Production, Income and Employment
|
|
|
- Marion Hutchinson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CAPTER 6 Production, Income and Employment Sasan ayazmanesh Summary Summary: This chapter deals with the following macroeconomic concepts: 1) National income accounting: how to measure the value of goods and services or national income. 2) Unemployment: how to measure the rate of unemployment. What is microeconomics? National Income Accounts Circular low of Spending We begin with what is called a circular flow of spending, which does not appear in this chapter (see Chapter 3). : Units of production ouseholds: actors of production Expenditures ($) Goods and services Goods and services Productive services and resources (land, labor and capital) Productive services and resources Income ($) 1
2 lows and Stocks Def. a flow measures something per unit of time. Example: the flow into the bathtub is 2 gallons per minute. Def. a stock measures something at a given time. Example: the stock of water in the bathtub is 10 gallons. Gross National Product (GNP) We will define Gross National Product and Gross National Income shortly. But first, let us define Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Def. GDP is the value of all goods and services produced. Gross National Income (GNI) GNP GNI Gross Domestic Product (GDP) More technically, Def. GDP is the monetary value of all final goods and services produced for the market place in one year, within a country. The meaning of each word: Monetary value: We need a unit of measurement, a common denominator. inal goods and services: We must avoid double counting by excluding all the intermediate stages of production and sales. 2
3 Example: Consider a gallon of gasoline: Stages of production Sales value Value added and sales Oil drilling $.50 $.50 Refining Shipping Retail sale $3.00 Note that one can calculate the GDP by adding up the values added. This is called the value added approach to GDP. Market place: We set aside those goods and services that are not bought or sold, for example: ousework: work that you do at home. If you hire a person to do the work, it enters the GDP. Underground economy: illegal drugs, gambling, prostitution, etc. Barter: direct exchange of goods and services. One year: All goods and services must be produced in the given year. Thus items produced in the previous years are excluded. This means that GDP is a flow, since it measures something per year. Within a country: We don t care whether the goods and services are produced by foreign or domestic firms, as long as they are produced in the country. The Expenditure Approach to GDP: The Components of GDP We can look at how money is spent on goods and services by dividing GDP into four components: GDP = C + Ig + G + (X-M) C: Personal consumption This is the total amount of spending by consumers on goods and services. It is the largest component of GDP (about 66% or 2/3 of GDP) 3
4 1) C consists of 1) durable goods (goods lasting 3 years or more), such as cars, refrigerators, computers, etc. 2) non-durable goods (goods lasting less than 3 years), such as food, clothing, soft drinks, etc. 3) services, such as transportation, education, health, etc. 2) Ig: Gross Private Investment This is the total spending on goods that are used to produce other goods. It consists of : 1) structures and equipments, 2) residential structures 3) changes in business inventories ( I) Changes in business inventories ( I ) can be positive, if some goods produced by the firms remain unsold: economy contracts. negative, if the firms have not produced enough: economy expands. zero, if the firms have produced just the right amount of goods and services: economy is stable, there is no expansion or contraction. Actual Investment and Planned Investment Since some of the investment is unintended changes in inventories, then Actual investment= Planned investment + Unintended changes in inventories I a = I p + I Gross Investment versus Net Investment Net investment = Gross Investment (Ig) Depreciation Expenditures Or In = Ig Depreciation Ig = In + Depreciation Depreciation Def. Depreciation (or capital consumption allowances ) is capital used up in the production process. Income 4
5 3) G: Government purchases: This is government expenditures on goods and service. It consists of 1) ederal expenditures on: a) Defense (the biggest component) b) Others 2) State and local government expenditures. Note G does not include transfer payment. Def. Transfer payments transfer income from one group of people to another, such as social security, welfare, unemployment compensation, etc. Q: Why are transfer payments not in in G? A: Because by definition G is government expenditure on goods and services and transfer payments are not expenditure on goods and services. 4) X-M: Net exports: This is the difference between total exports and total imports of goods and services, that is X M = exports imports X M could be negative, positive or zero. Summing up: GDP = C + Ig + G + (X-M) C: Personal consumption 1) durable goods 2) non-durable goods 3) services Ig: Gross Private Investment 1) structures and equipments 2) residential structures 3) changes in business inventories ( I) (Also, Ia, Ip, Ig, In, and depreciation) G: Government purchases 1) ederal expenditures a) Defense b) Others 2) State and local government X M: Net export See Econ 50 Website BEA Expenditures The Income (actor Payment) Approach to GDP We now look at the lower part of the flow, measuring the income or what the factors earn or receive: Gross National Product (GNP) Gross National Income (GNI) 5
6 Before discussing Gross National Products and Gross National Income identity, we look at Net National Income. Net National Income (NNI) or National Income (NI) Def. NNI or NI is the income earned by factors of production (labor, land and capital). NNI = Wages & Salaries + rent + interest + profit 1) Wages & salaries (or compensation to the employees ): income earned by the employees. 2) Rent: income earned for owning rental properties, imputed or otherwise. 3) Interest: interest earned by household from firms. 4) Profit: i) Corporate profit: a) dividends b) retained earnings c) corporate taxes ii) Income of unincorporated businesses, or proprietors income: Income of small businesses, partnerships, and self employed individuals, such as doctors and lawyers. NNI flow is not equal to GDP flow! In order to equalize the output flow with income flow we need to look at GNP and GNI. Gross National Product (GNP) Gross National Income (GNI) GNP GNI 6
7 GDP GNP Chinese US German Chinese US German US US Gross National Product (GNP) GNP = GDP Income earned by foreign firms in the US + Income earned by the US firms in foreign countries NNI and GNI NNI is income earned by factors of production. But factors don t earn 1) Depreciation (capital used up) 2) Indirect Business Taxes Def. Indirect Business Taxes (IBTs): These are mainly sales taxes, excise taxes, and utility taxes. NNI = GNI Depreciation IBTs Or Gross National Product (GNP) GNI = NNI + Depreciation + IBTs Depreciation IBTs NNI Government 7
8 Other Important National Income Categories Def. Personal Income (PI): income received as opposed to income earned. Some people receive (but don t earn) some income, such as transfer payments Some people earn (but don t receive) some income, such as retained earnings PI = NNI + Transfer payments retained earnings Def. Disposable Personal income (DPI): personal income after direct taxes: DPI = PI Direct taxes Example of direct taxes: Income tax, property tax, and inheritance tax Therefore: Real and Nominal (Money) GDP Def. Nominal GDP: GDP measured in current prices, i.e., GDP unadjusted for inflation. Def. Real GDP: GDP measured in constant prices, i.e., GDP adjusted for inflation. Real GDP = Nominal GDP / GDP Price Deflator We will define GDP Price Deflator in the next chapter Symbolically: y = Y/ GDP Price Deflator We will see how the adjustment is made in the next chapter. But in general: Note: You are expected to know the current values of nominal and real GDP. Visit US Department of Commerce BEA: GDP on your website! Is GDP a good measure of social welfare? No, not necessarily! Per capita GDP, i.e., GDP divided by the population is slightly a better measure. Even the latter is not a very good indicator of the quality of life, such as leisure, clean air, and water. 8
9 UNEMPLOYMENT Labor orce Def. Labor force consists of people (16 years or older) who either have a job or who are actively looking for a job. Given the definition of the labor force, discouraged workers are not in the labor force but part-time workers are. Def. Discouraged workers: those people who have given up actively looking for jobs. Def. Unemployed: those workers who are actively looking for jobs but can t find them. Def. Unemployment rate: Unemployed workers/ Labor force Example: Unemployed: 3 million people Employed: 9 million people Unemployment rate = 3/ (3 +9) = 3/12 = 25%! 1)rictional unemployment: Types of Unemployment unemployment due to changing jobs. 2) Seasonal unemployment: unemployment due to patterns of production or sales, such as production in agriculture or retail sales. Note: Unemployment reports are seasonally adjusted. 3) Structural unemployment: unemployment due to changes in the structure of the economy or the workforce. Examples: technological changes, making some jobs obsolete, or the baby boom of the1950s. 4) Cyclical unemployment: unemployment due to business cycle : a downturn in the economic activity. 9
10 ull Employment ull employment is when cyclical unemployment is zero. ull employment does not mean zero unemployment, since we still have some other types of unemployment. Note: You are expected to know the current rates of unemployment. Visit US Department of Labor and BLS: Employment on you website! It is argued that such unemployment as frictional unemployment is voluntary, while cyclical unemployment is involuntary. Summing up: GDP = C + Ig + G + (X-M) C: Personal consumption 1) durable goods 2) non-durable goods 3) services Ig: Gross Private Investment 1) structures and equipments 2) residential structures 3) changes in business inventories ( I) (Also, Ia, Ip, Ig, In, and depreciation) G: Government purchases 1) ederal expenditures a) Defense b) Others 2) State and local government X M: Net export Summing up: NNI=Wages & salaries + rent + interest + profit Profit i) Corporate profit: a) dividends b) retained earnings c) corporate taxes ii) Income of unincorporated businesses, or proprietors income GNP = GDP Income earned by foreign firms in the US + Income earned by the US firms in foreign countries NNI = GNI Depreciation IBTs PI = NNI + Transfer payments retained earnings DPI = PI Direct taxes Next stop: Chapter 7 10
MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME. Chapter 18
 1 MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME Chapter 18 national income and product accounts Data collected and published by the government describing the various components of national income and output
1 MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME Chapter 18 national income and product accounts Data collected and published by the government describing the various components of national income and output
MACROECONOMIC OUTPUT. Economy performance measurement
 MACROECONOMIC OUTPUT Economy performance measurement GDP Gross Domestic Product measures the monetary value of final goods and services that is, those that are bought by the final user produced in a country
MACROECONOMIC OUTPUT Economy performance measurement GDP Gross Domestic Product measures the monetary value of final goods and services that is, those that are bought by the final user produced in a country
8 THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS
 8 THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS Measuring a Nation s Income 23 Measuring a Nation s Income Microeconomics Microeconomics is the study of how individual households and firms make decisions and how they interact
8 THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS Measuring a Nation s Income 23 Measuring a Nation s Income Microeconomics Microeconomics is the study of how individual households and firms make decisions and how they interact
Measuring National Output and National Income. Gross Domestic Product. National Income and Product Accounts
 C H A P T E R 18 Measuring National Output and National Income Prepared by: Fernando Quijano and Yvonn Quijano Gross Domestic Product Gross domestic product (GDP) is the total market value of all final
C H A P T E R 18 Measuring National Output and National Income Prepared by: Fernando Quijano and Yvonn Quijano Gross Domestic Product Gross domestic product (GDP) is the total market value of all final
ECO 209Y MACROECONOMIC THEORY AND POLICY LECTURE 2: NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING
 ECO 209Y MACROECONOMIC THEORY AND POLICY LECTURE 2: NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING Gustavo Indart Slide1 GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of all final goods and services produced
ECO 209Y MACROECONOMIC THEORY AND POLICY LECTURE 2: NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING Gustavo Indart Slide1 GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of all final goods and services produced
Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics
 Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics slide 0 Learning Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) the Consumer Price Index (CPI) the Unemployment Rate slide 1 GROSS DOMESTIC
Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics slide 0 Learning Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) the Consumer Price Index (CPI) the Unemployment Rate slide 1 GROSS DOMESTIC
Macroeconomic Theory and Policy
 ECO 209Y Macroeconomic Theory and Policy Lecture 2: National Income Accounting Gustavo Indart Slide1 Gross Domestic Product Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of all final goods and services produced
ECO 209Y Macroeconomic Theory and Policy Lecture 2: National Income Accounting Gustavo Indart Slide1 Gross Domestic Product Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of all final goods and services produced
Measuring Domestic Output and National Income
 Chapter 27 Measuring Domestic Output and National Income Assessing the Economy s Performance National income accounting measures economy s overall performance Bureau of Economic Analysis compiles National
Chapter 27 Measuring Domestic Output and National Income Assessing the Economy s Performance National income accounting measures economy s overall performance Bureau of Economic Analysis compiles National
Chapter 5: Production, Income and Employment
 Chapter 5: Production, Income and Employment We will take our first look at production and employment, focusing on two key variables: Gross Domestic Product and Unemployment Rate The nation s Gross Domestic
Chapter 5: Production, Income and Employment We will take our first look at production and employment, focusing on two key variables: Gross Domestic Product and Unemployment Rate The nation s Gross Domestic
Economics 251 Examination I (100 points) To receive full credit, you must fully explain your answers and show all work.
 Economics 251 Examination I (100 points) To receive full credit, you must fully explain your answers and show all work. ANSWER ONE OF QUESTIONS 1 AND 2. 1. For each of the following events, show graphically
Economics 251 Examination I (100 points) To receive full credit, you must fully explain your answers and show all work. ANSWER ONE OF QUESTIONS 1 AND 2. 1. For each of the following events, show graphically
ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics. Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics
 ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics IN THIS CHAPTER, YOU WILL LEARN: the meaning and measurement of the most important macroeconomic statistics: gross domestic product
ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics IN THIS CHAPTER, YOU WILL LEARN: the meaning and measurement of the most important macroeconomic statistics: gross domestic product
Topic 2: Macroeconomic Data. (chapter 2) revised 9/15/09. CHAPTER 2 The Data of Macroeconomics slide 0
 Topic 2: Macroeconomic Data (chapter 2) revised 9/15/09 CHAPTER 2 The Data of Macroeconomics slide 0 Learning objectives In this chapter, you will learn about how we define and measure: Gross Domestic
Topic 2: Macroeconomic Data (chapter 2) revised 9/15/09 CHAPTER 2 The Data of Macroeconomics slide 0 Learning objectives In this chapter, you will learn about how we define and measure: Gross Domestic
Macroeconomic Data. Two definitions: In this chapter, you will learn about how we define and measure: Gross Domestic Product
 Topic 2: Macroeconomic Data (chapter 2) revised 9/15/09 CHAPTER 2 The Data of Macroeconomics slide 0 Learning objectives In this chapter, you will learn about how we define and measure: Gross Domestic
Topic 2: Macroeconomic Data (chapter 2) revised 9/15/09 CHAPTER 2 The Data of Macroeconomics slide 0 Learning objectives In this chapter, you will learn about how we define and measure: Gross Domestic
macro macroeconomics The Data of Macroeconomics N. Gregory Mankiw CHAPTER TWO 6 th edition
 macro CHAPTER TWO The Data of Macroeconomics macroeconomics 6 th edition N. Gregory Mankiw Learning objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) the Consumer Price Index
macro CHAPTER TWO The Data of Macroeconomics macroeconomics 6 th edition N. Gregory Mankiw Learning objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) the Consumer Price Index
Gross Domestic Product. National Income Determination. Topic 9: 10/7/2016
 The Economy s Income and Expenditure Topic 9: National Income Determination When judging whether the economy is doing well or poorly, it is natural to look at the total income that everyone in the economy
The Economy s Income and Expenditure Topic 9: National Income Determination When judging whether the economy is doing well or poorly, it is natural to look at the total income that everyone in the economy
Many of life s failures are people who did not realize how close they were to success when they gave up. Thomas Edison
 Many of life s failures are people who did not realize how close they were to success when they gave up. Thomas Edison National-income accounting is the system used to measure the aggregate income and
Many of life s failures are people who did not realize how close they were to success when they gave up. Thomas Edison National-income accounting is the system used to measure the aggregate income and
Unit 4: Measuring GDP and Prices
 Unit 4: Measuring GDP and Prices ECO 120 Global Macroeconomics 1 1.1 Reading Reading Gross Domestic Product (GDP): Module 11 Real vs Nominal GDP: Module 12 1.2 Goals Goals Specific Goals: Understand how
Unit 4: Measuring GDP and Prices ECO 120 Global Macroeconomics 1 1.1 Reading Reading Gross Domestic Product (GDP): Module 11 Real vs Nominal GDP: Module 12 1.2 Goals Goals Specific Goals: Understand how
MEASURING A NATION S INCOME
 10 MEASURING A NATION S INCOME LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this chapter, students should understand: why an economy s total income equals its total expenditure. how gross domestic product (GDP)
10 MEASURING A NATION S INCOME LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this chapter, students should understand: why an economy s total income equals its total expenditure. how gross domestic product (GDP)
National Income Accounting A macroeconomics way of calculating national income and its components (ex. GDP, NDP, NI, etc.)
 Meridian Notes By Tim Qi, Amy Young, Willy Zhang Economics AP Unit 3: Measuring the Economy s Performance Covers Ch 8 & 10 Economic Circulation Flow National Income Accounting A macroeconomics way of calculating
Meridian Notes By Tim Qi, Amy Young, Willy Zhang Economics AP Unit 3: Measuring the Economy s Performance Covers Ch 8 & 10 Economic Circulation Flow National Income Accounting A macroeconomics way of calculating
AGENDA Tues 1/26. QOD #8: GDP Calculations HW Review ( P #4,5,7) Partner Practice
 AGENDA Tues 1/26 QOD #8: GDP Calculations HW Review (494-500 P #4,5,7) Partner Practice Study for CH 23-24 Assessment Parent Syllabus review LO1 24-1 QOD #8: GDP Calculations-Part 1 Suppose that annual
AGENDA Tues 1/26 QOD #8: GDP Calculations HW Review (494-500 P #4,5,7) Partner Practice Study for CH 23-24 Assessment Parent Syllabus review LO1 24-1 QOD #8: GDP Calculations-Part 1 Suppose that annual
Gross entire; whole Domestic within a country s borders Product good or service
 OBJECTIVES Identify National Income and Product Accounts (NIPA). Explain how gross domestic product (GDP) is calculated. Explain the difference between nominal GDP and real GDP. List the main limitations
OBJECTIVES Identify National Income and Product Accounts (NIPA). Explain how gross domestic product (GDP) is calculated. Explain the difference between nominal GDP and real GDP. List the main limitations
MACROECONOMICS. The Data of Macroeconomics MANKIW. In this chapter, you will learn. Gross Domestic Product: Expenditure and Income.
 C H A P T E R 2 The Data of Macroeconomics MACROECONOMICS N. GREGORY MANKIW 2008 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved SIXTH EDITION PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich In this chapter, you will learn the
C H A P T E R 2 The Data of Macroeconomics MACROECONOMICS N. GREGORY MANKIW 2008 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved SIXTH EDITION PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich In this chapter, you will learn the
Chapter 1: The Data of Macroeconomics
 Chapter 1: The Data of Macroeconomics Econ206 - Francesc Ortega August 31, 2011 Outline 1. The GDP 2. The inflation rate 3. The unemployment rate Reading: Mankiw 7e, chapter 2 Definition The Gross Domestic
Chapter 1: The Data of Macroeconomics Econ206 - Francesc Ortega August 31, 2011 Outline 1. The GDP 2. The inflation rate 3. The unemployment rate Reading: Mankiw 7e, chapter 2 Definition The Gross Domestic
EXPENDITURE APPROACH: The expenditures on all final goods and services made by all sectors of the economy are added to calculate GDP. Expenditures are
 Chapter 1 MEASURING GDP AND PRICE LEVEL MEASURING EONOMIC ACTIVITY Macroeconomics studies the aggregate (or total) concept of economic activity. Its focus is on the aggregate output, the aggregate income,
Chapter 1 MEASURING GDP AND PRICE LEVEL MEASURING EONOMIC ACTIVITY Macroeconomics studies the aggregate (or total) concept of economic activity. Its focus is on the aggregate output, the aggregate income,
Learning objectives. Gross Domestic Product
 Learning objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) the Consumer Price Index (CPI) the Unemployment Rate The Data of Macroeconomics slide 1 Gross Domestic Product Two
Learning objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) the Consumer Price Index (CPI) the Unemployment Rate The Data of Macroeconomics slide 1 Gross Domestic Product Two
Macroeconomic Measurement and Business Cycles
 Macroeconomic Measurement and Business Cycles Economics 4353 - Intermediate Macroeconomics Aaron Hedlund University of Missouri Fall 2015 Econ 4353 (University of Missouri) Measurement and Business Cycles
Macroeconomic Measurement and Business Cycles Economics 4353 - Intermediate Macroeconomics Aaron Hedlund University of Missouri Fall 2015 Econ 4353 (University of Missouri) Measurement and Business Cycles
Measuring the Nation s Income and Growth
 Measuring the Nation s Income and Growth We will examine: GNP vs GDP income and expenditure approaches to measurement real versus Nominal GDP potential GDP what GDP does not measure Art Lightstone Gross
Measuring the Nation s Income and Growth We will examine: GNP vs GDP income and expenditure approaches to measurement real versus Nominal GDP potential GDP what GDP does not measure Art Lightstone Gross
Macroeconomic Measurement and Business Cycles
 Macroeconomic Measurement and Business Cycles Economics 3307 - Intermediate Macroeconomics Aaron Hedlund Baylor University Fall 2013 Econ 3307 (Baylor University) Measurement and Business Cycles Fall 2013
Macroeconomic Measurement and Business Cycles Economics 3307 - Intermediate Macroeconomics Aaron Hedlund Baylor University Fall 2013 Econ 3307 (Baylor University) Measurement and Business Cycles Fall 2013
Measuring a Nation s Income
 Measuring a Nation s Income Microeconomics is the study of how individual households and firms make decisions and how they interact with one another in markets. Macroeconomics is the study of the economy
Measuring a Nation s Income Microeconomics is the study of how individual households and firms make decisions and how they interact with one another in markets. Macroeconomics is the study of the economy
Econ COURSE 2 (Chapter 21) MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME
 COURSE 2 (Chapter 21) MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME Outline of today s lecture: 1. Gross Domestic Product 2. Calculating GDP A) Expenditure Approach B) Income Approach C) Output Approach
COURSE 2 (Chapter 21) MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME Outline of today s lecture: 1. Gross Domestic Product 2. Calculating GDP A) Expenditure Approach B) Income Approach C) Output Approach
Measuring the Economy. Measur
 Measuring the Economy Measur Economic indicators Economic indicators are statistics that help economists judge the health of an economy. They provide information about important aspects of the economy.
Measuring the Economy Measur Economic indicators Economic indicators are statistics that help economists judge the health of an economy. They provide information about important aspects of the economy.
Introduction. Learning Objectives. Chapter 8. Measuring the Economy s Performance
 Chapter 8 Measuring the Economy s Performance Introduction For a number of years, measured U.S. business investment spending on capital goods has declined relative to total national expenditures on goods
Chapter 8 Measuring the Economy s Performance Introduction For a number of years, measured U.S. business investment spending on capital goods has declined relative to total national expenditures on goods
MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC GROWTH. Objectives. Gross Domestic Product. An Economic Barometer. Gross Domestic Product. Gross Domestic Product CHAPTER
 MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC CHAPTER GROWTH Objectives After studying this chapter, you will able to Define GDP and use the circular flow model to explain why GDP equals aggregate expenditure and aggregate
MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC CHAPTER GROWTH Objectives After studying this chapter, you will able to Define GDP and use the circular flow model to explain why GDP equals aggregate expenditure and aggregate
Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income. Kazu Matsuda BIZ 203 Macroeconomics
 Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income Kazu Matsuda BIZ 203 Macroeconomics MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME National income and
Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income Kazu Matsuda BIZ 203 Macroeconomics MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME National income and
Macroeconomic Analysis Econ 6022 Level I
 1 / 37 Macroeconomic Analysis Econ 6022 Level I Lecture 2 Fall, 2011 2 / 37 Overview Let s start our tour in macroeconomics by introducing a few building blocks, which will be used repeatedly later on.
1 / 37 Macroeconomic Analysis Econ 6022 Level I Lecture 2 Fall, 2011 2 / 37 Overview Let s start our tour in macroeconomics by introducing a few building blocks, which will be used repeatedly later on.
Macroeconomic Measurements, Part II: GDP and Real GDP CHAPTER
 Macroeconomic Measurements, Part II: GDP and Real GDP 7 CHAPTER An Economic Barometer What exactly is GDP? How do we use it to tell us whether our economy is in a recession or how rapidly our economy is
Macroeconomic Measurements, Part II: GDP and Real GDP 7 CHAPTER An Economic Barometer What exactly is GDP? How do we use it to tell us whether our economy is in a recession or how rapidly our economy is
Measuring a Nation s Production and Income
 Chapter Summary 5 Measuring a Nation s Production and Income In this chapter, we learned how economists and government statisticians measure the income and production for an entire country and what those
Chapter Summary 5 Measuring a Nation s Production and Income In this chapter, we learned how economists and government statisticians measure the income and production for an entire country and what those
PART EIGHT: THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS. Measuring A Nation s Income
 ECON 102 Chapter 22 1 PART EIGHT: THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS Measuring A Nation s Income Chapter 23 What did we learn until now? In the first semester we covered microeconomics Microeconomics is the study
ECON 102 Chapter 22 1 PART EIGHT: THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS Measuring A Nation s Income Chapter 23 What did we learn until now? In the first semester we covered microeconomics Microeconomics is the study
Chapter 6 GDP, Unemployment and Inflation
 Chapter 6 GDP, Unemployment and Inflation - Microeconomics: study of how households and firms make choices & how they interact in markets. - Macroeconomics: study of the economy as a whole, including topics
Chapter 6 GDP, Unemployment and Inflation - Microeconomics: study of how households and firms make choices & how they interact in markets. - Macroeconomics: study of the economy as a whole, including topics
Economics. Economic Growth Session 1
 Economics Economic Growth Session 1 National Association of Credit Management Graduate School of Credit and Financial Management American University Washington, DC June 23, 2018 1 Business Cycles Stocks
Economics Economic Growth Session 1 National Association of Credit Management Graduate School of Credit and Financial Management American University Washington, DC June 23, 2018 1 Business Cycles Stocks
2/14/2008. The circular flow of goods and incomes. firms and households. goods markets. Goods and services. real flows: goods and services
 The circular flow of income Chapter 22 Introduction to Macroeconomics Economics, 4 th edition Stiglitz & Walsh firms and households goods markets real flows: goods and services The Economic Problem Goods
The circular flow of income Chapter 22 Introduction to Macroeconomics Economics, 4 th edition Stiglitz & Walsh firms and households goods markets real flows: goods and services The Economic Problem Goods
Chapter 8- Measuring Total Production & Income. Distribution of GDP
 Chapter 8- Measuring Total Production & Income Distribution of GDP 1 Keeping Tabs on the Economy You must be able to measure and track the economy in order to understand what is going on and react appropriately.
Chapter 8- Measuring Total Production & Income Distribution of GDP 1 Keeping Tabs on the Economy You must be able to measure and track the economy in order to understand what is going on and react appropriately.
Lecture 5: Measuring a Nation s Wealth. Rob Godby University of Wyoming
 Lecture 5: Measuring a Nation s Wealth Rob Godby University of Wyoming Macroeconomics Macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole. Its goal is to explain the economic changes that affect many
Lecture 5: Measuring a Nation s Wealth Rob Godby University of Wyoming Macroeconomics Macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole. Its goal is to explain the economic changes that affect many
Chapter 25 - Measuring domestic output and national income. National Income Accounting - measures the economy s overall performance
 Chapter 25 Chapter 25 - Measuring domestic output and national income Assessing the Economy s Performance National Income Accounting - measures the economy s overall performance Gross Domestic Product
Chapter 25 Chapter 25 - Measuring domestic output and national income Assessing the Economy s Performance National Income Accounting - measures the economy s overall performance Gross Domestic Product
Measuring a Nation s Income
 Chapter 22 Measuring a Nation s Income Test A 1. Macroeconomics is the study of a. market regulation. b. money and financial markets. c. economy-wide phenomena. d. how households and firms make decisions
Chapter 22 Measuring a Nation s Income Test A 1. Macroeconomics is the study of a. market regulation. b. money and financial markets. c. economy-wide phenomena. d. how households and firms make decisions
Gross Domestic Product. How Is The GDP Calculated? Net investment equals gross investment minus depreciation.
 Chapter 23: Measuring GDP, Inflation and Economic Growth Gross Domestic Product applegross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of aggregate or total production of goods and services in a country during
Chapter 23: Measuring GDP, Inflation and Economic Growth Gross Domestic Product applegross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of aggregate or total production of goods and services in a country during
Recall from Econ 200:
 Chapter 2: The Data of Macroeconomics Recall from Econ 200: Macroeconomics is the study of the economy a whole, including growth in incomes, changes in price, and the rate of unemployment. Macroeconomists
Chapter 2: The Data of Macroeconomics Recall from Econ 200: Macroeconomics is the study of the economy a whole, including growth in incomes, changes in price, and the rate of unemployment. Macroeconomists
MEASURING ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE PRODUCT MARKET
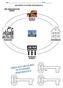 Name: Period THE CIRCULAR FLOW MODEL MEASURING ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE PRODUCT MARKET BUSINESSES HOUSEHOLDS RESOURCE MARKET 1. AKA: 2. 3. Additional Notes on Previous Page/Practice Workspace Quick Write Space
Name: Period THE CIRCULAR FLOW MODEL MEASURING ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE PRODUCT MARKET BUSINESSES HOUSEHOLDS RESOURCE MARKET 1. AKA: 2. 3. Additional Notes on Previous Page/Practice Workspace Quick Write Space
What is National Income? National income measures the total value of goods and services produced within the economy over a period of time.
 National Income What is National Income? National income measures the total value of goods and services produced within the economy over a period of time. Why is national income important? Measuring the
National Income What is National Income? National income measures the total value of goods and services produced within the economy over a period of time. Why is national income important? Measuring the
The Data of Macroeconomics
 C H A P T E R 2 MACROECONOMICS SIXTH EDITION N. GREGORY MANKIW PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2008 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved In this chapter, you will learn the meaning and measurement
C H A P T E R 2 MACROECONOMICS SIXTH EDITION N. GREGORY MANKIW PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2008 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved In this chapter, you will learn the meaning and measurement
Chapter 2: The Data of Macroeconomics*
 Chapter 2: The Data of Macroeconomics 1/40 *Slides based on Ron Cronovich's slides, adjusted by Marcel Bluhm for lecture in Macroeconomics at the Wang Yanan Institute for Studies in Economics at Xiamen
Chapter 2: The Data of Macroeconomics 1/40 *Slides based on Ron Cronovich's slides, adjusted by Marcel Bluhm for lecture in Macroeconomics at the Wang Yanan Institute for Studies in Economics at Xiamen
MACROECONOMICS - CLUTCH CH GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT (GDP) AND CONSUMER PRICE INDEX (CPI)
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CALCULATING GDP Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of the final goods and services produced by a country during a year GDP as a statistic is used to measure growth
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CALCULATING GDP Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of the final goods and services produced by a country during a year GDP as a statistic is used to measure growth
ECON 120 -ESSENTIALS OF ECONOMICS
 Name ECON 120 -ESSENTIALS OF ECONOMICS CH 21 Measuring National Inome MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The total market value of
Name ECON 120 -ESSENTIALS OF ECONOMICS CH 21 Measuring National Inome MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The total market value of
Lecture 4: Real GDP, the First of the Big 3 Economic Activity Variables
 Lecture 4: Real GDP, the First of the Big 3 Economic Activity Variables Economists focus on the outlook for material progress. To generate an opinion about overall economic activity, economists perform
Lecture 4: Real GDP, the First of the Big 3 Economic Activity Variables Economists focus on the outlook for material progress. To generate an opinion about overall economic activity, economists perform
Chapter Outline. Chapter 6 Every Macroeconomic Word You Have Ever Heard: Gross Domestic Product, Inflation, Unemployment, Recession and Depression
 Chapter 6 Every Macroeconomic Word You Have Ever Heard: Gross Domestic Product, Inflation, Unemployment, Recession and Depression Chapter Outline Measuring the Economy Real Gross Domestic Product and Why
Chapter 6 Every Macroeconomic Word You Have Ever Heard: Gross Domestic Product, Inflation, Unemployment, Recession and Depression Chapter Outline Measuring the Economy Real Gross Domestic Product and Why
Name (Please print) Assigned Seat. ECO202: PRINCIPLES OF MACROECONOMICS FIRST MIDTERM EXAM SPRING 2010 Prof. Bill Even FORM 3.
 Name (Please print) Assigned Seat ECO202: PRINCIPLES OF MACROECONOMICS FIRST MIDTERM EXAM SPRING 2010 Prof. Bill Even FORM 3 Directions 1. Fill in your scantron with your unique id and form number. Doing
Name (Please print) Assigned Seat ECO202: PRINCIPLES OF MACROECONOMICS FIRST MIDTERM EXAM SPRING 2010 Prof. Bill Even FORM 3 Directions 1. Fill in your scantron with your unique id and form number. Doing
Unit Two, Day One (pages , )
 Unit Two, Day One (pages 860-889, 585-608) What is the difference between macro and micro? National Debt v. Deficit (NOT THE SAME THING) National Debt Deficit In the circular flow the seller receives exactly
Unit Two, Day One (pages 860-889, 585-608) What is the difference between macro and micro? National Debt v. Deficit (NOT THE SAME THING) National Debt Deficit In the circular flow the seller receives exactly
Decision Makers and Markets
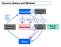 Decision Makers and Markets Households S FINANCIAL Wages Rent Interest Profit T Budget C I Factors M. (Capital Labor) Government G Goods & Services Rest of world Firms Decision Makers and Markets Households
Decision Makers and Markets Households S FINANCIAL Wages Rent Interest Profit T Budget C I Factors M. (Capital Labor) Government G Goods & Services Rest of world Firms Decision Makers and Markets Households
What is Macroeconomics? Data. Macroeconomics II. Lecture 1: Introduction to Macroeconomics
 Lecture 1: Introduction to Macroeconomics What is macroeconomics? What do we study? How do we study it? Macroeconomics: studies the whole economy main variables: real, inflation, unemployment usually dynamic
Lecture 1: Introduction to Macroeconomics What is macroeconomics? What do we study? How do we study it? Macroeconomics: studies the whole economy main variables: real, inflation, unemployment usually dynamic
Measurement. Chapter 2. Topics in Macroeconomics 2. Economics Division University of Southampton. February 8, 2008
 Measurement Chapter 2 Topics in Macroeconomics 2 Economics Division University of Southampton February 8, 2008 Chapter 2 1/42 Topics in Macroeconomics Gross Domestic Product Introduction Gross Domestic
Measurement Chapter 2 Topics in Macroeconomics 2 Economics Division University of Southampton February 8, 2008 Chapter 2 1/42 Topics in Macroeconomics Gross Domestic Product Introduction Gross Domestic
Unit 6 Measuring and Monitoring Economics (Ch 12 and 13)
 Unit 6 Measuring and Monitoring Economics (Ch 12 and 13) -Macroeconomics 0 & Microeconomics- Government tries to prevent free enterprise from having wild swings in economic behavior. Microeconomics - analyzes
Unit 6 Measuring and Monitoring Economics (Ch 12 and 13) -Macroeconomics 0 & Microeconomics- Government tries to prevent free enterprise from having wild swings in economic behavior. Microeconomics - analyzes
1 of 33. Measuring a Nation s Production and Income. 2 of 33
 1 of 33 2 of 33 The methods our government uses today to measure our economy, which we will study in this chapter, were developed in the 1930s. P R E P A R E D B Y FERNANDO QUIJANO, YVONN QUIJANO, AND
1 of 33 2 of 33 The methods our government uses today to measure our economy, which we will study in this chapter, were developed in the 1930s. P R E P A R E D B Y FERNANDO QUIJANO, YVONN QUIJANO, AND
"Data, data, data: how can I make bricks without clay?".
 1 Measurement As explained in the previous chapter, measurement is a key component of the scientific method and is necessary to develop and validate theories. Sherlock Holmes, one of the masters of (investigative
1 Measurement As explained in the previous chapter, measurement is a key component of the scientific method and is necessary to develop and validate theories. Sherlock Holmes, one of the masters of (investigative
Measurement. Chapter 2. Topics in Macroeconomics 2. Economics Division University of Southampton. February 2009
 Measurement Chapter 2 Topics in Macroeconomics 2 Economics Division University of Southampton February 2009 Chapter 2 1/45 Topics in Macroeconomics Gross Domestic Product Introduction Gross Domestic Product
Measurement Chapter 2 Topics in Macroeconomics 2 Economics Division University of Southampton February 2009 Chapter 2 1/45 Topics in Macroeconomics Gross Domestic Product Introduction Gross Domestic Product
Full file at
 MULTIPLE CHOICE Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question 1) Gross domestic product is defined as 1) A) the total market value of the final goods and services
MULTIPLE CHOICE Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question 1) Gross domestic product is defined as 1) A) the total market value of the final goods and services
Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income
 Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income 1 Multiple Choice 1) The total market value of all final goods and services produced within a given period by factors of production located within
Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income 1 Multiple Choice 1) The total market value of all final goods and services produced within a given period by factors of production located within
National Income Accounts, GDP and Real GDP. 2Topic
 National Income Accounts, GDP and Real GDP 2Topic National Income Accounting According to EconPort (http://www.econport.org/), National income accounting deals with the aggregate measure of the outcome
National Income Accounts, GDP and Real GDP 2Topic National Income Accounting According to EconPort (http://www.econport.org/), National income accounting deals with the aggregate measure of the outcome
Economic Performance. Sherif Khalifa. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 1 / 39
 Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 1 / 39 People earning higher income levels enjoy higher living standards. To judge economic well being, we consider the total income in an economy.
Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 1 / 39 People earning higher income levels enjoy higher living standards. To judge economic well being, we consider the total income in an economy.
MACROECONOMICS 201 Spring 2019 NOTES 5 NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING
 MACROECONOMICS 201 Spring 2019 NOTES 5 NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING Topics A. Methods of measuring national output B. Limitations of measures of national output Reading Assignment: Principles of Economics:
MACROECONOMICS 201 Spring 2019 NOTES 5 NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING Topics A. Methods of measuring national output B. Limitations of measures of national output Reading Assignment: Principles of Economics:
Economics Unit Four. Macroeconomics
 Economics Unit Four Macroeconomics Macroeconomics Macroeconomics is the study of the whole economy together the aggregated spending, saving, and investing decisions of all consumers and businesses describes
Economics Unit Four Macroeconomics Macroeconomics Macroeconomics is the study of the whole economy together the aggregated spending, saving, and investing decisions of all consumers and businesses describes
Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income. Kazu Matsuda IBEC 203 Macroeconomics
 Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income Kazu Matsuda IBEC 203 Macroeconomics MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME National income
Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income Kazu Matsuda IBEC 203 Macroeconomics MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME National income
Part V: Introduction to Macroeconomics 19. The Wealth of Nations: Defining and
 Part V: Introduction to s 19. 20. Aggregate Incomes 1 / 56 Chapter 19 Defining and 2017.8.9. 2 / 56 1 2 3 4 3 / 56 Chapter 19 Q: In the United States, what is the total market value of annual economic
Part V: Introduction to s 19. 20. Aggregate Incomes 1 / 56 Chapter 19 Defining and 2017.8.9. 2 / 56 1 2 3 4 3 / 56 Chapter 19 Q: In the United States, what is the total market value of annual economic
macroeconomics The Data of Macroeconomics N. Gregory Mankiw CHAPTER TWO PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich fifth edition
 CHAPTER TWO The Data of Macroeconomics macroeconomics fifth edition N. Gregory Mankiw PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2002 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved Learning objectives In this chapter,
CHAPTER TWO The Data of Macroeconomics macroeconomics fifth edition N. Gregory Mankiw PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2002 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved Learning objectives In this chapter,
Understanding Economics
 Understanding Economics 4th edition by Mark Lovewell, Khoa Nguyen and Brennan Thompson Understanding Economics 4 th edition by Mark Lovewell, Khoa Nguyen and Brennan Thompson Chapter 8 Measures of Economic
Understanding Economics 4th edition by Mark Lovewell, Khoa Nguyen and Brennan Thompson Understanding Economics 4 th edition by Mark Lovewell, Khoa Nguyen and Brennan Thompson Chapter 8 Measures of Economic
Introduction. Learning Objectives. Chapter 8. Measuring the Economy s Performance
 Copyright 2012 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Chapter 8 Measuring the Economy s Performance Introduction Does a general increase in the level of a nation s economic activity and the resulting
Copyright 2012 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Chapter 8 Measuring the Economy s Performance Introduction Does a general increase in the level of a nation s economic activity and the resulting
Macroeconomics, 12e (Gordon) Chapter 2 The Measurement of Income, Prices, and Unemployment
 Macroeconomics, 12e (Gordon) Chapter 2 The Measurement of Income, Prices, and Unemployment 2.1 Why We Care About Income 1) Job openings are plentiful when the A) actual real GDP is above the natural real
Macroeconomics, 12e (Gordon) Chapter 2 The Measurement of Income, Prices, and Unemployment 2.1 Why We Care About Income 1) Job openings are plentiful when the A) actual real GDP is above the natural real
NATIONAL INCOME AND RELATED AGGREGATES
 NATIONAL INCOME AND RELATED AGGREGATES The modern concept of National Income is more dynamic in the content than earlier concepts. The National Income Committee of India defined national income as: A National
NATIONAL INCOME AND RELATED AGGREGATES The modern concept of National Income is more dynamic in the content than earlier concepts. The National Income Committee of India defined national income as: A National
Indicators of National Econmoy. Ing. Mansoor Maitah Ph.D. et Ph.D.
 Indicators of National Econmoy Ing. Mansoor Maitah Ph.D. et Ph.D. Circular Flows in the Market Economy Describes the flow of resources, products, income, and revenue among the four decision makers (Households;
Indicators of National Econmoy Ing. Mansoor Maitah Ph.D. et Ph.D. Circular Flows in the Market Economy Describes the flow of resources, products, income, and revenue among the four decision makers (Households;
Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics
 Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics Zhengyu Cai Ph.D. Institute of Development Southwestern University of Finance and Economics All rights reserved http://www.escience.cn/people/zhengyucai/index.html
Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics Zhengyu Cai Ph.D. Institute of Development Southwestern University of Finance and Economics All rights reserved http://www.escience.cn/people/zhengyucai/index.html
Macroeconomics, 6e (Williamson) Chapter 2 Measurement. 2.1 Multiple-Choice Questions
 Macroeconomics, 6e (Williamson) Chapter 2 Measurement 2.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) NIPA means A) New Income and Price Accounting. B) National Investment and Productivity Approach. C) Neutral Increase
Macroeconomics, 6e (Williamson) Chapter 2 Measurement 2.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) NIPA means A) New Income and Price Accounting. B) National Investment and Productivity Approach. C) Neutral Increase
MEASURING A NATION S INCOME
 23 MEASURING A NATION S INCOME WHAT S NEW IN THE FOURTH EDITION: There is a new In the News box on The Underground Economy. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this chapter, students should understand:
23 MEASURING A NATION S INCOME WHAT S NEW IN THE FOURTH EDITION: There is a new In the News box on The Underground Economy. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this chapter, students should understand:
ECON 201. Learning Objectives. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) 9/25/2009. Chapter 5 GDP & Economic Growth
 ECON 201 Chapter 5 GDP & Economic Growth Learning Objectives How GDP is Defined and Measured. How economists distinguish between nominal GDP & real GDP. Long term trend of U.S. economic growth. Generalingredientsofeconomicgrowth
ECON 201 Chapter 5 GDP & Economic Growth Learning Objectives How GDP is Defined and Measured. How economists distinguish between nominal GDP & real GDP. Long term trend of U.S. economic growth. Generalingredientsofeconomicgrowth
Macroeconomics, 3e (Williamson) Chapter 2 Measurement
 Macroeconomics, 3e (Williamson) Chapter 2 Measurement 1) The principal printed source for reporting the US National Income and Product Accounts is called the A) Monthly Labor Review B) Survey of Current
Macroeconomics, 3e (Williamson) Chapter 2 Measurement 1) The principal printed source for reporting the US National Income and Product Accounts is called the A) Monthly Labor Review B) Survey of Current
ECONOMICS SOLUTION BOOK 2ND PUC. Unit 8. Part A
 Unit 8 Part A I. Choose the correct answer (each question carries 1 mark) 1. The study of National Income is related to: a) Micro economics b) Macro Economics c) Both Micro and Macro d) None of the above
Unit 8 Part A I. Choose the correct answer (each question carries 1 mark) 1. The study of National Income is related to: a) Micro economics b) Macro Economics c) Both Micro and Macro d) None of the above
Chapter 5: Gross Domestic Product Accounting GDP: What Approaches are used to measure GDP? Expenditure Income
 Chapter 5: Gross Domestic Product Accounting 2/7/00 GDP: GDP or Gross Domestic Product is the total value, measured in current prices, of all final goods and services, produced in the economy, during a
Chapter 5: Gross Domestic Product Accounting 2/7/00 GDP: GDP or Gross Domestic Product is the total value, measured in current prices, of all final goods and services, produced in the economy, during a
Distance Learning Programme. IAS Prelims INDIAN ECONOMY
 Distance Learning Programme IAS Prelims INDIAN ECONOMY CONTENTS 1. Introduction to Economics 5-11 2. Concepts of National Income 12-20 3. Human Development 21-30 4. Poverty, Unemployment & Inequality 31-49
Distance Learning Programme IAS Prelims INDIAN ECONOMY CONTENTS 1. Introduction to Economics 5-11 2. Concepts of National Income 12-20 3. Human Development 21-30 4. Poverty, Unemployment & Inequality 31-49
1. The economic statistic used to measure the level of prices is the: A) GDP. B) CPI. C) GNP. D) real GDP.
 1. The economic statistic used to measure the level of prices is the: A) GDP. B) CPI. C) GNP. D) real GDP. 2. The statistic used by economists to measure the value of economic output is the: A) CPI. B)
1. The economic statistic used to measure the level of prices is the: A) GDP. B) CPI. C) GNP. D) real GDP. 2. The statistic used by economists to measure the value of economic output is the: A) CPI. B)
Unemployment Rate = 1. A large number of economic statistics are released regularly. These include the following:
 CHAPTER The Data of Macroeconomics Questions for Review 1. GDP measures the total income earned from the production of the new final goods and services in the economy, and it measures the total expenditures
CHAPTER The Data of Macroeconomics Questions for Review 1. GDP measures the total income earned from the production of the new final goods and services in the economy, and it measures the total expenditures
file:///c:/users/moha/desktop/mac8e/new folder (2)/CourseCompas... Creation Settings
 1 of 24 12/8/2012 11:32 م COURSES > BA121 > CONTROL PANEL > POOL MANAGER > POOL CANVAS P Add, modify, and remove questions. Select a question type from the Add drop-down list and click Go to add questions.
1 of 24 12/8/2012 11:32 م COURSES > BA121 > CONTROL PANEL > POOL MANAGER > POOL CANVAS P Add, modify, and remove questions. Select a question type from the Add drop-down list and click Go to add questions.
Lecture 1 Endogenous variables: Exogenous variables: Pizza example:
 Lecture 1 Behavior of the whole is greater than the sum of individual actions and market outcomes Paradox of thrift: expectations of possible hardship in economy by families/businesses will cause them
Lecture 1 Behavior of the whole is greater than the sum of individual actions and market outcomes Paradox of thrift: expectations of possible hardship in economy by families/businesses will cause them
Chapter 8 GDP: # Measuring Total Production and Income
 Macroeconomics 6 th edition # Chapter 8 GDP: # Measuring Total Production and Income Modified by Yulin Hou For Principle of Macroeconomics Florida International University Summer 2017 pyright 2017 Pearson
Macroeconomics 6 th edition # Chapter 8 GDP: # Measuring Total Production and Income Modified by Yulin Hou For Principle of Macroeconomics Florida International University Summer 2017 pyright 2017 Pearson
Macroeconomics: New concepts
 Macroeconomics: New concepts Fatma September 2015 How to evaluate the performance of an economy? Some questions that can be asked about macroeconomies: How well Turkish economy is doiing now? How did the
Macroeconomics: New concepts Fatma September 2015 How to evaluate the performance of an economy? Some questions that can be asked about macroeconomies: How well Turkish economy is doiing now? How did the
Intro to macroeconomics. Rush October 2014
 Intro to macroeconomics Rush October 2014 Micro means small. Macro means big. We are moving from micro to macro What is microeconomics? Microeconomics is the study of SPECIFIC markets and the behavior
Intro to macroeconomics Rush October 2014 Micro means small. Macro means big. We are moving from micro to macro What is microeconomics? Microeconomics is the study of SPECIFIC markets and the behavior
Econ 311 Intermediate Macroeconomics Professor Eschker. Fall 2014
 Econ 311 Intermediate Macroeconomics Professor Eschker Fall 2014 Today s Topics Finish math refresher GDP Deflator Chain Weighting News CBO Projection: Budget Deficits in Future Years to be Smaller than
Econ 311 Intermediate Macroeconomics Professor Eschker Fall 2014 Today s Topics Finish math refresher GDP Deflator Chain Weighting News CBO Projection: Budget Deficits in Future Years to be Smaller than
Gross Domestic Product: Measuring the Nation s Output
 Measuring Economic Activity: GDP and Unemployment Gross Domestic Product (GDP) The market value of the final goods and services produced in a country during a given period Chapter 5: Measuring Economic
Measuring Economic Activity: GDP and Unemployment Gross Domestic Product (GDP) The market value of the final goods and services produced in a country during a given period Chapter 5: Measuring Economic
Chapter 2: The Data of Macroeconomics
 Chapter 2: The Data of Macroeconomics 0 IN THIS CHAPTER, YOU WILL LEARN: the meaning and measurement of the most important macroeconomic statistics:! gross domestic product (GDP)! the consumer price index
Chapter 2: The Data of Macroeconomics 0 IN THIS CHAPTER, YOU WILL LEARN: the meaning and measurement of the most important macroeconomic statistics:! gross domestic product (GDP)! the consumer price index
Unemployment Rate = 1. A large number of economic statistics are released regularly. These include the following:
 CHAPTER The Data of Macroeconomics Questions for Review 1. GDP measures the total income earned from the production of the new final goods and services in the economy, and it measures the total expenditures
CHAPTER The Data of Macroeconomics Questions for Review 1. GDP measures the total income earned from the production of the new final goods and services in the economy, and it measures the total expenditures
MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC GROWTH
 21 MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC GROWTH GDP Defined GDP or gross domestic product is the market value of all final goods and services produced in a country in a given time period. This definition has four
21 MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC GROWTH GDP Defined GDP or gross domestic product is the market value of all final goods and services produced in a country in a given time period. This definition has four
CHAPTER 3: MEASURING NATIONAL INCOME
 CHAPTER 3: MEASURING NATIONAL INCOME CIA4U Unit 2 Macroeconomics: Economic Indicators Households sell factor services to the business sector and earn income; with this income, they pay for the goods and
CHAPTER 3: MEASURING NATIONAL INCOME CIA4U Unit 2 Macroeconomics: Economic Indicators Households sell factor services to the business sector and earn income; with this income, they pay for the goods and
PART 6 The macroeconomic environment
 PART 6 The macroeconomic environment 1 of 38 Economy s Income & Expenditure Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Measures the total income of everyone in the economy Measures the total expenditure on the economy
PART 6 The macroeconomic environment 1 of 38 Economy s Income & Expenditure Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Measures the total income of everyone in the economy Measures the total expenditure on the economy
