STUDENT DETAIL REPORT
|
|
|
- Alannah Evans
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
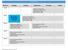
1 STUDENT DETAIL REPORT Sample Student Mathematics Student Performance J. Carpenter's Class Performance Class Performance Geometry 2.G.1 Recognize and draw shapes having specified attributes, such as a given number of angles or a given number of equal faces.5 Identify triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, hexagons, and cubes. 3.G.1 Understand that shapes in different categories (e.g., rhombuses, rectangles, and others) may share attributes (e.g., having four sides), and that the shared attributes can define a larger category (e.g., quadrilaterals). Recognize rhombuses, rectangles, and squares as examples of quadrilaterals, and draw examples of quadrilaterals that do not belong to any of these subcategories. 4.G.1 Draw points, lines, line segments, rays, angles (right, acute, obtuse), and perpendicular and parallel lines. Identify these in two-dimensional figures. 4.G.2 Classify two-dimensional figures based on the presence or absence of parallel or perpendicular lines, or the presence or absence of angles of a specified size. Recognize right triangles as a category, and identify right triangles. 5.G.1 Use a pair of perpendicular number lines, called axes, to define a coordinate system, with the intersection of the lines (the origin) arranged to coincide with the 0 on each line and a given point in the plane located by using an ordered pair of numbers, called its coordinates. Understand that the first number indicates how far to travel from the origin in the direction of one axis, and the second number indicates how far to travel in the direction of the second axis, with the convention that the names of the two axes and thcoordinates correspond (e.g., x-axis and x-coordinate, y-axis and y-coordinate). 6 of 7 86 % 61 % 100 of of % 83 % 19 of 23 7 of 9 78 % 56 % 80 of of % 45 % 27 of 60 0 of 1 0 % 48 % 14 of 29 Sample L-007e6f82965c4b64 Student, F-b9c89475b0 Page1 10/01/2012 -
2 8.G.3 Describe the effect of dilations, translations, rotations, and reflections on two-dimensional figures using coordinates. 4 of % 52 % 56 of 108 Measurement & Data 2.MD.8 Solve word problems involving dollar bills, quarters, dimes, nickels, and pennies, using $ and symbols appropriately. Example: If you have 2 dimes and 3 pennies, how many cents do you have? 3.MD.1 Tell and write time to the nearest minute and measure time intervals in minutes. Solve word problems involving addition and subtraction of time intervals in minutes, e.g., by representing the problem on a number line diagram. 3.MD.3 Draw a scaled picture graph and a scaled bar graph to represent a data set with several categories. Solve one- and two-step how many more and how many less problems using information presented in scaled bar graphs. 3.MD.4 Generate measurement data by measuring lengths using rulers marked with halves and fourths of an inch. Show the data by making a line plot, where the horizontal scale is marked off in appropriate units whole numbers, halves, or quarters. 4.MD.1 Know relative sizes of measurement units within one system of units including km, m, cm; kg, g; lb, oz.; l, ml; hr, min, sec. Within a single system of measurement, express measurements in a larger unit in terms of a smaller unit. Record measurement equivalents in a two column table. 4.MD.2 Use the four operations to solve word problems involving distances, intervals of time, liquid volumes, masses of objects, and money, including problems involving simple fractions or decimals, and problems that require expressing measurements given in a larger unit in terms of a smaller unit. Represent measurement quantities usindiagrams such as number line diagrams that feature a measurement scale. 4.MD.3 Apply the area and perimeter formulas for rectangles in real world and mathematical problems. 2 of 3 67 % 42 % 35 of 83 1 of % 85 % 22 of 26 3 of % 90 % 66 of 73 4 of % 81 % 88 of of % 43 % 13 of of % 75 % 96 of of % 45 % 142 of 315 Sample L-007e6f82965c4b64 Student, F-b9c89475b0 Page2 10/01/2012 -
3 4.MD.4 Make a line plot to display a data set of measurements in fractions of a unit (1/2, 1/4, 1/8). Solve problems involving addition and subtractioof fractions by using information presented in line plots. 2 of % 97 % 29 of 30 Number & Operations-Fractions 3.NF.1 Understand a fraction 1/b as the quantity formed by 1 part when a whole is partitioned into b equal parts; understand a fraction a/b as the quantity formed by a parts of size 1/b. 3.NF.2.a Represent a fraction 1/b on a number line diagram by defining the interval from 0 to 1 as the whole and partitioning it into b equal parts. Recognize that each part has size 1/b and that the endpoint of the part based at 0 locates the number 1/b on the number line. 3.NF.3.a Understand two fractions as equivalent (equal) if they are the same size, or the same point on a number line. 3.NF.3.d Compare two fractions with the same numerator or the same denominator by reasoning about their size. Recognize that comparisons are valid only when the two fractions refer to the same whole. Record the results of comparisons with the symbols >, =, or <, and justify the conclusions, e.g., by using a visual fraction model. 4.NF.1 Explain why a fraction a/b is equivalent to a fraction (n a)/(n b) by using visual fraction models, with attention to how the number and size of the parts differ even though the two fractions themselves are the same size. Use this principle to recognize and generate equivalentfractions. 4.NF.3.b Decompose a fraction into a sum of fractions with the same denominator in more than one way, recording each decomposition by an equation. Justify decompositions, e.g., busing a visual fraction model. 4.NF.3.c Add and subtract mixed numbers with like denominators, e.g., by replacing each mixed number with an equivalent fraction, and/oby using properties of operations and the relationship between addition and subtraction. 4.NF.6 Use decimal notation for fractions with denominators 10 or of % 72 % 56 of 78 1 of % 46 % 12 of 26 1 of % 27 % 7 of 26 2 of % 48 % 25 of of % 61 % 227 of of % 73 % 19 of 26 9 of % 48 % 11 of 23 4 of 8 50 % 47 % 67 of 142 Sample L-007e6f82965c4b64 Student, F-b9c89475b0 Page3 10/01/2012 -
4 Number &Operations in Base Ten 2.NBT.2 Count within 1000; skip-count by 5s, 10s, and 100s. 3.NBT.1 Use place value understanding to round whole numbers to the nearest 10 or NBT.2 Fluently add and subtract within 1000 using strategies and algorithms based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction. 3.NBT.3 Multiply one-digit whole numbers by multiples of 10 in the range 1090 (e.g., 9 80, 5 60) using strategies based on place value and properties of operations. 4.NBT.1 Recognize that in a multi-digit whole number, a digit in one place represents ten times what it represents in the place to its right. 4.NBT.2 Read and write multi-digit whole numbers using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form. Compare two multi-digit numbers based on meanings of the digits in each place, using >, =, and < symbols to record the results of comparisons. 4.NBT.3 Use place value understanding to round multidigit whole numbers to any place. 4.NBT.4 Fluently add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm. 5.NBT.1 Recognize that in a multi-digit number, a digit in one place represents 10 times as much as it represents in the place to its right and 1/10 owhat it represents in the place to its left. 5.NBT.7 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide decimals to hundredths, using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place valueproperties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition ansubtraction; relate the strategy to a written method and explain threasoning used. 9 of % 90 % 9 of 10 1 of 2 50 % 71 % 37 of of % 79 % 212 of of % 78 % 28 of of % 68 % 400 of of % 76 % 722 of of % 77 % 47 of of % 83 % 512 of of % 71 % 46 of of % 64 % 36 of 56 Number System Sample L-007e6f82965c4b64 Student, F-b9c89475b0 Page4 10/01/2012 -
5 6.NS.5 Understand that positive and negative numbers are used together to describe quantities having opposite directions or values (e.g., temperature above/below zero, elevation above/below sea level, credits/debits, positive/negative electric charge); use positive and negative numbers to represent quantities in real-world contexts, explaining the meaning of 0 in each situation. 10 of % 100 % 10 of 10 Operations and Algebraic Thinking 3.OA.1 Interpret products of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 5 7 as the total number of objects in 5 groups of 7 objects each. For example, describe a context in which a total number of objects can be expressed as OA.2 Interpret whole-number quotients of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 56 8 as the number of objects in each share when 56 objects are partitioned equally into 8 shares, or as a number of shares when 56 objects are partitioned into equal shares of 8 objects each. For example, describe a context in which a number of shares or a number of groups can be expressed as OA.3 Use multiplication and division within 100 to solve word problems in situations involving equal groups, arrays, and measurement quantities, e.g., by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem.1 3.OA.4 Determine the unknown whole number in a multiplication or division equation relating three whole numbers. For example, determine the unknown number that makes the equation true in each of the equations 8? = 48, 5 =?? 3, 6 6 =?. 3.OA.5 Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide.2 Examples: If 6 4 = 24 is known, then 4 6 = 24 is also known. (Commutative property of multiplication.) can be found by 3 5 = 15, then 15 2 = 30, or by 5 2 = 10, then 3 10 = OA.6 Understand division as an unknown-factor problem. For example, find 32 8 by finding the number that makes 32 when multiplied by of % 89 % 32 of of % 67 % 34 of of % 87 % 13 of of % 93 % 41 of of % 81 % 60 of of % 69 % 25 of 36 Sample L-007e6f82965c4b64 Student, F-b9c89475b0 Page5 10/01/2012 -
6 3.OA.7 Fluently multiply and divide within 100, using strategies such as the relationship between multiplication and division (e.g., knowing that 8 5 = 40, one knows 40 5 = 8) or properties of operations. By the end of Grade 3, know from memory all products of two one-digit numbers. 3.OA.8 Solve two-step word problems using the four operations. Represent these problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. Assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies including rounding. 3.OA.9 Identify arithmetic patterns (including patterns in the addition table or multiplication table), and explain them using properties of operations. 4.OA.3 Solve multistep word problems posed with whole numbers and having whole-number answers using the four operations, including problems in which remainders must be interpreted. Represent these problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. Assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies including rounding. 4.OA.4 Find all factor pairs for a whole number in the range Recognize that a whole number is a multiple of each of its factors. Determinwhether a given whole number in the range 1100 is a multiple of a given onedigit number. Determine whether a given whole number ithe range 1100 is prime or composite. 4.OA.5 Generate a number or shape pattern that follows a given rule. Identify apparent features of the pattern that were not explicit in the rule itself. Ratios & Proportional Relationships 61 of % 74 % 125 of of % 77 % 282 of of % 90 % 70 of of % 55 % 206 of of % 54 % 79 of of % 93 % 28 of 30 6.RP.1 Understand the concept of a ratio and use ratio language to describe a ratio relationship between two quantities. 2 of 7 29 % 29 % 2 of 7 Statistics & Probability 6.SP.4 Display numerical data in plots on a number line, including dot plots, histograms, and box plots. 20 of % 78 % 43 of 55 Sample L-007e6f82965c4b64 Student, F-b9c89475b0 Page6 10/01/2012 -
7 7.SP.5 Understand that the probability of a chance event is a number between 0 and 1 that expresses the likelihood of the event occurring. Larger numbers indicate greater likelihood. A probability near 0 indicates an unlikely event, a probability around 1/2 indicates an event that is neither unlikely nor likely, and a probability near 1 indicates a likely event. 7.SP.7 Develop a probability model and use it to find probabilities of events. Compare probabilities from a model to observed frequencies; if thagreement is not good, explain possible sources of the discrepancy. 2 of % 60 % 31 of 52 1 of % 73 % 19 of 26 Sample L-007e6f82965c4b64 Student, F-b9c89475b0 Page7 10/01/2012 -
8 Reading Student Performance J. Carpenter's Class Performance Class Performance Conventions of Standard English L.3.1 Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking 3 of % 67 % 41 of 61 L.3.1.a Explain the function of nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs in general and their functions in particular sentences. 4 of % 80 % 71 of 89 L.3.1.b Form and use regular and irregular plural nouns. 2 of % 74 % 32 of 43 L.3.1.f Ensure subject-verb and pronoun-antecedent agreement. 1 of % 50 % 10 of 20 L.3.1.g Form and use comparative and superlative adjectives and adverbs, and choose between them depending on what is to be modified. 2 of % 91 % 42 of 46 L.3.2 Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing. 3 of % 84 % 52 of 62 L.3.2.a Capitalize appropriate words in titles. 1 of % 52 % 12 of 23 L.3.2.c Use commas and quotation marks in dialogue. 2 of 3 67 % 56 % 35 of 62 L.3.2.e Use conventional spelling for high-frequency and other studied words and for adding suffixes to base words (e.g., sitting, smiled, cries, happiness). 3 of % 77 % 46 of 60 L.3.2.f Use spelling patterns and generalizations (e.g., word families, position-based spellings, syllable patterns, ending rules, meaningful word parts) in writing words. 1 of % 70 % 14 of 20 L.3.2.g Consult reference materials, including beginning dictionaries, as needed to check and correct spellings. 1 of % 56 % 10 of 18 Craft & Structure RI.3.5 Use text features and search tools (e.g., key words, sidebars, hyperlinks) to locate information relevant to a given topic efficiently. RI.3.6 Distinguish their own point of view from that of the author of a text. RI.4.4 Determine the meaning of general academic and domain-specific words or phrases in a text relevant to a grade 4 topic or subject area. 2 of % 78 % 31 of 40 1 of % 95 % 19 of 20 4 of % 49 % 27 of 55 Sample L-007e6f82965c4b64 Student, F-b9c89475b0 Page8 10/01/2012 -
9 RI.4.5 Describe the overall structure (e.g., chronology, comparison, cause/effect, problem/solution) of events, ideas, concepts, or information in a text or part of a text. RI.4.6 Compare and contrast a firsthand and secondhand account of the same event or topic; describe the differences in focus and the information provided. RL.3.4 Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in a text, distinguishing literal from nonliteral language. RL.4.4 Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in a text, including those that allude to significant characters found in mythology (e.g., Herculean). RL.4.5 Explain major differences between poems, drama, and prose, and refer to the structural elements of poems (e.g., verse, rhythm, meter) and drama (e.g., casts of characters, settings, descriptions, dialogue, stage directions) when writing or speaking about a text. RL.4.6 Compare and contrast the point of view from which different stories are narrated, including the difference between first- and third-person narrations. 7 of % 70 % 7 of 10 8 of % 53 % 66 of of 1 0 % 10 % 2 of 20 8 of % 56 % 100 of of % 70 % 7 of 10 8 of % 53 % 66 of 125 Foundational Skills RF.1.1 Demonstrate understanding of the organization and basic features of print. 10 of % 96 % 44 of 46 RF.1.3 Know and apply grade-level phonics and word 1 of 2 50 % 79 % 15 of 19 RF.1.3 Know and apply grade-level phonics and word 1 of 2 50 % 55 % 21 of 38 RF.1.3 Know and apply grade-level phonics and word 1 of 2 50 % 77 % 122 of 159 RF.2.3 Know and apply grade-level phonics and word 1 of % 79 % 15 of 19 RF.2.3 Know and apply grade-level phonics and word 1 of % 77 % 122 of 159 RF.2.3 Know and apply grade-level phonics and word 1 of % 55 % 21 of 38 RF.3.3.c Decode multisyllable words. 0 of 1 0 % 89 % 17 of 19 RF.4.3 Know and apply grade-level phonics and word 61 of % 79 % 15 of 19 RF.4.3 Know and apply grade-level phonics and word 61 of % 55 % 21 of 38 Sample L-007e6f82965c4b64 Student, F-b9c89475b0 Page9 10/01/2012 -
10 RF.4.3 Know and apply grade-level phonics and word RF.4.4 Read with sufficient accuracy and fluency to support comprehension. RF.5.3 Know and apply grade-level phonics and word analysis skills in decoding words RF.K.1.a Follow words from left to right, top to bottom, and page by page. RF.K.1.d Recognize and name all upper- and lowercase letters of the alphabet. RF.K.2 Demonstrate understanding of spoken words, syllables, and sounds (phonemes): a. Recognize and produce rhyming words; b. Count, pronounce, blend, and segment syllables in spoken words; c. Blend and segment onsets and rimes of single-syllable spoken words; d. Isolate and pronounce the initial, medial vowel, and final sounds (phonemes) in three-phoneme (consonent-vowelconsonent, or CVC) words.* (This does not include CVCs ending with /l/, /r/, or /x/.); e. Add or substitute individual sounds (phonemes) in simple, one-syllable words to make new words. 61 of % 77 % 122 of of % 70 % 7 of of % 77 % 44 of 57 9 of % 90 % 9 of of % 97 % 59 of 61 7 of % 55 % 26 of 47 RF.K.2.a Recognize and produce rhyming words. 1 of % 95 % 18 of 19 Intergration of Knowledge & Ideas RI.3.9 Compare and contrast the most important points and key details presented in two texts on the same topic. RI.4.8 Explain how an author uses reasons and evidence to support particular points in a text. RL.3.9 Compare and contrast the themes, settings, and plots of stories written by the same author about the same or similar characters (e.g., in books from a series). RL.4.9 Compare and contrast the treatment of similar themes and topics (e.g., opposition of good and evil) and patterns of events (e.g., the quest) in stories, myths, and traditional literature from different cultures. 0 of 1 0 % 45 % 9 of of % 60 % 137 of of 2 0 % 62 % 25 of 40 8 of 9 89 % 89 % 8 of 9 Key ideas & Details RI.3.1 Ask and answer questions to demonstrate understanding of a text, referring explicitly to the text as the basis for the answers. 3 of % 47 % 9 of 19 Sample L-007e6f82965c4b64 Student, F-b9c89475b0 Page10 10/01/2012 -
11 RI.3.1 Ask and answer questions to demonstrate understanding of a text, referring explicitly to the text as the basis for the answers. RI.3.2 Determine the main idea of a text; recount the key details and explain how they support the main idea. RI.3.3 Describe the relationship between a series of historical events, scientific ideas or concepts, or steps in technical procedures in a text, using language that pertains to time, sequence, and cause/effect. RI.4.1 Refer to details and examples in a text when explaining what the text says explicitly and when drawing inferences from the text. RI.4.1 Refer to details and examples in a text when explaining what the text says explicitly and when drawing inferences from the text. RI.4.2 Determine the main idea of a text and explain how it is supported by key details; summarize the text. RI.4.3 Explain events, procedures, ideas, or concepts in a historical, scientific, or technical text, including what happened and why, based on specific information in the text. RL.3.1 Ask and answer questions to demonstrate understanding of a text, referring explicitly to the text as the basis for the answers. RL.3.1 Ask and answer questions to demonstrate understanding of a text, referring explicitly to the text as the basis for the answers. RL.3.2 Recount stories, including fables, folktales, and myths from diverse cultures; determine the central message, lesson, or moral and explain how it is conveyed through key details in the text. RL.3.3 Describe characters in a story (e.g., their traits, motivations, or feelings) and explain how their actions contribute to the sequence of events. RL.4.1 Refer to details and examples in a text when explaining what the text says explicitly and when drawing inferences from the text. RL.4.1 Refer to details and examples in a text when explaining what the text says explicitly and when drawing inferences from the text. RL.4.2 Determine a theme of a story, drama, or poem from details in the text; summarize the text. 3 of % 67 % 38 of 57 2 of 4 50 % 45 % 35 of 77 0 of 1 0 % 79 % 15 of of % 57 % 170 of of % 63 % 114 of of % 50 % 194 of of % 50 % 61 of of % 67 % 38 of 57 1 of % 47 % 9 of 19 2 of 5 40 % 45 % 44 of 97 1 of 3 33 % 51 % 30 of of % 63 % 114 of of % 57 % 170 of of % 50 % 209 of 415 Sample L-007e6f82965c4b64 Student, F-b9c89475b0 Page11 10/01/2012 -
12 RL.4.3 Describe in depth a character, setting, or event in a story or drama, drawing on specific details in the text (e.g., a characters thoughts, words, or actions. 20 of % 49 % 190 of 387 Production and Distribution W.3.4 With guidance and support from adults, produce writing in which the development and organization are appropriate to task and purpose. W.3.5 With guidance and support from peers and adults, develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, and editing. (Editing for conventions should demonstrate command of Language standards 13 up to and including grade 3.) 1 of % 83 % 15 of 18 1 of % 61 % 11 of 18 Research to Build and Present Knowledge W.3.8 Recall information from experiences or gather information from print and digital sources; take brief notes on sources and sort evidence into provided categories. 1 of % 84 % 16 of 19 Vocabulary Acquistion & Use L.3.4.a Use sentence-level context as a clue to the meaning of a word or phrase. L.3.4.b Determine the meaning of the new word formed when a known affix is added to a known word (e.g., agreeable/disagreeable, comfortable/uncomfortable, care/carelessheat/preheat). L.3.4.d Use glossaries or beginning dictionaries, both print and digital, to determine or clarify the precise meaning of key words and phrases. L.3.6 Acquire and use accurately grade-appropriate conversational, general academic, and domainspecific words and phrases, including those that signal spatial and temporal relationships (e.g.,after dinner that night we went looking for them). L.4.4 Determine or clarify the meaning of unknown and multiple-meaning words and phrases based on grade 4 reading and content, choosing flexibly from a range of strategies. L.4.4.a Use context (e.g., definitions, examples, or restatements in text) as a clue to the meaning of a word or phrase. 1 of % 76 % 34 of 45 1 of % 71 % 30 of 42 1 of % 86 % 24 of 28 1 of % 87 % 74 of of % 77 % 46 of of % 55 % 58 of 106 Sample L-007e6f82965c4b64 Student, F-b9c89475b0 Page12 10/01/2012 -
13 L.4.4.b Use common, grade-appropriate Greek and Latin affixes and roots as clues to the meaning of a word (e.g., telegraph, photograph, autograph). L.4.4.c Consult reference materials (e.g., dictionaries, glossaries, thesauruses), both print and digital, to find the pronunciation and determine or clarify the precise meaning of key words and phrases. L.4.5 Demonstrate understanding of figurative language, word relationships, and nuances in word meanings. L.4.6 Acquire and use accurately grade-appropriate general academic and domain-specific words and phrases, including those that signal precise actions, emotions, or states of being (e.g., quizzed, whined, stammered) and that are basic to a particular topic (e.g., wildlife, conservation, and endangered when discussing animal preservation). L.5.5.c Use the relationship between particular words (e.g., synonyms, antonyms, homographs) to better understand each of the words. 28 of % 85 % 68 of of % 57 % 41 of 72 8 of % 80 % 8 of of % 62 % 10 of 16 2 of 7 29 % 68 % 25 of 37 Sample L-007e6f82965c4b64 Student, F-b9c89475b0 Page13 10/01/2012 -
14 Science Student Performance J. Carpenter's Class Performance Class Performance Earth & Space Science 3 4.ESS.1.a The solar system, galaxy, and universe 16 of % 49 % 49 of ESS.2.b Earth is made of rock, water, metal, air, and living organisms 13 of % 41 % 47 of ESS.3.a Properties and movements of water affect Earth's systems 8 of % 51 % 29 of 57 4.ESS.3.c What regulates weather and climate? 12 of % 35 % 28 of 81 4.ESS.4.b Humans depend on Earth's materials 7 of % 41 % 42 of 102 Engineering & Technology Science 4 4.ET.1.b Technology shapes our world 9 of % 64 % 21 of 33 4.ET.1.c People use materials and technology to modify or create new technology 9 of % 55 % 18 of 33 4.ET.2.a Technological problems defined and researched 13 of % 41 % 30 of 73 4.ET.2.b Creative solutions developed and evaluated 33 of % 52 % 63 of 121 Life Science 2 4.LS.1.a Organisms use their structures to grow, survive, and reproduce 11 of % 61 % 34 of 56 4.LS.1.c Organisms get the matter and energy they need from the environment 21 of % 52 % 59 of LS.2.a Offspring resemble their parents 8 of % 33 % 20 of 61 4.LS.3.a Organisms depend on the feeding relationships of one another and the physical environmnet 6 of % 42 % 34 of 81 4.LS.3.b Organisms get the matter and energy they need 5 of % 30 % 25 of 82 Physical Science 4.PS.3.b Energy for life and practical use 29 of % 48 % 143 of PS.3.c Relationship between energy and forces 13 of % 56 % 64 of PS.4.b Examining how light travels 15 of % 56 % 74 of 132 Sample L-007e6f82965c4b64 Student, F-b9c89475b0 Page14 10/01/2012 -
Common Core Georgia Performance Standards
 A Correlation of Pearson Connected Mathematics 2 2012 to the Common Core Georgia Performance s Grade 6 FORMAT FOR CORRELATION TO THE COMMON CORE GEORGIA PERFORMANCE STANDARDS (CCGPS) Subject Area: K-12
A Correlation of Pearson Connected Mathematics 2 2012 to the Common Core Georgia Performance s Grade 6 FORMAT FOR CORRELATION TO THE COMMON CORE GEORGIA PERFORMANCE STANDARDS (CCGPS) Subject Area: K-12
1 algebraic. expression. at least one operation. Any letter can be used as a variable. 2 + n. combination of numbers and variables
 1 algebraic expression at least one operation 2 + n r w q Any letter can be used as a variable. combination of numbers and variables DEFINE: A group of numbers, symbols, and variables that represent an
1 algebraic expression at least one operation 2 + n r w q Any letter can be used as a variable. combination of numbers and variables DEFINE: A group of numbers, symbols, and variables that represent an
Pearson Connected Mathematics Grade 7
 A Correlation of Pearson Connected Mathematics 2 2012 to the Common Core Georgia Performance s Grade 7 FORMAT FOR CORRELATION TO THE COMMON CORE GEORGIA PERFORMANCE STANDARDS (CCGPS) Subject Area: K-12
A Correlation of Pearson Connected Mathematics 2 2012 to the Common Core Georgia Performance s Grade 7 FORMAT FOR CORRELATION TO THE COMMON CORE GEORGIA PERFORMANCE STANDARDS (CCGPS) Subject Area: K-12
Prentice Hall Connected Mathematics, Grade 7 Unit 2004 Correlated to: Maine Learning Results for Mathematics (Grades 5-8)
 : Maine Learning Results for Mathematics (Grades 5-8) A. NUMBERS AND NUMBER SENSE Students will understand and demonstrate a sense of what numbers mean and how they are used. Students will be able to:
: Maine Learning Results for Mathematics (Grades 5-8) A. NUMBERS AND NUMBER SENSE Students will understand and demonstrate a sense of what numbers mean and how they are used. Students will be able to:
Connected Mathematics 2, 6 th and 7th Grade Units 2009 Correlated to: Washington Mathematics Standards (Grade 6)
 Grade 6 6.1. Core Content: Multiplication and division of fractions and decimals (Numbers, Operations, Algebra) 6.1.A Compare and order non-negative fractions, decimals, and integers using the number line,
Grade 6 6.1. Core Content: Multiplication and division of fractions and decimals (Numbers, Operations, Algebra) 6.1.A Compare and order non-negative fractions, decimals, and integers using the number line,
1 SE = Student Edition - TG = Teacher s Guide
 Mathematics State Goal 6: Number Sense Standard 6A Representations and Ordering Read, Write, and Represent Numbers 6.8.01 Read, write, and recognize equivalent representations of integer powers of 10.
Mathematics State Goal 6: Number Sense Standard 6A Representations and Ordering Read, Write, and Represent Numbers 6.8.01 Read, write, and recognize equivalent representations of integer powers of 10.
Forsyth Preparatory Academy
 Forsyth Preparatory Academy Community Support In an effort to inform prospective parents and the community about Forsyth Preparatory Academy, the start-up team created a website to describe the school,
Forsyth Preparatory Academy Community Support In an effort to inform prospective parents and the community about Forsyth Preparatory Academy, the start-up team created a website to describe the school,
Prentice Hall Connected Mathematics 2, 7th Grade Units 2009 Correlated to: Minnesota K-12 Academic Standards in Mathematics, 9/2008 (Grade 7)
 7.1.1.1 Know that every rational number can be written as the ratio of two integers or as a terminating or repeating decimal. Recognize that π is not rational, but that it can be approximated by rational
7.1.1.1 Know that every rational number can be written as the ratio of two integers or as a terminating or repeating decimal. Recognize that π is not rational, but that it can be approximated by rational
Levels 5 and 6 Grade Two Skill
 Correlation of the Superkids Second Grade Levels READING (1) Reading/Beginning Reading Skills/Print Awareness. Students understand how English is written and printed. Students are expected to distinguish
Correlation of the Superkids Second Grade Levels READING (1) Reading/Beginning Reading Skills/Print Awareness. Students understand how English is written and printed. Students are expected to distinguish
Mathematics Success Grade 8
 Mathematics Success Grade 8 T379 [OBJECTIVE] The student will derive the equation of a line and use this form to identify the slope and y-intercept of an equation. [PREREQUISITE SKILLS] Slope [MATERIALS]
Mathematics Success Grade 8 T379 [OBJECTIVE] The student will derive the equation of a line and use this form to identify the slope and y-intercept of an equation. [PREREQUISITE SKILLS] Slope [MATERIALS]
1.3 Real World and Mathematical Problems
 .3. Real World and Mathematical Problems with Rational Numbers - 7.NS.3 www.ck2.org.3 Real World and Mathematical Problems with Rational Numbers - 7.NS.3 Students will change between equivalent forms of
.3. Real World and Mathematical Problems with Rational Numbers - 7.NS.3 www.ck2.org.3 Real World and Mathematical Problems with Rational Numbers - 7.NS.3 Students will change between equivalent forms of
Contents. Heinemann Maths Zone
 Contents Chapter 1 Finance R1.1 Increasing a price by a percentage R1.2 Simple interest (1) R1.3 Simple interest (2) R1.4 Percentage profit (1) R1.5 Percentage profit (2) R1.6 The Distributive Law R1.7
Contents Chapter 1 Finance R1.1 Increasing a price by a percentage R1.2 Simple interest (1) R1.3 Simple interest (2) R1.4 Percentage profit (1) R1.5 Percentage profit (2) R1.6 The Distributive Law R1.7
Nuevo Siglo de Español correlated to New Jersey Reading First Standards (K-3)
 Nuevo Siglo de Español correlated to New Jersey Reading First Standards (K-3) Nuevo Siglo de Español- Kindergarten Materials: SANTILLANA NUEVO SIGLO DE ESPAÑOL (NSE) Mis Primeras Letras Activity Book (MPL)
Nuevo Siglo de Español correlated to New Jersey Reading First Standards (K-3) Nuevo Siglo de Español- Kindergarten Materials: SANTILLANA NUEVO SIGLO DE ESPAÑOL (NSE) Mis Primeras Letras Activity Book (MPL)
Contents. Heinemann Maths Zone Copyright Pearson Australia (a divsion of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd)
 Contents Chapter Money calculations R. Expressing fractions as decimals R.2 Expressing decimals as fractions R.3 Operating with fractions R.4 Simple decimal arithmetic R.5 Ratio and fractions R.6 Dividing
Contents Chapter Money calculations R. Expressing fractions as decimals R.2 Expressing decimals as fractions R.3 Operating with fractions R.4 Simple decimal arithmetic R.5 Ratio and fractions R.6 Dividing
Chapter 6: Quadratic Functions & Their Algebra
 Chapter 6: Quadratic Functions & Their Algebra Topics: 1. Quadratic Function Review. Factoring: With Greatest Common Factor & Difference of Two Squares 3. Factoring: Trinomials 4. Complete Factoring 5.
Chapter 6: Quadratic Functions & Their Algebra Topics: 1. Quadratic Function Review. Factoring: With Greatest Common Factor & Difference of Two Squares 3. Factoring: Trinomials 4. Complete Factoring 5.
Appendix A: Petition Signatures
 Appendix A: Petition Signatures Appendix B: School Compact Peak to Peak Mountain Charter School Compact It is important that families and schools work together to help students achieve high
Appendix A: Petition Signatures Appendix B: School Compact Peak to Peak Mountain Charter School Compact It is important that families and schools work together to help students achieve high
par ( 12). His closest competitor, Ernie Els, finished 3 strokes over par (+3). What was the margin of victory?
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. ) Tiger Woods won the 2000 U.S. Open golf tournament with a score of 2 strokes under par
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. ) Tiger Woods won the 2000 U.S. Open golf tournament with a score of 2 strokes under par
A C E. Answers Investigation 4. Applications. x y y
 Answers Applications 1. a. No; 2 5 = 0.4, which is less than 0.45. c. Answers will vary. Sample answer: 12. slope = 3; y-intercept can be found by counting back in the table: (0, 5); equation: y = 3x 5
Answers Applications 1. a. No; 2 5 = 0.4, which is less than 0.45. c. Answers will vary. Sample answer: 12. slope = 3; y-intercept can be found by counting back in the table: (0, 5); equation: y = 3x 5
GCSE Homework Unit 2 Foundation Tier Exercise Pack New AQA Syllabus
 GCSE Homework Unit 2 Foundation Tier Exercise Pack New AQA Syllabus The more negative a number, the smaller it is. The order of operations is Brackets, Indices, Division, Multiplication, Addition and Subtraction.
GCSE Homework Unit 2 Foundation Tier Exercise Pack New AQA Syllabus The more negative a number, the smaller it is. The order of operations is Brackets, Indices, Division, Multiplication, Addition and Subtraction.
Leith Academy. Numeracy Booklet Pupil Version. A guide for S1 and S2 pupils, parents and staff
 Leith Academy Numeracy Booklet Pupil Version A guide for S1 and S2 pupils, parents and staff Introduction What is the purpose of the booklet? This booklet has been produced to give guidance to pupils and
Leith Academy Numeracy Booklet Pupil Version A guide for S1 and S2 pupils, parents and staff Introduction What is the purpose of the booklet? This booklet has been produced to give guidance to pupils and
Ratios, Rates, and Conversions. Section 4-1 Part 1
 Ratios, Rates, and Conversions Section 4-1 Part 1 Vocabulary Ratio Rate Unit Rate Conversion Factor Unit Analysis Definition Ratio is a comparison of two quantities by division. The ratio of a to b can
Ratios, Rates, and Conversions Section 4-1 Part 1 Vocabulary Ratio Rate Unit Rate Conversion Factor Unit Analysis Definition Ratio is a comparison of two quantities by division. The ratio of a to b can
3.4.1 Convert Percents, Decimals, and Fractions
 3.4.1 Convert Percents, Decimals, and Fractions Learning Objective(s) 1 Describe the meaning of percent. 2 Represent a number as a decimal, percent, and fraction. Introduction Three common formats for
3.4.1 Convert Percents, Decimals, and Fractions Learning Objective(s) 1 Describe the meaning of percent. 2 Represent a number as a decimal, percent, and fraction. Introduction Three common formats for
NAME: DATE: MATHS: Arithmetic. Maths Arithmetic
 Maths Arithmetic It is not necessary to carry out all the activities contained in this unit. Please see Teachers Notes for explanations, additional activities, and tips and suggestions. Theme Arithmetic
Maths Arithmetic It is not necessary to carry out all the activities contained in this unit. Please see Teachers Notes for explanations, additional activities, and tips and suggestions. Theme Arithmetic
1 Interest: Investing Money
 1 Interest: Investing Money Relating Units of Time 1. Becky has been working at a flower shop for 2.1 yr. a) How long is this in weeks? Round up. 2.1 yr 3 wk/yr is about wk b) How long is this in days?
1 Interest: Investing Money Relating Units of Time 1. Becky has been working at a flower shop for 2.1 yr. a) How long is this in weeks? Round up. 2.1 yr 3 wk/yr is about wk b) How long is this in days?
ARITHMETIC CLAST MATHEMATICS COMPETENCIES. Solve real-world problems which do not require the use of variables and do
 ARITHMETIC CLAST MATHEMATICS COMPETENCIES IAa IAb: IA2a: IA2b: IA3: IA4: IIA: IIA2: IIA3: IIA4: IIA5: IIIA: IVA: IVA2: IVA3: Add and subtract rational numbers Multiply and divide rational numbers Add and
ARITHMETIC CLAST MATHEMATICS COMPETENCIES IAa IAb: IA2a: IA2b: IA3: IA4: IIA: IIA2: IIA3: IIA4: IIA5: IIIA: IVA: IVA2: IVA3: Add and subtract rational numbers Multiply and divide rational numbers Add and
The word gives a strong clue to its meaning. Per means out of and Cent means 100 so percentages are numbers out of 100 or 100
 Numeracy Introduction to percentages Percentages are commonly used in everyday language to express fractional numbers as whole numbers mostly between zero and one hundred which is the range of numbers
Numeracy Introduction to percentages Percentages are commonly used in everyday language to express fractional numbers as whole numbers mostly between zero and one hundred which is the range of numbers
par ( 12). His closest competitor, Ernie Els, finished 3 strokes over par (+3). What was the margin of victory?
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Tiger Woods won the 000 U.S. Open golf tournament with a score of 1 strokes under par
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Tiger Woods won the 000 U.S. Open golf tournament with a score of 1 strokes under par
Name For those going into. Algebra 1 Honors. School years that begin with an ODD year: do the odds
 Name For those going into LESSON 2.1 Study Guide For use with pages 64 70 Algebra 1 Honors GOAL: Graph and compare positive and negative numbers Date Natural numbers are the numbers 1,2,3, Natural numbers
Name For those going into LESSON 2.1 Study Guide For use with pages 64 70 Algebra 1 Honors GOAL: Graph and compare positive and negative numbers Date Natural numbers are the numbers 1,2,3, Natural numbers
The City School PAF Chapter Prep Section. Mathematics. Class 8. First Term. Workbook for Intervention Classes
 The City School PAF Chapter Prep Section Mathematics Class 8 First Term Workbook for Intervention Classes REVISION WORKSHEETS MATH CLASS 8 SIMULTANEOUS LINEAR EQUATIONS Q#1. 1000 tickets were sold. Adult
The City School PAF Chapter Prep Section Mathematics Class 8 First Term Workbook for Intervention Classes REVISION WORKSHEETS MATH CLASS 8 SIMULTANEOUS LINEAR EQUATIONS Q#1. 1000 tickets were sold. Adult
Superkids Levels 5 and 6 Units/Lessons and Materials*
 ENTRY LEVEL Spelling Students are asked to spell lists of words representing phonics features necessary to be successful at each grade level. Teachers score spelling based on the specific phonics features
ENTRY LEVEL Spelling Students are asked to spell lists of words representing phonics features necessary to be successful at each grade level. Teachers score spelling based on the specific phonics features
Arithmetic Revision Sheet Questions 1 and 2 of Paper 1
 Arithmetic Revision Sheet Questions and of Paper Basics Factors/ Divisors Numbers that divide evenly into a number. Factors of,,,, 6, Factors of 8,,, 6, 9, 8 Highest Common Factor of and 8 is 6 Multiples
Arithmetic Revision Sheet Questions and of Paper Basics Factors/ Divisors Numbers that divide evenly into a number. Factors of,,,, 6, Factors of 8,,, 6, 9, 8 Highest Common Factor of and 8 is 6 Multiples
Chapter 6. Percents and their Applications
 Chapter 6 Percents and their Applications What is a percent? A percent is 1 one hundredth of a number. For instance, a penny is 1/100 of a dollar. Each one hundredth is 1% A nickel is 5/100 of a dollar
Chapter 6 Percents and their Applications What is a percent? A percent is 1 one hundredth of a number. For instance, a penny is 1/100 of a dollar. Each one hundredth is 1% A nickel is 5/100 of a dollar
Essential Question: What is a probability distribution for a discrete random variable, and how can it be displayed?
 COMMON CORE N 3 Locker LESSON Distributions Common Core Math Standards The student is expected to: COMMON CORE S-IC.A. Decide if a specified model is consistent with results from a given data-generating
COMMON CORE N 3 Locker LESSON Distributions Common Core Math Standards The student is expected to: COMMON CORE S-IC.A. Decide if a specified model is consistent with results from a given data-generating
Math 110 Sample Final. 8) x = x 4
 Math 0 Sample Final Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve. ) Find the area.. miles.3 miles A) sq mi B). sq mi C). sq mi 0. sq
Math 0 Sample Final Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve. ) Find the area.. miles.3 miles A) sq mi B). sq mi C). sq mi 0. sq
4.1 Write Linear Equations by Using a Tables of Values
 4.1 Write Linear Equations by Using a Tables of Values Review: Write y = mx + b by finding the slope and y-intercept m = b = y = x + Every time x changes units, y changes units m = b = y = x + Every time
4.1 Write Linear Equations by Using a Tables of Values Review: Write y = mx + b by finding the slope and y-intercept m = b = y = x + Every time x changes units, y changes units m = b = y = x + Every time
3B titlepage.pdf 3/14/12 3:20:00 PM C M Y CM MY CY CMY K SAMPLE
 3/4/2 3:20:00 PM C M Y CM MY CY CMY SA K M PL E 3B titlepage.pdf Learning Maths Book 3B New Edition 208 Singapore Asia Publishers Pte Ltd Published and Distributed by: Singapore Asia Publishers Pte Ltd
3/4/2 3:20:00 PM C M Y CM MY CY CMY SA K M PL E 3B titlepage.pdf Learning Maths Book 3B New Edition 208 Singapore Asia Publishers Pte Ltd Published and Distributed by: Singapore Asia Publishers Pte Ltd
FOREWORD. I seek your valuable suggestions to improvement. - Niraj Kumar. 2 P a g e n i r a j k u m a r s w a m i. c o m
 SWAMI S WORK BOOK ON MATHS MCQ 4 Design & Developed by - Niraj Kumar (Primary Teacher) MA (English), B.Ed, CPPDPT (IGNOU) Kendriya Vidyalya Dipatoli,Ranchi 1 P a g e n i r a j k u m a r s w a m i. c o
SWAMI S WORK BOOK ON MATHS MCQ 4 Design & Developed by - Niraj Kumar (Primary Teacher) MA (English), B.Ed, CPPDPT (IGNOU) Kendriya Vidyalya Dipatoli,Ranchi 1 P a g e n i r a j k u m a r s w a m i. c o
SAMPLE. HSC formula sheet. Sphere V = 4 πr. Volume. A area of base
 Area of an annulus A = π(r 2 r 2 ) R radius of the outer circle r radius of the inner circle HSC formula sheet Area of an ellipse A = πab a length of the semi-major axis b length of the semi-minor axis
Area of an annulus A = π(r 2 r 2 ) R radius of the outer circle r radius of the inner circle HSC formula sheet Area of an ellipse A = πab a length of the semi-major axis b length of the semi-minor axis
Cost (in dollars) 0 (free) Number of magazines purchased
 Math 1 Midterm Review Name *****Don t forget to study the other methods for solving systems of equations (substitution and elimination) as well as systems of linear inequalities and line of best fit! Also,
Math 1 Midterm Review Name *****Don t forget to study the other methods for solving systems of equations (substitution and elimination) as well as systems of linear inequalities and line of best fit! Also,
Mutually Exclusive Exhaustive Categories
 Activity 1 1.1 Mutually Exclusive Exhaustive Categories As a small group, write a question and 4 to 6 mutually exclusive answers that encompass all possible responses. Make sure that everyone who is asked
Activity 1 1.1 Mutually Exclusive Exhaustive Categories As a small group, write a question and 4 to 6 mutually exclusive answers that encompass all possible responses. Make sure that everyone who is asked
A probability distribution shows the possible outcomes of an experiment and the probability of each of these outcomes.
 Introduction In the previous chapter we discussed the basic concepts of probability and described how the rules of addition and multiplication were used to compute probabilities. In this chapter we expand
Introduction In the previous chapter we discussed the basic concepts of probability and described how the rules of addition and multiplication were used to compute probabilities. In this chapter we expand
Grade 12 Essential Mathematics Achievement Test. Student Booklet
 Grade 12 Essential Mathematics Achievement Test Student Booklet June 2013 Manitoba Education Cataloguing in Publication Data Grade 12 essential mathematics achievement test. Student booklet. June 2013
Grade 12 Essential Mathematics Achievement Test Student Booklet June 2013 Manitoba Education Cataloguing in Publication Data Grade 12 essential mathematics achievement test. Student booklet. June 2013
Math 6 Unit 7 Notes: Proportional relationships
 Math 6 Unit 7 Notes: Proportional relationships Objectives: (3.2) The student will translate written forms of fractions, decimals, and percents to numerical form. (5.1) The student will apply ratios in
Math 6 Unit 7 Notes: Proportional relationships Objectives: (3.2) The student will translate written forms of fractions, decimals, and percents to numerical form. (5.1) The student will apply ratios in
Before How can lines on a graph show the effect of interest rates on savings accounts?
 Compound Interest LAUNCH (7 MIN) Before How can lines on a graph show the effect of interest rates on savings accounts? During How can you tell what the graph of simple interest looks like? After What
Compound Interest LAUNCH (7 MIN) Before How can lines on a graph show the effect of interest rates on savings accounts? During How can you tell what the graph of simple interest looks like? After What
Section 4.3 Objectives
 CHAPTER ~ Linear Equations in Two Variables Section Equation of a Line Section Objectives Write the equation of a line given its graph Write the equation of a line given its slope and y-intercept Write
CHAPTER ~ Linear Equations in Two Variables Section Equation of a Line Section Objectives Write the equation of a line given its graph Write the equation of a line given its slope and y-intercept Write
The Binomial Theorem. Step 1 Expand the binomials in column 1 on a CAS and record the results in column 2 of a table like the one below.
 Lesson 13-6 Lesson 13-6 The Binomial Theorem Vocabulary binomial coeffi cients BIG IDEA The nth row of Pascal s Triangle contains the coeffi cients of the terms of (a + b) n. You have seen patterns involving
Lesson 13-6 Lesson 13-6 The Binomial Theorem Vocabulary binomial coeffi cients BIG IDEA The nth row of Pascal s Triangle contains the coeffi cients of the terms of (a + b) n. You have seen patterns involving
Unit 3: Writing Equations Chapter Review
 Unit 3: Writing Equations Chapter Review Part 1: Writing Equations in Slope Intercept Form. (Lesson 1) 1. Write an equation that represents the line on the graph. 2. Write an equation that has a slope
Unit 3: Writing Equations Chapter Review Part 1: Writing Equations in Slope Intercept Form. (Lesson 1) 1. Write an equation that represents the line on the graph. 2. Write an equation that has a slope
Chapter 6 Diagnostic Test
 Chapter 6 Diagnostic Test STUDENT BOOK PAGES 310 364 1. Consider the quadratic relation y = x 2 6x + 3. a) Use partial factoring to locate two points with the same y-coordinate on the graph. b) Determine
Chapter 6 Diagnostic Test STUDENT BOOK PAGES 310 364 1. Consider the quadratic relation y = x 2 6x + 3. a) Use partial factoring to locate two points with the same y-coordinate on the graph. b) Determine
Continuous Probability Distributions
 8.1 Continuous Probability Distributions Distributions like the binomial probability distribution and the hypergeometric distribution deal with discrete data. The possible values of the random variable
8.1 Continuous Probability Distributions Distributions like the binomial probability distribution and the hypergeometric distribution deal with discrete data. The possible values of the random variable
Student-Built Glossary
 6 Student-Built Glossary This is an alphabetical list of key vocabulary terms you will learn in Chapter 6. As you study this chapter, complete each term s definition or description. Remember to add the
6 Student-Built Glossary This is an alphabetical list of key vocabulary terms you will learn in Chapter 6. As you study this chapter, complete each term s definition or description. Remember to add the
CCAC ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA
 CCAC ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA Sample Questions TOPICS TO STUDY: Evaluate expressions Add, subtract, multiply, and divide polynomials Add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational expressions Factor two and three
CCAC ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA Sample Questions TOPICS TO STUDY: Evaluate expressions Add, subtract, multiply, and divide polynomials Add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational expressions Factor two and three
Park Forest Math Team. Meet #2. Self-study Packet
 Park Forest Math Team Meet #2 Self-study Packet Problem Categories for this Meet: 1. Mystery: Problem solving 2. Geometry: Angle measures in plane figures including supplements and complements 3. Number
Park Forest Math Team Meet #2 Self-study Packet Problem Categories for this Meet: 1. Mystery: Problem solving 2. Geometry: Angle measures in plane figures including supplements and complements 3. Number
Basic Procedure for Histograms
 Basic Procedure for Histograms 1. Compute the range of observations (min. & max. value) 2. Choose an initial # of classes (most likely based on the range of values, try and find a number of classes that
Basic Procedure for Histograms 1. Compute the range of observations (min. & max. value) 2. Choose an initial # of classes (most likely based on the range of values, try and find a number of classes that
Topic #1: Evaluating and Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
 John Jay College of Criminal Justice The City University of New York Department of Mathematics and Computer Science MAT 105 - College Algebra Departmental Final Examination Review Topic #1: Evaluating
John Jay College of Criminal Justice The City University of New York Department of Mathematics and Computer Science MAT 105 - College Algebra Departmental Final Examination Review Topic #1: Evaluating
PART I: NO CALCULATOR (200 points)
 Prealgebra Practice Final Math 0 OER (Ch. -) PART I: NO CALCULATOR (00 points) (.). Find all divisors of the following numbers. a) b) 7 c) (.). Find the prime factorization of the following numbers. a)
Prealgebra Practice Final Math 0 OER (Ch. -) PART I: NO CALCULATOR (00 points) (.). Find all divisors of the following numbers. a) b) 7 c) (.). Find the prime factorization of the following numbers. a)
3.1 Factors and Multiples of Whole Numbers
 3.1 Factors and Multiples of Whole Numbers LESSON FOCUS: Determine prime factors, greatest common factors, and least common multiples of whole numbers. The prime factorization of a natural number is the
3.1 Factors and Multiples of Whole Numbers LESSON FOCUS: Determine prime factors, greatest common factors, and least common multiples of whole numbers. The prime factorization of a natural number is the
Chapter 4 Factoring and Quadratic Equations
 Chapter 4 Factoring and Quadratic Equations Lesson 1: Factoring by GCF, DOTS, and Case I Lesson : Factoring by Grouping & Case II Lesson 3: Factoring by Sum and Difference of Perfect Cubes Lesson 4: Solving
Chapter 4 Factoring and Quadratic Equations Lesson 1: Factoring by GCF, DOTS, and Case I Lesson : Factoring by Grouping & Case II Lesson 3: Factoring by Sum and Difference of Perfect Cubes Lesson 4: Solving
TABLE OF CONTENTS. About Finish Line PA Core Math 5. UNIT 1: Big Ideas from Grade 5 7 UNIT 1 REVIEW 39
 TABLE OF CONTENTS About Finish Line PA Core Math 5 UNIT 1: Big Ideas from Grade 5 7 LESSON 1 CC.2.1.5.C.2 Multiplying Fractions [connects to CC.2.3.6.A.1] 8 LESSON 2 CC.2.1.5.B.2 Operations with Decimals
TABLE OF CONTENTS About Finish Line PA Core Math 5 UNIT 1: Big Ideas from Grade 5 7 LESSON 1 CC.2.1.5.C.2 Multiplying Fractions [connects to CC.2.3.6.A.1] 8 LESSON 2 CC.2.1.5.B.2 Operations with Decimals
Chapter 2 Rocket Launch: AREA BETWEEN CURVES
 ANSWERS Mathematics (Mathematical Analysis) page 1 Chapter Rocket Launch: AREA BETWEEN CURVES RL-. a) 1,.,.; $8, $1, $18, $0, $, $6, $ b) x; 6(x ) + 0 RL-. a), 16, 9,, 1, 0; 1,,, 7, 9, 11 c) D = (-, );
ANSWERS Mathematics (Mathematical Analysis) page 1 Chapter Rocket Launch: AREA BETWEEN CURVES RL-. a) 1,.,.; $8, $1, $18, $0, $, $6, $ b) x; 6(x ) + 0 RL-. a), 16, 9,, 1, 0; 1,,, 7, 9, 11 c) D = (-, );
MATH SPEAK - TO BE UNDERSTOOD AND MEMORIZED
 FOM 11 T6 RATES AS GRAPHS 1 MATH SPEAK - TO BE UNDERSTOOD AND MEMORIZED 1) GRAPH a visual representation of a relationship between two different quantities. 2) SLOPE m a measure of the steepness of a graph
FOM 11 T6 RATES AS GRAPHS 1 MATH SPEAK - TO BE UNDERSTOOD AND MEMORIZED 1) GRAPH a visual representation of a relationship between two different quantities. 2) SLOPE m a measure of the steepness of a graph
Chapter 14 : Statistical Inference 1. Note : Here the 4-th and 5-th editions of the text have different chapters, but the material is the same.
 Chapter 14 : Statistical Inference 1 Chapter 14 : Introduction to Statistical Inference Note : Here the 4-th and 5-th editions of the text have different chapters, but the material is the same. Data x
Chapter 14 : Statistical Inference 1 Chapter 14 : Introduction to Statistical Inference Note : Here the 4-th and 5-th editions of the text have different chapters, but the material is the same. Data x
ASSIGNMENT 3 DYLAN ZWICK S MATH 1010 CLASS
 ASSIGNMENT 3 DYLAN ZWICK S MATH 1010 CLASS 1. Section 2.2 2.2.1: Find a number such that the sum of the number and 24 is 68. 2.2.3: You have accepted a job offer at an annual salary of $37,120. This salary
ASSIGNMENT 3 DYLAN ZWICK S MATH 1010 CLASS 1. Section 2.2 2.2.1: Find a number such that the sum of the number and 24 is 68. 2.2.3: You have accepted a job offer at an annual salary of $37,120. This salary
Answers. Cancelling Fractions - Page 15 Exercise 1
 Answers 0 s, 00 s and 000 s - Page 7 ) a) 0 0 c) 0 d),0 e) f). g). h) i). j).9 k) 0. l) 0. m) 0.0 n) 0.00 ) a) 00 700 c),900 d),00 e) 90 f),70 g). h) 70 i) 0. j) 0. k) 0. l) 0.0 m) 0. n).00 ) a),000,000
Answers 0 s, 00 s and 000 s - Page 7 ) a) 0 0 c) 0 d),0 e) f). g). h) i). j).9 k) 0. l) 0. m) 0.0 n) 0.00 ) a) 00 700 c),900 d),00 e) 90 f),70 g). h) 70 i) 0. j) 0. k) 0. l) 0.0 m) 0. n).00 ) a),000,000
Chapter 7 BUILD YOUR VOCABULARY
 C H A P T E R 7 BUILD YOUR VOCABULARY This is an alphabetical list of new vocabulary terms you will learn in Chapter 7. As you complete the study notes for the chapter, you will see Build Your Vocabulary
C H A P T E R 7 BUILD YOUR VOCABULARY This is an alphabetical list of new vocabulary terms you will learn in Chapter 7. As you complete the study notes for the chapter, you will see Build Your Vocabulary
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 INTRODUCTORY ALGEBRA/GRACEY CHAPTER 1-2.3 PRACTICE Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Evaluate the algebraic expression for the
INTRODUCTORY ALGEBRA/GRACEY CHAPTER 1-2.3 PRACTICE Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Evaluate the algebraic expression for the
Week of Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday
 Aug 29 Multiplication 3-digit by 2-digit Division 4-digit by 2-digit Add and subtract 2-digit Sept 5 No School Labor Day Holiday Multiplication 3-digit by 2-digit Division 4-digit by 2-digit Add and subtract
Aug 29 Multiplication 3-digit by 2-digit Division 4-digit by 2-digit Add and subtract 2-digit Sept 5 No School Labor Day Holiday Multiplication 3-digit by 2-digit Division 4-digit by 2-digit Add and subtract
CAMI Mathematics Literacy CAPS
 GRADE 12_CAPS Curriculum Numbers and calculations with numbers Number concepts to be used in the context of: Finance personal, household, business, workplace, national and global finance. Measurement complex
GRADE 12_CAPS Curriculum Numbers and calculations with numbers Number concepts to be used in the context of: Finance personal, household, business, workplace, national and global finance. Measurement complex
6th Grade Mathematics. STAAR Study Guide. This Study Guide belongs to:
 This Study Guide belongs to: TABLE OF CONTENTS Absolute Value & Opposite of a Number Page 7 Additive & Multiplicative Relationships Page 3 Area & Volume (Rec, Parallelogram) Page 1 Area & Volume (Trapezoid
This Study Guide belongs to: TABLE OF CONTENTS Absolute Value & Opposite of a Number Page 7 Additive & Multiplicative Relationships Page 3 Area & Volume (Rec, Parallelogram) Page 1 Area & Volume (Trapezoid
DATA HANDLING Five-Number Summary
 DATA HANDLING Five-Number Summary The five-number summary consists of the minimum and maximum values, the median, and the upper and lower quartiles. The minimum and the maximum are the smallest and greatest
DATA HANDLING Five-Number Summary The five-number summary consists of the minimum and maximum values, the median, and the upper and lower quartiles. The minimum and the maximum are the smallest and greatest
k x Unit 1 End of Module Assessment Study Guide: Module 1
 Unit 1 End of Module Assessment Study Guide: Module 1 vocabulary: Unit Rate: y x. How many y per each x. Proportional relationship: Has a constant unit rate. Constant of proportionality: Unit rate for
Unit 1 End of Module Assessment Study Guide: Module 1 vocabulary: Unit Rate: y x. How many y per each x. Proportional relationship: Has a constant unit rate. Constant of proportionality: Unit rate for
GOOD LUCK! 2. a b c d e 12. a b c d e. 3. a b c d e 13. a b c d e. 4. a b c d e 14. a b c d e. 5. a b c d e 15. a b c d e. 6. a b c d e 16.
 MA109 College Algebra Spring 2017 Exam2 2017-03-08 Name: Sec.: Do not remove this answer page you will turn in the entire exam. You have two hours to do this exam. No books or notes may be used. You may
MA109 College Algebra Spring 2017 Exam2 2017-03-08 Name: Sec.: Do not remove this answer page you will turn in the entire exam. You have two hours to do this exam. No books or notes may be used. You may
Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions
 COMMON CORE 4 Locker LESSON 9. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions Name Class Date 9. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions Essential Question: How can you multiply and divide rational
COMMON CORE 4 Locker LESSON 9. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions Name Class Date 9. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions Essential Question: How can you multiply and divide rational
Review of Beginning Algebra MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Review of Beginning Algebra MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Classify as an expression or an equation. 1) 2x + 9 1) A) Expression B)
Review of Beginning Algebra MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Classify as an expression or an equation. 1) 2x + 9 1) A) Expression B)
3 Ways to Write Ratios
 RATIO & PROPORTION Sec 1. Defining Ratio & Proportion A RATIO is a comparison between two quantities. We use ratios everyday; one Pepsi costs 50 cents describes a ratio. On a map, the legend might tell
RATIO & PROPORTION Sec 1. Defining Ratio & Proportion A RATIO is a comparison between two quantities. We use ratios everyday; one Pepsi costs 50 cents describes a ratio. On a map, the legend might tell
3 Ways to Write Ratios
 RATIO & PROPORTION Sec 1. Defining Ratio & Proportion A RATIO is a comparison between two quantities. We use ratios every day; one Pepsi costs 50 cents describes a ratio. On a map, the legend might tell
RATIO & PROPORTION Sec 1. Defining Ratio & Proportion A RATIO is a comparison between two quantities. We use ratios every day; one Pepsi costs 50 cents describes a ratio. On a map, the legend might tell
Proportional Relationships Unit
 Proportional Relationships Unit Reference Packet Need more help? Try any of the IXL 7 th grade standards for practice throughout the unit. Videos to view for help throughout the unit: Introduction to Ratio
Proportional Relationships Unit Reference Packet Need more help? Try any of the IXL 7 th grade standards for practice throughout the unit. Videos to view for help throughout the unit: Introduction to Ratio
Exercises. 140 Chapter 3: Factors and Products
 Exercises A 3. List the first 6 multiples of each number. a) 6 b) 13 c) 22 d) 31 e) 45 f) 27 4. List the prime factors of each number. a) 40 b) 75 c) 81 d) 120 e) 140 f) 192 5. Write each number as a product
Exercises A 3. List the first 6 multiples of each number. a) 6 b) 13 c) 22 d) 31 e) 45 f) 27 4. List the prime factors of each number. a) 40 b) 75 c) 81 d) 120 e) 140 f) 192 5. Write each number as a product
MENTAL CALCULATION. 1. RE-ARRANGING When trying to add a row of numbers, we should look for pairs that add up to make a multiple of 10 or 100
 MENTAL CALCULATION 1. RE-ARRANGING When trying to add a row of numbers, we should look for pairs that add up to make a multiple of 10 or 100 e.e. 13 + 8 + 7 + 6 + 2 13 + 8 + 7 + 6 + 2 20 10 2. UNITS, 20
MENTAL CALCULATION 1. RE-ARRANGING When trying to add a row of numbers, we should look for pairs that add up to make a multiple of 10 or 100 e.e. 13 + 8 + 7 + 6 + 2 13 + 8 + 7 + 6 + 2 20 10 2. UNITS, 20
Buying A Car. Mathematics Capstone Course
 Buying A Car Mathematics Capstone Course I. UNIT OVERVIEW & PURPOSE: In this lesson the student will be asked to search the Internet and find a car that he/she would like to purchase. The student will
Buying A Car Mathematics Capstone Course I. UNIT OVERVIEW & PURPOSE: In this lesson the student will be asked to search the Internet and find a car that he/she would like to purchase. The student will
Name: Period: Distance: Distance: Distance: Distance:
 Name: Period: Distance: Distance: Distance: Distance: 1 2 -2 + 2 + (-3) = -3 Shoes & Boots 3 4 1) Write each individual description below as an integer. Model the integer on the number line using an appropriate
Name: Period: Distance: Distance: Distance: Distance: 1 2 -2 + 2 + (-3) = -3 Shoes & Boots 3 4 1) Write each individual description below as an integer. Model the integer on the number line using an appropriate
Chapter Representing Patterns, pages MHR Answers
 . a) x -, x - b) Example: The processes are similar in that the like terms were combined. The processes are different in that one involved addition and the other involved subtraction.. Yes. Example: The
. a) x -, x - b) Example: The processes are similar in that the like terms were combined. The processes are different in that one involved addition and the other involved subtraction.. Yes. Example: The
Numeracy Booklet A guide for pupils, parents and staff
 Numeracy Booklet A guide for pupils, parents and staff The aim of this booklet is to ensure that there is a consistent approach throughout the academy and at home on basic mathematical concepts Place Value
Numeracy Booklet A guide for pupils, parents and staff The aim of this booklet is to ensure that there is a consistent approach throughout the academy and at home on basic mathematical concepts Place Value
Full download all chapters instantly please go to Solutions Manual, Test Bank site: testbanklive.com
 Beginning and Intermediate Algebra 5th Edition Tobey Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/beginning-and-intermediate-algebra-5th-edition-tobey-test-bank/ MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the
Beginning and Intermediate Algebra 5th Edition Tobey Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/beginning-and-intermediate-algebra-5th-edition-tobey-test-bank/ MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the
SESSION 3: GRAPHS THAT TELL A STORY. KEY CONCEPTS: Line Graphs Direct Proportion Inverse Proportion Tables Formulae X-PLANATION 1.
 SESSION 3: GRAPHS THAT TELL A STORY KEY CONCEPTS: Line Graphs Direct Proportion Inverse Proportion Tables Formulae X-PLANATION 1. DIRECT PROPORTION Two quantities are said to be in direct proportion if
SESSION 3: GRAPHS THAT TELL A STORY KEY CONCEPTS: Line Graphs Direct Proportion Inverse Proportion Tables Formulae X-PLANATION 1. DIRECT PROPORTION Two quantities are said to be in direct proportion if
2 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS
 Chapter 2 Descriptive Statistics 47 2 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Figure 2.1 When you have large amounts of data, you will need to organize it in a way that makes sense. These ballots from an election are rolled
Chapter 2 Descriptive Statistics 47 2 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Figure 2.1 When you have large amounts of data, you will need to organize it in a way that makes sense. These ballots from an election are rolled
elementary and intermediate Algebra Warm-up Name atfm0303mk2810yes
 MATH000 online PLACEMENT TEST 1 QUESTIONS 11-0-13 Fall 013 elementar and intermediate Algebra Warm-up Name atfm0303mkes www.alvarezmathhelp.com website PROGRAMS ALVAREZLAB (SAVE AND EXTRACT TO YOUR COMPUTER)
MATH000 online PLACEMENT TEST 1 QUESTIONS 11-0-13 Fall 013 elementar and intermediate Algebra Warm-up Name atfm0303mkes www.alvarezmathhelp.com website PROGRAMS ALVAREZLAB (SAVE AND EXTRACT TO YOUR COMPUTER)
Unit 8 - Math Review. Section 8: Real Estate Math Review. Reading Assignments (please note which version of the text you are using)
 Unit 8 - Math Review Unit Outline Using a Simple Calculator Math Refresher Fractions, Decimals, and Percentages Percentage Problems Commission Problems Loan Problems Straight-Line Appreciation/Depreciation
Unit 8 - Math Review Unit Outline Using a Simple Calculator Math Refresher Fractions, Decimals, and Percentages Percentage Problems Commission Problems Loan Problems Straight-Line Appreciation/Depreciation
GOOD LUCK! 2. a b c d e 12. a b c d e. 3. a b c d e 13. a b c d e. 4. a b c d e 14. a b c d e. 5. a b c d e 15. a b c d e. 6. a b c d e 16.
 MA109 College Algebra Fall 017 Exam 017-10-18 Name: Sec.: Do not remove this answer page you will turn in the entire exam. You have two hours to do this exam. No books or notes may be used. You may use
MA109 College Algebra Fall 017 Exam 017-10-18 Name: Sec.: Do not remove this answer page you will turn in the entire exam. You have two hours to do this exam. No books or notes may be used. You may use
HPISD 6/7 Math UNIT NAME ESTIMATED DURATION 9 WEEKS
 HPISD 6/7 Math UNIT NAME ESTIMATED DURATION 9 WEEKS UNIT 7: PERSONAL FINANCIAL LITERACY 12 DAYS 1 2 3 4 Unit Overview The student will apply mathematical process standards to develop an economic way of
HPISD 6/7 Math UNIT NAME ESTIMATED DURATION 9 WEEKS UNIT 7: PERSONAL FINANCIAL LITERACY 12 DAYS 1 2 3 4 Unit Overview The student will apply mathematical process standards to develop an economic way of
Not for sale or distribution
 TALK.9 Fractions, Decimals, and Percentages In this section you will convert between fractions, decimals, and percentages, and work with recurring decimals. Exercise.9 Warm Up Moza says, The numbers,.0
TALK.9 Fractions, Decimals, and Percentages In this section you will convert between fractions, decimals, and percentages, and work with recurring decimals. Exercise.9 Warm Up Moza says, The numbers,.0
Math Fundamentals for Statistics (Math 52) Homework Unit 6: Rates/Ratios/Proportions. Scott Fallstrom and Brent Pickett The How and Whys Guys
 Math Fundamentals for Statistics (Math 52) Homework Unit 6: Rates/Ratios/Proportions Scott Fallstrom and Brent Pickett The How and Whys Guys Homework Unit 6 Page 1 6.1: Comparing Objects Ratios and Rates
Math Fundamentals for Statistics (Math 52) Homework Unit 6: Rates/Ratios/Proportions Scott Fallstrom and Brent Pickett The How and Whys Guys Homework Unit 6 Page 1 6.1: Comparing Objects Ratios and Rates
troduction to Algebra
 Chapter Six Percent Percents, Decimals, and Fractions Understanding Percent The word percent comes from the Latin phrase per centum,, which means per 100. Percent means per one hundred. The % symbol is
Chapter Six Percent Percents, Decimals, and Fractions Understanding Percent The word percent comes from the Latin phrase per centum,, which means per 100. Percent means per one hundred. The % symbol is
ACCUPLACER Elementary Algebra Assessment Preparation Guide
 ACCUPLACER Elementary Algebra Assessment Preparation Guide Please note that the guide is for reference only and that it does not represent an exact match with the assessment content. The Assessment Centre
ACCUPLACER Elementary Algebra Assessment Preparation Guide Please note that the guide is for reference only and that it does not represent an exact match with the assessment content. The Assessment Centre
Learning Plan 3 Chapter 3
 Learning Plan 3 Chapter 3 Questions 1 and 2 (page 82) To convert a decimal into a percent, you must move the decimal point two places to the right. 0.72 = 72% 5.46 = 546% 3.0842 = 308.42% Question 3 Write
Learning Plan 3 Chapter 3 Questions 1 and 2 (page 82) To convert a decimal into a percent, you must move the decimal point two places to the right. 0.72 = 72% 5.46 = 546% 3.0842 = 308.42% Question 3 Write
Elementary Algebra Review for Exam 3
 Elementary Algebra Review for Exam ) After receiving a discount of 5% on its bulk order of typewriter ribbons, John's Office Supply pays $5882. What was the price of the order before the discount? Round
Elementary Algebra Review for Exam ) After receiving a discount of 5% on its bulk order of typewriter ribbons, John's Office Supply pays $5882. What was the price of the order before the discount? Round
Math 1205 Ch. 3 Problem Solving (Sec. 3.1)
 46 Math 1205 Ch. 3 Problem Solving (Sec. 3.1) Sec. 3.1 Ratios and Proportions Ratio comparison of two quantities with the same units Ex.: 2 cups to 6 cups Rate comparison of two quantities with different
46 Math 1205 Ch. 3 Problem Solving (Sec. 3.1) Sec. 3.1 Ratios and Proportions Ratio comparison of two quantities with the same units Ex.: 2 cups to 6 cups Rate comparison of two quantities with different
CAHSEE on Target UC Davis, School and University Partnerships
 UC Davis, School and University Partnerships CAHSEE on Target Mathematics Curriculum Published by The University of California, Davis, School/University Partnerships Program 2006 Director Sarah R. Martinez,
UC Davis, School and University Partnerships CAHSEE on Target Mathematics Curriculum Published by The University of California, Davis, School/University Partnerships Program 2006 Director Sarah R. Martinez,
BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE for Teachers and Students
 Pathway: Agribusiness Lesson: ABR B4 1: The Time Value of Money Common Core State Standards for Mathematics: 9-12.F-LE.1, 3 Domain: Linear, Quadratic, and Exponential Models F-LE Cluster: Construct and
Pathway: Agribusiness Lesson: ABR B4 1: The Time Value of Money Common Core State Standards for Mathematics: 9-12.F-LE.1, 3 Domain: Linear, Quadratic, and Exponential Models F-LE Cluster: Construct and
Math League SCASD. Meet #2. Self-study Packet
 Math League SCASD Meet #2 Self-study Packet Problem Categories for this Meet: 1. Mystery: Problem solving 2. Geometry: Angle measures in plane figures including supplements and complements 3. Number Theory:
Math League SCASD Meet #2 Self-study Packet Problem Categories for this Meet: 1. Mystery: Problem solving 2. Geometry: Angle measures in plane figures including supplements and complements 3. Number Theory:
MSM Course 1 Flashcards. Associative Property. base (in numeration) Commutative Property. Distributive Property. Chapter 1 (p.
 1 Chapter 1 (p. 26, 1-5) Associative Property Associative Property: The property that states that for three or more numbers, their sum or product is always the same, regardless of their grouping. 2 3 8
1 Chapter 1 (p. 26, 1-5) Associative Property Associative Property: The property that states that for three or more numbers, their sum or product is always the same, regardless of their grouping. 2 3 8
