Unit 5 Notes. National Economic Performance
|
|
|
- Brittney Fields
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit 5 Notes National Economic Performance
2 Economic Indicators Economic Indicators are statistics that economists use to determine the health of a nation s economy. We are going to focus on three statistics in this unit. Inflation Unemployment Gross Domestic Product
3 Inflation Inflation is defined as the increase in the general price level for goods and services over a period of time. When prices rise faster than income, buyers lose purchasing power.
4 Types of Inflation Demand-pull inflation - Occurs when consumers want to buy more goods than producers can supply. The Fed will try to create this to reduce unemployment. Cost-push inflation - Occurs when producers raise prices because input costs increase. Example: The price of a latte at Starbucks increases because the price of coffee beans increase.
5 Calculating the Inflation Rate The inflation rate is calculated by determining the change in the Consumer Price Index (CPI). The CPI is a statistical measure of the price of everything in a market basket of about 80,000 goods and services. Rate of Inflation = [CPI(new)-CPI(old)]/CPI(old)*100
6 Calculating the Inflation Rate The CPI for August 2013 is The CPI for August 2012 is Use the data above to calculate the inflation rate for the last 12 months.
7 Calculating the Inflation Rate = / = *100 = 1.52 Rate of inflation = 1.52 In plain English, prices went up an average of 1.52% in the last 12 months.
8 Patterns of Inflation Disinflation - Prices are rising, but at a decreasing rate. Hyperinflation - Prices are rising so rapidly (>50%) that they are out of control. Germany s inflation rate after WWI was over 300%. Deflation - The general level of prices is falling.
9 Calculating the Inflation Rate On a new sheet of paper, use the CPI data on page 342 to calculate the inflation rate in Use 2004 as CPI(old), and 2005 as CPI (new). Show your work. Turn in your work when you finish.
10 The Unemployment Rate Unemployment Rate - The percentage of the civilian labor force that is actively seeking work but is not employed. Unemployment Rate = unemployed/civilian labor force*100
11 The Civilian Labor Force Civilian Labor Force - The number of people aged 16 years and older that are employed or actively seeking employment. Those NOT in the civilian labor force: Armed Forces Retirees Institutionalized persons Students Disabled persons Stay-at-home parents Discouraged workers (people that have no job and have given up looking for a job.)
12 Types of Unemployment Frictional unemployment - temporary unemployment caused by the time required to move from one job to another Ex. Timmy is unemployed from the time he gets fired at Wendy s to the time he gets hired at Burger King. Seasonal unemployment - unemployment caused by a change in seasons Ex. Timmy, a construction worker, is unemployed during the winter.
13 Types of Unemployment Structural unemployment - unemployment caused by changes in the economy, such as change in consumer demand, globalization, or technology Timmy loses his job at the car wash; he is replaced by an automated car washer Cyclical unemployment - unemployment caused by changes in the business cycle Timmy loses his job during a recession; he gets re-hired when the economy recovers.
14 Gross Domestic Product (GDP) GDP is the total dollar value of all final goods and services produced in a country in a given year. Does not count intermediate goods. Does not count used goods. GDP is used to measure a nation s productivity. GDP per capita is used to compare the productivity of selected countries.
15 Gross Domestic Product (GDP) GDP = C+I+G+(X-M) C= Consumption -- household spending I = Investment -- business spending G = Government -- government spending (X-M) = Net Exports (Exports - Imports)
16 Gross Domestic Product (GDP) In the following table, list two expenditures for each GDP category: CONSUMPTION INVESTMENT GOVERNMENT NET EXPORTS
17 Measuring GDP Nominal GDP - measures total production in current year dollars Real GDP - measured total production in dollars, removing the effect of inflation GDP per capita - total production per person
18 October 30, 2013 Answer the following questions in complete sentences. Turn in this work by the end of the period. Page 345, #3 Page 362, #10, 12 Page 363, #23 (a,b,c) Page 445, #2 Work on Unit 5 Learning Guide if you finish early.
19 The Business Cycle GDP increases recovery or expansion GDP stops increasing (peak), and then... GDP decreases contraction or a recession recession - 2 consecutive quarters of negative GDP growth GDP stops decreasing (trough), and then... The cycle starts again
20 The Business Cycle G D P G r o w t h Wars are generally good for the economy. Productivity increases as the nation builds what is necessary to go to war. Recessions are indicated by two consecutive bars of negative (red) GDP growth.
21 Aggregate Supply Aggregate Supply - The total output a nation s firms are willing and able to produce, contingent on price. Aggregate Supply can be affected by: Weather changes Changes in the price of oil Technological changes
22 Aggregate Demand Aggregate Demand - The total amount of output purchased by all sectors of a nation s economy, contingent on price level. Aggregate demand can be affected by: Changes in household wealth Changes in consumer confidence Government policy
23 Changes in Aggregate Demand If aggregate demand increases, the aggregate demand curve will shift to the right. If aggregate demand increases: Prices will (increase/decrease). Unemployment will (increase/decrease).
24 Changes in Aggregate Demand If aggregate demand decrease, the aggreagate demand curve will shift to the left. If aggregate demand decreases: Prices will (increase/decrease). Unemployment will (increase/decrease).
25 Monetary/Fiscal Policies and AD Loose economic policy will cause aggregate demand (AD) to (increase/decrease). The purpose of loose economic policy is to reduce (unemployment/inflation). Tight economic policy will cause aggregate demand (AD) to (increase/decrease). The purpose of tight economic policy is to reduce (unemployment/inflation).
26 November 4, 2013 Finish and submit Unit 5 Learning Guide. Finish and submit questions assigned 10/30. Page 345, #3, Page 362, #10, 12, Page 363, #23 (a,b,c), Page 445, #2 Study for Unit 5 Test. Test is on Thursday.
The diagram above illustrates the pattern of: A) Wage movements over time B) Price level movements C) Economic growth patterns D) Business cycles
 Problem Set Econ 2013: Chapter 9: Business Cycles, Unemployment, and Inflation Name ID: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) 1) The
Problem Set Econ 2013: Chapter 9: Business Cycles, Unemployment, and Inflation Name ID: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) 1) The
Success is the sum of small efforts, repeated day in and day out. Robert Collier Test Yourself - Business Cycles and Unemployment
 Success is the sum of small efforts, repeated day in and day out. Robert Collier Test Yourself - Business Cycles and Unemployment What is a business cycle? A business cycle is alternating periods of economic
Success is the sum of small efforts, repeated day in and day out. Robert Collier Test Yourself - Business Cycles and Unemployment What is a business cycle? A business cycle is alternating periods of economic
The value of goods and services produced in a nation in a given time period is the definition of.
 Unit 4 Review The value of goods and services produced in a nation in a given time period is the definition of. GDP (gross domestic product) Which type of unemployment decreases during a recession? Which
Unit 4 Review The value of goods and services produced in a nation in a given time period is the definition of. GDP (gross domestic product) Which type of unemployment decreases during a recession? Which
Unit 6 Measuring and Monitoring Economics (Ch 12 and 13)
 Unit 6 Measuring and Monitoring Economics (Ch 12 and 13) -Macroeconomics 0 & Microeconomics- Government tries to prevent free enterprise from having wild swings in economic behavior. Microeconomics - analyzes
Unit 6 Measuring and Monitoring Economics (Ch 12 and 13) -Macroeconomics 0 & Microeconomics- Government tries to prevent free enterprise from having wild swings in economic behavior. Microeconomics - analyzes
CHAPTER 14 ECONOMIC INSTABILITY
 CHAPTER 14 ECONOMIC INSTABILITY Business Cycles Economic growth is something that is beneficial to almost everyone Sometimes though, economic growth is interrupted by business cycles largely systematic
CHAPTER 14 ECONOMIC INSTABILITY Business Cycles Economic growth is something that is beneficial to almost everyone Sometimes though, economic growth is interrupted by business cycles largely systematic
McGraw-Hill/Irwin 2002 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights Reserved.
 The Business Cycle Macroeconomics The Great Depression was the springboard for modern macroeconomics. Macroeconomics Macroeconomics is the study of aggregate economic behavior, of the economy as a whole.
The Business Cycle Macroeconomics The Great Depression was the springboard for modern macroeconomics. Macroeconomics Macroeconomics is the study of aggregate economic behavior, of the economy as a whole.
GEORGIA PERFORMANCE STANDARDS. Macroeconomics
 GEORGIA PERFORMANCE STANDARDS Macroeconomics GEORGIA PERFORMANCE STANDARDS INTERNATIONAL ECONOMICS Macroeconomic Concepts SSEMA1 The student will illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured.
GEORGIA PERFORMANCE STANDARDS Macroeconomics GEORGIA PERFORMANCE STANDARDS INTERNATIONAL ECONOMICS Macroeconomic Concepts SSEMA1 The student will illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured.
Chapter Outline. Chapter 6 Every Macroeconomic Word You Have Ever Heard: Gross Domestic Product, Inflation, Unemployment, Recession and Depression
 Chapter 6 Every Macroeconomic Word You Have Ever Heard: Gross Domestic Product, Inflation, Unemployment, Recession and Depression Chapter Outline Measuring the Economy Real Gross Domestic Product and Why
Chapter 6 Every Macroeconomic Word You Have Ever Heard: Gross Domestic Product, Inflation, Unemployment, Recession and Depression Chapter Outline Measuring the Economy Real Gross Domestic Product and Why
Measuring the Economy. Measur
 Measuring the Economy Measur Economic indicators Economic indicators are statistics that help economists judge the health of an economy. They provide information about important aspects of the economy.
Measuring the Economy Measur Economic indicators Economic indicators are statistics that help economists judge the health of an economy. They provide information about important aspects of the economy.
Economics Spring Benchmark 2
 Directions: Read and answer each question carefully. Mark your answers on your bubble sheet. Do NOT write on exam. 1. What does the GDP, gross domestic product, measure? A) the amount of goods bought and
Directions: Read and answer each question carefully. Mark your answers on your bubble sheet. Do NOT write on exam. 1. What does the GDP, gross domestic product, measure? A) the amount of goods bought and
Name Economics: Unit Three Study Guide Unit One Standards
 Name Economics: Unit Three Study Guide Unit One Standards Macroeconomic Concepts: SSEMA1 Illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. a. Identify and describe the macroeconomic goals of
Name Economics: Unit Three Study Guide Unit One Standards Macroeconomic Concepts: SSEMA1 Illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. a. Identify and describe the macroeconomic goals of
Economics Unit Four. Macroeconomics
 Economics Unit Four Macroeconomics Macroeconomics Macroeconomics is the study of the whole economy together the aggregated spending, saving, and investing decisions of all consumers and businesses describes
Economics Unit Four Macroeconomics Macroeconomics Macroeconomics is the study of the whole economy together the aggregated spending, saving, and investing decisions of all consumers and businesses describes
Introduction to Economic Growth and Instability
 on C H A P T E R Introduction to Economic Growth and Instability 8-1 ECONOMIC GROWTH Economic Growth on 8-2 An increase in real GDP over some time period An increase in real GDP per capita over some time
on C H A P T E R Introduction to Economic Growth and Instability 8-1 ECONOMIC GROWTH Economic Growth on 8-2 An increase in real GDP over some time period An increase in real GDP per capita over some time
ECON 201. The Business Cycle. Business Cycle 4 phases 10/1/2009. Chapter 6 Business Cycles, Unemployment, & Inflation
 ECON 201 Chapter 6 Business Cycles, Unemployment, & Inflation The Business Cycle The U.S. has experienced economic instability associated with business cycles. Business Cycles alternating rises and declines
ECON 201 Chapter 6 Business Cycles, Unemployment, & Inflation The Business Cycle The U.S. has experienced economic instability associated with business cycles. Business Cycles alternating rises and declines
SSEMA1 The student will illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. a. Explain that overall levels of income, employment, and prices
 SSEMA1 The student will illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. a. Explain that overall levels of income, employment, and prices are determined by the spending and production decisions
SSEMA1 The student will illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. a. Explain that overall levels of income, employment, and prices are determined by the spending and production decisions
Figure Sarver
 I. Learning Objectives In this chapter students will learn: A. About the business cycle and its primary phases. B. How unemployment and inflation are measured. C. About the types of unemployment and inflation
I. Learning Objectives In this chapter students will learn: A. About the business cycle and its primary phases. B. How unemployment and inflation are measured. C. About the types of unemployment and inflation
MONEY. Economics Unit 4 Macroeconomics Just the Facts Handout
 MONEY Economics Unit 4 Macroeconomics Just the Facts Handout Barter Economy A barter economy is an economy with no money. The only way you can get what you want in a barter economy is to trade something
MONEY Economics Unit 4 Macroeconomics Just the Facts Handout Barter Economy A barter economy is an economy with no money. The only way you can get what you want in a barter economy is to trade something
MEASURING ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE PRODUCT MARKET
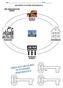 Name: Period THE CIRCULAR FLOW MODEL MEASURING ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE PRODUCT MARKET BUSINESSES HOUSEHOLDS RESOURCE MARKET 1. AKA: 2. 3. Additional Notes on Previous Page/Practice Workspace Quick Write Space
Name: Period THE CIRCULAR FLOW MODEL MEASURING ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE PRODUCT MARKET BUSINESSES HOUSEHOLDS RESOURCE MARKET 1. AKA: 2. 3. Additional Notes on Previous Page/Practice Workspace Quick Write Space
Date: Block # Economics Guided Notes Unit Four Day #2 CPI, Unemployment and the Business Cycle
 Name: Date: Block # Economics Guided Notes Unit Four Day #2 CPI, Unemployment and the Business Cycle Directions Activity listen and view today s PowerPoint lesson. As you view each slide, write in any
Name: Date: Block # Economics Guided Notes Unit Four Day #2 CPI, Unemployment and the Business Cycle Directions Activity listen and view today s PowerPoint lesson. As you view each slide, write in any
Introduction to Economic Growth, Unemployment, and Inflation McGraw-Hill Ryerson Ltd. Macroeconomics, Chapter 6 1
 Introduction to Economic Growth, Unemployment, and Inflation 2005 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Ltd. Macroeconomics, Chapter 6 1 In this chapter you will learn 6.1 The definition and causes of economic growth 6.2
Introduction to Economic Growth, Unemployment, and Inflation 2005 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Ltd. Macroeconomics, Chapter 6 1 In this chapter you will learn 6.1 The definition and causes of economic growth 6.2
What is Macroeconomics?
 MACRO ECONOMICS 1 What is Macroeconomics? Macroeconomics is the study of the large economy as a whole. It is the study of the big picture. Instead of analyzing one consumer, we analyze everyone. Instead
MACRO ECONOMICS 1 What is Macroeconomics? Macroeconomics is the study of the large economy as a whole. It is the study of the big picture. Instead of analyzing one consumer, we analyze everyone. Instead
Chapter 6 GDP, Unemployment and Inflation
 Chapter 6 GDP, Unemployment and Inflation - Microeconomics: study of how households and firms make choices & how they interact in markets. - Macroeconomics: study of the economy as a whole, including topics
Chapter 6 GDP, Unemployment and Inflation - Microeconomics: study of how households and firms make choices & how they interact in markets. - Macroeconomics: study of the economy as a whole, including topics
Unit 6 Measuring the Economy
 Unit 6 Measuring the Economy - Study Guide - Answer, Explain and define the following: 1) GNP 2) GDP 3) Dept. of Commerce 4) Intermediate goods 5) Disposable personal income 6) Contraction 7) Recession
Unit 6 Measuring the Economy - Study Guide - Answer, Explain and define the following: 1) GNP 2) GDP 3) Dept. of Commerce 4) Intermediate goods 5) Disposable personal income 6) Contraction 7) Recession
CIE Economics A-level
 CIE Economics A-level Topic 4: The Macroeconomy d) Employment and unemployment Notes Size and components of labour force The working age population is between the ages of 18 and 65 who are actively looking
CIE Economics A-level Topic 4: The Macroeconomy d) Employment and unemployment Notes Size and components of labour force The working age population is between the ages of 18 and 65 who are actively looking
MACROECONOMICS REVIEW FOR EXAM #1. 1. Real GDP is better than nominal GDP in making comparisons of GDP over time because:
 MACROECONOMICS REVIEW FOR EXAM #1 1. Real GDP is better than nominal GDP in making comparisons of GDP over time because: A. Nominal GDP can increase simply because of price increases over time. B. Real
MACROECONOMICS REVIEW FOR EXAM #1 1. Real GDP is better than nominal GDP in making comparisons of GDP over time because: A. Nominal GDP can increase simply because of price increases over time. B. Real
APE Unit 3 UGRP: Intro to Macroeconomics
 /40 UGRP Score: /10 UEQ Score: Name Date Period Time: 2.5 Weeks APE Unit 3 UGRP: Intro to Macroeconomics /50 Total Score Anchor Text and Video: Please visit: https://www.federalreserve.gov/faqs/what-is-macroeconomics.htm
/40 UGRP Score: /10 UEQ Score: Name Date Period Time: 2.5 Weeks APE Unit 3 UGRP: Intro to Macroeconomics /50 Total Score Anchor Text and Video: Please visit: https://www.federalreserve.gov/faqs/what-is-macroeconomics.htm
Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply. Chapter Objectives. AD AS Model
 10 Demand and Supply 10-1 Chapter Objectives Demand and the Factors That Cause it to Change. Supply and the Factors That Cause it to Change. How AD and AS Determine an Economy s and the Level of Real GDP.
10 Demand and Supply 10-1 Chapter Objectives Demand and the Factors That Cause it to Change. Supply and the Factors That Cause it to Change. How AD and AS Determine an Economy s and the Level of Real GDP.
Economic Ups and Downs: The PowerPoint
 : The PowerPoint Once you have finished reading and answering the questions in the attached Economic Ups and Downs worksheet, you should summarize the information in a PowerPoint presentation. Email the
: The PowerPoint Once you have finished reading and answering the questions in the attached Economic Ups and Downs worksheet, you should summarize the information in a PowerPoint presentation. Email the
Unit 7 Measuring the Economy
 Unit 7 Measuring the Economy - Study Guide - Answer, Explain and define the following: 1) GNP 2) GDP 3) Dept. of Commerce 4) Intermediate goods 5) Disposable personal income 6) Contraction 7) Recession
Unit 7 Measuring the Economy - Study Guide - Answer, Explain and define the following: 1) GNP 2) GDP 3) Dept. of Commerce 4) Intermediate goods 5) Disposable personal income 6) Contraction 7) Recession
Economics Unit 3. The Last Unit!!
 Economics Unit 3 The Last Unit!! Objective 3.01: Identify phases of the business cycle and the economic indicators used to measure economic activities and trends. Measuring the Economy GDP Gross Domestic
Economics Unit 3 The Last Unit!! Objective 3.01: Identify phases of the business cycle and the economic indicators used to measure economic activities and trends. Measuring the Economy GDP Gross Domestic
Print Your Name:. ID Number:.
 Econ2105, Professor Laury EXAM 1, FORM A (9/19/02) Print Your Name:. ID Number:. Multiple Choice (32 questions, 2.5 points each, 80 points total). Clearly indicate (by circling) the ONE BEST response to
Econ2105, Professor Laury EXAM 1, FORM A (9/19/02) Print Your Name:. ID Number:. Multiple Choice (32 questions, 2.5 points each, 80 points total). Clearly indicate (by circling) the ONE BEST response to
Macroeconomics CHAPTER 7. Tracking the Macroeconomy
 Macroeconomics CHAPTER 7 Tracking the Macroeconomy PowerPoint Slides by Can Erbil 2006 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved What you will learn in this chapter: How economists use aggregate measures to
Macroeconomics CHAPTER 7 Tracking the Macroeconomy PowerPoint Slides by Can Erbil 2006 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved What you will learn in this chapter: How economists use aggregate measures to
We use GDP to compare different economies or to track the same economy over time.
 Lecture Notes ECON 1A: Principles of Macroeconomics Chapter 5 - Introduction to Macroeconomics Introduction Macroeconomics looks at the big picture: Demand for: Average price of: Consumption by: Investment
Lecture Notes ECON 1A: Principles of Macroeconomics Chapter 5 - Introduction to Macroeconomics Introduction Macroeconomics looks at the big picture: Demand for: Average price of: Consumption by: Investment
Economic Growth, Business Cycles, Unemployment, and Inflation
 CHAPTER 24 Economic Growth, Business Cycles, Unemployment, and Inflation Remember that there is nothing stable in human affairs; therefore avoid undue elation in prosperity, or undue depression in adversity.
CHAPTER 24 Economic Growth, Business Cycles, Unemployment, and Inflation Remember that there is nothing stable in human affairs; therefore avoid undue elation in prosperity, or undue depression in adversity.
Economics. The last two weeks...
 Economics The last two weeks... Final Exam (Thursday, December 14) Practice tests and review materials on Wednesday Extra Credit Stock Project (due on Thursday, December 14) Today: Measuring Economic Performance
Economics The last two weeks... Final Exam (Thursday, December 14) Practice tests and review materials on Wednesday Extra Credit Stock Project (due on Thursday, December 14) Today: Measuring Economic Performance
Unemployment and Inflation. 1 of of 29
 1 of 29 2 of 29 In early June 2008, the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) announced that the unemployment rate for May 2008 was 5.5 percent. P R E P A R E D B Y FERNANDO QUIJANO, YVONN QUIJANO, AND XIAO
1 of 29 2 of 29 In early June 2008, the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) announced that the unemployment rate for May 2008 was 5.5 percent. P R E P A R E D B Y FERNANDO QUIJANO, YVONN QUIJANO, AND XIAO
MONITORING JOBS AND INFLATION
 21 MONITORING JOBS AND INFLATION After studying this chapter, you will be able to: Explain why unemployment is a problem and define the unemployment rate and other labour market indicators Explain why
21 MONITORING JOBS AND INFLATION After studying this chapter, you will be able to: Explain why unemployment is a problem and define the unemployment rate and other labour market indicators Explain why
Economic Changes and Cycles
 7 more class periods! Textbook Return Thursday 5/18 Final Exam Thursday 5/18 100 MC 5 Free Response 15% of grade Extra credit opportunities will be handed out on Thursday. Economic Changes and Cycles Chapter
7 more class periods! Textbook Return Thursday 5/18 Final Exam Thursday 5/18 100 MC 5 Free Response 15% of grade Extra credit opportunities will be handed out on Thursday. Economic Changes and Cycles Chapter
Introduction. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives. Chapter 7. Explain how the U.S. government calculates the official unemployment rate
 Chapter 7 The Macroeconomy:, Inflation, and Deflation Introduction Why is it that the responsibility for announcing the start of economic contractions and expansions does not rest with elected officials?
Chapter 7 The Macroeconomy:, Inflation, and Deflation Introduction Why is it that the responsibility for announcing the start of economic contractions and expansions does not rest with elected officials?
Practice Test 1: Multiple Choice
 Practice Test 1: Multiple Choice 1. If aggregate planned expenditure exceeds real GDP A. actual inventories decrease below their target. B. firms are not maximizing their profits. C. planned consumption
Practice Test 1: Multiple Choice 1. If aggregate planned expenditure exceeds real GDP A. actual inventories decrease below their target. B. firms are not maximizing their profits. C. planned consumption
Homework Assignment #3 (Due 10/10, Tuesday)
 Homework Assignment #3 (Due 10/10, Tuesday) Multiple Choice Questions: (Please use the green scantron to answer this part) 1) An observer of the economy notices that over the last nine months the unemployment
Homework Assignment #3 (Due 10/10, Tuesday) Multiple Choice Questions: (Please use the green scantron to answer this part) 1) An observer of the economy notices that over the last nine months the unemployment
Chapter 7 Unemployment, Inflation, and Long-Run Growth. Unemployment. Unemployment. Measuring Unemployment
 Chapter 7, Inflation, and Long-Run Growth Measuring Components of the Rate The Costs of Inflation The Consumer Price Index The Costs of Inflation Long-Run Growth Output and Productivity Growth Measuring
Chapter 7, Inflation, and Long-Run Growth Measuring Components of the Rate The Costs of Inflation The Consumer Price Index The Costs of Inflation Long-Run Growth Output and Productivity Growth Measuring
Test (1) Most of the direct spending at the state government level is on Defense. Public safety. Transportation. Education.
 Test 2 1. (1) If production in the economy is efficient, then changes in market prices Move us along the perimeter of the production possibilities curve. Move us to a point above the production possibilities
Test 2 1. (1) If production in the economy is efficient, then changes in market prices Move us along the perimeter of the production possibilities curve. Move us to a point above the production possibilities
MONITORING JOBS AND INFLATION*
 Chapt er 5 MONITORING JOBS AND INFLATION* Key Concepts Employment and Unemployment Unemployment is a problem for both the unemployed worker and for society. Unemployed workers lose income and, if prolonged,
Chapt er 5 MONITORING JOBS AND INFLATION* Key Concepts Employment and Unemployment Unemployment is a problem for both the unemployed worker and for society. Unemployed workers lose income and, if prolonged,
Business Cycle Theory
 Business Cycle Theory Changes in Business Activity Economics, Unit: 06 Lesson: 01 Objectives 1.Describe phases of business cycle 2.Identify and explain the factors that cause business cycles 3.Analyze
Business Cycle Theory Changes in Business Activity Economics, Unit: 06 Lesson: 01 Objectives 1.Describe phases of business cycle 2.Identify and explain the factors that cause business cycles 3.Analyze
Basic Concepts. MICROECONOMICS: deals with specific economic units and a detailed consideration of these individual units.
 Basic Concepts ECONOMICS: The study of how limited productive resources are efficiently allocated in a world of unlimited wants. SCARCITY: WANTS EXCEED RESOURCES We want more than we are capable of getting.
Basic Concepts ECONOMICS: The study of how limited productive resources are efficiently allocated in a world of unlimited wants. SCARCITY: WANTS EXCEED RESOURCES We want more than we are capable of getting.
Consequences of Business Fluctuations
 Aggregate Output Consequences of Business Fluctuations Parts of Chapter 14 + Other Issues Discussion Topics Fluctuations in business activity Consequences of business fluctuations Macroeconomic policy
Aggregate Output Consequences of Business Fluctuations Parts of Chapter 14 + Other Issues Discussion Topics Fluctuations in business activity Consequences of business fluctuations Macroeconomic policy
Practice Problems: Chapter 7 Tracking the Macroeconomy
 Practice Problems: Chapter 7 Tracking the Macroeconomy 1. The national accounts keep track of: A) the spending of consumers and the government. B) the sales of producers. C) business investment. D) all
Practice Problems: Chapter 7 Tracking the Macroeconomy 1. The national accounts keep track of: A) the spending of consumers and the government. B) the sales of producers. C) business investment. D) all
Chapter 7 Unemployment, Inflation, and Long-Run Growth
 Chapter 7 Unemployment, Inflation, and Long-Run Growth 7.1 Unemployment 1 Multiple Choice 1) We can safely say that total output can increase if there is a(n) A) increase in the size of the labor force
Chapter 7 Unemployment, Inflation, and Long-Run Growth 7.1 Unemployment 1 Multiple Choice 1) We can safely say that total output can increase if there is a(n) A) increase in the size of the labor force
Money. What is Money? 3 Uses of Money #1 Medium of Exchange #2 Unit of Account. #3 Store of Value. 6 Characteristics of. Money.
 What is Money? Suppose a generous relative gave you a gift of $1000 for your high school graduation. In a short paragraph outline what you would do with the money and the reason behind your decision. Can
What is Money? Suppose a generous relative gave you a gift of $1000 for your high school graduation. In a short paragraph outline what you would do with the money and the reason behind your decision. Can
OUTLINE October 18, Key concepts. Expenditure 10/16/ :53 PM. Focus: Total Expenditure
 OUTLINE October 18, 2017 Expenditure = C + I + G + (EX IM), continued 3 equations you must know Measuring Unemployment Measuring Inflation Key concepts When figuring out IF some activity is counted in
OUTLINE October 18, 2017 Expenditure = C + I + G + (EX IM), continued 3 equations you must know Measuring Unemployment Measuring Inflation Key concepts When figuring out IF some activity is counted in
SSEMA1 Unemployment, Inflation, CPI Notes
 SSEMA1 Unemployment, Inflation, CPI Notes SSEMA1: The student will illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. a. Define GDP, economic growth, unemployment, CPI, inflation, stagflation,
SSEMA1 Unemployment, Inflation, CPI Notes SSEMA1: The student will illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. a. Define GDP, economic growth, unemployment, CPI, inflation, stagflation,
Econ Department Final. Unit Three Macroeconomics Prepping for Success!
 Econ Department Final Unit Three Macroeconomics Prepping for Success! Econ Department Final Exam Your Economics Departmental Final Exam is cumulative and will count as 5% of your class grade. Following
Econ Department Final Unit Three Macroeconomics Prepping for Success! Econ Department Final Exam Your Economics Departmental Final Exam is cumulative and will count as 5% of your class grade. Following
2. In terms of dollar volume of exports and imports, the most important trading partner for the United States is:
 1. In the U.S. economy, all are generally accepted economic functions of government except: A) The provision of public goods B) The production and distribution of consumer goods C) Pursuing policies that
1. In the U.S. economy, all are generally accepted economic functions of government except: A) The provision of public goods B) The production and distribution of consumer goods C) Pursuing policies that
Macro Economic questions Part I
 Macro Economic questions Part I Question Budget Rental Car buys new automobiles for its business from a U.S. company. The value of transaction would be included in which category of the GDP? a. consumer
Macro Economic questions Part I Question Budget Rental Car buys new automobiles for its business from a U.S. company. The value of transaction would be included in which category of the GDP? a. consumer
Economics Chapters Duke Unit III Measuring Economic Performance
 Economics Chapters 12-16 Duke Unit III Measuring Economic Performance Chapter 12 Section 1 (Pgs. 301-308) Gross Domestic Product (GDP)- 1. What is the difference between final goods and services as opposed
Economics Chapters 12-16 Duke Unit III Measuring Economic Performance Chapter 12 Section 1 (Pgs. 301-308) Gross Domestic Product (GDP)- 1. What is the difference between final goods and services as opposed
Section 3 Mod Practice
 Class Period: Section 3 Mod 10-15 Practice Essay 1 (Module 10) Consider the following transactions involving the nation of Foxystan For each of the following, determine which transaction would be added
Class Period: Section 3 Mod 10-15 Practice Essay 1 (Module 10) Consider the following transactions involving the nation of Foxystan For each of the following, determine which transaction would be added
MAKING SENSE OF ECONOMIC INDICATORS
 WELCOME TO THE WEBINAR FRB MIAMI & FRB NASHVILLE TEACHERS! 1 WEBINAR LINK HTTP://FRBATL.ADOBECONNECT.COM/ECONINDICATORS/ DIAL-IN NUMBER (MUST USE FOR AUDIO) 855-377-2663 ACCESS CODE: 71032685 REMINDER:
WELCOME TO THE WEBINAR FRB MIAMI & FRB NASHVILLE TEACHERS! 1 WEBINAR LINK HTTP://FRBATL.ADOBECONNECT.COM/ECONINDICATORS/ DIAL-IN NUMBER (MUST USE FOR AUDIO) 855-377-2663 ACCESS CODE: 71032685 REMINDER:
Billions of dollars 7,500 1,300 1,
 Exam Name You may not discuss this test in any way shape or form with anyone before 1200 (Noon) Thursday, Dec. 9, 2010. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Circle the letter of the one alternative that best completes the
Exam Name You may not discuss this test in any way shape or form with anyone before 1200 (Noon) Thursday, Dec. 9, 2010. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Circle the letter of the one alternative that best completes the
Principles of Macroeconomics November 11th, Answer Key Midterm 2
 EC132.01(02) Serge Kasyanenko rinciples of Macroeconomics November 11th, 2005 I. Multiple Choice Section (30 points). Select one correct answer. Answer all questions. 1. A stable inflation can be achieved
EC132.01(02) Serge Kasyanenko rinciples of Macroeconomics November 11th, 2005 I. Multiple Choice Section (30 points). Select one correct answer. Answer all questions. 1. A stable inflation can be achieved
1. What was the unemployment rate in December 2001?
 EC2105, Spring 2002 Weekly Quiz 1 (January 16, 2002) 1. What was the unemployment rate in December 2001? 2. When the Fed meets later this month and decides whether to lower interest rates, it is conducting:
EC2105, Spring 2002 Weekly Quiz 1 (January 16, 2002) 1. What was the unemployment rate in December 2001? 2. When the Fed meets later this month and decides whether to lower interest rates, it is conducting:
Chapter 5: Production, Income and Employment
 Chapter 5: Production, Income and Employment We will take our first look at production and employment, focusing on two key variables: Gross Domestic Product and Unemployment Rate The nation s Gross Domestic
Chapter 5: Production, Income and Employment We will take our first look at production and employment, focusing on two key variables: Gross Domestic Product and Unemployment Rate The nation s Gross Domestic
Measurement. Chapter 2. Topics in Macroeconomics 2. Economics Division University of Southampton. February 8, 2008
 Measurement Chapter 2 Topics in Macroeconomics 2 Economics Division University of Southampton February 8, 2008 Chapter 2 1/42 Topics in Macroeconomics Gross Domestic Product Introduction Gross Domestic
Measurement Chapter 2 Topics in Macroeconomics 2 Economics Division University of Southampton February 8, 2008 Chapter 2 1/42 Topics in Macroeconomics Gross Domestic Product Introduction Gross Domestic
ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Solutions to the Final Exam
 ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Solutions to the Final Exam Multiple Choice Questions. (60 points; 2 pts each) #1. Which of the following is a stock variable? a) wealth b) consumption c) investment
ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Solutions to the Final Exam Multiple Choice Questions. (60 points; 2 pts each) #1. Which of the following is a stock variable? a) wealth b) consumption c) investment
Measurement. Chapter 2. Topics in Macroeconomics 2. Economics Division University of Southampton. February 2009
 Measurement Chapter 2 Topics in Macroeconomics 2 Economics Division University of Southampton February 2009 Chapter 2 1/45 Topics in Macroeconomics Gross Domestic Product Introduction Gross Domestic Product
Measurement Chapter 2 Topics in Macroeconomics 2 Economics Division University of Southampton February 2009 Chapter 2 1/45 Topics in Macroeconomics Gross Domestic Product Introduction Gross Domestic Product
AP Macroeconomics Unit 2: Measurement of Economic Performance 2-5. Unemployment. Unemployment
 1 Unemployment Business, Computers, & Information Technology Unit 2 Chapter 26 Review Identify the following: 1. What phase of the Business Cycle is the U.S. in? 2. What was the U.S. Real GDP Growth Rate
1 Unemployment Business, Computers, & Information Technology Unit 2 Chapter 26 Review Identify the following: 1. What phase of the Business Cycle is the U.S. in? 2. What was the U.S. Real GDP Growth Rate
Chapter 4: A First Look at Macroeconomics
 Chapter 4: A First Look at Macroeconomics Principles of Macroeconomics I. Economics as a Social Science A. Economics is the social science that studies the choices that individuals, businesses, governments,
Chapter 4: A First Look at Macroeconomics Principles of Macroeconomics I. Economics as a Social Science A. Economics is the social science that studies the choices that individuals, businesses, governments,
Name: Days/Times Class Meets: Today s Date:
 Name: _ Days/Times Class Meets: Today s Date: Macroeconomics, Spring 2008 Exam 3, TTh classes, various versions Read these Instructions carefully! You must follow them exactly! I) On your Scantron card
Name: _ Days/Times Class Meets: Today s Date: Macroeconomics, Spring 2008 Exam 3, TTh classes, various versions Read these Instructions carefully! You must follow them exactly! I) On your Scantron card
The Goals of Macroeconomic Policy
 The Goals of Macroeconomic Policy Dr. Ashraf Samir Website: ashraffeps.yolasite.com Contents Introduction I) The Goal of Economic Growth II) The Goal of Low Unemployment III) The Goal of Low Inflation
The Goals of Macroeconomic Policy Dr. Ashraf Samir Website: ashraffeps.yolasite.com Contents Introduction I) The Goal of Economic Growth II) The Goal of Low Unemployment III) The Goal of Low Inflation
Unit Two, Day One (pages , )
 Unit Two, Day One (pages 860-889, 585-608) What is the difference between macro and micro? National Debt v. Deficit (NOT THE SAME THING) National Debt Deficit In the circular flow the seller receives exactly
Unit Two, Day One (pages 860-889, 585-608) What is the difference between macro and micro? National Debt v. Deficit (NOT THE SAME THING) National Debt Deficit In the circular flow the seller receives exactly
Test bank for Macroeconomics 12th Edition by Rudiger Dornbusch Dr, Stanley Fischer, Richard Startz
 Test bank for Macroeconomics 12th Edition by Rudiger Dornbusch Dr, Stanley Fischer, Richard Startz Link full download : http://testbankcollection.com/download/test-bank-for-macroeconomics- 12th-edition-by-dornbusch-fischer-startz/
Test bank for Macroeconomics 12th Edition by Rudiger Dornbusch Dr, Stanley Fischer, Richard Startz Link full download : http://testbankcollection.com/download/test-bank-for-macroeconomics- 12th-edition-by-dornbusch-fischer-startz/
INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA UNIVERSITY FOUNDATION PROGRAMME ECO 183 : FOUNDATION ECONOMICS (MACROECONOMICS) RESIT EXAMINATION : AUGUST 2002 SESSION
 ECO 183 (R) / Page 1 of 9 INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA UNIVERSITY FOUNDATION PROGRAMME ECO 183 : FOUNDATION ECONOMICS (MACROECONOMICS) RESIT EXAMINATION : AUGUST 2002 SESSION Section A : Answer ALL questions.
ECO 183 (R) / Page 1 of 9 INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA UNIVERSITY FOUNDATION PROGRAMME ECO 183 : FOUNDATION ECONOMICS (MACROECONOMICS) RESIT EXAMINATION : AUGUST 2002 SESSION Section A : Answer ALL questions.
Butter Produced Price of Butter $5 40 $
 1) Gross domestic product is calculated by summing up A) the total quantity of goods and services in the economy. B) the total quantity of goods and services produced in the economy during a period of
1) Gross domestic product is calculated by summing up A) the total quantity of goods and services in the economy. B) the total quantity of goods and services produced in the economy during a period of
Economics Unit 3 Summary
 SSEMA1 Illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. Economic activity derives from the sectors of the economy explored in the fundamentals and microeconomics units. Individuals, businesses,
SSEMA1 Illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. Economic activity derives from the sectors of the economy explored in the fundamentals and microeconomics units. Individuals, businesses,
Your name (please print) ECO202: PRINCIPLES OF MACROECONOMICS FIRST MIDTERM EXAM Summer 2017 Prof. Bill Even
 Your name (please print) ECO202: PRINCIPLES OF MACROECONOMICS FIRST MIDTERM EXAM Summer 2017 Prof. Bill Even 1. You may have access to a pen or pencil and a calculator. Cell phones, watches, notes, and
Your name (please print) ECO202: PRINCIPLES OF MACROECONOMICS FIRST MIDTERM EXAM Summer 2017 Prof. Bill Even 1. You may have access to a pen or pencil and a calculator. Cell phones, watches, notes, and
Interview Preparation Lecture. Venue: Career Launcher Tambaram Centre Date: 26 th January, 2018
 Interview Preparation Lecture Venue: Career Launcher Tambaram Centre Date: 26 th January, 2018 Session One Duration: 1.5 hours What to expect from B-schools & what B-schools expects from you Why Economics??
Interview Preparation Lecture Venue: Career Launcher Tambaram Centre Date: 26 th January, 2018 Session One Duration: 1.5 hours What to expect from B-schools & what B-schools expects from you Why Economics??
Revision Sheets. AS Economics National Economy in a Global Context. Revision Sheets
 2018 http://www.publicdomainpictures.net/pictures/150000/velka/uk-map.jpg AS Economics National Economy in a Global Context Macroeconomic Objectives Low unemployment Improve external performance Objectives
2018 http://www.publicdomainpictures.net/pictures/150000/velka/uk-map.jpg AS Economics National Economy in a Global Context Macroeconomic Objectives Low unemployment Improve external performance Objectives
Chapter 11 Macroeconomic Issues: Economic Growth and the Business Cycle
 Chapter 11 Macroeconomic Issues: Economic Growth and the Business Cycle Multiple Choice Questions Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The sources of
Chapter 11 Macroeconomic Issues: Economic Growth and the Business Cycle Multiple Choice Questions Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The sources of
University of Lethbridge Department of Economics ECON 1012 Introduction to Microeconomics Instructor: Michael G. Lanyi. Chapter 21 Jobs & Infl
 University of Lethbridge Department of Economics ECON 1012 Introduction to Microeconomics Instructor: Michael G. Lanyi Chapter 21 Jobs & Infl 1) The working-age population is the total number of people
University of Lethbridge Department of Economics ECON 1012 Introduction to Microeconomics Instructor: Michael G. Lanyi Chapter 21 Jobs & Infl 1) The working-age population is the total number of people
E202-Fall 2009 Department Final Examination Version C
 Multiple Choice: On your answer sheet darken in the letter of your choice for each question. You should choose the suggested answer that BEST complete the statement or answers the question. 1) Suppose
Multiple Choice: On your answer sheet darken in the letter of your choice for each question. You should choose the suggested answer that BEST complete the statement or answers the question. 1) Suppose
Chapter 7 Introduction to Economic Growth and Instability
 Chapter 7 Introduction to Economic Growth and Instability Chapter Overview This chapter previews economic growth, the business cycle, unemployment, and inflation. It sets the stage for the analytical presentation
Chapter 7 Introduction to Economic Growth and Instability Chapter Overview This chapter previews economic growth, the business cycle, unemployment, and inflation. It sets the stage for the analytical presentation
Macroeconomics, 7e (Blanchard) Chapter 2: A Tour of the Book. 2.1 Aggregate Output.
 Macroeconomics, 7e (Blanchard) Chapter 2: A Tour of the Book 2.1 Aggregate Output. 1) Fill in the blank for the following: GDP is the value of all produced in a given period. A) final and intermediate
Macroeconomics, 7e (Blanchard) Chapter 2: A Tour of the Book 2.1 Aggregate Output. 1) Fill in the blank for the following: GDP is the value of all produced in a given period. A) final and intermediate
CHAPTER 6: MONITORING CYCLES, JOBS, AND THE PRICE LEVEL
 Principles of Macroeconomics CHAPTER 6: MONITORING CYCLES, JOBS, AND THE PRICE LEVEL Learning Goals: A. A recession started in March 2001 and ended in November 2001. What defines a recession, who makes
Principles of Macroeconomics CHAPTER 6: MONITORING CYCLES, JOBS, AND THE PRICE LEVEL Learning Goals: A. A recession started in March 2001 and ended in November 2001. What defines a recession, who makes
Macroeconomics. Economic Indicators. Reading and using global data sources CPI GDP per Capita Unemployment
 Macroeconomics Reading and using global data sources CPI GDP per Capita Unemployment What is this topic about? Why is it important? Assess this headline; is it good or bad? House sales rise 7% in March
Macroeconomics Reading and using global data sources CPI GDP per Capita Unemployment What is this topic about? Why is it important? Assess this headline; is it good or bad? House sales rise 7% in March
Chapter 02 National Income Accounting
 Chapter 02 National Income Accounting Multiple Choice Questions 1. In calculating this year's GDP, national income accountants a. Include any increase in stock values b. Include an estimate for income
Chapter 02 National Income Accounting Multiple Choice Questions 1. In calculating this year's GDP, national income accountants a. Include any increase in stock values b. Include an estimate for income
Inflation. Chapter Summary and Learning Objectives
 CHAPTER 9 Unemployment and Inflation Chapter Summary and Learning Objectives 9.1 Measuring the Unemployment Rate, the Labor Force Participation Rate, and the Employment-Population Ratio (pages 268 277)
CHAPTER 9 Unemployment and Inflation Chapter Summary and Learning Objectives 9.1 Measuring the Unemployment Rate, the Labor Force Participation Rate, and the Employment-Population Ratio (pages 268 277)
MACROECONOMICS - CLUTCH CH UNEMPLOYMENT AND INFLATION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: LABOR FORCE AND UNEMPLOYMENT Tracking levels of employment within an economy gives meaningful data regarding the nation s productivity Labor Force the total number of workers,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: LABOR FORCE AND UNEMPLOYMENT Tracking levels of employment within an economy gives meaningful data regarding the nation s productivity Labor Force the total number of workers,
ECON 1010 Principles of Macroeconomics. Midterm Exam #2. Professor: David Aadland. Spring Semester April 2 nd, 2019.
 ECON 1010 Principles of Macroeconomics Midterm Exam #2 Professor: David Aadland Spring Semester 2019 April 2 nd, 2019 Your Name Section 1: Multiple Choice (50 pts). Circle the correct answer; each is worth
ECON 1010 Principles of Macroeconomics Midterm Exam #2 Professor: David Aadland Spring Semester 2019 April 2 nd, 2019 Your Name Section 1: Multiple Choice (50 pts). Circle the correct answer; each is worth
Economics 102 NO CELL PHONES, CALCULATORS, OR FORMULA SHEETS ARE ALLOWED FOR THIS EXAM.
 Economics 102 Spring 2018 Second Midterm Date: Tuesday, April 10, 2018 Name TA Name Section The exam consists of three parts: (1) 11 Binary Choice Questions worth 2.5 points each (27.5 points total); (2)
Economics 102 Spring 2018 Second Midterm Date: Tuesday, April 10, 2018 Name TA Name Section The exam consists of three parts: (1) 11 Binary Choice Questions worth 2.5 points each (27.5 points total); (2)
ECNS Fall 2009 Practice Examination Opportunity
 ECNS 202 -- Fall 2009 Practice Examination Opportunity Mark the answer on the provided scantron sheet using a #2 lead pencil. Erase completely. I am not responsible for poorly marked or poorly erased asnwers.
ECNS 202 -- Fall 2009 Practice Examination Opportunity Mark the answer on the provided scantron sheet using a #2 lead pencil. Erase completely. I am not responsible for poorly marked or poorly erased asnwers.
Unemployment. What are the different types of unemployment? How are unemployment rates determined? What is full employment?
 Unemployment What are the different types of unemployment? How are unemployment rates determined? What is full employment? Types of Unemployment Frictional Unemployment Occurs when people change jobs,
Unemployment What are the different types of unemployment? How are unemployment rates determined? What is full employment? Types of Unemployment Frictional Unemployment Occurs when people change jobs,
Grade 11 Economics Unit #4: Macroeconomics Practice Test and Answer Key
 Name: Grade 11 Economics Unit #4: Macroeconomics Practice Test and Answer Key Note: Section A of the actual test will contain multiple-choice questions. You can practice this type of question within the
Name: Grade 11 Economics Unit #4: Macroeconomics Practice Test and Answer Key Note: Section A of the actual test will contain multiple-choice questions. You can practice this type of question within the
** Review ** For Test - 3
 ** Review ** For Test - 3 1. Gross domestic product or GDP is: A) the total dollar value intermediate goods and services produced in the economy in a given time period. B) the total dollar value of wages
** Review ** For Test - 3 1. Gross domestic product or GDP is: A) the total dollar value intermediate goods and services produced in the economy in a given time period. B) the total dollar value of wages
2) The four main categories of resources are. 3) Which of the following is the best example of physical capital used to produce a textbook?
 1) Economics is a. the narrow study of how to make money in financial markets b. the broad study of how to allocate unlimited resources to satisfy limited uses c. the broad study of how to allocate limited
1) Economics is a. the narrow study of how to make money in financial markets b. the broad study of how to allocate unlimited resources to satisfy limited uses c. the broad study of how to allocate limited
Gross Domestic Product
 Gross Domestic Product In this lesson, students will be able to identify characteristics of the Gross Domestic Product. Students will be able to identify and/or define the following terms: Gross Domestic
Gross Domestic Product In this lesson, students will be able to identify characteristics of the Gross Domestic Product. Students will be able to identify and/or define the following terms: Gross Domestic
3. The phase of the business cycle in which real GDP is at a minimum is called: A. the peak. B. a recession. C. the trough. D. the underside.
 1. Most economists agree that the immediate determinant of the volume of output and employment is the: A. composition of consumer spending. B. ratio of public goods to private goods production. C. level
1. Most economists agree that the immediate determinant of the volume of output and employment is the: A. composition of consumer spending. B. ratio of public goods to private goods production. C. level
Macroeconomic TOPIC Measurements, Part I: Prices and Unemployment
 1 Macroeconomic TOPIC Measurements, Part I: Prices and Unemployment Employment and Unemployment Population Survey In the U.S., the population is divided into two groups: The working-age population or civilian
1 Macroeconomic TOPIC Measurements, Part I: Prices and Unemployment Employment and Unemployment Population Survey In the U.S., the population is divided into two groups: The working-age population or civilian
Section 1: Guided Reading and Review Gross Domestic Product
 ) NAME CLASS ------------ DATE ------------- Section 1: Guided Reading and Review Gross Domestic Product r A. As You Read As you read Section 1, answer the following questions about gross domestic pr::jdt:ct.
) NAME CLASS ------------ DATE ------------- Section 1: Guided Reading and Review Gross Domestic Product r A. As You Read As you read Section 1, answer the following questions about gross domestic pr::jdt:ct.
WJEC (Wales) Economics A-level
 WJEC (Wales) Economics A-level Macroeconomics Topic 2: Macroeconomic Objectives 2.3 Inflation and deflation Notes Inflation is the sustained rise in the general price level over time. This means that the
WJEC (Wales) Economics A-level Macroeconomics Topic 2: Macroeconomic Objectives 2.3 Inflation and deflation Notes Inflation is the sustained rise in the general price level over time. This means that the
Lecture 6. Economic Fluctuations and Unemployment
 Lecture 6 Economic Fluctuations and Unemployment Growth and Fluctuations Growth and Fluctuations Growth and Fluctuations Growth and Fluctuations In 2002, economists calculated that the average British
Lecture 6 Economic Fluctuations and Unemployment Growth and Fluctuations Growth and Fluctuations Growth and Fluctuations Growth and Fluctuations In 2002, economists calculated that the average British
