Sandringham School Sixth Form. AS Maths. Bridging the gap
|
|
|
- Mark Horn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sandringham School Sixth Form AS Maths Bridging the gap
2 Section 1 - Factorising be able to factorise simple expressions be able to factorise quadratics The expression 4x + 8 can be written in factor form, the numbers 4 and x + 2 are the factors. The process of writing 4x + 8 in the form 4(x + 2) is called factorising. Example 1A Factorise (a) 6x + 10, (b) 2y + 12 (c) 5t 15 (d) 6a + 18 (e) ab + a 2 b (a) 6x (3x + 5) The number 2 divides into both terms of 6x + 10 (b) 2y (y 6) Notice the sign on both sides. (c) 5t 15 5(t + 3) Take care with the signs. You could also write 5( - t 3) (d) 6a (3a + 9) 6(a + 3) 2(3a + 9) is not completely factorised because (3a + 9) can be factorised as 3(a +3). (e) ab + a 2 b ab(1 a) a 2 b ab ab(a 1) Rearrange left hand side to move negative. ab divides both terms. Now have a go at section 1A questions 1,3,6,7,9 and 10. If the signs in a quadratic, for example x 2 + 7x + 10, are both positive, then the factors are of the form (x + )(x + ). If the sign of the constant term is positive, but the term involving x is negative, for example x 2 7x + 10,then the factors are of the form (x )(x ). If the sign of the constant term is negative, for example x 2 7x 10, or x 2 + 7x 10, then the factors are of the form (x )(x + ).
3 Example 1B Factorise (a) x 2 8x + 12, (b) x 2 + 3x 4, (c) x 2 7x 18 (x (a) )(x x 2 ). 8x + 12, x 2 8x + 12 (x 2)(x 6) The factors have the form (x -...) (x -...). 12 can be factorised as 1 x 12, 2 x 6, and 3 x 4. The possibilities are (x - 1) (x -12), (x - 2) (x -16) and (x - 3) (x - 4) Check which is correct. (b) x 2 + 3x 4, x 2 + 3x 4 (x 1)(x + 4) The factors have the form (x -...) (x +...). 4 can be factorised as 1 x 4, and 2 x 2. The possibilities are (x - 1) (x + 4), (x + 1) (x - 4), and (x - 2) (x + 2) Check which is correct. (c) x 2 7x 18, x 2 7x 18 (x 9)(x + 2) The factors have the form (x -...) (x +...). 18 can be factorised as 1 x 18, 2 x 9 and 3 x 6. The possibilities are (x - 1) (x + 18), (x - 18) (x + 1), (x - 2) (x + 9), (x - 9) (x + 2), (x - 3) (x + 6), (x - 6) (x + 3), Check which is correct. In practice, you would probably do much of the work in these examples in your head or on rough paper, and all you might write down is the very last line; the examples show the process in some detail. Now have a go at section 1B, questions, 11, 12, 14, 16, 17, 22, 23, 24 and 25.
4 Section 2 - The difference of two squares be able to apply the difference of two squares rule. Quadratics like x 2 16 and 100 4x 2 have no term involving x, and both the other terms are squares separated by a minus sign. They are referred to as the difference of two squares. Difference of two squares rule: x 2 k 2 (x + k)(x k) Example 2 Factorise (a) x 2 9, (b) 4x 2 81, (c) 25x 2 y 2 (d) (3y + 1) 2 (y + 2) 2 (a) x 2 9 (x + 3)(x 3) (b) 4x 2 81 (2x + 9)(2x 9) (c) 25x 2 y 2 (5x + y)(5x y) (d) (3y + 1) 2 (y + 2) 2 {(3y + 1) + (y + 2)}{(3y + 1) (y + 2)} {3y y + 2}{3y + 1 y 2} (4y + 3)(2y + 1) Use x 2 k 2 (x + k) (x k) with k 2 4x 2 81 is (2 x) Apply the difference of two squares rule. 25x 2 y 2 is (5 x) 2 y 2. Apply the difference of two squares rule. Use x 2 k 2 (x + k) (x k) with x 3y+ 1 and k y + 2. Then expand the inside brackets. Finally simplify the brackets. Now have a go at section 2,questions 1, 3, 4, 5 and 9.
5 Section 3 Changing the subject. be able to make x the subject of a formula A formula is a mathematical equation containing two or more letters, for example A(px + q) B The process for changing the subject of a formula is very similar to that for solving an equation. If there are brackets in it, then, just as with equations you should expand them first. Examples 1 In each case, make x the subject of the formula. (a) ax + a b + c (b) x+p p p q + q p (c) x2 a 2 y2 b 2 1 (a) ax + a b + c a + ax a b + c a ax b + c a x b+c a a Get the terms with x on one side, and everything else on the other. Do this by subtracting a from both sides. Divide through by a (b) x+p p p q + q p q(x + p) p 2 + q 2 qx + pq p 2 + q 2 qx p 2 + q 2 pq x p2 +q 2 pq q Recall that the fraction bar acts as a bracket, so put brackets in. Then multiply both sides by pq and cancel. Expand the bracket. Subtract pq from both sides. Divide both sides by q.
6 (c) x 2 a 2 y2 b 2 1 b 2 x 2 a 2 y 2 a 2 b 2 b 2 x 2 a 2 b 2 + a 2 y 2 x 2 a2 b 2 + a 2 y 2 b 2 x ± a2 b 2 + a 2 y 2 b 2 Clear the fractions by multiplying both sides by a 2 b 2. Then solve the equation for x 2. Finally, take the square root: the sign + means plus or minus, showing that there are two possible values of x. Now have a go at section 3, questions 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 9, 10, 12, 13 and 15. Section 4 Simplifying Algebraic Fractions. be able to simplify algebraic fractions by cancelling. Start by factorising the numerator and denominator if necessary. Then you can divide the numerator by any common factor to get the simplified fraction. Example Simplify 3x 2 8x + 4 6x 2 7x + 2 3x 2 8x + 4 6x 2 7x + 2 (x 2)(3x 2) (2x 1)(3x 2) x 2 2x 1 Factorise numerator and denominator Cancel common factors. Now have a go at section 4, questions 1, 3, 5, 7 and 9.
7 Section 5 Combining algebraic fractions be able to combine numbers and algebraic fractions be able to handle fractions that include brackets. Important rules to remember The multiplication rule for fractions is The division rule for fractions is a b c a c d b d ac bd a b c d a b d c ad bc The addition/ subtraction rule for fractions is a b ± c a d ± c b ad ± cb d bd bd Examples In each case express as a single fraction (a) 5 + x+2 x 1 (b) 2 + x+1 x 2 x 3 (c) x x 1 (x+3) 2 (x+3) (d) x2 6x 7 x 2 4 x2 x 2 x 2 7x (e) x 2 4 x 2 +3x+2 (x 2)2 x 2 +2x+1 (a) 5 + x+2 5(x 1)+(x 2) x 1 (x 1) 5x 5 + x 2 (x 1) 6x 7 x 1 The number 5 is the fraction 5 1. Multiply out brackets. Collect like terms.
8 (b) 2 + x+1 2(x 3)+(x+1)(x 2) x 2 x 3 (x 2)(x 3) 2x 6 + x2 x 2 (x 2)(x 3) x2 + x 8 (x 2)(x 3) The denominator is (x 2)(x 3) Multiply out brackets. Collect like terms. (c) x x 1 x(x+3) (x 1) (x+3) 2 (x+3) (x+3) 2 x2 + 3x x + 1 (x + 3) 2 x2 + 2x + 1 (x + 3) 2 (x + 1)2 (x + 3) 2 The denominator is (x + 3) 2 Multiply out brackets. Collect like terms. Factorise the top. (d) x2 6x 7 x 2 4 x2 x 2 x 2 7x (x+1)(x 7) (x+1)(x 2) (x 2)(x+2) (x)(x 7) (x + 1)2 x(x + 2) Factorise numerator and denominator where appropriate. Cancel common factors and apply rules for multiplying fractions. (e) x 2 4 (x 2)2 (x+2)(x 2) (x 2)2 x 2 +3x+2 x 2 +2x+1 (x+2)(x+1) (x+1) 2 (x + 2)(x 2) (x + 2)(x + 1) (x + 1) (x + 2) (x + 1)2 (x 2) 2 Factorise numerator and denominator where appropriate and apply rules for dividing fractions. Cancel common factors. Now have a go at section 5, questions 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 12, 18 and 19.
9 Section 6 Simultaneous equations Be able to solve simultaneous equations by both elimination and substitution. Be able to solve simultaneous equations where both equations are linear. Be able to solve simultaneous equations where one equation is linear and the other quadratic. Elimination In each case you need to reduce the equations to one involving x or y alone. This is called eliminating x or y. If you can t add or subtract to eliminate one of the letters straight away, chose the letter you want to eliminate and multiply one or both of the equations first to make the coefficients equal. Then you can eliminate that unknown. You may have to rearrange one of the equations so they are of a similar form. Example Solve the simultaneous equations 2x + 3y 1 7x y 2x + 3y 1 (1) 7x 5y 12 (2) 14x + 21y 7 (3) 14x 10y 24 (4) 31y 31 y 1 2x + 3 ( 1) 1 2x 3 1 2x 2 x 1. Rearrange the equations into a similar form. Multiply equation (1) by 7 and (2) by 2 to make the coefficients of x the same. Subtract (4) from (3) to eliminate x and solve to find y. Substitute y into a simpler equation and solve to find x. The solution is x 1, y 1.
10 Substitution This method is useful when one of the equations is a quadratic, but it can be used in examples like the one above. Rearrange the non-quadratic equation to find an expression for either x or y. Then substitute this into the quadratic and solve the resulting equation. Substitute the solutions to the quadratic back into the other equation to find the pairs of solutions required. Example Solve this pair of simultaneous equations. x 7 y (7 y) 2 + y 2 25 (49 14y + y 2 ) + y y 2 14y (2y 8)(y 3) 0 y 4 or y 3 When y 4, x When y 3, x Solutions are (3,4) or (4,3) x + y 7, x 2 + y 2 25 Rearrange to give x in terms of y. Substitute x into the quadratic. Multiply out the brackets. Collect like terms and factorise if possible. Solve to find y. Substitute y values into the nonquadratic equation to find pairs of solutions. Now have a go at section 6, questions 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10.
11 Section 7 know the rules for indices be able to simplify expressions that involve indices know the meaning of negative, zero and fractional indices be able to solve equations involving indices. You will have met all these rules before at GCSE, but it is essential you know them off by heart and are confident when using them. Rules for indices Addition rule for multiplication Subtraction rule for division The power-on-power rule The zero index Negative indices x m x n x m+n x m xm n xn (x m ) n x mn x 0 1, for all non-zero values of x. x n 1 x n Fractional indices x 1 n n x
12 Examples Evaluate (a) (b) ( ) 3 2 (C) write in the form 2 n (d) Solve 4 k+1 8 (a) Write as a fraction. Calculate the cube root of (b) ( 25 3 ) 2 ( 25 3 ) ( 5 7 ) Remember whole fraction is to the power of 3 2 Root then cube. (c) (2 2 ) 20 (2 3 ) (d) 4 k+1 8 (2 2 ) k+1 (2) 3 2 2k k k 1 2 Make the base of both the same. Use the power on power rule. Use the addition rule. Make bases the same. Use the power on power rule. Powers are equal. Solve to find k. Now have a go at section 7, questions 1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 9, 11 and 12.
13 Section 8 Surds be able to simplify expressions involving square roots. Be able to leave answers to questions in surd form A number written exactly using square roots is called a surd, e.g. 5 and Rules for surds Multiplication a b a b Examples Division a b a b (a) Express 28 in the form a b, (b) Work out and simplify (a) (b) Note Rationalising the denominator Simplified surds should never have a square root in the denominator. Simplifying the expression to remove the square root from the denominator is called rationalising. Examples (a) Rationalise 1 2 7, (b) Rationalise the denominator of (a) (b) (3 5) (3+ 5)(3 5) Note if the denominator contains an integer and a surd, then change the sign between them before multiplying top and bottom by them. (3 + 5)(3 5) Now have a go at section 8, questions 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 22, 27, 30, 31, 32.
14 Section 9 Solving quadratics by factorising. be able to solve quadratics by factorising. The simplest way to solve a quadratic is to factorise it if possible. Once it is factorised then use the fact that if the two factors multiply to give 0 then one of the factors must be zero. Example Solve x (x 1)(x + 4) x 2 + 3x 4 0 (x 1)(x + 4) 0 Either (x 1) 0 or (x + 4) 0 So x 1 or x 4 Factorise the quadratic. Make each factor equal to 0 and solve. Now have a go at section 9, questions 1, 4, 7, 9 and 10.
15 Section 10 Solving quadratics by completing the square. be able to solve quadratics by completing the square. Sometimes you need to solve a quadratic that does not factorise, one way of doing this is to complete the square. This method is also useful when you are asked to sketch the graph of a quadratic because it makes identifying the minimum/maximum point (vertex) and the line of symmetry easier. Example Solve x 2 6x by completing the square. x 2 6x Halve the coefficient of x, (-6) 2. Put it into a squared bracket with x, i.e. (x 3) Multiply this bracket out, i.e. x 2 6x Work out what you need to add/subtract to make this equal to the original equation, (-2) (x 2 6x + 9) 2 0 (x 3) (x 3) Put steps 2 and 4 together to give completed square form and solve the resulting equation. x 3 ± 2 x 3 ± 2 Now have a go at all of section 10.
16 Section 11 Solving quadratics using the formula. be able to solve quadratics by using the formula. The factorising method works well if the solutions are integers (whole numbers) or simple fractions. However, if there are no solutions, the solutions involve square roots or the coefficients are horrible then the quadratic formula should be used. The roots of the equation ax 2 + bx + c 0 are x b± b2 4ac 2a Example Use the quadratic formula to find the exact solutions to 2x 2 + 4x (a) 2x 2 + 4x Note x 4 ± ± ± ± The solutions are 1 ± or 1 ± Substitute a 1, b 4 and c1 into the formula. Leave the answer in surd form because this is exact, rounded decimals are not. Also be aware that in Core 1 you will not have a calculator. 1. A level questions will often ask for exact answers, this means if it contains a square root or pi, you should not turn it into a decimal. If it doesn t state otherwise it is ok to give decimal answers, work to 3 significant figures unless told differently. 2. You will not be given the formula you need to learn it. Now have a go at section 11, questions 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5.
1.4. Arithmetic of Algebraic Fractions. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Arithmetic of Algebraic Fractions 1.4 Introduction Just as one whole number divided by another is called a numerical fraction, so one algebraic expression divided by another is known as an algebraic fraction.
Arithmetic of Algebraic Fractions 1.4 Introduction Just as one whole number divided by another is called a numerical fraction, so one algebraic expression divided by another is known as an algebraic fraction.
ACCUPLACER Elementary Algebra Assessment Preparation Guide
 ACCUPLACER Elementary Algebra Assessment Preparation Guide Please note that the guide is for reference only and that it does not represent an exact match with the assessment content. The Assessment Centre
ACCUPLACER Elementary Algebra Assessment Preparation Guide Please note that the guide is for reference only and that it does not represent an exact match with the assessment content. The Assessment Centre
Chapter 2 Algebra Part 1
 Chapter 2 Algebra Part 1 Section 2.1 Expansion (Revision) In Mathematics EXPANSION really means MULTIPLY. For example 3(2x + 4) can be expanded by multiplying them out. Remember: There is an invisible
Chapter 2 Algebra Part 1 Section 2.1 Expansion (Revision) In Mathematics EXPANSION really means MULTIPLY. For example 3(2x + 4) can be expanded by multiplying them out. Remember: There is an invisible
CCAC ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA
 CCAC ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA Sample Questions TOPICS TO STUDY: Evaluate expressions Add, subtract, multiply, and divide polynomials Add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational expressions Factor two and three
CCAC ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA Sample Questions TOPICS TO STUDY: Evaluate expressions Add, subtract, multiply, and divide polynomials Add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational expressions Factor two and three
2-4 Completing the Square
 2-4 Completing the Square Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 2 Warm Up Write each expression as a trinomial. 1. (x 5) 2 x 2 10x + 25 2. (3x + 5) 2 9x 2 + 30x + 25 Factor each expression. 3.
2-4 Completing the Square Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 2 Warm Up Write each expression as a trinomial. 1. (x 5) 2 x 2 10x + 25 2. (3x + 5) 2 9x 2 + 30x + 25 Factor each expression. 3.
Quadratic Algebra Lesson #2
 Quadratic Algebra Lesson # Factorisation Of Quadratic Expressions Many of the previous expansions have resulted in expressions of the form ax + bx + c. Examples: x + 5x+6 4x 9 9x + 6x + 1 These are known
Quadratic Algebra Lesson # Factorisation Of Quadratic Expressions Many of the previous expansions have resulted in expressions of the form ax + bx + c. Examples: x + 5x+6 4x 9 9x + 6x + 1 These are known
S3 (3.1) Mutiplying out brackets & Factorising.notebook February 09, 2016
 Daily Practice 30.11.15 Q1. State the equation of the line that passes through (0, 8) and (3, 1) Q2. Simplify 500 Today we will be marking the check-up, homework and revising over multiplying out and simplifying.
Daily Practice 30.11.15 Q1. State the equation of the line that passes through (0, 8) and (3, 1) Q2. Simplify 500 Today we will be marking the check-up, homework and revising over multiplying out and simplifying.
FACTORISING EQUATIONS
 STRIVE FOR EXCELLENCE TUTORING www.striveforexcellence.com.au Factorising expressions with 2 terms FACTORISING EQUATIONS There are only 2 ways of factorising a quadratic with two terms: 1. Look for something
STRIVE FOR EXCELLENCE TUTORING www.striveforexcellence.com.au Factorising expressions with 2 terms FACTORISING EQUATIONS There are only 2 ways of factorising a quadratic with two terms: 1. Look for something
Accuplacer Review Workshop. Intermediate Algebra. Week Four. Includes internet links to instructional videos for additional resources:
 Accuplacer Review Workshop Intermediate Algebra Week Four Includes internet links to instructional videos for additional resources: http://www.mathispower4u.com (Arithmetic Video Library) http://www.purplemath.com
Accuplacer Review Workshop Intermediate Algebra Week Four Includes internet links to instructional videos for additional resources: http://www.mathispower4u.com (Arithmetic Video Library) http://www.purplemath.com
a*(variable) 2 + b*(variable) + c
 CH. 8. Factoring polynomials of the form: a*(variable) + b*(variable) + c Factor: 6x + 11x + 4 STEP 1: Is there a GCF of all terms? NO STEP : How many terms are there? Is it of degree? YES * Is it in the
CH. 8. Factoring polynomials of the form: a*(variable) + b*(variable) + c Factor: 6x + 11x + 4 STEP 1: Is there a GCF of all terms? NO STEP : How many terms are there? Is it of degree? YES * Is it in the
MATH 181-Quadratic Equations (7 )
 MATH 181-Quadratic Equations (7 ) 7.1 Solving a Quadratic Equation by Factoring I. Factoring Terms with Common Factors (Find the greatest common factor) a. 16 1x 4x = 4( 4 3x x ) 3 b. 14x y 35x y = 3 c.
MATH 181-Quadratic Equations (7 ) 7.1 Solving a Quadratic Equation by Factoring I. Factoring Terms with Common Factors (Find the greatest common factor) a. 16 1x 4x = 4( 4 3x x ) 3 b. 14x y 35x y = 3 c.
Decomposing Rational Expressions Into Partial Fractions
 Decomposing Rational Expressions Into Partial Fractions Say we are ked to add x to 4. The first step would be to write the two fractions in equivalent forms with the same denominators. Thus we write: x
Decomposing Rational Expressions Into Partial Fractions Say we are ked to add x to 4. The first step would be to write the two fractions in equivalent forms with the same denominators. Thus we write: x
Polynomial and Rational Expressions. College Algebra
 Polynomial and Rational Expressions College Algebra Polynomials A polynomial is an expression that can be written in the form a " x " + + a & x & + a ' x + a ( Each real number a i is called a coefficient.
Polynomial and Rational Expressions College Algebra Polynomials A polynomial is an expression that can be written in the form a " x " + + a & x & + a ' x + a ( Each real number a i is called a coefficient.
(8m 2 5m + 2) - (-10m 2 +7m 6) (8m 2 5m + 2) + (+10m 2-7m + 6)
 Adding Polynomials Adding & Subtracting Polynomials (Combining Like Terms) Subtracting Polynomials (if your nd polynomial is inside a set of parentheses). (x 8x + ) + (-x -x 7) FIRST, Identify the like
Adding Polynomials Adding & Subtracting Polynomials (Combining Like Terms) Subtracting Polynomials (if your nd polynomial is inside a set of parentheses). (x 8x + ) + (-x -x 7) FIRST, Identify the like
Edexcel past paper questions. Core Mathematics 4. Binomial Expansions
 Edexcel past paper questions Core Mathematics 4 Binomial Expansions Edited by: K V Kumaran Email: kvkumaran@gmail.com C4 Binomial Page Binomial Series C4 By the end of this unit you should be able to obtain
Edexcel past paper questions Core Mathematics 4 Binomial Expansions Edited by: K V Kumaran Email: kvkumaran@gmail.com C4 Binomial Page Binomial Series C4 By the end of this unit you should be able to obtain
Tool 1. Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
 Chapter 7: Factoring Review Tool 1 Greatest Common Factor (GCF) This is a very important tool. You must try to factor out the GCF first in every problem. Some problems do not have a GCF but many do. When
Chapter 7: Factoring Review Tool 1 Greatest Common Factor (GCF) This is a very important tool. You must try to factor out the GCF first in every problem. Some problems do not have a GCF but many do. When
Section 7.1 Common Factors in Polynomials
 Chapter 7 Factoring How Does GPS Work? 7.1 Common Factors in Polynomials 7.2 Difference of Two Squares 7.3 Perfect Trinomial Squares 7.4 Factoring Trinomials: (x 2 + bx + c) 7.5 Factoring Trinomials: (ax
Chapter 7 Factoring How Does GPS Work? 7.1 Common Factors in Polynomials 7.2 Difference of Two Squares 7.3 Perfect Trinomial Squares 7.4 Factoring Trinomials: (x 2 + bx + c) 7.5 Factoring Trinomials: (ax
5.1 Exponents and Scientific Notation
 5.1 Exponents and Scientific Notation Definition of an exponent a r = Example: Expand and simplify a) 3 4 b) ( 1 / 4 ) 2 c) (0.05) 3 d) (-3) 2 Difference between (-a) r (-a) r = and a r a r = Note: The
5.1 Exponents and Scientific Notation Definition of an exponent a r = Example: Expand and simplify a) 3 4 b) ( 1 / 4 ) 2 c) (0.05) 3 d) (-3) 2 Difference between (-a) r (-a) r = and a r a r = Note: The
Algebra Module A33. Factoring - 2. Copyright This publication The Northern Alberta Institute of Technology All Rights Reserved.
 Algebra Module A33 Factoring - 2 Copyright This publication The Northern Alberta Institute of Technology 2002. All Rights Reserved. LAST REVISED November, 2008 Factoring - 2 Statement of Prerequisite
Algebra Module A33 Factoring - 2 Copyright This publication The Northern Alberta Institute of Technology 2002. All Rights Reserved. LAST REVISED November, 2008 Factoring - 2 Statement of Prerequisite
3.1 Factors and Multiples of Whole Numbers
 3.1 Factors and Multiples of Whole Numbers LESSON FOCUS: Determine prime factors, greatest common factors, and least common multiples of whole numbers. The prime factorization of a natural number is the
3.1 Factors and Multiples of Whole Numbers LESSON FOCUS: Determine prime factors, greatest common factors, and least common multiples of whole numbers. The prime factorization of a natural number is the
Contents. Heinemann Maths Zone Copyright Pearson Australia (a divsion of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd)
 Contents Chapter Money calculations R. Expressing fractions as decimals R.2 Expressing decimals as fractions R.3 Operating with fractions R.4 Simple decimal arithmetic R.5 Ratio and fractions R.6 Dividing
Contents Chapter Money calculations R. Expressing fractions as decimals R.2 Expressing decimals as fractions R.3 Operating with fractions R.4 Simple decimal arithmetic R.5 Ratio and fractions R.6 Dividing
Algebra I EOC 10-Day STAAR Review. Hedgehog Learning
 Algebra I EOC 10-Day STAAR Review Hedgehog Learning Day 1 Day 2 STAAR Reporting Category Number and Algebraic Methods Readiness Standards 60% - 65% of STAAR A.10(E) - factor, if possible, trinomials with
Algebra I EOC 10-Day STAAR Review Hedgehog Learning Day 1 Day 2 STAAR Reporting Category Number and Algebraic Methods Readiness Standards 60% - 65% of STAAR A.10(E) - factor, if possible, trinomials with
Name. 5. Simplify. a) (6x)(2x 2 ) b) (5pq 2 )( 4p 2 q 2 ) c) (3ab)( 2ab 2 )(2a 3 ) d) ( 6x 2 yz)( 5y 3 z)
 3.1 Polynomials MATHPOWER TM 10, Ontario Edition, pp. 128 133 To add polynomials, collect like terms. To subtract a polynomial, add its opposite. To multiply monomials, multiply the numerical coefficients.
3.1 Polynomials MATHPOWER TM 10, Ontario Edition, pp. 128 133 To add polynomials, collect like terms. To subtract a polynomial, add its opposite. To multiply monomials, multiply the numerical coefficients.
TOPIC SKILLS R A G. Expand Double Brackets Including brackets with 3 terms. Squaring Brackets (x + 8) 2. Amber/Red Go to. Page 8-10.
 TOPIC SKILLS R A G Amber/Red Go to Expand Double Brackets Including brackets with 3 terms (x + 2)(x + 3) = x 2 + 2x + 3x + 6 = x 2 + 5x + 6 Page 8-10 (x + 2)(x 6) = x 2 + 2x 6x 12 = x 2 4x 12 (2x 8)(3x
TOPIC SKILLS R A G Amber/Red Go to Expand Double Brackets Including brackets with 3 terms (x + 2)(x + 3) = x 2 + 2x + 3x + 6 = x 2 + 5x + 6 Page 8-10 (x + 2)(x 6) = x 2 + 2x 6x 12 = x 2 4x 12 (2x 8)(3x
Chapter 6: Quadratic Functions & Their Algebra
 Chapter 6: Quadratic Functions & Their Algebra Topics: 1. Quadratic Function Review. Factoring: With Greatest Common Factor & Difference of Two Squares 3. Factoring: Trinomials 4. Complete Factoring 5.
Chapter 6: Quadratic Functions & Their Algebra Topics: 1. Quadratic Function Review. Factoring: With Greatest Common Factor & Difference of Two Squares 3. Factoring: Trinomials 4. Complete Factoring 5.
(x + 2)(x + 3) + (x + 2)(x + 3) 5(x + 3) (x + 2)(x + 3) + x(x + 2) 5x + 15 (x + 2)(x + 3) + x 2 + 2x. 5x x 2 + 2x. x 2 + 7x + 15 x 2 + 5x + 6
 Which is correct? Alex s add the numerators and the denominators way 5 x + 2 + x Morgan s find a common denominator way 5 x + 2 + x 5 x + 2 + x I added the numerator plus the numerator and the denominator
Which is correct? Alex s add the numerators and the denominators way 5 x + 2 + x Morgan s find a common denominator way 5 x + 2 + x 5 x + 2 + x I added the numerator plus the numerator and the denominator
Developmental Math An Open Program Unit 12 Factoring First Edition
 Developmental Math An Open Program Unit 12 Factoring First Edition Lesson 1 Introduction to Factoring TOPICS 12.1.1 Greatest Common Factor 1 Find the greatest common factor (GCF) of monomials. 2 Factor
Developmental Math An Open Program Unit 12 Factoring First Edition Lesson 1 Introduction to Factoring TOPICS 12.1.1 Greatest Common Factor 1 Find the greatest common factor (GCF) of monomials. 2 Factor
Worksheet A ALGEBRA PMT
 Worksheet A 1 Find the quotient obtained in dividing a (x 3 + 2x 2 x 2) by (x + 1) b (x 3 + 2x 2 9x + 2) by (x 2) c (20 + x + 3x 2 + x 3 ) by (x + 4) d (2x 3 x 2 4x + 3) by (x 1) e (6x 3 19x 2 73x + 90)
Worksheet A 1 Find the quotient obtained in dividing a (x 3 + 2x 2 x 2) by (x + 1) b (x 3 + 2x 2 9x + 2) by (x 2) c (20 + x + 3x 2 + x 3 ) by (x + 4) d (2x 3 x 2 4x + 3) by (x 1) e (6x 3 19x 2 73x + 90)
1.1 Forms for fractions px + q An expression of the form (x + r) (x + s) quadratic expression which factorises) may be written as
 1 Partial Fractions x 2 + 1 ny rational expression e.g. x (x 2 1) or x 4 x may be written () (x 3) as a sum of simpler fractions. This has uses in many areas e.g. integration or Laplace Transforms. The
1 Partial Fractions x 2 + 1 ny rational expression e.g. x (x 2 1) or x 4 x may be written () (x 3) as a sum of simpler fractions. This has uses in many areas e.g. integration or Laplace Transforms. The
Topic #1: Evaluating and Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
 John Jay College of Criminal Justice The City University of New York Department of Mathematics and Computer Science MAT 105 - College Algebra Departmental Final Examination Review Topic #1: Evaluating
John Jay College of Criminal Justice The City University of New York Department of Mathematics and Computer Science MAT 105 - College Algebra Departmental Final Examination Review Topic #1: Evaluating
Math 101, Basic Algebra Author: Debra Griffin
 Math 101, Basic Algebra Author: Debra Griffin Name Chapter 5 Factoring 5.1 Greatest Common Factor 2 GCF, factoring GCF, factoring common binomial factor 5.2 Factor by Grouping 5 5.3 Factoring Trinomials
Math 101, Basic Algebra Author: Debra Griffin Name Chapter 5 Factoring 5.1 Greatest Common Factor 2 GCF, factoring GCF, factoring common binomial factor 5.2 Factor by Grouping 5 5.3 Factoring Trinomials
Math 154 :: Elementary Algebra
 Math 1 :: Elementar Algebra Section.1 Exponents Section. Negative Exponents Section. Polnomials Section. Addition and Subtraction of Polnomials Section. Multiplication of Polnomials Section. Division of
Math 1 :: Elementar Algebra Section.1 Exponents Section. Negative Exponents Section. Polnomials Section. Addition and Subtraction of Polnomials Section. Multiplication of Polnomials Section. Division of
7.1 Simplifying Rational Expressions
 7.1 Simplifying Rational Expressions LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Determine the restrictions to the domain of a rational expression. 2. Simplify rational expressions. 3. Simplify expressions with opposite binomial
7.1 Simplifying Rational Expressions LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Determine the restrictions to the domain of a rational expression. 2. Simplify rational expressions. 3. Simplify expressions with opposite binomial
Alg2A Factoring and Equations Review Packet
 1 Factoring using GCF: Take the greatest common factor (GCF) for the numerical coefficient. When choosing the GCF for the variables, if all the terms have a common variable, take the one with the lowest
1 Factoring using GCF: Take the greatest common factor (GCF) for the numerical coefficient. When choosing the GCF for the variables, if all the terms have a common variable, take the one with the lowest
We begin, however, with the concept of prime factorization. Example: Determine the prime factorization of 12.
 Chapter 3: Factors and Products 3.1 Factors and Multiples of Whole Numbers In this chapter we will look at the topic of factors and products. In previous years, we examined these with only numbers, whereas
Chapter 3: Factors and Products 3.1 Factors and Multiples of Whole Numbers In this chapter we will look at the topic of factors and products. In previous years, we examined these with only numbers, whereas
GCSE Homework Unit 2 Foundation Tier Exercise Pack New AQA Syllabus
 GCSE Homework Unit 2 Foundation Tier Exercise Pack New AQA Syllabus The more negative a number, the smaller it is. The order of operations is Brackets, Indices, Division, Multiplication, Addition and Subtraction.
GCSE Homework Unit 2 Foundation Tier Exercise Pack New AQA Syllabus The more negative a number, the smaller it is. The order of operations is Brackets, Indices, Division, Multiplication, Addition and Subtraction.
Slide 1 / 128. Polynomials
 Slide 1 / 128 Polynomials Slide 2 / 128 Table of Contents Factors and GCF Factoring out GCF's Factoring Trinomials x 2 + bx + c Factoring Using Special Patterns Factoring Trinomials ax 2 + bx + c Factoring
Slide 1 / 128 Polynomials Slide 2 / 128 Table of Contents Factors and GCF Factoring out GCF's Factoring Trinomials x 2 + bx + c Factoring Using Special Patterns Factoring Trinomials ax 2 + bx + c Factoring
Contents. Heinemann Maths Zone
 Contents Chapter 1 Finance R1.1 Increasing a price by a percentage R1.2 Simple interest (1) R1.3 Simple interest (2) R1.4 Percentage profit (1) R1.5 Percentage profit (2) R1.6 The Distributive Law R1.7
Contents Chapter 1 Finance R1.1 Increasing a price by a percentage R1.2 Simple interest (1) R1.3 Simple interest (2) R1.4 Percentage profit (1) R1.5 Percentage profit (2) R1.6 The Distributive Law R1.7
(2/3) 3 ((1 7/8) 2 + 1/2) = (2/3) 3 ((8/8 7/8) 2 + 1/2) (Work from inner parentheses outward) = (2/3) 3 ((1/8) 2 + 1/2) = (8/27) (1/64 + 1/2)
 Exponents Problem: Show that 5. Solution: Remember, using our rules of exponents, 5 5, 5. Problems to Do: 1. Simplify each to a single fraction or number: (a) ( 1 ) 5 ( ) 5. And, since (b) + 9 + 1 5 /
Exponents Problem: Show that 5. Solution: Remember, using our rules of exponents, 5 5, 5. Problems to Do: 1. Simplify each to a single fraction or number: (a) ( 1 ) 5 ( ) 5. And, since (b) + 9 + 1 5 /
Name Date
 NEW DORP HIGH SCHOOL Deirdre A. DeAngelis, Principal MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT Li Pan, Assistant Principal Name Date Summer Math Assignment for a Student whose Official Class starts with 7, 8, and 9 Directions:
NEW DORP HIGH SCHOOL Deirdre A. DeAngelis, Principal MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT Li Pan, Assistant Principal Name Date Summer Math Assignment for a Student whose Official Class starts with 7, 8, and 9 Directions:
Unit 8 Notes: Solving Quadratics by Factoring Alg 1
 Unit 8 Notes: Solving Quadratics by Factoring Alg 1 Name Period Day Date Assignment (Due the next class meeting) Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Monday Tuesday
Unit 8 Notes: Solving Quadratics by Factoring Alg 1 Name Period Day Date Assignment (Due the next class meeting) Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Monday Tuesday
Mini-Lecture 6.1 The Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping
 Copyright 01 Pearson Education, Inc. Mini-Lecture 6.1 The Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping 1. Find the greatest common factor of a list of integers.. Find the greatest common factor of
Copyright 01 Pearson Education, Inc. Mini-Lecture 6.1 The Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping 1. Find the greatest common factor of a list of integers.. Find the greatest common factor of
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 10.1
 Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 10.1 Name Date Water Balloons Polynomials and Polynomial Functions Vocabulary Match each key term to its corresponding definition. 1. A polynomial written with
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 10.1 Name Date Water Balloons Polynomials and Polynomial Functions Vocabulary Match each key term to its corresponding definition. 1. A polynomial written with
Is the following a perfect cube? (use prime factorization to show if it is or isn't) 3456
 Is the following a perfect cube? (use prime factorization to show if it is or isn't) 3456 Oct 2 1:50 PM 1 Have you used algebra tiles before? X 2 X 2 X X X Oct 3 10:47 AM 2 Factor x 2 + 3x + 2 X 2 X X
Is the following a perfect cube? (use prime factorization to show if it is or isn't) 3456 Oct 2 1:50 PM 1 Have you used algebra tiles before? X 2 X 2 X X X Oct 3 10:47 AM 2 Factor x 2 + 3x + 2 X 2 X X
Downloaded from
 9. Algebraic Expressions and Identities Q 1 Using identity (x - a) (x + a) = x 2 a 2 find 6 2 5 2. Q 2 Find the product of (7x 4y) and (3x - 7y). Q 3 Using suitable identity find (a + 3)(a + 2). Q 4 Using
9. Algebraic Expressions and Identities Q 1 Using identity (x - a) (x + a) = x 2 a 2 find 6 2 5 2. Q 2 Find the product of (7x 4y) and (3x - 7y). Q 3 Using suitable identity find (a + 3)(a + 2). Q 4 Using
-5y 4 10y 3 7y 2 y 5: where y = -3-5(-3) 4 10(-3) 3 7(-3) 2 (-3) 5: Simplify -5(81) 10(-27) 7(9) (-3) 5: Evaluate = -200
 Polynomials: Objective Evaluate, add, subtract, multiply, and divide polynomials Definition: A Term is numbers or a product of numbers and/or variables. For example, 5x, 2y 2, -8, ab 4 c 2, etc. are all
Polynomials: Objective Evaluate, add, subtract, multiply, and divide polynomials Definition: A Term is numbers or a product of numbers and/or variables. For example, 5x, 2y 2, -8, ab 4 c 2, etc. are all
FACTORING HANDOUT. A General Factoring Strategy
 This Factoring Packet was made possible by a GRCC Faculty Excellence grant by Neesha Patel and Adrienne Palmer. FACTORING HANDOUT A General Factoring Strategy It is important to be able to recognize the
This Factoring Packet was made possible by a GRCC Faculty Excellence grant by Neesha Patel and Adrienne Palmer. FACTORING HANDOUT A General Factoring Strategy It is important to be able to recognize the
Mathematics Department A BLOCK EXAMINATION CORE MATHEMATICS PAPER 1 SEPTEMBER Time: 3 hours Marks: 150
 Mathematics Department A BLOCK EXAMINATION CORE MATHEMATICS PAPER 1 SEPTEMBER 2014 Examiner: Mr S B Coxon Moderator: Mr P Stevens Time: 3 hours Marks: 150 PLEASE READ THE INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY 1. This
Mathematics Department A BLOCK EXAMINATION CORE MATHEMATICS PAPER 1 SEPTEMBER 2014 Examiner: Mr S B Coxon Moderator: Mr P Stevens Time: 3 hours Marks: 150 PLEASE READ THE INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY 1. This
Equalities. Equalities
 Equalities Working with Equalities There are no special rules to remember when working with equalities, except for two things: When you add, subtract, multiply, or divide, you must perform the same operation
Equalities Working with Equalities There are no special rules to remember when working with equalities, except for two things: When you add, subtract, multiply, or divide, you must perform the same operation
Completing the Square. A trinomial that is the square of a binomial. x Square half the coefficient of x. AA65.pdf.
 AA65.pdf 6.5 Completing the Square 1. Converting from vertex form to standard form involves expanding the square of the binomial, distributing a, and then isolating y. What method does converting from
AA65.pdf 6.5 Completing the Square 1. Converting from vertex form to standard form involves expanding the square of the binomial, distributing a, and then isolating y. What method does converting from
Factoring is the process of changing a polynomial expression that is essentially a sum into an expression that is essentially a product.
 Ch. 8 Polynomial Factoring Sec. 1 Factoring is the process of changing a polynomial expression that is essentially a sum into an expression that is essentially a product. Factoring polynomials is not much
Ch. 8 Polynomial Factoring Sec. 1 Factoring is the process of changing a polynomial expression that is essentially a sum into an expression that is essentially a product. Factoring polynomials is not much
BINOMIAL SERIES PART 2
 BINOMIAL SERIES PART 2 SERIES 3 INU0114/514 (MATHS 1) Dr Adrian Jannetta MIMA CMath FRAS Binomial Series Part 2 1/ 28 Adrian Jannetta Objectives The purpose of this session is to introduce power series
BINOMIAL SERIES PART 2 SERIES 3 INU0114/514 (MATHS 1) Dr Adrian Jannetta MIMA CMath FRAS Binomial Series Part 2 1/ 28 Adrian Jannetta Objectives The purpose of this session is to introduce power series
Section 4.3 Objectives
 CHAPTER ~ Linear Equations in Two Variables Section Equation of a Line Section Objectives Write the equation of a line given its graph Write the equation of a line given its slope and y-intercept Write
CHAPTER ~ Linear Equations in Two Variables Section Equation of a Line Section Objectives Write the equation of a line given its graph Write the equation of a line given its slope and y-intercept Write
Question 3: How do you find the relative extrema of a function?
 Question 3: How do you find the relative extrema of a function? The strategy for tracking the sign of the derivative is useful for more than determining where a function is increasing or decreasing. It
Question 3: How do you find the relative extrema of a function? The strategy for tracking the sign of the derivative is useful for more than determining where a function is increasing or decreasing. It
Chapter 4 Partial Fractions
 Chapter 4 8 Partial Fraction Chapter 4 Partial Fractions 4. Introduction: A fraction is a symbol indicating the division of integers. For example,, are fractions and are called Common 9 Fraction. The dividend
Chapter 4 8 Partial Fraction Chapter 4 Partial Fractions 4. Introduction: A fraction is a symbol indicating the division of integers. For example,, are fractions and are called Common 9 Fraction. The dividend
Arithmetic Revision Sheet Questions 1 and 2 of Paper 1
 Arithmetic Revision Sheet Questions and of Paper Basics Factors/ Divisors Numbers that divide evenly into a number. Factors of,,,, 6, Factors of 8,,, 6, 9, 8 Highest Common Factor of and 8 is 6 Multiples
Arithmetic Revision Sheet Questions and of Paper Basics Factors/ Divisors Numbers that divide evenly into a number. Factors of,,,, 6, Factors of 8,,, 6, 9, 8 Highest Common Factor of and 8 is 6 Multiples
Factoring is the process of changing a polynomial expression that is essentially a sum into an expression that is essentially a product.
 Ch. 8 Polynomial Factoring Sec. 1 Factoring is the process of changing a polynomial expression that is essentially a sum into an expression that is essentially a product. Factoring polynomials is not much
Ch. 8 Polynomial Factoring Sec. 1 Factoring is the process of changing a polynomial expression that is essentially a sum into an expression that is essentially a product. Factoring polynomials is not much
Partial Fractions. A rational function is a fraction in which both the numerator and denominator are polynomials. For example, f ( x) = 4, g( x) =
 Partial Fractions A rational function is a fraction in which both the numerator and denominator are polynomials. For example, f ( x) = 4, g( x) = 3 x 2 x + 5, and h( x) = x + 26 x 2 are rational functions.
Partial Fractions A rational function is a fraction in which both the numerator and denominator are polynomials. For example, f ( x) = 4, g( x) = 3 x 2 x + 5, and h( x) = x + 26 x 2 are rational functions.
MATD 0370 ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA REVIEW FOR TEST 3 (New Material From: , , and 10.1)
 NOTE: In addition to the problems below, please study the handout Exercise Set 10.1 posted at http://www.austin.cc.tx.us/jbickham/handouts. 1. Simplify: 5 7 5. Simplify: ( 6ab 5 c )( a c 5 ). Simplify:
NOTE: In addition to the problems below, please study the handout Exercise Set 10.1 posted at http://www.austin.cc.tx.us/jbickham/handouts. 1. Simplify: 5 7 5. Simplify: ( 6ab 5 c )( a c 5 ). Simplify:
Section R.5 Review of Factoring. Factoring Out the Greatest Common Factor
 1 Section R.5 Review of Factoring Objective #1: Factoring Out the Greatest Common Factor The Greatest Common Factor (GCF) is the largest factor that can divide into the terms of an expression evenly with
1 Section R.5 Review of Factoring Objective #1: Factoring Out the Greatest Common Factor The Greatest Common Factor (GCF) is the largest factor that can divide into the terms of an expression evenly with
Unit 3: Writing Equations Chapter Review
 Unit 3: Writing Equations Chapter Review Part 1: Writing Equations in Slope Intercept Form. (Lesson 1) 1. Write an equation that represents the line on the graph. 2. Write an equation that has a slope
Unit 3: Writing Equations Chapter Review Part 1: Writing Equations in Slope Intercept Form. (Lesson 1) 1. Write an equation that represents the line on the graph. 2. Write an equation that has a slope
2.01 Products of Polynomials
 2.01 Products of Polynomials Recall from previous lessons that when algebraic expressions are added (or subtracted) they are called terms, while expressions that are multiplied are called factors. An algebraic
2.01 Products of Polynomials Recall from previous lessons that when algebraic expressions are added (or subtracted) they are called terms, while expressions that are multiplied are called factors. An algebraic
University of Phoenix Material
 1 University of Phoenix Material Factoring and Radical Expressions The goal of this week is to introduce the algebraic concept of factoring polynomials and simplifying radical expressions. Think of factoring
1 University of Phoenix Material Factoring and Radical Expressions The goal of this week is to introduce the algebraic concept of factoring polynomials and simplifying radical expressions. Think of factoring
Brackets and Factorising
 Brackets and Factorising Based on the quiz you have just done, give yourself a target: A1: I must learn to expand single brackets, such as 3(x + 5) A2: I must learn to expand double brackets, such as (x
Brackets and Factorising Based on the quiz you have just done, give yourself a target: A1: I must learn to expand single brackets, such as 3(x + 5) A2: I must learn to expand double brackets, such as (x
When Is Factoring Used?
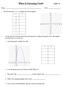 When Is Factoring Used? Name: DAY 9 Date: 1. Given the function, y = x 2 complete the table and graph. x y 2 1 0 1 2 3 1. A ball is thrown vertically upward from the ground according to the graph below.
When Is Factoring Used? Name: DAY 9 Date: 1. Given the function, y = x 2 complete the table and graph. x y 2 1 0 1 2 3 1. A ball is thrown vertically upward from the ground according to the graph below.
Factors of 10 = = 2 5 Possible pairs of factors:
 Factoring Trinomials Worksheet #1 1. b 2 + 8b + 7 Signs inside the two binomials are identical and positive. Factors of b 2 = b b Factors of 7 = 1 7 b 2 + 8b + 7 = (b + 1)(b + 7) 2. n 2 11n + 10 Signs
Factoring Trinomials Worksheet #1 1. b 2 + 8b + 7 Signs inside the two binomials are identical and positive. Factors of b 2 = b b Factors of 7 = 1 7 b 2 + 8b + 7 = (b + 1)(b + 7) 2. n 2 11n + 10 Signs
Chapter 6 Diagnostic Test
 Chapter 6 Diagnostic Test STUDENT BOOK PAGES 310 364 1. Consider the quadratic relation y = x 2 6x + 3. a) Use partial factoring to locate two points with the same y-coordinate on the graph. b) Determine
Chapter 6 Diagnostic Test STUDENT BOOK PAGES 310 364 1. Consider the quadratic relation y = x 2 6x + 3. a) Use partial factoring to locate two points with the same y-coordinate on the graph. b) Determine
Alg2A Factoring and Equations Review Packet
 1 Multiplying binomials: We have a special way of remembering how to multiply binomials called FOIL: F: first x x = x 2 (x + 7)(x + 5) O: outer x 5 = 5x I: inner 7 x = 7x x 2 + 5x +7x + 35 (then simplify)
1 Multiplying binomials: We have a special way of remembering how to multiply binomials called FOIL: F: first x x = x 2 (x + 7)(x + 5) O: outer x 5 = 5x I: inner 7 x = 7x x 2 + 5x +7x + 35 (then simplify)
Week 19 Algebra 2 Assignment:
 Week 9 Algebra Assignment: Day : pp. 66-67 #- odd, omit #, 7 Day : pp. 66-67 #- even, omit #8 Day : pp. 7-7 #- odd Day 4: pp. 7-7 #-4 even Day : pp. 77-79 #- odd, 7 Notes on Assignment: Pages 66-67: General
Week 9 Algebra Assignment: Day : pp. 66-67 #- odd, omit #, 7 Day : pp. 66-67 #- even, omit #8 Day : pp. 7-7 #- odd Day 4: pp. 7-7 #-4 even Day : pp. 77-79 #- odd, 7 Notes on Assignment: Pages 66-67: General
Math1090 Midterm 2 Review Sections , Solve the system of linear equations using Gauss-Jordan elimination.
 Math1090 Midterm 2 Review Sections 2.1-2.5, 3.1-3.3 1. Solve the system of linear equations using Gauss-Jordan elimination. 5x+20y 15z = 155 (a) 2x 7y+13z=85 3x+14y +6z= 43 x+z= 2 (b) x= 6 y+z=11 x y+
Math1090 Midterm 2 Review Sections 2.1-2.5, 3.1-3.3 1. Solve the system of linear equations using Gauss-Jordan elimination. 5x+20y 15z = 155 (a) 2x 7y+13z=85 3x+14y +6z= 43 x+z= 2 (b) x= 6 y+z=11 x y+
Common Core Algebra L clone 4 review R Final Exam
 1) Which graph represents an exponential function? A) B) 2) Which relation is a function? A) {(12, 13), (14, 19), (11, 17), (14, 17)} B) {(20, -2), (24, 10), (-21, -5), (22, 4)} C) {(34, 8), (32, -3),
1) Which graph represents an exponential function? A) B) 2) Which relation is a function? A) {(12, 13), (14, 19), (11, 17), (14, 17)} B) {(20, -2), (24, 10), (-21, -5), (22, 4)} C) {(34, 8), (32, -3),
Multiply the binomials. Add the middle terms. 2x 2 7x 6. Rewrite the middle term as 2x 2 a sum or difference of terms. 12x 321x 22
 Section 5.5 Factoring Trinomials 349 Factoring Trinomials 1. Factoring Trinomials: AC-Method In Section 5.4, we learned how to factor out the greatest common factor from a polynomial and how to factor
Section 5.5 Factoring Trinomials 349 Factoring Trinomials 1. Factoring Trinomials: AC-Method In Section 5.4, we learned how to factor out the greatest common factor from a polynomial and how to factor
Section 7.4 Additional Factoring Techniques
 Section 7.4 Additional Factoring Techniques Objectives In this section, you will learn to: To successfully complete this section, you need to understand: Factor trinomials when a = 1. Multiplying binomials
Section 7.4 Additional Factoring Techniques Objectives In this section, you will learn to: To successfully complete this section, you need to understand: Factor trinomials when a = 1. Multiplying binomials
Factor Trinomials When the Coefficient of the Second-Degree Term is 1 (Objective #1)
 Factoring Trinomials (5.2) Factor Trinomials When the Coefficient of the Second-Degree Term is 1 EXAMPLE #1: Factor the trinomials. = = Factor Trinomials When the Coefficient of the Second-Degree Term
Factoring Trinomials (5.2) Factor Trinomials When the Coefficient of the Second-Degree Term is 1 EXAMPLE #1: Factor the trinomials. = = Factor Trinomials When the Coefficient of the Second-Degree Term
UNIT 5 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Lesson 2: Creating and Solving Quadratic Equations in One Variable Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: multiplying polynomials working with complex numbers Introduction 2 b 2 A trinomial of the form x + bx + that can be written as
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: multiplying polynomials working with complex numbers Introduction 2 b 2 A trinomial of the form x + bx + that can be written as
Chapter 4 Factoring and Quadratic Equations
 Chapter 4 Factoring and Quadratic Equations Lesson 1: Factoring by GCF, DOTS, and Case I Lesson : Factoring by Grouping & Case II Lesson 3: Factoring by Sum and Difference of Perfect Cubes Lesson 4: Solving
Chapter 4 Factoring and Quadratic Equations Lesson 1: Factoring by GCF, DOTS, and Case I Lesson : Factoring by Grouping & Case II Lesson 3: Factoring by Sum and Difference of Perfect Cubes Lesson 4: Solving
Factoring Quadratic Expressions VOCABULARY
 5-5 Factoring Quadratic Expressions TEKS FOCUS Foundational to TEKS (4)(F) Solve quadratic and square root equations. TEKS (1)(C) Select tools, including real objects, manipulatives, paper and pencil,
5-5 Factoring Quadratic Expressions TEKS FOCUS Foundational to TEKS (4)(F) Solve quadratic and square root equations. TEKS (1)(C) Select tools, including real objects, manipulatives, paper and pencil,
Polynomial is a general description on any algebraic expression with 1 term or more. To add or subtract polynomials, we combine like terms.
 Polynomials Lesson 5.0 Re-Introduction to Polynomials Let s start with some definition. Monomial - an algebraic expression with ONE term. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Polynomials Lesson 5.0 Re-Introduction to Polynomials Let s start with some definition. Monomial - an algebraic expression with ONE term. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Final Project. College Algebra. Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to:
 COURSE OBJECTIVES Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: 1. Perform operations on algebraic expressions 2. Perform operations on functions expressed in standard function
COURSE OBJECTIVES Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: 1. Perform operations on algebraic expressions 2. Perform operations on functions expressed in standard function
SCHOOL OF ACCOUNTING AND BUSINESS BSc. (APPLIED ACCOUNTING) GENERAL / SPECIAL DEGREE PROGRAMME
 All Rights Reserved No. of Pages - 06 No of Questions - 06 SCHOOL OF ACCOUNTING AND BUSINESS BSc. (APPLIED ACCOUNTING) GENERAL / SPECIAL DEGREE PROGRAMME YEAR I SEMESTER I (Group B) END SEMESTER EXAMINATION
All Rights Reserved No. of Pages - 06 No of Questions - 06 SCHOOL OF ACCOUNTING AND BUSINESS BSc. (APPLIED ACCOUNTING) GENERAL / SPECIAL DEGREE PROGRAMME YEAR I SEMESTER I (Group B) END SEMESTER EXAMINATION
4.1 Write Linear Equations by Using a Tables of Values
 4.1 Write Linear Equations by Using a Tables of Values Review: Write y = mx + b by finding the slope and y-intercept m = b = y = x + Every time x changes units, y changes units m = b = y = x + Every time
4.1 Write Linear Equations by Using a Tables of Values Review: Write y = mx + b by finding the slope and y-intercept m = b = y = x + Every time x changes units, y changes units m = b = y = x + Every time
3.1 Solutions to Exercises
 .1 Solutions to Exercises 1. (a) f(x) will approach + as x approaches. (b) f(x) will still approach + as x approaches -, because any negative integer x will become positive if it is raised to an even exponent,
.1 Solutions to Exercises 1. (a) f(x) will approach + as x approaches. (b) f(x) will still approach + as x approaches -, because any negative integer x will become positive if it is raised to an even exponent,
SYLLABUS. Class B.Com. I Year(Hons) Business Mathematics
 SYLLABUS Class B.Com. I Year(Hons) Business Mathematics UNIT I Average, Ratio and Proportion, Percentage UNIT II Profit and Loss, Simple Interest, Compound Interest UNIT III UNIT IV UNIT V UNIT-I AVERAGE
SYLLABUS Class B.Com. I Year(Hons) Business Mathematics UNIT I Average, Ratio and Proportion, Percentage UNIT II Profit and Loss, Simple Interest, Compound Interest UNIT III UNIT IV UNIT V UNIT-I AVERAGE
3 Ways to Write Ratios
 RATIO & PROPORTION Sec 1. Defining Ratio & Proportion A RATIO is a comparison between two quantities. We use ratios every day; one Pepsi costs 50 cents describes a ratio. On a map, the legend might tell
RATIO & PROPORTION Sec 1. Defining Ratio & Proportion A RATIO is a comparison between two quantities. We use ratios every day; one Pepsi costs 50 cents describes a ratio. On a map, the legend might tell
TERMINOLOGY 4.1. READING ASSIGNMENT 4.2 Sections 5.4, 6.1 through 6.5. Binomial. Factor (verb) GCF. Monomial. Polynomial.
 Section 4. Factoring Polynomials TERMINOLOGY 4.1 Prerequisite Terms: Binomial Factor (verb) GCF Monomial Polynomial Trinomial READING ASSIGNMENT 4. Sections 5.4, 6.1 through 6.5 160 READING AND SELF-DISCOVERY
Section 4. Factoring Polynomials TERMINOLOGY 4.1 Prerequisite Terms: Binomial Factor (verb) GCF Monomial Polynomial Trinomial READING ASSIGNMENT 4. Sections 5.4, 6.1 through 6.5 160 READING AND SELF-DISCOVERY
Factoring completely is factoring a product down to a product of prime factors. 24 (2)(12) (2)(2)(6) (2)(2)(2)(3)
 Factoring Contents Introduction... 2 Factoring Polynomials... 4 Greatest Common Factor... 4 Factoring by Grouping... 5 Factoring a Trinomial with a Table... 5 Factoring a Trinomial with a Leading Coefficient
Factoring Contents Introduction... 2 Factoring Polynomials... 4 Greatest Common Factor... 4 Factoring by Grouping... 5 Factoring a Trinomial with a Table... 5 Factoring a Trinomial with a Leading Coefficient
3 Ways to Write Ratios
 RATIO & PROPORTION Sec 1. Defining Ratio & Proportion A RATIO is a comparison between two quantities. We use ratios everyday; one Pepsi costs 50 cents describes a ratio. On a map, the legend might tell
RATIO & PROPORTION Sec 1. Defining Ratio & Proportion A RATIO is a comparison between two quantities. We use ratios everyday; one Pepsi costs 50 cents describes a ratio. On a map, the legend might tell
Prerequisites. Introduction CHAPTER OUTLINE
 Prerequisites 1 Figure 1 Credit: Andreas Kambanls CHAPTER OUTLINE 1.1 Real Numbers: Algebra Essentials 1.2 Exponents and Scientific Notation 1.3 Radicals and Rational Expressions 1.4 Polynomials 1.5 Factoring
Prerequisites 1 Figure 1 Credit: Andreas Kambanls CHAPTER OUTLINE 1.1 Real Numbers: Algebra Essentials 1.2 Exponents and Scientific Notation 1.3 Radicals and Rational Expressions 1.4 Polynomials 1.5 Factoring
Name Class Date. Adding and Subtracting Polynomials
 8-1 Reteaching Adding and Subtracting Polynomials You can add and subtract polynomials by lining up like terms and then adding or subtracting each part separately. What is the simplified form of (3x 4x
8-1 Reteaching Adding and Subtracting Polynomials You can add and subtract polynomials by lining up like terms and then adding or subtracting each part separately. What is the simplified form of (3x 4x
Section 5.3 Practice Exercises Vocabulary and Key Concepts
 Section 5.3 Practice Exercises Vocabulary and Key Concepts 1. a. To multiply 2(4x 5), apply the property. b. The conjugate of 4x + 7 is. c. When two conjugates are multiplied the resulting binomial is
Section 5.3 Practice Exercises Vocabulary and Key Concepts 1. a. To multiply 2(4x 5), apply the property. b. The conjugate of 4x + 7 is. c. When two conjugates are multiplied the resulting binomial is
Multiplication of Polynomials
 Multiplication of Polynomials In multiplying polynomials, we need to consider the following cases: Case 1: Monomial times Polynomial In this case, you can use the distributive property and laws of exponents
Multiplication of Polynomials In multiplying polynomials, we need to consider the following cases: Case 1: Monomial times Polynomial In this case, you can use the distributive property and laws of exponents
Quadratic Functions. As review, we will look at the definition of a quadratic function. A quadratic function is a function f of the form
 Quadratic Functions To this point, we have had some experience with quadratic equations. We know that the graph of a quadratic equation gives us a parabola. In this section, we will see how quadratic equations
Quadratic Functions To this point, we have had some experience with quadratic equations. We know that the graph of a quadratic equation gives us a parabola. In this section, we will see how quadratic equations
MTH 110-College Algebra
 MTH 110-College Algebra Chapter R-Basic Concepts of Algebra R.1 I. Real Number System Please indicate if each of these numbers is a W (Whole number), R (Real number), Z (Integer), I (Irrational number),
MTH 110-College Algebra Chapter R-Basic Concepts of Algebra R.1 I. Real Number System Please indicate if each of these numbers is a W (Whole number), R (Real number), Z (Integer), I (Irrational number),
POD. Combine these like terms: 1) 3x 2 4x + 5x x 7x ) 7y 2 + 2y y + 5y 2. 3) 5x 4 + 2x x 7x 4 + 3x x
 POD Combine these like terms: 1) 3x 2 4x + 5x 2 6 + 9x 7x 2 + 2 2) 7y 2 + 2y 3 + 2 4y + 5y 2 3) 5x 4 + 2x 5 5 10x 7x 4 + 3x 5 12 + 2x 1 Definitions! Monomial: a single term ex: 4x Binomial: two terms separated
POD Combine these like terms: 1) 3x 2 4x + 5x 2 6 + 9x 7x 2 + 2 2) 7y 2 + 2y 3 + 2 4y + 5y 2 3) 5x 4 + 2x 5 5 10x 7x 4 + 3x 5 12 + 2x 1 Definitions! Monomial: a single term ex: 4x Binomial: two terms separated
Chapter 6.1: Introduction to parabolas and solving equations by factoring
 Chapter 6 Solving Quadratic Equations and Factoring Chapter 6.1: Introduction to parabolas and solving equations by factoring If you push a pen off a table, how does it fall? Does it fall like this? Or
Chapter 6 Solving Quadratic Equations and Factoring Chapter 6.1: Introduction to parabolas and solving equations by factoring If you push a pen off a table, how does it fall? Does it fall like this? Or
3.1 Solutions to Exercises
 .1 Solutions to Exercises 1. (a) f(x) will approach + as x approaches. (b) f(x) will still approach + as x approaches -, because any negative integer x will become positive if it is raised to an even exponent,
.1 Solutions to Exercises 1. (a) f(x) will approach + as x approaches. (b) f(x) will still approach + as x approaches -, because any negative integer x will become positive if it is raised to an even exponent,
Topic 12 Factorisation
 Topic 12 Factorisation 1. How to find the greatest common factors of an algebraic expression. Definition: A factor of a number is an integer that divides the number exactly. So for example, the factors
Topic 12 Factorisation 1. How to find the greatest common factors of an algebraic expression. Definition: A factor of a number is an integer that divides the number exactly. So for example, the factors
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL M ATHEMATICAL P RELIMINARIES. Chapter Objectives
 M ATHEMATICAL P RELIMINARIES. Some Mathematical Preliminaries. Arithmetic Operations.3 Fractions.4 Solving Equations.5 Currency Conversions.6 Simple Inequalities.7 Calculating Percentages.8 The Calculator.
M ATHEMATICAL P RELIMINARIES. Some Mathematical Preliminaries. Arithmetic Operations.3 Fractions.4 Solving Equations.5 Currency Conversions.6 Simple Inequalities.7 Calculating Percentages.8 The Calculator.
The Zero Product Law. Standards:
 Objective: Students will be able to (SWBAT) use complex numbers in polynomial identities and equations, in order to (IOT) solve quadratic equations with real coefficient that have complex solutions. Standards:
Objective: Students will be able to (SWBAT) use complex numbers in polynomial identities and equations, in order to (IOT) solve quadratic equations with real coefficient that have complex solutions. Standards:
MATD 0370 ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA REVIEW FOR TEST 3 (New Material From: , , and 10.1)
 NOTE: In addition to the problems below, please study the handout Exercise Set 10.1 posted at http://www.austincc.edu/jbickham/handouts. 1. Simplify: 5 7 5. Simplify: ( ab 5 c )( a c 5 ). Simplify: 4x
NOTE: In addition to the problems below, please study the handout Exercise Set 10.1 posted at http://www.austincc.edu/jbickham/handouts. 1. Simplify: 5 7 5. Simplify: ( ab 5 c )( a c 5 ). Simplify: 4x
