Theorem (CLT) to 1. estimate a population parameter (such as the mean or proportion) using a sample, and. determine
Confidence Intervals and Sample Size Chapter 6 shows us how we can use the Central Limit Theorem (CLT) to 1. estimate a population parameter (such as the mean or proportion) using a sample, and. determine
In a binomial experiment of n trials, where p = probability of success and q = probability of failure. mean variance standard deviation
 Name In a binomial experiment of n trials, where p = probability of success and q = probability of failure mean variance standard deviation µ = n p σ = n p q σ = n p q Notation X ~ B(n, p) The probability
Name In a binomial experiment of n trials, where p = probability of success and q = probability of failure mean variance standard deviation µ = n p σ = n p q σ = n p q Notation X ~ B(n, p) The probability
Using the Central Limit Theorem It is important for you to understand when to use the CLT. If you are being asked to find the probability of the
 Using the Central Limit Theorem It is important for you to understand when to use the CLT. If you are being asked to find the probability of the mean, use the CLT for the mean. If you are being asked to
Using the Central Limit Theorem It is important for you to understand when to use the CLT. If you are being asked to find the probability of the mean, use the CLT for the mean. If you are being asked to
Homework: Due Wed, Feb 20 th. Chapter 8, # 60a + 62a (count together as 1), 74, 82
 Announcements: Week 5 quiz begins at 4pm today and ends at 3pm on Wed If you take more than 20 minutes to complete your quiz, you will only receive partial credit. (It doesn t cut you off.) Today: Sections
Announcements: Week 5 quiz begins at 4pm today and ends at 3pm on Wed If you take more than 20 minutes to complete your quiz, you will only receive partial credit. (It doesn t cut you off.) Today: Sections
Discrete Probability Distribution
 1 Discrete Probability Distribution Key Definitions Discrete Random Variable: Has a countable number of values. This means that each data point is distinct and separate. Continuous Random Variable: Has
1 Discrete Probability Distribution Key Definitions Discrete Random Variable: Has a countable number of values. This means that each data point is distinct and separate. Continuous Random Variable: Has
Chapter 7. Random Variables
 Chapter 7 Random Variables Making quantifiable meaning out of categorical data Toss three coins. What does the sample space consist of? HHH, HHT, HTH, HTT, TTT, TTH, THT, THH In statistics, we are most
Chapter 7 Random Variables Making quantifiable meaning out of categorical data Toss three coins. What does the sample space consist of? HHH, HHT, HTH, HTT, TTT, TTH, THT, THH In statistics, we are most
AMS7: WEEK 4. CLASS 3
 AMS7: WEEK 4. CLASS 3 Sampling distributions and estimators. Central Limit Theorem Normal Approximation to the Binomial Distribution Friday April 24th, 2015 Sampling distributions and estimators REMEMBER:
AMS7: WEEK 4. CLASS 3 Sampling distributions and estimators. Central Limit Theorem Normal Approximation to the Binomial Distribution Friday April 24th, 2015 Sampling distributions and estimators REMEMBER:
MATH 104 CHAPTER 5 page 1 NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
 MATH 104 CHAPTER 5 page 1 NORMAL DISTRIBUTION We have examined discrete random variables, those random variables for which we can list the possible values. We will now look at continuous random variables.
MATH 104 CHAPTER 5 page 1 NORMAL DISTRIBUTION We have examined discrete random variables, those random variables for which we can list the possible values. We will now look at continuous random variables.
MAS1403. Quantitative Methods for Business Management. Semester 1, Module leader: Dr. David Walshaw
 MAS1403 Quantitative Methods for Business Management Semester 1, 2018 2019 Module leader: Dr. David Walshaw Additional lecturers: Dr. James Waldren and Dr. Stuart Hall Announcements: Written assignment
MAS1403 Quantitative Methods for Business Management Semester 1, 2018 2019 Module leader: Dr. David Walshaw Additional lecturers: Dr. James Waldren and Dr. Stuart Hall Announcements: Written assignment
Binomial Distribution. Normal Approximation to the Binomial
 Binomial Distribution Normal Approximation to the Binomial /29 Homework Read Sec 6-6. Discussion Question pg 337 Do Ex 6-6 -4 2 /29 Objectives Objective: Use the normal approximation to calculate 3 /29
Binomial Distribution Normal Approximation to the Binomial /29 Homework Read Sec 6-6. Discussion Question pg 337 Do Ex 6-6 -4 2 /29 Objectives Objective: Use the normal approximation to calculate 3 /29
Section Distributions of Random Variables
 Section 8.1 - Distributions of Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
Section 8.1 - Distributions of Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
Standard Normal Calculations
 Standard Normal Calculations Section 4.3 Cathy Poliak, Ph.D. cathy@math.uh.edu Office in Fleming 11c Department of Mathematics University of Houston Lecture 10-2311 Cathy Poliak, Ph.D. cathy@math.uh.edu
Standard Normal Calculations Section 4.3 Cathy Poliak, Ph.D. cathy@math.uh.edu Office in Fleming 11c Department of Mathematics University of Houston Lecture 10-2311 Cathy Poliak, Ph.D. cathy@math.uh.edu
The Normal Distribution. (Ch 4.3)
 5 The Normal Distribution (Ch 4.3) The Normal Distribution The normal distribution is probably the most important distribution in all of probability and statistics. Many populations have distributions
5 The Normal Distribution (Ch 4.3) The Normal Distribution The normal distribution is probably the most important distribution in all of probability and statistics. Many populations have distributions
Chapter ! Bell Shaped
 Chapter 6 6-1 Business Statistics: A First Course 5 th Edition Chapter 7 Continuous Probability Distributions Learning Objectives In this chapter, you learn:! To compute probabilities from the normal distribution!
Chapter 6 6-1 Business Statistics: A First Course 5 th Edition Chapter 7 Continuous Probability Distributions Learning Objectives In this chapter, you learn:! To compute probabilities from the normal distribution!
The "bell-shaped" curve, or normal curve, is a probability distribution that describes many real-life situations.
 6.1 6.2 The Standard Normal Curve The "bell-shaped" curve, or normal curve, is a probability distribution that describes many real-life situations. Basic Properties 1. The total area under the curve is.
6.1 6.2 The Standard Normal Curve The "bell-shaped" curve, or normal curve, is a probability distribution that describes many real-life situations. Basic Properties 1. The total area under the curve is.
Lecture 9. Probability Distributions. Outline. Outline
 Outline Lecture 9 Probability Distributions 6-1 Introduction 6- Probability Distributions 6-3 Mean, Variance, and Expectation 6-4 The Binomial Distribution Outline 7- Properties of the Normal Distribution
Outline Lecture 9 Probability Distributions 6-1 Introduction 6- Probability Distributions 6-3 Mean, Variance, and Expectation 6-4 The Binomial Distribution Outline 7- Properties of the Normal Distribution
Chapter 6. The Normal Probability Distributions
 Chapter 6 The Normal Probability Distributions 1 Chapter 6 Overview Introduction 6-1 Normal Probability Distributions 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution 6-3 Applications of the Normal Distribution 6-5
Chapter 6 The Normal Probability Distributions 1 Chapter 6 Overview Introduction 6-1 Normal Probability Distributions 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution 6-3 Applications of the Normal Distribution 6-5
Math 120 Introduction to Statistics Mr. Toner s Lecture Notes. Standardizing normal distributions The Standard Normal Curve
 6.1 6.2 The Standard Normal Curve Standardizing normal distributions The "bell-shaped" curve, or normal curve, is a probability distribution that describes many reallife situations. Basic Properties 1.
6.1 6.2 The Standard Normal Curve Standardizing normal distributions The "bell-shaped" curve, or normal curve, is a probability distribution that describes many reallife situations. Basic Properties 1.
Inverse Normal Distribution and Approximation to Binomial
 Inverse Normal Distribution and Approximation to Binomial Section 5.5 Cathy Poliak, Ph.D. cathy@math.uh.edu Office in Fleming 11c Department of Mathematics University of Houston Lecture 16-3339 Cathy Poliak,
Inverse Normal Distribution and Approximation to Binomial Section 5.5 Cathy Poliak, Ph.D. cathy@math.uh.edu Office in Fleming 11c Department of Mathematics University of Houston Lecture 16-3339 Cathy Poliak,
Lecture 9. Probability Distributions
 Lecture 9 Probability Distributions Outline 6-1 Introduction 6-2 Probability Distributions 6-3 Mean, Variance, and Expectation 6-4 The Binomial Distribution Outline 7-2 Properties of the Normal Distribution
Lecture 9 Probability Distributions Outline 6-1 Introduction 6-2 Probability Distributions 6-3 Mean, Variance, and Expectation 6-4 The Binomial Distribution Outline 7-2 Properties of the Normal Distribution
23.1 Probability Distributions
 3.1 Probability Distributions Essential Question: What is a probability distribution for a discrete random variable, and how can it be displayed? Explore Using Simulation to Obtain an Empirical Probability
3.1 Probability Distributions Essential Question: What is a probability distribution for a discrete random variable, and how can it be displayed? Explore Using Simulation to Obtain an Empirical Probability
Chapter 4 Probability Distributions
 Slide 1 Chapter 4 Probability Distributions Slide 2 4-1 Overview 4-2 Random Variables 4-3 Binomial Probability Distributions 4-4 Mean, Variance, and Standard Deviation for the Binomial Distribution 4-5
Slide 1 Chapter 4 Probability Distributions Slide 2 4-1 Overview 4-2 Random Variables 4-3 Binomial Probability Distributions 4-4 Mean, Variance, and Standard Deviation for the Binomial Distribution 4-5
Expected Value of a Random Variable
 Knowledge Article: Probability and Statistics Expected Value of a Random Variable Expected Value of a Discrete Random Variable You're familiar with a simple mean, or average, of a set. The mean value of
Knowledge Article: Probability and Statistics Expected Value of a Random Variable Expected Value of a Discrete Random Variable You're familiar with a simple mean, or average, of a set. The mean value of
STAT Chapter 5: Continuous Distributions. Probability distributions are used a bit differently for continuous r.v. s than for discrete r.v. s.
 STAT 515 -- Chapter 5: Continuous Distributions Probability distributions are used a bit differently for continuous r.v. s than for discrete r.v. s. Continuous distributions typically are represented by
STAT 515 -- Chapter 5: Continuous Distributions Probability distributions are used a bit differently for continuous r.v. s than for discrete r.v. s. Continuous distributions typically are represented by
A continuous random variable is one that can theoretically take on any value on some line interval. We use f ( x)
 Section 6-2 I. Continuous Probability Distributions A continuous random variable is one that can theoretically take on any value on some line interval. We use f ( x) to represent a probability density
Section 6-2 I. Continuous Probability Distributions A continuous random variable is one that can theoretically take on any value on some line interval. We use f ( x) to represent a probability density
Chapter 14 - Random Variables
 Chapter 14 - Random Variables October 29, 2014 There are many scenarios where probabilities are used to determine risk factors. Examples include Insurance, Casino, Lottery, Business, Medical, and other
Chapter 14 - Random Variables October 29, 2014 There are many scenarios where probabilities are used to determine risk factors. Examples include Insurance, Casino, Lottery, Business, Medical, and other
Chapter 4 and Chapter 5 Test Review Worksheet
 Name: Date: Hour: Chapter 4 and Chapter 5 Test Review Worksheet You must shade all provided graphs, you must round all z-scores to 2 places after the decimal, you must round all probabilities to at least
Name: Date: Hour: Chapter 4 and Chapter 5 Test Review Worksheet You must shade all provided graphs, you must round all z-scores to 2 places after the decimal, you must round all probabilities to at least
Derived copy of Using the Normal Distribution *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m62375 1 Derived copy of Using the Normal Distribution * Cindy Sun Based on Using the Normal Distribution by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative
OpenStax-CNX module: m62375 1 Derived copy of Using the Normal Distribution * Cindy Sun Based on Using the Normal Distribution by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Chapter 6 Exam A Name The given values are discrete. Use the continuity correction and describe the region of the normal distribution that corresponds to the indicated probability. 1) The probability of
Chapter 6 Exam A Name The given values are discrete. Use the continuity correction and describe the region of the normal distribution that corresponds to the indicated probability. 1) The probability of
The Normal Approximation to the Binomial
 Lecture 16 The Normal Approximation to the Binomial We can calculate l binomial i probabilities bbilii using The binomial formula The cumulative binomial tables When n is large, and p is not too close
Lecture 16 The Normal Approximation to the Binomial We can calculate l binomial i probabilities bbilii using The binomial formula The cumulative binomial tables When n is large, and p is not too close
5.2 Random Variables, Probability Histograms and Probability Distributions
 Chapter 5 5.2 Random Variables, Probability Histograms and Probability Distributions A random variable (r.v.) can be either continuous or discrete. It takes on the possible values of an experiment. It
Chapter 5 5.2 Random Variables, Probability Histograms and Probability Distributions A random variable (r.v.) can be either continuous or discrete. It takes on the possible values of an experiment. It
NORMAL PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS
 5 CHAPTER NORMAL PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS 5.1 Introduction to Normal Distributions and the Standard Normal Distribution 5.2 Normal Distributions: Finding Probabilities 5.3 Normal Distributions: Finding
5 CHAPTER NORMAL PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS 5.1 Introduction to Normal Distributions and the Standard Normal Distribution 5.2 Normal Distributions: Finding Probabilities 5.3 Normal Distributions: Finding
Chapter 8 Homework Solutions Compiled by Joe Kahlig. speed(x) freq 25 x < x < x < x < x < x < 55 5
 H homework problems, C-copyright Joe Kahlig Chapter Solutions, Page Chapter Homework Solutions Compiled by Joe Kahlig. (a) finite discrete (b) infinite discrete (c) continuous (d) finite discrete (e) continuous.
H homework problems, C-copyright Joe Kahlig Chapter Solutions, Page Chapter Homework Solutions Compiled by Joe Kahlig. (a) finite discrete (b) infinite discrete (c) continuous (d) finite discrete (e) continuous.
Continuous Random Variables and Probability Distributions
 CHAPTER 5 CHAPTER OUTLINE Continuous Random Variables and Probability Distributions 5.1 Continuous Random Variables The Uniform Distribution 5.2 Expectations for Continuous Random Variables 5.3 The Normal
CHAPTER 5 CHAPTER OUTLINE Continuous Random Variables and Probability Distributions 5.1 Continuous Random Variables The Uniform Distribution 5.2 Expectations for Continuous Random Variables 5.3 The Normal
Math Week in Review #10. Experiments with two outcomes ( success and failure ) are called Bernoulli or binomial trials.
 Math 141 Spring 2006 c Heather Ramsey Page 1 Section 8.4 - Binomial Distribution Math 141 - Week in Review #10 Experiments with two outcomes ( success and failure ) are called Bernoulli or binomial trials.
Math 141 Spring 2006 c Heather Ramsey Page 1 Section 8.4 - Binomial Distribution Math 141 - Week in Review #10 Experiments with two outcomes ( success and failure ) are called Bernoulli or binomial trials.
Chapter 6 Analyzing Accumulated Change: Integrals in Action
 Chapter 6 Analyzing Accumulated Change: Integrals in Action 6. Streams in Business and Biology You will find Excel very helpful when dealing with streams that are accumulated over finite intervals. Finding
Chapter 6 Analyzing Accumulated Change: Integrals in Action 6. Streams in Business and Biology You will find Excel very helpful when dealing with streams that are accumulated over finite intervals. Finding
2011 Pearson Education, Inc
 Statistics for Business and Economics Chapter 4 Random Variables & Probability Distributions Content 1. Two Types of Random Variables 2. Probability Distributions for Discrete Random Variables 3. The Binomial
Statistics for Business and Economics Chapter 4 Random Variables & Probability Distributions Content 1. Two Types of Random Variables 2. Probability Distributions for Discrete Random Variables 3. The Binomial
Examples: Random Variables. Discrete and Continuous Random Variables. Probability Distributions
 Random Variables Examples: Random variable a variable (typically represented by x) that takes a numerical value by chance. Number of boys in a randomly selected family with three children. Possible values:
Random Variables Examples: Random variable a variable (typically represented by x) that takes a numerical value by chance. Number of boys in a randomly selected family with three children. Possible values:
CHAPTER 8 PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS AND STATISTICS
 CHAPTER 8 PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS AND STATISTICS 8.1 Distribution of Random Variables Random Variable Probability Distribution of Random Variables 8.2 Expected Value Mean Mean is the average value of
CHAPTER 8 PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS AND STATISTICS 8.1 Distribution of Random Variables Random Variable Probability Distribution of Random Variables 8.2 Expected Value Mean Mean is the average value of
These Statistics NOTES Belong to:
 These Statistics NOTES Belong to: Topic Notes Questions Date 1 2 3 4 5 6 REVIEW DO EVERY QUESTION IN YOUR PROVINCIAL EXAM BINDER Important Calculator Functions to know for this chapter Normal Distributions
These Statistics NOTES Belong to: Topic Notes Questions Date 1 2 3 4 5 6 REVIEW DO EVERY QUESTION IN YOUR PROVINCIAL EXAM BINDER Important Calculator Functions to know for this chapter Normal Distributions
