BANK OF CANADA RENEWAL OF BACKGROUND INFORMATION THE INFLATION-CONTROL TARGET. May 2001
|
|
|
- Marlene Adela Williams
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BANK OF CANADA May RENEWAL OF THE INFLATION-CONTROL TARGET BACKGROUND INFORMATION
2 Bank of Canada Wellington Street Ottawa, Ontario KA G9 78 ISBN: Printed in Canada on recycled paper
3 B A N K O F C A N A D A RENEWAL OF THE INFLATION-CONTROL TARGET BACKGROUND INFORMATION
4
5 RENEWAL OF THE INFLATION-CONTROL TARGET BACKGROUND INFORMATION MAY INTRODUCTION As noted in the joint statement issued on 7 May, the Government of Canada and the Bank of Canada have renewed the inflation-control target for a five-year period from the end of. This background note provides additional information on the target arrangements and on the refinements in the way that the Bank plans to implement these arrangements in order to increase the predictability of inflation over the longer term. It also sets out some changes in the way that the Bank will explain inflation developments to the Canadian public. BACKGROUND In February 99, the Government and the Bank introduced targets aimed at reducing the rate of inflation. The objective was to achieve a per cent inflation rate by the end of 99 (the lowest inflation rate in almost two decades) and to gradually reduce the rate of inflation to per cent by the end of 99. The targets were extended twice first from the end of 99 to the end of 998 and then from the end of 998 to the end of. Both extensions involved maintaining a target range of to per cent with a midpoint of per cent. As was explained when the targets were extended, it was considered important to allow the Canadian economy and the Canadian public sufficient time to adjust to inflation targeting, and it was also considered helpful to see how the Canadian economy functioned throughout a full economic cycle, including a period in which economic activity was at or near the economy s productive capacity. After a decade of experience, it is clear that focusing monetary policy on keeping inflation low, stable, and predictable makes an important contribution to a wellfunctioning Canadian economy. The inflation targets have proven to be an effective way of maintaining a low-inflation environment and have provided an anchor for inflation expectations. To achieve the best economic outcomes, it is, of course, essential that other policies, both macro and micro, also have the appropriate focus. But low inflation provides the crucial underpinning that enables the economy to perform well. A framework in which inflation-control targets assure Canadians that inflation will remain low, stable, and predictable leads to less-pronounced cycles and to higher growth of production capacity. The reduced amplitude of the business cycle stems from the stabilizing properties of the inflation targets as the Bank focuses on the effects of demand pressures on the future rate of inflation. Thus, when demand presses against the economy s capacity to produce, there will be upward pressure on inflation relative to the target, and the Bank will act to tighten monetary conditions. This, in turn, will moderate demand and activity and thus reduce the inflationary pressures. Conversely, when demand is weak, there will be downward pressure on inflation relative to the target, and the Bank will act to ease monetary conditions. This will support economic activity and offset the downward pressures on demand and inflation. The latter part of the 99s has provided strong evidence that, by fostering an environment of low and predictable rates of inflation, the targets contribute to the achievement of sustained, robust growth. Low and predictable inflation supports growth in capacity output through various channels. Among the most important are the ability of businesses and households to make better long-term plans for saving and investment, the increased incentives for business to control costs and increase productivity, the cost reductions that arise from the interaction of inflation and the nonindexed components of the tax system, and
6 RENEWAL OF THE INFLATION-CONTROL TARGET BACKGROUND INFORMATION MAY the reduced need to divert resources towards protection from inflation. STRENGTHENING THE TARGETING ARRANGEMENTS The basic framework for conducting monetary policy under the inflation-control target is being maintained, and the Bank is making a number of modifications to strengthen the way the target arrangements are implemented.. The inflation target The to per cent inflation-control target range that has been in place for the last six years has proved capable of delivering good economic performance and has therefore been retained for the next five years. The Bank has carefully examined the arguments that the target should be raised. These arguments relate to concerns about downward wage rigidity, the inability of interest rates to decline below zero, and the potential risk of deflation. The Bank has concluded that the evidence does not support these concerns for the current target range. The Bank has also carefully examined the arguments for a lower target. Good theoretical arguments can be made that support further reduction in the target, but it has thus far proven difficult to quantify the longer-term benefits of such a change. Consequently, the Bank decided that it was best to maintain the current target range. To maximize the likelihood that inflation stays within the to per cent target range, the Bank needs to aim at the per cent target midpoint. It is not possible, however, to maintain inflation precisely at the target. See Technical Background Document on the Bank s Web site ( for a brief review of the literature on whether the current low-inflation regime leads to economic difficulties. References to the research that has been done on these issues are provided there.. See Technical Background Document on the Bank s Web site for a brief review of the arguments that reducing the rate of inflation further would improve economic outcomes. midpoint all the time. Shocks to demand and supply may push inflation in ways that cannot be offset in the short run because there are lags in the effect of monetary policy. Monetary policy will therefore be directed to moving inflation to the target midpoint over a six- to eight-quarter horizon. In this way, policy aims at keeping the trend of inflation at the per cent target midpoint. The target range of ± per cent around the target midpoint thus encompasses the outcomes for inflation that are likely to occur most of the time. This range should be interpreted as a reflection of the short-run uncertainty of outcomes stemming from unpredictable shocks and not as a measure of the indifference of the Bank as to the outcome.. Measurement of the target rate of inflation The inflation target will continue to be set in terms of the -month increase in the total consumer price index (CPI). The use of the CPI as the basis for the target reflects its role as the most commonly used indicator of inflation in the Canadian economy. Because it measures the prices of consumer goods and services, the CPI is the most relevant estimate of the cost of living for most Canadians. Moreover, from a technical viewpoint, the Canadian CPI is a sound measure of changes in the price level. The CPI also has some important practical advantages: it is available monthly so that it can be tracked regularly; it is published in a timely fashion without long delays; and it is, for all practical purposes, never revised.. Term of agreement The earlier inflation-control agreements had a three-year horizon. On this occasion, the Bank and the government have agreed on a five-year horizon. This reflects the wide acceptance of the targets after almost a. The bias of CPI inflation in measuring the increase in the true cost of living is low, at about. per cent per year (Crawford 998).
7 RENEWAL OF THE INFLATION-CONTROL TARGET BACKGROUND INFORMATION MAY decade of operation. Indeed, they have become a central element in the Canadian economic policy framework. A longer period for the agreement will give Canadians greater assurance that low inflation will be a continuing feature of the Canadian economic environment and will facilitate long-term planning.. Use and measurement of core inflation as an operational guide to policy While the overall target is defined in terms of the total CPI, the Bank finds it very helpful to use a core measure of inflation as a shorter-term operational guide to policy. One reason for this focus on core inflation is the considerable short-run volatility in certain components of the CPI. Since movements in these volatile elements tend to reverse themselves fairly quickly, and since monetary policy actions affect inflation over a longer period, it would be inappropriate for monetary policy to try to offset the short-run movements in the total CPI caused by these fluctuations. Over longer periods of time, the total CPI and core measures of the CPI that exclude components with considerable shortrun volatility have tended to move in a very similar fashion and are likely to continue to do so in the future. Hence, achieving the target rate of increase for the core measure of the CPI will tend to bring about a similar rate of increase for the total CPI over time. Another reason for this focus on core inflation is to adjust for the first-round effects of changes in indirect taxes (such as sales and excise taxes) on inflation. The Bank has always made it clear that it would accommodate the first-round effects of a change in indirect taxes, i.e., not try to offset its direct effect on the total CPI. However, the Bank has also made it clear that it would take whatever actions were necessary to prevent second-round effects, in which the taxinduced rise or fall in the CPI led to subsequent broader effects on wage and price inflation. To the extent that it isolates the underlying trend in inflation, core inflation tends to be a better predictor of future changes in the total CPI than does the recent history of CPI inflation. That is, using core inflation as the operational guide increases the likelihood of keeping future CPI inflation on target. Since the inception of the targeting regime in 99, the Bank has used as its core measure of inflation the CPI excluding food, energy, and the effect of changes in indirect taxes. For the past several years, the Bank has also been monitoring and reporting a number of other measures of underlying inflation, including one called CPIX. CPIX excludes the eight most volatile components of the CPI: fruit, vegetables, gasoline, fuel oil, natural gas, intercity transportation, tobacco, and mortgage-interest costs. It also excludes the effect of changes in indirect taxes on the other CPI components. After a thorough assessment, the Bank has concluded that this measure has a number of advantages over the current measure of core inflation in capturing the underlying trend of inflation. The Bank has therefore chosen it as its new measure of core inflation and as its new operating guide for policy. The new measure of core inflation has the following benefits: It includes 8 per cent of the consumer basket, as opposed to the 7 per cent included in the current measure of core CPI. It excludes only the five food and energy components that are most volatile because they are directly affected by supply shocks: fruit, vegetables, gasoline, fuel oil, and natural gas. It excludes intercity transportation prices, which are volatile because they are heavily influenced by supply shocks to the price of aviation fuel and by temporary airline seat sales.
8 RENEWAL OF THE INFLATION-CONTROL TARGET BACKGROUND INFORMATION MAY It excludes tobacco prices, which are volatile because of changes in tobacco taxes and other factors. It excludes the costs of mortgage interest, which tend to rise (at least for short-term maturities) when monetary policy is tightened and thus give a misleading signal of coming inflation trends. Because it removes additional volatile components of the consumer basket and retains other non-volatile components, the new measure of core inflation is somewhat less volatile than the current measure. The new measure performs better than the current measure of core inflation in explaining future changes in total CPI inflation adjusted for the effect of changes in indirect taxes. Chart shows the movements in the current and new measures of core inflation, and Chart shows the new measure of core inflation along with total CPI inflation. Over the period January 99 to March, the average rates of inflation based on the new measure of core CPI, the current measure of core CPI, and total CPI are very close within. per cent of one another. We expect that, in the future, the measures of inflation based on the total CPI and the new core CPI will continue to exhibit similar trends. In the event of anticipated persistent differences for a number of years between the trends of the. Most major inflation-targeting central banks exclude mortgage-interest costs from either their targeted measure of inflation or their underlying measure of inflation. These include the Bank of England, the Reserve Bank of New Zealand, the Swedish Riksbank, and the Reserve Bank of Australia.. This better performance is judged by regressions in which the future changes in -month CPI inflation adjusted for the effect of changes in indirect taxes are explained by the current difference between a core measure of inflation and CPI inflation adjusted for the effect of changes in indirect taxes. (That is, taxadjusted CPI inflation tends to decline when it is above core inflation and to rise when it is below core inflation.) The better performance holds whether the future change is over or 8 months and whether the period considered starts in 98 or 99. Other empirical work on various measures of core inflation can be found in Hogan, Johnson, and Laflèche (). An article in the Autumn Bank of Canada Review will contain further discussion of the properties of the new measure of core inflation. Chart Two Measures of Core Inflation Year-over-year percentage change New measure Current measure (CPI excluding food, energy, and effect of changes in indirect taxes) Chart Total CPI and the New Measure of Core Inflation Year-over-year percentage change New measure of core inflation Total CPI two measures, the Bank would adjust its desired path for core CPI inflation so that it is effectively aiming to keep future total CPI inflation close to the target midpoint. Starting in June, Statistics Canada will publish in its monthly CPI release the CPI excluding the eight most volatile components identified by the Bank and listed above. And the Bank will publish both the effect of changes in indirect taxes on this measure and the new measure of core inflation.. Explanation by the Bank of inflation outcomes As noted earlier, the target range for inflation around the target midpoint indicates that the Bank expects the outcome to be relatively close to the target midpoint 7
9 RENEWAL OF THE INFLATION-CONTROL TARGET BACKGROUND INFORMATION MAY most of the time. For the official target measure, the -month increase in the total CPI, the range will be ± per cent; that is, we would expect inflation to fall between per cent and per cent most of the time (Chart ). When CPI inflation persistently deviates from the target midpoint, the Bank will give special attention in its Monetary Policy Reports orupdates to explaining why inflation has deviated to such an extent from the target midpoint, what steps (if any) are being taken to ensure that inflation moves back to the target midpoint, and when inflation is expected to return to the target midpoint. These explanations will focus on the movements in total CPI inflation, core inflation, and the components excluded from the core measure, as well as on changes in indirect taxes. Chart Total CPI and CPI Adjusted for the Effect of Changes in Indirect Taxes Year-over-year percentage change Chart CPI Adjusted for the Effect of Changes in Indirect Taxes Average percentage change from December 99 at annual rates Interval for average inflation since December aiming at per cent for the -month rate of inflation. In these circumstances, the longer the averaging period, the more likely it is that average inflation will approach per cent. Chart illustrates the interval for the likely outcomes for the average of CPI inflation, excluding the effect of indirect taxes, for the period since the end of 99, when the current target first took effect. 8 Target range (upper limit) - Total CPI Target midpoint CPI adjusted for the effect of changes in indirect taxes Target range (lower limit) Predictability of average inflation over longer time horizons is desirable. Because unpredictable shocks to inflation should tend to average out over time, 7 monetary policy can deliver this predictability by consistently - REFERENCES Crawford, Allan Measurement biases in Canadian CPI: An update. Bank of Canada Review (Spring): 9. Hogan, Seamus, Marianne Johnson, and Thérèse Laflèche.. Core Inflation. Technical Report No. 89. Ottawa: Bank of Canada.. The largest movement of the total CPI outside the target range occurred in 99 as a result of the reduction in tobacco excise taxes. The tax effect is reflected in the difference between the total CPI and the CPI adjusted for the effect of indirect taxes, as shown in Chart. 7. One type of shock that would not average out over time would be repeated changes in the same direction in indirect taxes. 8. If there is no autocorrelation from year to year (as appears to be the case in the targeting period for total CPI inflation, abstracting from the effect of large indirect tax changes), the statistical formula for the variance of an average implies that the width of the interval will be inversely proportional to the square root of the length of the period over which the average is being calculated. For a range of ±. per cent for the -month inflation rate, the interval becomes ±.7 per cent after years and ±. per cent after years. 7
10
Monetary policy in Sweden
 PM DATE: 2006-05-18 SVERIGES RIKSBANK SE-103 37 Stockholm (Brunkebergstorg 11) Tel +46 8 787 00 00 Fax +46 8 21 05 31 registratorn@riksbank.se www.riksbank.se DNR 2006-631-STA Monetary policy in Sweden
PM DATE: 2006-05-18 SVERIGES RIKSBANK SE-103 37 Stockholm (Brunkebergstorg 11) Tel +46 8 787 00 00 Fax +46 8 21 05 31 registratorn@riksbank.se www.riksbank.se DNR 2006-631-STA Monetary policy in Sweden
The Exchange Rate and Canadian Inflation Targeting
 The Exchange Rate and Canadian Inflation Targeting Christopher Ragan* An essential part of the Bank of Canada s inflation-control strategy is a flexible exchange rate that is free to adjust to various
The Exchange Rate and Canadian Inflation Targeting Christopher Ragan* An essential part of the Bank of Canada s inflation-control strategy is a flexible exchange rate that is free to adjust to various
Measuring Inflation: Methodology and Misconceptions
 Remarks by John Murray Deputy Governor of the Bank of Canada to the Certified General Accountants of Ontario Toronto, ON 18 September 2008 CHECK AGAINST DELIVERY Measuring Inflation: Methodology and Misconceptions
Remarks by John Murray Deputy Governor of the Bank of Canada to the Certified General Accountants of Ontario Toronto, ON 18 September 2008 CHECK AGAINST DELIVERY Measuring Inflation: Methodology and Misconceptions
Inflation Targeting and Inflation Prospects in Canada
 Inflation Targeting and Inflation Prospects in Canada CPP Interdisciplinary Seminar March 2006 Don Coletti Research Director International Department Bank of Canada Overview Objective: answer questions
Inflation Targeting and Inflation Prospects in Canada CPP Interdisciplinary Seminar March 2006 Don Coletti Research Director International Department Bank of Canada Overview Objective: answer questions
What Operating Procedures Should Be Adopted to Maintain Price Stability? Practical Issues
 What Operating Procedures Should Be Adopted to Maintain Price Stability? Practical Issues Charles Freedman In this paper I provide a broad-brush examination from a practitioner s point of view, of some
What Operating Procedures Should Be Adopted to Maintain Price Stability? Practical Issues Charles Freedman In this paper I provide a broad-brush examination from a practitioner s point of view, of some
Bank of Canada to adopt fixed dates for announcing Bank Rate changes
 BANK OF CANADA FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE CONTACT: Pierre Laprise 19 September 2000 (613) 782-8782 Bank of Canada to adopt fixed dates for announcing Bank Rate changes OTTAWA The Bank of Canada today outlined
BANK OF CANADA FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE CONTACT: Pierre Laprise 19 September 2000 (613) 782-8782 Bank of Canada to adopt fixed dates for announcing Bank Rate changes OTTAWA The Bank of Canada today outlined
Inflation Targeting and Output Stabilization in Australia
 6 Inflation Targeting and Output Stabilization in Australia Guy Debelle 1 Inflation targeting has been adopted as the framework for monetary policy in a number of countries, including Australia, over the
6 Inflation Targeting and Output Stabilization in Australia Guy Debelle 1 Inflation targeting has been adopted as the framework for monetary policy in a number of countries, including Australia, over the
A Primer on Inflation Targeting
 A Primer on Inflation Targeting Publication No. 2011-111-E 9 November 2011 Brett Stuckey International Affairs, Trade and Finance Division Parliamentary Information and Research Service A Primer on Inflation
A Primer on Inflation Targeting Publication No. 2011-111-E 9 November 2011 Brett Stuckey International Affairs, Trade and Finance Division Parliamentary Information and Research Service A Primer on Inflation
Barbro Wickman-Parak: The Riksbank's inflation target
 Barbro Wickman-Parak: The Riksbank's inflation target Speech by Ms Barbro Wickman-Parak, Deputy Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, at Swedbank, Stockholm, 9 June 8. * * * The CPI, other measures of inflation
Barbro Wickman-Parak: The Riksbank's inflation target Speech by Ms Barbro Wickman-Parak, Deputy Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, at Swedbank, Stockholm, 9 June 8. * * * The CPI, other measures of inflation
Core Indicators of Japan s Consumer Price Index
 -E-7 Core Indicators of Japan s Consumer Price Index Monetary Affairs Department (currently Financial Systems and Bank Examination Department) Shigenori Shiratsuka November The primary objective of the
-E-7 Core Indicators of Japan s Consumer Price Index Monetary Affairs Department (currently Financial Systems and Bank Examination Department) Shigenori Shiratsuka November The primary objective of the
MID-TERM REVIEW OF MONETARY POLICY STATEMENT 2006
 MID-TERM REVIEW OF MONETARY POLICY STATEMENT 1. Introduction 1.1 There are three objectives to undertake a mid-term review of the Monetary Policy Statement (MPS). First, it is intended to review progress
MID-TERM REVIEW OF MONETARY POLICY STATEMENT 1. Introduction 1.1 There are three objectives to undertake a mid-term review of the Monetary Policy Statement (MPS). First, it is intended to review progress
Gordon Thiesssen: The outlook for the Canadian economy and the conduct of monetary policy
 Gordon Thiesssen: The outlook for the Canadian economy and the conduct of monetary policy Remarks by Mr Gordon Thiessen, Governor of the Bank of Canada, to the Calgary Chamber of Commerce, Calgary, on
Gordon Thiesssen: The outlook for the Canadian economy and the conduct of monetary policy Remarks by Mr Gordon Thiessen, Governor of the Bank of Canada, to the Calgary Chamber of Commerce, Calgary, on
Discussion. Benoît Carmichael
 Discussion Benoît Carmichael The two studies presented in the first session of the conference take quite different approaches to the question of price indexes. On the one hand, Coulombe s study develops
Discussion Benoît Carmichael The two studies presented in the first session of the conference take quite different approaches to the question of price indexes. On the one hand, Coulombe s study develops
The Future Performance of the Canadian Economy
 Remarks by Gordon Thiessen Governor of the Bank of Canada to the Canadian Club of Winnipeg Winnipeg, Manitoba 25 March 1998 The Future Performance of the Canadian Economy It can take anywhere from one
Remarks by Gordon Thiessen Governor of the Bank of Canada to the Canadian Club of Winnipeg Winnipeg, Manitoba 25 March 1998 The Future Performance of the Canadian Economy It can take anywhere from one
Independent Review of the Operation of Monetary Policy in New Zealand: Report to the Minister of Finance
 Independent Review of the Operation of Monetary Policy in New Zealand: Report to the Minister of Finance Lars E.O. Svensson Institute for International Economic Studies, Stockholm University February 2001
Independent Review of the Operation of Monetary Policy in New Zealand: Report to the Minister of Finance Lars E.O. Svensson Institute for International Economic Studies, Stockholm University February 2001
Economic and Fiscal Assessment Update. Ottawa, Canada November 2,
 Economic and Fiscal Assessment Update Ottawa, Canada November 2, 29 www.parl.gc.ca/pbo-dpb The Federal Accountability Act mandates the Parliamentary Budget Officer (PBO) to provide independent analysis
Economic and Fiscal Assessment Update Ottawa, Canada November 2, 29 www.parl.gc.ca/pbo-dpb The Federal Accountability Act mandates the Parliamentary Budget Officer (PBO) to provide independent analysis
UPDATE MONETARY POLICY REPORT. Highlights. January 2004
 B A N K O F C A N A D A MONETARY POLICY REPORT UPDATE January This text is a commentary of the Governing Council of the Bank of Canada. It presents the Bank s updated outlook based on information received
B A N K O F C A N A D A MONETARY POLICY REPORT UPDATE January This text is a commentary of the Governing Council of the Bank of Canada. It presents the Bank s updated outlook based on information received
Evaluation of Norges Bank's projections for 2004
 Evaluation of Norges Bank's projections for 2004 Per Espen Lilleås, economist in the Economics Department 1 The assessments of capacity utilisation in the Norwegian economy in 2004, measured by estimates
Evaluation of Norges Bank's projections for 2004 Per Espen Lilleås, economist in the Economics Department 1 The assessments of capacity utilisation in the Norwegian economy in 2004, measured by estimates
* + p t. i t. = r t. + a(p t
 REAL INTEREST RATE AND MONETARY POLICY There are various approaches to the question of what is a desirable long-term level for monetary policy s instrumental rate. The matter is discussed here with reference
REAL INTEREST RATE AND MONETARY POLICY There are various approaches to the question of what is a desirable long-term level for monetary policy s instrumental rate. The matter is discussed here with reference
Irma Rosenberg: Assessment of monetary policy
 Irma Rosenberg: Assessment of monetary policy Speech by Ms Irma Rosenberg, Deputy Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, at Norges Bank s conference on monetary policy 2006, Oslo, 30 March 2006. * * * Let
Irma Rosenberg: Assessment of monetary policy Speech by Ms Irma Rosenberg, Deputy Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, at Norges Bank s conference on monetary policy 2006, Oslo, 30 March 2006. * * * Let
Measuring Uncertainty in Monetary Policy Using Realized and Implied Volatility
 32 Measuring Uncertainty in Monetary Policy Using Realized and Implied Volatility Bo Young Chang and Bruno Feunou, Financial Markets Department Measuring the degree of uncertainty in the financial markets
32 Measuring Uncertainty in Monetary Policy Using Realized and Implied Volatility Bo Young Chang and Bruno Feunou, Financial Markets Department Measuring the degree of uncertainty in the financial markets
Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (July 2018)
 Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (July 2018) July 31, 2018 Bank of Japan The Bank's View 1 Summary Japan's economy is likely to continue growing at a pace above its potential in fiscal 2018, mainly
Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (July 2018) July 31, 2018 Bank of Japan The Bank's View 1 Summary Japan's economy is likely to continue growing at a pace above its potential in fiscal 2018, mainly
QED. Queen s Economics Department Working Paper No Core inflation at the Bank of Canada A critique. Kevin Clinton Queen s University
 QED Queen s Economics Department Working Paper No. 1077 Core inflation at the Bank of Canada A critique Kevin Clinton Queen s University Department of Economics Queen s University 94 University Avenue
QED Queen s Economics Department Working Paper No. 1077 Core inflation at the Bank of Canada A critique Kevin Clinton Queen s University Department of Economics Queen s University 94 University Avenue
Monetary policy in Sweden
 Monetary policy in Sweden 2010 S V E R I G E S R I K S B A N K Addendum 7 September 2017 The CPIF as target variable for monetary policy As of September 2017, the Riksbank uses the CPIF, the consumer price
Monetary policy in Sweden 2010 S V E R I G E S R I K S B A N K Addendum 7 September 2017 The CPIF as target variable for monetary policy As of September 2017, the Riksbank uses the CPIF, the consumer price
Notes on the monetary transmission mechanism in the Czech economy
 Notes on the monetary transmission mechanism in the Czech economy Luděk Niedermayer 1 This paper discusses several empirical aspects of the monetary transmission mechanism in the Czech economy. The introduction
Notes on the monetary transmission mechanism in the Czech economy Luděk Niedermayer 1 This paper discusses several empirical aspects of the monetary transmission mechanism in the Czech economy. The introduction
Monetary Policy Update December 2007
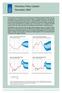 Monetary Policy Update December 7 At its meeting on 8 December, the Executive Board of the Riksbank decided to hold the repo rate unchanged at per cent. During the first half of 8 it is expected that the
Monetary Policy Update December 7 At its meeting on 8 December, the Executive Board of the Riksbank decided to hold the repo rate unchanged at per cent. During the first half of 8 it is expected that the
Svein Gjedrem: The conduct of monetary policy
 Svein Gjedrem: The conduct of monetary policy Introductory statement by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the hearing before the Standing Committee on Finance and Economic
Svein Gjedrem: The conduct of monetary policy Introductory statement by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the hearing before the Standing Committee on Finance and Economic
MONETARY POLICY REPORT April 2002
 B A N K O F C A N A D A MONETARY POLICY REPORT April This 1995 $ gold coin, designed by artist John Mantha, celebrates the Canadian tradition of producing maple syrup. Canada s First Peoples taught the
B A N K O F C A N A D A MONETARY POLICY REPORT April This 1995 $ gold coin, designed by artist John Mantha, celebrates the Canadian tradition of producing maple syrup. Canada s First Peoples taught the
The anchoring of inflation expectations in Singapore
 The anchoring of inflation expectations in Singapore Khor Hoe Ee 1 and Saktiandi Supaat 2 Introduction The credibility of a central bank is probably one of the most important factors determining whether
The anchoring of inflation expectations in Singapore Khor Hoe Ee 1 and Saktiandi Supaat 2 Introduction The credibility of a central bank is probably one of the most important factors determining whether
Developments in inflation and its determinants
 INFLATION REPORT February 2018 Summary Developments in inflation and its determinants The annual CPI inflation rate strengthened its upward trend in the course of 2017 Q4, standing at 3.32 percent in December,
INFLATION REPORT February 2018 Summary Developments in inflation and its determinants The annual CPI inflation rate strengthened its upward trend in the course of 2017 Q4, standing at 3.32 percent in December,
Mr Bäckström elucidates the economic situation in Sweden and describes the consequences it may have for future monetary policy
 Mr Bäckström elucidates the economic situation in Sweden and describes the consequences it may have for future monetary policy Speech given by Mr Urban Bäckström, Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank at Föreningssparbanken,
Mr Bäckström elucidates the economic situation in Sweden and describes the consequences it may have for future monetary policy Speech given by Mr Urban Bäckström, Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank at Föreningssparbanken,
Monetary Policy Report. May 1997
 B A N K O F C A N A D A Monetary Policy Report May 1997 The silver dollar on the cover was issued to mark the 1th anniversary of the Stanley Cup. Donated by Governor General Lord Stanley in 193, the Cup
B A N K O F C A N A D A Monetary Policy Report May 1997 The silver dollar on the cover was issued to mark the 1th anniversary of the Stanley Cup. Donated by Governor General Lord Stanley in 193, the Cup
Inflation target misses: A comparison of countries on inflation targets
 Appendix 1 Inflation target misses: A comparison of countries on inflation targets Just over four years have elapsed since the Central Bank of Iceland moved onto an inflation target as its new monetary
Appendix 1 Inflation target misses: A comparison of countries on inflation targets Just over four years have elapsed since the Central Bank of Iceland moved onto an inflation target as its new monetary
BANK OF BOTSWANA MONETARY POLICY STATEMENT Mid-Year Review
 BANK OF BOTSWANA MONETARY POLICY STATEMENT 00 Mid-Year Review 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1 The Monetary Policy Statement (MPS) released in February 00 specified several objectives that the Bank of Botswana intended
BANK OF BOTSWANA MONETARY POLICY STATEMENT 00 Mid-Year Review 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1 The Monetary Policy Statement (MPS) released in February 00 specified several objectives that the Bank of Botswana intended
Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (April 2014)
 April 30, 2014 Bank of Japan Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (April 2014) The Bank's View 1 Summary From fiscal 2014 through fiscal 2016, Japan's economy is likely to continue growing at a pace
April 30, 2014 Bank of Japan Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (April 2014) The Bank's View 1 Summary From fiscal 2014 through fiscal 2016, Japan's economy is likely to continue growing at a pace
FINAL EXAM: Macro 302 Winter 2014
 FINAL EXAM: Macro 32 Winter 214 Surname: Name: Student Number: State clearly your assumptions when you derive a result. ou must always show your thinking to get full credit. ou have 3 hours to answer all
FINAL EXAM: Macro 32 Winter 214 Surname: Name: Student Number: State clearly your assumptions when you derive a result. ou must always show your thinking to get full credit. ou have 3 hours to answer all
September 21, 2016 Bank of Japan
 September 21, 2016 Bank of Japan Comprehensive Assessment: Developments in Economic Activity and Prices as well as Policy Effects since the Introduction of Quantitative and Qualitative Monetary Easing
September 21, 2016 Bank of Japan Comprehensive Assessment: Developments in Economic Activity and Prices as well as Policy Effects since the Introduction of Quantitative and Qualitative Monetary Easing
Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (January 2018)
 Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (January 2018) January 23, 2018 Bank of Japan The Bank's View 1 Summary Japan's economy is likely to continue expanding on the back of highly accommodative financial
Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (January 2018) January 23, 2018 Bank of Japan The Bank's View 1 Summary Japan's economy is likely to continue expanding on the back of highly accommodative financial
Deepak Mohanty: Perspectives on inflation in India
 Deepak Mohanty: Perspectives on inflation in India Speech by Mr Deepak Mohanty, Executive Director of the Reserve Bank of India, at the Bankers Club, Chennai, 28 September 2010. * * * The assistance provided
Deepak Mohanty: Perspectives on inflation in India Speech by Mr Deepak Mohanty, Executive Director of the Reserve Bank of India, at the Bankers Club, Chennai, 28 September 2010. * * * The assistance provided
Nigeria s Experience with Monetary Policy Transmission
 Nigeria s Experience with Monetary Policy Transmission Usman Okpanachi Monetary Policy Department Outline Introduction Current Monetary Policy Framework Transmission Mechanism of policy Some Outputs and
Nigeria s Experience with Monetary Policy Transmission Usman Okpanachi Monetary Policy Department Outline Introduction Current Monetary Policy Framework Transmission Mechanism of policy Some Outputs and
Why Monetary Policy Matters: A Canadian Perspective
 Why Monetary Policy Matters: A Canadian Perspective Christopher Ragan* This article provides answers to several key questions about Canadian monetary policy. First, what is monetary policy? Second, why
Why Monetary Policy Matters: A Canadian Perspective Christopher Ragan* This article provides answers to several key questions about Canadian monetary policy. First, what is monetary policy? Second, why
Monetary Policy Report
 Monetary Policy Report October 7 www.bankofcanada.ca CANADA S INFLATION-CONTROL STRATEGY* Inflation control and the economy Inflation control is not an end in itself; it is the means whereby monetary policy
Monetary Policy Report October 7 www.bankofcanada.ca CANADA S INFLATION-CONTROL STRATEGY* Inflation control and the economy Inflation control is not an end in itself; it is the means whereby monetary policy
Changes to the Bank of Canada s Framework for Financial Market Operations
 Changes to the Bank of Canada s Framework for Financial Market Operations A consultation paper by the Bank of Canada 5 May 2015 Operations Consultation Financial Markets Department Bank of Canada 234 Laurier
Changes to the Bank of Canada s Framework for Financial Market Operations A consultation paper by the Bank of Canada 5 May 2015 Operations Consultation Financial Markets Department Bank of Canada 234 Laurier
Review of the literature on the comparison
 Review of the literature on the comparison of price level targeting and inflation targeting Florin V Citu, Economics Department Introduction This paper assesses some of the literature that compares price
Review of the literature on the comparison of price level targeting and inflation targeting Florin V Citu, Economics Department Introduction This paper assesses some of the literature that compares price
Irma Rosenberg: Monetary policy and the Swedish economy
 Irma Rosenberg: Monetary policy and the Swedish economy Speech by Ms Irma Rosenberg, Deputy Governor of Sveriges Riksbank, to the Swedish Society of Financial Analysts, Stockholm, 5 March 2003. * * * Thank
Irma Rosenberg: Monetary policy and the Swedish economy Speech by Ms Irma Rosenberg, Deputy Governor of Sveriges Riksbank, to the Swedish Society of Financial Analysts, Stockholm, 5 March 2003. * * * Thank
monetary policy monthly report
 monetary policy monthly report Current and expected inflation performance and monetary policy SUMMARY Inflation highlights Annual inflation rate of recorded +3.2 percent, the highest upward trend of this
monetary policy monthly report Current and expected inflation performance and monetary policy SUMMARY Inflation highlights Annual inflation rate of recorded +3.2 percent, the highest upward trend of this
David Dodge: Canada s experience with inflation targets and a flexible exchange rate: lessons learned
 David Dodge: Canada s experience with inflation targets and a flexible exchange rate: lessons learned Remarks by Mr David Dodge, Governor of the Bank of Canada, to the Canadian Society of New York, New
David Dodge: Canada s experience with inflation targets and a flexible exchange rate: lessons learned Remarks by Mr David Dodge, Governor of the Bank of Canada, to the Canadian Society of New York, New
Bank of Japan Review. The Uncertainty of the Economic Outlook and Central Banks Communications
 Bank of Japan Review 8-E- The Uncertainty of the Economic Outlook and Central Banks Communications Monetary Affairs Department Koji Nakamura and Shinichiro Nagae June 8 Central Banks make policy decisions
Bank of Japan Review 8-E- The Uncertainty of the Economic Outlook and Central Banks Communications Monetary Affairs Department Koji Nakamura and Shinichiro Nagae June 8 Central Banks make policy decisions
Are we there yet? Adjustment paths in response to Tariff shocks: a CGE Analysis.
 Are we there yet? Adjustment paths in response to Tariff shocks: a CGE Analysis. This paper takes the mini USAGE model developed by Dixon and Rimmer (2005) and modifies it in order to better mimic the
Are we there yet? Adjustment paths in response to Tariff shocks: a CGE Analysis. This paper takes the mini USAGE model developed by Dixon and Rimmer (2005) and modifies it in order to better mimic the
Irma Rosenberg: Riksbank to introduce own path for the repo rate
 Irma Rosenberg: Riksbank to introduce own path for the repo rate Speech by Ms Irma Rosenberg, Deputy Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, at Danske Bank, Stockholm, 17 January 2007. * * * Thank you for the
Irma Rosenberg: Riksbank to introduce own path for the repo rate Speech by Ms Irma Rosenberg, Deputy Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, at Danske Bank, Stockholm, 17 January 2007. * * * Thank you for the
Advanced Topic 7: Exchange Rate Determination IV
 Advanced Topic 7: Exchange Rate Determination IV John E. Floyd University of Toronto May 10, 2013 Our major task here is to look at the evidence regarding the effects of unanticipated money shocks on real
Advanced Topic 7: Exchange Rate Determination IV John E. Floyd University of Toronto May 10, 2013 Our major task here is to look at the evidence regarding the effects of unanticipated money shocks on real
The Characteristics of Stock Market Volatility. By Daniel R Wessels. June 2006
 The Characteristics of Stock Market Volatility By Daniel R Wessels June 2006 Available at: www.indexinvestor.co.za 1. Introduction Stock market volatility is synonymous with the uncertainty how macroeconomic
The Characteristics of Stock Market Volatility By Daniel R Wessels June 2006 Available at: www.indexinvestor.co.za 1. Introduction Stock market volatility is synonymous with the uncertainty how macroeconomic
Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (October 2014)
 October 31, 2014 Bank of Japan Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (October 2014) The Bank's View 1 Summary From fiscal 2014 through fiscal 2016, Japan's economy is likely to continue growing at a
October 31, 2014 Bank of Japan Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (October 2014) The Bank's View 1 Summary From fiscal 2014 through fiscal 2016, Japan's economy is likely to continue growing at a
Guidelines for Central Government Debt Management Decision taken at the Cabinet meeting 10 November 2005
 Guidelines for Central Government Debt Management 2006 Decision taken at the Cabinet meeting 10 November 2005 006 Guidelines for Central Government Debt Management 2006 1 Contents Appendix 1 Summary...3
Guidelines for Central Government Debt Management 2006 Decision taken at the Cabinet meeting 10 November 2005 006 Guidelines for Central Government Debt Management 2006 1 Contents Appendix 1 Summary...3
: Monetary Economics and the European Union. Lecture 5. Instructor: Prof Robert Hill. Inflation Targeting
 320.326: Monetary Economics and the European Union Lecture 5 Instructor: Prof Robert Hill Inflation Targeting Note: The extra class on Monday 11 Nov is cancelled. This lecture will take place in the normal
320.326: Monetary Economics and the European Union Lecture 5 Instructor: Prof Robert Hill Inflation Targeting Note: The extra class on Monday 11 Nov is cancelled. This lecture will take place in the normal
An Assessment of the Revisions to the Government s Fiscal Outlook. Ottawa, Canada November 29,
 An Assessment of the Revisions to the Government s Fiscal Outlook Ottawa, Canada November 29, 2012 www.pbo-dpb.gc.ca The mandate of the Parliamentary Budget Officer (PBO) is to provide independent analysis
An Assessment of the Revisions to the Government s Fiscal Outlook Ottawa, Canada November 29, 2012 www.pbo-dpb.gc.ca The mandate of the Parliamentary Budget Officer (PBO) is to provide independent analysis
MONETARY POLICY REPORT May 2001
 B A N K O F C A N A D A MONETARY POLICY REPORT May 1 The 1985 silver dollar on the cover was designed by Karel Roblicek and marks the 1th anniversary of Canada s National Parks. The national parks system
B A N K O F C A N A D A MONETARY POLICY REPORT May 1 The 1985 silver dollar on the cover was designed by Karel Roblicek and marks the 1th anniversary of Canada s National Parks. The national parks system
Canada s Economic Future: What Have We Learned from the 1990s?
 Remarks by Gordon Thiessen Governor of the Bank of Canada to the Canadian Club of Toronto Toronto, Ontario 22 January 2001 Canada s Economic Future: What Have We Learned from the 1990s? It was to the Canadian
Remarks by Gordon Thiessen Governor of the Bank of Canada to the Canadian Club of Toronto Toronto, Ontario 22 January 2001 Canada s Economic Future: What Have We Learned from the 1990s? It was to the Canadian
Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (April 2010)
 April 30, 2010 Bank of Japan Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (April 2010) The Bank's View 1 The global economy has emerged from the sharp deterioration triggered by the financial crisis and has
April 30, 2010 Bank of Japan Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (April 2010) The Bank's View 1 The global economy has emerged from the sharp deterioration triggered by the financial crisis and has
Monetary Policy Objectives
 Monetary Policy Objectives Purpose Phase 1 of the Review of the Reserve Bank Act considers changes to the Act to provide for requiring monetary policy decision-makers to give due consideration to maximising
Monetary Policy Objectives Purpose Phase 1 of the Review of the Reserve Bank Act considers changes to the Act to provide for requiring monetary policy decision-makers to give due consideration to maximising
Monetary Policy Objectives Options for Reform
 Monetary Policy Objectives Options for Reform Contents 2 Objectives for reform (slides 3-4) The existing regime (slides 5-7) Updating section 1A (slide 8) Criteria for objectives reform (slide 9) Options
Monetary Policy Objectives Options for Reform Contents 2 Objectives for reform (slides 3-4) The existing regime (slides 5-7) Updating section 1A (slide 8) Criteria for objectives reform (slide 9) Options
Another Milestone on the Road to Policy Normalization
 LEADERSHIP SERIES OCTOBER 2017 A feature article from our U.S. partners Another Milestone on the Road to Policy Normalization The twin tailwinds of strong earnings and easing financial conditions are unlikely
LEADERSHIP SERIES OCTOBER 2017 A feature article from our U.S. partners Another Milestone on the Road to Policy Normalization The twin tailwinds of strong earnings and easing financial conditions are unlikely
TURKEY S DISINFLATION EXPERIENCE: THE ROAD TO PRICE STABILITY Erdem Başçi*
 TURKEY S DISINFLATION EXPERIENCE: THE ROAD TO PRICE STABILITY Erdem Başçi* ABSTRACT This paper aims to analyze the disinflation experience of the Turkish economy after adopting the floating exchange rate
TURKEY S DISINFLATION EXPERIENCE: THE ROAD TO PRICE STABILITY Erdem Başçi* ABSTRACT This paper aims to analyze the disinflation experience of the Turkish economy after adopting the floating exchange rate
Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (October 2017)
 Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (October 2017) October 31, 2017 Bank of Japan The Bank's View 1 Summary Japan's economy is likely to continue expanding on the back of highly accommodative financial
Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (October 2017) October 31, 2017 Bank of Japan The Bank's View 1 Summary Japan's economy is likely to continue expanding on the back of highly accommodative financial
Characteristics of the euro area business cycle in the 1990s
 Characteristics of the euro area business cycle in the 1990s As part of its monetary policy strategy, the ECB regularly monitors the development of a wide range of indicators and assesses their implications
Characteristics of the euro area business cycle in the 1990s As part of its monetary policy strategy, the ECB regularly monitors the development of a wide range of indicators and assesses their implications
THE BEHAVIOUR OF GOVERNMENT OF CANADA REAL RETURN BOND RETURNS: AN EMPIRICAL STUDY
 ASAC 2005 Toronto, Ontario David W. Peters Faculty of Social Sciences University of Western Ontario THE BEHAVIOUR OF GOVERNMENT OF CANADA REAL RETURN BOND RETURNS: AN EMPIRICAL STUDY The Government of
ASAC 2005 Toronto, Ontario David W. Peters Faculty of Social Sciences University of Western Ontario THE BEHAVIOUR OF GOVERNMENT OF CANADA REAL RETURN BOND RETURNS: AN EMPIRICAL STUDY The Government of
Dnr RG 2013/ September Central Government Debt Management
 Dnr RG 2013/339 27 September 2013 Central Government Debt Management Proposed guidelines 2014 2017 SUMMARY 1 1 PREREQUISITES 2 1 The development of central government debt until 2017 2 PROPOSED GUIDELINES
Dnr RG 2013/339 27 September 2013 Central Government Debt Management Proposed guidelines 2014 2017 SUMMARY 1 1 PREREQUISITES 2 1 The development of central government debt until 2017 2 PROPOSED GUIDELINES
Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (April 2018)
 Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (April 2018) The Bank's View 1 Summary April 27, 2018 Bank of Japan Japan's economy is likely to continue growing at a pace above its potential in fiscal 2018,
Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (April 2018) The Bank's View 1 Summary April 27, 2018 Bank of Japan Japan's economy is likely to continue growing at a pace above its potential in fiscal 2018,
Household Balance Sheets and Debt an International Country Study
 47 Household Balance Sheets and Debt an International Country Study Jacob Isaksen, Paul Lassenius Kramp, Louise Funch Sørensen and Søren Vester Sørensen, Economics INTRODUCTION AND SUMMARY What are the
47 Household Balance Sheets and Debt an International Country Study Jacob Isaksen, Paul Lassenius Kramp, Louise Funch Sørensen and Søren Vester Sørensen, Economics INTRODUCTION AND SUMMARY What are the
Transparency and the Response of Interest Rates to the Publication of Macroeconomic Data
 Transparency and the Response of Interest Rates to the Publication of Macroeconomic Data Nicolas Parent, Financial Markets Department It is now widely recognized that greater transparency facilitates the
Transparency and the Response of Interest Rates to the Publication of Macroeconomic Data Nicolas Parent, Financial Markets Department It is now widely recognized that greater transparency facilitates the
Monetary Policy Report: Using Rules for Benchmarking
 Monetary Policy Report: Using Rules for Benchmarking Michael Dotsey Executive Vice President and Director of Research Keith Sill Senior Vice President and Director, Real-Time Data Research Center Federal
Monetary Policy Report: Using Rules for Benchmarking Michael Dotsey Executive Vice President and Director of Research Keith Sill Senior Vice President and Director, Real-Time Data Research Center Federal
An Improved Framework for Assessing the Risks Arising from Elevated Household Debt
 51 An Improved Framework for Assessing the Risks Arising from Elevated Household Debt Umar Faruqui, Xuezhi Liu and Tom Roberts Introduction Since 2008, the Bank of Canada has used a microsimulation model
51 An Improved Framework for Assessing the Risks Arising from Elevated Household Debt Umar Faruqui, Xuezhi Liu and Tom Roberts Introduction Since 2008, the Bank of Canada has used a microsimulation model
A measure of supercore inflation for the eurozone
 Inflation A measure of supercore inflation for the eurozone Global Macroeconomic Scenarios Introduction Core inflation measures are developed to clean headline inflation from those price items that are
Inflation A measure of supercore inflation for the eurozone Global Macroeconomic Scenarios Introduction Core inflation measures are developed to clean headline inflation from those price items that are
The Riksbank's monetary policy strategy
 SPEECH DATE: 14 September 2006 SPEAKER: LOCALITY: Deputy Governor Lars Nyberg Foreign Banker s Association SVERIGES RIKSBANK SE-103 37 Stockholm (Brunkebergstorg 11) Tel +46 8 787 00 00 Fax +46 8 21 05
SPEECH DATE: 14 September 2006 SPEAKER: LOCALITY: Deputy Governor Lars Nyberg Foreign Banker s Association SVERIGES RIKSBANK SE-103 37 Stockholm (Brunkebergstorg 11) Tel +46 8 787 00 00 Fax +46 8 21 05
Predicting a US recession: has the yield curve lost its relevance?
 Global Perspective Predicting a US recession: has the yield curve lost its relevance? For professional investor use only Asset Management August 2018 Executive summary It is becoming apparent the US economy
Global Perspective Predicting a US recession: has the yield curve lost its relevance? For professional investor use only Asset Management August 2018 Executive summary It is becoming apparent the US economy
Øystein Olsen: Monetary policy and interrelationships in the Norwegian economy
 Øystein Olsen: Monetary policy and interrelationships in the Norwegian economy Address by Mr Øystein Olsen, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the Centre for Monetary Economics (CME)/BI
Øystein Olsen: Monetary policy and interrelationships in the Norwegian economy Address by Mr Øystein Olsen, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the Centre for Monetary Economics (CME)/BI
Monetary Policy Objectives During the Crisis: An Overview of Selected Southeast European Countries
 Monetary Policy Objectives During the Crisis: An Overview of Selected Southeast European Countries 35 UDK: 338.23:336.74(4-12) DOI: 10.1515/jcbtp-2015-0003 Journal of Central Banking Theory and Practice,
Monetary Policy Objectives During the Crisis: An Overview of Selected Southeast European Countries 35 UDK: 338.23:336.74(4-12) DOI: 10.1515/jcbtp-2015-0003 Journal of Central Banking Theory and Practice,
STEPHEN NICKELL BANK OF ENGLAND MONETARY POLICY COMMITTEE. The Budget of 1981 was over the top
 STEPHEN NICKELL BANK OF ENGLAND MONETARY POLICY COMMITTEE The Budget of 1981 was over the top To be delivered at the Institute of Economic Affairs Panel Discussion in London Monday 13 March 2006 Prepared
STEPHEN NICKELL BANK OF ENGLAND MONETARY POLICY COMMITTEE The Budget of 1981 was over the top To be delivered at the Institute of Economic Affairs Panel Discussion in London Monday 13 March 2006 Prepared
Durmuş Yilmaz: Press conference for the presentation of the inflation report
 Durmuş Yilmaz: Press conference for the presentation of the inflation report Speech by Mr Durmuş Yilmaz, Governor of the Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey, at the press conference for the presentation
Durmuş Yilmaz: Press conference for the presentation of the inflation report Speech by Mr Durmuş Yilmaz, Governor of the Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey, at the press conference for the presentation
Stochastic Modelling: The power behind effective financial planning. Better Outcomes For All. Good for the consumer. Good for the Industry.
 Stochastic Modelling: The power behind effective financial planning Better Outcomes For All Good for the consumer. Good for the Industry. Introduction This document aims to explain what stochastic modelling
Stochastic Modelling: The power behind effective financial planning Better Outcomes For All Good for the consumer. Good for the Industry. Introduction This document aims to explain what stochastic modelling
End of year fiscal report. November 2008
 End of year fiscal report November 2008 End of year fiscal report November 2008 Crown copyright 2008 The text in this document (excluding the Royal Coat of Arms and departmental logos) may be reproduced
End of year fiscal report November 2008 End of year fiscal report November 2008 Crown copyright 2008 The text in this document (excluding the Royal Coat of Arms and departmental logos) may be reproduced
The Bank of Canada s Business Outlook Survey
 The Bank of Canada s Business Outlook Survey Monica Martin, Ontario Regional Office Since the autumn of 1997, the regional offices of the Bank of Canada have conducted quarterly consultations with businesses
The Bank of Canada s Business Outlook Survey Monica Martin, Ontario Regional Office Since the autumn of 1997, the regional offices of the Bank of Canada have conducted quarterly consultations with businesses
Session 9. The Interactions Between Cyclical and Long-term Dynamics: The Role of Inflation
 Session 9. The Interactions Between Cyclical and Long-term Dynamics: The Role of Inflation Potential Output and Inflation Inflation as a Mechanism of Adjustment The Role of Expectations and the Phillips
Session 9. The Interactions Between Cyclical and Long-term Dynamics: The Role of Inflation Potential Output and Inflation Inflation as a Mechanism of Adjustment The Role of Expectations and the Phillips
MINUTES OF THE MONETARY COUNCIL MEETING 16 October 2018
 MINUTES OF THE MONETARY COUNCIL MEETING 16 October 2018 Time of publication: 2 p.m. on 7 November 2018 Article 3 (1) of the MNB Act (Act CXXXIX of 2013 on the Magyar Nemzeti Bank) defines achieving and
MINUTES OF THE MONETARY COUNCIL MEETING 16 October 2018 Time of publication: 2 p.m. on 7 November 2018 Article 3 (1) of the MNB Act (Act CXXXIX of 2013 on the Magyar Nemzeti Bank) defines achieving and
Erdem Başçi: Recent economic and financial developments in Turkey
 Erdem Başçi: Recent economic and financial developments in Turkey Speech by Mr Erdem Başçi, Governor of the Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey, at the press conference for the presentation of the April
Erdem Başçi: Recent economic and financial developments in Turkey Speech by Mr Erdem Başçi, Governor of the Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey, at the press conference for the presentation of the April
Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (January 2019)
 January 23, 2019 Bank of Japan Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (January 2019) The Bank's View 1 Summary Japan's economy is likely to continue on an expanding trend throughout the projection period
January 23, 2019 Bank of Japan Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (January 2019) The Bank's View 1 Summary Japan's economy is likely to continue on an expanding trend throughout the projection period
Measures of inflation used in inflation projections- experiences of the selected European countries. Karolina Tura * November 2014
 Measures of inflation used in inflation projections- experiences of the selected European countries Karolina Tura * November 2014 Abstract The article describes the study of central paths projections of
Measures of inflation used in inflation projections- experiences of the selected European countries Karolina Tura * November 2014 Abstract The article describes the study of central paths projections of
Commentary: Housing is the Business Cycle
 Commentary: Housing is the Business Cycle Frank Smets Prof. Leamer s paper is witty, provocative and very timely. It is also written with a certain passion. Now, passion and central banking do not necessarily
Commentary: Housing is the Business Cycle Frank Smets Prof. Leamer s paper is witty, provocative and very timely. It is also written with a certain passion. Now, passion and central banking do not necessarily
Adopting Inflation Targeting: Overview of Economic Preconditions and Institutional Requirements
 GERMAN ECONOMIC TEAM IN BELARUS 76 Zakharova Str., 220088 Minsk, Belarus. Tel./fax: +375 (17) 210 0105 E-mail: research@research.by. Internet: http://research.by/ PP/06/07 Adopting Inflation Targeting:
GERMAN ECONOMIC TEAM IN BELARUS 76 Zakharova Str., 220088 Minsk, Belarus. Tel./fax: +375 (17) 210 0105 E-mail: research@research.by. Internet: http://research.by/ PP/06/07 Adopting Inflation Targeting:
Assessing the Spillover Effects of Changes in Bank Capital Regulation Using BoC-GEM-Fin: A Non-Technical Description
 Assessing the Spillover Effects of Changes in Bank Capital Regulation Using BoC-GEM-Fin: A Non-Technical Description Carlos de Resende, Ali Dib, and Nikita Perevalov International Economic Analysis Department
Assessing the Spillover Effects of Changes in Bank Capital Regulation Using BoC-GEM-Fin: A Non-Technical Description Carlos de Resende, Ali Dib, and Nikita Perevalov International Economic Analysis Department
THE U.S. ECONOMY IN 1986
 of women in the labor force. Over the past decade, women have accounted for 62 percent of total labor force growth. Increasing labor force participation of women has not led to large increases in unemployment
of women in the labor force. Over the past decade, women have accounted for 62 percent of total labor force growth. Increasing labor force participation of women has not led to large increases in unemployment
Inflation Targeting A Matter of Time
 Remarks by Timothy Lane Deputy Governor of the Bank of Canada CFA Society Atlantic Canada Halifax, Nova Scotia 27 October 215 Inflation Targeting A Matter of Time Introduction Thank you for inviting me
Remarks by Timothy Lane Deputy Governor of the Bank of Canada CFA Society Atlantic Canada Halifax, Nova Scotia 27 October 215 Inflation Targeting A Matter of Time Introduction Thank you for inviting me
INTERNATIONAL MONETARY FUND. Information Note on Modifications to the Fund s Debt Sustainability Assessment Framework for Market Access Countries
 INTERNATIONAL MONETARY FUND Information Note on Modifications to the Fund s Debt Sustainability Assessment Framework for Market Access Countries Prepared by the Policy Development and Review Department
INTERNATIONAL MONETARY FUND Information Note on Modifications to the Fund s Debt Sustainability Assessment Framework for Market Access Countries Prepared by the Policy Development and Review Department
Monetary Policy. Modern Monetary Policy Regimes: Mandate, Independence, and Accountability. 1. Mandate. 1. Mandate. Monetary Policy: Outline
 Monetary Policy Lars E.O. Svensson Sveriges Riksbank Monetary Policy: Outline. Modern monetary policy: Mandate, independence, and accountability. Monetary policy in Sweden. Flexible inflation targeting
Monetary Policy Lars E.O. Svensson Sveriges Riksbank Monetary Policy: Outline. Modern monetary policy: Mandate, independence, and accountability. Monetary policy in Sweden. Flexible inflation targeting
Saving, wealth and consumption
 By Melissa Davey of the Bank s Structural Economic Analysis Division. The UK household saving ratio has recently fallen to its lowest level since 19. A key influence has been the large increase in the
By Melissa Davey of the Bank s Structural Economic Analysis Division. The UK household saving ratio has recently fallen to its lowest level since 19. A key influence has been the large increase in the
THE ROLE OF EXCHANGE RATES IN MONETARY POLICY RULE: THE CASE OF INFLATION TARGETING COUNTRIES
 THE ROLE OF EXCHANGE RATES IN MONETARY POLICY RULE: THE CASE OF INFLATION TARGETING COUNTRIES Mahir Binici Central Bank of Turkey Istiklal Cad. No:10 Ulus, Ankara/Turkey E-mail: mahir.binici@tcmb.gov.tr
THE ROLE OF EXCHANGE RATES IN MONETARY POLICY RULE: THE CASE OF INFLATION TARGETING COUNTRIES Mahir Binici Central Bank of Turkey Istiklal Cad. No:10 Ulus, Ankara/Turkey E-mail: mahir.binici@tcmb.gov.tr
CHAPTER 13: Monetary Policy
 CHAPTER 13: Monetary Policy 1a. FIGURE 13A 1 An Expansionary Monetary Policy Nominal Interest Rate (%) Price level (GDP deflator, 2002= 100) Quantity of Money ($ billions) Real GDP (2002 $billions) An
CHAPTER 13: Monetary Policy 1a. FIGURE 13A 1 An Expansionary Monetary Policy Nominal Interest Rate (%) Price level (GDP deflator, 2002= 100) Quantity of Money ($ billions) Real GDP (2002 $billions) An
Svein Gjedrem: On business cycles, monetary policy and property markets
 Svein Gjedrem: On business cycles, monetary policy and property markets Speech by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the Næringseiendom conference, Bergen, 12 May 2006.
Svein Gjedrem: On business cycles, monetary policy and property markets Speech by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the Næringseiendom conference, Bergen, 12 May 2006.
HOW WE INVEST WHITE PAPER STRATEGIC TILTING. By David Iverson and Alex Bacchus JULY
 HOW WE INVEST WHITE PAPER STRATEGIC TILTING By David Iverson and Alex Bacchus JULY 2017 www.nzsuperfund.co.nz email:enquiries@nzsuperfund.co.nz PREFACE The Guardians of New Zealand Superannuation uses
HOW WE INVEST WHITE PAPER STRATEGIC TILTING By David Iverson and Alex Bacchus JULY 2017 www.nzsuperfund.co.nz email:enquiries@nzsuperfund.co.nz PREFACE The Guardians of New Zealand Superannuation uses
Edexcel (A) Economics A-level
 Edexcel (A) Economics A-level Theme 2: The UK Economy, Performance and Policies 2.1 Measures of Economic Performance 2.1.2 Inflation Notes Inflation is the sustained rise in the general price level over
Edexcel (A) Economics A-level Theme 2: The UK Economy, Performance and Policies 2.1 Measures of Economic Performance 2.1.2 Inflation Notes Inflation is the sustained rise in the general price level over
