Strategy -1- Strategy
|
|
|
- Marcus Fields
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Strategy -- Strategy A Duopoly, Cournot equilibrium 2 B Mixed strategies: Rock, Scissors, Paper, Nash equilibrium 5 C Games with private information 8 D Additional exercises pages
2 Strategy -2- A Cournot Duopoly Two firms produce related products Demands are linear q p 0 p2, q p 20 p2 The demand price functions are as follows: p 9 q q, p 2 q q The cost of production in firm is C ( q ) 4q and in firm 2 is C2( q2) 7q2 Cournot (842) Firm : Computes its marginal revenue and adjusts its output until MR ( q, q2) MC 4 R ( q) p ( q) q 9q q q q R MR 9 q q q
3 Strategy -3- Firm then chooses q to satisfy MR MC 9 q q q q Therefore q ( q ) q 2 2 Best response function q( q 2) is firm s best (ie profit-maximizing) response for any choice by firm 2 We can similarly derive firm 2 s best response function q2( q ) Exercise: Show that q2( q ) q
4 Strategy -4- The two best response lines are depicted Cournot visualized an adjustment process With each firm adjusting to the other as depicted Note that the adjustment process converges to a q ( q, q ) where * * * 2 q ( q ) q and * * 2 q ( q ) q * * 2 2 At this point the strategy if the firms are said to be mutual best responses Then the stable outcome of this adjustment process satisfies the two first order conditions q ( q, q ) and ( q, q2) 0 q 2
5 Strategy -5- B Rock Scissors Paper Suppose that the game is to be played 00 times for $20 per round A pure strategy is a choice from the set of possible actions A { a, a2, a3} { R, S, P} A mixed strategy p ( p, p2, p3) places positive probability on at least two of these actions The probabilities are positive and sum to one Suppose that player 2 adopts the strategy 2 p ( p, p2, p3) ***
6 Strategy -6- B Rock Scissors Paper Suppose that the game is to be played 00 times for $20 per round A pure strategy is a choice from the set of possible actions A { a, a2, a3} { R, S, P} A mixed strategy p ( p, p2, p3) places positive probability on at least two of these actions The probabilities are positive and sum to one Suppose that player 2 adopts the strategy 2 p ( p, p2, p3) Player s expected payoffs are as follows: U ( a ) 20( p p ) 2 3 U ( a ) 20( p p ) 2 3 U ( a ) 20( p p ) 3 2 **
7 Strategy -7- B Rock Scissors Paper Suppose that the game is to be played 00 times for $20 per round A pure strategy is a choice from the set of possible actions A { a, a2, a3} { R, S, P} A mixed strategy p ( p, p2, p3) places positive probability on at least two of these actions The probabilities are positive and sum to one Suppose that player 2 adopts the strategy 2 p ( p, p2, p3) Player s expected payoffs are as follows: U ( a ) 20( p p ) 2 3 U ( a ) 20( p p ) 2 3 U ( a ) 20( p p ) 3 2 It is easy to see that if p (,, ), then player s payoff is the same (zero) for all three strategies Then * p (,, ) is a best response to p (,, )
8 Strategy -8- B Rock Scissors Paper Suppose that the game is to be played 00 times for $20 per round A pure strategy is a choice from the set of possible actions A { a, a2, a3} { R, S, P} A mixed strategy p ( p, p2, p3) places positive probability on at least two of these actions The probabilities are positive and sum to one Suppose that player 2 adopts the strategy 2 p ( p, p2, p3) Player s expected payoffs are as follows: U ( a ) 20( p p ) 2 3 U ( a ) 20( p p ) 2 3 U ( a ) 20( p p ) 3 2 It is easy to see that if p (,, ), then player s payoff is the same (zero) for all three strategies Then p (,, ) is a best response to p (,, ) By a symmetric argument, mutual best responses p (,, ) is a best response to p (,, ) So the strategies are 3 3 3
9 Strategy -9- Suppose instead that p (,, ) Then U ( a ) 20( p p ) 20( ) 2 3 U ( a ) 20( p p ) 20( ) 2 3 U ( a ) 20( p p ) 20(2 ) 3 2 **
10 Strategy -0- Suppose instead that p (,, ) Then U ( a ) 20( p p ) 20( ) 2 3 U ( a ) 20( p p ) 20( ) 2 3 U ( a ) 20( p p ) 20(2 ) 3 2 So player s best response is p for all 0 (0,0,) Thus the dynamic process underlying Cournot s solution concept does not converge to the mutual best response outcome *
11 Strategy -- Suppose instead that p (,, ) Then U ( a ) 20( p p ) 20( ) 2 3 U ( a ) 20( p p ) 20( ) 2 3 U ( a ) 20( p p ) 20(2 ) 3 2 So player s best response is p for all 0 (0,0,) Thus the dynamic process underlying Cournot s solution concept does not converge to the mutual best response outcome Despite this is does seem a very reasonable outcome In modern economic modelling of strategy, economists solve for the mutual best response outcome and remain silent as to how it might be learned/discovered
12 Strategy -2- Nash equilibrium Let S i be the set of feasible strategies (pure or mixed) for player i I {,, I} The strategies s i S i and Nash Equilibrium strategies if they are mutual best response strategies That is, for each i and strategies of the other players, s ( s,, s, s,, s ), i i i I s i is a best response for player i
13 Strategy -3- C A game with private information Sealed bid auction There are I bidders Each of the buyers may submit a non-negative sealed bid **
14 Strategy -4- C A game with private information Sealed bid auction There are I bidders Each of the buyers may submit a non-negative sealed bid Allocation rule Bidder i with bid b i loses if another bid is higher If there are m bidders who submit the tying high bid, the winner is selected randomly from one of these high bidders so that win probability of each such bidder is /m *
15 Strategy -5- C A game with private information Sealed bid auction There are I bidders Each of the buyers may submit a non-negative sealed bid Allocation rule Bidder i with bid b i loses if another bid is higher If there are m bidders who submit the tying high bid, the winner is selected randomly from one of these high bidders so that win probability of each such bidder is /m Payment rule (i) Sealed high-bid auction The winner pays his or her bid Losers pay nothing (ii) Sealed second-bid auction The winner pays the highest of the losing bids (the second highest bid)
16 Strategy -6- The model Private information: Each buyer s value is private information ****
17 Strategy -7- The model Private information: Each buyer s value is private information Common knowledge: It is common knowledge that buyer i s value is an independent random draw from a continuous distribution We define F( ) Pr{ v i } This is called the cumulative distribution function (cdf) ***
18 Strategy -8- The model Private information: Each buyer s value is private information Common knowledge: It is common knowledge that buyer i s value is an independent random draw from a continuous distribution We define F( ) Pr{ v i } This is called the cumulative distribution function (cdf) The derivative, f( ) F ( ), is called the probability density function (pdf) **
19 Strategy -9- The model Private information: Each buyer s value is private information Common knowledge: It is common knowledge that buyer i s value is an independent random draw from a continuous distribution We define F( ) Pr{ v i } This is called the cumulative distribution function (cdf) The derivative, f( ) F ( ), is called the probability density function (pdf) The values: The values lie on an interval [0, ] *
20 Strategy -20- The model Private information: Each buyer s value is private information Common knowledge: It is common knowledge that buyer i s value is an independent random draw from a continuous distribution We define F( ) Pr{ v i } This is called the cumulative distribution function (cdf) The derivative, f( ) F ( ), is called the probability density function (pdf) The values: The values lie on an interval [, ] Pure strategy With private information a pure strategy is a mapping b B( ) from every possible value (ie every i into a non-negative bid i i i Bayesian Nash Equilibrium (BNE) strategies: With private information mutual best response strategies are called Bayesian Nash Equilibrium strategies
21 Strategy -2- An example: Sealed high-bid auction bidders We first examine the special case of a uniform distribution in which the values lie in the interval [0, ] i F( ) Pr( v i ) 00 As we shall see, there is an equilibrium in which the bidding strategies are linear B( ) k, i I {,, I} i i With two bidders the equilibrium bid function is B( ) Method: To check whether any proposed pair of strategies are mutual best response (BNE) strategies all we need to do is show that they are mutual best responses i 2 i
22 Strategy -22- Step : Equilibrium win probability W() b We use the proposed equilibrium strategy of buyer 2 to obtain the equilibrium win probability for buyer If buyer bids b he wins if b b and loses if b b Since the tie occurs with probability zero, the win probability is W ( b) Pr{ b b} 2 Since b B( ) the win probability is W ( b) Pr { b} Pr{ 2b} F( 2b) For the uniform case, F( ) 00 Therefore 2b W ( b) F(2 b) 00
23 Strategy -23- Step 2: Solve for buyer s best response Buyer s expected payoff is the win probability Wb () multiplied by the profit if she wins, b 2b 2 2 u(, b) W ( b)( b) ( b) ( b b ) u 2 (, b) ( 2 b) b 00 0, if b 2 Therefore buyer s best response to buyer 2 s proposed strategy B ( ) is the strategy B ( ) 2 By an identical argument, B ( ) is a best response to B ( ) Therefore the pair of strategies { B ( )} { ( )} 2 2 i i i 2 i i are mutual best responses
24 Strategy -24- D Exercises: Pricing game If a firm cannot change its capacity quickly then the quantity setting model makes sense But what if capacity can be easily changed Then a firm can lower a price and still guarantee delivery, or raise a price and sell off unused capacity C ( q ) c q where c 4 and c2 7 Demands are f f f f q p 0 p2, q p 20 p2 Then the profit of firm f is ( p, q ( p)) p q ( p) C ( q ( p)) ( p c ) q ( p) f f f f f f f f f f (a) For each firm solve for the best response function p b ( q2) and p2 b2 ( p ) (b) Depict these in a neat figure What are the equilibrium prices in this game? (c) If firm 2 produces nothing what will firm do? Plot a price vector p ( p, p ) indicating the monopoly outcome with only firm producing Hint: The price of commodity 2 must be chosen so that demand for firm 2 s output is zero (d) Starting from this price pair, examine the adjustment process proposed by Cournot
25 Strategy -25- (e) Compare the equilibrium profits with those in the quantity setting game Exercise 2: Dominant strategy equilibrium in a pricing game with two firms producing the same product Firm has a constant marginal cost c and firm 2 a constant marginal cost c 2 Let q f ( p, p 2) be the demand for the goods produced by firm f And let q( p) q( p) q2( p) be the market demand If one sets a lower price then the other it sells to the entire market If the firms sets equal prices consumers are indifferent so any demands q ˆ ˆ ( p, p ) and q ˆ ˆ 2( p, p ) satisfying q ( pˆ, pˆ ) q ( pˆ, pˆ ) q( pˆ, pˆ ) 2 are best responses by consumers (a) Suppose that c c2 c Show that the unique equilibrium pair of prices is ( p, p2) ( c, c) (b) Explain why there is a continuum of equilibrium demands (c) Suppose next that c c2 Show that there is a unique equilibrium pair of prices (d) Is there more than one pair of equilibrium demands?
Strategy -1- Strategic equilibrium in auctions
 Strategy -- Strategic equilibrium in auctions A. Sealed high-bid auction 2 B. Sealed high-bid auction: a general approach 6 C. Other auctions: revenue equivalence theorem 27 D. Reserve price in the sealed
Strategy -- Strategic equilibrium in auctions A. Sealed high-bid auction 2 B. Sealed high-bid auction: a general approach 6 C. Other auctions: revenue equivalence theorem 27 D. Reserve price in the sealed
Games of Incomplete Information ( 資訊不全賽局 ) Games of Incomplete Information
 1 Games of Incomplete Information ( 資訊不全賽局 ) Wang 2012/12/13 (Lecture 9, Micro Theory I) Simultaneous Move Games An Example One or more players know preferences only probabilistically (cf. Harsanyi, 1976-77)
1 Games of Incomplete Information ( 資訊不全賽局 ) Wang 2012/12/13 (Lecture 9, Micro Theory I) Simultaneous Move Games An Example One or more players know preferences only probabilistically (cf. Harsanyi, 1976-77)
Bayesian Nash Equilibrium
 Bayesian Nash Equilibrium We have already seen that a strategy for a player in a game of incomplete information is a function that specifies what action or actions to take in the game, for every possibletypeofthatplayer.
Bayesian Nash Equilibrium We have already seen that a strategy for a player in a game of incomplete information is a function that specifies what action or actions to take in the game, for every possibletypeofthatplayer.
Games with Private Information 資訊不透明賽局
 Games with Private Information 資訊不透明賽局 Joseph Tao-yi Wang 00/0/5 (Lecture 9, Micro Theory I-) Market Entry Game with Private Information (-,4) (-,) BE when p < /: (,, ) (-,4) (-,) BE when p < /: (,, )
Games with Private Information 資訊不透明賽局 Joseph Tao-yi Wang 00/0/5 (Lecture 9, Micro Theory I-) Market Entry Game with Private Information (-,4) (-,) BE when p < /: (,, ) (-,4) (-,) BE when p < /: (,, )
Problem Set 3: Suggested Solutions
 Microeconomics: Pricing 3E00 Fall 06. True or false: Problem Set 3: Suggested Solutions (a) Since a durable goods monopolist prices at the monopoly price in her last period of operation, the prices must
Microeconomics: Pricing 3E00 Fall 06. True or false: Problem Set 3: Suggested Solutions (a) Since a durable goods monopolist prices at the monopoly price in her last period of operation, the prices must
Auction is a commonly used way of allocating indivisible
 Econ 221 Fall, 2018 Li, Hao UBC CHAPTER 16. BIDDING STRATEGY AND AUCTION DESIGN Auction is a commonly used way of allocating indivisible goods among interested buyers. Used cameras, Salvator Mundi, and
Econ 221 Fall, 2018 Li, Hao UBC CHAPTER 16. BIDDING STRATEGY AND AUCTION DESIGN Auction is a commonly used way of allocating indivisible goods among interested buyers. Used cameras, Salvator Mundi, and
AS/ECON 2350 S2 N Answers to Mid term Exam July time : 1 hour. Do all 4 questions. All count equally.
 AS/ECON 2350 S2 N Answers to Mid term Exam July 2017 time : 1 hour Do all 4 questions. All count equally. Q1. Monopoly is inefficient because the monopoly s owner makes high profits, and the monopoly s
AS/ECON 2350 S2 N Answers to Mid term Exam July 2017 time : 1 hour Do all 4 questions. All count equally. Q1. Monopoly is inefficient because the monopoly s owner makes high profits, and the monopoly s
Economics Honors Exam 2009 Solutions: Microeconomics, Questions 1-2
 Economics Honors Exam 2009 Solutions: Microeconomics, Questions 1-2 Question 1 (Microeconomics, 30 points). A ticket to a newly staged opera is on sale through sealed-bid auction. There are three bidders,
Economics Honors Exam 2009 Solutions: Microeconomics, Questions 1-2 Question 1 (Microeconomics, 30 points). A ticket to a newly staged opera is on sale through sealed-bid auction. There are three bidders,
Econ 101A Final exam May 14, 2013.
 Econ 101A Final exam May 14, 2013. Do not turn the page until instructed to. Do not forget to write Problems 1 in the first Blue Book and Problems 2, 3 and 4 in the second Blue Book. 1 Econ 101A Final
Econ 101A Final exam May 14, 2013. Do not turn the page until instructed to. Do not forget to write Problems 1 in the first Blue Book and Problems 2, 3 and 4 in the second Blue Book. 1 Econ 101A Final
Notes for Section: Week 7
 Economics 160 Professor Steven Tadelis Stanford University Spring Quarter, 004 Notes for Section: Week 7 Notes prepared by Paul Riskind (pnr@stanford.edu). spot errors or have questions about these notes.
Economics 160 Professor Steven Tadelis Stanford University Spring Quarter, 004 Notes for Section: Week 7 Notes prepared by Paul Riskind (pnr@stanford.edu). spot errors or have questions about these notes.
Notes on Auctions. Theorem 1 In a second price sealed bid auction bidding your valuation is always a weakly dominant strategy.
 Notes on Auctions Second Price Sealed Bid Auctions These are the easiest auctions to analyze. Theorem In a second price sealed bid auction bidding your valuation is always a weakly dominant strategy. Proof
Notes on Auctions Second Price Sealed Bid Auctions These are the easiest auctions to analyze. Theorem In a second price sealed bid auction bidding your valuation is always a weakly dominant strategy. Proof
CUR 412: Game Theory and its Applications, Lecture 4
 CUR 412: Game Theory and its Applications, Lecture 4 Prof. Ronaldo CARPIO March 22, 2015 Homework #1 Homework #1 will be due at the end of class today. Please check the website later today for the solutions
CUR 412: Game Theory and its Applications, Lecture 4 Prof. Ronaldo CARPIO March 22, 2015 Homework #1 Homework #1 will be due at the end of class today. Please check the website later today for the solutions
CUR 412: Game Theory and its Applications, Lecture 4
 CUR 412: Game Theory and its Applications, Lecture 4 Prof. Ronaldo CARPIO March 27, 2015 Homework #1 Homework #1 will be due at the end of class today. Please check the website later today for the solutions
CUR 412: Game Theory and its Applications, Lecture 4 Prof. Ronaldo CARPIO March 27, 2015 Homework #1 Homework #1 will be due at the end of class today. Please check the website later today for the solutions
Today. Applications of NE and SPNE Auctions English Auction Second-Price Sealed-Bid Auction First-Price Sealed-Bid Auction
 Today Applications of NE and SPNE Auctions English Auction Second-Price Sealed-Bid Auction First-Price Sealed-Bid Auction 2 / 26 Auctions Used to allocate: Art Government bonds Radio spectrum Forms: Sequential
Today Applications of NE and SPNE Auctions English Auction Second-Price Sealed-Bid Auction First-Price Sealed-Bid Auction 2 / 26 Auctions Used to allocate: Art Government bonds Radio spectrum Forms: Sequential
Econ 101A Final exam May 14, 2013.
 Econ 101A Final exam May 14, 2013. Do not turn the page until instructed to. Do not forget to write Problems 1 in the first Blue Book and Problems 2, 3 and 4 in the second Blue Book. 1 Econ 101A Final
Econ 101A Final exam May 14, 2013. Do not turn the page until instructed to. Do not forget to write Problems 1 in the first Blue Book and Problems 2, 3 and 4 in the second Blue Book. 1 Econ 101A Final
Microeconomics Comprehensive Exam
 Microeconomics Comprehensive Exam June 2009 Instructions: (1) Please answer each of the four questions on separate pieces of paper. (2) When finished, please arrange your answers alphabetically (in the
Microeconomics Comprehensive Exam June 2009 Instructions: (1) Please answer each of the four questions on separate pieces of paper. (2) When finished, please arrange your answers alphabetically (in the
The Ohio State University Department of Economics Second Midterm Examination Answers
 Econ 5001 Spring 2018 Prof. James Peck The Ohio State University Department of Economics Second Midterm Examination Answers Note: There were 4 versions of the test: A, B, C, and D, based on player 1 s
Econ 5001 Spring 2018 Prof. James Peck The Ohio State University Department of Economics Second Midterm Examination Answers Note: There were 4 versions of the test: A, B, C, and D, based on player 1 s
1 Theory of Auctions. 1.1 Independent Private Value Auctions
 1 Theory of Auctions 1.1 Independent Private Value Auctions for the moment consider an environment in which there is a single seller who wants to sell one indivisible unit of output to one of n buyers
1 Theory of Auctions 1.1 Independent Private Value Auctions for the moment consider an environment in which there is a single seller who wants to sell one indivisible unit of output to one of n buyers
HW Consider the following game:
 HW 1 1. Consider the following game: 2. HW 2 Suppose a parent and child play the following game, first analyzed by Becker (1974). First child takes the action, A 0, that produces income for the child,
HW 1 1. Consider the following game: 2. HW 2 Suppose a parent and child play the following game, first analyzed by Becker (1974). First child takes the action, A 0, that produces income for the child,
Noncooperative Market Games in Normal Form
 Chapter 6 Noncooperative Market Games in Normal Form 1 Market game: one seller and one buyer 2 players, a buyer and a seller Buyer receives red card Ace=11, King = Queen = Jack = 10, 9,, 2 Number represents
Chapter 6 Noncooperative Market Games in Normal Form 1 Market game: one seller and one buyer 2 players, a buyer and a seller Buyer receives red card Ace=11, King = Queen = Jack = 10, 9,, 2 Number represents
In Class Exercises. Problem 1
 In Class Exercises Problem 1 A group of n students go to a restaurant. Each person will simultaneously choose his own meal but the total bill will be shared amongst all the students. If a student chooses
In Class Exercises Problem 1 A group of n students go to a restaurant. Each person will simultaneously choose his own meal but the total bill will be shared amongst all the students. If a student chooses
In the Name of God. Sharif University of Technology. Graduate School of Management and Economics
 In the Name of God Sharif University of Technology Graduate School of Management and Economics Microeconomics (for MBA students) 44111 (1393-94 1 st term) - Group 2 Dr. S. Farshad Fatemi Game Theory Game:
In the Name of God Sharif University of Technology Graduate School of Management and Economics Microeconomics (for MBA students) 44111 (1393-94 1 st term) - Group 2 Dr. S. Farshad Fatemi Game Theory Game:
Microeconomic Theory II Preliminary Examination Solutions Exam date: June 5, 2017
 Microeconomic Theory II Preliminary Examination Solutions Exam date: June 5, 07. (40 points) Consider a Cournot duopoly. The market price is given by q q, where q and q are the quantities of output produced
Microeconomic Theory II Preliminary Examination Solutions Exam date: June 5, 07. (40 points) Consider a Cournot duopoly. The market price is given by q q, where q and q are the quantities of output produced
Auctions. Agenda. Definition. Syllabus: Mansfield, chapter 15 Jehle, chapter 9
 Auctions Syllabus: Mansfield, chapter 15 Jehle, chapter 9 1 Agenda Types of auctions Bidding behavior Buyer s maximization problem Seller s maximization problem Introducing risk aversion Winner s curse
Auctions Syllabus: Mansfield, chapter 15 Jehle, chapter 9 1 Agenda Types of auctions Bidding behavior Buyer s maximization problem Seller s maximization problem Introducing risk aversion Winner s curse
MA300.2 Game Theory 2005, LSE
 MA300.2 Game Theory 2005, LSE Answers to Problem Set 2 [1] (a) This is standard (we have even done it in class). The one-shot Cournot outputs can be computed to be A/3, while the payoff to each firm can
MA300.2 Game Theory 2005, LSE Answers to Problem Set 2 [1] (a) This is standard (we have even done it in class). The one-shot Cournot outputs can be computed to be A/3, while the payoff to each firm can
Microeconomics II. CIDE, MsC Economics. List of Problems
 Microeconomics II CIDE, MsC Economics List of Problems 1. There are three people, Amy (A), Bart (B) and Chris (C): A and B have hats. These three people are arranged in a room so that B can see everything
Microeconomics II CIDE, MsC Economics List of Problems 1. There are three people, Amy (A), Bart (B) and Chris (C): A and B have hats. These three people are arranged in a room so that B can see everything
ECON Microeconomics II IRYNA DUDNYK. Auctions.
 Auctions. What is an auction? When and whhy do we need auctions? Auction is a mechanism of allocating a particular object at a certain price. Allocating part concerns who will get the object and the price
Auctions. What is an auction? When and whhy do we need auctions? Auction is a mechanism of allocating a particular object at a certain price. Allocating part concerns who will get the object and the price
March 30, Why do economists (and increasingly, engineers and computer scientists) study auctions?
 March 3, 215 Steven A. Matthews, A Technical Primer on Auction Theory I: Independent Private Values, Northwestern University CMSEMS Discussion Paper No. 196, May, 1995. This paper is posted on the course
March 3, 215 Steven A. Matthews, A Technical Primer on Auction Theory I: Independent Private Values, Northwestern University CMSEMS Discussion Paper No. 196, May, 1995. This paper is posted on the course
ECON 459 Game Theory. Lecture Notes Auctions. Luca Anderlini Spring 2017
 ECON 459 Game Theory Lecture Notes Auctions Luca Anderlini Spring 2017 These notes have been used and commented on before. If you can still spot any errors or have any suggestions for improvement, please
ECON 459 Game Theory Lecture Notes Auctions Luca Anderlini Spring 2017 These notes have been used and commented on before. If you can still spot any errors or have any suggestions for improvement, please
Math 135: Answers to Practice Problems
 Math 35: Answers to Practice Problems Answers to problems from the textbook: Many of the problems from the textbook have answers in the back of the book. Here are the answers to the problems that don t
Math 35: Answers to Practice Problems Answers to problems from the textbook: Many of the problems from the textbook have answers in the back of the book. Here are the answers to the problems that don t
x. The saver is John Riley 7 December 2016 Econ 401a Final Examination Sketch of answers 1. Choice over time Then Adding,
 John Riley 7 December 06 Econ 40a Final Eamination Sketch of answers Choice over time (a) y s, Adding, y ( r) s y s r r y y r r (b) The slope of the life-time budget line is r When r The initial optimum
John Riley 7 December 06 Econ 40a Final Eamination Sketch of answers Choice over time (a) y s, Adding, y ( r) s y s r r y y r r (b) The slope of the life-time budget line is r When r The initial optimum
Chapter 10: Mixed strategies Nash equilibria, reaction curves and the equality of payoffs theorem
 Chapter 10: Mixed strategies Nash equilibria reaction curves and the equality of payoffs theorem Nash equilibrium: The concept of Nash equilibrium can be extended in a natural manner to the mixed strategies
Chapter 10: Mixed strategies Nash equilibria reaction curves and the equality of payoffs theorem Nash equilibrium: The concept of Nash equilibrium can be extended in a natural manner to the mixed strategies
Elements of Economic Analysis II Lecture XI: Oligopoly: Cournot and Bertrand Competition
 Elements of Economic Analysis II Lecture XI: Oligopoly: Cournot and Bertrand Competition Kai Hao Yang /2/207 In this lecture, we will apply the concepts in game theory to study oligopoly. In short, unlike
Elements of Economic Analysis II Lecture XI: Oligopoly: Cournot and Bertrand Competition Kai Hao Yang /2/207 In this lecture, we will apply the concepts in game theory to study oligopoly. In short, unlike
Francesco Nava Microeconomic Principles II EC202 Lent Term 2010
 Answer Key Problem Set 1 Francesco Nava Microeconomic Principles II EC202 Lent Term 2010 Please give your answers to your class teacher by Friday of week 6 LT. If you not to hand in at your class, make
Answer Key Problem Set 1 Francesco Nava Microeconomic Principles II EC202 Lent Term 2010 Please give your answers to your class teacher by Friday of week 6 LT. If you not to hand in at your class, make
Lecture #6: Auctions: Theory and Applications. Prof. Dr. Sven Seuken
 Lecture #6: Auctions: Theory and Applications Prof. Dr. Sven Seuken 15.3.2012 Housekeeping Questions? Concerns? BitTorrent homework assignment? Posting on NB: do not copy/paste from PDFs Game Theory Homework:
Lecture #6: Auctions: Theory and Applications Prof. Dr. Sven Seuken 15.3.2012 Housekeeping Questions? Concerns? BitTorrent homework assignment? Posting on NB: do not copy/paste from PDFs Game Theory Homework:
When one firm considers changing its price or output level, it must make assumptions about the reactions of its rivals.
 Chapter 3 Oligopoly Oligopoly is an industry where there are relatively few sellers. The product may be standardized (steel) or differentiated (automobiles). The firms have a high degree of interdependence.
Chapter 3 Oligopoly Oligopoly is an industry where there are relatively few sellers. The product may be standardized (steel) or differentiated (automobiles). The firms have a high degree of interdependence.
Optimal Auctions. Game Theory Course: Jackson, Leyton-Brown & Shoham
 Game Theory Course: Jackson, Leyton-Brown & Shoham So far we have considered efficient auctions What about maximizing the seller s revenue? she may be willing to risk failing to sell the good she may be
Game Theory Course: Jackson, Leyton-Brown & Shoham So far we have considered efficient auctions What about maximizing the seller s revenue? she may be willing to risk failing to sell the good she may be
Oligopoly Games and Voting Games. Cournot s Model of Quantity Competition:
 Oligopoly Games and Voting Games Cournot s Model of Quantity Competition: Supposetherearetwofirms, producing an identical good. (In his 1838 book, Cournot thought of firms filling bottles with mineral
Oligopoly Games and Voting Games Cournot s Model of Quantity Competition: Supposetherearetwofirms, producing an identical good. (In his 1838 book, Cournot thought of firms filling bottles with mineral
S 2,2-1, x c C x r, 1 0,0
 Problem Set 5 1. There are two players facing each other in the following random prisoners dilemma: S C S, -1, x c C x r, 1 0,0 With probability p, x c = y, and with probability 1 p, x c = 0. With probability
Problem Set 5 1. There are two players facing each other in the following random prisoners dilemma: S C S, -1, x c C x r, 1 0,0 With probability p, x c = y, and with probability 1 p, x c = 0. With probability
MA200.2 Game Theory II, LSE
 MA200.2 Game Theory II, LSE Problem Set 1 These questions will go over basic game-theoretic concepts and some applications. homework is due during class on week 4. This [1] In this problem (see Fudenberg-Tirole
MA200.2 Game Theory II, LSE Problem Set 1 These questions will go over basic game-theoretic concepts and some applications. homework is due during class on week 4. This [1] In this problem (see Fudenberg-Tirole
Final Examination December 14, Economics 5010 AF3.0 : Applied Microeconomics. time=2.5 hours
 YORK UNIVERSITY Faculty of Graduate Studies Final Examination December 14, 2010 Economics 5010 AF3.0 : Applied Microeconomics S. Bucovetsky time=2.5 hours Do any 6 of the following 10 questions. All count
YORK UNIVERSITY Faculty of Graduate Studies Final Examination December 14, 2010 Economics 5010 AF3.0 : Applied Microeconomics S. Bucovetsky time=2.5 hours Do any 6 of the following 10 questions. All count
M.Phil. Game theory: Problem set II. These problems are designed for discussions in the classes of Week 8 of Michaelmas term. 1
 M.Phil. Game theory: Problem set II These problems are designed for discussions in the classes of Week 8 of Michaelmas term.. Private Provision of Public Good. Consider the following public good game:
M.Phil. Game theory: Problem set II These problems are designed for discussions in the classes of Week 8 of Michaelmas term.. Private Provision of Public Good. Consider the following public good game:
UC Berkeley Haas School of Business Game Theory (EMBA 296 & EWMBA 211) Summer 2016
 UC Berkeley Haas School of Business Game Theory (EMBA 296 & EWMBA 211) Summer 2016 More on strategic games and extensive games with perfect information Block 2 Jun 11, 2017 Auctions results Histogram of
UC Berkeley Haas School of Business Game Theory (EMBA 296 & EWMBA 211) Summer 2016 More on strategic games and extensive games with perfect information Block 2 Jun 11, 2017 Auctions results Histogram of
Bayesian games and their use in auctions. Vincent Conitzer
 Bayesian games and their use in auctions Vincent Conitzer conitzer@cs.duke.edu What is mechanism design? In mechanism design, we get to design the game (or mechanism) e.g. the rules of the auction, marketplace,
Bayesian games and their use in auctions Vincent Conitzer conitzer@cs.duke.edu What is mechanism design? In mechanism design, we get to design the game (or mechanism) e.g. the rules of the auction, marketplace,
Duopoly models Multistage games with observed actions Subgame perfect equilibrium Extensive form of a game Two-stage prisoner s dilemma
 Recap Last class (September 20, 2016) Duopoly models Multistage games with observed actions Subgame perfect equilibrium Extensive form of a game Two-stage prisoner s dilemma Today (October 13, 2016) Finitely
Recap Last class (September 20, 2016) Duopoly models Multistage games with observed actions Subgame perfect equilibrium Extensive form of a game Two-stage prisoner s dilemma Today (October 13, 2016) Finitely
Answer Key for M. A. Economics Entrance Examination 2017 (Main version)
 Answer Key for M. A. Economics Entrance Examination 2017 (Main version) July 4, 2017 1. Person A lexicographically prefers good x to good y, i.e., when comparing two bundles of x and y, she strictly prefers
Answer Key for M. A. Economics Entrance Examination 2017 (Main version) July 4, 2017 1. Person A lexicographically prefers good x to good y, i.e., when comparing two bundles of x and y, she strictly prefers
Microeconomics III. Oligopoly prefacetogametheory (Mar 11, 2012) School of Economics The Interdisciplinary Center (IDC), Herzliya
 Microeconomics III Oligopoly prefacetogametheory (Mar 11, 01) School of Economics The Interdisciplinary Center (IDC), Herzliya Oligopoly is a market in which only a few firms compete with one another,
Microeconomics III Oligopoly prefacetogametheory (Mar 11, 01) School of Economics The Interdisciplinary Center (IDC), Herzliya Oligopoly is a market in which only a few firms compete with one another,
Problem Set 3: Suggested Solutions
 Microeconomics: Pricing 3E Fall 5. True or false: Problem Set 3: Suggested Solutions (a) Since a durable goods monopolist prices at the monopoly price in her last period of operation, the prices must be
Microeconomics: Pricing 3E Fall 5. True or false: Problem Set 3: Suggested Solutions (a) Since a durable goods monopolist prices at the monopoly price in her last period of operation, the prices must be
Answers to Microeconomics Prelim of August 24, In practice, firms often price their products by marking up a fixed percentage over (average)
 Answers to Microeconomics Prelim of August 24, 2016 1. In practice, firms often price their products by marking up a fixed percentage over (average) cost. To investigate the consequences of markup pricing,
Answers to Microeconomics Prelim of August 24, 2016 1. In practice, firms often price their products by marking up a fixed percentage over (average) cost. To investigate the consequences of markup pricing,
Game Theory. Lecture Notes By Y. Narahari. Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science Bangalore, India July 2012
 Game Theory Lecture Notes By Y. Narahari Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science Bangalore, India July 2012 The Revenue Equivalence Theorem Note: This is a only a draft
Game Theory Lecture Notes By Y. Narahari Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science Bangalore, India July 2012 The Revenue Equivalence Theorem Note: This is a only a draft
Simon Fraser University Spring 2014
 Simon Fraser University Spring 2014 Econ 302 D200 Final Exam Solution This brief solution guide does not have the explanations necessary for full marks. NE = Nash equilibrium, SPE = subgame perfect equilibrium,
Simon Fraser University Spring 2014 Econ 302 D200 Final Exam Solution This brief solution guide does not have the explanations necessary for full marks. NE = Nash equilibrium, SPE = subgame perfect equilibrium,
CS711 Game Theory and Mechanism Design
 CS711 Game Theory and Mechanism Design Problem Set 1 August 13, 2018 Que 1. [Easy] William and Henry are participants in a televised game show, seated in separate booths with no possibility of communicating
CS711 Game Theory and Mechanism Design Problem Set 1 August 13, 2018 Que 1. [Easy] William and Henry are participants in a televised game show, seated in separate booths with no possibility of communicating
Mechanism Design and Auctions
 Multiagent Systems (BE4M36MAS) Mechanism Design and Auctions Branislav Bošanský and Michal Pěchouček Artificial Intelligence Center, Department of Computer Science, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Czech
Multiagent Systems (BE4M36MAS) Mechanism Design and Auctions Branislav Bošanský and Michal Pěchouček Artificial Intelligence Center, Department of Computer Science, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Czech
Mixed Strategies. In the previous chapters we restricted players to using pure strategies and we
 6 Mixed Strategies In the previous chapters we restricted players to using pure strategies and we postponed discussing the option that a player may choose to randomize between several of his pure strategies.
6 Mixed Strategies In the previous chapters we restricted players to using pure strategies and we postponed discussing the option that a player may choose to randomize between several of his pure strategies.
Auctions: Types and Equilibriums
 Auctions: Types and Equilibriums Emrah Cem and Samira Farhin University of Texas at Dallas emrah.cem@utdallas.edu samira.farhin@utdallas.edu April 25, 2013 Emrah Cem and Samira Farhin (UTD) Auctions April
Auctions: Types and Equilibriums Emrah Cem and Samira Farhin University of Texas at Dallas emrah.cem@utdallas.edu samira.farhin@utdallas.edu April 25, 2013 Emrah Cem and Samira Farhin (UTD) Auctions April
Advanced Microeconomics
 Advanced Microeconomics ECON5200 - Fall 2014 Introduction What you have done: - consumers maximize their utility subject to budget constraints and firms maximize their profits given technology and market
Advanced Microeconomics ECON5200 - Fall 2014 Introduction What you have done: - consumers maximize their utility subject to budget constraints and firms maximize their profits given technology and market
ECO 426 (Market Design) - Lecture 9
 ECO 426 (Market Design) - Lecture 9 Ettore Damiano November 30, 2015 Common Value Auction In a private value auction: the valuation of bidder i, v i, is independent of the other bidders value In a common
ECO 426 (Market Design) - Lecture 9 Ettore Damiano November 30, 2015 Common Value Auction In a private value auction: the valuation of bidder i, v i, is independent of the other bidders value In a common
Simon Fraser University Fall Econ 302 D200 Final Exam Solution Instructor: Songzi Du Wednesday December 16, 2015, 8:30 11:30 AM
 Simon Fraser University Fall 2015 Econ 302 D200 Final Exam Solution Instructor: Songzi Du Wednesday December 16, 2015, 8:30 11:30 AM NE = Nash equilibrium, SPE = subgame perfect equilibrium, PBE = perfect
Simon Fraser University Fall 2015 Econ 302 D200 Final Exam Solution Instructor: Songzi Du Wednesday December 16, 2015, 8:30 11:30 AM NE = Nash equilibrium, SPE = subgame perfect equilibrium, PBE = perfect
MA200.2 Game Theory II, LSE
 MA200.2 Game Theory II, LSE Answers to Problem Set [] In part (i), proceed as follows. Suppose that we are doing 2 s best response to. Let p be probability that player plays U. Now if player 2 chooses
MA200.2 Game Theory II, LSE Answers to Problem Set [] In part (i), proceed as follows. Suppose that we are doing 2 s best response to. Let p be probability that player plays U. Now if player 2 chooses
Solution Problem Set 2
 ECON 282, Intro Game Theory, (Fall 2008) Christoph Luelfesmann, SFU Solution Problem Set 2 Due at the beginning of class on Tuesday, Oct. 7. Please let me know if you have problems to understand one of
ECON 282, Intro Game Theory, (Fall 2008) Christoph Luelfesmann, SFU Solution Problem Set 2 Due at the beginning of class on Tuesday, Oct. 7. Please let me know if you have problems to understand one of
Chapter 11: Dynamic Games and First and Second Movers
 Chapter : Dynamic Games and First and Second Movers Learning Objectives Students should learn to:. Extend the reaction function ideas developed in the Cournot duopoly model to a model of sequential behavior
Chapter : Dynamic Games and First and Second Movers Learning Objectives Students should learn to:. Extend the reaction function ideas developed in the Cournot duopoly model to a model of sequential behavior
Microeconomic Theory II Preliminary Examination Solutions Exam date: August 7, 2017
 Microeconomic Theory II Preliminary Examination Solutions Exam date: August 7, 017 1. Sheila moves first and chooses either H or L. Bruce receives a signal, h or l, about Sheila s behavior. The distribution
Microeconomic Theory II Preliminary Examination Solutions Exam date: August 7, 017 1. Sheila moves first and chooses either H or L. Bruce receives a signal, h or l, about Sheila s behavior. The distribution
ISSN BWPEF Uninformative Equilibrium in Uniform Price Auctions. Arup Daripa Birkbeck, University of London.
 ISSN 1745-8587 Birkbeck Working Papers in Economics & Finance School of Economics, Mathematics and Statistics BWPEF 0701 Uninformative Equilibrium in Uniform Price Auctions Arup Daripa Birkbeck, University
ISSN 1745-8587 Birkbeck Working Papers in Economics & Finance School of Economics, Mathematics and Statistics BWPEF 0701 Uninformative Equilibrium in Uniform Price Auctions Arup Daripa Birkbeck, University
On Existence of Equilibria. Bayesian Allocation-Mechanisms
 On Existence of Equilibria in Bayesian Allocation Mechanisms Northwestern University April 23, 2014 Bayesian Allocation Mechanisms In allocation mechanisms, agents choose messages. The messages determine
On Existence of Equilibria in Bayesian Allocation Mechanisms Northwestern University April 23, 2014 Bayesian Allocation Mechanisms In allocation mechanisms, agents choose messages. The messages determine
PAULI MURTO, ANDREY ZHUKOV
 GAME THEORY SOLUTION SET 1 WINTER 018 PAULI MURTO, ANDREY ZHUKOV Introduction For suggested solution to problem 4, last year s suggested solutions by Tsz-Ning Wong were used who I think used suggested
GAME THEORY SOLUTION SET 1 WINTER 018 PAULI MURTO, ANDREY ZHUKOV Introduction For suggested solution to problem 4, last year s suggested solutions by Tsz-Ning Wong were used who I think used suggested
PAULI MURTO, ANDREY ZHUKOV. If any mistakes or typos are spotted, kindly communicate them to
 GAME THEORY PROBLEM SET 1 WINTER 2018 PAULI MURTO, ANDREY ZHUKOV Introduction If any mistakes or typos are spotted, kindly communicate them to andrey.zhukov@aalto.fi. Materials from Osborne and Rubinstein
GAME THEORY PROBLEM SET 1 WINTER 2018 PAULI MURTO, ANDREY ZHUKOV Introduction If any mistakes or typos are spotted, kindly communicate them to andrey.zhukov@aalto.fi. Materials from Osborne and Rubinstein
Auction Theory: Some Basics
 Auction Theory: Some Basics Arunava Sen Indian Statistical Institute, New Delhi ICRIER Conference on Telecom, March 7, 2014 Outline Outline Single Good Problem Outline Single Good Problem First Price Auction
Auction Theory: Some Basics Arunava Sen Indian Statistical Institute, New Delhi ICRIER Conference on Telecom, March 7, 2014 Outline Outline Single Good Problem Outline Single Good Problem First Price Auction
Game Theory: Additional Exercises
 Game Theory: Additional Exercises Problem 1. Consider the following scenario. Players 1 and 2 compete in an auction for a valuable object, for example a painting. Each player writes a bid in a sealed envelope,
Game Theory: Additional Exercises Problem 1. Consider the following scenario. Players 1 and 2 compete in an auction for a valuable object, for example a painting. Each player writes a bid in a sealed envelope,
ECE 586GT: Problem Set 1: Problems and Solutions Analysis of static games
 University of Illinois Fall 2018 ECE 586GT: Problem Set 1: Problems and Solutions Analysis of static games Due: Tuesday, Sept. 11, at beginning of class Reading: Course notes, Sections 1.1-1.4 1. [A random
University of Illinois Fall 2018 ECE 586GT: Problem Set 1: Problems and Solutions Analysis of static games Due: Tuesday, Sept. 11, at beginning of class Reading: Course notes, Sections 1.1-1.4 1. [A random
EC 202. Lecture notes 14 Oligopoly I. George Symeonidis
 EC 202 Lecture notes 14 Oligopoly I George Symeonidis Oligopoly When only a small number of firms compete in the same market, each firm has some market power. Moreover, their interactions cannot be ignored.
EC 202 Lecture notes 14 Oligopoly I George Symeonidis Oligopoly When only a small number of firms compete in the same market, each firm has some market power. Moreover, their interactions cannot be ignored.
Economics 171: Final Exam
 Question 1: Basic Concepts (20 points) Economics 171: Final Exam 1. Is it true that every strategy is either strictly dominated or is a dominant strategy? Explain. (5) No, some strategies are neither dominated
Question 1: Basic Concepts (20 points) Economics 171: Final Exam 1. Is it true that every strategy is either strictly dominated or is a dominant strategy? Explain. (5) No, some strategies are neither dominated
PhD Qualifier Examination
 PhD Qualifier Examination Department of Agricultural Economics May 29, 2014 Instructions This exam consists of six questions. You must answer all questions. If you need an assumption to complete a question,
PhD Qualifier Examination Department of Agricultural Economics May 29, 2014 Instructions This exam consists of six questions. You must answer all questions. If you need an assumption to complete a question,
University of Hong Kong
 University of Hong Kong ECON6036 Game Theory and Applications Problem Set I 1 Nash equilibrium, pure and mixed equilibrium 1. This exercise asks you to work through the characterization of all the Nash
University of Hong Kong ECON6036 Game Theory and Applications Problem Set I 1 Nash equilibrium, pure and mixed equilibrium 1. This exercise asks you to work through the characterization of all the Nash
Microeconomics II. CIDE, Spring 2011 List of Problems
 Microeconomics II CIDE, Spring 2011 List of Prolems 1. There are three people, Amy (A), Bart (B) and Chris (C): A and B have hats. These three people are arranged in a room so that B can see everything
Microeconomics II CIDE, Spring 2011 List of Prolems 1. There are three people, Amy (A), Bart (B) and Chris (C): A and B have hats. These three people are arranged in a room so that B can see everything
Chapter 3. Dynamic discrete games and auctions: an introduction
 Chapter 3. Dynamic discrete games and auctions: an introduction Joan Llull Structural Micro. IDEA PhD Program I. Dynamic Discrete Games with Imperfect Information A. Motivating example: firm entry and
Chapter 3. Dynamic discrete games and auctions: an introduction Joan Llull Structural Micro. IDEA PhD Program I. Dynamic Discrete Games with Imperfect Information A. Motivating example: firm entry and
Exercise Chapter 10
 Exercise 10.8.1 Where the isoprofit curves touch the gradients of the profits of Alice and Bob point in the opposite directions. Thus, increasing one agent s profit will necessarily decrease the other
Exercise 10.8.1 Where the isoprofit curves touch the gradients of the profits of Alice and Bob point in the opposite directions. Thus, increasing one agent s profit will necessarily decrease the other
EconS Games with Incomplete Information II and Auction Theory
 EconS 424 - Games with Incomplete Information II and Auction Theory Félix Muñoz-García Washington State University fmunoz@wsu.edu April 28, 2014 Félix Muñoz-García (WSU) EconS 424 - Recitation 9 April
EconS 424 - Games with Incomplete Information II and Auction Theory Félix Muñoz-García Washington State University fmunoz@wsu.edu April 28, 2014 Félix Muñoz-García (WSU) EconS 424 - Recitation 9 April
Lecture Notes on Anticommons T. Bergstrom, April 2010 These notes illustrate the problem of the anticommons for one particular example.
 Lecture Notes on Anticommons T Bergstrom, April 2010 These notes illustrate the problem of the anticommons for one particular example Sales with incomplete information Bilateral Monopoly We start with
Lecture Notes on Anticommons T Bergstrom, April 2010 These notes illustrate the problem of the anticommons for one particular example Sales with incomplete information Bilateral Monopoly We start with
UCLA Department of Economics Ph.D. Preliminary Exam Industrial Organization Field Exam (Spring 2010) Use SEPARATE booklets to answer each question
 Wednesday, June 23 2010 Instructions: UCLA Department of Economics Ph.D. Preliminary Exam Industrial Organization Field Exam (Spring 2010) You have 4 hours for the exam. Answer any 5 out 6 questions. All
Wednesday, June 23 2010 Instructions: UCLA Department of Economics Ph.D. Preliminary Exam Industrial Organization Field Exam (Spring 2010) You have 4 hours for the exam. Answer any 5 out 6 questions. All
Consider the following (true) preference orderings of 4 agents on 4 candidates.
 Part 1: Voting Systems Consider the following (true) preference orderings of 4 agents on 4 candidates. Agent #1: A > B > C > D Agent #2: B > C > D > A Agent #3: C > B > D > A Agent #4: D > C > A > B Assume
Part 1: Voting Systems Consider the following (true) preference orderings of 4 agents on 4 candidates. Agent #1: A > B > C > D Agent #2: B > C > D > A Agent #3: C > B > D > A Agent #4: D > C > A > B Assume
CUR 412: Game Theory and its Applications, Lecture 9
 CUR 412: Game Theory and its Applications, Lecture 9 Prof. Ronaldo CARPIO May 22, 2015 Announcements HW #3 is due next week. Ch. 6.1: Ultimatum Game This is a simple game that can model a very simplified
CUR 412: Game Theory and its Applications, Lecture 9 Prof. Ronaldo CARPIO May 22, 2015 Announcements HW #3 is due next week. Ch. 6.1: Ultimatum Game This is a simple game that can model a very simplified
Outline for today. Stat155 Game Theory Lecture 13: General-Sum Games. General-sum games. General-sum games. Dominated pure strategies
 Outline for today Stat155 Game Theory Lecture 13: General-Sum Games Peter Bartlett October 11, 2016 Two-player general-sum games Definitions: payoff matrices, dominant strategies, safety strategies, Nash
Outline for today Stat155 Game Theory Lecture 13: General-Sum Games Peter Bartlett October 11, 2016 Two-player general-sum games Definitions: payoff matrices, dominant strategies, safety strategies, Nash
Introduction to Political Economy Problem Set 3
 Introduction to Political Economy 14.770 Problem Set 3 Due date: Question 1: Consider an alternative model of lobbying (compared to the Grossman and Helpman model with enforceable contracts), where lobbies
Introduction to Political Economy 14.770 Problem Set 3 Due date: Question 1: Consider an alternative model of lobbying (compared to the Grossman and Helpman model with enforceable contracts), where lobbies
Econ 101A Final exam Th 15 December. Do not turn the page until instructed to.
 Econ 101A Final exam Th 15 December. Do not turn the page until instructed to. 1 Econ 101A Final Exam Th 15 December. Please solve Problem 1, 2, and 3 in the first blue book and Problems 4 and 5 in the
Econ 101A Final exam Th 15 December. Do not turn the page until instructed to. 1 Econ 101A Final Exam Th 15 December. Please solve Problem 1, 2, and 3 in the first blue book and Problems 4 and 5 in the
Lecture 9: Basic Oligopoly Models
 Lecture 9: Basic Oligopoly Models Managerial Economics November 16, 2012 Prof. Dr. Sebastian Rausch Centre for Energy Policy and Economics Department of Management, Technology and Economics ETH Zürich
Lecture 9: Basic Oligopoly Models Managerial Economics November 16, 2012 Prof. Dr. Sebastian Rausch Centre for Energy Policy and Economics Department of Management, Technology and Economics ETH Zürich
Economics 101A (Lecture 21) Stefano DellaVigna
 Economics 101A (Lecture 21) Stefano DellaVigna April 14, 2015 Outline 1. Oligopoly: Cournot 2. Oligopoly: Bertrand 3. Second-price Auction 4. Auctions: ebay Evidence 1 Oligopoly: Cournot Nicholson, Ch.
Economics 101A (Lecture 21) Stefano DellaVigna April 14, 2015 Outline 1. Oligopoly: Cournot 2. Oligopoly: Bertrand 3. Second-price Auction 4. Auctions: ebay Evidence 1 Oligopoly: Cournot Nicholson, Ch.
Game Theory with Applications to Finance and Marketing, I
 Game Theory with Applications to Finance and Marketing, I Homework 1, due in recitation on 10/18/2018. 1. Consider the following strategic game: player 1/player 2 L R U 1,1 0,0 D 0,0 3,2 Any NE can be
Game Theory with Applications to Finance and Marketing, I Homework 1, due in recitation on 10/18/2018. 1. Consider the following strategic game: player 1/player 2 L R U 1,1 0,0 D 0,0 3,2 Any NE can be
UC Berkeley Haas School of Business Economic Analysis for Business Decisions (EWMBA 201A) Fall 2012
 UC Berkeley Haas School of Business Economic Analysis for Business Decisions (EWMBA 01A) Fall 01 Oligopolistic markets (PR 1.-1.5) Lectures 11-1 Sep., 01 Oligopoly (preface to game theory) Another form
UC Berkeley Haas School of Business Economic Analysis for Business Decisions (EWMBA 01A) Fall 01 Oligopolistic markets (PR 1.-1.5) Lectures 11-1 Sep., 01 Oligopoly (preface to game theory) Another form
ECON106P: Pricing and Strategy
 ECON106P: Pricing and Strategy Yangbo Song Economics Department, UCLA June 30, 2014 Yangbo Song UCLA June 30, 2014 1 / 31 Game theory Game theory is a methodology used to analyze strategic situations in
ECON106P: Pricing and Strategy Yangbo Song Economics Department, UCLA June 30, 2014 Yangbo Song UCLA June 30, 2014 1 / 31 Game theory Game theory is a methodology used to analyze strategic situations in
This is page 5 Printer: Opaq
 9 Mixed Strategies This is page 5 Printer: Opaq The basic idea of Nash equilibria, that is, pairs of actions where each player is choosing a particular one of his possible actions, is an appealing one.
9 Mixed Strategies This is page 5 Printer: Opaq The basic idea of Nash equilibria, that is, pairs of actions where each player is choosing a particular one of his possible actions, is an appealing one.
Introduction to Industrial Organization Professor: Caixia Shen Fall 2014 Lecture Note 5 Games and Strategy (Ch. 4)
 Introduction to Industrial Organization Professor: Caixia Shen Fall 2014 Lecture Note 5 Games and Strategy (Ch. 4) Outline: Modeling by means of games Normal form games Dominant strategies; dominated strategies,
Introduction to Industrial Organization Professor: Caixia Shen Fall 2014 Lecture Note 5 Games and Strategy (Ch. 4) Outline: Modeling by means of games Normal form games Dominant strategies; dominated strategies,
GS/ECON 5010 Answers to Assignment 3 November 2005
 GS/ECON 5010 Answers to Assignment November 005 Q1. What are the market price, and aggregate quantity sold, in long run equilibrium in a perfectly competitive market for which the demand function has the
GS/ECON 5010 Answers to Assignment November 005 Q1. What are the market price, and aggregate quantity sold, in long run equilibrium in a perfectly competitive market for which the demand function has the
by open ascending bid ("English") auction Auctioneer raises asking price until all but one bidder drops out
 Auctions. Auction off a single item (a) () (c) (d) y open ascending id ("English") auction Auctioneer raises asking price until all ut one idder drops out y Dutch auction (descending asking price) Auctioneer
Auctions. Auction off a single item (a) () (c) (d) y open ascending id ("English") auction Auctioneer raises asking price until all ut one idder drops out y Dutch auction (descending asking price) Auctioneer
October An Equilibrium of the First Price Sealed Bid Auction for an Arbitrary Distribution.
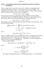 October 13..18.4 An Equilibrium of the First Price Sealed Bid Auction for an Arbitrary Distribution. We now assume that the reservation values of the bidders are independently and identically distributed
October 13..18.4 An Equilibrium of the First Price Sealed Bid Auction for an Arbitrary Distribution. We now assume that the reservation values of the bidders are independently and identically distributed
DUOPOLY. MICROECONOMICS Principles and Analysis Frank Cowell. July 2017 Frank Cowell: Duopoly. Almost essential Monopoly
 Prerequisites Almost essential Monopoly Useful, but optional Game Theory: Strategy and Equilibrium DUOPOLY MICROECONOMICS Principles and Analysis Frank Cowell 1 Overview Duopoly Background How the basic
Prerequisites Almost essential Monopoly Useful, but optional Game Theory: Strategy and Equilibrium DUOPOLY MICROECONOMICS Principles and Analysis Frank Cowell 1 Overview Duopoly Background How the basic
Challenge to Hotelling s Principle of Minimum
 Challenge to Hotelling s Principle of Minimum Differentiation Two conclusions 1. There is no equilibrium when sellers are too close i.e., Hotelling is wrong 2. Under a slightly modified version, get maximum
Challenge to Hotelling s Principle of Minimum Differentiation Two conclusions 1. There is no equilibrium when sellers are too close i.e., Hotelling is wrong 2. Under a slightly modified version, get maximum
ECON/MGMT 115. Industrial Organization
 ECON/MGMT 115 Industrial Organization 1. Cournot Model, reprised 2. Bertrand Model of Oligopoly 3. Cournot & Bertrand First Hour Reviewing the Cournot Duopoloy Equilibria Cournot vs. competitive markets
ECON/MGMT 115 Industrial Organization 1. Cournot Model, reprised 2. Bertrand Model of Oligopoly 3. Cournot & Bertrand First Hour Reviewing the Cournot Duopoloy Equilibria Cournot vs. competitive markets
Multiunit Auctions: Package Bidding October 24, Multiunit Auctions: Package Bidding
 Multiunit Auctions: Package Bidding 1 Examples of Multiunit Auctions Spectrum Licenses Bus Routes in London IBM procurements Treasury Bills Note: Heterogenous vs Homogenous Goods 2 Challenges in Multiunit
Multiunit Auctions: Package Bidding 1 Examples of Multiunit Auctions Spectrum Licenses Bus Routes in London IBM procurements Treasury Bills Note: Heterogenous vs Homogenous Goods 2 Challenges in Multiunit
Networks: Fall 2010 Homework 3 David Easley and Jon Kleinberg Due in Class September 29, 2010
 Networks: Fall 00 Homework David Easley and Jon Kleinberg Due in Class September 9, 00 As noted on the course home page, homework solutions must be submitted by upload to the CMS site, at https://cms.csuglab.cornell.edu/.
Networks: Fall 00 Homework David Easley and Jon Kleinberg Due in Class September 9, 00 As noted on the course home page, homework solutions must be submitted by upload to the CMS site, at https://cms.csuglab.cornell.edu/.
Ideal Bootstrapping and Exact Recombination: Applications to Auction Experiments
 Ideal Bootstrapping and Exact Recombination: Applications to Auction Experiments Carl T. Bergstrom University of Washington, Seattle, WA Theodore C. Bergstrom University of California, Santa Barbara Rodney
Ideal Bootstrapping and Exact Recombination: Applications to Auction Experiments Carl T. Bergstrom University of Washington, Seattle, WA Theodore C. Bergstrom University of California, Santa Barbara Rodney
