Data analysis methods in weather and climate research
|
|
|
- Felicity Strickland
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Data analysis methods in weather and climate research Dr. David B. Stephenson Department of Meteorology University of Reading 5. Parameter estimation Fitting probability models he sampling distribution of an estimator Error bars and Confidence intervals ypes of estimator Accuracy bias and efficiency of estimators (c Probability modelling in 6 steps Modelling strategy: 1. Explore the data sample (EDA. Identify a suitable distribution 3. Fit the distribution to the data by estimation of the parameters 4. Check the goodness-of-fit 5. Make out-of-sample predictions 6. Go back to 1 or if needed (c 004 D.B.Stephenson@reading.ac.uk 5. Parameter estimation Estimate the values of population parameter(s that give the best fit of the probability model ~ f ( x; to the observed sample of data. Note: we fit the model to the data NO the data to the model! (c 004 D.B.Stephenson@reading.ac.uk 3 (c 000 Dr. David Stephenson
2 5. Sample statistics and estimators Parameters are estimated by using sample statistics [] of the original random variables. Such sample statistics are known as estimators. For example the population mean parameter in the Normal distribution N ( can be estimated by the sample mean x. his is known as a point estimate. he hat symbol denotes estimate of. (c 004 D.B.Stephenson@reading.ac.uk 4 5. Interval estimates Rather than just give a single best estimate of a parameter ( point estimate it is more informative to give a likely range of possible values in other words an interval estimate. he simplest way to do this is to quote the best estimate plus/minus the standard deviation in this estimate: he standard deviation quantifies the amount of uncertainty in the estimate caused by sampling. (c 004 D.B.Stephenson@reading.ac.uk 5 5. Sampling distribution Each sample statistic [] is distributed with its own sampling distribution : ~ f ( n he sampling distribution depends on: Choice of sample statistic; Sample size n; Parameters of the original distribution f ( ~ (c 004 D.B.Stephenson@reading.ac.uk 6 (c 000 Dr. David Stephenson
3 5. Mean of iid normally distributed variables For iid ( independent and identically distributed normally distributed random variables: E( ~ N( ~ N( Var ( / n (c 004 D.B.Stephenson@reading.ac.uk 7 Sampling distribution of sample mean / n 5. Central Limit heorem ~ lim n f ( ~ and independen t N( / n his works for ANY f( with finite mean and variance and explains why we see so many variables that are normally distributed e.g. mean errors due to many random effects. (c 004 D.B.Stephenson@reading.ac.uk 8 5. Definition of standard error he standard error is the standard deviation of the sample statistic. i.e. Var( e.g. for sample mean of iid variables: n (c 004 D.B.Stephenson@reading.ac.uk 9 (c 000 Dr. David Stephenson
4 5. Confidence intervals (C.I. s he (1 100% confidence interval of a sample statistic is the interval between the / and the 1 / quantiles of the sampling distribution. Pr{ t t } 1 / confidence level 1 / here is probability 1 overlap the true value. that the interval will (c 004 D.B.Stephenson@reading.ac.uk Examples of confidence intervals (c 004 D.B.Stephenson@reading.ac.uk Some commonly used C.I. s Alpha 1-alpha Zc Description % C.I. +/- probable error % C.I. +/- 1 std. errors ~ 95% C.I. ~+/- std. errors % C.I. ~+/- 3 std. errors (c 004 D.B.Stephenson@reading.ac.uk 1 (c 000 Dr. David Stephenson
5 5. Choice of estimator Many ways to choose the estimators such as: Method of moments use sample moments e.g. mean variance skewness etc. Robust estimation use rank statistics such as the median IQR etc. instead. Maximum Likelihood Estimation choose estimator so that it maximises the likelihood of our data sampling occurring. (c Accuracy bias and efficiency he accuracy of an estimator can be quantified as follows: Mean Squared Error E (( ( E( Var( squared " bias" " efficiency" here is invariably a trade-off between bias and efficiency. (c 004 D.B.Stephenson@reading.ac.uk Summary Model is fit to the data by using sample statistics (estimators to estimate the true model parameters Interval estimates give a range of probable values rather than a single point estimate Each estimator has its own probability distribution known as a sampling distribution he standard deviation of the estimator is known as the standard error he sampling distribution can be used to construct confidence intervals in which the true value is most likely to be found. here are several methods for estimating parameters: moment method robust estimation maximum likelihood estimation. Different estimators have different accuracies bias and efficiency. (c 004 D.B.Stephenson@reading.ac.uk 15 (c 000 Dr. David Stephenson
STAT 509: Statistics for Engineers Dr. Dewei Wang. Copyright 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
 STAT 509: Statistics for Engineers Dr. Dewei Wang Applied Statistics and Probability for Engineers Sixth Edition Douglas C. Montgomery George C. Runger 7 Point CHAPTER OUTLINE 7-1 Point Estimation 7-2
STAT 509: Statistics for Engineers Dr. Dewei Wang Applied Statistics and Probability for Engineers Sixth Edition Douglas C. Montgomery George C. Runger 7 Point CHAPTER OUTLINE 7-1 Point Estimation 7-2
STATISTICS and PROBABILITY
 Introduction to Statistics Atatürk University STATISTICS and PROBABILITY LECTURE: SAMPLING DISTRIBUTIONS and POINT ESTIMATIONS Prof. Dr. İrfan KAYMAZ Atatürk University Engineering Faculty Department of
Introduction to Statistics Atatürk University STATISTICS and PROBABILITY LECTURE: SAMPLING DISTRIBUTIONS and POINT ESTIMATIONS Prof. Dr. İrfan KAYMAZ Atatürk University Engineering Faculty Department of
Chapter 8. Introduction to Statistical Inference
 Chapter 8. Introduction to Statistical Inference Point Estimation Statistical inference is to draw some type of conclusion about one or more parameters(population characteristics). Now you know that a
Chapter 8. Introduction to Statistical Inference Point Estimation Statistical inference is to draw some type of conclusion about one or more parameters(population characteristics). Now you know that a
MODELLING OF INCOME AND WAGE DISTRIBUTION USING THE METHOD OF L-MOMENTS OF PARAMETER ESTIMATION
 International Days of Statistics and Economics, Prague, September -3, MODELLING OF INCOME AND WAGE DISTRIBUTION USING THE METHOD OF L-MOMENTS OF PARAMETER ESTIMATION Diana Bílková Abstract Using L-moments
International Days of Statistics and Economics, Prague, September -3, MODELLING OF INCOME AND WAGE DISTRIBUTION USING THE METHOD OF L-MOMENTS OF PARAMETER ESTIMATION Diana Bílková Abstract Using L-moments
Applied Statistics I
 Applied Statistics I Liang Zhang Department of Mathematics, University of Utah July 14, 2008 Liang Zhang (UofU) Applied Statistics I July 14, 2008 1 / 18 Point Estimation Liang Zhang (UofU) Applied Statistics
Applied Statistics I Liang Zhang Department of Mathematics, University of Utah July 14, 2008 Liang Zhang (UofU) Applied Statistics I July 14, 2008 1 / 18 Point Estimation Liang Zhang (UofU) Applied Statistics
Lecture Data Science
 Web Science & Technologies University of Koblenz Landau, Germany Lecture Data Science Statistics Foundations JProf. Dr. Claudia Wagner Learning Goals How to describe sample data? What is mode/median/mean?
Web Science & Technologies University of Koblenz Landau, Germany Lecture Data Science Statistics Foundations JProf. Dr. Claudia Wagner Learning Goals How to describe sample data? What is mode/median/mean?
Point Estimation. Some General Concepts of Point Estimation. Example. Estimator quality
 Point Estimation Some General Concepts of Point Estimation Statistical inference = conclusions about parameters Parameters == population characteristics A point estimate of a parameter is a value (based
Point Estimation Some General Concepts of Point Estimation Statistical inference = conclusions about parameters Parameters == population characteristics A point estimate of a parameter is a value (based
Financial Econometrics Jeffrey R. Russell. Midterm 2014 Suggested Solutions. TA: B. B. Deng
 Financial Econometrics Jeffrey R. Russell Midterm 2014 Suggested Solutions TA: B. B. Deng Unless otherwise stated, e t is iid N(0,s 2 ) 1. (12 points) Consider the three series y1, y2, y3, and y4. Match
Financial Econometrics Jeffrey R. Russell Midterm 2014 Suggested Solutions TA: B. B. Deng Unless otherwise stated, e t is iid N(0,s 2 ) 1. (12 points) Consider the three series y1, y2, y3, and y4. Match
Midterm Exam. b. What are the continuously compounded returns for the two stocks?
 University of Washington Fall 004 Department of Economics Eric Zivot Economics 483 Midterm Exam This is a closed book and closed note exam. However, you are allowed one page of notes (double-sided). Answer
University of Washington Fall 004 Department of Economics Eric Zivot Economics 483 Midterm Exam This is a closed book and closed note exam. However, you are allowed one page of notes (double-sided). Answer
Financial Econometrics Jeffrey R. Russell Midterm 2014
 Name: Financial Econometrics Jeffrey R. Russell Midterm 2014 You have 2 hours to complete the exam. Use can use a calculator and one side of an 8.5x11 cheat sheet. Try to fit all your work in the space
Name: Financial Econometrics Jeffrey R. Russell Midterm 2014 You have 2 hours to complete the exam. Use can use a calculator and one side of an 8.5x11 cheat sheet. Try to fit all your work in the space
Module 4: Point Estimation Statistics (OA3102)
 Module 4: Point Estimation Statistics (OA3102) Professor Ron Fricker Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, California Reading assignment: WM&S chapter 8.1-8.4 Revision: 1-12 1 Goals for this Module Define
Module 4: Point Estimation Statistics (OA3102) Professor Ron Fricker Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, California Reading assignment: WM&S chapter 8.1-8.4 Revision: 1-12 1 Goals for this Module Define
Chapter 7: Point Estimation and Sampling Distributions
 Chapter 7: Point Estimation and Sampling Distributions Seungchul Baek Department of Statistics, University of South Carolina STAT 509: Statistics for Engineers 1 / 20 Motivation In chapter 3, we learned
Chapter 7: Point Estimation and Sampling Distributions Seungchul Baek Department of Statistics, University of South Carolina STAT 509: Statistics for Engineers 1 / 20 Motivation In chapter 3, we learned
The Range, the Inter Quartile Range (or IQR), and the Standard Deviation (which we usually denote by a lower case s).
 We will look the three common and useful measures of spread. The Range, the Inter Quartile Range (or IQR), and the Standard Deviation (which we usually denote by a lower case s). 1 Ameasure of the center
We will look the three common and useful measures of spread. The Range, the Inter Quartile Range (or IQR), and the Standard Deviation (which we usually denote by a lower case s). 1 Ameasure of the center
Chapter 3. Numerical Descriptive Measures. Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd. Chapter 3, Slide 1
 Chapter 3 Numerical Descriptive Measures Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd. Chapter 3, Slide 1 Objectives In this chapter, you learn to: Describe the properties of central tendency, variation, and
Chapter 3 Numerical Descriptive Measures Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Ltd. Chapter 3, Slide 1 Objectives In this chapter, you learn to: Describe the properties of central tendency, variation, and
Subject CS1 Actuarial Statistics 1 Core Principles. Syllabus. for the 2019 exams. 1 June 2018
 ` Subject CS1 Actuarial Statistics 1 Core Principles Syllabus for the 2019 exams 1 June 2018 Copyright in this Core Reading is the property of the Institute and Faculty of Actuaries who are the sole distributors.
` Subject CS1 Actuarial Statistics 1 Core Principles Syllabus for the 2019 exams 1 June 2018 Copyright in this Core Reading is the property of the Institute and Faculty of Actuaries who are the sole distributors.
Data Distributions and Normality
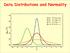 Data Distributions and Normality Definition (Non)Parametric Parametric statistics assume that data come from a normal distribution, and make inferences about parameters of that distribution. These statistical
Data Distributions and Normality Definition (Non)Parametric Parametric statistics assume that data come from a normal distribution, and make inferences about parameters of that distribution. These statistical
EVA Tutorial #1 BLOCK MAXIMA APPROACH IN HYDROLOGIC/CLIMATE APPLICATIONS. Rick Katz
 1 EVA Tutorial #1 BLOCK MAXIMA APPROACH IN HYDROLOGIC/CLIMATE APPLICATIONS Rick Katz Institute for Mathematics Applied to Geosciences National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, CO USA email: rwk@ucar.edu
1 EVA Tutorial #1 BLOCK MAXIMA APPROACH IN HYDROLOGIC/CLIMATE APPLICATIONS Rick Katz Institute for Mathematics Applied to Geosciences National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, CO USA email: rwk@ucar.edu
Random Variables and Probability Distributions
 Chapter 3 Random Variables and Probability Distributions Chapter Three Random Variables and Probability Distributions 3. Introduction An event is defined as the possible outcome of an experiment. In engineering
Chapter 3 Random Variables and Probability Distributions Chapter Three Random Variables and Probability Distributions 3. Introduction An event is defined as the possible outcome of an experiment. In engineering
Point Estimation. Stat 4570/5570 Material from Devore s book (Ed 8), and Cengage
 6 Point Estimation Stat 4570/5570 Material from Devore s book (Ed 8), and Cengage Point Estimation Statistical inference: directed toward conclusions about one or more parameters. We will use the generic
6 Point Estimation Stat 4570/5570 Material from Devore s book (Ed 8), and Cengage Point Estimation Statistical inference: directed toward conclusions about one or more parameters. We will use the generic
Introduction to Statistical Data Analysis II
 Introduction to Statistical Data Analysis II JULY 2011 Afsaneh Yazdani Preface Major branches of Statistics: - Descriptive Statistics - Inferential Statistics Preface What is Inferential Statistics? Preface
Introduction to Statistical Data Analysis II JULY 2011 Afsaneh Yazdani Preface Major branches of Statistics: - Descriptive Statistics - Inferential Statistics Preface What is Inferential Statistics? Preface
Key Objectives. Module 2: The Logic of Statistical Inference. Z-scores. SGSB Workshop: Using Statistical Data to Make Decisions
 SGSB Workshop: Using Statistical Data to Make Decisions Module 2: The Logic of Statistical Inference Dr. Tom Ilvento January 2006 Dr. Mugdim Pašić Key Objectives Understand the logic of statistical inference
SGSB Workshop: Using Statistical Data to Make Decisions Module 2: The Logic of Statistical Inference Dr. Tom Ilvento January 2006 Dr. Mugdim Pašić Key Objectives Understand the logic of statistical inference
Financial Time Series and Their Characteristics
 Financial Time Series and Their Characteristics Egon Zakrajšek Division of Monetary Affairs Federal Reserve Board Summer School in Financial Mathematics Faculty of Mathematics & Physics University of Ljubljana
Financial Time Series and Their Characteristics Egon Zakrajšek Division of Monetary Affairs Federal Reserve Board Summer School in Financial Mathematics Faculty of Mathematics & Physics University of Ljubljana
Probability & Statistics
 Probability & Statistics BITS Pilani K K Birla Goa Campus Dr. Jajati Keshari Sahoo Department of Mathematics Statistics Descriptive statistics Inferential statistics /38 Inferential Statistics 1. Involves:
Probability & Statistics BITS Pilani K K Birla Goa Campus Dr. Jajati Keshari Sahoo Department of Mathematics Statistics Descriptive statistics Inferential statistics /38 Inferential Statistics 1. Involves:
Chapter 5. Statistical inference for Parametric Models
 Chapter 5. Statistical inference for Parametric Models Outline Overview Parameter estimation Method of moments How good are method of moments estimates? Interval estimation Statistical Inference for Parametric
Chapter 5. Statistical inference for Parametric Models Outline Overview Parameter estimation Method of moments How good are method of moments estimates? Interval estimation Statistical Inference for Parametric
12 The Bootstrap and why it works
 12 he Bootstrap and why it works For a review of many applications of bootstrap see Efron and ibshirani (1994). For the theory behind the bootstrap see the books by Hall (1992), van der Waart (2000), Lahiri
12 he Bootstrap and why it works For a review of many applications of bootstrap see Efron and ibshirani (1994). For the theory behind the bootstrap see the books by Hall (1992), van der Waart (2000), Lahiri
Confidence Intervals Introduction
 Confidence Intervals Introduction A point estimate provides no information about the precision and reliability of estimation. For example, the sample mean X is a point estimate of the population mean μ
Confidence Intervals Introduction A point estimate provides no information about the precision and reliability of estimation. For example, the sample mean X is a point estimate of the population mean μ
Financial Econometrics (FinMetrics04) Time-series Statistics Concepts Exploratory Data Analysis Testing for Normality Empirical VaR
 Financial Econometrics (FinMetrics04) Time-series Statistics Concepts Exploratory Data Analysis Testing for Normality Empirical VaR Nelson Mark University of Notre Dame Fall 2017 September 11, 2017 Introduction
Financial Econometrics (FinMetrics04) Time-series Statistics Concepts Exploratory Data Analysis Testing for Normality Empirical VaR Nelson Mark University of Notre Dame Fall 2017 September 11, 2017 Introduction
Much of what appears here comes from ideas presented in the book:
 Chapter 11 Robust statistical methods Much of what appears here comes from ideas presented in the book: Huber, Peter J. (1981), Robust statistics, John Wiley & Sons (New York; Chichester). There are many
Chapter 11 Robust statistical methods Much of what appears here comes from ideas presented in the book: Huber, Peter J. (1981), Robust statistics, John Wiley & Sons (New York; Chichester). There are many
Chapter 7 - Lecture 1 General concepts and criteria
 Chapter 7 - Lecture 1 General concepts and criteria January 29th, 2010 Best estimator Mean Square error Unbiased estimators Example Unbiased estimators not unique Special case MVUE Bootstrap General Question
Chapter 7 - Lecture 1 General concepts and criteria January 29th, 2010 Best estimator Mean Square error Unbiased estimators Example Unbiased estimators not unique Special case MVUE Bootstrap General Question
MgtOp S 215 Chapter 8 Dr. Ahn
 MgtOp S 215 Chapter 8 Dr. Ahn An estimator of a population parameter is a rule that tells us how to use the sample values,,, to estimate the parameter, and is a statistic. An estimate is the value obtained
MgtOp S 215 Chapter 8 Dr. Ahn An estimator of a population parameter is a rule that tells us how to use the sample values,,, to estimate the parameter, and is a statistic. An estimate is the value obtained
Application of the Bootstrap Estimating a Population Mean
 Application of the Bootstrap Estimating a Population Mean Movie Average Shot Lengths Sources: Barry Sands Average Shot Length Movie Database L. Chihara and T. Hesterberg (2011). Mathematical Statistics
Application of the Bootstrap Estimating a Population Mean Movie Average Shot Lengths Sources: Barry Sands Average Shot Length Movie Database L. Chihara and T. Hesterberg (2011). Mathematical Statistics
Are Market Neutral Hedge Funds Really Market Neutral?
 Are Market Neutral Hedge Funds Really Market Neutral? Andrew Patton London School of Economics June 2005 1 Background The hedge fund industry has grown from about $50 billion in 1990 to $1 trillion in
Are Market Neutral Hedge Funds Really Market Neutral? Andrew Patton London School of Economics June 2005 1 Background The hedge fund industry has grown from about $50 billion in 1990 to $1 trillion in
Statistics for Business and Economics
 Statistics for Business and Economics Chapter 7 Estimation: Single Population Copyright 010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Ch. 7-1 Confidence Intervals Contents of this chapter: Confidence
Statistics for Business and Economics Chapter 7 Estimation: Single Population Copyright 010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Ch. 7-1 Confidence Intervals Contents of this chapter: Confidence
Point Estimators. STATISTICS Lecture no. 10. Department of Econometrics FEM UO Brno office 69a, tel
 STATISTICS Lecture no. 10 Department of Econometrics FEM UO Brno office 69a, tel. 973 442029 email:jiri.neubauer@unob.cz 8. 12. 2009 Introduction Suppose that we manufacture lightbulbs and we want to state
STATISTICS Lecture no. 10 Department of Econometrics FEM UO Brno office 69a, tel. 973 442029 email:jiri.neubauer@unob.cz 8. 12. 2009 Introduction Suppose that we manufacture lightbulbs and we want to state
A NEW POINT ESTIMATOR FOR THE MEDIAN OF GAMMA DISTRIBUTION
 Banneheka, B.M.S.G., Ekanayake, G.E.M.U.P.D. Viyodaya Journal of Science, 009. Vol 4. pp. 95-03 A NEW POINT ESTIMATOR FOR THE MEDIAN OF GAMMA DISTRIBUTION B.M.S.G. Banneheka Department of Statistics and
Banneheka, B.M.S.G., Ekanayake, G.E.M.U.P.D. Viyodaya Journal of Science, 009. Vol 4. pp. 95-03 A NEW POINT ESTIMATOR FOR THE MEDIAN OF GAMMA DISTRIBUTION B.M.S.G. Banneheka Department of Statistics and
Linda Allen, Jacob Boudoukh and Anthony Saunders, Understanding Market, Credit and Operational Risk: The Value at Risk Approach
 P1.T4. Valuation & Risk Models Linda Allen, Jacob Boudoukh and Anthony Saunders, Understanding Market, Credit and Operational Risk: The Value at Risk Approach Bionic Turtle FRM Study Notes Reading 26 By
P1.T4. Valuation & Risk Models Linda Allen, Jacob Boudoukh and Anthony Saunders, Understanding Market, Credit and Operational Risk: The Value at Risk Approach Bionic Turtle FRM Study Notes Reading 26 By
AP Statistics Chapter 6 - Random Variables
 AP Statistics Chapter 6 - Random 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Objective: Recognize and define discrete random variables, and construct a probability distribution table and a probability histogram
AP Statistics Chapter 6 - Random 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Objective: Recognize and define discrete random variables, and construct a probability distribution table and a probability histogram
درس هفتم یادگیري ماشین. (Machine Learning) دانشگاه فردوسی مشهد دانشکده مهندسی رضا منصفی
 یادگیري ماشین توزیع هاي نمونه و تخمین نقطه اي پارامترها Sampling Distributions and Point Estimation of Parameter (Machine Learning) دانشگاه فردوسی مشهد دانشکده مهندسی رضا منصفی درس هفتم 1 Outline Introduction
یادگیري ماشین توزیع هاي نمونه و تخمین نقطه اي پارامترها Sampling Distributions and Point Estimation of Parameter (Machine Learning) دانشگاه فردوسی مشهد دانشکده مهندسی رضا منصفی درس هفتم 1 Outline Introduction
Point Estimation. Principle of Unbiased Estimation. When choosing among several different estimators of θ, select one that is unbiased.
 Point Estimation Point Estimation Definition A point estimate of a parameter θ is a single number that can be regarded as a sensible value for θ. A point estimate is obtained by selecting a suitable statistic
Point Estimation Point Estimation Definition A point estimate of a parameter θ is a single number that can be regarded as a sensible value for θ. A point estimate is obtained by selecting a suitable statistic
Module 3: Sampling Distributions and the CLT Statistics (OA3102)
 Module 3: Sampling Distributions and the CLT Statistics (OA3102) Professor Ron Fricker Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, California Reading assignment: WM&S chpt 7.1-7.3, 7.5 Revision: 1-12 1 Goals for
Module 3: Sampling Distributions and the CLT Statistics (OA3102) Professor Ron Fricker Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, California Reading assignment: WM&S chpt 7.1-7.3, 7.5 Revision: 1-12 1 Goals for
Chapter 9. Sampling Distributions. A sampling distribution is created by, as the name suggests, sampling.
 Chapter 9 Sampling Distributions 9.1 Sampling Distributions A sampling distribution is created by, as the name suggests, sampling. The method we will employ on the rules of probability and the laws of
Chapter 9 Sampling Distributions 9.1 Sampling Distributions A sampling distribution is created by, as the name suggests, sampling. The method we will employ on the rules of probability and the laws of
MATH 3200 Exam 3 Dr. Syring
 . Suppose n eligible voters are polled (randomly sampled) from a population of size N. The poll asks voters whether they support or do not support increasing local taxes to fund public parks. Let M be
. Suppose n eligible voters are polled (randomly sampled) from a population of size N. The poll asks voters whether they support or do not support increasing local taxes to fund public parks. Let M be
Topic 8: Model Diagnostics
 Topic 8: Model Diagnostics Outline Diagnostics to check model assumptions Diagnostics concerning X Diagnostics using the residuals Diagnostics and remedial measures Diagnostics: look at the data to diagnose
Topic 8: Model Diagnostics Outline Diagnostics to check model assumptions Diagnostics concerning X Diagnostics using the residuals Diagnostics and remedial measures Diagnostics: look at the data to diagnose
Market Risk Analysis Volume IV. Value-at-Risk Models
 Market Risk Analysis Volume IV Value-at-Risk Models Carol Alexander John Wiley & Sons, Ltd List of Figures List of Tables List of Examples Foreword Preface to Volume IV xiii xvi xxi xxv xxix IV.l Value
Market Risk Analysis Volume IV Value-at-Risk Models Carol Alexander John Wiley & Sons, Ltd List of Figures List of Tables List of Examples Foreword Preface to Volume IV xiii xvi xxi xxv xxix IV.l Value
Modelling of Long-Term Risk
 Modelling of Long-Term Risk Roger Kaufmann Swiss Life roger.kaufmann@swisslife.ch 15th International AFIR Colloquium 6-9 September 2005, Zurich c 2005 (R. Kaufmann, Swiss Life) Contents A. Basel II B.
Modelling of Long-Term Risk Roger Kaufmann Swiss Life roger.kaufmann@swisslife.ch 15th International AFIR Colloquium 6-9 September 2005, Zurich c 2005 (R. Kaufmann, Swiss Life) Contents A. Basel II B.
Discrete probability distributions
 Discrete probability distributions Probability distributions Discrete random variables Expected values (mean) Variance Linear functions - mean & standard deviation Standard deviation 1 Probability distributions
Discrete probability distributions Probability distributions Discrete random variables Expected values (mean) Variance Linear functions - mean & standard deviation Standard deviation 1 Probability distributions
Asymptotic Distribution Free Interval Estimation
 D.L. Coffman et al.: ADF Intraclass Correlation 2008 Methodology Hogrefe Coefficient 2008; & Huber Vol. Publishers for 4(1):4 9 ICC Asymptotic Distribution Free Interval Estimation for an Intraclass Correlation
D.L. Coffman et al.: ADF Intraclass Correlation 2008 Methodology Hogrefe Coefficient 2008; & Huber Vol. Publishers for 4(1):4 9 ICC Asymptotic Distribution Free Interval Estimation for an Intraclass Correlation
Basic Procedure for Histograms
 Basic Procedure for Histograms 1. Compute the range of observations (min. & max. value) 2. Choose an initial # of classes (most likely based on the range of values, try and find a number of classes that
Basic Procedure for Histograms 1. Compute the range of observations (min. & max. value) 2. Choose an initial # of classes (most likely based on the range of values, try and find a number of classes that
Lecture 9 - Sampling Distributions and the CLT
 Lecture 9 - Sampling Distributions and the CLT Sta102/BME102 Colin Rundel September 23, 2015 1 Variability of Estimates Activity Sampling distributions - via simulation Sampling distributions - via CLT
Lecture 9 - Sampling Distributions and the CLT Sta102/BME102 Colin Rundel September 23, 2015 1 Variability of Estimates Activity Sampling distributions - via simulation Sampling distributions - via CLT
Point Estimation. Edwin Leuven
 Point Estimation Edwin Leuven Introduction Last time we reviewed statistical inference We saw that while in probability we ask: given a data generating process, what are the properties of the outcomes?
Point Estimation Edwin Leuven Introduction Last time we reviewed statistical inference We saw that while in probability we ask: given a data generating process, what are the properties of the outcomes?
CS145: Probability & Computing
 CS145: Probability & Computing Lecture 8: Variance of Sums, Cumulative Distribution, Continuous Variables Instructor: Eli Upfal Brown University Computer Science Figure credits: Bertsekas & Tsitsiklis,
CS145: Probability & Computing Lecture 8: Variance of Sums, Cumulative Distribution, Continuous Variables Instructor: Eli Upfal Brown University Computer Science Figure credits: Bertsekas & Tsitsiklis,
Definition 9.1 A point estimate is any function T (X 1,..., X n ) of a random sample. We often write an estimator of the parameter θ as ˆθ.
 9 Point estimation 9.1 Rationale behind point estimation When sampling from a population described by a pdf f(x θ) or probability function P [X = x θ] knowledge of θ gives knowledge of the entire population.
9 Point estimation 9.1 Rationale behind point estimation When sampling from a population described by a pdf f(x θ) or probability function P [X = x θ] knowledge of θ gives knowledge of the entire population.
Descriptive Statistics
 Petra Petrovics Descriptive Statistics 2 nd seminar DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Definition: Descriptive statistics is concerned only with collecting and describing data Methods: - statistical tables and graphs
Petra Petrovics Descriptive Statistics 2 nd seminar DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Definition: Descriptive statistics is concerned only with collecting and describing data Methods: - statistical tables and graphs
PRMIA Exam 8002 PRM Certification - Exam II: Mathematical Foundations of Risk Measurement Version: 6.0 [ Total Questions: 132 ]
![PRMIA Exam 8002 PRM Certification - Exam II: Mathematical Foundations of Risk Measurement Version: 6.0 [ Total Questions: 132 ] PRMIA Exam 8002 PRM Certification - Exam II: Mathematical Foundations of Risk Measurement Version: 6.0 [ Total Questions: 132 ]](/thumbs/74/69839183.jpg) s@lm@n PRMIA Exam 8002 PRM Certification - Exam II: Mathematical Foundations of Risk Measurement Version: 6.0 [ Total Questions: 132 ] Question No : 1 A 2-step binomial tree is used to value an American
s@lm@n PRMIA Exam 8002 PRM Certification - Exam II: Mathematical Foundations of Risk Measurement Version: 6.0 [ Total Questions: 132 ] Question No : 1 A 2-step binomial tree is used to value an American
Measures of Center. Mean. 1. Mean 2. Median 3. Mode 4. Midrange (rarely used) Measure of Center. Notation. Mean
 Measure of Center Measures of Center The value at the center or middle of a data set 1. Mean 2. Median 3. Mode 4. Midrange (rarely used) 1 2 Mean Notation The measure of center obtained by adding the values
Measure of Center Measures of Center The value at the center or middle of a data set 1. Mean 2. Median 3. Mode 4. Midrange (rarely used) 1 2 Mean Notation The measure of center obtained by adding the values
9/17/2015. Basic Statistics for the Healthcare Professional. Relax.it won t be that bad! Purpose of Statistic. Objectives
 Basic Statistics for the Healthcare Professional 1 F R A N K C O H E N, M B B, M P A D I R E C T O R O F A N A L Y T I C S D O C T O R S M A N A G E M E N T, LLC Purpose of Statistic 2 Provide a numerical
Basic Statistics for the Healthcare Professional 1 F R A N K C O H E N, M B B, M P A D I R E C T O R O F A N A L Y T I C S D O C T O R S M A N A G E M E N T, LLC Purpose of Statistic 2 Provide a numerical
M249 Diagnostic Quiz
 THE OPEN UNIVERSITY Faculty of Mathematics and Computing M249 Diagnostic Quiz Prepared by the Course Team [Press to begin] c 2005, 2006 The Open University Last Revision Date: May 19, 2006 Version 4.2
THE OPEN UNIVERSITY Faculty of Mathematics and Computing M249 Diagnostic Quiz Prepared by the Course Team [Press to begin] c 2005, 2006 The Open University Last Revision Date: May 19, 2006 Version 4.2
Analysis of truncated data with application to the operational risk estimation
 Analysis of truncated data with application to the operational risk estimation Petr Volf 1 Abstract. Researchers interested in the estimation of operational risk often face problems arising from the structure
Analysis of truncated data with application to the operational risk estimation Petr Volf 1 Abstract. Researchers interested in the estimation of operational risk often face problems arising from the structure
Notice that X2 and Y2 are skewed. Taking the SQRT of Y2 reduces the skewness greatly.
 Notice that X2 and Y2 are skewed. Taking the SQRT of Y2 reduces the skewness greatly. The MEANS Procedure Variable Mean Std Dev Minimum Maximum Skewness ƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒ
Notice that X2 and Y2 are skewed. Taking the SQRT of Y2 reduces the skewness greatly. The MEANS Procedure Variable Mean Std Dev Minimum Maximum Skewness ƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒƒ
Computing Statistics ID1050 Quantitative & Qualitative Reasoning
 Computing Statistics ID1050 Quantitative & Qualitative Reasoning Single-variable Statistics We will be considering six statistics of a data set Three measures of the middle Mean, median, and mode Two measures
Computing Statistics ID1050 Quantitative & Qualitative Reasoning Single-variable Statistics We will be considering six statistics of a data set Three measures of the middle Mean, median, and mode Two measures
Continuous Probability Distributions & Normal Distribution
 Mathematical Methods Units 3/4 Student Learning Plan Continuous Probability Distributions & Normal Distribution 7 lessons Notes: Students need practice in recognising whether a problem involves a discrete
Mathematical Methods Units 3/4 Student Learning Plan Continuous Probability Distributions & Normal Distribution 7 lessons Notes: Students need practice in recognising whether a problem involves a discrete
Week 1 Variables: Exploration, Familiarisation and Description. Descriptive Statistics.
 Week 1 Variables: Exploration, Familiarisation and Description. Descriptive Statistics. Convergent validity: the degree to which results/evidence from different tests/sources, converge on the same conclusion.
Week 1 Variables: Exploration, Familiarisation and Description. Descriptive Statistics. Convergent validity: the degree to which results/evidence from different tests/sources, converge on the same conclusion.
Chapter 6 Confidence Intervals
 Chapter 6 Confidence Intervals Section 6-1 Confidence Intervals for the Mean (Large Samples) VOCABULARY: Point Estimate A value for a parameter. The most point estimate of the population parameter is the
Chapter 6 Confidence Intervals Section 6-1 Confidence Intervals for the Mean (Large Samples) VOCABULARY: Point Estimate A value for a parameter. The most point estimate of the population parameter is the
On Some Test Statistics for Testing the Population Skewness and Kurtosis: An Empirical Study
 Florida International University FIU Digital Commons FIU Electronic Theses and Dissertations University Graduate School 8-26-2016 On Some Test Statistics for Testing the Population Skewness and Kurtosis:
Florida International University FIU Digital Commons FIU Electronic Theses and Dissertations University Graduate School 8-26-2016 On Some Test Statistics for Testing the Population Skewness and Kurtosis:
Statistical analysis and bootstrapping
 Statistical analysis and bootstrapping p. 1/15 Statistical analysis and bootstrapping Michel Bierlaire michel.bierlaire@epfl.ch Transport and Mobility Laboratory Statistical analysis and bootstrapping
Statistical analysis and bootstrapping p. 1/15 Statistical analysis and bootstrapping Michel Bierlaire michel.bierlaire@epfl.ch Transport and Mobility Laboratory Statistical analysis and bootstrapping
Two hours. To be supplied by the Examinations Office: Mathematical Formula Tables and Statistical Tables THE UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER
 Two hours MATH20802 To be supplied by the Examinations Office: Mathematical Formula Tables and Statistical Tables THE UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER STATISTICAL METHODS Answer any FOUR of the SIX questions.
Two hours MATH20802 To be supplied by the Examinations Office: Mathematical Formula Tables and Statistical Tables THE UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER STATISTICAL METHODS Answer any FOUR of the SIX questions.
Examples: Random Variables. Discrete and Continuous Random Variables. Probability Distributions
 Random Variables Examples: Random variable a variable (typically represented by x) that takes a numerical value by chance. Number of boys in a randomly selected family with three children. Possible values:
Random Variables Examples: Random variable a variable (typically represented by x) that takes a numerical value by chance. Number of boys in a randomly selected family with three children. Possible values:
CHAPTER 5. Introduction to Risk, Return, and the Historical Record INVESTMENTS BODIE, KANE, MARCUS
 CHAPTER 5 Introduction to Risk, Return, and the Historical Record INVESTMENTS BODIE, KANE, MARCUS McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 5-2 Supply Interest
CHAPTER 5 Introduction to Risk, Return, and the Historical Record INVESTMENTS BODIE, KANE, MARCUS McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 5-2 Supply Interest
Quantitative Methods
 THE ASSOCIATION OF BUSINESS EXECUTIVES DIPLOMA PART 2 QM Quantitative Methods afternoon 26 May 2004 1 Time allowed: 3 hours. 2 Answer any FOUR questions. 3 All questions carry 25 marks. Marks for subdivisions
THE ASSOCIATION OF BUSINESS EXECUTIVES DIPLOMA PART 2 QM Quantitative Methods afternoon 26 May 2004 1 Time allowed: 3 hours. 2 Answer any FOUR questions. 3 All questions carry 25 marks. Marks for subdivisions
STA Module 3B Discrete Random Variables
 STA 2023 Module 3B Discrete Random Variables Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. Determine the probability distribution of a discrete random variable. 2. Construct
STA 2023 Module 3B Discrete Random Variables Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. Determine the probability distribution of a discrete random variable. 2. Construct
Contents. 1 Introduction. Math 321 Chapter 5 Confidence Intervals. 1 Introduction 1
 Math 321 Chapter 5 Confidence Intervals (draft version 2019/04/11-11:17:37) Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Confidence interval for mean µ 2 2.1 Known variance................................. 2 2.2 Unknown
Math 321 Chapter 5 Confidence Intervals (draft version 2019/04/11-11:17:37) Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Confidence interval for mean µ 2 2.1 Known variance................................. 2 2.2 Unknown
Econ 6900: Statistical Problems. Instructor: Yogesh Uppal
 Econ 6900: Statistical Problems Instructor: Yogesh Uppal Email: yuppal@ysu.edu Lecture Slides 4 Random Variables Probability Distributions Discrete Distributions Discrete Uniform Probability Distribution
Econ 6900: Statistical Problems Instructor: Yogesh Uppal Email: yuppal@ysu.edu Lecture Slides 4 Random Variables Probability Distributions Discrete Distributions Discrete Uniform Probability Distribution
Contents Part I Descriptive Statistics 1 Introduction and Framework Population, Sample, and Observations Variables Quali
 Part I Descriptive Statistics 1 Introduction and Framework... 3 1.1 Population, Sample, and Observations... 3 1.2 Variables.... 4 1.2.1 Qualitative and Quantitative Variables.... 5 1.2.2 Discrete and Continuous
Part I Descriptive Statistics 1 Introduction and Framework... 3 1.1 Population, Sample, and Observations... 3 1.2 Variables.... 4 1.2.1 Qualitative and Quantitative Variables.... 5 1.2.2 Discrete and Continuous
Chapter 8: Sampling distributions of estimators Sections
 Chapter 8 continued Chapter 8: Sampling distributions of estimators Sections 8.1 Sampling distribution of a statistic 8.2 The Chi-square distributions 8.3 Joint Distribution of the sample mean and sample
Chapter 8 continued Chapter 8: Sampling distributions of estimators Sections 8.1 Sampling distribution of a statistic 8.2 The Chi-square distributions 8.3 Joint Distribution of the sample mean and sample
Analysis of 2x2 Cross-Over Designs using T-Tests for Non-Inferiority
 Chapter 235 Analysis of 2x2 Cross-Over Designs using -ests for Non-Inferiority Introduction his procedure analyzes data from a two-treatment, two-period (2x2) cross-over design where the goal is to demonstrate
Chapter 235 Analysis of 2x2 Cross-Over Designs using -ests for Non-Inferiority Introduction his procedure analyzes data from a two-treatment, two-period (2x2) cross-over design where the goal is to demonstrate
Tests for One Variance
 Chapter 65 Introduction Occasionally, researchers are interested in the estimation of the variance (or standard deviation) rather than the mean. This module calculates the sample size and performs power
Chapter 65 Introduction Occasionally, researchers are interested in the estimation of the variance (or standard deviation) rather than the mean. This module calculates the sample size and performs power
Chapter 5: Statistical Inference (in General)
 Chapter 5: Statistical Inference (in General) Shiwen Shen University of South Carolina 2016 Fall Section 003 1 / 17 Motivation In chapter 3, we learn the discrete probability distributions, including Bernoulli,
Chapter 5: Statistical Inference (in General) Shiwen Shen University of South Carolina 2016 Fall Section 003 1 / 17 Motivation In chapter 3, we learn the discrete probability distributions, including Bernoulli,
STA Rev. F Learning Objectives. What is a Random Variable? Module 5 Discrete Random Variables
 STA 2023 Module 5 Discrete Random Variables Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Determine the probability distribution of a discrete random variable. 2. Construct
STA 2023 Module 5 Discrete Random Variables Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Determine the probability distribution of a discrete random variable. 2. Construct
Mixed models in R using the lme4 package Part 3: Inference based on profiled deviance
 Mixed models in R using the lme4 package Part 3: Inference based on profiled deviance Douglas Bates Department of Statistics University of Wisconsin - Madison Madison January 11, 2011
Mixed models in R using the lme4 package Part 3: Inference based on profiled deviance Douglas Bates Department of Statistics University of Wisconsin - Madison Madison January 11, 2011
STAT/MATH 395 PROBABILITY II
 STAT/MATH 395 PROBABILITY II Distribution of Random Samples & Limit Theorems Néhémy Lim University of Washington Winter 2017 Outline Distribution of i.i.d. Samples Convergence of random variables The Laws
STAT/MATH 395 PROBABILITY II Distribution of Random Samples & Limit Theorems Néhémy Lim University of Washington Winter 2017 Outline Distribution of i.i.d. Samples Convergence of random variables The Laws
Can we use kernel smoothing to estimate Value at Risk and Tail Value at Risk?
 Can we use kernel smoothing to estimate Value at Risk and Tail Value at Risk? Ramon Alemany, Catalina Bolancé and Montserrat Guillén Riskcenter - IREA Universitat de Barcelona http://www.ub.edu/riskcenter
Can we use kernel smoothing to estimate Value at Risk and Tail Value at Risk? Ramon Alemany, Catalina Bolancé and Montserrat Guillén Riskcenter - IREA Universitat de Barcelona http://www.ub.edu/riskcenter
Chapter 7 presents the beginning of inferential statistics. The two major activities of inferential statistics are
 Chapter 7 presents the beginning of inferential statistics. Concept: Inferential Statistics The two major activities of inferential statistics are 1 to use sample data to estimate values of population
Chapter 7 presents the beginning of inferential statistics. Concept: Inferential Statistics The two major activities of inferential statistics are 1 to use sample data to estimate values of population
Simulation Lecture Notes and the Gentle Lentil Case
 Simulation Lecture Notes and the Gentle Lentil Case General Overview of the Case What is the decision problem presented in the case? What are the issues Sanjay must consider in deciding among the alternative
Simulation Lecture Notes and the Gentle Lentil Case General Overview of the Case What is the decision problem presented in the case? What are the issues Sanjay must consider in deciding among the alternative
Shifting our focus. We were studying statistics (data, displays, sampling...) The next few lectures focus on probability (randomness) Why?
 Probability Introduction Shifting our focus We were studying statistics (data, displays, sampling...) The next few lectures focus on probability (randomness) Why? What is Probability? Probability is used
Probability Introduction Shifting our focus We were studying statistics (data, displays, sampling...) The next few lectures focus on probability (randomness) Why? What is Probability? Probability is used
Chapter 5 Discrete Probability Distributions. Random Variables Discrete Probability Distributions Expected Value and Variance
 Chapter 5 Discrete Probability Distributions Random Variables Discrete Probability Distributions Expected Value and Variance.40.30.20.10 0 1 2 3 4 Random Variables A random variable is a numerical description
Chapter 5 Discrete Probability Distributions Random Variables Discrete Probability Distributions Expected Value and Variance.40.30.20.10 0 1 2 3 4 Random Variables A random variable is a numerical description
Chapter 7. Sampling Distributions
 Chapter 7 Sampling Distributions Section 7.1 Sampling Distributions and the Central Limit Theorem Sampling Distributions Sampling distribution The probability distribution of a sample statistic. Formed
Chapter 7 Sampling Distributions Section 7.1 Sampling Distributions and the Central Limit Theorem Sampling Distributions Sampling distribution The probability distribution of a sample statistic. Formed
PIVOTAL QUANTILE ESTIMATES IN VAR CALCULATIONS. Peter Schaller, Bank Austria Creditanstalt (BA-CA) Wien,
 PIVOTAL QUANTILE ESTIMATES IN VAR CALCULATIONS Peter Schaller, Bank Austria Creditanstalt (BA-CA) Wien, peter@ca-risc.co.at c Peter Schaller, BA-CA, Strategic Riskmanagement 1 Contents Some aspects of
PIVOTAL QUANTILE ESTIMATES IN VAR CALCULATIONS Peter Schaller, Bank Austria Creditanstalt (BA-CA) Wien, peter@ca-risc.co.at c Peter Schaller, BA-CA, Strategic Riskmanagement 1 Contents Some aspects of
Paper Reference. Paper Reference(s) 6683/01 Edexcel GCE Statistics S1 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 6 6 8 3 0 1 Surname Paper Reference(s) 6683/01 Edexcel GCE Statistics S1 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary Wednesday 20 May 2009 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Signature
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 6 6 8 3 0 1 Surname Paper Reference(s) 6683/01 Edexcel GCE Statistics S1 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary Wednesday 20 May 2009 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Signature
Back to estimators...
 Back to estimators... So far, we have: Identified estimators for common parameters Discussed the sampling distributions of estimators Introduced ways to judge the goodness of an estimator (bias, MSE, etc.)
Back to estimators... So far, we have: Identified estimators for common parameters Discussed the sampling distributions of estimators Introduced ways to judge the goodness of an estimator (bias, MSE, etc.)
Chapter 4: Estimation
 Slide 4.1 Chapter 4: Estimation Estimation is the process of using sample data to draw inferences about the population Sample information x, s Inferences Population parameters µ,σ Slide 4. Point and interval
Slide 4.1 Chapter 4: Estimation Estimation is the process of using sample data to draw inferences about the population Sample information x, s Inferences Population parameters µ,σ Slide 4. Point and interval
Section 7.2. Estimating a Population Proportion
 Section 7.2 Estimating a Population Proportion Overview Section 7.2 Estimating a Population Proportion Section 7.3 Estimating a Population Mean Section 7.4 Estimating a Population Standard Deviation or
Section 7.2 Estimating a Population Proportion Overview Section 7.2 Estimating a Population Proportion Section 7.3 Estimating a Population Mean Section 7.4 Estimating a Population Standard Deviation or
Chapter 11: Inference for Distributions Inference for Means of a Population 11.2 Comparing Two Means
 Chapter 11: Inference for Distributions 11.1 Inference for Means of a Population 11.2 Comparing Two Means 1 Population Standard Deviation In the previous chapter, we computed confidence intervals and performed
Chapter 11: Inference for Distributions 11.1 Inference for Means of a Population 11.2 Comparing Two Means 1 Population Standard Deviation In the previous chapter, we computed confidence intervals and performed
1. The number of dental claims for each insured in a calendar year is distributed as a Geometric distribution with variance of
 1. The number of dental claims for each insured in a calendar year is distributed as a Geometric distribution with variance of 7.315. The amount of each claim is distributed as a Pareto distribution with
1. The number of dental claims for each insured in a calendar year is distributed as a Geometric distribution with variance of 7.315. The amount of each claim is distributed as a Pareto distribution with
Hypothesis Tests: One Sample Mean Cal State Northridge Ψ320 Andrew Ainsworth PhD
 Hypothesis Tests: One Sample Mean Cal State Northridge Ψ320 Andrew Ainsworth PhD MAJOR POINTS Sampling distribution of the mean revisited Testing hypotheses: sigma known An example Testing hypotheses:
Hypothesis Tests: One Sample Mean Cal State Northridge Ψ320 Andrew Ainsworth PhD MAJOR POINTS Sampling distribution of the mean revisited Testing hypotheses: sigma known An example Testing hypotheses:
The SAS System 11:03 Monday, November 11,
 The SAS System 11:3 Monday, November 11, 213 1 The CONTENTS Procedure Data Set Name BIO.AUTO_PREMIUMS Observations 5 Member Type DATA Variables 3 Engine V9 Indexes Created Monday, November 11, 213 11:4:19
The SAS System 11:3 Monday, November 11, 213 1 The CONTENTS Procedure Data Set Name BIO.AUTO_PREMIUMS Observations 5 Member Type DATA Variables 3 Engine V9 Indexes Created Monday, November 11, 213 11:4:19
Value (x) probability Example A-2: Construct a histogram for population Ψ.
 Calculus 111, section 08.x The Central Limit Theorem notes by Tim Pilachowski If you haven t done it yet, go to the Math 111 page and download the handout: Central Limit Theorem supplement. Today s lecture
Calculus 111, section 08.x The Central Limit Theorem notes by Tim Pilachowski If you haven t done it yet, go to the Math 111 page and download the handout: Central Limit Theorem supplement. Today s lecture
Modelling catastrophic risk in international equity markets: An extreme value approach. JOHN COTTER University College Dublin
 Modelling catastrophic risk in international equity markets: An extreme value approach JOHN COTTER University College Dublin Abstract: This letter uses the Block Maxima Extreme Value approach to quantify
Modelling catastrophic risk in international equity markets: An extreme value approach JOHN COTTER University College Dublin Abstract: This letter uses the Block Maxima Extreme Value approach to quantify
physicsandmathstutor.com Paper Reference Statistics S1 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary Wednesday 20 May 2009 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
 Centre No. Candidate No. physicsandmathstutor.com Paper Reference 6 6 8 3 0 1 Surname Paper Reference(s) 6683/01 Edexcel GCE Statistics S1 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary Wednesday 20 May 2009 Afternoon Time:
Centre No. Candidate No. physicsandmathstutor.com Paper Reference 6 6 8 3 0 1 Surname Paper Reference(s) 6683/01 Edexcel GCE Statistics S1 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary Wednesday 20 May 2009 Afternoon Time:
Chapter 7 Sampling Distributions and Point Estimation of Parameters
 Chapter 7 Sampling Distributions and Point Estimation of Parameters Part 1: Sampling Distributions, the Central Limit Theorem, Point Estimation & Estimators Sections 7-1 to 7-2 1 / 25 Statistical Inferences
Chapter 7 Sampling Distributions and Point Estimation of Parameters Part 1: Sampling Distributions, the Central Limit Theorem, Point Estimation & Estimators Sections 7-1 to 7-2 1 / 25 Statistical Inferences
2011 Pearson Education, Inc
 Statistics for Business and Economics Chapter 4 Random Variables & Probability Distributions Content 1. Two Types of Random Variables 2. Probability Distributions for Discrete Random Variables 3. The Binomial
Statistics for Business and Economics Chapter 4 Random Variables & Probability Distributions Content 1. Two Types of Random Variables 2. Probability Distributions for Discrete Random Variables 3. The Binomial
