U.S. Job Flows and the China Shock
|
|
|
- Georgiana O’Brien’
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 U.S. Job Flows and the China Shock Appendix For Online Publication Brian Asquith, Sanjana Goswami, David Neumark, and Antonio Rodriguez-Lopez November 2017 A Supporting Figures and Tables Millions % 51% Births Expansions Births Expansions (a) Job creation decomposition (b) Job creation shares (average) Millions % 59% Deaths Contractions Deaths Contractions (c) Job destruction decomposition (d) Job destruction shares (average) Figure A.1: Employment creation and destruction in the manufacturing industry (three-year windows) 1
2 Millions % 63% Births Expansions Births Expansions (a) Job creation decomposition (b) Job creation shares (average) Millions % 68% Deaths Contractions Deaths Contractions (c) Job destruction decomposition (d) Job destruction shares (average) Figure A.2: Employment creation and destruction in the non-manufacturing industry (three-year windows) 2
3 Table A.1: Job Flows Decomposition in All Industries (in Thousands) Employment at initial year 102, , , , , , , , ,499 Employment at final year 111, , , , , , , , ,779 Change in employment Due to births 16,887 19,498 18,377 17,571 16,814 19,176 24,060 21,893 18,758 Due to deaths -8,953-9,261-10,699-11,067-11,618-12,716-12,989-14,223-16,854 Due to expansions 8,331 9,366 11,658 13,472 14,404 14,688 14,610 13,565 13,151 Due to contractions -6,995-6,896-7,739-7,338-7,417-7,184-8,347-9,946-11,775 Net changes Net extensive margin 7,933 10,237 7,678 6,504 5,196 6,460 11,071 7,670 1,904 Net intensive margin 1,336 2,471 3,919 6,134 6,987 7,505 6,263 3,620 1,376 Net employment change 9,270 12,708 11,598 12,638 12,183 13,965 17,334 11,289 3, Employment at initial year 141, , , , , , , , ,508 Employment at final year 139, , , , , , , , ,794 Change in employment Due to births 15,350 16,789 16,909 15,952 15,053 16,058 19,464 22,178 19,159 Due to deaths -17,571-17,061-14,161-12,987-12,189-21,996-23,762-26,870-19,155 Due to expansions 13,126 13,028 11,906 10,925 10,183 8,190 7,418 7,416 7,544 Due to contractions -13,532-11,041-9,559-8,040-7,124-5,618-4,256-3,924-3,262 Net changes Net extensive margin -2, ,748 2,966 2,864-5,938-4,298-4,691 3 Net intensive margin ,986 2,347 2,885 3,060 2,572 3,162 3,492 4,282 Net employment change -2,627 1,713 5,095 5,851 5,924-3,365-1,135-1,199 4,285 Notes: This table reports employment levels and three-year job flows for the overall U.S. economy. It uses NETS data from the universe of U.S. establishments with two or more employees in at least one year during the period.
4 Table A.2: Predicted U.S. Net Employment Changes due to the China Shock with NETS Data and CBP Data (in Thousands) Import exposure PNTR status Specification Exposure type Sector NETS CBP NETS CBP : Table 1, cols. 2 and 6 Direct Manufacturing ,496-4,165 Tables 4 and 5, col. 2 Combined I Total ,567-2,484-7,495 Tables 4 and 5, col. 5 Combined II Total ,918-2,825-10,200 Tables 6 and 7, col. 1 Local Exposed -2,128-2,078-3,896-3,153 Tables 6 and 7, col. 2 Nonexposed tradable ,103 Tables 6 and 7, col. 3 Nonexposed nontradable 2,225 2,331 2,792 1, : Table 1, cols. 5 and 7 Direct Manufacturing ,707-4,819 Tables 4 and 5, col. 3 Combined I Total ,549-3,693-8,345 Tables 4 and 5, col. 6 Combined II Total ,009-5,261-13,200 Tables A.5 and A.6, col. 1 Local Exposed -2,515-2,758-6,620-5,282 Tables A.5 and A.6, col. 2 Nonexposed tradable ,269-1,736 Tables A.5 and A.6, col. 3 Nonexposed nontradable 2,222 2,684 4,693 4,145 Notes: For the specifications described in the first column, and using either Chinese import exposure or China s PNTR status as the China-shock variable, this table compares predicted net employment changes with NETS data vs. predicted net employment changes with CBP data. Negative values indicate that the China-shock variable reduces employment. Equations (6) and (7) show general formulas to calculate predicted employment changes from Tables 1, 4, and 5, and equations (16) and (17) show the general formulas to calculate predicted employment changes from Tables 6, 7, A.5, and A.6. The numbers in bold denote predicted changes corresponding to statistically significant coefficients in the corresponding tables. 4
5 Table A.3: IV Estimation of the Effects of Chinese Import Exposure on U.S. Employment with Higher-Order Upstream and Downstream Linkages Across Industries Combined measure I (direct+upstream) Combined measure II (direct+upstream+downstream) (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) Net employment growth -0.35** -0.42*** -0.47*** -0.31** -0.36*** -0.38*** (0.15) (0.15) (0.16) (0.14) (0.13) (0.11) Job flows Births (0.09) (0.07) (0.09) (0.08) (0.06) (0.07) Deaths 0.33*** 0.40*** 0.47*** 0.33*** 0.38*** 0.42*** (0.10) (0.10) (0.12) (0.09) (0.09) (0.10) Expansions (0.03) (0.02) (0.02) (0.05) (0.03) (0.04) Contractions 0.12** 0.11* 0.08* 0.11** 0.12** 0.08** (0.06) (0.06) (0.05) (0.06) (0.06) (0.04) Net extensive margin -0.25** -0.33*** -0.43*** -0.24*** -0.29*** -0.36*** (0.12) (0.11) (0.15) (0.09) (0.08) (0.10) Net intensive margin (0.07) (0.08) (0.05) (0.08) (0.07) (0.05) Job creation * 0.12 (0.10) (0.07) (0.09) (0.10) (0.07) (0.08) Job destruction 0.44*** 0.52*** 0.55*** 0.44*** 0.50*** 0.50*** (0.14) (0.14) (0.13) (0.13) (0.12) (0.10) CBP data: Net employment growth -0.94*** -1.31*** -1.34*** -0.85*** -1.14*** -1.21*** (0.25) (0.35) (0.39) (0.22) (0.30) (0.36) Sector period controls Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Manf. sector controls Yes No No Yes No No Include No No Yes No No Yes Observations Notes: This table reports results for the effects of direct + upstream, and direct + upstream + downstream higher-order Chinese import exposure on annualized log-employment changes and job flows. All regressions include 479 industries, two subperiods ( and either or ), and are weighted by 1992 employment. The net growth regression with CBP data is weighted by 1992 CBP employment, and is reported for the purpose of comparison with the net growth regression with NETS data. Standard errors (in parentheses) are clustered at the three-digit industry level. The coefficients are statistically significant at the *10%, **5%, or ***1% level. 5
6 Table A.4: OLS Estimation of the Effects of China s PNTR Status on U.S. Employment with Higher-Order Upstream and Downstream Linkages Across Industries Combined measure I (direct+upstream) Combined measure II (direct+upstream+downstream) (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) Net employment growth ** ** (0.14) (0.12) (0.17) (0.12) (0.10) (0.14) Job flows Births (0.14) (0.12) (0.16) (0.11) (0.10) (0.12) Deaths 0.24*** 0.28*** 0.44*** 0.17*** 0.22*** 0.39*** (0.05) (0.05) (0.10) (0.06) (0.05) (0.09) Expansions (0.03) (0.03) (0.03) (0.04) (0.03) (0.03) Contractions (0.04) (0.03) (0.03) (0.04) (0.03) (0.03) Net extensive margin ** *** (0.14) (0.12) (0.18) (0.11) (0.10) (0.14) Net intensive margin (0.05) (0.04) (0.04) (0.05) (0.04) (0.04) Job creation (0.14) (0.12) (0.15) (0.11) (0.10) (0.11) Job destruction 0.26*** 0.30*** 0.45*** 0.18** 0.24*** 0.39*** (0.07) (0.06) (0.10) (0.07) (0.06) (0.09) CBP data: Net employment growth -0.52*** -0.70*** -0.90*** -0.43*** -0.66*** -0.97*** (0.11) (0.11) (0.16) (0.10) (0.11) (0.16) Sector period controls Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Manf. sector controls Yes No No Yes No No Include No No Yes No No Yes Observations Notes: This table reports results for the effects of direct + upstream, and direct + upstream + downstream higher-order exposure to China s PNTR status on annualized log-employment changes and job flows. All regressions include 479 industries, two subperiods ( and either or ), and are weighted by 1992 employment. The net growth regression with CBP data is weighted by 1992 CBP employment, and is reported for the purpose of comparison with the net growth regression with NETS data. Standard errors (in parentheses) are clustered at the three-digit industry level. The coefficients are statistically significant at the *10%, **5%, or ***1% level. 6
7 Table A.5: IV Estimation of the Effects of Chinese Import Exposure on U.S. Commuting Zones by Sectoral Employment ( ) Chinese Import Exposure Bartik Shock Exposed Nonexposed Nonexposed Exposed Nonexposed Nonexposed tradable nontradable tradable nontradable (Employment/Population) -1.12*** * 0.19*** -0.04** 0.73*** (0.22) (0.09) (0.51) (0.04) (0.02) (0.11) Job flows Births * 1.89*** 0.22*** 0.03*** 1.36*** (0.12) (0.07) (0.55) (0.03) (0.01) (0.11) Deaths 1.05*** -0.17* 1.16** 0.17*** 0.05*** 0.84*** (0.18) (0.09) (0.51) (0.03) (0.01) (0.07) Expansions ** 0.46* 0.15*** 0.02** 0.37*** (0.08) (0.06) (0.27) (0.02) (0.01) (0.05) Contractions 0.26*** -0.15* *** 0.15*** (0.06) (0.08) (0.18) (0.01) (0.01) (0.04) 7 Net extensive margin -0.86*** ** -0.02** 0.52*** (0.20) (0.06) (0.46) (0.03) (0.01) (0.09) Net intensive margin -0.25*** *** *** (0.08) (0.05) (0.19) (0.02) (0.01) (0.04) Job creation ** 2.35*** 0.37*** 0.05*** 1.72*** (0.18) (0.12) (0.69) (0.05) (0.02) (0.14) Job destruction 1.31*** -0.32** 1.37** 0.18*** 0.09*** 0.99*** (0.18) (0.15) (0.64) (0.03) (0.02) (0.10) CBP data: (Employment/Population) -1.42*** * 0.15*** *** (0.23) (0.11) (0.74) (0.02) (0.01) (0.09) Notes: Using subperiods , , and import exposure as the China shock, this table reports ˆβ k, ˆγ k, ˆβ F k, and ˆγ F k, for k {1(exposed), 2(nonexposed tradable), 3(nonexposed nontradable)}, from the estimation of specifications (14) and (15). All regressions include 4,332 observations (722 commuting zones, three sectors, and two subperiods) and the following controls: sectortime fixed effects, the commuting zone s manufacturing share (at the beginning of each period) interacted with sector dummies, and regional Census division dummies interacted with sector dummies. Regressions are weighted by 1992 commuting-zone population. The net regression with CBP data is reported for the purpose of comparison with the net regression with NETS data. Standard errors (in parentheses) are clustered at the commuting-zone level. The coefficients are statistically significant at the *10%, **5%, or ***1% level.
8 Table A.6: OLS Estimation of the Effects of China s PNTR Status on U.S. Commuting Zones by Sectoral Employment ( ) PNTR Status Bartik Shock Exposed Nonexposed Nonexposed Exposed Nonexposed Nonexposed tradable nontradable tradable nontradable (Employment/Population) -0.73*** -0.14*** 0.52** 0.14*** -0.04** 0.77*** (0.08) (0.05) (0.21) (0.04) (0.02) (0.11) Job flows Births -0.13*** *** 0.21*** 0.03*** 1.40*** (0.04) (0.02) (0.16) (0.03) (0.01) (0.12) Deaths 0.47*** 0.10*** 0.40** 0.21*** 0.06*** 0.87*** (0.06) (0.02) (0.16) (0.03) (0.01) (0.08) Expansions -0.13*** *** 0.14*** 0.02* 0.39*** (0.03) (0.02) (0.12) (0.02) (0.01) (0.05) Contractions * *** 0.16*** (0.03) (0.02) (0.05) (0.01) (0.01) (0.05) 8 Net extensive margin -0.60*** -0.11*** *** 0.53*** (0.06) (0.03) (0.16) (0.02) (0.01) (0.09) Net intensive margin -0.13*** ** 0.13*** *** (0.04) (0.03) (0.11) (0.02) (0.02) (0.04) Job creation -0.25*** *** 0.36*** 0.05*** 1.80*** (0.07) (0.03) (0.22) (0.05) (0.02) (0.14) Job destruction 0.47*** 0.11*** 0.49*** 0.22*** 0.09*** 1.03*** (0.07) (0.03) (0.18) (0.04) (0.02) (0.11) CBP data: (Employment/Population) -0.56*** -0.18*** 0.44* 0.15*** *** (0.06) (0.03) (0.26) (0.02) (0.01) (0.09) Notes: Using subperiods , , and PNTR status as the China shock, this table reports ˆβ k, ˆγ k, ˆβF k, and ˆγ F k, for k {1(exposed), 2(nonexposed tradable), 3(nonexposed nontradable)}, from the estimation of specifications (14) and (15). All regressions include 4,332 observations (722 commuting zones, three sectors, and two subperiods) and the following controls: sectortime fixed effects, the commuting zone s manufacturing share (at the beginning of each period) interacted with sector dummies, and regional Census division dummies interacted with sector dummies. Regressions are weighted by 1992 commuting-zone population. The net regression with CBP data is reported for the purpose of comparison with the net regression with NETS data. Standard errors (in parentheses) are clustered at the commuting-zone level. The coefficients are statistically significant at the *10%, **5%, or ***1% level.
U.S. Job Flows and the China Shock
 U.S. Job Flows and the China Shock Brian Asquith, Sanjana Goswami, David Neumark, and Antonio Rodriguez-Lopez November 2017 Abstract International trade exposure affects job creation and destruction along
U.S. Job Flows and the China Shock Brian Asquith, Sanjana Goswami, David Neumark, and Antonio Rodriguez-Lopez November 2017 Abstract International trade exposure affects job creation and destruction along
Table IA.1 CEO Pay-Size Elasticity and Increased Labor Demand Panel A: IPOs Scaled by Full Sample Industry Average
 Table IA.1 CEO Pay-Size Elasticity and Increased Labor Demand Panel A: IPOs Scaled by Industry Average (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) Ln(Market Value) 0.423 0.419 0.423 0.423 0.255 (33.29) (30.84) (33.29) (33.29)
Table IA.1 CEO Pay-Size Elasticity and Increased Labor Demand Panel A: IPOs Scaled by Industry Average (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) Ln(Market Value) 0.423 0.419 0.423 0.423 0.255 (33.29) (30.84) (33.29) (33.29)
Trade Costs and Job Flows: Evidence from Establishment-Level Data
 Trade Costs and Job Flows: Evidence from Establishment-Level Data Appendix For Online Publication Jose L. Groizard, Priya Ranjan, and Antonio Rodriguez-Lopez March 2014 A A Model of Input Trade and Firm-Level
Trade Costs and Job Flows: Evidence from Establishment-Level Data Appendix For Online Publication Jose L. Groizard, Priya Ranjan, and Antonio Rodriguez-Lopez March 2014 A A Model of Input Trade and Firm-Level
Do Domestic Chinese Firms Benefit from Foreign Direct Investment?
 Do Domestic Chinese Firms Benefit from Foreign Direct Investment? Chang-Tai Hsieh, University of California Working Paper Series Vol. 2006-30 December 2006 The views expressed in this publication are those
Do Domestic Chinese Firms Benefit from Foreign Direct Investment? Chang-Tai Hsieh, University of California Working Paper Series Vol. 2006-30 December 2006 The views expressed in this publication are those
APPENDIX to Pyramidal Ownership and the Creation of New Firms
 APPENDIX to Pyramidal Ownership and the Creation of New Firms This Appendix reports additional results that we discuss but do not tabulate in the main text of the paper. The content is summarized below,
APPENDIX to Pyramidal Ownership and the Creation of New Firms This Appendix reports additional results that we discuss but do not tabulate in the main text of the paper. The content is summarized below,
Internet Appendix for Collateral Shocks and Corporate Employment
 Internet Appendix for Collateral Shocks and Corporate Employment Nuri Ersahin Rustom M. Irani University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign March 1, 2018 Appendix IA.I: First-stage for IV estimation This
Internet Appendix for Collateral Shocks and Corporate Employment Nuri Ersahin Rustom M. Irani University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign March 1, 2018 Appendix IA.I: First-stage for IV estimation This
Chinese imports and US labour market adjustment: Insights from value-added trade flows
 Chinese imports and US labour market adjustment: Insights from value-added trade flows Adam Jakubik & Victor Kummritz ERSD, WTO 6 July 2017, ILO 1 / 34 Overview We study the impact of the increased volume
Chinese imports and US labour market adjustment: Insights from value-added trade flows Adam Jakubik & Victor Kummritz ERSD, WTO 6 July 2017, ILO 1 / 34 Overview We study the impact of the increased volume
Import Competition and Household Debt
 Import Competition and Household Debt Barrot (MIT) Plosser (NY Fed) Loualiche (MIT) Sauvagnat (Bocconi) USC Spring 2017 The views expressed in this paper are those of the authors and do not necessarily
Import Competition and Household Debt Barrot (MIT) Plosser (NY Fed) Loualiche (MIT) Sauvagnat (Bocconi) USC Spring 2017 The views expressed in this paper are those of the authors and do not necessarily
No Place Like Home: Familiarity in Mutual Fund Manager Portfolio Choice
 Web Appendix to No Place Like Home: Familiarity in Mutual Fund Manager Portfolio Choice Veronika K. Pool, Noah Stoffman, and Scott E. Yonker April 22, 2012 Kelley School of Business, Indiana University.
Web Appendix to No Place Like Home: Familiarity in Mutual Fund Manager Portfolio Choice Veronika K. Pool, Noah Stoffman, and Scott E. Yonker April 22, 2012 Kelley School of Business, Indiana University.
 TABLE I SUMMARY STATISTICS Panel A: Loan-level Variables (22,176 loans) Variable Mean S.D. Pre-nuclear Test Total Lending (000) 16,479 60,768 Change in Log Lending -0.0028 1.23 Post-nuclear Test Default
TABLE I SUMMARY STATISTICS Panel A: Loan-level Variables (22,176 loans) Variable Mean S.D. Pre-nuclear Test Total Lending (000) 16,479 60,768 Change in Log Lending -0.0028 1.23 Post-nuclear Test Default
Internet Appendix for Bankruptcy Spillovers
 Internet Appendix for Bankruptcy Spillovers Shai Bernstein, Emanuele Colonnelli, Xavier Giroud, and Benjamin Iverson August 21, 2018 This appendix contains additional analysis that demonstrates and supports
Internet Appendix for Bankruptcy Spillovers Shai Bernstein, Emanuele Colonnelli, Xavier Giroud, and Benjamin Iverson August 21, 2018 This appendix contains additional analysis that demonstrates and supports
Services Reform and Manufacturing Performance: Evidence from India
 Services Reform and Manufacturing Performance: Evidence from India Jens M. Arnold, OECD Economics Dept. Molly Lipscomb, Notre Dame Beata S. Javorcik, Oxford Aaditya Mattoo, World Bank India: Strong performance
Services Reform and Manufacturing Performance: Evidence from India Jens M. Arnold, OECD Economics Dept. Molly Lipscomb, Notre Dame Beata S. Javorcik, Oxford Aaditya Mattoo, World Bank India: Strong performance
Import Competition and the Great U.S. Employment Sag of the 2000s
 Import Competition and the Great U.S. Employment Sag of the 2000s Daron Acemoglu David Autor David Dorn Gordon H. Hanson MIT and NBER MIT and NBER CEMFI and IZA UCSD and NBER Brendan Price MIT August 2014
Import Competition and the Great U.S. Employment Sag of the 2000s Daron Acemoglu David Autor David Dorn Gordon H. Hanson MIT and NBER MIT and NBER CEMFI and IZA UCSD and NBER Brendan Price MIT August 2014
Technology and the China Shock: Evidence from France
 Technology and the China Shock: Evidence from France Clément Malgouyres, Institut des politiques publiques June 19, 2018 DARES Job polarization 1 / 29 Motivation China went from 3 to 25% of world manufacturing
Technology and the China Shock: Evidence from France Clément Malgouyres, Institut des politiques publiques June 19, 2018 DARES Job polarization 1 / 29 Motivation China went from 3 to 25% of world manufacturing
The Labor Market Consequences of Adverse Financial Shocks
 The Labor Market Consequences of Adverse Financial Shocks November 2012 Unemployment rate on the two sides of the Atlantic Credit to the private sector over GDP Credit to private sector as a percentage
The Labor Market Consequences of Adverse Financial Shocks November 2012 Unemployment rate on the two sides of the Atlantic Credit to the private sector over GDP Credit to private sector as a percentage
Magnification of the China Shock Through the U.S. Housing Market
 Magnification of the China Shock Through the U.S. Housing Market Robert Feenstra University of California, Davis and NBER Yuan Xu Tsinghua University Hong Ma Tsinghua University December 1, 2018 Abstract
Magnification of the China Shock Through the U.S. Housing Market Robert Feenstra University of California, Davis and NBER Yuan Xu Tsinghua University Hong Ma Tsinghua University December 1, 2018 Abstract
Identifying FDI Spillovers Online Appendix
 Identifying FDI Spillovers Online Appendix Yi Lu Tsinghua University and National University of Singapore, Zhigang Tao University of Hong Kong Lianming Zhu Waseda University This Version: December 2016
Identifying FDI Spillovers Online Appendix Yi Lu Tsinghua University and National University of Singapore, Zhigang Tao University of Hong Kong Lianming Zhu Waseda University This Version: December 2016
Supplemental Table I. WTO impact by industry
 Supplemental Table I. WTO impact by industry This table presents the influence of WTO accessions on each three-digit NAICS code based industry for the manufacturing sector. The WTO impact is estimated
Supplemental Table I. WTO impact by industry This table presents the influence of WTO accessions on each three-digit NAICS code based industry for the manufacturing sector. The WTO impact is estimated
ONLINE APPENDIX (NOT FOR PUBLICATION) Appendix A: Appendix Figures and Tables
 ONLINE APPENDIX (NOT FOR PUBLICATION) Appendix A: Appendix Figures and Tables 34 Figure A.1: First Page of the Standard Layout 35 Figure A.2: Second Page of the Credit Card Statement 36 Figure A.3: First
ONLINE APPENDIX (NOT FOR PUBLICATION) Appendix A: Appendix Figures and Tables 34 Figure A.1: First Page of the Standard Layout 35 Figure A.2: Second Page of the Credit Card Statement 36 Figure A.3: First
Import Competition and the Great U.S. Employment Sag of the 2000s
 Import Competition and the Great U.S. Employment Sag of the 2000s Daron Acemoglu David Autor David Dorn Gordon Hanson Brendan Price February 2015 From the Roaring 90 s to the Great Sag Growth of U.S. employment
Import Competition and the Great U.S. Employment Sag of the 2000s Daron Acemoglu David Autor David Dorn Gordon Hanson Brendan Price February 2015 From the Roaring 90 s to the Great Sag Growth of U.S. employment
Interest Rate Pass-Through: Mortgage Rates, Household Consumption, and Voluntary Deleveraging. Online Appendix
 Interest Rate Pass-Through: Mortgage Rates, Household Consumption, and Voluntary Deleveraging Marco Di Maggio, Amir Kermani, Benjamin J. Keys, Tomasz Piskorski, Rodney Ramcharan, Amit Seru, Vincent Yao
Interest Rate Pass-Through: Mortgage Rates, Household Consumption, and Voluntary Deleveraging Marco Di Maggio, Amir Kermani, Benjamin J. Keys, Tomasz Piskorski, Rodney Ramcharan, Amit Seru, Vincent Yao
Online Appendices for
 Online Appendices for From Made in China to Innovated in China : Necessity, Prospect, and Challenges Shang-Jin Wei, Zhuan Xie, and Xiaobo Zhang Journal of Economic Perspectives, (31)1, Winter 2017 Online
Online Appendices for From Made in China to Innovated in China : Necessity, Prospect, and Challenges Shang-Jin Wei, Zhuan Xie, and Xiaobo Zhang Journal of Economic Perspectives, (31)1, Winter 2017 Online
Investment and Employment Responses to State Adoption of Federal Accelerated Depreciation Policies
 Investment and Employment Responses to State Adoption of Federal Accelerated Depreciation Policies Eric Ohrn Grinnell College 72nd Annual Congress of the IIPF August 10, 2016 Introduction During the 2000s,
Investment and Employment Responses to State Adoption of Federal Accelerated Depreciation Policies Eric Ohrn Grinnell College 72nd Annual Congress of the IIPF August 10, 2016 Introduction During the 2000s,
Can Information Change Personal Retirement Savings? Evidence from Social Security Benefits Statement Mailings. Susan Payne Carter William Skimmyhorn
 Can Information Change Personal Retirement Savings? Evidence from Social Security Benefits Statement Mailings Susan Payne Carter William Skimmyhorn Online Appendix Appendix Table 1. Summary Statistics
Can Information Change Personal Retirement Savings? Evidence from Social Security Benefits Statement Mailings Susan Payne Carter William Skimmyhorn Online Appendix Appendix Table 1. Summary Statistics
Fabien Rozzi Technische Universität München. Junior Management Science 3(2) (2018) 33-56
 Fabien Rozzi Technische Universität München Junior Management Science 3(2) (2018) 33-56 Appendix 52 Appendix Tables Table 1: Selective Overview of Online Labor Platforms and Markets Platform Type/ Field
Fabien Rozzi Technische Universität München Junior Management Science 3(2) (2018) 33-56 Appendix 52 Appendix Tables Table 1: Selective Overview of Online Labor Platforms and Markets Platform Type/ Field
Stock Liquidity and Default Risk *
 Stock Liquidity and Default Risk * Jonathan Brogaard Dan Li Ying Xia Internet Appendix A1. Cox Proportional Hazard Model As a robustness test, we examine actual bankruptcies instead of the risk of default.
Stock Liquidity and Default Risk * Jonathan Brogaard Dan Li Ying Xia Internet Appendix A1. Cox Proportional Hazard Model As a robustness test, we examine actual bankruptcies instead of the risk of default.
The Labor Market Consequences of Adverse Financial Shocks
 13TH JACQUES POLAK ANNUAL RESEARCH CONFERENCE NOVEMBER 8 9, 2012 The Labor Market Consequences of Adverse Financial Shocks Tito Boeri Bocconi University and frdb Pietro Garibaldi University of Torino and
13TH JACQUES POLAK ANNUAL RESEARCH CONFERENCE NOVEMBER 8 9, 2012 The Labor Market Consequences of Adverse Financial Shocks Tito Boeri Bocconi University and frdb Pietro Garibaldi University of Torino and
Web Appendix: Do Arbitrageurs Amplify Economic Shocks?
 Web Appendix: Do Arbitrageurs Amplify Economic Shocks? Harrison Hong Princeton University Jeffrey D. Kubik Syracuse University Tal Fishman Parkcentral Capital Management We have carried out a number of
Web Appendix: Do Arbitrageurs Amplify Economic Shocks? Harrison Hong Princeton University Jeffrey D. Kubik Syracuse University Tal Fishman Parkcentral Capital Management We have carried out a number of
Firing Costs, Employment and Misallocation
 Firing Costs, Employment and Misallocation Evidence from Randomly Assigned Judges Omar Bamieh University of Vienna November 13th 2018 1 / 27 Why should we care about firing costs? Firing costs make it
Firing Costs, Employment and Misallocation Evidence from Randomly Assigned Judges Omar Bamieh University of Vienna November 13th 2018 1 / 27 Why should we care about firing costs? Firing costs make it
Early Retirement Incentives and Student Achievement. Maria D. Fitzpatrick and Michael F. Lovenheim. Online Appendix
 Early Retirement Incentives and Student Achievement Maria D. Fitzpatrick and Michael F. Lovenheim Online Appendix Table A-1. OLS Estimates of the Effect of the Early Retirement Incentive Program on the
Early Retirement Incentives and Student Achievement Maria D. Fitzpatrick and Michael F. Lovenheim Online Appendix Table A-1. OLS Estimates of the Effect of the Early Retirement Incentive Program on the
How Do Households Adjust to Trade Liberalization? Evidence from China s WTO Accession
 How Do Households Adjust to Trade Liberalization? Evidence from China s WTO Accession Mi Dai Beijing Normal University Wei Huang National University of Singapore Yifan Zhang Chinese University of Hong
How Do Households Adjust to Trade Liberalization? Evidence from China s WTO Accession Mi Dai Beijing Normal University Wei Huang National University of Singapore Yifan Zhang Chinese University of Hong
Response to Robert Feenstra, Hong Ma, and Yuan Xu s Comment on Autor, Dorn, and Hanson (AER 2013)
 Response to Robert Feenstra, Hong Ma, and Yuan Xu s Comment on Autor, Dorn, and Hanson (AER 2013) David Autor David Dorn Gordon Hanson April 2, 2017 A 2017 comment by Feenstra, Ma, and Xu (FMX) claims
Response to Robert Feenstra, Hong Ma, and Yuan Xu s Comment on Autor, Dorn, and Hanson (AER 2013) David Autor David Dorn Gordon Hanson April 2, 2017 A 2017 comment by Feenstra, Ma, and Xu (FMX) claims
institution Top 10 to 20 undergraduate
 Appendix Table A1 Who Responded to the Survey Dynamics of the Gender Gap for Young Professionals in the Financial and Corporate Sectors By Marianne Bertrand, Claudia Goldin, Lawrence F. Katz On-Line Appendix
Appendix Table A1 Who Responded to the Survey Dynamics of the Gender Gap for Young Professionals in the Financial and Corporate Sectors By Marianne Bertrand, Claudia Goldin, Lawrence F. Katz On-Line Appendix
Import Protection, Business Cycles, and Exchange Rates:
 Import Protection, Business Cycles, and Exchange Rates: Evidence from the Great Recession Chad P. Bown The World Bank Meredith A. Crowley Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago Preliminary, comments welcome Any
Import Protection, Business Cycles, and Exchange Rates: Evidence from the Great Recession Chad P. Bown The World Bank Meredith A. Crowley Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago Preliminary, comments welcome Any
Peer Effects in Retirement Decisions
 Peer Effects in Retirement Decisions Mario Meier 1 & Andrea Weber 2 1 University of Mannheim 2 Vienna University of Economics and Business, CEPR, IZA Meier & Weber (2016) Peers in Retirement 1 / 35 Motivation
Peer Effects in Retirement Decisions Mario Meier 1 & Andrea Weber 2 1 University of Mannheim 2 Vienna University of Economics and Business, CEPR, IZA Meier & Weber (2016) Peers in Retirement 1 / 35 Motivation
Organizing the Global Value Chain: Online Appendix
 Organizing the Global Value Chain: Online Appendix Pol Antràs Harvard University Davin Chor Singapore anagement University ay 23, 22 Abstract This online Appendix documents several detailed proofs from
Organizing the Global Value Chain: Online Appendix Pol Antràs Harvard University Davin Chor Singapore anagement University ay 23, 22 Abstract This online Appendix documents several detailed proofs from
How Do Households Adjust to Trade Liberalization? Evidence from China s WTO Accession
 How Do Households Adjust to Trade Liberalization? Evidence from China s WTO Accession Mi Dai, Wei Huang, Yifan Zhang December 15, 2017 Abstract We investigate the impacts of trade liberalization on household
How Do Households Adjust to Trade Liberalization? Evidence from China s WTO Accession Mi Dai, Wei Huang, Yifan Zhang December 15, 2017 Abstract We investigate the impacts of trade liberalization on household
Employment Adjustments to Increased Imports: Evidence from a Developing Country
 Employment Adjustments to Increased Imports: Evidence from a Developing Country Beyza Ural Marchand University of Alberta 2016 Introduction Motivation Motivation International trade is one of the most
Employment Adjustments to Increased Imports: Evidence from a Developing Country Beyza Ural Marchand University of Alberta 2016 Introduction Motivation Motivation International trade is one of the most
Online Appendix: Tariffs and Firm Performance in Ethiopia
 Online Appendix: Tariffs and Firm Performance in Ethiopia Arne Bigsten, Mulu Gebreeyesus and Måns Söderbom $ August 2015 Document description: This appendix contains additional material for the study Tariffs
Online Appendix: Tariffs and Firm Performance in Ethiopia Arne Bigsten, Mulu Gebreeyesus and Måns Söderbom $ August 2015 Document description: This appendix contains additional material for the study Tariffs
Really Uncertain Business Cycles
 Really Uncertain Business Cycles Nick Bloom (Stanford & NBER) Max Floetotto (McKinsey) Nir Jaimovich (Duke & NBER) Itay Saporta-Eksten (Stanford) Stephen J. Terry (Stanford) SITE, August 31 st 2011 1 Uncertainty
Really Uncertain Business Cycles Nick Bloom (Stanford & NBER) Max Floetotto (McKinsey) Nir Jaimovich (Duke & NBER) Itay Saporta-Eksten (Stanford) Stephen J. Terry (Stanford) SITE, August 31 st 2011 1 Uncertainty
Introduction to Econometrics (3 rd Updated Edition) Solutions to Odd- Numbered End- of- Chapter Exercises: Chapter 6
 Introduction to Econometrics (3 rd Updated Edition) by James H. Stock and Mark W. Watson Solutions to Odd- Numbered End- of- Chapter Exercises: Chapter 6 (This version August 17, 014) 015 Pearson Education,
Introduction to Econometrics (3 rd Updated Edition) by James H. Stock and Mark W. Watson Solutions to Odd- Numbered End- of- Chapter Exercises: Chapter 6 (This version August 17, 014) 015 Pearson Education,
Mining closures, gender, and employment reallocations: the case of UK coal mines
 Mining closures, gender, and employment reallocations: the case of UK coal mines Fernando Aragon (SFU), Juan Pablo Rud (Royal Holloway) and Gerhard Toews (Oxcarre) November 24, 2016 Collapse In December
Mining closures, gender, and employment reallocations: the case of UK coal mines Fernando Aragon (SFU), Juan Pablo Rud (Royal Holloway) and Gerhard Toews (Oxcarre) November 24, 2016 Collapse In December
Measures of Participation in Global Value Chains. and Global Business Cycles
 Measures of Participation in Global Value Chains and Global Business Cycles (Draft for comments) Zhi Wang University of International Business and Economics & George Mason University Shang-Jin Wei Columbia
Measures of Participation in Global Value Chains and Global Business Cycles (Draft for comments) Zhi Wang University of International Business and Economics & George Mason University Shang-Jin Wei Columbia
The Margins of Global Sourcing: Theory and Evidence from U.S. Firms by Pol Antràs, Teresa C. Fort and Felix Tintelnot
 The Margins of Global Sourcing: Theory and Evidence from U.S. Firms by Pol Antràs, Teresa C. Fort and Felix Tintelnot Online Theory Appendix Not for Publication) Equilibrium in the Complements-Pareto Case
The Margins of Global Sourcing: Theory and Evidence from U.S. Firms by Pol Antràs, Teresa C. Fort and Felix Tintelnot Online Theory Appendix Not for Publication) Equilibrium in the Complements-Pareto Case
Gains from Trade 1-3
 Trade and Income We discusses the study by Frankel and Romer (1999). Does trade cause growth? American Economic Review 89(3), 379-399. Frankel and Romer examine the impact of trade on real income using
Trade and Income We discusses the study by Frankel and Romer (1999). Does trade cause growth? American Economic Review 89(3), 379-399. Frankel and Romer examine the impact of trade on real income using
Figure 2.1 The Longitudinal Employer-Household Dynamics Program
 Figure 2.1 The Longitudinal Employer-Household Dynamics Program Demographic Surveys Household Record Household-ID Data Integration Record Person-ID Employer-ID Data Economic Censuses and Surveys Census
Figure 2.1 The Longitudinal Employer-Household Dynamics Program Demographic Surveys Household Record Household-ID Data Integration Record Person-ID Employer-ID Data Economic Censuses and Surveys Census
Supplement materials for Early network events in the later success of Chinese entrepreneurs
 Supplement materials for Early network events in the later success of Chinese entrepreneurs Figure S1 Kinds of Event Sequences by Years Since Business Founding A1 A2 A3 B4 B5 B6 B7 C8 C9 C10 Profile A
Supplement materials for Early network events in the later success of Chinese entrepreneurs Figure S1 Kinds of Event Sequences by Years Since Business Founding A1 A2 A3 B4 B5 B6 B7 C8 C9 C10 Profile A
NOT FOR PUBLICATION. Theory Appendix for The China Syndrome. Small Open Economy Model
 NOT FOR PUBLICATION Theory Appendix for The China Syndrome Small Open Economy Model In this appendix, we develop a general equilibrium model of how increased import competition from China affects employment
NOT FOR PUBLICATION Theory Appendix for The China Syndrome Small Open Economy Model In this appendix, we develop a general equilibrium model of how increased import competition from China affects employment
Supplemental Appendix for Cost Pass-Through to Higher Ethanol Blends at the Pump: Evidence from Minnesota Gas Station Data.
 November 18, 2018 Supplemental Appendix for Cost Pass-Through to Higher Ethanol Blends at the Pump: Evidence from Minnesota Gas Station Data Jing Li, MIT James H. Stock, Harvard University and NBER This
November 18, 2018 Supplemental Appendix for Cost Pass-Through to Higher Ethanol Blends at the Pump: Evidence from Minnesota Gas Station Data Jing Li, MIT James H. Stock, Harvard University and NBER This
Credit Cycles and Financial Verification
 Online Appendix to: Credit Cycles and Financial Verification Petro Lisowsky University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Massachusetts Institute of Technology Sloan School of Management and Norwegian Center
Online Appendix to: Credit Cycles and Financial Verification Petro Lisowsky University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Massachusetts Institute of Technology Sloan School of Management and Norwegian Center
Internet Appendix for Corporate Cash Shortfalls and Financing Decisions. Rongbing Huang and Jay R. Ritter. August 31, 2017
 Internet Appendix for Corporate Cash Shortfalls and Financing Decisions Rongbing Huang and Jay R. Ritter August 31, 2017 Our Figure 1 finds that firms that have a larger are more likely to run out of cash
Internet Appendix for Corporate Cash Shortfalls and Financing Decisions Rongbing Huang and Jay R. Ritter August 31, 2017 Our Figure 1 finds that firms that have a larger are more likely to run out of cash
H-share IPO date. A-share IPO. No. Name Sector H-Shares
 Internet Appendix 1: Sample Cross-Listed Stocks The table below reports all 53 firms with cross-listed A-shares and H-shares in our sample. The time for cross-listing is in boldface. No. Name Sector H-Shares
Internet Appendix 1: Sample Cross-Listed Stocks The table below reports all 53 firms with cross-listed A-shares and H-shares in our sample. The time for cross-listing is in boldface. No. Name Sector H-Shares
The Great Recession and Job Loss Spillovers
 Policy Research Working Paper 7543 WPS7543 The Great Recession and Job Loss Spillovers Impact of Tradable Employment Shocks on Supporting Services Ha Nguyen Shawheen Rezaei Public Disclosure Authorized
Policy Research Working Paper 7543 WPS7543 The Great Recession and Job Loss Spillovers Impact of Tradable Employment Shocks on Supporting Services Ha Nguyen Shawheen Rezaei Public Disclosure Authorized
Who is internationally diversified? Evidence from the 401(k) plans of 296 firms*
 Online Appendix for Who is internationally diversified? Evidence from the 401(k) plans of 296 firms* Geert Bekaert a,b, Kenton Hoyem c, Wei-Yin Hu c, Enrichetta Ravina a, * a Columbia Business School,
Online Appendix for Who is internationally diversified? Evidence from the 401(k) plans of 296 firms* Geert Bekaert a,b, Kenton Hoyem c, Wei-Yin Hu c, Enrichetta Ravina a, * a Columbia Business School,
1 Payroll Tax Legislation 2. 2 Severance Payments Legislation 3
 Web Appendix Contents 1 Payroll Tax Legislation 2 2 Severance Payments Legislation 3 3 Difference-in-Difference Results 5 3.1 Senior Workers, 1997 Change............................... 5 3.2 Young Workers,
Web Appendix Contents 1 Payroll Tax Legislation 2 2 Severance Payments Legislation 3 3 Difference-in-Difference Results 5 3.1 Senior Workers, 1997 Change............................... 5 3.2 Young Workers,
Online Appendix. Moral Hazard in Health Insurance: Do Dynamic Incentives Matter? by Aron-Dine, Einav, Finkelstein, and Cullen
 Online Appendix Moral Hazard in Health Insurance: Do Dynamic Incentives Matter? by Aron-Dine, Einav, Finkelstein, and Cullen Appendix A: Analysis of Initial Claims in Medicare Part D In this appendix we
Online Appendix Moral Hazard in Health Insurance: Do Dynamic Incentives Matter? by Aron-Dine, Einav, Finkelstein, and Cullen Appendix A: Analysis of Initial Claims in Medicare Part D In this appendix we
Working Paper Series / Cahiers de recherche
 Working Paper Series / Cahiers de recherche August 2018 août Productivity Gains from International Trade: Does Firm Age Matter? M. Jahangir Alam (HEC Montréal / Statistics Canada) Productivity Partnership
Working Paper Series / Cahiers de recherche August 2018 août Productivity Gains from International Trade: Does Firm Age Matter? M. Jahangir Alam (HEC Montréal / Statistics Canada) Productivity Partnership
Housing Market Trends
 Housing Market Trends Lessons from International Comparisons Grace Wong The Wharton School, Univ of Penn wongg@wharton.upenn.edu May 10, 2007 International comparisons The impact of macroeconomic variables
Housing Market Trends Lessons from International Comparisons Grace Wong The Wharton School, Univ of Penn wongg@wharton.upenn.edu May 10, 2007 International comparisons The impact of macroeconomic variables
Plant Scale and Exchange-Rate-Induced Productivity Growth. May 25, Abstract
 Plant Scale and Exchange-Rate-Induced Productivity Growth Jen Baggs, Eugene Beaulieu + and Loretta Fung May 25, 2007 Preliminary Draft: Please do not quote without permission Abstract In the last two decades,
Plant Scale and Exchange-Rate-Induced Productivity Growth Jen Baggs, Eugene Beaulieu + and Loretta Fung May 25, 2007 Preliminary Draft: Please do not quote without permission Abstract In the last two decades,
R&D, International Sourcing and the Joint Impact on Firm Performance
 R&D, International Sourcing and the Joint Impact on Firm Performance Esther Ann Bøler Andreas Moxnes Karen Helene Ulltveit-Moe Published in American Economic Review 105(12): 3704-3739 Abstract This paper
R&D, International Sourcing and the Joint Impact on Firm Performance Esther Ann Bøler Andreas Moxnes Karen Helene Ulltveit-Moe Published in American Economic Review 105(12): 3704-3739 Abstract This paper
Online Appendix. Manisha Goel. April 2016
 Online Appendix Manisha Goel April 2016 Appendix A Appendix A.1 Empirical Appendix Data Sources U.S. Imports and Exports Data The imports data for the United States are obtained from the Center for International
Online Appendix Manisha Goel April 2016 Appendix A Appendix A.1 Empirical Appendix Data Sources U.S. Imports and Exports Data The imports data for the United States are obtained from the Center for International
Internet Appendix for: Does Going Public Affect Innovation?
 Internet Appendix for: Does Going Public Affect Innovation? July 3, 2014 I Variable Definitions Innovation Measures 1. Citations - Number of citations a patent receives in its grant year and the following
Internet Appendix for: Does Going Public Affect Innovation? July 3, 2014 I Variable Definitions Innovation Measures 1. Citations - Number of citations a patent receives in its grant year and the following
Solution to Exercise E5.
 Solution to Exercise E5. The Multiple Regression Model. Estimation. Exercise E5.1. Beach umbrella rental Part I. Simple Linear Regression Model. a. Regression model: U t = β 1 + β 2 T t + u t t = 1,...,
Solution to Exercise E5. The Multiple Regression Model. Estimation. Exercise E5.1. Beach umbrella rental Part I. Simple Linear Regression Model. a. Regression model: U t = β 1 + β 2 T t + u t t = 1,...,
Deviations from Optimal Corporate Cash Holdings and the Valuation from a Shareholder s Perspective
 Deviations from Optimal Corporate Cash Holdings and the Valuation from a Shareholder s Perspective Zhenxu Tong * University of Exeter Abstract The tradeoff theory of corporate cash holdings predicts that
Deviations from Optimal Corporate Cash Holdings and the Valuation from a Shareholder s Perspective Zhenxu Tong * University of Exeter Abstract The tradeoff theory of corporate cash holdings predicts that
Online Appendix Long-Lasting Effects of Socialist Education
 Online Appendix Long-Lasting Effects of Socialist Education Nicola Fuchs-Schündeln Goethe University Frankfurt, CEPR, and IZA Paolo Masella University of Sussex and IZA December 11, 2015 1 Temporary Disruptions
Online Appendix Long-Lasting Effects of Socialist Education Nicola Fuchs-Schündeln Goethe University Frankfurt, CEPR, and IZA Paolo Masella University of Sussex and IZA December 11, 2015 1 Temporary Disruptions
Venting Out: Exports During a Domestic Slump
 Venting Out: Exports During a Domestic Slump Miguel Almunia Pol Antràs David Lopez-Rodriguez Eduardo Morales CUNEF Harvard University Banco de España Princeton University November 2018 Almunia, Antras,
Venting Out: Exports During a Domestic Slump Miguel Almunia Pol Antràs David Lopez-Rodriguez Eduardo Morales CUNEF Harvard University Banco de España Princeton University November 2018 Almunia, Antras,
The causal effects of an industrial policy
 The causal effects of an industrial policy Chiara Criscuolo (OECD), Ralf Martin (Imperial), Henry Overman (LSE) and John Van Reenen (LSE) Bruegel,6 th December 2012 1 MOTIVATION Industrial policies pervasive
The causal effects of an industrial policy Chiara Criscuolo (OECD), Ralf Martin (Imperial), Henry Overman (LSE) and John Van Reenen (LSE) Bruegel,6 th December 2012 1 MOTIVATION Industrial policies pervasive
Loss Aversion and Seller Behavior: Evidence from the Housing Market
 Loss Aversion and Seller Behavior: Evidence from the Housing Market Chris Mayer (The Wharton School) Joint with David Genesove (Hebrew University) Behavioral Economics Summer Camp August 5, 2002 Published
Loss Aversion and Seller Behavior: Evidence from the Housing Market Chris Mayer (The Wharton School) Joint with David Genesove (Hebrew University) Behavioral Economics Summer Camp August 5, 2002 Published
Does Inequality Reduce Happiness? Evidence from the States of the USA from the 1970s to the 1990s
 For Milan, March 2003. To be presented by Andrew Oswald, Warwick University. Email: andrew.oswald@warwick.ac.uk Does Inequality Reduce Happiness? Evidence from the States of the USA from the 1970s to the
For Milan, March 2003. To be presented by Andrew Oswald, Warwick University. Email: andrew.oswald@warwick.ac.uk Does Inequality Reduce Happiness? Evidence from the States of the USA from the 1970s to the
This document consists of three sections: Section IA.1 examines the sensitivity of our
 Internet Appendix for Determinants and Consequences of Information Processing Delay: Evidence from Thomson Reuters Institutional Brokers Estimate System This document consists of three sections: Section
Internet Appendix for Determinants and Consequences of Information Processing Delay: Evidence from Thomson Reuters Institutional Brokers Estimate System This document consists of three sections: Section
Friendship at Work: Can Peer Effects Catalyze Female Entrepreneurship? Erica Field, Seema Jayachandran, Rohini Pande, and Natalia Rigol
 Friendship at Work: Can Peer Effects Catalyze Female Entrepreneurship? Erica Field, Seema Jayachandran, Rohini Pande, and Natalia Rigol Online Appendix Appendix Table 1: Heterogeneous Impact of Business
Friendship at Work: Can Peer Effects Catalyze Female Entrepreneurship? Erica Field, Seema Jayachandran, Rohini Pande, and Natalia Rigol Online Appendix Appendix Table 1: Heterogeneous Impact of Business
A Rising Tide Lifts All Boats? IT growth in the US over the last 30 years
 A Rising Tide Lifts All Boats? IT growth in the US over the last 30 years Nicholas Bloom (Stanford) and Nicola Pierri (Stanford)1 March 25 th 2017 1) Executive Summary Using a new survey of IT usage from
A Rising Tide Lifts All Boats? IT growth in the US over the last 30 years Nicholas Bloom (Stanford) and Nicola Pierri (Stanford)1 March 25 th 2017 1) Executive Summary Using a new survey of IT usage from
Long Term Effects of Temporary Labor Demand: Free Trade Zones, Female Education and Marriage Market Outcomes in the Dominican Republic
 Long Term Effects of Temporary Labor Demand: Free Trade Zones, Female Education and Marriage Market Outcomes in the Dominican Republic Maria Micaela Sviatschi Columbia University June 15, 2015 Introduction
Long Term Effects of Temporary Labor Demand: Free Trade Zones, Female Education and Marriage Market Outcomes in the Dominican Republic Maria Micaela Sviatschi Columbia University June 15, 2015 Introduction
Volume 37, Issue 3. The effects of capital buffers on profitability: An empirical study. Benjamin M Tabak Universidade Católica de Brasília
 Volume 37, Issue 3 The effects of capital buffers on profitability: An empirical study Benjamin M Tabak Universidade Católica de Brasília Dimas M Fazio London Business School Joao M. T. Amaral Universidade
Volume 37, Issue 3 The effects of capital buffers on profitability: An empirical study Benjamin M Tabak Universidade Católica de Brasília Dimas M Fazio London Business School Joao M. T. Amaral Universidade
Estimating the U.S. Consumer Gains from Chinese Import Penetration
 Estimating the U.S. Consumer Gains from Chinese Import Penetration Liang Bai University of Edinburgh Sebastian Stumpner Université de Montréal February 15, 2017 Abstract This paper investigates the size
Estimating the U.S. Consumer Gains from Chinese Import Penetration Liang Bai University of Edinburgh Sebastian Stumpner Université de Montréal February 15, 2017 Abstract This paper investigates the size
TRADE ADJUSTMENT: WORKER-LEVEL EVIDENCE* David H. Autor David Dorn Gordon H. Hanson Jae Song
 TRADE ADJUSTMENT: WORKER-LEVEL EVIDENCE* David H. Autor David Dorn Gordon H. Hanson Jae Song We analyze the effect of exposure to international trade on earnings and employment of U.S. workers from 1992
TRADE ADJUSTMENT: WORKER-LEVEL EVIDENCE* David H. Autor David Dorn Gordon H. Hanson Jae Song We analyze the effect of exposure to international trade on earnings and employment of U.S. workers from 1992
Health Returns to Public Funds Across Tiers of Local Government: The Case of the Philippine Devolution
 Health Returns to Public Funds Across Tiers of Local Government: The Case of the Philippine Devolution Sharon Maccini* Ph.D. Candidate in Health Policy Harvard University May 2005 Abstract In this paper,
Health Returns to Public Funds Across Tiers of Local Government: The Case of the Philippine Devolution Sharon Maccini* Ph.D. Candidate in Health Policy Harvard University May 2005 Abstract In this paper,
Loan Originations and Defaults in the Mortgage Crisis: The Role of the Middle Class. Internet Appendix. Manuel Adelino, Duke University
 Loan Originations and Defaults in the Mortgage Crisis: The Role of the Middle Class Internet Appendix Manuel Adelino, Duke University Antoinette Schoar, MIT and NBER Felipe Severino, Dartmouth College
Loan Originations and Defaults in the Mortgage Crisis: The Role of the Middle Class Internet Appendix Manuel Adelino, Duke University Antoinette Schoar, MIT and NBER Felipe Severino, Dartmouth College
Does Crop Insurance Enrollment Exacerbate the Negative Effects of Extreme Heat? A Farm-level Analysis
 Does Crop Insurance Enrollment Exacerbate the Negative Effects of Extreme Heat? A Farm-level Analysis Madhav Regmi and Jesse B. Tack Department of Agricultural Economics, Kansas State University August
Does Crop Insurance Enrollment Exacerbate the Negative Effects of Extreme Heat? A Farm-level Analysis Madhav Regmi and Jesse B. Tack Department of Agricultural Economics, Kansas State University August
The Spillover Effect of Municipal Bond Insurers on Uninsured Municipal Bonds
 The Spillover Effect of Municipal Bond Insurers on Uninsured Municipal Bonds January 8, 2017 Abstract This paper examines the adverse spillover effect of the municipal bond insurance company on uninsured
The Spillover Effect of Municipal Bond Insurers on Uninsured Municipal Bonds January 8, 2017 Abstract This paper examines the adverse spillover effect of the municipal bond insurance company on uninsured
Company Stock Price Reactions to the 2016 Election Shock: Trump, Taxes, and Trade INTERNET APPENDIX. August 11, 2017
 Company Stock Price Reactions to the 2016 Election Shock: Trump, Taxes, and Trade INTERNET APPENDIX August 11, 2017 A. News coverage and major events Section 5 of the paper examines the speed of pricing
Company Stock Price Reactions to the 2016 Election Shock: Trump, Taxes, and Trade INTERNET APPENDIX August 11, 2017 A. News coverage and major events Section 5 of the paper examines the speed of pricing
EXAMINATIONS OF THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY
 EXAMINATIONS OF THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY HIGHER CERTIFICATE IN STATISTICS, 2010 MODULE 7 : Time series and index numbers Time allowed: One and a half hours Candidates should answer THREE questions.
EXAMINATIONS OF THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY HIGHER CERTIFICATE IN STATISTICS, 2010 MODULE 7 : Time series and index numbers Time allowed: One and a half hours Candidates should answer THREE questions.
Public-private sector pay differential in UK: A recent update
 Public-private sector pay differential in UK: A recent update by D H Blackaby P D Murphy N C O Leary A V Staneva No. 2013-01 Department of Economics Discussion Paper Series Public-private sector pay differential
Public-private sector pay differential in UK: A recent update by D H Blackaby P D Murphy N C O Leary A V Staneva No. 2013-01 Department of Economics Discussion Paper Series Public-private sector pay differential
Appendix F K F M M Y L Y Y F
 Appendix Theoretical Model In the analysis of our article, we test whether there are increasing returns in U.S. manufacturing and what is driving these returns. In the first step, we estimate overall returns
Appendix Theoretical Model In the analysis of our article, we test whether there are increasing returns in U.S. manufacturing and what is driving these returns. In the first step, we estimate overall returns
Can t Pay or Won t Pay? Unemployment, Negative Equity, and Strategic Default ONLINE APPENDIX
 Can t Pay or Won t Pay? Unemployment, Negative Equity, and Strategic Default ONLINE APPENDIX Kristopher Gerardi FRB Atlanta Kyle Herkenhoff University of Minnesota Paul Willen FRB Boston May 2017 Lee Ohanian
Can t Pay or Won t Pay? Unemployment, Negative Equity, and Strategic Default ONLINE APPENDIX Kristopher Gerardi FRB Atlanta Kyle Herkenhoff University of Minnesota Paul Willen FRB Boston May 2017 Lee Ohanian
Internet Appendix for. Using Product Text to Capture Vertical Integration and Firm Boundaries
 Internet Appendix for Using Product Text to Capture Vertical Integration and Firm Boundaries (Not for publication) Laurent Frésard, Gerard Hoberg, and Gordon Phillips August 28, 2017 This appendix contains
Internet Appendix for Using Product Text to Capture Vertical Integration and Firm Boundaries (Not for publication) Laurent Frésard, Gerard Hoberg, and Gordon Phillips August 28, 2017 This appendix contains
Online Appendix to. The Value of Crowdsourced Earnings Forecasts
 Online Appendix to The Value of Crowdsourced Earnings Forecasts This online appendix tabulates and discusses the results of robustness checks and supplementary analyses mentioned in the paper. A1. Estimating
Online Appendix to The Value of Crowdsourced Earnings Forecasts This online appendix tabulates and discusses the results of robustness checks and supplementary analyses mentioned in the paper. A1. Estimating
Web Appendix Figure 1. Operational Steps of Experiment
 Web Appendix Figure 1. Operational Steps of Experiment 57,533 direct mail solicitations with randomly different offer interest rates sent out to former clients. 5,028 clients go to branch and apply for
Web Appendix Figure 1. Operational Steps of Experiment 57,533 direct mail solicitations with randomly different offer interest rates sent out to former clients. 5,028 clients go to branch and apply for
Tobin's Q and the Gains from Takeovers
 THE JOURNAL OF FINANCE VOL. LXVI, NO. 1 MARCH 1991 Tobin's Q and the Gains from Takeovers HENRI SERVAES* ABSTRACT This paper analyzes the relation between takeover gains and the q ratios of targets and
THE JOURNAL OF FINANCE VOL. LXVI, NO. 1 MARCH 1991 Tobin's Q and the Gains from Takeovers HENRI SERVAES* ABSTRACT This paper analyzes the relation between takeover gains and the q ratios of targets and
Financial Literacy, Social Networks, & Index Insurance
 Financial Literacy, Social Networks, and Index-Based Weather Insurance Xavier Giné, Dean Karlan and Mũthoni Ngatia Building Financial Capability January 2013 Introduction Introduction Agriculture in developing
Financial Literacy, Social Networks, and Index-Based Weather Insurance Xavier Giné, Dean Karlan and Mũthoni Ngatia Building Financial Capability January 2013 Introduction Introduction Agriculture in developing
Trade Policy Uncertainty and Stock Returns
 Trade Policy Uncertainty and Stock Returns Marcelo Bianconi Tufts Federico Esposito Tufts February 2019 Marco Sammon Kellogg Abstract This paper documents new stylized facts on the effects of trade policy
Trade Policy Uncertainty and Stock Returns Marcelo Bianconi Tufts Federico Esposito Tufts February 2019 Marco Sammon Kellogg Abstract This paper documents new stylized facts on the effects of trade policy
Online Appendix What Does Health Reform Mean for the Healthcare Industry? Evidence from the Massachusetts Special Senate Election.
 Online Appendix What Does Health Reform Mean for the Healthcare Industry? Evidence from the Massachusetts Special Senate Election. BY MOHAMAD M. AL-ISSISS AND NOLAN H. MILLER Appendix A: Extended Event
Online Appendix What Does Health Reform Mean for the Healthcare Industry? Evidence from the Massachusetts Special Senate Election. BY MOHAMAD M. AL-ISSISS AND NOLAN H. MILLER Appendix A: Extended Event
Online Appendix Only Funding forms, market conditions and dynamic effects of government R&D subsidies: evidence from China
 Online Appendix Only Funding forms, market conditions and dynamic effects of government R&D subsidies: evidence from China By Di Guo a, Yan Guo b, Kun Jiang c Appendix A: TFP estimation Firm TFP is measured
Online Appendix Only Funding forms, market conditions and dynamic effects of government R&D subsidies: evidence from China By Di Guo a, Yan Guo b, Kun Jiang c Appendix A: TFP estimation Firm TFP is measured
Beggar-Thy-Neighbor or Beneficial Spillover: Effect of Exchange Rates on GVC Trade
 Beggar-Thy-Neighbor or Beneficial Spillover: Effect of Exchange Rates on GVC Trade 5 th IMF WB WTO Joint Trade Research Workshop November 30, 2016 Gee Hee Hong (IMF) (with Kevin Cheng, Dulani Seneviratne,
Beggar-Thy-Neighbor or Beneficial Spillover: Effect of Exchange Rates on GVC Trade 5 th IMF WB WTO Joint Trade Research Workshop November 30, 2016 Gee Hee Hong (IMF) (with Kevin Cheng, Dulani Seneviratne,
Tax Gap Map Tax Year 2006 ($ billions)
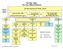 Tax Gap Map Tax Year 2006 ($ billions) Total Tax Liability $2,660 Gross Tax Gap: $450 (Voluntary Compliance Rate = 83.1%) Tax Paid Voluntarily & Timely: $2,210 Enforced & Other Late Payments of Tax $65
Tax Gap Map Tax Year 2006 ($ billions) Total Tax Liability $2,660 Gross Tax Gap: $450 (Voluntary Compliance Rate = 83.1%) Tax Paid Voluntarily & Timely: $2,210 Enforced & Other Late Payments of Tax $65
Intellectual Property-Related Preferential Trade Agreements and the Composition of Trade
 Intellectual Property-Related Preferential Trade Agreements and the Composition of Trade Keith E. Maskus and William Ridley Presentation at IPSDM November 14, 2017 Introduction International economists
Intellectual Property-Related Preferential Trade Agreements and the Composition of Trade Keith E. Maskus and William Ridley Presentation at IPSDM November 14, 2017 Introduction International economists
Incidence of Social Security Contributions: Evidence from France
 Incidence of Social Security Contributions: Evidence from France Antoine Bozio, Thomas Breda et Julien Grenet Paris School of Economics PSE Public and Labour Economics Seminar Paris, 15 September 2016
Incidence of Social Security Contributions: Evidence from France Antoine Bozio, Thomas Breda et Julien Grenet Paris School of Economics PSE Public and Labour Economics Seminar Paris, 15 September 2016
Advanced Topics in Trade
 Advanced Topics in Trade Lectures 10-11 - Trade and Inequality Heiwai Tang - SAIS April 11-18, 2017 Today s Agenda Evidence on inequality in developed countries (developing countries next lecture). Can
Advanced Topics in Trade Lectures 10-11 - Trade and Inequality Heiwai Tang - SAIS April 11-18, 2017 Today s Agenda Evidence on inequality in developed countries (developing countries next lecture). Can
Equality and Fertility: Evidence from China
 Equality and Fertility: Evidence from China Chen Wei Center for Population and Development Studies, People s University of China Liu Jinju School of Labour and Human Resources, People s University of China
Equality and Fertility: Evidence from China Chen Wei Center for Population and Development Studies, People s University of China Liu Jinju School of Labour and Human Resources, People s University of China
Errata for Actuarial Mathematics for Life Contingent Risks
 Errata for Actuarial Mathematics for Life Contingent Risks David C M Dickson, Mary R Hardy, Howard R Waters Note: These errata refer to the first printing of Actuarial Mathematics for Life Contingent Risks.
Errata for Actuarial Mathematics for Life Contingent Risks David C M Dickson, Mary R Hardy, Howard R Waters Note: These errata refer to the first printing of Actuarial Mathematics for Life Contingent Risks.
