Macro CH 20 - multiple choice 80
|
|
|
- Dora Carroll
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Class: Date: Macro CH 20 - multiple choice 80 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. GDP is measured by a. adding units of all goods and services. b. adding the market value of total final production. c. adding the value of total production at original cost. d. multiplying total production by the difference between the market value and original cost. e. adding the difference between the market price and the cost for all final goods and services produced. 2. Gross Domestic Product measures the a. quantity of the goods and services produced in a given year, listed item by item, within a country. b. income of the business sector within a country. c. market value of the final goods and services produced in a given year within a country. d. measures the market value of the domestic labor in a given year within a country. e. market value of the final goods and services consumed by households in a given year within a country. 3. GDP equals the value of all a. goods and only goods produced. b. services and only services produced. c. final goods and services produced. d. goods and services produced. e. final goods and services consumed by households. 4. Gross domestic product is the market value of all the a. goods and services produced by corporations in a given time period. b. final goods and services produced by corporations in a given time period. c. final goods and services produced within a country in a given time period. d. intermediate goods and services and final goods and services produced within a country in a given time period. e. final goods and services produced by a country's citizens no matter where they are located in a given time period. 5. Which of the following most correctly describes GDP? GDP is the sum of the market value of all a. goods and services purchased within a country in a given time period. b. final goods and services produced within a country in a given time period. c. final goods and services purchased within a country in a given time period. d. intermediate goods and services produced within a country in a given time period. e. final goods and services produced by a country's citizens no matter where they are located in a given time period. 4
2 6. Of the following, which best describes how GDP is computed? a. by adding the market value of everything produced b. by adding the market value of all final goods and services c. by asking all households what they produced during the current year d. by multiplying the total number of hours worked by the average wage rate e. by surveying households on what they purchased during the current year 7. If you make dinner for yourself a. the market value of your dinner is added to GDP. b. your service in preparing the meal is valued at a cook's wage and added to GDP. c. none of what you bought to prepare for dinner is included in GDP. d. only the market value of ingredients that you purchased this year is added to GDP. e. the difference between the cost of the ingredients that you purchased this year and the market value of the dinner is added to GDP. 8. Honda has an assembly plant for Civics in Ohio. The production of U.S.-made Civics is a. added to U.S. GDP. b. added to Japan's GDP because Honda is a Japanese company. c. not included in either the U.S. or Japanese GDP. d. added to U.S. GDP only if the Civic is sold in the United States in the year it is produced. e. added to both U.S. GDP, because the car is produced in the United States, and to Japan's GDP, because Honda is a Japanese company. 9. Which of the following is included in Germany's GDP? i. BMWs produced in a German owned factory in South Carolina ii. the value of the stocks sold on the German stock exchange, the Frankfurt Stock Exchange iii. china produced by the English owned Wedgewood Company at a factory in Berlin, Germany a. i only. b. ii only. c. iii only. d. i and ii. e. i and iii. 10. The measurement of GDP makes a distinction between a. goods and services, including goods and excluding services. b. final goods and services and intermediate goods and services, so that GDP includes intermediate goods and services but excludes final goods and services. c. goods and services, including services but excluding goods. d. final goods and services and intermediate goods and services, so that GDP includes final goods and services but excludes intermediate goods and services. e. durable goods and nondurable goods so that GDP includes only durable goods. 2
3 11. To calculate GDP, we use the market value of a. only final goods and services. b. only intermediate goods and services. c. both final goods and services and intermediate goods and services. d. final goods and services or intermediate goods and services because it does not matter which we use. e. only final goods because services are not durable enough to include in GDP. 12. Which of the following is a final good or service? a. tires purchased by Ford for use on one of their SUV's b. the new economics textbook you are using c. the hair gels used by a hair stylist at the local hair salon d. the butter used by a chef to make butter cream frosting e. the taco shells purchased by Taco Bell for use in their tacos 13. Which of the following would NOT be directly included in the U.S. GDP in 2006? a. the market value of restaurant meals sold in 2006 b. the market value of the computer chips produced in 2006 and used by Dell in their latest personal computer c. the value of the automobiles produced in 2006 at the Toyota plant located in Georgetown, KY d. legal services provided to first time home buyers during 2006 e. the purchase of a new home in Walnut Creek, California in Investment is defined as the purchase of a. any financial asset only. b. additions to inventories only. c. financial assets and inventories only. d. the purchase of new capital goods and additions to inventories. e. the purchase of new capital goods but not additions to inventories. 15. Which of the following is included as investment in GDP? i. cars produced during the year but unsold at the end of the year ii. new capital equipment produced and purchased during the year iii. purchases of a company's stocks and bonds a. i only. b. ii only. c. iii only. d. i and ii. e. i, ii, and iii. 16. The purchase of stocks and bonds is a. included in GDP as investment. b. included in GDP as a consumption expenditure. c. included in GDP as an intermediate good. d. not included in GDP as investment. e. not included in GDP because these are intermediate goods. 3
4 17. In measuring GDP, which of the following is included? a. the value of preparing meals at home b. the value of stocks and bonds bought and sold c. the value of used goods when they are sold d. the value of increases in business inventories e. the value of durable consumption goods but not the value of nondurable consumption goods. 18. When measuring GDP, a. the government sector is not included because it is the public sector not the private sector. b. the government sector is counted, and the value of the government sector in GDP is equal to its tax revenue. c. only the federal government's expenditures on goods and services are included. d. the expenditures on goods and services by all levels of government are included. e. the government sector is not counted because it does not produce goods and services. 19. Net exports of goods and services is defined as equal to a. the value of exports of goods and services minus the value of imports of goods and services. b. U.S. sales of goods and services to the rest of the world plus U.S. purchases of goods and services from the rest of the world. c. U.S. sales of goods and services to the rest of the world. d. U.S. purchases of goods and services from the rest of the world. e. the value of imports of goods and services minus the value of exports of goods and services. 20. In calculating GDP, we must a. add the market value of imports and subtract the market value of exports. b. add the market value of exports and subtract the market value of imports. c. exclude net exports of goods and services (NX). d. add the value of the goods produced outside of the United States by American firms. e. subtract the market value of imports, because these goods are produced in a country other than the United States, and subtract the market value of exports, because these goods are consumed in a country other than the United States. 21. Which of the following expenditure components of GDP can be negative or positive? a. Consumption expenditures. b. Investment expenditures. c. Government purchases of goods and services. d. Net exports of goods and services. e. None of the above because expenditure can never be negative. 22. Last year the United States net exports of goods and services was negative. This fact means that last year a. there was an error made when calculating net exports of goods and services for the United States. b. the value of U.S. exports were greater than the value of U.S. imports. c. the value of U.S. exports were less than the value of U.S. imports. d. U.S. consumption expenditure plus investment was less than the value of exports plus the value of imports. e. U.S. consumption expenditure plus investment plus government expenditures on goods and services was less than the value of exports plus the value of imports. 4
5 23. The value of production equals consumption expenditure plus a. investment plus government expenditures on goods and services. b. investment plus government expenditures on goods and services minus net exports of goods and services. c. investment plus government expenditures on goods and services plus net exports of goods and services. d. money plus government expenditures on goods and services plus net exports of goods and services. e. saving plus investment plus government expenditures on goods and services plus net exports of goods and services. 24. Gross Domestic Product equals a. Y = C + I G + NX. b. Y = C - I + G + NX. c. Y = C + I + G + NX. d. Y = C I G NX. e. Y = C + I + G NX. 25. In year 2004, in Candamica, consumption expenditure was $13 billion, interest, rent, and profit were $1.5 billion, government expenditures on goods and services were $3 billion, net exports of goods and services amounted to $2 billion, and investment was $8 billion. Hence total expenditure was a. $24.5 billion. b. $27.5 billion. c. $22.5 billion. d. $26 billion. e. $16 billion. 26. Everything else the same, if consumption expenditure increases by $200 billion and imports increase by $200 billion, then GDP a. increases by $400 billion. b. increases by $200 billion. c. decreases by $400 billion. d. does not change. e. decreases by $200 billion. 27. In order to measure gross domestic product, we can follow a. only one approach: the circular flow approach. b. only one approach: the national accounts approach. c. two approaches: the expenditure approach and the income approach. d. three approaches: the expenditure approach, the income approach, and the production approach. e. three approaches: the expenditure approach, the income approach, and the market-based approach 28. The expenditure approach to measuring GDP is done by using data on only a. consumption expenditure. b. consumption expenditure and investment. c. consumption expenditure, investment, government expenditures on goods and services, and net exports of goods and services. d. consumption expenditure, investment, and government expenditures. e. wages, rent, interest, and profit. 5
6 29. In comparing the magnitudes of the components of GDP according to the expenditure approach, we see that in the United States a. government expenditures on goods and services is the largest category. b. investment is the largest category. c. investment is much larger than government expenditures on goods and services. d. investment is about the same size as government expenditures on goods and services. e. investment, government expenditures on goods and services, and consumption expenditure are all about the same size. 30. In comparing the magnitudes of the components of GDP according to the expenditure approach, we see that in the United States a. net exports of goods and services is about the same size as investment. b. consumption expenditures is the largest category. c. government expenditures on goods and services is larger than consumption expenditures. d. net exports of goods and services is larger than investment. e. investment is the largest category. 31. If consumption was 70 percent of GDP and both investment and government expenditure were 18 percent each, then we see that a. GDP can be over 100 percent because it is "gross" rather than "net." b. the error is due to rounding. c. exports must be less than imports. d. exports must be more than imports. e. we must subtract depreciation from investment so that the components of GDP do not exceed 100 percent. 32. Based on the data in the table above, what does GDP equal? a. $10,200 billion b. $10,400 billion c. $10,000 billion d. $9,800 billion e. $8,900 billion 6
7 33. The table gives data for a nation. What is the amount of the country's GDP? a. $6,000 billion b. $6,200 billion c. $6,600 billion d. $6,900 billion e. $5,800 billion. 34. When using the expenditure approach to measure U.S. GDP, a. all expenditures within the United States count toward U.S. GDP. b. used goods and financial assets purchased in a year are not included in the measure of U.S. GDP. c. all expenditures on final goods and services produced by U.S. owned companies and only U.S. owned companies count toward U.S. GDP. d. expenditures on used goods counts toward U.S. GDP, but expenditures on financial assets do not count toward U.S. GDP. e. expenditures on used goods count towards U.S. GDP only if the goods were initially produced in the United States. 35. When calculating GDP, purchases of used goods are a. included at the original price. b. included by taking the original price and subtracting the (current) used price. c. included at the (current) used price. d. not included. e. included at the original price minus any depreciation. 36. The purchase of the financial assets, such as stocks and bonds, is not included in GDP because a. they are too expensive. b. taxes are paid on them. c. brokerage firms don't want them to be included. d. they don't represent the production of goods or services. e. The question errs because the purchase of financial assets is counted as part of GDP. 37. Recently, the government made adjustments to how GDP is calculated that included placing software purchases into the category of a. intermediate goods because software is not a final good. b. inventory and now software purchases are not directly counted as part of GDP. c. investment and now directly counts software purchases as part of GDP. d. net exports of goods and services because most software is written abroad. e. net operating surplus. 7
8 38. The income approach measures GDP by summing a. C + I + G + NX. b. the total production of all final goods and services produced in a year within a country's borders. c. the wealth of households, business and government. d. the incomes paid households for the resources they own. e. Both answers A and D are correct. 39. When measuring GDP by the income approach, wages, also called "compensation of employees," includes only a. net wages and salaries. b. net wages, salaries, and fringe benefits. c. fringe benefits, such as health care. d. social security payments and pension fund payments. e. net wages and salaries plus fringe benefits paid by private businesses but not the net wages and salaries plus fringe benefits paid by governments. 40. The category of "rent" in the income approach to GDP a. includes the money paid to rent apartments only. b. includes the money paid to rent machinery only. c. includes the money paid to use land and other rented inputs. d. does not have any connection to owner-occupied housing. e. includes only the imputed rent for owner-occupied housing. 41. Once the categories of income are totaled, the sum is called a. "GDP measured by the income approach." b. "net domestic product at factor cost" and is not equal to GDP. c. "net domestic product at factor cost" and is equal to GDP. d. "total income earned" and is equal to GDP. e. GNP and is not equal to GDP. 42. After calculating net domestic product at factor cost, to calculate GDP using the income approach, in part we must add a. wages. b. net operating surplus. c. indirect taxes and depreciation. d. interest, rent, and profit. e. subsidies. 43. To measure GDP by using the income approach, we must add all incomes and then depreciation and net taxes less subsidies. a. neither add nor subtract; add b. add; neither add nor subtract c. add; add d. add; subtract e. subtract; add 8
9 44. To calculate GDP using the income approach, one of the adjustments made to net domestic product at factor cost is to a. add depreciation. b. add investment. c. subtract investment. d. add consumption expenditure. e. subtract indirect taxes less subsidies. 45. When calculating GDP, depreciation must be when using the approach. a. subtracted; income b. added; income c. added; expenditure d. subtracted; expenditure e. ignored; income 46. The table above has information about an economy. Using this information, GDP equals a. $5,600 billion. b. $7,100 billion. c. $8,300 billion. d. $9,500 billion. e. some amount that cannot be calculated without information on the amount of government expenditures. 47. Using the information in the table above, what does GDP equal? a. $300 billion b. $306 billion c. $326 billion d. $316 billion e. GDP cannot be calculated without information on the amount of investment. 9
10 48. Real GDP measures the value of goods and services produced in a given year valued using a. base year prices. b. prices that prevail the same year. c. no prices. d. future prices. e. real rather than nominal prices. 49. Real GDP is all final goods and services produced in a year within a country valued at a. market prices prevailing in the current year. b. current prices. c. nominal prices. d. base year prices. e. real prices. 50. Real GDP can increase if the i. quantities of goods and services produced decrease and prices fall by a smaller percentage. ii. quantities of goods and services produced decrease and prices fall by a larger percentage. iii. quantities of goods and services produced decrease and prices do not change. iv. quantities of goods and services produced increase. a. i only. b. iii only. c. iv only. d. i and iii. e. i, ii, and iii. 51. Nominal GDP is defined as GDP a. minus taxes and subsidies. b. corrected for price changes. c. measured at prices that prevailed during the year GDP was measured. d. measured by using quantities only. e. measured using base year prices. 52. Nominal GDP measures the value of goods and services produced in a given year valued using a. constant prices. b. prices of the same year. c. no prices. d. future prices. e. base year prices. 10
11 53. An increase in nominal GDP could result from an increase in i. production ii. prices iii. taxes and subsidies a. i only. b. ii only. c. i and ii. d. i and iii. e. i, ii, and iii. 54. Which of the following statement is correct? a. If nominal GDP increases, then real GDP must increase. b. If nominal GDP decreases, then real GDP must increase. c. If real GDP decreases, then nominal GDP must decrease. d. Nominal and real GDP can change either in the same direction or the opposite direction. e. If nominal GDP does not change, then real GDP cannot change. 55. Bobby was researching the economic growth of a country between 2003 and Using 2003 as the base year, he calculated a twelve percent increase for real GDP and a ten percent increase for nominal GDP. His results indicate that a. he made an error when calculating nominal GDP. b. the quantity of goods and services produced decreased over the period. c. the quantity of goods and services produced increased and prices decreased over the period. d. the quantity of goods and services produced and prices both decreased over the period. e. the quantity of goods and services produced did not change and prices decreased over the period. 56. During last year, a country produced 10,000 pizzas and 30,000 hamburgers and nothing else. The pizzas sold for $9.00 each and the hamburgers for $2.00 each. Nominal GDP was a. $150,000. b. $220,000. c. $290,000. d. $440,000. e. $360, The base year is A country only produces CD players. The price of a CD player in 2005 was $100. The price of a CD player was $90 in The quantity of CD players produced in 2005 was 10,000 units and in 2006 was 10,500 units. Nominal GDP in 2006 equals a. $900,000. b. $945,000. c. $1,000,000. d. $1,050,000. e. an amount that cannot be determined without information about nominal GDP in
12 58. The base year is A country only produces CD players. The price of a CD player in 2005 was $100. The price of a CD player was $90 in The quantity of CD players produced in 2005 was 10,000 units and in 2006 was 10,500 units. Real GDP in 2005 equals a. $900,000. b. $945,000. c. $1,000,000. d. $1,050,000. e. an amount that cannot be determined without information about real GDP in The table above gives the production and prices for a small nation that produces only bread and soda. The base year is What is nominal GDP in 2005? a. $425 b. $320 c. $205 d. $640 e. $ The table above gives the production and prices for a small nation that produces only bread and soda. The base year is What is real GDP in 2005? a. $300 b. $425 c. $320 d. $240 e. $ The table above gives the production and prices for a small nation that produces only bread and soda. The base year is What is nominal GDP in 2006? a. $240 b. $320 c. $425 d. $300 e. $460 12
13 62. The table above gives some data about GDP in a country for two years. Using these data, real GDP increased by percent between these two years. a. 4 b. 5 c. 6 d. 10 e Between the base period and the next period, prices stay constant. The GDP deflator in the next period a. can not be calculated without knowing how much the quantity changed. b. will equal 0 because there is no change. c. is equal to 100 because there is no change. d. is equal to 1 because there is no change. e. is equal to 50 because there is no change. 64. Real GDP is $1,500 billion and nominal GDP is $1,650. The GDP deflator equals a b c d e As measured, GDP omits which of the following? i. Illegal sales of goods and services. ii. Changes in the amount of leisure time. iii. Household production of goods and services. a. i only. b. i and ii. c. ii and iii. d. i and iii. e. i, ii, and iii. 66. Excluding household and underground production leads to a. underestimation of real GDP but not nominal GDP. b. overestimation of real GDP but not nominal GDP. c. overestimation of both real GDP and nominal GDP. d. underestimation of both real GDP and nominal GDP. e. underestimation of real GDP an an overestimation of nominal GDP. 13
14 67. Goods and services such as environmental quality, leisure time, and household production are not included in GDP because they are not a. productive activities. b. for consumption. c. bought in markets. d. made for profit. e. really durable goods. 68. Household production, such as baking bread at home, is not included in GDP because it a. has better quality than the bread in the store. b. has lower quality than the bread in the store. c. does not add anything of value to GDP. d. does not involve a market transaction. e. it is not really production. 69. The calculation of GDP excludes a. government expenditures on office supplies. b. households' purchases of shampoo. c. businesses' purchase of new machine tools. d. a family member painting the family home. e. expenditures on durable goods. 70. An example of household production excluded from GDP is a. household cleaning services provided by Merry Maids Incorporated. b. childcare provided by a certified nanny. c. tree trimming you provide at your parent's home. d. plumbing work completed by Joe Fix-it. e. lawn care provided by a local lawn care company. 71. Which of the following is likely to be an unreported economic activity? a. a $25,000 bonus paid to the CEO of a company b. tips paid to a taxi driver c. the minimum wage paid to a teenager working at a McDonalds d. the brokerage fees paid to a broker at Merrill Lynch e. the purchase of shares of stock in Walgreen's Pharmacy 72. The measurement of GDP handles underground production by a. including the amount produced in this sector of the economy in exactly the same way that all other production is included. b. omitting it because underground production is difficult to measure. c. adding it at a fixed rate of prices. d. adding an estimate of it because it is difficult to precisely measure underground production. e. omitting it because, being illegal, it has no effect on the nation's total production. 73. Leisure time is ignored when calculating GDP because leisure time a. does not effect our standard of living. b. has been declining over time. c. is not an economic good. d. does not involve a measurable market transaction. e. is not productive. 14
15 74. Which of the following is not included in measured GDP? a. the value of the pizzas produced at Pizza Hut b. the value of leisure time c. the value of the goods produced at a French owned plant in Atlanta, GA d. the value of the services produced by a lawyer in Tampa, FL e. the value of a plane produced by Boeing in Washington and sold to Air France. 75. Mexico City is notorious for its excessive pollution. Mexico's measure of GDP is a. decreased by the estimated value of the pollution's harm. b. not affected by the value of the pollution's harm. c. increased by the estimated value of the pollution's harm. d. changed by the pollution only when comparing its GDP with the U.S. GDP. e. None of the above answers is correct. 76. The Human Development Index was proposed because a. people confuse nominal GDP and real GDP. b. nominal GDP and real GDP are subjective measures. c. of the limitations of real GDP as a measure comparing the standard of living in different nations. d. the GDP deflator changes if the base year is changed. e. different nations have different populations. 77. Depreciation is a. fall in the value of an exchange rate. b. the decrease in the value of capital resulting from its use and obsolescence. c. the decrease in the purchasing power of a dollar because of inflation. d. part of consumption expenditure. e. part of net domestic product at factor cost. 78. Comparing nominal GDP of 2005 to nominal GDP of twenty years ago a. is an inaccurate measure of the change in total production. b. has no economic meaning. c. will be an accurate measure of the change in total production. d. determines the extent to which the cost of living changed. e. cannot be done because the two GDP measures use different prices. 79. If real GDP increases over time, the cost of living will a. always remain constant. b. always decrease. c. always increase. d. either remain constant or increase. e. More information is needed to determine how the cost of living changes. 80. If both the production of goods and services increase and prices rise, then the change in nominal GDP a. definitely understates the change in production. b. definitely accurately reflect the change in production. c. definitely overstates the change in production. d. either understates or might accurately reflect the change in production. e. More information is needed to determine how the change in nominal GDP compares to the change in production. 15
Decision Makers and Markets
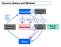 Decision Makers and Markets Households S FINANCIAL Wages Rent Interest Profit T Budget C I Factors M. (Capital Labor) Government G Goods & Services Rest of world Firms Decision Makers and Markets Households
Decision Makers and Markets Households S FINANCIAL Wages Rent Interest Profit T Budget C I Factors M. (Capital Labor) Government G Goods & Services Rest of world Firms Decision Makers and Markets Households
ECON 120 -ESSENTIALS OF ECONOMICS
 Name ECON 120 -ESSENTIALS OF ECONOMICS CH 21 Measuring National Inome MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The total market value of
Name ECON 120 -ESSENTIALS OF ECONOMICS CH 21 Measuring National Inome MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The total market value of
Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income
 Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income 1 Multiple Choice 1) The total market value of all final goods and services produced within a given period by factors of production located within
Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income 1 Multiple Choice 1) The total market value of all final goods and services produced within a given period by factors of production located within
GOAL #3 PROMOTE ECONOMIC GROWTH
 GOAL #3 PROMOTE ECONOMIC GROWTH CH. 12.1 How does a country measure economic growth? 3 How is the economy doing? The Bureau of Economic Analysis collect statistics on production, income, investment, and
GOAL #3 PROMOTE ECONOMIC GROWTH CH. 12.1 How does a country measure economic growth? 3 How is the economy doing? The Bureau of Economic Analysis collect statistics on production, income, investment, and
Economic Performance. Sherif Khalifa. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 1 / 39
 Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 1 / 39 People earning higher income levels enjoy higher living standards. To judge economic well being, we consider the total income in an economy.
Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 1 / 39 People earning higher income levels enjoy higher living standards. To judge economic well being, we consider the total income in an economy.
MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC GROWTH. Objectives. Gross Domestic Product. An Economic Barometer. Gross Domestic Product. Gross Domestic Product CHAPTER
 MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC CHAPTER GROWTH Objectives After studying this chapter, you will able to Define GDP and use the circular flow model to explain why GDP equals aggregate expenditure and aggregate
MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC CHAPTER GROWTH Objectives After studying this chapter, you will able to Define GDP and use the circular flow model to explain why GDP equals aggregate expenditure and aggregate
National Income. Sherif Khalifa. Sherif Khalifa () National Income 1 / 28
 National Income Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () National Income 1 / 28 People with higher incomes enjoy higher standards of living. To judge whether the economy is doing well, we look at the total income
National Income Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () National Income 1 / 28 People with higher incomes enjoy higher standards of living. To judge whether the economy is doing well, we look at the total income
LECTURE NOTES ON MACROECONOMIC PRINCIPLES
 LECTURE NOTES ON MACROECONOMIC PRINCIPLES Peter Ireland Department of Economics Boston College peter.ireland@bc.edu http://www2.bc.edu/peter-ireland/ec132.html Copyright (c) 2013 by Peter Ireland. Redistribution
LECTURE NOTES ON MACROECONOMIC PRINCIPLES Peter Ireland Department of Economics Boston College peter.ireland@bc.edu http://www2.bc.edu/peter-ireland/ec132.html Copyright (c) 2013 by Peter Ireland. Redistribution
1. The economic statistic used to measure the level of prices is the: A) GDP. B) CPI. C) GNP. D) real GDP.
 1. The economic statistic used to measure the level of prices is the: A) GDP. B) CPI. C) GNP. D) real GDP. 2. The statistic used by economists to measure the value of economic output is the: A) CPI. B)
1. The economic statistic used to measure the level of prices is the: A) GDP. B) CPI. C) GNP. D) real GDP. 2. The statistic used by economists to measure the value of economic output is the: A) CPI. B)
Measuring the Production, Income, and Spending of Nations
 6 Measuring the Production, Income, and Spending of Nations A Precise Definition of GDP GDP: a measure of the value of all newly produced 1 goods and services in a country 2 during some period of time
6 Measuring the Production, Income, and Spending of Nations A Precise Definition of GDP GDP: a measure of the value of all newly produced 1 goods and services in a country 2 during some period of time
Introduction. Learning Objectives. Chapter 8. Measuring the Economy s Performance
 Chapter 8 Measuring the Economy s Performance Introduction For a number of years, measured U.S. business investment spending on capital goods has declined relative to total national expenditures on goods
Chapter 8 Measuring the Economy s Performance Introduction For a number of years, measured U.S. business investment spending on capital goods has declined relative to total national expenditures on goods
MEASURING A NATION S INCOME
 10 MEASURING A NATION S INCOME LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this chapter, students should understand: why an economy s total income equals its total expenditure. how gross domestic product (GDP)
10 MEASURING A NATION S INCOME LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this chapter, students should understand: why an economy s total income equals its total expenditure. how gross domestic product (GDP)
EXPENDITURE APPROACH: The expenditures on all final goods and services made by all sectors of the economy are added to calculate GDP. Expenditures are
 Chapter 1 MEASURING GDP AND PRICE LEVEL MEASURING EONOMIC ACTIVITY Macroeconomics studies the aggregate (or total) concept of economic activity. Its focus is on the aggregate output, the aggregate income,
Chapter 1 MEASURING GDP AND PRICE LEVEL MEASURING EONOMIC ACTIVITY Macroeconomics studies the aggregate (or total) concept of economic activity. Its focus is on the aggregate output, the aggregate income,
file:///c:/users/moha/desktop/mac8e/new folder (2)/CourseCompas... Creation Settings
 1 of 24 12/8/2012 11:32 م COURSES > BA121 > CONTROL PANEL > POOL MANAGER > POOL CANVAS P Add, modify, and remove questions. Select a question type from the Add drop-down list and click Go to add questions.
1 of 24 12/8/2012 11:32 م COURSES > BA121 > CONTROL PANEL > POOL MANAGER > POOL CANVAS P Add, modify, and remove questions. Select a question type from the Add drop-down list and click Go to add questions.
Gross Domestic Product. How Is The GDP Calculated? Net investment equals gross investment minus depreciation.
 Chapter 23: Measuring GDP, Inflation and Economic Growth Gross Domestic Product applegross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of aggregate or total production of goods and services in a country during
Chapter 23: Measuring GDP, Inflation and Economic Growth Gross Domestic Product applegross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of aggregate or total production of goods and services in a country during
Gross Domestic Product. National Income Determination. Topic 9: 10/7/2016
 The Economy s Income and Expenditure Topic 9: National Income Determination When judging whether the economy is doing well or poorly, it is natural to look at the total income that everyone in the economy
The Economy s Income and Expenditure Topic 9: National Income Determination When judging whether the economy is doing well or poorly, it is natural to look at the total income that everyone in the economy
Measuring National Output and National Income. Gross Domestic Product. National Income and Product Accounts
 C H A P T E R 18 Measuring National Output and National Income Prepared by: Fernando Quijano and Yvonn Quijano Gross Domestic Product Gross domestic product (GDP) is the total market value of all final
C H A P T E R 18 Measuring National Output and National Income Prepared by: Fernando Quijano and Yvonn Quijano Gross Domestic Product Gross domestic product (GDP) is the total market value of all final
Economic Performance. Sherif Khalifa. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 1 / 55
 Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 1 / 55 People earning higher income levels also enjoy higher living standards. To judge economic well being, we consider the total income of an economy.
Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 1 / 55 People earning higher income levels also enjoy higher living standards. To judge economic well being, we consider the total income of an economy.
Chapter 8 GDP: # Measuring Total Production and Income
 Macroeconomics 6 th edition # Chapter 8 GDP: # Measuring Total Production and Income Modified by Yulin Hou For Principle of Macroeconomics Florida International University Summer 2017 pyright 2017 Pearson
Macroeconomics 6 th edition # Chapter 8 GDP: # Measuring Total Production and Income Modified by Yulin Hou For Principle of Macroeconomics Florida International University Summer 2017 pyright 2017 Pearson
Macroeconomic Measurement 1: Values and Prices
 International Economics and Business Dynamics Class Notes Macroeconomic Measurement 1: Values and Prices Revised: September 25, 2012 Latest version available at http://www.fperri.net/teaching/20205.htm
International Economics and Business Dynamics Class Notes Macroeconomic Measurement 1: Values and Prices Revised: September 25, 2012 Latest version available at http://www.fperri.net/teaching/20205.htm
CHAPTER 2: MEASUREMENT OF MACROECONOMIC VARIABLES
 Additional Questions Problems and/or essay questions: CHAPTER 2: MEASUREMENT OF MACROECONOMIC VARIABLES 1. What impact do you think that the movement of women from working in the household to working in
Additional Questions Problems and/or essay questions: CHAPTER 2: MEASUREMENT OF MACROECONOMIC VARIABLES 1. What impact do you think that the movement of women from working in the household to working in
Full file at Macroeconomics, 11e (Gordon) Chapter 2 The Measurement of Income, Prices, and Unemployment
 Macroeconomics, 11e (Gordon) Chapter 2 The Measurement of Income, Prices, and Unemployment 1) Job openings are plentiful when the A) actual real GDP is above the natural real GDP. B) natural real GDP is
Macroeconomics, 11e (Gordon) Chapter 2 The Measurement of Income, Prices, and Unemployment 1) Job openings are plentiful when the A) actual real GDP is above the natural real GDP. B) natural real GDP is
ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics. Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics
 ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics IN THIS CHAPTER, YOU WILL LEARN: the meaning and measurement of the most important macroeconomic statistics: gross domestic product
ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics IN THIS CHAPTER, YOU WILL LEARN: the meaning and measurement of the most important macroeconomic statistics: gross domestic product
W8- GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT MEASURES TOTAL PRODUCTION BSB113
 W8- GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT MEASURES TOTAL PRODUCTION BSB113 Gross Domestic Product (GDP): the market value of all final goods and services produced in a country during a period. In measuring GDP, we include
W8- GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT MEASURES TOTAL PRODUCTION BSB113 Gross Domestic Product (GDP): the market value of all final goods and services produced in a country during a period. In measuring GDP, we include
Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income. Kazu Matsuda IBEC 203 Macroeconomics
 Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income Kazu Matsuda IBEC 203 Macroeconomics MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME National income
Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income Kazu Matsuda IBEC 203 Macroeconomics MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME National income
Full file at
 ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS Problems and/or Essay Questions: CHAPTER 2: MEASUREMENT OF MACROECONOMIC VARIABLES 1. What impact do you think that the movement of women from working in the household to working in
ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS Problems and/or Essay Questions: CHAPTER 2: MEASUREMENT OF MACROECONOMIC VARIABLES 1. What impact do you think that the movement of women from working in the household to working in
Macroeconomics Canadian 7th Edition Abel SOLUTIONS MANUAL
 Macroeconomics Canadian 7th Edition Abel TEST BANK Full download at: Macroeconomics Canadian 7th Edition Abel SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/macroeconomics-canadian-7th-editionabel-test-bank/
Macroeconomics Canadian 7th Edition Abel TEST BANK Full download at: Macroeconomics Canadian 7th Edition Abel SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/macroeconomics-canadian-7th-editionabel-test-bank/
GDP: Measuring Total Production and Income
 Chapter 7 7.1 GDP: Measuring Total Production and Income Gross Domestic Product Measures Total Production 1. In 2007, American Airlines experienced an increase in the demand for its services and this fueled
Chapter 7 7.1 GDP: Measuring Total Production and Income Gross Domestic Product Measures Total Production 1. In 2007, American Airlines experienced an increase in the demand for its services and this fueled
Macroeconomics, 12e (Gordon) Chapter 2 The Measurement of Income, Prices, and Unemployment
 Macroeconomics, 12e (Gordon) Chapter 2 The Measurement of Income, Prices, and Unemployment 2.1 Why We Care About Income 1) Job openings are plentiful when the A) actual real GDP is above the natural real
Macroeconomics, 12e (Gordon) Chapter 2 The Measurement of Income, Prices, and Unemployment 2.1 Why We Care About Income 1) Job openings are plentiful when the A) actual real GDP is above the natural real
Ch 2. National Income Accounting ECO 402
 Ch 2. National Income Accounting ECO 402 Key Words The circular flow Three approaches to measuring national income Production Income Expenditure Value added Final goods and intermediate goods Gross domestic
Ch 2. National Income Accounting ECO 402 Key Words The circular flow Three approaches to measuring national income Production Income Expenditure Value added Final goods and intermediate goods Gross domestic
1. The economic statistic used to measure the level of prices is: A) GDP. B) CPI. C) GNP. D) real GDP.
 1. The economic statistic used to measure the level of prices is: A) GDP. B) CPI. C) GNP. D) real GDP. 2. The statistic used by economists to measure the value of economic output is: A) the CPI. B) GDP.
1. The economic statistic used to measure the level of prices is: A) GDP. B) CPI. C) GNP. D) real GDP. 2. The statistic used by economists to measure the value of economic output is: A) the CPI. B) GDP.
Text transcription of Chapter 5 Measuring a Nation s Income
 Text transcription of Chapter 5 Measuring a Nation s Income Welcome to the Chapter 5 Lecture on the Measuring a Nation s Income. We are going to start working with statistics to measure the size of economies
Text transcription of Chapter 5 Measuring a Nation s Income Welcome to the Chapter 5 Lecture on the Measuring a Nation s Income. We are going to start working with statistics to measure the size of economies
Chapter 02 National Income Accounting
 Chapter 02 National Income Accounting Multiple Choice Questions 1. In calculating this year's GDP, national income accountants a. Include any increase in stock values b. Include an estimate for income
Chapter 02 National Income Accounting Multiple Choice Questions 1. In calculating this year's GDP, national income accountants a. Include any increase in stock values b. Include an estimate for income
Measuring a Nation s Income
 Wojciech Gerson (1831-1901) Seventh Edition Principles of Economics N. Gregory Mankiw CHAPTER 23 Measuring a Nation s Income In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions What is Gross Domestic
Wojciech Gerson (1831-1901) Seventh Edition Principles of Economics N. Gregory Mankiw CHAPTER 23 Measuring a Nation s Income In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions What is Gross Domestic
Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income. Kazu Matsuda BIZ 203 Macroeconomics
 Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income Kazu Matsuda BIZ 203 Macroeconomics MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME National income and
Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income Kazu Matsuda BIZ 203 Macroeconomics MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME National income and
BEFORE YOU BEGIN Looking at the Chapter
 Name Date Period MEASURING ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE Chapter 12 BEFORE YOU BEGIN Looking at the Chapter Fill in the blank spaces with the missing words. GDP is the total value of all goods and services produced
Name Date Period MEASURING ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE Chapter 12 BEFORE YOU BEGIN Looking at the Chapter Fill in the blank spaces with the missing words. GDP is the total value of all goods and services produced
MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME. Chapter 18
 1 MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME Chapter 18 national income and product accounts Data collected and published by the government describing the various components of national income and output
1 MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME Chapter 18 national income and product accounts Data collected and published by the government describing the various components of national income and output
Measuring a Nation s Production and Income
 Chapter Summary 5 Measuring a Nation s Production and Income In this chapter, we learned how economists and government statisticians measure the income and production for an entire country and what those
Chapter Summary 5 Measuring a Nation s Production and Income In this chapter, we learned how economists and government statisticians measure the income and production for an entire country and what those
Measuring a Nation s Income
 C H A P T E R 23 Measuring a Nation s Income Economics P R I N C I P L E S O F N. Gregory Mankiw Premium PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2009 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning, all rights reserved
C H A P T E R 23 Measuring a Nation s Income Economics P R I N C I P L E S O F N. Gregory Mankiw Premium PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2009 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning, all rights reserved
Macroeconomics Sixth Edition
 N. Gregory Mankiw Principles of Macroeconomics Sixth Edition 10 Measuring a Nation s Income Premium PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2012 UPDATE In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions:
N. Gregory Mankiw Principles of Macroeconomics Sixth Edition 10 Measuring a Nation s Income Premium PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2012 UPDATE In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions:
William A. McEachern Macro3 ECON
 William A. McEachern Macro3 ECON 6 1 The Product of a Nation 17 th and 18 th century Mercantilism 1758 Economic prosperity: stock of precious metals Circular flow of output and income National income accounting
William A. McEachern Macro3 ECON 6 1 The Product of a Nation 17 th and 18 th century Mercantilism 1758 Economic prosperity: stock of precious metals Circular flow of output and income National income accounting
Introduction to Macroeconomics
 Week 1: General notes: o Macroeconomics studies the aggregate impact of individual decisions. Microeconomics studies decision-making by individual economic agents o In the study of macroeconomics, an economist
Week 1: General notes: o Macroeconomics studies the aggregate impact of individual decisions. Microeconomics studies decision-making by individual economic agents o In the study of macroeconomics, an economist
National Income. Sherif Khalifa. Sherif Khalifa () National Income 1 / 44
 National Income Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () National Income 1 / 44 People with higher incomes enjoy higher standards of living. To judge how the economy is doing, we look at the total income of everyone
National Income Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () National Income 1 / 44 People with higher incomes enjoy higher standards of living. To judge how the economy is doing, we look at the total income of everyone
Week 1. H1 Notes ECON10003
 Week 1 Some output produced by the government is free. Education is a classic example. This is still viewed as a service and valued at the cost of production which is primarily the salary of the workers
Week 1 Some output produced by the government is free. Education is a classic example. This is still viewed as a service and valued at the cost of production which is primarily the salary of the workers
Chapter 2: The Data of Macroeconomics
 Chapter 2: The Data of Macroeconomics 0 IN THIS CHAPTER, YOU WILL LEARN: the meaning and measurement of the most important macroeconomic statistics:! gross domestic product (GDP)! the consumer price index
Chapter 2: The Data of Macroeconomics 0 IN THIS CHAPTER, YOU WILL LEARN: the meaning and measurement of the most important macroeconomic statistics:! gross domestic product (GDP)! the consumer price index
Full file at
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The accounting framework used in measuring current economic activity is called 1) A) the flow of
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The accounting framework used in measuring current economic activity is called 1) A) the flow of
Macroeconomics. Measuring a Nation s Income. Income and Expenditure. The Circular-Flow Diagram. Micro vs. Macro. Principles of
 N. Gregory Mankiw Principles of Macroeconomics Sixth Edition 10 Measuring a Nation s Income Premium PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich Income and Expenditure Gross Domestic Product () measures total income
N. Gregory Mankiw Principles of Macroeconomics Sixth Edition 10 Measuring a Nation s Income Premium PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich Income and Expenditure Gross Domestic Product () measures total income
In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions
 In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions What is Gross Domestic Product (GDP)? How is GDP related to a nation s total income and spending? What are the components of GDP? How is GDP corrected
In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions What is Gross Domestic Product (GDP)? How is GDP related to a nation s total income and spending? What are the components of GDP? How is GDP corrected
Macroeconomics, 8e (Abel/Bernanke/Croushore) Chapter 2 The Measurement and Structure of the National Economy
 Macroeconomics 8th Edition Abel Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/macroeconomics-8th-edition-abel-test-bank/ Macroeconomics, 8e (Abel/Bernanke/Croushore) Chapter 2 The Measurement
Macroeconomics 8th Edition Abel Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/macroeconomics-8th-edition-abel-test-bank/ Macroeconomics, 8e (Abel/Bernanke/Croushore) Chapter 2 The Measurement
GDP can be measured in mainly two ways. 1. Income Approach. 2. Expenditure Approach. Expenditure Approach:
 Gross Domestic Product is the total market value of all goods and services produced in the country in a particular year. It is equal to total consumer, investment and government spending, plus the value
Gross Domestic Product is the total market value of all goods and services produced in the country in a particular year. It is equal to total consumer, investment and government spending, plus the value
Macroeonomics. Measuring a Nation s Income 8/29/2012. Micro vs. Macro. In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions: N.
 C H A P T E R 10 Measuring a Nation s Income P R I N C I P L E S O F Macroeonomics N. Gregory Mankiw Premium PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2009 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning, all rights
C H A P T E R 10 Measuring a Nation s Income P R I N C I P L E S O F Macroeonomics N. Gregory Mankiw Premium PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2009 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning, all rights
Macroeconomics, 6e (Williamson) Chapter 2 Measurement. 2.1 Multiple-Choice Questions
 Macroeconomics, 6e (Williamson) Chapter 2 Measurement 2.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) NIPA means A) New Income and Price Accounting. B) National Investment and Productivity Approach. C) Neutral Increase
Macroeconomics, 6e (Williamson) Chapter 2 Measurement 2.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) NIPA means A) New Income and Price Accounting. B) National Investment and Productivity Approach. C) Neutral Increase
Learning objectives. Gross Domestic Product
 Learning objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) the Consumer Price Index (CPI) the Unemployment Rate The Data of Macroeconomics slide 1 Gross Domestic Product Two
Learning objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) the Consumer Price Index (CPI) the Unemployment Rate The Data of Macroeconomics slide 1 Gross Domestic Product Two
Introduction. Learning Objectives. Chapter 8. Measuring the Economy s Performance
 Copyright 2012 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Chapter 8 Measuring the Economy s Performance Introduction Does a general increase in the level of a nation s economic activity and the resulting
Copyright 2012 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Chapter 8 Measuring the Economy s Performance Introduction Does a general increase in the level of a nation s economic activity and the resulting
Chapter 8- Measuring Total Production & Income. Distribution of GDP
 Chapter 8- Measuring Total Production & Income Distribution of GDP 1 Keeping Tabs on the Economy You must be able to measure and track the economy in order to understand what is going on and react appropriately.
Chapter 8- Measuring Total Production & Income Distribution of GDP 1 Keeping Tabs on the Economy You must be able to measure and track the economy in order to understand what is going on and react appropriately.
MEASURING A NATION S INCOME
 23 MEASURING A NATION S INCOME WHAT S NEW IN THE FOURTH EDITION: There is a new In the News box on The Underground Economy. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this chapter, students should understand:
23 MEASURING A NATION S INCOME WHAT S NEW IN THE FOURTH EDITION: There is a new In the News box on The Underground Economy. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this chapter, students should understand:
8 THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS
 8 THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS Measuring a Nation s Income 23 Measuring a Nation s Income Microeconomics Microeconomics is the study of how individual households and firms make decisions and how they interact
8 THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS Measuring a Nation s Income 23 Measuring a Nation s Income Microeconomics Microeconomics is the study of how individual households and firms make decisions and how they interact
Chapter 2 The Measurement of Income, Prices, and Unemployment
 Chapter 2 The Measurement of Income, Prices, and Unemployment Chapter Outline 2-1 Why We Care About Income 2-2 The Circular Flow of Income and Expenditure 2-3 What GDP Is, and What GDP Is Not a. Defining
Chapter 2 The Measurement of Income, Prices, and Unemployment Chapter Outline 2-1 Why We Care About Income 2-2 The Circular Flow of Income and Expenditure 2-3 What GDP Is, and What GDP Is Not a. Defining
1 of 22 9/24/2013 2:14 PM
 1 of 22 9/24/2013 2:14 PM National income accounts assist Market investors in making more profitable investments. Individuals in maximizing their incomes. Economic policy makers in formulating policies
1 of 22 9/24/2013 2:14 PM National income accounts assist Market investors in making more profitable investments. Individuals in maximizing their incomes. Economic policy makers in formulating policies
Indicators of National Econmoy. Ing. Mansoor Maitah Ph.D. et Ph.D.
 Indicators of National Econmoy Ing. Mansoor Maitah Ph.D. et Ph.D. Circular Flows in the Market Economy Describes the flow of resources, products, income, and revenue among the four decision makers (Households;
Indicators of National Econmoy Ing. Mansoor Maitah Ph.D. et Ph.D. Circular Flows in the Market Economy Describes the flow of resources, products, income, and revenue among the four decision makers (Households;
Full file at
 MULTIPLE CHOICE Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question 1) Gross domestic product is defined as 1) A) the total market value of the final goods and services
MULTIPLE CHOICE Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question 1) Gross domestic product is defined as 1) A) the total market value of the final goods and services
ECON 201. Learning Objectives. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) 9/25/2009. Chapter 5 GDP & Economic Growth
 ECON 201 Chapter 5 GDP & Economic Growth Learning Objectives How GDP is Defined and Measured. How economists distinguish between nominal GDP & real GDP. Long term trend of U.S. economic growth. Generalingredientsofeconomicgrowth
ECON 201 Chapter 5 GDP & Economic Growth Learning Objectives How GDP is Defined and Measured. How economists distinguish between nominal GDP & real GDP. Long term trend of U.S. economic growth. Generalingredientsofeconomicgrowth
Test bank for Macroeconomics 12th Edition by Rudiger Dornbusch Dr, Stanley Fischer, Richard Startz
 Test bank for Macroeconomics 12th Edition by Rudiger Dornbusch Dr, Stanley Fischer, Richard Startz Link full download : http://testbankcollection.com/download/test-bank-for-macroeconomics- 12th-edition-by-dornbusch-fischer-startz/
Test bank for Macroeconomics 12th Edition by Rudiger Dornbusch Dr, Stanley Fischer, Richard Startz Link full download : http://testbankcollection.com/download/test-bank-for-macroeconomics- 12th-edition-by-dornbusch-fischer-startz/
E 11) Stay-at-home mothers create community garden. E 2) Honda purchases steel for producing new cars. I 12) Chevrolet purchases a new factory.
 Lecture (6.2.2) Is This Part of GDP? GDP is made up of many different factors. While working in pairs, decide whether you think each economic event below is included in GDP or excluded from GDP. If you
Lecture (6.2.2) Is This Part of GDP? GDP is made up of many different factors. While working in pairs, decide whether you think each economic event below is included in GDP or excluded from GDP. If you
Unemployment Rate = 1. A large number of economic statistics are released regularly. These include the following:
 CHAPTER The Data of Macroeconomics Questions for Review 1. GDP measures the total income earned from the production of the new final goods and services in the economy, and it measures the total expenditures
CHAPTER The Data of Macroeconomics Questions for Review 1. GDP measures the total income earned from the production of the new final goods and services in the economy, and it measures the total expenditures
Macroeconomic Measurements, Part II: GDP and Real GDP CHAPTER
 Macroeconomic Measurements, Part II: GDP and Real GDP 7 CHAPTER An Economic Barometer What exactly is GDP? How do we use it to tell us whether our economy is in a recession or how rapidly our economy is
Macroeconomic Measurements, Part II: GDP and Real GDP 7 CHAPTER An Economic Barometer What exactly is GDP? How do we use it to tell us whether our economy is in a recession or how rapidly our economy is
Parkin/Bade, Economics: Canada in the Global Environment, 8e
 Chapter 20 Measuring GDP and Economic Growth 20.1 Gross Domestic Product 1) Gross domestic product is A) the final value of all goods produced in a country in a given time period. B) the market value of
Chapter 20 Measuring GDP and Economic Growth 20.1 Gross Domestic Product 1) Gross domestic product is A) the final value of all goods produced in a country in a given time period. B) the market value of
Economics Chapter 11: MEASURING ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE
 SECTION 1 National Income Accounting Economics Chapter 11: MEASURING ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE What Is Gross Domestic Product? Gross domestic product (GDP) is the total value of all goods and services produced
SECTION 1 National Income Accounting Economics Chapter 11: MEASURING ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE What Is Gross Domestic Product? Gross domestic product (GDP) is the total value of all goods and services produced
k-2/ Macroeconomics 9th Edition Abel SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full download at:
 Macroeconomics 9th Edition Abel TEST BANK Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/macroeconomics-9th-edition-abel-test-ban k-2/ Macroeconomics 9th Edition Abel SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full download
Macroeconomics 9th Edition Abel TEST BANK Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/macroeconomics-9th-edition-abel-test-ban k-2/ Macroeconomics 9th Edition Abel SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full download
Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics
 Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics slide 0 Learning Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) the Consumer Price Index (CPI) the Unemployment Rate slide 1 GROSS DOMESTIC
Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics slide 0 Learning Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) the Consumer Price Index (CPI) the Unemployment Rate slide 1 GROSS DOMESTIC
ECO 209Y MACROECONOMIC THEORY AND POLICY LECTURE 2: NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING
 ECO 209Y MACROECONOMIC THEORY AND POLICY LECTURE 2: NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING Gustavo Indart Slide1 GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of all final goods and services produced
ECO 209Y MACROECONOMIC THEORY AND POLICY LECTURE 2: NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING Gustavo Indart Slide1 GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of all final goods and services produced
Lecture Investment and Saving
 Lecture 3-1 4. Investment and Saving Investment is the portion of final product that adds to the nation s stock of income-yielding physical assets or that replaces old, worn-out physical assets. The goods
Lecture 3-1 4. Investment and Saving Investment is the portion of final product that adds to the nation s stock of income-yielding physical assets or that replaces old, worn-out physical assets. The goods
Part V: Introduction to Macroeconomics 19. The Wealth of Nations: Defining and
 Part V: Introduction to s 19. 20. Aggregate Incomes 1 / 56 Chapter 19 Defining and 2017.8.9. 2 / 56 1 2 3 4 3 / 56 Chapter 19 Q: In the United States, what is the total market value of annual economic
Part V: Introduction to s 19. 20. Aggregate Incomes 1 / 56 Chapter 19 Defining and 2017.8.9. 2 / 56 1 2 3 4 3 / 56 Chapter 19 Q: In the United States, what is the total market value of annual economic
Unemployment Rate = 1. A large number of economic statistics are released regularly. These include the following:
 CHAPTER The Data of Macroeconomics Questions for Review 1. GDP measures the total income earned from the production of the new final goods and services in the economy, and it measures the total expenditures
CHAPTER The Data of Macroeconomics Questions for Review 1. GDP measures the total income earned from the production of the new final goods and services in the economy, and it measures the total expenditures
Taking an Economic Pulse: Measuring National Output
 Chapter 2 Taking an Economic Pulse: Measuring National Output Review Questions 1. Distinguish between GNP and GDP. What is included, and what is excluded? Gross domestic product (GDP) and gross national
Chapter 2 Taking an Economic Pulse: Measuring National Output Review Questions 1. Distinguish between GNP and GDP. What is included, and what is excluded? Gross domestic product (GDP) and gross national
1. A large number of economic statistics are released regularly. These include the following:
 CHAPTER The Data of Macroeconomics Questions for Review 1. GDP measures the total income earned from the production of the new final goods and services in the economy, and it measures the total expenditures
CHAPTER The Data of Macroeconomics Questions for Review 1. GDP measures the total income earned from the production of the new final goods and services in the economy, and it measures the total expenditures
E) price level and the total output that firms wish to produce and sell, as technology and input prices vary.
 Exam Name 1) The economyʹs aggregate supply (AS) curve shows the relationship between the A) price level and the marginal propensity to consume (MPC). B) equilibrium real GDP and marginal cost. C) price
Exam Name 1) The economyʹs aggregate supply (AS) curve shows the relationship between the A) price level and the marginal propensity to consume (MPC). B) equilibrium real GDP and marginal cost. C) price
Many of life s failures are people who did not realize how close they were to success when they gave up. Thomas Edison
 Many of life s failures are people who did not realize how close they were to success when they gave up. Thomas Edison National-income accounting is the system used to measure the aggregate income and
Many of life s failures are people who did not realize how close they were to success when they gave up. Thomas Edison National-income accounting is the system used to measure the aggregate income and
"Data, data, data: how can I make bricks without clay?".
 1 Measurement As explained in the previous chapter, measurement is a key component of the scientific method and is necessary to develop and validate theories. Sherlock Holmes, one of the masters of (investigative
1 Measurement As explained in the previous chapter, measurement is a key component of the scientific method and is necessary to develop and validate theories. Sherlock Holmes, one of the masters of (investigative
MACROECONOMICS. The Data of Macroeconomics MANKIW. In this chapter, you will learn. Gross Domestic Product: Expenditure and Income.
 C H A P T E R 2 The Data of Macroeconomics MACROECONOMICS N. GREGORY MANKIW 2008 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved SIXTH EDITION PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich In this chapter, you will learn the
C H A P T E R 2 The Data of Macroeconomics MACROECONOMICS N. GREGORY MANKIW 2008 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved SIXTH EDITION PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich In this chapter, you will learn the
Unit 4: Measuring GDP and Prices
 Unit 4: Measuring GDP and Prices ECO 120 Global Macroeconomics 1 1.1 Reading Reading Gross Domestic Product (GDP): Module 11 Real vs Nominal GDP: Module 12 1.2 Goals Goals Specific Goals: Understand how
Unit 4: Measuring GDP and Prices ECO 120 Global Macroeconomics 1 1.1 Reading Reading Gross Domestic Product (GDP): Module 11 Real vs Nominal GDP: Module 12 1.2 Goals Goals Specific Goals: Understand how
Measuring the Aggregate Economy
 CHAPTER 25 Measuring the Aggregate Economy The government is very keen on amassing statistics... They collect them, add them, raise them to the n th power, take the cube root and prepare wonderful diagrams.
CHAPTER 25 Measuring the Aggregate Economy The government is very keen on amassing statistics... They collect them, add them, raise them to the n th power, take the cube root and prepare wonderful diagrams.
Homework 2 of ETP Economics
 Homework 2 of ETP Economics Winter Term 2014 Due: April 2 1. Which of the following is not included in GDP? a. unpaid cleaning and maintenance of houses b. services such as those provided by lawyers and
Homework 2 of ETP Economics Winter Term 2014 Due: April 2 1. Which of the following is not included in GDP? a. unpaid cleaning and maintenance of houses b. services such as those provided by lawyers and
GDP and The Measurement of Progress
 GDP and The Measurement of Progress What is GDP Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a year. GDP per capita GDP divided by population
GDP and The Measurement of Progress What is GDP Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a year. GDP per capita GDP divided by population
Macroeconomics 5th Edition Williamson Test Bank Full Download:
 Macroeconomics 5th Edition Williamson Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/macroeconomics-5th-edition-williamson-test-bank/ Macroeconomics, 5e (Williamson) Chapter 2 Measurement 1)
Macroeconomics 5th Edition Williamson Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/macroeconomics-5th-edition-williamson-test-bank/ Macroeconomics, 5e (Williamson) Chapter 2 Measurement 1)
NATIONAL INCOME AND RELATED AGGREGATES
 NATIONAL INCOME AND RELATED AGGREGATES The modern concept of National Income is more dynamic in the content than earlier concepts. The National Income Committee of India defined national income as: A National
NATIONAL INCOME AND RELATED AGGREGATES The modern concept of National Income is more dynamic in the content than earlier concepts. The National Income Committee of India defined national income as: A National
Economics. The last two weeks...
 Economics The last two weeks... Final Exam (Thursday, December 14) Practice tests and review materials on Wednesday Extra Credit Stock Project (due on Thursday, December 14) Today: Measuring Economic Performance
Economics The last two weeks... Final Exam (Thursday, December 14) Practice tests and review materials on Wednesday Extra Credit Stock Project (due on Thursday, December 14) Today: Measuring Economic Performance
macro macroeconomics The Data of Macroeconomics N. Gregory Mankiw CHAPTER TWO 6 th edition
 macro CHAPTER TWO The Data of Macroeconomics macroeconomics 6 th edition N. Gregory Mankiw Learning objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) the Consumer Price Index
macro CHAPTER TWO The Data of Macroeconomics macroeconomics 6 th edition N. Gregory Mankiw Learning objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) the Consumer Price Index
PART EIGHT: THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS. Measuring A Nation s Income
 ECON 102 Chapter 22 1 PART EIGHT: THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS Measuring A Nation s Income Chapter 23 What did we learn until now? In the first semester we covered microeconomics Microeconomics is the study
ECON 102 Chapter 22 1 PART EIGHT: THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS Measuring A Nation s Income Chapter 23 What did we learn until now? In the first semester we covered microeconomics Microeconomics is the study
Final goods and services. Produced in a country in a given period of time
 Chapter 4 1. Explain how economists define and measure an economy's output 2. Apply the expenditure method for measuring GDP to analyze economic activity 3. Define and compute nominal GDP and real GDP
Chapter 4 1. Explain how economists define and measure an economy's output 2. Apply the expenditure method for measuring GDP to analyze economic activity 3. Define and compute nominal GDP and real GDP
Macroeconomic Measurement and Business Cycles
 Macroeconomic Measurement and Business Cycles Economics 4353 - Intermediate Macroeconomics Aaron Hedlund University of Missouri Fall 2015 Econ 4353 (University of Missouri) Measurement and Business Cycles
Macroeconomic Measurement and Business Cycles Economics 4353 - Intermediate Macroeconomics Aaron Hedlund University of Missouri Fall 2015 Econ 4353 (University of Missouri) Measurement and Business Cycles
Answers to Text Questions and Problems to Chapter 5
 Answers to Text Questions and Problems to Chapter 5 Answers to Review Questions 1. Using market values permits economists to add together different goods and services to get a measure of total output.
Answers to Text Questions and Problems to Chapter 5 Answers to Review Questions 1. Using market values permits economists to add together different goods and services to get a measure of total output.
Macroeconomic Measurement and Business Cycles
 Macroeconomic Measurement and Business Cycles Economics 3307 - Intermediate Macroeconomics Aaron Hedlund Baylor University Fall 2013 Econ 3307 (Baylor University) Measurement and Business Cycles Fall 2013
Macroeconomic Measurement and Business Cycles Economics 3307 - Intermediate Macroeconomics Aaron Hedlund Baylor University Fall 2013 Econ 3307 (Baylor University) Measurement and Business Cycles Fall 2013
Test Yourself: National-Income Accounting
 Test Yourself: National-Income Accounting Nothing is more destructive than the gap between people's perceptions of their own day-to-day economic well-being and what politicians and statisticians are telling
Test Yourself: National-Income Accounting Nothing is more destructive than the gap between people's perceptions of their own day-to-day economic well-being and what politicians and statisticians are telling
AGENDA Tues 1/26. QOD #8: GDP Calculations HW Review ( P #4,5,7) Partner Practice
 AGENDA Tues 1/26 QOD #8: GDP Calculations HW Review (494-500 P #4,5,7) Partner Practice Study for CH 23-24 Assessment Parent Syllabus review LO1 24-1 QOD #8: GDP Calculations-Part 1 Suppose that annual
AGENDA Tues 1/26 QOD #8: GDP Calculations HW Review (494-500 P #4,5,7) Partner Practice Study for CH 23-24 Assessment Parent Syllabus review LO1 24-1 QOD #8: GDP Calculations-Part 1 Suppose that annual
Welcome to Econ20B The Principle of Macroeconomics
 Welcome to Econ20B The Principle of Macroeconomics CHAPTER 23 MEASURING A NATION S INCOME 0 Professor Min Ouyang Office: 3101 Social Science Plaza A Office Hours: Tuesdays 3:30 5:30 p. Office Phone: 9498249698
Welcome to Econ20B The Principle of Macroeconomics CHAPTER 23 MEASURING A NATION S INCOME 0 Professor Min Ouyang Office: 3101 Social Science Plaza A Office Hours: Tuesdays 3:30 5:30 p. Office Phone: 9498249698
Macroeconomics, 3e (Williamson) Chapter 2 Measurement
 Macroeconomics, 3e (Williamson) Chapter 2 Measurement 1) The principal printed source for reporting the US National Income and Product Accounts is called the A) Monthly Labor Review B) Survey of Current
Macroeconomics, 3e (Williamson) Chapter 2 Measurement 1) The principal printed source for reporting the US National Income and Product Accounts is called the A) Monthly Labor Review B) Survey of Current
Econ COURSE 2 (Chapter 21) MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME
 COURSE 2 (Chapter 21) MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME Outline of today s lecture: 1. Gross Domestic Product 2. Calculating GDP A) Expenditure Approach B) Income Approach C) Output Approach
COURSE 2 (Chapter 21) MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME Outline of today s lecture: 1. Gross Domestic Product 2. Calculating GDP A) Expenditure Approach B) Income Approach C) Output Approach
A. Adding the monetary value of all final goods and services produced during a given period of
 Chapter 02 The U.S. Economy Multiple Choice Questions 1. In order to measure what a country produces, we: A. Summarize total output in physical terms. B. Count units of output. C. Count the weight of different
Chapter 02 The U.S. Economy Multiple Choice Questions 1. In order to measure what a country produces, we: A. Summarize total output in physical terms. B. Count units of output. C. Count the weight of different
MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC GROWTH
 21 MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC GROWTH GDP Defined GDP or gross domestic product is the market value of all final goods and services produced in a country in a given time period. This definition has four
21 MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC GROWTH GDP Defined GDP or gross domestic product is the market value of all final goods and services produced in a country in a given time period. This definition has four
