Parkes Mechanism Design 1. Mechanism Design I. David C. Parkes. Division of Engineering and Applied Science, Harvard University
|
|
|
- George Lyons
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Parkes Mechanism Design 1 Mechanism Design I David C. Parkes Division of Engineering and Applied Science, Harvard University CS 286r Spring 2003
2 Parkes Mechanism Design 2 Mechanism Design Central question: what social choice functions can be implemented in distributed systems with private information and rational agents? impose incentive based constraints Note: Mechanism design assumes unlimited computation and communication. Key concept is that of a rational agent.
3 Parkes Mechanism Design 3 Central Ideas Design criteria participation constraints incentive-compatibility constraints budget-balance constraints Revelation principle Impossibility and possibility results what are the limits that the information problem and rationality place on implementation?
4 Parkes Mechanism Design 4 Basic Definitions Set of possible outcomes Agents, with preference types. Utility,, over outcome, and Mechanism! " defines a strategy space $#&% '(')'*%,+, and an outcome function -. + /. Agent 0 plays strategy 12 the mechanism implements outcome 6 1 #7 #89:'('('( 1 + +;!., given type 354, and Defines a game: Utility to agent from strategy profile 1, is <=6 1!>, which we write as shorthand? 1.
5 + Parkes Mechanism Design 5 Classic Implementation Concept implements SCF D if: 6 1FE# G# >(':')'( 1FE + H+! D 9 I for an equil. strategy 1 E# )'(':'( 1 JE.
6 Parkes Mechanism Design 6 Equilibrium Concepts " implements D in eq. if, for all,? 1 E! D, where 1 E is a eq. Nash: 1 E > 1 EK K 9 ML 12N 9 1 EK K 9 > I OI PI 12N RQ Bayesian-Nash: (need a common prior S T3VU ) WYX8Z\[^] WaX9Z\[2] 1FE 9 1FEK K _> `,L < 1 N > 1FEK K > `b Dominant strategy: 1 E 9 1 K < K _> ML < 12N > 1 K < K _> _9 I OI OI 12N Q 1 E I PI PI 1 N cq 1 E PI 1 K 1 E
7 i Parkes Mechanism Design 7 d efhg Bayes-Nash sgt gqeuwv?xhu i j kml npoqeo"r
8 Parkes Mechanism Design 8 Mechanism Desiderata Allocative Efficiency select the outcome that maximizes total utility Fairness select the outcome that minimizes the variance in utility Revenue maximization select the outcome that maximizes revenue to a seller (or more generally, utility to one of the agents) Budget-balanced implement outcomes that have balanced transfers across agents Pareto Optimal
9 { { Parkes Mechanism Design 9 Direct Revelation Mechanisms (DRM) In a DRM, y ", the strategy space, z {, and an agent simply reports a type to the mechanism, with outcome rule, - /. Def. [incentive-compatible] A DRM is (Bayes-)Nash incentive-compatible if truth-revelation is a (Bayes-)Nash equilibrium, i.e. for all agent 0 and 3 4~} 4, X8Z\[^]? A K > ` L X8Z\[2] <? ƒ y K _> `b I;ƒ Q Def. [strategyproof] A DRM is strategyproof if truth-revelation is a dominant strategy eq., i.e. for all agent 0 4, and 3 4~} =6 A K _> YL < 6 ƒ O K _9 _> I K _I;ƒ Q We say that T3mU is truthfully implementable.
10 Parkes Mechanism Design 10 The Revelation Principle [Gibbard 73;Green & Laffont 77] Thm. For any mechanism,, there is a direct and incentive-compatible mechanism with the same outcome. the computations that go on within the mind of any bidder in the nondirect mechanism are shifted to become part of the mechanism in the direct mechanism. [McAfee&McMillan, 87] Consider: the IC direct-revelation implementation of a first-price sealed-bid auction the IC direct-revelation implementation of an English (ascending-price) auction.
11 { Parkes Mechanism Design 11 Proof Consider mechanism, Am, that implements SCF, T3mU, in a dominant strategy equilibrium. In otherwords, ˆTP ŠT3VU9U strategy eq. T3mU, for all 3 }, where Š is a dominant Construct direct mechanism, N D. By contradicton, suppose: cq N Œ ' Ž2' D N K 9 M D K 9 for some N Q, some K. But, because D 6 1 E!, this implies that =6 1FE N 9 1FEK K _!> Y!=6 1HE > 1FEK K!9 which contradicts the strategyproofness of.š in mechanism,.
12 Parkes Mechanism Design 12 Theoretical Implications Putting computational constraints to one side, we can limit the search for a useful mechanism to the class of direct and incentive-compatible mechanisms. Focus goals. Formulate as an explicit optimization problem; e.g. maximize expected payoff to the seller across all DRM s that satisfy IC and IR constraints (Myerson 81). Impossibility. If no DRM,, can implement SCF, 6, then no mechanism can implement SCF?.
13 Parkes Mechanism Design 13 Practical Implications? Incentive-compatibility is free from an implementation perspective (but NOT strategyproofness) any outcome implemented by mechanism,, can be implemented by incentive-compatible mechanism,. BUT BUT BUT, what about computation? few procedures in practical use are direct and incentive-compatible, perhaps their are some unmodeled costs, computational problems? Problems include: Shifts computation to center; Pref. elicitation costs; Not transparent; Requires a center.
14 + Parkes Mechanism Design 14 Introducing Payments Define the outcome space, % outcome rule, y ># :'('('(y <+, defines a choice,? 1, and a transfer, y < 1 from agent 0 to the mechanism, given strategy profile 1. Assume quasilinear preferences,, such that an š < y where < is the valuation function of agent 0. General/No-transfer i sgt x ef9nžxhu Quasi-linear/Transfer
15 Parkes Mechanism Design 15 Individual Rationality Constraints Let < denote the (expected) utility to agent 0 with type 3 4 of its outside option, and let! D > denote the equilibrium utility to agent 0 in the mechanism. ex ante individual-rationality agents choose to participate before they know their own types; XhŸ5 ]? D > ` L interim individual-rationality X [ Ÿ [ agents can withdraw once they know their own type; X9Z"[yŸ ˆZ\[ ] D K > ` L ex post individual-rationality agents can withdraw from the mechanism at the end; D 9 YL <. ex ante i interim i ex post sgt gqeuwv?xhu
16 Parkes Mechanism Design 16 Groves Mechanisms [Groves 73] Def. A Groves mechanism, 9 y # ('('(':A + is defined with choice rule, E ƒ F ª ŸG«< mƒ and transfer rules ƒ ƒ K 7 E ƒ >*ƒ where yb is an (arbitrary) function that does not depend on the reported type, ƒ, of agent 0 ; abstract choice set. Thm. [Groves 73] Groves mechanisms are strategyproof and efficient.
17 Parkes Mechanism Design 17 Proof. Agent 0 s utility for strategy 3 4 ±, given 3 ± s 4 from agents ² ³ 0, is: ƒ E ƒ 9 ƒ E ƒ 9 q E ƒ 9mƒ ƒ K Ignore V ƒ K, and notice that choice E ƒ F ª ŸG«< mƒ i.e. it maximizes the sum of reported values, and therefore the agent should announce ƒ to maximize its own payoff. Thm. Groves mechanisms are unique, in the sense that any mechanism that implements efficient choice, µ,št3mu, in truthful dominant strategy must implement Groves transfers. (Green & Laffont 77)
18 Parkes Mechanism Design 18 Vickrey-Clarke-Groves Mechanism [Vickrey61, Clarke71, Groves73] Def. [VCG mechanism] Implement efficient outcome, E ª Vƒ, and compute transfers where ƒ K ª K *ƒ mƒ. E *ƒ Thm. The VCG mechanism is strategyproof, efficient, and interim IR. Alternative description: V¹wº¼»b½7¾ ]¼ ÀM ` where is the value of the efficient allocation in the subproblem restricted to agents Á.
19 ] Parkes Mechanism Design 19 [Note 1:] given strategies ƒ payment, < E ]Â < E ƒ ÀM ]Â K, each agent s ÀM `, sets ÀM `Ã E ƒ i.e., this is the least value agent could have bid and maintained outcome E. [Note 2:] Each agent s equilibrium utility is: Ä < E < E _@ ÀM, ÀM ` i.e., equal to its marginal contribution to the welfare of the system. * potential for a budget-balance problem here!
20 Ì Parkes Mechanism Design 20 Example: Shortest Path. [Nisan 99] S T Biconnected graph, Å bæ, cost Ç2ÈÊÉ } Í, edges srategic. Assume large value Î to send message. Ë per edge Goal: route packets along the lowest-cost path from z to Ï. VCG Payment edge Ð : ¹wºÑ»Ò½ ¾ÔÓ Õ Ó Ö Ø Õ Ó Ø Ù Ó.ØÛ Ø Ù Ó Ú
21 Parkes Mechanism Design 21 [Krishna & Perry 98] The Centrality of VCG Thm. Among all efficient and interim IR mechanisms, the VCG maximizes the expected transfers from agents. In other words, the VCG mechanism maximizes the expected revenue to a seller across all efficient mechanisms. (BNE does not help). note. VCG & reserve prices also maximizes revenue across all mechanisms when there is a perfectly efficient aftermarket. (Ausubel& Cramton) This unification provides quite direct results of a number of central negative results in the mechanism design literature. Next time!
Mechanism Design and Auctions
 Multiagent Systems (BE4M36MAS) Mechanism Design and Auctions Branislav Bošanský and Michal Pěchouček Artificial Intelligence Center, Department of Computer Science, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Czech
Multiagent Systems (BE4M36MAS) Mechanism Design and Auctions Branislav Bošanský and Michal Pěchouček Artificial Intelligence Center, Department of Computer Science, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Czech
Parkes Auction Theory 1. Auction Theory. Jacomo Corbo. School of Engineering and Applied Science, Harvard University
 Parkes Auction Theory 1 Auction Theory Jacomo Corbo School of Engineering and Applied Science, Harvard University CS 286r Spring 2007 Parkes Auction Theory 2 Auctions: A Special Case of Mech. Design Allocation
Parkes Auction Theory 1 Auction Theory Jacomo Corbo School of Engineering and Applied Science, Harvard University CS 286r Spring 2007 Parkes Auction Theory 2 Auctions: A Special Case of Mech. Design Allocation
Parkes Auction Theory 1. Auction Theory. David C. Parkes. Division of Engineering and Applied Science, Harvard University
 Parkes Auction Theory 1 Auction Theory David C. Parkes Division of Engineering and Applied Science, Harvard University CS 286r Spring 2003 Parkes Auction Theory 2 Auctions: A Special Case of Mech. Design
Parkes Auction Theory 1 Auction Theory David C. Parkes Division of Engineering and Applied Science, Harvard University CS 286r Spring 2003 Parkes Auction Theory 2 Auctions: A Special Case of Mech. Design
Mechanism Design and Auctions
 Mechanism Design and Auctions Kevin Leyton-Brown & Yoav Shoham Chapter 7 of Multiagent Systems (MIT Press, 2012) Drawing on material that first appeared in our own book, Multiagent Systems: Algorithmic,
Mechanism Design and Auctions Kevin Leyton-Brown & Yoav Shoham Chapter 7 of Multiagent Systems (MIT Press, 2012) Drawing on material that first appeared in our own book, Multiagent Systems: Algorithmic,
Auctions Introduction
 Auctions Introduction CPSC 532A Lecture 20 November 21, 2006 Auctions Introduction CPSC 532A Lecture 20, Slide 1 Lecture Overview 1 Recap 2 VCG caveats 3 Auctions 4 Standard auctions 5 More exotic auctions
Auctions Introduction CPSC 532A Lecture 20 November 21, 2006 Auctions Introduction CPSC 532A Lecture 20, Slide 1 Lecture Overview 1 Recap 2 VCG caveats 3 Auctions 4 Standard auctions 5 More exotic auctions
Matching Markets and Google s Sponsored Search
 Matching Markets and Google s Sponsored Search Part III: Dynamics Episode 9 Baochun Li Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Matching Markets (Required reading: Chapter
Matching Markets and Google s Sponsored Search Part III: Dynamics Episode 9 Baochun Li Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Matching Markets (Required reading: Chapter
April 29, X ( ) for all. Using to denote a true type and areport,let
 April 29, 2015 "A Characterization of Efficient, Bayesian Incentive Compatible Mechanisms," by S. R. Williams. Economic Theory 14, 155-180 (1999). AcommonresultinBayesianmechanismdesignshowsthatexpostefficiency
April 29, 2015 "A Characterization of Efficient, Bayesian Incentive Compatible Mechanisms," by S. R. Williams. Economic Theory 14, 155-180 (1999). AcommonresultinBayesianmechanismdesignshowsthatexpostefficiency
2534 Lecture 9: Bayesian Games, Mechanism Design and Auctions
 2534 Lecture 9: Bayesian Games, Mechanism Design and Auctions Wrap up (quickly) extensive form/dynamic games Mechanism Design Bayesian games, mechanisms, auctions (a bit) will focus on Shoham and Leyton-Brown
2534 Lecture 9: Bayesian Games, Mechanism Design and Auctions Wrap up (quickly) extensive form/dynamic games Mechanism Design Bayesian games, mechanisms, auctions (a bit) will focus on Shoham and Leyton-Brown
Game Theory Lecture #16
 Game Theory Lecture #16 Outline: Auctions Mechanism Design Vickrey-Clarke-Groves Mechanism Optimizing Social Welfare Goal: Entice players to select outcome which optimizes social welfare Examples: Traffic
Game Theory Lecture #16 Outline: Auctions Mechanism Design Vickrey-Clarke-Groves Mechanism Optimizing Social Welfare Goal: Entice players to select outcome which optimizes social welfare Examples: Traffic
Truthful Double Auction Mechanisms
 OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 56, No. 1, January February 2008, pp. 102 120 issn 0030-364X eissn 1526-5463 08 5601 0102 informs doi 10.1287/opre.1070.0458 2008 INFORMS Truthful Double Auction Mechanisms Leon
OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 56, No. 1, January February 2008, pp. 102 120 issn 0030-364X eissn 1526-5463 08 5601 0102 informs doi 10.1287/opre.1070.0458 2008 INFORMS Truthful Double Auction Mechanisms Leon
Multiunit Auctions: Package Bidding October 24, Multiunit Auctions: Package Bidding
 Multiunit Auctions: Package Bidding 1 Examples of Multiunit Auctions Spectrum Licenses Bus Routes in London IBM procurements Treasury Bills Note: Heterogenous vs Homogenous Goods 2 Challenges in Multiunit
Multiunit Auctions: Package Bidding 1 Examples of Multiunit Auctions Spectrum Licenses Bus Routes in London IBM procurements Treasury Bills Note: Heterogenous vs Homogenous Goods 2 Challenges in Multiunit
CS599: Algorithm Design in Strategic Settings Fall 2012 Lecture 4: Prior-Free Single-Parameter Mechanism Design. Instructor: Shaddin Dughmi
 CS599: Algorithm Design in Strategic Settings Fall 2012 Lecture 4: Prior-Free Single-Parameter Mechanism Design Instructor: Shaddin Dughmi Administrivia HW out, due Friday 10/5 Very hard (I think) Discuss
CS599: Algorithm Design in Strategic Settings Fall 2012 Lecture 4: Prior-Free Single-Parameter Mechanism Design Instructor: Shaddin Dughmi Administrivia HW out, due Friday 10/5 Very hard (I think) Discuss
Auction Theory: Some Basics
 Auction Theory: Some Basics Arunava Sen Indian Statistical Institute, New Delhi ICRIER Conference on Telecom, March 7, 2014 Outline Outline Single Good Problem Outline Single Good Problem First Price Auction
Auction Theory: Some Basics Arunava Sen Indian Statistical Institute, New Delhi ICRIER Conference on Telecom, March 7, 2014 Outline Outline Single Good Problem Outline Single Good Problem First Price Auction
Revenue Equivalence and Mechanism Design
 Equivalence and Design Daniel R. 1 1 Department of Economics University of Maryland, College Park. September 2017 / Econ415 IPV, Total Surplus Background the mechanism designer The fact that there are
Equivalence and Design Daniel R. 1 1 Department of Economics University of Maryland, College Park. September 2017 / Econ415 IPV, Total Surplus Background the mechanism designer The fact that there are
Game Theory. Lecture Notes By Y. Narahari. Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science Bangalore, India July 2012
 Game Theory Lecture Notes By Y. Narahari Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science Bangalore, India July 2012 The Revenue Equivalence Theorem Note: This is a only a draft
Game Theory Lecture Notes By Y. Narahari Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science Bangalore, India July 2012 The Revenue Equivalence Theorem Note: This is a only a draft
CS 573: Algorithmic Game Theory Lecture date: 22 February Combinatorial Auctions 1. 2 The Vickrey-Clarke-Groves (VCG) Mechanism 3
 CS 573: Algorithmic Game Theory Lecture date: 22 February 2008 Instructor: Chandra Chekuri Scribe: Daniel Rebolledo Contents 1 Combinatorial Auctions 1 2 The Vickrey-Clarke-Groves (VCG) Mechanism 3 3 Examples
CS 573: Algorithmic Game Theory Lecture date: 22 February 2008 Instructor: Chandra Chekuri Scribe: Daniel Rebolledo Contents 1 Combinatorial Auctions 1 2 The Vickrey-Clarke-Groves (VCG) Mechanism 3 3 Examples
Mechanism Design and Auctions
 Mechanism Design and Auctions Game Theory Algorithmic Game Theory 1 TOC Mechanism Design Basics Myerson s Lemma Revenue-Maximizing Auctions Near-Optimal Auctions Multi-Parameter Mechanism Design and the
Mechanism Design and Auctions Game Theory Algorithmic Game Theory 1 TOC Mechanism Design Basics Myerson s Lemma Revenue-Maximizing Auctions Near-Optimal Auctions Multi-Parameter Mechanism Design and the
Introduction to mechanism design. Lirong Xia
 Introduction to mechanism design Lirong Xia Fall, 2016 1 Last class: game theory R 1 * s 1 Strategy Profile D Mechanism R 2 * s 2 Outcome R n * s n Game theory: predicting the outcome with strategic agents
Introduction to mechanism design Lirong Xia Fall, 2016 1 Last class: game theory R 1 * s 1 Strategy Profile D Mechanism R 2 * s 2 Outcome R n * s n Game theory: predicting the outcome with strategic agents
CSV 886 Social Economic and Information Networks. Lecture 4: Auctions, Matching Markets. R Ravi
 CSV 886 Social Economic and Information Networks Lecture 4: Auctions, Matching Markets R Ravi ravi+iitd@andrew.cmu.edu Schedule 2 Auctions 3 Simple Models of Trade Decentralized Buyers and sellers have
CSV 886 Social Economic and Information Networks Lecture 4: Auctions, Matching Markets R Ravi ravi+iitd@andrew.cmu.edu Schedule 2 Auctions 3 Simple Models of Trade Decentralized Buyers and sellers have
Dynamic Marginal Contribution Mechanism
 Dynamic Marginal Contribution Mechanism Dirk Bergemann and Juuso Välimäki DIMACS: Economics and Computer Science October 2007 Intertemporal Efciency with Private Information random arrival of buyers, sellers
Dynamic Marginal Contribution Mechanism Dirk Bergemann and Juuso Välimäki DIMACS: Economics and Computer Science October 2007 Intertemporal Efciency with Private Information random arrival of buyers, sellers
Deep Learning for Revenue-Optimal Auctions with Budgets
 Deep Learning for Revenue-Optimal Auctions with Budgets Zhe Feng Harvard SEAS Based on joint work with Harikrishna Narasimhan (Harvard) and David C. Parkes (Harvard) 7/11/2018 AAMAS'18, Stockholm, Sweden
Deep Learning for Revenue-Optimal Auctions with Budgets Zhe Feng Harvard SEAS Based on joint work with Harikrishna Narasimhan (Harvard) and David C. Parkes (Harvard) 7/11/2018 AAMAS'18, Stockholm, Sweden
Decentralized supply chain formation using an incentive compatible mechanism
 formation using an incentive compatible mechanism N. Hemachandra IE&OR, IIT Bombay Joint work with Prof Y Narahari and Nikesh Srivastava Symposium on Optimization in Supply Chains IIT Bombay, Oct 27, 2007
formation using an incentive compatible mechanism N. Hemachandra IE&OR, IIT Bombay Joint work with Prof Y Narahari and Nikesh Srivastava Symposium on Optimization in Supply Chains IIT Bombay, Oct 27, 2007
Path Auction Games When an Agent Can Own Multiple Edges
 Path Auction Games When an Agent Can Own Multiple Edges Ye Du Rahul Sami Yaoyun Shi Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, University of Michigan 2260 Hayward Ave, Ann Arbor, MI 48109-2121,
Path Auction Games When an Agent Can Own Multiple Edges Ye Du Rahul Sami Yaoyun Shi Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, University of Michigan 2260 Hayward Ave, Ann Arbor, MI 48109-2121,
Introduction to mechanism design. Lirong Xia
 Introduction to mechanism design Lirong Xia Feb. 9, 2016 1 Last class: game theory R 1 * s 1 Strategy Profile D Mechanism R 2 * s 2 Outcome R n * s n Game theory: predicting the outcome with strategic
Introduction to mechanism design Lirong Xia Feb. 9, 2016 1 Last class: game theory R 1 * s 1 Strategy Profile D Mechanism R 2 * s 2 Outcome R n * s n Game theory: predicting the outcome with strategic
Auction Theory Lecture Note, David McAdams, Fall Bilateral Trade
 Auction Theory Lecture Note, Daid McAdams, Fall 2008 1 Bilateral Trade ** Reised 10-17-08: An error in the discussion after Theorem 4 has been corrected. We shall use the example of bilateral trade to
Auction Theory Lecture Note, Daid McAdams, Fall 2008 1 Bilateral Trade ** Reised 10-17-08: An error in the discussion after Theorem 4 has been corrected. We shall use the example of bilateral trade to
Game Theory. Jiang, Bo ( 江波 )
 Game Theory Jiang, Bo ( 江波 ) jiang.bo@mail.shufe.edu.cn Majority voting Mechanism Design Three candidates: x, y, z. Three voters: a, b, c. Voter a: x>y>z; voter b: y>z>x; voter c: z>x>y What is the final
Game Theory Jiang, Bo ( 江波 ) jiang.bo@mail.shufe.edu.cn Majority voting Mechanism Design Three candidates: x, y, z. Three voters: a, b, c. Voter a: x>y>z; voter b: y>z>x; voter c: z>x>y What is the final
How Pervasive is the Myerson-Satterthwaite Impossibility?
 How Pervasive is the Myerson-Satterthwaite Impossibility? Abraham Othman and Tuomas Sandholm Computer Science Department Carnegie Mellon University {aothman,sandholm}@cs.cmu.edu Abstract The Myerson-Satterthwaite
How Pervasive is the Myerson-Satterthwaite Impossibility? Abraham Othman and Tuomas Sandholm Computer Science Department Carnegie Mellon University {aothman,sandholm}@cs.cmu.edu Abstract The Myerson-Satterthwaite
Mechanism design with correlated distributions. Michael Albert and Vincent Conitzer and
 Mechanism design with correlated distributions Michael Albert and Vincent Conitzer malbert@cs.duke.edu and conitzer@cs.duke.edu Impossibility results from mechanism design with independent valuations Myerson
Mechanism design with correlated distributions Michael Albert and Vincent Conitzer malbert@cs.duke.edu and conitzer@cs.duke.edu Impossibility results from mechanism design with independent valuations Myerson
Ascending Price Vickrey Auctions for General Valuations
 Ascending Price Vickrey Auctions for General Valuations The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation Mishra, Debasis,
Ascending Price Vickrey Auctions for General Valuations The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation Mishra, Debasis,
Bayesian games and their use in auctions. Vincent Conitzer
 Bayesian games and their use in auctions Vincent Conitzer conitzer@cs.duke.edu What is mechanism design? In mechanism design, we get to design the game (or mechanism) e.g. the rules of the auction, marketplace,
Bayesian games and their use in auctions Vincent Conitzer conitzer@cs.duke.edu What is mechanism design? In mechanism design, we get to design the game (or mechanism) e.g. the rules of the auction, marketplace,
From the Assignment Model to Combinatorial Auctions
 From the Assignment Model to Combinatorial Auctions IPAM Workshop, UCLA May 7, 2008 Sushil Bikhchandani & Joseph Ostroy Overview LP formulations of the (package) assignment model Sealed-bid and ascending-price
From the Assignment Model to Combinatorial Auctions IPAM Workshop, UCLA May 7, 2008 Sushil Bikhchandani & Joseph Ostroy Overview LP formulations of the (package) assignment model Sealed-bid and ascending-price
Information, efficiency and the core of an economy: Comments on Wilson s paper
 Information, efficiency and the core of an economy: Comments on Wilson s paper Dionysius Glycopantis 1 and Nicholas C. Yannelis 2 1 Department of Economics, City University, Northampton Square, London
Information, efficiency and the core of an economy: Comments on Wilson s paper Dionysius Glycopantis 1 and Nicholas C. Yannelis 2 1 Department of Economics, City University, Northampton Square, London
COS 445 Final. Due online Monday, May 21st at 11:59 pm. Please upload each problem as a separate file via MTA.
 COS 445 Final Due online Monday, May 21st at 11:59 pm All problems on this final are no collaboration problems. You may not discuss any aspect of any problems with anyone except for the course staff. You
COS 445 Final Due online Monday, May 21st at 11:59 pm All problems on this final are no collaboration problems. You may not discuss any aspect of any problems with anyone except for the course staff. You
Algorithmic Game Theory
 Algorithmic Game Theory Lecture 10 06/15/10 1 A combinatorial auction is defined by a set of goods G, G = m, n bidders with valuation functions v i :2 G R + 0. $5 Got $6! More? Example: A single item for
Algorithmic Game Theory Lecture 10 06/15/10 1 A combinatorial auction is defined by a set of goods G, G = m, n bidders with valuation functions v i :2 G R + 0. $5 Got $6! More? Example: A single item for
University of Michigan. July 1994
 Preliminary Draft Generalized Vickrey Auctions by Jerey K. MacKie-Mason Hal R. Varian University of Michigan July 1994 Abstract. We describe a generalization of the Vickrey auction. Our mechanism extends
Preliminary Draft Generalized Vickrey Auctions by Jerey K. MacKie-Mason Hal R. Varian University of Michigan July 1994 Abstract. We describe a generalization of the Vickrey auction. Our mechanism extends
Auctioning one item. Tuomas Sandholm Computer Science Department Carnegie Mellon University
 Auctioning one item Tuomas Sandholm Computer Science Department Carnegie Mellon University Auctions Methods for allocating goods, tasks, resources... Participants: auctioneer, bidders Enforced agreement
Auctioning one item Tuomas Sandholm Computer Science Department Carnegie Mellon University Auctions Methods for allocating goods, tasks, resources... Participants: auctioneer, bidders Enforced agreement
Optimal Auctions. Game Theory Course: Jackson, Leyton-Brown & Shoham
 Game Theory Course: Jackson, Leyton-Brown & Shoham So far we have considered efficient auctions What about maximizing the seller s revenue? she may be willing to risk failing to sell the good she may be
Game Theory Course: Jackson, Leyton-Brown & Shoham So far we have considered efficient auctions What about maximizing the seller s revenue? she may be willing to risk failing to sell the good she may be
Algorithmic Game Theory (a primer) Depth Qualifying Exam for Ashish Rastogi (Ph.D. candidate)
 Algorithmic Game Theory (a primer) Depth Qualifying Exam for Ashish Rastogi (Ph.D. candidate) 1 Game Theory Theory of strategic behavior among rational players. Typical game has several players. Each player
Algorithmic Game Theory (a primer) Depth Qualifying Exam for Ashish Rastogi (Ph.D. candidate) 1 Game Theory Theory of strategic behavior among rational players. Typical game has several players. Each player
CS364B: Frontiers in Mechanism Design Lecture #18: Multi-Parameter Revenue-Maximization
 CS364B: Frontiers in Mechanism Design Lecture #18: Multi-Parameter Revenue-Maximization Tim Roughgarden March 5, 2014 1 Review of Single-Parameter Revenue Maximization With this lecture we commence the
CS364B: Frontiers in Mechanism Design Lecture #18: Multi-Parameter Revenue-Maximization Tim Roughgarden March 5, 2014 1 Review of Single-Parameter Revenue Maximization With this lecture we commence the
On the impossibility of core-selecting auctions
 Theoretical Economics 11 (2016), 41 52 1555-7561/20160041 On the impossibility of core-selecting auctions Jacob K. Goeree Economics Discipline Group, University of Technology Sydney Yuanchuan Lien Department
Theoretical Economics 11 (2016), 41 52 1555-7561/20160041 On the impossibility of core-selecting auctions Jacob K. Goeree Economics Discipline Group, University of Technology Sydney Yuanchuan Lien Department
The Optimality of Being Efficient. Lawrence Ausubel and Peter Cramton Department of Economics University of Maryland
 The Optimality of Being Efficient Lawrence Ausubel and Peter Cramton Department of Economics University of Maryland 1 Common Reaction Why worry about efficiency, when there is resale? Our Conclusion Why
The Optimality of Being Efficient Lawrence Ausubel and Peter Cramton Department of Economics University of Maryland 1 Common Reaction Why worry about efficiency, when there is resale? Our Conclusion Why
2534 Lecture 10: Mechanism Design and Auctions
 2534 Lecture 10: Mechanism Design and Auctions Mechanism Design re-introduce mechanisms and mechanism design key results in mechanism design, auctions as an illustration we ll briefly discuss (though we
2534 Lecture 10: Mechanism Design and Auctions Mechanism Design re-introduce mechanisms and mechanism design key results in mechanism design, auctions as an illustration we ll briefly discuss (though we
SPECTRUM MARKETS. Randall Berry, Michael Honig Department of EECS Northwestern University. DySPAN Conference, Aachen, Germany
 1 SPECTRUM MARKETS Randall Berry, Michael Honig Department of EECS Northwestern University DySPAN Conference, Aachen, Germany Spectrum Management 2 Economics Policy Communications Engineering Why This
1 SPECTRUM MARKETS Randall Berry, Michael Honig Department of EECS Northwestern University DySPAN Conference, Aachen, Germany Spectrum Management 2 Economics Policy Communications Engineering Why This
Single-Parameter Mechanisms
 Algorithmic Game Theory, Summer 25 Single-Parameter Mechanisms Lecture 9 (6 pages) Instructor: Xiaohui Bei In the previous lecture, we learned basic concepts about mechanism design. The goal in this area
Algorithmic Game Theory, Summer 25 Single-Parameter Mechanisms Lecture 9 (6 pages) Instructor: Xiaohui Bei In the previous lecture, we learned basic concepts about mechanism design. The goal in this area
auction terminates to compute minimal competitive equilibrium prices. With this approach the auction does not need to terminate with minimal CE prices
 Chapter 7 ibundle Extend & Adjust Much of my dissertation addresses a fundamental problem with the GVA, which is that it requires agents to compute and reveal their values for all combinations of items.
Chapter 7 ibundle Extend & Adjust Much of my dissertation addresses a fundamental problem with the GVA, which is that it requires agents to compute and reveal their values for all combinations of items.
Auctions. Michal Jakob Agent Technology Center, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, FEE, Czech Technical University
 Auctions Michal Jakob Agent Technology Center, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, FEE, Czech Technical University AE4M36MAS Autumn 2014 - Lecture 12 Where are We? Agent architectures (inc. BDI
Auctions Michal Jakob Agent Technology Center, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, FEE, Czech Technical University AE4M36MAS Autumn 2014 - Lecture 12 Where are We? Agent architectures (inc. BDI
Consider the following (true) preference orderings of 4 agents on 4 candidates.
 Part 1: Voting Systems Consider the following (true) preference orderings of 4 agents on 4 candidates. Agent #1: A > B > C > D Agent #2: B > C > D > A Agent #3: C > B > D > A Agent #4: D > C > A > B Assume
Part 1: Voting Systems Consider the following (true) preference orderings of 4 agents on 4 candidates. Agent #1: A > B > C > D Agent #2: B > C > D > A Agent #3: C > B > D > A Agent #4: D > C > A > B Assume
Mechanism Design: Groves Mechanisms and Clarke Tax
 Mechanism Design: Groves Mechanisms and Clarke Tax (Based on Shoham and Leyton-Brown (2008). Multiagent Systems: Algorithmic, Game-Theoretic, and Logical Foundations, Cambridge.) Leen-Kiat Soh Grove Mechanisms
Mechanism Design: Groves Mechanisms and Clarke Tax (Based on Shoham and Leyton-Brown (2008). Multiagent Systems: Algorithmic, Game-Theoretic, and Logical Foundations, Cambridge.) Leen-Kiat Soh Grove Mechanisms
Mechanism Design for Multi-Agent Meeting Scheduling Including Time Preferences, Availability, and Value of Presence
 Mechanism Design for Multi-Agent Meeting Scheduling Including Time Preferences, Availability, and Value of Presence Elisabeth Crawford and Manuela Veloso Computer Science Department, Carnegie Mellon University,
Mechanism Design for Multi-Agent Meeting Scheduling Including Time Preferences, Availability, and Value of Presence Elisabeth Crawford and Manuela Veloso Computer Science Department, Carnegie Mellon University,
On the Impossibility of Core-Selecting Auctions
 On the Impossibility of Core-Selecting Auctions Jacob K. Goeree and Yuanchuan Lien November 10, 009 Abstract When goods are substitutes, the Vickrey auction produces efficient, core outcomes that yield
On the Impossibility of Core-Selecting Auctions Jacob K. Goeree and Yuanchuan Lien November 10, 009 Abstract When goods are substitutes, the Vickrey auction produces efficient, core outcomes that yield
Recap First-Price Revenue Equivalence Optimal Auctions. Auction Theory II. Lecture 19. Auction Theory II Lecture 19, Slide 1
 Auction Theory II Lecture 19 Auction Theory II Lecture 19, Slide 1 Lecture Overview 1 Recap 2 First-Price Auctions 3 Revenue Equivalence 4 Optimal Auctions Auction Theory II Lecture 19, Slide 2 Motivation
Auction Theory II Lecture 19 Auction Theory II Lecture 19, Slide 1 Lecture Overview 1 Recap 2 First-Price Auctions 3 Revenue Equivalence 4 Optimal Auctions Auction Theory II Lecture 19, Slide 2 Motivation
Side-Communication Yields Efficiency of Ascending Auctions: The Two-Items Case
 Side-Communication Yields Efficiency of Ascending Auctions: The Two-Items Case Ron Lavi Faculty of Industrial Engineering and Management The Technion Israel Institute of Technology ronlavi@ie.technion.ac.il
Side-Communication Yields Efficiency of Ascending Auctions: The Two-Items Case Ron Lavi Faculty of Industrial Engineering and Management The Technion Israel Institute of Technology ronlavi@ie.technion.ac.il
Auctions. Michal Jakob Agent Technology Center, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, FEE, Czech Technical University
 Auctions Michal Jakob Agent Technology Center, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, FEE, Czech Technical University AE4M36MAS Autumn 2015 - Lecture 12 Where are We? Agent architectures (inc. BDI
Auctions Michal Jakob Agent Technology Center, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, FEE, Czech Technical University AE4M36MAS Autumn 2015 - Lecture 12 Where are We? Agent architectures (inc. BDI
Core Deviation Minimizing Auctions
 Core Deviation Minimizing Auctions Isa E. Hafalir and Hadi Yektaş April 4, 014 Abstract In a stylized environment with complementary products, we study a class of dominant strategy implementable direct
Core Deviation Minimizing Auctions Isa E. Hafalir and Hadi Yektaş April 4, 014 Abstract In a stylized environment with complementary products, we study a class of dominant strategy implementable direct
October An Equilibrium of the First Price Sealed Bid Auction for an Arbitrary Distribution.
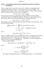 October 13..18.4 An Equilibrium of the First Price Sealed Bid Auction for an Arbitrary Distribution. We now assume that the reservation values of the bidders are independently and identically distributed
October 13..18.4 An Equilibrium of the First Price Sealed Bid Auction for an Arbitrary Distribution. We now assume that the reservation values of the bidders are independently and identically distributed
Auctions with Severely Bounded Communication
 Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research 8 (007) 33 66 Submitted 05/06; published 3/07 Auctions with Severely Bounded Communication Liad Blumrosen Microsoft Research 065 La Avenida Mountain View, CA
Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research 8 (007) 33 66 Submitted 05/06; published 3/07 Auctions with Severely Bounded Communication Liad Blumrosen Microsoft Research 065 La Avenida Mountain View, CA
Preference Networks in Matching Markets
 Preference Networks in Matching Markets CSE 5339: Topics in Network Data Analysis Samir Chowdhury April 5, 2016 Market interactions between buyers and sellers form an interesting class of problems in network
Preference Networks in Matching Markets CSE 5339: Topics in Network Data Analysis Samir Chowdhury April 5, 2016 Market interactions between buyers and sellers form an interesting class of problems in network
Ad Auctions October 8, Ad Auctions October 8, 2010
 Ad Auctions October 8, 2010 1 Ad Auction Theory: Literature Old: Shapley-Shubik (1972) Leonard (1983) Demange-Gale (1985) Demange-Gale-Sotomayor (1986) New: Varian (2006) Edelman-Ostrovsky-Schwarz (2007)
Ad Auctions October 8, 2010 1 Ad Auction Theory: Literature Old: Shapley-Shubik (1972) Leonard (1983) Demange-Gale (1985) Demange-Gale-Sotomayor (1986) New: Varian (2006) Edelman-Ostrovsky-Schwarz (2007)
On Existence of Equilibria. Bayesian Allocation-Mechanisms
 On Existence of Equilibria in Bayesian Allocation Mechanisms Northwestern University April 23, 2014 Bayesian Allocation Mechanisms In allocation mechanisms, agents choose messages. The messages determine
On Existence of Equilibria in Bayesian Allocation Mechanisms Northwestern University April 23, 2014 Bayesian Allocation Mechanisms In allocation mechanisms, agents choose messages. The messages determine
Microeconomic Theory II Preliminary Examination Solutions
 Microeconomic Theory II Preliminary Examination Solutions 1. (45 points) Consider the following normal form game played by Bruce and Sheila: L Sheila R T 1, 0 3, 3 Bruce M 1, x 0, 0 B 0, 0 4, 1 (a) Suppose
Microeconomic Theory II Preliminary Examination Solutions 1. (45 points) Consider the following normal form game played by Bruce and Sheila: L Sheila R T 1, 0 3, 3 Bruce M 1, x 0, 0 B 0, 0 4, 1 (a) Suppose
COMP/MATH 553 Algorithmic Game Theory Lecture 2: Mechanism Design Basics. Sep 8, Yang Cai
 COMP/MATH 553 Algorithmic Game Theory Lecture 2: Mechanism Design Basics Sep 8, 2014 Yang Cai An overview of the class Broad View: Mechanism Design and Auctions First Price Auction Second Price/Vickrey
COMP/MATH 553 Algorithmic Game Theory Lecture 2: Mechanism Design Basics Sep 8, 2014 Yang Cai An overview of the class Broad View: Mechanism Design and Auctions First Price Auction Second Price/Vickrey
On Indirect and Direct Implementations of Core Outcomes in Combinatorial Auctions
 On Indirect and Direct Implementations of Core Outcomes in Combinatorial Auctions David C. Parkes Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University parkes@eecs.harvard.edu draft, comments
On Indirect and Direct Implementations of Core Outcomes in Combinatorial Auctions David C. Parkes Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University parkes@eecs.harvard.edu draft, comments
The Duo-Item Bisection Auction
 Comput Econ DOI 10.1007/s10614-013-9380-0 Albin Erlanson Accepted: 2 May 2013 Springer Science+Business Media New York 2013 Abstract This paper proposes an iterative sealed-bid auction for selling multiple
Comput Econ DOI 10.1007/s10614-013-9380-0 Albin Erlanson Accepted: 2 May 2013 Springer Science+Business Media New York 2013 Abstract This paper proposes an iterative sealed-bid auction for selling multiple
Optimization in the Private Value Model: Competitive Analysis Applied to Auction Design
 Optimization in the Private Value Model: Competitive Analysis Applied to Auction Design Jason D. Hartline A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of
Optimization in the Private Value Model: Competitive Analysis Applied to Auction Design Jason D. Hartline A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of
Combinatorial Exchanges. David C. Parkes Harvard University
 Combinatorial Exchanges David C. Parkes Harvard University What is a combinatorial exchange? Two-sided Complex valuations (swaps, contingent swaps, all-or-nothing sells, etc.) Fragmented Spectrum (E.Kwerel)
Combinatorial Exchanges David C. Parkes Harvard University What is a combinatorial exchange? Two-sided Complex valuations (swaps, contingent swaps, all-or-nothing sells, etc.) Fragmented Spectrum (E.Kwerel)
Pareto optimal budgeted combinatorial auctions
 Theoretical Economics 13 2018), 831 868 1555-7561/20180831 Pareto optimal budgeted combinatorial auctions Phuong Le Analysis Group, Inc. This paper studies the possibility of implementing Pareto optimal
Theoretical Economics 13 2018), 831 868 1555-7561/20180831 Pareto optimal budgeted combinatorial auctions Phuong Le Analysis Group, Inc. This paper studies the possibility of implementing Pareto optimal
A Nearly Optimal Auction for an Uninformed Seller
 A Nearly Optimal Auction for an Uninformed Seller Natalia Lazzati y Matt Van Essen z December 9, 2013 Abstract This paper describes a nearly optimal auction mechanism that does not require previous knowledge
A Nearly Optimal Auction for an Uninformed Seller Natalia Lazzati y Matt Van Essen z December 9, 2013 Abstract This paper describes a nearly optimal auction mechanism that does not require previous knowledge
Trade reduction vs. multi-stage: A comparison of double auction design approaches
 European Journal of Operational Research 180 (2007) 677 691 Decision Support Trade reduction vs. multi-stage: A comparison of double auction design approaches Leon Yang Chu a,b, Zuo-Jun Max Shen b, * a
European Journal of Operational Research 180 (2007) 677 691 Decision Support Trade reduction vs. multi-stage: A comparison of double auction design approaches Leon Yang Chu a,b, Zuo-Jun Max Shen b, * a
Auctions That Implement Efficient Investments
 Auctions That Implement Efficient Investments Kentaro Tomoeda October 31, 215 Abstract This article analyzes the implementability of efficient investments for two commonly used mechanisms in single-item
Auctions That Implement Efficient Investments Kentaro Tomoeda October 31, 215 Abstract This article analyzes the implementability of efficient investments for two commonly used mechanisms in single-item
Multi-Item Vickrey-Dutch Auctions
 Multi-Item Vickrey-Dutch Auctions Debasis Mishra David C. Parkes June 5, 2007 Abstract Descending price auctions are adopted for goods that must be sold quickly and in private values environments, for
Multi-Item Vickrey-Dutch Auctions Debasis Mishra David C. Parkes June 5, 2007 Abstract Descending price auctions are adopted for goods that must be sold quickly and in private values environments, for
Games of Incomplete Information ( 資訊不全賽局 ) Games of Incomplete Information
 1 Games of Incomplete Information ( 資訊不全賽局 ) Wang 2012/12/13 (Lecture 9, Micro Theory I) Simultaneous Move Games An Example One or more players know preferences only probabilistically (cf. Harsanyi, 1976-77)
1 Games of Incomplete Information ( 資訊不全賽局 ) Wang 2012/12/13 (Lecture 9, Micro Theory I) Simultaneous Move Games An Example One or more players know preferences only probabilistically (cf. Harsanyi, 1976-77)
Notes on Auctions. Theorem 1 In a second price sealed bid auction bidding your valuation is always a weakly dominant strategy.
 Notes on Auctions Second Price Sealed Bid Auctions These are the easiest auctions to analyze. Theorem In a second price sealed bid auction bidding your valuation is always a weakly dominant strategy. Proof
Notes on Auctions Second Price Sealed Bid Auctions These are the easiest auctions to analyze. Theorem In a second price sealed bid auction bidding your valuation is always a weakly dominant strategy. Proof
Optimal Mixed Spectrum Auction
 Optimal Mixed Spectrum Auction Alonso Silva Fernando Beltran Jean Walrand Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley Technical Report No. UCB/EECS-13-19 http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/pubs/techrpts/13/eecs-13-19.html
Optimal Mixed Spectrum Auction Alonso Silva Fernando Beltran Jean Walrand Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley Technical Report No. UCB/EECS-13-19 http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/pubs/techrpts/13/eecs-13-19.html
Revenue Equivalence and Income Taxation
 Journal of Economics and Finance Volume 24 Number 1 Spring 2000 Pages 56-63 Revenue Equivalence and Income Taxation Veronika Grimm and Ulrich Schmidt* Abstract This paper considers the classical independent
Journal of Economics and Finance Volume 24 Number 1 Spring 2000 Pages 56-63 Revenue Equivalence and Income Taxation Veronika Grimm and Ulrich Schmidt* Abstract This paper considers the classical independent
Problem Set 2 - SOLUTIONS
 Problem Set - SOLUTONS 1. Consider the following two-player game: L R T 4, 4 1, 1 B, 3, 3 (a) What is the maxmin strategy profile? What is the value of this game? Note, the question could be solved like
Problem Set - SOLUTONS 1. Consider the following two-player game: L R T 4, 4 1, 1 B, 3, 3 (a) What is the maxmin strategy profile? What is the value of this game? Note, the question could be solved like
II-5. Intermediaries. Outline. Introduction. SponSearch. Introduction. II-5. Intermediaries. Introduction. SponSearch. II-5.
 Outline (Part II: Security of Economics) Lecture 5: Market with intermediaries and advertising Sponsored search Market with intermediaries Spring 2013 Outline Market is a system of exchange protocols Sponsored
Outline (Part II: Security of Economics) Lecture 5: Market with intermediaries and advertising Sponsored search Market with intermediaries Spring 2013 Outline Market is a system of exchange protocols Sponsored
Practice Problems 2: Asymmetric Information
 Practice Problems 2: Asymmetric Information November 25, 2013 1 Single-Agent Problems 1. Nonlinear Pricing with Two Types Suppose a seller of wine faces two types of customers, θ 1 and θ 2, where θ 2 >
Practice Problems 2: Asymmetric Information November 25, 2013 1 Single-Agent Problems 1. Nonlinear Pricing with Two Types Suppose a seller of wine faces two types of customers, θ 1 and θ 2, where θ 2 >
Ex post renegotiation-proof mechanism design
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Journal of Economic Theory 148 2013 473 501 www.elsevier.com/locate/jet Ex post renegotiation-proof mechanism design Zvika Neeman a,1, Gregory Pavlov b, a The
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Journal of Economic Theory 148 2013 473 501 www.elsevier.com/locate/jet Ex post renegotiation-proof mechanism design Zvika Neeman a,1, Gregory Pavlov b, a The
Auctions 1: Common auctions & Revenue equivalence & Optimal mechanisms. 1 Notable features of auctions. use. A lot of varieties.
 1 Notable features of auctions Ancient market mechanisms. use. A lot of varieties. Widespread in Auctions 1: Common auctions & Revenue equivalence & Optimal mechanisms Simple and transparent games (mechanisms).
1 Notable features of auctions Ancient market mechanisms. use. A lot of varieties. Widespread in Auctions 1: Common auctions & Revenue equivalence & Optimal mechanisms Simple and transparent games (mechanisms).
Microeconomic Theory II Preliminary Examination Solutions Exam date: June 5, 2017
 Microeconomic Theory II Preliminary Examination Solutions Exam date: June 5, 07. (40 points) Consider a Cournot duopoly. The market price is given by q q, where q and q are the quantities of output produced
Microeconomic Theory II Preliminary Examination Solutions Exam date: June 5, 07. (40 points) Consider a Cournot duopoly. The market price is given by q q, where q and q are the quantities of output produced
Practice Problems. U(w, e) = p w e 2,
 Practice Problems Information Economics (Ec 515) George Georgiadis Problem 1. Static Moral Hazard Consider an agency relationship in which the principal contracts with the agent. The monetary result of
Practice Problems Information Economics (Ec 515) George Georgiadis Problem 1. Static Moral Hazard Consider an agency relationship in which the principal contracts with the agent. The monetary result of
Auctions. Episode 8. Baochun Li Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto
 Auctions Episode 8 Baochun Li Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Paying Per Click 3 Paying Per Click Ads in Google s sponsored links are based on a cost-per-click
Auctions Episode 8 Baochun Li Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Paying Per Click 3 Paying Per Click Ads in Google s sponsored links are based on a cost-per-click
Microeconomic Theory II Preliminary Examination Solutions Exam date: August 7, 2017
 Microeconomic Theory II Preliminary Examination Solutions Exam date: August 7, 017 1. Sheila moves first and chooses either H or L. Bruce receives a signal, h or l, about Sheila s behavior. The distribution
Microeconomic Theory II Preliminary Examination Solutions Exam date: August 7, 017 1. Sheila moves first and chooses either H or L. Bruce receives a signal, h or l, about Sheila s behavior. The distribution
Lecture 5: Iterative Combinatorial Auctions
 COMS 6998-3: Algorithmic Game Theory October 6, 2008 Lecture 5: Iterative Combinatorial Auctions Lecturer: Sébastien Lahaie Scribe: Sébastien Lahaie In this lecture we examine a procedure that generalizes
COMS 6998-3: Algorithmic Game Theory October 6, 2008 Lecture 5: Iterative Combinatorial Auctions Lecturer: Sébastien Lahaie Scribe: Sébastien Lahaie In this lecture we examine a procedure that generalizes
Ex-Post Incentive Compatible Mechanism Design
 Ex-Post Incentive Compatible Mechanism Design Kim-Sau Chung and Jeffrey C. Ely Department of Economics Northwestern University 2003 Sheridan Road Evanston IL 60208 May 17, 2006 Abstract We characterize
Ex-Post Incentive Compatible Mechanism Design Kim-Sau Chung and Jeffrey C. Ely Department of Economics Northwestern University 2003 Sheridan Road Evanston IL 60208 May 17, 2006 Abstract We characterize
Practice Problems. w U(w, e) = p w e 2,
 Practice Problems nformation Economics (Ec 55) George Georgiadis Problem. Static Moral Hazard Consider an agency relationship in which the principal contracts with the agent. The monetary result of the
Practice Problems nformation Economics (Ec 55) George Georgiadis Problem. Static Moral Hazard Consider an agency relationship in which the principal contracts with the agent. The monetary result of the
Econ 804 with Shih En January 10, 2012
 Econ 804 with Shih En January 10, 2012 Dynamic Games Review Multi-stage games with observed actions with observed actions requires that at the end of each stage, the players observe what everyone else
Econ 804 with Shih En January 10, 2012 Dynamic Games Review Multi-stage games with observed actions with observed actions requires that at the end of each stage, the players observe what everyone else
Bayesian Nash Equilibrium
 Bayesian Nash Equilibrium We have already seen that a strategy for a player in a game of incomplete information is a function that specifies what action or actions to take in the game, for every possibletypeofthatplayer.
Bayesian Nash Equilibrium We have already seen that a strategy for a player in a game of incomplete information is a function that specifies what action or actions to take in the game, for every possibletypeofthatplayer.
A simulation study of two combinatorial auctions
 A simulation study of two combinatorial auctions David Nordström Department of Economics Lund University Supervisor: Tommy Andersson Co-supervisor: Albin Erlanson May 24, 2012 Abstract Combinatorial auctions
A simulation study of two combinatorial auctions David Nordström Department of Economics Lund University Supervisor: Tommy Andersson Co-supervisor: Albin Erlanson May 24, 2012 Abstract Combinatorial auctions
Introduction to Multi-Agent Systems. Yoav Shoham (Written with Trond Grenager)
 Introduction to Multi-Agent Systems Yoav Shoham (Written with Trond Grenager) April 30, 2002 152 Chapter 7 Mechanism Design 7.1 Overview In the preceding chapters we presented essential elements of game
Introduction to Multi-Agent Systems Yoav Shoham (Written with Trond Grenager) April 30, 2002 152 Chapter 7 Mechanism Design 7.1 Overview In the preceding chapters we presented essential elements of game
Answers to Microeconomics Prelim of August 24, In practice, firms often price their products by marking up a fixed percentage over (average)
 Answers to Microeconomics Prelim of August 24, 2016 1. In practice, firms often price their products by marking up a fixed percentage over (average) cost. To investigate the consequences of markup pricing,
Answers to Microeconomics Prelim of August 24, 2016 1. In practice, firms often price their products by marking up a fixed percentage over (average) cost. To investigate the consequences of markup pricing,
Inefficiencies in Bargaining: Departing from Akerlof and Myerson-Satterthwaite
 Inefficiencies in Bargaining: Departing from Akerlof and Myerson-Satterthwaite Olivier Compte and Philippe Jehiel October 2004 Abstract We consider bargaining problems in which parties have access to outside
Inefficiencies in Bargaining: Departing from Akerlof and Myerson-Satterthwaite Olivier Compte and Philippe Jehiel October 2004 Abstract We consider bargaining problems in which parties have access to outside
Independent Private Value Auctions
 John Nachbar April 16, 214 ndependent Private Value Auctions The following notes are based on the treatment in Krishna (29); see also Milgrom (24). focus on only the simplest auction environments. Consider
John Nachbar April 16, 214 ndependent Private Value Auctions The following notes are based on the treatment in Krishna (29); see also Milgrom (24). focus on only the simplest auction environments. Consider
Robust Trading Mechanisms with Budget Surplus and Partial Trade
 Robust Trading Mechanisms with Budget Surplus and Partial Trade Jesse A. Schwartz Kennesaw State University Quan Wen Vanderbilt University May 2012 Abstract In a bilateral bargaining problem with private
Robust Trading Mechanisms with Budget Surplus and Partial Trade Jesse A. Schwartz Kennesaw State University Quan Wen Vanderbilt University May 2012 Abstract In a bilateral bargaining problem with private
2 Comparison Between Truthful and Nash Auction Games
 CS 684 Algorithmic Game Theory December 5, 2005 Instructor: Éva Tardos Scribe: Sameer Pai 1 Current Class Events Problem Set 3 solutions are available on CMS as of today. The class is almost completely
CS 684 Algorithmic Game Theory December 5, 2005 Instructor: Éva Tardos Scribe: Sameer Pai 1 Current Class Events Problem Set 3 solutions are available on CMS as of today. The class is almost completely
The Cascade Auction A Mechanism For Deterring Collusion In Auctions
 The Cascade Auction A Mechanism For Deterring Collusion In Auctions Uriel Feige Weizmann Institute Gil Kalai Hebrew University and Microsoft Research Moshe Tennenholtz Technion and Microsoft Research Abstract
The Cascade Auction A Mechanism For Deterring Collusion In Auctions Uriel Feige Weizmann Institute Gil Kalai Hebrew University and Microsoft Research Moshe Tennenholtz Technion and Microsoft Research Abstract
Definition of Incomplete Contracts
 Definition of Incomplete Contracts Susheng Wang 1 2 nd edition 2 July 2016 This note defines incomplete contracts and explains simple contracts. Although widely used in practice, incomplete contracts have
Definition of Incomplete Contracts Susheng Wang 1 2 nd edition 2 July 2016 This note defines incomplete contracts and explains simple contracts. Although widely used in practice, incomplete contracts have
Auctions. Economics Auction Theory. Instructor: Songzi Du. Simon Fraser University. November 17, 2016
 Auctions Economics 383 - Auction Theory Instructor: Songzi Du Simon Fraser University November 17, 2016 ECON 383 (SFU) Auctions November 17, 2016 1 / 28 Auctions Mechanisms of transaction: bargaining,
Auctions Economics 383 - Auction Theory Instructor: Songzi Du Simon Fraser University November 17, 2016 ECON 383 (SFU) Auctions November 17, 2016 1 / 28 Auctions Mechanisms of transaction: bargaining,
Problem Set 3: Suggested Solutions
 Microeconomics: Pricing 3E00 Fall 06. True or false: Problem Set 3: Suggested Solutions (a) Since a durable goods monopolist prices at the monopoly price in her last period of operation, the prices must
Microeconomics: Pricing 3E00 Fall 06. True or false: Problem Set 3: Suggested Solutions (a) Since a durable goods monopolist prices at the monopoly price in her last period of operation, the prices must
Comparing Allocations under Asymmetric Information: Coase Theorem Revisited
 Comparing Allocations under Asymmetric Information: Coase Theorem Revisited Shingo Ishiguro Graduate School of Economics, Osaka University 1-7 Machikaneyama, Toyonaka, Osaka 560-0043, Japan August 2002
Comparing Allocations under Asymmetric Information: Coase Theorem Revisited Shingo Ishiguro Graduate School of Economics, Osaka University 1-7 Machikaneyama, Toyonaka, Osaka 560-0043, Japan August 2002
