Supplementary Expert Report to the Land Court by Marcus Brown
|
|
|
- Ambrose McLaughlin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Expert Report to the Land Court by Marcus Brown 1. Experts Details & Qualifications 1.1 Name My name is Marcus Robert Brown. 1.2 Address My business address is: Economic Associates Pty Ltd 6/220 Boundary Street Spring Hill Qld Qualifications 1. I hold the following qualifications: (a) (b) Bachelor of Economics (Hons); and Master of Business Administration. 2. Opinion and Findings 2. This supplementary report seeks to expand on and/or respond to disagreements noted in the Joint Expert Report (JER) prepared by Roderick Duncan and me. 3. Primarily I wish to address the following points: (a) (b) (c) (d) Roderick Duncan s assertion that, the opinion of Marcus Brown that the mining boom has had no impact on the manufacturing sector runs counter to most economic analysis, including the recently released Grattan Institute report Roderick Duncan s assertion that, The assumption of perfect elasticity of supply for materials means that the additional materials for the Alpha mine can be supplied with zero cost for any other industry or firm in Queensland. This assumes that the orders of materials for Alpha mine can be met without delaying materials for any other project in Queensland. Roderick Duncan s assertion that, The skilled labour required for mining operations is not a type of labour in abundance in Australia, or those workers would not be earning the average annual income of over $100,000 that the ABS records workers in the sector as earning. The relevance or scenario analysis in the preparation of the EIS. The Mining Boom and its Impact on the Tradables (or Trade Exposed) Sector 4. At page 8 of the JER Roderick Duncan stated, the opinion of Marcus Brown that the mining boom has had no impact on the manufacturing sector runs counter to most economic analysis, including the recently released Grattan Institute report 1
2 5. To be clear, at no point in either my first individual statement nor in the JER did I contend that the mining boom had no impact on the manufacturing sector (or on other tradables sectors more broadly speaking). Rather I contended that: It is my view that the decline in non-mining sectors over the last five years is likely more attributable to broader global factors than to the mining industry per se (Subparagraph (c), page 4 of the JER) It is my view that based on available economic data that broader global factors have been primarily attributable to the poor performance of Australian non-mining sectors over the last five years (Subparagraph (e), page 5 of the JER) I do not believe that the reduction in manufacturing employment post 2008 is entirely attributable to the growth in mining employment. (Subparagraph (i), page 5 of the JER) 6. To clarify, it is my view that the decline in the manufacturing sector is primarily being driven by factors apart from the recent mining boom. The mining boom has had some impact on the manufacturing sector, but it has been a secondary influence. Furthermore, the mining investment boom is generally considered to have commenced around 2004 and has now ended. This is not to say that the mining sector will not continue to expand, rather that it is likely to grow at levels more in line with whole-of-economy growth. The Alpha Coal Mine is a post-boom project. 7. As indicated in the JER, the Australian economy began to experience capacity constraints in 2007 as reflected by the unemployment rate approaching 4%. However, with the onset of the Global Financial Crisis in the first half of 2008, unemployment increased and industry experienced significant declines in capacity utilization. 8. The impact of the mining sector on other tradables (or trade exposed) sectors has been overstated by some commentators. For example, Gary Banks, the former Chairman of the Productivity Commission 1 acknowledges that the mining boom has had some effect on other sectors, however points out: 9. But the pressures being placed on our traded goods sector are mainly due to us being richer than we were, and consuming more goods and (especially) services, rather than because mining draws labour or capital from manufacturing and agriculture. (page 2) Banks later went on to say: Delving a bit further into the manufacturing employment story reveals that, in the recent two speed years, the main causalities in employment terms within that sector have been the relatively highly assisted motor vehicle and TCF (Textiles, Clothing & Footwear) industries. (page 4) In addition, Banks commented that: 1 Gary Banks, Chairman, Productivity Commission Address to the Melbourne Institute and the Australian Economic and Social Outlook Conference, 30 June
3 Those longer term trends the relative rise of the services sector and the decline of manufacturing and agriculture are a manifestation of the process of advanced economic development, observable in all OECD countries. (page 5) 10. I note that Roderick Duncan cited the recent Grattan Institute Report, The Mining Boom: Impacts and Prospects, July 2013 in support of his proposition that I have ignored the impact of the mining boom on other sectors. In fact, the Grattan Institute report makes similar arguments to those made by the former Chairman of the Productivity Commission and by me, stating: The high exchange rate has hurt many trade-exposed businesses, including manufacturing. But it would be wrong to conclude that the boom is primarily responsible for the relative decline of the manufacturing sector, or for the sharper declines of individual industries, such as car manufacturing. Longer-term trends are at work.. In the 2000s, manufacturing s relative decline continued even in economies that did not experience Australia s exchange rate appreciation. (Grattan Institute, page 23) 11. Figure 1 below illustrates the historic decline of manufacturing employment since the mid- 1980s through to the most recent available data in May I have calculated a trend line for the decline in manufacturing employment from May 1985 to May 2004 (the start of the mining boom). I have extrapolated that trend from May 2004 to May 2013 to identify what would be the trend decline of the sector in the absence of the mining boom. The graph also shows the movement of the Trade Weighted Index (a measure of the strength of the Australian dollar against a basket of currencies of our major trading partners). Figure 1 shows that in the period between May 2004 and May 2008 (onset of GFC), manufacturing employment followed the long term trend. That is, the sector experienced decline consistent with historical trends despite the mining boom. 12. Figure 1 shows that it was not until after the GFC that manufacturing employment collapsed, as shown by the divergence of the actual employment from the extrapolated trendline. As I have stated in previous reports this was a trend across most developed countries. Notably, the Trade Weighted Index rebounded after its significant fall at the onset of the GFC to levels previously not experienced in our trend horizon. The high Trade Weighted Index (reflected in a high Australian dollar) would have had some impact on the Australian manufacturing industry; however as stated by the IMF 2, the Australian dollar was inflated well above levels explained by Australia s trading performance (by 10% to 20%). Excluding that 10%-20% premium on the value of the Australian dollar estimated by the IMF, the Trade Weighted Index would have been below the levels recorded prior to May International Monetary Fund (2012) Australia: 2012 Article IV Consultation Staff Report, IMF Country Report No. 12/305 3
4 Figure 1: Manufacturing employment (original and trend) and Trade Weighted Index 13. I note Roderick Duncan s argument that the negative impact of the mining boom is so widely known that it has its own name, that is the Dutch Disease. The Dutch Disease refers to a phenomenon whereby as a result of one part of the economy is booming 3 as a result of a short term stimulus, other parts of the economy (known as lagging sectors) suffer long term declines due to increased competition for resources (the Resource Movement Effect) and reduced international competitiveness due to an appreciating exchange rate (the Spending Effect). While it may be convenient to make arguments that adjustments in the Australian economy are part of the so called Dutch Disease, it is not a universally held view, with David Gruen the Head of the Australian Treasury s Macroeconomic Group pointing out: this global changing of the Guard (from the economic re-emergence of China and India) seems more like a generational change in Australia s comparative advantage than it does an example of the Dutch Disease, in which we might wish to return Australia to its pre-boom industrial structure once a short lived disturbance has passed (Gruen, D The Resources Boom and Structural Change in the Australian Economy, address to the CEDA 2011 Economic & Political Overview, 24 Feb 2011) 14. Much of the discussion regarding the decline in the manufacturing industry has related to either employment or percentage GDP contribution. Notably however, the value of manufacturing exports has shown an upward trend over the long term (including the period after 2004) (as shown in Figure 4 of my first individual statement). Also, manufacturing s industry value added (i.e. industry contribution to GDP) has remained stable despite sharp 3 Typically, the comparison is between a booming resources sector and lagging manufacturing and agricultural sectors. 4
5 declines in textile, clothing & other manufacturing as a result of significant reduction in trade protection available to that sector (see Figure 5 of my first individual statement). Growth in export values and stabilised industry contribution in the face of declining employment would tend to suggest productivity improvement, rather than industry collapse. This tends to reinforce the proposition that Australia is moving through a long term readjustment rather than the so called Dutch Disease. 15. The Grattan Institute report and Gary Banks (former Chairman, Productivity Commission) largely focuses on the exchange rate effect of a peaking Terms of Trade as the potential adverse impact of the mining boom, which in the context of the literature of the Dutch Disease would be described as the Spending Effect, while Roderick Duncan appears more focussed on the Resource Movement Effect. 16. The Spending Effect focusses on the impact of an appreciating dollar. Australia s strong trade performance has most certainly been a contributing factor to the strength of our currency during the mining boom. However, as I explained in my first individual statement the value of the Australian dollar up until recently had been inflated by a suite of global monetary factors with the IMF estimating in November 2012 that the Australian dollar was 10% to 20% above levels that might be explained by Australia-specific factors 4. The recent devaluation of the Australian currency has seen the Australian dollar fall from its November 2012 average of US$1.041 to approximately US$ In terms of the Resource Movement Effect, I would agree with Corder (2011), a paper cited frequently in the Grattan Institute report, that the resource movement effect (i.e. the movement of resources from a lagging sector to a booming sector) is not particularly significant in an Australian context insofar as the constraints on the movement of labour between sectors are somewhat reduced by Australia s skilled immigration policy, and secondly that the movement of capital between sectors is mitigated by high international capital mobility. Furthermore, the presence of considerable spare capacity in the Australian economy post the GFC (and particularly at present 5 ) means that the potential for the Resource Movement Effect in relation to the Alpha Coal Project is highly unlikely. 18. Hence, I reiterate my previously made point that the strong growth in the Australian mining industry is not primarily responsible for the decline in the Australian manufacturing sector. 19. With regards to the potential crowding out effects of the Alpha Coal Mine, the somewhat secondary impacts of the mining boom on the manufacturing sector were a result of confluence of resource sector investment activity across a large number of projects which has since peaked and is subsiding. As I stated in the JER the potential for this one single project to cause crowding out is limited; however despite this the risk has been addressed in the EIS. 20. The issue of structural adjustment within the Australian economy (that is the long term reorganisation of the structure of the Australian economy in terms of the relative size and 4 The reported influence on the Australian dollar of factors other than the Terms of Trade would tend to suggest that the impact on the tradables sector of the exchange rate appreciation is not wholly a Dutch Disease type phenomenon. 5 As I stated in my first individual statement industry capacity utilisation economy-wide is currently estimated at less than 80%, lowest levels since the GFC, while mining s industry capacity utilisation is approximately 75%. 5
6 contribution of component industry sectors) is not one that would be dealt with on a project by project basis because it requires coordinated consideration at the macro-economic level. Elasticity in Supply Markets 21. In paragraphs (g) and (h) on page 4 of the JER, Roderick Duncan makes comments regarding assumptions of perfect elasticity of supply and the likely absence (in his opinion) of indirect impacts of project purchases on the Queensland economy. 22. Elasticity refers to the responsiveness of changes in quantities demand or supplied to changes in prices (and vice versa). For example, say the price of petrol increased by 20% there would be a change in the amount of petrol consumed. Conversely, where the amount of petrol demand to increase by say 20% then the price of petrol would in all likelihood increase. 23. The issue of elasticities is a subtle one insofar as elasticities are not constant. Elasticities are a measure of the slope of the supply or demand curve from one point to another. Supply and demand curves are not linear, rather they are typically concave. Figure 2: Example of supply and demand curves Price Supply Quantity Demand 24. Because of the concave nature of supply and demand curves there are typically two measures of elasticity of relevance to economists, firstly point elasticity which relates to the changes in quantities supplied or demanded in response to marginal changes in prices (and vice versa), and secondly arc elasticity which is the changes in quantities supplied or demanded in response to significant changes in prices (and vice versa). 25. The point raised by Roderick Duncan relates to supplier markets. Roderick Duncan s point appears to be that the increase in demand for materials created by the Alpha Coal Mine is significant, and therefore the relevant elasticity is arc elasticity. Accordingly, Roderick Duncan implies that the increased demand for materials from suppliers would have a material impact on prices charged by suppliers, which would negatively affect demand from other projects. Hence there would be no net gain to production in Queensland. 6
7 26. To a lay person the Alpha Coal Mine appears to be a very large project, but in the broader context of the Queensland economy it represents a marginal change to the Queensland economy. For example, Queensland Gross State Product in was estimated at $258 billion 6, while the peak estimated value added effect of the supply chain stimulus of the Alpha Coal Mine in its first five years of operation is estimated in the EIS at approximately $0.92 billion 7. This represents approximately 0.35% of current Gross State Product. 27. In the context that industry capacity utilization is at comparatively low levels and the change across the broader economy is marginal, it would be more appropriate to consider elasticity in the context of a point elasticity. In the context of the supply curve illustrated above, supply markets with underutilized capacity that experience a marginal change in demand operate at the flatter part of the supply curve. The supply curve at that point is highly elastic as illustrated in Figure 3 shown below (Note: moving from Q 0 to Q 1 results in a very small change in price from P 0 to P 1 ). Hence, a small movement along the supply curve would not be accompanied by a material change in price - that is, the change in materials supplied would not have a material impact on prices and hence other projects would not be affected. Figure 3: Implications of a marginal change in quantity supplied on price Price Supply P 0 1 Demand Q 0 Q 1 Quantity Remuneration of Mining Workers 28. In the JER Roderick Duncan states, The skilled labour required for mining operations is not a type of labour in abundance in Australia, or those workers would not be earning the average annual income of over $100,000 that the ABS records workers in the sector as earning. 6 Australian Bureau of Statistics (2013), Australian National Accounts-State Accounts, Catalogue No Based on addition of 2017 construction and operational total value added impacts (that is including both direct and indirect impacts). 7
8 29. Roderick Duncan s inference that mining labour is in short supply in Australia is not consistent with ABS evidence (Catalogue no ) that mining employment has declined from a peak of approximately 277,000 mining workers in May 2012 to approximately 261,100 mining workers in Australia in May The remuneration of mine workers is driven by a number of factors apart from their skill levels, including: (a) (b) (c) The need to compensate workers for working in remote areas; A higher occupational health and safety risk than other lines of work; and A significant difference in average hours worked, when compared with workers in other industries. 31. Roderick Duncan s estimate of average mine worker income of $100,000 per annum appears to come from the 2011 Census of Population & Housing, although I cannot be sure of this in the absence of any referencing. 32. Assuming that Roderick Duncan s estimate relates to the 2011 Census data, according to the ABS (Catalogue No ) the average weekly hours worked by mining workers in Queensland during 2011 was approximately 44 hours per week as compared with: (a) (b) (c) (d) Queensland average hours worked of 34 hours per week; Queensland Manufacturing Industry average of 37 hours per week; Queensland construction industry average of 38 hours per week; and Utilities sector average of 37 hours per week. 33. The difference in hours worked alone accounts for 15% to 20% of the difference in remuneration. 34. Therefore, I consider Roderick Duncan's approach of simply inferring from a given average wage that labour of a particular type must be in short supply is inappropriate. Relevance of Scenario Analysis in the EIS 35. Roderick Duncan is critical that the analysis does not consider the various risks associated with the project. He does not specifically identify the risks he is concerned about. However, his individual statement suggests falling coal prices as a significant risk to the project s viability, a risk which, if realized, could see the mine prematurely close. 36. The regulatory environment guiding the approval and development of mines throughout Queensland incorporates a number of risk management and mitigation measure to address the issue alluded to by Roderick Duncan. For example, the Alpha coal mine will be subject to a remediation bond (which I understand is known as a 'financial assurance' under the Environmental Protection Act 1994 (Qld)) to ensure that the mine site is appropriately remediated in the event of the financial failure of the mine. Additionally, the mine approval is specific as to the operating parameters of the mine, with any significant departures from the approval requiring a further approval. Therefore, the EIS responds to the approval to being sought, not some other version of it. 8
9 37. Finally, the mine would be developed in stages meaning that, were the mine to prematurely close, the mine would not be fully developed; hence the adverse impacts of the mine in say environmental terms would be generally commensurate with the level of development achieved. 38. Hence, the regulatory framework addresses risk management issues, limiting their relevance to the EIS. 39. If a 'multi-scenario' approach was run with respect to the economic impact assessment, for consistency, it would seem appropriate and necessary to adopt the same approach for the various other impact assessments that comprise the broader EIS including, for example, groundwater, flora and fauna, etc. Given the lack of guidance (or sensible or obvious limit) as to the number or combination of 'scenarios' to assess, to me this would seem impracticable. 40. To the extent Roderick Duncan is suggesting that economic modelling would normally look at the profitability of the mine under various scenarios to determine the return the owner might expect, I consider this is a commercial risk for the owner of the mine to assess, and, in my experience, it is not common for an economic impact assessment under an EIS process to consider this. Rather, commonly economic impact assessments seek to identify the scope and scale of economic impacts on the economic environment and this is what has been done as part of the Alpha Coal Mine economic impact assessment. 41. It is important to note that the EIS responds to the requirements of a development approval process rather than determining whether a project is economically viable. 42. I note that Roderick Duncan has raised concerns about the ownership of the proponent and its implications for consideration of approving the mining lease. The application for a mining lease relates to the project, not the proponent. The ownership or control of a company with a mining lease can change (particularly if the company is publicly listed), furthermore approvals can be transferred. Concerns about foreign ownership of resource projects and the loss of project income through repatriation is largely misguided as pointed out by Gary Banks 8 (former Chairman of the Productivity Commission) who stated: Some have claimed that we are not benefiting from the mining boom because companies are foreign owned. But if this were the case, and income were going abroad, we wouldn t have a two speed economy. (page 2) 3. Expert's Statement I confirm the following: (a) (b) (c) the factual matters stated in this report are, as far as I know, true; I have made all enquiries that I consider appropriate; the opinions stated in this report are genuinely held by me; 8 Gary Banks, Chairman, Productivity Commission Address to the Melbourne Institute and the Australian Economic and Social Outlook Conference, 30 June
10 (d) (e) the report contains reference to all matters I consider significant; and I understand my duty to the court and have complied with the duty. Marcus Brown 20 August
Potential Output in Denmark
 43 Potential Output in Denmark Asger Lau Andersen and Morten Hedegaard Rasmussen, Economics 1 INTRODUCTION AND SUMMARY The concepts of potential output and output gap are among the most widely used concepts
43 Potential Output in Denmark Asger Lau Andersen and Morten Hedegaard Rasmussen, Economics 1 INTRODUCTION AND SUMMARY The concepts of potential output and output gap are among the most widely used concepts
Victoria University. David Gruen Australian Treasury 23 February Is the resources boom an example of Dutch
 The resources boom and structural change in the Australian economy Victoria University David Gruen Australian Treasury February Outline The resources boom Structural change in the Australian traded sector
The resources boom and structural change in the Australian economy Victoria University David Gruen Australian Treasury February Outline The resources boom Structural change in the Australian traded sector
2018 HSC Economics Marking Guidelines
 NSW Education Standards Authority 2018 HSC Economics Marking Guidelines Section I Multiple-choice Answer Key Question Answer 1 C 2 A 3 A 4 D 5 D 6 B 7 A 8 C 9 A 10 D 11 D 12 C 13 B 14 C 15 B 16 D 17 B
NSW Education Standards Authority 2018 HSC Economics Marking Guidelines Section I Multiple-choice Answer Key Question Answer 1 C 2 A 3 A 4 D 5 D 6 B 7 A 8 C 9 A 10 D 11 D 12 C 13 B 14 C 15 B 16 D 17 B
Hunter Economic Indicators
 Hunter Economic Indicators June Quarter 2017 Dr Anthea Bill, Lead Economist Presentation Friday 4 August 2017 Presentation outline International: moderate growth, Euro-zone improves National: GDP slows
Hunter Economic Indicators June Quarter 2017 Dr Anthea Bill, Lead Economist Presentation Friday 4 August 2017 Presentation outline International: moderate growth, Euro-zone improves National: GDP slows
Australian. Manufacturing. Sector. Executive Summary. Impacts of new and retained business in the
 Executive Summary Impacts of new and retained business in the Australian Since 1984, ICN has monitored the economic impact of its services and the benefits to the economy Manufacturing when a local supplier
Executive Summary Impacts of new and retained business in the Australian Since 1984, ICN has monitored the economic impact of its services and the benefits to the economy Manufacturing when a local supplier
Botswana s exchange rate policy
 BIS Botswana s exchange rate policy Kealeboga Masalila and Oduetse Motshidisi 1. Introduction In the construction of a market-based development strategy, a key policy consideration is the selection of
BIS Botswana s exchange rate policy Kealeboga Masalila and Oduetse Motshidisi 1. Introduction In the construction of a market-based development strategy, a key policy consideration is the selection of
Australia s productivity performance & drivers of future prosperity
 Australia s productivity performance & drivers of future prosperity ABS NatStats conference 16 September 2010 Session 3A: Policy, Finance and Productivity Saul Eslake Grattan Institute Australia s productivity
Australia s productivity performance & drivers of future prosperity ABS NatStats conference 16 September 2010 Session 3A: Policy, Finance and Productivity Saul Eslake Grattan Institute Australia s productivity
EQUIPMENT DEMAND INDEX
 THE ALLEASING EQUIPMENT DEMAND INDEX 2O17. SO FAR, SO GOOD APRIL 2O17 AUSTRALIA IT S ABOUT THE DOMESTIC ECONOMY When businesses decide to make an asset acquisition or not, what are the dominant factors
THE ALLEASING EQUIPMENT DEMAND INDEX 2O17. SO FAR, SO GOOD APRIL 2O17 AUSTRALIA IT S ABOUT THE DOMESTIC ECONOMY When businesses decide to make an asset acquisition or not, what are the dominant factors
: Monetary Economics and the European Union. Lecture 8. Instructor: Prof Robert Hill. The Costs and Benefits of Monetary Union II
 320.326: Monetary Economics and the European Union Lecture 8 Instructor: Prof Robert Hill The Costs and Benefits of Monetary Union II De Grauwe Chapters 3, 4, 5 1 1. Countries in Trouble in the Eurozone
320.326: Monetary Economics and the European Union Lecture 8 Instructor: Prof Robert Hill The Costs and Benefits of Monetary Union II De Grauwe Chapters 3, 4, 5 1 1. Countries in Trouble in the Eurozone
VICTORIAN BUILDING & CONSTRUCTION INDUSTRY OUTLOOK
 VICTORIAN BUILDING & CONSTRUCTION INDUSTRY OUTLOOK MARCH 2017 QUARTERLY UPDATE 15 JUNE 2017 PREPARED FOR THE MASTER BUILDERS ASSOCIATION OF VICTORIA STAFF RESPONSIBLE FOR THIS REPORT WERE: Director Senior
VICTORIAN BUILDING & CONSTRUCTION INDUSTRY OUTLOOK MARCH 2017 QUARTERLY UPDATE 15 JUNE 2017 PREPARED FOR THE MASTER BUILDERS ASSOCIATION OF VICTORIA STAFF RESPONSIBLE FOR THIS REPORT WERE: Director Senior
2017 VCE Economics examination report
 General comments The 2017 VCE Economics examination was the first for the new VCE Economics Study Design (2017 2021). The examination was generally well handled by the majority of students. Most students
General comments The 2017 VCE Economics examination was the first for the new VCE Economics Study Design (2017 2021). The examination was generally well handled by the majority of students. Most students
Article published in the Quarterly Review 2014:2, pp
 Estimating the Cyclically Adjusted Budget Balance Article published in the Quarterly Review 2014:2, pp. 59-66 BOX 6: ESTIMATING THE CYCLICALLY ADJUSTED BUDGET BALANCE 1 In the wake of the financial crisis,
Estimating the Cyclically Adjusted Budget Balance Article published in the Quarterly Review 2014:2, pp. 59-66 BOX 6: ESTIMATING THE CYCLICALLY ADJUSTED BUDGET BALANCE 1 In the wake of the financial crisis,
NAB MONTHLY BUSINESS SURVEY JUNE 2018
 EMBARGOED UNTIL: 11:3AM AEST, 1 JULY 218 NAB MONTHLY BUSINESS SURVEY JUNE 218 CONFIDENCE AND CONDITIONS HOLD STEADY NAB Australian Economics There was little change in headline business conditions and
EMBARGOED UNTIL: 11:3AM AEST, 1 JULY 218 NAB MONTHLY BUSINESS SURVEY JUNE 218 CONFIDENCE AND CONDITIONS HOLD STEADY NAB Australian Economics There was little change in headline business conditions and
Melbourne Mining Club Being lucky is not enough. Don Argus, Chairman 22 October 2009
 Melbourne Mining Club Being lucky is not enough Don Argus, Chairman 22 October 2009 Economic Activity Contracted in All Countries Global GDP Growth (%, Quarter-Over-Quarter, Annualised) 9 7 5 3 1 (1) (3)
Melbourne Mining Club Being lucky is not enough Don Argus, Chairman 22 October 2009 Economic Activity Contracted in All Countries Global GDP Growth (%, Quarter-Over-Quarter, Annualised) 9 7 5 3 1 (1) (3)
Table 1: Arithmetic contributions to June 2016 CPl inflation relative to the pre-crisis average
 BANK OF ENGLAND Mark Carney Governor The Rt Hon Philip Hammond Chancellor of the Exchequer HM Treasury 1 Horse Guards Road London SW1A2HQ 4 August 2016 On 19 July, the Office for National Statistics published
BANK OF ENGLAND Mark Carney Governor The Rt Hon Philip Hammond Chancellor of the Exchequer HM Treasury 1 Horse Guards Road London SW1A2HQ 4 August 2016 On 19 July, the Office for National Statistics published
9. IMPACT OF INCREASING THE MINIMUM WAGE
 9. IMPACT OF INCREASING THE MINIMUM WAGE [9.1] The ACTU has discussed a number of academic studies on the minimum wage in its submission which require a reply from employers. In dealing with this material,
9. IMPACT OF INCREASING THE MINIMUM WAGE [9.1] The ACTU has discussed a number of academic studies on the minimum wage in its submission which require a reply from employers. In dealing with this material,
SUBMISSION TO THE AUSTRALIAN INDUSTRIAL RELATIONS COMMISSION REGARDING THE ACTU LIVING WAGE APPLICATIONS. by Leigh Harkness
 SUBMISSION TO THE AUSTRALIAN INDUSTRIAL RELATIONS COMMISSION REGARDING THE ACTU LIVING WAGE APPLICATIONS 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1 Economic rational 1.1.1 This submission contends that wages generally, and award
SUBMISSION TO THE AUSTRALIAN INDUSTRIAL RELATIONS COMMISSION REGARDING THE ACTU LIVING WAGE APPLICATIONS 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1 Economic rational 1.1.1 This submission contends that wages generally, and award
CRS Report for Congress
 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Order Code RS21409 January 31, 2003 The Budget Deficit and the Trade Deficit: What Is Their Relationship? Summary Marc Labonte Analyst in Economics
CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Order Code RS21409 January 31, 2003 The Budget Deficit and the Trade Deficit: What Is Their Relationship? Summary Marc Labonte Analyst in Economics
Comprehensive Analysis on Australian Dollar
 Comprehensive Analysis on Australian Dollar Summary on AUD: Bearish This report is an analysis on the AUD/USD currency pair. Australia s currency is called a commodity currency as its economy depends on
Comprehensive Analysis on Australian Dollar Summary on AUD: Bearish This report is an analysis on the AUD/USD currency pair. Australia s currency is called a commodity currency as its economy depends on
Employment Outlook to November 2019
 Employment Outlook to November 2019 Based on the Department of Employment s 2015 employment projections Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 Introduction... 2 Projected employment growth by industry...
Employment Outlook to November 2019 Based on the Department of Employment s 2015 employment projections Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 Introduction... 2 Projected employment growth by industry...
CHANGING THE TAXATION REGIME FOR INVESTORS IN THE HOUSING MARKET
 CHANGING THE TAXATION REGIME FOR INVESTORS IN THE HOUSING MARKET BRIEFING REPORT FOR MASTER BUILDERS AUSTRALIA APRIL 2018 SUMMARY REPORT Housing affordability, particularly for first home buyers, is an
CHANGING THE TAXATION REGIME FOR INVESTORS IN THE HOUSING MARKET BRIEFING REPORT FOR MASTER BUILDERS AUSTRALIA APRIL 2018 SUMMARY REPORT Housing affordability, particularly for first home buyers, is an
Introduction. ECON204 Notes. Response to the GFC Crisis Monetary policy Cut interest rates Quantitative easing
 Introduction ECON204 Notes Response to the GFC Crisis Monetary policy Cut interest rates Quantitative easing Fiscal policy Governments spent and borrowed a lot Fiscal deficits funded by debt Many have
Introduction ECON204 Notes Response to the GFC Crisis Monetary policy Cut interest rates Quantitative easing Fiscal policy Governments spent and borrowed a lot Fiscal deficits funded by debt Many have
NAB MONTHLY BUSINESS SURVEY APRIL 2018 BUSINESS CONDITIONS AT RECORD LEVELS
 EMBARGOED UNTIL: 11:3AM AEST, 7 MAY 218 NAB MONTHLY BUSINESS SURVEY APRIL 218 BUSINESS CONDITIONS AT RECORD LEVELS NAB Australian Economics There was a significant improvement in business conditions in
EMBARGOED UNTIL: 11:3AM AEST, 7 MAY 218 NAB MONTHLY BUSINESS SURVEY APRIL 218 BUSINESS CONDITIONS AT RECORD LEVELS NAB Australian Economics There was a significant improvement in business conditions in
Glenn Stevens: The resources boom
 Glenn Stevens: The resources boom Remarks by Mr Glenn Stevens, Governor of the Reserve Bank of Australia, at the Victoria University public conference on The Resources Boom: Understanding National and
Glenn Stevens: The resources boom Remarks by Mr Glenn Stevens, Governor of the Reserve Bank of Australia, at the Victoria University public conference on The Resources Boom: Understanding National and
Growth and change. Australian jobs in Conrad Liveris conradliveris.com
 Growth and change Australian jobs in 2018 Conrad Liveris conradliveris.com +61 430 449 116 Executive Summary The labour market is more complex than month-to-month statistical releases. A more meaningful
Growth and change Australian jobs in 2018 Conrad Liveris conradliveris.com +61 430 449 116 Executive Summary The labour market is more complex than month-to-month statistical releases. A more meaningful
An analysis of Victoria s labour productivity performance
 An analysis of Victoria s labour productivity performance Presentation to a forum hosted by Victorian Department of Innovation, Industry and Regional Development Melbourne 14 th April Saul Eslake Program
An analysis of Victoria s labour productivity performance Presentation to a forum hosted by Victorian Department of Innovation, Industry and Regional Development Melbourne 14 th April Saul Eslake Program
The Long Term View. Patricia Scott Commissioner, Productivity Commission
 The Long Term View Patricia Scott Commissioner, Productivity Commission Melbourne Institute Economic and Social Outlook Conference 2 nd November 2012 Productivity Commission What is the Productivity Commission?
The Long Term View Patricia Scott Commissioner, Productivity Commission Melbourne Institute Economic and Social Outlook Conference 2 nd November 2012 Productivity Commission What is the Productivity Commission?
Diversification and Macro Policy Coordination Challenges
 Diversification and Macro Policy Coordination Challenges: An Illustration with the Experience of Argentina 23-214 Columbia IPD and Renmin University of China Conference Beijing August 29, 215 Motivation
Diversification and Macro Policy Coordination Challenges: An Illustration with the Experience of Argentina 23-214 Columbia IPD and Renmin University of China Conference Beijing August 29, 215 Motivation
Exam Number. Section
 Exam Number Section MACROECONOMICS IN THE GLOBAL ECONOMY Core Course Professor Antonio Fatás Final Exam February 24, 2011 9:00-12:00 Instructions: (PLEASE READ) SUGGESTED ANSWERS Space to answer the questions
Exam Number Section MACROECONOMICS IN THE GLOBAL ECONOMY Core Course Professor Antonio Fatás Final Exam February 24, 2011 9:00-12:00 Instructions: (PLEASE READ) SUGGESTED ANSWERS Space to answer the questions
Australia s productivity performance
 Australia s productivity performance Seminar Presentation to Australian Treasury Canberra, 22 nd September 2010 Saul Eslake Grattan Institute Australia s productivity growth has slowed over the last five
Australia s productivity performance Seminar Presentation to Australian Treasury Canberra, 22 nd September 2010 Saul Eslake Grattan Institute Australia s productivity growth has slowed over the last five
Economics is the study of decision making
 TOPIC 1 - INTRODUCTION TO THE GLOBAL ECONOMY WHAT IS ECONOMICS Economics is the study of decision making Every time we take a decision, we are choosing between at least two possibilities How do you take
TOPIC 1 - INTRODUCTION TO THE GLOBAL ECONOMY WHAT IS ECONOMICS Economics is the study of decision making Every time we take a decision, we are choosing between at least two possibilities How do you take
Economic Growth and Development Prof. Rajashree Bedamatta Department of Humanities and Social Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Economic Growth and Development Prof. Rajashree Bedamatta Department of Humanities and Social Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Lecture 01 Concepts of Economic Growth Hello and welcome
Economic Growth and Development Prof. Rajashree Bedamatta Department of Humanities and Social Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Lecture 01 Concepts of Economic Growth Hello and welcome
Business Expectations Survey March 2014 Summary Review
 Business Expectations Survey March 2014 Summary Review 1. Introduction The BES reports on current confidence levels among local businesses as well as their expectations of movements in key economic indicators.
Business Expectations Survey March 2014 Summary Review 1. Introduction The BES reports on current confidence levels among local businesses as well as their expectations of movements in key economic indicators.
Consumption expenditure The five most important variables that determine the level of consumption are:
 The aggregate expenditure model: A macroeconomic model that focuses on the relationship between total spending and real GDP, assuming the price level is constant. Macroeconomic equilibrium: AE = GDP Consumption
The aggregate expenditure model: A macroeconomic model that focuses on the relationship between total spending and real GDP, assuming the price level is constant. Macroeconomic equilibrium: AE = GDP Consumption
A HIGH YIELDING RESILIENT ECONOMY:
 A HIGH YIELDING RESILIENT ECONOMY: January 2017 BetaShares Strong Australian Dollar Fund (hedge fund) (ASX: AUDS) The BetaShares Strong Australian Dollar Fund (hedge fund) (ASX: AUDS) and the BetaShares
A HIGH YIELDING RESILIENT ECONOMY: January 2017 BetaShares Strong Australian Dollar Fund (hedge fund) (ASX: AUDS) The BetaShares Strong Australian Dollar Fund (hedge fund) (ASX: AUDS) and the BetaShares
Notes on the monetary transmission mechanism in the Czech economy
 Notes on the monetary transmission mechanism in the Czech economy Luděk Niedermayer 1 This paper discusses several empirical aspects of the monetary transmission mechanism in the Czech economy. The introduction
Notes on the monetary transmission mechanism in the Czech economy Luděk Niedermayer 1 This paper discusses several empirical aspects of the monetary transmission mechanism in the Czech economy. The introduction
$57.2bn. Why the US trade deficit is heading the wrong way. Economic and Financial Analysis
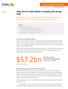 Economic and Financial Analysis 6 April 2018 Global Economics 6 April 2018 Article Why the US trade deficit is heading the wrong way Macroeconomic policy, not just trade barriers, affects the trade deficit.
Economic and Financial Analysis 6 April 2018 Global Economics 6 April 2018 Article Why the US trade deficit is heading the wrong way Macroeconomic policy, not just trade barriers, affects the trade deficit.
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science. August Examination 2006 ECO 209Y
 UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science August Examination 2006 ECO 209Y Duration: 2 hours Examination Aids allowed: Non-programmable calculators only INSTRUCTIONS: Students are required to answer
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science August Examination 2006 ECO 209Y Duration: 2 hours Examination Aids allowed: Non-programmable calculators only INSTRUCTIONS: Students are required to answer
Diamonds aren t Forever: A Dynamic CGE Analysis of the Mineral Sector in Botswana Preliminary DRAFT
 Diamonds aren t Forever: A Dynamic CGE Analysis of the Mineral Sector in Botswana Preliminary DRAFT Authors: Delfin Go (The World Bank) Scott McDonald (Oxford Brookes University) Karen Thierfelder (U.S.
Diamonds aren t Forever: A Dynamic CGE Analysis of the Mineral Sector in Botswana Preliminary DRAFT Authors: Delfin Go (The World Bank) Scott McDonald (Oxford Brookes University) Karen Thierfelder (U.S.
The reasons why inflation has moved away from the target, and the outlook for inflation.
 BANK OF ENGLAND Mark Carney Governor The Rt Hon Philip Hammond Chancellor of the Exchequer HM Treasury 1 Horse Guards Road London SW1A2HQ 8 February 2018 On 12 December, the Office for National Statistics
BANK OF ENGLAND Mark Carney Governor The Rt Hon Philip Hammond Chancellor of the Exchequer HM Treasury 1 Horse Guards Road London SW1A2HQ 8 February 2018 On 12 December, the Office for National Statistics
Research report South Australian Economic and Budget Outlook
 4 Research report South Australian Economic and Budget Outlook Associate Professor John Spoehr and Eric Parnis July 2010 Report prepared for: Public Service Association of South Australia AISR South Australian
4 Research report South Australian Economic and Budget Outlook Associate Professor John Spoehr and Eric Parnis July 2010 Report prepared for: Public Service Association of South Australia AISR South Australian
Submitted by Western Power
 Final Determination on the New Facilities Investment Test for a 66/11 kv Medical Centre Zone Substation Expansion and Voltage Conversion of the Distribution Network Submitted by Western Power 19 February
Final Determination on the New Facilities Investment Test for a 66/11 kv Medical Centre Zone Substation Expansion and Voltage Conversion of the Distribution Network Submitted by Western Power 19 February
Financing the U.S. Trade Deficit
 Order Code RL33274 Financing the U.S. Trade Deficit Updated January 31, 2008 James K. Jackson Specialist in International Trade and Finance Foreign Affairs, Defense, and Trade Division Financing the U.S.
Order Code RL33274 Financing the U.S. Trade Deficit Updated January 31, 2008 James K. Jackson Specialist in International Trade and Finance Foreign Affairs, Defense, and Trade Division Financing the U.S.
Competition Policy Review Panel Research Paper Summary. Author: Walid Hejazi, Rotman School of Management, University of Toronto
 Competition Policy Review Panel Research Paper Summary Author: Walid Hejazi, Rotman School of Management, University of Toronto Title: Inward Foreign Direct Investment and the Canadian Economy Subjects
Competition Policy Review Panel Research Paper Summary Author: Walid Hejazi, Rotman School of Management, University of Toronto Title: Inward Foreign Direct Investment and the Canadian Economy Subjects
Frameworks for economic impact analysis and benefit-cost analysis
 Frameworks for economic impact analysis and benefit-cost analysis A report prepared by Marsden Jacob Associates for the Economic Regulation Authority, WA 22 July 2005 This report has been prepared in accordance
Frameworks for economic impact analysis and benefit-cost analysis A report prepared by Marsden Jacob Associates for the Economic Regulation Authority, WA 22 July 2005 This report has been prepared in accordance
The Victorian economy and government financial position
 The n economy and government financial position Presentation to n Council of Social Service 26 Congress Saul Eslake Chief Economist ANZ RACV Centre Melbourne th August 26 4 th www.anz.com/go/economics
The n economy and government financial position Presentation to n Council of Social Service 26 Congress Saul Eslake Chief Economist ANZ RACV Centre Melbourne th August 26 4 th www.anz.com/go/economics
Macroeconomic Outlook: Implications for Agriculture. It has been 26 years since we have experienced a significant recession
 Macroeconomic Outlook: Implications for Agriculture John B. Penson, Jr. Regents Professor and Stiles Professor of Agriculture Texas A&M University Our Recession History September 1902 August1904 23 May
Macroeconomic Outlook: Implications for Agriculture John B. Penson, Jr. Regents Professor and Stiles Professor of Agriculture Texas A&M University Our Recession History September 1902 August1904 23 May
Chapter 77: HL extension Consequences of a change in the terms of trade (3.5)
 Chapter 77: HL extension Consequences of a change in the terms of trade (3.5) HL extensions Terms of trade and redistribution effects Terms of trade, PED and the balance of payments Terms of trade, commodities
Chapter 77: HL extension Consequences of a change in the terms of trade (3.5) HL extensions Terms of trade and redistribution effects Terms of trade, PED and the balance of payments Terms of trade, commodities
Global Macroeconomic Monthly Review
 Global Macroeconomic Monthly Review August 14 th, 2018 Arie Tal, Research Economist Capital Markets Division, Economics Department 1 Please see disclaimer on the last page of this report Key Issues Global
Global Macroeconomic Monthly Review August 14 th, 2018 Arie Tal, Research Economist Capital Markets Division, Economics Department 1 Please see disclaimer on the last page of this report Key Issues Global
Two New Indexes Offer a Broad View of Economic Activity in the New York New Jersey Region
 C URRENT IN ECONOMICS FEDERAL RESERVE BANK OF NEW YORK Second I SSUES AND FINANCE district highlights Volume 5 Number 14 October 1999 Two New Indexes Offer a Broad View of Economic Activity in the New
C URRENT IN ECONOMICS FEDERAL RESERVE BANK OF NEW YORK Second I SSUES AND FINANCE district highlights Volume 5 Number 14 October 1999 Two New Indexes Offer a Broad View of Economic Activity in the New
MANAGEMENT INFORMATION
 CERTIFICATE LEVEL EXAMINATION SAMPLE PAPER 3 (90 MINUTES) MANAGEMENT INFORMATION This assessment consists of ONE scenario based question worth 20 marks and 32 short questions each worth 2.5 marks. At least
CERTIFICATE LEVEL EXAMINATION SAMPLE PAPER 3 (90 MINUTES) MANAGEMENT INFORMATION This assessment consists of ONE scenario based question worth 20 marks and 32 short questions each worth 2.5 marks. At least
Mr. Bäckström explains why price stability ought to be a central bank s principle monetary policy objective
 Mr. Bäckström explains why price stability ought to be a central bank s principle monetary policy objective Address by the Governor of the Bank of Sweden, Mr. Urban Bäckström, at Handelsbanken seminar
Mr. Bäckström explains why price stability ought to be a central bank s principle monetary policy objective Address by the Governor of the Bank of Sweden, Mr. Urban Bäckström, at Handelsbanken seminar
20 July 2018 AUSTRALIAN ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS
 20 July 2018 AUSTRALIAN ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS This week the RBA reiterated its view that there is no case for a near-term change in the cash rate. Eventually the next move in the cash rate would more likely
20 July 2018 AUSTRALIAN ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS This week the RBA reiterated its view that there is no case for a near-term change in the cash rate. Eventually the next move in the cash rate would more likely
National Accounts - GDP A Game Changer?
 Wednesday, March 1 National Accounts - GDP A Game r? GDP growth was stronger than expected, rising by.% in the December quarter. Moreover, September s quarterly growth was revised upwards from.9% to 1.1%.
Wednesday, March 1 National Accounts - GDP A Game r? GDP growth was stronger than expected, rising by.% in the December quarter. Moreover, September s quarterly growth was revised upwards from.9% to 1.1%.
ECO401 Quiz # 5 February 15, 2010 Total questions: 15
 ECO401 Quiz # 5 February 15, 2010 Total questions: 15 Question # 1 of 15 ( Start time: 09:37:50 PM ) Total Marks: 1 Economic activity moves from a trough into a period of until it reaches a and then into
ECO401 Quiz # 5 February 15, 2010 Total questions: 15 Question # 1 of 15 ( Start time: 09:37:50 PM ) Total Marks: 1 Economic activity moves from a trough into a period of until it reaches a and then into
23 February 2018 AUSTRALIAN ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS. IMF updates assessment and forecasts for Australia
 AUSTRALIAN ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS 23 February 2018 This week the IMF updated its assessment of Australia s economy. It noted Australia has been relatively successful in adjusting to the end of the mining
AUSTRALIAN ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS 23 February 2018 This week the IMF updated its assessment of Australia s economy. It noted Australia has been relatively successful in adjusting to the end of the mining
Solution Problem Set #1
 INTB 334 Yoto V. Yotov Drexel University Solution Problem Set #1 This problem set is designed to help you master the concepts and tools covered in class so far and to prepare you better for the coming
INTB 334 Yoto V. Yotov Drexel University Solution Problem Set #1 This problem set is designed to help you master the concepts and tools covered in class so far and to prepare you better for the coming
Economics 2005 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION. Total marks 100. Section I. Pages 2 8
 2005 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION Economics Total marks 100 Section I Pages 2 8 General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time 3 hours Write using black or blue pen Board-approved calculators
2005 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION Economics Total marks 100 Section I Pages 2 8 General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time 3 hours Write using black or blue pen Board-approved calculators
Impact of Next Generation Infrastructure on Australian Cities
 Impact of Next Generation Infrastructure on Australian Cities ISNGI 2017 Institution of Civil Engineers, London 13 September 2017 Dr. Fariba Ramezani Associate Research Fellow SMART Infrastructure Facility
Impact of Next Generation Infrastructure on Australian Cities ISNGI 2017 Institution of Civil Engineers, London 13 September 2017 Dr. Fariba Ramezani Associate Research Fellow SMART Infrastructure Facility
Previsions Macroeconòmiques. Macroeconomic scenario for the Catalan economy 2017 and June 2017
 PM Previsions Macroeconòmiques Macroeconomic scenario for the Catalan economy 2017 and 2018 June 2017 Previsions macroeconòmiques Macroeconomic scenario for the Catalan economy June 2017 ISSN: 2013-2182
PM Previsions Macroeconòmiques Macroeconomic scenario for the Catalan economy 2017 and 2018 June 2017 Previsions macroeconòmiques Macroeconomic scenario for the Catalan economy June 2017 ISSN: 2013-2182
Monthly Bulletin of Economic Trends: Economic Activity in the Major States
 MELBOURNE INSTITUTE Applied Economic & Social Research Monthly Bulletin of Economic Trends: Economic Activity in the Major States January 2018 Monthly Bulletin of Economic Trends January 2018 Released
MELBOURNE INSTITUTE Applied Economic & Social Research Monthly Bulletin of Economic Trends: Economic Activity in the Major States January 2018 Monthly Bulletin of Economic Trends January 2018 Released
An overview of the South African macroeconomic. environment
 An overview of the South African macroeconomic environment 1 Study instruction Study Study guide: study unit 1 Study unit outcomes Once you have worked through this study unit, you should be able to give
An overview of the South African macroeconomic environment 1 Study instruction Study Study guide: study unit 1 Study unit outcomes Once you have worked through this study unit, you should be able to give
Model Question Paper Economics - II (MSF1A4)
 Model Question Paper Economics - II (MSF1A4) Answer all 74 questions. Marks are indicated against each question. 1. Which of the following is true if the central bank of a country sells government securities
Model Question Paper Economics - II (MSF1A4) Answer all 74 questions. Marks are indicated against each question. 1. Which of the following is true if the central bank of a country sells government securities
Macroeconomic Theory and Stabilization Policy. Multiple Choice Problems [Select the best alternative]
![Macroeconomic Theory and Stabilization Policy. Multiple Choice Problems [Select the best alternative] Macroeconomic Theory and Stabilization Policy. Multiple Choice Problems [Select the best alternative]](/thumbs/77/75538231.jpg) 1 Macroeconomic Theory and Stabilization Policy Module 1: Introduction Multiple Choice Problems [Select the best alternative] 1. In stagflation potential output of the economy declines. the inflation rate
1 Macroeconomic Theory and Stabilization Policy Module 1: Introduction Multiple Choice Problems [Select the best alternative] 1. In stagflation potential output of the economy declines. the inflation rate
ECONOMIC ANALYSIS OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA
 ECONOMIC ANALYSIS OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA DAVID OSBORNE, ROBERT HARDEN, CHRISTOPHER HOY PNG COUNTRY ASSESSMENT AUGUST 2017 The Lowy Institute is an independent policy think tank. Its mandate ranges across
ECONOMIC ANALYSIS OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA DAVID OSBORNE, ROBERT HARDEN, CHRISTOPHER HOY PNG COUNTRY ASSESSMENT AUGUST 2017 The Lowy Institute is an independent policy think tank. Its mandate ranges across
The Use of Profit by the Five Major Oil Companies
 Order Code RL34044 The Use of Profit by the Five Major Oil Companies June 19, 2007 Robert Pirog Specialist in Energy Economics and Policy Resources, Science, and Industry Division The Use of Profit by
Order Code RL34044 The Use of Profit by the Five Major Oil Companies June 19, 2007 Robert Pirog Specialist in Energy Economics and Policy Resources, Science, and Industry Division The Use of Profit by
Trade deficits and the US economy Part I
 Trade deficits and the US economy Part I by Michael Knetter Globalization is frequently identified as a primary force affecting the structure and development of the US economy as we enter a new millennium.
Trade deficits and the US economy Part I by Michael Knetter Globalization is frequently identified as a primary force affecting the structure and development of the US economy as we enter a new millennium.
Questions to Adani from Four Corners. Responses by Adani Spokesperson
 Questions to Adani from Four Corners Responses by Adani Spokesperson Q: Will the whole project- mine, rail and port development will attract finance? A: Yes. Q: Which entity or entities are committed to
Questions to Adani from Four Corners Responses by Adani Spokesperson Q: Will the whole project- mine, rail and port development will attract finance? A: Yes. Q: Which entity or entities are committed to
Synthesis for Macroeconomics Summary of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Relevance of Fiscal and Monetary Policy. Fernando Nandy T. Aldaba, Ph.
 Synthesis for Macroeconomics Summary of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Relevance of Fiscal and Monetary Policy Fernando Nandy T. Aldaba, Ph.D Senior Executives Class Batc 3 Sinagtala APPLIED PUBLIC
Synthesis for Macroeconomics Summary of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Relevance of Fiscal and Monetary Policy Fernando Nandy T. Aldaba, Ph.D Senior Executives Class Batc 3 Sinagtala APPLIED PUBLIC
MERCHANDISE EXPORTS OF ASEAN, CHINA AND INDIA 1. Highlights
 ASEAN Secretariat Studies unit brief Studies Unit Paper No. 10-2006 December 2006 MERCHANDISE EXPORTS OF ASEAN, CHINA AND INDIA 1 Highlights ASEAN: more open to external trade than China or India, and
ASEAN Secretariat Studies unit brief Studies Unit Paper No. 10-2006 December 2006 MERCHANDISE EXPORTS OF ASEAN, CHINA AND INDIA 1 Highlights ASEAN: more open to external trade than China or India, and
Ricardian Model part 1
 Lecture 2a: Ricardian Model part 1 Thibault FALLY C181 International Trade Spring 2018 In this chapter we will examine the following topics: Brief summary of reasons to trade and specialize Brief history
Lecture 2a: Ricardian Model part 1 Thibault FALLY C181 International Trade Spring 2018 In this chapter we will examine the following topics: Brief summary of reasons to trade and specialize Brief history
An updated estimate of the market risk premium
 An updated estimate of the market risk premium REPORT PREPARED FOR AURIZON NETWORK September 2017 Frontier Economics Pty. Ltd., Australia. i Frontier Economics September 2017 An updated estimate of the
An updated estimate of the market risk premium REPORT PREPARED FOR AURIZON NETWORK September 2017 Frontier Economics Pty. Ltd., Australia. i Frontier Economics September 2017 An updated estimate of the
2017 PNG Economic Survey. Rohan Fox (ANU), Stephen Howes (ANU), Nelson Atip Nema (UPNG), Marcel Schröder (UPNG and ANU)
 2017 PNG Economic Survey Rohan Fox (ANU), Stephen Howes (ANU), Nelson Atip Nema (UPNG), Marcel Schröder (UPNG and ANU) Introduction Survey is written at the time of a new government and new 100-day plan
2017 PNG Economic Survey Rohan Fox (ANU), Stephen Howes (ANU), Nelson Atip Nema (UPNG), Marcel Schröder (UPNG and ANU) Introduction Survey is written at the time of a new government and new 100-day plan
CIE Economics A-level
 CIE Economics A-level Topic 4: The Macroeconomy d) Employment and unemployment Notes Size and components of labour force The working age population is between the ages of 18 and 65 who are actively looking
CIE Economics A-level Topic 4: The Macroeconomy d) Employment and unemployment Notes Size and components of labour force The working age population is between the ages of 18 and 65 who are actively looking
EXTERNAL STABILITY & THE EXCHANGE RATE
 EXTERNAL STABILITY & THE EXCHANGE RATE Peter Kennedy Head Teacher Teaching & Learning CHHS HSC Senior Marker Economics Tutor Macquarie University 1 Australia s External Stability Let s start with some
EXTERNAL STABILITY & THE EXCHANGE RATE Peter Kennedy Head Teacher Teaching & Learning CHHS HSC Senior Marker Economics Tutor Macquarie University 1 Australia s External Stability Let s start with some
WEST AFRICAN SENIOR SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION ECONOMICS
 PREAMBLE This syllabus is designed to expose students to the basic economic principles as useful guide to rational decision-making relating to individuals, business, government and society in general;
PREAMBLE This syllabus is designed to expose students to the basic economic principles as useful guide to rational decision-making relating to individuals, business, government and society in general;
How to note. MACROECONOMICS NOTE No. 2. Macroeconomic Issues for Scaling-Up Aid Flows
 How to note Part of a series of four notes on macroeconomics for DFID staff OCTOBER 2004 MACROECONOMICS NOTE No. 2 Macroeconomic Issues for Scaling-Up Aid Flows This note is concerned with the macroeconomic
How to note Part of a series of four notes on macroeconomics for DFID staff OCTOBER 2004 MACROECONOMICS NOTE No. 2 Macroeconomic Issues for Scaling-Up Aid Flows This note is concerned with the macroeconomic
Chart 4: Other key indicators (Australia) Chart 5: Other key indicators (NSW FO firms v Other state FO firms)
 NAB MULTINATIONAL BUSINESS SURVEY December Quarter 216 (Embargoed until 11.3am Tuesday 14 th March) By Group Economics FOREIGN OWNED MULTINATIONALS ENJOY STRONG CONDITIONS IN THEIR AUSTRALIAN OPERATIONS.
NAB MULTINATIONAL BUSINESS SURVEY December Quarter 216 (Embargoed until 11.3am Tuesday 14 th March) By Group Economics FOREIGN OWNED MULTINATIONALS ENJOY STRONG CONDITIONS IN THEIR AUSTRALIAN OPERATIONS.
Economics 2006 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION. Total marks 100. Section I Pages 2 8
 2006 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION Economics Total marks 100 Section I Pages 2 8 General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time 3 hours Write using black or blue pen Board-approved calculators
2006 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION Economics Total marks 100 Section I Pages 2 8 General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time 3 hours Write using black or blue pen Board-approved calculators
2c Tax Incidence : General Equilibrium
 2c Tax Incidence : General Equilibrium Partial equilibrium tax incidence misses out on a lot of important aspects of economic activity. Among those aspects : markets are interrelated, so that prices of
2c Tax Incidence : General Equilibrium Partial equilibrium tax incidence misses out on a lot of important aspects of economic activity. Among those aspects : markets are interrelated, so that prices of
CRS Report for Congress
 Order Code RS21409 Updated March 24, 2005 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web The Budget Deficit and the Trade Deficit: What Is Their Relationship? Summary Marc Labonte and Gail Makinen
Order Code RS21409 Updated March 24, 2005 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web The Budget Deficit and the Trade Deficit: What Is Their Relationship? Summary Marc Labonte and Gail Makinen
Otaviano Canuto Vice President & Head of Network Poverty Reduction and Economic Management The World Bank
 Otaviano Canuto Vice President & Head of Network Poverty Reduction and Economic Management The World Bank The 11th International Academic Conference on Economic and Social Development April 6-8, 2010 Moscow
Otaviano Canuto Vice President & Head of Network Poverty Reduction and Economic Management The World Bank The 11th International Academic Conference on Economic and Social Development April 6-8, 2010 Moscow
The Yield Curve WHAT IT IS AND WHY IT MATTERS. UWA Student Managed Investment Fund ECONOMICS TEAM ALEX DYKES ARKA CHANDA ANDRE CHINNERY
 The Yield Curve WHAT IT IS AND WHY IT MATTERS UWA Student Managed Investment Fund ECONOMICS TEAM ALEX DYKES ARKA CHANDA ANDRE CHINNERY What is it? The Yield Curve: What It Is and Why It Matters The yield
The Yield Curve WHAT IT IS AND WHY IT MATTERS UWA Student Managed Investment Fund ECONOMICS TEAM ALEX DYKES ARKA CHANDA ANDRE CHINNERY What is it? The Yield Curve: What It Is and Why It Matters The yield
SUGGESTED ANSWERS TO PROBLEM SET
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA Economics 134 DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS Spring 2018 Professor David Romer SUGGESTED ANSWERS TO PROBLEM SET 1 1. a. The conditions indicate that we should consider the IS-MP model,
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA Economics 134 DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS Spring 2018 Professor David Romer SUGGESTED ANSWERS TO PROBLEM SET 1 1. a. The conditions indicate that we should consider the IS-MP model,
Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 6
 Department of Economics University of California, Berkeley Spring 2006 Economics 182 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 6 Problem 1: International diversification Because raspberries are nontradable, asset
Department of Economics University of California, Berkeley Spring 2006 Economics 182 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 6 Problem 1: International diversification Because raspberries are nontradable, asset
Economy Report - Malaysia
 Economy Report - Malaysia (Extracted from 2001 Economic Outlook) REAL GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT Economic activity in Malaysia expanded strongly in 2000 under the stimulus of strong export growth as well as
Economy Report - Malaysia (Extracted from 2001 Economic Outlook) REAL GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT Economic activity in Malaysia expanded strongly in 2000 under the stimulus of strong export growth as well as
QUEENSLAND SUNCORP GROUP CCIQ PULSE SURVEY OF BUSINESS CONDITIONS
 QUEENSLAND SUNCORP GROUP CCIQ PULSE SURVEY OF BUSINESS CONDITIONS DECEMBER QUARTER 16 SECTION 1 The CCIQ Pulse Survey of Business Conditions is the largest survey of businesses, providing critical insights
QUEENSLAND SUNCORP GROUP CCIQ PULSE SURVEY OF BUSINESS CONDITIONS DECEMBER QUARTER 16 SECTION 1 The CCIQ Pulse Survey of Business Conditions is the largest survey of businesses, providing critical insights
The U.S. Economy: An Optimistic Outlook, But With Some Important Risks
 EMBARGOED UNTIL 8:10 A.M. Eastern Time on Friday, April 13, 2018 OR UPON DELIVERY The U.S. Economy: An Optimistic Outlook, But With Some Important Risks Eric S. Rosengren President & Chief Executive Officer
EMBARGOED UNTIL 8:10 A.M. Eastern Time on Friday, April 13, 2018 OR UPON DELIVERY The U.S. Economy: An Optimistic Outlook, But With Some Important Risks Eric S. Rosengren President & Chief Executive Officer
Financing the U.S. Trade Deficit
 Order Code RL33274 Financing the U.S. Trade Deficit Updated September 4, 2007 James K. Jackson Specialist in International Trade and Finance Foreign Affairs, Defense, and Trade Division Financing the U.S.
Order Code RL33274 Financing the U.S. Trade Deficit Updated September 4, 2007 James K. Jackson Specialist in International Trade and Finance Foreign Affairs, Defense, and Trade Division Financing the U.S.
Appendix 4.2 Yukon Macroeconomic Model
 Appendix 4.2 Yukon Macroeconomic Model 2016 2035 14 July 2016 Revised: 16 March 2017 Executive Summary The Yukon Macroeconomic Model (MEM) is a tool for generating future economic and demographic indicators
Appendix 4.2 Yukon Macroeconomic Model 2016 2035 14 July 2016 Revised: 16 March 2017 Executive Summary The Yukon Macroeconomic Model (MEM) is a tool for generating future economic and demographic indicators
Monetary Policy Summary and minutes of the Monetary Policy Committee meeting ending on 13 December 2017
 Monetary Policy Summary and minutes of the Monetary Policy Committee meeting ending on 13 December 2017 Publication date: 14 December 2017 These are the minutes of the Monetary Policy Committee meeting
Monetary Policy Summary and minutes of the Monetary Policy Committee meeting ending on 13 December 2017 Publication date: 14 December 2017 These are the minutes of the Monetary Policy Committee meeting
Transcript of Larry Summers NBER Macro Annual 2018
 Transcript of Larry Summers NBER Macro Annual 2018 I salute the authors endeavor to use market price to examine the riskiness of the financial system and to evaluate the change in the subsidy represented
Transcript of Larry Summers NBER Macro Annual 2018 I salute the authors endeavor to use market price to examine the riskiness of the financial system and to evaluate the change in the subsidy represented
28 October 2016 AUSTRALIAN ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS. Inflation remains weak in the Q3 2016
 28 October 2016 AUSTRALIAN ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS This week s ABS inflation data (CPI) for the September quarter (Q3) showed headline inflation picking up to 1.3% p.a. (from 1.0% p.a.). Fruit and electricity
28 October 2016 AUSTRALIAN ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS This week s ABS inflation data (CPI) for the September quarter (Q3) showed headline inflation picking up to 1.3% p.a. (from 1.0% p.a.). Fruit and electricity
Christopher Kent: Financial conditions and the Australian dollar - recent developments
 Christopher Kent: Financial conditions and the Australian dollar - recent developments Address by Mr Christopher Kent, Assistant Governor (Financial Markets) of the Reserve Bank of Australia, to the XE
Christopher Kent: Financial conditions and the Australian dollar - recent developments Address by Mr Christopher Kent, Assistant Governor (Financial Markets) of the Reserve Bank of Australia, to the XE
27 March Dr Malcolm Roberts Chairman Queensland Competition Authority. Dear Malcolm. DBCT Post 85 Mtpa Expansion Study
 27 March 2013 Dr Malcolm Roberts Chairman Queensland Competition Authority Dear Malcolm DBCT Post 85 Mtpa Expansion Study On 23 September 2010, the Queensland Competition Authority (the Authority) approved
27 March 2013 Dr Malcolm Roberts Chairman Queensland Competition Authority Dear Malcolm DBCT Post 85 Mtpa Expansion Study On 23 September 2010, the Queensland Competition Authority (the Authority) approved
5. Bulgarian National Bank Forecast of Key
 5. Bulgarian National Bank Forecast of Key Macroeconomic Indicators for 2018 2020 The BNB forecast of key macroeconomic indicators is based on data published as of 15 June 2018. ECB, EC and IMF assumptions
5. Bulgarian National Bank Forecast of Key Macroeconomic Indicators for 2018 2020 The BNB forecast of key macroeconomic indicators is based on data published as of 15 June 2018. ECB, EC and IMF assumptions
Market Bulletin. Chinese yuan: Walking on a tight rope. 16 August 2016 MARKET INSIGHTS. In brief
 MARKET INSIGHTS Market Bulletin 16 August 2016 Chinese yuan: Walking on a tight rope In brief Recent trends suggest the Chinese authorities are allowing the Chinese yuan to depreciate against a basket
MARKET INSIGHTS Market Bulletin 16 August 2016 Chinese yuan: Walking on a tight rope In brief Recent trends suggest the Chinese authorities are allowing the Chinese yuan to depreciate against a basket
1: Challenges for Australia s tax system
 1: Challenges for Australia s tax system Overview This chapter sets out the major challenges that confront the Australian tax system. Key points Australia s tax system faces challenges from a changing
1: Challenges for Australia s tax system Overview This chapter sets out the major challenges that confront the Australian tax system. Key points Australia s tax system faces challenges from a changing
Attachment 7.4 Wage price index (WPI) and Consumer price index (CPI) forecasts Access Arrangement Information
 Attachment 7.4 Wage price index (WPI) and Consumer price index (CPI) forecasts Access Arrangement Information 2 October 2017 Access Arrangement Information (AAI) for the period 1 July 2017 to 30 June 2022
Attachment 7.4 Wage price index (WPI) and Consumer price index (CPI) forecasts Access Arrangement Information 2 October 2017 Access Arrangement Information (AAI) for the period 1 July 2017 to 30 June 2022
Online Appendix to: The Composition Effects of Tax-Based Consolidations on Income Inequality. June 19, 2017
 Online Appendix to: The Composition Effects of Tax-Based Consolidations on Income Inequality June 19, 2017 1 Table of contents 1 Robustness checks on baseline regression... 1 2 Robustness checks on composition
Online Appendix to: The Composition Effects of Tax-Based Consolidations on Income Inequality June 19, 2017 1 Table of contents 1 Robustness checks on baseline regression... 1 2 Robustness checks on composition
