COMP/MATH 553 Algorithmic Game Theory Lecture 2: Mechanism Design Basics. Sep 8, Yang Cai
|
|
|
- Dominick Houston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 COMP/MATH 553 Algorithmic Game Theory Lecture 2: Mechanism Design Basics Sep 8, 2014 Yang Cai
2 An overview of the class Broad View: Mechanism Design and Auctions First Price Auction Second Price/Vickrey Auction Case Study: Sponsored Search Auction
3 [1] Broader View Mechanism Design (MD) Auction
4 ? What is It s the Science of Rule Mechanism Making. Design?
5 What is Mechanism Design? Understanding an existing game/economic system. Engineering part of Game Theory/Economics Existing System Predict Most of Game Theory/Economics devoted to Explain/predict the outcome. Outcome Mechanism Design reverse the direction Identifies the desired outcome/goal first! Achievable? Goal Asks whether the goals are achievable? If so, how? System Mechanism Design
6 Auctions Auctions Elections, fair division, etc. (will cover if time permits) MD Auction [1] Broader View
7 Auction example 1 Online Marketplace MD Auction [1] Broader View
8 Auction example 2 Sponsored Search MD Auction [1] Broader View
9 Auction example 3 Spectrum Auctions MD Auction [1] Broader View
10 SINGLE ITEM AUCTION
11 Single-item Auctions: Set-up Bidders Auctioneer v1 1 vi i Bidders: n vn have values on the item. These values are Private. Quasilinear utility: vi p, if wins. 0, if loses. Item
12 Auction Format: Sealed-Bid Auction Bidders v1 1 Auctioneer Item vi i n vn Sealed-Bid Auctions: 1. Each bidder i privately communicates a bid bi to the auctioneer in a sealed envelope, if you like. 2. The auctioneer decides who gets the good (if anyone). 3. The auctioneer decides on a selling price.
13 Auction Format: Sealed-Bid Auction Bidders v1 1 Auctioneer Item vi i n vn Sealed-Bid Auctions: Goal:1.Maximize social welfare. (Give itcommunicates to the bidder withathe value) Each bidder i privately bidhighest bi to the Natural Choice: Give it to the bidder with the highest bid. The only auctioneer selection rule wein use this lecture. a insealed envelope, if you like. 2. The auctioneer decides who gets the good (if anyone). 3. The auctioneer decides on a selling price.
14 Auction Format: Sealed-Bid Auction Bidders v1 1 Auctioneer Item vi i n vn Sealed-Bid Auctions: about athe 1. Each bidder i privatelyhow communicates bid bi to the selling price? auctioneer in a sealed envelope, if you like. 2. The auctioneer decides who gets the good (if anyone). 3. The auctioneer decides on a selling price.
15 Auction Format: Sealed-Bid Auction How about the selling price? Altruistic and charge nothing? Name the largest number you can... Fails terribly...
16 First Price Auction Pay you bid (First Price)? Hard to reason about. What did you guys bid? For two bidders,each bidding half of her value is a Nash eq. Why?
17 First Price Auction Game played last time Assume your value vi is sampled from U[0,1]. You won t overbid, so you will discount your value. Your strategy is a number di in [0,1] which specifies how much you want to discount your value, e.g. bi = (1 di) vi Game 1: What will you do if you are playing with only one student (picked random) from the class? Game 2: Will you change your strategy if you are playing with two other students? If yes, what will it be?
18 First Price Auction Pay you bid (First Price)? For two bidders,each bidding half of her value is a Nash eq. Why? How about three bidders? n bidders? Discounting a factor of 1/n is a Nash eq.
19 First Price Auction Pay you bid (First Price)? What if the values are not drawn from U[0,1], but from some arbitrary distribution F? bi(v) = E[maxj i vj vj v ] What if different bidders have their values drawn from different distributions? Eq. strategies could get really complicated...
20 First Price Auction Example [Kaplan and Zamir 11]: Bidder 1 s value is drawn from U[0,5], bidder 2 s value is drawn from U[6,7].
21 First Price Auction Example [Kaplan and Zamir 11]: Bidder 1 s value is drawn from U[0,5], bidder 2 s value is drawn from U[6,7]. o Nash eq. : bidder 1 bids 3 if his value is in [0,3], otherwise for b in (3, 13/3]:
22 First Price Auction Pay you bid (First Price)? Depends on the number of bidders. Depends on your information about other bidders. Optimal bidding strategy complicated! Nash eq. might not be reached. Winner might not value the item the most.
23 Second Price/Vickrey Auction Another idea Charge the winner the second highest bid. Seems arbitrary... But actually used in Ebay.
24 Second-Price/Vickrey Auction Lemma 1: In a second-price auction, every bidder has a dominant strategy: set its bid bi equal to its private valuation vi. That is, this strategy maximizes the utility of bidder i, no matter what the other bidders do. Super easy to participate in. (unlike first price) Proof: See the board.
25 Second-Price/Vickrey Auction Lemma 2: In a second-price auction, every truthful bidder is guaranteed non-negative utility. Proof: See the board.
26 Second Price/Vickrey Auction [Vickrey 61 ] The Vickrey auction is has three quite different and desirable properties: (1) [strong incentive guarantees] It is dominant-strategy incentivecompatible (DSIC), i.e., Lemma 1 and 2 hold. (2) [strong performance guarantees] If bidders report truthfully, then the auction maximizes the social welfare Σi vixi, where xi is 1 if i wins and 0 if i loses. (3) [computational efficiency] The auction can be implemented in polynomial (indeed linear) time.
27 What s next? These three properties are criteria for a good auction: More complicated allocation problem Optimize Revenue
28 Case Study: Sponsored Search Auction
29 Sponsored Search Auction
30
31 Sponsored Search Auctions: Set-up Bidders (advertisers) Slots v1 1 vn k slots for sale. Slot j has click-through-rate (CTR) αj. Bidder i s value for slot j is αjvi. Two complications: o Multiple items o Items are non identical 1 αj j n α1 vi i Auctioneer/ Google αk k
32 Sponsored Search Auction: Goal (1)DSIC. That is, truthful bidding should be a dominant strategy, and never leads to negative utility. (2) Social welfare maximization. That is, the assignment of bidders to slots should maximize Σvixi, where xi now denotes the CTR of the slot to which i is assigned (or 0 if i is not assigned to a slot). Each slot can only be assigned to one bidder, and each bidder gets only one slot. (3) Polynomial running time. Remember zillions of these auctions need to be run every day!
Mechanism Design and Auctions
 Mechanism Design and Auctions Game Theory Algorithmic Game Theory 1 TOC Mechanism Design Basics Myerson s Lemma Revenue-Maximizing Auctions Near-Optimal Auctions Multi-Parameter Mechanism Design and the
Mechanism Design and Auctions Game Theory Algorithmic Game Theory 1 TOC Mechanism Design Basics Myerson s Lemma Revenue-Maximizing Auctions Near-Optimal Auctions Multi-Parameter Mechanism Design and the
CS364A: Algorithmic Game Theory Lecture #3: Myerson s Lemma
 CS364A: Algorithmic Game Theory Lecture #3: Myerson s Lemma Tim Roughgarden September 3, 23 The Story So Far Last time, we introduced the Vickrey auction and proved that it enjoys three desirable and different
CS364A: Algorithmic Game Theory Lecture #3: Myerson s Lemma Tim Roughgarden September 3, 23 The Story So Far Last time, we introduced the Vickrey auction and proved that it enjoys three desirable and different
CS269I: Incentives in Computer Science Lecture #14: More on Auctions
 CS69I: Incentives in Computer Science Lecture #14: More on Auctions Tim Roughgarden November 9, 016 1 First-Price Auction Last lecture we ran an experiment demonstrating that first-price auctions are not
CS69I: Incentives in Computer Science Lecture #14: More on Auctions Tim Roughgarden November 9, 016 1 First-Price Auction Last lecture we ran an experiment demonstrating that first-price auctions are not
Matching Markets and Google s Sponsored Search
 Matching Markets and Google s Sponsored Search Part III: Dynamics Episode 9 Baochun Li Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Matching Markets (Required reading: Chapter
Matching Markets and Google s Sponsored Search Part III: Dynamics Episode 9 Baochun Li Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Matching Markets (Required reading: Chapter
CSV 886 Social Economic and Information Networks. Lecture 4: Auctions, Matching Markets. R Ravi
 CSV 886 Social Economic and Information Networks Lecture 4: Auctions, Matching Markets R Ravi ravi+iitd@andrew.cmu.edu Schedule 2 Auctions 3 Simple Models of Trade Decentralized Buyers and sellers have
CSV 886 Social Economic and Information Networks Lecture 4: Auctions, Matching Markets R Ravi ravi+iitd@andrew.cmu.edu Schedule 2 Auctions 3 Simple Models of Trade Decentralized Buyers and sellers have
Auctions. Episode 8. Baochun Li Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto
 Auctions Episode 8 Baochun Li Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Paying Per Click 3 Paying Per Click Ads in Google s sponsored links are based on a cost-per-click
Auctions Episode 8 Baochun Li Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Paying Per Click 3 Paying Per Click Ads in Google s sponsored links are based on a cost-per-click
Single-Parameter Mechanisms
 Algorithmic Game Theory, Summer 25 Single-Parameter Mechanisms Lecture 9 (6 pages) Instructor: Xiaohui Bei In the previous lecture, we learned basic concepts about mechanism design. The goal in this area
Algorithmic Game Theory, Summer 25 Single-Parameter Mechanisms Lecture 9 (6 pages) Instructor: Xiaohui Bei In the previous lecture, we learned basic concepts about mechanism design. The goal in this area
CS364B: Frontiers in Mechanism Design Lecture #18: Multi-Parameter Revenue-Maximization
 CS364B: Frontiers in Mechanism Design Lecture #18: Multi-Parameter Revenue-Maximization Tim Roughgarden March 5, 2014 1 Review of Single-Parameter Revenue Maximization With this lecture we commence the
CS364B: Frontiers in Mechanism Design Lecture #18: Multi-Parameter Revenue-Maximization Tim Roughgarden March 5, 2014 1 Review of Single-Parameter Revenue Maximization With this lecture we commence the
ECON Microeconomics II IRYNA DUDNYK. Auctions.
 Auctions. What is an auction? When and whhy do we need auctions? Auction is a mechanism of allocating a particular object at a certain price. Allocating part concerns who will get the object and the price
Auctions. What is an auction? When and whhy do we need auctions? Auction is a mechanism of allocating a particular object at a certain price. Allocating part concerns who will get the object and the price
CS599: Algorithm Design in Strategic Settings Fall 2012 Lecture 4: Prior-Free Single-Parameter Mechanism Design. Instructor: Shaddin Dughmi
 CS599: Algorithm Design in Strategic Settings Fall 2012 Lecture 4: Prior-Free Single-Parameter Mechanism Design Instructor: Shaddin Dughmi Administrivia HW out, due Friday 10/5 Very hard (I think) Discuss
CS599: Algorithm Design in Strategic Settings Fall 2012 Lecture 4: Prior-Free Single-Parameter Mechanism Design Instructor: Shaddin Dughmi Administrivia HW out, due Friday 10/5 Very hard (I think) Discuss
Social Network Analysis
 Lecture IV Auctions Kyumars Sheykh Esmaili Where Are Auctions Appropriate? Where sellers do not have a good estimate of the buyers true values for an item, and where buyers do not know each other s values
Lecture IV Auctions Kyumars Sheykh Esmaili Where Are Auctions Appropriate? Where sellers do not have a good estimate of the buyers true values for an item, and where buyers do not know each other s values
Auction Theory: Some Basics
 Auction Theory: Some Basics Arunava Sen Indian Statistical Institute, New Delhi ICRIER Conference on Telecom, March 7, 2014 Outline Outline Single Good Problem Outline Single Good Problem First Price Auction
Auction Theory: Some Basics Arunava Sen Indian Statistical Institute, New Delhi ICRIER Conference on Telecom, March 7, 2014 Outline Outline Single Good Problem Outline Single Good Problem First Price Auction
Today. Applications of NE and SPNE Auctions English Auction Second-Price Sealed-Bid Auction First-Price Sealed-Bid Auction
 Today Applications of NE and SPNE Auctions English Auction Second-Price Sealed-Bid Auction First-Price Sealed-Bid Auction 2 / 26 Auctions Used to allocate: Art Government bonds Radio spectrum Forms: Sequential
Today Applications of NE and SPNE Auctions English Auction Second-Price Sealed-Bid Auction First-Price Sealed-Bid Auction 2 / 26 Auctions Used to allocate: Art Government bonds Radio spectrum Forms: Sequential
ECO 426 (Market Design) - Lecture 11
 ECO 426 (Market Design) - Lecture 11 Ettore Damiano December 7, 2015 Sponsored search auctions Google, Yahoo etc.. sell ad spaces linked to keyword searches Google advertising revenue: USD 42.5bn in 2012
ECO 426 (Market Design) - Lecture 11 Ettore Damiano December 7, 2015 Sponsored search auctions Google, Yahoo etc.. sell ad spaces linked to keyword searches Google advertising revenue: USD 42.5bn in 2012
Game Theory Lecture #16
 Game Theory Lecture #16 Outline: Auctions Mechanism Design Vickrey-Clarke-Groves Mechanism Optimizing Social Welfare Goal: Entice players to select outcome which optimizes social welfare Examples: Traffic
Game Theory Lecture #16 Outline: Auctions Mechanism Design Vickrey-Clarke-Groves Mechanism Optimizing Social Welfare Goal: Entice players to select outcome which optimizes social welfare Examples: Traffic
Bayesian games and their use in auctions. Vincent Conitzer
 Bayesian games and their use in auctions Vincent Conitzer conitzer@cs.duke.edu What is mechanism design? In mechanism design, we get to design the game (or mechanism) e.g. the rules of the auction, marketplace,
Bayesian games and their use in auctions Vincent Conitzer conitzer@cs.duke.edu What is mechanism design? In mechanism design, we get to design the game (or mechanism) e.g. the rules of the auction, marketplace,
Algorithmic Game Theory
 Algorithmic Game Theory Lecture 10 06/15/10 1 A combinatorial auction is defined by a set of goods G, G = m, n bidders with valuation functions v i :2 G R + 0. $5 Got $6! More? Example: A single item for
Algorithmic Game Theory Lecture 10 06/15/10 1 A combinatorial auction is defined by a set of goods G, G = m, n bidders with valuation functions v i :2 G R + 0. $5 Got $6! More? Example: A single item for
Auction is a commonly used way of allocating indivisible
 Econ 221 Fall, 2018 Li, Hao UBC CHAPTER 16. BIDDING STRATEGY AND AUCTION DESIGN Auction is a commonly used way of allocating indivisible goods among interested buyers. Used cameras, Salvator Mundi, and
Econ 221 Fall, 2018 Li, Hao UBC CHAPTER 16. BIDDING STRATEGY AND AUCTION DESIGN Auction is a commonly used way of allocating indivisible goods among interested buyers. Used cameras, Salvator Mundi, and
ECON 459 Game Theory. Lecture Notes Auctions. Luca Anderlini Spring 2017
 ECON 459 Game Theory Lecture Notes Auctions Luca Anderlini Spring 2017 These notes have been used and commented on before. If you can still spot any errors or have any suggestions for improvement, please
ECON 459 Game Theory Lecture Notes Auctions Luca Anderlini Spring 2017 These notes have been used and commented on before. If you can still spot any errors or have any suggestions for improvement, please
Notes on Auctions. Theorem 1 In a second price sealed bid auction bidding your valuation is always a weakly dominant strategy.
 Notes on Auctions Second Price Sealed Bid Auctions These are the easiest auctions to analyze. Theorem In a second price sealed bid auction bidding your valuation is always a weakly dominant strategy. Proof
Notes on Auctions Second Price Sealed Bid Auctions These are the easiest auctions to analyze. Theorem In a second price sealed bid auction bidding your valuation is always a weakly dominant strategy. Proof
CS 573: Algorithmic Game Theory Lecture date: 22 February Combinatorial Auctions 1. 2 The Vickrey-Clarke-Groves (VCG) Mechanism 3
 CS 573: Algorithmic Game Theory Lecture date: 22 February 2008 Instructor: Chandra Chekuri Scribe: Daniel Rebolledo Contents 1 Combinatorial Auctions 1 2 The Vickrey-Clarke-Groves (VCG) Mechanism 3 3 Examples
CS 573: Algorithmic Game Theory Lecture date: 22 February 2008 Instructor: Chandra Chekuri Scribe: Daniel Rebolledo Contents 1 Combinatorial Auctions 1 2 The Vickrey-Clarke-Groves (VCG) Mechanism 3 3 Examples
Auctions. Michal Jakob Agent Technology Center, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, FEE, Czech Technical University
 Auctions Michal Jakob Agent Technology Center, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, FEE, Czech Technical University AE4M36MAS Autumn 2014 - Lecture 12 Where are We? Agent architectures (inc. BDI
Auctions Michal Jakob Agent Technology Center, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, FEE, Czech Technical University AE4M36MAS Autumn 2014 - Lecture 12 Where are We? Agent architectures (inc. BDI
Mechanism Design and Auctions
 Multiagent Systems (BE4M36MAS) Mechanism Design and Auctions Branislav Bošanský and Michal Pěchouček Artificial Intelligence Center, Department of Computer Science, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Czech
Multiagent Systems (BE4M36MAS) Mechanism Design and Auctions Branislav Bošanský and Michal Pěchouček Artificial Intelligence Center, Department of Computer Science, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Czech
Revenue Equivalence and Mechanism Design
 Equivalence and Design Daniel R. 1 1 Department of Economics University of Maryland, College Park. September 2017 / Econ415 IPV, Total Surplus Background the mechanism designer The fact that there are
Equivalence and Design Daniel R. 1 1 Department of Economics University of Maryland, College Park. September 2017 / Econ415 IPV, Total Surplus Background the mechanism designer The fact that there are
CMSC 474, Introduction to Game Theory Introduction to Auctions
 CMSC 474, Introduction to Game Theory Introduction to Auctions Mohammad T. Hajiaghayi University of Maryland Auctions An auction is a way (other than bargaining) to sell a fixed supply of a commodity (an
CMSC 474, Introduction to Game Theory Introduction to Auctions Mohammad T. Hajiaghayi University of Maryland Auctions An auction is a way (other than bargaining) to sell a fixed supply of a commodity (an
Recap First-Price Revenue Equivalence Optimal Auctions. Auction Theory II. Lecture 19. Auction Theory II Lecture 19, Slide 1
 Auction Theory II Lecture 19 Auction Theory II Lecture 19, Slide 1 Lecture Overview 1 Recap 2 First-Price Auctions 3 Revenue Equivalence 4 Optimal Auctions Auction Theory II Lecture 19, Slide 2 Motivation
Auction Theory II Lecture 19 Auction Theory II Lecture 19, Slide 1 Lecture Overview 1 Recap 2 First-Price Auctions 3 Revenue Equivalence 4 Optimal Auctions Auction Theory II Lecture 19, Slide 2 Motivation
Econ 101A Final exam May 14, 2013.
 Econ 101A Final exam May 14, 2013. Do not turn the page until instructed to. Do not forget to write Problems 1 in the first Blue Book and Problems 2, 3 and 4 in the second Blue Book. 1 Econ 101A Final
Econ 101A Final exam May 14, 2013. Do not turn the page until instructed to. Do not forget to write Problems 1 in the first Blue Book and Problems 2, 3 and 4 in the second Blue Book. 1 Econ 101A Final
Auctions. Michal Jakob Agent Technology Center, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, FEE, Czech Technical University
 Auctions Michal Jakob Agent Technology Center, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, FEE, Czech Technical University AE4M36MAS Autumn 2015 - Lecture 12 Where are We? Agent architectures (inc. BDI
Auctions Michal Jakob Agent Technology Center, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, FEE, Czech Technical University AE4M36MAS Autumn 2015 - Lecture 12 Where are We? Agent architectures (inc. BDI
Multiunit Auctions: Package Bidding October 24, Multiunit Auctions: Package Bidding
 Multiunit Auctions: Package Bidding 1 Examples of Multiunit Auctions Spectrum Licenses Bus Routes in London IBM procurements Treasury Bills Note: Heterogenous vs Homogenous Goods 2 Challenges in Multiunit
Multiunit Auctions: Package Bidding 1 Examples of Multiunit Auctions Spectrum Licenses Bus Routes in London IBM procurements Treasury Bills Note: Heterogenous vs Homogenous Goods 2 Challenges in Multiunit
Lecture 6 Applications of Static Games of Incomplete Information
 Lecture 6 Applications of Static Games of Incomplete Information Good to be sold at an auction. Which auction design should be used in order to maximize expected revenue for the seller, if the bidders
Lecture 6 Applications of Static Games of Incomplete Information Good to be sold at an auction. Which auction design should be used in order to maximize expected revenue for the seller, if the bidders
Subjects: What is an auction? Auction formats. True values & known values. Relationships between auction formats
 Auctions Subjects: What is an auction? Auction formats True values & known values Relationships between auction formats Auctions as a game and strategies to win. All-pay auctions What is an auction? An
Auctions Subjects: What is an auction? Auction formats True values & known values Relationships between auction formats Auctions as a game and strategies to win. All-pay auctions What is an auction? An
CSV 886 Social Economic and Information Networks. Lecture 5: Matching Markets, Sponsored Search. R Ravi
 CSV 886 Social Economic and Information Networks Lecture 5: Matching Markets, Sponsored Search R Ravi ravi+iitd@andrew.cmu.edu Simple Models of Trade Decentralized Buyers and sellers have to find each
CSV 886 Social Economic and Information Networks Lecture 5: Matching Markets, Sponsored Search R Ravi ravi+iitd@andrew.cmu.edu Simple Models of Trade Decentralized Buyers and sellers have to find each
Econ 101A Final exam May 14, 2013.
 Econ 101A Final exam May 14, 2013. Do not turn the page until instructed to. Do not forget to write Problems 1 in the first Blue Book and Problems 2, 3 and 4 in the second Blue Book. 1 Econ 101A Final
Econ 101A Final exam May 14, 2013. Do not turn the page until instructed to. Do not forget to write Problems 1 in the first Blue Book and Problems 2, 3 and 4 in the second Blue Book. 1 Econ 101A Final
Games of Incomplete Information ( 資訊不全賽局 ) Games of Incomplete Information
 1 Games of Incomplete Information ( 資訊不全賽局 ) Wang 2012/12/13 (Lecture 9, Micro Theory I) Simultaneous Move Games An Example One or more players know preferences only probabilistically (cf. Harsanyi, 1976-77)
1 Games of Incomplete Information ( 資訊不全賽局 ) Wang 2012/12/13 (Lecture 9, Micro Theory I) Simultaneous Move Games An Example One or more players know preferences only probabilistically (cf. Harsanyi, 1976-77)
6.254 : Game Theory with Engineering Applications Lecture 3: Strategic Form Games - Solution Concepts
 6.254 : Game Theory with Engineering Applications Lecture 3: Strategic Form Games - Solution Concepts Asu Ozdaglar MIT February 9, 2010 1 Introduction Outline Review Examples of Pure Strategy Nash Equilibria
6.254 : Game Theory with Engineering Applications Lecture 3: Strategic Form Games - Solution Concepts Asu Ozdaglar MIT February 9, 2010 1 Introduction Outline Review Examples of Pure Strategy Nash Equilibria
Economics 101A (Lecture 21) Stefano DellaVigna
 Economics 101A (Lecture 21) Stefano DellaVigna April 14, 2015 Outline 1. Oligopoly: Cournot 2. Oligopoly: Bertrand 3. Second-price Auction 4. Auctions: ebay Evidence 1 Oligopoly: Cournot Nicholson, Ch.
Economics 101A (Lecture 21) Stefano DellaVigna April 14, 2015 Outline 1. Oligopoly: Cournot 2. Oligopoly: Bertrand 3. Second-price Auction 4. Auctions: ebay Evidence 1 Oligopoly: Cournot Nicholson, Ch.
II-5. Intermediaries. Outline. Introduction. SponSearch. Introduction. II-5. Intermediaries. Introduction. SponSearch. II-5.
 Outline (Part II: Security of Economics) Lecture 5: Market with intermediaries and advertising Sponsored search Market with intermediaries Spring 2013 Outline Market is a system of exchange protocols Sponsored
Outline (Part II: Security of Economics) Lecture 5: Market with intermediaries and advertising Sponsored search Market with intermediaries Spring 2013 Outline Market is a system of exchange protocols Sponsored
CUR 412: Game Theory and its Applications, Lecture 4
 CUR 412: Game Theory and its Applications, Lecture 4 Prof. Ronaldo CARPIO March 22, 2015 Homework #1 Homework #1 will be due at the end of class today. Please check the website later today for the solutions
CUR 412: Game Theory and its Applications, Lecture 4 Prof. Ronaldo CARPIO March 22, 2015 Homework #1 Homework #1 will be due at the end of class today. Please check the website later today for the solutions
CUR 412: Game Theory and its Applications, Lecture 4
 CUR 412: Game Theory and its Applications, Lecture 4 Prof. Ronaldo CARPIO March 27, 2015 Homework #1 Homework #1 will be due at the end of class today. Please check the website later today for the solutions
CUR 412: Game Theory and its Applications, Lecture 4 Prof. Ronaldo CARPIO March 27, 2015 Homework #1 Homework #1 will be due at the end of class today. Please check the website later today for the solutions
Chapter 10: Mixed strategies Nash equilibria, reaction curves and the equality of payoffs theorem
 Chapter 10: Mixed strategies Nash equilibria reaction curves and the equality of payoffs theorem Nash equilibrium: The concept of Nash equilibrium can be extended in a natural manner to the mixed strategies
Chapter 10: Mixed strategies Nash equilibria reaction curves and the equality of payoffs theorem Nash equilibrium: The concept of Nash equilibrium can be extended in a natural manner to the mixed strategies
The Complexity of Simple and Optimal Deterministic Mechanisms for an Additive Buyer. Xi Chen, George Matikas, Dimitris Paparas, Mihalis Yannakakis
 The Complexity of Simple and Optimal Deterministic Mechanisms for an Additive Buyer Xi Chen, George Matikas, Dimitris Paparas, Mihalis Yannakakis Seller has n items for sale The Set-up Seller has n items
The Complexity of Simple and Optimal Deterministic Mechanisms for an Additive Buyer Xi Chen, George Matikas, Dimitris Paparas, Mihalis Yannakakis Seller has n items for sale The Set-up Seller has n items
COS 445 Final. Due online Monday, May 21st at 11:59 pm. Please upload each problem as a separate file via MTA.
 COS 445 Final Due online Monday, May 21st at 11:59 pm All problems on this final are no collaboration problems. You may not discuss any aspect of any problems with anyone except for the course staff. You
COS 445 Final Due online Monday, May 21st at 11:59 pm All problems on this final are no collaboration problems. You may not discuss any aspect of any problems with anyone except for the course staff. You
Simultaneous Multi-round Auctions
 Simultaneous Multi-round Auctions Daniel R. 1 1 Department of Economics University of Maryland, College Park. October / Econ415 Outline 1 2 3 4 5 Outline and Focus of Presentation The talk will focus on
Simultaneous Multi-round Auctions Daniel R. 1 1 Department of Economics University of Maryland, College Park. October / Econ415 Outline 1 2 3 4 5 Outline and Focus of Presentation The talk will focus on
Game Theory. Lecture Notes By Y. Narahari. Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science Bangalore, India July 2012
 Game Theory Lecture Notes By Y. Narahari Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science Bangalore, India July 2012 The Revenue Equivalence Theorem Note: This is a only a draft
Game Theory Lecture Notes By Y. Narahari Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science Bangalore, India July 2012 The Revenue Equivalence Theorem Note: This is a only a draft
Economics 101A (Lecture 21) Stefano DellaVigna
 Economics 101A (Lecture 21) Stefano DellaVigna November 11, 2009 Outline 1. Oligopoly: Cournot 2. Oligopoly: Bertrand 3. Second-price Auction 4. Auctions: ebay Evidence 1 Oligopoly: Cournot Nicholson,
Economics 101A (Lecture 21) Stefano DellaVigna November 11, 2009 Outline 1. Oligopoly: Cournot 2. Oligopoly: Bertrand 3. Second-price Auction 4. Auctions: ebay Evidence 1 Oligopoly: Cournot Nicholson,
Ad Auctions October 8, Ad Auctions October 8, 2010
 Ad Auctions October 8, 2010 1 Ad Auction Theory: Literature Old: Shapley-Shubik (1972) Leonard (1983) Demange-Gale (1985) Demange-Gale-Sotomayor (1986) New: Varian (2006) Edelman-Ostrovsky-Schwarz (2007)
Ad Auctions October 8, 2010 1 Ad Auction Theory: Literature Old: Shapley-Shubik (1972) Leonard (1983) Demange-Gale (1985) Demange-Gale-Sotomayor (1986) New: Varian (2006) Edelman-Ostrovsky-Schwarz (2007)
Lecture #6: Auctions: Theory and Applications. Prof. Dr. Sven Seuken
 Lecture #6: Auctions: Theory and Applications Prof. Dr. Sven Seuken 15.3.2012 Housekeeping Questions? Concerns? BitTorrent homework assignment? Posting on NB: do not copy/paste from PDFs Game Theory Homework:
Lecture #6: Auctions: Theory and Applications Prof. Dr. Sven Seuken 15.3.2012 Housekeeping Questions? Concerns? BitTorrent homework assignment? Posting on NB: do not copy/paste from PDFs Game Theory Homework:
Auctions That Implement Efficient Investments
 Auctions That Implement Efficient Investments Kentaro Tomoeda October 31, 215 Abstract This article analyzes the implementability of efficient investments for two commonly used mechanisms in single-item
Auctions That Implement Efficient Investments Kentaro Tomoeda October 31, 215 Abstract This article analyzes the implementability of efficient investments for two commonly used mechanisms in single-item
Auctions Introduction
 Auctions Introduction CPSC 532A Lecture 20 November 21, 2006 Auctions Introduction CPSC 532A Lecture 20, Slide 1 Lecture Overview 1 Recap 2 VCG caveats 3 Auctions 4 Standard auctions 5 More exotic auctions
Auctions Introduction CPSC 532A Lecture 20 November 21, 2006 Auctions Introduction CPSC 532A Lecture 20, Slide 1 Lecture Overview 1 Recap 2 VCG caveats 3 Auctions 4 Standard auctions 5 More exotic auctions
Mechanism Design and Auctions
 Mechanism Design and Auctions Kevin Leyton-Brown & Yoav Shoham Chapter 7 of Multiagent Systems (MIT Press, 2012) Drawing on material that first appeared in our own book, Multiagent Systems: Algorithmic,
Mechanism Design and Auctions Kevin Leyton-Brown & Yoav Shoham Chapter 7 of Multiagent Systems (MIT Press, 2012) Drawing on material that first appeared in our own book, Multiagent Systems: Algorithmic,
Consider the following (true) preference orderings of 4 agents on 4 candidates.
 Part 1: Voting Systems Consider the following (true) preference orderings of 4 agents on 4 candidates. Agent #1: A > B > C > D Agent #2: B > C > D > A Agent #3: C > B > D > A Agent #4: D > C > A > B Assume
Part 1: Voting Systems Consider the following (true) preference orderings of 4 agents on 4 candidates. Agent #1: A > B > C > D Agent #2: B > C > D > A Agent #3: C > B > D > A Agent #4: D > C > A > B Assume
On the Impossibility of Core-Selecting Auctions
 On the Impossibility of Core-Selecting Auctions Jacob K. Goeree and Yuanchuan Lien November 10, 009 Abstract When goods are substitutes, the Vickrey auction produces efficient, core outcomes that yield
On the Impossibility of Core-Selecting Auctions Jacob K. Goeree and Yuanchuan Lien November 10, 009 Abstract When goods are substitutes, the Vickrey auction produces efficient, core outcomes that yield
The Vickrey-Clarke-Groves Mechanism
 July 8, 2009 This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License. Dealing with Externalities We saw that the Vickrey auction was no longer efficient when there
July 8, 2009 This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License. Dealing with Externalities We saw that the Vickrey auction was no longer efficient when there
Auctions. N i k o l a o s L i o n i s U n i v e r s i t y O f A t h e n s. ( R e v i s e d : J a n u a r y )
 Auctions 1 N i k o l a o s L i o n i s U n i v e r s i t y O f A t h e n s ( R e v i s e d : J a n u a r y 2 0 1 7 ) Common definition What is an auction? A usually public sale of goods where people make
Auctions 1 N i k o l a o s L i o n i s U n i v e r s i t y O f A t h e n s ( R e v i s e d : J a n u a r y 2 0 1 7 ) Common definition What is an auction? A usually public sale of goods where people make
October An Equilibrium of the First Price Sealed Bid Auction for an Arbitrary Distribution.
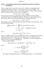 October 13..18.4 An Equilibrium of the First Price Sealed Bid Auction for an Arbitrary Distribution. We now assume that the reservation values of the bidders are independently and identically distributed
October 13..18.4 An Equilibrium of the First Price Sealed Bid Auction for an Arbitrary Distribution. We now assume that the reservation values of the bidders are independently and identically distributed
Strategy -1- Strategy
 Strategy -- Strategy A Duopoly, Cournot equilibrium 2 B Mixed strategies: Rock, Scissors, Paper, Nash equilibrium 5 C Games with private information 8 D Additional exercises 24 25 pages Strategy -2- A
Strategy -- Strategy A Duopoly, Cournot equilibrium 2 B Mixed strategies: Rock, Scissors, Paper, Nash equilibrium 5 C Games with private information 8 D Additional exercises 24 25 pages Strategy -2- A
Optimal Auctions. Game Theory Course: Jackson, Leyton-Brown & Shoham
 Game Theory Course: Jackson, Leyton-Brown & Shoham So far we have considered efficient auctions What about maximizing the seller s revenue? she may be willing to risk failing to sell the good she may be
Game Theory Course: Jackson, Leyton-Brown & Shoham So far we have considered efficient auctions What about maximizing the seller s revenue? she may be willing to risk failing to sell the good she may be
Introduction to mechanism design. Lirong Xia
 Introduction to mechanism design Lirong Xia Fall, 2016 1 Last class: game theory R 1 * s 1 Strategy Profile D Mechanism R 2 * s 2 Outcome R n * s n Game theory: predicting the outcome with strategic agents
Introduction to mechanism design Lirong Xia Fall, 2016 1 Last class: game theory R 1 * s 1 Strategy Profile D Mechanism R 2 * s 2 Outcome R n * s n Game theory: predicting the outcome with strategic agents
CS 573: Algorithmic Game Theory Lecture date: March 26th, 2008
 CS 573: Algorithmic Game Theory Lecture date: March 26th, 28 Instructor: Chandra Chekuri Scribe: Qi Li Contents Overview: Auctions in the Bayesian setting 1 1 Single item auction 1 1.1 Setting............................................
CS 573: Algorithmic Game Theory Lecture date: March 26th, 28 Instructor: Chandra Chekuri Scribe: Qi Li Contents Overview: Auctions in the Bayesian setting 1 1 Single item auction 1 1.1 Setting............................................
Auctions. Book Pages Auction. Auction types. Rules to Auctions
 Auctions An auction is a mechanism for trading items by means of bidding. Dates back to BC where Babylonians auctioned of women as wives. Position of Emperor of Rome was auctioned off in ad Can have the
Auctions An auction is a mechanism for trading items by means of bidding. Dates back to BC where Babylonians auctioned of women as wives. Position of Emperor of Rome was auctioned off in ad Can have the
KIER DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES
 KIER DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES KYOTO INSTITUTE OF ECONOMIC RESEARCH http://www.kier.kyoto-u.ac.jp/index.html Discussion Paper No. 657 The Buy Price in Auctions with Discrete Type Distributions Yusuke Inami
KIER DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES KYOTO INSTITUTE OF ECONOMIC RESEARCH http://www.kier.kyoto-u.ac.jp/index.html Discussion Paper No. 657 The Buy Price in Auctions with Discrete Type Distributions Yusuke Inami
A simulation study of two combinatorial auctions
 A simulation study of two combinatorial auctions David Nordström Department of Economics Lund University Supervisor: Tommy Andersson Co-supervisor: Albin Erlanson May 24, 2012 Abstract Combinatorial auctions
A simulation study of two combinatorial auctions David Nordström Department of Economics Lund University Supervisor: Tommy Andersson Co-supervisor: Albin Erlanson May 24, 2012 Abstract Combinatorial auctions
Auctions. Economics Auction Theory. Instructor: Songzi Du. Simon Fraser University. November 17, 2016
 Auctions Economics 383 - Auction Theory Instructor: Songzi Du Simon Fraser University November 17, 2016 ECON 383 (SFU) Auctions November 17, 2016 1 / 28 Auctions Mechanisms of transaction: bargaining,
Auctions Economics 383 - Auction Theory Instructor: Songzi Du Simon Fraser University November 17, 2016 ECON 383 (SFU) Auctions November 17, 2016 1 / 28 Auctions Mechanisms of transaction: bargaining,
University of Michigan. July 1994
 Preliminary Draft Generalized Vickrey Auctions by Jerey K. MacKie-Mason Hal R. Varian University of Michigan July 1994 Abstract. We describe a generalization of the Vickrey auction. Our mechanism extends
Preliminary Draft Generalized Vickrey Auctions by Jerey K. MacKie-Mason Hal R. Varian University of Michigan July 1994 Abstract. We describe a generalization of the Vickrey auction. Our mechanism extends
Auctions. Market Design. University of Notre Dame. Market Design (ND) Auctions 1 / 61
 Auctions Market Design University of Notre Dame Market Design (ND) Auctions 1 / 61 Game theory review A game is a collection of players, the actions those players can take, and their preferences over the
Auctions Market Design University of Notre Dame Market Design (ND) Auctions 1 / 61 Game theory review A game is a collection of players, the actions those players can take, and their preferences over the
Algorithmic Game Theory (a primer) Depth Qualifying Exam for Ashish Rastogi (Ph.D. candidate)
 Algorithmic Game Theory (a primer) Depth Qualifying Exam for Ashish Rastogi (Ph.D. candidate) 1 Game Theory Theory of strategic behavior among rational players. Typical game has several players. Each player
Algorithmic Game Theory (a primer) Depth Qualifying Exam for Ashish Rastogi (Ph.D. candidate) 1 Game Theory Theory of strategic behavior among rational players. Typical game has several players. Each player
Introduction to mechanism design. Lirong Xia
 Introduction to mechanism design Lirong Xia Feb. 9, 2016 1 Last class: game theory R 1 * s 1 Strategy Profile D Mechanism R 2 * s 2 Outcome R n * s n Game theory: predicting the outcome with strategic
Introduction to mechanism design Lirong Xia Feb. 9, 2016 1 Last class: game theory R 1 * s 1 Strategy Profile D Mechanism R 2 * s 2 Outcome R n * s n Game theory: predicting the outcome with strategic
Parkes Mechanism Design 1. Mechanism Design I. David C. Parkes. Division of Engineering and Applied Science, Harvard University
 Parkes Mechanism Design 1 Mechanism Design I David C. Parkes Division of Engineering and Applied Science, Harvard University CS 286r Spring 2003 Parkes Mechanism Design 2 Mechanism Design Central question:
Parkes Mechanism Design 1 Mechanism Design I David C. Parkes Division of Engineering and Applied Science, Harvard University CS 286r Spring 2003 Parkes Mechanism Design 2 Mechanism Design Central question:
Dynamic Marginal Contribution Mechanism
 Dynamic Marginal Contribution Mechanism Dirk Bergemann and Juuso Välimäki DIMACS: Economics and Computer Science October 2007 Intertemporal Efciency with Private Information random arrival of buyers, sellers
Dynamic Marginal Contribution Mechanism Dirk Bergemann and Juuso Välimäki DIMACS: Economics and Computer Science October 2007 Intertemporal Efciency with Private Information random arrival of buyers, sellers
Agent-Based Systems. Agent-Based Systems. Michael Rovatsos. Lecture 11 Resource Allocation 1 / 18
 Agent-Based Systems Michael Rovatsos mrovatso@inf.ed.ac.uk Lecture 11 Resource Allocation 1 / 18 Where are we? Coalition formation The core and the Shapley value Different representations Simple games
Agent-Based Systems Michael Rovatsos mrovatso@inf.ed.ac.uk Lecture 11 Resource Allocation 1 / 18 Where are we? Coalition formation The core and the Shapley value Different representations Simple games
Single Price Mechanisms for Revenue Maximization in Unlimited Supply Combinatorial Auctions
 Single Price Mechanisms for Revenue Maximization in Unlimited Supply Combinatorial Auctions Maria-Florina Balcan Avrim Blum Yishay Mansour February 2007 CMU-CS-07-111 School of Computer Science Carnegie
Single Price Mechanisms for Revenue Maximization in Unlimited Supply Combinatorial Auctions Maria-Florina Balcan Avrim Blum Yishay Mansour February 2007 CMU-CS-07-111 School of Computer Science Carnegie
Optimization in the Private Value Model: Competitive Analysis Applied to Auction Design
 Optimization in the Private Value Model: Competitive Analysis Applied to Auction Design Jason D. Hartline A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of
Optimization in the Private Value Model: Competitive Analysis Applied to Auction Design Jason D. Hartline A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of
EconS Games with Incomplete Information II and Auction Theory
 EconS 424 - Games with Incomplete Information II and Auction Theory Félix Muñoz-García Washington State University fmunoz@wsu.edu April 28, 2014 Félix Muñoz-García (WSU) EconS 424 - Recitation 9 April
EconS 424 - Games with Incomplete Information II and Auction Theory Félix Muñoz-García Washington State University fmunoz@wsu.edu April 28, 2014 Félix Muñoz-García (WSU) EconS 424 - Recitation 9 April
Problem Set 3: Suggested Solutions
 Microeconomics: Pricing 3E00 Fall 06. True or false: Problem Set 3: Suggested Solutions (a) Since a durable goods monopolist prices at the monopoly price in her last period of operation, the prices must
Microeconomics: Pricing 3E00 Fall 06. True or false: Problem Set 3: Suggested Solutions (a) Since a durable goods monopolist prices at the monopoly price in her last period of operation, the prices must
ECON20710 Lecture Auction as a Bayesian Game
 ECON7 Lecture Auction as a Bayesian Game Hanzhe Zhang Tuesday, November 3, Introduction Auction theory has been a particularly successful application of game theory ideas to the real world, with its uses
ECON7 Lecture Auction as a Bayesian Game Hanzhe Zhang Tuesday, November 3, Introduction Auction theory has been a particularly successful application of game theory ideas to the real world, with its uses
CMSC 858F: Algorithmic Game Theory Fall 2010 Introduction to Algorithmic Game Theory
 CMSC 858F: Algorithmic Game Theory Fall 2010 Introduction to Algorithmic Game Theory Instructor: Mohammad T. Hajiaghayi Scribe: Hyoungtae Cho October 13, 2010 1 Overview In this lecture, we introduce the
CMSC 858F: Algorithmic Game Theory Fall 2010 Introduction to Algorithmic Game Theory Instructor: Mohammad T. Hajiaghayi Scribe: Hyoungtae Cho October 13, 2010 1 Overview In this lecture, we introduce the
In the Name of God. Sharif University of Technology. Graduate School of Management and Economics
 In the Name of God Sharif University of Technology Graduate School of Management and Economics Microeconomics (for MBA students) 44111 (1393-94 1 st term) - Group 2 Dr. S. Farshad Fatemi Game Theory Game:
In the Name of God Sharif University of Technology Graduate School of Management and Economics Microeconomics (for MBA students) 44111 (1393-94 1 st term) - Group 2 Dr. S. Farshad Fatemi Game Theory Game:
The Duo-Item Bisection Auction
 Comput Econ DOI 10.1007/s10614-013-9380-0 Albin Erlanson Accepted: 2 May 2013 Springer Science+Business Media New York 2013 Abstract This paper proposes an iterative sealed-bid auction for selling multiple
Comput Econ DOI 10.1007/s10614-013-9380-0 Albin Erlanson Accepted: 2 May 2013 Springer Science+Business Media New York 2013 Abstract This paper proposes an iterative sealed-bid auction for selling multiple
Auctions. Agenda. Definition. Syllabus: Mansfield, chapter 15 Jehle, chapter 9
 Auctions Syllabus: Mansfield, chapter 15 Jehle, chapter 9 1 Agenda Types of auctions Bidding behavior Buyer s maximization problem Seller s maximization problem Introducing risk aversion Winner s curse
Auctions Syllabus: Mansfield, chapter 15 Jehle, chapter 9 1 Agenda Types of auctions Bidding behavior Buyer s maximization problem Seller s maximization problem Introducing risk aversion Winner s curse
ECO 426 (Market Design) - Lecture 8
 ECO 426 (Market Design) - Lecture 8 Ettore Damiano November 23, 2015 Revenue equivalence Model: N bidders Bidder i has valuation v i Each v i is drawn independently from the same distribution F (e.g. U[0,
ECO 426 (Market Design) - Lecture 8 Ettore Damiano November 23, 2015 Revenue equivalence Model: N bidders Bidder i has valuation v i Each v i is drawn independently from the same distribution F (e.g. U[0,
POSITION AUCTIONS: DESIGN, INCENTIVES AND STRATEGIES. Matr ANNO ACCADEMICO. Dipartimento di Economia e Finanza
 Dipartimento di Economia e Finanza Cattedra di Games and Strategies POSITION AUCTIONS: DESIGN, INCENTIVES AND STRATEGIES Relatore Prof. Marco Dall Aglio Candidato Karin Guetta Matr. 165721 ANNO ACCADEMICO
Dipartimento di Economia e Finanza Cattedra di Games and Strategies POSITION AUCTIONS: DESIGN, INCENTIVES AND STRATEGIES Relatore Prof. Marco Dall Aglio Candidato Karin Guetta Matr. 165721 ANNO ACCADEMICO
Applicant Auction Conference
 Applicant Auction Conference Using auctions to resolve string contentions efficiently and fairly in a simple and transparent process Peter Cramton, Chairman Cramton Associates www.applicantauction.com
Applicant Auction Conference Using auctions to resolve string contentions efficiently and fairly in a simple and transparent process Peter Cramton, Chairman Cramton Associates www.applicantauction.com
Auction types. All Pay Auction: Everyone writes down a bid in secret. The person with the highest bid wins. Everyone pays.
 Auctions An auction is a mechanism for trading items by means of bidding. Dates back to 500 BC where Babylonians auctioned off women as wives. Position of Emperor of Rome was auctioned off in 193 ad Can
Auctions An auction is a mechanism for trading items by means of bidding. Dates back to 500 BC where Babylonians auctioned off women as wives. Position of Emperor of Rome was auctioned off in 193 ad Can
Truthful Auctions for Pricing Search Keywords
 Truthful Auctions for Pricing Search Keywords Gagan Aggarwal Ashish Goel Rajeev Motwani Abstract We present a truthful auction for pricing advertising slots on a web-page assuming that advertisements for
Truthful Auctions for Pricing Search Keywords Gagan Aggarwal Ashish Goel Rajeev Motwani Abstract We present a truthful auction for pricing advertising slots on a web-page assuming that advertisements for
Parkes Auction Theory 1. Auction Theory. Jacomo Corbo. School of Engineering and Applied Science, Harvard University
 Parkes Auction Theory 1 Auction Theory Jacomo Corbo School of Engineering and Applied Science, Harvard University CS 286r Spring 2007 Parkes Auction Theory 2 Auctions: A Special Case of Mech. Design Allocation
Parkes Auction Theory 1 Auction Theory Jacomo Corbo School of Engineering and Applied Science, Harvard University CS 286r Spring 2007 Parkes Auction Theory 2 Auctions: A Special Case of Mech. Design Allocation
Mechanism Design: Groves Mechanisms and Clarke Tax
 Mechanism Design: Groves Mechanisms and Clarke Tax (Based on Shoham and Leyton-Brown (2008). Multiagent Systems: Algorithmic, Game-Theoretic, and Logical Foundations, Cambridge.) Leen-Kiat Soh Grove Mechanisms
Mechanism Design: Groves Mechanisms and Clarke Tax (Based on Shoham and Leyton-Brown (2008). Multiagent Systems: Algorithmic, Game-Theoretic, and Logical Foundations, Cambridge.) Leen-Kiat Soh Grove Mechanisms
Game theory review. The English Auction How should bidders behave in the English auction?
 Game theory review A game is a collection of players, the actions those players can take, and their preferences over the selection of actions taken by all the players A strategy s i is dominant for player
Game theory review A game is a collection of players, the actions those players can take, and their preferences over the selection of actions taken by all the players A strategy s i is dominant for player
Mechanism design with correlated distributions. Michael Albert and Vincent Conitzer and
 Mechanism design with correlated distributions Michael Albert and Vincent Conitzer malbert@cs.duke.edu and conitzer@cs.duke.edu Impossibility results from mechanism design with independent valuations Myerson
Mechanism design with correlated distributions Michael Albert and Vincent Conitzer malbert@cs.duke.edu and conitzer@cs.duke.edu Impossibility results from mechanism design with independent valuations Myerson
Auction Theory for Undergrads
 Auction Theory for Undergrads Felix Munoz-Garcia School of Economic Sciences Washington State University September 2012 Introduction Auctions are a large part of the economic landscape: Since Babylon in
Auction Theory for Undergrads Felix Munoz-Garcia School of Economic Sciences Washington State University September 2012 Introduction Auctions are a large part of the economic landscape: Since Babylon in
Truthful Double Auction Mechanisms
 OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 56, No. 1, January February 2008, pp. 102 120 issn 0030-364X eissn 1526-5463 08 5601 0102 informs doi 10.1287/opre.1070.0458 2008 INFORMS Truthful Double Auction Mechanisms Leon
OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 56, No. 1, January February 2008, pp. 102 120 issn 0030-364X eissn 1526-5463 08 5601 0102 informs doi 10.1287/opre.1070.0458 2008 INFORMS Truthful Double Auction Mechanisms Leon
Problem Set 3: Suggested Solutions
 Microeconomics: Pricing 3E Fall 5. True or false: Problem Set 3: Suggested Solutions (a) Since a durable goods monopolist prices at the monopoly price in her last period of operation, the prices must be
Microeconomics: Pricing 3E Fall 5. True or false: Problem Set 3: Suggested Solutions (a) Since a durable goods monopolist prices at the monopoly price in her last period of operation, the prices must be
CS711 Game Theory and Mechanism Design
 CS711 Game Theory and Mechanism Design Problem Set 1 August 13, 2018 Que 1. [Easy] William and Henry are participants in a televised game show, seated in separate booths with no possibility of communicating
CS711 Game Theory and Mechanism Design Problem Set 1 August 13, 2018 Que 1. [Easy] William and Henry are participants in a televised game show, seated in separate booths with no possibility of communicating
Budget Management In GSP (2018)
 Budget Management In GSP (2018) Yahoo! March 18, 2018 Miguel March 18, 2018 1 / 26 Today s Presentation: Budget Management Strategies in Repeated auctions, Balseiro, Kim, and Mahdian, WWW2017 Learning
Budget Management In GSP (2018) Yahoo! March 18, 2018 Miguel March 18, 2018 1 / 26 Today s Presentation: Budget Management Strategies in Repeated auctions, Balseiro, Kim, and Mahdian, WWW2017 Learning
Single Price Mechanisms for Revenue Maximization in Unlimited Supply Combinatorial Auctions
 Single Price Mechanisms for Revenue Maximization in Unlimited Supply Combinatorial Auctions Maria-Florina Balcan Avrim Blum Yishay Mansour December 7, 2006 Abstract In this note we generalize a result
Single Price Mechanisms for Revenue Maximization in Unlimited Supply Combinatorial Auctions Maria-Florina Balcan Avrim Blum Yishay Mansour December 7, 2006 Abstract In this note we generalize a result
Decentralized supply chain formation using an incentive compatible mechanism
 formation using an incentive compatible mechanism N. Hemachandra IE&OR, IIT Bombay Joint work with Prof Y Narahari and Nikesh Srivastava Symposium on Optimization in Supply Chains IIT Bombay, Oct 27, 2007
formation using an incentive compatible mechanism N. Hemachandra IE&OR, IIT Bombay Joint work with Prof Y Narahari and Nikesh Srivastava Symposium on Optimization in Supply Chains IIT Bombay, Oct 27, 2007
Mechanism Design for Multi-Agent Meeting Scheduling Including Time Preferences, Availability, and Value of Presence
 Mechanism Design for Multi-Agent Meeting Scheduling Including Time Preferences, Availability, and Value of Presence Elisabeth Crawford and Manuela Veloso Computer Science Department, Carnegie Mellon University,
Mechanism Design for Multi-Agent Meeting Scheduling Including Time Preferences, Availability, and Value of Presence Elisabeth Crawford and Manuela Veloso Computer Science Department, Carnegie Mellon University,
Lecture 10: The knapsack problem
 Optimization Methods in Finance (EPFL, Fall 2010) Lecture 10: The knapsack problem 24.11.2010 Lecturer: Prof. Friedrich Eisenbrand Scribe: Anu Harjula The knapsack problem The Knapsack problem is a problem
Optimization Methods in Finance (EPFL, Fall 2010) Lecture 10: The knapsack problem 24.11.2010 Lecturer: Prof. Friedrich Eisenbrand Scribe: Anu Harjula The knapsack problem The Knapsack problem is a problem
Game theory and applications: Lecture 1
 Game theory and applications: Lecture 1 Adam Szeidl September 20, 2018 Outline for today 1 Some applications of game theory 2 Games in strategic form 3 Dominance 4 Nash equilibrium 1 / 8 1. Some applications
Game theory and applications: Lecture 1 Adam Szeidl September 20, 2018 Outline for today 1 Some applications of game theory 2 Games in strategic form 3 Dominance 4 Nash equilibrium 1 / 8 1. Some applications
Preference Networks in Matching Markets
 Preference Networks in Matching Markets CSE 5339: Topics in Network Data Analysis Samir Chowdhury April 5, 2016 Market interactions between buyers and sellers form an interesting class of problems in network
Preference Networks in Matching Markets CSE 5339: Topics in Network Data Analysis Samir Chowdhury April 5, 2016 Market interactions between buyers and sellers form an interesting class of problems in network
6.207/14.15: Networks Lecture 10: Introduction to Game Theory 2
 6.207/14.15: Networks Lecture 10: Introduction to Game Theory 2 Daron Acemoglu and Asu Ozdaglar MIT October 14, 2009 1 Introduction Outline Review Examples of Pure Strategy Nash Equilibria Mixed Strategies
6.207/14.15: Networks Lecture 10: Introduction to Game Theory 2 Daron Acemoglu and Asu Ozdaglar MIT October 14, 2009 1 Introduction Outline Review Examples of Pure Strategy Nash Equilibria Mixed Strategies
