MATH 116: Material Covered in Class and Quiz/Exam Information
|
|
|
- Phyllis McDowell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MATH 116: Material Covered in Class and Quiz/Exam Information August 23 rd. Syllabus. Divisibility and linear combinations. Example 1: Proof of Theorem 2.4 parts (a), (c), and (g). Example 2: Exercise 2.7 parts (a) and (b). Example 3: Prove that if a b and b c then a c. Example 4: Exercise 2.8 parts (a) and (b). Example 5: Exercise 2.14 parts (a) and (b). August 28 th. gcd(a, b) and Worksheet. Example 6: Discussion on Exercise 2.14 with 5 2. Example 7: gcd(6, 9) = gcd( 3, 9) = 3. Example 8: Lemma Example 9: Exercise August 30 th. Prime numbers. Quiz 1 (up to 2.17). Example 10: Exercise Example 11: Using Lemma 2.43, prove Lemma Example 12: Theorem Example 13: Use Theorem 2.49 to get the sieve of Eratosthenes. Example 14: After rambling a bit about prime distribution we solved Exercise September 6 th. Prime factorization and gcd (again). Quiz 2 (up to 2.58). Example 15: Exercise Example 16: Exercise Example 17: Find gcd( , ) Example 18: Various examples of squares and/or square-free numbers. Example 19: Exercise Example 20: Exercise 3.4. Example 21: Exercise 3.6. September 11 th. The Euclidean algorithm and Worksheet. Example 22: Exercise 3.7. Example 23: gcd(3172, 793) and gcd(3175, 793) Example 24: Lemma Example 25: Exercise
2 September 13 th. Bézout s Lemma. Quiz 3 (up to 3.22). Example 26: Exercise 3.32(f). Example 27: Find s and t in Bézout s Lemma for the numbers in Exercise 3.32(f). Example 28: Exercise Example 29: Exercise Example 30: Exercise September 18 th. Diophantine Equations and Worksheet. Example 31: Lemma 4.7 Example 32: Find solutions of 3x 9y = 12 in Z. Example 33: Find solutions of 2017x + 31y = 4 in Z. September 20 th. 8:00-8:50 Missing Proofs. 8:50-9:50 Exam 1 (Chapters 2 and 3). Example 34: Proof of Bézout s Lemma. Example 35: Proof of Theorem 4.9. September 25 th. Diophantine Equations, Z m, and Worksheet. Example 36: Exercise 4.11 (c). Example 37: Exercise Example 38: We found all equivalence classes modulo 5. September 27 th. Z m. Quiz 4 (Linear Diophantine equations). Example 39: Compute the following in Z 78 : Example 40: Exercise 6.23, parts (a) and (b). Example 41: Exercise 6.30(a). October 2 nd. More computations modulo m. Congruence equations. Example 42: Exercise Example 43: Exercise Not complete, though. Example 44: Exercise 7.10 (e). October 4 th. Congruence equations. Chinese remainder theorem. Quiz 5 (Chapter 5, and Chapter 6 up to Exercise 6.23). Example 45: Theorem 7.5. Example 46: Theorem 7.8. Example 47: Exercise 7.10 parts (a) and (f). 2
3 Example 48: Solve 2x 3 (mod 5). October 9 th. The Chinese remainder theorem. Worksheet. Example 49: Solve in two different ways. x 1 (mod 2) x 2 (mod 5) x 3 (mod 7) October 11 th. Z m. Exam 2 (Chapters 4 6, and Chapter 7 up to Section 7.2, included). Example 50: Find all the elements in Z 8, Z 10, and Z p for p prime. Example 51: Theorem Example 52: Compute φ( ) October 16 th. Properties of the Euler-φ function. Worksheet. Example 53: Theorem Example 54: Theorem 8.21 for k = 1 and k = 2. October 18 th. Euler s Theorem. Order of an element. Quiz 6 (Chinese remainder theorem and basic properties of Z m and φ). Example 55: Exercise 8.21 for k = 4. Example 56: is divisible by 7. Example 57: Prove that if gcd(a, b) = 1 then a φ(b) + b φ(a) 1 (mod ab). October 23 th. Order of an element. Worksheet. Example 58: Theorem 9.5 and Exercise 9.6. Example 59: Corollary 9.7. Example 60: Find Example 61: Exercise 9.149a). October 25 th. Primitive elements. Quiz 7 (Euler s φ-function and Euler s theorem). Example 62: Exercise 9.16(a). Example 63: Found primitive roots of n = 2, 3, 23, and 9. Checked that n = 8 and n = 12 do not have primitive roots. October 30 th. Existence of primitive roots. Example 64: Exercise
4 Example 65: Theorem Example 66: Exercise While solving this we looked at Corollaries 9.35 and November 1 st. Discrete logarithms. Solving equations using logarithms. Worksheet/Quiz. Example 67: Solve 7x 7 3 (mod 11). Example 68: Solve 21x (mod 38). November 6 th. Missing proofs and squares in Z n. Example 69: Theorem Example 70: Theorem Example 71: If r is a primitive root of p (odd prime) then r (p 1)/2 1 (mod p). November 8 th. Squares in Z n. Exam 3 (Section 7.3 to Chapter 9, both included). Example 72: If n has a primitive root, then the number of quadratic residues of n is φ(n) 2. Example 73: If n has a primitive root r, then the quadratic residues of n are exactly the even powers of r. Example 74: If n has a primitive root r, then the product of two non-quadratic residues is a quadratic residue. November 13 th. The quadratic reciprocity. Example 75: Theorem Example 76: Theorem Example 77: Exercise 10.20(a). Example 78: Exercise Example 79: Exercise November 15 th. The quadratic reciprocity. Worksheet on Chapter 10. Example 80: Proof of Corollary Example 81: Proof of Theorem November 20 th. Multiplicative functions. σ and τ. Example 82: Example 11.3 and Exercise 11.5(e). Example 83: Theorem (one way only). Example 84: Theorem Example 85: Lemma Example 86: Exercise 11.28(a) (incomplete). 4
5 November 27 th. The Möbius inversion formula. Example 87: Exercise 11.28(a) (the other half). Example 88: Exercise Example 89: Exercise November 29 th. Fermat primes and Mersenne primes. Worksheet on Chapter 11. Example 90: Lemma Example 91: Theorem December 4 th. Review and missing proofs. Example 92: Theorem Example 93: Lemma December 6 th. Review.. Exam 4 (Chapters 10, 11, and 12). December 7 th and 8 th. Consultation Days. Office hours: Thursday: 8:00-10:00 AM and 3:00-5:00 PM. Friday: 2:00-4:00 PM. December 13 th. Final Exam: 08:45-10:45AM in S 139. This exam is comprehensive, so it tests Chapters 2-12, except Sections 3.4 and
Homework #5 7 th week Math 240 Thursday October 24, 2013
 . Let a, b > be integers and g : = gcd(a, b) its greatest common divisor. Show that if a = g q a and b = g q b then q a and q b are relatively rime. Since gcd(κ a, κ b) = κ gcd(a, b) in articular, for
. Let a, b > be integers and g : = gcd(a, b) its greatest common divisor. Show that if a = g q a and b = g q b then q a and q b are relatively rime. Since gcd(κ a, κ b) = κ gcd(a, b) in articular, for
Algebra homework 8 Homomorphisms, isomorphisms
 MATH-UA.343.005 T.A. Louis Guigo Algebra homework 8 Homomorphisms, isomorphisms For every n 1 we denote by S n the n-th symmetric group. Exercise 1. Consider the following permutations: ( ) ( 1 2 3 4 5
MATH-UA.343.005 T.A. Louis Guigo Algebra homework 8 Homomorphisms, isomorphisms For every n 1 we denote by S n the n-th symmetric group. Exercise 1. Consider the following permutations: ( ) ( 1 2 3 4 5
A generalization of Sylvester s and Frobenius problems on numerical semigroups
 ACTA ARITHMETICA LXV.4 (1993) A generalization of Sylvester s and Frobenius problems on numerical semigroups by Zdzis law Skupień (Kraków) 1. Introduction. Our aim is to formulate and study a modular change
ACTA ARITHMETICA LXV.4 (1993) A generalization of Sylvester s and Frobenius problems on numerical semigroups by Zdzis law Skupień (Kraków) 1. Introduction. Our aim is to formulate and study a modular change
Algebra and Number Theory Exercise Set
 Algebra and Number Theory Exercise Set Kamil Niedzia lomski 1 Algebra 1.1 Complex Numbers Exercise 1. Find real and imaginary part of complex numbers (1) 1 i 2+i (2) (3 + 7i)( 3 + i) (3) ( 3+i)( 1+i 3)
Algebra and Number Theory Exercise Set Kamil Niedzia lomski 1 Algebra 1.1 Complex Numbers Exercise 1. Find real and imaginary part of complex numbers (1) 1 i 2+i (2) (3 + 7i)( 3 + i) (3) ( 3+i)( 1+i 3)
Partial Fractions. A rational function is a fraction in which both the numerator and denominator are polynomials. For example, f ( x) = 4, g( x) =
 Partial Fractions A rational function is a fraction in which both the numerator and denominator are polynomials. For example, f ( x) = 4, g( x) = 3 x 2 x + 5, and h( x) = x + 26 x 2 are rational functions.
Partial Fractions A rational function is a fraction in which both the numerator and denominator are polynomials. For example, f ( x) = 4, g( x) = 3 x 2 x + 5, and h( x) = x + 26 x 2 are rational functions.
Worksheet A ALGEBRA PMT
 Worksheet A 1 Find the quotient obtained in dividing a (x 3 + 2x 2 x 2) by (x + 1) b (x 3 + 2x 2 9x + 2) by (x 2) c (20 + x + 3x 2 + x 3 ) by (x + 4) d (2x 3 x 2 4x + 3) by (x 1) e (6x 3 19x 2 73x + 90)
Worksheet A 1 Find the quotient obtained in dividing a (x 3 + 2x 2 x 2) by (x + 1) b (x 3 + 2x 2 9x + 2) by (x 2) c (20 + x + 3x 2 + x 3 ) by (x + 4) d (2x 3 x 2 4x + 3) by (x 1) e (6x 3 19x 2 73x + 90)
On equation. Boris Bartolomé. January 25 th, Göttingen Universität & Institut de Mathémathiques de Bordeaux
 Göttingen Universität & Institut de Mathémathiques de Bordeaux Boris.Bartolome@mathematik.uni-goettingen.de Boris.Bartolome@math.u-bordeaux1.fr January 25 th, 2016 January 25 th, 2016 1 / 19 Overview 1
Göttingen Universität & Institut de Mathémathiques de Bordeaux Boris.Bartolome@mathematik.uni-goettingen.de Boris.Bartolome@math.u-bordeaux1.fr January 25 th, 2016 January 25 th, 2016 1 / 19 Overview 1
WEIGHTED SUM OF THE EXTENSIONS OF THE REPRESENTATIONS OF QUADRATIC FORMS
 WEIGHTED SUM OF THE EXTENSIONS OF THE REPRESENTATIONS OF QUADRATIC FORMS BYEONG-KWEON OH Abstract Let L, N and M be positive definite integral Z-lattices In this paper, we show some relation between the
WEIGHTED SUM OF THE EXTENSIONS OF THE REPRESENTATIONS OF QUADRATIC FORMS BYEONG-KWEON OH Abstract Let L, N and M be positive definite integral Z-lattices In this paper, we show some relation between the
2-4 Completing the Square
 2-4 Completing the Square Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 2 Warm Up Write each expression as a trinomial. 1. (x 5) 2 x 2 10x + 25 2. (3x + 5) 2 9x 2 + 30x + 25 Factor each expression. 3.
2-4 Completing the Square Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 2 Warm Up Write each expression as a trinomial. 1. (x 5) 2 x 2 10x + 25 2. (3x + 5) 2 9x 2 + 30x + 25 Factor each expression. 3.
QUADRATIC. Parent Graph: How to Tell it's a Quadratic: Helpful Hints for Calculator Usage: Domain of Parent Graph:, Range of Parent Graph: 0,
 Parent Graph: How to Tell it's a Quadratic: If the equation's largest exponent is 2 If the graph is a parabola ("U"-Shaped) Opening up or down. QUADRATIC f x = x 2 Domain of Parent Graph:, Range of Parent
Parent Graph: How to Tell it's a Quadratic: If the equation's largest exponent is 2 If the graph is a parabola ("U"-Shaped) Opening up or down. QUADRATIC f x = x 2 Domain of Parent Graph:, Range of Parent
A Result on the Distribution of Quadratic Residues with Applications to Elliptic Curve Cryptography
 A Result on the Distribution of Quadratic Residues with Applications to Elliptic Curve Cryptography Muralidhara V.N. and Sandeep Sen {murali, ssen}@cse.iitd.ernet.in Department of Computer Science and
A Result on the Distribution of Quadratic Residues with Applications to Elliptic Curve Cryptography Muralidhara V.N. and Sandeep Sen {murali, ssen}@cse.iitd.ernet.in Department of Computer Science and
Factor Trinomials When the Coefficient of the Second-Degree Term is 1 (Objective #1)
 Factoring Trinomials (5.2) Factor Trinomials When the Coefficient of the Second-Degree Term is 1 EXAMPLE #1: Factor the trinomials. = = Factor Trinomials When the Coefficient of the Second-Degree Term
Factoring Trinomials (5.2) Factor Trinomials When the Coefficient of the Second-Degree Term is 1 EXAMPLE #1: Factor the trinomials. = = Factor Trinomials When the Coefficient of the Second-Degree Term
Writing Exponential Equations Day 2
 Writing Exponential Equations Day 2 MGSE9 12.A.CED.1 Create equations and inequalities in one variable and use them to solve problems. Include equations arising from linear, quadratic, simple rational,
Writing Exponential Equations Day 2 MGSE9 12.A.CED.1 Create equations and inequalities in one variable and use them to solve problems. Include equations arising from linear, quadratic, simple rational,
Version A. Problem 1. Let X be the continuous random variable defined by the following pdf: 1 x/2 when 0 x 2, f(x) = 0 otherwise.
 Math 224 Q Exam 3A Fall 217 Tues Dec 12 Version A Problem 1. Let X be the continuous random variable defined by the following pdf: { 1 x/2 when x 2, f(x) otherwise. (a) Compute the mean µ E[X]. E[X] x
Math 224 Q Exam 3A Fall 217 Tues Dec 12 Version A Problem 1. Let X be the continuous random variable defined by the following pdf: { 1 x/2 when x 2, f(x) otherwise. (a) Compute the mean µ E[X]. E[X] x
Algebra 2 Final Exam
 Algebra 2 Final Exam Name: Read the directions below. You may lose points if you do not follow these instructions. The exam consists of 30 Multiple Choice questions worth 1 point each and 5 Short Answer
Algebra 2 Final Exam Name: Read the directions below. You may lose points if you do not follow these instructions. The exam consists of 30 Multiple Choice questions worth 1 point each and 5 Short Answer
Study Guide and Review - Chapter 2
 Divide using long division. 31. (x 3 + 8x 2 5) (x 2) So, (x 3 + 8x 2 5) (x 2) = x 2 + 10x + 20 +. 33. (2x 5 + 5x 4 5x 3 + x 2 18x + 10) (2x 1) So, (2x 5 + 5x 4 5x 3 + x 2 18x + 10) (2x 1) = x 4 + 3x 3
Divide using long division. 31. (x 3 + 8x 2 5) (x 2) So, (x 3 + 8x 2 5) (x 2) = x 2 + 10x + 20 +. 33. (2x 5 + 5x 4 5x 3 + x 2 18x + 10) (2x 1) So, (2x 5 + 5x 4 5x 3 + x 2 18x + 10) (2x 1) = x 4 + 3x 3
REMARKS ON K3 SURFACES WITH NON-SYMPLECTIC AUTOMORPHISMS OF ORDER 7
 REMARKS ON K3 SURFACES WTH NON-SYMPLECTC AUTOMORPHSMS OF ORDER 7 SHNGO TAK Abstract. n this note, we treat a pair of a K3 surface and a non-symplectic automorphism of order 7m (m = 1, 3 and 6) on it. We
REMARKS ON K3 SURFACES WTH NON-SYMPLECTC AUTOMORPHSMS OF ORDER 7 SHNGO TAK Abstract. n this note, we treat a pair of a K3 surface and a non-symplectic automorphism of order 7m (m = 1, 3 and 6) on it. We
How can we factor polynomials?
 How can we factor polynomials? Factoring refers to writing something as a product. Factoring completely means that all of the factors are relatively prime (they have a GCF of 1). Methods of factoring:
How can we factor polynomials? Factoring refers to writing something as a product. Factoring completely means that all of the factors are relatively prime (they have a GCF of 1). Methods of factoring:
Topic #1: Evaluating and Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
 John Jay College of Criminal Justice The City University of New York Department of Mathematics and Computer Science MAT 105 - College Algebra Departmental Final Examination Review Topic #1: Evaluating
John Jay College of Criminal Justice The City University of New York Department of Mathematics and Computer Science MAT 105 - College Algebra Departmental Final Examination Review Topic #1: Evaluating
Page Points Score Total: 100
 Math 1130 Spring 2019 Sample Midterm 2b 2/28/19 Name (Print): Username.#: Lecturer: Rec. Instructor: Rec. Time: This exam contains 10 pages (including this cover page) and 9 problems. Check to see if any
Math 1130 Spring 2019 Sample Midterm 2b 2/28/19 Name (Print): Username.#: Lecturer: Rec. Instructor: Rec. Time: This exam contains 10 pages (including this cover page) and 9 problems. Check to see if any
Lattice based cryptography
 Lattice based cryptography Abderrahmane Nitaj University of Caen Basse Normandie, France Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, June 23, 2014 Abderrahmane Nitaj (LMNO) Q AK ËAÓ Lattice based cryptography 1 / 54 Contents
Lattice based cryptography Abderrahmane Nitaj University of Caen Basse Normandie, France Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, June 23, 2014 Abderrahmane Nitaj (LMNO) Q AK ËAÓ Lattice based cryptography 1 / 54 Contents
A note on the number of (k, l)-sum-free sets
 A note on the number of (k, l)-sum-free sets Tomasz Schoen Mathematisches Seminar Universität zu Kiel Ludewig-Meyn-Str. 4, 4098 Kiel, Germany tos@numerik.uni-kiel.de and Department of Discrete Mathematics
A note on the number of (k, l)-sum-free sets Tomasz Schoen Mathematisches Seminar Universität zu Kiel Ludewig-Meyn-Str. 4, 4098 Kiel, Germany tos@numerik.uni-kiel.de and Department of Discrete Mathematics
Final Study Guide MATH 111
 Final Study Guide MATH 111 The final will be cumulative. There will probably be a very slight emphasis on the material from the second half of the class. In terms of the material in the first half, please
Final Study Guide MATH 111 The final will be cumulative. There will probably be a very slight emphasis on the material from the second half of the class. In terms of the material in the first half, please
Discrete Mathematics for CS Spring 2008 David Wagner Final Exam
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Spring 2008 David Wagner Final Exam PRINT your name:, (last) SIGN your name: (first) PRINT your Unix account login: Your section time (e.g., Tue 3pm): Name of the person
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Spring 2008 David Wagner Final Exam PRINT your name:, (last) SIGN your name: (first) PRINT your Unix account login: Your section time (e.g., Tue 3pm): Name of the person
3 The Model Existence Theorem
 3 The Model Existence Theorem Although we don t have compactness or a useful Completeness Theorem, Henkinstyle arguments can still be used in some contexts to build models. In this section we describe
3 The Model Existence Theorem Although we don t have compactness or a useful Completeness Theorem, Henkinstyle arguments can still be used in some contexts to build models. In this section we describe
Contents. Heinemann Maths Zone
 Contents Chapter 1 Finance R1.1 Increasing a price by a percentage R1.2 Simple interest (1) R1.3 Simple interest (2) R1.4 Percentage profit (1) R1.5 Percentage profit (2) R1.6 The Distributive Law R1.7
Contents Chapter 1 Finance R1.1 Increasing a price by a percentage R1.2 Simple interest (1) R1.3 Simple interest (2) R1.4 Percentage profit (1) R1.5 Percentage profit (2) R1.6 The Distributive Law R1.7
Unit 1 Maths Methods (CAS) Exam 2013 Thursday June 6th pm
 Name: Teacher: Unit 1 Maths Methods (CAS) Exam 2013 Thursday June 6th 1.50-3.20 pm Reading time: 10 Minutes Writing time: 80 Minutes Instruction to candidates: Students are permitted to bring into the
Name: Teacher: Unit 1 Maths Methods (CAS) Exam 2013 Thursday June 6th 1.50-3.20 pm Reading time: 10 Minutes Writing time: 80 Minutes Instruction to candidates: Students are permitted to bring into the
Unit 8 Notes: Solving Quadratics by Factoring Alg 1
 Unit 8 Notes: Solving Quadratics by Factoring Alg 1 Name Period Day Date Assignment (Due the next class meeting) Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Monday Tuesday
Unit 8 Notes: Solving Quadratics by Factoring Alg 1 Name Period Day Date Assignment (Due the next class meeting) Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Monday Tuesday
Alg2A Factoring and Equations Review Packet
 1 Factoring using GCF: Take the greatest common factor (GCF) for the numerical coefficient. When choosing the GCF for the variables, if all the terms have a common variable, take the one with the lowest
1 Factoring using GCF: Take the greatest common factor (GCF) for the numerical coefficient. When choosing the GCF for the variables, if all the terms have a common variable, take the one with the lowest
Determinants II Linear Algebra, Fall 2008
 Determinants II Linear Algebra, Fall 2008 1 Basic Properties of Determinants Here are the basic properties of determinants which you proved in the exercises to the previous handout Theorem 1 Let A be an
Determinants II Linear Algebra, Fall 2008 1 Basic Properties of Determinants Here are the basic properties of determinants which you proved in the exercises to the previous handout Theorem 1 Let A be an
Notes on the symmetric group
 Notes on the symmetric group 1 Computations in the symmetric group Recall that, given a set X, the set S X of all bijections from X to itself (or, more briefly, permutations of X) is group under function
Notes on the symmetric group 1 Computations in the symmetric group Recall that, given a set X, the set S X of all bijections from X to itself (or, more briefly, permutations of X) is group under function
Slide 1 / 128. Polynomials
 Slide 1 / 128 Polynomials Slide 2 / 128 Table of Contents Factors and GCF Factoring out GCF's Factoring Trinomials x 2 + bx + c Factoring Using Special Patterns Factoring Trinomials ax 2 + bx + c Factoring
Slide 1 / 128 Polynomials Slide 2 / 128 Table of Contents Factors and GCF Factoring out GCF's Factoring Trinomials x 2 + bx + c Factoring Using Special Patterns Factoring Trinomials ax 2 + bx + c Factoring
Applications of Data Dispersions
 1 Applications of Data Dispersions Key Definitions Standard Deviation: The standard deviation shows how far away each value is from the mean on average. Z-Scores: The distance between the mean and a given
1 Applications of Data Dispersions Key Definitions Standard Deviation: The standard deviation shows how far away each value is from the mean on average. Z-Scores: The distance between the mean and a given
MATD 0370 ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA REVIEW FOR TEST 3 (New Material From: , , and 10.1)
 NOTE: In addition to the problems below, please study the handout Exercise Set 10.1 posted at http://www.austin.cc.tx.us/jbickham/handouts. 1. Simplify: 5 7 5. Simplify: ( 6ab 5 c )( a c 5 ). Simplify:
NOTE: In addition to the problems below, please study the handout Exercise Set 10.1 posted at http://www.austin.cc.tx.us/jbickham/handouts. 1. Simplify: 5 7 5. Simplify: ( 6ab 5 c )( a c 5 ). Simplify:
Math1090 Midterm 2 Review Sections , Solve the system of linear equations using Gauss-Jordan elimination.
 Math1090 Midterm 2 Review Sections 2.1-2.5, 3.1-3.3 1. Solve the system of linear equations using Gauss-Jordan elimination. 5x+20y 15z = 155 (a) 2x 7y+13z=85 3x+14y +6z= 43 x+z= 2 (b) x= 6 y+z=11 x y+
Math1090 Midterm 2 Review Sections 2.1-2.5, 3.1-3.3 1. Solve the system of linear equations using Gauss-Jordan elimination. 5x+20y 15z = 155 (a) 2x 7y+13z=85 3x+14y +6z= 43 x+z= 2 (b) x= 6 y+z=11 x y+
CCAC ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA
 CCAC ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA Sample Questions TOPICS TO STUDY: Evaluate expressions Add, subtract, multiply, and divide polynomials Add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational expressions Factor two and three
CCAC ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA Sample Questions TOPICS TO STUDY: Evaluate expressions Add, subtract, multiply, and divide polynomials Add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational expressions Factor two and three
MATD 0370 ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA REVIEW FOR TEST 3 (New Material From: , , and 10.1)
 NOTE: In addition to the problems below, please study the handout Exercise Set 10.1 posted at http://www.austincc.edu/jbickham/handouts. 1. Simplify: 5 7 5. Simplify: ( ab 5 c )( a c 5 ). Simplify: 4x
NOTE: In addition to the problems below, please study the handout Exercise Set 10.1 posted at http://www.austincc.edu/jbickham/handouts. 1. Simplify: 5 7 5. Simplify: ( ab 5 c )( a c 5 ). Simplify: 4x
On Machin s formula with Powers of the Golden Section
 On Machin s formula with Powers of the Golden Section Florian Luca Instituto de Matemáticas Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México C.P. 58089, Morelia, Michoacán, México fluca@matmor.unam.mx Pantelimon
On Machin s formula with Powers of the Golden Section Florian Luca Instituto de Matemáticas Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México C.P. 58089, Morelia, Michoacán, México fluca@matmor.unam.mx Pantelimon
Monte Carlo and Empirical Methods for Stochastic Inference (MASM11/FMSN50)
 Monte Carlo and Empirical Methods for Stochastic Inference (MASM11/FMSN50) Magnus Wiktorsson Centre for Mathematical Sciences Lund University, Sweden Lecture 2 Random number generation January 18, 2018
Monte Carlo and Empirical Methods for Stochastic Inference (MASM11/FMSN50) Magnus Wiktorsson Centre for Mathematical Sciences Lund University, Sweden Lecture 2 Random number generation January 18, 2018
Writing Exponential Equations Day 2
 Writing Exponential Equations Day 2 MGSE9 12.A.CED.1 Create equations and inequalities in one variable and use them to solve problems. Include equations arising from linear, quadratic, simple rational,
Writing Exponential Equations Day 2 MGSE9 12.A.CED.1 Create equations and inequalities in one variable and use them to solve problems. Include equations arising from linear, quadratic, simple rational,
Lecture 5: Tuesday, January 27, Peterson s Algorithm satisfies the No Starvation property (Theorem 1)
 Com S 611 Spring Semester 2015 Advanced Topics on Distributed and Concurrent Algorithms Lecture 5: Tuesday, January 27, 2015 Instructor: Soma Chaudhuri Scribe: Nik Kinkel 1 Introduction This lecture covers
Com S 611 Spring Semester 2015 Advanced Topics on Distributed and Concurrent Algorithms Lecture 5: Tuesday, January 27, 2015 Instructor: Soma Chaudhuri Scribe: Nik Kinkel 1 Introduction This lecture covers
Factoring. (5) Page 600 #21 43 Right **********Quiz Tomorrow********** (10) Page #20 32 Right; #35 47 Right *****Quiz tomorrow****
 Algebra Unit 6: Factoring Name: Date: Period: # Factoring (1) Page 629 #6 8; #15 20 (2) Page 629 #21, 22, 29-32 (3) Worksheet (4) Page 600 #19 42 Left (5) Page 600 #21 43 Right **********Quiz Tomorrow**********
Algebra Unit 6: Factoring Name: Date: Period: # Factoring (1) Page 629 #6 8; #15 20 (2) Page 629 #21, 22, 29-32 (3) Worksheet (4) Page 600 #19 42 Left (5) Page 600 #21 43 Right **********Quiz Tomorrow**********
Hedging under Arbitrage
 Hedging under Arbitrage Johannes Ruf Columbia University, Department of Statistics Modeling and Managing Financial Risks January 12, 2011 Motivation Given: a frictionless market of stocks with continuous
Hedging under Arbitrage Johannes Ruf Columbia University, Department of Statistics Modeling and Managing Financial Risks January 12, 2011 Motivation Given: a frictionless market of stocks with continuous
7-5 Factoring Special Products
 7-5 Factoring Special Products Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 1 Warm Up Determine whether the following are perfect squares. If so, find the square root. 1. 64 yes; 8 2. 36 3. 45 no 4.
7-5 Factoring Special Products Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 1 Warm Up Determine whether the following are perfect squares. If so, find the square root. 1. 64 yes; 8 2. 36 3. 45 no 4.
TWO-PERIODIC TERNARY RECURRENCES AND THEIR BINET-FORMULA 1. INTRODUCTION
 TWO-PERIODIC TERNARY RECURRENCES AND THEIR BINET-FORMULA M. ALP, N. IRMAK and L. SZALAY Abstract. The properties of k-periodic binary recurrences have been discussed by several authors. In this paper,
TWO-PERIODIC TERNARY RECURRENCES AND THEIR BINET-FORMULA M. ALP, N. IRMAK and L. SZALAY Abstract. The properties of k-periodic binary recurrences have been discussed by several authors. In this paper,
Math Analysis Midterm Review. Directions: This assignment is due at the beginning of class on Friday, January 9th
 Math Analysis Midterm Review Name Directions: This assignment is due at the beginning of class on Friday, January 9th This homework is intended to help you prepare for the midterm exam. The questions are
Math Analysis Midterm Review Name Directions: This assignment is due at the beginning of class on Friday, January 9th This homework is intended to help you prepare for the midterm exam. The questions are
Handout 4: Gains from Diversification for 2 Risky Assets Corporate Finance, Sections 001 and 002
 Handout 4: Gains from Diversification for 2 Risky Assets Corporate Finance, Sections 001 and 002 Suppose you are deciding how to allocate your wealth between two risky assets. Recall that the expected
Handout 4: Gains from Diversification for 2 Risky Assets Corporate Finance, Sections 001 and 002 Suppose you are deciding how to allocate your wealth between two risky assets. Recall that the expected
3.1 Properties of Binomial Coefficients
 3 Properties of Binomial Coefficients 31 Properties of Binomial Coefficients Here is the famous recursive formula for binomial coefficients Lemma 31 For 1 < n, 1 1 ( n 1 ) This equation can be proven by
3 Properties of Binomial Coefficients 31 Properties of Binomial Coefficients Here is the famous recursive formula for binomial coefficients Lemma 31 For 1 < n, 1 1 ( n 1 ) This equation can be proven by
Yao s Minimax Principle
 Complexity of algorithms The complexity of an algorithm is usually measured with respect to the size of the input, where size may for example refer to the length of a binary word describing the input,
Complexity of algorithms The complexity of an algorithm is usually measured with respect to the size of the input, where size may for example refer to the length of a binary word describing the input,
Orthogonality to the value group is the same as generic stability in C-minimal expansions of ACVF
 Orthogonality to the value group is the same as generic stability in C-minimal expansions of ACVF Will Johnson February 18, 2014 1 Introduction Let T be some C-minimal expansion of ACVF. Let U be the monster
Orthogonality to the value group is the same as generic stability in C-minimal expansions of ACVF Will Johnson February 18, 2014 1 Introduction Let T be some C-minimal expansion of ACVF. Let U be the monster
n - 1 PMT = 2) ( ) + ( ) + (9 1) A) 7,002,009 B) 70,002,009 C) 70,020,009 D) 700,020,009
 MGF 1107-Math for Liberal Arts II-Final Eam Stud Guide Spring 015 The final eam will consist of three parts: both a multiple choice and free response section allowing a scientific calculator, and a free
MGF 1107-Math for Liberal Arts II-Final Eam Stud Guide Spring 015 The final eam will consist of three parts: both a multiple choice and free response section allowing a scientific calculator, and a free
CS227-Scientific Computing. Lecture 6: Nonlinear Equations
 CS227-Scientific Computing Lecture 6: Nonlinear Equations A Financial Problem You invest $100 a month in an interest-bearing account. You make 60 deposits, and one month after the last deposit (5 years
CS227-Scientific Computing Lecture 6: Nonlinear Equations A Financial Problem You invest $100 a month in an interest-bearing account. You make 60 deposits, and one month after the last deposit (5 years
Quadrant marked mesh patterns in 123-avoiding permutations
 Quadrant marked mesh patterns in 23-avoiding permutations Dun Qiu Department of Mathematics University of California, San Diego La Jolla, CA 92093-02. USA duqiu@math.ucsd.edu Jeffrey Remmel Department
Quadrant marked mesh patterns in 23-avoiding permutations Dun Qiu Department of Mathematics University of California, San Diego La Jolla, CA 92093-02. USA duqiu@math.ucsd.edu Jeffrey Remmel Department
Multiple Eisenstein series
 Heilbronn Workshop on String Theory and Arithmetic Geometry University of Bristol - 5th September 2012 Multiple zeta-values Definition For natural numbers s 1 2, s 2,..., s l 1 the multiple zeta-value
Heilbronn Workshop on String Theory and Arithmetic Geometry University of Bristol - 5th September 2012 Multiple zeta-values Definition For natural numbers s 1 2, s 2,..., s l 1 the multiple zeta-value
Math Computational Finance Option pricing using Brownian bridge and Stratified samlping
 . Math 623 - Computational Finance Option pricing using Brownian bridge and Stratified samlping Pratik Mehta pbmehta@eden.rutgers.edu Masters of Science in Mathematical Finance Department of Mathematics,
. Math 623 - Computational Finance Option pricing using Brownian bridge and Stratified samlping Pratik Mehta pbmehta@eden.rutgers.edu Masters of Science in Mathematical Finance Department of Mathematics,
SYLLABUS AND SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR MSQE (Program Code: MQEK and MQED) Syllabus for PEA (Mathematics), 2013
 SYLLABUS AND SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR MSQE (Program Code: MQEK and MQED) 2013 Syllabus for PEA (Mathematics), 2013 Algebra: Binomial Theorem, AP, GP, HP, Exponential, Logarithmic Series, Sequence, Permutations
SYLLABUS AND SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR MSQE (Program Code: MQEK and MQED) 2013 Syllabus for PEA (Mathematics), 2013 Algebra: Binomial Theorem, AP, GP, HP, Exponential, Logarithmic Series, Sequence, Permutations
Errata and Updates for the 12 th Edition of the ASM Manual for Exam FM/2 (Last updated 5/4/2018) sorted by page
 Errata and Updates for the 12 th Edition of the ASM Manual for Exam FM/2 (Last updated 5/4/2018) sorted by page [2/28/18] Page 255, Question 47. The last answer should be 7.98 without the % sign. [7/30/17]
Errata and Updates for the 12 th Edition of the ASM Manual for Exam FM/2 (Last updated 5/4/2018) sorted by page [2/28/18] Page 255, Question 47. The last answer should be 7.98 without the % sign. [7/30/17]
Factoring. Difference of Two Perfect Squares (DOTS) Greatest Common Factor (GCF) Factoring Completely Trinomials. Factor Trinomials by Grouping
 Unit 6 Name Factoring Day 1 Difference of Two Perfect Squares (DOTS) Day Greatest Common Factor (GCF) Day 3 Factoring Completely Binomials Day 4 QUIZ Day 5 Factor by Grouping Day 6 Factor Trinomials by
Unit 6 Name Factoring Day 1 Difference of Two Perfect Squares (DOTS) Day Greatest Common Factor (GCF) Day 3 Factoring Completely Binomials Day 4 QUIZ Day 5 Factor by Grouping Day 6 Factor Trinomials by
Pricing Kernel. v,x = p,y = p,ax, so p is a stochastic discount factor. One refers to p as the pricing kernel.
 Payoff Space The set of possible payoffs is the range R(A). This payoff space is a subspace of the state space and is a Euclidean space in its own right. 1 Pricing Kernel By the law of one price, two portfolios
Payoff Space The set of possible payoffs is the range R(A). This payoff space is a subspace of the state space and is a Euclidean space in its own right. 1 Pricing Kernel By the law of one price, two portfolios
On the Optimality of a Family of Binary Trees Techical Report TR
 On the Optimality of a Family of Binary Trees Techical Report TR-011101-1 Dana Vrajitoru and William Knight Indiana University South Bend Department of Computer and Information Sciences Abstract In this
On the Optimality of a Family of Binary Trees Techical Report TR-011101-1 Dana Vrajitoru and William Knight Indiana University South Bend Department of Computer and Information Sciences Abstract In this
BF212 Mathematical Methods for Finance
 BF212 Mathematical Methods for Finance Academic Year: 2009-10 Semester: 2 Course Coordinator: William Leon Other Instructor(s): Pre-requisites: No. of AUs: 4 Cambridge G.C.E O Level Mathematics AB103 Business
BF212 Mathematical Methods for Finance Academic Year: 2009-10 Semester: 2 Course Coordinator: William Leon Other Instructor(s): Pre-requisites: No. of AUs: 4 Cambridge G.C.E O Level Mathematics AB103 Business
Contents. Heinemann Maths Zone Copyright Pearson Australia (a divsion of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd)
 Contents Chapter Money calculations R. Expressing fractions as decimals R.2 Expressing decimals as fractions R.3 Operating with fractions R.4 Simple decimal arithmetic R.5 Ratio and fractions R.6 Dividing
Contents Chapter Money calculations R. Expressing fractions as decimals R.2 Expressing decimals as fractions R.3 Operating with fractions R.4 Simple decimal arithmetic R.5 Ratio and fractions R.6 Dividing
Collinear Triple Hypergraphs and the Finite Plane Kakeya Problem
 Collinear Triple Hypergraphs and the Finite Plane Kakeya Problem Joshua Cooper August 14, 006 Abstract We show that the problem of counting collinear points in a permutation (previously considered by the
Collinear Triple Hypergraphs and the Finite Plane Kakeya Problem Joshua Cooper August 14, 006 Abstract We show that the problem of counting collinear points in a permutation (previously considered by the
McGILL UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS MATH THEORY OF INTEREST
 McGILL UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS MATH 329 2004 01 THEORY OF INTEREST Information for Students (Winter Term, 2003/2004) Pages 1-8 of these notes may be considered
McGILL UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS MATH 329 2004 01 THEORY OF INTEREST Information for Students (Winter Term, 2003/2004) Pages 1-8 of these notes may be considered
5.6 Special Products of Polynomials
 5.6 Special Products of Polynomials Learning Objectives Find the square of a binomial Find the product of binomials using sum and difference formula Solve problems using special products of polynomials
5.6 Special Products of Polynomials Learning Objectives Find the square of a binomial Find the product of binomials using sum and difference formula Solve problems using special products of polynomials
Optimal Search for Parameters in Monte Carlo Simulation for Derivative Pricing
 Optimal Search for Parameters in Monte Carlo Simulation for Derivative Pricing Prof. Chuan-Ju Wang Department of Computer Science University of Taipei Joint work with Prof. Ming-Yang Kao March 28, 2014
Optimal Search for Parameters in Monte Carlo Simulation for Derivative Pricing Prof. Chuan-Ju Wang Department of Computer Science University of Taipei Joint work with Prof. Ming-Yang Kao March 28, 2014
Name: Common Core Algebra L R Final Exam 2015 CLONE 3 Teacher:
 1) Which graph represents a linear function? 2) Which relation is a function? A) B) A) {(2, 3), (3, 9), (4, 7), (5, 7)} B) {(0, -2), (3, 10), (-2, -4), (3, 4)} C) {(2, 7), (2, -3), (1, 1), (3, -1)} D)
1) Which graph represents a linear function? 2) Which relation is a function? A) B) A) {(2, 3), (3, 9), (4, 7), (5, 7)} B) {(0, -2), (3, 10), (-2, -4), (3, 4)} C) {(2, 7), (2, -3), (1, 1), (3, -1)} D)
MA 1125 Lecture 05 - Measures of Spread. Wednesday, September 6, Objectives: Introduce variance, standard deviation, range.
 MA 115 Lecture 05 - Measures of Spread Wednesday, September 6, 017 Objectives: Introduce variance, standard deviation, range. 1. Measures of Spread In Lecture 04, we looked at several measures of central
MA 115 Lecture 05 - Measures of Spread Wednesday, September 6, 017 Objectives: Introduce variance, standard deviation, range. 1. Measures of Spread In Lecture 04, we looked at several measures of central
Page Points Score Total: 100
 Math 1130 Autumn 2018 Sample Midterm 2c 2/28/19 Name (Print): Username.#: Lecturer: Rec. Instructor: Rec. Time: This exam contains 8 pages (including this cover page) and 6 problems. Check to see if any
Math 1130 Autumn 2018 Sample Midterm 2c 2/28/19 Name (Print): Username.#: Lecturer: Rec. Instructor: Rec. Time: This exam contains 8 pages (including this cover page) and 6 problems. Check to see if any
CATEGORICAL SKEW LATTICES
 CATEGORICAL SKEW LATTICES MICHAEL KINYON AND JONATHAN LEECH Abstract. Categorical skew lattices are a variety of skew lattices on which the natural partial order is especially well behaved. While most
CATEGORICAL SKEW LATTICES MICHAEL KINYON AND JONATHAN LEECH Abstract. Categorical skew lattices are a variety of skew lattices on which the natural partial order is especially well behaved. While most
A THREE-FACTOR CONVERGENCE MODEL OF INTEREST RATES
 Proceedings of ALGORITMY 01 pp. 95 104 A THREE-FACTOR CONVERGENCE MODEL OF INTEREST RATES BEÁTA STEHLÍKOVÁ AND ZUZANA ZÍKOVÁ Abstract. A convergence model of interest rates explains the evolution of the
Proceedings of ALGORITMY 01 pp. 95 104 A THREE-FACTOR CONVERGENCE MODEL OF INTEREST RATES BEÁTA STEHLÍKOVÁ AND ZUZANA ZÍKOVÁ Abstract. A convergence model of interest rates explains the evolution of the
SELF-ADJOINT BOUNDARY-VALUE PROBLEMS ON TIME-SCALES
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2007(2007), No. 175, pp. 1 10. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) SELF-ADJOINT
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2007(2007), No. 175, pp. 1 10. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) SELF-ADJOINT
Introductory Mathematics for Economics MSc s: Course Outline. Huw David Dixon. Cardiff Business School. September 2008.
 Introductory Maths: course outline Huw Dixon. Introductory Mathematics for Economics MSc s: Course Outline. Huw David Dixon Cardiff Business School. September 008. The course will consist of five hour
Introductory Maths: course outline Huw Dixon. Introductory Mathematics for Economics MSc s: Course Outline. Huw David Dixon Cardiff Business School. September 008. The course will consist of five hour
Part 3: Trust-region methods for unconstrained optimization. Nick Gould (RAL)
 Part 3: Trust-region methods for unconstrained optimization Nick Gould (RAL) minimize x IR n f(x) MSc course on nonlinear optimization UNCONSTRAINED MINIMIZATION minimize x IR n f(x) where the objective
Part 3: Trust-region methods for unconstrained optimization Nick Gould (RAL) minimize x IR n f(x) MSc course on nonlinear optimization UNCONSTRAINED MINIMIZATION minimize x IR n f(x) where the objective
The Binomial Theorem and Consequences
 The Binomial Theorem and Consequences Juris Steprāns York University November 17, 2011 Fermat s Theorem Pierre de Fermat claimed the following theorem in 1640, but the first published proof (by Leonhard
The Binomial Theorem and Consequences Juris Steprāns York University November 17, 2011 Fermat s Theorem Pierre de Fermat claimed the following theorem in 1640, but the first published proof (by Leonhard
Final Project. College Algebra. Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to:
 COURSE OBJECTIVES Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: 1. Perform operations on algebraic expressions 2. Perform operations on functions expressed in standard function
COURSE OBJECTIVES Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: 1. Perform operations on algebraic expressions 2. Perform operations on functions expressed in standard function
A DNC function that computes no effectively bi-immune set
 A DNC function that computes no effectively bi-immune set Achilles A. Beros Laboratoire d Informatique de Nantes Atlantique, Université de Nantes July 5, 204 Standard Definitions Definition f is diagonally
A DNC function that computes no effectively bi-immune set Achilles A. Beros Laboratoire d Informatique de Nantes Atlantique, Université de Nantes July 5, 204 Standard Definitions Definition f is diagonally
22. Construct a bond amortization table for a $1000 two-year bond with 7% coupons paid semi-annually bought to yield 8% semi-annually.
 Chapter 6 Exercises 22. Construct a bond amortization table for a $1000 two-year bond with 7% coupons paid semi-annually bought to yield 8% semi-annually. 23. Construct a bond amortization table for a
Chapter 6 Exercises 22. Construct a bond amortization table for a $1000 two-year bond with 7% coupons paid semi-annually bought to yield 8% semi-annually. 23. Construct a bond amortization table for a
Haiyang Feng College of Management and Economics, Tianjin University, Tianjin , CHINA
 RESEARCH ARTICLE QUALITY, PRICING, AND RELEASE TIME: OPTIMAL MARKET ENTRY STRATEGY FOR SOFTWARE-AS-A-SERVICE VENDORS Haiyang Feng College of Management and Economics, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072,
RESEARCH ARTICLE QUALITY, PRICING, AND RELEASE TIME: OPTIMAL MARKET ENTRY STRATEGY FOR SOFTWARE-AS-A-SERVICE VENDORS Haiyang Feng College of Management and Economics, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072,
Dr. Maddah ENMG 625 Financial Eng g II 10/16/06
 Dr. Maddah ENMG 65 Financial Eng g II 10/16/06 Chapter 11 Models of Asset Dynamics () Random Walk A random process, z, is an additive process defined over times t 0, t 1,, t k, t k+1,, such that z( t )
Dr. Maddah ENMG 65 Financial Eng g II 10/16/06 Chapter 11 Models of Asset Dynamics () Random Walk A random process, z, is an additive process defined over times t 0, t 1,, t k, t k+1,, such that z( t )
Functions - Compound Interest
 10.6 Functions - Compound Interest Objective: Calculate final account balances using the formulas for compound and continuous interest. An application of exponential functions is compound interest. When
10.6 Functions - Compound Interest Objective: Calculate final account balances using the formulas for compound and continuous interest. An application of exponential functions is compound interest. When
Identifying & Factoring: x 2 + bx + c
 Identifying & Factoring: x 2 + bx + c Apr 13 11:04 AM 1 May 16 8:52 AM 2 A polynomial that can be simplified to the form ax + bx + c, where a 0, is called a quadratic polynomial. Linear term. Quadratic
Identifying & Factoring: x 2 + bx + c Apr 13 11:04 AM 1 May 16 8:52 AM 2 A polynomial that can be simplified to the form ax + bx + c, where a 0, is called a quadratic polynomial. Linear term. Quadratic
Unit 2: Modeling in the Frequency Domain Part 2: The Laplace Transform
 The Laplace Transform Unit 2: Modeling in the Frequency Domain Part 2: The Laplace Transform Engineering 5821: Control Systems I Faculty of Engineering & Applied Science Memorial University of Newfoundland
The Laplace Transform Unit 2: Modeling in the Frequency Domain Part 2: The Laplace Transform Engineering 5821: Control Systems I Faculty of Engineering & Applied Science Memorial University of Newfoundland
TABLEAU-BASED DECISION PROCEDURES FOR HYBRID LOGIC
 TABLEAU-BASED DECISION PROCEDURES FOR HYBRID LOGIC THOMAS BOLANDER AND TORBEN BRAÜNER Abstract. Hybrid logics are a principled generalization of both modal logics and description logics. It is well-known
TABLEAU-BASED DECISION PROCEDURES FOR HYBRID LOGIC THOMAS BOLANDER AND TORBEN BRAÜNER Abstract. Hybrid logics are a principled generalization of both modal logics and description logics. It is well-known
maps 1 to 5. Similarly, we compute (1 2)(4 7 8)(2 1)( ) = (1 5 8)(2 4 7).
 Math 430 Dr. Songhao Li Spring 2016 HOMEWORK 3 SOLUTIONS Due 2/15/16 Part II Section 9 Exercises 4. Find the orbits of σ : Z Z defined by σ(n) = n + 1. Solution: We show that the only orbit is Z. Let i,
Math 430 Dr. Songhao Li Spring 2016 HOMEWORK 3 SOLUTIONS Due 2/15/16 Part II Section 9 Exercises 4. Find the orbits of σ : Z Z defined by σ(n) = n + 1. Solution: We show that the only orbit is Z. Let i,
Solve the matrix equation for X. 1) A = 6 0, B = , AX = B A) D) -2 2 B) -12 0
 MATH 1324 FINAL EXAM. ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS. TIME 1.5HRS. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the matrix equation for X. 1) A = 3-2
MATH 1324 FINAL EXAM. ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS. TIME 1.5HRS. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the matrix equation for X. 1) A = 3-2
MA131 Lecture 8.2. The normal distribution curve can be considered as a probability distribution curve for normally distributed variables.
 Normal distribution curve as probability distribution curve The normal distribution curve can be considered as a probability distribution curve for normally distributed variables. The area under the normal
Normal distribution curve as probability distribution curve The normal distribution curve can be considered as a probability distribution curve for normally distributed variables. The area under the normal
When Is Factoring Used?
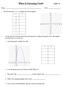 When Is Factoring Used? Name: DAY 9 Date: 1. Given the function, y = x 2 complete the table and graph. x y 2 1 0 1 2 3 1. A ball is thrown vertically upward from the ground according to the graph below.
When Is Factoring Used? Name: DAY 9 Date: 1. Given the function, y = x 2 complete the table and graph. x y 2 1 0 1 2 3 1. A ball is thrown vertically upward from the ground according to the graph below.
Sandringham School Sixth Form. AS Maths. Bridging the gap
 Sandringham School Sixth Form AS Maths Bridging the gap Section 1 - Factorising be able to factorise simple expressions be able to factorise quadratics The expression 4x + 8 can be written in factor form,
Sandringham School Sixth Form AS Maths Bridging the gap Section 1 - Factorising be able to factorise simple expressions be able to factorise quadratics The expression 4x + 8 can be written in factor form,
FIT5124 Advanced Topics in Security. Lecture 1: Lattice-Based Crypto. I
 FIT5124 Advanced Topics in Security Lecture 1: Lattice-Based Crypto. I Ron Steinfeld Clayton School of IT Monash University March 2016 Acknowledgements: Some figures sourced from Oded Regev s Lecture Notes
FIT5124 Advanced Topics in Security Lecture 1: Lattice-Based Crypto. I Ron Steinfeld Clayton School of IT Monash University March 2016 Acknowledgements: Some figures sourced from Oded Regev s Lecture Notes
Mathematics Notes for Class 12 chapter 1. Relations and Functions
 1 P a g e Mathematics Notes for Class 12 chapter 1. Relations and Functions Relation If A and B are two non-empty sets, then a relation R from A to B is a subset of A x B. If R A x B and (a, b) R, then
1 P a g e Mathematics Notes for Class 12 chapter 1. Relations and Functions Relation If A and B are two non-empty sets, then a relation R from A to B is a subset of A x B. If R A x B and (a, b) R, then
Outline. 1 Introduction. 2 Algorithms. 3 Examples. Algorithm 1 General coordinate minimization framework. 1: Choose x 0 R n and set k 0.
 Outline Coordinate Minimization Daniel P. Robinson Department of Applied Mathematics and Statistics Johns Hopkins University November 27, 208 Introduction 2 Algorithms Cyclic order with exact minimization
Outline Coordinate Minimization Daniel P. Robinson Department of Applied Mathematics and Statistics Johns Hopkins University November 27, 208 Introduction 2 Algorithms Cyclic order with exact minimization
Hints on Some of the Exercises
 Hints on Some of the Exercises of the book R. Seydel: Tools for Computational Finance. Springer, 00/004/006/009/01. Preparatory Remarks: Some of the hints suggest ideas that may simplify solving the exercises
Hints on Some of the Exercises of the book R. Seydel: Tools for Computational Finance. Springer, 00/004/006/009/01. Preparatory Remarks: Some of the hints suggest ideas that may simplify solving the exercises
Math Computational Finance Double barrier option pricing using Quasi Monte Carlo and Brownian Bridge methods
 . Math 623 - Computational Finance Double barrier option pricing using Quasi Monte Carlo and Brownian Bridge methods Pratik Mehta pbmehta@eden.rutgers.edu Masters of Science in Mathematical Finance Department
. Math 623 - Computational Finance Double barrier option pricing using Quasi Monte Carlo and Brownian Bridge methods Pratik Mehta pbmehta@eden.rutgers.edu Masters of Science in Mathematical Finance Department
Algebra I EOC 10-Day STAAR Review. Hedgehog Learning
 Algebra I EOC 10-Day STAAR Review Hedgehog Learning Day 1 Day 2 STAAR Reporting Category Number and Algebraic Methods Readiness Standards 60% - 65% of STAAR A.10(E) - factor, if possible, trinomials with
Algebra I EOC 10-Day STAAR Review Hedgehog Learning Day 1 Day 2 STAAR Reporting Category Number and Algebraic Methods Readiness Standards 60% - 65% of STAAR A.10(E) - factor, if possible, trinomials with
Chapter 10. Rational Numbers
 Chapter 0 Rational Numbers The Histor of Chess 0. Rational Epressions 0. Multipling Rational Epressions 0.3 Dividing Rational Epressions 0. Dividing Polnomials 0.5 Addition and Subtraction of Rational
Chapter 0 Rational Numbers The Histor of Chess 0. Rational Epressions 0. Multipling Rational Epressions 0.3 Dividing Rational Epressions 0. Dividing Polnomials 0.5 Addition and Subtraction of Rational
lecture 31: The Secant Method: Prototypical Quasi-Newton Method
 169 lecture 31: The Secant Method: Prototypical Quasi-Newton Method Newton s method is fast if one has a good initial guess x 0 Even then, it can be inconvenient and expensive to compute the derivatives
169 lecture 31: The Secant Method: Prototypical Quasi-Newton Method Newton s method is fast if one has a good initial guess x 0 Even then, it can be inconvenient and expensive to compute the derivatives
AS Mathematics Assignment 7 Due Date: Friday 14 th February 2014
 AS Mathematics Assignment 7 Due Date: Friday 14 th February 2014 NAME. GROUP: MECHANICS/STATS Instructions to Students All questions must be attempted. You should present your solutions on file paper and
AS Mathematics Assignment 7 Due Date: Friday 14 th February 2014 NAME. GROUP: MECHANICS/STATS Instructions to Students All questions must be attempted. You should present your solutions on file paper and
Abstract Algebra Solution of Assignment-1
 Abstract Algebra Solution of Assignment-1 P. Kalika & Kri. Munesh [ M.Sc. Tech Mathematics ] 1. Illustrate Cayley s Theorem by calculating the left regular representation for the group V 4 = {e, a, b,
Abstract Algebra Solution of Assignment-1 P. Kalika & Kri. Munesh [ M.Sc. Tech Mathematics ] 1. Illustrate Cayley s Theorem by calculating the left regular representation for the group V 4 = {e, a, b,
Gödel algebras free over finite distributive lattices
 TANCL, Oxford, August 4-9, 2007 1 Gödel algebras free over finite distributive lattices Stefano Aguzzoli Brunella Gerla Vincenzo Marra D.S.I. D.I.COM. D.I.C.O. University of Milano University of Insubria
TANCL, Oxford, August 4-9, 2007 1 Gödel algebras free over finite distributive lattices Stefano Aguzzoli Brunella Gerla Vincenzo Marra D.S.I. D.I.COM. D.I.C.O. University of Milano University of Insubria
