Quadratic Functions. As review, we will look at the definition of a quadratic function. A quadratic function is a function f of the form
|
|
|
- Eleanor Stone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Quadratic Functions To this point, we have had some experience with quadratic equations. We know that the graph of a quadratic equation gives us a parabola. In this section, we will see how quadratic equations (and their corresponding parabolas) can give us some valuable information in real-life situations. If a parabola opens upward, then we know that there is a point at which the graph reaches its minimum value. Likewise, if we have a parabola that opens downward, we know that there must be a maximum value for that function. These maximum and minimum values are referred to as extreme values. There are many practical situations, which can be represented by such functions. In these situations, the extreme values can often give us valuable pieces of information. For example, the owner of a clothing store might be interested in knowing her maximum profit or minimum cost. As review, we will look at the definition of a quadratic function. Def: A quadratic function is a function f of the form = ax + bx + c where a, b, and c are real numbers and a 0. Standard Form and Completing the Square: In determining extreme values, it is very helpful to put the quadratic function into standard form. This can be done by completing the square. Now, I can already hear the collective groan at the mention of completing the square, but it is a very necessary skill in determining extreme values. I am confident that you can learn it well if you just take it step-by-step. First, let s take a look at standard form. Def: A quadratic function can be expressed in the standard form = a( x h) + k by completing the square. The graph of f is a parabola with vertex (h,k); the parabola opens upward if a > 0 or downward if a < 0.
2 If a > 0, then the minimum value of f occurs at x = h and this value is in other words, the point with coordinates (h,k). f ( h) = k, If a < 0, then the maximum value of f occurs at x = h and this value is also the point (h,k). f ( h) = k, Example 1: Sketch the graph of the function = x + 10x 0 and state the vertex. Begin by completing the square. Solution: Comparing this with the form a = 1 b = 10 c = 0 = ax + bx + c, we can see that
3 Example 1 (Continued): Step 1: Group the x and x terms, and factor out any a value. In this case, since a = 1, we simply have to group the first two terms. = ( x + 10x) 0 Step : After grouping the first two terms and factoring out a, consider the coefficient of x, in this case 10. Divide this value by and take the square. 10 = 5 = 5 Step 3: Complete the square by adding the above value inside the parentheses. Note: Any value that is added to one side of the equation must also be subtracted from that side of the equation in order to keep from changing the value. i.e.- add a value of zero to the equation. Therefore, we must subtract the total value outside the parentheses. (Here is where you must be careful to pay attention to any common value that has been factored out. We will see this in the next example.) = ( x + 10x + 5) 0 5 Step 4: Factor the portion of the equation in parentheses and combine any other like terms. = ( x + 10x + 5) 0 5 = ( x + 10x + 5) 45 = ( x + 5) 45 OR = ( x ( 5)) 45 (which will be helpful, as you will see now) The function should be in the form = a( x h) + k. In this case, a = 1 h = 5 k = 45
4 Example 1 (Continued): Notice: You must pay special attention to the sign of h. Rewriting the equation as we did above will be helpful in seeing the sign of h more clearly. Now that we have completed the square, the remainder of the solution is very simple. By definition, we know the parabola opens upward, since a > 0, and we have a minimum value at the point (-5,-45) which is also the vertex of the parabola. We are simply asked to sketch the parabola, so it is not necessary in this case to find multiple points on the graph. We can simply sketch the graph using what we know. Let s look at one more example. Example : For the function = x 16x + 1 (a) Express the function in standard form. (b) Sketch its graph. (c) Find its maximum or minimum value. Solution: (a) We can put the function into standard form by completing the square. Step 1: Group the x and x terms, and factor out any a value. = (x = ( x 8x) x) + 1
5 Example (Continued): Step : After grouping the first two terms and factoring out a, consider the coefficient of x, in this case ( 8). Divide this value by and take the square. 8 = ( 4) = 16 (Notice that the sign of the x coefficient does not really matter at this point, because after squaring the term, you will always have a positive number.) Step 3: Complete the square by adding the above value inside the parentheses and subtracting the total value outside the parentheses. = ( x 8x + 16) Note: Special attention must be given to the value that was factored out. This will affect the value which is subtracted outside the parentheses. i.e.- (16)=3 Step 4: Factor the portion of the equation in parentheses and combine any other like terms. = ( x 8x + 16) = ( x 8x + 16) 0 = ( x 4) 0 So, we have the graph in standard form. (b) To sketch the graph, let s combine the information we have from the standard form of the equation. a = h = 4 k = 0 Since a > 0, the parabola opens upward; therefore, we have a minimum value at x = 4. This value occurs at the point (4,-0) which is also the vertex. With this information, we can easily sketch the graph.
6 Example (Continued): (c) The minimum value of the graph occurs at x = 4, and the value there is ( 0). This is the value f ( h) = k. Maximum or Minimum Value of a Quadratic Equation: In the examples so far, we have been asked to graph the function, etc. Sometimes is simply necessary to know the maximum or minimum value. In this case, you do not need to complete the square, because you do not need the equation to be in standard form. Def: The maximum or minimum value of a quadratic function = ax + bx + c occurs at x = b a If a > 0, then the minimum value is f b a. b If a < 0, then the maximum value is f. a
7 Example 3: A coffee shop on the SAC campus has a sales analyst consider the store s sales records for a month. The analyst produces a formula in order to help the store generate more profit. He finds that if the shop cells l orders of latte in one day, the profit (in dollars) is given by the following function 1 P ( l) = x + 3x 1800 What is the maximum profit possible for the store in one day, and how many lattes must they sell in order to reach this maximum? Solution: First, it is important to notice that they asked for a maximum profit. We know we will have a maximum instead of a minimum, because a < 0. Using the definition above, the maximum occurs at b a l = = 3 ( 1 ) 3() = ( 1) = 3000 = 1500 This means that in order to receive a maximum profit, the coffee shop must sell 1500 lattes per day. In order to find out what the maximum profit actually is (in dollars), we have to evaluate the function at this value, l. b 1 P = P (1500) = (1500) a = = = 450 The maximum profit would be $ (1500) 1800
2-4 Completing the Square
 2-4 Completing the Square Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 2 Warm Up Write each expression as a trinomial. 1. (x 5) 2 x 2 10x + 25 2. (3x + 5) 2 9x 2 + 30x + 25 Factor each expression. 3.
2-4 Completing the Square Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 2 Warm Up Write each expression as a trinomial. 1. (x 5) 2 x 2 10x + 25 2. (3x + 5) 2 9x 2 + 30x + 25 Factor each expression. 3.
Stats for Exam 1. Letter Score Range Frequency A 90 to B 80 to 89 3 C 70 to 79 4 D 60 to 69 4 F 59 and below 8
 Stats for Exam 1 Letter Score Range Frequency A 90 to 100 14 B 80 to 89 3 C 70 to 79 4 D 60 to 69 4 F 59 and below 8 High Score 100 two of them 75th percentile 94 Median 81 25th percentile 60 Low Score
Stats for Exam 1 Letter Score Range Frequency A 90 to 100 14 B 80 to 89 3 C 70 to 79 4 D 60 to 69 4 F 59 and below 8 High Score 100 two of them 75th percentile 94 Median 81 25th percentile 60 Low Score
Completing the Square. A trinomial that is the square of a binomial. x Square half the coefficient of x. AA65.pdf.
 AA65.pdf 6.5 Completing the Square 1. Converting from vertex form to standard form involves expanding the square of the binomial, distributing a, and then isolating y. What method does converting from
AA65.pdf 6.5 Completing the Square 1. Converting from vertex form to standard form involves expanding the square of the binomial, distributing a, and then isolating y. What method does converting from
Chapter 6: Quadratic Functions & Their Algebra
 Chapter 6: Quadratic Functions & Their Algebra Topics: 1. Quadratic Function Review. Factoring: With Greatest Common Factor & Difference of Two Squares 3. Factoring: Trinomials 4. Complete Factoring 5.
Chapter 6: Quadratic Functions & Their Algebra Topics: 1. Quadratic Function Review. Factoring: With Greatest Common Factor & Difference of Two Squares 3. Factoring: Trinomials 4. Complete Factoring 5.
When Is Factoring Used?
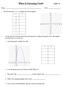 When Is Factoring Used? Name: DAY 9 Date: 1. Given the function, y = x 2 complete the table and graph. x y 2 1 0 1 2 3 1. A ball is thrown vertically upward from the ground according to the graph below.
When Is Factoring Used? Name: DAY 9 Date: 1. Given the function, y = x 2 complete the table and graph. x y 2 1 0 1 2 3 1. A ball is thrown vertically upward from the ground according to the graph below.
Common Core Algebra L clone 4 review R Final Exam
 1) Which graph represents an exponential function? A) B) 2) Which relation is a function? A) {(12, 13), (14, 19), (11, 17), (14, 17)} B) {(20, -2), (24, 10), (-21, -5), (22, 4)} C) {(34, 8), (32, -3),
1) Which graph represents an exponential function? A) B) 2) Which relation is a function? A) {(12, 13), (14, 19), (11, 17), (14, 17)} B) {(20, -2), (24, 10), (-21, -5), (22, 4)} C) {(34, 8), (32, -3),
Chapter 4 Factoring and Quadratic Equations
 Chapter 4 Factoring and Quadratic Equations Lesson 1: Factoring by GCF, DOTS, and Case I Lesson : Factoring by Grouping & Case II Lesson 3: Factoring by Sum and Difference of Perfect Cubes Lesson 4: Solving
Chapter 4 Factoring and Quadratic Equations Lesson 1: Factoring by GCF, DOTS, and Case I Lesson : Factoring by Grouping & Case II Lesson 3: Factoring by Sum and Difference of Perfect Cubes Lesson 4: Solving
Factor Trinomials When the Coefficient of the Second-Degree Term is 1 (Objective #1)
 Factoring Trinomials (5.2) Factor Trinomials When the Coefficient of the Second-Degree Term is 1 EXAMPLE #1: Factor the trinomials. = = Factor Trinomials When the Coefficient of the Second-Degree Term
Factoring Trinomials (5.2) Factor Trinomials When the Coefficient of the Second-Degree Term is 1 EXAMPLE #1: Factor the trinomials. = = Factor Trinomials When the Coefficient of the Second-Degree Term
Math1090 Midterm 2 Review Sections , Solve the system of linear equations using Gauss-Jordan elimination.
 Math1090 Midterm 2 Review Sections 2.1-2.5, 3.1-3.3 1. Solve the system of linear equations using Gauss-Jordan elimination. 5x+20y 15z = 155 (a) 2x 7y+13z=85 3x+14y +6z= 43 x+z= 2 (b) x= 6 y+z=11 x y+
Math1090 Midterm 2 Review Sections 2.1-2.5, 3.1-3.3 1. Solve the system of linear equations using Gauss-Jordan elimination. 5x+20y 15z = 155 (a) 2x 7y+13z=85 3x+14y +6z= 43 x+z= 2 (b) x= 6 y+z=11 x y+
(x + 3) 2 = (x + 3)(x + 3) = x 2 + 3x + 3x + 9 = x 2 + 6x + 9 Perfect Square Trinomials
 Perfect Square Trinomials Perfect Square Trinomials are trinomials that have: 1. a product (ax 2 + bx + c) that is a perfect square 2. a sum that has the same factors of the product when added together
Perfect Square Trinomials Perfect Square Trinomials are trinomials that have: 1. a product (ax 2 + bx + c) that is a perfect square 2. a sum that has the same factors of the product when added together
3.1 Solutions to Exercises
 .1 Solutions to Exercises 1. (a) f(x) will approach + as x approaches. (b) f(x) will still approach + as x approaches -, because any negative integer x will become positive if it is raised to an even exponent,
.1 Solutions to Exercises 1. (a) f(x) will approach + as x approaches. (b) f(x) will still approach + as x approaches -, because any negative integer x will become positive if it is raised to an even exponent,
A. B. C. D. Graphing Quadratics Practice Quiz. Question 1. Select the graph of the quadratic function. f (x ) = 2x 2. 2/26/2018 Print Assignment
 Question 1. Select the graph of the quadratic function. f (x ) = 2x 2 C. D. https://my.hrw.com/wwtb2/viewer/printall_vs23.html?umk5tfdnj31tcldd29v4nnzkclztk3w8q6wgvr2629ca0a5fsymn1tfv8j1vs4qotwclvofjr8uon4cldd29v4
Question 1. Select the graph of the quadratic function. f (x ) = 2x 2 C. D. https://my.hrw.com/wwtb2/viewer/printall_vs23.html?umk5tfdnj31tcldd29v4nnzkclztk3w8q6wgvr2629ca0a5fsymn1tfv8j1vs4qotwclvofjr8uon4cldd29v4
a*(variable) 2 + b*(variable) + c
 CH. 8. Factoring polynomials of the form: a*(variable) + b*(variable) + c Factor: 6x + 11x + 4 STEP 1: Is there a GCF of all terms? NO STEP : How many terms are there? Is it of degree? YES * Is it in the
CH. 8. Factoring polynomials of the form: a*(variable) + b*(variable) + c Factor: 6x + 11x + 4 STEP 1: Is there a GCF of all terms? NO STEP : How many terms are there? Is it of degree? YES * Is it in the
The Zero Product Law. Standards:
 Objective: Students will be able to (SWBAT) use complex numbers in polynomial identities and equations, in order to (IOT) solve quadratic equations with real coefficient that have complex solutions. Standards:
Objective: Students will be able to (SWBAT) use complex numbers in polynomial identities and equations, in order to (IOT) solve quadratic equations with real coefficient that have complex solutions. Standards:
3.1 Solutions to Exercises
 .1 Solutions to Exercises 1. (a) f(x) will approach + as x approaches. (b) f(x) will still approach + as x approaches -, because any negative integer x will become positive if it is raised to an even exponent,
.1 Solutions to Exercises 1. (a) f(x) will approach + as x approaches. (b) f(x) will still approach + as x approaches -, because any negative integer x will become positive if it is raised to an even exponent,
UNIT 5 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Lesson 2: Creating and Solving Quadratic Equations in One Variable Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: multiplying polynomials working with complex numbers Introduction 2 b 2 A trinomial of the form x + bx + that can be written as
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: multiplying polynomials working with complex numbers Introduction 2 b 2 A trinomial of the form x + bx + that can be written as
Forms of Quadratic Functions
 MBF3C U3L1 Forms of the Quadratic Functions Topic : Goal : Forms of Quadratic Functions I know the three forms that a quadratic function can be written in and what information can be taken directly from
MBF3C U3L1 Forms of the Quadratic Functions Topic : Goal : Forms of Quadratic Functions I know the three forms that a quadratic function can be written in and what information can be taken directly from
Sandringham School Sixth Form. AS Maths. Bridging the gap
 Sandringham School Sixth Form AS Maths Bridging the gap Section 1 - Factorising be able to factorise simple expressions be able to factorise quadratics The expression 4x + 8 can be written in factor form,
Sandringham School Sixth Form AS Maths Bridging the gap Section 1 - Factorising be able to factorise simple expressions be able to factorise quadratics The expression 4x + 8 can be written in factor form,
Solving Problems Involving Cost, Revenue, Profit. Max and Min Problems
 Solving Problems Involving Cost, Revenue, Profit The cost function C(x) is the total cost of making x items. If the cost per item is fixed, it is equal to the cost per item (c) times the number of items
Solving Problems Involving Cost, Revenue, Profit The cost function C(x) is the total cost of making x items. If the cost per item is fixed, it is equal to the cost per item (c) times the number of items
MLC at Boise State Polynomials Activity 3 Week #5
 Polynomials Activity 3 Week #5 This activity will be discuss maximums, minimums and zeros of a quadratic function and its application to business, specifically maximizing profit, minimizing cost and break-even
Polynomials Activity 3 Week #5 This activity will be discuss maximums, minimums and zeros of a quadratic function and its application to business, specifically maximizing profit, minimizing cost and break-even
Name: Common Core Algebra L R Final Exam 2015 CLONE 3 Teacher:
 1) Which graph represents a linear function? 2) Which relation is a function? A) B) A) {(2, 3), (3, 9), (4, 7), (5, 7)} B) {(0, -2), (3, 10), (-2, -4), (3, 4)} C) {(2, 7), (2, -3), (1, 1), (3, -1)} D)
1) Which graph represents a linear function? 2) Which relation is a function? A) B) A) {(2, 3), (3, 9), (4, 7), (5, 7)} B) {(0, -2), (3, 10), (-2, -4), (3, 4)} C) {(2, 7), (2, -3), (1, 1), (3, -1)} D)
Algebra I EOC 10-Day STAAR Review. Hedgehog Learning
 Algebra I EOC 10-Day STAAR Review Hedgehog Learning Day 1 Day 2 STAAR Reporting Category Number and Algebraic Methods Readiness Standards 60% - 65% of STAAR A.10(E) - factor, if possible, trinomials with
Algebra I EOC 10-Day STAAR Review Hedgehog Learning Day 1 Day 2 STAAR Reporting Category Number and Algebraic Methods Readiness Standards 60% - 65% of STAAR A.10(E) - factor, if possible, trinomials with
Chapter 6 Diagnostic Test
 Chapter 6 Diagnostic Test STUDENT BOOK PAGES 310 364 1. Consider the quadratic relation y = x 2 6x + 3. a) Use partial factoring to locate two points with the same y-coordinate on the graph. b) Determine
Chapter 6 Diagnostic Test STUDENT BOOK PAGES 310 364 1. Consider the quadratic relation y = x 2 6x + 3. a) Use partial factoring to locate two points with the same y-coordinate on the graph. b) Determine
Topic #1: Evaluating and Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
 John Jay College of Criminal Justice The City University of New York Department of Mathematics and Computer Science MAT 105 - College Algebra Departmental Final Examination Review Topic #1: Evaluating
John Jay College of Criminal Justice The City University of New York Department of Mathematics and Computer Science MAT 105 - College Algebra Departmental Final Examination Review Topic #1: Evaluating
How can we factor polynomials?
 How can we factor polynomials? Factoring refers to writing something as a product. Factoring completely means that all of the factors are relatively prime (they have a GCF of 1). Methods of factoring:
How can we factor polynomials? Factoring refers to writing something as a product. Factoring completely means that all of the factors are relatively prime (they have a GCF of 1). Methods of factoring:
We can solve quadratic equations by transforming the. left side of the equation into a perfect square trinomial
 Introduction We can solve quadratic equations by transforming the left side of the equation into a perfect square trinomial and using square roots to solve. Previously, you may have explored perfect square
Introduction We can solve quadratic equations by transforming the left side of the equation into a perfect square trinomial and using square roots to solve. Previously, you may have explored perfect square
Quadratic Modeling Elementary Education 10 Business 10 Profits
 Quadratic Modeling Elementary Education 10 Business 10 Profits This week we are asking elementary education majors to complete the same activity as business majors. Our first goal is to give elementary
Quadratic Modeling Elementary Education 10 Business 10 Profits This week we are asking elementary education majors to complete the same activity as business majors. Our first goal is to give elementary
CCAC ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA
 CCAC ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA Sample Questions TOPICS TO STUDY: Evaluate expressions Add, subtract, multiply, and divide polynomials Add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational expressions Factor two and three
CCAC ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA Sample Questions TOPICS TO STUDY: Evaluate expressions Add, subtract, multiply, and divide polynomials Add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational expressions Factor two and three
Lesson 11. Ma February 8 th, 2017
 Lesson 11 Ma 15800 February 8 th, 2017 This lesson focuses on applications of quadratics.the nice thing about quadratic expressions is that it is very easy to find their maximum or minimum values, namely
Lesson 11 Ma 15800 February 8 th, 2017 This lesson focuses on applications of quadratics.the nice thing about quadratic expressions is that it is very easy to find their maximum or minimum values, namely
Algebra 7-4 Study Guide: Factoring (pp & 487) Page 1! of 11!
 Page 1! of 11! Attendance Problems. Find each product. 1.(x 2)(2x + 7) 2. (3y + 4)(2y + 9) 3. (3n 5)(n 7) Factor each trinomial. 4. x 2 +4x 32 5. z 2 + 15z + 36 6. h 2 17h + 72 I can factor quadratic trinomials
Page 1! of 11! Attendance Problems. Find each product. 1.(x 2)(2x + 7) 2. (3y + 4)(2y + 9) 3. (3n 5)(n 7) Factor each trinomial. 4. x 2 +4x 32 5. z 2 + 15z + 36 6. h 2 17h + 72 I can factor quadratic trinomials
FACTORISING EQUATIONS
 STRIVE FOR EXCELLENCE TUTORING www.striveforexcellence.com.au Factorising expressions with 2 terms FACTORISING EQUATIONS There are only 2 ways of factorising a quadratic with two terms: 1. Look for something
STRIVE FOR EXCELLENCE TUTORING www.striveforexcellence.com.au Factorising expressions with 2 terms FACTORISING EQUATIONS There are only 2 ways of factorising a quadratic with two terms: 1. Look for something
(2/3) 3 ((1 7/8) 2 + 1/2) = (2/3) 3 ((8/8 7/8) 2 + 1/2) (Work from inner parentheses outward) = (2/3) 3 ((1/8) 2 + 1/2) = (8/27) (1/64 + 1/2)
 Exponents Problem: Show that 5. Solution: Remember, using our rules of exponents, 5 5, 5. Problems to Do: 1. Simplify each to a single fraction or number: (a) ( 1 ) 5 ( ) 5. And, since (b) + 9 + 1 5 /
Exponents Problem: Show that 5. Solution: Remember, using our rules of exponents, 5 5, 5. Problems to Do: 1. Simplify each to a single fraction or number: (a) ( 1 ) 5 ( ) 5. And, since (b) + 9 + 1 5 /
Final Project. College Algebra. Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to:
 COURSE OBJECTIVES Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: 1. Perform operations on algebraic expressions 2. Perform operations on functions expressed in standard function
COURSE OBJECTIVES Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: 1. Perform operations on algebraic expressions 2. Perform operations on functions expressed in standard function
5.1 Exponents and Scientific Notation
 5.1 Exponents and Scientific Notation Definition of an exponent a r = Example: Expand and simplify a) 3 4 b) ( 1 / 4 ) 2 c) (0.05) 3 d) (-3) 2 Difference between (-a) r (-a) r = and a r a r = Note: The
5.1 Exponents and Scientific Notation Definition of an exponent a r = Example: Expand and simplify a) 3 4 b) ( 1 / 4 ) 2 c) (0.05) 3 d) (-3) 2 Difference between (-a) r (-a) r = and a r a r = Note: The
Week 19 Algebra 2 Assignment:
 Week 9 Algebra Assignment: Day : pp. 66-67 #- odd, omit #, 7 Day : pp. 66-67 #- even, omit #8 Day : pp. 7-7 #- odd Day 4: pp. 7-7 #-4 even Day : pp. 77-79 #- odd, 7 Notes on Assignment: Pages 66-67: General
Week 9 Algebra Assignment: Day : pp. 66-67 #- odd, omit #, 7 Day : pp. 66-67 #- even, omit #8 Day : pp. 7-7 #- odd Day 4: pp. 7-7 #-4 even Day : pp. 77-79 #- odd, 7 Notes on Assignment: Pages 66-67: General
TERMINOLOGY 4.1. READING ASSIGNMENT 4.2 Sections 5.4, 6.1 through 6.5. Binomial. Factor (verb) GCF. Monomial. Polynomial.
 Section 4. Factoring Polynomials TERMINOLOGY 4.1 Prerequisite Terms: Binomial Factor (verb) GCF Monomial Polynomial Trinomial READING ASSIGNMENT 4. Sections 5.4, 6.1 through 6.5 160 READING AND SELF-DISCOVERY
Section 4. Factoring Polynomials TERMINOLOGY 4.1 Prerequisite Terms: Binomial Factor (verb) GCF Monomial Polynomial Trinomial READING ASSIGNMENT 4. Sections 5.4, 6.1 through 6.5 160 READING AND SELF-DISCOVERY
Name Date
 NEW DORP HIGH SCHOOL Deirdre A. DeAngelis, Principal MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT Li Pan, Assistant Principal Name Date Summer Math Assignment for a Student whose Official Class starts with 7, 8, and 9 Directions:
NEW DORP HIGH SCHOOL Deirdre A. DeAngelis, Principal MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT Li Pan, Assistant Principal Name Date Summer Math Assignment for a Student whose Official Class starts with 7, 8, and 9 Directions:
Partial Fractions. A rational function is a fraction in which both the numerator and denominator are polynomials. For example, f ( x) = 4, g( x) =
 Partial Fractions A rational function is a fraction in which both the numerator and denominator are polynomials. For example, f ( x) = 4, g( x) = 3 x 2 x + 5, and h( x) = x + 26 x 2 are rational functions.
Partial Fractions A rational function is a fraction in which both the numerator and denominator are polynomials. For example, f ( x) = 4, g( x) = 3 x 2 x + 5, and h( x) = x + 26 x 2 are rational functions.
2.8 Absolute Value Functions
 2.8 Absolute Value Functions Algebra III Mr. Niedert Algebra III 2.8 Absolute Value Functions Mr. Niedert 1 / 8 Today s Learning Target(s) 1 I can graph absolute value functions and apply them to real-life
2.8 Absolute Value Functions Algebra III Mr. Niedert Algebra III 2.8 Absolute Value Functions Mr. Niedert 1 / 8 Today s Learning Target(s) 1 I can graph absolute value functions and apply them to real-life
TCM Final Review Packet Name Per.
 TCM Final Review Packet Name Per. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Translate the statement into a formula. 1) The total distance traveled,
TCM Final Review Packet Name Per. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Translate the statement into a formula. 1) The total distance traveled,
Completing the Square. A trinomial that is the square of a binomial. x Squaring half the coefficient of x. AA65.pdf.
 AA65.pdf 6.5 Completing the Square 1. Converting from vertex form to standard form involves expanding the square of the binomial, distributing a, and then isolating y. What method does converting from
AA65.pdf 6.5 Completing the Square 1. Converting from vertex form to standard form involves expanding the square of the binomial, distributing a, and then isolating y. What method does converting from
Tool 1. Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
 Chapter 7: Factoring Review Tool 1 Greatest Common Factor (GCF) This is a very important tool. You must try to factor out the GCF first in every problem. Some problems do not have a GCF but many do. When
Chapter 7: Factoring Review Tool 1 Greatest Common Factor (GCF) This is a very important tool. You must try to factor out the GCF first in every problem. Some problems do not have a GCF but many do. When
Lesson 7.1: Factoring a GCF
 Name Lesson 7.1: Factoring a GCF Date Algebra I Factoring expressions is one of the gateway skills that is necessary for much of what we do in algebra for the rest of the course. The word factor has two
Name Lesson 7.1: Factoring a GCF Date Algebra I Factoring expressions is one of the gateway skills that is necessary for much of what we do in algebra for the rest of the course. The word factor has two
WEEK 1 REVIEW Lines and Linear Models. A VERTICAL line has NO SLOPE. All other lines have change in y rise y2-
 WEEK 1 REVIEW Lines and Linear Models SLOPE A VERTICAL line has NO SLOPE. All other lines have change in y rise y- y1 slope = m = = = change in x run x - x 1 Find the slope of the line passing through
WEEK 1 REVIEW Lines and Linear Models SLOPE A VERTICAL line has NO SLOPE. All other lines have change in y rise y- y1 slope = m = = = change in x run x - x 1 Find the slope of the line passing through
Section 7.1 Common Factors in Polynomials
 Chapter 7 Factoring How Does GPS Work? 7.1 Common Factors in Polynomials 7.2 Difference of Two Squares 7.3 Perfect Trinomial Squares 7.4 Factoring Trinomials: (x 2 + bx + c) 7.5 Factoring Trinomials: (ax
Chapter 7 Factoring How Does GPS Work? 7.1 Common Factors in Polynomials 7.2 Difference of Two Squares 7.3 Perfect Trinomial Squares 7.4 Factoring Trinomials: (x 2 + bx + c) 7.5 Factoring Trinomials: (ax
9/16/ (1) Review of Factoring trinomials. (2) Develop the graphic significance of factors/roots. Math 2 Honors - Santowski
 (1) Review of Factoring trinomials (2) Develop the graphic significance of factors/roots (3) Solving Eqn (algebra/graphic connection) 1 2 To expand means to write a product of expressions as a sum or difference
(1) Review of Factoring trinomials (2) Develop the graphic significance of factors/roots (3) Solving Eqn (algebra/graphic connection) 1 2 To expand means to write a product of expressions as a sum or difference
Factoring is the process of changing a polynomial expression that is essentially a sum into an expression that is essentially a product.
 Ch. 8 Polynomial Factoring Sec. 1 Factoring is the process of changing a polynomial expression that is essentially a sum into an expression that is essentially a product. Factoring polynomials is not much
Ch. 8 Polynomial Factoring Sec. 1 Factoring is the process of changing a polynomial expression that is essentially a sum into an expression that is essentially a product. Factoring polynomials is not much
Math Performance Task Teacher Instructions
 Math Performance Task Teacher Instructions Stock Market Research Instructions for the Teacher The Stock Market Research performance task centers around the concepts of linear and exponential functions.
Math Performance Task Teacher Instructions Stock Market Research Instructions for the Teacher The Stock Market Research performance task centers around the concepts of linear and exponential functions.
Semester Exam Review
 Semester Exam Review Name Date Block MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. For the given equation, find the values of a, b, and c, determine
Semester Exam Review Name Date Block MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. For the given equation, find the values of a, b, and c, determine
Unit 8 Notes: Solving Quadratics by Factoring Alg 1
 Unit 8 Notes: Solving Quadratics by Factoring Alg 1 Name Period Day Date Assignment (Due the next class meeting) Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Monday Tuesday
Unit 8 Notes: Solving Quadratics by Factoring Alg 1 Name Period Day Date Assignment (Due the next class meeting) Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Monday Tuesday
-5y 4 10y 3 7y 2 y 5: where y = -3-5(-3) 4 10(-3) 3 7(-3) 2 (-3) 5: Simplify -5(81) 10(-27) 7(9) (-3) 5: Evaluate = -200
 Polynomials: Objective Evaluate, add, subtract, multiply, and divide polynomials Definition: A Term is numbers or a product of numbers and/or variables. For example, 5x, 2y 2, -8, ab 4 c 2, etc. are all
Polynomials: Objective Evaluate, add, subtract, multiply, and divide polynomials Definition: A Term is numbers or a product of numbers and/or variables. For example, 5x, 2y 2, -8, ab 4 c 2, etc. are all
8-7 Solving ax^2 + bx + c = 0
 29. BASKETBALL When Jerald shoots a free throw, the ball is 6 feet from the floor and has an initial upward velocity of 20 feet per second. The hoop is 10 feet from the floor. a. Use the vertical motion
29. BASKETBALL When Jerald shoots a free throw, the ball is 6 feet from the floor and has an initial upward velocity of 20 feet per second. The hoop is 10 feet from the floor. a. Use the vertical motion
(8m 2 5m + 2) - (-10m 2 +7m 6) (8m 2 5m + 2) + (+10m 2-7m + 6)
 Adding Polynomials Adding & Subtracting Polynomials (Combining Like Terms) Subtracting Polynomials (if your nd polynomial is inside a set of parentheses). (x 8x + ) + (-x -x 7) FIRST, Identify the like
Adding Polynomials Adding & Subtracting Polynomials (Combining Like Terms) Subtracting Polynomials (if your nd polynomial is inside a set of parentheses). (x 8x + ) + (-x -x 7) FIRST, Identify the like
Quadratic Algebra Lesson #2
 Quadratic Algebra Lesson # Factorisation Of Quadratic Expressions Many of the previous expansions have resulted in expressions of the form ax + bx + c. Examples: x + 5x+6 4x 9 9x + 6x + 1 These are known
Quadratic Algebra Lesson # Factorisation Of Quadratic Expressions Many of the previous expansions have resulted in expressions of the form ax + bx + c. Examples: x + 5x+6 4x 9 9x + 6x + 1 These are known
Unit 3: Writing Equations Chapter Review
 Unit 3: Writing Equations Chapter Review Part 1: Writing Equations in Slope Intercept Form. (Lesson 1) 1. Write an equation that represents the line on the graph. 2. Write an equation that has a slope
Unit 3: Writing Equations Chapter Review Part 1: Writing Equations in Slope Intercept Form. (Lesson 1) 1. Write an equation that represents the line on the graph. 2. Write an equation that has a slope
Solutions to Extra Business Problems
 Solutions to Extra Business Problems 5/28/11 1. (a).taking the derivative of C(q), we find that MC(q) = 12q + 14. Thus MC(5) = 74 - the marginal cost at a production level of 5 is 74 thousand dollars/unit.
Solutions to Extra Business Problems 5/28/11 1. (a).taking the derivative of C(q), we find that MC(q) = 12q + 14. Thus MC(5) = 74 - the marginal cost at a production level of 5 is 74 thousand dollars/unit.
Check that your exam contains 20 questions numbered sequentially.
 MATH 22 EXAM II SAMPLE EXAM VERSION A NAME STUDENT NUMBER INSTRUCTOR SECTION NUMBER On your scantron, write and bubble your PSU ID, Section Number, and Test Version. Failure to correctly code these items
MATH 22 EXAM II SAMPLE EXAM VERSION A NAME STUDENT NUMBER INSTRUCTOR SECTION NUMBER On your scantron, write and bubble your PSU ID, Section Number, and Test Version. Failure to correctly code these items
Developmental Math An Open Program Unit 12 Factoring First Edition
 Developmental Math An Open Program Unit 12 Factoring First Edition Lesson 1 Introduction to Factoring TOPICS 12.1.1 Greatest Common Factor 1 Find the greatest common factor (GCF) of monomials. 2 Factor
Developmental Math An Open Program Unit 12 Factoring First Edition Lesson 1 Introduction to Factoring TOPICS 12.1.1 Greatest Common Factor 1 Find the greatest common factor (GCF) of monomials. 2 Factor
Section 7.4 Additional Factoring Techniques
 Section 7.4 Additional Factoring Techniques Objectives In this section, you will learn to: To successfully complete this section, you need to understand: Factor trinomials when a = 1. Multiplying binomials
Section 7.4 Additional Factoring Techniques Objectives In this section, you will learn to: To successfully complete this section, you need to understand: Factor trinomials when a = 1. Multiplying binomials
ST. DAVID S MARIST INANDA
 ST. DAVID S MARIST INANDA MATHEMATICS NOVEMBER EXAMINATION GRADE 11 PAPER 1 8 th NOVEMBER 2016 EXAMINER: MRS S RICHARD MARKS: 125 MODERATOR: MRS C KENNEDY TIME: 2 1 Hours 2 NAME: PLEASE PUT A CROSS NEXT
ST. DAVID S MARIST INANDA MATHEMATICS NOVEMBER EXAMINATION GRADE 11 PAPER 1 8 th NOVEMBER 2016 EXAMINER: MRS S RICHARD MARKS: 125 MODERATOR: MRS C KENNEDY TIME: 2 1 Hours 2 NAME: PLEASE PUT A CROSS NEXT
Economics 307: Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory A Brief Mathematical Primer
 Economics 07: Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory A Brief Mathematical Primer Calculus: Much of economics is based upon mathematical models that attempt to describe various economic relationships. You have
Economics 07: Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory A Brief Mathematical Primer Calculus: Much of economics is based upon mathematical models that attempt to describe various economic relationships. You have
Alg2A Factoring and Equations Review Packet
 1 Factoring using GCF: Take the greatest common factor (GCF) for the numerical coefficient. When choosing the GCF for the variables, if all the terms have a common variable, take the one with the lowest
1 Factoring using GCF: Take the greatest common factor (GCF) for the numerical coefficient. When choosing the GCF for the variables, if all the terms have a common variable, take the one with the lowest
CH 39 CREATING THE EQUATION OF A LINE
 9 CH 9 CREATING THE EQUATION OF A LINE Introduction S ome chapters back we played around with straight lines. We graphed a few, and we learned how to find their intercepts and slopes. Now we re ready to
9 CH 9 CREATING THE EQUATION OF A LINE Introduction S ome chapters back we played around with straight lines. We graphed a few, and we learned how to find their intercepts and slopes. Now we re ready to
Name Date Student id #:
 Math1090 Final Exam Spring, 2016 Instructor: Name Date Student id #: Instructions: Please show all of your work as partial credit will be given where appropriate, and there may be no credit given for problems
Math1090 Final Exam Spring, 2016 Instructor: Name Date Student id #: Instructions: Please show all of your work as partial credit will be given where appropriate, and there may be no credit given for problems
University of Phoenix Material
 1 University of Phoenix Material Factoring and Radical Expressions The goal of this week is to introduce the algebraic concept of factoring polynomials and simplifying radical expressions. Think of factoring
1 University of Phoenix Material Factoring and Radical Expressions The goal of this week is to introduce the algebraic concept of factoring polynomials and simplifying radical expressions. Think of factoring
8-4 Factoring ax 2 + bx + c. (3x + 2)(2x + 5) = 6x x + 10
 When you multiply (3x + 2)(2x + 5), the coefficient of the x 2 -term is the product of the coefficients of the x-terms. Also, the constant term in the trinomial is the product of the constants in the binomials.
When you multiply (3x + 2)(2x + 5), the coefficient of the x 2 -term is the product of the coefficients of the x-terms. Also, the constant term in the trinomial is the product of the constants in the binomials.
Page Points Score Total: 100
 Math 1130 Spring 2019 Sample Midterm 2b 2/28/19 Name (Print): Username.#: Lecturer: Rec. Instructor: Rec. Time: This exam contains 10 pages (including this cover page) and 9 problems. Check to see if any
Math 1130 Spring 2019 Sample Midterm 2b 2/28/19 Name (Print): Username.#: Lecturer: Rec. Instructor: Rec. Time: This exam contains 10 pages (including this cover page) and 9 problems. Check to see if any
Section R.4 Review of Factoring. Factoring Out the Greatest Common Factor
 1 Section R.4 Review of Factoring Objective #1: Factoring Out the Greatest Common Factor The Greatest Common Factor (GCF) is the largest factor that can divide into the terms of an expression evenly with
1 Section R.4 Review of Factoring Objective #1: Factoring Out the Greatest Common Factor The Greatest Common Factor (GCF) is the largest factor that can divide into the terms of an expression evenly with
Review Exercise Set 13. Find the slope and the equation of the line in the following graph. If the slope is undefined, then indicate it as such.
 Review Exercise Set 13 Exercise 1: Find the slope and the equation of the line in the following graph. If the slope is undefined, then indicate it as such. Exercise 2: Write a linear function that can
Review Exercise Set 13 Exercise 1: Find the slope and the equation of the line in the following graph. If the slope is undefined, then indicate it as such. Exercise 2: Write a linear function that can
Chapter 8: Factoring Polynomials. Algebra 1 Mr. Barr
 p. 1 Chapter 8: Factoring Polynomials Algebra 1 Mr. Barr Name: p. 2 Date Schedule Lesson/Activity 8.1 Monomials & Factoring 8.2 Using the Distributive Property 8.3 Quadratics in the form x 2 +bx+c Quiz
p. 1 Chapter 8: Factoring Polynomials Algebra 1 Mr. Barr Name: p. 2 Date Schedule Lesson/Activity 8.1 Monomials & Factoring 8.2 Using the Distributive Property 8.3 Quadratics in the form x 2 +bx+c Quiz
5.6 Special Products of Polynomials
 5.6 Special Products of Polynomials Learning Objectives Find the square of a binomial Find the product of binomials using sum and difference formula Solve problems using special products of polynomials
5.6 Special Products of Polynomials Learning Objectives Find the square of a binomial Find the product of binomials using sum and difference formula Solve problems using special products of polynomials
SCHOOL OF ACCOUNTING AND BUSINESS BSc. (APPLIED ACCOUNTING) GENERAL / SPECIAL DEGREE PROGRAMME
 All Rights Reserved No. of Pages - 06 No of Questions - 06 SCHOOL OF ACCOUNTING AND BUSINESS BSc. (APPLIED ACCOUNTING) GENERAL / SPECIAL DEGREE PROGRAMME YEAR I SEMESTER I (Group B) END SEMESTER EXAMINATION
All Rights Reserved No. of Pages - 06 No of Questions - 06 SCHOOL OF ACCOUNTING AND BUSINESS BSc. (APPLIED ACCOUNTING) GENERAL / SPECIAL DEGREE PROGRAMME YEAR I SEMESTER I (Group B) END SEMESTER EXAMINATION
Algebra/Geometry Blend Unit #5: Factoring and Quadratic Functions Lesson 2: Factoring Trinomials. What does factoring really mean?
 Algebra/Geometry Blend Unit #5: Factoring and Quadratic Functions Lesson 2: Factoring Trinomials Name Period Date [page 1] Before you embark on your next factoring adventure, it is important to ask yourself
Algebra/Geometry Blend Unit #5: Factoring and Quadratic Functions Lesson 2: Factoring Trinomials Name Period Date [page 1] Before you embark on your next factoring adventure, it is important to ask yourself
Algebra with Calculus for Business: Review (Summer of 07)
 Algebra with Calculus for Business: Review (Summer of 07) 1. Simplify (5 1 m 2 ) 3 (5m 2 ) 4. 2. Simplify (cd) 3 2 (c 3 ) 1 4 (d 1 4 ) 3. 3. Simplify (x 1 2 + y 1 2 )(x 1 2 y 1 2 ) 4. Solve the equation
Algebra with Calculus for Business: Review (Summer of 07) 1. Simplify (5 1 m 2 ) 3 (5m 2 ) 4. 2. Simplify (cd) 3 2 (c 3 ) 1 4 (d 1 4 ) 3. 3. Simplify (x 1 2 + y 1 2 )(x 1 2 y 1 2 ) 4. Solve the equation
Chapter 6.1: Introduction to parabolas and solving equations by factoring
 Chapter 6 Solving Quadratic Equations and Factoring Chapter 6.1: Introduction to parabolas and solving equations by factoring If you push a pen off a table, how does it fall? Does it fall like this? Or
Chapter 6 Solving Quadratic Equations and Factoring Chapter 6.1: Introduction to parabolas and solving equations by factoring If you push a pen off a table, how does it fall? Does it fall like this? Or
PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION 2018 MATHEMATICS GRADE 12 PAPER 1. Time: 3 hours Total: 150 PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY
 PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION 2018 MATHEMATICS GRADE 12 PAPER 1 Time: 3 hours Total: 150 Examiner: P R Mhuka Moderators: J Scalla E Zachariou PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY 1. This question
PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION 2018 MATHEMATICS GRADE 12 PAPER 1 Time: 3 hours Total: 150 Examiner: P R Mhuka Moderators: J Scalla E Zachariou PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY 1. This question
Unit 8: Quadratic Expressions (Polynomials)
 Name: Period: Algebra 1 Unit 8: Quadratic Expressions (Polynomials) Note Packet Date Topic/Assignment HW Page Due Date 8-A Naming Polynomials and Combining Like Terms 8-B Adding and Subtracting Polynomials
Name: Period: Algebra 1 Unit 8: Quadratic Expressions (Polynomials) Note Packet Date Topic/Assignment HW Page Due Date 8-A Naming Polynomials and Combining Like Terms 8-B Adding and Subtracting Polynomials
Factoring is the process of changing a polynomial expression that is essentially a sum into an expression that is essentially a product.
 Ch. 8 Polynomial Factoring Sec. 1 Factoring is the process of changing a polynomial expression that is essentially a sum into an expression that is essentially a product. Factoring polynomials is not much
Ch. 8 Polynomial Factoring Sec. 1 Factoring is the process of changing a polynomial expression that is essentially a sum into an expression that is essentially a product. Factoring polynomials is not much
Factoring Quadratic Expressions VOCABULARY
 5-5 Factoring Quadratic Expressions TEKS FOCUS Foundational to TEKS (4)(F) Solve quadratic and square root equations. TEKS (1)(C) Select tools, including real objects, manipulatives, paper and pencil,
5-5 Factoring Quadratic Expressions TEKS FOCUS Foundational to TEKS (4)(F) Solve quadratic and square root equations. TEKS (1)(C) Select tools, including real objects, manipulatives, paper and pencil,
Section R.5 Review of Factoring. Factoring Out the Greatest Common Factor
 1 Section R.5 Review of Factoring Objective #1: Factoring Out the Greatest Common Factor The Greatest Common Factor (GCF) is the largest factor that can divide into the terms of an expression evenly with
1 Section R.5 Review of Factoring Objective #1: Factoring Out the Greatest Common Factor The Greatest Common Factor (GCF) is the largest factor that can divide into the terms of an expression evenly with
WEEK 2 REVIEW. Straight Lines (1.2) Linear Models (1.3) Intersection Points (1.4) Least Squares (1.5)
 WEEK 2 REVIEW Straight Lines (1.2) Linear Models (1.3) Intersection Points (1.4) Least Squares (1.5) 1 STRAIGHT LINES SLOPE A VERTICAL line has NO SLOPE. All other lines have a slope given by m = rise
WEEK 2 REVIEW Straight Lines (1.2) Linear Models (1.3) Intersection Points (1.4) Least Squares (1.5) 1 STRAIGHT LINES SLOPE A VERTICAL line has NO SLOPE. All other lines have a slope given by m = rise
MATH 181-Quadratic Equations (7 )
 MATH 181-Quadratic Equations (7 ) 7.1 Solving a Quadratic Equation by Factoring I. Factoring Terms with Common Factors (Find the greatest common factor) a. 16 1x 4x = 4( 4 3x x ) 3 b. 14x y 35x y = 3 c.
MATH 181-Quadratic Equations (7 ) 7.1 Solving a Quadratic Equation by Factoring I. Factoring Terms with Common Factors (Find the greatest common factor) a. 16 1x 4x = 4( 4 3x x ) 3 b. 14x y 35x y = 3 c.
Worksheet 1 Laws of Integral Indices
 Worksheet 1 Laws of Integral Indices 1. Simplify a 4 b a 5 4 and express your answer with positive indices.. Simplify 6 x y x 3 and express your answer with positive indices. 3. Simplify x x 3 5 y 4 and
Worksheet 1 Laws of Integral Indices 1. Simplify a 4 b a 5 4 and express your answer with positive indices.. Simplify 6 x y x 3 and express your answer with positive indices. 3. Simplify x x 3 5 y 4 and
Study Guide - Part 1
 Math 116 Spring 2015 Study Guide - Part 1 1. Find the slope of a line that goes through the points (1, 5) and ( 3, 13). The slope is (A) Less than -1 (B) Between -1 and 1 (C) Between 1 and 3 (D) More than
Math 116 Spring 2015 Study Guide - Part 1 1. Find the slope of a line that goes through the points (1, 5) and ( 3, 13). The slope is (A) Less than -1 (B) Between -1 and 1 (C) Between 1 and 3 (D) More than
notebook October 08, What are the x and y intercepts? (write your answers as coordinates).
 3.4 Opening Activity: Draw a graph of the equation y = 5x + 20 What are the x and y intercepts? (write your answers as coordinates). How are you able to use the equation but NOT the graph to find the x
3.4 Opening Activity: Draw a graph of the equation y = 5x + 20 What are the x and y intercepts? (write your answers as coordinates). How are you able to use the equation but NOT the graph to find the x
QUADRATIC. Parent Graph: How to Tell it's a Quadratic: Helpful Hints for Calculator Usage: Domain of Parent Graph:, Range of Parent Graph: 0,
 Parent Graph: How to Tell it's a Quadratic: If the equation's largest exponent is 2 If the graph is a parabola ("U"-Shaped) Opening up or down. QUADRATIC f x = x 2 Domain of Parent Graph:, Range of Parent
Parent Graph: How to Tell it's a Quadratic: If the equation's largest exponent is 2 If the graph is a parabola ("U"-Shaped) Opening up or down. QUADRATIC f x = x 2 Domain of Parent Graph:, Range of Parent
Math 101, Basic Algebra Author: Debra Griffin
 Math 101, Basic Algebra Author: Debra Griffin Name Chapter 5 Factoring 5.1 Greatest Common Factor 2 GCF, factoring GCF, factoring common binomial factor 5.2 Factor by Grouping 5 5.3 Factoring Trinomials
Math 101, Basic Algebra Author: Debra Griffin Name Chapter 5 Factoring 5.1 Greatest Common Factor 2 GCF, factoring GCF, factoring common binomial factor 5.2 Factor by Grouping 5 5.3 Factoring Trinomials
2) Endpoints of a diameter (-1, 6), (9, -2) A) (x - 2)2 + (y - 4)2 = 41 B) (x - 4)2 + (y - 2)2 = 41 C) (x - 4)2 + y2 = 16 D) x2 + (y - 2)2 = 25
 Math 101 Final Exam Review Revised FA17 (through section 5.6) The following problems are provided for additional practice in preparation for the Final Exam. You should not, however, rely solely upon these
Math 101 Final Exam Review Revised FA17 (through section 5.6) The following problems are provided for additional practice in preparation for the Final Exam. You should not, however, rely solely upon these
Section 6.4 Adding & Subtracting Like Fractions
 Section 6.4 Adding & Subtracting Like Fractions ADDING ALGEBRAIC FRACTIONS As you now know, a rational expression is an algebraic fraction in which the numerator and denominator are both polynomials. Just
Section 6.4 Adding & Subtracting Like Fractions ADDING ALGEBRAIC FRACTIONS As you now know, a rational expression is an algebraic fraction in which the numerator and denominator are both polynomials. Just
FACTORING HANDOUT. A General Factoring Strategy
 This Factoring Packet was made possible by a GRCC Faculty Excellence grant by Neesha Patel and Adrienne Palmer. FACTORING HANDOUT A General Factoring Strategy It is important to be able to recognize the
This Factoring Packet was made possible by a GRCC Faculty Excellence grant by Neesha Patel and Adrienne Palmer. FACTORING HANDOUT A General Factoring Strategy It is important to be able to recognize the
Elementary Algebra Review for Exam 3
 Elementary Algebra Review for Exam ) After receiving a discount of 5% on its bulk order of typewriter ribbons, John's Office Supply pays $5882. What was the price of the order before the discount? Round
Elementary Algebra Review for Exam ) After receiving a discount of 5% on its bulk order of typewriter ribbons, John's Office Supply pays $5882. What was the price of the order before the discount? Round
1/14/15. Objectives. 7-5 Factoring Special Products. Factor perfect-square trinomials. Factor the difference of two squares.
 Objectives Factor perfect-square trinomials. Factor the difference A trinomial is a perfect square if: The first and last terms are perfect squares. The middle term is two times one factor from the first
Objectives Factor perfect-square trinomials. Factor the difference A trinomial is a perfect square if: The first and last terms are perfect squares. The middle term is two times one factor from the first
Worksheet A ALGEBRA PMT
 Worksheet A 1 Find the quotient obtained in dividing a (x 3 + 2x 2 x 2) by (x + 1) b (x 3 + 2x 2 9x + 2) by (x 2) c (20 + x + 3x 2 + x 3 ) by (x + 4) d (2x 3 x 2 4x + 3) by (x 1) e (6x 3 19x 2 73x + 90)
Worksheet A 1 Find the quotient obtained in dividing a (x 3 + 2x 2 x 2) by (x + 1) b (x 3 + 2x 2 9x + 2) by (x 2) c (20 + x + 3x 2 + x 3 ) by (x + 4) d (2x 3 x 2 4x + 3) by (x 1) e (6x 3 19x 2 73x + 90)
MATD 0370 ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA REVIEW FOR TEST 3 (New Material From: , , and 10.1)
 NOTE: In addition to the problems below, please study the handout Exercise Set 10.1 posted at http://www.austin.cc.tx.us/jbickham/handouts. 1. Simplify: 5 7 5. Simplify: ( 6ab 5 c )( a c 5 ). Simplify:
NOTE: In addition to the problems below, please study the handout Exercise Set 10.1 posted at http://www.austin.cc.tx.us/jbickham/handouts. 1. Simplify: 5 7 5. Simplify: ( 6ab 5 c )( a c 5 ). Simplify:
Accuplacer Review Workshop. Intermediate Algebra. Week Four. Includes internet links to instructional videos for additional resources:
 Accuplacer Review Workshop Intermediate Algebra Week Four Includes internet links to instructional videos for additional resources: http://www.mathispower4u.com (Arithmetic Video Library) http://www.purplemath.com
Accuplacer Review Workshop Intermediate Algebra Week Four Includes internet links to instructional videos for additional resources: http://www.mathispower4u.com (Arithmetic Video Library) http://www.purplemath.com
BARUCH COLLEGE MATH 2003 SPRING 2006 MANUAL FOR THE UNIFORM FINAL EXAMINATION
 BARUCH COLLEGE MATH 003 SPRING 006 MANUAL FOR THE UNIFORM FINAL EXAMINATION The final examination for Math 003 will consist of two parts. Part I: Part II: This part will consist of 5 questions similar
BARUCH COLLEGE MATH 003 SPRING 006 MANUAL FOR THE UNIFORM FINAL EXAMINATION The final examination for Math 003 will consist of two parts. Part I: Part II: This part will consist of 5 questions similar
LINES AND SLOPES. Required concepts for the courses : Micro economic analysis, Managerial economy.
 LINES AND SLOPES Summary 1. Elements of a line equation... 1 2. How to obtain a straight line equation... 2 3. Microeconomic applications... 3 3.1. Demand curve... 3 3.2. Elasticity problems... 7 4. Exercises...
LINES AND SLOPES Summary 1. Elements of a line equation... 1 2. How to obtain a straight line equation... 2 3. Microeconomic applications... 3 3.1. Demand curve... 3 3.2. Elasticity problems... 7 4. Exercises...
8.1 Functions Practice Problems
 8. Functions Practice Problems. Which of the following tables could describe a function? Explain your answer. (a) (b) Input Output Input Output. Which of the following equations define q as a function
8. Functions Practice Problems. Which of the following tables could describe a function? Explain your answer. (a) (b) Input Output Input Output. Which of the following equations define q as a function
Mix Review» Form A (Master Copy)» Teacher Version. Directions: Please choose the best answer choice for each of the following questions.
 Directions: Please choose the best answer choice for each of the following questions. 1. What is the value of 3. Nature's Nursery had maple trees on sale for 15% off the original price of $30.00. When
Directions: Please choose the best answer choice for each of the following questions. 1. What is the value of 3. Nature's Nursery had maple trees on sale for 15% off the original price of $30.00. When
MATD 0370 ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA REVIEW FOR TEST 3 (New Material From: , , and 10.1)
 NOTE: In addition to the problems below, please study the handout Exercise Set 10.1 posted at http://www.austincc.edu/jbickham/handouts. 1. Simplify: 5 7 5. Simplify: ( ab 5 c )( a c 5 ). Simplify: 4x
NOTE: In addition to the problems below, please study the handout Exercise Set 10.1 posted at http://www.austincc.edu/jbickham/handouts. 1. Simplify: 5 7 5. Simplify: ( ab 5 c )( a c 5 ). Simplify: 4x
