Class-12 NATIONAL INCOME What is National Income? 1. Concept and Meaning of National Income
|
|
|
- Sandra Ellis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
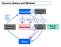
1 Class-12 NATIONAL INCOME What is National Income? 1. Concept and Meaning of National Income National Income is a measure of the total flow of earning of the factor-owners through the production of goods and services. In simple words, it is the total amount of income earned by the aggregate output. The total value of the level of aggregate output is called Gross National Product or GNP. GNP is a measure of the total market value of all final goods and services currently produced by all the citizens of a nation within a period, usually a year. Focus on the important points mentioned below:- It Measures how much people produce. It Counts current production only It Counts the level of output with a market value. It relies on the market prices of goods and services as a measure. 2. Methods of Measuring National Income There are mainly Three Approaches to measure GNP 5 The relationship of these approaches is shown in the diagram given below. Product market Households Firms The 3 arrows in the diagram show the overall level of economics activities. Based on these 3 directions of Flows i.e. Flow of output, Flow of Income and a Flow of Expenditure, economists develop three approaches to measure GNP. 2.1 Output or value added approach The total value of all final goods and services (i.e. outputs) can be found out by adding up the total values of outputs produced at different stages of production.this method it to avoid the socalled double-counting or an over-estimation of GNP. However, there are difficulties in the collection and calculation of data obtained; caution should be taken to take Final Goods not Intermediate goods as it will result in Double Counting. For example in a Cycle Manufacturing Unit, computing the total value of cycles produced in a year the final value of the cycle ( Multiplied by total no of units produced) which is ready to be marketed for sale will be taken not the cost of intermediate goods which are used in the process of manufacture as it will result in double counting. i.e. The market price of a cycle is suppose Rs.2000 which includes say profit margin of Rs.200 besides the cost of manufacturing of Rs.1800.This 1800 includes all costs including components and parts etc. (these are intermediate goods which are used in the process of production.)if the costs of parts etc. are
2 also taken while computing final value of total units produced, it will give inflated figure and hence result in double counting error. Same way at macro level, while computing the National Income under Value Added Method the value of final goods and services should be taken up to avoid the double counting error as the cost of Intermediate Goods are already counted in the final value of the product Expenditure approach Amount of Expenditure refers to all spending on currently-produced final goods and services only in an economy. In an economy, there are three main agencies which buy goods and services. These are: Households, Firms and the Government In Economics, we use the following Terms: C = Private Consumption Expenditure (of all Households) I = Investment Expenditure (of all firms) G = Government Consumption Expenditure (of the local government) In an economy the entire output which is produced in a year is not fully consumed by that economy as some goods are exported and in the similar way the domestic consumption (expenditure) may also include imports. Hence under the expenditure approach to measure the GNP, the value of exports must be added to C, I and G whereas the values of imports must be deducted from the above amount. Finally, we have: GNP at market prices = C+I+G+X-M (Where X-M = Exports Imports) Gross Domestic Product (GDP) We can only find the amount of outputs which are produced within the domestic boundary of an economy in a specific period, say a year. To arrive at the value of GNP, Net Factor Income Earned from Abroad (NFIA) has to be added to the GDP. Income from abroad = income earned by local citizens form the provision of factors services abroad Income to abroad = income earned by foreign citizens form the provision of factors services locally Net Factor Income from abroad Income earned from abroad Income sent to abroad GNP = GDP + Net Factor Income Earned from Abroad Income approach The Income approach tries to measure the total flows of income earned by the factor-owners in the provision of final goods and services in a current period. There are four types of factors of production and four types of factors incomes accordingly i.e. Land, Labour, Capital, and Organization as Factors of Production and Rent, Wages, Interest and Profit as Factor Incomes correspondingly. National Income = Wages+ Interest Income + Rental Income +*Profit The term* Profit can be further sub-divided into; profit tax; dividend to all those shareholders; and retained profit (or retained earnings). 3. Relevant concepts of National Income 3.1 Net National Product (NNP)
3 The investment expenditure of the firms is made up of two parts. One part is to buy new capital goods and machinery for production. It is called net investment because the production capacity of the firms can be expanded. Another part- consumption allowance or depreciation- is spent on replacing the used-up capital goods or the maintenance of existing capital goods will face wear and tear out over time. Depreciation refers to all non cash provision charged against profit each year to replace the fixed assets due to wear and tear, obsolescence, destruction and accidental loss etc. The sum of these two amounts is called Gross Investment in economics. Gross Investment= Net investment + Depreciation Net investment will increase the production capacity and output of a nation, but not by depreciation expenditure. So we have, NNP = GNP-Depreciation 3.2 GNP at Factor Cost The amount of National Income calculated under the Income Approach will not be the same as the amount of GNP at market prices found by the expenditure approach. In the expenditure approach, the value of GNP included some types of expenses which are not factor incomes earned by the citizens. They include depreciation, indirect business taxes, and government subsidies. GNP at factor Cost = GNP at market price = Indirect Business Taxes + Subsidies = GNP at market price = Indirect Business Taxes less Subsidies 8 GNP at factor cost carries the meaning that we are measuring the total output by their costs of production. As output generates income to the factor-owners, it is also related with the value of national income. GNP at factor Cost = National Income + Depreciation Depreciation is also a type of costs of production but will not become a source of income directly. So it is included in the factor cost but excluded in the value of national income. 3.3 GNP (GNP at Current Market Prices) GNP is a measure based on market prices which are expressed in terms of money. In reality, market prices changes all the time. The same amount of outputs may different total market values provided that price change. In order to isolate the effect of prices change on the value of GNP, economists have developed the concept and techniques of constant market prices. GNP at the base year (1990) = 1X x 4 +2 x 2m. = 18 million GNP at current market prices in 1995 = 1x 6 +2 x6 +3 x 4m. = 30 Million The 2 value of GNP at current market prices in 1995 & 2000 are calculated by using the money prices in that year, eg. The nominal growth rate is % between 1990 to GNP at constant market prices of 1995 = 1 x x 6 +2 x 4m. = 26 million The real output changes from 18 to 26 million from 1990 to GNP at constant marker prices is called real GNP. The growth rate of real GNP is called real growth rate of GNP. Real GNP
4 The value of the real GNP is based on the prices of the base year. However, there are too many different values of prices of goods and services. To make the calculation of GNP easier, economists use a price index to find the real GNP. A Price index is a number showing the changes in the overall level of prices. It shows a change in the general price level of an economy. With the value of the price index, the real GNP of anyone year can be found Real GNP = Nominal GNP x (Price Index at base year/price index at current year) 9 4. Factors Affecting National Income 4.1 Factors of production Normally the more efficient and richer the resources, higher will be the level of National Income or GNP Land Resources like coal, iron and timber are essential for heavy industries so that they must be available and accessible. In other words, the geographical location of these natural resources affects the level of GNP Capital Capital is generally determined by investment. Investment in turn depends on other factors like profitability, political stability etc Labour and Entrepreneur The quality or productivity of human resources is more important than quantity. Manpower planning and education affect the productivity and production capacity of an economy Technology This factor is more important for Nations with fewer natural resources. The development in technology is affected by the level of invention and innovation in production Government Government can help to provide a favorable business environment for investment. It provides law and order, regulations Political Stability A stable economy and political system helps in appropriate allocation of resources. Wars, strikes and social unrests will discourage investment and business activities. 5. Uses of National Income Statistics 5.1 Standard of living The per capita GNP allows us to compare the standard of living of different nations. In general, a nation has a higher standard of living if its per capita GNP is higher than that of another nation Policy formulation In the compilation of GNP statistics, the Government gathers lot of information of the economy. The Government can use this as base to plan and decide its policies International comparison By converting the local GNP figures into a common unit (usually in US$), we can compare the standard of living of different nations. It helps to show the rate of growth or development of different nations. 5.4 Business Decision The GNP figures can show the level of development of different industries and sectors of an economy. It
5 helps the business to plan for production. 6. Limitations of National Income Statistics GNP is a measure of the overall flow of goods and services, as well as to show the general welfare of the people. It aims not only at the level of cost of living but also the standard of living. It is quite correct to show the cost of living but there are some limitations on the GNP statistics to indicate the standard of living of an economy like 6.1 Price Changes A higher nominal GNP of a nation may not mean that the standard of living is better. If the price increases at a high rate, the real GNP may even fall. 6.2 Omission or under-estimation 6.3 Voluntary services GNP figures do not include the contribution of the voluntary agencies which raise the general welfare, e.g. the Tung Wah group of Hospitals. In this respect, the GNP figures under-estimate the level of welfare. The voluntary work of housewives is also neglected by the GNP figures. It again underestimates welfare of people or standard of living. It is also a source of welfare and raises our standard of living e.g. the welfare enjoyed with a New Year holiday, however, the monetary value is difficult to calculate. 6.4 Illegal Activities Drug trafficking and illegal gambling are activities omitted in the value of GNP. It is difficult to determine its effect on the welfare of an economy. 6.5 Undesirable Effects of Production GNP figures have not considered the effects of pollution, traffic congestion on the economy. They have lowered our standard of living. 6.6 Problem of Comparison 6.7 Output Composition 11 Nations with the same GNP may have different living standard because their output composition may be different. In general, a higher level of consumer goods and services in the GNP indicates a higher current level of living standard Distribution of National Income and wealth If income is obtained by a small rate of people in a nation, the general living standard is still low compared with a nation having a more evenly distributed income or GNP 6.9 Population Size A large population has a lower living standard even if its GNP is the same as that of a small population. The per capita GNP is more useful to compare the two nations National Defense If a nation has spent a lot of resources in the production of weapons and so on, its living standard may not be improved Time Technology will be improved overtime; this may not be shown in GNP figures because there may be small changes in cost and price only. Besides, durable goods provide welfare to us over a period of time (usually more than 1 year). This cannot be shown by GNP figures within a year. COMPONENTS OF VALUE OF OUTPUT AND VALUE ADDED Gross output of the Market Or Sales + change in stock Or Sales +closing stock opening stock = Gross value of output at MP
6 Less Intermediate consumption = Gross value added at MP Less Consumption of fixed capital (Depreciation) (Fall in the value of fixed assets) = Net value added at MP Less Net direct taxes = Net value added at FC 12 Check your progress/examples 1. Calculate Gross value added at factor cost from the following :- (i) Gross value of output at MP 10,500 (ii) Depreciation 1000 (iii) Indirect taxes 750 (iv) Economic subsidies 200 (v) Intermediate consumption 4000 (vi) Compensation of employees 2000 Solution Gross value added at Factor cost will be calculated as under:- Gross value of output at MP 10,500 + Economic Subsidies Intermediate Consumption Indirect Taxes -750 Rs.5950/- 2. From the following data, estimate the net value added at factor cost and show that it is equal to the sum of factor incomes :- (i) Sales 9600 (ii) Increase in stock 2080 (iii) Intermediate Consumption 2370 (iv) Depreciation 450 (v) Wages and salaries 5400 (vi) Internet 250 (vii) Rent 750 (viii) Profit 2150 (ix) Net indirect Taxes 310 Solution Value added at FC = Sales + increase in stock Intermediate Consumption Depreciation- Net Indirect Taxes = = Rs. 8550/- 13 Sum of Factor Incomes Wages & salaries = Interest = Rent = Profit = Hence value added at FC cost equals sum of factor incomes
7 Check your progress Q. 1 Find out Net value added at FC by an enterprise from the following data: Rs. In crores (i) Consumption of Fixed Capital 10 (ii) Subsidies 5 (iii) Indirect Taxes 25 (iv) Purchase of material and 75 Services from other production units (v) Value of output 125 (Ans. = 70 Corers) Q 2. Calculate value added by Firm A & B from the following data:- Rs. (Lakh) (i) Purchase by Firms B from Firm A 40 (ii) Sales by Firm B 80 (iii) Imports by Firm B 10 (iv) Rent Paid by Firm B 05 (v) Opening stock of Firm B 15 (vi) Closing stock of Firm B 20 (vii) Purchases by Firm A from Firm B 20 (viii) Closing stock of Firm A 20 (ix) Opening stock of Firm A Solution Value of output of Firm A = Sales + stock = 40 + (20-10) = 50 Lakhs Value added By Firm A Value of output Intermediate Consumption = = 30 Lakhs Value of output of Firm B = Sales + change in stock = (20-15) = 105 Lakhs Value added By Firm B Value of output Purchase-Imports Rent = = 50 Lakhs 15 II Income Method of Computing National Income Steps involved in calculating NI by Income method Step 1. Identification and classification of producing enterprises which employ factor inputs into primary, secondary and territory sector Step 2. Classification of factors income into Compensation to Employees, Operating Surplus & Mixed Income. Step 3 Estimation of National Income NNP at fc (National Income) 1. Compensation to employees 2. Operating surplus 3. Mixed income and self employed = Net domestic product at factor cost
8 4. Net factor income from abroad 5. Net national product at factor cost Process involved in estimating NI by Income method Any income corresponding to which there is no flow of goods and services or value added, it should not be included in calculation of National Income 1. Transfer payment like scholarships, olf age pensions, gifts etc. is not a productive activity. So they are excluded. These are unilateral payments. A distinction is made between old age pension is a transfer payment and retirement pension is a part of compensation of employees. 2. Income from the sale of second hand goods or capital gains is excluded from national income because their sale has been accounted in the year they were purchased. However the brakeage/commission paid is included as factor income. 3. Illegal income from smuggling, black marketing, theft, scarcity. Gambling is net included as it is not only illegal but also difficult to count as nobody reveals it. 4. Income arising from sales of financial assets like shares, bonds, debentures in the market is not treated as income as there is no corresponding production of goods and services when such sales are made. It reflects a mere transfer of ownership rights. 5. Imputed value of services rendered by owners of production units are to be included e.g. rental of owner-occupied houses on the basis of prevailing market rate Imputed value of own account production must be included as it is equivalent to selling the good to himself and earning factor income. 7. Income from windfall gains like lotteries is not included, as its is not earned by providing any productive activity. It is a transfer receipt. Numerical Example 1. Calculate national income from the following data:- (Rs. Crores) (i) Consumption of fixed capital 50 (ii) Employers contribution to social security 75 (iii) Interest 160 (iv) Net Indirect Taxes 55 (v) Rent 130 (vi) Dividends 45 (vii) Corporate Tax 15 (viii) Undistributed profit 10 (ix) Net factor income from abroad -10 (x) Wages and salaries 450 Solution NDP fc = (X) + (ii) + (iii) + (v) + (vi) + (Vii) + (Viii) = * = 885 Cr. NNP at fc = NDP fc + (ix) = (-10) = 875 Cr. Notes of solution *Since wages and salaries and employees contribution to social security are given separately, these must be added to obtain compensation to employees. Dividend, undistributed profit and corporate taxes are to be added to get Total profit/ Retained Earnings. Net indirect taxes, is not required in this question. Similarly consumption of fixed capital
9 is also not required in this question. 17 III Expenditure Method The other way of calculating National Income is to measure total spending on final good by the different sectors of the economy. Expenditure method is National Income Accounting method that measures GDP by adding all the spending for final goods during a period of time. GNP mp = C+I+G+(X-M) The Factors Income earned by the Factors of Production is spent on (Disposed off) goods and services that are produced by firms. That is why expenditure method is also called income disposal method. Expenditure is undertaken by all sectors of an Economy-Households, Government, Firms and Rest of the World. Let us understand the kind of expenditure that is incurred by the different sectors. 1. Personal or Private Consumption Expenditure (C) Private Consumption Expenditure is the money value of final goods and services purchased by the resident households, including non-profit institutions of an economy in a given year. 2. Gross Domestic Capital Formation (I) Capital formation or investment is an addition to capital stock of an economy in a given time period. This is the sum of two components i.e. (i) Gross Domestic fixed capital formation and (ii) Change in stock This includes investments by firms as well as governments sectors 3. Government Final Consumption Expenditure (G) This category includes the value of goods and service purchased by Government. 4. Net Exports (X-M) The last component in GDP Expenditure Account is Net Exports, expressed in the formula (X-M). Exports (X) are expenditure by foreigners for Indian domestic product. Imports (M) is the expenditure on goods and services produced by the rest of the world by resident household firms and government. 18 Steps involved in calculation of National Income ( NI) by expenditure method Step 1. Identification of economic units incurring final expenditure Step 2. Classification of final expenditure (C+I+G+(X-M)) Step 3 Estimation of NI by expenditure Method:- Please Note 1. Only final expenditure is to be included to avoid double counting. 2. Intermediate expenditure like on raw materials, etc, is not included in the calculation of National Income. 3. Expenditure on second-hand goods is not included as they have already been included when they were purchased originally. 4. Expenditure on shares and bonds is not included because buying financial assets is not a production activity because financial assets are neither good nor services. These are also known as Paper Money or Barren Money. 5. Expenditure on transfer payments by the government is excluded in total expenditure because transfer payment is a payment against which no services are rendered therefore, no production takes place and hence are not considered
10 in computing National Income. 6. The imputed expenditure value or self use of own produced final products is included. 19 Numerical Example Calculate national income from the data given below by expenditure method. Item Rs. (In crores) (i) Personal consumption expenditure 3500 (ii) Consumption of fixed capital 50 (iii) Net fixed capital formation 1250 (iv) Change in stock 500 (v) Exports 400 (vi) Imports 750 (vii) Net indirect taxes 40 (viii) Governments consumption expenditure 1600 (ix) Net factor income from abroad (-) 10 (x) Wages and salaries 450 Solution Rs. (In crores) Personal Consumption expenditure Net fixed Capital Formation Change in Stock Govt. Consumption Expenditure Net Exports (Exports-Imports) -350 Net Domestic product at market price 6500 (-) Net Indirect Taxes 40 Net Domestic product at Factor Cost Net factor Income from abroad (-) 10 NNP FC (National Income) 6450 Please Note 1. Since Net Fixed Capital Formation is given, we are asked to calculate net National Product at factor cost. Thus, consumption of fixed capital is not required here. 2. Since, fixed capital is given, we need to add change in stock to get the total domestic capital formation (Investment) 3. The entry wages and salaries are not required here.
1 What do you mean by Net Export? 2 Define Current Transfers? 3 Who is considered as normal resident of country?
 1 What do you mean by Net Export? 2 Define Current Transfers? 3 Who is considered as normal resident of country? 4 What do you ean by economic territory? 5. When will be NDP MP be less than NDP FC? 6.
1 What do you mean by Net Export? 2 Define Current Transfers? 3 Who is considered as normal resident of country? 4 What do you ean by economic territory? 5. When will be NDP MP be less than NDP FC? 6.
UNIT 6 NATIONAL INCOME POINTS TO REMEMBER
 1 COMPREHENSIVE COMMERCE UNIT 6 NATIONAL INCOME POINTS TO REMEMBER Good : In economics a good is defined as any physical object, natural or man-made, that could command a price in the market. Consumption
1 COMPREHENSIVE COMMERCE UNIT 6 NATIONAL INCOME POINTS TO REMEMBER Good : In economics a good is defined as any physical object, natural or man-made, that could command a price in the market. Consumption
 UNIT 6 NATIONAL INCOME POINTS TO REMEMBER Good : In economics a good is defined as any physical object, natural or man-made, that could command a price in the market. Consumption Goods : Those goods which
UNIT 6 NATIONAL INCOME POINTS TO REMEMBER Good : In economics a good is defined as any physical object, natural or man-made, that could command a price in the market. Consumption Goods : Those goods which
What is National Income? National income measures the total value of goods and services produced within the economy over a period of time.
 National Income What is National Income? National income measures the total value of goods and services produced within the economy over a period of time. Why is national income important? Measuring the
National Income What is National Income? National income measures the total value of goods and services produced within the economy over a period of time. Why is national income important? Measuring the
National Income Accounting
 National Income Accounting Notes: Net Investment = Gross Investment Deprecation Net Indirect tax= Indirect tax subsidy NFIA (Net factor Income from abroad) = Factor Income from Abroad Factor income paid
National Income Accounting Notes: Net Investment = Gross Investment Deprecation Net Indirect tax= Indirect tax subsidy NFIA (Net factor Income from abroad) = Factor Income from Abroad Factor income paid
NATIONAL INCOME AND RELATED AGGREGATES
 NATIONAL INCOME AND RELATED AGGREGATES The modern concept of National Income is more dynamic in the content than earlier concepts. The National Income Committee of India defined national income as: A National
NATIONAL INCOME AND RELATED AGGREGATES The modern concept of National Income is more dynamic in the content than earlier concepts. The National Income Committee of India defined national income as: A National
NATIONAL INCOME. be less than NDP FC. State the meaning of injection in income flow, with the help of an example.
 NATIONAL INCOME Q. 1. When will be NDP MP be less than NDP FC? Q.2. State the meaning of consumption of fixed capital? Q.3. State the meaning of injection in income flow, with the help of an example. Q.4.
NATIONAL INCOME Q. 1. When will be NDP MP be less than NDP FC? Q.2. State the meaning of consumption of fixed capital? Q.3. State the meaning of injection in income flow, with the help of an example. Q.4.
ECONOMICS SOLUTION BOOK 2ND PUC. Unit 8. Part A
 Unit 8 Part A I. Choose the correct answer (each question carries 1 mark) 1. The study of National Income is related to: a) Micro economics b) Macro Economics c) Both Micro and Macro d) None of the above
Unit 8 Part A I. Choose the correct answer (each question carries 1 mark) 1. The study of National Income is related to: a) Micro economics b) Macro Economics c) Both Micro and Macro d) None of the above
Distance Learning Programme. IAS Prelims INDIAN ECONOMY
 Distance Learning Programme IAS Prelims INDIAN ECONOMY CONTENTS 1. Introduction to Economics 5-11 2. Concepts of National Income 12-20 3. Human Development 21-30 4. Poverty, Unemployment & Inequality 31-49
Distance Learning Programme IAS Prelims INDIAN ECONOMY CONTENTS 1. Introduction to Economics 5-11 2. Concepts of National Income 12-20 3. Human Development 21-30 4. Poverty, Unemployment & Inequality 31-49
MACROECONOMICS NATIONAL INCOME
 MACROECONOMICS Q. 1. Define intermediate goods. NATIONAL INCOME Q.2. Q.3. Q.4. State the meaning of consumption of fixed capital? State the meaning of injection in income flow, with the help of an example.
MACROECONOMICS Q. 1. Define intermediate goods. NATIONAL INCOME Q.2. Q.3. Q.4. State the meaning of consumption of fixed capital? State the meaning of injection in income flow, with the help of an example.
Macro Economics & National Income Accounting. Samir K Mahajan
 Macro Economics & National Income Accounting MACROECONOMICS (Ragner Frisch ) Macroeconomics looks at the economy as an organic whole. Macroeconomics studies economic aggregates such as: total output, total
Macro Economics & National Income Accounting MACROECONOMICS (Ragner Frisch ) Macroeconomics looks at the economy as an organic whole. Macroeconomics studies economic aggregates such as: total output, total
NATIONAL INCOME AND RELATED AGGREGATES
 National Income and Related Aggregates MODULE - 9 National Income Accounting 24 NATIONAL INCOME AND RELATED AGGREGATES The main objective of an economy is to provide goods and services for the satisfaction
National Income and Related Aggregates MODULE - 9 National Income Accounting 24 NATIONAL INCOME AND RELATED AGGREGATES The main objective of an economy is to provide goods and services for the satisfaction
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT FIRST ASSESSMENT 2018 VALUE POINTS-ECONOMICS CLASS XII SECTION A
 INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT FIRST ASSESSMENT 208 VALUE POINTS-ECONOMICS CLASS XII SECTION A What shape will Production Possibility Curve take when Marginal Rate of Transformation values decrease? Ans: PPC becomes
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT FIRST ASSESSMENT 208 VALUE POINTS-ECONOMICS CLASS XII SECTION A What shape will Production Possibility Curve take when Marginal Rate of Transformation values decrease? Ans: PPC becomes
Goods and Services. Consumption Expenditure On Goods and Services. Factor Payments Rent, Wages, Interest and Profits
 Q.1 Define the following. (i) Stock Stock variable refers to that variable, which is measured at a particular point of time. Examples: stock of goods on 31st March 2017, National wealth, National Capital,
Q.1 Define the following. (i) Stock Stock variable refers to that variable, which is measured at a particular point of time. Examples: stock of goods on 31st March 2017, National wealth, National Capital,
Test Yourself: National-Income Accounting
 Test Yourself: National-Income Accounting Nothing is more destructive than the gap between people's perceptions of their own day-to-day economic well-being and what politicians and statisticians are telling
Test Yourself: National-Income Accounting Nothing is more destructive than the gap between people's perceptions of their own day-to-day economic well-being and what politicians and statisticians are telling
MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC GROWTH. Objectives. Gross Domestic Product. An Economic Barometer. Gross Domestic Product. Gross Domestic Product CHAPTER
 MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC CHAPTER GROWTH Objectives After studying this chapter, you will able to Define GDP and use the circular flow model to explain why GDP equals aggregate expenditure and aggregate
MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC CHAPTER GROWTH Objectives After studying this chapter, you will able to Define GDP and use the circular flow model to explain why GDP equals aggregate expenditure and aggregate
ECONOMICS. Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 100 QUESTION PAPER CODE 58/1/1 SECTION - A. 1. Define an indifference curve. 1
 ECONOMICS Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 100 General Instructions: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) All questions in both the sections are compulsory. Marks for questions are indicated against each.
ECONOMICS Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 100 General Instructions: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) All questions in both the sections are compulsory. Marks for questions are indicated against each.
National Income Accounts
 National Income Accounts What is National Income Accounting? National income accounting is a term which is applied to the description of the various types of economic activities that are taking place in
National Income Accounts What is National Income Accounting? National income accounting is a term which is applied to the description of the various types of economic activities that are taking place in
EXPENDITURE APPROACH: The expenditures on all final goods and services made by all sectors of the economy are added to calculate GDP. Expenditures are
 Chapter 1 MEASURING GDP AND PRICE LEVEL MEASURING EONOMIC ACTIVITY Macroeconomics studies the aggregate (or total) concept of economic activity. Its focus is on the aggregate output, the aggregate income,
Chapter 1 MEASURING GDP AND PRICE LEVEL MEASURING EONOMIC ACTIVITY Macroeconomics studies the aggregate (or total) concept of economic activity. Its focus is on the aggregate output, the aggregate income,
National Income. What is National Income?
 National Income What is National Income? This is income accruing to the permanent residents of a country from current economic activity during a specified period, usually one year. What determines the
National Income What is National Income? This is income accruing to the permanent residents of a country from current economic activity during a specified period, usually one year. What determines the
ECO 209Y MACROECONOMIC THEORY AND POLICY LECTURE 2: NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING
 ECO 209Y MACROECONOMIC THEORY AND POLICY LECTURE 2: NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING Gustavo Indart Slide1 GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of all final goods and services produced
ECO 209Y MACROECONOMIC THEORY AND POLICY LECTURE 2: NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING Gustavo Indart Slide1 GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of all final goods and services produced
 Six Marks Questions (6 M) 1. Explain the determinants of supply? 2. Explain the relationship between Total Revenue and marginal Revenue using a Schedule and diagram? ********** UNIT IV: FORMS OF MARKET
Six Marks Questions (6 M) 1. Explain the determinants of supply? 2. Explain the relationship between Total Revenue and marginal Revenue using a Schedule and diagram? ********** UNIT IV: FORMS OF MARKET
NATIONAL INCOME. Traditional Definition
 NATIONAL INCOME The definitions of national income can be classified into two groups: Definitions of National Income Traditional Definition Modern Definition "The labour and capital of country acting on
NATIONAL INCOME The definitions of national income can be classified into two groups: Definitions of National Income Traditional Definition Modern Definition "The labour and capital of country acting on
Economic Growth and Development Prof. Rajashree Bedamatta Department of Humanities and Social Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Economic Growth and Development Prof. Rajashree Bedamatta Department of Humanities and Social Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Lecture 01 Concepts of Economic Growth Hello and welcome
Economic Growth and Development Prof. Rajashree Bedamatta Department of Humanities and Social Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Lecture 01 Concepts of Economic Growth Hello and welcome
Gross Domestic Product. National Income Determination. Topic 9: 10/7/2016
 The Economy s Income and Expenditure Topic 9: National Income Determination When judging whether the economy is doing well or poorly, it is natural to look at the total income that everyone in the economy
The Economy s Income and Expenditure Topic 9: National Income Determination When judging whether the economy is doing well or poorly, it is natural to look at the total income that everyone in the economy
Na#onal Income Mr Traynor
 Na#onal Income Mr Traynor Economics Pack 4 Exam Prep 6 th Year, Ailesbury Rd 1) Short Ques+ons Study the table below and calculate (i) and (ii), showing all your workings. (i) Year National Income Consumption
Na#onal Income Mr Traynor Economics Pack 4 Exam Prep 6 th Year, Ailesbury Rd 1) Short Ques+ons Study the table below and calculate (i) and (ii), showing all your workings. (i) Year National Income Consumption
Chapter 8- Measuring Total Production & Income. Distribution of GDP
 Chapter 8- Measuring Total Production & Income Distribution of GDP 1 Keeping Tabs on the Economy You must be able to measure and track the economy in order to understand what is going on and react appropriately.
Chapter 8- Measuring Total Production & Income Distribution of GDP 1 Keeping Tabs on the Economy You must be able to measure and track the economy in order to understand what is going on and react appropriately.
India s New GDP Series : Everything You Need To Know
 India s New GDP Series 2011-12: Everything You Need To Know India has shifted to a new GDP series. The organisation responsible for calculating national income CSO (Central Statistical Organisation) adopted
India s New GDP Series 2011-12: Everything You Need To Know India has shifted to a new GDP series. The organisation responsible for calculating national income CSO (Central Statistical Organisation) adopted
Gross Domestic Product. How Is The GDP Calculated? Net investment equals gross investment minus depreciation.
 Chapter 23: Measuring GDP, Inflation and Economic Growth Gross Domestic Product applegross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of aggregate or total production of goods and services in a country during
Chapter 23: Measuring GDP, Inflation and Economic Growth Gross Domestic Product applegross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of aggregate or total production of goods and services in a country during
Macroeconomic Measurements, Part II: GDP and Real GDP CHAPTER
 Macroeconomic Measurements, Part II: GDP and Real GDP 7 CHAPTER An Economic Barometer What exactly is GDP? How do we use it to tell us whether our economy is in a recession or how rapidly our economy is
Macroeconomic Measurements, Part II: GDP and Real GDP 7 CHAPTER An Economic Barometer What exactly is GDP? How do we use it to tell us whether our economy is in a recession or how rapidly our economy is
NATIONAL INCOME AND THE ECONOMY
 UNIT 1 NATIONAL INCOME AND THE ECONOMY Structure 1.0 Objectives 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Meaning of an Economy 1.3 Meaning of National Income 1.4 Questions About an Economy That Interest Us 1.4.1 Is the Economy
UNIT 1 NATIONAL INCOME AND THE ECONOMY Structure 1.0 Objectives 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Meaning of an Economy 1.3 Meaning of National Income 1.4 Questions About an Economy That Interest Us 1.4.1 Is the Economy
CHAPTER 2: MEASUREMENT OF MACROECONOMIC VARIABLES
 Additional Questions Problems and/or essay questions: CHAPTER 2: MEASUREMENT OF MACROECONOMIC VARIABLES 1. What impact do you think that the movement of women from working in the household to working in
Additional Questions Problems and/or essay questions: CHAPTER 2: MEASUREMENT OF MACROECONOMIC VARIABLES 1. What impact do you think that the movement of women from working in the household to working in
Q.1 Calculate GNP at MP by (a) income method, and (b) expenditure method.
 Q.1 Calculate GNP at MP by (a) income method, and (b) expenditure method. (Rs. in crores) (i) Net exports 10 (ii) Rent 20 (iii) Private final consumption expenditure 400 (iv) Interest 30 (v) Dividends
Q.1 Calculate GNP at MP by (a) income method, and (b) expenditure method. (Rs. in crores) (i) Net exports 10 (ii) Rent 20 (iii) Private final consumption expenditure 400 (iv) Interest 30 (v) Dividends
Module 1 Introduction
 Module 1 Introduction 1 Unit Structure : 1.0 Objectives 1.1 Distinction between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics 1.2 Circular flow of Economic activities 1.3 Gross National Product (GNP) 1.4 Net National
Module 1 Introduction 1 Unit Structure : 1.0 Objectives 1.1 Distinction between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics 1.2 Circular flow of Economic activities 1.3 Gross National Product (GNP) 1.4 Net National
MEASURING A NATION S INCOME
 10 MEASURING A NATION S INCOME LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this chapter, students should understand: why an economy s total income equals its total expenditure. how gross domestic product (GDP)
10 MEASURING A NATION S INCOME LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this chapter, students should understand: why an economy s total income equals its total expenditure. how gross domestic product (GDP)
Macroeconomic Theory and Policy
 ECO 209Y Macroeconomic Theory and Policy Lecture 2: National Income Accounting Gustavo Indart Slide1 Gross Domestic Product Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of all final goods and services produced
ECO 209Y Macroeconomic Theory and Policy Lecture 2: National Income Accounting Gustavo Indart Slide1 Gross Domestic Product Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of all final goods and services produced
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER II ECONOMICS Class - XII BLUE PRINT
 SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER II ECONOMICS Class - XII Maximum Marks 100 Time : 3 hrs. BLUE PRINT Sl. No. Form of Very Short Short Answer Long Answer Total Questions (1 Mark) (3, 4 Marks) (6 Marks) Content Unit
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER II ECONOMICS Class - XII Maximum Marks 100 Time : 3 hrs. BLUE PRINT Sl. No. Form of Very Short Short Answer Long Answer Total Questions (1 Mark) (3, 4 Marks) (6 Marks) Content Unit
Measuring a Nation s Production and Income
 Chapter Summary 5 Measuring a Nation s Production and Income In this chapter, we learned how economists and government statisticians measure the income and production for an entire country and what those
Chapter Summary 5 Measuring a Nation s Production and Income In this chapter, we learned how economists and government statisticians measure the income and production for an entire country and what those
/
 SAMPLE QUESTIN PAPER 2 Economics Class II Time allowed: 3hrs Maximum Marks: 100 General Instructions: i. All questions in both the sections are compulsory. ii. Marks for questions are indicated against
SAMPLE QUESTIN PAPER 2 Economics Class II Time allowed: 3hrs Maximum Marks: 100 General Instructions: i. All questions in both the sections are compulsory. ii. Marks for questions are indicated against
SYLLABUS UNIT I UNIT II UNIT III UNIT IV UNIT V. B.Com I YEAR (Hons.) Subject MACRO ECONOMICS
 SYLLABUS B.Com I YEAR (Hons.) Subject MACRO ECONOMICS UNIT I UNIT II UNIT III UNIT IV UNIT V Macro economics concept, nature, importance, limitations, difference between micro and macro economics, significance.
SYLLABUS B.Com I YEAR (Hons.) Subject MACRO ECONOMICS UNIT I UNIT II UNIT III UNIT IV UNIT V Macro economics concept, nature, importance, limitations, difference between micro and macro economics, significance.
MACROECONOMIC OUTPUT. Economy performance measurement
 MACROECONOMIC OUTPUT Economy performance measurement GDP Gross Domestic Product measures the monetary value of final goods and services that is, those that are bought by the final user produced in a country
MACROECONOMIC OUTPUT Economy performance measurement GDP Gross Domestic Product measures the monetary value of final goods and services that is, those that are bought by the final user produced in a country
Full file at
 ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS Problems and/or Essay Questions: CHAPTER 2: MEASUREMENT OF MACROECONOMIC VARIABLES 1. What impact do you think that the movement of women from working in the household to working in
ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS Problems and/or Essay Questions: CHAPTER 2: MEASUREMENT OF MACROECONOMIC VARIABLES 1. What impact do you think that the movement of women from working in the household to working in
Introduction. Learning Objectives. Chapter 8. Measuring the Economy s Performance
 Chapter 8 Measuring the Economy s Performance Introduction For a number of years, measured U.S. business investment spending on capital goods has declined relative to total national expenditures on goods
Chapter 8 Measuring the Economy s Performance Introduction For a number of years, measured U.S. business investment spending on capital goods has declined relative to total national expenditures on goods
National Income Accounts, GDP and Real GDP. 2Topic
 National Income Accounts, GDP and Real GDP 2Topic National Income Accounting According to EconPort (http://www.econport.org/), National income accounting deals with the aggregate measure of the outcome
National Income Accounts, GDP and Real GDP 2Topic National Income Accounting According to EconPort (http://www.econport.org/), National income accounting deals with the aggregate measure of the outcome
Full file at
 MULTIPLE CHOICE Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question 1) Gross domestic product is defined as 1) A) the total market value of the final goods and services
MULTIPLE CHOICE Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question 1) Gross domestic product is defined as 1) A) the total market value of the final goods and services
MACROECONOMICS ESSENTIALS FOR CIVIL SERVICE EXAMINATIONS
 2018 WWW.OBJECTIVEIAS.IN MACROECONOMICS ESSENTIALS FOR CIVIL SERVICE EXAMINATIONS Special Features: 1. Detailed Explanation of Each Concept 2. Important Key Words at the end of Each Unit 3. Check your
2018 WWW.OBJECTIVEIAS.IN MACROECONOMICS ESSENTIALS FOR CIVIL SERVICE EXAMINATIONS Special Features: 1. Detailed Explanation of Each Concept 2. Important Key Words at the end of Each Unit 3. Check your
Measures of Economic Activity PART II
 Measures of Economic Activity PART II Microeconomics: - the branch of economics that studies the economy of consumers or households or individual firms VS. Macroeconomics: - The Study of the economy as
Measures of Economic Activity PART II Microeconomics: - the branch of economics that studies the economy of consumers or households or individual firms VS. Macroeconomics: - The Study of the economy as
Adam Smith Aggregate monetary resources Automatic stabilisers Autonomous change Autonomous expenditure multiplier Balance of payments
 Glossary Adam Smith (1723 1790) Regarded as the father of modern Economics. Author of Wealth of Nations. Aggregate monetary resources Broad money without time deposits of post office savings organisation
Glossary Adam Smith (1723 1790) Regarded as the father of modern Economics. Author of Wealth of Nations. Aggregate monetary resources Broad money without time deposits of post office savings organisation
HKAL Economics Past Examination Papers Multiple-choice Questions Chapter 1: National Income Accounting
 PASTpaper\AlmAcro\MCQ\CH1-National Income Accounting-SV.doc/P.1 of 7 HKAL Economics Past Examination Papers Multiple-choice Questions Chapter 1: National Income Accounting 1- The value of the vegetables
PASTpaper\AlmAcro\MCQ\CH1-National Income Accounting-SV.doc/P.1 of 7 HKAL Economics Past Examination Papers Multiple-choice Questions Chapter 1: National Income Accounting 1- The value of the vegetables
Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income
 Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income 1 Multiple Choice 1) The total market value of all final goods and services produced within a given period by factors of production located within
Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income 1 Multiple Choice 1) The total market value of all final goods and services produced within a given period by factors of production located within
National Income Accounting
 National Income Accounting Expenditure and Output Measures Example from Ghana - Newsletter Limitations of the GDP Measure Production that is not bought or sold does not generally get counted. Although
National Income Accounting Expenditure and Output Measures Example from Ghana - Newsletter Limitations of the GDP Measure Production that is not bought or sold does not generally get counted. Although
Studymate Solutions to CBSE Board Examination
 Studymate Solutions to CBSE Board Examination 2017-2018 Series : SGN Code No. 58/1 Roll No. Candidates must write the Code on the title page of the answer-book. 4 Please check that this question paper
Studymate Solutions to CBSE Board Examination 2017-2018 Series : SGN Code No. 58/1 Roll No. Candidates must write the Code on the title page of the answer-book. 4 Please check that this question paper
2.1 Economic activity The level of overall economic activity
 2.1 Economic activity The level of overall economic activity Learning Outcomes Describe, using a diagram, the circular flow of income between households and firms in a closed economy with no government.
2.1 Economic activity The level of overall economic activity Learning Outcomes Describe, using a diagram, the circular flow of income between households and firms in a closed economy with no government.
ECON 1102: MACROECONOMICS 1 Chapter 1: Measuring Macroeconomic Performance, Output and Prices
 ECON 1102: MACROECONOMICS 1 Chapter 1: Measuring Macroeconomic Performance, Output and Prices 1.1 Measuring Macroeconomic Performance 1. Rising Living Standards Economic growth is the tendency for output
ECON 1102: MACROECONOMICS 1 Chapter 1: Measuring Macroeconomic Performance, Output and Prices 1.1 Measuring Macroeconomic Performance 1. Rising Living Standards Economic growth is the tendency for output
MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC GROWTH
 21 MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC GROWTH GDP Defined GDP or gross domestic product is the market value of all final goods and services produced in a country in a given time period. This definition has four
21 MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC GROWTH GDP Defined GDP or gross domestic product is the market value of all final goods and services produced in a country in a given time period. This definition has four
Measuring the Aggregate Economy
 CHAPTER 25 Measuring the Aggregate Economy The government is very keen on amassing statistics... They collect them, add them, raise them to the n th power, take the cube root and prepare wonderful diagrams.
CHAPTER 25 Measuring the Aggregate Economy The government is very keen on amassing statistics... They collect them, add them, raise them to the n th power, take the cube root and prepare wonderful diagrams.
01 Measuring a Nation s Income Econ 111
 01 Measuring a Nation s Income Econ 111 Measuring a Nation s Income (Chapter 10) Macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole. Its goal is to explain the economic changes that affect many households,
01 Measuring a Nation s Income Econ 111 Measuring a Nation s Income (Chapter 10) Macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole. Its goal is to explain the economic changes that affect many households,
Many of life s failures are people who did not realize how close they were to success when they gave up. Thomas Edison
 Many of life s failures are people who did not realize how close they were to success when they gave up. Thomas Edison National-income accounting is the system used to measure the aggregate income and
Many of life s failures are people who did not realize how close they were to success when they gave up. Thomas Edison National-income accounting is the system used to measure the aggregate income and
National Income Accounting we ll define it as the process of developing and analyzing measures of economic output and performance
 National Income Accounting Essentials National Income Accounting we ll define it as the process of developing and analyzing measures of economic output and performance rooted in the national Income and
National Income Accounting Essentials National Income Accounting we ll define it as the process of developing and analyzing measures of economic output and performance rooted in the national Income and
MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME. Chapter 18
 1 MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME Chapter 18 national income and product accounts Data collected and published by the government describing the various components of national income and output
1 MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME Chapter 18 national income and product accounts Data collected and published by the government describing the various components of national income and output
SYLLABUS ECONOMICS (CODE NO. 30) Class XII
 Annexure O SYLLABUS ECONOMICS (CODE NO. 30) Class XII 2013-14 Paper I 3 Hours 100 Marks ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Units
Annexure O SYLLABUS ECONOMICS (CODE NO. 30) Class XII 2013-14 Paper I 3 Hours 100 Marks ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Units
B) Income Statement (2.5 mrks for each company) Particulars Company A Company B Sales. (reverse working) (Contrib + V Cost) 91,000
 INTER CA MAY 2018 PAPER 8 : FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT AND ECONOMICS FOR FINANCE Branch: Multiple Date: PART- A : FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT (60 marks) Note: Question 1 is compulsory. Attempt any five from the rest.
INTER CA MAY 2018 PAPER 8 : FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT AND ECONOMICS FOR FINANCE Branch: Multiple Date: PART- A : FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT (60 marks) Note: Question 1 is compulsory. Attempt any five from the rest.
Chapter 5 Measuring a Nation's Income
 Chapter 5 Measuring a Nation's Income Problem set 1. Which of the following headlines would be most closely related to what macroeconomists study? a. Unemployment rate rises from 5 percent to 5.5 percent.
Chapter 5 Measuring a Nation's Income Problem set 1. Which of the following headlines would be most closely related to what macroeconomists study? a. Unemployment rate rises from 5 percent to 5.5 percent.
BEFORE YOU BEGIN Looking at the Chapter
 Name Date Period MEASURING ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE Chapter 12 BEFORE YOU BEGIN Looking at the Chapter Fill in the blank spaces with the missing words. GDP is the total value of all goods and services produced
Name Date Period MEASURING ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE Chapter 12 BEFORE YOU BEGIN Looking at the Chapter Fill in the blank spaces with the missing words. GDP is the total value of all goods and services produced
MARKING SCHEME Section A: Microeconomics
 MARKING SCHEME Section A: Microeconomics 1. c) 2. - Give subsidies to reduce price. - Undertake health campaigns to promote the positive effects of milk consumption. (Any 1) 3. c) 4. If the river Kosi
MARKING SCHEME Section A: Microeconomics 1. c) 2. - Give subsidies to reduce price. - Undertake health campaigns to promote the positive effects of milk consumption. (Any 1) 3. c) 4. If the river Kosi
Gross Domestic Product: What It Is and How It Is Measured. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the market value of all final user goods and services
 Gross Domestic Product: What It Is and How It Is Measured Tawni Hunt Ferrarini Northern Michigan University James Gwartney Florida State University Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the market value of all
Gross Domestic Product: What It Is and How It Is Measured Tawni Hunt Ferrarini Northern Michigan University James Gwartney Florida State University Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the market value of all
Measuring Domestic Output and National Income
 Chapter 27 Measuring Domestic Output and National Income Assessing the Economy s Performance National income accounting measures economy s overall performance Bureau of Economic Analysis compiles National
Chapter 27 Measuring Domestic Output and National Income Assessing the Economy s Performance National income accounting measures economy s overall performance Bureau of Economic Analysis compiles National
Lecture Investment and Saving
 Lecture 3-1 4. Investment and Saving Investment is the portion of final product that adds to the nation s stock of income-yielding physical assets or that replaces old, worn-out physical assets. The goods
Lecture 3-1 4. Investment and Saving Investment is the portion of final product that adds to the nation s stock of income-yielding physical assets or that replaces old, worn-out physical assets. The goods
The primary purpose of the International Comparison Program (ICP) is to provide the purchasing
 CHAPTER 3 National Accounts Framework for International Comparisons: GDP Compilation and Breakdown Process Paul McCarthy The primary purpose of the International Comparison Program (ICP) is to provide
CHAPTER 3 National Accounts Framework for International Comparisons: GDP Compilation and Breakdown Process Paul McCarthy The primary purpose of the International Comparison Program (ICP) is to provide
MARKING SCHEME 1. D. 2Y
 Mid-year Exam 07-8 SUJBECT ECONOMICS M.M =80 MARKING SCHEME. D. Y. c. both a and b.. c. both a and b. 4. b. equal to AR 5. Demand of a single consumer for a good and summation of all individual demand
Mid-year Exam 07-8 SUJBECT ECONOMICS M.M =80 MARKING SCHEME. D. Y. c. both a and b.. c. both a and b. 4. b. equal to AR 5. Demand of a single consumer for a good and summation of all individual demand
National-Income Accounting Part II
 National-Income Accounting Part II Nothing is more destructive than the gap between people's perceptions of their own day-to-day economic well-being and what politicians and statisticians are telling them
National-Income Accounting Part II Nothing is more destructive than the gap between people's perceptions of their own day-to-day economic well-being and what politicians and statisticians are telling them
MOCK PRE-BOARD ECONOMICS MARKING SCHEME
 Q N o MC = TVCn TVC n- MC = 500 000 MOCK PRE-BOARD 07-8 ECONOMICS MARKING SCHEME MC = 500 Demand for desert cooler will increase All the above 4 Demand can be postpone 5 PPC to show economic problem :
Q N o MC = TVCn TVC n- MC = 500 000 MOCK PRE-BOARD 07-8 ECONOMICS MARKING SCHEME MC = 500 Demand for desert cooler will increase All the above 4 Demand can be postpone 5 PPC to show economic problem :
DEHRADUN PUBLIC SCHOOL ASSIGNMENT ( ) SUBJECT: ECONOMICS (030) CLASS -XII
 DEHRADUN PUBLIC SCHOOL ASSIGNMENT (2017-18) SUBJECT: ECONOMICS (030) CLASS -XII UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION 1. Discuss the central problem of Economy? 2. What do you mean by production possibility frontier? 3.
DEHRADUN PUBLIC SCHOOL ASSIGNMENT (2017-18) SUBJECT: ECONOMICS (030) CLASS -XII UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION 1. Discuss the central problem of Economy? 2. What do you mean by production possibility frontier? 3.
Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics
 Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics Zhengyu Cai Ph.D. Institute of Development Southwestern University of Finance and Economics All rights reserved http://www.escience.cn/people/zhengyucai/index.html
Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics Zhengyu Cai Ph.D. Institute of Development Southwestern University of Finance and Economics All rights reserved http://www.escience.cn/people/zhengyucai/index.html
DESIGN OF QUESTION PAPER ECONOMICS (030) CLASS-XII
 DESIGN OF QUESTION PAPER ECONOMICS (030) CLASS-XII Marks 100 Duration 3 hrs. 1. Weightage by type of questions Type Number of questions Marks Total Estimated time a candidate is expected to take to answer
DESIGN OF QUESTION PAPER ECONOMICS (030) CLASS-XII Marks 100 Duration 3 hrs. 1. Weightage by type of questions Type Number of questions Marks Total Estimated time a candidate is expected to take to answer
h) Did we have to go through all the questions from 11a) to 11g) to know that saving would not change? Why or Why?
 Study Guide # 1 Definitions 1- Who is counted as unemployed? How is defined the unemployment rate? What about the employment rate? 2- What is inflation? Disinflation? Deflation? 3- What is the Gross Domestic
Study Guide # 1 Definitions 1- Who is counted as unemployed? How is defined the unemployment rate? What about the employment rate? 2- What is inflation? Disinflation? Deflation? 3- What is the Gross Domestic
Answer Key Economics Class 12 (Pre Board)
 Answer Key Economics Class 2 (Pre Board) Part A (Micro Economics). Which of the following is not an assumption of the theory of demand based on analysis of indifference curve? c) Constant marginal utility
Answer Key Economics Class 2 (Pre Board) Part A (Micro Economics). Which of the following is not an assumption of the theory of demand based on analysis of indifference curve? c) Constant marginal utility
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER 2 ECONOMICS Class XII BLUE PRINT
 SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER 2 ECONOMICS Class XII Maximum Marks: 00 Time: 3 hours BLUE PRINT Sl. No. Forms of Questions Content Unit Very Short ( Mark) Short Answer (3,4 Marks) Long Answer (6 Marks) Total. Unit
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER 2 ECONOMICS Class XII Maximum Marks: 00 Time: 3 hours BLUE PRINT Sl. No. Forms of Questions Content Unit Very Short ( Mark) Short Answer (3,4 Marks) Long Answer (6 Marks) Total. Unit
1. For information about the Mid-Decade Review, see Mid-Decade Strategic Review of BEA s Economic Accounts: Maintaining and Improving
 September 1995 SURVEY OF CURRENT BUSINESS 33 Preview of the Comprehensive Revision of the National Income and Product Accounts: Recognition of Government Investment and Incorporation of a New Methodology
September 1995 SURVEY OF CURRENT BUSINESS 33 Preview of the Comprehensive Revision of the National Income and Product Accounts: Recognition of Government Investment and Incorporation of a New Methodology
14 October 2013 Rev 25 SNA BASIC CONCEPTS (BASED ON SNA 2008)
 14 October 2013 Rev 25 SNA BASIC CONCEPTS (BASED ON SNA 2008) CONCEPT Accumulation Asset Assets (produced) Assets (nonproduced) Asset (fixed) goods and services are used for the three economic activities
14 October 2013 Rev 25 SNA BASIC CONCEPTS (BASED ON SNA 2008) CONCEPT Accumulation Asset Assets (produced) Assets (nonproduced) Asset (fixed) goods and services are used for the three economic activities
Economics 251 Examination I (100 points) To receive full credit, you must fully explain your answers and show all work.
 Economics 251 Examination I (100 points) To receive full credit, you must fully explain your answers and show all work. ANSWER ONE OF QUESTIONS 1 AND 2. 1. For each of the following events, show graphically
Economics 251 Examination I (100 points) To receive full credit, you must fully explain your answers and show all work. ANSWER ONE OF QUESTIONS 1 AND 2. 1. For each of the following events, show graphically
Test bank for Macroeconomics 12th Edition by Rudiger Dornbusch Dr, Stanley Fischer, Richard Startz
 Test bank for Macroeconomics 12th Edition by Rudiger Dornbusch Dr, Stanley Fischer, Richard Startz Link full download : http://testbankcollection.com/download/test-bank-for-macroeconomics- 12th-edition-by-dornbusch-fischer-startz/
Test bank for Macroeconomics 12th Edition by Rudiger Dornbusch Dr, Stanley Fischer, Richard Startz Link full download : http://testbankcollection.com/download/test-bank-for-macroeconomics- 12th-edition-by-dornbusch-fischer-startz/
MEASURING A NATION S INCOME
 23 MEASURING A NATION S INCOME WHAT S NEW IN THE FOURTH EDITION: There is a new In the News box on The Underground Economy. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this chapter, students should understand:
23 MEASURING A NATION S INCOME WHAT S NEW IN THE FOURTH EDITION: There is a new In the News box on The Underground Economy. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this chapter, students should understand:
Economic Performance. Sherif Khalifa. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 1 / 39
 Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 1 / 39 People earning higher income levels enjoy higher living standards. To judge economic well being, we consider the total income in an economy.
Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 1 / 39 People earning higher income levels enjoy higher living standards. To judge economic well being, we consider the total income in an economy.
Decision Makers and Markets
 Decision Makers and Markets Households S FINANCIAL Wages Rent Interest Profit T Budget C I Factors M. (Capital Labor) Government G Goods & Services Rest of world Firms Decision Makers and Markets Households
Decision Makers and Markets Households S FINANCIAL Wages Rent Interest Profit T Budget C I Factors M. (Capital Labor) Government G Goods & Services Rest of world Firms Decision Makers and Markets Households
Chapter 2. The Measurement and Structure of the Canadian Economy. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education Canada
 Chapter 2 The Measurement and Structure of the Canadian Economy Copyright 2009 Pearson Education Canada National Income Accounting The national income accounts is an accounting framework used in measuring
Chapter 2 The Measurement and Structure of the Canadian Economy Copyright 2009 Pearson Education Canada National Income Accounting The national income accounts is an accounting framework used in measuring
DESIGN OF QUESTION PAPER ECONOMICS Class - XII. 1. Weightage by types of questions Type Number of Marks Total Estimated
 DESIGN OF QUESTION PAPER ECONOMICS Class - XII Marks - 100 Duration - 3 hrs. 1. Weightage by types of questions Type Number of Marks Total Estimated questions time a candidate is expected to take to answer
DESIGN OF QUESTION PAPER ECONOMICS Class - XII Marks - 100 Duration - 3 hrs. 1. Weightage by types of questions Type Number of Marks Total Estimated questions time a candidate is expected to take to answer
II. Comparing Levels Of Development
 II. Comparing Levels Of Development Countries are unequally endowed with natural resources. For example, some countries benefit from fertile agricultural soils, while others have to put a lot of effort
II. Comparing Levels Of Development Countries are unequally endowed with natural resources. For example, some countries benefit from fertile agricultural soils, while others have to put a lot of effort
National Accounting. Introduction to Macroeconomics. October 7 th, 2011 WS 2011
 National Accounting Introduction to Macroeconomics WS 2011 October 7 th, 2011 Introduction to Macroeconomics (WS 2011) National Accounting October 7 th, 2011 1 / 35 Why study National Accounting? National
National Accounting Introduction to Macroeconomics WS 2011 October 7 th, 2011 Introduction to Macroeconomics (WS 2011) National Accounting October 7 th, 2011 1 / 35 Why study National Accounting? National
Macro CH 20 - multiple choice 80
 Class: Date: Macro CH 20 - multiple choice 80 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. GDP is measured by a. adding units of all goods and services.
Class: Date: Macro CH 20 - multiple choice 80 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. GDP is measured by a. adding units of all goods and services.
"Data, data, data: how can I make bricks without clay?".
 1 Measurement As explained in the previous chapter, measurement is a key component of the scientific method and is necessary to develop and validate theories. Sherlock Holmes, one of the masters of (investigative
1 Measurement As explained in the previous chapter, measurement is a key component of the scientific method and is necessary to develop and validate theories. Sherlock Holmes, one of the masters of (investigative
Measuring the Nation s Income and Growth
 Measuring the Nation s Income and Growth We will examine: GNP vs GDP income and expenditure approaches to measurement real versus Nominal GDP potential GDP what GDP does not measure Art Lightstone Gross
Measuring the Nation s Income and Growth We will examine: GNP vs GDP income and expenditure approaches to measurement real versus Nominal GDP potential GDP what GDP does not measure Art Lightstone Gross
Production, Income and Employment
 CAPTER 6 Production, Income and Employment Sasan ayazmanesh Summary Summary: This chapter deals with the following macroeconomic concepts: 1) National income accounting: how to measure the value of goods
CAPTER 6 Production, Income and Employment Sasan ayazmanesh Summary Summary: This chapter deals with the following macroeconomic concepts: 1) National income accounting: how to measure the value of goods
Exhaustiveness, part 2 Illegal Economy 1
 Exhaustiveness, part 2 Illegal Economy 1 Introduction This paper continues the series dedicated to extending the contents of the Handbook Essential SNA: Building the Basics 2. One of the main themes in
Exhaustiveness, part 2 Illegal Economy 1 Introduction This paper continues the series dedicated to extending the contents of the Handbook Essential SNA: Building the Basics 2. One of the main themes in
National Accounts of Tajikistan
 National Accounts of Tajikistan Nilyufar Khuseynova Spesialist of SNA and financial statistics department Introduction of SNA -93 The practical introduction of System of National Accounts in Tajikistan
National Accounts of Tajikistan Nilyufar Khuseynova Spesialist of SNA and financial statistics department Introduction of SNA -93 The practical introduction of System of National Accounts in Tajikistan
Introduction. Learning Objectives. Chapter 8. Measuring the Economy s Performance
 Copyright 2012 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Chapter 8 Measuring the Economy s Performance Introduction Does a general increase in the level of a nation s economic activity and the resulting
Copyright 2012 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Chapter 8 Measuring the Economy s Performance Introduction Does a general increase in the level of a nation s economic activity and the resulting
DESIGN OF QUESTION PAPER ECONOMICS Class - XII. 1. Weightage by types of questions Type Number of Marks Total Estimated
 DESIGN OF QUESTION PAPER ECONOMICS Class - XII Marks - 100 Duration - 3 hrs. 1. Weightage by types of questions Type Number of Marks Total Estimated questions time a candidate is expected to take to answer
DESIGN OF QUESTION PAPER ECONOMICS Class - XII Marks - 100 Duration - 3 hrs. 1. Weightage by types of questions Type Number of Marks Total Estimated questions time a candidate is expected to take to answer
MARKING SCHEME. Economics ( ) - SET 2 SECTION-A. Q.No. Value points to answers Marks Allocation SECTION A : MICRO ECONOMICS
 MARKING SCHEME Economics (2016-17) - SET 2 SECTION-A Q.No. Value points to answers Marks Allocation SECTION A : MICRO ECONOMICS 1. A consumer is said to be rational when he aims at maximizing his utility
MARKING SCHEME Economics (2016-17) - SET 2 SECTION-A Q.No. Value points to answers Marks Allocation SECTION A : MICRO ECONOMICS 1. A consumer is said to be rational when he aims at maximizing his utility
METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME
 1) What is meant by circular flow of income? 1 2) What are the two types of circular flow of income? 1 3) What do you mean by real flow? 1 4) What do you mean by money flow? 1 5) Differentiate between
1) What is meant by circular flow of income? 1 2) What are the two types of circular flow of income? 1 3) What do you mean by real flow? 1 4) What do you mean by money flow? 1 5) Differentiate between
Assignment 1 Deadline: September 23, 2004
 ECN 204 Introductory Macroeconomics Instructor: Sharif F. Khan Department of Economics Ryerson University Fall 2005 Assignment 1 Deadline: September 23, 2004 Part A Multiple-Choice Questions [30 marks]
ECN 204 Introductory Macroeconomics Instructor: Sharif F. Khan Department of Economics Ryerson University Fall 2005 Assignment 1 Deadline: September 23, 2004 Part A Multiple-Choice Questions [30 marks]
