Recent Swedish Monetary Policy
|
|
|
- Herbert Sullivan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 To Mr. Eccles From Mr, Edmlston Recent Swedish Monetary Policy
2 Brief Survey of Swedish Economic Activity Sweden has a population of about 6,000,000. In normal times about 58% of the population are engaged in agriculture and fishing while 51% are engaged in industries, including forestry and mining* Trade and transport occupies 1Z% of the population with the rest economically inactive or scattered among the professions and handicraft industries. Foreign trade plays a very large part in the Swedish economy. Its chief exports are iron ore and iron products and lumber and wood products. Also there is a certain amount of animal products, such as butter and bacon, which are exported. The most important imports are food stuffs, luxuries and textiles. The foreign trade is principally concerned with European markets with Great Britain being the largest market for Swedish products, while Germany imports more goods to Sweden than any other country. Because of this large foreign trade and because England is so important in it, it is not surprising that Sweden has followed the lead of England in going off gold and has kept its monetary unit tied relatively closely to the pound in the last few years. The Swedish Banking System Before going into a discussion of the recent monetary policy of the country it is well to have a general picture of the characteristics of the Swedish banking system within which this policy must operate. The Central Bank The central bank of Sweden, the Riksbank, holds a unique place among the world central banking institutions. It is completely owned by the State, but is a bank directly supervised by the Parliament, and not administered by the executive Government.
3 2 - Management - The management of the bank is in the hands of a Board of Governors, six members of which are appointed by the Parliament, while the seventh, who is designated as chairman, is appointed by the Crown. Their term of office is three years. Although the Board is appointed by Parliament it has a considerable amount of independence in action and this freedom is guarded carefully by both Parliament itself and by the Board of Governors. Ho?<rever, the Bank! s operations are examined periodically by 12 auditors who are nominated by Parliament and governed by special instructions. Note Issue Powers - The Riksbank has the sole power of note issue. It has authority to issue notes up to twice the amount of its gold reserve and also under emergency circumstances may issue an additional 125 million kronor currency backed by specified security. Powers of the Bank - The Riksbank is purely a banker*s bank. Although under the law it does have power to accept private deposits, this power has never been used. The deposits of the Bank consist of bankers 1 balances and Government noninterest bearing deposits. Power to control the credit situation. The Riksbank f s power here centers around its discount rate. As the banks of the country are normally indebted to the Riksbank any changes in the rediscount rate (particularly upward) tend to have a considerable affect upon the rates in the open market and hence give the Bank considerable control of the general credit situation. Also the bank has the power to purchase and sell Government securities. However, these operations are seldom undertaken by the Bank except in times of emergency. The Riksbank holds the gold reserves of the country and also deals in foreign exchange.
4 - 3 - These transactions in foreign exchange serve as a substitute, at least in part, for open market operations. In case the Bank is purchasing foreign exchange it means that funds are placed into the hands of the commercial banks to use for expanding credit for domestic needs* On the other hand, if the bank is selling foreign exchange, it usually means that funds are flowing abroad to meet commercial or capital payments and the banks of the country are forced to pay the Riksbank to meet these withdrawals thus curtailing their domestic loaning power. Other Financial Institutions The Commercial Banks There are two types of commercial banking institutions. The first, the so-called "aktie" banks which are institutions in which the liability of the shareholders is limited to the original paid-in capital. Half of the countrys banking business is done by the three largest of this type of banks, which have branches throughout the country. The other class of banks are the "enskilda" banks which are private institutions with unlimited shareholder liability. The commercial banks of Sweden have always experienced difficulty in increasing deposits because of the relative scarcity of circulating capital in the country. Therefore, they have set up various classifications of deposit accounts so as to best satisfy the desires of various classes of depositors and thus keep deposits at a maximum. The proportionate line-up o~ deposits is: long term money (four months) 57$; short term money (two to fjur weeks), 8$} demand deposits, 12$: and savings deposits (one*weeks notice), 23$. Thus about 80$ of the total deposits are of a long-term variety. On the credit extension side Swedish banks have also gone into the long term market to a considerable extent and provide a large amount
5 - 4 - of ftmds for capital purposes to industry. Another noteworthy feature of the Swedish banks is that they are consistently over-loaned, in that their total loans exceed deposits by some 25$. However, inasmuch as the Swedish law requires a ratio of capital to deposits of one to five this large capital holding provides a buffer against difficulties arising from this over-loaned condition. Moreover the Swedish banks have very small holdings of cash in relation to their deposits. However, inasmuch as the majority of their deposits are on a long term basis and the commercial banks have recourse to the Riksbank bank in case of need, this situation is not particularly serious. The Savings Banks In addition there are some 500 savings banks over the country which have deposits approximately equal to those of the commercial banks. These savings banks compete with the commercial banks especially in acquiring deposits. They have been, on the whole, conservative institutions and have been more prevalent through the rural areas of the country. In recent years, however, they have become more important in urban centers. Approximately 50$ of the savings banks 1 loans are on real estate mortgages. Also there are a small number of mortgage institutions which loan on rural and urban real estate. Survey of Sweden f s "Managed Currency" Sweden abandoned the gold standard in September Undoubtedly this suspension was chiefly due to the abandonment of the gold standard by Great Britain a week previously. The situation was that Sweden had an excess of imports over exports, and along with many other countries was at this time undergoing a withdrawal of foreign capital, which had been placed in Sweden in previous years, and which now lead to an adverse bal-
6 - 5 - ance of payments position for the country. These adverse payments could not easily be met by the Riksbank because its holdings of foreign exchange had already been drawn down to a very low level and it was losing gold at a comparatively rapid rate. In order to maintain the gold reserves of the country the Swedish Government, failing to obtain loans from foreign sources was forced to abandon gold and to declare an export embargo on gold* First declaration of future monetary policy* - In conjunction with the suspension of gold payments the Government declared that its future monetary policy was to have as its objective the "preservation of the domestic purchasing power of the krona t!. The change in the monetary standard was met with general approval throughout the countiy, but it was recognized that the program was one of emergency character as Sweden had been forced off gold and as the Minister of Finance had announced that it was the desire of the Government to return to gold as soon as the conditions abroad would permit it. In order to preserve the internal purchasing power of the krona the Government took immediate steps to remove all fears of monetary inflation and to show that^abandonment of the gold standard did not mean that there would be a relinquishmerit of all control over the Swedish currency. The first step was to raise the rediscount rate from 6 to 8/6, which it was hoped would have two effects* First, to prevent a severe decline in the krona internationally and second, to curtail any speculative purchasing of securities and commodities. While ordinarily a raise in the rediscount rate in this way is a signal that difficulties are ahead and hence often leads to a rapid withdrawal of foreign funds from the country f s market, this was not of any great significance in Sweden as already foreign balances held there had been drawn down to negligible amounts.. This of course was an abnormally high rate and it
7 - 6 - was soon lowered, as the risk of deflation was seen to be greater than the risk of inflation. The next step was for the Riksbank to enter into an agreement with the important commercial banks of the country wherein the latter banks agreed to be extremely cautious in their extension of credit and to particularly avoid credits which were intended for import purposes The immediate effect of these measures was to reestablish the confidence of the public in the country f s monetary unit and as shown by the accompanying chart a small rise in wholesale prices and in the index of production followed. The Monetary Policy of When Parliament convened in January 1932 the Minister of Finance proposed a revision of the monetary policy. He suggested that it would be wise for the Riksbank to make a public statement as to the future monetary policy of the Government and to attempt through monetary control to achieve a slow rise in wholesale prices in order to stimulate the industry and commerce of the country. It was also proposed that the Riksbank should limit so far as possible the fluctuations in foreign exchange. This had been attempted to some extent in 1931, but now the Riksbank was in much better position to cope with the program of limiting such fluctuations because of its larger holdings in foreign exchange and its better reserve position in general. Subsequently the Governors of the Riksbank made a public statement in February 1932 which set up the aims of the monetary policy which the Bank was to follow substantially along the lines which were suggested by the Minister of Finance which were outlined above. In reality, the objective of the program was to adjust the wholesale price level to the prevailing costs of production, thereby increasing the possibilities of profit and
8 SWEDEN Gold Standard Abandoned Wholesale Price Index Digitized for FRASER SJ.X3SI-IHDYSSVW QOOMbON 'ONI 'ANVdWCO MOOS X3QOO SNOISIAIQ on xa osi -HONI
9 WHOLESALE PRICE INDEX Swedish Board of Trade ( ) All commodities Month Jan Feb March April May June July Aug Sept Oct Nov. n7 no 109 no Dec. 117 in 108 no Source of data Skandinaviska Kreditaktiebolaget.
10 INDEX OP PRODUCTION According to Federation of Swedish Industries ( ) Month Jan Feb March April May June July Aug Sept Oct Nov Dec Seasonal change removed - Revised Figures* Source of data - Skandinaviska Kreditaktiebolaget,
11 «. 7 consequently the volume of physical production. There was no desire to tie the krona to any particular foreign currency, but because of the fact that England was so important as a market for Swedish goods it is to be noted that the krona was in effect tied fairly closely to the pound although there were certain deviations for limited periods. In order to carry out this proposed policy, the Riksbank continually lowered its rediscount rate until on March 5rd of 1932 it had reached the rate of 5$. On June 3rd the rate was lowered to 4% and in August 1932 it was quoted at 5^$. It is shown in the accompanying chart that the level of wholesale prices stayed fairly constaat throughout the year of However, industrial production fell off from the first quarter very rapidly until July of that year. This can be accounted for in several ways. In the first place, mounting obstacles were being placed in the way of Swedish export industries by the aggravation of the world depression and the general rise of tariff barriers during the first part of this year. In addition, there was a strike in the paper pulp industry, which is one of the most important in the country, and labor difficulties lasted throughout the entire second quarter of the year. But probably of most importance was the Kreuger 'crisis of March 1932 which caused a temporary shock to confidence in the Swedish economic situation both at home and abroad. Thus, the Swedish monetary policy appears during the course of this year not to have been particularly effective. But this is not surprising considering the general uncertainty which hung over the country following the Kreuger crisis and the continual aggravation of the world depression up to the middle of the year. The price level as noted above tended slightly to decline if anything and while it may have been possible to, as some observers like Professor Ohlin have held, have obtained a certain rise in prices provided the central bank had purchased Government securities, and in con-
12 - 8 - junction the Government itself had started an effective public works program. However, the later measure was not inaugurated* The bank actually bought approximately 200,000,000 kronor of Government securities during the spring of These purchases were evidently not intended as a means to raise the price level but rather to aid the banking system to meet the shock of the Kreuger failure. Secondary vision of the Swedish monetary policy Because of the large volume of unemployment and the fall in the wholesale price level from October 1952 through the first quarter of 1955, it was decided that more definite instructions in regard to the Swedish monetary policy should be given by the Parliament in the year of Accordingly, therefore the Government appointed a committee of representatives of industry, agriculture and banking, along with experts in economics to make a study of the problems facing the country and to consider what steps should be taken by the Government in view of the probable development abroad. In its deliberation the committee proceeded from two assumptions. The first of these was that a rise in the world price level would actually be brought about by cooperative action on the part of the central banks of the world following the World Economic Conference to be held in June of that year. If such action was taken it was deemed desirable for Sweden to tie their currency with those of the leading nations and to assist and cooperate in carrying out the program for raising the price level throughout the world. On the other hand if no such joint action was to be forth-coming the committee thought that Sweden should continue to follow an independent policy of regulating the internal purchasing power of the krona and to hold down the value to which the krona had been driven by speculation in the foreign exchange markets of the world. There was to be no attempt, however, to de-
13 - 9 - value the krona with a view of gaining commercial advantages because the committee thought that competition in depreciation of foreign values of currencies below their purchasing-power parities had in the last few years contributed more disastrously perhaps than any other single factor to the continuous decline in the world economy* As the means to be used to bring about a rise in the domestic price level the committee recommended further decreases of the bank rate and grants of credit It was proposed also that Riksbank should intervene actively for the stated purpose of aiding in the financing of expenditures for the relief of unemployment. As there is no established market for short-term State bonds in Sweden the Riksbank does not have the same opportunity for pushing out funds as exists in England and the United States, but it was thought that the Treasury could issue short term bills which would be readily taken by the commercial banks inasmuch as these banks had large reserves of cash and the Riksbank would be prepared to rediscount these bills so that commercial banks could at any time get funds to meet any needs which might come from commerce and industry with an expansion of business activity. It was hoped also that the Government would start a program of public works and in this way put funds out into the hands of spenders and thus affect the price level favorably. The lines of the monetary program outlined above were enbodied in the bill submitted by the Government to Parliament on the 26th of May. The Parliament approved the recommendations. The results of the policy which was set up are to some extent difficult to trace. Fran the middle of the year 1953 there has been a continual increase in the wholesale price level as shown by the accompanying chart, as well as a considerable increase in the volume of production. However, this was a time of general business revival throughout the world and it was to be expected that Sweden would follow along with this general improvement. There was no appreciable expansion of public works during this
14 period and hence this feature the policy did not actually ha,ve a trial. Also, there was never throughout the whole period of the depression aijy budgetary inflation of considerable amounts, as shown by the table below: Total public debt of Sweden June (Dec. 3D 1934 (Jan. 31) In million Rronor 1, , , , , , ,350.5 In million dollars (Converted at par) table shows that the public debt was increased slightly up to the middle of 1933 but from then on it has been relatively stationary and in fact slightly declined during January 1934 It is true that the policy followed by the Riksbank in purchasing foreign exchange has put funds into the hands of the commercial banks. Consequently, the banks have paid off their entire indebtedness to the Riksbank and have large excess reserves. The money market has been eased and was characterized by a surplus in funds which has led to a marked reduction of money rates, but the mere existence of these surplus funds has led to no greater increase in the loans of the commercial banks. Summary and Conclusions There has grown up a rather widespread superstition in many circles regarding the Swedish tt managed currency* The impression has been given in some quarters that the Swedish experience proves that by monetary manipulation it is possible to move price levels about almost at will* However, in the Swedish situation there are many complicating factors and it is difficult to say with assurance just how effective the monetary program has been. Moreover, among the various writers on the subject there is no strik-
15 ing unanimity of opinion as to the results of the "management" Thus it is with considerable trepidation that I set down the following conclusions* (1) Sweden was clearly forced off gold* The action was not as a result of any voluntary policy seeking to attain a healthier monetary situation* (2) Sweden is a small country and largely dependant upon foreign trade* Therefore her price level and economic prosperity is greatly dependant upon conditions over which she can exert relatively slight control* Of necessity she had to tie rather closely to the English pound in monetary affairs, but it is to the credit of the authorities that they saw this and acted accordingly* (3) By formulating and publishing a definite monetary policy the Swedish Government has set a good example for other countries* Fears of inflation were quickly allayed in the first instance* Later this policy served to maintain confidence in the future value of the krona* (4) The process of deflation was halted and this in itself was a great achievement considering the rapid deflation which had taken place before gold was abandoned. Swedish wholesale prices maintained relative stability at a time when gold prices were continuing to fall* Thus the situation in Sweden was improved in spite of trying times of strikes and the period of unrest attending the Kreuger failure* (5) Undoubtedly the Riksbank, by holding down the value of the krona to the level it had been driven by speculation in foreign exchange markets, by its purchases of large amounts of foreign exchange, eased the situation in Sweden and tended to hold up the general price level* Here its policies in influencing the price level have been more successful than by its discount rate action*
16 (6) The attempts to raise the level of domestic wholesale prices cannot be said to have attained much success. While funds were placed in the hands of banks, they were not used to make loans and thus initiate a credit expansion* Instead the banks of Sweden, as those in other countries, paid off indebtedness (which is quite unusual for Swedish banks), and strengthened their position generally. The lowering of the Riskbank rediscount rate accompanied by decline in open-market rates merely eased the money market and to some extent stimulated the bond market* The rise in prices and production which has been noted in the last half of 1933 and the first part of 1934 must however be attributed to the general improving business outlook throughout the world rather than to the Swedish monetary policy* However the Swedish policy has aided and abetted the possibility of such improvement*
Does the Riksbank have to make a profit?
 SPEECH DATE: 23 January 2015 SPEAKER: First Deputy Governor Kerstin af Jochnick LOCATION: Swedish House of Finance (SHoF), Stockholm SVERIGES RIKSBANK SE-103 37 Stockholm (Brunkebergstorg 11) Tel +46 8
SPEECH DATE: 23 January 2015 SPEAKER: First Deputy Governor Kerstin af Jochnick LOCATION: Swedish House of Finance (SHoF), Stockholm SVERIGES RIKSBANK SE-103 37 Stockholm (Brunkebergstorg 11) Tel +46 8
Mr. Bäckström explains why price stability ought to be a central bank s principle monetary policy objective
 Mr. Bäckström explains why price stability ought to be a central bank s principle monetary policy objective Address by the Governor of the Bank of Sweden, Mr. Urban Bäckström, at Handelsbanken seminar
Mr. Bäckström explains why price stability ought to be a central bank s principle monetary policy objective Address by the Governor of the Bank of Sweden, Mr. Urban Bäckström, at Handelsbanken seminar
PRESENTATION BY PROF. E. TUMUSIIME-MUTEBILE, GOVERNOR, BANK OF UGANDA, TO THE NRM RETREAT, KYANKWANZI, JANUARY
 BANK OF UGANDA PRESENTATION BY PROF. E. TUMUSIIME-MUTEBILE, GOVERNOR, BANK OF UGANDA, TO THE NRM RETREAT, KYANKWANZI, JANUARY 19, 2012 MACROECONOMIC MANAGEMENT IN TURBULENT TIMES Introduction I want to
BANK OF UGANDA PRESENTATION BY PROF. E. TUMUSIIME-MUTEBILE, GOVERNOR, BANK OF UGANDA, TO THE NRM RETREAT, KYANKWANZI, JANUARY 19, 2012 MACROECONOMIC MANAGEMENT IN TURBULENT TIMES Introduction I want to
Lars Nyberg: Developments in the property market
 Lars Nyberg: Developments in the property market Speech by Mr Lars Nyberg, Deputy Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, at Fastighetsvärlden (Swedish newspaper), Stockholm, 30 May 2007. * * * I would like
Lars Nyberg: Developments in the property market Speech by Mr Lars Nyberg, Deputy Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, at Fastighetsvärlden (Swedish newspaper), Stockholm, 30 May 2007. * * * I would like
1 World Economy. about 0.5% for the full year Its GDP in 2012 is forecast to grow by 2 3%.
 1 World Economy The short-term outlook on the Finnish forest industry s exports markets is overshadowed by uncertainty and a new setback for growth in the world economy. GDP growth in the world economy
1 World Economy The short-term outlook on the Finnish forest industry s exports markets is overshadowed by uncertainty and a new setback for growth in the world economy. GDP growth in the world economy
Chapter 18: Output and the Exchange Rate in the Short Run
 Chapter 18: Output and the Exchange Rate in the Short Run Krugman, P.R., Obstfeld, M.: International Economics: Theory and Policy, 8th Edition, Pearson Addison-Wesley, 460-500 1 Preview Balance sheets
Chapter 18: Output and the Exchange Rate in the Short Run Krugman, P.R., Obstfeld, M.: International Economics: Theory and Policy, 8th Edition, Pearson Addison-Wesley, 460-500 1 Preview Balance sheets
Statement by. David M. Lilly Member, Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. Before the
 F O R RELEASE ON DELIVERY Statement by David M. Lilly Member, Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System Before the Subcommittee on Economic Stabilization of the Committee on Banking, Finance and
F O R RELEASE ON DELIVERY Statement by David M. Lilly Member, Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System Before the Subcommittee on Economic Stabilization of the Committee on Banking, Finance and
Monetary policy operating procedures: the Peruvian case
 Monetary policy operating procedures: the Peruvian case Marylin Choy Chong 1. Background (i) Reforms At the end of 1990 Peru initiated a financial reform process as part of a broad set of structural reforms
Monetary policy operating procedures: the Peruvian case Marylin Choy Chong 1. Background (i) Reforms At the end of 1990 Peru initiated a financial reform process as part of a broad set of structural reforms
FEDERAL RESERVE BULLETIN
 March 9 FEDERAL RESERVE BULLETIN VOLUME 0 March 9 NUMBER The rebuilding of foreign gold and dollar to more adequate levels continued in 9, especially in Continental Western Europe and the Sterling Area.
March 9 FEDERAL RESERVE BULLETIN VOLUME 0 March 9 NUMBER The rebuilding of foreign gold and dollar to more adequate levels continued in 9, especially in Continental Western Europe and the Sterling Area.
Economics of Money, Banking, and Fin. Markets, 10e (Mishkin) Chapter 18 The International Financial System
 Economics of Money, Banking, and Fin. Markets, 10e (Mishkin) Chapter 18 The International Financial System 18.1 Intervention in the Foreign Exchange Market 1) A central bank of domestic currency and corresponding
Economics of Money, Banking, and Fin. Markets, 10e (Mishkin) Chapter 18 The International Financial System 18.1 Intervention in the Foreign Exchange Market 1) A central bank of domestic currency and corresponding
Irma Rosenberg: Monetary policy and the Swedish economy
 Irma Rosenberg: Monetary policy and the Swedish economy Speech by Ms Irma Rosenberg, Deputy Governor of Sveriges Riksbank, to the Swedish Society of Financial Analysts, Stockholm, 5 March 2003. * * * Thank
Irma Rosenberg: Monetary policy and the Swedish economy Speech by Ms Irma Rosenberg, Deputy Governor of Sveriges Riksbank, to the Swedish Society of Financial Analysts, Stockholm, 5 March 2003. * * * Thank
II BANKING SECTOR STABILITY AND RISKS
 II BANKING SECTOR STABILITY AND RISKS Strategic development of the banking sector The influence of economic adjustment in the last half-year is reflected in the changes in the structure of domestic financial
II BANKING SECTOR STABILITY AND RISKS Strategic development of the banking sector The influence of economic adjustment in the last half-year is reflected in the changes in the structure of domestic financial
Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 4
 Department of Economics University of California, Berkeley Spring 2006 Economics 182 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 4 Problem 1 : True, False, Uncertain (a) False or Uncertain. In first generation
Department of Economics University of California, Berkeley Spring 2006 Economics 182 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 4 Problem 1 : True, False, Uncertain (a) False or Uncertain. In first generation
SUMMARY OF MACROECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS
 SUMMARY OF MACROECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS FEBRUARY 2018 2 Summary of macroeconomic developments, February 2018 Forecasts for global economic developments over the medium term are optimistic. In its January
SUMMARY OF MACROECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS FEBRUARY 2018 2 Summary of macroeconomic developments, February 2018 Forecasts for global economic developments over the medium term are optimistic. In its January
Background to the Recent Decline in the Growth Rate of Banknotes in Circulation
 Bank of Japan Review -E-3 Background to the Recent Decline in the Growth Rate of Banknotes in Circulation Yoshihito Saito and Hideki Takada October The year-on-year growth rate of banknotes in circulation
Bank of Japan Review -E-3 Background to the Recent Decline in the Growth Rate of Banknotes in Circulation Yoshihito Saito and Hideki Takada October The year-on-year growth rate of banknotes in circulation
Viet Nam GDP growth by sector Crude oil output Million metric tons 20
 Viet Nam This economy is weathering the global economic crisis relatively well due largely to swift and strong policy responses. The GDP growth forecast for 29 is revised up from that made in March and
Viet Nam This economy is weathering the global economic crisis relatively well due largely to swift and strong policy responses. The GDP growth forecast for 29 is revised up from that made in March and
Leading Economic Indicator Nebraska
 Nebraska Monthly Economic Indicators: December 20, 2017 Prepared by the UNL College of Business Administration, Bureau of Business Research Author: Dr. Eric Thompson Leading Economic Indicator...1 Coincident
Nebraska Monthly Economic Indicators: December 20, 2017 Prepared by the UNL College of Business Administration, Bureau of Business Research Author: Dr. Eric Thompson Leading Economic Indicator...1 Coincident
"THE FEDERAL RESERVE SYSTEM AND THE BANKING ACT OF 1935." Address by M. S. SZYMCZAK, MEMBER BOARD OF GOVERNORS OF THE FEDERAL RESERVE SYSTEM
 X-9356 "THE FEDERAL RESERVE SYSTEM AND THE BANKING ACT OF 1935." Address by M. S. SZYMCZAK, MEMBER BOARD OF GOVERNORS OF THE FEDERAL RESERVE SYSTEM before the Cleveland Chapter, American Institute of Banking,
X-9356 "THE FEDERAL RESERVE SYSTEM AND THE BANKING ACT OF 1935." Address by M. S. SZYMCZAK, MEMBER BOARD OF GOVERNORS OF THE FEDERAL RESERVE SYSTEM before the Cleveland Chapter, American Institute of Banking,
Barbro Wickman-Parak: The Riksbank's inflation target
 Barbro Wickman-Parak: The Riksbank's inflation target Speech by Ms Barbro Wickman-Parak, Deputy Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, at Swedbank, Stockholm, 9 June 8. * * * The CPI, other measures of inflation
Barbro Wickman-Parak: The Riksbank's inflation target Speech by Ms Barbro Wickman-Parak, Deputy Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, at Swedbank, Stockholm, 9 June 8. * * * The CPI, other measures of inflation
Interest Rates in Leading Countries
 Interest Rates in Leading Countries have been generally rising since 1954 in the leading countries of the free world, as economic activity has been increasing to record levels. The economic expansion has
Interest Rates in Leading Countries have been generally rising since 1954 in the leading countries of the free world, as economic activity has been increasing to record levels. The economic expansion has
Chapter 18. The International Financial System Intervention in the Foreign Exchange Market
 Chapter 18 The International Financial System 18.1 Intervention in the Foreign Exchange Market 1) A central bank of domestic currency and corresponding of foreign assets in the foreign exchange market
Chapter 18 The International Financial System 18.1 Intervention in the Foreign Exchange Market 1) A central bank of domestic currency and corresponding of foreign assets in the foreign exchange market
Irma Rosenberg: Assessment of monetary policy
 Irma Rosenberg: Assessment of monetary policy Speech by Ms Irma Rosenberg, Deputy Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, at Norges Bank s conference on monetary policy 2006, Oslo, 30 March 2006. * * * Let
Irma Rosenberg: Assessment of monetary policy Speech by Ms Irma Rosenberg, Deputy Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, at Norges Bank s conference on monetary policy 2006, Oslo, 30 March 2006. * * * Let
SPEECH. Monetary policy and the current economic situation. Well-balanced monetary policy in July
 SPEECH DATE: 22 August 2013 SPEAKER: First Deputy Governor Kerstin af Jochnick LOCATION: County Administrative Board in Kalmar SVERIGES RIKSBANK SE-103 37 Stockholm (Brunkebergstorg 11) Tel +46 8 787 00
SPEECH DATE: 22 August 2013 SPEAKER: First Deputy Governor Kerstin af Jochnick LOCATION: County Administrative Board in Kalmar SVERIGES RIKSBANK SE-103 37 Stockholm (Brunkebergstorg 11) Tel +46 8 787 00
INCREASING THE RATE OF CAPITAL FORMATION (Investment Policy Report)
 policies can increase our supply of goods and services, improve our efficiency in using the Nation's human resources, and help people lead more satisfying lives. INCREASING THE RATE OF CAPITAL FORMATION
policies can increase our supply of goods and services, improve our efficiency in using the Nation's human resources, and help people lead more satisfying lives. INCREASING THE RATE OF CAPITAL FORMATION
Central Government Borrowing:
 2004:3 Central Government Borrowing: Forecast and Analysis Borrowing requirement Forecast for 2004 3 Forecast for 2005 4 Comparisons 5 Monthly forecasts 6 The central government debt 6 Funding Gross borrowing
2004:3 Central Government Borrowing: Forecast and Analysis Borrowing requirement Forecast for 2004 3 Forecast for 2005 4 Comparisons 5 Monthly forecasts 6 The central government debt 6 Funding Gross borrowing
The Riksbank's monetary policy strategy
 SPEECH DATE: 14 September 2006 SPEAKER: LOCALITY: Deputy Governor Lars Nyberg Foreign Banker s Association SVERIGES RIKSBANK SE-103 37 Stockholm (Brunkebergstorg 11) Tel +46 8 787 00 00 Fax +46 8 21 05
SPEECH DATE: 14 September 2006 SPEAKER: LOCALITY: Deputy Governor Lars Nyberg Foreign Banker s Association SVERIGES RIKSBANK SE-103 37 Stockholm (Brunkebergstorg 11) Tel +46 8 787 00 00 Fax +46 8 21 05
Monetary policy in Sweden
 Monetary policy in Sweden 2010 S V E R I G E S R I K S B A N K Addendum 7 September 2017 The CPIF as target variable for monetary policy As of September 2017, the Riksbank uses the CPIF, the consumer price
Monetary policy in Sweden 2010 S V E R I G E S R I K S B A N K Addendum 7 September 2017 The CPIF as target variable for monetary policy As of September 2017, the Riksbank uses the CPIF, the consumer price
Capital Flows and International Payments
 Capital Flows and International Payments THE UNITED STATES had a smaller deficit in its international transactions in 1961 than in any of the three preceding years, but the deficit was still uncomfortably
Capital Flows and International Payments THE UNITED STATES had a smaller deficit in its international transactions in 1961 than in any of the three preceding years, but the deficit was still uncomfortably
Quarterly Statistical Digest
 Quarterly Statistical Digest February 2019 Volume 28, No. 1 The Statistical Digest is a quarterly publication of the Central Bank of The Bahamas, prepared by the Research Department for issue in February,
Quarterly Statistical Digest February 2019 Volume 28, No. 1 The Statistical Digest is a quarterly publication of the Central Bank of The Bahamas, prepared by the Research Department for issue in February,
Malawi Tea 2020 Revitalisation programme towards living wage. Wages Committee progress report 2016
 Malawi Tea 2020 Revitalisation programme towards living wage Wages Committee progress report 2016 By Richard Anker and Martha Anker October 2016 This paper provides an update to October 2016 (date of
Malawi Tea 2020 Revitalisation programme towards living wage Wages Committee progress report 2016 By Richard Anker and Martha Anker October 2016 This paper provides an update to October 2016 (date of
Lars Heikensten: Monetary policy and the economic situation
 Lars Heikensten: Monetary policy and the economic situation Speech by Mr Lars Heikensten, Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, at Handelsbanken, Karlstad, 26 January 2004. * * * It is nice to meet a group
Lars Heikensten: Monetary policy and the economic situation Speech by Mr Lars Heikensten, Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, at Handelsbanken, Karlstad, 26 January 2004. * * * It is nice to meet a group
The Banker's Responsibility
 The Banker's Responsibility Address delivered by ROY A. YOUNG Governor, Federal Reserve Board before the AMERICAN BANKERS ASSOCIATION at its Annual Convention at Philadelphia, Pa. October 3, 1928 14 G-.VS
The Banker's Responsibility Address delivered by ROY A. YOUNG Governor, Federal Reserve Board before the AMERICAN BANKERS ASSOCIATION at its Annual Convention at Philadelphia, Pa. October 3, 1928 14 G-.VS
Leading Economic Indicator Nebraska
 Nebraska Monthly Economic Indicators: July 29, 2016 Prepared by the UNL College of Business Administration, Department of Economics Authors: Dr. Eric Thompson, Dr. William Walstad Leading Economic Indicator...1
Nebraska Monthly Economic Indicators: July 29, 2016 Prepared by the UNL College of Business Administration, Department of Economics Authors: Dr. Eric Thompson, Dr. William Walstad Leading Economic Indicator...1
Is China the New France?
 Is China the New France? August 6, 2013 by Marianne Brunet Imagine a country that grows its economy by greatly devaluing against the reserve currency to develop a strong export sector. As the country becomes
Is China the New France? August 6, 2013 by Marianne Brunet Imagine a country that grows its economy by greatly devaluing against the reserve currency to develop a strong export sector. As the country becomes
made available a few days after the next regularly scheduled and the Board's Annual Report. The summary descriptions of
 FEDERAL RESERVE press release For Use at 4:00 p.m. October 20, 1978 The Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System and the Federal Open Market Committee today released the attached record of policy
FEDERAL RESERVE press release For Use at 4:00 p.m. October 20, 1978 The Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System and the Federal Open Market Committee today released the attached record of policy
LETTER. economic THE CANADA / U.S. PRODUCTIVITY GAP: THE EFFECT OF FIRM SIZE FEBRUARY Canada. United States. Interest rates.
 economic LETTER FEBRUARY 2014 THE CANADA / U.S. PRODUCTIVITY GAP: THE EFFECT OF FIRM SIZE For many years now, Canada s labour productivity has been weaker than that of the United States. One of the theories
economic LETTER FEBRUARY 2014 THE CANADA / U.S. PRODUCTIVITY GAP: THE EFFECT OF FIRM SIZE For many years now, Canada s labour productivity has been weaker than that of the United States. One of the theories
Guidelines for central government debt management Decision taken at the government meeting 15 November 2018
 Guidelines for central government debt management 2019 Decision taken at the government meeting 15 November 2018 Contents Summary... 2 1 Decision on guidelines for central government debt management 2019...
Guidelines for central government debt management 2019 Decision taken at the government meeting 15 November 2018 Contents Summary... 2 1 Decision on guidelines for central government debt management 2019...
INFLATION AND THE ECONOMIC OUTLOOK By Darryl R. Francis, President. Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis
 INFLATION AND THE ECONOMIC OUTLOOK By Darryl R. Francis, President To Steel Plate Fabricators Association Key Biscayne, Florida April 29, 1974 It is good to have this opportunity to present my views regarding
INFLATION AND THE ECONOMIC OUTLOOK By Darryl R. Francis, President To Steel Plate Fabricators Association Key Biscayne, Florida April 29, 1974 It is good to have this opportunity to present my views regarding
World Payments Stresses in
 World Payments Stresses in 1956-57 INTERNATIONAL TRANSACTIONS in the year ending June 1957 resulted in net transfers of gold and dollars from foreign countries to the United States. In the four preceding
World Payments Stresses in 1956-57 INTERNATIONAL TRANSACTIONS in the year ending June 1957 resulted in net transfers of gold and dollars from foreign countries to the United States. In the four preceding
FEDERAL RESERVE BULLETIN
 FEDERAL RESERVE BULLETIN VOLUME 40 NUMBER 2 Demand deposits and currency increased about 1.5 per cent in 1953. Demand deposits held by individuals and businesses showed a less than seasonal decline early
FEDERAL RESERVE BULLETIN VOLUME 40 NUMBER 2 Demand deposits and currency increased about 1.5 per cent in 1953. Demand deposits held by individuals and businesses showed a less than seasonal decline early
The transmission mechanism of monetary policy in Peru
 The transmission mechanism of monetary policy in Peru Javier de la Rocha Overview The far-reaching structural transformation that began in August 1990 has significantly changed the way in which monetary
The transmission mechanism of monetary policy in Peru Javier de la Rocha Overview The far-reaching structural transformation that began in August 1990 has significantly changed the way in which monetary
London Borough of Barnet Treasury Management Strategy Statement and Annual Investment Strategy
 London Borough of Barnet Mid-year Treasury Report 2017-18 London Borough of Barnet Treasury Management Strategy Statement and Annual Investment Strategy Quarter Ended 30th March 2014 Mid-year Review Report
London Borough of Barnet Mid-year Treasury Report 2017-18 London Borough of Barnet Treasury Management Strategy Statement and Annual Investment Strategy Quarter Ended 30th March 2014 Mid-year Review Report
1 World Economy. Value of Finnish Forest Industry Exports Fell by Almost a Quarter in 2009
 1 World Economy The recovery in the world economy that began during 2009 has started to slow since spring 2010 as stocks are replenished and government stimulus packages are gradually brought to an end.
1 World Economy The recovery in the world economy that began during 2009 has started to slow since spring 2010 as stocks are replenished and government stimulus packages are gradually brought to an end.
Figure 1: Change in LEI-N August 2018
 Nebraska Monthly Economic Indicators: September 26, 2018 Prepared by the UNL College of Business, Bureau of Business Research Author: Dr. Eric Thompson Leading Economic Indicator...1 Coincident Economic
Nebraska Monthly Economic Indicators: September 26, 2018 Prepared by the UNL College of Business, Bureau of Business Research Author: Dr. Eric Thompson Leading Economic Indicator...1 Coincident Economic
THE MUTUAL INTEREST OF COMMERCIAL BANKS AND THE FEDERAL RESERVE. Delivered by Harry A. Shuford, President. Federal Reserve Bank of St.
 THE MUTUAL INTEREST OF COMMERCIAL BANKS AND THE FEDERAL RESERVE Delivered by Harry A. Shuford, President at the Arkansas Bankers Association Annual Convention Hot Springs, Arkansas May 22, 1963 THE MUTUAL
THE MUTUAL INTEREST OF COMMERCIAL BANKS AND THE FEDERAL RESERVE Delivered by Harry A. Shuford, President at the Arkansas Bankers Association Annual Convention Hot Springs, Arkansas May 22, 1963 THE MUTUAL
How costly is for Spain to be in the EURO?
 How costly is for to be in the EURO? Are members of a monetary Union fatally handicapped to recover from recessions and solve financial crisis? By Domingo Cavallo 1 Countries with a long history of low
How costly is for to be in the EURO? Are members of a monetary Union fatally handicapped to recover from recessions and solve financial crisis? By Domingo Cavallo 1 Countries with a long history of low
Statement of William McChesney Martin, Jr., Chairman, Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. before the. Joint Economic Committee
 For release on delivery Statement of William McChesney Martin, Jr., Chairman, Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System before the Joint Economic Committee July 27, 1959 THE GOVERNMENT SECURITIES
For release on delivery Statement of William McChesney Martin, Jr., Chairman, Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System before the Joint Economic Committee July 27, 1959 THE GOVERNMENT SECURITIES
Economic & Revenue Forecast Tracking
 Economic & Revenue Forecast Tracking April 2011 Employment and Financial Statement Data through 03/11 503-378-3455 OEA.info@state.or.us http://www.oregon.gov/das/oea/index.shtml A. Macroeconomic Environment
Economic & Revenue Forecast Tracking April 2011 Employment and Financial Statement Data through 03/11 503-378-3455 OEA.info@state.or.us http://www.oregon.gov/das/oea/index.shtml A. Macroeconomic Environment
Dynamic Change, Economic Fluctuations, and the AD-AS Model
 Dynamic Change, Economic Fluctuations, and the AD-AS Model Full Length Text Part: Macro Only Text Part: 3 Chapter: 10 3 Chapter: 10 To Accompany Economics: Private and Public Choice 13th ed. James Gwartney,
Dynamic Change, Economic Fluctuations, and the AD-AS Model Full Length Text Part: Macro Only Text Part: 3 Chapter: 10 3 Chapter: 10 To Accompany Economics: Private and Public Choice 13th ed. James Gwartney,
The Asian Face of the Global Recession
 The Asian Face of the Global Recession C.P. Chandrasekhar & Jayati Ghosh Delegates to the World Economic Forum at Davos this year came despondent and left in despair. Both the discussions and the new evidence
The Asian Face of the Global Recession C.P. Chandrasekhar & Jayati Ghosh Delegates to the World Economic Forum at Davos this year came despondent and left in despair. Both the discussions and the new evidence
Lars Heikensten: The Swedish economy and monetary policy
 Lars Heikensten: The Swedish economy and monetary policy Speech by Mr Lars Heikensten, Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, at a seminar arranged by the Stockholm Chamber of Commerce and Veckans Affärer,
Lars Heikensten: The Swedish economy and monetary policy Speech by Mr Lars Heikensten, Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, at a seminar arranged by the Stockholm Chamber of Commerce and Veckans Affärer,
Mr Bäckström elucidates the economic situation in Sweden and describes the consequences it may have for future monetary policy
 Mr Bäckström elucidates the economic situation in Sweden and describes the consequences it may have for future monetary policy Speech given by Mr Urban Bäckström, Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank at Föreningssparbanken,
Mr Bäckström elucidates the economic situation in Sweden and describes the consequences it may have for future monetary policy Speech given by Mr Urban Bäckström, Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank at Föreningssparbanken,
DEVELOPMENTS IN THE COST COMPETITIVENESS OF THE EUROPEAN UNION, THE UNITED STATES AND JAPAN MAIN FEATURES
 DEVELOPMENTS IN THE COST COMPETITIVENESS OF THE EUROPEAN UNION, THE UNITED STATES AND JAPAN MAIN FEATURES The euro against major international currencies: During the second quarter of 2000, the US dollar,
DEVELOPMENTS IN THE COST COMPETITIVENESS OF THE EUROPEAN UNION, THE UNITED STATES AND JAPAN MAIN FEATURES The euro against major international currencies: During the second quarter of 2000, the US dollar,
BANKERS' ACCEPTANCE FINANCING IN THE UNITED STATES 1
 ' ACCEPTANCE FINANCING IN THE UNITED STATES 1 Recent growth in acceptances outstanding reflects renewed interest by United States bankers and traders in this form of financing and in the extension of short-term
' ACCEPTANCE FINANCING IN THE UNITED STATES 1 Recent growth in acceptances outstanding reflects renewed interest by United States bankers and traders in this form of financing and in the extension of short-term
Karnit Flug: Macroeconomic policy and the performance of the Israeli economy
 Karnit Flug: Macroeconomic policy and the performance of the Israeli economy Remarks by Dr Karnit Flug, Governor of the Bank of Israel, to the conference of the Israel Economic Association, Tel Aviv, 18
Karnit Flug: Macroeconomic policy and the performance of the Israeli economy Remarks by Dr Karnit Flug, Governor of the Bank of Israel, to the conference of the Israel Economic Association, Tel Aviv, 18
Leading Economic Indicator Nebraska
 Nebraska Monthly Economic Indicators: September 20, 2017 Prepared by the UNL College of Business Administration, Bureau of Business Research Author: Dr. Eric Thompson Leading Economic Indicator...1 Coincident
Nebraska Monthly Economic Indicators: September 20, 2017 Prepared by the UNL College of Business Administration, Bureau of Business Research Author: Dr. Eric Thompson Leading Economic Indicator...1 Coincident
CONTENTS. 2. Implementation of monetary policy Inflation Money market Capital market... 10
 CONTENTS 1. Monetary developments... 3 1.1. Factors affecting the development of the money supply... 3 1.2. Structure of the money supply... 5 1.3. Bank lending... 6 1.4. Interest rate development in October
CONTENTS 1. Monetary developments... 3 1.1. Factors affecting the development of the money supply... 3 1.2. Structure of the money supply... 5 1.3. Bank lending... 6 1.4. Interest rate development in October
Chapter 19 (8) International Monetary Systems: An Historical Overview
 Chapter 19 (8) International Monetary Systems: An Historical Overview Preview Goals of macroeconomic policies internal and external balance Gold standard era 1870 1914 International monetary system during
Chapter 19 (8) International Monetary Systems: An Historical Overview Preview Goals of macroeconomic policies internal and external balance Gold standard era 1870 1914 International monetary system during
Svein Gjedrem: The conduct of monetary policy
 Svein Gjedrem: The conduct of monetary policy Introductory statement by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the hearing before the Standing Committee on Finance and Economic
Svein Gjedrem: The conduct of monetary policy Introductory statement by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the hearing before the Standing Committee on Finance and Economic
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from the National Bureau of Economic Research
 This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from the National Bureau of Economic Research Volume Title: Business Cycles, Inflation, and Forecasting, 2nd edition Volume Author/Editor: Geoffrey H.
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from the National Bureau of Economic Research Volume Title: Business Cycles, Inflation, and Forecasting, 2nd edition Volume Author/Editor: Geoffrey H.
A Primer on Inflation Targeting
 A Primer on Inflation Targeting Publication No. 2011-111-E 9 November 2011 Brett Stuckey International Affairs, Trade and Finance Division Parliamentary Information and Research Service A Primer on Inflation
A Primer on Inflation Targeting Publication No. 2011-111-E 9 November 2011 Brett Stuckey International Affairs, Trade and Finance Division Parliamentary Information and Research Service A Primer on Inflation
102 FEDERAL RESERVE BULLETIN FEBRUARY 1938
 102 FEDERAL RESERVE BULLETIN FEBRUARY 1938 TRENDS IN RATES OF BANK EARNINGS AND EXPENSES profits of banks in relation to the volume of earning assets have declined over the past half century. The rate
102 FEDERAL RESERVE BULLETIN FEBRUARY 1938 TRENDS IN RATES OF BANK EARNINGS AND EXPENSES profits of banks in relation to the volume of earning assets have declined over the past half century. The rate
Guidelines for Central Government Debt Management Decision taken at the Cabinet meeting 10 November 2005
 Guidelines for Central Government Debt Management 2006 Decision taken at the Cabinet meeting 10 November 2005 006 Guidelines for Central Government Debt Management 2006 1 Contents Appendix 1 Summary...3
Guidelines for Central Government Debt Management 2006 Decision taken at the Cabinet meeting 10 November 2005 006 Guidelines for Central Government Debt Management 2006 1 Contents Appendix 1 Summary...3
Financing the U.S. Trade Deficit
 Order Code RL33274 Financing the U.S. Trade Deficit Updated January 31, 2008 James K. Jackson Specialist in International Trade and Finance Foreign Affairs, Defense, and Trade Division Financing the U.S.
Order Code RL33274 Financing the U.S. Trade Deficit Updated January 31, 2008 James K. Jackson Specialist in International Trade and Finance Foreign Affairs, Defense, and Trade Division Financing the U.S.
Svante Öberg: The economic situation
 Svante Öberg: The economic situation Speech by Mr Svante Öberg, First Deputy Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, to the Västerbotten Chamber of Commerce, Umeå, 5 August. * * * My message today can be summarised
Svante Öberg: The economic situation Speech by Mr Svante Öberg, First Deputy Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, to the Västerbotten Chamber of Commerce, Umeå, 5 August. * * * My message today can be summarised
Quarterly Statistical Digest
 Quarterly Statistical Digest August Volume 27, No. 3 The Statistical Digest is a quarterly publication of the Central Bank of The Bahamas, prepared by the Research Department for issue in February, May,
Quarterly Statistical Digest August Volume 27, No. 3 The Statistical Digest is a quarterly publication of the Central Bank of The Bahamas, prepared by the Research Department for issue in February, May,
Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (July 2018)
 Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (July 2018) July 31, 2018 Bank of Japan The Bank's View 1 Summary Japan's economy is likely to continue growing at a pace above its potential in fiscal 2018, mainly
Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (July 2018) July 31, 2018 Bank of Japan The Bank's View 1 Summary Japan's economy is likely to continue growing at a pace above its potential in fiscal 2018, mainly
Don t Raise the Federal Debt Ceiling, Torpedo the U.S. Housing Market
 Don t Raise the Federal Debt Ceiling, Torpedo the U.S. Housing Market Failure to Act Would Have Serious Consequences for Housing Just as the Market Is Showing Signs of Recovery Christian E. Weller May
Don t Raise the Federal Debt Ceiling, Torpedo the U.S. Housing Market Failure to Act Would Have Serious Consequences for Housing Just as the Market Is Showing Signs of Recovery Christian E. Weller May
GUIDELINES FOR CENTRAL GOVERNMENT DEBT MANAGEMENT 2018
 GUIDELINES FOR CENTRAL GOVERNMENT DEBT MANAGEMENT 2018 Decision taken at the Cabinet meeting November 9 2017 2018 LONG-TERM PERSPECTIVES COST MINIMISATION FLEXIBILITY Contents Summary... 2 1 Decision on
GUIDELINES FOR CENTRAL GOVERNMENT DEBT MANAGEMENT 2018 Decision taken at the Cabinet meeting November 9 2017 2018 LONG-TERM PERSPECTIVES COST MINIMISATION FLEXIBILITY Contents Summary... 2 1 Decision on
Leading Economic Indicator Nebraska
 Nebraska Monthly Economic Indicators: October 24, 2018 Prepared by the UNL College of Business, Bureau of Business Research Author: Dr. Eric Thompson Leading Economic Indicator...1 Coincident Economic
Nebraska Monthly Economic Indicators: October 24, 2018 Prepared by the UNL College of Business, Bureau of Business Research Author: Dr. Eric Thompson Leading Economic Indicator...1 Coincident Economic
SEB FX Ringside 13 January 2016
 SEB FX Ringside 13 January 2016 Swedish FX intervention is now a policy tool Author: Carl Hammer The theme of diverging fortunes for Scandinavian currencies continues this year based on underlying fundamentals.
SEB FX Ringside 13 January 2016 Swedish FX intervention is now a policy tool Author: Carl Hammer The theme of diverging fortunes for Scandinavian currencies continues this year based on underlying fundamentals.
9.3 The Federal Reserve System L E A R N I N G O B JE C T I V E S
 2. Acme Bank s balance sheet after losing $1,000 in deposits: Figure 9.11 Required reserves are deficient by $800. Acme must hold 20% of its deposits, in this case $1,800 (0.2 x $9,000=$1,800), as reserves,
2. Acme Bank s balance sheet after losing $1,000 in deposits: Figure 9.11 Required reserves are deficient by $800. Acme must hold 20% of its deposits, in this case $1,800 (0.2 x $9,000=$1,800), as reserves,
The hnpact of Energy Prices and Money Growth on Five Industrial Countries
 The hnpact of Energy Prices and Money Growth on Five Industrial Countries R. W. HAFER N the winter of 1973-7, the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) quadrupled the price of oil from $3
The hnpact of Energy Prices and Money Growth on Five Industrial Countries R. W. HAFER N the winter of 1973-7, the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) quadrupled the price of oil from $3
The Riksbank s Company Interviews
 The Riksbank s Company Interviews DECEMBER 2008 JANUARY 2009 2 the riksbank s company interviews n The Riksbank s company interviews December 2008 January 2009 Ongoing decline in economic activity and
The Riksbank s Company Interviews DECEMBER 2008 JANUARY 2009 2 the riksbank s company interviews n The Riksbank s company interviews December 2008 January 2009 Ongoing decline in economic activity and
BOJ December 2015 Tankan Survey
 Japan's Economy 15 December 15 (No. of pages: 6) Japanese report: 14 Dec 15 BOJ December 15 Tankan Survey Business sentiment marking time, future uncertain Economic Intelligence Team Satoshi Osanai Shunsuke
Japan's Economy 15 December 15 (No. of pages: 6) Japanese report: 14 Dec 15 BOJ December 15 Tankan Survey Business sentiment marking time, future uncertain Economic Intelligence Team Satoshi Osanai Shunsuke
CIE Economics A-level
 CIE Economics A-level Topic 4: The Macroeconomy f) Money supply (theory) Notes Quantity theory of money (MV = PT) The Quantity Theory of Money states that there is inflation if the money supply increases
CIE Economics A-level Topic 4: The Macroeconomy f) Money supply (theory) Notes Quantity theory of money (MV = PT) The Quantity Theory of Money states that there is inflation if the money supply increases
Investment assets totalled EUR billion at the end of 2016 return for the past 20 years 4.3 per cent in real terms
 1/13 Investment assets totalled EUR 188.5 billion at the end of 2016 return for the past 20 years 4.3 per cent in real terms At the end of 2016, the total net amount of assets put into funds by earnings-related
1/13 Investment assets totalled EUR 188.5 billion at the end of 2016 return for the past 20 years 4.3 per cent in real terms At the end of 2016, the total net amount of assets put into funds by earnings-related
HOUSEHOLD SECTOR FINANCIAL VULNERABILITY
 September 213 JOHN LOOS: HOUSEHOLD AND PROPERTY SECTOR STRATEGIST: FNB HOME LOANS 11-12 John.loos@fnb.co.za The information in this publication is derived from sources which are regarded as accurate and
September 213 JOHN LOOS: HOUSEHOLD AND PROPERTY SECTOR STRATEGIST: FNB HOME LOANS 11-12 John.loos@fnb.co.za The information in this publication is derived from sources which are regarded as accurate and
Outlook for the Chilean Economy
 Outlook for the Chilean Economy Jorge Marshall, Vice-President of the Board, Central Bank of Chile. Address to the Fifth Annual Latin American Banking Conference, Salomon Smith Barney, New York, March
Outlook for the Chilean Economy Jorge Marshall, Vice-President of the Board, Central Bank of Chile. Address to the Fifth Annual Latin American Banking Conference, Salomon Smith Barney, New York, March
Svante Öberg: Potential GDP, resource utilisation and monetary policy
 Svante Öberg: Potential GDP, resource utilisation and monetary policy Speech by Mr Svante Öberg, First Deputy Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, at the Statistics Sweden s annual conference, Saltsjöbaden,
Svante Öberg: Potential GDP, resource utilisation and monetary policy Speech by Mr Svante Öberg, First Deputy Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, at the Statistics Sweden s annual conference, Saltsjöbaden,
LESSON - 26 FOREIGN EXCHANGE - 1. Learning outcomes
 LESSON - 26 FOREIGN EXCHANGE - 1 Learning outcomes After studying this unit, you should be able to: Define foreign exchange Know foreign exchange markets functions of foreign exchange market methods affecting
LESSON - 26 FOREIGN EXCHANGE - 1 Learning outcomes After studying this unit, you should be able to: Define foreign exchange Know foreign exchange markets functions of foreign exchange market methods affecting
The Vice-Grip of Finance
 The Vice-Grip of Finance C.P. Chandrasekhar and Jayati Ghosh On December 19 th a bunch of foreign investors dumped their holdings in the Thai stock market, triggering a collapse of the stock exchange of
The Vice-Grip of Finance C.P. Chandrasekhar and Jayati Ghosh On December 19 th a bunch of foreign investors dumped their holdings in the Thai stock market, triggering a collapse of the stock exchange of
Monetary Policy. Confidence in the kina exchange rate and management of the economy; A foundation for stable fiscal operations of the Government;
 Bank of Papua New Guinea PRESENTATION - ON THE MARCH 2012 MONETARY POLICY STATEMENT BY MR. LOI M. BAKANI - GOVERNOR BANK OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA TUESDAY 3 RD APRIL 2012 LAE INTERNATIONAL HOTEL, LAE Monetary
Bank of Papua New Guinea PRESENTATION - ON THE MARCH 2012 MONETARY POLICY STATEMENT BY MR. LOI M. BAKANI - GOVERNOR BANK OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA TUESDAY 3 RD APRIL 2012 LAE INTERNATIONAL HOTEL, LAE Monetary
Updated macroeconomic forecast
 Prepare for landing: Updated macroeconomic forecast 217-219 26 January 218 Íslandsbanki Research Executive summary The Icelandic economy has been buoyant in the past few years, after the deep recession
Prepare for landing: Updated macroeconomic forecast 217-219 26 January 218 Íslandsbanki Research Executive summary The Icelandic economy has been buoyant in the past few years, after the deep recession
Mr Thiessen converses on the conduct of monetary policy in Canada under a floating exchange rate system
 Mr Thiessen converses on the conduct of monetary policy in Canada under a floating exchange rate system Speech by Mr Gordon Thiessen, Governor of the Bank of Canada, to the Canadian Society of New York,
Mr Thiessen converses on the conduct of monetary policy in Canada under a floating exchange rate system Speech by Mr Gordon Thiessen, Governor of the Bank of Canada, to the Canadian Society of New York,
Leading Economic Indicator Nebraska
 Nebraska Monthly Economic Indicators: August 19, 2016 Prepared by the UNL College of Business Administration, Department of Economics Authors: Dr. Eric Thompson, Dr. William Walstad Leading Economic Indicator...1
Nebraska Monthly Economic Indicators: August 19, 2016 Prepared by the UNL College of Business Administration, Department of Economics Authors: Dr. Eric Thompson, Dr. William Walstad Leading Economic Indicator...1
Annual General Meeting 2017 Chairman s statement CHAIRMAN S STATEMENT ÍSLANDSBANKI ANNUAL GENERAL MEETING 2017
 Annual General Meeting 2017 Chairman s statement CHAIRMAN S STATEMENT ÍSLANDSBANKI ANNUAL GENERAL MEETING 2017 Íslandsbanki Annual General Meeting, 23 March 2017 Friðrik Sophusson, Chairman of the Board
Annual General Meeting 2017 Chairman s statement CHAIRMAN S STATEMENT ÍSLANDSBANKI ANNUAL GENERAL MEETING 2017 Íslandsbanki Annual General Meeting, 23 March 2017 Friðrik Sophusson, Chairman of the Board
Canada s Economic Future: What Have We Learned from the 1990s?
 Remarks by Gordon Thiessen Governor of the Bank of Canada to the Canadian Club of Toronto Toronto, Ontario 22 January 2001 Canada s Economic Future: What Have We Learned from the 1990s? It was to the Canadian
Remarks by Gordon Thiessen Governor of the Bank of Canada to the Canadian Club of Toronto Toronto, Ontario 22 January 2001 Canada s Economic Future: What Have We Learned from the 1990s? It was to the Canadian
Digitized for FRASER Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis
 Minutes of the meeting of the Open Market Investment Committee for the Federal Reserve System in Washington on July 2, 192 at 11:00 a.m. PRESENT: Messrs. Crissinger, Platt, Hardin, James and McIntosh,
Minutes of the meeting of the Open Market Investment Committee for the Federal Reserve System in Washington on July 2, 192 at 11:00 a.m. PRESENT: Messrs. Crissinger, Platt, Hardin, James and McIntosh,
Øystein Olsen: The economic outlook
 Øystein Olsen: The economic outlook Address by Mr Øystein Olsen, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), to invited foreign embassy representatives, Oslo, 29 March 2011. The address is based
Øystein Olsen: The economic outlook Address by Mr Øystein Olsen, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), to invited foreign embassy representatives, Oslo, 29 March 2011. The address is based
Monetary Policy Update December 2007
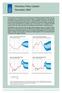 Monetary Policy Update December 7 At its meeting on 8 December, the Executive Board of the Riksbank decided to hold the repo rate unchanged at per cent. During the first half of 8 it is expected that the
Monetary Policy Update December 7 At its meeting on 8 December, the Executive Board of the Riksbank decided to hold the repo rate unchanged at per cent. During the first half of 8 it is expected that the
BANK OF CANADA RENEWAL OF BACKGROUND INFORMATION THE INFLATION-CONTROL TARGET. May 2001
 BANK OF CANADA May RENEWAL OF THE INFLATION-CONTROL TARGET BACKGROUND INFORMATION Bank of Canada Wellington Street Ottawa, Ontario KA G9 78 ISBN: --89- Printed in Canada on recycled paper B A N K O F C
BANK OF CANADA May RENEWAL OF THE INFLATION-CONTROL TARGET BACKGROUND INFORMATION Bank of Canada Wellington Street Ottawa, Ontario KA G9 78 ISBN: --89- Printed in Canada on recycled paper B A N K O F C
PNC Investment Perspective
 March/April 2014 PNC Investment Perspective Decoupling of Developed and Emerging Markets? Jim Dunigan Mr. Dunigan is Executive Vice President and Managing Executive, Investments for PNC Asset Management
March/April 2014 PNC Investment Perspective Decoupling of Developed and Emerging Markets? Jim Dunigan Mr. Dunigan is Executive Vice President and Managing Executive, Investments for PNC Asset Management
and loan balances Treasury to invest surplus tax
 Treasury to invest surplus tax and loan balances Legislation signed by the President on October 28, 1977, will allow the Treasury Department to earn a direct return on temporary cash surpluses. The new
Treasury to invest surplus tax and loan balances Legislation signed by the President on October 28, 1977, will allow the Treasury Department to earn a direct return on temporary cash surpluses. The new
Volume Author/Editor: Neil H. Jacoby and Raymond J. Saulnier. Volume URL:
 This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from the National Bureau of Economic Research Volume Title: Term Lending to Business Volume Author/Editor: Neil H. Jacoby and Raymond J. Saulnier Volume
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from the National Bureau of Economic Research Volume Title: Term Lending to Business Volume Author/Editor: Neil H. Jacoby and Raymond J. Saulnier Volume
Corporate and Household Sectors in Austria: Subdued Growth of Indebtedness
 Corporate and Household Sectors in Austria: Subdued Growth of Indebtedness Stabilization of Corporate Sector Risk Indicators The Austrian Economy Slows Down Against the background of the renewed recession
Corporate and Household Sectors in Austria: Subdued Growth of Indebtedness Stabilization of Corporate Sector Risk Indicators The Austrian Economy Slows Down Against the background of the renewed recession
Ms Hessius comments on the inflation target and the state of the economy in Sweden
 Ms Hessius comments on the inflation target and the state of the economy in Sweden Speech given by Ms Kerstin Hessius, Deputy Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, before the Swedish Economic Association,
Ms Hessius comments on the inflation target and the state of the economy in Sweden Speech given by Ms Kerstin Hessius, Deputy Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, before the Swedish Economic Association,
DEVELOPMENTS IN THE COST COMPETITIVENESS OF THE EUROPEAN UNION, THE UNITED STATES AND JAPAN MAIN FEATURES
 DEVELOPMENTS IN THE COST COMPETITIVENESS OF THE EUROPEAN UNION, THE UNITED STATES AND JAPAN MAIN FEATURES The euro against major international currencies: During the first quarter of 2001, the euro appreciated
DEVELOPMENTS IN THE COST COMPETITIVENESS OF THE EUROPEAN UNION, THE UNITED STATES AND JAPAN MAIN FEATURES The euro against major international currencies: During the first quarter of 2001, the euro appreciated
Eva Srejber: How the Riksbank's financial assets are managed
 Eva Srejber: How the Riksbank's financial assets are managed Speech by Ms Eva Srejber, First Deputy Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, at the Handelsbanken, Stockholm, 25 April 2006. References and diagrams
Eva Srejber: How the Riksbank's financial assets are managed Speech by Ms Eva Srejber, First Deputy Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, at the Handelsbanken, Stockholm, 25 April 2006. References and diagrams
Full report. Value for money in foreign aid? - Currency management in international development cooperation (RiR 2014:19) AUDIT REPORT
 AUDIT REPORT 1 Full report Value for money in foreign aid? - Currency management in international development cooperation (RiR 2014:19) SWEDISH NATIONAL AUDIT OFFICE Contents Summary 3 1 Introduction
AUDIT REPORT 1 Full report Value for money in foreign aid? - Currency management in international development cooperation (RiR 2014:19) SWEDISH NATIONAL AUDIT OFFICE Contents Summary 3 1 Introduction
