Country report BRAZIL
|
|
|
- Miles Blair
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Summary Brazil s economy grew by only.7% in 11, after the high 7.5% growth of 1. In particular industry has been under pressure, as the competitiveness of the sector has been hit by the appreciation of the real. The government has tried to stem the appreciation by further tightening its capital controls. The sudden way in which the central bank thereby changed trade finance regulations bodes ill for policy predictability. Meanwhile, the central bank has aggressively eased monetary policy by reducing its main policy rate from 1.5% to 9%. After breaking the upper bound of the inflation target range during 9 months in 11, inflation has fallen back within the range. However, the labor market remains very tight. Brazil s current account deficit may grow somewhat in the coming years, but the foreign exchange reserves have grown further during 11. Meanwhile, the government of Dilma Rousseff is popular, partially thanks to the president s reputation of being a competent manager. Things to watch: Possibility of new capital controls. Prices of commodities. Author: Contact details: Herwin Loman Country Risk Research Economic Research Department Rabobank Nederland P.O.Box 171, 35 HG Utrecht, The Netherlands +31-() H.Loman@rn.rabobank.nl April 1 Rabobank Economic Research Department Page: 1/7
2 Brazil National facts Social and governance indicators rank / total Type of government Federal Republic Human Development Index (rank) 8 / 187 Capital Brasilia Ease of doing business (rank) 16 / 183 Surface area (thousand sq km) 8,51 Economic freedom index (rank) 99 / 179 Population (millions) 19.8 Corruption perceptions index (rank) 73 / 183 Main religions Roman Catholic (7%) Press freedom index (rank) 99 / 178 Protestant (15%) Gini index (income distribution) 53.9 Main ethnic groups White (5%) Population below $1.5 per day (PPP) 6.1% Mulatto (39%) Black (6%) Foreign trade 1 Head of State (president) Dilma Rousseff Main export partners (%) Main import partners (%) Head of Government Dilma Rousseff China 15 US 17 Monetary unit real (BRL) US 1 China 15 Argentina 9 Argentina 9 Economy 11 Netherlands 5 Germany 8 Economic size bn USD % world total Main export products (%) Nominal GDP Primary products 5 Nominal GDP at PPP 8.89 Manufactured products 39 Export value of goods and services Semimanufactured products 1 IMF quotum (in mln SDR) Special operations Economic structure 11 5-year av. Main import products (%) Real GDP growth (%).7.5 Intermediate products and raw materials 6 Agriculture (% of GDP) 6 6 Capital gppds 3 Industry (% of GDP) 8 8 Consumer goods 17 Services (% of GDP) Fuels and lubricants 1 Standards of living USD % world av. Openness of the economy 11 Nominal GDP per head Export value of G&S (% of GDP) 1 Nominal GDP per head at PPP Import value of G&S (% of GDP) 1 Real GDP per head Inward FDI (% of GDP).7, CIA World Factbook, UN, Heritage Foundation, Transparency International, Reporters Without Borders, World Bank. Economic structure and growth Brazil s economic growth strongly decelerated in 11, with the growth rate falling from 7.5% in 1 to.7% in 11. In the fourth quarter of 11, the economy grew by a meager.3% quarter-on-quarter only. The weak growth was partially the result of efforts by the central bank in early 11 to control inflation, and the problems in the euro zone. In particular Brazil s manufacturing sector suffered, as the appreciation of the real reduced the competitiveness of its products. As a result, the manufacturing sector grew only by.1% in 11, against 1.6% for the industrial sector as a whole, while the services sector grew by.7% and the agricultural sector by 3.9%. Helped by a strong fall in interest rates during the second half of 11 and some improvement in global economist sentiment, we expect a modest recovery in 1. Although a fall of GDP growth of almost 5 percentage points may look dramatic, it primarily shows that Brazil s structural growth rate lies at about %. This is due to a number of factors. First, there are strong human capital constraints. Even after a year of disappointing growth, the labor market has remained extremely tight, with particularly the demand for higher educated people being very strong. Supply is held back by Brazil s educational system (see also Political and social situation chapter). Another important constraint is Brazil s infrastructure. Recently, investment in infrastructure has grown somewhat, but the country is still struggling with the effects of decades of underinvestment. Other factors that are holding back growth in Brazil are the tax system, with its high rates and its extremely complicated structure, and bureaucracy. April 1 Rabobank Economic Research Department Page: /7
3 Luckily, Brazil also has a number of powerful strengths. The country is a global commodity powerhouse. It is already a very important agricultural producer and agricultural production can still be raised strongly, even without using more land. Brazil is also a very important producer of iron ore. Meanwhile, Brazil s role in the oil industry is expected to increase strongly in the coming years, as the country hopes to bring large pre-salt fields into production. However, this will require massive investment and a lot of advanced technology. Partially thanks to the growth of the middle class, Brazil also has a rapidly growing domestic market and consumption has boomed in the past decade. However, as consumers have seen debt payments increase strongly, there are clear limits to consumption growth. Despite this increasing repayment burden, the overall health of the financial sector remains good. The sector is well regulated and the capital ratios and liquidity are good. However, the attempts by the government to reduce the lending spreads (see also Economic policy chapter) are likely to result in lower profitability. Figure 1: Growth performance % change p.a. % change p.a. 1 1 Figure : Public finances % of GDP % of GDP e 1f 13f External demand Gross fixed investment Inventory changes Government consumption Private consumption Overall economic growth e 1f 13f Public debt (l) Budget balance (r ) - Political and social situation Dilma Rousseff, who succeeded Lula da Silva as Brazil s president more than a year ago, has so far managed to be a popular president. In a recently published poll, 6% of the respondents said that they considered her government to be good or very good. This makes Rousseff the most popular president after 15 months being in office, although a majority of the people polled also indicated that they would like Lula da Silva to succeed her in 1. Rousseff thanks her popularity to a large extent to her image of being a capable manager. We consider this image to be well deserved. First, she has skillfully held together a multiparty coalition, despite the fact that already eight cabinet ministers have resigned. Out of these resignations, seven were due to corruption. The hardline approach of Rousseff against corruption is a welcome break with the policy of Lula in this field. However, making politics less corrupt is extremely difficult, as coalitions in Brazil rely on many parties, who tend to consider the ministries they run as personal fiefdoms. Nonetheless, the president has tried to reduce the power of parties over key cabinet appointments. This has led to the departure of a party from her coalition, but it could help to make Brazil s politics cleaner. Meanwhile, partially thanks to the support of a newly formed center party, the government has historically high levels of support in both the lower and the upper house. Second, Rousseff has been able to take a number of reforms. Although she has avoided sweeping reforms, she has been able to tackle a number of issues in a gradualist way. For example, recently, she managed to implement a controversial reform to the public sector pension system. April 1 Rabobank Economic Research Department Page: 3/7
4 Meanwhile, income inequality has continued to fall. According to the CIA, Brazil s Gini index fell to 51.9 in 1. Brazil has traditionally been a society with a high level of inequality. This high inequality is often associated with crime, which indeed is also traditionally high in Brazil, and less political stability. The Gini index peaked at an extremely high level of 63.3 in 1989, but has fallen afterwards. In particular in the last decade it has declined steadily. If the current trends continue, Brazil may thus become a less unequal country than China or the USA in the medium term. The decline in inequality has meant a strong fall in the number of poor, while the middle class has grown strongly. The decrease in inequality has not been limited to income only, as the access to health and education has also improved markedly in the past decade. Nevertheless, the quality of the public health and education systems is often still poor and there is a lot of inefficiency and wasteful spending. Economic policy Attempts to boost growth, in particular in the industrial sector, have dominated Brazil s policy agenda recently. In early 1, the government intensified its fight against the appreciation of the real by tightening its controls on capital inflows a number of times. The last tightening round was a rather dramatic one, as the central bank not only decided that all foreign loans of Brazilian companies with a maturity up to five years have to be taxed, but it also suddenly changed trade finance regulations. The sudden and drastic way in which the central bank implemented these measures has raised fears about Brazil s policy predictability. So far, it seems that the measures have been effective, as the real has depreciated recently (see figure 5), although part of the depreciation also seems linked to the recent decline of global economic sentiment as result of the return of some stress in the euro zone. President Dilma Rousseff also personally got involved in to so called currency wars, as she recently accused developed countries of engaging in the fiercest protectionism that exists through their easy monetary policies, as these result in upward pressure on the real. However, the high real might be here to stay, as the prices of Brazil s export commodities may remain high and Brazil is set to become an important oil producer in the coming years. Meanwhile, the government has also introduced some protectionist measures, reduced payroll taxes for struggling sectors and increased subsidized lending. Although the fiscal costs of these measures are limited, we think broader tax and red tape reform would be much more effective. However, as we already explained in the previous chapter, only some limited gradual reform at best can be expected. Brazil will therefore remain a country with a high level of taxation and a high level of public expenditure in the near future. Public debt equaled 5% of GDP in 11, and is expected to stay at roughly that level in the coming years. The government has been under strong pressure from congress to increase spending, but it still managed to increase Brazil s primary surplus somewhat to 3.1% of GDP in 11. This positive trend has continued in the first months of 1, as the government posted a primary surplus of 3.3% of GDP in the 1 months ending in February, against a target of 3.1% of GDP for the whole of 1. Meanwhile, the central bank has tried to boost growth by aggressively easing monetary policy. The latest ease of policy took place in mid-april, when the central bank lowered its main policy by 75 basis points to 9%. Last year the rate reached a peak of 1.5%, but the interest rate is now nearing the all-time low of 8.75%. Thus, the new central bank president Alexandre Tombini seems less of an inflation hawk then his predecessor, Henrique Meirelles. April 1 Rabobank Economic Research Department Page: /7
5 Some monetary easing was possible though, as inflation went down in late 11. After breaking the inflation target range during nine consecutive months in 11, inflation has fallen back within the.5%-6.5% inflation target range. Year-on-year inflation has fallen from a peak of 7.3% in September to 5.9% in February 1. However, we note that Brazil s labor market has remained very tight despite a year of low growth, which implies that the extent to which the central bank can boost growth without raising the inflation rate seems limited. The government has also tried to boost growth by pressing banks to lower their spread between lending and borrowing. The government has forced state banks to lower their lending rates and private banks have recently lowered their rates as well. Traditionally this spread has been extremely large in Brazil. Figure 3: Current account % of GDP % of GDP 6 6 Figure : Debt-creating inflows bn USD 5 bn USD e 1f 13f Trade Services Income Transfers Current account e 1f 13f Short-term debt Private MLT Public MLT 1 Balance of Payments Thanks to the commodity boom of the past years, Brazil has become increasingly reliant on exports of primary products, with primary products accounting for 5% of all exports in 1, up from 9% in 6. Therefore, we consider a large and sustained fall of commodity prices, for instance as a result of a strong decrease of growth in China, as the biggest risk to Brazil s balance of payments position. Nevertheless, compared to other important commodity exporters, Brazil s exports remain relatively diversified, as a significant share of exports still consists of manufactured products, while the range of the commodities the country exports is also very wide. Meanwhile, the boom of the domestic economy and the appreciation of the real have resulted in a strong growth of imports of goods and services. Thus, Brazil s current account has deteriorated in the past five years (see figure 3). Thanks to the strong slowdown of growth in 11, the current account deficit decreased somewhat between 1 and 11 by falling from.% of GDP to.1% of GDP, but it is expected to grow once again in the coming years. In 11 Brazil s current account deficit could easily be financed by FDI inflows, as inward FDI grew to.7% of GDP. However, in the coming years the current account deficit is expected to be larger than the inward FDI flows. Brazil s current account deficit points at a structural weakness of the economy: a lack of savings. With a gross national savings rate of only 17% of GDP, Brazil needs foreign money to bring its gross fixed investment to a still very low level of 19% of GDP. External position Brazil has large and growing holdings of foreign reserves, with the total reserves increasing from USD 87bn in 1 to USD 35bn in 11. This means that Brazil s foreign debt, which totaled USD 397bn in 11, is almost fully covered by foreign reserves. As Brazil s government debt has almost fully been issued in local currency, the government is a net external creditor. April 1 Rabobank Economic Research Department Page: 5/7
6 Meanwhile, the external liquidity of Brazil has also remained good. The large foreign reserves stock was equal to almost 1 months of imports in 11. Brazil s liquidity ratio was a comfortable 16% in the same year. The weakness of Brazil s external position is its negative net international investment position of 1% of GDP in 1. However, the risks due to this position are strongly mitigated by the fact that most of Brazil s foreign assets are highly liquid, while a large part of Brazil s foreign liabilities are in the form of FDI stock. In total, in 1, 5% of foreign liabilities were in the form of FDI stock, while % consisted of portfolio investments. More than half of the strong increase of foreign liabilities between 9 and 1 was accounted for by FDI. Figure 5: Exchange rate BRL/EUR (LHS) BRL/USD (RHS) Source: EcoWin Figure 6: External liquidity months % e 1f 13f Import cover (l) Short-term debt cover (r) Debt service cover (r ) Total foreign debt cover (r) April 1 Rabobank Economic Research Department Page: 6/7
7 Brazil Selection of economic indicators e 1f 13f Key country risk indicators GDP (% real change pa) Consumer prices (average % change pa) Current account balance (% of GDP) Total foreign exchange reserves (mln USD) Economic growth GDP (% real change pa) Gross fixed investment (% real change pa) Private consumption (real % change pa) Government consumption (% real change pa), SA Exports of G&S (% real change pa) Imports of G&S (% real change pa) Economic policy Budget balance (% of GDP) Public debt (% of GDP) Money market interest rate (%) M growth (% change pa) Consumer prices (average % change pa) Exchange rate LCU to USD (average) Recorded unemployment (%) Balance of payments (mln USD) Current account balance Trade balance Export value of goods Import value of goods Services balance Income balance Transfer balance Net direct investment flows Net portfolio investment flows Net debt flows Other capital flows (negative is flight) Change in international reserves External position (mln USD) Total foreign debt Short-term debt Total debt service due, incl. short-term debt Total foreign exchange reserves International investment position n.a. n.a. n.a. Total assets n.a. n.a. n.a. Total liabilities n.a. n.a. n.a. Key ratios for balance of payments, external solvency and external liquidity Trade balance (% of GDP) Current account balance (% of GDP) Inward FDI (% of GDP) Foreign debt (% of GDP) Foreign debt (% of XGSIT) International investment position (% of GDP) n.a. n.a. n.a. Debt service ratio (% of XGSIT) Interest service ratio incl. arrears (% of XGSIT) FX-reserves import cover (months) FX-reserves debt service cover (%) Liquidity ratio Disclaimer This document is issued by Coöperatieve Centrale Raiffeisen-Boerenleenbank B.A. incorporated in the Netherlands, trading as Rabobank Nederland, and regulated by the FSA. The information and opinions contained herein have been compiled or arrived at from sources believed to be reliable, but no representation or warranty, express or implied, is made as to their accuracy or completeness. It is for information purposes only and should not be construed as an offer for sale or subscription of, or solicitation of an offer to buy or subscribe for any securities or derivatives. The information contained herein is not to be relied upon as authoritative or taken in substitution for the exercise of judgement by any recipient. All opinions expressed herein are subject to change without notice. Neither Rabobank Nederland, nor other legal entities in the group to which it belongs accept any liability whatsoever for any direct or consequential loss howsoever arising from any use of this document or its contents or otherwise arising in connection therewith, and their directors, officers and/or employees may have had a long or short position and may have traded or acted as principal in the securities described within this report, or related securities. Further it may have or have had a relationship with or may provide or have provided corporate finance or other services to companies whose securities are described in this report, or any related investment. This document is for distribution in or from the Netherlands and the United Kingdom, and is directed only at authorised or exempted persons within the meaning of the Financial Services and Markets Act or to persons described in Part IV Article 19 of the Financial Services and Markets Act (Financial Promotions) Order 1, or to persons categorised as a market counterparty or intermediate customer in accordance with COBS The document is not intended to be distributed, or passed on, directly or indirectly, to those who may not have professional experience in matters relating to investments, nor should it be relied upon by such persons. The distribution of this document in other jurisdictions may be restricted by law and recipients into whose possession this document comes from should inform themselves about, and observe any such restrictions. Neither this document nor any copy of it may be taken or transmitted, or distributed directly or indirectly into the United States, Canada, and Japan or to any US-person. This document may not be reproduced, distributed or published, in whole or in part, for any purpose, except with the prior written consent of Rabobank Nederland. By accepting this document you agree to be bound by the foregoing restrictions. April 1 Rabobank Economic Research Department Page: 7/7
Country update URUGUAY
 Summary Uruguay s economy continued to grow quickly in 2011, although growth decelerated in the course of the year. The deceleration has been welcome, as the economy was close to overheating, with especially
Summary Uruguay s economy continued to grow quickly in 2011, although growth decelerated in the course of the year. The deceleration has been welcome, as the economy was close to overheating, with especially
Country update PARAGUAY
 Summary Right when Paraguay seemed to be have recovered from an earlier outbreak of foot and mouth disease, a new outbreak was reported in early January. Meanwhile, Paraguay has also been hit by a drought,
Summary Right when Paraguay seemed to be have recovered from an earlier outbreak of foot and mouth disease, a new outbreak was reported in early January. Meanwhile, Paraguay has also been hit by a drought,
Country report ALGERIA
 Summary Growth slowed in Algeria on account of reduced energy production and weaker demand from Europe. Still, due to an expected increase in oil production and further economic diversification, we expect
Summary Growth slowed in Algeria on account of reduced energy production and weaker demand from Europe. Still, due to an expected increase in oil production and further economic diversification, we expect
Country report MAURITIUS
 Summary Mauritius is a politically and socially stable island in the Indian Ocean. The economic diversification is limited, partly due to its size, and provides the highest vulnerability. This is mostly
Summary Mauritius is a politically and socially stable island in the Indian Ocean. The economic diversification is limited, partly due to its size, and provides the highest vulnerability. This is mostly
Country update MAURITIUS
 Summary Mauritius open economy is very vulnerable to the eurozone crisis and the global economic slowdown. As a result of subdued external demand, a weaker tourism sector and lower sugar production, economic
Summary Mauritius open economy is very vulnerable to the eurozone crisis and the global economic slowdown. As a result of subdued external demand, a weaker tourism sector and lower sugar production, economic
Country report NEW ZEALAND
 Summary Economic and financial developments in New Zealand have continued to be impacted by the aftershocks from the 4 September 2010 Canterbury earthquake. Absent further disruptions, rebuilding should
Summary Economic and financial developments in New Zealand have continued to be impacted by the aftershocks from the 4 September 2010 Canterbury earthquake. Absent further disruptions, rebuilding should
Country update TURKEY
 Summary Turkey s economy appears to be headed for a soft-landing, after nearly overheating in 211. While domestic demand growth came to a halt, exports took over as the main driver of growth. For 2, we
Summary Turkey s economy appears to be headed for a soft-landing, after nearly overheating in 211. While domestic demand growth came to a halt, exports took over as the main driver of growth. For 2, we
Country report THE NETHERLANDS
 Summary In the aftermath of the financial crisis the Dutch economy managed to recover as it was able to benefit from expanding world trade. Lately however the economy has slowed down, ending up in recession
Summary In the aftermath of the financial crisis the Dutch economy managed to recover as it was able to benefit from expanding world trade. Lately however the economy has slowed down, ending up in recession
Country Report BRAZIL
 Country Report BRAZIL Summary After posting 7.5% economic growth in 1, the highest growth rate in years, we expect the economy to grow at a slower pace in 11. This is welcome, as inflation has been approaching
Country Report BRAZIL Summary After posting 7.5% economic growth in 1, the highest growth rate in years, we expect the economy to grow at a slower pace in 11. This is welcome, as inflation has been approaching
Country report BRUNEI
 Country report BRUNEI Summary The prosperous country of Brunei derives its wealth from an abundance of oil and gas resources. The economy contracted 1.8% yoy in 2009 and is estimated to have grown over
Country report BRUNEI Summary The prosperous country of Brunei derives its wealth from an abundance of oil and gas resources. The economy contracted 1.8% yoy in 2009 and is estimated to have grown over
Country report PARAGUAY
 Country report PARAGUAY Summary Paraguay has posted a very high economic growth rate in 21, thanks to rapid growth of exports of soybeans and meat. However, the economic structure of the country remains
Country report PARAGUAY Summary Paraguay has posted a very high economic growth rate in 21, thanks to rapid growth of exports of soybeans and meat. However, the economic structure of the country remains
Country update OMAN. Country Risk Research Economic Research Department Rabobank Nederland
 Summary Oman is a middle-income economy that is heavily dependent on its dwindling oil resources. Because of declining oil reserves and a rapidly growing labour force, the government is actively pursuing
Summary Oman is a middle-income economy that is heavily dependent on its dwindling oil resources. Because of declining oil reserves and a rapidly growing labour force, the government is actively pursuing
Country report KENYA. Author: Elena Saputo Country Risk Research Economic Research Department Rabobank Nederland
 Summary Kenya has regained a sense of political stability after the political turmoil that followed general elections in 7. In August 1, a new constitution was adopted in a peaceful vote. However, the
Summary Kenya has regained a sense of political stability after the political turmoil that followed general elections in 7. In August 1, a new constitution was adopted in a peaceful vote. However, the
Country report AZERBAIJAN
 Summary The economic base of Azerbaijan is very narrow as the country is highly dependent on its energy sector and oil exports in particular. As oil production plateaued in 11, economic growth was weak
Summary The economic base of Azerbaijan is very narrow as the country is highly dependent on its energy sector and oil exports in particular. As oil production plateaued in 11, economic growth was weak
Country update INDIA
 Summary Economic growth in 211/12 slowed to 6.% from 8%+ growth figures in the two years before. For this fiscal year, economic growth is expected to be around 6% to 6.%, although downside side risks are
Summary Economic growth in 211/12 slowed to 6.% from 8%+ growth figures in the two years before. For this fiscal year, economic growth is expected to be around 6% to 6.%, although downside side risks are
Country report MOROCCO
 Country report MOROCCO Summary Morocco s stable growth and banking sector, despite the global crisis, mark the county s present relatively sound economic state. Although Morocco suffered from lower inflows
Country report MOROCCO Summary Morocco s stable growth and banking sector, despite the global crisis, mark the county s present relatively sound economic state. Although Morocco suffered from lower inflows
Country report LATVIA
 Summary Latvia s economy has gradually recovered from its 28/1 recession, when GDP fell by about 2%. Last year, driven by strongly rising investments and exports, as well as recovering private consumption,
Summary Latvia s economy has gradually recovered from its 28/1 recession, when GDP fell by about 2%. Last year, driven by strongly rising investments and exports, as well as recovering private consumption,
Country report KUWAIT
 Summary The turmoil in the Arab world had little impact on Kuwait, although concerns of contagion remain. A large risk lies in the political sphere, where the frequent frictions within the government and
Summary The turmoil in the Arab world had little impact on Kuwait, although concerns of contagion remain. A large risk lies in the political sphere, where the frequent frictions within the government and
Country report ARGENTINA
 Summary On 23 October 211, Cristina Fernández de Kirchner won the presidential elections convincingly with 5% of the votes. Her party also regained the majority in congress which it lost in 29. This will
Summary On 23 October 211, Cristina Fernández de Kirchner won the presidential elections convincingly with 5% of the votes. Her party also regained the majority in congress which it lost in 29. This will
Country report GHANA. Author: Reinier Meijer Country Risk Research Economic Research Department Rabobank Nederland
 Summary Ghana s main economic risk is the country s persisting twin deficit on the current account balance (of 9.% in 211) and fiscal balance (of % of GDP in 211). The fiscal deficit is expected to widen
Summary Ghana s main economic risk is the country s persisting twin deficit on the current account balance (of 9.% in 211) and fiscal balance (of % of GDP in 211). The fiscal deficit is expected to widen
Country report INDONESIA
 Summary Based on strong economic growth (6.% in 11), solid public finances, and a balanced current account, Indonesia s star has been rising. Moody s and Fitch have upgraded Indonesia back to investment
Summary Based on strong economic growth (6.% in 11), solid public finances, and a balanced current account, Indonesia s star has been rising. Moody s and Fitch have upgraded Indonesia back to investment
Brazil. Mauricio Oreng Senior Brazil Strategist Aug-17. Macroeconomic outlook. Marketing communication
 Mauricio Oreng Senior Brazil Strategist Aug-17 Brazil Macroeconomic outlook Marketing communication Brazil s worst recession on record... 12 10 % real annual growth 8 6 4 2 0 GDP forecast 2017: 0.1% -2
Mauricio Oreng Senior Brazil Strategist Aug-17 Brazil Macroeconomic outlook Marketing communication Brazil s worst recession on record... 12 10 % real annual growth 8 6 4 2 0 GDP forecast 2017: 0.1% -2
Country report KENYA. Author: Reinier Meijer Country Risk Research Economic Research Department Rabobank Nederland
 Summary Kenya's 27 presidential elections, which were marred by severe unrest and violence, have led to a recent constitutional reform meant to curb new unrest. Nevertheless, the upcoming general elections,
Summary Kenya's 27 presidential elections, which were marred by severe unrest and violence, have led to a recent constitutional reform meant to curb new unrest. Nevertheless, the upcoming general elections,
Strengths + and weaknesses
 Chile: economic reality holds back reforms Country Report Ester Barendregt The Bachelet government is facing popular discontent on both the left and the right as well as a deteriorated economic environment,
Chile: economic reality holds back reforms Country Report Ester Barendregt The Bachelet government is facing popular discontent on both the left and the right as well as a deteriorated economic environment,
Country report Cameroon
 Country report Cameroon Summary In the past, Cameroon benefited from being a small oil-exporting economy (1% of GDP, but % of exports and fiscal revenues in ). Oil exploitation created fluctuating trade
Country report Cameroon Summary In the past, Cameroon benefited from being a small oil-exporting economy (1% of GDP, but % of exports and fiscal revenues in ). Oil exploitation created fluctuating trade
Strengths (+) and weaknesses ( )
 Country Report Chile Country Report Alexandra Dumitru A new government took office in March 2014 and has been pushing through a bold reform agenda. In the meantime, the economy took a downturn, but economic
Country Report Chile Country Report Alexandra Dumitru A new government took office in March 2014 and has been pushing through a bold reform agenda. In the meantime, the economy took a downturn, but economic
Outlook 2013: China. Growth expected to accelerate again
 Outlook 13: China Growth expected to accelerate again Weakened external demand and only limited growth supporting policies from the Chinese government were the main factors explaining China s slowing growth
Outlook 13: China Growth expected to accelerate again Weakened external demand and only limited growth supporting policies from the Chinese government were the main factors explaining China s slowing growth
2014 Fiscal Balance: Short-Term Improvement
 BLOMINVEST BANK In June 2014, oil prices were slashed from a high of $112 to a low of $58 in December 2014. This bearish trend meant different things to the fiscal balances of oil importing countries and
BLOMINVEST BANK In June 2014, oil prices were slashed from a high of $112 to a low of $58 in December 2014. This bearish trend meant different things to the fiscal balances of oil importing countries and
The Turkish Economy. Dynamics of Growth
 The Economy in Turkey in 2018 2018 1 The Turkish Economy The Turkish economy grew at a rate of 3.2% in 2016, largely due to the attempted coup and terror attacks. The outlook was negative in the beginning
The Economy in Turkey in 2018 2018 1 The Turkish Economy The Turkish economy grew at a rate of 3.2% in 2016, largely due to the attempted coup and terror attacks. The outlook was negative in the beginning
CAN BRAZIL S ECONOMY REGAIN ITS STRENGTH?
 1 CAN BRAZIL S ECONOMY REGAIN ITS STRENGTH? Osamu Katano North America & Latin America Dept., Mitsui Global Strategic Studies Institute Brazil s economy is recovering from a terrible period. Real GDP growth
1 CAN BRAZIL S ECONOMY REGAIN ITS STRENGTH? Osamu Katano North America & Latin America Dept., Mitsui Global Strategic Studies Institute Brazil s economy is recovering from a terrible period. Real GDP growth
Country Insight Snapshot Australia March 2018
 Country Insight Snapshot Australia Written 02 OVERVIEW O V E R A L L C O U N T R Y R I S K R A T I N G : D B 2 c Low risk: Low degree of uncertainty associated with expected returns. However, country-wide
Country Insight Snapshot Australia Written 02 OVERVIEW O V E R A L L C O U N T R Y R I S K R A T I N G : D B 2 c Low risk: Low degree of uncertainty associated with expected returns. However, country-wide
Strengths (+) and weaknesses ( )
 Country Report Australia Country Report Marcel Weernink Economic growth in Australia decelerates due to lower mining investments. The outlook depends heavily on demand from China for its commodities and
Country Report Australia Country Report Marcel Weernink Economic growth in Australia decelerates due to lower mining investments. The outlook depends heavily on demand from China for its commodities and
Uzbekistan. Cautious improvement after the power shift in Uzbekistan 14/06/2017 COUNTRY RISK CLASSIFICATION
 14/6/217 6/7 COUNTRY RISK CLASSIFICATION COUNTRY RISK CLASSIFICATION 1 2 3 4 6 7 The country risk classifications are on a scale of to 7. The lower the number, the better the credit rating. Cautious improvement
14/6/217 6/7 COUNTRY RISK CLASSIFICATION COUNTRY RISK CLASSIFICATION 1 2 3 4 6 7 The country risk classifications are on a scale of to 7. The lower the number, the better the credit rating. Cautious improvement
Nigeria Economic Update QNB Group. September 2014
 Nigeria Economic Update QNB Group September 21 Nigeria Overview A rebasing of GDP in 213 has made Nigeria the biggest economy in Africa with the largest population; the economy is growing rapidly but remains
Nigeria Economic Update QNB Group September 21 Nigeria Overview A rebasing of GDP in 213 has made Nigeria the biggest economy in Africa with the largest population; the economy is growing rapidly but remains
MUFG LATIN AMERICA TOPICS
 MUFG LATIN AMERICA TOPICS Mexico s Macroeconomic Performance: Q3 217 GDP and Current Economic Indicators MUFG UNION BANK, N.A. ECONOMIC RESEARCH (NEW YORK) KAREN MARTINEZ Latin America Economist +1(212)72-57
MUFG LATIN AMERICA TOPICS Mexico s Macroeconomic Performance: Q3 217 GDP and Current Economic Indicators MUFG UNION BANK, N.A. ECONOMIC RESEARCH (NEW YORK) KAREN MARTINEZ Latin America Economist +1(212)72-57
Strenghts (+) and weaknesses ( )
 Country Report Singapore Country Report Maartje Wijffelaars Strong institutions and effective policymaking support (potential) GDP growth, while the state s small size and ageing pose challenges. Healthy
Country Report Singapore Country Report Maartje Wijffelaars Strong institutions and effective policymaking support (potential) GDP growth, while the state s small size and ageing pose challenges. Healthy
Brazil: A New Horizon?
 Bert Hoffmann GIGA Institute of Latin American Studies Hamburg, Germany Brazil: A New Horizon? ERA Conference Novara, 5-6 November 2013 Which Brazil? This one?? Or this one? A New Reality Sept. 6, 2002:
Bert Hoffmann GIGA Institute of Latin American Studies Hamburg, Germany Brazil: A New Horizon? ERA Conference Novara, 5-6 November 2013 Which Brazil? This one?? Or this one? A New Reality Sept. 6, 2002:
Game-Changers in the Era of Dissonance
 Game-Changers in the Era of Dissonance The research views expressed herein are those of the author and do not necessarily represent the views of the CME Group or its affiliates. All examples in this presentation
Game-Changers in the Era of Dissonance The research views expressed herein are those of the author and do not necessarily represent the views of the CME Group or its affiliates. All examples in this presentation
NATIONAL BANK OF SERBIA. Speech at the presentation of the Inflation Report November 2018
 NATIONAL BANK OF SERBIA Speech at the presentation of the Inflation Report November 8 Savo Jakovljević, Acting General Manager of the Economic Research and Statistics Department Belgrade, November 8 Ladies
NATIONAL BANK OF SERBIA Speech at the presentation of the Inflation Report November 8 Savo Jakovljević, Acting General Manager of the Economic Research and Statistics Department Belgrade, November 8 Ladies
Monthly Bulletin of Economic Trends: Review of the Australian Economy
 MELBOURNE INSTITUTE Applied Economic & Social Research Monthly Bulletin of Economic Trends: Review of the Australian Economy December 7 Released on December 7 Outlook for Australia Economic Activity Actual
MELBOURNE INSTITUTE Applied Economic & Social Research Monthly Bulletin of Economic Trends: Review of the Australian Economy December 7 Released on December 7 Outlook for Australia Economic Activity Actual
Country Risk Analytics
 Emerging Markets Country Risk Analytics MacroFinance Research Quarterly - 2018 Q2 www.taceconomics.com www.taceconomics.com 2 Country Risk Analytics EM Quarterly MacroFinance Research 2018 Q2 Description
Emerging Markets Country Risk Analytics MacroFinance Research Quarterly - 2018 Q2 www.taceconomics.com www.taceconomics.com 2 Country Risk Analytics EM Quarterly MacroFinance Research 2018 Q2 Description
MACRO-ECONOMICS AND MACRO FINANCIAL CRISIS
 MACRO-ECONOMICS AND MACRO FINANCIAL CRISIS Dr. Lê Xuân Ngh a 1. The world economy and perspectives. The recovery of the US economy continues to face difficulties. The CPI decreased by 0.1% in June indicating
MACRO-ECONOMICS AND MACRO FINANCIAL CRISIS Dr. Lê Xuân Ngh a 1. The world economy and perspectives. The recovery of the US economy continues to face difficulties. The CPI decreased by 0.1% in June indicating
Australian Dollar Outlook
 Tuesday, 31 March 015 Australian Dollar Outlook Still Under Pressure We have revised our AUD forecasts for this year down slightly to reflect developments over recent months. We now expect the AUD to end
Tuesday, 31 March 015 Australian Dollar Outlook Still Under Pressure We have revised our AUD forecasts for this year down slightly to reflect developments over recent months. We now expect the AUD to end
Implementation of Pheu Thai Party Policy Key to Thailand s Success
 Analyst Tan Xuan +6631179 tanx@phillip.com.sg 14 Jul 211 Implementation of Pheu Thai Party Policy Key to Thailand s Success Executive Summary Bright spot in private consumption to be supported by rising
Analyst Tan Xuan +6631179 tanx@phillip.com.sg 14 Jul 211 Implementation of Pheu Thai Party Policy Key to Thailand s Success Executive Summary Bright spot in private consumption to be supported by rising
Economic Outlook. December Dan McLaughlin. Chief Economist
 Economic Outlook December 211 Chief Economist Dan McLaughlin 11q3(e) 11q1 1q3 Global growth has slowed this year... Global Growth (%) 6 4 2-2 -4-6 1q1 9q3 9q1 8q3 8q1 7q3 7q1 World US Euro And OECD expects
Economic Outlook December 211 Chief Economist Dan McLaughlin 11q3(e) 11q1 1q3 Global growth has slowed this year... Global Growth (%) 6 4 2-2 -4-6 1q1 9q3 9q1 8q3 8q1 7q3 7q1 World US Euro And OECD expects
Main Economic & Financial Indicators Poland
 Main Economic & Financial Indicators Poland. 6 OCTOBER 2015 NAOKO ISHIHARA ECONOMIST ECONOMIC RESEARCH OFFICE (LONDON) T +44-(0)20-7577-2179 E naoko.ishihara@uk.mufg.jp The Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi UFJ,
Main Economic & Financial Indicators Poland. 6 OCTOBER 2015 NAOKO ISHIHARA ECONOMIST ECONOMIC RESEARCH OFFICE (LONDON) T +44-(0)20-7577-2179 E naoko.ishihara@uk.mufg.jp The Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi UFJ,
D&B Country Insight Snapshot: Portugal January 2015
 D&B Country Insight Snapshot: Portugal January 2015 Overview Overall Country Risk Rating : DB4c Moderate risk: Significant uncertainty over expected returns. Risk-averse customers are advised to protect
D&B Country Insight Snapshot: Portugal January 2015 Overview Overall Country Risk Rating : DB4c Moderate risk: Significant uncertainty over expected returns. Risk-averse customers are advised to protect
Leumi. Global Economics Monthly Review. Arie Tal, Research Economist. May 8, The Finance Division, Economics Department. leumiusa.
 Global Economics Monthly Review May 8, 2018 Arie Tal, Research Economist The Finance Division, Economics Department Leumi leumiusa.com Please see important disclaimer on the last page of this report Key
Global Economics Monthly Review May 8, 2018 Arie Tal, Research Economist The Finance Division, Economics Department Leumi leumiusa.com Please see important disclaimer on the last page of this report Key
Global Economics Monthly Review
 Global Economics Monthly Review January 8 th, 2018 Arie Tal, Research Economist The Finance Division, Economics Department Please see important disclaimer on the last page of this report 1 Key Issues Global
Global Economics Monthly Review January 8 th, 2018 Arie Tal, Research Economist The Finance Division, Economics Department Please see important disclaimer on the last page of this report 1 Key Issues Global
The Forex Market in March 2007
 1 The Forex Market in March 2007 US Dollar : USD The US dollar in March continued to weaken from prior month compared with the euro and the yen with exchange rates averaging at US$ 1.3251 per euro and
1 The Forex Market in March 2007 US Dollar : USD The US dollar in March continued to weaken from prior month compared with the euro and the yen with exchange rates averaging at US$ 1.3251 per euro and
Colombia. 1. General trends. The Colombian economy grew by 2.5% in 2008, a lower rate than the sustained growth of
 Economic Survey of Latin America and the Caribbean 2008-2009 129 Colombia 1. General trends The Colombian economy grew by 2.5% in 2008, a lower rate than the sustained growth of recent years. Indicators
Economic Survey of Latin America and the Caribbean 2008-2009 129 Colombia 1. General trends The Colombian economy grew by 2.5% in 2008, a lower rate than the sustained growth of recent years. Indicators
Global Macroeconomic Monthly Review
 Global Macroeconomic Monthly Review August 14 th, 2018 Arie Tal, Research Economist Capital Markets Division, Economics Department 1 Please see disclaimer on the last page of this report Key Issues Global
Global Macroeconomic Monthly Review August 14 th, 2018 Arie Tal, Research Economist Capital Markets Division, Economics Department 1 Please see disclaimer on the last page of this report Key Issues Global
Gauging Current Conditions:
 Gauging Current Conditions: The Economic Outlook and Its Impact on Workers Compensation Vol. 2 2005 The gauges below indicate the economic outlook for the current year and for 2006 for factors that typically
Gauging Current Conditions: The Economic Outlook and Its Impact on Workers Compensation Vol. 2 2005 The gauges below indicate the economic outlook for the current year and for 2006 for factors that typically
D&B Country Insight Snapshot: Belgium April 2015
 D&B Country Insight Snapshot: Belgium April 2015 Overview Overall Country Risk Rating : DB2d Low risk: Low degree of uncertainty associated with expected returns. However, country-wide factors may result
D&B Country Insight Snapshot: Belgium April 2015 Overview Overall Country Risk Rating : DB2d Low risk: Low degree of uncertainty associated with expected returns. However, country-wide factors may result
NATIONAL BANK OF SERBIA. Speech at the presentation of the Inflation Report May Dr Jorgovanka Tabaković, Governor
 NATIONAL BANK OF SERBIA Speech at the presentation of the Inflation Report May Dr Jorgovanka Tabaković, Governor Belgrade, May Ladies and gentlemen, representatives of the press, dear colleagues, Welcome
NATIONAL BANK OF SERBIA Speech at the presentation of the Inflation Report May Dr Jorgovanka Tabaković, Governor Belgrade, May Ladies and gentlemen, representatives of the press, dear colleagues, Welcome
$57.2bn. Why the US trade deficit is heading the wrong way. Economic and Financial Analysis
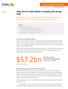 Economic and Financial Analysis 6 April 2018 Global Economics 6 April 2018 Article Why the US trade deficit is heading the wrong way Macroeconomic policy, not just trade barriers, affects the trade deficit.
Economic and Financial Analysis 6 April 2018 Global Economics 6 April 2018 Article Why the US trade deficit is heading the wrong way Macroeconomic policy, not just trade barriers, affects the trade deficit.
Real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of Hong Kong increased 0.9 percent in the first half
 Economic Prospects of Hong Kong in 2012-13 Win Lin Chou, City University of Hong Kong Prepared for United Nations Project LINK Meeting in New York, October 22-24, 2012 I. The Current Trends Real Gross
Economic Prospects of Hong Kong in 2012-13 Win Lin Chou, City University of Hong Kong Prepared for United Nations Project LINK Meeting in New York, October 22-24, 2012 I. The Current Trends Real Gross
North American Economic Outlook: Climbing Out of Recession
 North American Economic Outlook: Climbing Out of Recession Presentation to the Canadian Association of Movers Paul Ferley (1) 97-731 Assistant Chief Economist paul.ferley@rbc.com November 17, 9 U.S. Economic
North American Economic Outlook: Climbing Out of Recession Presentation to the Canadian Association of Movers Paul Ferley (1) 97-731 Assistant Chief Economist paul.ferley@rbc.com November 17, 9 U.S. Economic
Macro Research Economic outlook
 Macro Research Economic outlook Macroeconomic Research Itaú Unibanco April 2017 Roadmap Global Economy The global outlook remains favorable Global growth positive momentum continues, with a synchronized
Macro Research Economic outlook Macroeconomic Research Itaú Unibanco April 2017 Roadmap Global Economy The global outlook remains favorable Global growth positive momentum continues, with a synchronized
SEB MERCHANT BANKING COUNTRY RISK ANALYSIS 28 September 2016
 SEB MERCHANT BANKING COUNTRY RISK ANALYSIS 28 September 2016 Higher foreign reserves and lower financing needs following the debt restructuring in 2015 have reduced external vulnerability. In addition,
SEB MERCHANT BANKING COUNTRY RISK ANALYSIS 28 September 2016 Higher foreign reserves and lower financing needs following the debt restructuring in 2015 have reduced external vulnerability. In addition,
growth but still remains at approximately 1.5% of potential GDP.
 THE UK ECONOMY IN FOCUS/APPLICATIONS Reminder of key objectives: Low and positive inflation (inflation rate target of 2%/- 1%) Sustainable growth of real GDP (no target) falling unemployment (no target)
THE UK ECONOMY IN FOCUS/APPLICATIONS Reminder of key objectives: Low and positive inflation (inflation rate target of 2%/- 1%) Sustainable growth of real GDP (no target) falling unemployment (no target)
PROJECT LINK FALL MEETING NEW YORK, OCTOBER 2015 COUNTRY REPORT : SWITZERLAND
 PROJECT LINK FALL MEETING NEW YORK, OCTOBER 2015 COUNTRY REPORT : SWITZERLAND Délia NILLES 1 1. Recent Trends and Selected Key Forecasts 1.1 Recent trends Switzerland's real GDP grew by 1.9% in 2014, but
PROJECT LINK FALL MEETING NEW YORK, OCTOBER 2015 COUNTRY REPORT : SWITZERLAND Délia NILLES 1 1. Recent Trends and Selected Key Forecasts 1.1 Recent trends Switzerland's real GDP grew by 1.9% in 2014, but
South Korea: new growth model emerging?
 ING Business Opportunity Report Economics Department South Korea: new growth model emerging? Summary conclusions The growth outlook for Korea in the short to medium term is positive. ING forecasts economic
ING Business Opportunity Report Economics Department South Korea: new growth model emerging? Summary conclusions The growth outlook for Korea in the short to medium term is positive. ING forecasts economic
$3.56 trillion. $2.216 trillion
 ECONOMY SUMMARY INTRODUCTION The main goal of this macro-study is to investigate Brazil and to get a global view of its economy. This chapter will focus on Brazil s economy by giving an answer to the following
ECONOMY SUMMARY INTRODUCTION The main goal of this macro-study is to investigate Brazil and to get a global view of its economy. This chapter will focus on Brazil s economy by giving an answer to the following
ECONOMY REPORT - CHINESE TAIPEI
 ECONOMY REPORT - CHINESE TAIPEI (Extracted from 2001 Economic Outlook) REAL GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT The Chinese Taipei economy grew strongly during the first three quarters of 2000, thanks largely to robust
ECONOMY REPORT - CHINESE TAIPEI (Extracted from 2001 Economic Outlook) REAL GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT The Chinese Taipei economy grew strongly during the first three quarters of 2000, thanks largely to robust
Fund Management Diary
 Fund Management Diary Meeting held on 16 th October 2018 Euro-zone competitiveness imbalances In the run up to the global financial crisis differing competitiveness levels across the euro-zone contributed
Fund Management Diary Meeting held on 16 th October 2018 Euro-zone competitiveness imbalances In the run up to the global financial crisis differing competitiveness levels across the euro-zone contributed
D&B Country Insight Snapshot: Lithuania November 2014
 D&B Country Insight Snapshot: Lithuania November 2014 Overview Overall Country Risk Rating : DB3b Slight risk : Enough uncertainty over expected returns to warrant close monitoring of country risk. Customers
D&B Country Insight Snapshot: Lithuania November 2014 Overview Overall Country Risk Rating : DB3b Slight risk : Enough uncertainty over expected returns to warrant close monitoring of country risk. Customers
Country Insight Snapshot United Kingdom April 2018
 Country Insight Snapshot United Kingdom Written 30 March 2018 OVERVIEW O V E R A L L C O U N T R Y R I S K R A T I N G : D B 2 d Low risk: Low degree of uncertainty associated with expected returns. However,
Country Insight Snapshot United Kingdom Written 30 March 2018 OVERVIEW O V E R A L L C O U N T R Y R I S K R A T I N G : D B 2 d Low risk: Low degree of uncertainty associated with expected returns. However,
Teetering on the brink: is the world heading for another financial crisis?
 Teetering on the brink: is the world heading for another financial crisis? Adrian Cooper CEO & Chief Economist acooper@oxfordeconomics.com Peter Suomi Director petersuomi@oxfordeconomics.com October 2011
Teetering on the brink: is the world heading for another financial crisis? Adrian Cooper CEO & Chief Economist acooper@oxfordeconomics.com Peter Suomi Director petersuomi@oxfordeconomics.com October 2011
Main Economic & Financial Indicators The Czech Republic
 Main Economic & Financial Indicators The Czech Republic 15 OCTOBER 215 NAOKO ISHIHARA ECONOMIST ECONOMIC RESEARCH OFFICE (LONDON) T +44-()2-7577-2179 E naoko.ishihara@uk.mufg.jp The Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi
Main Economic & Financial Indicators The Czech Republic 15 OCTOBER 215 NAOKO ISHIHARA ECONOMIST ECONOMIC RESEARCH OFFICE (LONDON) T +44-()2-7577-2179 E naoko.ishihara@uk.mufg.jp The Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi
The U.S. Current Account Balance and the Business Cycle
 The U.S. Current Account Balance and the Business Cycle Prepared for: Macroeconomic Theory American University Prof. R. Blecker Author: Brian Dew brianwdew@gmail.com November 19, 2015 November 19, 2015
The U.S. Current Account Balance and the Business Cycle Prepared for: Macroeconomic Theory American University Prof. R. Blecker Author: Brian Dew brianwdew@gmail.com November 19, 2015 November 19, 2015
Global PMI. Global economy set for robust Q2 growth. June 8 th IHS Markit. All Rights Reserved.
 Global PMI Global economy set for robust Q2 growth June 8 th 2017 2 PMI indicates robust global growth in Q2 The global economy is on course for a robust second quarter, according to PMI survey data. The
Global PMI Global economy set for robust Q2 growth June 8 th 2017 2 PMI indicates robust global growth in Q2 The global economy is on course for a robust second quarter, according to PMI survey data. The
An Overview of World Goods and Services Trade
 Appendix IV An Overview of World Goods and Services Trade An overview of the size and composition of U.S. and world trade is useful to provide perspective for the large U.S. trade and current account deficits
Appendix IV An Overview of World Goods and Services Trade An overview of the size and composition of U.S. and world trade is useful to provide perspective for the large U.S. trade and current account deficits
Vietnam. HSBC Global Connections Report. October 2013
 HSBC Global Connections Report October 2013 Vietnam The pick-up in GDP growth will be modest this year, with weak domestic demand and exports still dampening industrial confidence. A stronger recovery
HSBC Global Connections Report October 2013 Vietnam The pick-up in GDP growth will be modest this year, with weak domestic demand and exports still dampening industrial confidence. A stronger recovery
Asset Allocation Model March Update
 The month of February was marked by a sell-off in global equity markets and a sudden increase in market volatility with the CBOE Volatility Index reaching its highest level since August 2015. The rout
The month of February was marked by a sell-off in global equity markets and a sudden increase in market volatility with the CBOE Volatility Index reaching its highest level since August 2015. The rout
The yellow highlighted areas are bear markets with NO recession.
 Part 3, Final Report: Major Market Reversal Model This is the third and final report on my major market reversal model. This portion of the model focuses on the domestic and international economy. I ve
Part 3, Final Report: Major Market Reversal Model This is the third and final report on my major market reversal model. This portion of the model focuses on the domestic and international economy. I ve
Current Economic Conditions and Selected Forecasts
 Order Code RL30329 Current Economic Conditions and Selected Forecasts Updated May 20, 2008 Gail E. Makinen Economic Policy Consultant Government and Finance Division Current Economic Conditions and Selected
Order Code RL30329 Current Economic Conditions and Selected Forecasts Updated May 20, 2008 Gail E. Makinen Economic Policy Consultant Government and Finance Division Current Economic Conditions and Selected
The Saturday Economist UK Economic Outlook Q1 2015
 The Saturday Economist The Saturday Economist UK Economic Outlook Q1 2015 Leisure and Construction driving recovery UK Economic Outlook March 2015 Page 1 The UK recovery continues. We expect growth of
The Saturday Economist The Saturday Economist UK Economic Outlook Q1 2015 Leisure and Construction driving recovery UK Economic Outlook March 2015 Page 1 The UK recovery continues. We expect growth of
Slovenia. Eurozone rebalancing. EY Eurozone Forecast June Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain. Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Netherlands
 EY Forecast June 215 rebalancing recovery Outlook for Activity to remain solid this year, after growing 2.4% in 214 Published in collaboration with Highlights n GDP grew by 2.4% in 214 and 3% in Q1 215,
EY Forecast June 215 rebalancing recovery Outlook for Activity to remain solid this year, after growing 2.4% in 214 Published in collaboration with Highlights n GDP grew by 2.4% in 214 and 3% in Q1 215,
TURKEY: RECENT DEVELOPMENTS January March 2018
 TURKEY: RECENT DEVELOPMENTS January March 218 3 81 4 698 961 7 34 7 96 9 66 8 98 1 931 1 6 11 2 11 88 11 19 1 883 1 97 12 48 12 112 Per capita GDP tripled while nominal GDP quadrupled in last 1 years 237
TURKEY: RECENT DEVELOPMENTS January March 218 3 81 4 698 961 7 34 7 96 9 66 8 98 1 931 1 6 11 2 11 88 11 19 1 883 1 97 12 48 12 112 Per capita GDP tripled while nominal GDP quadrupled in last 1 years 237
Eurozone. EY Eurozone Forecast September 2014
 Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast September 2014 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for
Eurozone EY Eurozone Forecast September 2014 Austria Belgium Cyprus Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Ireland Italy Latvia Luxembourg Malta Netherlands Portugal Slovakia Slovenia Spain Outlook for
Economic activity gathers pace
 Produced by the Economic Research Unit October 2014 A quarterly analysis of trends in the Irish economy Economic activity gathers pace Positive data flow Recovery broadening out GDP growth revised up to
Produced by the Economic Research Unit October 2014 A quarterly analysis of trends in the Irish economy Economic activity gathers pace Positive data flow Recovery broadening out GDP growth revised up to
Press Release December adjustment of monetary policy, allowed for a substantial reduction in new credit to Government by the Central Bank.
 Press Release December 2017 Overview During 2017, the Barbados economy continued to face significant macroeconomic challenges associated with declining international reserves, weak public finances and
Press Release December 2017 Overview During 2017, the Barbados economy continued to face significant macroeconomic challenges associated with declining international reserves, weak public finances and
Macroeconomic overview
 Macroeconomic overview APRIL 2009 Analyst: Ruta Arumäe, SEB Estonia Phone: +372 665 5578 E-mail: ruta.arumae@seb.ee KEY ECONOMIC NEWS Industrial production 1Q -26% Retail sales 1Q -14.6%, export ca -27%
Macroeconomic overview APRIL 2009 Analyst: Ruta Arumäe, SEB Estonia Phone: +372 665 5578 E-mail: ruta.arumae@seb.ee KEY ECONOMIC NEWS Industrial production 1Q -26% Retail sales 1Q -14.6%, export ca -27%
TURKEY: RECENT DEVELOPMENTS January June 2018
 TURKEY: RECENT DEVELOPMENTS January June 218 3 81 4 698 961 7 34 7 96 9 66 8 98 1 931 1 6 11 2 11 88 11 19 1 883 1 97 12 48 12 112 Per capita GDP tripled while nominal GDP quadrupled in last 1 years 237
TURKEY: RECENT DEVELOPMENTS January June 218 3 81 4 698 961 7 34 7 96 9 66 8 98 1 931 1 6 11 2 11 88 11 19 1 883 1 97 12 48 12 112 Per capita GDP tripled while nominal GDP quadrupled in last 1 years 237
MUFG LATIN AMERICA TOPICS
 MUFG LATIN AMERICA TOPICS Mexico s Macroeconomic Performance: Q1 2017 and Current Economic Indicators MUFG UNION BANK, N.A. ECONOMIC RESEARCH (NEW YORK) KAREN MARTINEZ Latin America Economist +1(212)782-5708
MUFG LATIN AMERICA TOPICS Mexico s Macroeconomic Performance: Q1 2017 and Current Economic Indicators MUFG UNION BANK, N.A. ECONOMIC RESEARCH (NEW YORK) KAREN MARTINEZ Latin America Economist +1(212)782-5708
Switzerland Economic Update QNB Group. September 2014
 Switzerland Economic Update QNB Group September 14 Switzerland Overview Switzerland s efficient capital markets, highly skilled human capital and low corporate tax rates make it the world's most competitive
Switzerland Economic Update QNB Group September 14 Switzerland Overview Switzerland s efficient capital markets, highly skilled human capital and low corporate tax rates make it the world's most competitive
Emerging Markets Debt: Outlook for the Asset Class
 Emerging Markets Debt: Outlook for the Asset Class By Steffen Reichold Emerging Markets Economist May 2, 211 Emerging market debt has been one of the best performing asset classes in recent years due to
Emerging Markets Debt: Outlook for the Asset Class By Steffen Reichold Emerging Markets Economist May 2, 211 Emerging market debt has been one of the best performing asset classes in recent years due to
The usage of surveys to overrun data gaps: Bank Indonesia s experience
 The usage of surveys to overrun data gaps: Bank Indonesia s experience Hendy Sulistiowaty and Ari Nopianti I. Introduction The global economic recession that triggered in late 2007 in the United States
The usage of surveys to overrun data gaps: Bank Indonesia s experience Hendy Sulistiowaty and Ari Nopianti I. Introduction The global economic recession that triggered in late 2007 in the United States
Trade in 2018: Nowhere close to its heyday
 Economic and Financial Analysis 5 December 2017 Article 5 December 2017 Trade in 2018: Nowhere close to its heyday Trade Trade in 2018 will pick up speed but rebalancing of the Chinese economy and global
Economic and Financial Analysis 5 December 2017 Article 5 December 2017 Trade in 2018: Nowhere close to its heyday Trade Trade in 2018 will pick up speed but rebalancing of the Chinese economy and global
Latvia SEB MERCHANT BANKING COUNTRY RISK ANALYSIS 18 June 2012
 Latvia SEB MERCHANT BANKING COUNTRY RISK ANALYSIS 18 June 1 Analyst: Per A. Hammarlund. Tel: +()8-7 9. E-mail: per.hammarlund@seb.se Strengths Country Risk Factors: Latvia Weaknesses Recovering GDP growth
Latvia SEB MERCHANT BANKING COUNTRY RISK ANALYSIS 18 June 1 Analyst: Per A. Hammarlund. Tel: +()8-7 9. E-mail: per.hammarlund@seb.se Strengths Country Risk Factors: Latvia Weaknesses Recovering GDP growth
Outlook 2013: Latin America
 Latin America and Caribbean Figure 1: Goods and services exports (% of GDP) % of GDP % of GDP 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 While a more challenging external environment has contributed to somewhat slower economic
Latin America and Caribbean Figure 1: Goods and services exports (% of GDP) % of GDP % of GDP 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 While a more challenging external environment has contributed to somewhat slower economic
WTO lowers forecast after sub-par trade growth in first half of 2014
 PRESS RELEASE PRESS/722 26 September 214 (-) WTO lowers forecast after sub-par trade growth in first half of 214 TRADE STATISTICS WTO economists have reduced their forecast for world trade growth in 214
PRESS RELEASE PRESS/722 26 September 214 (-) WTO lowers forecast after sub-par trade growth in first half of 214 TRADE STATISTICS WTO economists have reduced their forecast for world trade growth in 214
Economic Profile of Bhutan
 Economic Profile of Bhutan Submitted to: Dr. Ahmed Tazmeen Assistant Professor, Department of Economics North South University Submitted By: Namgay Wangmo MPPG 6th Batch ID # 1612872085 Date of Submission:
Economic Profile of Bhutan Submitted to: Dr. Ahmed Tazmeen Assistant Professor, Department of Economics North South University Submitted By: Namgay Wangmo MPPG 6th Batch ID # 1612872085 Date of Submission:
Finland's Balance of Payments. Preliminary Review 2007
 Finland's Balance of Payments Preliminary Review 27 1 Current account, 198 27 1 Credit Net - -1 198 198 199 199 2 2 Current transfers Income Services Goods Curent account, net Debit Bank of Finland Financial
Finland's Balance of Payments Preliminary Review 27 1 Current account, 198 27 1 Credit Net - -1 198 198 199 199 2 2 Current transfers Income Services Goods Curent account, net Debit Bank of Finland Financial
Monthly Report of Prospects for Japan's Economy
 Monthly Report of Prospects for Japan's Economy March 15 Macro Economic Research Centre Economics Department http://www.jri.co.jp/english/periodical/ This report is the revised English version of the February
Monthly Report of Prospects for Japan's Economy March 15 Macro Economic Research Centre Economics Department http://www.jri.co.jp/english/periodical/ This report is the revised English version of the February
A Bull Call Spread for Brazil
 A Bull Call Spread for Brazil Brazil is coming from a three-year recessionary period, with an unemployment rate still above 12%. Despite this, the Bovespa index (IBOV), which is the top equity index for
A Bull Call Spread for Brazil Brazil is coming from a three-year recessionary period, with an unemployment rate still above 12%. Despite this, the Bovespa index (IBOV), which is the top equity index for
The Economic Outlook. Emerging Risks in the International Economy. May 27, 2016
 The Economic Outlook May 27, 2016 Emerging Risks in the International Economy The international economy will likely continue to pose risks to the U.S. economy in 2016. Weaknesses globally are broad based
The Economic Outlook May 27, 2016 Emerging Risks in the International Economy The international economy will likely continue to pose risks to the U.S. economy in 2016. Weaknesses globally are broad based
Economic Research KDN No.: PP14787/11/2012(030811)
 wider Economic Research KDN No.: PP14787/11/2012(030811) Vol.: ER/014/2015 State of Kuwait: Country Risk Insights Economic Research Led By: Nor Zahidi Alias Chief Economist +603 2082 2277 zahidi@marc.com.my
wider Economic Research KDN No.: PP14787/11/2012(030811) Vol.: ER/014/2015 State of Kuwait: Country Risk Insights Economic Research Led By: Nor Zahidi Alias Chief Economist +603 2082 2277 zahidi@marc.com.my
TransGraph Research Consulting Technology
 Research Consulting Technology Agriculture Metals Energy Dairy Currency Economy Brands Medium term outlook on Lead July 217 2 Market Recap LME Lead remained weak last month but recovered towards the end
Research Consulting Technology Agriculture Metals Energy Dairy Currency Economy Brands Medium term outlook on Lead July 217 2 Market Recap LME Lead remained weak last month but recovered towards the end
