Economic Performance. Sherif Khalifa. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 1 / 55
|
|
|
- Hortense Stevens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 1 / 55
2 People earning higher income levels also enjoy higher living standards. To judge economic well being, we consider the total income of an economy. Economies with a larger output satisfy the demands of their inhabitants. Gross Domestic Product measures the total income and output of a nation. Gross Domestic product is the best assessment of economic performance. Provides a number for the dollar value of economic activity in a period of time. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 2 / 55
3 Definition Gross Domestic Product is the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period of time. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 3 / 55
4 Definition Gross Domestic Product is the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period of time. GDP adds together diverse products into one value of economic activity. The value of economic activity is calculated using market prices. Market prices is the amount people are willing to pay for products. Market prices reflect the value of those products to people. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 4 / 55
5 Definition Gross Domestic Product is the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period of time. GDP includes items produced and sold in markets legally. GDP excludes items produced and sold illicitly. GDP excludes items produced and consumed at home. GDP excludes items sold in black markets or informal markets. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 5 / 55
6 Definition Gross Domestic Product is the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period of time. Final goods are ready for consumption and intended for the end user. Intermediate goods are ingredients in the production of other goods. The value of intermediate goods is included in the prices of the final goods. GDP includes only the value of final goods to avoid double counting. An exception when an intermediate good is added to a firm s inventory for sale at a later date. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 6 / 55
7 Definition Gross Domestic Product is the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period of time. GDP includes tangible goods and intangible services. Tangible goods include durable and non-durable goods. Durable goods are goods that last for a long period of time. Non-durable goods are goods that do not last for a long period of time. Services include work done for consumers by individuals and by firms. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 7 / 55
8 Definition Gross Domestic Product is the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period of time. GDP includes goods and services currently produced. GDP does not include items produced in the past. GDP does not include the sale of old and used items. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 8 / 55
9 Definition Gross Domestic Product is the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period of time. GDP is the value of production within the geographic confines of a country. GDP includes items that are produced domestically by nationals and foreigners. The production of citizens abroad is not included in the GDP of the citizen s country. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 9 / 55
10 Definition Gross Domestic Product is the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period of time. GDP is the value of production that takes place within a specific interval of time, a year or a quarter. When GDP is reported for a quarter, it represents GDP at an annual rate. This is the amount of income and expenditure during a quarter multiplied by 4. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 10 / 55
11 The performance of the economy reflects the ability to produce more products. Gross Domestic Product increases from one year to another either because: 1 The economy is producing a larger quantity of goods and services. 2 Goods and services are being sold at higher prices. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 11 / 55
12 Definition Nominal GDP is the production of goods and services valued at current prices. Definition Nominal GDP uses current prices to place a value on the economy s production of goods and services. Nominal GDP 2017 = [(P 2017 Q 2017 ) Item1 + (P 2017 Q 2017 ) Item2 +...] Nominal GDP 2018 = [(P 2018 Q 2018 ) Item1 + (P 2018 Q 2018 ) Item2 +...] Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 12 / 55
13 Definition Real GDP is the production of goods and services valued at constant prices. Definition Real GDP uses constant base year prices to place a value on the economy s production of goods and services. Real GDP 2017 = [(P base Q 2017 ) Item1 + (P base Q 2017 ) Item2 +...] Real GDP 2018 = [(P base Q 2018 ) Item1 + (P base Q 2018 ) Item2 +...] Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 13 / 55
14 Billions $12,000 Nominal and Real GDP in the U.S., $10,000 $8,000 $6,000 Real GDP (base year 2000) $4,000 $2,000 Nominal GDP $ Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 14 / 55
15 Example Assume an economy produces hot dogs and burgers only. Calculate Nominal GDP and Real GDP. Year Hot Dogs Burgers Price Quantity Price Quantity 2015 $1 100 $ $2 150 $ $3 200 $4 150 Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 15 / 55
16 Year Hot Dogs Burgers Nominal GDP 2015 $1x100=$100 $2x50=$100 $ $2x150=$300 $3x100=$300 $ $3x200=$600 $4x150=$600 $1200 Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 16 / 55
17 Year Hot Dogs Burgers Real GDP 2015 $1x100=$100 $2x50=$100 $ $1x150=$150 $2x100=$200 $ $1x200=$200 $2x150=$300 $500 Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 17 / 55
18 Definition The GDP Deflator measures the current level of prices relative to the level of prices in the base year. [ ] Nominal GDP GDP Deflator = X 100 Real GDP [ ] (P2018 Q 2018 ) GDP Deflator 2018 = Item1 + (P 2018 Q 2018 ) Item X 100 (P base Q 2018 ) Item1 + (P base Q 2018 ) Item Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 18 / 55
19 Year Nominal GDP Real GDP ( GDP Deflator 2015 $200 $ ) 200 x100 = $600 $ $1200 $500 ( 600 ) 350 x100 =171 ( 1200 ) 500 x100 =240 Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 19 / 55
20 GDP does not take into account activity in black markets or informal markets. GDP does not take into account the effect of production on the environment. GDP does not take into account subsistence production and volunteer work. GDP does not take into account human happiness and life satisfaction. GDP does not take into account the impact of leisure on the quality of life. GDP does not take into account income inequality between rich and poor. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 20 / 55
21 GDP is the income of everyone in the economy and the total expenditure on the economy s output. Total expenditure has to equal total income because every transaction has a buyer and a seller. Every dollar of spending on a product by some buyer is a dollar of income for some seller. The expenditure of buyers on purchasing a product is income to the sellers of the product. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 21 / 55
22 Revenue (=GDP) G & S sold Markets for Goods & Services Spending (=GDP) G & S bought Firms Households Factors of production Wages, rent, profit (=GDP) Markets for Factors of Production Labor, land, capital Income (=GDP) Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 22 / 55
23 Economists care not only about the economy s total output but also about the allocation of this output among alternative uses. GDP is allocated among four categories: consumption spending, investment spending, government spending and net exports. These categories consider expenditure by domestic and foreign households, firms and governments on goods and services. This equation is an identity that holds at all times, and is called the national income accounts identity. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 23 / 55
24 Y : Gross Domestic Product C: Consumption Spending I : Investment Spending G: Government Spending NX : Net exports Y = C + I + G + NX Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 24 / 55
25 Definition Consumption Spending is spending by households on goods and services, with the exception of purchases of new housing. Goods include durable goods and non-durable goods. Durable goods are goods that last for a long period of time. Non-durable goods are goods that do not last a long period of time. A service is the non material equivalent of a good. A service is an economic activity that does not result in ownership. For renters, consumption includes rent payments. For homeowners, consumption includes the imputed rental value of the house. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 25 / 55
26 Definitions The relationship between consumption and disposable income is called the consumption function. C = C (Y T ) Definition The marginal propensity to consume is the amount by which consumption changes when disposable income increases by one dollar. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 26 / 55
27 C = C(Y T) depends on consumption spending by households C disposable income C C = = C( C( Y T) Y T) Y T The slope of the consumption function is the MPC. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 27 / 55
28 Definition Investment Spending is spending on capital equipment, structures, and inventories, and household purchases of new housing. Investment spending is divided into business fixed investment, residential investment, and changes in inventory. Business fixed investment is spending on new plant, factories, machines, equipment and tools by firms. Residential investment is the purchase of new housing by households and landlords. Residential investment includes the purchase price, down payment and mortgage payments. Inventory includes items produced in a given year, but may be sold in a later year. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 28 / 55
29 Definition The relationship between investment spending and the interest rate is called the investment function. I = I (r) Definition The interest rate measures the cost of the funds used to finance investment. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 29 / 55
30 Investment spending I = I(r) depends on real interest rate Real interest rate, r Investment function, I(r) Quantity of investment, I Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 30 / 55
31 Definition Government Spending is spending by local, state and federal governments on goods and services. Federal government spending includes defense and non-defense spending. State and local government spending includes only non-defense spending. Non defense includes the salaries of government workers and spending on public works. Excludes transfer payments, such as social security or unemployment benefits. Transfer payments are not made in exchange for a currently produced good or service. Government spending depends on the government ideology and the budget deficit. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 31 / 55
32 Definition Net Exports equal the purchases of domestically produced goods by foreigners minus the domestic purchases of foreign goods. Net Exports = Exports Imports The purchases of domestically produced goods by foreigners is a country s exports. The domestic purchases of foreign goods is a country s imports. When a household, a firm or the government buys a good or a service from abroad, it increases imports. This also increases either consumption, investment, or government spending, and does not affect GDP. The trade balance depends on trade policy, the exchange rate and transportation costs. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 32 / 55
33 Gross Domestic Product Personal Consumption Expenditures Durable Goods (Cars, Household Durables, Computers) Nondurable Goods (Food & Clothes) Services (Travel, Entertainment, Imputed Costs Of Home Ownership) Gross Private Domestic Investment Fixed Investment Nonresidential Structures Equipment & Software Residential Change In Private Inventories (End Of Period To End Of Period) Government Consumption Expenditures & Gross Investment Federal National Defense Nondefense State & Local Net Exports Of Goods & Services Exports Goods Services Imports Goods Services Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 33 / 55
34 Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 34 / 55
35 Y = Wage + Rent + Interest + Profit Compensation of employees or wages and fringe benefits earned by workers. Proprietor s income which is the income of non-corporate businesses. Rental income include the imputed rent that homeowners pay to themselves less depreciation. Corporate profits is the income of corporations after payments to their workers and creditors. Net interest is the interest businesses pay less the interest they receive, plus interest earned from foreigners. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 35 / 55
36 GDP exclusively measures the market value of finished goods and services. GDP completely captures the net contributions or the value added of intermediate producers. Total dollars spent on finished goods and services equals the total dollars collected by economic entities involved in the production of economic output. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 36 / 55
37 An economy solely in the business of the production and sale of rocking chairs. Value Price Income Wage Rent Interest Profits Added Alpha $10 $10 $10 $8 $1 $1 Lumber Beta $60 $70 $60 $55 $5 Furniture Gamma $30 $100 $30 $20 $2 $3 $5 Retailer Total $100 $100 $83 $3 $3 $11 Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 37 / 55
38 Example Drug Lords increase their production and sale of cocaine. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 38 / 55
39 Example Drug Lords increase their production and sale of cocaine. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 38 / 55
40 Example Drug Lords increase their production and sale of cocaine. A cattle rancher sells beef to McDonald s to prepare Big Macs. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 38 / 55
41 Example Drug Lords increase their production and sale of cocaine. A cattle rancher sells beef to McDonald s to prepare Big Macs. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 38 / 55
42 Example Drug Lords increase their production and sale of cocaine. A cattle rancher sells beef to McDonald s to prepare Big Macs. A company increases production of paper used in Hallmark cards. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 38 / 55
43 Example Drug Lords increase their production and sale of cocaine. A cattle rancher sells beef to McDonald s to prepare Big Macs. A company increases production of paper used in Hallmark cards. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 38 / 55
44 Example Drug Lords increase their production and sale of cocaine. A cattle rancher sells beef to McDonald s to prepare Big Macs. A company increases production of paper used in Hallmark cards. A chef cooks a gourmet meal to his family. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 38 / 55
45 Example Drug Lords increase their production and sale of cocaine. A cattle rancher sells beef to McDonald s to prepare Big Macs. A company increases production of paper used in Hallmark cards. A chef cooks a gourmet meal to his family. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 38 / 55
46 Example Drug Lords increase their production and sale of cocaine. A cattle rancher sells beef to McDonald s to prepare Big Macs. A company increases production of paper used in Hallmark cards. A chef cooks a gourmet meal to his family. You grow oranges in your garden that your kids eat. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 38 / 55
47 Example Drug Lords increase their production and sale of cocaine. A cattle rancher sells beef to McDonald s to prepare Big Macs. A company increases production of paper used in Hallmark cards. A chef cooks a gourmet meal to his family. You grow oranges in your garden that your kids eat. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 38 / 55
48 Example A collector sells a Mickey Mantle card to another collector. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 39 / 55
49 Example A collector sells a Mickey Mantle card to another collector. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 39 / 55
50 Example A collector sells a Mickey Mantle card to another collector. Ford produces cars in France. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 39 / 55
51 Example A collector sells a Mickey Mantle card to another collector. Ford produces cars in France. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 39 / 55
52 Example A collector sells a Mickey Mantle card to another collector. Ford produces cars in France. A family buys a new car. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 39 / 55
53 Example A collector sells a Mickey Mantle card to another collector. Ford produces cars in France. A family buys a new car. Consumption. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 39 / 55
54 Example A collector sells a Mickey Mantle card to another collector. Ford produces cars in France. A family buys a new car. Consumption. A family buys a new house. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 39 / 55
55 Example A collector sells a Mickey Mantle card to another collector. Ford produces cars in France. A family buys a new car. Consumption. A family buys a new house. Investment. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 39 / 55
56 Example A collector sells a Mickey Mantle card to another collector. Ford produces cars in France. A family buys a new car. Consumption. A family buys a new house. Investment. Ford expands its factory. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 39 / 55
57 Example A collector sells a Mickey Mantle card to another collector. Ford produces cars in France. A family buys a new car. Consumption. A family buys a new house. Investment. Ford expands its factory. Investment. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 39 / 55
58 Example Ford adds some Mustang cars to its inventory. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 40 / 55
59 Example Ford adds some Mustang cars to its inventory. Investment. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 40 / 55
60 Example Ford adds some Mustang cars to its inventory. Investment. Ford sells a Mustang car from its inventory. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 40 / 55
61 Example Ford adds some Mustang cars to its inventory. Investment. Ford sells a Mustang car from its inventory. Investment & Consumption. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 40 / 55
62 Example Ford adds some Mustang cars to its inventory. Investment. Ford sells a Mustang car from its inventory. Investment & Consumption. California paves Highway 101. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 40 / 55
63 Example Ford adds some Mustang cars to its inventory. Investment. Ford sells a Mustang car from its inventory. Investment & Consumption. California paves Highway 101. Government Expenditure. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 40 / 55
64 Example Ford adds some Mustang cars to its inventory. Investment. Ford sells a Mustang car from its inventory. Investment & Consumption. California paves Highway 101. Government Expenditure. You buy a bottle of French wine. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 40 / 55
65 Example Ford adds some Mustang cars to its inventory. Investment. Ford sells a Mustang car from its inventory. Investment & Consumption. California paves Highway 101. Government Expenditure. You buy a bottle of French wine. Imports & Consumption. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 40 / 55
66 Example Ford adds some Mustang cars to its inventory. Investment. Ford sells a Mustang car from its inventory. Investment & Consumption. California paves Highway 101. Government Expenditure. You buy a bottle of French wine. Imports & Consumption. Federal Government increases unemployment benefits. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 40 / 55
67 Example Ford adds some Mustang cars to its inventory. Investment. Ford sells a Mustang car from its inventory. Investment & Consumption. California paves Highway 101. Government Expenditure. You buy a bottle of French wine. Imports & Consumption. Federal Government increases unemployment benefits. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 40 / 55
68 Definition Gross Domestic Product GDP is total income earned domestically. GDP includes income earned domestically by foreigners, but it does not include income earned by nationals abroad. Definition Gross National Product GNP is the market value of all final goods and services produced by factors of production owned by a country s citizens. Definition Gross National Product GNP is total income earned by nationals. GNP includes the income that nationals earn abroad, but it does not include the income earned by foreigners within a country. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 41 / 55
69 Definition Net National Product NNP is the market value of all final goods and services produced by factors of production owned by a country s citizens, after depreciation of capital has been allowed for. Definition Depreciation is the amount of the economy s stock of plants, equipment and residential structures that wears out during the year. NNP = GNP Depreciation Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 42 / 55
70 Gross Domestic Product (Flow Of Output On U.S. Soil) Plus: Income Receipts From The Rest Of World (e.i. IBM Profits Earned In Europe) Less: Income Payments To The Rest Of World (e.i. U.S. Government Interest Payment To Japanese Owners Of Treasuries) Equals: Gross National Product (Flow Of Output To U.S. Citizens/U.S. Companies) Less: Consumption Of Fixed Capital (Depreciation) Private Domestic Business Capital Consumption Allowances Less: Capital Consumption Adjustment Households And Institutions Government General Government Government Enterprises Equals: Net National Product Less: Statistical Discrepancy Equal: National Income Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 43 / 55
71 Income Markets for factors of Production Factor Payments Private Saving Financial Markets Households Taxes Government Public Saving Firms Government Purchases Investment Consumption Markets for Goods and Services Firm Revenue Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 44 / 55
72 Definition Factors of production are the inputs used to produce goods and services. The two critical factors of production are capital and labor. Capital is the set of tools that workers use. Labor is the time people spend working. Factors of production are fully utilized. K = K L = L Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 45 / 55
73 Definition The production technology determines how much output is produced from given amounts of capital and labor. Y = F (K, L) Y = F ( K, L ) Definition A production function has constant returns to scale if an increase of an equal percentage in all factors of production cause an increase in output of the same percentage. zy = F (zk, zl) Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 46 / 55
74 The kitchen and its equipment are the Bakery capital. The workers hired to make the bread are its labor. The loaves of bread are its output. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 47 / 55
75 To make a product, the firm needs two factors of production, capital and labor. Let s represent the firm s technology by the usual production function: Y = F (K, L) Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 48 / 55
76 A competitive firm is small relative to the markets in which it trades. The competitive firm has no influence on market prices. The competitive firm has no influence on the wages of the workers. The competitive firm has no influence on the rents of the capital. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 49 / 55
77 The firm sells output at a price P, hires workers at wage W, and rents capital at a rate R. The goal of the firm is to choose L and K to maximize profit. Firm profits equal sales revenues minus production costs. Profit = Revenue Labor Costs Capital Costs = PY WL RK = PF (K, L) WL RK Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 50 / 55
78 Definition The marginal product of labor is the extra amount of output the firm gets from one extra unit of labor, holding the amount of capital constant. Definition Diminishing marginal productivity means that, holding capital fixed, the marginal product of labor decreases as the amount of labor increases. Profit = Revenue Cost (P) (MPL) = W 0 = (P) (MPL) W Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 51 / 55
79 Definition The marginal product of capital is the amount of extra output the firm gets from an extra unit of capital, holding the amount of labor constant. Definition Diminishing marginal productivity means that, holding labor fixed, the marginal product of capital decreases as the amount of capital increases. Profit = Revenue Cost (P) (MPK ) = R 0 = (P) (MPK ) R Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 52 / 55
80 Y = F (K, L) = AK α L 1 α MPL = AK α (1 α) L 1 α 1 MPK = AL 1 α αk α 1 W = (P) (MPL) = PAK α (1 α) L 1 α 1 R = (P) (MPK ) = PAL 1 α αk α 1 Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 53 / 55
81 Y = F (K, L) = AK 1 2 L 1 2 A = 100, K = 100, L = 100, P = 10 MPL = 1 2 AK 1 2 L 1 2 = 1 2 (100) (100) 1 2 (100) 1 2 = 50 MPK = 1 2 AK 1 2 L 1 2 = 1 2 (100) (100) 1 2 (100) 1 2 = 50 W = P (MPL) = 50P = 500 R = P (MPK ) = 50P = 500 Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 54 / 55
82 Y C G = I Y = C + I + G Y C G + T T = I Y } {{ T C } + T }{{ G } = I Private Saving Public Saving S = I Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 55 / 55
Economic Performance. Sherif Khalifa. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 1 / 39
 Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 1 / 39 People earning higher income levels enjoy higher living standards. To judge economic well being, we consider the total income in an economy.
Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () Economic Performance 1 / 39 People earning higher income levels enjoy higher living standards. To judge economic well being, we consider the total income in an economy.
National Income. Sherif Khalifa. Sherif Khalifa () National Income 1 / 44
 National Income Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () National Income 1 / 44 People with higher incomes enjoy higher standards of living. To judge how the economy is doing, we look at the total income of everyone
National Income Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () National Income 1 / 44 People with higher incomes enjoy higher standards of living. To judge how the economy is doing, we look at the total income of everyone
National Income. Sherif Khalifa. Sherif Khalifa () National Income 1 / 28
 National Income Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () National Income 1 / 28 People with higher incomes enjoy higher standards of living. To judge whether the economy is doing well, we look at the total income
National Income Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () National Income 1 / 28 People with higher incomes enjoy higher standards of living. To judge whether the economy is doing well, we look at the total income
Gross Domestic Product. National Income Determination. Topic 9: 10/7/2016
 The Economy s Income and Expenditure Topic 9: National Income Determination When judging whether the economy is doing well or poorly, it is natural to look at the total income that everyone in the economy
The Economy s Income and Expenditure Topic 9: National Income Determination When judging whether the economy is doing well or poorly, it is natural to look at the total income that everyone in the economy
8 THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS
 8 THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS Measuring a Nation s Income 23 Measuring a Nation s Income Microeconomics Microeconomics is the study of how individual households and firms make decisions and how they interact
8 THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS Measuring a Nation s Income 23 Measuring a Nation s Income Microeconomics Microeconomics is the study of how individual households and firms make decisions and how they interact
Lecture 4: Real GDP, the First of the Big 3 Economic Activity Variables
 Lecture 4: Real GDP, the First of the Big 3 Economic Activity Variables Economists focus on the outlook for material progress. To generate an opinion about overall economic activity, economists perform
Lecture 4: Real GDP, the First of the Big 3 Economic Activity Variables Economists focus on the outlook for material progress. To generate an opinion about overall economic activity, economists perform
MEASURING A NATION S INCOME
 10 MEASURING A NATION S INCOME LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this chapter, students should understand: why an economy s total income equals its total expenditure. how gross domestic product (GDP)
10 MEASURING A NATION S INCOME LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this chapter, students should understand: why an economy s total income equals its total expenditure. how gross domestic product (GDP)
MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME. Chapter 18
 1 MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME Chapter 18 national income and product accounts Data collected and published by the government describing the various components of national income and output
1 MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME Chapter 18 national income and product accounts Data collected and published by the government describing the various components of national income and output
Measuring a Nation s Income
 Measuring a Nation s Income Microeconomics is the study of how individual households and firms make decisions and how they interact with one another in markets. Macroeconomics is the study of the economy
Measuring a Nation s Income Microeconomics is the study of how individual households and firms make decisions and how they interact with one another in markets. Macroeconomics is the study of the economy
Chapter 3 National Income: Where It Comes From And Where It Goes
 Chapter 3 National Income: Where It Comes From And Where It Goes 0 1 1 2 The Neo-Classical Model Goal: to explain the more realistic circular flow Supply Side (firms): how total output(=income; GDP) is
Chapter 3 National Income: Where It Comes From And Where It Goes 0 1 1 2 The Neo-Classical Model Goal: to explain the more realistic circular flow Supply Side (firms): how total output(=income; GDP) is
ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics. Chapter 3 National Income: Where It Comes From and Where It Goes
 ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Chapter 3 National Income: Where It Comes From and Where It Goes Outline of model A closed economy, market-clearing model Supply side factors of production determination
ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Chapter 3 National Income: Where It Comes From and Where It Goes Outline of model A closed economy, market-clearing model Supply side factors of production determination
Chapter 5 Measuring a Nation's Income
 Chapter 5 Measuring a Nation's Income Problem set 1. Which of the following headlines would be most closely related to what macroeconomists study? a. Unemployment rate rises from 5 percent to 5.5 percent.
Chapter 5 Measuring a Nation's Income Problem set 1. Which of the following headlines would be most closely related to what macroeconomists study? a. Unemployment rate rises from 5 percent to 5.5 percent.
In this chapter, you will learn C H A P T E R National Income: Where it Comes From and Where it Goes CHAPTER 3
 C H A P T E R 3 National Income: Where it Comes From and Where it Goes MACROECONOMICS N. GREGORY MANKIW 007 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved SIXTH EDITION PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich In this
C H A P T E R 3 National Income: Where it Comes From and Where it Goes MACROECONOMICS N. GREGORY MANKIW 007 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved SIXTH EDITION PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich In this
7. a. i. Nominal GDP is the total value of goods and services measured at current prices. Therefore, ( ) ( Q burgers ) ( Q hotdogs ) + P burgers
 Macroeconomics ECON 2204 Prof. Murphy Problem Set 1 Answers Chapter 2 #2, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, and 11 (on pages 44-45) 2. Value added by each person is equal to the value of the good produced minus the amount
Macroeconomics ECON 2204 Prof. Murphy Problem Set 1 Answers Chapter 2 #2, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, and 11 (on pages 44-45) 2. Value added by each person is equal to the value of the good produced minus the amount
Chapter 2: The Data of Macroeconomics*
 Chapter 2: The Data of Macroeconomics 1/40 *Slides based on Ron Cronovich's slides, adjusted by Marcel Bluhm for lecture in Macroeconomics at the Wang Yanan Institute for Studies in Economics at Xiamen
Chapter 2: The Data of Macroeconomics 1/40 *Slides based on Ron Cronovich's slides, adjusted by Marcel Bluhm for lecture in Macroeconomics at the Wang Yanan Institute for Studies in Economics at Xiamen
Macroeconomic Analysis Econ 6022 Level I
 1 / 37 Macroeconomic Analysis Econ 6022 Level I Lecture 2 Fall, 2011 2 / 37 Overview Let s start our tour in macroeconomics by introducing a few building blocks, which will be used repeatedly later on.
1 / 37 Macroeconomic Analysis Econ 6022 Level I Lecture 2 Fall, 2011 2 / 37 Overview Let s start our tour in macroeconomics by introducing a few building blocks, which will be used repeatedly later on.
Lecture notes: 101/105 (revised 9/27/00) Lecture 3: national Income: Production, Distribution and Allocation (chapter 3)
 Lecture notes: 101/105 (revised 9/27/00) Lecture 3: national Income: Production, Distribution and Allocation (chapter 3) 1) Intro Have given definitions of some key macroeconomic variables. Now start building
Lecture notes: 101/105 (revised 9/27/00) Lecture 3: national Income: Production, Distribution and Allocation (chapter 3) 1) Intro Have given definitions of some key macroeconomic variables. Now start building
CHAPTER 3 National Income: Where It Comes From and Where It Goes
 CHAPTER 3 National Income: Where It Comes From and Where It Goes A PowerPoint Tutorial To Accompany MACROECONOMICS, 7th. Edition N. Gregory Mankiw Tutorial written by: Mannig J. Simidian B.A. in Economics
CHAPTER 3 National Income: Where It Comes From and Where It Goes A PowerPoint Tutorial To Accompany MACROECONOMICS, 7th. Edition N. Gregory Mankiw Tutorial written by: Mannig J. Simidian B.A. in Economics
Where does stuff come from?
 Where does stuff come from? Factors of production Technology Factors of production: Thanks, Marx! The stuff we use to make other stuff Factors of production: Thanks, Marx! The stuff we use to make other
Where does stuff come from? Factors of production Technology Factors of production: Thanks, Marx! The stuff we use to make other stuff Factors of production: Thanks, Marx! The stuff we use to make other
Scientists, economists, and detectives have much in common: they all
 CHAPTER 2 The Data of Macroeconomics It is a capital mistake to theorize before one has data. Insensibly one begins to twist facts to suit theories, instead of theories to fit facts. Sherlock Holmes Scientists,
CHAPTER 2 The Data of Macroeconomics It is a capital mistake to theorize before one has data. Insensibly one begins to twist facts to suit theories, instead of theories to fit facts. Sherlock Holmes Scientists,
EXPENDITURE APPROACH: The expenditures on all final goods and services made by all sectors of the economy are added to calculate GDP. Expenditures are
 Chapter 1 MEASURING GDP AND PRICE LEVEL MEASURING EONOMIC ACTIVITY Macroeconomics studies the aggregate (or total) concept of economic activity. Its focus is on the aggregate output, the aggregate income,
Chapter 1 MEASURING GDP AND PRICE LEVEL MEASURING EONOMIC ACTIVITY Macroeconomics studies the aggregate (or total) concept of economic activity. Its focus is on the aggregate output, the aggregate income,
1. The economic statistic used to measure the level of prices is the: A) GDP. B) CPI. C) GNP. D) real GDP.
 1. The economic statistic used to measure the level of prices is the: A) GDP. B) CPI. C) GNP. D) real GDP. 2. The statistic used by economists to measure the value of economic output is the: A) CPI. B)
1. The economic statistic used to measure the level of prices is the: A) GDP. B) CPI. C) GNP. D) real GDP. 2. The statistic used by economists to measure the value of economic output is the: A) CPI. B)
PART II CLASSICAL THEORY. Chapter 3: National Income: Where it Comes From and Where it Goes 1/64
 PART II CLASSICAL THEORY Chapter 3: National Income: Where it Comes From and Where it Goes 1/64 Chapter 3: National Income: Where it Comes From and Where it Goes 2/64 * Slides based on Ron Cronovich's
PART II CLASSICAL THEORY Chapter 3: National Income: Where it Comes From and Where it Goes 1/64 Chapter 3: National Income: Where it Comes From and Where it Goes 2/64 * Slides based on Ron Cronovich's
Macroeconomcs. Factors of production. Outline of model. In this chapter you will learn:
 In this chapter you will learn: Macroeconomcs Professor Hisahiro Naito what determines the economy s total output/income how the prices of the factors of production are determined how total income is distributed
In this chapter you will learn: Macroeconomcs Professor Hisahiro Naito what determines the economy s total output/income how the prices of the factors of production are determined how total income is distributed
Macro CH 20 - multiple choice 80
 Class: Date: Macro CH 20 - multiple choice 80 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. GDP is measured by a. adding units of all goods and services.
Class: Date: Macro CH 20 - multiple choice 80 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. GDP is measured by a. adding units of all goods and services.
MEASURING A NATION S INCOME
 23 MEASURING A NATION S INCOME WHAT S NEW IN THE FOURTH EDITION: There is a new In the News box on The Underground Economy. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this chapter, students should understand:
23 MEASURING A NATION S INCOME WHAT S NEW IN THE FOURTH EDITION: There is a new In the News box on The Underground Economy. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this chapter, students should understand:
W8- GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT MEASURES TOTAL PRODUCTION BSB113
 W8- GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT MEASURES TOTAL PRODUCTION BSB113 Gross Domestic Product (GDP): the market value of all final goods and services produced in a country during a period. In measuring GDP, we include
W8- GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT MEASURES TOTAL PRODUCTION BSB113 Gross Domestic Product (GDP): the market value of all final goods and services produced in a country during a period. In measuring GDP, we include
Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics
 Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics slide 0 Learning Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) the Consumer Price Index (CPI) the Unemployment Rate slide 1 GROSS DOMESTIC
Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics slide 0 Learning Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) the Consumer Price Index (CPI) the Unemployment Rate slide 1 GROSS DOMESTIC
file:///c:/users/moha/desktop/mac8e/new folder (2)/CourseCompas... Creation Settings
 1 of 24 12/8/2012 11:32 م COURSES > BA121 > CONTROL PANEL > POOL MANAGER > POOL CANVAS P Add, modify, and remove questions. Select a question type from the Add drop-down list and click Go to add questions.
1 of 24 12/8/2012 11:32 م COURSES > BA121 > CONTROL PANEL > POOL MANAGER > POOL CANVAS P Add, modify, and remove questions. Select a question type from the Add drop-down list and click Go to add questions.
Recall from Econ 200:
 Chapter 2: The Data of Macroeconomics Recall from Econ 200: Macroeconomics is the study of the economy a whole, including growth in incomes, changes in price, and the rate of unemployment. Macroeconomists
Chapter 2: The Data of Macroeconomics Recall from Econ 200: Macroeconomics is the study of the economy a whole, including growth in incomes, changes in price, and the rate of unemployment. Macroeconomists
1. The economic statistic used to measure the level of prices is: A) GDP. B) CPI. C) GNP. D) real GDP.
 1. The economic statistic used to measure the level of prices is: A) GDP. B) CPI. C) GNP. D) real GDP. 2. The statistic used by economists to measure the value of economic output is: A) the CPI. B) GDP.
1. The economic statistic used to measure the level of prices is: A) GDP. B) CPI. C) GNP. D) real GDP. 2. The statistic used by economists to measure the value of economic output is: A) the CPI. B) GDP.
PART II CLASSICAL THEORY. Chapter 3: National Income: Where it Comes From and Where it Goes 1/51
 PART II CLASSICAL THEORY Chapter 3: National Income: Where it Comes From and Where it Goes 1/51 Chapter 3: National Income: Where it Comes From and Where it Goes 2/51 *Slides based on Ron Cronovich's slides,
PART II CLASSICAL THEORY Chapter 3: National Income: Where it Comes From and Where it Goes 1/51 Chapter 3: National Income: Where it Comes From and Where it Goes 2/51 *Slides based on Ron Cronovich's slides,
IN THIS LECTURE, YOU WILL LEARN:
 IN THIS LECTURE, YOU WILL LEARN: Am simple perfect competition production medium-run model view of what determines the economy s total output/income how the prices of the factors of production are determined
IN THIS LECTURE, YOU WILL LEARN: Am simple perfect competition production medium-run model view of what determines the economy s total output/income how the prices of the factors of production are determined
ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics. Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics
 ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics IN THIS CHAPTER, YOU WILL LEARN: the meaning and measurement of the most important macroeconomic statistics: gross domestic product
ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics IN THIS CHAPTER, YOU WILL LEARN: the meaning and measurement of the most important macroeconomic statistics: gross domestic product
9/10/2017. National Income: Where it Comes From and Where it Goes (in the long-run) Introduction. The Neoclassical model
 Chapter 3 - The Long-run Model National Income: Where it Comes From and Where it Goes (in the long-run) Introduction In chapter 2 we defined and measured some key macroeconomic variables. Now we start
Chapter 3 - The Long-run Model National Income: Where it Comes From and Where it Goes (in the long-run) Introduction In chapter 2 we defined and measured some key macroeconomic variables. Now we start
MACROECONOMICS - CLUTCH CH GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT (GDP) AND CONSUMER PRICE INDEX (CPI)
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CALCULATING GDP Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of the final goods and services produced by a country during a year GDP as a statistic is used to measure growth
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CALCULATING GDP Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of the final goods and services produced by a country during a year GDP as a statistic is used to measure growth
Text transcription of Chapter 5 Measuring a Nation s Income
 Text transcription of Chapter 5 Measuring a Nation s Income Welcome to the Chapter 5 Lecture on the Measuring a Nation s Income. We are going to start working with statistics to measure the size of economies
Text transcription of Chapter 5 Measuring a Nation s Income Welcome to the Chapter 5 Lecture on the Measuring a Nation s Income. We are going to start working with statistics to measure the size of economies
ECON 120 -ESSENTIALS OF ECONOMICS
 Name ECON 120 -ESSENTIALS OF ECONOMICS CH 21 Measuring National Inome MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The total market value of
Name ECON 120 -ESSENTIALS OF ECONOMICS CH 21 Measuring National Inome MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The total market value of
PART 6 The macroeconomic environment
 PART 6 The macroeconomic environment 1 of 38 Economy s Income & Expenditure Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Measures the total income of everyone in the economy Measures the total expenditure on the economy
PART 6 The macroeconomic environment 1 of 38 Economy s Income & Expenditure Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Measures the total income of everyone in the economy Measures the total expenditure on the economy
01 Measuring a Nation s Income Econ 111
 01 Measuring a Nation s Income Econ 111 Measuring a Nation s Income (Chapter 10) Macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole. Its goal is to explain the economic changes that affect many households,
01 Measuring a Nation s Income Econ 111 Measuring a Nation s Income (Chapter 10) Macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole. Its goal is to explain the economic changes that affect many households,
LECTURE NOTES ON MACROECONOMIC PRINCIPLES
 LECTURE NOTES ON MACROECONOMIC PRINCIPLES Peter Ireland Department of Economics Boston College peter.ireland@bc.edu http://www2.bc.edu/peter-ireland/ec132.html Copyright (c) 2013 by Peter Ireland. Redistribution
LECTURE NOTES ON MACROECONOMIC PRINCIPLES Peter Ireland Department of Economics Boston College peter.ireland@bc.edu http://www2.bc.edu/peter-ireland/ec132.html Copyright (c) 2013 by Peter Ireland. Redistribution
ECO 209Y MACROECONOMIC THEORY AND POLICY LECTURE 2: NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING
 ECO 209Y MACROECONOMIC THEORY AND POLICY LECTURE 2: NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING Gustavo Indart Slide1 GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of all final goods and services produced
ECO 209Y MACROECONOMIC THEORY AND POLICY LECTURE 2: NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING Gustavo Indart Slide1 GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of all final goods and services produced
Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income
 Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income 1 Multiple Choice 1) The total market value of all final goods and services produced within a given period by factors of production located within
Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income 1 Multiple Choice 1) The total market value of all final goods and services produced within a given period by factors of production located within
Learning objectives. Gross Domestic Product
 Learning objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) the Consumer Price Index (CPI) the Unemployment Rate The Data of Macroeconomics slide 1 Gross Domestic Product Two
Learning objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) the Consumer Price Index (CPI) the Unemployment Rate The Data of Macroeconomics slide 1 Gross Domestic Product Two
Lecture 3: National Income: Where it comes from and where it goes
 Class Notes Intermediate Macroeconomics Li Gan Lecture 3: National Income: Where it comes from and where it goes Production Function: Y = F(K, L) = K α L 1-α Returns to scale: Constant Return to Scale:
Class Notes Intermediate Macroeconomics Li Gan Lecture 3: National Income: Where it comes from and where it goes Production Function: Y = F(K, L) = K α L 1-α Returns to scale: Constant Return to Scale:
Lecture 5: Measuring a Nation s Wealth. Rob Godby University of Wyoming
 Lecture 5: Measuring a Nation s Wealth Rob Godby University of Wyoming Macroeconomics Macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole. Its goal is to explain the economic changes that affect many
Lecture 5: Measuring a Nation s Wealth Rob Godby University of Wyoming Macroeconomics Macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole. Its goal is to explain the economic changes that affect many
ECF2331 Final Revision
 Table of Contents Week 1 Introduction to Macroeconomics... 5 What Macroeconomics is about... 5 Macroeconomics 5 Issues addressed by macroeconomists 5 What Macroeconomists Do... 5 Macro Research 5 Develop
Table of Contents Week 1 Introduction to Macroeconomics... 5 What Macroeconomics is about... 5 Macroeconomics 5 Issues addressed by macroeconomists 5 What Macroeconomists Do... 5 Macro Research 5 Develop
Full file at
 MULTIPLE CHOICE Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question 1) Gross domestic product is defined as 1) A) the total market value of the final goods and services
MULTIPLE CHOICE Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question 1) Gross domestic product is defined as 1) A) the total market value of the final goods and services
Principles of Macroeconomics Introductory quiz
 Principles of Macroeconomics Introductory quiz Academic Program: MSc in Banking and Finance Semester: Fall 2011/12 Instructor: Dr. Nikolaos I. Papanikolaou Office: Luxembourg School of Finance, KB2-E02
Principles of Macroeconomics Introductory quiz Academic Program: MSc in Banking and Finance Semester: Fall 2011/12 Instructor: Dr. Nikolaos I. Papanikolaou Office: Luxembourg School of Finance, KB2-E02
Measuring a Nation s Production and Income
 Chapter Summary 5 Measuring a Nation s Production and Income In this chapter, we learned how economists and government statisticians measure the income and production for an entire country and what those
Chapter Summary 5 Measuring a Nation s Production and Income In this chapter, we learned how economists and government statisticians measure the income and production for an entire country and what those
Macroeconomic Theory and Policy
 ECO 209Y Macroeconomic Theory and Policy Lecture 2: National Income Accounting Gustavo Indart Slide1 Gross Domestic Product Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of all final goods and services produced
ECO 209Y Macroeconomic Theory and Policy Lecture 2: National Income Accounting Gustavo Indart Slide1 Gross Domestic Product Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of all final goods and services produced
Lecture 1: Gross Domestic Product
 Lecture 1: Gross Domestic Product August 25, 2016 Prof. Wyatt Brooks MEASURING A NATION S INCOME 0 Structure of the Course First Part of the Class: The macroeconomy in the long run Why are countries rich
Lecture 1: Gross Domestic Product August 25, 2016 Prof. Wyatt Brooks MEASURING A NATION S INCOME 0 Structure of the Course First Part of the Class: The macroeconomy in the long run Why are countries rich
Measuring National Output and National Income. Gross Domestic Product. National Income and Product Accounts
 C H A P T E R 18 Measuring National Output and National Income Prepared by: Fernando Quijano and Yvonn Quijano Gross Domestic Product Gross domestic product (GDP) is the total market value of all final
C H A P T E R 18 Measuring National Output and National Income Prepared by: Fernando Quijano and Yvonn Quijano Gross Domestic Product Gross domestic product (GDP) is the total market value of all final
ECON Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory
 ECON 3510 - Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory Fall 2015 Mankiw, Macroeconomics, 8th ed., Chapter 3 Chapter 3: A Theory of National Income Key points: Understand the aggregate production function Understand
ECON 3510 - Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory Fall 2015 Mankiw, Macroeconomics, 8th ed., Chapter 3 Chapter 3: A Theory of National Income Key points: Understand the aggregate production function Understand
MACROECONOMICS. The Data of Macroeconomics MANKIW. In this chapter, you will learn. Gross Domestic Product: Expenditure and Income.
 C H A P T E R 2 The Data of Macroeconomics MACROECONOMICS N. GREGORY MANKIW 2008 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved SIXTH EDITION PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich In this chapter, you will learn the
C H A P T E R 2 The Data of Macroeconomics MACROECONOMICS N. GREGORY MANKIW 2008 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved SIXTH EDITION PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich In this chapter, you will learn the
Macroeconomic Measurement and Business Cycles
 Macroeconomic Measurement and Business Cycles Economics 4353 - Intermediate Macroeconomics Aaron Hedlund University of Missouri Fall 2015 Econ 4353 (University of Missouri) Measurement and Business Cycles
Macroeconomic Measurement and Business Cycles Economics 4353 - Intermediate Macroeconomics Aaron Hedlund University of Missouri Fall 2015 Econ 4353 (University of Missouri) Measurement and Business Cycles
Macroeconomic Measurement and Business Cycles
 Macroeconomic Measurement and Business Cycles Economics 3307 - Intermediate Macroeconomics Aaron Hedlund Baylor University Fall 2013 Econ 3307 (Baylor University) Measurement and Business Cycles Fall 2013
Macroeconomic Measurement and Business Cycles Economics 3307 - Intermediate Macroeconomics Aaron Hedlund Baylor University Fall 2013 Econ 3307 (Baylor University) Measurement and Business Cycles Fall 2013
Week 1. H1 Notes ECON10003
 Week 1 Some output produced by the government is free. Education is a classic example. This is still viewed as a service and valued at the cost of production which is primarily the salary of the workers
Week 1 Some output produced by the government is free. Education is a classic example. This is still viewed as a service and valued at the cost of production which is primarily the salary of the workers
Lecture 1 Endogenous variables: Exogenous variables: Pizza example:
 Lecture 1 Behavior of the whole is greater than the sum of individual actions and market outcomes Paradox of thrift: expectations of possible hardship in economy by families/businesses will cause them
Lecture 1 Behavior of the whole is greater than the sum of individual actions and market outcomes Paradox of thrift: expectations of possible hardship in economy by families/businesses will cause them
Macroeconomics EC1001
 Macroeconomics EC1001 Lecturer: Professor James Mitchell Room: 107 Astley Clarke Building Email: jm463@le.ac.uk Office hours: Thursday 9.30am-11.30am Module website: www.le.ac.uk/economics/teach/ec1001/ec1001.html
Macroeconomics EC1001 Lecturer: Professor James Mitchell Room: 107 Astley Clarke Building Email: jm463@le.ac.uk Office hours: Thursday 9.30am-11.30am Module website: www.le.ac.uk/economics/teach/ec1001/ec1001.html
PART EIGHT: THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS. Measuring A Nation s Income
 ECON 102 Chapter 22 1 PART EIGHT: THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS Measuring A Nation s Income Chapter 23 What did we learn until now? In the first semester we covered microeconomics Microeconomics is the study
ECON 102 Chapter 22 1 PART EIGHT: THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS Measuring A Nation s Income Chapter 23 What did we learn until now? In the first semester we covered microeconomics Microeconomics is the study
GDP Measuring Output and Income Part II. Alternative Measures Real World Approximations. September 13 th, 2017
 GDP Measuring Output and Income Part II Alternative Measures Real World Approximations September 13 th, 2017 But First: A Continual Challenge: Connecting words and equations We describe economic circumstances
GDP Measuring Output and Income Part II Alternative Measures Real World Approximations September 13 th, 2017 But First: A Continual Challenge: Connecting words and equations We describe economic circumstances
Topic 2: Macroeconomic Data. (chapter 2) revised 9/15/09. CHAPTER 2 The Data of Macroeconomics slide 0
 Topic 2: Macroeconomic Data (chapter 2) revised 9/15/09 CHAPTER 2 The Data of Macroeconomics slide 0 Learning objectives In this chapter, you will learn about how we define and measure: Gross Domestic
Topic 2: Macroeconomic Data (chapter 2) revised 9/15/09 CHAPTER 2 The Data of Macroeconomics slide 0 Learning objectives In this chapter, you will learn about how we define and measure: Gross Domestic
Econ COURSE 2 (Chapter 21) MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME
 COURSE 2 (Chapter 21) MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME Outline of today s lecture: 1. Gross Domestic Product 2. Calculating GDP A) Expenditure Approach B) Income Approach C) Output Approach
COURSE 2 (Chapter 21) MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME Outline of today s lecture: 1. Gross Domestic Product 2. Calculating GDP A) Expenditure Approach B) Income Approach C) Output Approach
macro macroeconomics The Data of Macroeconomics N. Gregory Mankiw CHAPTER TWO 6 th edition
 macro CHAPTER TWO The Data of Macroeconomics macroeconomics 6 th edition N. Gregory Mankiw Learning objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) the Consumer Price Index
macro CHAPTER TWO The Data of Macroeconomics macroeconomics 6 th edition N. Gregory Mankiw Learning objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) the Consumer Price Index
Gross Domestic Product: Measuring the Nation s Output
 Measuring Economic Activity: GDP and Unemployment Gross Domestic Product (GDP) The market value of the final goods and services produced in a country during a given period Chapter 5: Measuring Economic
Measuring Economic Activity: GDP and Unemployment Gross Domestic Product (GDP) The market value of the final goods and services produced in a country during a given period Chapter 5: Measuring Economic
"Data, data, data: how can I make bricks without clay?".
 1 Measurement As explained in the previous chapter, measurement is a key component of the scientific method and is necessary to develop and validate theories. Sherlock Holmes, one of the masters of (investigative
1 Measurement As explained in the previous chapter, measurement is a key component of the scientific method and is necessary to develop and validate theories. Sherlock Holmes, one of the masters of (investigative
Ch 2. National Income Accounting ECO 402
 Ch 2. National Income Accounting ECO 402 Key Words The circular flow Three approaches to measuring national income Production Income Expenditure Value added Final goods and intermediate goods Gross domestic
Ch 2. National Income Accounting ECO 402 Key Words The circular flow Three approaches to measuring national income Production Income Expenditure Value added Final goods and intermediate goods Gross domestic
Chapter 3. National Income: Where it Comes from and Where it Goes
 ECONOMY IN THE LONG RUN Chapter 3 National Income: Where it Comes from and Where it Goes 1 QUESTIONS ABOUT THE SOURCES AND USES OF GDP Here we develop a static classical model of the macroeconomy: prices
ECONOMY IN THE LONG RUN Chapter 3 National Income: Where it Comes from and Where it Goes 1 QUESTIONS ABOUT THE SOURCES AND USES OF GDP Here we develop a static classical model of the macroeconomy: prices
Chapter 2: The Data of Macroeconomics
 Chapter 2: The Data of Macroeconomics 0 IN THIS CHAPTER, YOU WILL LEARN: the meaning and measurement of the most important macroeconomic statistics:! gross domestic product (GDP)! the consumer price index
Chapter 2: The Data of Macroeconomics 0 IN THIS CHAPTER, YOU WILL LEARN: the meaning and measurement of the most important macroeconomic statistics:! gross domestic product (GDP)! the consumer price index
Macroeconomic Data. Two definitions: In this chapter, you will learn about how we define and measure: Gross Domestic Product
 Topic 2: Macroeconomic Data (chapter 2) revised 9/15/09 CHAPTER 2 The Data of Macroeconomics slide 0 Learning objectives In this chapter, you will learn about how we define and measure: Gross Domestic
Topic 2: Macroeconomic Data (chapter 2) revised 9/15/09 CHAPTER 2 The Data of Macroeconomics slide 0 Learning objectives In this chapter, you will learn about how we define and measure: Gross Domestic
Chapter 8- Measuring Total Production & Income. Distribution of GDP
 Chapter 8- Measuring Total Production & Income Distribution of GDP 1 Keeping Tabs on the Economy You must be able to measure and track the economy in order to understand what is going on and react appropriately.
Chapter 8- Measuring Total Production & Income Distribution of GDP 1 Keeping Tabs on the Economy You must be able to measure and track the economy in order to understand what is going on and react appropriately.
Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income. Kazu Matsuda BIZ 203 Macroeconomics
 Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income Kazu Matsuda BIZ 203 Macroeconomics MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME National income and
Chapter 6 Measuring National Output and National Income Kazu Matsuda BIZ 203 Macroeconomics MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME MEASURING NATIONAL OUTPUT AND NATIONAL INCOME National income and
Introduction. Learning Objectives. Chapter 8. Measuring the Economy s Performance
 Chapter 8 Measuring the Economy s Performance Introduction For a number of years, measured U.S. business investment spending on capital goods has declined relative to total national expenditures on goods
Chapter 8 Measuring the Economy s Performance Introduction For a number of years, measured U.S. business investment spending on capital goods has declined relative to total national expenditures on goods
Measuring a Nation s Income
 Wojciech Gerson (1831-1901) Seventh Edition Principles of Economics N. Gregory Mankiw CHAPTER 23 Measuring a Nation s Income In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions What is Gross Domestic
Wojciech Gerson (1831-1901) Seventh Edition Principles of Economics N. Gregory Mankiw CHAPTER 23 Measuring a Nation s Income In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions What is Gross Domestic
Chapter 2: The Measurement and Structure of the National Economy
 Chapter 2: The Measurement and Structure of the National Economy Yulei Luo SEF of HKU January 22, 2014 Luo, Y. (SEF of HKU) ECON2220: Macro Theory January 22, 2014 1 / 26 Chapter Outline National Income
Chapter 2: The Measurement and Structure of the National Economy Yulei Luo SEF of HKU January 22, 2014 Luo, Y. (SEF of HKU) ECON2220: Macro Theory January 22, 2014 1 / 26 Chapter Outline National Income
Decision Makers and Markets
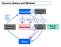 Decision Makers and Markets Households S FINANCIAL Wages Rent Interest Profit T Budget C I Factors M. (Capital Labor) Government G Goods & Services Rest of world Firms Decision Makers and Markets Households
Decision Makers and Markets Households S FINANCIAL Wages Rent Interest Profit T Budget C I Factors M. (Capital Labor) Government G Goods & Services Rest of world Firms Decision Makers and Markets Households
Economics 251 Examination I (100 points) To receive full credit, you must fully explain your answers and show all work.
 Economics 251 Examination I (100 points) To receive full credit, you must fully explain your answers and show all work. ANSWER ONE OF QUESTIONS 1 AND 2. 1. For each of the following events, show graphically
Economics 251 Examination I (100 points) To receive full credit, you must fully explain your answers and show all work. ANSWER ONE OF QUESTIONS 1 AND 2. 1. For each of the following events, show graphically
William A. McEachern Macro3 ECON
 William A. McEachern Macro3 ECON 6 1 The Product of a Nation 17 th and 18 th century Mercantilism 1758 Economic prosperity: stock of precious metals Circular flow of output and income National income accounting
William A. McEachern Macro3 ECON 6 1 The Product of a Nation 17 th and 18 th century Mercantilism 1758 Economic prosperity: stock of precious metals Circular flow of output and income National income accounting
Chapter 5: Gross Domestic Product Accounting GDP: What Approaches are used to measure GDP? Expenditure Income
 Chapter 5: Gross Domestic Product Accounting 2/7/00 GDP: GDP or Gross Domestic Product is the total value, measured in current prices, of all final goods and services, produced in the economy, during a
Chapter 5: Gross Domestic Product Accounting 2/7/00 GDP: GDP or Gross Domestic Product is the total value, measured in current prices, of all final goods and services, produced in the economy, during a
Full file at
 ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS Problems and/or Essay Questions: CHAPTER 2: MEASUREMENT OF MACROECONOMIC VARIABLES 1. What impact do you think that the movement of women from working in the household to working in
ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS Problems and/or Essay Questions: CHAPTER 2: MEASUREMENT OF MACROECONOMIC VARIABLES 1. What impact do you think that the movement of women from working in the household to working in
Measuring the Production, Income, and Spending of Nations
 6 Measuring the Production, Income, and Spending of Nations A Precise Definition of GDP GDP: a measure of the value of all newly produced 1 goods and services in a country 2 during some period of time
6 Measuring the Production, Income, and Spending of Nations A Precise Definition of GDP GDP: a measure of the value of all newly produced 1 goods and services in a country 2 during some period of time
Macroeconomics Sixth Edition
 N. Gregory Mankiw Principles of Macroeconomics Sixth Edition 10 Measuring a Nation s Income Premium PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2012 UPDATE In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions:
N. Gregory Mankiw Principles of Macroeconomics Sixth Edition 10 Measuring a Nation s Income Premium PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2012 UPDATE In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions:
The Data of Macroeconomics
 C H A P T E R 2 MACROECONOMICS SIXTH EDITION N. GREGORY MANKIW PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2008 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved In this chapter, you will learn the meaning and measurement
C H A P T E R 2 MACROECONOMICS SIXTH EDITION N. GREGORY MANKIW PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2008 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved In this chapter, you will learn the meaning and measurement
Chapter 2. The Measurement and Structure of the Canadian Economy. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education Canada
 Chapter 2 The Measurement and Structure of the Canadian Economy Copyright 2009 Pearson Education Canada National Income Accounting The national income accounts is an accounting framework used in measuring
Chapter 2 The Measurement and Structure of the Canadian Economy Copyright 2009 Pearson Education Canada National Income Accounting The national income accounts is an accounting framework used in measuring
334 Appendix B. Fixed investment. Gross domestic product (percent change) Change in private inventories. Year or quarter. Nonresidential Residential
 2010 Table B 5. Contributions to percent change in real gross domestic product, 1960 2009 Personal consumption expenditures Gross private domestic investment Gross domestic product (percent change) Goods
2010 Table B 5. Contributions to percent change in real gross domestic product, 1960 2009 Personal consumption expenditures Gross private domestic investment Gross domestic product (percent change) Goods
file:///c:/users/moha/desktop/mac8e/new folder/coursecompass_fi... Creation Settings
 file:///c:/users/moha/desktop/mac8e/new folder/coursecompass_fi... COURSES > BA121 > CONTROL PANEL > POOL MANAGER > POOL CANVAS Add, modify, and remove questions. Select a question type from the Add drop-down
file:///c:/users/moha/desktop/mac8e/new folder/coursecompass_fi... COURSES > BA121 > CONTROL PANEL > POOL MANAGER > POOL CANVAS Add, modify, and remove questions. Select a question type from the Add drop-down
Economics. The last two weeks...
 Economics The last two weeks... Final Exam (Thursday, December 14) Practice tests and review materials on Wednesday Extra Credit Stock Project (due on Thursday, December 14) Today: Measuring Economic Performance
Economics The last two weeks... Final Exam (Thursday, December 14) Practice tests and review materials on Wednesday Extra Credit Stock Project (due on Thursday, December 14) Today: Measuring Economic Performance
Principles of Macroeconomics Fall Answer Key - Problem Set 1
 EC132.01(02) Serge Kasyanenko Principles of Macroeconomics Fall 2005 Answer Key - Problem Set 1 1. Gross Domestic Product, 2004 (millions of current dollars) I. Personal consumption expenditures 8214.3
EC132.01(02) Serge Kasyanenko Principles of Macroeconomics Fall 2005 Answer Key - Problem Set 1 1. Gross Domestic Product, 2004 (millions of current dollars) I. Personal consumption expenditures 8214.3
In understanding the behavior of aggregate demand we must take a close look at its individual components: Figure 1, Aggregate Demand
 The Digital Economist Lecture 4 -- The Real Economy and Aggregate Demand The concept of aggregate demand is used to understand and measure the ability, and willingness, of individuals and institutions
The Digital Economist Lecture 4 -- The Real Economy and Aggregate Demand The concept of aggregate demand is used to understand and measure the ability, and willingness, of individuals and institutions
Macroeconomics, 3e (Williamson) Chapter 2 Measurement
 Macroeconomics, 3e (Williamson) Chapter 2 Measurement 1) The principal printed source for reporting the US National Income and Product Accounts is called the A) Monthly Labor Review B) Survey of Current
Macroeconomics, 3e (Williamson) Chapter 2 Measurement 1) The principal printed source for reporting the US National Income and Product Accounts is called the A) Monthly Labor Review B) Survey of Current
macroeconomics The Data of Macroeconomics N. Gregory Mankiw CHAPTER TWO PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich fifth edition
 CHAPTER TWO The Data of Macroeconomics macroeconomics fifth edition N. Gregory Mankiw PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2002 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved Learning objectives In this chapter,
CHAPTER TWO The Data of Macroeconomics macroeconomics fifth edition N. Gregory Mankiw PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2002 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved Learning objectives In this chapter,
Gross Domestic Product. How Is The GDP Calculated? Net investment equals gross investment minus depreciation.
 Chapter 23: Measuring GDP, Inflation and Economic Growth Gross Domestic Product applegross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of aggregate or total production of goods and services in a country during
Chapter 23: Measuring GDP, Inflation and Economic Growth Gross Domestic Product applegross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of aggregate or total production of goods and services in a country during
Introduction. Learning Objectives. Chapter 8. Measuring the Economy s Performance
 Copyright 2012 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Chapter 8 Measuring the Economy s Performance Introduction Does a general increase in the level of a nation s economic activity and the resulting
Copyright 2012 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Chapter 8 Measuring the Economy s Performance Introduction Does a general increase in the level of a nation s economic activity and the resulting
Chapter 1: The Data of Macroeconomics
 Chapter 1: The Data of Macroeconomics Econ206 - Francesc Ortega August 31, 2011 Outline 1. The GDP 2. The inflation rate 3. The unemployment rate Reading: Mankiw 7e, chapter 2 Definition The Gross Domestic
Chapter 1: The Data of Macroeconomics Econ206 - Francesc Ortega August 31, 2011 Outline 1. The GDP 2. The inflation rate 3. The unemployment rate Reading: Mankiw 7e, chapter 2 Definition The Gross Domestic
Econ 311 Intermediate Macroeconomics Professor Eschker. Fall 2014
 Econ 311 Intermediate Macroeconomics Professor Eschker Fall 2014 Today s Topics Finish math refresher GDP Deflator Chain Weighting News CBO Projection: Budget Deficits in Future Years to be Smaller than
Econ 311 Intermediate Macroeconomics Professor Eschker Fall 2014 Today s Topics Finish math refresher GDP Deflator Chain Weighting News CBO Projection: Budget Deficits in Future Years to be Smaller than
CHAPTER 2: MEASUREMENT OF MACROECONOMIC VARIABLES
 Additional Questions Problems and/or essay questions: CHAPTER 2: MEASUREMENT OF MACROECONOMIC VARIABLES 1. What impact do you think that the movement of women from working in the household to working in
Additional Questions Problems and/or essay questions: CHAPTER 2: MEASUREMENT OF MACROECONOMIC VARIABLES 1. What impact do you think that the movement of women from working in the household to working in
Macroeconomics 5th Edition Williamson Test Bank Full Download:
 Macroeconomics 5th Edition Williamson Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/macroeconomics-5th-edition-williamson-test-bank/ Macroeconomics, 5e (Williamson) Chapter 2 Measurement 1)
Macroeconomics 5th Edition Williamson Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/macroeconomics-5th-edition-williamson-test-bank/ Macroeconomics, 5e (Williamson) Chapter 2 Measurement 1)
Measuring a Nation s Income
 C H A P T E R 23 Measuring a Nation s Income Economics P R I N C I P L E S O F N. Gregory Mankiw Premium PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2009 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning, all rights reserved
C H A P T E R 23 Measuring a Nation s Income Economics P R I N C I P L E S O F N. Gregory Mankiw Premium PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2009 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning, all rights reserved
ECO 1002 IN CLASS QUESTIONS
 Dokuz Eylül University Faculty of Business Department of Economics Spring 2018 Question 1. ECO 1002 IN CLASS QUESTIONS Which of the following transactions or activities would be counted in your country
Dokuz Eylül University Faculty of Business Department of Economics Spring 2018 Question 1. ECO 1002 IN CLASS QUESTIONS Which of the following transactions or activities would be counted in your country
