Macroeconomics. Macroeconomics. Study of economics at aggregate level. Measurement. National Output(Q) or Income (Y) or Expenditure(Z)
|
|
|
- Chad Bruce
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Macroeconomics Study of economics at aggregate level. 1 Macroeconomics Measurement National Output(Q) or Income (Y) or Expenditure(Z) Price Levels or Inflation (P) Unemployment (U) and Poverty Policy Monetary Policy (RBI) Fiscal Policy ( Central Govt.) CSO:NAS in India 2 1
2 Q I. National Output Concept and Measurement 3 National Output: Introduction National output is the nation s aggregate output of goods and services during a given year. Nations Total Production/Output(Q) Total Income (Y) Total Expenditure(Z) For an economy as a whole during a given year, Output Income Expenditure because: All output produced is for transaction purpose Every transaction has a buyer and a seller. Every rupee of spending by some buyer is a rupee of income for some seller. 2
3 National Output: The Circular Flow of Income and Expenditure Economy an integrated system of production, exchange and consumption, it has two types of decision makers 1. Producers(Seller): Sales goods and services; receives income. 2. Consumer ( Buyer): Buys goods and services; made expenditure Buy and sell goods and services Production flow ( Income) Money Flow ( Expenditure) Economic Agents are both buyer and seller 1. Individual/Households/Society 2. Firms/Industry 3. Government 4. External Sector Total Output= Total Income = Total Expenditure at a point of time 5 Govt Purchse and Subsidies Wages, Salaries and transfer Payment Direct and indirect Taxes Government Direct Taxes Revenue Spending Goods & Services sold Market for Goods and Services (Goods Flow) Goods & Services bought Firms Investment Capital Market Savings Households Inputs for production Rent, wages, interest and profit Payments for imports Receipts from exports Market for Factors of Production (Factor Flow) Foreign Sector Land, Labor, Capital and Entrepreneur Income Export of man power Foreign Remittance 3
4 National Output: Concepts & Measurement 1 GDP: GDP M, and GDP F 2 NDP: NDP M, and NGP F 3 GNP: GNP M, and GNP F 4 NNP : NNP M, and NNP F (= National Income) 5 Private Income 6 Personal Income 7 Personal Disposable Income All Output are express with current and constant prices. Output at Current Price is called Nominal Output Output at Constant Price is called Real Output. 1.1.The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) GDP is the total market value of all final goods and services produced within country s borders during a given period of time (generally a year) irrespective of ownership of resources. Ex. Phillips produces tube light with in India; GDP of India TATA produces car in UK; GDP of UK but GNP of India. Does not include: Intermediate goods, Ex. Intel chips Goods produced in the past Non market production Black market: hawkers selling coconut Underground economy: drugs, prostitution, Household production: self consumption item, not sold in mkt 8 4
5 1.1.The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Current Prices=> ( Nominal term) Constant Prices=> ( Real Term) GDP: ( GDP F and GDP M ) a. GDP M (GDP at Market Prices): When the output of all final goods and services are valued at market prices and the values thus obtained are added is known as GDP M. It includes Indirect Taxes (Ti) and net of Subsidies (S) GDP M =GDP F + (Ti-S) b. GDP F (GDP at Factor Costs/Prices): GDP F =GDP M - (Ti-S) => GDP F =GDP M Ti+S 10 5
6 1.2. Net Domestic Product(NDP): NDP is obtained by subtracting depreciation from GDP NDP F =GDP F - depreciation NDP M =GDP M - depreciation Gross National Product (GNP): GNP is the monetary value of all final goods and services (Σpiqi) that are currently produced in a year and valued at market price. 1. Produced by National owned Resources only Ex. visiting Prof, banks profits, Indian company produces out side India included 2. Sold through the official market Self consumption- included Rent on owner-living houses is computed included Do it yourself activities excluded Black economy: legal/illegal difficult to estimate: excluded 3. Not resold or used in further productions Final goods: Included: Intermediate goods, Non-productive transactions: such as (i) Public and private transfer payment, (ii) buying and selling of securities, and Second hand sales: Excluded 12 6
7 1.2 GNP : GNP M and GNP F A) GNP at Market Price (GNP M ): When the output of all final goods and services are valued at market prices (current price) and the values thus obtained are added is known as GNP M. It includes Indirect Taxes (Ti) and net of Subsidies (S) GNP M = GNP F +Ti-S B) GNP at Factor Cost (GNP F ): GNP F = GNP M T i +S For National Income identity purpose we use the following identity GNP F C + I +G+X-M Hence GNP GNI GNE Net National Product (NNP) NNP is total value of final goods and services produced in the economy during a year after deducting depreciation plus net income from abroad NNP F =GNP F -depreciation NNP M =GNP M -depreciation NNP F is known as National Income 14 7
8 1.4 Private Sector s Income a.private Income: Income earned by households Pvt.I=NNP F IAD-END+NDI+TAD+OTA b. Personal Income: Income received by households: PI=Pvt.I-RE-CT c. Personal Disposal Income: Income available for dispose PDI=PI-HDT-MAD IAD- Income from entrepreneurship and property accruing to govt administrative deps ex. Railways END- earnings of Govt non-departmental enterprises (PSUs) NDI- National Debt Interest TAD- Current Transfer from Govt administration Dept OTA- Other net current transfer from abroad RE- retained earnings of nations s private corporate sector CT- corporate tax HDT- Household direct tax MAD- Miscellaneous receipts of govt administrative dept ex. Fines, fees
9 How is GDP and GNP Related???? GNP= GDP + Net Income from abroad. => GDP=GNP- GDP + Net Income from abroad Similarly, 1. GNP F =GDP F + Net income from abroad GNP M =GDP M + Net income from abroad 2. GDP F =GNP F -Net income from abroad GDP M =GNP M -Net income from abroad We know that GDP F =GDP M -Ti + S A region's GDP is one of the ways of measuring the size of its local economy whereas the GNP measures the overall economic strength of a country. 17 Nominal & Real GDP: ( GDP at Current and Constant Price) All Output are expressed with Current and Constant prices. Output at Current Price is called Nominal Output Output at Constant Price is called Real Output. GDP F with Constant Price is called as Real GDP which is used to measure the growth rate of the economy. GDP F with Current Price is called as Nominal GDP. 18 9
10 Nominal & Real GDP: ( GDP at Current and Constant Price) Current Prices=> ( Nominal term) Constant Prices=> ( Real Term) 19 The GDP Deflator The GDP deflator is a measure of the price level calculated as the ratio of nominal GDP to real GDP times 100. It tells us what portion of the rise in nominal GDP that is attributable to a rise in prices rather than a rise in the quantities produced. Calculations: GDP deflator = Real GDP 20XX Nominal GDP Real GDP Nominal GDP GDP deflator XX 20XX
11 Nominal Vs Real GDP(GDP F ) GDPF at current prices(base Year ) GDP F at Constant Price( ) Nominal GDP in cr GDP Deflator Growth Rates (GDP) Real GDP in Cr Growth rate: (Y t -Y t-1 )/Y t-1 *100 Economic Growth rate is measured in terms of real GDP growth rate Real GDP Growth Rate Trend Line Real GDP Growth Rate i.e. GDP at FC (constant price) base year ( )
12 Real Growth Rate of different measurement of National Income accounting (constant price) base year ( ) GDPFC NDPFC GNPFC NNPFC Business Cycle Potential or Natural Real GDP growth rate 24 12
13 Business Cycle Trough: High unemployment, low demand, unused productive capacity, low profits, low investments and lack of confidence about economic prospects Peak: top of cycle high capacity utilisation shortage of skill labour and raw material excess demand, etc Recovery or Expansion: employment, income, consumer spending, demand, etc. increases Business opinions changes from pessimism to optimism Recession or contraction: is downturn in economic activity. Recession is fall in real GDP for two quarters. Depression Recession that is deep and long lasting is Depression. Demand, production and employment falls Boom and Slump: Non- technical but descriptive terms. Falling half of cycle is slump. Rising half of cycle is often called boom. 25 National Output: The Methods of Measurement 26 13
14 2.0. India s National Output: Methods of Measurement Base year No of Items to calculate GDP (for monthly) 124 ( for annual) Annual Series( ) Quarterly Series (since 1997 Q1) No Series Less than Quarterly is available IIP used as proxy for GDP India uses Laspeyer s Methods to calculate IIP Weights are based on value added methods ( new included old deleted) National Output: Methods of Measurement a. Product Methods (GNP): GNP is the value added by the various industries and activities of the economy in a particular year. Q=f(L,N,K,O)= Σp i Q i a. Income Methods (GNI): We added up the income earned by the owners of factors of productions in a particular year Y=(R L)+(w N) + (i K) + (profit E) b. Expenditure Methods (GNE): We added up the final expenditure of all residents (eco agents) in a country. Z= (C+I+G+X-M) National Income Identity: Q Y Z 28 14
15 2.1. Product Methods: GDP F =ΣP i Q i Pi= Price of final good i Qi= Output of final good i A. Primary (i) Agriculture + (ii) forestry and Fishing + (iii) Mining and Quarrying B. Secondary (i) Manufacturing + (ii) Electricity, gas and water supply + (iii )Construction C. Tertiary (Services) Trade, hotels and restaurant Transport, storage and communication Banking and insurance Real estate, dwelling and business services Public administration and defense Other services
16 2.1. Net Product Methods: Value Added Approach
17 2.2. Income Approach: A. Compensation of employee (W) B. Operating surplus rent (R) interest (i) profits and dividends (Profit) C. Mixed Income (self employed) Transfer payments, employees benefit, pensions etc not included here as income. GDP F = R+W+i+Profit + Mixed Income
18 2.3. Expenditure Approach: A. Private Consumption (C) B. Investments (gross) (I) C. Government Expenditure (G) D. Exports (X) E. Imports (M) (minus) GDP M = C+I+G+X M
19 Sectoral Contributions of GDP at FC at Const Price (%) Agriculture & Allied Activities Agriculture Industry Mining & Quarrying Manufacturing Electricity, Gas & Water Supply Services Construction Trade, Hotels, Transport & Communication Financing, Insurance, Real Estate & Business Services Community, Social & Personal Services Sectoral Contributions of GDP at FC at Const Price (%) 38 19
20 Is GDP A Good Measure Of Economic Well-being? GDP is the best single measure of the economic wellbeing of a society. GDP per person tells us the income and expenditure of the average person in the economy. Higher GDP per person indicates a higher standard of living. GDP is not a perfect measure of the happiness or quality of life, however. 39 Is GDP A Good Measure Of Economic Well-being? Some things that contribute to well-being are not included in GDP. The value of. The value of a clean environment. The value of almost all activity that takes place outside of markets, such as the value of the time parents spend with their children and the value of volunteer work. GDP Measures the Size of the Pie but Not How the Pie Is Divided Up 40 20
21 Did World War II Bring Prosperity? Implications for Managers -Movement in national Income helps the manager to figure out the state of the economy -Component of the national income helps to determine the production, distribution, demand structure etc. of the economy. -Expenditure pattern indicates the role of govt in economic activity -Role of govt enhances private competitions -Pattern of govt finances thorough direct and indirect axes affects the disposable income of the households thereby their consumption pattern -Level of imports and exports provides information to the managers about the demand pattern and the potential customers in the international markets 42 21
22 P II. Price Levels: Concept & Measurement GDP Deflator, WPI, CPI, PPI 43 Price Data Bulk Transactions Implicit Small Transaction WPI Deflator CPI Data Sources : Central Statistical Organization(CSO) National Sample Surveys Organization (NSSO) Director of Economics and Statistics (DES) Labor Bureau (LB) National Buildings Organization (NBO) Indian Bureau of Mines (IBM) Reserve Banks of India (RBI) Director General of Commercial Intelligence and Statistics (DGCIS) Office of the Coal Controller and Textile Commissioner (OCC&TC)tec
23 Measuring Price Changes: Price Indices GDP Deflator Implicit Price Index. Calculated from Nominal and Real GDP WPI (676 item with base year) started since 1902 AC All commodities (by Office of Economic Advisor, Ministry of Industry) PA Primary articles.»fa Food articles.»nf Non food articles.»minerals. FPL& L i.e. Fuel, power, light & lubricants MP Manufactured products CPI (200+) (1970s) UNME Urban non manual employees ( by CSO) IW Industrial workers. AL Agricultural labors. (Labor Bureau) RL Rural Labors Producer Price Index (PPI) ( Dr Abhijit Sen Suggestions) Includes only manufacturing goods 45 Price Index in India 46 23
24 Measuring Price Changes: Index Number Basic Concepts: Index No: It is a statistical device (measure) to express average changes in related variables. Price Index: Measures relative changes in average prices over time. India Uses Laspeyres Method 47 Measuring Price Changes: CPI Average Prices Quantity Sold % Change Food Rs 12 Rs % 4 5 Housing % 3 3 Fun % 3 4 Machines % 2 2 Calculations: Laspeyer s Method CPI = (Σp t q 0 / Σp 0 q 0 )x 100 Σp t q 0= = 1992 Quantities x 1992 Prices = 4 Rs Rs Rs.4 = Rs.48 + Rs.27 + Rs.12 = Rs.87 Σp 0 q 0 = 1992 Quantities x 1994 Prices = 4 Rs Rs Rs.5 = Rs.56 + Rs.30 + Rs.15 = Rs.101 CPI: - Machines not included. - Base year (1992) quantities (market basket) rather than base year prices used. CPI for 1994 is = Σp t q 0 / Σp 0 q 0 x 100 = (101 / 87) = => 1.16% 48 24
25 Measuring Price Changes: Chain base methods 49 Measuring Price Changes: Inflation Rate Inflation ( ) is the rate of changes in price levels: Inflation ( ) rate: CPI Inflation: P P t t P P P t 1 P t 1 t 1 t Inflation from 1993 to 1994: = (CPI 1994 CPI 1993 ) 100 CPI 1993 = ( ) 100 = = 2.20% 50 25
26 Measuring Price Changes: Methods Existing ( ) series Total: 447 commodities i) Primary article: 93( Food 93, non food 28 and minerals 21) ii) Fuel, power etc: 20 iii) Manufactured Items: 334 WPI Weights Existing ( ) series Total: 435 commodities i) Primary article: 98( Food 98, non food 25 and minerals 19) ii) Fuel, power etc: 19 iii) Manufactured Items: 318 Weights are assigned in proportion to their share in the total value of transaction (output) 52 in the economy. 26
27 WPI Weights Weight No. of items No. of Quotations Major Group / Group All Commodities I Primary Articles II Fuel & Power III Manufactured Products Weights are assigned in proportion to their share in the total value of transaction (output) in the economy. 53 CPI Weights Weights are assigned as the ratio of total consumption expenditure of estimated number of 54 families allocated to a center in the state to the sum of all such expenditures over all centers in the country 27
28 CPI Weights 55 Inflation Rate in India 56 28
29 Types of Inflation >10% in P per year >100% in P with in a year Prices rise with Govt interruption slow Increase in price < 3% 3 to 7%per year in P prices rise without any Govt interruption 57 Extremely rapid or out of control inflation. Hyper Inflation There is no precise numerical definition to hyperinflation. The most famous example of hyperinflation occurred in Germany between January 1922 and November Germany: WPI 140% in % % 1923 Hungary: the inflation rate was 20,000% Country Argentina % % 416.9% Brazil % % Peru % % 287.3% Sources: CMIE World Economy and India's place, Oct
30 Core vs Headline Inflation: Core Inflation: Core inflation is generally a chosen measure of inflation that excludes the more volatile price categories e.g. food and energy prices, otherwise it will give a false measure of inflation. Usually calculated from CPI excluding energy and food product from CPI Headline Inflation: A measurement of price inflation that takes into account all types of inflation that an economy can experience. Unlike core inflation, headline inflation also counts changes in the price of food and energy. Because food and energy prices can rapidly increase while other types of inflation can remain low, headline inflation may not give an accurate picture of how an economy is behaving. Headline inflation is more useful for the typical household because it reflects changes in the cost of living, while core inflation is used by central banks because core inflation is less volatile and shows the effects 59 of supply and demand on GDP better. Threshold Inflation and Stagflation Threshold Inflation: " acceptable rise in prices purported to reflect changes in relative prices necessary to attract resources to growth sector. Threshold level of inflation can be described as that inflexion point beyond which the output growth is not optimal Chakravarty Committee Report : 4% C Rangarajan : 6 to7% Stagflation A condition of slow economic growth and relatively high unemployment accompanied by inflation. This happened to a great extent during the 1970s, when world oil prices rose dramatically, fueling sharp inflation in developed countries. We have seen that this happened in later At least some central banks have expressed concern over inflation even as the global economy seems to be slowing down
31 Relation between Inflation and Interest Rates Interest rates reported in the media are nominal rates Real interest rate = nominal interest rate -(expected) inflation rate A 10-year Treasury bond paying 6.08% p.a. with 1.6% annual inflation rate has a real return of? Real return = 6.08% - 1.6% = 4.28% Causes of Inflation Price is determined when AD=AS 1. Demand pull inflation (AD>AS) may be due to : a)increase in money supply (M) b)increase in government purchases (G) or cut in Tax (T) c)increase in exports (X) or decrease in Import (M) 2. Cost push inflation may arise due of : a)increase in money wage rates (W) b)increase in money prices of raw materials (P). c)decrease in supply ( Supply shocks) 31
32 Structuralists Theories of Inflation a. Food Scarcity: Low monsoon Causes of Inflation b. Resources Imbalance: ( imbalance between demand and supply of industrial inputs) c. Balance of Payment deficits (M>X) Heavily dependent on imports of capital goods, raw materials, oil etc. d. Infrastructural Bottlenecks Scare and unequal distribution of Electricity, means of transport, etc. e. Social and Political Constraints Corruption, Black money, Trade unions and wage bargain Methods of Controlling Inflation 32
33 Methods of Controlling Inflation U III. Measurement of Employment (E) and Unemployment (U) 66 33
34 Definition of Unemployment Definition: An Unemployed person is Not working, willing and able to work Actively seeking a job and willing to accept a job at the prevailing market wage Not counted as unemployed Unable or unwilling to work, underage, college students, home makers, retired, in the military. Measurement: Total labor force (L) = Employed persons (E)+ Unemployed persons Civilian noninstitutional population (16 and over)= Total labor force (L) + Not in labor force 67 Unemployment Rates Unemployment Rate (percent) = Unemployed * 100 Total Labor Force Participation Rate (percent) = Total Labor Force * 100 Civilian Population 68 34
35 Employment - Unemployment U.S. Unemployment Rate Great Depression ( ) 25% Unemployment rate, % 20% 15% 10% 5% World War II ( ) recession recession recession Fairfax Co., VA. U.S. 0% Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics 69 Types of Unemployment Frictional Unemployment - where people become unemployed between jobs. Due to imperfect information. Structural Unemployment - caused by changes to the structure of industry in the economy e.g. the decline of the coal, iron and steel industries. The mismatch between skills of labor and skills demanded. Seasonal Unemployment - unemployment that results from the normal seasonal change in aggregate economic activity. e.g. holiday resorts Cyclical Unemployment - stable labor force in an unstable economy. Unemployment that results from a decline in aggregate economic activity Demand Deficient Unemployment where AD is less than AS Technological Unemployment caused where people are put out of work by changes in technology Real Wage or Classical Unemployment caused by wage rates being held above market clearing levels 70 35
36 Natural Rate of Unemployment Natural Rate of Unemployment: consistent with frictional, structural, and seasonal unemployment. Full Employment Output: total output of economy when unemployment is at the natural rate. During the business cycle total output fluctuates around the full employment level leading to changes in the cyclical unemployment. 71 Thank You All 72 36
MACROECONOMICS. Ankur Jain Chief Knowledge Expert, T.I.M.E.
 MACROECONOMICS Ankur Jain Chief Knowledge Expert, T.I.M.E. www.time4education.com THE 3 SECTORS OF THE ECONOMY Primary agriculture, forestry, fishery, animal husbandry Secondary mineral, power, mining,
MACROECONOMICS Ankur Jain Chief Knowledge Expert, T.I.M.E. www.time4education.com THE 3 SECTORS OF THE ECONOMY Primary agriculture, forestry, fishery, animal husbandry Secondary mineral, power, mining,
National Income Accounting
 National Income Accounting Notes: Net Investment = Gross Investment Deprecation Net Indirect tax= Indirect tax subsidy NFIA (Net factor Income from abroad) = Factor Income from Abroad Factor income paid
National Income Accounting Notes: Net Investment = Gross Investment Deprecation Net Indirect tax= Indirect tax subsidy NFIA (Net factor Income from abroad) = Factor Income from Abroad Factor income paid
Gross Domestic Product. National Income Determination. Topic 9: 10/7/2016
 The Economy s Income and Expenditure Topic 9: National Income Determination When judging whether the economy is doing well or poorly, it is natural to look at the total income that everyone in the economy
The Economy s Income and Expenditure Topic 9: National Income Determination When judging whether the economy is doing well or poorly, it is natural to look at the total income that everyone in the economy
EXPENDITURE APPROACH: The expenditures on all final goods and services made by all sectors of the economy are added to calculate GDP. Expenditures are
 Chapter 1 MEASURING GDP AND PRICE LEVEL MEASURING EONOMIC ACTIVITY Macroeconomics studies the aggregate (or total) concept of economic activity. Its focus is on the aggregate output, the aggregate income,
Chapter 1 MEASURING GDP AND PRICE LEVEL MEASURING EONOMIC ACTIVITY Macroeconomics studies the aggregate (or total) concept of economic activity. Its focus is on the aggregate output, the aggregate income,
Chapter 6 GDP, Unemployment and Inflation
 Chapter 6 GDP, Unemployment and Inflation - Microeconomics: study of how households and firms make choices & how they interact in markets. - Macroeconomics: study of the economy as a whole, including topics
Chapter 6 GDP, Unemployment and Inflation - Microeconomics: study of how households and firms make choices & how they interact in markets. - Macroeconomics: study of the economy as a whole, including topics
Model Question Paper Economics - II (MSF1A4)
 Model Question Paper Economics - II (MSF1A4) Answer all 74 questions. Marks are indicated against each question. 1. Which of the following is true if the central bank of a country sells government securities
Model Question Paper Economics - II (MSF1A4) Answer all 74 questions. Marks are indicated against each question. 1. Which of the following is true if the central bank of a country sells government securities
National Accounting. Introduction to Macroeconomics. October 7 th, 2011 WS 2011
 National Accounting Introduction to Macroeconomics WS 2011 October 7 th, 2011 Introduction to Macroeconomics (WS 2011) National Accounting October 7 th, 2011 1 / 35 Why study National Accounting? National
National Accounting Introduction to Macroeconomics WS 2011 October 7 th, 2011 Introduction to Macroeconomics (WS 2011) National Accounting October 7 th, 2011 1 / 35 Why study National Accounting? National
8 THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS
 8 THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS Measuring a Nation s Income 23 Measuring a Nation s Income Microeconomics Microeconomics is the study of how individual households and firms make decisions and how they interact
8 THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS Measuring a Nation s Income 23 Measuring a Nation s Income Microeconomics Microeconomics is the study of how individual households and firms make decisions and how they interact
Inflation Unit V[ Part1/2]
![Inflation Unit V[ Part1/2] Inflation Unit V[ Part1/2]](/thumbs/86/93637821.jpg) Inflation Unit V[ Part1/2] CPT General Economics Chapter - 6 Select Aspects of Indian Economy CA. Dipti Lunawat Learning Objectives Meaning & Types of Inflation Price Trends in India Causes of Inflation
Inflation Unit V[ Part1/2] CPT General Economics Chapter - 6 Select Aspects of Indian Economy CA. Dipti Lunawat Learning Objectives Meaning & Types of Inflation Price Trends in India Causes of Inflation
What is Macroeconomics?
 MACRO ECONOMICS 1 What is Macroeconomics? Macroeconomics is the study of the large economy as a whole. It is the study of the big picture. Instead of analyzing one consumer, we analyze everyone. Instead
MACRO ECONOMICS 1 What is Macroeconomics? Macroeconomics is the study of the large economy as a whole. It is the study of the big picture. Instead of analyzing one consumer, we analyze everyone. Instead
NATIONAL INCOME AND RELATED AGGREGATES
 NATIONAL INCOME AND RELATED AGGREGATES The modern concept of National Income is more dynamic in the content than earlier concepts. The National Income Committee of India defined national income as: A National
NATIONAL INCOME AND RELATED AGGREGATES The modern concept of National Income is more dynamic in the content than earlier concepts. The National Income Committee of India defined national income as: A National
Inflation and Its Effect On Economics Development
 Inflation and Its Effect On Economics Development Ms. SEEMA YADAV Assistant Professor, Dept of Economics, S.K.Govt. College, Rewari. Abstract Inflation is the burning issue for the economic development
Inflation and Its Effect On Economics Development Ms. SEEMA YADAV Assistant Professor, Dept of Economics, S.K.Govt. College, Rewari. Abstract Inflation is the burning issue for the economic development
Unemployment and Inflation
 Unemployment and Inflation By A. V. Vedpuriswar October 15, 2016 Inflation This refers to the phenomenon by which the price level rises and money loses value. There are two kinds of inflation: Demand pull
Unemployment and Inflation By A. V. Vedpuriswar October 15, 2016 Inflation This refers to the phenomenon by which the price level rises and money loses value. There are two kinds of inflation: Demand pull
Full file at
 ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS Problems and/or Essay Questions: CHAPTER 2: MEASUREMENT OF MACROECONOMIC VARIABLES 1. What impact do you think that the movement of women from working in the household to working in
ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS Problems and/or Essay Questions: CHAPTER 2: MEASUREMENT OF MACROECONOMIC VARIABLES 1. What impact do you think that the movement of women from working in the household to working in
India s New GDP Series : Everything You Need To Know
 India s New GDP Series 2011-12: Everything You Need To Know India has shifted to a new GDP series. The organisation responsible for calculating national income CSO (Central Statistical Organisation) adopted
India s New GDP Series 2011-12: Everything You Need To Know India has shifted to a new GDP series. The organisation responsible for calculating national income CSO (Central Statistical Organisation) adopted
PART EIGHT: THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS. Measuring A Nation s Income
 ECON 102 Chapter 22 1 PART EIGHT: THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS Measuring A Nation s Income Chapter 23 What did we learn until now? In the first semester we covered microeconomics Microeconomics is the study
ECON 102 Chapter 22 1 PART EIGHT: THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS Measuring A Nation s Income Chapter 23 What did we learn until now? In the first semester we covered microeconomics Microeconomics is the study
CHAPTER 2: MEASUREMENT OF MACROECONOMIC VARIABLES
 Additional Questions Problems and/or essay questions: CHAPTER 2: MEASUREMENT OF MACROECONOMIC VARIABLES 1. What impact do you think that the movement of women from working in the household to working in
Additional Questions Problems and/or essay questions: CHAPTER 2: MEASUREMENT OF MACROECONOMIC VARIABLES 1. What impact do you think that the movement of women from working in the household to working in
Adam Smith Aggregate monetary resources Automatic stabilisers Autonomous change Autonomous expenditure multiplier Balance of payments
 Glossary Adam Smith (1723 1790) Regarded as the father of modern Economics. Author of Wealth of Nations. Aggregate monetary resources Broad money without time deposits of post office savings organisation
Glossary Adam Smith (1723 1790) Regarded as the father of modern Economics. Author of Wealth of Nations. Aggregate monetary resources Broad money without time deposits of post office savings organisation
2.1 Economic activity The level of overall economic activity
 2.1 Economic activity The level of overall economic activity Learning Outcomes Describe, using a diagram, the circular flow of income between households and firms in a closed economy with no government.
2.1 Economic activity The level of overall economic activity Learning Outcomes Describe, using a diagram, the circular flow of income between households and firms in a closed economy with no government.
Macro Economics & National Income Accounting. Samir K Mahajan
 Macro Economics & National Income Accounting MACROECONOMICS (Ragner Frisch ) Macroeconomics looks at the economy as an organic whole. Macroeconomics studies economic aggregates such as: total output, total
Macro Economics & National Income Accounting MACROECONOMICS (Ragner Frisch ) Macroeconomics looks at the economy as an organic whole. Macroeconomics studies economic aggregates such as: total output, total
Distance Learning Programme. IAS Prelims INDIAN ECONOMY
 Distance Learning Programme IAS Prelims INDIAN ECONOMY CONTENTS 1. Introduction to Economics 5-11 2. Concepts of National Income 12-20 3. Human Development 21-30 4. Poverty, Unemployment & Inequality 31-49
Distance Learning Programme IAS Prelims INDIAN ECONOMY CONTENTS 1. Introduction to Economics 5-11 2. Concepts of National Income 12-20 3. Human Development 21-30 4. Poverty, Unemployment & Inequality 31-49
NATIONAL ACCOUNTING. Government Sector
 NATIONAL ACCOUNTING Three different methods that must provide same result. 1) Expenditure (final G+S) 2) Income (adding factor incomes paid; gross operating surplus) 3) Value added (value added onto intermediate
NATIONAL ACCOUNTING Three different methods that must provide same result. 1) Expenditure (final G+S) 2) Income (adding factor incomes paid; gross operating surplus) 3) Value added (value added onto intermediate
SSEMA1 The student will illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. a. Explain that overall levels of income, employment, and prices
 SSEMA1 The student will illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. a. Explain that overall levels of income, employment, and prices are determined by the spending and production decisions
SSEMA1 The student will illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. a. Explain that overall levels of income, employment, and prices are determined by the spending and production decisions
MACROECONOMICS ESSENTIALS FOR CIVIL SERVICE EXAMINATIONS
 2018 WWW.OBJECTIVEIAS.IN MACROECONOMICS ESSENTIALS FOR CIVIL SERVICE EXAMINATIONS Special Features: 1. Detailed Explanation of Each Concept 2. Important Key Words at the end of Each Unit 3. Check your
2018 WWW.OBJECTIVEIAS.IN MACROECONOMICS ESSENTIALS FOR CIVIL SERVICE EXAMINATIONS Special Features: 1. Detailed Explanation of Each Concept 2. Important Key Words at the end of Each Unit 3. Check your
 Six Marks Questions (6 M) 1. Explain the determinants of supply? 2. Explain the relationship between Total Revenue and marginal Revenue using a Schedule and diagram? ********** UNIT IV: FORMS OF MARKET
Six Marks Questions (6 M) 1. Explain the determinants of supply? 2. Explain the relationship between Total Revenue and marginal Revenue using a Schedule and diagram? ********** UNIT IV: FORMS OF MARKET
01 Measuring a Nation s Income Econ 111
 01 Measuring a Nation s Income Econ 111 Measuring a Nation s Income (Chapter 10) Macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole. Its goal is to explain the economic changes that affect many households,
01 Measuring a Nation s Income Econ 111 Measuring a Nation s Income (Chapter 10) Macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole. Its goal is to explain the economic changes that affect many households,
ECO 209Y MACROECONOMIC THEORY AND POLICY LECTURE 2: NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING
 ECO 209Y MACROECONOMIC THEORY AND POLICY LECTURE 2: NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING Gustavo Indart Slide1 GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of all final goods and services produced
ECO 209Y MACROECONOMIC THEORY AND POLICY LECTURE 2: NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING Gustavo Indart Slide1 GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of all final goods and services produced
2/14/2008. The circular flow of goods and incomes. firms and households. goods markets. Goods and services. real flows: goods and services
 The circular flow of income Chapter 22 Introduction to Macroeconomics Economics, 4 th edition Stiglitz & Walsh firms and households goods markets real flows: goods and services The Economic Problem Goods
The circular flow of income Chapter 22 Introduction to Macroeconomics Economics, 4 th edition Stiglitz & Walsh firms and households goods markets real flows: goods and services The Economic Problem Goods
UNIT 6 NATIONAL INCOME POINTS TO REMEMBER
 1 COMPREHENSIVE COMMERCE UNIT 6 NATIONAL INCOME POINTS TO REMEMBER Good : In economics a good is defined as any physical object, natural or man-made, that could command a price in the market. Consumption
1 COMPREHENSIVE COMMERCE UNIT 6 NATIONAL INCOME POINTS TO REMEMBER Good : In economics a good is defined as any physical object, natural or man-made, that could command a price in the market. Consumption
Class-12 NATIONAL INCOME What is National Income? 1. Concept and Meaning of National Income
 Class-12 NATIONAL INCOME What is National Income? 1. Concept and Meaning of National Income National Income is a measure of the total flow of earning of the factor-owners through the production of goods
Class-12 NATIONAL INCOME What is National Income? 1. Concept and Meaning of National Income National Income is a measure of the total flow of earning of the factor-owners through the production of goods
 UNIT 6 NATIONAL INCOME POINTS TO REMEMBER Good : In economics a good is defined as any physical object, natural or man-made, that could command a price in the market. Consumption Goods : Those goods which
UNIT 6 NATIONAL INCOME POINTS TO REMEMBER Good : In economics a good is defined as any physical object, natural or man-made, that could command a price in the market. Consumption Goods : Those goods which
Unemployment Rate = 1. A large number of economic statistics are released regularly. These include the following:
 CHAPTER The Data of Macroeconomics Questions for Review 1. GDP measures the total income earned from the production of the new final goods and services in the economy, and it measures the total expenditures
CHAPTER The Data of Macroeconomics Questions for Review 1. GDP measures the total income earned from the production of the new final goods and services in the economy, and it measures the total expenditures
Principles of Macroeconomics
 Principles of Macroeconomics Academic Program: MSc in Banking and Finance Semester: Spring 2012/13 Instructor: Dr. Nikolaos I. Papanikolaou Office: Luxembourg School of Finance, KB2-E02-21 Phone: (00352)
Principles of Macroeconomics Academic Program: MSc in Banking and Finance Semester: Spring 2012/13 Instructor: Dr. Nikolaos I. Papanikolaou Office: Luxembourg School of Finance, KB2-E02-21 Phone: (00352)
We use GDP to compare different economies or to track the same economy over time.
 Lecture Notes ECON 1A: Principles of Macroeconomics Chapter 5 - Introduction to Macroeconomics Introduction Macroeconomics looks at the big picture: Demand for: Average price of: Consumption by: Investment
Lecture Notes ECON 1A: Principles of Macroeconomics Chapter 5 - Introduction to Macroeconomics Introduction Macroeconomics looks at the big picture: Demand for: Average price of: Consumption by: Investment
Unemployment Rate = 1. A large number of economic statistics are released regularly. These include the following:
 CHAPTER The Data of Macroeconomics Questions for Review 1. GDP measures the total income earned from the production of the new final goods and services in the economy, and it measures the total expenditures
CHAPTER The Data of Macroeconomics Questions for Review 1. GDP measures the total income earned from the production of the new final goods and services in the economy, and it measures the total expenditures
Macroeconomic Theory and Policy
 ECO 209Y Macroeconomic Theory and Policy Lecture 2: National Income Accounting Gustavo Indart Slide1 Gross Domestic Product Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of all final goods and services produced
ECO 209Y Macroeconomic Theory and Policy Lecture 2: National Income Accounting Gustavo Indart Slide1 Gross Domestic Product Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of all final goods and services produced
macro macroeconomics The Data of Macroeconomics N. Gregory Mankiw CHAPTER TWO 6 th edition
 macro CHAPTER TWO The Data of Macroeconomics macroeconomics 6 th edition N. Gregory Mankiw Learning objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) the Consumer Price Index
macro CHAPTER TWO The Data of Macroeconomics macroeconomics 6 th edition N. Gregory Mankiw Learning objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) the Consumer Price Index
Lecture notes 1 Macroeconomic data and history Facts to explain
 Kevin Clinton Winter 2005 Lecture notes 1 Macroeconomic data and history Facts to explain 1. Facts, theory, and policy In macroeconomics we deal with the big picture i.e. major aggregates in the economy.
Kevin Clinton Winter 2005 Lecture notes 1 Macroeconomic data and history Facts to explain 1. Facts, theory, and policy In macroeconomics we deal with the big picture i.e. major aggregates in the economy.
Unit 5 Notes. National Economic Performance
 Unit 5 Notes National Economic Performance Economic Indicators Economic Indicators are statistics that economists use to determine the health of a nation s economy. We are going to focus on three statistics
Unit 5 Notes National Economic Performance Economic Indicators Economic Indicators are statistics that economists use to determine the health of a nation s economy. We are going to focus on three statistics
Unit 6 Measuring and Monitoring Economics (Ch 12 and 13)
 Unit 6 Measuring and Monitoring Economics (Ch 12 and 13) -Macroeconomics 0 & Microeconomics- Government tries to prevent free enterprise from having wild swings in economic behavior. Microeconomics - analyzes
Unit 6 Measuring and Monitoring Economics (Ch 12 and 13) -Macroeconomics 0 & Microeconomics- Government tries to prevent free enterprise from having wild swings in economic behavior. Microeconomics - analyzes
ECF2331 Final Revision
 Table of Contents Week 1 Introduction to Macroeconomics... 5 What Macroeconomics is about... 5 Macroeconomics 5 Issues addressed by macroeconomists 5 What Macroeconomists Do... 5 Macro Research 5 Develop
Table of Contents Week 1 Introduction to Macroeconomics... 5 What Macroeconomics is about... 5 Macroeconomics 5 Issues addressed by macroeconomists 5 What Macroeconomists Do... 5 Macro Research 5 Develop
ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics. Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics
 ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics IN THIS CHAPTER, YOU WILL LEARN: the meaning and measurement of the most important macroeconomic statistics: gross domestic product
ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics IN THIS CHAPTER, YOU WILL LEARN: the meaning and measurement of the most important macroeconomic statistics: gross domestic product
Chapter 5: Production, Income and Employment
 Chapter 5: Production, Income and Employment We will take our first look at production and employment, focusing on two key variables: Gross Domestic Product and Unemployment Rate The nation s Gross Domestic
Chapter 5: Production, Income and Employment We will take our first look at production and employment, focusing on two key variables: Gross Domestic Product and Unemployment Rate The nation s Gross Domestic
Interview Preparation Lecture. Venue: Career Launcher Tambaram Centre Date: 26 th January, 2018
 Interview Preparation Lecture Venue: Career Launcher Tambaram Centre Date: 26 th January, 2018 Session One Duration: 1.5 hours What to expect from B-schools & what B-schools expects from you Why Economics??
Interview Preparation Lecture Venue: Career Launcher Tambaram Centre Date: 26 th January, 2018 Session One Duration: 1.5 hours What to expect from B-schools & what B-schools expects from you Why Economics??
Week 1. H1 Notes ECON10003
 Week 1 Some output produced by the government is free. Education is a classic example. This is still viewed as a service and valued at the cost of production which is primarily the salary of the workers
Week 1 Some output produced by the government is free. Education is a classic example. This is still viewed as a service and valued at the cost of production which is primarily the salary of the workers
GEORGIA PERFORMANCE STANDARDS. Macroeconomics
 GEORGIA PERFORMANCE STANDARDS Macroeconomics GEORGIA PERFORMANCE STANDARDS INTERNATIONAL ECONOMICS Macroeconomic Concepts SSEMA1 The student will illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured.
GEORGIA PERFORMANCE STANDARDS Macroeconomics GEORGIA PERFORMANCE STANDARDS INTERNATIONAL ECONOMICS Macroeconomic Concepts SSEMA1 The student will illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured.
ECONOMICS SOLUTION BOOK 2ND PUC. Unit 8. Part A
 Unit 8 Part A I. Choose the correct answer (each question carries 1 mark) 1. The study of National Income is related to: a) Micro economics b) Macro Economics c) Both Micro and Macro d) None of the above
Unit 8 Part A I. Choose the correct answer (each question carries 1 mark) 1. The study of National Income is related to: a) Micro economics b) Macro Economics c) Both Micro and Macro d) None of the above
Assignment 1 Deadline: September 23, 2004
 ECN 204 Introductory Macroeconomics Instructor: Sharif F. Khan Department of Economics Ryerson University Fall 2005 Assignment 1 Deadline: September 23, 2004 Part A Multiple-Choice Questions [30 marks]
ECN 204 Introductory Macroeconomics Instructor: Sharif F. Khan Department of Economics Ryerson University Fall 2005 Assignment 1 Deadline: September 23, 2004 Part A Multiple-Choice Questions [30 marks]
Consequences of Business Fluctuations
 Aggregate Output Consequences of Business Fluctuations Parts of Chapter 14 + Other Issues Discussion Topics Fluctuations in business activity Consequences of business fluctuations Macroeconomic policy
Aggregate Output Consequences of Business Fluctuations Parts of Chapter 14 + Other Issues Discussion Topics Fluctuations in business activity Consequences of business fluctuations Macroeconomic policy
Unit 7 Measuring the Economy
 Unit 7 Measuring the Economy - Study Guide - Answer, Explain and define the following: 1) GNP 2) GDP 3) Dept. of Commerce 4) Intermediate goods 5) Disposable personal income 6) Contraction 7) Recession
Unit 7 Measuring the Economy - Study Guide - Answer, Explain and define the following: 1) GNP 2) GDP 3) Dept. of Commerce 4) Intermediate goods 5) Disposable personal income 6) Contraction 7) Recession
Date: Block # Economics Guided Notes Unit Four Day #2 CPI, Unemployment and the Business Cycle
 Name: Date: Block # Economics Guided Notes Unit Four Day #2 CPI, Unemployment and the Business Cycle Directions Activity listen and view today s PowerPoint lesson. As you view each slide, write in any
Name: Date: Block # Economics Guided Notes Unit Four Day #2 CPI, Unemployment and the Business Cycle Directions Activity listen and view today s PowerPoint lesson. As you view each slide, write in any
1. A large number of economic statistics are released regularly. These include the following:
 CHAPTER The Data of Macroeconomics Questions for Review 1. GDP measures the total income earned from the production of the new final goods and services in the economy, and it measures the total expenditures
CHAPTER The Data of Macroeconomics Questions for Review 1. GDP measures the total income earned from the production of the new final goods and services in the economy, and it measures the total expenditures
Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics
 Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics slide 0 Learning Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) the Consumer Price Index (CPI) the Unemployment Rate slide 1 GROSS DOMESTIC
Chapter 2 The Data of Macroeconomics slide 0 Learning Objectives In this chapter, you will learn about: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) the Consumer Price Index (CPI) the Unemployment Rate slide 1 GROSS DOMESTIC
Economics Unit Four. Macroeconomics
 Economics Unit Four Macroeconomics Macroeconomics Macroeconomics is the study of the whole economy together the aggregated spending, saving, and investing decisions of all consumers and businesses describes
Economics Unit Four Macroeconomics Macroeconomics Macroeconomics is the study of the whole economy together the aggregated spending, saving, and investing decisions of all consumers and businesses describes
INFLATION SHYAM S KAGGOD
 INFLATION BY SHYAM S KAGGOD INTRODUCTION Inflation is the persistent increase in the price levels of basket of commodities Inflation is nothing more than a sharp upward rise in price level. Too much money
INFLATION BY SHYAM S KAGGOD INTRODUCTION Inflation is the persistent increase in the price levels of basket of commodities Inflation is nothing more than a sharp upward rise in price level. Too much money
What is Macroeconomics?
 Lecture 1-1 What is Macroeconomics? 1. Macroeconomics Macroeconomics: the study of the major economic totals (aggregates). Issues involving the overall economic performance of the nation: do people find
Lecture 1-1 What is Macroeconomics? 1. Macroeconomics Macroeconomics: the study of the major economic totals (aggregates). Issues involving the overall economic performance of the nation: do people find
Economics Unit 3 Summary
 SSEMA1 Illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. Economic activity derives from the sectors of the economy explored in the fundamentals and microeconomics units. Individuals, businesses,
SSEMA1 Illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. Economic activity derives from the sectors of the economy explored in the fundamentals and microeconomics units. Individuals, businesses,
Part V: Introduction to Macroeconomics 19. The Wealth of Nations: Defining and
 Part V: Introduction to s 19. 20. Aggregate Incomes 1 / 56 Chapter 19 Defining and 2017.8.9. 2 / 56 1 2 3 4 3 / 56 Chapter 19 Q: In the United States, what is the total market value of annual economic
Part V: Introduction to s 19. 20. Aggregate Incomes 1 / 56 Chapter 19 Defining and 2017.8.9. 2 / 56 1 2 3 4 3 / 56 Chapter 19 Q: In the United States, what is the total market value of annual economic
CHAPTER 14 ECONOMIC INSTABILITY
 CHAPTER 14 ECONOMIC INSTABILITY Business Cycles Economic growth is something that is beneficial to almost everyone Sometimes though, economic growth is interrupted by business cycles largely systematic
CHAPTER 14 ECONOMIC INSTABILITY Business Cycles Economic growth is something that is beneficial to almost everyone Sometimes though, economic growth is interrupted by business cycles largely systematic
An empirical study on the causes and impacts on inflation in India
 2017; 3(4): 42-46 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2017; 3(4): 42-46 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 09-02-2017 Accepted: 10-03-2017 Monica Mahbubani Vignesh Chandramouli
2017; 3(4): 42-46 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2017; 3(4): 42-46 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 09-02-2017 Accepted: 10-03-2017 Monica Mahbubani Vignesh Chandramouli
Chapter 2: The Data of Macroeconomics
 Chapter 2: The Data of Macroeconomics 0 IN THIS CHAPTER, YOU WILL LEARN: the meaning and measurement of the most important macroeconomic statistics:! gross domestic product (GDP)! the consumer price index
Chapter 2: The Data of Macroeconomics 0 IN THIS CHAPTER, YOU WILL LEARN: the meaning and measurement of the most important macroeconomic statistics:! gross domestic product (GDP)! the consumer price index
Economics is the study of decision making
 TOPIC 1 - INTRODUCTION TO THE GLOBAL ECONOMY WHAT IS ECONOMICS Economics is the study of decision making Every time we take a decision, we are choosing between at least two possibilities How do you take
TOPIC 1 - INTRODUCTION TO THE GLOBAL ECONOMY WHAT IS ECONOMICS Economics is the study of decision making Every time we take a decision, we are choosing between at least two possibilities How do you take
Chapter 2: The Data of Macroeconomics*
 Chapter 2: The Data of Macroeconomics 1/40 *Slides based on Ron Cronovich's slides, adjusted by Marcel Bluhm for lecture in Macroeconomics at the Wang Yanan Institute for Studies in Economics at Xiamen
Chapter 2: The Data of Macroeconomics 1/40 *Slides based on Ron Cronovich's slides, adjusted by Marcel Bluhm for lecture in Macroeconomics at the Wang Yanan Institute for Studies in Economics at Xiamen
Introduction. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives. Chapter 7. Explain how the U.S. government calculates the official unemployment rate
 Chapter 7 The Macroeconomy:, Inflation, and Deflation Introduction Why is it that the responsibility for announcing the start of economic contractions and expansions does not rest with elected officials?
Chapter 7 The Macroeconomy:, Inflation, and Deflation Introduction Why is it that the responsibility for announcing the start of economic contractions and expansions does not rest with elected officials?
Dunbar s Big Review Sheet AP Macroeconomics Exam Content Area [Hubbard Textbook pages] (percentage coverage on AP Macroeconomics Exam) I.
![Dunbar s Big Review Sheet AP Macroeconomics Exam Content Area [Hubbard Textbook pages] (percentage coverage on AP Macroeconomics Exam) I. Dunbar s Big Review Sheet AP Macroeconomics Exam Content Area [Hubbard Textbook pages] (percentage coverage on AP Macroeconomics Exam) I.](/thumbs/77/76534172.jpg) Dunbar s Big Review Sheet AP Macroeconomics Exam Content Area [Hubbard Textbook pages] (percentage coverage on AP Macroeconomics Exam) I. Basic Economic Concepts (8-12%) Three Fundamental Questions [8]:
Dunbar s Big Review Sheet AP Macroeconomics Exam Content Area [Hubbard Textbook pages] (percentage coverage on AP Macroeconomics Exam) I. Basic Economic Concepts (8-12%) Three Fundamental Questions [8]:
Introduction to Economics
 Introduction to Economics Topic 6 (Macroeconomics): Measuring aggregate production and income Coordinator lecturer: Levi Pérez (lperez@uniovi.es) University of Oviedo (Spain, ES EU) Overview 1. Basic macroeconomic
Introduction to Economics Topic 6 (Macroeconomics): Measuring aggregate production and income Coordinator lecturer: Levi Pérez (lperez@uniovi.es) University of Oviedo (Spain, ES EU) Overview 1. Basic macroeconomic
Subject: Economics. Grade / Group: 1201/1202. Teacher s Name: Ana Isabel Almeida L. Semester Examination or Guide: Date:
 Westhill Institute Vestigia Nulla Retrorsum Department of Curriculum and Academic Programs Subject: Economics Grade / Group: 1201/1202 Teacher s Name: Ana Isabel Almeida L. Semester Examination or Guide:
Westhill Institute Vestigia Nulla Retrorsum Department of Curriculum and Academic Programs Subject: Economics Grade / Group: 1201/1202 Teacher s Name: Ana Isabel Almeida L. Semester Examination or Guide:
ECON 201. The Business Cycle. Business Cycle 4 phases 10/1/2009. Chapter 6 Business Cycles, Unemployment, & Inflation
 ECON 201 Chapter 6 Business Cycles, Unemployment, & Inflation The Business Cycle The U.S. has experienced economic instability associated with business cycles. Business Cycles alternating rises and declines
ECON 201 Chapter 6 Business Cycles, Unemployment, & Inflation The Business Cycle The U.S. has experienced economic instability associated with business cycles. Business Cycles alternating rises and declines
Unit 6 Measuring the Economy
 Unit 6 Measuring the Economy - Study Guide - Answer, Explain and define the following: 1) GNP 2) GDP 3) Dept. of Commerce 4) Intermediate goods 5) Disposable personal income 6) Contraction 7) Recession
Unit 6 Measuring the Economy - Study Guide - Answer, Explain and define the following: 1) GNP 2) GDP 3) Dept. of Commerce 4) Intermediate goods 5) Disposable personal income 6) Contraction 7) Recession
What is National Income? National income measures the total value of goods and services produced within the economy over a period of time.
 National Income What is National Income? National income measures the total value of goods and services produced within the economy over a period of time. Why is national income important? Measuring the
National Income What is National Income? National income measures the total value of goods and services produced within the economy over a period of time. Why is national income important? Measuring the
SYLLABUS UNIT I UNIT II UNIT III UNIT IV UNIT V. B.Com I YEAR (Hons.) Subject MACRO ECONOMICS
 SYLLABUS B.Com I YEAR (Hons.) Subject MACRO ECONOMICS UNIT I UNIT II UNIT III UNIT IV UNIT V Macro economics concept, nature, importance, limitations, difference between micro and macro economics, significance.
SYLLABUS B.Com I YEAR (Hons.) Subject MACRO ECONOMICS UNIT I UNIT II UNIT III UNIT IV UNIT V Macro economics concept, nature, importance, limitations, difference between micro and macro economics, significance.
MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC GROWTH
 21 MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC GROWTH GDP Defined GDP or gross domestic product is the market value of all final goods and services produced in a country in a given time period. This definition has four
21 MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC GROWTH GDP Defined GDP or gross domestic product is the market value of all final goods and services produced in a country in a given time period. This definition has four
Indian Economy. GDP growth slowed down but remained above the comfortable 7% Manufacturing GVAbp
 Indian Economy Economic Growth GDP growth slowed down but remained above the comfortable 7% Domestic economy witnessed 7.1% GDP growth during the first quarter (Apr - Jun) of fiscal 2016-17 (Q1FY17) as
Indian Economy Economic Growth GDP growth slowed down but remained above the comfortable 7% Domestic economy witnessed 7.1% GDP growth during the first quarter (Apr - Jun) of fiscal 2016-17 (Q1FY17) as
ECO403 - Macroeconomics Faqs For Midterm Exam Preparation Spring 2013
 ECO403 - Macroeconomics Faqs For Midterm Exam Preparation Spring 2013 FAQs Question: 53-How the consumer can get the optimal level of satisfaction? Answer: A point where the indifference curve is tangent
ECO403 - Macroeconomics Faqs For Midterm Exam Preparation Spring 2013 FAQs Question: 53-How the consumer can get the optimal level of satisfaction? Answer: A point where the indifference curve is tangent
NATIONAL ECONOMIC ACCOUNTS 2010 (Provisional Estimates)
 REPUBLIC OF CYPRUS NATIONAL ECONOMIC ACCOUNTS 2010 (Provisional Estimates) STATISTICAL SERVICE National Accounts Statistics Series II Report No. 27 Obtainable from the Printing Office of the Republic of
REPUBLIC OF CYPRUS NATIONAL ECONOMIC ACCOUNTS 2010 (Provisional Estimates) STATISTICAL SERVICE National Accounts Statistics Series II Report No. 27 Obtainable from the Printing Office of the Republic of
Macroeconomic Analysis Econ 6022 Level I
 1 / 37 Macroeconomic Analysis Econ 6022 Level I Lecture 2 Fall, 2011 2 / 37 Overview Let s start our tour in macroeconomics by introducing a few building blocks, which will be used repeatedly later on.
1 / 37 Macroeconomic Analysis Econ 6022 Level I Lecture 2 Fall, 2011 2 / 37 Overview Let s start our tour in macroeconomics by introducing a few building blocks, which will be used repeatedly later on.
Measuring the Nation s Income and Growth
 Measuring the Nation s Income and Growth We will examine: GNP vs GDP income and expenditure approaches to measurement real versus Nominal GDP potential GDP what GDP does not measure Art Lightstone Gross
Measuring the Nation s Income and Growth We will examine: GNP vs GDP income and expenditure approaches to measurement real versus Nominal GDP potential GDP what GDP does not measure Art Lightstone Gross
** Review ** For Test - 3
 ** Review ** For Test - 3 1. Gross domestic product or GDP is: A) the total dollar value intermediate goods and services produced in the economy in a given time period. B) the total dollar value of wages
** Review ** For Test - 3 1. Gross domestic product or GDP is: A) the total dollar value intermediate goods and services produced in the economy in a given time period. B) the total dollar value of wages
ECONOMICS EXAMINATION OBJECTIVES
 ECONOMICS EXAMINATION OBJECTIVES The following objectives of the examination are to test whether the candidates have acquired a basic understanding of economics with special emphasis on Hong Kong conditions
ECONOMICS EXAMINATION OBJECTIVES The following objectives of the examination are to test whether the candidates have acquired a basic understanding of economics with special emphasis on Hong Kong conditions
National Economic Performance
 National Economic Performance Andrew B. Abel January 20, 1999 A. Abel: National Economic Performance 1 Overview I. Measuring Economic Activity II. Fundamentals of National Income Accounting III. Determinants
National Economic Performance Andrew B. Abel January 20, 1999 A. Abel: National Economic Performance 1 Overview I. Measuring Economic Activity II. Fundamentals of National Income Accounting III. Determinants
1 of 33. Measuring a Nation s Production and Income. 2 of 33
 1 of 33 2 of 33 The methods our government uses today to measure our economy, which we will study in this chapter, were developed in the 1930s. P R E P A R E D B Y FERNANDO QUIJANO, YVONN QUIJANO, AND
1 of 33 2 of 33 The methods our government uses today to measure our economy, which we will study in this chapter, were developed in the 1930s. P R E P A R E D B Y FERNANDO QUIJANO, YVONN QUIJANO, AND
MACROECONOMICS NATIONAL INCOME
 MACROECONOMICS Q. 1. Define intermediate goods. NATIONAL INCOME Q.2. Q.3. Q.4. State the meaning of consumption of fixed capital? State the meaning of injection in income flow, with the help of an example.
MACROECONOMICS Q. 1. Define intermediate goods. NATIONAL INCOME Q.2. Q.3. Q.4. State the meaning of consumption of fixed capital? State the meaning of injection in income flow, with the help of an example.
ECON 1102: MACROECONOMICS 1 Chapter 1: Measuring Macroeconomic Performance, Output and Prices
 ECON 1102: MACROECONOMICS 1 Chapter 1: Measuring Macroeconomic Performance, Output and Prices 1.1 Measuring Macroeconomic Performance 1. Rising Living Standards Economic growth is the tendency for output
ECON 1102: MACROECONOMICS 1 Chapter 1: Measuring Macroeconomic Performance, Output and Prices 1.1 Measuring Macroeconomic Performance 1. Rising Living Standards Economic growth is the tendency for output
SSC 260 : Introduction to Social Sciences : Economic Section
 SSC 260 : Introduction to Social Sciences : Economic Section Jaruwan Chontanawat Topic 2: Economic force in Daily life (II) : Introduction to Macroeconomics Outlines: Overview of Macroeconomics & Development
SSC 260 : Introduction to Social Sciences : Economic Section Jaruwan Chontanawat Topic 2: Economic force in Daily life (II) : Introduction to Macroeconomics Outlines: Overview of Macroeconomics & Development
PRESS NOTE ON QUARTERLY ESTIMATES OF GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT FOR THE THIRD QUARTER (OCTOBER-DECEMBER) OF CENTRAL STATISTICS OFFICE
 PRESS NOTE ON QUARTERLY ESTIMATES OF GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT FOR THE THIRD QUARTER (OCTOBER-DECEMBER) OF 2012-13 CENTRAL STATISTICS OFFICE MINISTRY OF STATISTICS AND PROGRAMME IMPLEMENTATION GOVERNMENT
PRESS NOTE ON QUARTERLY ESTIMATES OF GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT FOR THE THIRD QUARTER (OCTOBER-DECEMBER) OF 2012-13 CENTRAL STATISTICS OFFICE MINISTRY OF STATISTICS AND PROGRAMME IMPLEMENTATION GOVERNMENT
MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC GROWTH. Objectives. Gross Domestic Product. An Economic Barometer. Gross Domestic Product. Gross Domestic Product CHAPTER
 MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC CHAPTER GROWTH Objectives After studying this chapter, you will able to Define GDP and use the circular flow model to explain why GDP equals aggregate expenditure and aggregate
MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC CHAPTER GROWTH Objectives After studying this chapter, you will able to Define GDP and use the circular flow model to explain why GDP equals aggregate expenditure and aggregate
THE ASIAN SCHOOL, DEHRADUN
 CLASS 12 SUBJECT Economics CHAPTER- 1 Micro (Introduction to Micro Economics MM-30 Q1. Define the following : 1X4 a) PPC b) MRT c) MOC d) Resource Q2. State the causes of Economic problem. 1 Q3. What is
CLASS 12 SUBJECT Economics CHAPTER- 1 Micro (Introduction to Micro Economics MM-30 Q1. Define the following : 1X4 a) PPC b) MRT c) MOC d) Resource Q2. State the causes of Economic problem. 1 Q3. What is
Gross entire; whole Domestic within a country s borders Product good or service
 OBJECTIVES Identify National Income and Product Accounts (NIPA). Explain how gross domestic product (GDP) is calculated. Explain the difference between nominal GDP and real GDP. List the main limitations
OBJECTIVES Identify National Income and Product Accounts (NIPA). Explain how gross domestic product (GDP) is calculated. Explain the difference between nominal GDP and real GDP. List the main limitations
Introduction to Macroeconomics
 Week 1: General notes: o Macroeconomics studies the aggregate impact of individual decisions. Microeconomics studies decision-making by individual economic agents o In the study of macroeconomics, an economist
Week 1: General notes: o Macroeconomics studies the aggregate impact of individual decisions. Microeconomics studies decision-making by individual economic agents o In the study of macroeconomics, an economist
Answer Key Economics Class 12 (Pre Board)
 Answer Key Economics Class 2 (Pre Board) Part A (Micro Economics). Which of the following is not an assumption of the theory of demand based on analysis of indifference curve? c) Constant marginal utility
Answer Key Economics Class 2 (Pre Board) Part A (Micro Economics). Which of the following is not an assumption of the theory of demand based on analysis of indifference curve? c) Constant marginal utility
BRICS Academy MINI GRAND TEST 9. TIME: 50 Min NO. QUESTION : 50 MARKS: 100 / Neg.M s : 1/3. released by the CSO with a time lag of:
 BANGALORE HYDERABAD DATE: 01-03-2018 SUBJECT: ECONOMY LEVEL - 1 MINI GRAND TEST 9 TIME: 50 Min NO. QUESTION : 50 MARKS: 100 / Neg.M s : 1/3 1. The Quarterly and Annual GDP data is 5. Consider the following
BANGALORE HYDERABAD DATE: 01-03-2018 SUBJECT: ECONOMY LEVEL - 1 MINI GRAND TEST 9 TIME: 50 Min NO. QUESTION : 50 MARKS: 100 / Neg.M s : 1/3 1. The Quarterly and Annual GDP data is 5. Consider the following
PART 6 The macroeconomic environment
 PART 6 The macroeconomic environment 1 of 38 Economy s Income & Expenditure Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Measures the total income of everyone in the economy Measures the total expenditure on the economy
PART 6 The macroeconomic environment 1 of 38 Economy s Income & Expenditure Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Measures the total income of everyone in the economy Measures the total expenditure on the economy
GLS UNIVERSITY, Faculty of Commerce B.Com Semester-II, Macro Economics
 GLS UNIVERSITY, Faculty of Commerce B.Com Semester-II, Macro Economics Unit I National Income 1. National income includes contribution of a) Agriculture b) Industry c) Services d) All of the above 2. Which
GLS UNIVERSITY, Faculty of Commerce B.Com Semester-II, Macro Economics Unit I National Income 1. National income includes contribution of a) Agriculture b) Industry c) Services d) All of the above 2. Which
Measuring a Nation s Income
 Measuring a Nation s Income Microeconomics is the study of how individual households and firms make decisions and how they interact with one another in markets. Macroeconomics is the study of the economy
Measuring a Nation s Income Microeconomics is the study of how individual households and firms make decisions and how they interact with one another in markets. Macroeconomics is the study of the economy
Chapter 02 National Income Accounting
 Chapter 02 National Income Accounting Multiple Choice Questions 1. In calculating this year's GDP, national income accountants a. Include any increase in stock values b. Include an estimate for income
Chapter 02 National Income Accounting Multiple Choice Questions 1. In calculating this year's GDP, national income accountants a. Include any increase in stock values b. Include an estimate for income
What is Macroeconomics?
 Introduction ti to Macroeconomics MSc Induction Simon Hayley Simon.Hayley.1@city.ac.uk it What is Macroeconomics? Macroeconomics looks at the economy as a whole. It studies aggregate effects, such as:
Introduction ti to Macroeconomics MSc Induction Simon Hayley Simon.Hayley.1@city.ac.uk it What is Macroeconomics? Macroeconomics looks at the economy as a whole. It studies aggregate effects, such as:
A. unchanged decrease B. surplus decrease C. unchanged no change D. surplus increase E. unchanged increase A. A B. B C. C D. D E. E.
 AP Macroeconomics Test (Answers on last Page) 1. Which of the following correctly describes the components of Aggregate Demand? A. Consumption expenditures + Investment expenditures + Government expenditures
AP Macroeconomics Test (Answers on last Page) 1. Which of the following correctly describes the components of Aggregate Demand? A. Consumption expenditures + Investment expenditures + Government expenditures
MEASURING ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE PRODUCT MARKET
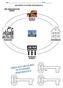 Name: Period THE CIRCULAR FLOW MODEL MEASURING ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE PRODUCT MARKET BUSINESSES HOUSEHOLDS RESOURCE MARKET 1. AKA: 2. 3. Additional Notes on Previous Page/Practice Workspace Quick Write Space
Name: Period THE CIRCULAR FLOW MODEL MEASURING ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE PRODUCT MARKET BUSINESSES HOUSEHOLDS RESOURCE MARKET 1. AKA: 2. 3. Additional Notes on Previous Page/Practice Workspace Quick Write Space
Irish Economic Environment. Contact Details. Office Hours: by appointment KB3-46
 Irish Economic Environment Dr. Stephen Kinsella & Ms. Claire Hurst Department of Economics University of Limerick http://stephenkinsella.net Contact Details Office Hours: by appointment KB3-46 stephen.kinsella@ul.ie/
Irish Economic Environment Dr. Stephen Kinsella & Ms. Claire Hurst Department of Economics University of Limerick http://stephenkinsella.net Contact Details Office Hours: by appointment KB3-46 stephen.kinsella@ul.ie/
NATIONAL INCOME. be less than NDP FC. State the meaning of injection in income flow, with the help of an example.
 NATIONAL INCOME Q. 1. When will be NDP MP be less than NDP FC? Q.2. State the meaning of consumption of fixed capital? Q.3. State the meaning of injection in income flow, with the help of an example. Q.4.
NATIONAL INCOME Q. 1. When will be NDP MP be less than NDP FC? Q.2. State the meaning of consumption of fixed capital? Q.3. State the meaning of injection in income flow, with the help of an example. Q.4.
