DISASTER RECOVERY. Challenges and Lessons. Empowered lives. Resilient nations.
|
|
|
- Georgina Kennedy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DISASTER RECOVERY Challenges and Lessons Empowered lives. Resilient nations.
2 2
3 Contents THE COST OF DISASTERS IS HIGH EXPOSURE TO DISASTER RISK IS GROWING A FAILED RECOVERY PROCESS UNDERMINES DEVELOPMENT RECOVERY IS AN OPPORTUNITY TO BUILD BACK BETTER SUCCESSFUL RECOVERY IS A PLANNED EFFORT UNDP SUPPORTS RECOVERY AS A PATHWAY TO DEVELOPMENT
4 THE COST OF DISASTERS IS HIGH Disasters occur on a continual basis across the globe, bringing in their wake large-scale damages and losses to countries and communities. They destroy public infrastructure, disrupt basic services, cause loss of lives and disrupt livelihoods. Disasters often make the world s poor fall further into poverty. In fact, developing countries with highly vulnerable populations face the highest risk. Moreover, with rapid population growth and more people living in cities than ever before, overcrowded urban centres are putting people, assets and critical infrastructure at extreme risk.
5 The Impact of Global Disasters An average of 216 million people are affected by disasters each year percent of the world s population was affected by disasters between 2002 and 2012, resulting in 1.2 million fatalities and an economic cost of US$1.7 trillion. 2 During , approximately 23 million people were left homeless due to the impact of disasters. 3 As per the Emergency Events Database (EM-DAT) 4, an average of 30 earthquakes occur every year. Asia experiences the highest number of earthquakes, with an average of 55 percent of the yearly total, followed by the Americas with 21 percent. 5 ASIA 55% THE AMERICAS 21% 5
6 The Economic Cost of Disasters Losses due to disasters have risen significantly over the last three decades, as seen in the graphs below showing three decades of economic losses. 6 US Natural Catastrophe Update Number of events in the U.S (January June only) 120 Geophysical events (Earthquake, tsunami, volcanic activity) Meteorological events (Tropical storm, extratropical storm, convective storm, local storm) Hydrological events (Flood, mass movement) Climatological events (Extreme temperature, drought, forest fire) Source: Munich Re, NatCatSERVICE Munich Re. 6
7 First Six Months in Events Overall losses totalled US$ 12.6bn Insured losses totalled US$ 8.2bn US Natural Catastrophe Update Overall and insured losses in the U.S (January June only) Overall losses (in 2015 values)* Insured losses (in 2015 values)* Source: Munich Re, NatCatSERVICE Munich Re. * Losses adjusted to inflation based on country CPI 7
8 Wildfires are a growing problem with annual losses reaching US $190 billion a year. 8 Earthquakes, tsunamis, hurricanes and floods now cause economic losses that average between US $250 and US $300 billion each year. 7 Global economic losses from weather-related disasters increased by US $2.7 billion a year in real terms between 1980 and
9 Disasters Affect Livelihoods and Business Sustainability The port of Kobe, Japan was the world s sixth busiest before the 1995 Great Hanshin earthquake. By 2010, it had fallen to 47th place, despite major investments in reconstruction and efforts to improve competitiveness. 10 THE PORT OF KOBE In Thailand, tourism contributes to 5-6 percent of the country s GDP. Most of the areas worst hit by the 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami have economies that depend on tourism. For example, Phang Nga, Phuket and Krabi contribute to approximately 50 percent of the country s tourism-based GDP. With an array of informal and home industries (e.g. fishing, food vendors, handicraft making) connected to tourism, an estimated 64.4 percent of the population s livelihood depends on tourism and related industries. Following the 2004 Tsunami, hotels, restaurants and souvenir shops closed, leaving 5,000 people unemployed. In Phang Nga alone 3,638 claimed unemployment insurance, but this amounted to only 10 percent of their monthly salaries. 11 CONTRIBUTION TO COUNTRY'S TOURISM-BASED GDP PHANG NGA PHUKET KRABI 50% 9
10 EXPOSURE TO DISASTER RISK IS GROWING As a result of climate change, the frequency and intensity of weather-related disasters are increasing. Changing temperatures, extreme weather patterns, variations in precipitation and rising sea levels are modifying hazard levels and exacerbating disaster risks. Heat waves, droughts, floods, cyclones, wildfires and other such disasters are taking a heavier toll on human and natural environments. Future predictions suggest that these trends will not only continue, but dramatically worsen. Across the globe, these trends threaten to increase poverty levels, fueling more rural to urban migration and further destroying the ecosystems to new dangerous and unpredictable levels.
11 How Risks are Increasing Compared to only 30 percent in 1950, 54 percent of the world's population resided in urban areas as of This trend is predicated to increase to 66 percent by Unplanned urbanization, particularly of the rural poor to cities, often results in people living in slums with inadequate civic amenities and housing, thus exposing more people and assets to risks of loss in a disaster. Estimates suggest that by 2050, 40 percent of the global population will live in river basins exposed to severe droughts or floods, mostly affecting countries in Africa and Asia. 13 Almost 3.6 billion people, or two-thirds of the world s population, live on or within 100 miles of a coastline. Estimates project that nearly 75 percent of the world s population (6 billion people) will live along coasts in the next three decades. Much of this coastal population growth is occurring in Southeast Asia, Latin America and other parts of the developing world. 14 This exposes a huge number of people to storm surges, typhoons, floods and tsunami. 30% 54% 66% 75% percent of all coastal wetlands were lost between 1980 and the early 2000s and natural storm surge barriers such as mangrove forests and coral reefs are in rapid decline
12 1 By the end of the 21st century, it is predicted that global warming will likely cause a 2 to 11 percent increase in the intensity of tropical cyclones meaning a much higher destructive potential of these storms. 16 The productivity of fisheries and farming (wheat, rice and maize) is predicted to drop in coming decades due to temperature increases of 2 C or more above 1990s levels. Temperature rises of 4 C or more combined with continued population growth and increased demand will negatively impact food security C +2 C +3 C +4 C 2 Renewable surface water and groundwater resources, already under strain, will decline further as competition for water resources grows
13 The Cost of Future Disasters The global average for annual economic losses due to natural disasters is projected to increase from the current US $250 - $300 billion to US $415 billion by 2030 for urban infrastructure alone. 19 By 2030, climate risks could cost countries up to 19 percent of their total gross domestic product $250 - $300 billion 2030 $415 billion In the Caribbean, hurricane wind damage is projected to cost an additional US$ 1.4 billion in average annual losses
14 A FAILED RECOVERY PROCESS UNDERMINES DEVELOPMENT The failure to recover adequately from a disaster in any context may result in secondary disasters, with equally grave effects. A failed recovery can contribute to disasters becoming endemic, as it derails development gains and results in widespread losses. When combined with poorly carried out recovery processes, recurrent disasters increase vulnerability and create chronic conditions of risk.
15 Why Do Recovery Efforts So Often Fail? Recovery needs are not properly identified through a formal assessment process. Recovery programming is ad hoc and not based on an overarching recovery strategy and clear set of recovery priorities. Recovery strategies do not take into account vulnerabilities and cultural considerations. Recovery is not supported by adequate financial resources. Aid for disasters is typically provided for immediate humanitarian relief with few resources for longer-term recovery needs. Recovery favours rebuilding infrastructure over social and household recovery needs. Recovery efforts often fail to encourage local participation and ownership. 15
16 How Disasters Increase the Incidence of Poverty A large-scale disaster can cause economic slowdown, loss of employment and decreased entrepreneurial activity, pushing more people into poverty. The Post-Disaster Needs Assessment (PDNA) conducted following the earthquakes in Nepal in April and May 2015 estimated that as a result of the disaster the number of poor people would increase an additional 2.5 to 3.5 percent (estimated to represent at least 700,000 people). If a disaster recovery programme fails to restore livelihoods and assets, people find themselves even more vulnerable in the face of future disasters and climate events. Data collected from Rizal Province in the Philippines which was affected by typhoons Ondoy and Pepeng in 2009 showed poverty almost doubled within three years. +1% 16
17 A Persistent Funding Gap in Recovery Furthermore, when recovery efforts are not well funded, a country or region can continue to suffer long after the disaster is over. A recovery and preparedness plan drafted following Cyclone Nargis that hit Myanmar in presented a budget for US $691 million in recovery needs, but only US $100 million had been raised one year later. Following Typhoon Haiyan in the Philippines in 2013, the Office of the Presidential Assistant for Rehabilitation and Recovery reported an average funding gap of 67 percent for key sectors of the recovery process. 23 $691 million $100 million GAP 17
18 RECOVERY IS AN OPPORTUNITY TO BUILD BACK BETTER Disaster recovery periods are opportunities for reflecting on the root causes of a disaster and recasting development priorities to reduce human vulnerability to natural hazards. Simply reinventing pre-disaster conditions is a wasted opportunity. United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA). World Urbanization Prospects: The 2014 Revision.
19 Disaster recovery efforts aim to restore peoples lives and livelihoods, re-establish institutions and social networks and foster sustainable development. And, importantly, disaster recovery work offers an opportunity to build back better meaning it is a time to not only restore conditions to pre-disaster levels, but to improve them by addressing the underlying risks and vulnerabilities that caused the natural hazard to turn into a disaster in the first place. For recovery processes to be efficient and effective, it is critical that recovery institutions have strong management capacities and enabling policies in place. To this end, governments are placing greater emphasis on shoring up institutional capacity, adopting supportive policies and securing resources for recovery. Several disaster prone countries Bolivia, Ecuador and Indonesia have established institutions with dedicated personnel and resources, making recovery assistance more predictable and better tailored to local needs and contexts. 19
20 UNDP s Support to Building Back Better After the 2004 Tsunami in the Maldives, UNDP built harbours and jetties to restore sea transport of essential supplies and resume business with the mainland and other islands. Following major disasters in Bangladesh, India, Indonesia, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka, UNDP supported local governments to design and build low-cost disaster resilient houses. This included training masons in disasterresilient technologies that could help structures to withstand future impacts. In India, Indonesia and several other countries following major disasters, UNDP provided technical assistance to review building codes and develop land use plans for reconstruction and recovery. In Haiti, Malawi, the Philippines and Vanuatu, UNDP gave livelihood assistance that helped thousands of families restore existing businesses and start new ones. 20
21 UNDP's Support to Pakistan s Earthquake Reconstruction and Rehabilitation Authority Following a 7.6 magnitude earthquake in Kashmir in 2005, the Government of Pakistan set up the Earthquake Reconstruction and Rehabilitation Authority (ERRA), a dedicated agency to manage and coordinate the recovery process. Over a three-year period, UNDP supported this agency with funds from the Government of Germany and the UK Department for International Development (DFID). UNDP donated equipment to set up the institution, worked with ERRA to identify and recruit national and international experts to lead recovery work and provided project technical assistance. UNDP also funded positions within the agency to support government coordination and oversee recovery programmes in housing, livelihoods, legal aid and education. UNDP s contributions to the functioning of ERRA helped establish it as a strong technical entity with clear operating procedures. 21
22 SUCCESSFUL RECOVERY IS A PLANNED EFFORT Effective recovery interventions require conducting a needs assessment across all affected sectors of society and using this information to create a recovery strategy. A good assessment provides a clear picture of the damages, losses and needs of all affected people and sectors. It also identifies existing capacities of affected populations so that local resources, abilities and knowledge can play a primary role in recovery processes. Effective recovery interventions help affected communities address early recovery challenges at the same time as they tackle longer-term issues in sustainable and innovative ways. Interventions that focus on measures such as capacity development, coordination and information management can make recovery much more effective.
23 What Underlies Successful Recovery Efforts? Needs are assessed in order to design an actionable recovery strategy. Recovery efforts focus on reducing risk and vulnerabilities. Recovery efforts draw on and learn from past experiences. Policy frameworks and clear institutional roles and responsibilities are established. Robust resource mobilization strategies ensure adequate financial resources. Recovery actors and organizations communicate openly with the public and encourage participation. Information management and continuous monitoring and evaluation of recovery progress is supported. Dedicated personnel and resources are critical for delivering successful recovery programmes in an effective and timely manner. Recovery processes are transparent and accountable. 23
24 UNDP's Support to Recovery Planning Around the World UNDP has been instrumental in supporting governments and regional bodies across the globe to develop frameworks and guidelines for recovery. UNDP helped the Government of Indonesia with its Guidelines for Formulation of Post-Disaster Reconstruction Plan, the Government of India to prepare a Recovery Framework, the Government of Rwanda with a Recovery Strategy and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) with a Disaster Recovery Guidance Note. UNDP is also working with the governments of Angola, Cape Verde and Niger to develop recovery frameworks. 24
25 25
26 UNDP SUPPORTS RECOVERY AS A PATHWAY TO DEVELOPMENT
27 As the lead implementing agency in the area of recovery in the United Nations system, UNDP plays a vital role in disaster recovery, providing advisory and technical support to governments so that they can establish institutions and design recovery interventions that lay the foundation for future resilience. UNDP assists in the following areas: assessments and analysis, recovery planning and resource mobilization, early recovery interventions, assistance to national and local governments, technical and financial support for medium to long-term recovery programmes, coordination and information management, strengthening disaster risk reduction systems, promoting community participation and social cohesion in recovery, monitoring and evaluation for recovery, and South-South cooperation and sharing of international best practices. For UNDP, recovery efforts begin in the immediate aftermath of a disaster during the relief phase and continue until full recovery is achieved. UNDP s approach involves planning for recovery in three stages early, medium and long-term recovery. Fundamental to UNDP s work in recovery is the application of principles that reduce the risk of future events, decrease the vulnerability of impacted populations, promote building back better and ensure sustainability of recovery efforts. 27
28 UNDP's Key Achievements in Support of DRR and Recovery UNDP Country Offices have provided technical and financial assistance for recovery programming after major disasters in 112 countries. UNDP has supported recovery preparedness and PDNA training and capacity development for recovery in 25 countries. UNDP s financial investment in disaster recovery in the Asia Pacific region has totalled US$ 50 million since the year 2000 covering 17 countries. UNDP has supported more than 40 Post-Disaster Needs Assessments (PDNAs) after catastrophic events across the globe. UNDP has set up early recovery coordination structures, including working groups on livelihoods, governance, community infrastructure and other areas of recovery. These working groups were established in 19 countries for 22 disasters and helped to coordinate recovery efforts and manage successful recovery operations. 28
29 UNDP s Disaster Risk Reduction Efforts Working toward the adoption of disaster risk reduction measures and building resilience is a major focus of UNDP. Building resilience can be defined as a transformative process of strengthening the capacity of men, women, communities, institutions and countries to anticipate, prevent, recover from, and transform in, the aftermath of shocks, stresses and change. 24 UNDP is a leading implementer of Disaster Risk Reduction programmes with $1.7 billion invested in the ten years from 2005 to 2014 in 163 countries. UNDP s disaster risk reduction investment by region is: The breakdown of UNDP s disaster risk reduction work by focus area is: GLOBAL HQ 5% LATIN AMERICA 7% EUROPE - CIS 10% ARAB STATES 10% AFRICA 38% ASIA AND THE PACIFIC 30% Institutional Development Legal Frameworks DRR Policy and Strategy Mainstreaming DRR Local and Urban Risk Management Risk Assessments Disaster Loss Databases Early Warning Systems COUNTRIES
30 Building a Resilient Habitat in Bangladesh 25 In the aftermath of Cyclone Sidr in 2007, UNDP teamed up with architects from BRAC in Bangladesh to design and build a disaster-resilient habitat that would protect property against cyclones striking the Bay of Bengal with increasing frequency. A habitat in Shyamnagar consists of 43 houses built on two metres (six feet) concrete stilts designed to withstand a tidal surge of up to two metre and winds of up to 235km/h (150mph). Trees close to the village help prevent topsoil from washing away, while taller trees in the distance act as windbreaks. Primary and secondary embankments protect livestock and assets against high sea levels. Over the course of two years, UNDP constructed 25,000 core family shelters in five districts affected by Cyclone Sidr. 30
31 Reducing Gender-Based Vulnerability in India Recovery provides an opportunity to redress gender disparities and empower women by targeting them to receive livelihoods assets, access to credit and skills training. Following the Odisha Super Cyclone, Gujarat earthquake, and tsunami in Tamil Nadu, land and property titles were given directly to women or to both husband and wife. This changed the status of women in communities where men traditionally held exclusive land tenure and property rights. 31
32 End Notes 1 Guha-Sapir, D., Hoyois, Ph., Below, R Annual Disaster Statistical Review 2013: The Numbers and Trends. Brussels: Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters (CRED). 2 The United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNISDR). Disaster Impacts (chart). 3 United Nations Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction Database managed by CRED, Brussels. 5 Guha-Sapir, D. Human Casualties in Earthquakes: Progress in Modelling and Mitigation. 6 Munich Re Loss events worldwide from E /mram/assetpool.mr_america/PDFs/4_Events/MunichRe_III_NatCatWebinar_071415_pdf.pdf 7 UNISDR Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction: Making Development Sustainable: The Future of Disaster Risk Management. 8 UNISDR Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction: From Shared Risk to Shared Value: The Business Case for Disaster Risk Reduction. 9 Ward, R. and Ranger, N Insurance Industry Brief: Trends in Economic and Insured Losses from Weather-Related Events: A new analysis. The Munich Re Programme of the Centre for Climate Change Economics and Policy, Munich, Germany. 10 UNISDR Rego, Loy. Social and Economic Impact of December 2004 Tsunami. Asian Disaster Preparedness Center United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA) World Urbanization Prospects: The 2014 Revision. 32
33 13 UNISDR The National Academies of Science Ocean Science Series: Coastal Hazards. National Academies Press, Washington, D.C UNISDR Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory/National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). 30 September Global Warming and Hurricanes: An Overview of Current Research Results Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report Summary for Policy Makers. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the IPCC. [Pachauri, R.K. and Meyer, L.A. (eds.)]. 18 Ibid. 19 UNISDR Swiss Re Report of the Economics of Climate Adaptation working group (ECA). Economics of Climate Adaptation (ECA) - Shaping climate-resilient development, A framework for decision-making. 21 UNISDR Fan, Lilianne. November HPG Working Paper: Disaster as opportunity? Building back better in Aceh, Myanmar and Haiti. Humanitarian Policy Group Overseas Development Institute: London. 23 Office of the President of the Philippines, Office of the Presidential Assistant for Rehabilitation and Recovery, UNDP Empowered Lives, Resilient Bangladesh: Results achieved with our partners,
34 UNDP partners with people at all levels of society to help build nations that can withstand crisis, and drive and sustain the kind of growth that improves the quality of life for everyone. On the ground in nearly 170 countries and territories, we offer global perspective and local insight to help empower lives and build resilient nations.
35
36 Empowered lives. Resilient nations. United Nations Development Programme Bureau for Policy and Programme Support One United Nations Plaza New York, NY, USA Tel: For more information: Copyright 2016, UNDP
Economic Risk and Potential of Climate Change
 Economic Risk and Potential of Climate Change Prof. Dr. Peter Hoeppe; Dr. Ernst Rauch This document appeared in Detlef Stolten, Bernd Emonts (Eds.): 18th World Hydrogen Energy Conference 2010 - WHEC 2010
Economic Risk and Potential of Climate Change Prof. Dr. Peter Hoeppe; Dr. Ernst Rauch This document appeared in Detlef Stolten, Bernd Emonts (Eds.): 18th World Hydrogen Energy Conference 2010 - WHEC 2010
Disaster Risk Reduction
 Disaster Risk Reduction AHI M2 Extreme Environement Risk and vulnerability UPEC Universityof Creteil-Paris XII Aloysius John March 2012 Introduction There is growing international concern at the present
Disaster Risk Reduction AHI M2 Extreme Environement Risk and vulnerability UPEC Universityof Creteil-Paris XII Aloysius John March 2012 Introduction There is growing international concern at the present
Regional trends on gender data collection and analysis
 Sex-disaggregated data for the SDG indicators in Asia and the Pacific: What and how? Regional trends on gender data collection and analysis Rajesh Sharma UNDP Bangkok Regional Hub ISSUES (1) In the past,
Sex-disaggregated data for the SDG indicators in Asia and the Pacific: What and how? Regional trends on gender data collection and analysis Rajesh Sharma UNDP Bangkok Regional Hub ISSUES (1) In the past,
Southeast Asia Disaster Risk Insurance Facility
 Southeast Asia Disaster Risk Insurance Facility PROTECT THE GREATEST HOME OF ALL: OUR COUNTRIES SEADRIF is a regional platform to provide ASEAN countries with financial solutions and technical advice to
Southeast Asia Disaster Risk Insurance Facility PROTECT THE GREATEST HOME OF ALL: OUR COUNTRIES SEADRIF is a regional platform to provide ASEAN countries with financial solutions and technical advice to
ADB s Experiences in Disaster Management. Neil Britton Senior Disaster Risk Management Specialist Asian Development Bank 25 November 2007
 ADB s Experiences in Disaster Management Neil Britton Senior Disaster Risk Management Specialist Asian Development Bank 25 November 2007 Presentation Format Asia s changing hazardscape and vulnerability
ADB s Experiences in Disaster Management Neil Britton Senior Disaster Risk Management Specialist Asian Development Bank 25 November 2007 Presentation Format Asia s changing hazardscape and vulnerability
9,697 Dead people. 96 million People affected. Lower mortality, higher cost
 335 Reported disasters 9,697 Dead people 96 million People affected 334 billion US$ economic damage Lower mortality, higher cost Executive Summary In, 335 natural disasters affected over 95.6 million people,
335 Reported disasters 9,697 Dead people 96 million People affected 334 billion US$ economic damage Lower mortality, higher cost Executive Summary In, 335 natural disasters affected over 95.6 million people,
SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): FINANCE (DISASTER RISK MANAGEMENT) 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities
 National Disaster Risk Management Fund (RRP PAK 50316) SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): FINANCE (DISASTER RISK MANAGEMENT) A. Sector Road Map 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities a. Performance
National Disaster Risk Management Fund (RRP PAK 50316) SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): FINANCE (DISASTER RISK MANAGEMENT) A. Sector Road Map 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities a. Performance
Chapter 2: Natural Disasters and Sustainable Development
 Chapter 2: Natural Disasters and Sustainable Development This Chapter deals with the importance of the link between disaster reduction frameworks and development initiatives, as well as frameworks based
Chapter 2: Natural Disasters and Sustainable Development This Chapter deals with the importance of the link between disaster reduction frameworks and development initiatives, as well as frameworks based
Sendai Cooperation Initiative for Disaster Risk Reduction
 Sendai Cooperation Initiative for Disaster Risk Reduction March 14, 2015 Disasters are a threat to which human being has long been exposed. A disaster deprives people of their lives instantly and afflicts
Sendai Cooperation Initiative for Disaster Risk Reduction March 14, 2015 Disasters are a threat to which human being has long been exposed. A disaster deprives people of their lives instantly and afflicts
DEFINING THE PROTECTION GAP. 1: Decide who /what should be protected:
 DEFINING THE PROTECTION GAP Introduction In recent years, we ve seen a considerable increase in disasters, both in their frequency and severity. Overall economic losses from such disasters currently average
DEFINING THE PROTECTION GAP Introduction In recent years, we ve seen a considerable increase in disasters, both in their frequency and severity. Overall economic losses from such disasters currently average
Natural Disasters in 2007: An Analytical Overview
 Natural Disasters in 2007: An Analytical Overview Chapter 1: Impact of Natural Disasters This chapter deals with the overall trends in natural disasters and their impacts for the year 2007. It also addresses
Natural Disasters in 2007: An Analytical Overview Chapter 1: Impact of Natural Disasters This chapter deals with the overall trends in natural disasters and their impacts for the year 2007. It also addresses
Quantifying Disaster Risk: measuring progress in the path towards resilience
 Quantifying Disaster Risk: measuring progress in the path towards resilience Sujit Mohanty UNISDR -ROAP Expert Group Meeting (EGM) on Improving Disaster Data to Build Resilience in Asia and the Pacific,
Quantifying Disaster Risk: measuring progress in the path towards resilience Sujit Mohanty UNISDR -ROAP Expert Group Meeting (EGM) on Improving Disaster Data to Build Resilience in Asia and the Pacific,
Reducing vulnerability to disasters is an integral part of the fight against
 IDA at Work Managing Natural Hazards, Reducing Risks to Development Reducing vulnerability to disasters is an integral part of the fight against poverty. A natural disaster can destroy decades of development
IDA at Work Managing Natural Hazards, Reducing Risks to Development Reducing vulnerability to disasters is an integral part of the fight against poverty. A natural disaster can destroy decades of development
National disaster loss and damage databases UNDP s experience and lessons learned Presented by Sanny Jegillos Senior Adviser
 National disaster loss and damage databases UNDP s experience and lessons learned Presented by Sanny Jegillos Senior Adviser Bureau for Policy and Programme Support UNDP Bangkok Regional Hub 1 Why disaster
National disaster loss and damage databases UNDP s experience and lessons learned Presented by Sanny Jegillos Senior Adviser Bureau for Policy and Programme Support UNDP Bangkok Regional Hub 1 Why disaster
The Lessons of 2017 Perspective from the World Bank Group
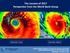 The Lessons of 2017 Perspective from the World Bank Group Barbuda Dominica Hurricane Irma Hurricane Maria Rebuild, Rethink, Resilience: Lessons for economic and security partnerships following after the
The Lessons of 2017 Perspective from the World Bank Group Barbuda Dominica Hurricane Irma Hurricane Maria Rebuild, Rethink, Resilience: Lessons for economic and security partnerships following after the
OVERVIEW. Linking disaster risk reduction and climate change adaptation. Disaster reduction - trends Trends in economic impact of disasters
 Linking disaster risk reduction and climate change adaptation Inter-Agency Secretariat for the International Strategy for Disaster Reduction (UNISDR) A. Trends OVERVIEW B. Disaster reduction a tool for
Linking disaster risk reduction and climate change adaptation Inter-Agency Secretariat for the International Strategy for Disaster Reduction (UNISDR) A. Trends OVERVIEW B. Disaster reduction a tool for
Chapter 2: Natural Disasters and Sustainable Development
 Chapter 2: Natural Disasters and Sustainable Development This chapter addresses the importance of the link between disaster reduction frameworks and development initiatives, based on the disaster trends
Chapter 2: Natural Disasters and Sustainable Development This chapter addresses the importance of the link between disaster reduction frameworks and development initiatives, based on the disaster trends
Building. Resilience. Integrating Climate and Disaster Risk into Development The World Bank Group Experience. Public Disclosure Authorized
 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Building Resilience Integrating Climate and Disaster Risk into Development The World
Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Building Resilience Integrating Climate and Disaster Risk into Development The World
Insurers as Data Providers. Raising Awareness of Changing Risks. What can Insurers Contribute to Increase Resilience Against Weather Extremes?
 What can Insurers Contribute to Increase Resilience Against Weather Extremes? Prof. Dr. Peter Hoeppe, Head Geo Risks Research/Corporate Climate Centre, Munich Re 5 th European Communications Workshop for
What can Insurers Contribute to Increase Resilience Against Weather Extremes? Prof. Dr. Peter Hoeppe, Head Geo Risks Research/Corporate Climate Centre, Munich Re 5 th European Communications Workshop for
REDUCING DISASTER RISK a challenge for development
 Reducing Disaster Risk: a challenge for development REDUCING DISASTER RISK a challenge for development A Global Report from : United Nations Development Programme Bureau for Crisis Prevention and Recovery
Reducing Disaster Risk: a challenge for development REDUCING DISASTER RISK a challenge for development A Global Report from : United Nations Development Programme Bureau for Crisis Prevention and Recovery
The Emerging Importance of Improving Resilience to Hazards. Presentation to: West Michigan Sustainable Business Forum November 14, 2016 Dale Sands
 The Emerging Importance of Improving Resilience to Hazards Presentation to: West Michigan Sustainable Business Forum November 14, 216 Dale Sands Agenda Resilience Defined Driving Forces Of Resilience Improvement
The Emerging Importance of Improving Resilience to Hazards Presentation to: West Michigan Sustainable Business Forum November 14, 216 Dale Sands Agenda Resilience Defined Driving Forces Of Resilience Improvement
Palu, Indonesia. Local progress report on the implementation of the 10 Essentials for Making Cities Resilient ( )
 Palu, Indonesia Local progress report on the implementation of the 10 Essentials for Making Cities Resilient (2013-2014) Name of focal point: Yusniar Nurdin Organization: BNPB Title/Position: Technical
Palu, Indonesia Local progress report on the implementation of the 10 Essentials for Making Cities Resilient (2013-2014) Name of focal point: Yusniar Nurdin Organization: BNPB Title/Position: Technical
EXPERIENCES IN ECONOMIC ASSESSSMET OF DISASTERS IMPACT
 EXPERIENCES IN ECONOMIC ASSESSSMET OF DISASTERS IMPACT AS A TOOL FOR RISK REDUCTION AND MAINSTREAMING DISASTER REDUCTION IN DEVELOPMENT POLICY Ricardo Zapata-Marti, Focal Point for Disaster Evaluation
EXPERIENCES IN ECONOMIC ASSESSSMET OF DISASTERS IMPACT AS A TOOL FOR RISK REDUCTION AND MAINSTREAMING DISASTER REDUCTION IN DEVELOPMENT POLICY Ricardo Zapata-Marti, Focal Point for Disaster Evaluation
Addressing Loss and Damage with Microinsurance
 Addressing Loss and Damage with Microinsurance Kees van der Geest, Michael Zissener & Koko Warner 2014 To be cited as: Van der Geest, K., Zissener, M. & Warner, K. (2014). Addressing Loss and Damage with
Addressing Loss and Damage with Microinsurance Kees van der Geest, Michael Zissener & Koko Warner 2014 To be cited as: Van der Geest, K., Zissener, M. & Warner, K. (2014). Addressing Loss and Damage with
Regional Capacity Development Workshop: Mainstreaming DRR in Sustainable Development Planning Myanmar s Country Disaster Profile
 Regional Capacity Development Workshop: Mainstreaming DRR in Sustainable Development Planning Myanmar s Country Disaster Profile 13-16 September 2016 New Delhi, India Key Disaster Impacts: Overview Myanmar
Regional Capacity Development Workshop: Mainstreaming DRR in Sustainable Development Planning Myanmar s Country Disaster Profile 13-16 September 2016 New Delhi, India Key Disaster Impacts: Overview Myanmar
PROGRAM INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) CONCEPT STAGE Report No.: Second Disaster Risk Management Development Policy Loan with a CAT-DDO Region
 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized PROGRAM INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) CONCEPT STAGE Report No.: Operation Name Second Disaster
Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized PROGRAM INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) CONCEPT STAGE Report No.: Operation Name Second Disaster
Achievements and Challenges
 LDCs Graduation in Asia-Pacific: Achievements and Challenges Ministerial Meeting of Asia-Pacific Least Developed Countries on Graduation and Post 2015 Development Agenda Kathmandu, Nepal 16-18 December
LDCs Graduation in Asia-Pacific: Achievements and Challenges Ministerial Meeting of Asia-Pacific Least Developed Countries on Graduation and Post 2015 Development Agenda Kathmandu, Nepal 16-18 December
The Costs of Climate Change
 BACKGROUNDER The Costs of Climate Change Prepared by Clare Demerse, federal policy advisor, Clean Energy Canada November 17, 2016 CLIMATE COSTS IN CONTEXT Canada s governments are developing a climate
BACKGROUNDER The Costs of Climate Change Prepared by Clare Demerse, federal policy advisor, Clean Energy Canada November 17, 2016 CLIMATE COSTS IN CONTEXT Canada s governments are developing a climate
Chapter 2: Natural Disasters and Sustainable Development
 Chapter 2: Natural Disasters and Sustainable Development This chapter addresses the importance of the link between disaster reduction frameworks and development initiatives, based on the disaster trends
Chapter 2: Natural Disasters and Sustainable Development This chapter addresses the importance of the link between disaster reduction frameworks and development initiatives, based on the disaster trends
WEATHER EXTREMES, CLIMATE CHANGE,
 WEATHER EXTREMES, CLIMATE CHANGE, DURBAN 2011 ELECTRONIC PRESS FOLDER Status: 25.11.2011 Contents 1. Current meteorological knowledge 2. Extreme weather events 3. Political action required 4. Insurance
WEATHER EXTREMES, CLIMATE CHANGE, DURBAN 2011 ELECTRONIC PRESS FOLDER Status: 25.11.2011 Contents 1. Current meteorological knowledge 2. Extreme weather events 3. Political action required 4. Insurance
DISASTER RISK FINANCING AND INSURANCE PROGRAM
 DISASTER RISK FINANCING AND INSURANCE PROGRAM Strengthening Financial Resilience to Disasters What We Do DRFIP helps developing countries manage the cost of disaster and climate shocks. The initiative
DISASTER RISK FINANCING AND INSURANCE PROGRAM Strengthening Financial Resilience to Disasters What We Do DRFIP helps developing countries manage the cost of disaster and climate shocks. The initiative
Sri Lanka: Preliminary Damage and Needs Assessment Page 25 of 29
 Sri Lanka: Preliminary Damage and Needs Assessment Page 25 of 29 F. IMMEDIATE AND MEDIUM TERM RECOVERY STRATEGY Implementation Approach 75. One of the main challenges of developing a comprehensive, as
Sri Lanka: Preliminary Damage and Needs Assessment Page 25 of 29 F. IMMEDIATE AND MEDIUM TERM RECOVERY STRATEGY Implementation Approach 75. One of the main challenges of developing a comprehensive, as
Innovating to Reduce Risk
 E X E C U T I V E S U M M A R Y Innovating to Reduce Risk This publication is driven by input provided by the disaster risk community. The Global Facility of Disaster Risk and Recovery facilitated the
E X E C U T I V E S U M M A R Y Innovating to Reduce Risk This publication is driven by input provided by the disaster risk community. The Global Facility of Disaster Risk and Recovery facilitated the
Preliminary Damage and Loss Assessment
 The 15th Meeting of The Consultative Group on Indonesia Jakarta, June 14, 2006 Yogyakarta and Central Java Natural Disaster A Joint Report from BAPPENAS, the Provincial and Local Governments of D.I.Yogyakarta,
The 15th Meeting of The Consultative Group on Indonesia Jakarta, June 14, 2006 Yogyakarta and Central Java Natural Disaster A Joint Report from BAPPENAS, the Provincial and Local Governments of D.I.Yogyakarta,
Mainstreaming Disaster Risk Reduction into National Development Planning and Financing in Asia-Pacific
 Mainstreaming Disaster Risk Reduction into National Development Planning and Financing in Asia-Pacific Outline 1. Development, sustainable development and disaster 2. Guidelines for mainstreaming Disaster
Mainstreaming Disaster Risk Reduction into National Development Planning and Financing in Asia-Pacific Outline 1. Development, sustainable development and disaster 2. Guidelines for mainstreaming Disaster
CONCEPT NOTE (DRAFT)
 2015 MEETING OF THE WMO DISASTER RISK REDUCTION USER-INTERFACE EXPERT ADVISORY GROUP ON HAZARD AND RISK ANALYSIS (WMO DRR UI-EAG HRA) 15-17 December 2015 WMO Headquarters Geneva, Switzerland Room: Salle
2015 MEETING OF THE WMO DISASTER RISK REDUCTION USER-INTERFACE EXPERT ADVISORY GROUP ON HAZARD AND RISK ANALYSIS (WMO DRR UI-EAG HRA) 15-17 December 2015 WMO Headquarters Geneva, Switzerland Room: Salle
Disasters and Climate Change: Hazards of Nature or Risks from Development
 Disasters and Climate Change: Hazards of Nature or Risks from Development Ajay Chhibber Director, Independent Evaluation Group World Bank Fourth Disasters and Development Seminar Tuesday, November 28,
Disasters and Climate Change: Hazards of Nature or Risks from Development Ajay Chhibber Director, Independent Evaluation Group World Bank Fourth Disasters and Development Seminar Tuesday, November 28,
Sustainable Recovery and Reconstruction Framework (SURRF)
 Sustainable Recovery and Reconstruction Framework (SURRF) Saroj Kumar Jha Program Manager Global Facility for Disaster Reduction and Recovery The World Bank Group, Washington DC 1 The definitional challenge
Sustainable Recovery and Reconstruction Framework (SURRF) Saroj Kumar Jha Program Manager Global Facility for Disaster Reduction and Recovery The World Bank Group, Washington DC 1 The definitional challenge
Rationalle for the Sendai Framework for DRR Evidence from the 2009, 2011 and 2013 Global Assessment Report on DRR
 Rationalle for the Sendai Framework for DRR Evidence from the 2009, 2011 and 2013 Global Assessment Report on DRR Good progress in Hyogo Framework for Action (HFA) implementation has been made, but more
Rationalle for the Sendai Framework for DRR Evidence from the 2009, 2011 and 2013 Global Assessment Report on DRR Good progress in Hyogo Framework for Action (HFA) implementation has been made, but more
Preparedness through DDR and DRM can help to adapt for climate change The central message of chapter 9
 Preparedness through DDR and DRM can help to adapt for climate change The central message of chapter 9 Case Studies: Virginia Murray, Gordon McBean, Mihir Bhatt, Sergey Borsch, Tae Sung Cheong, Wadid Fawzy
Preparedness through DDR and DRM can help to adapt for climate change The central message of chapter 9 Case Studies: Virginia Murray, Gordon McBean, Mihir Bhatt, Sergey Borsch, Tae Sung Cheong, Wadid Fawzy
RESILIENCE Provisional copy
 RESILIENCE Promoting Disaster and Climate Risk Resilience Through Regional Programmatic and Risk Financing Mechanisms Action Statement and Action Plan Provisional copy Overview and Context Climate change
RESILIENCE Promoting Disaster and Climate Risk Resilience Through Regional Programmatic and Risk Financing Mechanisms Action Statement and Action Plan Provisional copy Overview and Context Climate change
Source: NOAA 2011 NATURAL CATASTROPHE YEAR IN REVIEW
 Source: NOAA 2011 NATURAL CATASTROPHE YEAR IN REVIEW January 4, 4 2012 U.S. NATURAL CATASTROPHE UPDATE Carl Hedde, SVP, Head of Risk Accumulation Munich Reinsurance America, Inc. MR NatCatSERVICE One of
Source: NOAA 2011 NATURAL CATASTROPHE YEAR IN REVIEW January 4, 4 2012 U.S. NATURAL CATASTROPHE UPDATE Carl Hedde, SVP, Head of Risk Accumulation Munich Reinsurance America, Inc. MR NatCatSERVICE One of
Type and nature of actions to address loss and damage for which finance will be required
 Submission to support the UNFCCC secretariat in determining the scope of a technical paper which will serve as an input to the review of the Warsaw International Mechanism for Loss and Damage in 2019:
Submission to support the UNFCCC secretariat in determining the scope of a technical paper which will serve as an input to the review of the Warsaw International Mechanism for Loss and Damage in 2019:
Dr. Joseph A. Weinstock Asian Development Bank
 New Directions of Asian Development Bank in Reducing Disaster Risk Dr. Joseph A. Weinstock Asian Development Bank January 20, 2005 Kobe, Japan Global Disasters 1974 2003: People Affected Region Mean Annual
New Directions of Asian Development Bank in Reducing Disaster Risk Dr. Joseph A. Weinstock Asian Development Bank January 20, 2005 Kobe, Japan Global Disasters 1974 2003: People Affected Region Mean Annual
COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES
 EN EN EN COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, 23.2.2009 COM(2009) 82 final COMMUNICATION FROM THE COMMISSION TO THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT, THE COUNCIL, THE EUROPEAN ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COMMITTEE
EN EN EN COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, 23.2.2009 COM(2009) 82 final COMMUNICATION FROM THE COMMISSION TO THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT, THE COUNCIL, THE EUROPEAN ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COMMITTEE
PROJECT INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) ADDITIONAL FINANCING Report No.: PIDA5305. Project Name. Parent Project Name. Region Country Sector(s) Theme(s)
 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Project Name Parent Project Name Region Country Sector(s) Theme(s) Lending Instrument
Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Project Name Parent Project Name Region Country Sector(s) Theme(s) Lending Instrument
Decision-makers Barriers to Climate and Extreme Weather Adaptation for Seaports
 Decision-makers Barriers to Climate and Extreme Weather Adaptation for Seaports ELIZABETH L MCLEAN, PHD AUSTIN BECKER, PHD DUNCAN MCINTOSH, PHD DEPARTMENT OF MARINE AFFAIRS UNIVERSITY OF RHODE ISLAND Chris
Decision-makers Barriers to Climate and Extreme Weather Adaptation for Seaports ELIZABETH L MCLEAN, PHD AUSTIN BECKER, PHD DUNCAN MCINTOSH, PHD DEPARTMENT OF MARINE AFFAIRS UNIVERSITY OF RHODE ISLAND Chris
Palu, Indonesia. Local progress report on the implementation of the Hyogo Framework for Action ( )
 Palu, Indonesia Local progress report on the implementation of the Hyogo Framework for Action (2013-2014) Name of focal point: Yusniar Nurdin Organization: BNPB Title/Position: Technical Support Consultant
Palu, Indonesia Local progress report on the implementation of the Hyogo Framework for Action (2013-2014) Name of focal point: Yusniar Nurdin Organization: BNPB Title/Position: Technical Support Consultant
Economic impact of disasters:
 S E R I E ECLAC SUBREGIONAL OFFICE IN MEXICO estudios y perspectivas 117 Economic impact of disasters: Evidence from DALA assessments by ECLAC in Latin America and the Caribbean Ricardo Zapata Benjamín
S E R I E ECLAC SUBREGIONAL OFFICE IN MEXICO estudios y perspectivas 117 Economic impact of disasters: Evidence from DALA assessments by ECLAC in Latin America and the Caribbean Ricardo Zapata Benjamín
ANNOUNCEMENT. EXPERT MEETING DRR4NAP Integrating Disaster Risk Reduction into National Adaptation Plans November 2017 Bonn, Germany
 ANNOUNCEMENT EXPERT MEETING DRR4NAP Integrating Disaster Risk Reduction into National Adaptation Plans 27-28 November 2017 Bonn, Germany Organized by the United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction
ANNOUNCEMENT EXPERT MEETING DRR4NAP Integrating Disaster Risk Reduction into National Adaptation Plans 27-28 November 2017 Bonn, Germany Organized by the United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction
Global Facility for Disaster Reduction and Recovery. of the Hyogo Framework for Action. Kobe, January 15, 2007
 Global Facility for Disaster Reduction and Recovery New Initiative to Enable / Accelerate the Implementation of the Hyogo Framework for Action Kobe, January 15, 2007 Maryvonne Plessis-Fraissard Senior
Global Facility for Disaster Reduction and Recovery New Initiative to Enable / Accelerate the Implementation of the Hyogo Framework for Action Kobe, January 15, 2007 Maryvonne Plessis-Fraissard Senior
Introduction to Disaster Management
 Introduction to Disaster Management Definitions Adopted By Few Important Agencies WHO; A disaster is an occurrence disrupting the normal conditions of existence and causing a level of suffering that exceeds
Introduction to Disaster Management Definitions Adopted By Few Important Agencies WHO; A disaster is an occurrence disrupting the normal conditions of existence and causing a level of suffering that exceeds
Vulnerability and Adaptation to Climate Change in Small Island Developing States BACKGROUND
 Vulnerability and Adaptation to Climate Change in Small Island Developing States BACKGROUND Dr. Graham Sem Sustainable Environment Management Limited 53 Warwick Avenue, Westmere Auckland, New Zealand E-mail:
Vulnerability and Adaptation to Climate Change in Small Island Developing States BACKGROUND Dr. Graham Sem Sustainable Environment Management Limited 53 Warwick Avenue, Westmere Auckland, New Zealand E-mail:
World Meteorological Organization Role of WMO and National Meteorological and Hydrological Services in Disaster Risk Reduction
 World Meteorological Organization Role of WMO and National Meteorological and Hydrological Services in Disaster Risk Reduction By Maryam Golnaraghi, Ph.D. Chief of Disaster Risk Reduction Programme Extreme
World Meteorological Organization Role of WMO and National Meteorological and Hydrological Services in Disaster Risk Reduction By Maryam Golnaraghi, Ph.D. Chief of Disaster Risk Reduction Programme Extreme
Evaluation Approach Project Performance Evaluation Report for Loan 2167 and Grant 0006-SRI: Tsunami-Affected Areas Rebuilding Project September 2015
 Asian Development Bank 6 ADB Avenue, Mandaluyong City, 1550 Metro Manila, Philippines Tel +63 2 632 4444; Fax +63 2 636 2163; evaluation@adb.org www.adb.org/evaluation Evaluation Approach Project Performance
Asian Development Bank 6 ADB Avenue, Mandaluyong City, 1550 Metro Manila, Philippines Tel +63 2 632 4444; Fax +63 2 636 2163; evaluation@adb.org www.adb.org/evaluation Evaluation Approach Project Performance
Need for a Closer Look
 Need for a Closer Look - Natural Catastrophes in India Anup Jindal emphasizes that if a realistic assessment of the catastrophe risks is to be made, one should also take into account the future projections;
Need for a Closer Look - Natural Catastrophes in India Anup Jindal emphasizes that if a realistic assessment of the catastrophe risks is to be made, one should also take into account the future projections;
Recent weather disasters Statistics of natural catastrophes Reasons for increasing losses Risk reduction strategies Conclusions
 Geo Risks Research Munich Reinsurance Company Topics Recent weather disasters Statistics of natural catastrophes Reasons for increasing losses Risk reduction strategies Conclusions Weather records and
Geo Risks Research Munich Reinsurance Company Topics Recent weather disasters Statistics of natural catastrophes Reasons for increasing losses Risk reduction strategies Conclusions Weather records and
Towards a Post-2015 Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction
 Towards a Post-2015 Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction Introduction 1. The Hyogo Framework for Action 2005-2015 (HFA) Building the Resilience of Nations and Communities to Disasters, is the inspiration
Towards a Post-2015 Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction Introduction 1. The Hyogo Framework for Action 2005-2015 (HFA) Building the Resilience of Nations and Communities to Disasters, is the inspiration
Sharm El Sheikh Declaration on Disaster Risk Reduction. 16 September Adopted at the Second Arab Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction
 Sharm El Sheikh Declaration on Disaster Risk Reduction 16 September 2014 Adopted at the Second Arab Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction City of Sharm El Sheikh, Arab Republic of Egypt, 14 16 September
Sharm El Sheikh Declaration on Disaster Risk Reduction 16 September 2014 Adopted at the Second Arab Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction City of Sharm El Sheikh, Arab Republic of Egypt, 14 16 September
things to know about finance for reducing disaster risk
 10 things to know about finance for reducing disaster risk Charlene Watson Alice Caravani Tom Mitchell Jan Kellett Katie Peters March 2015 Design: Steven Dickie - stevendickie.com/design Photo: NASA Goddard
10 things to know about finance for reducing disaster risk Charlene Watson Alice Caravani Tom Mitchell Jan Kellett Katie Peters March 2015 Design: Steven Dickie - stevendickie.com/design Photo: NASA Goddard
PROPOSAL FOR AN IPCC SPECIAL REPORT ON MANAGING THE RISK OF EXTREME EVENTS 1 TO ADVANCE CLIMATE CHANGE ADAPTATION
 PROPOSAL FOR AN IPCC SPECIAL REPORT ON MANAGING THE RISK OF EXTREME EVENTS 1 TO ADVANCE CLIMATE CHANGE ADAPTATION PROPOSED BY NORWAY AND THE SECRETARIAT OF THE INTERNATIONAL STRATEGY FOR DISASTER REDUCTION
PROPOSAL FOR AN IPCC SPECIAL REPORT ON MANAGING THE RISK OF EXTREME EVENTS 1 TO ADVANCE CLIMATE CHANGE ADAPTATION PROPOSED BY NORWAY AND THE SECRETARIAT OF THE INTERNATIONAL STRATEGY FOR DISASTER REDUCTION
Disaster Risk Management
 Disaster Risk Management Managing The Impacts of Extreme Weather and Climate Events Workshop on Climate Change and Disaster Risk Management in Planning and Investment Projects Session 8: Climate Change
Disaster Risk Management Managing The Impacts of Extreme Weather and Climate Events Workshop on Climate Change and Disaster Risk Management in Planning and Investment Projects Session 8: Climate Change
Workshop Climate Change Adaptation (CCA)
 Workshop Climate Change Adaptation (CCA) March 24th 27th, 2014 Manila, Philippines Tuesday, March 25th, 2014 09.00h 09.30h: Exchange of Experiences and Key Learning Points Resty Lou Talamayan (PRC) Session
Workshop Climate Change Adaptation (CCA) March 24th 27th, 2014 Manila, Philippines Tuesday, March 25th, 2014 09.00h 09.30h: Exchange of Experiences and Key Learning Points Resty Lou Talamayan (PRC) Session
Third Session: Small Island Developing States: Transport and Trade Logistics Challenges
 Multi-year Expert Meeting on Transport, Trade Logistics and Trade Facilitation: Third Session: Small Island Developing States: Transport and Trade Logistics Challenges 24 26 November 2014 Disaster Risk
Multi-year Expert Meeting on Transport, Trade Logistics and Trade Facilitation: Third Session: Small Island Developing States: Transport and Trade Logistics Challenges 24 26 November 2014 Disaster Risk
Reconstruction after the March 2011 Disaster in Japan: issues, policy options and prospects
 Reconstruction after the March 2011 Disaster in Japan: issues, policy options and prospects Presentation at the XVI conference on Dynamics, Economic Growth, and International Trade (DEGIT-XVI) at the Saint-Petersburg
Reconstruction after the March 2011 Disaster in Japan: issues, policy options and prospects Presentation at the XVI conference on Dynamics, Economic Growth, and International Trade (DEGIT-XVI) at the Saint-Petersburg
AXA AND CLIMATE RISKS Why does climate change warrant our attention?
 AXA AND CLIMATE RISKS Why does climate change warrant our attention? Climate change is increasingly impacting the world s populations and economies The latest scientific findings have reinforced the message
AXA AND CLIMATE RISKS Why does climate change warrant our attention? Climate change is increasingly impacting the world s populations and economies The latest scientific findings have reinforced the message
Batam, Indonesia. Local progress report on the implementation of the 10 Essentials for Making Cities Resilient ( )
 Batam, Indonesia Local progress report on the implementation of the 10 Essentials for Making Cities Resilient (2013-2014) Name of focal point: Yusniar Nurdin Organization: BNPB Title/Position: Technical
Batam, Indonesia Local progress report on the implementation of the 10 Essentials for Making Cities Resilient (2013-2014) Name of focal point: Yusniar Nurdin Organization: BNPB Title/Position: Technical
THE CLIMATE RISK INSURANCE INITIATIVE
 THE CLIMATE RISK INSURANCE INITIATIVE InsuResilience at a glance The InsuResilience Climate Risk Insurance Initiative was adopted by the G7 partner countries Germany, France, Italy, Japan, Canada, the
THE CLIMATE RISK INSURANCE INITIATIVE InsuResilience at a glance The InsuResilience Climate Risk Insurance Initiative was adopted by the G7 partner countries Germany, France, Italy, Japan, Canada, the
Disaster risk reduction and climate change adaptation suggested reading list
 Workshop on integrating practices, tools and systems for climate risk assessment and management and disaster risk reduction strategies into national policies and programmes The UNFCCC workshop will be
Workshop on integrating practices, tools and systems for climate risk assessment and management and disaster risk reduction strategies into national policies and programmes The UNFCCC workshop will be
Skardu, Pakistan. Local progress report on the implementation of the 10 Essentials for Making Cities Resilient (First Cycle)
 Skardu, Pakistan Local progress report on the implementation of the 10 Essentials for Making Cities Resilient (First Cycle) Name of focal point: Habib Mughal Organization: UN-HABITAT - Pakistan Title/Position:
Skardu, Pakistan Local progress report on the implementation of the 10 Essentials for Making Cities Resilient (First Cycle) Name of focal point: Habib Mughal Organization: UN-HABITAT - Pakistan Title/Position:
Mournag, Tunisia. Local progress report on the implementation of the 10 Essentials for Making Cities Resilient ( )
 Mournag, Tunisia Local progress report on the implementation of the 10 Essentials for Making Cities Resilient (2013-2014) Name of focal point: Kamal Alelwy Organization: La ville de Mournag Title/Position:
Mournag, Tunisia Local progress report on the implementation of the 10 Essentials for Making Cities Resilient (2013-2014) Name of focal point: Kamal Alelwy Organization: La ville de Mournag Title/Position:
Birgunj Sub metropolitan City, Nepal
 Birgunj Sub metropolitan City, Nepal Local progress report on the implementation of the 10 Essentials for Making Cities Resilient (2013-2014) Name of focal point: - - Organization: - Title/Position: -
Birgunj Sub metropolitan City, Nepal Local progress report on the implementation of the 10 Essentials for Making Cities Resilient (2013-2014) Name of focal point: - - Organization: - Title/Position: -
Insuring Climate Change-related Risks
 Insuring Climate Change-related Risks 19 February 2016 Austrian Climate Change Workshop Day 2 Tobias Grimm Senior Project Manager Corporate Climate Centre Climate & Renewables Munich Re some facts About
Insuring Climate Change-related Risks 19 February 2016 Austrian Climate Change Workshop Day 2 Tobias Grimm Senior Project Manager Corporate Climate Centre Climate & Renewables Munich Re some facts About
Sint Maarten National Recovery and Resilience Plan A Roadmap to Building Back Better
 Sint Maarten National Recovery and Resilience Plan A Roadmap to Building Back Better EXECUTIVE BRIEF 2 Executive Brief Background Sint Maarten and Saint Martin 1 Saint Martin Sint Maarten Copyright 2018
Sint Maarten National Recovery and Resilience Plan A Roadmap to Building Back Better EXECUTIVE BRIEF 2 Executive Brief Background Sint Maarten and Saint Martin 1 Saint Martin Sint Maarten Copyright 2018
Barito Kuala, Indonesia
 Barito Kuala, Indonesia Local progress report on the implementation of the Hyogo Framework for Action (2013-2014) Name of focal point: Yusniar Nurdin Organization: BNPB Title/Position: Technical Support
Barito Kuala, Indonesia Local progress report on the implementation of the Hyogo Framework for Action (2013-2014) Name of focal point: Yusniar Nurdin Organization: BNPB Title/Position: Technical Support
Workshop on. Bangkok from October 2012
 Workshop on Promoting community-based disaster risk reduction, CCA and emergency response for older people and other vulnerable groups in ASEAN and Japan Background: Bangkok from 15 19 October 2012 Asia
Workshop on Promoting community-based disaster risk reduction, CCA and emergency response for older people and other vulnerable groups in ASEAN and Japan Background: Bangkok from 15 19 October 2012 Asia
Disaster risk management for climate change adaptation: Experiences from German development cooperation
 Disaster risk management for climate change adaptation: Experiences from German development cooperation Britta Heine 1, Jens Etter 2 1 Deutsche Gesellschaft für Technische Zusammenarbeit (GTZ) GmbH, Postfach
Disaster risk management for climate change adaptation: Experiences from German development cooperation Britta Heine 1, Jens Etter 2 1 Deutsche Gesellschaft für Technische Zusammenarbeit (GTZ) GmbH, Postfach
Disaster Risk Management
 Disaster Risk Management Approach and Contributions of German Development Cooperation Contents Foreword................................................................. 3 Section 1 What does Disaster Risk
Disaster Risk Management Approach and Contributions of German Development Cooperation Contents Foreword................................................................. 3 Section 1 What does Disaster Risk
Policy Implementation for Enhancing Community. Resilience in Malawi
 Volume 10 Issue 1 May 2014 Status of Policy Implementation for Enhancing Community Resilience in Malawi Policy Brief ECRP and DISCOVER Disclaimer This policy brief has been financed by United Kingdom (UK)
Volume 10 Issue 1 May 2014 Status of Policy Implementation for Enhancing Community Resilience in Malawi Policy Brief ECRP and DISCOVER Disclaimer This policy brief has been financed by United Kingdom (UK)
CARIBBEAN DEVELOPMENT BANK SUPPORT FOR HAITI TO MEET COMMITMENT TO CARIBBEAN CATASTROPHE RISK INSURANCE FACILITY FOR THE HURRICANE SEASON
 PUBLIC DISCLOSURE AUTHORISED CARIBBEAN DEVELOPMENT BANK SUPPORT FOR HAITI TO MEET COMMITMENT TO CARIBBEAN CATASTROPHE RISK INSURANCE FACILITY FOR THE 2017-2018 HURRICANE SEASON This Document is being made
PUBLIC DISCLOSURE AUTHORISED CARIBBEAN DEVELOPMENT BANK SUPPORT FOR HAITI TO MEET COMMITMENT TO CARIBBEAN CATASTROPHE RISK INSURANCE FACILITY FOR THE 2017-2018 HURRICANE SEASON This Document is being made
Interfacing Climate Change and Disaster Risk Reduction
 Interfacing Climate Change and Disaster Risk Reduction GIDMC 11 July 2018 DR. PARIVELAN K.M. ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR TATA INSTITUTE OF SOCIAL SCIENCES MUMBAI TISS TISS- working with disasters since post independence
Interfacing Climate Change and Disaster Risk Reduction GIDMC 11 July 2018 DR. PARIVELAN K.M. ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR TATA INSTITUTE OF SOCIAL SCIENCES MUMBAI TISS TISS- working with disasters since post independence
Innovative finance for resilient infrastructure
 Innovative finance for resilient infrastructure Preliminary findings Centre for Global Disaster Protection & Lloyd s of London Partners: The Centre for Global Disaster Protection, in partnership with Lloyd
Innovative finance for resilient infrastructure Preliminary findings Centre for Global Disaster Protection & Lloyd s of London Partners: The Centre for Global Disaster Protection, in partnership with Lloyd
Cayman Islands. National progress report on the implementation of the Hyogo Framework for Action ( ) - interim
 Cayman Islands National progress report on the implementation of the Hyogo Framework for Action (2009-2011) - interim Name of focal point : McCleary Frederick Organization : Hazard Management Cayman Islands
Cayman Islands National progress report on the implementation of the Hyogo Framework for Action (2009-2011) - interim Name of focal point : McCleary Frederick Organization : Hazard Management Cayman Islands
Managing Natural Disasters
 Managing Natural Disasters Lucy Conger With research assistant from Cory Siskind, Inter-American Dialogue Prepared for the Colombian Government for the Sixth Summit of the Americas August 2011 Managing
Managing Natural Disasters Lucy Conger With research assistant from Cory Siskind, Inter-American Dialogue Prepared for the Colombian Government for the Sixth Summit of the Americas August 2011 Managing
Munich Re THE RISKS OF CLIMATE CHANGE INNOVATIVE PROJECTS OF MUNICH RE. Prof. Dr. Peter Hoeppe Head of Geo Risks Research/Corporate Climate Centre
 THE RISKS OF CLIMATE CHANGE INNOVATIVE PROJECTS OF MUNICH RE Prof. Dr. Peter Hoeppe Head of Geo Risks Research/Corporate Climate Centre Lunchtime Colloquium, Rachel Carson Center, Munich, April 12, 2012
THE RISKS OF CLIMATE CHANGE INNOVATIVE PROJECTS OF MUNICH RE Prof. Dr. Peter Hoeppe Head of Geo Risks Research/Corporate Climate Centre Lunchtime Colloquium, Rachel Carson Center, Munich, April 12, 2012
Investing in Business Continuity Planning (BCP) for Coastal Community
 Advancing Business Continuity in a Challenging Environment Investing in Business Continuity Planning (BCP) for Coastal Community Dr. Khairul Hisyam Kamarudin May 2018 INTRODUCTION Malaysia has a tropical
Advancing Business Continuity in a Challenging Environment Investing in Business Continuity Planning (BCP) for Coastal Community Dr. Khairul Hisyam Kamarudin May 2018 INTRODUCTION Malaysia has a tropical
REDUCING DISASTER RISK a challenge for development
 REDUCING DISASTER RISK a challenge for development A Global Report from : United Nations Development Programme Bureau for Crisis Prevention and Recovery Why a global UNDP Report on Disaster Risk Economic
REDUCING DISASTER RISK a challenge for development A Global Report from : United Nations Development Programme Bureau for Crisis Prevention and Recovery Why a global UNDP Report on Disaster Risk Economic
Resilient Coasts: A Blueprint for Action
 Resilient Coasts: A Blueprint for Action The Resilient Coasts Blueprint was authored and endorsed by the following organizations: Risk Management Solutions The Resilient Coasts Initiative was made possible
Resilient Coasts: A Blueprint for Action The Resilient Coasts Blueprint was authored and endorsed by the following organizations: Risk Management Solutions The Resilient Coasts Initiative was made possible
Asia is the most risk-prone disaster in the world.
 Key Note Address Business Resilience and Implication for ASEAN Economic Community by Mr. Isara Vongkusolkit, Chairman of TCC and BOT On April 20 th, 2016 during 11.10-11.35 hrs., Dusit Thani Hotel, Bangkok
Key Note Address Business Resilience and Implication for ASEAN Economic Community by Mr. Isara Vongkusolkit, Chairman of TCC and BOT On April 20 th, 2016 during 11.10-11.35 hrs., Dusit Thani Hotel, Bangkok
Patika, Pakistan. Local progress report on the implementation of the 10 Essentials for Making Cities Resilient (First Cycle)
 Patika, Pakistan Local progress report on the implementation of the 10 Essentials for Making Cities Resilient (First Cycle) Name of focal point: Habib Mughal Organization: UN-HABITAT - Pakistan Title/Position:
Patika, Pakistan Local progress report on the implementation of the 10 Essentials for Making Cities Resilient (First Cycle) Name of focal point: Habib Mughal Organization: UN-HABITAT - Pakistan Title/Position:
Disaster Risk Reduction : The Hyogo Framework For Action
 Disaster Risk Reduction : The Hyogo Framework For Action 2005-2015 Manoj Kumar Mishra Introduction Every year, more than 200 million people are affected by droughts, floods, cyclones, earth quake, wild
Disaster Risk Reduction : The Hyogo Framework For Action 2005-2015 Manoj Kumar Mishra Introduction Every year, more than 200 million people are affected by droughts, floods, cyclones, earth quake, wild
Beirut, Lebanon. Local progress report on the implementation of the 10 Essentials for Making Cities Resilient ( )
 Beirut, Lebanon Local progress report on the implementation of the 10 Essentials for Making Cities Resilient (2013-2014) Name of focal point: Bilal Hamad Organization: - Title/Position: - E-mail address:
Beirut, Lebanon Local progress report on the implementation of the 10 Essentials for Making Cities Resilient (2013-2014) Name of focal point: Bilal Hamad Organization: - Title/Position: - E-mail address:
ESTABLISHMENT OF COUNTRY-BASED FLOOD RISK INDEX
 ESTABLISHMENT OF COUNTRY-BASED FLOOD RISK INDEX Yasuo KANNAMI MEE07182 Supervisor: Kuniyoshi TAKEUCHI ABSTRACT This thesis offers a measure to assess the country-wise flood risk, namely Flood Risk Index
ESTABLISHMENT OF COUNTRY-BASED FLOOD RISK INDEX Yasuo KANNAMI MEE07182 Supervisor: Kuniyoshi TAKEUCHI ABSTRACT This thesis offers a measure to assess the country-wise flood risk, namely Flood Risk Index
INDEX BASED RISK TRANSFER AND INSURANCE MECHANISMS FOR ADAPTATION. Abedalrazq Khalil, PhD Water Resources Specialist, World Bank
 INDEX BASED RISK TRANSFER AND INSURANCE MECHANISMS FOR ADAPTATION Abedalrazq Khalil, PhD Water Resources Specialist, World Bank Outline Introduction: Climate Change and Extremes Index Based Risk Transfer:
INDEX BASED RISK TRANSFER AND INSURANCE MECHANISMS FOR ADAPTATION Abedalrazq Khalil, PhD Water Resources Specialist, World Bank Outline Introduction: Climate Change and Extremes Index Based Risk Transfer:
Business for Resilience
 Business for Resilience ARISE is the private sector initiative of the UN Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNISDR). Its main role is to mobilize business in support of the goals of the 2015 Sendai Framework.
Business for Resilience ARISE is the private sector initiative of the UN Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNISDR). Its main role is to mobilize business in support of the goals of the 2015 Sendai Framework.
Pidie Jaya, Indonesia
 Pidie Jaya, Indonesia Local progress report on the implementation of the 10 Essentials for Making Cities Resilient (2013-2014) Name of focal point: Yusniar Nurdin Organization: BNPB Title/Position: Technical
Pidie Jaya, Indonesia Local progress report on the implementation of the 10 Essentials for Making Cities Resilient (2013-2014) Name of focal point: Yusniar Nurdin Organization: BNPB Title/Position: Technical
Trade and Natural Disaster Response. Ricardo James, Charge d Affaires, Permanent Delegation of the Organization of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS)
 Trade and Natural Disaster Response Ricardo James, Charge d Affaires, Permanent Delegation of the Organization of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS) Natural Disaster Threats in the Caribbean Hurricanes and
Trade and Natural Disaster Response Ricardo James, Charge d Affaires, Permanent Delegation of the Organization of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS) Natural Disaster Threats in the Caribbean Hurricanes and
Binjai, Indonesia. Local progress report on the implementation of the 10 Essentials for Making Cities Resilient ( )
 Binjai, Indonesia Local progress report on the implementation of the 10 Essentials for Making Cities Resilient (2013-2014) Name of focal point: Yusniar Nurdin Organization: BNPB Title/Position: Technical
Binjai, Indonesia Local progress report on the implementation of the 10 Essentials for Making Cities Resilient (2013-2014) Name of focal point: Yusniar Nurdin Organization: BNPB Title/Position: Technical
Skardu, Pakistan. Local progress report on the implementation of the Hyogo Framework for Action (First Cycle)
 Skardu, Pakistan Local progress report on the implementation of the Hyogo Framework for Action (First Cycle) Name of focal point: Habib Mughal Organization: UN-HABITAT - Pakistan Title/Position: Manager
Skardu, Pakistan Local progress report on the implementation of the Hyogo Framework for Action (First Cycle) Name of focal point: Habib Mughal Organization: UN-HABITAT - Pakistan Title/Position: Manager
Disaster Risk Management & Mitigation
 Disaster Risk Management & Mitigation 1 The concept of DRM accepts that some hazard events may occur But tries to lessen the impact by improving the community s ability to absorb the impact with minimum
Disaster Risk Management & Mitigation 1 The concept of DRM accepts that some hazard events may occur But tries to lessen the impact by improving the community s ability to absorb the impact with minimum
