DazStat. Introduction. Installation. DazStat is an Excel add-in for Excel 2003 and Excel 2007.
|
|
|
- Cory Sparks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DazStat Introduction DazStat is an Excel add-in for Excel 2003 and Excel DazStat is one of a series of Daz add-ins that are planned to provide increasingly sophisticated analytical functions particularly suited to investment analysts. Existing and planned modules include: DazRatio analytical estimates of performance and risk DazBeta analytical and functional estimates of correlation, covariance, and Beta DazAlpha analytical estimates of Alpha, functional Alpha and Alpha stability DazUtility other functions that are useful and productive Installation DazStat is provided as an add-in application provided with an installer application. Double-click on the DazStatSetup installer, acknowledge the License Agreement, select whether to install for just the current user or all users on your computer and click through to completion. DazStat uses a license manager application. This requires you to select the type of license you are registering. The license will be verified automatically.
2 After registration the License Manager will check the registration periodically when activated in Excel, but this takes just a moment. The License Manager is quite sophisticated and should not cause any problems if you need to re-install on a new drive, etc. If you have any problems please contact Information@DazRisk.com. In Excel 2003, go to Menu Tools/Add-ins. Select the Automation option, scroll down to DazStat (press D to get there fast) and click OK. DazStat will now show in the add-in list with a check mark to show that it is active. In Excel 2007, go to the Microsoft Office Button and select Excel Options at the bottom. Select Addin from the options on the left and click Go at the bottom. Select the Automation option, scroll down to DazStat (press D to get there fast) and click OK. DazStat will now show in the add-in list with a check mark to show that it is active. DazStat has been tested with Excel 2003, 2007 and 2010 Beta on Windows XP, Vista and Windows 7. The DazStat Examples file is a standard Excel worksheet that includes examples of the DazStat functions and how they may be used. These examples include the use with vertical return series, horizontal return series and return series in the percent not decimals. Note that the Stat switch can be referenced outside the function making it easy to select and change functions within an existing worksheet.
3 General Function Variables The function structure of DazStat is as follows: =DazStat(Stat, Data, Freq, Pct, Label) Stat (required) The specific function result to be returned. The switch choices are listed below. Data (required) The data range for values to be used in the function. Freq (optional) The number of periods in a year to be used for annualized return values. The default value is 12. Pct (optional) A flag that forces DazStat to convert the data series into decimals (i.e. 4.32% or ) from percentages (i.e ). The default value is True. Label (optional) A flag that forces DazStat to return the label (name) of the function rather than the result. The default value is False. Note that in most cases you will only need to add the first two variables as the others are optional with reasonable defaults. Rows and Columns The data range specified in DazStat can be for either a row or column orientation. Empty Values As you can see in the Examples worksheet, DazStat allows you to run the analytics against data that may have initial and final empty values. Certain Excel function will automatically exclude empty values in the results while others treat an empty value as a zero value. DazStat creates its own internal array of valid values from the data range you specify to give you consistency and also ease in replicating the function across a range of data series. Help Unfortunately, no help structure is provided for so-called User-Defined Functions (UDF) in Excel. Some assistance is available in Excel if you enter =DazStat() in a cell and select the function builder fx next to the formula bar.
4 Statistics Arrays are created by entering the DazStat function, selecting the number of cells for the array and pressing Ctrl-Shift-Enter. 0 Count Cell: Returns the number of values included in the data range. 1 Positive Cell: Returns the number of positive values included in the data range (includes zero). 2 Negative Cell: Returns the number of negative values included in the data range. 3 Mean Cell: Returns the mean (average) of the values included in the data range. Note: First moment of the Normal distribution. 4 Median Cell: Returns the median of the values included in the data range. Note: Should be the same as the Mean if the distribution is Normal. One test of Normal-ity. 5 Max Cell: Returns the maximum of the values included in the data range. 6 Min Cell: Returns the minimum of the values included in the data range. 7 Standard Deviation Cell: Returns the standard deviation of the values included in the data range. Note: Second moment of the Normal distribution measures the dispersion of expected returns: 68.27% within +/- one Standard Deviation of the Mean. The basis for most investment risk measures Annualized Volatility. 8 Skew Cell: Returns the skew of the distribution of the values included in the data range. Note: Third moment of the Normal distribution. Should be zero. One test of Normal-ity. Comparison with the Skew of the underlying asset returns would indicate active management, illiquidity or non-market pricing. 9 Excess Kurtosis Cell: Returns the excess kurtosis of the distribution of the values included in the data range. This is equivalent to Excel s Kurt() function and is not the same as the actual Kurtosis of the distribution. Note: Fourth moment of the Normal distribution. The expected Kurtosis is 3, so the actual value would be 3 + Excess Kurtosis. One test of Normal-ity.
5 Comparison with the Kurtosis of the underlying asset returns would indicate active management, illiquidity or non-market pricing. 10 Jarque-Bera Cell: Returns a label describing the distribution of the values included in the data range as Normal or Non-Normal. Using a P-value of 0.05 as an acceptance level. Array: Returns the label, the Jarque-Bera statistic (JB) and the Chi value for the 0.05 confidence. Note: If the JB statistic is greater than the Chi value, then the Jarque-Bera test implies that the distribution of values departs from the Normal null-hypothesis with a greater than 0.05 confidence. Note that this implementation of the Jarque-Bera test is not robust with fewer observations than PPCC Cell: Returns a label describing the distribution of the values included in the data range as Normal or Non-Normal using 0.99 as an acceptance level. Array: Returns the label and the Probability Plot Correlation Coefficient for the data relative to a Normal distribution with the same mean and standard deviation. Note: PPCC correlates the expected Normal distribution and the actual distribution, which produces a simple and easily understood result. However, the correlation coefficient should be above to have confidence that the actual distribution is Normal in a statistical sense. 12 Kolmogorov Smirnov Cell: Returns a label describing the distribution of the values included in the data range as Normal or Non-Normal using a P-value of 0.05 as an acceptance level. Array: Returns the label, the Kolmogorov Smirnov Z statistic for the differences between the expected Normal distribution and the actual data distribution and the approximate acceptance level of 1.36/Sqrt(n). Note: Kolmogorov Smirnov is a non-parametric statistic similar to PPCC, but measuring only a single point the greatest distance between the expected and actual data. 13 Anderson-Darling Cell: Returns a label describing the distribution of the values included in the data range as Normal or Non-Normal using a P-value of 0.05 as an acceptance level. Array: Returns the label, the Anderson-Darling A *2 statistic for the differences between the expected Normal distribution and the actual data distribution and the P-value. Note: Anderson-Darling is a powerful parametric test for goodness-of-fit to a parameterized distribution Normal in this case. 14 Ljung-Box Cell: Returns a label describing the distribution of the values included in the data range as Independent or Autocorrelated. Array: Returns the label, the Ljung-Box Q statistic, the Chi value for the 0.05 acceptance level and the number of lag steps (k). Note: If the Q statistic is greater than the Chi value, then the Ljung-Box test implies that the distribution
6 of returns is autocorrelated. Note that the Ljung-Box test is considered to be very robust but depends on the number of lag steps used. DazStat sets the number of lag steps to 50 if the number of values is greater than 200, 3 if the number of values is less than 50 and otherwise uses 10 lag steps. 15 Wald-Wolfowitz Cell: Returns a label describing the distribution of the values included in the data range as Random or Non-random. Array: Returns the label, the Wald-Wolfowitz Z statistic and the P-value. Note: Wald-Wolfowitz is a non-parametric test for randomness based on the number of observed runs in the data. Randomness is one of the properties that leads to a Normal distribution. Non-random may imply momentum, in-efficient market behavior and technical factors. 16 Cumulative Return Cell: Returns the cumulative return of the values in the data range. 17 CAGR Cell: Returns the Compound Annual Growth Rate of the values in the data range based on the Freq value entered into the function. 18 Annualized Volatility Cell: Returns the annualized volatility of the values in the data range based on the Freq value entered into the function. Note: Calculated as the Standard Deviation of the returns times the square root of the Freq. Not reliable as an estimate of risk if the distribution of returns is not Normal. See Non-parametric Standard Deviation. 19 Non-parametric Standard Deviation - Proprietary Cell: Returns the Non-parametric Standard Deviation. Array: Returns the Non-parametric Standard Deviation, the Non-parametric Downside Dispersion and the Non-parametric Upside Dispersion. Note: A Normal distribution has an expected 68.27% of the sample within +/- one Standard Deviation. The Non-parametric Standard Deviation measures the actual 68.27% range of the sample around the Mean return. 20 Non-parametric Annualized Volatility - Proprietary Cell: Returns the Non-parametric Annualized Volatility derived from the Non-parametric Standard Deviation times the square root of the Freq. Note: This is closer to the real volatility experienced by the return series. The Standard Deviation measured used for conventional Annualized Volatility assumes that the returns have a Normal distribution: symmetrical gains and losses, no excess Kurtosis or Skew. The Non-parametric Annualized
7 Volatility measures the actual range of returns (volatility or risk ) rather than the expected range of returns. 21 Inter-quartile Volatility Cell: Returns the annualized value of the inter-quartile volatility. Array: returns the annualized value of the inter-quartile volatility, and the first and third quartile values. Note: Measured as the difference between the 75 and 25 percentile values. This has been used as a non-parametric alternative to Standard Deviation, but it is measuring a different distribution (50%) rather than 69.27% - use Non-Parametric Standard Deviation for 68.27%. It is also measured without removing the Mean return. Inter-quartile Volatility is the 50% range of returns around the Median, which is assumed to be zero. 22Max Drawdown Cell: Returns the maximum cumulative drawdown of the returns. Array: Returns the maximum, second and third non-overlapping cumulative drawdowns of the returns. 23 Max Run-up Cell: Returns the maximum cumulative run-up of the returns. Array: Returns the maximum, second and third non-overlapping cumulative run-ups of the values in the data range. Ratios 98 and 99 are designed to provide a faster and more efficient method of producing all the DazRatio results by using an array rather than individual cell calculations. 98 All Results Returns all 45 results in a single horizontal array. 99 All Results Returns all 45 results in a single vertical array.
8 Tips Take a look at the DazStat Examples spreadsheet for ideas on how to use DazStat. Note that the DazStat structure is the same for all functions. This allows you to easily switch from one function to another or to use a cell value to determine the Stat result you want. That is one benefit of the DazStat module you do not have to learn the eccentricities of Excel s implementation of functions. Use the array results, even for individual functions. The array results provide information on the underlying or associated values to help you understand what is driving the value of the specific function result. Use the Index function if you want to have a single cell that accesses a result from inside an array. For example, INDEX(DazStat(15,B$2:B$65,12),2) will return the Wald-Wolfowitz runs test Z score directly for the returns in B2:B65. Look at the alternate functions for the same concept. For example, there are four different functions that measure the data s fit to a Normal distribution: Jarque-Bera, PPCC, Kolmogorov-Smirnov and Anderson-Darling. The differences tell you something about what happens when you change the assumptions.
Descriptive Statistics
 Chapter 3 Descriptive Statistics Chapter 2 presented graphical techniques for organizing and displaying data. Even though such graphical techniques allow the researcher to make some general observations
Chapter 3 Descriptive Statistics Chapter 2 presented graphical techniques for organizing and displaying data. Even though such graphical techniques allow the researcher to make some general observations
1.2 Describing Distributions with Numbers, Continued
 1.2 Describing Distributions with Numbers, Continued Ulrich Hoensch Thursday, September 6, 2012 Interquartile Range and 1.5 IQR Rule for Outliers The interquartile range IQR is the distance between the
1.2 Describing Distributions with Numbers, Continued Ulrich Hoensch Thursday, September 6, 2012 Interquartile Range and 1.5 IQR Rule for Outliers The interquartile range IQR is the distance between the
MATHEMATICS APPLIED TO BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES MVE PA 07. LP07 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS - Calculating of statistical indicators (1)
 LP07 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS - Calculating of statistical indicators (1) Descriptive statistics are ways of summarizing large sets of quantitative (numerical) information. The best way to reduce a set of
LP07 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS - Calculating of statistical indicators (1) Descriptive statistics are ways of summarizing large sets of quantitative (numerical) information. The best way to reduce a set of
Lecture 1: Empirical Properties of Returns
 Lecture 1: Empirical Properties of Returns Econ 589 Eric Zivot Spring 2011 Updated: March 29, 2011 Daily CC Returns on MSFT -0.3 r(t) -0.2-0.1 0.1 1986 1987 1988 1989 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996
Lecture 1: Empirical Properties of Returns Econ 589 Eric Zivot Spring 2011 Updated: March 29, 2011 Daily CC Returns on MSFT -0.3 r(t) -0.2-0.1 0.1 1986 1987 1988 1989 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996
2018 AAPM: Normal and non normal distributions: Why understanding distributions are important when designing experiments and analyzing data
 Statistical Failings that Keep Us All in the Dark Normal and non normal distributions: Why understanding distributions are important when designing experiments and Conflict of Interest Disclosure I have
Statistical Failings that Keep Us All in the Dark Normal and non normal distributions: Why understanding distributions are important when designing experiments and Conflict of Interest Disclosure I have
Washington University Fall Economics 487. Project Proposal due Monday 10/22 Final Project due Monday 12/3
 Washington University Fall 2001 Department of Economics James Morley Economics 487 Project Proposal due Monday 10/22 Final Project due Monday 12/3 For this project, you will analyze the behaviour of 10
Washington University Fall 2001 Department of Economics James Morley Economics 487 Project Proposal due Monday 10/22 Final Project due Monday 12/3 For this project, you will analyze the behaviour of 10
Washington University Fall Economics 487
 Washington University Fall 2009 Department of Economics James Morley Economics 487 Project Proposal due Tuesday 11/10 Final Project due Wednesday 12/9 (by 5:00pm) (20% penalty per day if the project is
Washington University Fall 2009 Department of Economics James Morley Economics 487 Project Proposal due Tuesday 11/10 Final Project due Wednesday 12/9 (by 5:00pm) (20% penalty per day if the project is
Financial Time Series and Their Characteristics
 Financial Time Series and Their Characteristics Egon Zakrajšek Division of Monetary Affairs Federal Reserve Board Summer School in Financial Mathematics Faculty of Mathematics & Physics University of Ljubljana
Financial Time Series and Their Characteristics Egon Zakrajšek Division of Monetary Affairs Federal Reserve Board Summer School in Financial Mathematics Faculty of Mathematics & Physics University of Ljubljana
Vivid Reports 2.0 Budget User Guide
 B R I S C O E S O L U T I O N S Vivid Reports 2.0 Budget User Guide Briscoe Solutions Inc PO BOX 2003 Station Main Winnipeg, MB R3C 3R3 Phone 204.975.9409 Toll Free 1.866.484.8778 Copyright 2009-2014 Briscoe
B R I S C O E S O L U T I O N S Vivid Reports 2.0 Budget User Guide Briscoe Solutions Inc PO BOX 2003 Station Main Winnipeg, MB R3C 3R3 Phone 204.975.9409 Toll Free 1.866.484.8778 Copyright 2009-2014 Briscoe
WEB APPENDIX 8A 7.1 ( 8.9)
 WEB APPENDIX 8A CALCULATING BETA COEFFICIENTS The CAPM is an ex ante model, which means that all of the variables represent before-the-fact expected values. In particular, the beta coefficient used in
WEB APPENDIX 8A CALCULATING BETA COEFFICIENTS The CAPM is an ex ante model, which means that all of the variables represent before-the-fact expected values. In particular, the beta coefficient used in
Creating and Assigning Targets
 Creating and Assigning Targets Targets are a powerful reporting tool in PortfolioCenter that allow you to mix index returns for several indexes, based on the portfolio s asset class allocation. For example,
Creating and Assigning Targets Targets are a powerful reporting tool in PortfolioCenter that allow you to mix index returns for several indexes, based on the portfolio s asset class allocation. For example,
DECISION SUPPORT Risk handout. Simulating Spreadsheet models
 DECISION SUPPORT MODELS @ Risk handout Simulating Spreadsheet models using @RISK 1. Step 1 1.1. Open Excel and @RISK enabling any macros if prompted 1.2. There are four on-line help options available.
DECISION SUPPORT MODELS @ Risk handout Simulating Spreadsheet models using @RISK 1. Step 1 1.1. Open Excel and @RISK enabling any macros if prompted 1.2. There are four on-line help options available.
The Advanced Budget Project Part D The Budget Report
 The Advanced Budget Project Part D The Budget Report A budget is probably the most important spreadsheet you can create. A good budget will keep you focused on your ultimate financial goal and help you
The Advanced Budget Project Part D The Budget Report A budget is probably the most important spreadsheet you can create. A good budget will keep you focused on your ultimate financial goal and help you
SUMMARY STATISTICS EXAMPLES AND ACTIVITIES
 Session 6 SUMMARY STATISTICS EXAMPLES AD ACTIVITIES Example 1.1 Expand the following: 1. X 2. 2 6 5 X 3. X 2 4 3 4 4. X 4 2 Solution 1. 2 3 2 X X X... X 2. 6 4 X X X X 4 5 6 5 3. X 2 X 3 2 X 4 2 X 5 2
Session 6 SUMMARY STATISTICS EXAMPLES AD ACTIVITIES Example 1.1 Expand the following: 1. X 2. 2 6 5 X 3. X 2 4 3 4 4. X 4 2 Solution 1. 2 3 2 X X X... X 2. 6 4 X X X X 4 5 6 5 3. X 2 X 3 2 X 4 2 X 5 2
MBEJ 1023 Dr. Mehdi Moeinaddini Dept. of Urban & Regional Planning Faculty of Built Environment
 MBEJ 1023 Planning Analytical Methods Dr. Mehdi Moeinaddini Dept. of Urban & Regional Planning Faculty of Built Environment Contents What is statistics? Population and Sample Descriptive Statistics Inferential
MBEJ 1023 Planning Analytical Methods Dr. Mehdi Moeinaddini Dept. of Urban & Regional Planning Faculty of Built Environment Contents What is statistics? Population and Sample Descriptive Statistics Inferential
Creating a Rolling Income Statement
 Creating a Rolling Income Statement This is a demonstration on how to create an Income Statement that will always return the current month s data as well as the prior 12 months data. The report will be
Creating a Rolling Income Statement This is a demonstration on how to create an Income Statement that will always return the current month s data as well as the prior 12 months data. The report will be
Risk Analysis. å To change Benchmark tickers:
 Property Sheet will appear. The Return/Statistics page will be displayed. 2. Use the five boxes in the Benchmark section of this page to enter or change the tickers that will appear on the Performance
Property Sheet will appear. The Return/Statistics page will be displayed. 2. Use the five boxes in the Benchmark section of this page to enter or change the tickers that will appear on the Performance
Written by N.Nilgün Çokça. Advance Excel. Part One. Using Excel for Data Analysis
 Written by N.Nilgün Çokça Advance Excel Part One Using Excel for Data Analysis March, 2018 P a g e 1 Using Excel for Calculations Arithmetic operations Arithmetic operators: To perform basic mathematical
Written by N.Nilgün Çokça Advance Excel Part One Using Excel for Data Analysis March, 2018 P a g e 1 Using Excel for Calculations Arithmetic operations Arithmetic operators: To perform basic mathematical
Spreadsheet Directions
 The Best Summer Job Offer Ever! Spreadsheet Directions Before beginning, answer questions 1 through 4. Now let s see if you made a wise choice of payment plan. Complete all the steps outlined below in
The Best Summer Job Offer Ever! Spreadsheet Directions Before beginning, answer questions 1 through 4. Now let s see if you made a wise choice of payment plan. Complete all the steps outlined below in
Ti 83/84. Descriptive Statistics for a List of Numbers
 Ti 83/84 Descriptive Statistics for a List of Numbers Quiz scores in a (fictitious) class were 10.5, 13.5, 8, 12, 11.3, 9, 9.5, 5, 15, 2.5, 10.5, 7, 11.5, 10, and 10.5. It s hard to get much of a sense
Ti 83/84 Descriptive Statistics for a List of Numbers Quiz scores in a (fictitious) class were 10.5, 13.5, 8, 12, 11.3, 9, 9.5, 5, 15, 2.5, 10.5, 7, 11.5, 10, and 10.5. It s hard to get much of a sense
LAB 2 INSTRUCTIONS PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS IN EXCEL
 LAB 2 INSTRUCTIONS PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS IN EXCEL There is a wide range of probability distributions (both discrete and continuous) available in Excel. They can be accessed through the Insert Function
LAB 2 INSTRUCTIONS PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS IN EXCEL There is a wide range of probability distributions (both discrete and continuous) available in Excel. They can be accessed through the Insert Function
ExcelSim 2003 Documentation
 ExcelSim 2003 Documentation Note: The ExcelSim 2003 add-in program is copyright 2001-2003 by Timothy R. Mayes, Ph.D. It is free to use, but it is meant for educational use only. If you wish to perform
ExcelSim 2003 Documentation Note: The ExcelSim 2003 add-in program is copyright 2001-2003 by Timothy R. Mayes, Ph.D. It is free to use, but it is meant for educational use only. If you wish to perform
Introduction to Basic Excel Functions and Formulae Note: Basic Functions Note: Function Key(s)/Input Description 1. Sum 2. Product
 Introduction to Basic Excel Functions and Formulae Excel has some very useful functions that you can use when working with formulae. This worksheet has been designed using Excel 2010 however the basic
Introduction to Basic Excel Functions and Formulae Excel has some very useful functions that you can use when working with formulae. This worksheet has been designed using Excel 2010 however the basic
Tests for One Variance
 Chapter 65 Introduction Occasionally, researchers are interested in the estimation of the variance (or standard deviation) rather than the mean. This module calculates the sample size and performs power
Chapter 65 Introduction Occasionally, researchers are interested in the estimation of the variance (or standard deviation) rather than the mean. This module calculates the sample size and performs power
University of Texas at Dallas School of Management. Investment Management Spring Estimation of Systematic and Factor Risks (Due April 1)
 University of Texas at Dallas School of Management Finance 6310 Professor Day Investment Management Spring 2008 Estimation of Systematic and Factor Risks (Due April 1) This assignment requires you to perform
University of Texas at Dallas School of Management Finance 6310 Professor Day Investment Management Spring 2008 Estimation of Systematic and Factor Risks (Due April 1) This assignment requires you to perform
starting on 5/1/1953 up until 2/1/2017.
 An Actuary s Guide to Financial Applications: Examples with EViews By William Bourgeois An actuary is a business professional who uses statistics to determine and analyze risks for companies. In this guide,
An Actuary s Guide to Financial Applications: Examples with EViews By William Bourgeois An actuary is a business professional who uses statistics to determine and analyze risks for companies. In this guide,
Basic Procedure for Histograms
 Basic Procedure for Histograms 1. Compute the range of observations (min. & max. value) 2. Choose an initial # of classes (most likely based on the range of values, try and find a number of classes that
Basic Procedure for Histograms 1. Compute the range of observations (min. & max. value) 2. Choose an initial # of classes (most likely based on the range of values, try and find a number of classes that
1 Exercise One. 1.1 Calculate the mean ROI. Note that the data is not grouped! Below you find the raw data in tabular form:
 1 Exercise One Note that the data is not grouped! 1.1 Calculate the mean ROI Below you find the raw data in tabular form: Obs Data 1 18.5 2 18.6 3 17.4 4 12.2 5 19.7 6 5.6 7 7.7 8 9.8 9 19.9 10 9.9 11
1 Exercise One Note that the data is not grouped! 1.1 Calculate the mean ROI Below you find the raw data in tabular form: Obs Data 1 18.5 2 18.6 3 17.4 4 12.2 5 19.7 6 5.6 7 7.7 8 9.8 9 19.9 10 9.9 11
Monte Carlo Simulation (Random Number Generation)
 Monte Carlo Simulation (Random Number Generation) Revised: 10/11/2017 Summary... 1 Data Input... 1 Analysis Options... 6 Summary Statistics... 6 Box-and-Whisker Plots... 7 Percentiles... 9 Quantile Plots...
Monte Carlo Simulation (Random Number Generation) Revised: 10/11/2017 Summary... 1 Data Input... 1 Analysis Options... 6 Summary Statistics... 6 Box-and-Whisker Plots... 7 Percentiles... 9 Quantile Plots...
Handout 5: Summarizing Numerical Data STAT 100 Spring 2016
 In this handout, we will consider methods that are appropriate for summarizing a single set of numerical measurements. Definition Numerical Data: A set of measurements that are recorded on a naturally
In this handout, we will consider methods that are appropriate for summarizing a single set of numerical measurements. Definition Numerical Data: A set of measurements that are recorded on a naturally
Two-Sample T-Test for Superiority by a Margin
 Chapter 219 Two-Sample T-Test for Superiority by a Margin Introduction This procedure provides reports for making inference about the superiority of a treatment mean compared to a control mean from data
Chapter 219 Two-Sample T-Test for Superiority by a Margin Introduction This procedure provides reports for making inference about the superiority of a treatment mean compared to a control mean from data
NCSS Statistical Software. Reference Intervals
 Chapter 586 Introduction A reference interval contains the middle 95% of measurements of a substance from a healthy population. It is a type of prediction interval. This procedure calculates one-, and
Chapter 586 Introduction A reference interval contains the middle 95% of measurements of a substance from a healthy population. It is a type of prediction interval. This procedure calculates one-, and
DATA HANDLING Five-Number Summary
 DATA HANDLING Five-Number Summary The five-number summary consists of the minimum and maximum values, the median, and the upper and lower quartiles. The minimum and the maximum are the smallest and greatest
DATA HANDLING Five-Number Summary The five-number summary consists of the minimum and maximum values, the median, and the upper and lower quartiles. The minimum and the maximum are the smallest and greatest
Workshop 1. Descriptive Statistics, Distributions, Sampling and Monte Carlo Simulation. Part I: The Firestone Case 1
 Sami Najafi Asadolahi Statistics for Managers Workshop 1 Descriptive Statistics, Distributions, Sampling and Monte Carlo Simulation The purpose of the workshops is to give you hands-on experience with
Sami Najafi Asadolahi Statistics for Managers Workshop 1 Descriptive Statistics, Distributions, Sampling and Monte Carlo Simulation The purpose of the workshops is to give you hands-on experience with
Two-Sample T-Test for Non-Inferiority
 Chapter 198 Two-Sample T-Test for Non-Inferiority Introduction This procedure provides reports for making inference about the non-inferiority of a treatment mean compared to a control mean from data taken
Chapter 198 Two-Sample T-Test for Non-Inferiority Introduction This procedure provides reports for making inference about the non-inferiority of a treatment mean compared to a control mean from data taken
Point-Biserial and Biserial Correlations
 Chapter 302 Point-Biserial and Biserial Correlations Introduction This procedure calculates estimates, confidence intervals, and hypothesis tests for both the point-biserial and the biserial correlations.
Chapter 302 Point-Biserial and Biserial Correlations Introduction This procedure calculates estimates, confidence intervals, and hypothesis tests for both the point-biserial and the biserial correlations.
Table of Contents. New to the Second Edition... Chapter 1: Introduction : Social Research...
 iii Table of Contents Preface... xiii Purpose... xiii Outline of Chapters... xiv New to the Second Edition... xvii Acknowledgements... xviii Chapter 1: Introduction... 1 1.1: Social Research... 1 Introduction...
iii Table of Contents Preface... xiii Purpose... xiii Outline of Chapters... xiv New to the Second Edition... xvii Acknowledgements... xviii Chapter 1: Introduction... 1 1.1: Social Research... 1 Introduction...
An application program that can quickly handle calculations. A spreadsheet uses numbers like a word processor uses words.
 An application program that can quickly handle calculations A spreadsheet uses numbers like a word processor uses words. WHAT IF? Columns run vertically & are identified by letters A, B, etc. Rows run
An application program that can quickly handle calculations A spreadsheet uses numbers like a word processor uses words. WHAT IF? Columns run vertically & are identified by letters A, B, etc. Rows run
Project your expenses
 Welcome to the Victory Cashflow worksheet. Spending just half an hour each month will ensure your budget is maintained and your finances are in order. The objective of this budget is to predict the future
Welcome to the Victory Cashflow worksheet. Spending just half an hour each month will ensure your budget is maintained and your finances are in order. The objective of this budget is to predict the future
Data Distributions and Normality
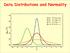 Data Distributions and Normality Definition (Non)Parametric Parametric statistics assume that data come from a normal distribution, and make inferences about parameters of that distribution. These statistical
Data Distributions and Normality Definition (Non)Parametric Parametric statistics assume that data come from a normal distribution, and make inferences about parameters of that distribution. These statistical
Using an Excel spreadsheet to calculate Andrew s 18th birthday costs
 Using an Excel spreadsheet to calculate Andrew s 18th birthday costs Open a new spreadsheet in Excel. Highlight cells A1 to J1. Prevocational Mathematics 1 of 17 Planning an event Using an Excel spreadsheet
Using an Excel spreadsheet to calculate Andrew s 18th birthday costs Open a new spreadsheet in Excel. Highlight cells A1 to J1. Prevocational Mathematics 1 of 17 Planning an event Using an Excel spreadsheet
Copyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 6-1
 Copyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 6-1 Chapter 6 Copyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Measures of Center in a Distribution 6-A The mean is what we most commonly call the average value. It is
Copyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 6-1 Chapter 6 Copyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Measures of Center in a Distribution 6-A The mean is what we most commonly call the average value. It is
Chapter 3. Numerical Descriptive Measures. Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd. Chapter 3, Slide 1
 Chapter 3 Numerical Descriptive Measures Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd. Chapter 3, Slide 1 Objectives In this chapter, you learn to: Describe the properties of central tendency, variation, and
Chapter 3 Numerical Descriptive Measures Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd. Chapter 3, Slide 1 Objectives In this chapter, you learn to: Describe the properties of central tendency, variation, and
Introduction to Computational Finance and Financial Econometrics Descriptive Statistics
 You can t see this text! Introduction to Computational Finance and Financial Econometrics Descriptive Statistics Eric Zivot Summer 2015 Eric Zivot (Copyright 2015) Descriptive Statistics 1 / 28 Outline
You can t see this text! Introduction to Computational Finance and Financial Econometrics Descriptive Statistics Eric Zivot Summer 2015 Eric Zivot (Copyright 2015) Descriptive Statistics 1 / 28 Outline
Morningstar Direct SM 3.16 Release Aug 2014
 The Morningstar Direct team is pleased to announce the new features and enhancements in version 3.16. In this release, you can now search for Strategic Beta products in addition to taking action on new
The Morningstar Direct team is pleased to announce the new features and enhancements in version 3.16. In this release, you can now search for Strategic Beta products in addition to taking action on new
You should already have a worksheet with the Basic Plus Plan details in it as well as another plan you have chosen from ehealthinsurance.com.
 In earlier technology assignments, you identified several details of a health plan and created a table of total cost. In this technology assignment, you ll create a worksheet which calculates the total
In earlier technology assignments, you identified several details of a health plan and created a table of total cost. In this technology assignment, you ll create a worksheet which calculates the total
Simple Descriptive Statistics
 Simple Descriptive Statistics These are ways to summarize a data set quickly and accurately The most common way of describing a variable distribution is in terms of two of its properties: Central tendency
Simple Descriptive Statistics These are ways to summarize a data set quickly and accurately The most common way of describing a variable distribution is in terms of two of its properties: Central tendency
How To: Perform a Process Capability Analysis Using STATGRAPHICS Centurion
 How To: Perform a Process Capability Analysis Using STATGRAPHICS Centurion by Dr. Neil W. Polhemus July 17, 2005 Introduction For individuals concerned with the quality of the goods and services that they
How To: Perform a Process Capability Analysis Using STATGRAPHICS Centurion by Dr. Neil W. Polhemus July 17, 2005 Introduction For individuals concerned with the quality of the goods and services that they
Decision Trees Using TreePlan
 Decision Trees Using TreePlan 6 6. TREEPLAN OVERVIEW TreePlan is a decision tree add-in for Microsoft Excel 7 & & & 6 (Windows) and Microsoft Excel & 6 (Macintosh). TreePlan helps you build a decision
Decision Trees Using TreePlan 6 6. TREEPLAN OVERVIEW TreePlan is a decision tree add-in for Microsoft Excel 7 & & & 6 (Windows) and Microsoft Excel & 6 (Macintosh). TreePlan helps you build a decision
Web Extension: Continuous Distributions and Estimating Beta with a Calculator
 19878_02W_p001-008.qxd 3/10/06 9:51 AM Page 1 C H A P T E R 2 Web Extension: Continuous Distributions and Estimating Beta with a Calculator This extension explains continuous probability distributions
19878_02W_p001-008.qxd 3/10/06 9:51 AM Page 1 C H A P T E R 2 Web Extension: Continuous Distributions and Estimating Beta with a Calculator This extension explains continuous probability distributions
REGIONAL WORKSHOP ON TRAFFIC FORECASTING AND ECONOMIC PLANNING
 International Civil Aviation Organization 27/8/10 WORKING PAPER REGIONAL WORKSHOP ON TRAFFIC FORECASTING AND ECONOMIC PLANNING Cairo 2 to 4 November 2010 Agenda Item 3 a): Forecasting Methodology (Presented
International Civil Aviation Organization 27/8/10 WORKING PAPER REGIONAL WORKSHOP ON TRAFFIC FORECASTING AND ECONOMIC PLANNING Cairo 2 to 4 November 2010 Agenda Item 3 a): Forecasting Methodology (Presented
Tests for Two Variances
 Chapter 655 Tests for Two Variances Introduction Occasionally, researchers are interested in comparing the variances (or standard deviations) of two groups rather than their means. This module calculates
Chapter 655 Tests for Two Variances Introduction Occasionally, researchers are interested in comparing the variances (or standard deviations) of two groups rather than their means. This module calculates
Chapter 4 Level of Volatility in the Indian Stock Market
 Chapter 4 Level of Volatility in the Indian Stock Market Measurement of volatility is an important issue in financial econometrics. The main reason for the prominent role that volatility plays in financial
Chapter 4 Level of Volatility in the Indian Stock Market Measurement of volatility is an important issue in financial econometrics. The main reason for the prominent role that volatility plays in financial
Monte Carlo Simulation (General Simulation Models)
 Monte Carlo Simulation (General Simulation Models) Revised: 10/11/2017 Summary... 1 Example #1... 1 Example #2... 10 Summary Monte Carlo simulation is used to estimate the distribution of variables when
Monte Carlo Simulation (General Simulation Models) Revised: 10/11/2017 Summary... 1 Example #1... 1 Example #2... 10 Summary Monte Carlo simulation is used to estimate the distribution of variables when
Data screening, transformations: MRC05
 Dale Berger Data screening, transformations: MRC05 This is a demonstration of data screening and transformations for a regression analysis. Our interest is in predicting current salary from education level
Dale Berger Data screening, transformations: MRC05 This is a demonstration of data screening and transformations for a regression analysis. Our interest is in predicting current salary from education level
Review: Types of Summary Statistics
 Review: Types of Summary Statistics We re often interested in describing the following characteristics of the distribution of a data series: Central tendency - where is the middle of the distribution?
Review: Types of Summary Statistics We re often interested in describing the following characteristics of the distribution of a data series: Central tendency - where is the middle of the distribution?
Statistical Analysis of Data from the Stock Markets. UiO-STK4510 Autumn 2015
 Statistical Analysis of Data from the Stock Markets UiO-STK4510 Autumn 2015 Sampling Conventions We observe the price process S of some stock (or stock index) at times ft i g i=0,...,n, we denote it by
Statistical Analysis of Data from the Stock Markets UiO-STK4510 Autumn 2015 Sampling Conventions We observe the price process S of some stock (or stock index) at times ft i g i=0,...,n, we denote it by
Bidding Decision Example
 Bidding Decision Example SUPERTREE EXAMPLE In this chapter, we demonstrate Supertree using the simple bidding problem portrayed by the decision tree in Figure 5.1. The situation: Your company is bidding
Bidding Decision Example SUPERTREE EXAMPLE In this chapter, we demonstrate Supertree using the simple bidding problem portrayed by the decision tree in Figure 5.1. The situation: Your company is bidding
Sample Reports for The Expert Allocator by Investment Technologies
 Sample Reports for The Expert Allocator by Investment Technologies Telephone 212/724-7535 Fax 212/208-4384 Support Telephone 203/364-9915 Fax 203/547-6164 e-mail support@investmenttechnologies.com Website
Sample Reports for The Expert Allocator by Investment Technologies Telephone 212/724-7535 Fax 212/208-4384 Support Telephone 203/364-9915 Fax 203/547-6164 e-mail support@investmenttechnologies.com Website
Jacob: The illustrative worksheet shows the values of the simulation parameters in the upper left section (Cells D5:F10). Is this for documentation?
 PROJECT TEMPLATE: DISCRETE CHANGE IN THE INFLATION RATE (The attached PDF file has better formatting.) {This posting explains how to simulate a discrete change in a parameter and how to use dummy variables
PROJECT TEMPLATE: DISCRETE CHANGE IN THE INFLATION RATE (The attached PDF file has better formatting.) {This posting explains how to simulate a discrete change in a parameter and how to use dummy variables
Prepared By. Handaru Jati, Ph.D. Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta.
 Prepared By Handaru Jati, Ph.D Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta handaru@uny.ac.id Chapter 7 Statistical Analysis with Excel Chapter Overview 7.1 Introduction 7.2 Understanding Data 7.2.1 Descriptive Statistics
Prepared By Handaru Jati, Ph.D Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta handaru@uny.ac.id Chapter 7 Statistical Analysis with Excel Chapter Overview 7.1 Introduction 7.2 Understanding Data 7.2.1 Descriptive Statistics
Software Tutorial ormal Statistics
 Software Tutorial ormal Statistics The example session with the teaching software, PG2000, which is described below is intended as an example run to familiarise the user with the package. This documented
Software Tutorial ormal Statistics The example session with the teaching software, PG2000, which is described below is intended as an example run to familiarise the user with the package. This documented
Common Risk Factors in the Cross-Section of Corporate Bond Returns
 Common Risk Factors in the Cross-Section of Corporate Bond Returns Online Appendix Section A.1 discusses the results from orthogonalized risk characteristics. Section A.2 reports the results for the downside
Common Risk Factors in the Cross-Section of Corporate Bond Returns Online Appendix Section A.1 discusses the results from orthogonalized risk characteristics. Section A.2 reports the results for the downside
Financial Econometrics (FinMetrics04) Time-series Statistics Concepts Exploratory Data Analysis Testing for Normality Empirical VaR
 Financial Econometrics (FinMetrics04) Time-series Statistics Concepts Exploratory Data Analysis Testing for Normality Empirical VaR Nelson Mark University of Notre Dame Fall 2017 September 11, 2017 Introduction
Financial Econometrics (FinMetrics04) Time-series Statistics Concepts Exploratory Data Analysis Testing for Normality Empirical VaR Nelson Mark University of Notre Dame Fall 2017 September 11, 2017 Introduction
ก ก ก ก ก ก ก. ก (Food Safety Risk Assessment Workshop) 1 : Fundamental ( ก ( NAC 2010)) 2 3 : Excel and Statistics Simulation Software\
 ก ก ก ก (Food Safety Risk Assessment Workshop) ก ก ก ก ก ก ก ก 5 1 : Fundamental ( ก 29-30.. 53 ( NAC 2010)) 2 3 : Excel and Statistics Simulation Software\ 1 4 2553 4 5 : Quantitative Risk Modeling Microbial
ก ก ก ก (Food Safety Risk Assessment Workshop) ก ก ก ก ก ก ก ก 5 1 : Fundamental ( ก 29-30.. 53 ( NAC 2010)) 2 3 : Excel and Statistics Simulation Software\ 1 4 2553 4 5 : Quantitative Risk Modeling Microbial
Computing interest and composition of functions:
 Computing interest and composition of functions: In this week, we are creating a simple and compound interest calculator in EXCEL. These two calculators will be used to solve interest questions in week
Computing interest and composition of functions: In this week, we are creating a simple and compound interest calculator in EXCEL. These two calculators will be used to solve interest questions in week
Elementary Statistics
 Chapter 7 Estimation Goal: To become familiar with how to use Excel 2010 for Estimation of Means. There is one Stat Tool in Excel that is used with estimation of means, T.INV.2T. Open Excel and click on
Chapter 7 Estimation Goal: To become familiar with how to use Excel 2010 for Estimation of Means. There is one Stat Tool in Excel that is used with estimation of means, T.INV.2T. Open Excel and click on
Equivalence Tests for Two Correlated Proportions
 Chapter 165 Equivalence Tests for Two Correlated Proportions Introduction The two procedures described in this chapter compute power and sample size for testing equivalence using differences or ratios
Chapter 165 Equivalence Tests for Two Correlated Proportions Introduction The two procedures described in this chapter compute power and sample size for testing equivalence using differences or ratios
Graphing Calculator Appendix
 Appendix GC GC-1 This appendix contains some keystroke suggestions for many graphing calculator operations that are featured in this text. The keystrokes are for the TI-83/ TI-83 Plus calculators. The
Appendix GC GC-1 This appendix contains some keystroke suggestions for many graphing calculator operations that are featured in this text. The keystrokes are for the TI-83/ TI-83 Plus calculators. The
Exploring Microsoft Office Excel 2007 Comprehensive Grauer Scheeren Mulbery Second Edition
 Exploring Microsoft Office Excel 2007 Comprehensive Grauer Scheeren Mulbery Second Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the
Exploring Microsoft Office Excel 2007 Comprehensive Grauer Scheeren Mulbery Second Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the
What's new in Invest for Excel 3.6
 What's new in Invest for Excel 3.6 Microsoft Excel versions supported... 2 Russian user manual... 2 Digitally signed program code... 2 Template folders... 2 Goodwill depreciation tax-deductibility option...
What's new in Invest for Excel 3.6 Microsoft Excel versions supported... 2 Russian user manual... 2 Digitally signed program code... 2 Template folders... 2 Goodwill depreciation tax-deductibility option...
TESTING STATISTICAL HYPOTHESES
 TESTING STATISTICAL HYPOTHESES In order to apply different stochastic models like Black-Scholes, it is necessary to check the two basic assumption: the return rates are normally distributed the return
TESTING STATISTICAL HYPOTHESES In order to apply different stochastic models like Black-Scholes, it is necessary to check the two basic assumption: the return rates are normally distributed the return
PASS Sample Size Software
 Chapter 850 Introduction Cox proportional hazards regression models the relationship between the hazard function λ( t X ) time and k covariates using the following formula λ log λ ( t X ) ( t) 0 = β1 X1
Chapter 850 Introduction Cox proportional hazards regression models the relationship between the hazard function λ( t X ) time and k covariates using the following formula λ log λ ( t X ) ( t) 0 = β1 X1
Learning The Expert Allocator by Investment Technologies
 Learning The Expert Allocator by Investment Technologies Telephone 212/724-7535 Fax 212/208-4384 228 West 71st Street, Suite Support 7I, New Telephone York, NY 203703 203/364-9915 Fax 203/547-6164 Technical
Learning The Expert Allocator by Investment Technologies Telephone 212/724-7535 Fax 212/208-4384 228 West 71st Street, Suite Support 7I, New Telephone York, NY 203703 203/364-9915 Fax 203/547-6164 Technical
ESTIMATING THE DISTRIBUTION OF DEMAND USING BOUNDED SALES DATA
 ESTIMATING THE DISTRIBUTION OF DEMAND USING BOUNDED SALES DATA Michael R. Middleton, McLaren School of Business, University of San Francisco 0 Fulton Street, San Francisco, CA -00 -- middleton@usfca.edu
ESTIMATING THE DISTRIBUTION OF DEMAND USING BOUNDED SALES DATA Michael R. Middleton, McLaren School of Business, University of San Francisco 0 Fulton Street, San Francisco, CA -00 -- middleton@usfca.edu
Exploring Data and Graphics
 Exploring Data and Graphics Rick White Department of Statistics, UBC Graduate Pathways to Success Graduate & Postdoctoral Studies November 13, 2013 Outline Summarizing Data Types of Data Visualizing Data
Exploring Data and Graphics Rick White Department of Statistics, UBC Graduate Pathways to Success Graduate & Postdoctoral Studies November 13, 2013 Outline Summarizing Data Types of Data Visualizing Data
What s Normal? Chapter 8. Hitting the Curve. In This Chapter
 Chapter 8 What s Normal? In This Chapter Meet the normal distribution Standard deviations and the normal distribution Excel s normal distribution-related functions A main job of statisticians is to estimate
Chapter 8 What s Normal? In This Chapter Meet the normal distribution Standard deviations and the normal distribution Excel s normal distribution-related functions A main job of statisticians is to estimate
Math 2311 Bekki George Office Hours: MW 11am to 12:45pm in 639 PGH Online Thursdays 4-5:30pm And by appointment
 Math 2311 Bekki George bekki@math.uh.edu Office Hours: MW 11am to 12:45pm in 639 PGH Online Thursdays 4-5:30pm And by appointment Class webpage: http://www.math.uh.edu/~bekki/math2311.html Math 2311 Class
Math 2311 Bekki George bekki@math.uh.edu Office Hours: MW 11am to 12:45pm in 639 PGH Online Thursdays 4-5:30pm And by appointment Class webpage: http://www.math.uh.edu/~bekki/math2311.html Math 2311 Class
23.1 Probability Distributions
 3.1 Probability Distributions Essential Question: What is a probability distribution for a discrete random variable, and how can it be displayed? Explore Using Simulation to Obtain an Empirical Probability
3.1 Probability Distributions Essential Question: What is a probability distribution for a discrete random variable, and how can it be displayed? Explore Using Simulation to Obtain an Empirical Probability
Morningstar Hedge Fund Operational Risk Flags Methodology
 Morningstar Hedge Fund Operational Risk Flags Methodology Morningstar Methodology Paper December 4, 009 009 Morningstar, Inc. All rights reserved. The information in this document is the property of Morningstar,
Morningstar Hedge Fund Operational Risk Flags Methodology Morningstar Methodology Paper December 4, 009 009 Morningstar, Inc. All rights reserved. The information in this document is the property of Morningstar,
TIE2140 / IE2140e Engineering Economy Tutorial 6 (Lab 2) Engineering-Economic Decision Making Process using EXCEL
 TIE2140 / IE2140e Engineering Economy Tutorial 6 (Lab 2) Engineering-Economic Decision Making Process using EXCEL Solutions Guide by Wang Xin, Hong Lanqing & Mei Wenjie 1. Learning Objectives In this lab-based
TIE2140 / IE2140e Engineering Economy Tutorial 6 (Lab 2) Engineering-Economic Decision Making Process using EXCEL Solutions Guide by Wang Xin, Hong Lanqing & Mei Wenjie 1. Learning Objectives In this lab-based
Measures of Center. Mean. 1. Mean 2. Median 3. Mode 4. Midrange (rarely used) Measure of Center. Notation. Mean
 Measure of Center Measures of Center The value at the center or middle of a data set 1. Mean 2. Median 3. Mode 4. Midrange (rarely used) 1 2 Mean Notation The measure of center obtained by adding the values
Measure of Center Measures of Center The value at the center or middle of a data set 1. Mean 2. Median 3. Mode 4. Midrange (rarely used) 1 2 Mean Notation The measure of center obtained by adding the values
2 Exploring Univariate Data
 2 Exploring Univariate Data A good picture is worth more than a thousand words! Having the data collected we examine them to get a feel for they main messages and any surprising features, before attempting
2 Exploring Univariate Data A good picture is worth more than a thousand words! Having the data collected we examine them to get a feel for they main messages and any surprising features, before attempting
HandDA program instructions
 HandDA program instructions All materials referenced in these instructions can be downloaded from: http://www.umass.edu/resec/faculty/murphy/handda/handda.html Background The HandDA program is another
HandDA program instructions All materials referenced in these instructions can be downloaded from: http://www.umass.edu/resec/faculty/murphy/handda/handda.html Background The HandDA program is another
Statistics TI-83 Usage Handout
 Statistics TI-83 Usage Handout This handout includes instructions for performing several different functions on a TI-83 calculator for use in Statistics. The Contents table below lists the topics covered
Statistics TI-83 Usage Handout This handout includes instructions for performing several different functions on a TI-83 calculator for use in Statistics. The Contents table below lists the topics covered
XLSTAT TIP SHEET FOR BUSINESS STATISTICS CENGAGE LEARNING
 XLSTAT TIP SHEET FOR BUSINESS STATISTICS CENGAGE LEARNING INTRODUCTION XLSTAT makes accessible to anyone a powerful, complete and user-friendly data analysis and statistical solution. Accessibility to
XLSTAT TIP SHEET FOR BUSINESS STATISTICS CENGAGE LEARNING INTRODUCTION XLSTAT makes accessible to anyone a powerful, complete and user-friendly data analysis and statistical solution. Accessibility to
SFSU FIN822 Project 1
 SFSU FIN822 Project 1 This project can be done in a team of up to 3 people. Your project report must be accompanied by printouts of programming outputs. You could use any software to solve the problems.
SFSU FIN822 Project 1 This project can be done in a team of up to 3 people. Your project report must be accompanied by printouts of programming outputs. You could use any software to solve the problems.
Frequency Distribution and Summary Statistics
 Frequency Distribution and Summary Statistics Dongmei Li Department of Public Health Sciences Office of Public Health Studies University of Hawai i at Mānoa Outline 1. Stemplot 2. Frequency table 3. Summary
Frequency Distribution and Summary Statistics Dongmei Li Department of Public Health Sciences Office of Public Health Studies University of Hawai i at Mānoa Outline 1. Stemplot 2. Frequency table 3. Summary
Categorical. A general name for non-numerical data; the data is separated into categories of some kind.
 Chapter 5 Categorical A general name for non-numerical data; the data is separated into categories of some kind. Nominal data Categorical data with no implied order. Eg. Eye colours, favourite TV show,
Chapter 5 Categorical A general name for non-numerical data; the data is separated into categories of some kind. Nominal data Categorical data with no implied order. Eg. Eye colours, favourite TV show,
2.4 STATISTICAL FOUNDATIONS
 2.4 STATISTICAL FOUNDATIONS Characteristics of Return Distributions Moments of Return Distribution Correlation Standard Deviation & Variance Test for Normality of Distributions Time Series Return Volatility
2.4 STATISTICAL FOUNDATIONS Characteristics of Return Distributions Moments of Return Distribution Correlation Standard Deviation & Variance Test for Normality of Distributions Time Series Return Volatility
Real Options Valuation, Inc. Software Technical Support
 Real Options Valuation, Inc. Software Technical Support HELPFUL TIPS AND TECHNIQUES Johnathan Mun, Ph.D., MBA, MS, CFC, CRM, FRM, MIFC 1 P a g e Helpful Tips and Techniques The following are some quick
Real Options Valuation, Inc. Software Technical Support HELPFUL TIPS AND TECHNIQUES Johnathan Mun, Ph.D., MBA, MS, CFC, CRM, FRM, MIFC 1 P a g e Helpful Tips and Techniques The following are some quick
CHAPTER TOPICS STATISTIK & PROBABILITAS. Copyright 2017 By. Ir. Arthur Daniel Limantara, MM, MT.
 Distribusi Normal CHAPTER TOPICS The Normal Distribution The Standardized Normal Distribution Evaluating the Normality Assumption The Uniform Distribution The Exponential Distribution 2 CONTINUOUS PROBABILITY
Distribusi Normal CHAPTER TOPICS The Normal Distribution The Standardized Normal Distribution Evaluating the Normality Assumption The Uniform Distribution The Exponential Distribution 2 CONTINUOUS PROBABILITY
Appendix A (Pornprasertmanit & Little, in press) Mathematical Proof
 Appendix A (Pornprasertmanit & Little, in press) Mathematical Proof Definition We begin by defining notations that are needed for later sections. First, we define moment as the mean of a random variable
Appendix A (Pornprasertmanit & Little, in press) Mathematical Proof Definition We begin by defining notations that are needed for later sections. First, we define moment as the mean of a random variable
9/17/2015. Basic Statistics for the Healthcare Professional. Relax.it won t be that bad! Purpose of Statistic. Objectives
 Basic Statistics for the Healthcare Professional 1 F R A N K C O H E N, M B B, M P A D I R E C T O R O F A N A L Y T I C S D O C T O R S M A N A G E M E N T, LLC Purpose of Statistic 2 Provide a numerical
Basic Statistics for the Healthcare Professional 1 F R A N K C O H E N, M B B, M P A D I R E C T O R O F A N A L Y T I C S D O C T O R S M A N A G E M E N T, LLC Purpose of Statistic 2 Provide a numerical
Tests for Multiple Correlated Proportions (McNemar-Bowker Test of Symmetry)
 Chapter 151 Tests for Multiple Correlated Proportions (McNemar-Bowker Test of Symmetry) Introduction McNemar s test for correlated proportions requires that there be only possible categories for each outcome.
Chapter 151 Tests for Multiple Correlated Proportions (McNemar-Bowker Test of Symmetry) Introduction McNemar s test for correlated proportions requires that there be only possible categories for each outcome.
Where Vami 0 = 1000 and Where R N = Return for period N. Vami N = ( 1 + R N ) Vami N-1. Where R I = Return for period I. Average Return = ( S R I ) N
 The following section provides a brief description of each statistic used in PerTrac and gives the formula used to calculate each. PerTrac computes annualized statistics based on monthly data, unless Quarterly
The following section provides a brief description of each statistic used in PerTrac and gives the formula used to calculate each. PerTrac computes annualized statistics based on monthly data, unless Quarterly
This homework assignment uses the material on pages ( A moving average ).
 Module 2: Time series concepts HW Homework assignment: equally weighted moving average This homework assignment uses the material on pages 14-15 ( A moving average ). 2 Let Y t = 1/5 ( t + t-1 + t-2 +
Module 2: Time series concepts HW Homework assignment: equally weighted moving average This homework assignment uses the material on pages 14-15 ( A moving average ). 2 Let Y t = 1/5 ( t + t-1 + t-2 +
STAT 113 Variability
 STAT 113 Variability Colin Reimer Dawson Oberlin College September 14, 2017 1 / 48 Outline Last Time: Shape and Center Variability Boxplots and the IQR Variance and Standard Deviaton Transformations 2
STAT 113 Variability Colin Reimer Dawson Oberlin College September 14, 2017 1 / 48 Outline Last Time: Shape and Center Variability Boxplots and the IQR Variance and Standard Deviaton Transformations 2
Summary of Statistical Analysis Tools EDAD 5630
 Summary of Statistical Analysis Tools EDAD 5630 Test Name Program Used Purpose Steps Main Uses/Applications in Schools Principal Component Analysis SPSS Measure Underlying Constructs Reliability SPSS Measure
Summary of Statistical Analysis Tools EDAD 5630 Test Name Program Used Purpose Steps Main Uses/Applications in Schools Principal Component Analysis SPSS Measure Underlying Constructs Reliability SPSS Measure
Personal Finance Amortization Table. Name: Period:
 Personal Finance Amortization Table Name: Period: Ch 8 Project using Excel In this project you will complete a loan amortization table (payment schedule) for the purchase of a home with a $235,500 loan
Personal Finance Amortization Table Name: Period: Ch 8 Project using Excel In this project you will complete a loan amortization table (payment schedule) for the purchase of a home with a $235,500 loan
