Chapter 6 Diagnostic Test
|
|
|
- Edwina Garrett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 6 Diagnostic Test STUDENT BOOK PAGES Consider the quadratic relation y = x 2 6x + 3. a) Use partial factoring to locate two points with the same y-coordinate on the graph. b) Determine the coordinates of the vertex. c) Sketch the graph. 2. Sketch the graph of each quadratic relation. a) y = (x 3)(x + 1) c) y = 4(x + 2) b) y = 2x x 12 d) y = 3 1 (x + 2)(x 4) 3. Factor each expression, if possible. a) x 2 5x 24 c) 9x 2 9x 10 b) x 2 4x + 8 d) 2x 2 + 7x Expand and simplify. a) (2x 5)(x + 7) c) (2m 3)(2m + 3) b) (3 2q) 2 d) (5c 3)(11 c) 5. For each quadratic relation, determine the zeros, the y-intercept, the equation of the axis of symmetry, the vertex, and the equation in standard form. a) b) 6. For each quadratic relation, determine the equation of the axis of symmetry, the vertex, and the zeros (if any). a) y = 2(x + 4)(x + 8) c) y = 3x(x 4) + 12 b) y = (x + 1) d) y = 3 1 (x 5) Use graphing technology to graph each quadratic relation. Then explain why the relation cannot be written as y = a(x r)(x s), where r and s are integers. a) y = 2x 2 + 6x + 7 b) y = x 2 8x + 5 Chapter 6 Diagnostic Test 411
2 Chapter 6 Diagnostic Test Answers 1. a) y = x(x 6) + 3; (0, 3), (6, 3) c) b) (3, 6) 2. The points that are labelled may vary, e.g., a) c) b) d) 3. a) (x + 3)(x 8) b) cannot be factored c) (3x + 2)(3x 5) d) (2x + 1)(x 4) 4. a) 2x 2 + 9x 35 b) 9 12q + 4q 2 c) 4m 2 9 d) 5c c a) 3, 5; 7.5; x = 1; (1, 8); y = 0.5x 2 x 7.5 b) 3, 4; 12; x = 3.5; (3.5, 0.25); y = x 2 + 7x a) x = 6; ( 6, 8); 4, 8 b) x = 1; ( 1, 9); 2, 4 c) x = 2; (2, 0); 2 d) x = 5; (5, 2); no zeros 7. a) b) There are no x-intercepts, so the relation cannot be factored. The x-intercepts are not integers, so r and s are not integers. If students have difficulty with the questions in the Diagnostic Test, it may be necessary to review the following topics: graphing a quadratic relation given in standard form, factored form, and vertex form using technology to graph a quadratic relation determining the equation of the axis of symmetry, the vertex, and the zeros of a quadratic relation expanding and simplifying expressions factoring quadratic expressions 412 Principles of Mathematics 10: Chapter 6 Diagnostic Test Answers
3 Lesson 6.1 Extra Practice STUDENT BOOK PAGES Use each graph to determine the roots of the quadratic equation, where y = 0. a) 4. Solve by graphing. Round your answers to two decimal places. a) x 2 6x 4 = 0 b) x 2 7x + 5 = 2 c) 4x 2 12x + 15 = 0 d) 32x 4x 2 = 52 b) 2. Determine whether 3 is a root of each equation. a) (x 3)(x + 6) = 0 b) x 2 + 5x + 6 = 0 c) 5x x + 5 = 11 d) 4x 2 = Solve by factoring. a) 2x 2 + x 10 = 0 b) x 2 2x 9 = 6 c) 3x x 15 = 5 d) 3x 2 6x = 0 5. The height, h, in metres, of a football can be modelled by h = 5t t, where t is the time, in seconds, after kickoff. The football lands on the ground without being caught. How long is the football in the air? 6. Tracy runs a small business doing tax returns. If she charges a fee of F dollars per tax return, the amount of money she will earn, E, in dollars, each 1 tax season can be modelled by E = F(480 F). 5 a) How much will Tracy earn if she charges $375 per tax return? b) If Tracy wants to earn at least $9000, between what two amounts should she charge? 7. a) Use algebra to determine the points of intersection of the line y = 4 3x and the parabola y = 3x 2 + 4x 2. b) Verify your answers for part a) using a graphing calculator. Lesson 6.1 Extra Practice 413
4 Lesson 6.1 Extra Practice Answers 1. a) 3, 3 b) 5, 2 2. a) no b) yes c) yes d) no 1 3. a) 2, 2 2 b) 5, 3 4 c), a) $7875 b) between $ and $ a), 2, ( 3, 13) 3 b) d) 0, 2 4. a) 0.61, 6.61 b) 0.46, 6.54 c) 3.95, 0.95 d) 2.27, s 414 Principles of Mathematics 10: Lesson 6.1 Extra Practice Answers
5 Lesson 6.3 Extra Practice STUDENT BOOK PAGES Write each relation in vertex form by completing the square. a) y = x 2 12x b) y = 3x 2 + 6x a) Complete the square to write the relation y = 5x 2 20x 13 in vertex form. b) Graph the relation. 3. Copy and complete this area model. Then express the relation y = x x + 8 in vertex form. 4. Benoît has a home business making fancy gift boxes. If he sells each box for x dollars, his monthly profit, P, in dollars, can be modelled by P = 50x x 520. a) What is the maximum profit that Benoît can make per month? b) How much should he charge to make this profit? 5. Kara wants to make a square and a rectangle with a piece of flexible wire that is 102 cm long. The length of the rectangle will be twice its width. Kara decides to represent the length of wire, measured in centimetres, that she will use for the square as 12x. a) Write expressions for the dimensions of the square and the rectangle in centimetres. b) Show that the combined area of the square and the rectangle, in square centimetres, is 17(x 2 8x + 34). c) Determine the minimum combined area that Kara can make. What are the lengths of wire that she must use for each shape? 6. a) Determine the vertex and the equation of the axis of symmetry of the quadratic relation y = 3x 2 12x + 5 by completing the square. b) How does doubling the coefficient of x in the relation affect the position of the axis of symmetry? 7. a) Continue the following pattern of perfect-square trinomials for three more terms: 100x 2 20x + 1, 100x 2 40x + 4, b) Express 100x 2 140x + 65 as the sum of a perfect-square expression and the square of an integer. Lesson 6.3 Extra Practice 415
6 Lesson 6.3 Extra Practice Answers a) y = (x 6) 2 36 b) y = 3(x + 1) a) y = 5(x + 2) b) 4. a) $92.50 b) $ a) 3x by 3x, (34 4x) by (17 2x) b) Answers may vary, e.g., A = (3x) 2 + (34 4x)(17 2x) A = 9x (34) 34(2x) 17(4x) + 8x 2 A = 17x 2 17(8x) + 17(34) A = 17(x 2 8x + 34) c) 306 cm 2 ; square: 48 cm; rectangle: 54 cm 6. a) (2, 7), x = 2 b) Answers may vary, e.g., after doubling, the axis of symmetry is twice as far from the y-axis. 7. a) 100x 2 60x + 9, 100x 2 80x + 16, 100x 2 100x + 25 b) (10x 7) y = (x + 5.5) Principles of Mathematics 10: Lesson 6.3 Extra Practice Answers
7 Chapter 6 Mid-Chapter Review Extra Practice STUDENT BOOK PAGES Solve each quadratic equation by factoring. a) x 2 13x + 30 = 0 b) x 2 = 6(12 x) c) (x + 1) 2 = 16 d) x(x + 4) = Solve each quadratic equation by factoring or by using a graphing calculator. Round your answers to two decimal places, if necessary. a) 2x 2 + 9x 5 = 0 b) x = 3x c) 3x 2 5x = 7 d) 3(x 2 5) = 4x 3. A rectangular theatre stage, with an area of 84 m 2, is 5 m longer than it is wide. How long is the stage? 4. Determine the value of c that makes each expression a multiple of a perfect-square trinomial. a) x 2 + 8x + c b) 2x x + c c) 5x 2 60x + c d) 7x 2 42x + c 6. Armin charges $50/h to repair computers. If he charges for x hours per month, his monthly profit, P, in dollars, can be modelled by the relation P = x x a) What is Armin s maximum monthly profit? b) How many hours should he work each month to achieve this profit? 7. A suborbital space plane is designed to give space tourists a brief experience of zero-g flight. According to the flight plan, when the engine shuts down at an altitude of m, the space plane gains altitude at a speed of 1250 m/s. Its height, t seconds after engine shutdown, can be modelled by 5t t a) What is the maximum altitude of the space plane? b) The period of freefall lasts from engine shutdown to re-entry. Assuming that the space plane starts to re-enter the atmosphere at the same altitude of m, how long is the space plane in freefall? 5. Complete the square to express each relation in vertex form. Then describe the transformations that must be applied to the graph of y = x 2 to graph the relation. a) y = x x + 29 b) y = 3x 2 18x + 14 Chapter 6 Mid-Chapter Review Extra Practice 417
8 Chapter 6 Mid-Chapter Review Extra Practice Answers 1. a) 3, 10 b) 6, 12 c) 3, 5 d) 2, 6 2. a) 0.5, 5 b) no solutions c) about 0.91, about 2.57 d) about 1.67, 3 6. a) $3950 b) 90 h 7. a) m b) 250 s, or 4 min 10 s m 4. a) 16 b) 18 c) 180 d) a) y = (x + 7) 2 20; translation 7 units left and 20 units down b) y = 3(x 3) 2 13; vertical stretch by a factor of 3, translation 3 units right and 13 units down 418 Principles of Mathematics 10: Chapter 6 Mid-Chapter Review Extra Practice Answers
9 Lesson 6.4 Extra Practice STUDENT BOOK PAGES a) Solve the equation 2x 2 27x 80 = 0 by factoring. b) Solve the same equation using the quadratic formula. c) Identify one advantage of each strategy over the other. 2. Solve each equation using the quadratic formula. a) x 2 16 = 49 b) 3x(x 5) = 5(15 3x) 3. Determine the roots of each equation. Round the roots to two decimal places, if necessary. a) 2x 2 10 = 0 b) 3(x 3) = 0 c) 3(x + 3) 2 75 = 0 d) 0.5(x 0.5) = 0 6. A baseball is bunted so that its height, h, in metres, after t seconds is modelled by h = 4.9t t a) How long is the baseball in the air, to the nearest tenth of a second? b) How long is the baseball above 25 m, to the nearest tenth of a second? 7. A landscape architect is planning a circular flower bed that will be surrounded by a ring of paving stones, 25 cm wide. The area of the ring of paving stones will be half the area of the flower bed. Determine the diameter of the flower bed, to the nearest centimetre. 4. Solve each equation. Round your solutions to two decimal places, if necessary. a) 2x 2 10x 6 = 0 b) (x 1)(2x + 3) = 0 c) 2(x 2 + 1) = 7x d) 2x(2 x) = 1 x 5. Calculate the value of x, to two decimal places. Lesson 6.4 Extra Practice 419
10 Lesson 6.4 Extra Practice Answers 1. a) b) 16, 2.5 c) Answers may vary, e.g., factoring makes it easier to check that the solutions are correct; the quadratic formula can be used directly, without checking all the factor pairs of a) about 8.06, about 8.06 b) 5, 5 3. a) 2.24, 2.24 b) 0.55, 5.45 c) 2, 8 d) 1.91, a) 5.54, 0.54 b) 1, 1.5 c) 0.31, 3.19 d) 0.22, a) 4.8 s b) 1.9 s cm 420 Principles of Mathematics 10: Lesson 6.4 Extra Practice Answers
11 Lesson 6.5 Extra Practice STUDENT BOOK PAGES a) Determine the roots of 2x 2 9x 35 = 0 using the strategy of your choice. b) What do your results for part a) tell you about the graph of y = 2x 2 9x 35? c) Predict whether the discriminant of the equation in part a) is positive, negative, or zero. Justify your prediction. d) Confirm your prediction by calculating the value of D. 2. Calculate the discriminant of each equation, and state the number of real roots. a) x 2 + 5x 3 = 0 b) 4x(x 1) + 1 = 0 c) 2x = 3x d) 3x(x + 5) = x How many times does each relation cross or touch the x-axis? Justify your answer in terms of the graph of the relation. a) y = (x 3) 2 7 b) y = 2x 2 13 c) y = 5(x + 2) 2 d) y = (x + 10) Determine whether the vertex of each parabola lies above, below, or on the x-axis. Explain your answers. a) y = x 2 + 7x + 5 b) y = (x + 2) 2 + 2x + 7 c) y = 4x 2 20x + 25 d) y = 5x(x 3) For what value(s) of k does the relation y = 4x 2 kx + 9 have each number of zeros? a) two zeros b) one zero c) no zeros 7. Suppose that a and c have opposite signs in the quadratic relation y = ax 2 + bx + c. a) What does this tell you about the y-intercept and the direction of opening of the graph of the relation? b) Use sketches, without a grid, to show why the relation must have two roots. c) Give an algebraic reason why the discriminant must be positive when a and c have opposite signs. 4. The support rails of a suspension bridge over a river are modelled by the relation h = x 2, where x is the distance, in metres, from the middle of the bridge and h is the height, in metres, above the river. Explain why, in terms of the bridge and the river, the discriminant of the relation must be negative. Lesson 6.5 Extra Practice 421
12 Lesson 6.5 Extra Practice Answers 1. a) 7, 2.5 b) The parabola crosses the x-axis twice. c) From parts a) and b), the parabola has two roots. The discriminant must be positive. d) D = 361; my prediction is correct. 7. Answers may vary, e.g., a) Either the y-intercept is positive and the graph opens downward, or the y-intercept is negative and the graph opens upward. b) Answers may vary slightly, e.g., 2. a) 37; two real roots c) 31; no real roots b) 0; one real root d) 289; two real roots 3. Answers may vary, e.g., a) 2; the vertex is below the x-axis, and the graph opens upward. b) 0; the vertex is below the x-axis, and the graph opens downward. c) 1; the vertex is on the x-axis. d) 2; the vertex is above the x-axis, and the graph opens downward. 4. Answers may vary, e.g., the bridge is above the river, so the height of the rail is always positive. Therefore, the relation has no zeros. 5. Answers may vary, e.g., a) Above the x-axis; the relation opens downward and, because the discriminant is positive, has two zeros. b) Above the x-axis; the relation opens upward and, because the discriminant is negative, has no zeros. c) On the x-axis; the discriminant is zero, so the relation has one zero. d) Below the x-axis; the relation opens downward and, because the discriminant is negative, has no zeros. 6. a) k < 12 or k > 12 b) k = ±12 c) 12 < k < 12 In each case, the vertex is farther from the x-axis than the y-intercept, so the graph must cross the x-axis twice. c) Since a and c have opposite signs, ac < 0, so 4ac > 0. Therefore, b 2 4ac > Principles of Mathematics 10: Lesson 6.5 Extra Practice Answers
13 Lesson 6.6 Extra Practice STUDENT BOOK PAGES For each relation, explain what each coordinate of the vertex represents and what the zeros represent. a) a relation that models the height, h, of a diver who jumps upward from a board, after time t b) a relation that models the monthly profit, P, earned for a given number of clients per month, x c) a relation that models the area, A, of a rectangle with a fixed perimeter and width w For questions 2 to 7, round your answers to two decimal places, if necessary. 2. The height, h, in metres, of a football is modelled by h = 1 + 5t(4 t), where t is the time, in seconds, after the football is punted. a) What is the maximum height of the football? b) How long is the football in the air? 3. Carly is diving from the 10 m board at her local pool. During her descent underwater, her depth, d, in metres, is modelled by d = 7.5t t, where t is the time, in seconds, after she enters the water. a) What is Carly s maximum depth? b) How long does Carly take to reach this depth? 6. Darya attempts a high jump of 2.22 m. Her centre of mass is initially at a height of 1.0 m, passes 1.8 m after 0.2 s, and passes 1.8 m again after 0.8 s. a) The height of Darya s centre of mass, in metres, is modelled by y = a(t h) 2 + k. Show that h = 0.5, 0.25a + k = 1, and 0.09a + k = 1.8. b) Write the relation that models the height of Darya s centre of mass in vertex form. c) Does Darya clear the attempted height? Explain. 7. Rashid is planning six cubicles for an office. He wants each cubicle to have the same dimensions, and he has chosen an L-shaped layout. He has written the relation P = 9l + 10w for the length of cubicle wall needed. If he has 72 m of cubicle wall to use, what dimensions will maximize the area of each cubicle? 4. The sum of the squares of three consecutive positive odd integers is 515. Determine the integers. 5. Karsten, a tennis pro, is attempting a drop shot so that the ball just clears the net. The ball is 1.3 m above the ground when Karsten hits it. The ball reaches its maximum height, 3.1 m, after it has travelled 2.5 m horizontally. a) Write an equation to model this situation. b) The height of the net is 0.92 m in the middle of the court. Assuming that Karsten s shot is aimed down the centre line, how far away from the net must he be to make the shot? Lesson 6.6 Extra Practice 423
14 Lesson 6.6 Extra Practice Answers 1. a) vertex: maximum height, h, and time, t, when the maximum height is reached; first zero: no meaning; second zero: time when the diver enters the water b) vertex: maximum profit, P, and number of clients per month, x, for the maximum profit; zeros: break-even points c) vertex: maximum area, A, and width, w, for the maximum area; zeros: dimensions of the rectangles with zero length or width 2. a) 21 m b) 4.05 s 3. a) 6.82 m b) 0.95 s 4. 11, 13, a) h = 0.29(x 2.5) b) 5.24 m a) h = = 0.5; 1 = a(0 0.5) 2 + k, so a + k = 1; 1.8 = a( ) 2 + k, so 0.09a + k = 1.8 b) h = 5(t 0.5) c) Yes. The maximum height of Darya s centre of mass is greater than 2.22 m m by 3.6 m 424 Principles of Mathematics 10: Lesson 6.6 Extra Practice Answers
15 Chapter 6 Review Extra Practice STUDENT BOOK PAGES Solve each equation by factoring. Check your solutions with graphing technology. a) x = 7x b) 2x 2 + 9x 35 = 0 c) 17(x + 5) = 5(x 2 + 9) d) 3x(x 6) = 5(2 x) 2. The quadratic relation y = 5x x + c has a minimum value of 0. What is the value of c? Explain. 3. Write each relation in vertex form by completing the square. Then describe the transformations that must be applied to the graph of y = x 2 to graph the relation. a) y = x 2 12x + 50 b) y = 4x x c) y = 0.25x x d) y = 2x x 15 For questions 4 to 8, round your answers to two decimal places, if necessary. 4. A bridge with a parabolic inner arch is being constructed over a canal. The arch will just touch the water on each side of the canal, which is 27.2 m wide. The arch must have a clearance of 6.4 m at a horizontal distance of 9.5 m from either bank of the canal. a) Write a relation, in factored form, to model the height, h, in metres, of the bridge at a horizontal distance of x metres from one bank of the canal. b) Rewrite your relation for part a) in vertex form by expanding and completing the square. c) How high above the water will the arch be, at its highest point, to the nearest hundredth of a metre? 5. Solve each equation using the quadratic formula. a) x 2 7x + 9 = 0 b) 2.5x 2 = 16x c) 2x(x + 3) = 14(1 x) d) 2x(2x 5) = Kaneisha owns a business that produces and sells handmade carriage clocks. She models her monthly revenue, in dollars, as R = 0.2x x, where x is the price, in dollars, of each clock. She models her monthly costs, in dollars, as C = x. She calculates her monthly profit, in dollars, as P = R C. Between what prices should Kaneisha charge to break even? 7. The height of a football, h, in metres, can be modelled by h = 5t t + 1.5, where t is the time, in seconds, after it is punted. a) Write an equation for the time(s) at which the football is c metres high. Determine an expression for the discriminant, D, of this equation in terms of c. b) Use your expression for the discriminant to determine the maximum height of the football. Explain your reasoning. c) How many realistic solutions does your equation from part a) have for each case below? Explain your reasoning. i) 1.50 c < ii) 0 c < 1.50 iii) c < 0 8. The hourly cost, C, in dollars, of running a printing press is modelled as C = x x + 965, where x is the number of pages that are printed per hour. a) How many pages should be printed each hour to minimize the cost? b) What rates of printing will keep the cost below $800? Chapter 6 Review Extra Practice Answers 425
16 Chapter 6 Review Extra Practice Answers 1. a) 3, 4 b) 7, ; answers may vary, e.g., only a perfect-square trinomial could have a minimum value of zero because it has only one root, so 5x x + c = 5(x 2 + 8x + 16) = 5x x a) y = (x 6) ; translation 6 units right and 14 units up b) y = 4(x + 6) 2 ; vertical stretch by a factor of 4, translation 6 units left c) y = 0.25(x 7) ; reflection in the x-axis, vertical compression by a factor of 0.25, translation 7 units right and 19 units up d) y = 2(x 2.5) 2 2.5; reflection in the x-axis, vertical stretch by a factor of 2, translation 2.5 units right and 2.5 units down 4. a) h = 0.04x(x 27.2) b) h = 0.04(x 13.6) c) 7.40 m c) 1.6, 5 5. a) about 1.70, about 5.30 b) 7, 0.6 c) about 0.66, about d) about 3.55, about between $97.87 and $ d) 2, a) 5t t c = 0; D = c b) m; answers may vary, e.g., there is exactly one solution for the time to reach maximum height, and the equation has exactly one solution for c = c) i) D > 0, so there are two solutions; both solutions are realistic, since the height is between the starting value of 1.5 m and the maximum height. ii) D > 0, so there are two solutions; only one solution is realistic, since the height is less than the starting value of 1.5 m. iii) D > 0, so there are two solutions; neither solution is realistic, since the height cannot be negative. 8. a) 6000 b) between 1000 and pages per hour 426 Principles of Mathematics 10: Chapter 6 Review Extra Practice Answers
17 Chapters 4 6 Cumulative Review Extra Practice STUDENT BOOK PAGES What is the factored form of 12a 2 7a 10? A. (6a 2)(2a + 5) B. (4a 5)(3a + 2) C. (4a + 2)(3a 5) D. (4a + 2)(3a 2) 2. What is the factored form of 16c 2 56c + 49? A. (4c 7) 2 B. (4c + 7)(4c 7) C. (4c + 7) 2 D. (8c 7)(2c 7) 3. What is the factored form of 81x 2 y 2 49? A. (9xy 7) 2 B. (9x 7y)(9x + 7y) C. (9xy + 7) 2 D. (9xy 7)(9xy + 7) 4. The following transformations were applied to the graph of y = x 2 : a reflection in the x-axis, a vertical compression by a factor of 2 1, and a translation 3 units right and 7 units down. What is the equation of the transformed graph? A. y = 2 1 (x 3) B. y = (x 7) C. y = 2(x 3) D. y = (x 3) The vertex of a parabola is ( 4, 5), and the parabola passes through ( 6, 3). What is the equation of the parabola? A. y = 11(x + 4) B. y = 2(x + 4) C. y = 2(x 4) D. y = 11(x 5) What is the vertex form of the quadratic relation y = 4x(x 5) 10? A. y = 4(x + 2.5) B. y = 4(x 2.5) 2 15 C. y = 4(x 2.5) 2 35 D. y = 4(x 2.5) Which values of x are solutions to the equation 8x 2 2x 3 = 0? 1 3 A. x =, x = B. x =, x = C. x =, x = D. x =, x = Which expression is not a perfect-square trinomial? A. 9x 2 6x + 1 B. x x + 25 C. x 2 x + 1 D. 4x 2 12x What is the minimum value of the quadratic equation y = 2x x + 17? A. 81 B. 81 C. 32 D Which equation is equivalent to x 2 + 8x + 15? A. y = (x + 8) 2 1 B. y = (x + 4) 2 1 C. y = (x + 4) D. y = (x + 2) Which value of b will make the quadratic equation 6x 2 + bx + 5 have no real solutions? A. 11 B. 17 C. 4 D. 12 Chapters 4 6 Cumulative Review Extra Practice 427
18 Chapters 4 6 Cumulative Review Extra Practice Answers 1. B 2. A 3. D 4. D 5. B 6. C 7. B 8. C 9. A 10. B 11. C 428 Principles of Mathematics 10: Chapters 4 6 Cumulative Review Extra Practice Answers
Chapter 6: Quadratic Functions & Their Algebra
 Chapter 6: Quadratic Functions & Their Algebra Topics: 1. Quadratic Function Review. Factoring: With Greatest Common Factor & Difference of Two Squares 3. Factoring: Trinomials 4. Complete Factoring 5.
Chapter 6: Quadratic Functions & Their Algebra Topics: 1. Quadratic Function Review. Factoring: With Greatest Common Factor & Difference of Two Squares 3. Factoring: Trinomials 4. Complete Factoring 5.
Factoring Quadratic Expressions VOCABULARY
 5-5 Factoring Quadratic Expressions TEKS FOCUS Foundational to TEKS (4)(F) Solve quadratic and square root equations. TEKS (1)(C) Select tools, including real objects, manipulatives, paper and pencil,
5-5 Factoring Quadratic Expressions TEKS FOCUS Foundational to TEKS (4)(F) Solve quadratic and square root equations. TEKS (1)(C) Select tools, including real objects, manipulatives, paper and pencil,
A. B. C. D. Graphing Quadratics Practice Quiz. Question 1. Select the graph of the quadratic function. f (x ) = 2x 2. 2/26/2018 Print Assignment
 Question 1. Select the graph of the quadratic function. f (x ) = 2x 2 C. D. https://my.hrw.com/wwtb2/viewer/printall_vs23.html?umk5tfdnj31tcldd29v4nnzkclztk3w8q6wgvr2629ca0a5fsymn1tfv8j1vs4qotwclvofjr8uon4cldd29v4
Question 1. Select the graph of the quadratic function. f (x ) = 2x 2 C. D. https://my.hrw.com/wwtb2/viewer/printall_vs23.html?umk5tfdnj31tcldd29v4nnzkclztk3w8q6wgvr2629ca0a5fsymn1tfv8j1vs4qotwclvofjr8uon4cldd29v4
Solving Problems Involving Cost, Revenue, Profit. Max and Min Problems
 Solving Problems Involving Cost, Revenue, Profit The cost function C(x) is the total cost of making x items. If the cost per item is fixed, it is equal to the cost per item (c) times the number of items
Solving Problems Involving Cost, Revenue, Profit The cost function C(x) is the total cost of making x items. If the cost per item is fixed, it is equal to the cost per item (c) times the number of items
Chapter 4 Factoring and Quadratic Equations
 Chapter 4 Factoring and Quadratic Equations Lesson 1: Factoring by GCF, DOTS, and Case I Lesson : Factoring by Grouping & Case II Lesson 3: Factoring by Sum and Difference of Perfect Cubes Lesson 4: Solving
Chapter 4 Factoring and Quadratic Equations Lesson 1: Factoring by GCF, DOTS, and Case I Lesson : Factoring by Grouping & Case II Lesson 3: Factoring by Sum and Difference of Perfect Cubes Lesson 4: Solving
3.1 Factors and Multiples of Whole Numbers
 3.1 Factors and Multiples of Whole Numbers LESSON FOCUS: Determine prime factors, greatest common factors, and least common multiples of whole numbers. The prime factorization of a natural number is the
3.1 Factors and Multiples of Whole Numbers LESSON FOCUS: Determine prime factors, greatest common factors, and least common multiples of whole numbers. The prime factorization of a natural number is the
3.1 Solutions to Exercises
 .1 Solutions to Exercises 1. (a) f(x) will approach + as x approaches. (b) f(x) will still approach + as x approaches -, because any negative integer x will become positive if it is raised to an even exponent,
.1 Solutions to Exercises 1. (a) f(x) will approach + as x approaches. (b) f(x) will still approach + as x approaches -, because any negative integer x will become positive if it is raised to an even exponent,
Name. 5. Simplify. a) (6x)(2x 2 ) b) (5pq 2 )( 4p 2 q 2 ) c) (3ab)( 2ab 2 )(2a 3 ) d) ( 6x 2 yz)( 5y 3 z)
 3.1 Polynomials MATHPOWER TM 10, Ontario Edition, pp. 128 133 To add polynomials, collect like terms. To subtract a polynomial, add its opposite. To multiply monomials, multiply the numerical coefficients.
3.1 Polynomials MATHPOWER TM 10, Ontario Edition, pp. 128 133 To add polynomials, collect like terms. To subtract a polynomial, add its opposite. To multiply monomials, multiply the numerical coefficients.
MATH 181-Quadratic Equations (7 )
 MATH 181-Quadratic Equations (7 ) 7.1 Solving a Quadratic Equation by Factoring I. Factoring Terms with Common Factors (Find the greatest common factor) a. 16 1x 4x = 4( 4 3x x ) 3 b. 14x y 35x y = 3 c.
MATH 181-Quadratic Equations (7 ) 7.1 Solving a Quadratic Equation by Factoring I. Factoring Terms with Common Factors (Find the greatest common factor) a. 16 1x 4x = 4( 4 3x x ) 3 b. 14x y 35x y = 3 c.
3.1 Solutions to Exercises
 .1 Solutions to Exercises 1. (a) f(x) will approach + as x approaches. (b) f(x) will still approach + as x approaches -, because any negative integer x will become positive if it is raised to an even exponent,
.1 Solutions to Exercises 1. (a) f(x) will approach + as x approaches. (b) f(x) will still approach + as x approaches -, because any negative integer x will become positive if it is raised to an even exponent,
Chapter 5 Self-Assessment
 Chapter 5 Self-Assessment. BLM 5 1 Concept BEFORE DURING (What I can do) AFTER (Proof that I can do this) 5.1 I can multiply binomials. I can multiply trinomials. I can explain how multiplication of binomials
Chapter 5 Self-Assessment. BLM 5 1 Concept BEFORE DURING (What I can do) AFTER (Proof that I can do this) 5.1 I can multiply binomials. I can multiply trinomials. I can explain how multiplication of binomials
Factor Quadratic Expressions of the Form ax 2 + bx + c. How can you use a model to factor quadratic expressions of the form ax 2 + bx + c?
 5.5 Factor Quadratic Expressions of the Form ax 2 + bx + c The Ontario Summer Games are held every two years in even-numbered years to provide sports competition for youth between the ages of 11 and 22.
5.5 Factor Quadratic Expressions of the Form ax 2 + bx + c The Ontario Summer Games are held every two years in even-numbered years to provide sports competition for youth between the ages of 11 and 22.
Topic #1: Evaluating and Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
 John Jay College of Criminal Justice The City University of New York Department of Mathematics and Computer Science MAT 105 - College Algebra Departmental Final Examination Review Topic #1: Evaluating
John Jay College of Criminal Justice The City University of New York Department of Mathematics and Computer Science MAT 105 - College Algebra Departmental Final Examination Review Topic #1: Evaluating
Elementary Algebra Review for Exam 3
 Elementary Algebra Review for Exam ) After receiving a discount of 5% on its bulk order of typewriter ribbons, John's Office Supply pays $5882. What was the price of the order before the discount? Round
Elementary Algebra Review for Exam ) After receiving a discount of 5% on its bulk order of typewriter ribbons, John's Office Supply pays $5882. What was the price of the order before the discount? Round
Exercises. 140 Chapter 3: Factors and Products
 Exercises A 3. List the first 6 multiples of each number. a) 6 b) 13 c) 22 d) 31 e) 45 f) 27 4. List the prime factors of each number. a) 40 b) 75 c) 81 d) 120 e) 140 f) 192 5. Write each number as a product
Exercises A 3. List the first 6 multiples of each number. a) 6 b) 13 c) 22 d) 31 e) 45 f) 27 4. List the prime factors of each number. a) 40 b) 75 c) 81 d) 120 e) 140 f) 192 5. Write each number as a product
MATD 0370 ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA REVIEW FOR TEST 3 (New Material From: , , and 10.1)
 NOTE: In addition to the problems below, please study the handout Exercise Set 10.1 posted at http://www.austincc.edu/jbickham/handouts. 1. Simplify: 5 7 5. Simplify: ( ab 5 c )( a c 5 ). Simplify: 4x
NOTE: In addition to the problems below, please study the handout Exercise Set 10.1 posted at http://www.austincc.edu/jbickham/handouts. 1. Simplify: 5 7 5. Simplify: ( ab 5 c )( a c 5 ). Simplify: 4x
Name Class Date. Adding and Subtracting Polynomials
 8-1 Reteaching Adding and Subtracting Polynomials You can add and subtract polynomials by lining up like terms and then adding or subtracting each part separately. What is the simplified form of (3x 4x
8-1 Reteaching Adding and Subtracting Polynomials You can add and subtract polynomials by lining up like terms and then adding or subtracting each part separately. What is the simplified form of (3x 4x
Name: Class: Date: in general form.
 Write the equation in general form. Mathematical Applications for the Management Life and Social Sciences 11th Edition Harshbarger TEST BANK Full clear download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/mathematical-applications-management-life-socialsciences-11th-edition-harshbarger-test-bank/
Write the equation in general form. Mathematical Applications for the Management Life and Social Sciences 11th Edition Harshbarger TEST BANK Full clear download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/mathematical-applications-management-life-socialsciences-11th-edition-harshbarger-test-bank/
2-4 Completing the Square
 2-4 Completing the Square Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 2 Warm Up Write each expression as a trinomial. 1. (x 5) 2 x 2 10x + 25 2. (3x + 5) 2 9x 2 + 30x + 25 Factor each expression. 3.
2-4 Completing the Square Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 2 Warm Up Write each expression as a trinomial. 1. (x 5) 2 x 2 10x + 25 2. (3x + 5) 2 9x 2 + 30x + 25 Factor each expression. 3.
MATD 0370 ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA REVIEW FOR TEST 3 (New Material From: , , and 10.1)
 NOTE: In addition to the problems below, please study the handout Exercise Set 10.1 posted at http://www.austin.cc.tx.us/jbickham/handouts. 1. Simplify: 5 7 5. Simplify: ( 6ab 5 c )( a c 5 ). Simplify:
NOTE: In addition to the problems below, please study the handout Exercise Set 10.1 posted at http://www.austin.cc.tx.us/jbickham/handouts. 1. Simplify: 5 7 5. Simplify: ( 6ab 5 c )( a c 5 ). Simplify:
Name: Common Core Algebra L R Final Exam 2015 CLONE 3 Teacher:
 1) Which graph represents a linear function? 2) Which relation is a function? A) B) A) {(2, 3), (3, 9), (4, 7), (5, 7)} B) {(0, -2), (3, 10), (-2, -4), (3, 4)} C) {(2, 7), (2, -3), (1, 1), (3, -1)} D)
1) Which graph represents a linear function? 2) Which relation is a function? A) B) A) {(2, 3), (3, 9), (4, 7), (5, 7)} B) {(0, -2), (3, 10), (-2, -4), (3, 4)} C) {(2, 7), (2, -3), (1, 1), (3, -1)} D)
ST. DAVID S MARIST INANDA
 ST. DAVID S MARIST INANDA MATHEMATICS NOVEMBER EXAMINATION GRADE 11 PAPER 1 8 th NOVEMBER 2016 EXAMINER: MRS S RICHARD MARKS: 125 MODERATOR: MRS C KENNEDY TIME: 2 1 Hours 2 NAME: PLEASE PUT A CROSS NEXT
ST. DAVID S MARIST INANDA MATHEMATICS NOVEMBER EXAMINATION GRADE 11 PAPER 1 8 th NOVEMBER 2016 EXAMINER: MRS S RICHARD MARKS: 125 MODERATOR: MRS C KENNEDY TIME: 2 1 Hours 2 NAME: PLEASE PUT A CROSS NEXT
BARUCH COLLEGE MATH 2003 SPRING 2006 MANUAL FOR THE UNIFORM FINAL EXAMINATION
 BARUCH COLLEGE MATH 003 SPRING 006 MANUAL FOR THE UNIFORM FINAL EXAMINATION The final examination for Math 003 will consist of two parts. Part I: Part II: This part will consist of 5 questions similar
BARUCH COLLEGE MATH 003 SPRING 006 MANUAL FOR THE UNIFORM FINAL EXAMINATION The final examination for Math 003 will consist of two parts. Part I: Part II: This part will consist of 5 questions similar
Unit 8: Quadratic Expressions (Polynomials)
 Name: Period: Algebra 1 Unit 8: Quadratic Expressions (Polynomials) Note Packet Date Topic/Assignment HW Page Due Date 8-A Naming Polynomials and Combining Like Terms 8-B Adding and Subtracting Polynomials
Name: Period: Algebra 1 Unit 8: Quadratic Expressions (Polynomials) Note Packet Date Topic/Assignment HW Page Due Date 8-A Naming Polynomials and Combining Like Terms 8-B Adding and Subtracting Polynomials
When Is Factoring Used?
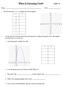 When Is Factoring Used? Name: DAY 9 Date: 1. Given the function, y = x 2 complete the table and graph. x y 2 1 0 1 2 3 1. A ball is thrown vertically upward from the ground according to the graph below.
When Is Factoring Used? Name: DAY 9 Date: 1. Given the function, y = x 2 complete the table and graph. x y 2 1 0 1 2 3 1. A ball is thrown vertically upward from the ground according to the graph below.
Developmental Math An Open Program Unit 12 Factoring First Edition
 Developmental Math An Open Program Unit 12 Factoring First Edition Lesson 1 Introduction to Factoring TOPICS 12.1.1 Greatest Common Factor 1 Find the greatest common factor (GCF) of monomials. 2 Factor
Developmental Math An Open Program Unit 12 Factoring First Edition Lesson 1 Introduction to Factoring TOPICS 12.1.1 Greatest Common Factor 1 Find the greatest common factor (GCF) of monomials. 2 Factor
Math1090 Midterm 2 Review Sections , Solve the system of linear equations using Gauss-Jordan elimination.
 Math1090 Midterm 2 Review Sections 2.1-2.5, 3.1-3.3 1. Solve the system of linear equations using Gauss-Jordan elimination. 5x+20y 15z = 155 (a) 2x 7y+13z=85 3x+14y +6z= 43 x+z= 2 (b) x= 6 y+z=11 x y+
Math1090 Midterm 2 Review Sections 2.1-2.5, 3.1-3.3 1. Solve the system of linear equations using Gauss-Jordan elimination. 5x+20y 15z = 155 (a) 2x 7y+13z=85 3x+14y +6z= 43 x+z= 2 (b) x= 6 y+z=11 x y+
Common Core Algebra L clone 4 review R Final Exam
 1) Which graph represents an exponential function? A) B) 2) Which relation is a function? A) {(12, 13), (14, 19), (11, 17), (14, 17)} B) {(20, -2), (24, 10), (-21, -5), (22, 4)} C) {(34, 8), (32, -3),
1) Which graph represents an exponential function? A) B) 2) Which relation is a function? A) {(12, 13), (14, 19), (11, 17), (14, 17)} B) {(20, -2), (24, 10), (-21, -5), (22, 4)} C) {(34, 8), (32, -3),
Name Date
 NEW DORP HIGH SCHOOL Deirdre A. DeAngelis, Principal MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT Li Pan, Assistant Principal Name Date Summer Math Assignment for a Student whose Official Class starts with 7, 8, and 9 Directions:
NEW DORP HIGH SCHOOL Deirdre A. DeAngelis, Principal MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT Li Pan, Assistant Principal Name Date Summer Math Assignment for a Student whose Official Class starts with 7, 8, and 9 Directions:
Unit 3: Writing Equations Chapter Review
 Unit 3: Writing Equations Chapter Review Part 1: Writing Equations in Slope Intercept Form. (Lesson 1) 1. Write an equation that represents the line on the graph. 2. Write an equation that has a slope
Unit 3: Writing Equations Chapter Review Part 1: Writing Equations in Slope Intercept Form. (Lesson 1) 1. Write an equation that represents the line on the graph. 2. Write an equation that has a slope
Firrhill High School. Mathematics Department. Level 5
 Firrhill High School Mathematics Department Level 5 Home Exercise 1 - Basic Calculations Int 2 Unit 1 1. Round these numbers to 2 significant figures a) 409000 (b) 837500000 (c) 562 d) 0.00000009 (e)
Firrhill High School Mathematics Department Level 5 Home Exercise 1 - Basic Calculations Int 2 Unit 1 1. Round these numbers to 2 significant figures a) 409000 (b) 837500000 (c) 562 d) 0.00000009 (e)
Section 4.3 Objectives
 CHAPTER ~ Linear Equations in Two Variables Section Equation of a Line Section Objectives Write the equation of a line given its graph Write the equation of a line given its slope and y-intercept Write
CHAPTER ~ Linear Equations in Two Variables Section Equation of a Line Section Objectives Write the equation of a line given its graph Write the equation of a line given its slope and y-intercept Write
8-7 Solving ax^2 + bx + c = 0
 29. BASKETBALL When Jerald shoots a free throw, the ball is 6 feet from the floor and has an initial upward velocity of 20 feet per second. The hoop is 10 feet from the floor. a. Use the vertical motion
29. BASKETBALL When Jerald shoots a free throw, the ball is 6 feet from the floor and has an initial upward velocity of 20 feet per second. The hoop is 10 feet from the floor. a. Use the vertical motion
9/16/ (1) Review of Factoring trinomials. (2) Develop the graphic significance of factors/roots. Math 2 Honors - Santowski
 (1) Review of Factoring trinomials (2) Develop the graphic significance of factors/roots (3) Solving Eqn (algebra/graphic connection) 1 2 To expand means to write a product of expressions as a sum or difference
(1) Review of Factoring trinomials (2) Develop the graphic significance of factors/roots (3) Solving Eqn (algebra/graphic connection) 1 2 To expand means to write a product of expressions as a sum or difference
Factoring. (5) Page 600 #21 43 Right **********Quiz Tomorrow********** (10) Page #20 32 Right; #35 47 Right *****Quiz tomorrow****
 Algebra Unit 6: Factoring Name: Date: Period: # Factoring (1) Page 629 #6 8; #15 20 (2) Page 629 #21, 22, 29-32 (3) Worksheet (4) Page 600 #19 42 Left (5) Page 600 #21 43 Right **********Quiz Tomorrow**********
Algebra Unit 6: Factoring Name: Date: Period: # Factoring (1) Page 629 #6 8; #15 20 (2) Page 629 #21, 22, 29-32 (3) Worksheet (4) Page 600 #19 42 Left (5) Page 600 #21 43 Right **********Quiz Tomorrow**********
Special Binomial Products
 Lesson 11-6 Lesson 11-6 Special Binomial Products Vocabulary perfect square trinomials difference of squares BIG IDEA The square of a binomial a + b is the expression (a + b) 2 and can be found by multiplying
Lesson 11-6 Lesson 11-6 Special Binomial Products Vocabulary perfect square trinomials difference of squares BIG IDEA The square of a binomial a + b is the expression (a + b) 2 and can be found by multiplying
Mathematics 10C. UNIT THREE Polynomials. 3x 3-6x 2. 3x 2 (x - 2) 4x 2-3x - 1. Unit. Student Workbook. FOIL (2x - 3)(x + 1) A C = -4.
 Mathematics 10C FOIL (2x - 3)(x + 1) Student Workbook Lesson 1: Expanding Approximate Completion Time: 4 Days Unit 3 3x 3-6x 2 Factor Expand 3x 2 (x - 2) Lesson 2: Greatest Common Factor Approximate Completion
Mathematics 10C FOIL (2x - 3)(x + 1) Student Workbook Lesson 1: Expanding Approximate Completion Time: 4 Days Unit 3 3x 3-6x 2 Factor Expand 3x 2 (x - 2) Lesson 2: Greatest Common Factor Approximate Completion
Math Analysis Midterm Review. Directions: This assignment is due at the beginning of class on Friday, January 9th
 Math Analysis Midterm Review Name Directions: This assignment is due at the beginning of class on Friday, January 9th This homework is intended to help you prepare for the midterm exam. The questions are
Math Analysis Midterm Review Name Directions: This assignment is due at the beginning of class on Friday, January 9th This homework is intended to help you prepare for the midterm exam. The questions are
1 algebraic. expression. at least one operation. Any letter can be used as a variable. 2 + n. combination of numbers and variables
 1 algebraic expression at least one operation 2 + n r w q Any letter can be used as a variable. combination of numbers and variables DEFINE: A group of numbers, symbols, and variables that represent an
1 algebraic expression at least one operation 2 + n r w q Any letter can be used as a variable. combination of numbers and variables DEFINE: A group of numbers, symbols, and variables that represent an
Chapter Representing Patterns, pages MHR Answers
 . a) x -, x - b) Example: The processes are similar in that the like terms were combined. The processes are different in that one involved addition and the other involved subtraction.. Yes. Example: The
. a) x -, x - b) Example: The processes are similar in that the like terms were combined. The processes are different in that one involved addition and the other involved subtraction.. Yes. Example: The
Sandringham School Sixth Form. AS Maths. Bridging the gap
 Sandringham School Sixth Form AS Maths Bridging the gap Section 1 - Factorising be able to factorise simple expressions be able to factorise quadratics The expression 4x + 8 can be written in factor form,
Sandringham School Sixth Form AS Maths Bridging the gap Section 1 - Factorising be able to factorise simple expressions be able to factorise quadratics The expression 4x + 8 can be written in factor form,
Laurie s Notes. Overview of Section 7.6. (1x + 6)(2x + 1)
 Laurie s Notes Overview of Section 7.6 Introduction In this lesson, students factor trinomials of the form ax 2 + bx + c. In factoring trinomials, an common factor should be factored out first, leaving
Laurie s Notes Overview of Section 7.6 Introduction In this lesson, students factor trinomials of the form ax 2 + bx + c. In factoring trinomials, an common factor should be factored out first, leaving
Unit 8 Notes: Solving Quadratics by Factoring Alg 1
 Unit 8 Notes: Solving Quadratics by Factoring Alg 1 Name Period Day Date Assignment (Due the next class meeting) Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Monday Tuesday
Unit 8 Notes: Solving Quadratics by Factoring Alg 1 Name Period Day Date Assignment (Due the next class meeting) Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Monday Tuesday
Semester Exam Review
 Semester Exam Review Name Date Block MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. For the given equation, find the values of a, b, and c, determine
Semester Exam Review Name Date Block MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. For the given equation, find the values of a, b, and c, determine
GCSE Homework Unit 2 Foundation Tier Exercise Pack New AQA Syllabus
 GCSE Homework Unit 2 Foundation Tier Exercise Pack New AQA Syllabus The more negative a number, the smaller it is. The order of operations is Brackets, Indices, Division, Multiplication, Addition and Subtraction.
GCSE Homework Unit 2 Foundation Tier Exercise Pack New AQA Syllabus The more negative a number, the smaller it is. The order of operations is Brackets, Indices, Division, Multiplication, Addition and Subtraction.
Algebra I EOC 10-Day STAAR Review. Hedgehog Learning
 Algebra I EOC 10-Day STAAR Review Hedgehog Learning Day 1 Day 2 STAAR Reporting Category Number and Algebraic Methods Readiness Standards 60% - 65% of STAAR A.10(E) - factor, if possible, trinomials with
Algebra I EOC 10-Day STAAR Review Hedgehog Learning Day 1 Day 2 STAAR Reporting Category Number and Algebraic Methods Readiness Standards 60% - 65% of STAAR A.10(E) - factor, if possible, trinomials with
Section 13.1 The Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping. to continue. Also, circle your answer to each numbered exercise.
 Algebra Foundations First Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 13.1 Section 13.1 The Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping Complete the outline as you view Video Lecture 13.1. Pause the video as needed
Algebra Foundations First Edition, Elayn Martin-Gay Sec. 13.1 Section 13.1 The Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping Complete the outline as you view Video Lecture 13.1. Pause the video as needed
Algebra. Chapter 8: Factoring Polynomials. Name: Teacher: Pd:
 Algebra Chapter 8: Factoring Polynomials Name: Teacher: Pd: Table of Contents o Day 1: SWBAT: Factor polynomials by using the GCF. Pgs: 1-6 HW: Pages 7-8 o Day 2: SWBAT: Factor quadratic trinomials of
Algebra Chapter 8: Factoring Polynomials Name: Teacher: Pd: Table of Contents o Day 1: SWBAT: Factor polynomials by using the GCF. Pgs: 1-6 HW: Pages 7-8 o Day 2: SWBAT: Factor quadratic trinomials of
(x + 3) 2 = (x + 3)(x + 3) = x 2 + 3x + 3x + 9 = x 2 + 6x + 9 Perfect Square Trinomials
 Perfect Square Trinomials Perfect Square Trinomials are trinomials that have: 1. a product (ax 2 + bx + c) that is a perfect square 2. a sum that has the same factors of the product when added together
Perfect Square Trinomials Perfect Square Trinomials are trinomials that have: 1. a product (ax 2 + bx + c) that is a perfect square 2. a sum that has the same factors of the product when added together
a*(variable) 2 + b*(variable) + c
 CH. 8. Factoring polynomials of the form: a*(variable) + b*(variable) + c Factor: 6x + 11x + 4 STEP 1: Is there a GCF of all terms? NO STEP : How many terms are there? Is it of degree? YES * Is it in the
CH. 8. Factoring polynomials of the form: a*(variable) + b*(variable) + c Factor: 6x + 11x + 4 STEP 1: Is there a GCF of all terms? NO STEP : How many terms are there? Is it of degree? YES * Is it in the
WEEK 1 REVIEW Lines and Linear Models. A VERTICAL line has NO SLOPE. All other lines have change in y rise y2-
 WEEK 1 REVIEW Lines and Linear Models SLOPE A VERTICAL line has NO SLOPE. All other lines have change in y rise y- y1 slope = m = = = change in x run x - x 1 Find the slope of the line passing through
WEEK 1 REVIEW Lines and Linear Models SLOPE A VERTICAL line has NO SLOPE. All other lines have change in y rise y- y1 slope = m = = = change in x run x - x 1 Find the slope of the line passing through
The Zero Product Law. Standards:
 Objective: Students will be able to (SWBAT) use complex numbers in polynomial identities and equations, in order to (IOT) solve quadratic equations with real coefficient that have complex solutions. Standards:
Objective: Students will be able to (SWBAT) use complex numbers in polynomial identities and equations, in order to (IOT) solve quadratic equations with real coefficient that have complex solutions. Standards:
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission. Leaving Certificate Examination Mathematics
 2016. M27 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission Leaving Certificate Examination 2016 Paper 1 Ordinary Level Friday 10 June Afternoon 2:00 4:30 300 marks Running total Examination
2016. M27 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission Leaving Certificate Examination 2016 Paper 1 Ordinary Level Friday 10 June Afternoon 2:00 4:30 300 marks Running total Examination
Lesson 2: Multiplication of Numbers in Exponential Form
 : Classwork In general, if x is any number and m, n are positive integers, then because x m x n = x m+n x m x n = (x x) m times (x x) n times = (x x) = x m+n m+n times Exercise 1 14 23 14 8 = Exercise
: Classwork In general, if x is any number and m, n are positive integers, then because x m x n = x m+n x m x n = (x x) m times (x x) n times = (x x) = x m+n m+n times Exercise 1 14 23 14 8 = Exercise
par ( 12). His closest competitor, Ernie Els, finished 3 strokes over par (+3). What was the margin of victory?
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Tiger Woods won the 000 U.S. Open golf tournament with a score of 1 strokes under par
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Tiger Woods won the 000 U.S. Open golf tournament with a score of 1 strokes under par
Math 8. Quarter 4. Name Teacher Period
 Math 8 Quarter 4 Name Teacher Period 1 Unit 12 2 Released Questions 201 For the following questions Calculators are NOT permitted 1) 2) ) 4) 5) 6) 4 For the following questions Calculators are permitted
Math 8 Quarter 4 Name Teacher Period 1 Unit 12 2 Released Questions 201 For the following questions Calculators are NOT permitted 1) 2) ) 4) 5) 6) 4 For the following questions Calculators are permitted
Chapter 2 Rocket Launch: AREA BETWEEN CURVES
 ANSWERS Mathematics (Mathematical Analysis) page 1 Chapter Rocket Launch: AREA BETWEEN CURVES RL-. a) 1,.,.; $8, $1, $18, $0, $, $6, $ b) x; 6(x ) + 0 RL-. a), 16, 9,, 1, 0; 1,,, 7, 9, 11 c) D = (-, );
ANSWERS Mathematics (Mathematical Analysis) page 1 Chapter Rocket Launch: AREA BETWEEN CURVES RL-. a) 1,.,.; $8, $1, $18, $0, $, $6, $ b) x; 6(x ) + 0 RL-. a), 16, 9,, 1, 0; 1,,, 7, 9, 11 c) D = (-, );
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 10.1
 Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 10.1 Name Date Water Balloons Polynomials and Polynomial Functions Vocabulary Match each key term to its corresponding definition. 1. A polynomial written with
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 10.1 Name Date Water Balloons Polynomials and Polynomial Functions Vocabulary Match each key term to its corresponding definition. 1. A polynomial written with
5.1 Exponents and Scientific Notation
 5.1 Exponents and Scientific Notation Definition of an exponent a r = Example: Expand and simplify a) 3 4 b) ( 1 / 4 ) 2 c) (0.05) 3 d) (-3) 2 Difference between (-a) r (-a) r = and a r a r = Note: The
5.1 Exponents and Scientific Notation Definition of an exponent a r = Example: Expand and simplify a) 3 4 b) ( 1 / 4 ) 2 c) (0.05) 3 d) (-3) 2 Difference between (-a) r (-a) r = and a r a r = Note: The
PART I: NO CALCULATOR (200 points)
 Prealgebra Practice Final Math 0 OER (Ch. -) PART I: NO CALCULATOR (00 points) (.). Find all divisors of the following numbers. a) b) 7 c) (.). Find the prime factorization of the following numbers. a)
Prealgebra Practice Final Math 0 OER (Ch. -) PART I: NO CALCULATOR (00 points) (.). Find all divisors of the following numbers. a) b) 7 c) (.). Find the prime factorization of the following numbers. a)
TCM Final Review Packet Name Per.
 TCM Final Review Packet Name Per. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Translate the statement into a formula. 1) The total distance traveled,
TCM Final Review Packet Name Per. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Translate the statement into a formula. 1) The total distance traveled,
Lesson 7.1: Factoring a GCF
 Name Lesson 7.1: Factoring a GCF Date Algebra I Factoring expressions is one of the gateway skills that is necessary for much of what we do in algebra for the rest of the course. The word factor has two
Name Lesson 7.1: Factoring a GCF Date Algebra I Factoring expressions is one of the gateway skills that is necessary for much of what we do in algebra for the rest of the course. The word factor has two
Name Date. Key Math Concepts
 2-1 Interpret Scatterplots Key Math Concepts Bivariate data is pairs of numbers, (x,y), that represent variables. Positive correlation: the value of one variable increases as the other increases. Negative
2-1 Interpret Scatterplots Key Math Concepts Bivariate data is pairs of numbers, (x,y), that represent variables. Positive correlation: the value of one variable increases as the other increases. Negative
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 INTRODUCTORY ALGEBRA/GRACEY CHAPTER 1-2.3 PRACTICE Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Evaluate the algebraic expression for the
INTRODUCTORY ALGEBRA/GRACEY CHAPTER 1-2.3 PRACTICE Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Evaluate the algebraic expression for the
PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION 2018 MATHEMATICS GRADE 12 PAPER 1. Time: 3 hours Total: 150 PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY
 PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION 2018 MATHEMATICS GRADE 12 PAPER 1 Time: 3 hours Total: 150 Examiner: P R Mhuka Moderators: J Scalla E Zachariou PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY 1. This question
PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION 2018 MATHEMATICS GRADE 12 PAPER 1 Time: 3 hours Total: 150 Examiner: P R Mhuka Moderators: J Scalla E Zachariou PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY 1. This question
Contents. Heinemann Maths Zone Copyright Pearson Australia (a divsion of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd)
 Contents Chapter Money calculations R. Expressing fractions as decimals R.2 Expressing decimals as fractions R.3 Operating with fractions R.4 Simple decimal arithmetic R.5 Ratio and fractions R.6 Dividing
Contents Chapter Money calculations R. Expressing fractions as decimals R.2 Expressing decimals as fractions R.3 Operating with fractions R.4 Simple decimal arithmetic R.5 Ratio and fractions R.6 Dividing
(2/3) 3 ((1 7/8) 2 + 1/2) = (2/3) 3 ((8/8 7/8) 2 + 1/2) (Work from inner parentheses outward) = (2/3) 3 ((1/8) 2 + 1/2) = (8/27) (1/64 + 1/2)
 Exponents Problem: Show that 5. Solution: Remember, using our rules of exponents, 5 5, 5. Problems to Do: 1. Simplify each to a single fraction or number: (a) ( 1 ) 5 ( ) 5. And, since (b) + 9 + 1 5 /
Exponents Problem: Show that 5. Solution: Remember, using our rules of exponents, 5 5, 5. Problems to Do: 1. Simplify each to a single fraction or number: (a) ( 1 ) 5 ( ) 5. And, since (b) + 9 + 1 5 /
Chapter 2-4 Review. Find the equation of the following graphs. Then state the domain and range: 1a) 1b) 1c)
 Chapter - Review Find the equation of the following graphs. Then state the domain and range: a) b) c) a) b) c) a) b) c) Find the domain of the following functions. Write your answer in interval notation:
Chapter - Review Find the equation of the following graphs. Then state the domain and range: a) b) c) a) b) c) a) b) c) Find the domain of the following functions. Write your answer in interval notation:
Name Date Student id #:
 Math1090 Final Exam Spring, 2016 Instructor: Name Date Student id #: Instructions: Please show all of your work as partial credit will be given where appropriate, and there may be no credit given for problems
Math1090 Final Exam Spring, 2016 Instructor: Name Date Student id #: Instructions: Please show all of your work as partial credit will be given where appropriate, and there may be no credit given for problems
ACCUPLACER Elementary Algebra Assessment Preparation Guide
 ACCUPLACER Elementary Algebra Assessment Preparation Guide Please note that the guide is for reference only and that it does not represent an exact match with the assessment content. The Assessment Centre
ACCUPLACER Elementary Algebra Assessment Preparation Guide Please note that the guide is for reference only and that it does not represent an exact match with the assessment content. The Assessment Centre
Forms of Quadratic Functions
 MBF3C U3L1 Forms of the Quadratic Functions Topic : Goal : Forms of Quadratic Functions I know the three forms that a quadratic function can be written in and what information can be taken directly from
MBF3C U3L1 Forms of the Quadratic Functions Topic : Goal : Forms of Quadratic Functions I know the three forms that a quadratic function can be written in and what information can be taken directly from
Math 10 Lesson 2-3 Factoring trinomials
 I. Lesson Objectives: Math 10 Lesson 2-3 Factoring trinomials a) To see the patterns in multiplying binomials that can be used to factor trinomials into binomials. b) To factor trinomials of the form ax
I. Lesson Objectives: Math 10 Lesson 2-3 Factoring trinomials a) To see the patterns in multiplying binomials that can be used to factor trinomials into binomials. b) To factor trinomials of the form ax
Section 7.1 Common Factors in Polynomials
 Chapter 7 Factoring How Does GPS Work? 7.1 Common Factors in Polynomials 7.2 Difference of Two Squares 7.3 Perfect Trinomial Squares 7.4 Factoring Trinomials: (x 2 + bx + c) 7.5 Factoring Trinomials: (ax
Chapter 7 Factoring How Does GPS Work? 7.1 Common Factors in Polynomials 7.2 Difference of Two Squares 7.3 Perfect Trinomial Squares 7.4 Factoring Trinomials: (x 2 + bx + c) 7.5 Factoring Trinomials: (ax
Prentice Hall Connected Mathematics 2, 7th Grade Units 2009 Correlated to: Minnesota K-12 Academic Standards in Mathematics, 9/2008 (Grade 7)
 7.1.1.1 Know that every rational number can be written as the ratio of two integers or as a terminating or repeating decimal. Recognize that π is not rational, but that it can be approximated by rational
7.1.1.1 Know that every rational number can be written as the ratio of two integers or as a terminating or repeating decimal. Recognize that π is not rational, but that it can be approximated by rational
Quadratic Functions. As review, we will look at the definition of a quadratic function. A quadratic function is a function f of the form
 Quadratic Functions To this point, we have had some experience with quadratic equations. We know that the graph of a quadratic equation gives us a parabola. In this section, we will see how quadratic equations
Quadratic Functions To this point, we have had some experience with quadratic equations. We know that the graph of a quadratic equation gives us a parabola. In this section, we will see how quadratic equations
Final Exam Review. 1. Simplify each of the following. Express each answer with positive exponents.
 1 1. Simplify each of the following. Express each answer with positive exponents. a a) 4 b 1x xy b) 1 x y 1. Evaluate without the use of a calculator. Express answers as integers or rational numbers. a)
1 1. Simplify each of the following. Express each answer with positive exponents. a a) 4 b 1x xy b) 1 x y 1. Evaluate without the use of a calculator. Express answers as integers or rational numbers. a)
( ) 4 ( )! x f) h(x) = 2cos x + 1
 Chapter Prerequisite Skills BLM -.. Identifying Types of Functions. Identify the type of function (polynomial, rational, logarithmic, etc.) represented by each of the following. Justify your response.
Chapter Prerequisite Skills BLM -.. Identifying Types of Functions. Identify the type of function (polynomial, rational, logarithmic, etc.) represented by each of the following. Justify your response.
2.01 Products of Polynomials
 2.01 Products of Polynomials Recall from previous lessons that when algebraic expressions are added (or subtracted) they are called terms, while expressions that are multiplied are called factors. An algebraic
2.01 Products of Polynomials Recall from previous lessons that when algebraic expressions are added (or subtracted) they are called terms, while expressions that are multiplied are called factors. An algebraic
Algebra I April 2017 EOC Study Guide Practice Test 1
 Name: Algebra I April 2017 EOC Study Guide Practice Test 1 Score: Top 3 Items to Study: 1. 2. 3. 1) The distance a car travels can be found using the formula d = rt, where d is the distance, r is the rate
Name: Algebra I April 2017 EOC Study Guide Practice Test 1 Score: Top 3 Items to Study: 1. 2. 3. 1) The distance a car travels can be found using the formula d = rt, where d is the distance, r is the rate
List the quadrant(s) in which the given point is located. 1) (-10, 0) A) On an axis B) II C) IV D) III
 MTH 55 Chapter 2 HW List the quadrant(s) in which the given point is located. 1) (-10, 0) 1) A) On an axis B) II C) IV D) III 2) The first coordinate is positive. 2) A) I, IV B) I, II C) III, IV D) II,
MTH 55 Chapter 2 HW List the quadrant(s) in which the given point is located. 1) (-10, 0) 1) A) On an axis B) II C) IV D) III 2) The first coordinate is positive. 2) A) I, IV B) I, II C) III, IV D) II,
Completing the Square. A trinomial that is the square of a binomial. x Square half the coefficient of x. AA65.pdf.
 AA65.pdf 6.5 Completing the Square 1. Converting from vertex form to standard form involves expanding the square of the binomial, distributing a, and then isolating y. What method does converting from
AA65.pdf 6.5 Completing the Square 1. Converting from vertex form to standard form involves expanding the square of the binomial, distributing a, and then isolating y. What method does converting from
Lesson 11. Ma February 8 th, 2017
 Lesson 11 Ma 15800 February 8 th, 2017 This lesson focuses on applications of quadratics.the nice thing about quadratic expressions is that it is very easy to find their maximum or minimum values, namely
Lesson 11 Ma 15800 February 8 th, 2017 This lesson focuses on applications of quadratics.the nice thing about quadratic expressions is that it is very easy to find their maximum or minimum values, namely
Unit 1 Maths Methods (CAS) Exam 2013 Thursday June 6th pm
 Name: Teacher: Unit 1 Maths Methods (CAS) Exam 2013 Thursday June 6th 1.50-3.20 pm Reading time: 10 Minutes Writing time: 80 Minutes Instruction to candidates: Students are permitted to bring into the
Name: Teacher: Unit 1 Maths Methods (CAS) Exam 2013 Thursday June 6th 1.50-3.20 pm Reading time: 10 Minutes Writing time: 80 Minutes Instruction to candidates: Students are permitted to bring into the
CCAC ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA
 CCAC ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA Sample Questions TOPICS TO STUDY: Evaluate expressions Add, subtract, multiply, and divide polynomials Add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational expressions Factor two and three
CCAC ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA Sample Questions TOPICS TO STUDY: Evaluate expressions Add, subtract, multiply, and divide polynomials Add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational expressions Factor two and three
PRINTABLE VERSION. Practice Final Exam
 Page 1 of 25 PRINTABLE VERSION Practice Final Exam Question 1 The following table of values gives a company's annual profits in millions of dollars. Rescale the data so that the year 2003 corresponds to
Page 1 of 25 PRINTABLE VERSION Practice Final Exam Question 1 The following table of values gives a company's annual profits in millions of dollars. Rescale the data so that the year 2003 corresponds to
Factoring Quadratics: ax 2 + bx + c
 4.4 Factoring Quadratics: a 2 + b + c GOAL Factor quadratic epressions of the form a 2 + b + c, where a. LEARN ABOUT the Math Kellie was asked to determine the -intercepts of y = 2 + + 6 algebraically.
4.4 Factoring Quadratics: a 2 + b + c GOAL Factor quadratic epressions of the form a 2 + b + c, where a. LEARN ABOUT the Math Kellie was asked to determine the -intercepts of y = 2 + + 6 algebraically.
M14/5/MATSD/SP2/ENG/TZ2/XX. mathematical STUDIES. Wednesday 14 May 2014 (morning) 1 hour 30 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
 M14/5/MATSD/SP2/ENG/TZ2/XX 22147406 mathematical STUDIES STANDARD level Paper 2 Wednesday 14 May 2014 (morning) 1 hour 30 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Do not open this examination paper until instructed
M14/5/MATSD/SP2/ENG/TZ2/XX 22147406 mathematical STUDIES STANDARD level Paper 2 Wednesday 14 May 2014 (morning) 1 hour 30 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Do not open this examination paper until instructed
Factor Trinomials When the Coefficient of the Second-Degree Term is 1 (Objective #1)
 Factoring Trinomials (5.2) Factor Trinomials When the Coefficient of the Second-Degree Term is 1 EXAMPLE #1: Factor the trinomials. = = Factor Trinomials When the Coefficient of the Second-Degree Term
Factoring Trinomials (5.2) Factor Trinomials When the Coefficient of the Second-Degree Term is 1 EXAMPLE #1: Factor the trinomials. = = Factor Trinomials When the Coefficient of the Second-Degree Term
Chapter 5 Polynomials 5.1 Multiplying Polynomials
 Chapter 5 Polynomials 5.1 Multiplying Polynomials 1. a) 3x 2 5x + 2; (3x 2)(x 1) b) 2x 2 + x 6; (2x 3)(x + 2) 2. a) b) c) d) e) f) 3. a) 2x 2 4x 16 b) t 2 + 9t + 20 c) 6w 2 23w 18 d) z 2 4 e) a 2 + 2ab
Chapter 5 Polynomials 5.1 Multiplying Polynomials 1. a) 3x 2 5x + 2; (3x 2)(x 1) b) 2x 2 + x 6; (2x 3)(x + 2) 2. a) b) c) d) e) f) 3. a) 2x 2 4x 16 b) t 2 + 9t + 20 c) 6w 2 23w 18 d) z 2 4 e) a 2 + 2ab
Mathematics Success Level H
 Mathematics Success Level H T473 [OBJECTIVE] The student will graph a line given the slope and y-intercept. [MATERIALS] Student pages S160 S169 Transparencies T484, T486, T488, T490, T492, T494, T496 Wall-size
Mathematics Success Level H T473 [OBJECTIVE] The student will graph a line given the slope and y-intercept. [MATERIALS] Student pages S160 S169 Transparencies T484, T486, T488, T490, T492, T494, T496 Wall-size
Quadratic Modeling Elementary Education 10 Business 10 Profits
 Quadratic Modeling Elementary Education 10 Business 10 Profits This week we are asking elementary education majors to complete the same activity as business majors. Our first goal is to give elementary
Quadratic Modeling Elementary Education 10 Business 10 Profits This week we are asking elementary education majors to complete the same activity as business majors. Our first goal is to give elementary
Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping
 mil84488_ch06_409-419.qxd 2/8/12 3:11 PM Page 410 410 Chapter 6 Factoring Polynomials Section 6.1 Concepts 1. Identifying the Greatest Common Factor 2. Factoring out the Greatest Common Factor 3. Factoring
mil84488_ch06_409-419.qxd 2/8/12 3:11 PM Page 410 410 Chapter 6 Factoring Polynomials Section 6.1 Concepts 1. Identifying the Greatest Common Factor 2. Factoring out the Greatest Common Factor 3. Factoring
Name: Period: Date: FOMP 10 Final Review Part 2 v1. Short Answer. Level 1-2 Questions. 1. What expression does the diagram represent?
 Period: Date: FOMP 10 Final Review Part 2 v1 Short Answer Level 1-2 Questions 1. What expression does the diagram represent? 2. What is the factored form of the expression 5x 2 45? 3. What value of k makes
Period: Date: FOMP 10 Final Review Part 2 v1 Short Answer Level 1-2 Questions 1. What expression does the diagram represent? 2. What is the factored form of the expression 5x 2 45? 3. What value of k makes
7-5 Factoring Special Products
 7-5 Factoring Special Products Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 1 Warm Up Determine whether the following are perfect squares. If so, find the square root. 1. 64 yes; 8 2. 36 3. 45 no 4.
7-5 Factoring Special Products Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 1 Warm Up Determine whether the following are perfect squares. If so, find the square root. 1. 64 yes; 8 2. 36 3. 45 no 4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MGF 1107 Practice Final Dr. Schnackenberg MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Graph the equation. Select integers for x, -3 x 3. 1) y
MGF 1107 Practice Final Dr. Schnackenberg MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Graph the equation. Select integers for x, -3 x 3. 1) y
UNIT 5 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Lesson 2: Creating and Solving Quadratic Equations in One Variable Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: multiplying polynomials working with complex numbers Introduction 2 b 2 A trinomial of the form x + bx + that can be written as
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: multiplying polynomials working with complex numbers Introduction 2 b 2 A trinomial of the form x + bx + that can be written as
Chapter 9. Chapters 5 8 Review, pages Analysing Graphs of Linear Relations, pages
 1. a) -7 No. Different sets of integers can have the same mean. Eample: {-, -1, 1, -,, -1} and {-, 9, -, 1,, } both have a sum of - and a mean of -7.. a decrease of 31 people per ear 3. 7 s. $7 Chapters
1. a) -7 No. Different sets of integers can have the same mean. Eample: {-, -1, 1, -,, -1} and {-, 9, -, 1,, } both have a sum of - and a mean of -7.. a decrease of 31 people per ear 3. 7 s. $7 Chapters
Lesson 10: Interpreting Quadratic Functions from Graphs and Tables
 : Interpreting Quadratic Functions from Graphs and Tables Student Outcomes Students interpret quadratic functions from graphs and tables: zeros ( intercepts), intercept, the minimum or maximum value (vertex),
: Interpreting Quadratic Functions from Graphs and Tables Student Outcomes Students interpret quadratic functions from graphs and tables: zeros ( intercepts), intercept, the minimum or maximum value (vertex),
How can we factor polynomials?
 How can we factor polynomials? Factoring refers to writing something as a product. Factoring completely means that all of the factors are relatively prime (they have a GCF of 1). Methods of factoring:
How can we factor polynomials? Factoring refers to writing something as a product. Factoring completely means that all of the factors are relatively prime (they have a GCF of 1). Methods of factoring:
MATH 1015 Final Exam Review Rev 02/2018
 MATH 1 Final Exam Review Rev 0/018 ============================================================================== 1)Find the domain and range for the function. 1) 3 1-7 - - - -3 - -1 1 3 7 - -3 - - - -7
MATH 1 Final Exam Review Rev 0/018 ============================================================================== 1)Find the domain and range for the function. 1) 3 1-7 - - - -3 - -1 1 3 7 - -3 - - - -7
