Consumption and Investment. Graduate Macroeconomics I ECON Cunningham
|
|
|
- Wilfred Floyd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Consumpion and Invesmen Graduae Macroeconomics I ECON Cunningham
2 Keynesian Theory Recall ha Keynes argues ha C= C 0 +cy, wih C 0 > 0 and he average propensiy o consume (APC = C/Y) is greaer han he marginal propensiy o consume (MPC = c): C/Y = (C 0 + cy)/y > c, or (1) APC > MPC (2) Moreover, he APC should no be a consan if C 0 is no zero. If C 0 = 0, hen he consumpion funcion reduces o he absolue income hypohesis consumpion is proporionae o income which is no consisen wih Keynes. 2
3 Empirical Verificaion? Keynes followers esimaed he consumpion funcion for he U.S. using he daa from : C = Yd C 0 =26.5 billion > 0 APC > MPC Increases in consumer spending seemed o be less han increases in disposable income, supporing MPC < 1. 3
4 Kuznes Consumpion Daa Kuznes, Simon. Uses of Naional Income in Peace and War, Occasional Paper 6. NY: NBER, Time series esimaes of consumpion and naional income Overlapping decades , 5 year seps Each esimae is a decade average Kuznes, Simon. Naional Produc Since NY: NBER, Exended daa backward o
5 Kuznes Sudy (1) Assumpions: Personal axes and ransfer paymens are small (in his period) Therefore, i is reasonable o use oal income (GNP) as a proxy for disposable income. If a relaionship beween consumpion and disposable income exiss, here should also be a relaionship beween consumpion and GNP. 5
6 Kuznes Sudy (2) Resuls: (1946 sudy) Beween , real income expanded o seven (7) imes is 1869 level ($9.3 billion o $69 billion) Bu he average propensiy o consume ranged beween and Tha is, APC did no vary significanly in he face of vasly expanding income. Problem! 6
7 Kuznes Sudy (3) Years Y C C/Y
8 Second Failure Predicions of pos-wwii period are grossly wrong Keynesian Theory argues ha he average propensiy o save (APS) rises wih income (S = S 0 +sy). Higher pos-war incomes should imply excess saving. Excess saving is more han can be absorbed by invesmen. Therefore he excess saving will resul over-invesmen or hoarding, and herefore in unemploymen. Will we go sraigh back o he Depression? Comparison of he forecass wih he acual resuls sugges ha: consumpion was under -prediced saving was over -prediced IMPLICATION: major deerminans in he behavioral equaions mus be missing! 8
9 9
10 Reconciliaion wih Keynes Theory? (1) Arhur Smihies, Economerica, Uses per capia Yd and C, and a ime rend. Argues ha he Cons. Funcion is really Keynesian, bu jus looks Kuznesian because of he shifs in he funcion. C * Kuznes = 1925 = 1924 = 1923 Says he daa poins jus happen o line up o fi Kuznes consumpion funcion. Y * 10
11 Smihies Resul Smihies esimaes yielded he equaion: C * = Y * (-1922) Or equivalenly, C * = [ (-1922)] Y * Which is of he form C = C 0 + cy, he equaion of a line. 11
12 Reconciliaion (2) Reasons for shifs: Migraion of people from farms o ciies (mus buy goods) Shif in disribuion oward greaer equaliy (poorer save less) Rise in he perceived sandard of living (luxuries become necessiies) For hese reasons each agen (per capia) should increase his or her consumpion. 12
13 Modigliani ges involved Modigliani, Franco. Flucuaions in he saving-income raion: a problem in economic forecasing, in Sudies in Income and Wealh vol. 11, Conference on Research in Income and Wealh. NY: NBER, 1949, pp When Franco Modigliani (1949) esimaes Smihies relaion over a differen ime period, he analysis compleely breaks down. Bu, Modigliani is hooked... 13
14 More Problems 14
15 15
16 Habi Persisence Theory Noe: Duesenberry and Modigliani boh presened similar resuls a he Economeric Sociey Meeing of Duesenberry (1947) noed ha in 1935 dissaving grew as a percenage of income. Dissaving was greaer in1935 han in he relaively prosperous year Why? Households mus sacrifice saving o defend (aemp o mainain) heir sandard of living. Duesenberry and Modigliani can reconcile he shor-run and long-run consumpion funcions, bu canno explain he negaive relaionship beweem curren income and consumpion ha someimes occurs. 16
17 Duesenberry s Habi Persisence Duesenberry assumes ha he consumers defend heir highes level of consumpion. Thus: S Y = Y F Y peak For no oher reason han simpliciy, he assumes lineariy. S Y = a + Y b Y peak 17
18 18 More More Duesenberry Duesenberry Noe: Y C Y S and Y C Y S so C S Y = + = + = 1 1 = peak Y Y b a Y C ) (1 So ha peak Y Y Y b a C = 1 If Y grows seadily, hen ) (1,, ) (1, 1 bk a wih Y C or Y bk a C and k Y Y Y Y peak = = = = = λ λ Kuzne s Kuzne s Resul Resul
19 Dusesenberry s Rache Effec C C Y 19
20 Brown s Habi Persisence Brown. Habi Persisence and Lags in Consumer Behavior, Economerica 20 (July 1952). Brown ries: C = a 0 + a Y 1 + a 2 C peak and C = a 0 + a Y 1 + a 2 C 1 He finds he second specificaion slighly superior and more easily consisen wih he downward shifs. (Economeric ess.) 20
21 Hamburger and Wealh Theories Hamburger (1951, 1954, 1955) Argues an alernaive explanaion for slugglishness ies consumer response formally o ineremporal uiliy maximizaion. Household ies curren consumpion o a lifeime plan of consumpion: u = u ( c, c +, c + 2,..., c + 1 i Wealh arises from propery wealh and human wealh (invesmens and income). Households consume less under an esae moive. Explains habi persisence rigorously. ) 21
22 Life Cycle Hypohesis (LCH) Franco Modigliani, Alber Ando, and Richard Bloomberg Assumes ha each represenaive agen will die, and knows: when he/she will die, how many periods T he/she will live, and How much his/her life-ime income will be. The consumer smoohs consumpion expendiure over his/her life, spending 1/T of his/her life-ime income each period. 22
23 LCH (2) The consumpion funcion implied by his logic is: 1 C = + T [ 1 1e Y + ( N 1) Y A ] wih he aggregae esimable consumpion funcion look like his: 1 1e C = by 1 + b2y + b3 A 23
24 Income and Consumpion LCH deah Consumpion Saving Income Dissaving T 24
25 Tesing he LCH If he funcion form looks like his: 1 1e C = by 1 + b2y + b3 Ando and Modigliani argue ha expeced fuure labor income is proporional o curren income, so ha he funcion can be reduced o: 1 C = ( b1 + b2β ) Y + b3 When hey esimae his funcion, hey ge: 1 + A A C = 0.72Y 0. 06A 25
26 Criicisms of LCH The households, a all imes, have a definie, conscious vision of: The family s fuure size and composiion, including he life expecancy of each member, The enire lifeime profile of he labor income of each member afer he applicable axes, The presen and fuure exen and erms of any credi available, and The fuure emergencies, opporuniies, and social pressures which migh affec is consumpion spending. I does no ake ino accoun liquidiy consrains. 26
27 Policy Implicaions of LCH Changes in curren income have a srong effec on curren consumpion ONLY if hey affec expeced lifeime income. In Q2 1975, a one-ime ax rebae of $8 billion was paid ou o axpayers o simulae AD. The rebae had lile effec. Maybe George W. hadn heard abou his? The only way here can be a significan effec is if here is a srong liquidiy consrain operaing. This has implicaions for moneary policy. 27
28 Permanen Income Hypohesis (PIH) Milon Friedman (A Theory of he Consumpion Funcion. Princeon Univ. Press, 1957) Assumpions: Perfec cerainy abou: Fuure receips Fuure ineres raes Fuure prices, ec. People save o reduce flucuaions in expendiures People are immoral (or leave bequess) Individual s uiliy funcion: u = u(c,c 1 ) where c is curren period consumpion and c 1 is nex period consumpion. 28
29 PIH, Coninued Assume posiive bu diminishing reurns and posiive cross parials. Also assume ha u is homogeneous of degree one. The budge consrain is: 1 1 c + c1 = q + q = 1+ r 1+ r w e Where q,q 1 are planned real receips from human and nonhuman wealh in each period, and w e is expeced wealh. Opimizaion yields: c = i c 1 = A i ( r ) w B e ( r ) w e 29
30 PIH, Coninued This implies ha consumpion depends upon income only if he income affecs expeced wealh. Therefore, changes in income need no affec curren consumpion. We may view y p = rw e as permanen income wha really affecs he consumpion decision. c = c P + c T y = y P + y T 30
31 PIH, Coninued Where is has permanen (p) and ransiory (T) componens. For each individual agen: c P = k(r,v,x)y P Where r = rae of reurn v = he raio of human o nonhuman wealh (permanen income) x = demographics By summing across individuals (aggregaing), we have: C P = κy P, ha permanen consumpion is proporional o permanen income. 31
32 PIH, Coninued When reduced o a esimable form, his becomes: c = κa 0 Y + λc -1 + θ Which looks remarkably like he Brown (1952) resul. The resul can explain he unusual changes in MPC due o changes in income: If income changes, individuals end o decrease saving (or dissave) o mainain a more uniform spending paern over heir lives. 32
33 PIH (2) Individuals updae adapively heir esimaes of permanen income based on changes in curren income. Tha is, hey learn. Y p p = Y p ( ), 1 + j Y Y 1 0 < j < 1 The resul is ha changes o curren income have lile effec on curren consumpion unless he individual believes ha he changes has long-erm consequences. 33
34 Invesmen Spending Invesmen is he change in he capial sock I n, = K K -1 = Ne Invesmen I g, = K K -1 δk = Gross Invesmen (δk is depreciaion) I = I(r,E) = I(r) Wha abou he expecaions erm? 34
35 The Acceleraor Model (1) Aemps o capure some measure of curren business condiions (growh of he economy or lack of i), and use ha o explain he level of invesmen. 35
36 Acceleraor Model (2) The desired capial sock is proporional o he level of oupu: d K = αy Invesmen is he process of moving from he curren level of capial o a desired level: d I K K n, = 1 We assume ha whaever he capial sock ended up being las period was he level of capial ha businesses acually waned: K d 1 = K 1 = αy 1 36
37 Acceleraor Model (3) This allows us o rewrie: d In, = K K 1 As d I K K = αy αy I n, = 1 1 = α( Y Y 1) n, = α Y Thus invesmen is relaed o he rae of change in oupu. If he economy is growing rapidly, hen invesmen grows rapidly. If he economy is no growing, hen invesmen slows, and ne invesmen (afer depreciaion) may acually be negaive. 37
38 Acceleraor Model (4) As a resul of adjusmen coss and pracical ime-o-build consideraions, he enire adjusmen o he desired capial sock may no be done in one period. The firms may only finance a parial adjusmen. Le λ be he fracion of he gap beween he desired and acual capial sock ha he firms pursue. This leads o: Or, equivalenly, I n d, = λ( K K 1), 0 < λ < 1. I λ( αy K 1) n, = This is referred o as he flexible acceleraor model of invesmen. 38
39 Cos of Capial Approach MEC all over again? Recall ha Keynes argued ha business decision makers compare he expeced revenue sream from he new capial o he cos of capial. The user cos of capial is he oal cos o he firm of employing an addiional uni of capial for one period. The new capial migh be funded by borrowing, selling sock shares, reained earnings, ec. 39
40 Cos of Capial Approach (2) This suggess an invesmen funcion of he form: I I Y, CC, K ) n, = ( 1 If a firm invesed is reained earnings or monies raised by selling sock shares, i could earn he curren ineres rae. So his mus be he opporuniy cos we are looking for. Invesmen mus be relaed o his ineres rae specifically, o he real ineres rae φ, where: φ = r p& e 40
41 Cos of Capial Approach (3) Par of he user cos of capial is he depreciaion rae δ. e So CC = φ + δ = r p& + δ. Bu some governmen programs provide subsidies o firms for purchasing capial. For example, he gov may offer invesmen ax credis. If he porion paid by governmen is τ, hen he effecive cos of capial o he firm is: CC e = ( 1 τ )( r p& + δ ). This leads o an invesmen funcion of he form: e I I Y, r, p&, τ, K ) n, = ( 1 41
Inventory Investment. Investment Decision and Expected Profit. Lecture 5
 Invenory Invesmen. Invesmen Decision and Expeced Profi Lecure 5 Invenory Accumulaion 1. Invenory socks 1) Changes in invenory holdings represen an imporan and highly volaile ype of invesmen spending. 2)
Invenory Invesmen. Invesmen Decision and Expeced Profi Lecure 5 Invenory Accumulaion 1. Invenory socks 1) Changes in invenory holdings represen an imporan and highly volaile ype of invesmen spending. 2)
Economic Growth Continued: From Solow to Ramsey
 Economic Growh Coninued: From Solow o Ramsey J. Bradford DeLong May 2008 Choosing a Naional Savings Rae Wha can we say abou economic policy and long-run growh? To keep maers simple, le us assume ha he
Economic Growh Coninued: From Solow o Ramsey J. Bradford DeLong May 2008 Choosing a Naional Savings Rae Wha can we say abou economic policy and long-run growh? To keep maers simple, le us assume ha he
THE MALAYSIAN PRIVATE CONSUMER EXPENDITURE: RECONCILING BETWEEN THEORIES AND DATA. Eu Chye Tan
 THE MALAYSIAN PRIVATE CONSUMER EXPENDITURE: RECONCILING BETWEEN THEORIES AND DATA Eu Chye Tan Faculy of Economics & Adminisraion Universiy of Malaya I. Overview This paper aemps o examine he Malaysian
THE MALAYSIAN PRIVATE CONSUMER EXPENDITURE: RECONCILING BETWEEN THEORIES AND DATA Eu Chye Tan Faculy of Economics & Adminisraion Universiy of Malaya I. Overview This paper aemps o examine he Malaysian
UCLA Department of Economics Fall PhD. Qualifying Exam in Macroeconomic Theory
 UCLA Deparmen of Economics Fall 2016 PhD. Qualifying Exam in Macroeconomic Theory Insrucions: This exam consiss of hree pars, and you are o complee each par. Answer each par in a separae bluebook. All
UCLA Deparmen of Economics Fall 2016 PhD. Qualifying Exam in Macroeconomic Theory Insrucions: This exam consiss of hree pars, and you are o complee each par. Answer each par in a separae bluebook. All
Macroeconomics. Part 3 Macroeconomics of Financial Markets. Lecture 8 Investment: basic concepts
 Macroeconomics Par 3 Macroeconomics of Financial Markes Lecure 8 Invesmen: basic conceps Moivaion General equilibrium Ramsey and OLG models have very simple assumpions ha invesmen ino producion capial
Macroeconomics Par 3 Macroeconomics of Financial Markes Lecure 8 Invesmen: basic conceps Moivaion General equilibrium Ramsey and OLG models have very simple assumpions ha invesmen ino producion capial
Process of convergence dr Joanna Wolszczak-Derlacz. Lecture 4 and 5 Solow growth model (a)
 Process of convergence dr Joanna Wolszczak-Derlacz ecure 4 and 5 Solow growh model a Solow growh model Rober Solow "A Conribuion o he Theory of Economic Growh." Quarerly Journal of Economics 70 February
Process of convergence dr Joanna Wolszczak-Derlacz ecure 4 and 5 Solow growh model a Solow growh model Rober Solow "A Conribuion o he Theory of Economic Growh." Quarerly Journal of Economics 70 February
Wealth Effects (Plural) and U.S. Consumer Spending *
 Wealh Effecs (Plural) and U.S. Consumer Spending * John Duca, Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas & Oberlin College John Muellbauer, Oxford Universiy & INET Anhony Murphy, Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas December
Wealh Effecs (Plural) and U.S. Consumer Spending * John Duca, Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas & Oberlin College John Muellbauer, Oxford Universiy & INET Anhony Murphy, Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas December
CHAPTER CHAPTER26. Fiscal Policy: A Summing Up. Prepared by: Fernando Quijano and Yvonn Quijano
 Fiscal Policy: A Summing Up Prepared by: Fernando Quijano and vonn Quijano CHAPTER CHAPTER26 2006 Prenice Hall usiness Publishing Macroeconomics, 4/e Olivier lanchard Chaper 26: Fiscal Policy: A Summing
Fiscal Policy: A Summing Up Prepared by: Fernando Quijano and vonn Quijano CHAPTER CHAPTER26 2006 Prenice Hall usiness Publishing Macroeconomics, 4/e Olivier lanchard Chaper 26: Fiscal Policy: A Summing
You should turn in (at least) FOUR bluebooks, one (or more, if needed) bluebook(s) for each question.
 UCLA Deparmen of Economics Spring 05 PhD. Qualifying Exam in Macroeconomic Theory Insrucions: This exam consiss of hree pars, and each par is worh 0 poins. Pars and have one quesion each, and Par 3 has
UCLA Deparmen of Economics Spring 05 PhD. Qualifying Exam in Macroeconomic Theory Insrucions: This exam consiss of hree pars, and each par is worh 0 poins. Pars and have one quesion each, and Par 3 has
Output: The Demand for Goods and Services
 IN CHAPTER 15 how o incorporae dynamics ino he AD-AS model we previously sudied how o use he dynamic AD-AS model o illusrae long-run economic growh how o use he dynamic AD-AS model o race ou he effecs
IN CHAPTER 15 how o incorporae dynamics ino he AD-AS model we previously sudied how o use he dynamic AD-AS model o illusrae long-run economic growh how o use he dynamic AD-AS model o race ou he effecs
CHAPTER CHAPTER18. Openness in Goods. and Financial Markets. Openness in Goods, and Financial Markets. Openness in Goods,
 Openness in Goods and Financial Markes CHAPTER CHAPTER18 Openness in Goods, and Openness has hree disinc dimensions: 1. Openness in goods markes. Free rade resricions include ariffs and quoas. 2. Openness
Openness in Goods and Financial Markes CHAPTER CHAPTER18 Openness in Goods, and Openness has hree disinc dimensions: 1. Openness in goods markes. Free rade resricions include ariffs and quoas. 2. Openness
Appendix B: DETAILS ABOUT THE SIMULATION MODEL. contained in lookup tables that are all calculated on an auxiliary spreadsheet.
 Appendix B: DETAILS ABOUT THE SIMULATION MODEL The simulaion model is carried ou on one spreadshee and has five modules, four of which are conained in lookup ables ha are all calculaed on an auxiliary
Appendix B: DETAILS ABOUT THE SIMULATION MODEL The simulaion model is carried ou on one spreadshee and has five modules, four of which are conained in lookup ables ha are all calculaed on an auxiliary
Macroeconomics II A dynamic approach to short run economic fluctuations. The DAD/DAS model.
 Macroeconomics II A dynamic approach o shor run economic flucuaions. The DAD/DAS model. Par 2. The demand side of he model he dynamic aggregae demand (DAD) Inflaion and dynamics in he shor run So far,
Macroeconomics II A dynamic approach o shor run economic flucuaions. The DAD/DAS model. Par 2. The demand side of he model he dynamic aggregae demand (DAD) Inflaion and dynamics in he shor run So far,
Li Gan Guan Gong Michael Hurd. April, 2006
 Ne Inergeneraional Transfers from an Increase in Social Securiy Benefis Li Gan Guan Gong Michael Hurd April, 2006 ABSTRACT When he age of deah is uncerain, individuals will leave bequess even if hey have
Ne Inergeneraional Transfers from an Increase in Social Securiy Benefis Li Gan Guan Gong Michael Hurd April, 2006 ABSTRACT When he age of deah is uncerain, individuals will leave bequess even if hey have
Stylized fact: high cyclical correlation of monetary aggregates and output
 SIMPLE DSGE MODELS OF MONEY PART II SEPTEMBER 27, 2011 Inroducion BUSINESS CYCLE IMPLICATIONS OF MONEY Sylized fac: high cyclical correlaion of moneary aggregaes and oupu Convenional Keynesian view: nominal
SIMPLE DSGE MODELS OF MONEY PART II SEPTEMBER 27, 2011 Inroducion BUSINESS CYCLE IMPLICATIONS OF MONEY Sylized fac: high cyclical correlaion of moneary aggregaes and oupu Convenional Keynesian view: nominal
Problem Set 1 Answers. a. The computer is a final good produced and sold in Hence, 2006 GDP increases by $2,000.
 Social Analysis 10 Spring 2006 Problem Se 1 Answers Quesion 1 a. The compuer is a final good produced and sold in 2006. Hence, 2006 GDP increases by $2,000. b. The bread is a final good sold in 2006. 2006
Social Analysis 10 Spring 2006 Problem Se 1 Answers Quesion 1 a. The compuer is a final good produced and sold in 2006. Hence, 2006 GDP increases by $2,000. b. The bread is a final good sold in 2006. 2006
Spring 2011 Social Sciences 7418 University of Wisconsin-Madison
 Economics 32, Sec. 1 Menzie D. Chinn Spring 211 Social Sciences 7418 Universiy of Wisconsin-Madison Noes for Econ 32-1 FALL 21 Miderm 1 Exam The Fall 21 Econ 32-1 course used Hall and Papell, Macroeconomics
Economics 32, Sec. 1 Menzie D. Chinn Spring 211 Social Sciences 7418 Universiy of Wisconsin-Madison Noes for Econ 32-1 FALL 21 Miderm 1 Exam The Fall 21 Econ 32-1 course used Hall and Papell, Macroeconomics
Aid, Policies, and Growth
 Aid, Policies, and Growh By Craig Burnside and David Dollar APPENDIX ON THE NEOCLASSICAL MODEL Here we use a simple neoclassical growh model o moivae he form of our empirical growh equaion. Our inenion
Aid, Policies, and Growh By Craig Burnside and David Dollar APPENDIX ON THE NEOCLASSICAL MODEL Here we use a simple neoclassical growh model o moivae he form of our empirical growh equaion. Our inenion
a. If Y is 1,000, M is 100, and the growth rate of nominal money is 1 percent, what must i and P be?
 Problem Se 4 ECN 101 Inermediae Macroeconomics SOLUTIONS Numerical Quesions 1. Assume ha he demand for real money balance (M/P) is M/P = 0.6-100i, where is naional income and i is he nominal ineres rae.
Problem Se 4 ECN 101 Inermediae Macroeconomics SOLUTIONS Numerical Quesions 1. Assume ha he demand for real money balance (M/P) is M/P = 0.6-100i, where is naional income and i is he nominal ineres rae.
ECONOMIC GROWTH. Student Assessment. Macroeconomics II. Class 1
 Suden Assessmen You will be graded on he basis of In-class aciviies (quizzes worh 30 poins) which can be replaced wih he number of marks from he regular uorial IF i is >=30 (capped a 30, i.e. marks from
Suden Assessmen You will be graded on he basis of In-class aciviies (quizzes worh 30 poins) which can be replaced wih he number of marks from he regular uorial IF i is >=30 (capped a 30, i.e. marks from
TAX SMOOTHING: TESTS ON INDONESIAN DATA
 TAX SMOOTHING: TESTS ON INDONESIAN DATA Rudi Kurniawan Deparmen of Economics Macquarie Universiy Macquarie Park, Sydney NSW 3 Ausralia rudi.kurniawan@mq.edu.au Absrac This paper conribues o he lieraure
TAX SMOOTHING: TESTS ON INDONESIAN DATA Rudi Kurniawan Deparmen of Economics Macquarie Universiy Macquarie Park, Sydney NSW 3 Ausralia rudi.kurniawan@mq.edu.au Absrac This paper conribues o he lieraure
1. To express the production function in terms of output per worker and capital per worker, divide by N: K f N
 THE LOG RU Exercise 8 The Solow Model Suppose an economy is characerized by he aggregae producion funcion / /, where is aggregae oupu, is capial and is employmen. Suppose furher ha aggregae saving is proporional
THE LOG RU Exercise 8 The Solow Model Suppose an economy is characerized by he aggregae producion funcion / /, where is aggregae oupu, is capial and is employmen. Suppose furher ha aggregae saving is proporional
Final Exam Answers Exchange Rate Economics
 Kiel Insiu für Welwirhschaf Advanced Sudies in Inernaional Economic Policy Research Spring 2005 Menzie D. Chinn Final Exam Answers Exchange Rae Economics This exam is 1 ½ hours long. Answer all quesions.
Kiel Insiu für Welwirhschaf Advanced Sudies in Inernaional Economic Policy Research Spring 2005 Menzie D. Chinn Final Exam Answers Exchange Rae Economics This exam is 1 ½ hours long. Answer all quesions.
EVA NOPAT Capital charges ( = WACC * Invested Capital) = EVA [1 P] each
![EVA NOPAT Capital charges ( = WACC * Invested Capital) = EVA [1 P] each EVA NOPAT Capital charges ( = WACC * Invested Capital) = EVA [1 P] each](/thumbs/92/109302006.jpg) VBM Soluion skech SS 2012: Noe: This is a soluion skech, no a complee soluion. Disribuion of poins is no binding for he correcor. 1 EVA, free cash flow, and financial raios (45) 1.1 EVA wihou adjusmens
VBM Soluion skech SS 2012: Noe: This is a soluion skech, no a complee soluion. Disribuion of poins is no binding for he correcor. 1 EVA, free cash flow, and financial raios (45) 1.1 EVA wihou adjusmens
Aggregate Demand Aggregate Supply 1 Y. f P
 ublic Aairs 974 Menzie D. Chinn Fall 202 Social Sciences 748 Universiy o Wisconsin-Madison Aggregae Demand Aggregae Supply. The Basic Model wih Expeced Inlaion Se o Zero Consider he hillips curve relaionship:
ublic Aairs 974 Menzie D. Chinn Fall 202 Social Sciences 748 Universiy o Wisconsin-Madison Aggregae Demand Aggregae Supply. The Basic Model wih Expeced Inlaion Se o Zero Consider he hillips curve relaionship:
Macroeconomics II THE AD-AS MODEL. A Road Map
 Macroeconomics II Class 4 THE AD-AS MODEL Class 8 A Road Map THE AD-AS MODEL: MICROFOUNDATIONS 1. Aggregae Supply 1.1 The Long-Run AS Curve 1.2 rice and Wage Sickiness 2.1 Aggregae Demand 2.2 Equilibrium
Macroeconomics II Class 4 THE AD-AS MODEL Class 8 A Road Map THE AD-AS MODEL: MICROFOUNDATIONS 1. Aggregae Supply 1.1 The Long-Run AS Curve 1.2 rice and Wage Sickiness 2.1 Aggregae Demand 2.2 Equilibrium
Econ 546 Lecture 4. The Basic New Keynesian Model Michael Devereux January 2011
 Econ 546 Lecure 4 The Basic New Keynesian Model Michael Devereux January 20 Road map for his lecure We are evenually going o ge 3 equaions, fully describing he NK model The firs wo are jus he same as before:
Econ 546 Lecure 4 The Basic New Keynesian Model Michael Devereux January 20 Road map for his lecure We are evenually going o ge 3 equaions, fully describing he NK model The firs wo are jus he same as before:
FINAL EXAM EC26102: MONEY, BANKING AND FINANCIAL MARKETS MAY 11, 2004
 FINAL EXAM EC26102: MONEY, BANKING AND FINANCIAL MARKETS MAY 11, 2004 This exam has 50 quesions on 14 pages. Before you begin, please check o make sure ha your copy has all 50 quesions and all 14 pages.
FINAL EXAM EC26102: MONEY, BANKING AND FINANCIAL MARKETS MAY 11, 2004 This exam has 50 quesions on 14 pages. Before you begin, please check o make sure ha your copy has all 50 quesions and all 14 pages.
OPTIMUM FISCAL AND MONETARY POLICY USING THE MONETARY OVERLAPPING GENERATION MODELS
 Kuwai Chaper of Arabian Journal of Business and Managemen Review Vol. 3, No.6; Feb. 2014 OPTIMUM FISCAL AND MONETARY POLICY USING THE MONETARY OVERLAPPING GENERATION MODELS Ayoub Faramarzi 1, Dr.Rahim
Kuwai Chaper of Arabian Journal of Business and Managemen Review Vol. 3, No.6; Feb. 2014 OPTIMUM FISCAL AND MONETARY POLICY USING THE MONETARY OVERLAPPING GENERATION MODELS Ayoub Faramarzi 1, Dr.Rahim
Economics 301 Fall Name. Answer all questions. Each sub-question is worth 7 points (except 4d).
 Name Answer all quesions. Each sub-quesion is worh 7 poins (excep 4d). 1. (42 ps) The informaion below describes he curren sae of a growing closed economy. Producion funcion: α 1 Y = K ( Q N ) α Producion
Name Answer all quesions. Each sub-quesion is worh 7 poins (excep 4d). 1. (42 ps) The informaion below describes he curren sae of a growing closed economy. Producion funcion: α 1 Y = K ( Q N ) α Producion
Supplement to Chapter 3
 Supplemen o Chaper 3 I. Measuring Real GD and Inflaion If here were only one good in he world, anchovies, hen daa and prices would deermine real oupu and inflaion perfecly: GD Q ; GD Q. + + + Then, he
Supplemen o Chaper 3 I. Measuring Real GD and Inflaion If here were only one good in he world, anchovies, hen daa and prices would deermine real oupu and inflaion perfecly: GD Q ; GD Q. + + + Then, he
ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS. CHAPTERS 6-9; (Blanchard)
 ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS CHAPTERS 6-9; 18-20 (Blanchard) Quesion 1 Discuss in deail he following: a) The sacrifice raio b) Okun s law c) The neuraliy of money d) Bargaining power e) NAIRU f) Wage indexaion
ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS CHAPTERS 6-9; 18-20 (Blanchard) Quesion 1 Discuss in deail he following: a) The sacrifice raio b) Okun s law c) The neuraliy of money d) Bargaining power e) NAIRU f) Wage indexaion
Unemployment and Phillips curve
 Unemploymen and Phillips curve 2 of The Naural Rae of Unemploymen and he Phillips Curve Figure 1 Inflaion versus Unemploymen in he Unied Saes, 1900 o 1960 During he period 1900 o 1960 in he Unied Saes,
Unemploymen and Phillips curve 2 of The Naural Rae of Unemploymen and he Phillips Curve Figure 1 Inflaion versus Unemploymen in he Unied Saes, 1900 o 1960 During he period 1900 o 1960 in he Unied Saes,
Two ways to we learn the model
 Two ways o we learn he model Graphical Inerface: Model Algebra: The equaion you used in your SPREADSHEET. Corresponding equaion in he MODEL. There are four core relaionships in he model: you have already
Two ways o we learn he model Graphical Inerface: Model Algebra: The equaion you used in your SPREADSHEET. Corresponding equaion in he MODEL. There are four core relaionships in he model: you have already
THE TWO-PERIOD MODEL (CONTINUED)
 GOVERNMENT AND FISCAL POLICY IN THE TWO-PERIOD MODEL (CONTINUED) MAY 25, 20 A Governmen in he Two-Period Model ADYNAMIC MODEL OF THE GOVERNMENT So far only consumers in our wo-period framework Inroduce
GOVERNMENT AND FISCAL POLICY IN THE TWO-PERIOD MODEL (CONTINUED) MAY 25, 20 A Governmen in he Two-Period Model ADYNAMIC MODEL OF THE GOVERNMENT So far only consumers in our wo-period framework Inroduce
Chapter 8 Consumption and Portfolio Choice under Uncertainty
 George Alogoskoufis, Dynamic Macroeconomic Theory, 2015 Chaper 8 Consumpion and Porfolio Choice under Uncerainy In his chaper we examine dynamic models of consumer choice under uncerainy. We coninue, as
George Alogoskoufis, Dynamic Macroeconomic Theory, 2015 Chaper 8 Consumpion and Porfolio Choice under Uncerainy In his chaper we examine dynamic models of consumer choice under uncerainy. We coninue, as
The macroeconomic effects of fiscal policy in Greece
 The macroeconomic effecs of fiscal policy in Greece Dimiris Papageorgiou Economic Research Deparmen, Bank of Greece Naional and Kapodisrian Universiy of Ahens May 22, 23 Email: dpapag@aueb.gr, and DPapageorgiou@bankofgreece.gr.
The macroeconomic effecs of fiscal policy in Greece Dimiris Papageorgiou Economic Research Deparmen, Bank of Greece Naional and Kapodisrian Universiy of Ahens May 22, 23 Email: dpapag@aueb.gr, and DPapageorgiou@bankofgreece.gr.
The Economic Impact of the Proposed Gasoline Tax Cut In Connecticut
 The Economic Impac of he Proposed Gasoline Tax Cu In Connecicu By Hemana Shresha, Research Assisan Bobur Alimov, Research Assisan Sanley McMillen, Manager, Research Projecs June 21, 2000 CONNECTICUT CENTER
The Economic Impac of he Proposed Gasoline Tax Cu In Connecicu By Hemana Shresha, Research Assisan Bobur Alimov, Research Assisan Sanley McMillen, Manager, Research Projecs June 21, 2000 CONNECTICUT CENTER
Chapter VI. Consumption Function
 Macroeconomics 1 Ch VI. Consumpion Theory Secoral Analysis Chaper VI. Consumpion Funcion As elsewhere, he Keynesians and he classical economiss have compleely differen views on consumpion. The consumpion
Macroeconomics 1 Ch VI. Consumpion Theory Secoral Analysis Chaper VI. Consumpion Funcion As elsewhere, he Keynesians and he classical economiss have compleely differen views on consumpion. The consumpion
SMALL MENU COSTS AND LARGE BUSINESS CYCLES: AN EXTENSION OF THE MANKIW MODEL
 SMALL MENU COSTS AND LARGE BUSINESS CYCLES: AN EXTENSION OF THE MANKIW MODEL 2 Hiranya K. Nah, Sam Houson Sae Universiy Rober Srecher, Sam Houson Sae Universiy ABSTRACT Using a muli-period general equilibrium
SMALL MENU COSTS AND LARGE BUSINESS CYCLES: AN EXTENSION OF THE MANKIW MODEL 2 Hiranya K. Nah, Sam Houson Sae Universiy Rober Srecher, Sam Houson Sae Universiy ABSTRACT Using a muli-period general equilibrium
Problem 1 / 25 Problem 2 / 25 Problem 3 / 30 Problem 4 / 20 TOTAL / 100
 Deparmen of Economics Universiy of Maryland Economics 325 Inermediae Macroeconomic Analysis Final Exam Professor Sanjay Chugh Spring 2009 May 16, 2009 NAME: TA S NAME: The Exam has a oal of four (4) problems
Deparmen of Economics Universiy of Maryland Economics 325 Inermediae Macroeconomic Analysis Final Exam Professor Sanjay Chugh Spring 2009 May 16, 2009 NAME: TA S NAME: The Exam has a oal of four (4) problems
Economics 2450A: Public Economics Section 9: Linear Capital Taxation
 Economics 2450A: Public Economics Secion 9: Linear Capial Taxaion Maeo Paradisi November 7, 206 In his secion we inroduce a framework o sudy opimal linear capial axaion. We firs focus on a wo-period model,
Economics 2450A: Public Economics Secion 9: Linear Capial Taxaion Maeo Paradisi November 7, 206 In his secion we inroduce a framework o sudy opimal linear capial axaion. We firs focus on a wo-period model,
Government Expenditure Composition and Growth in Chile
 Governmen Expendiure Composiion and Growh in Chile January 2007 Carlos J. García Cenral Bank of Chile Saniago Herrera World Bank Jorge E. Resrepo Cenral Bank of Chile Organizaion of he presenaion:. Inroducion
Governmen Expendiure Composiion and Growh in Chile January 2007 Carlos J. García Cenral Bank of Chile Saniago Herrera World Bank Jorge E. Resrepo Cenral Bank of Chile Organizaion of he presenaion:. Inroducion
Problem 1 / 25 Problem 2 / 25 Problem 3 / 11 Problem 4 / 15 Problem 5 / 24 TOTAL / 100
 Deparmen of Economics Universiy of Maryland Economics 35 Inermediae Macroeconomic Analysis Miderm Exam Suggesed Soluions Professor Sanjay Chugh Fall 008 NAME: The Exam has a oal of five (5) problems and
Deparmen of Economics Universiy of Maryland Economics 35 Inermediae Macroeconomic Analysis Miderm Exam Suggesed Soluions Professor Sanjay Chugh Fall 008 NAME: The Exam has a oal of five (5) problems and
ECO 301 MACROECONOMIC THEORY UNIVERSITY OF MIAMI DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Instructor: Dr. S. Nuray Akin
 ECO 301 MACROECONOMIC THEORY UNIVERSITY OF MIAMI DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Insrucor: Dr. S. Nuray Akin Name: ID: Insrucions: This exam consiss of 12 pages; please check your examinaion
ECO 301 MACROECONOMIC THEORY UNIVERSITY OF MIAMI DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Insrucor: Dr. S. Nuray Akin Name: ID: Insrucions: This exam consiss of 12 pages; please check your examinaion
Empirical analysis on China money multiplier
 Aug. 2009, Volume 8, No.8 (Serial No.74) Chinese Business Review, ISSN 1537-1506, USA Empirical analysis on China money muliplier SHANG Hua-juan (Financial School, Shanghai Universiy of Finance and Economics,
Aug. 2009, Volume 8, No.8 (Serial No.74) Chinese Business Review, ISSN 1537-1506, USA Empirical analysis on China money muliplier SHANG Hua-juan (Financial School, Shanghai Universiy of Finance and Economics,
(a) Assume that the entrepreneur is willing to undertake the project, and analyze the problem from the point of view of the outside investor.
 Problem Se # Soluions Course 4.454 Macro IV TA: Todd Gormley, gormley@mi.edu Disribued: November 9, 004 Due: Tuesday, November 3, 004 [in class]. Financial Consrains (via Cosly Sae Verificaion) Consider
Problem Se # Soluions Course 4.454 Macro IV TA: Todd Gormley, gormley@mi.edu Disribued: November 9, 004 Due: Tuesday, November 3, 004 [in class]. Financial Consrains (via Cosly Sae Verificaion) Consider
A NOTE ON BUSINESS CYCLE NON-LINEARITY IN U.S. CONSUMPTION 247
 Journal of Applied Economics, Vol. VI, No. 2 (Nov 2003), 247-253 A NOTE ON BUSINESS CYCLE NON-LINEARITY IN U.S. CONSUMPTION 247 A NOTE ON BUSINESS CYCLE NON-LINEARITY IN U.S. CONSUMPTION STEVEN COOK *
Journal of Applied Economics, Vol. VI, No. 2 (Nov 2003), 247-253 A NOTE ON BUSINESS CYCLE NON-LINEARITY IN U.S. CONSUMPTION 247 A NOTE ON BUSINESS CYCLE NON-LINEARITY IN U.S. CONSUMPTION STEVEN COOK *
Commentary: Housing, Credit and Consumer Expenditure
 Commenary: Housing, Credi and Consumer Expendiure Sydney C. Ludvigson The subjec of his working session is housing and consumer behavior. As emphasized by John Muellbauer, one possible way in which house
Commenary: Housing, Credi and Consumer Expendiure Sydney C. Ludvigson The subjec of his working session is housing and consumer behavior. As emphasized by John Muellbauer, one possible way in which house
PRESS RELEASE EURO AREA ECONOMIC AND FINANCIAL DEVELOPMENTS BY INSTITUTIONAL SECTOR - FIRST QUARTER August 2012
 1 Augus 212 PRESS RELEASE EURO AREA ECONOMIC AND FINANCIAL DEVELOPMENTS BY INSTITUTIONAL SECTOR - FIRST QUARTER 212 In he firs quarer of 212, he annual growh rae 1 of households gross disposable income
1 Augus 212 PRESS RELEASE EURO AREA ECONOMIC AND FINANCIAL DEVELOPMENTS BY INSTITUTIONAL SECTOR - FIRST QUARTER 212 In he firs quarer of 212, he annual growh rae 1 of households gross disposable income
Section 4 The Exchange Rate in the Long Run
 Secion 4 he Exchange Rae in he Long Run 1 Conen Objecives Purchasing Power Pariy A Long-Run PPP Model he Real Exchange Rae Summary 2 Objecives o undersand he law of one price and purchasing power pariy
Secion 4 he Exchange Rae in he Long Run 1 Conen Objecives Purchasing Power Pariy A Long-Run PPP Model he Real Exchange Rae Summary 2 Objecives o undersand he law of one price and purchasing power pariy
Anticipation Effects in Fiscal
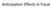 Anicipaion Effecs in Fiscal Ramey QJE (211) .5.4.5.6.7 1 Defense Spending During Korean War Defense Spending During Vienam War 1948 1949 195 1951 1952 1953 1954 1955 1964 1965 1966 1967 1968 1969 197 -.1
Anicipaion Effecs in Fiscal Ramey QJE (211) .5.4.5.6.7 1 Defense Spending During Korean War Defense Spending During Vienam War 1948 1949 195 1951 1952 1953 1954 1955 1964 1965 1966 1967 1968 1969 197 -.1
Money in a Real Business Cycle Model
 Money in a Real Business Cycle Model Graduae Macro II, Spring 200 The Universiy of Nore Dame Professor Sims This documen describes how o include money ino an oherwise sandard real business cycle model.
Money in a Real Business Cycle Model Graduae Macro II, Spring 200 The Universiy of Nore Dame Professor Sims This documen describes how o include money ino an oherwise sandard real business cycle model.
Exam 1. Econ520. Spring 2017
 Exam 1. Econ520. Spring 2017 Professor Luz Hendricks UNC Insrucions: Answer all quesions. Clearly number your answers. Wrie legibly. Do no wrie your answers on he quesion shees. Explain your answers do
Exam 1. Econ520. Spring 2017 Professor Luz Hendricks UNC Insrucions: Answer all quesions. Clearly number your answers. Wrie legibly. Do no wrie your answers on he quesion shees. Explain your answers do
San Francisco State University ECON 560 Summer 2018 Problem set 3 Due Monday, July 23
 San Francisco Sae Universiy Michael Bar ECON 56 Summer 28 Problem se 3 Due Monday, July 23 Name Assignmen Rules. Homework assignmens mus be yped. For insrucions on how o ype equaions and mah objecs please
San Francisco Sae Universiy Michael Bar ECON 56 Summer 28 Problem se 3 Due Monday, July 23 Name Assignmen Rules. Homework assignmens mus be yped. For insrucions on how o ype equaions and mah objecs please
Money/monetary policy issues an enduring fascination in macroeconomics. How can/should central bank control the economy? Should it/can it at all?
 SIMPLE DSGE MODELS OF MONEY PART I SEPTEMBER 22, 211 Inroducion BASIC ISSUES Money/moneary policy issues an enduring fascinaion in macroeconomics How can/should cenral bank conrol he economy? Should i/can
SIMPLE DSGE MODELS OF MONEY PART I SEPTEMBER 22, 211 Inroducion BASIC ISSUES Money/moneary policy issues an enduring fascinaion in macroeconomics How can/should cenral bank conrol he economy? Should i/can
Optimal Tax-Timing and Asset Allocation when Tax Rebates on Capital Losses are Limited
 Opimal Tax-Timing and Asse Allocaion when Tax Rebaes on Capial Losses are Limied Marcel Marekwica This version: January 15, 2007 Absrac Since Consaninides (1983) i is well known ha in a marke where capial
Opimal Tax-Timing and Asse Allocaion when Tax Rebaes on Capial Losses are Limied Marcel Marekwica This version: January 15, 2007 Absrac Since Consaninides (1983) i is well known ha in a marke where capial
Suggested Template for Rolling Schemes for inclusion in the future price regulation of Dublin Airport
 Suggesed Templae for Rolling Schemes for inclusion in he fuure price regulaion of Dublin Airpor. In line wih sandard inernaional regulaory pracice, he regime operaed since 00 by he Commission fixes in
Suggesed Templae for Rolling Schemes for inclusion in he fuure price regulaion of Dublin Airpor. In line wih sandard inernaional regulaory pracice, he regime operaed since 00 by he Commission fixes in
R e. Y R, X R, u e, and. Use the attached excel spreadsheets to
 HW # Saisical Financial Modeling ( P Theodossiou) 1 The following are annual reurns for US finance socks (F) and he S&P500 socks index (M) Year Reurn Finance Socks Reurn S&P500 Year Reurn Finance Socks
HW # Saisical Financial Modeling ( P Theodossiou) 1 The following are annual reurns for US finance socks (F) and he S&P500 socks index (M) Year Reurn Finance Socks Reurn S&P500 Year Reurn Finance Socks
Portfolio investments accounted for the largest outflow of SEK 77.5 billion in the financial account, which gave a net outflow of SEK billion.
 BALANCE OF PAYMENTS DATE: 27-11-27 PUBLISHER: Saisics Sweden Balance of Paymens and Financial Markes (BFM) Maria Falk +46 8 6 94 72, maria.falk@scb.se Camilla Bergeling +46 8 6 942 6, camilla.bergeling@scb.se
BALANCE OF PAYMENTS DATE: 27-11-27 PUBLISHER: Saisics Sweden Balance of Paymens and Financial Markes (BFM) Maria Falk +46 8 6 94 72, maria.falk@scb.se Camilla Bergeling +46 8 6 942 6, camilla.bergeling@scb.se
Volume 31, Issue 1. Pitfall of simple permanent income hypothesis model
 Volume 31, Issue 1 ifall of simple permanen income hypohesis model Kazuo Masuda Bank of Japan Absrac ermanen Income Hypohesis (hereafer, IH) is one of he cenral conceps in macroeconomics. Single equaion
Volume 31, Issue 1 ifall of simple permanen income hypohesis model Kazuo Masuda Bank of Japan Absrac ermanen Income Hypohesis (hereafer, IH) is one of he cenral conceps in macroeconomics. Single equaion
STATIONERY REQUIREMENTS SPECIAL REQUIREMENTS 20 Page booklet List of statistical formulae New Cambridge Elementary Statistical Tables
 ECONOMICS RIPOS Par I Friday 7 June 005 9 Paper Quaniaive Mehods in Economics his exam comprises four secions. Secions A and B are on Mahemaics; Secions C and D are on Saisics. You should do he appropriae
ECONOMICS RIPOS Par I Friday 7 June 005 9 Paper Quaniaive Mehods in Economics his exam comprises four secions. Secions A and B are on Mahemaics; Secions C and D are on Saisics. You should do he appropriae
Current vs. Permanent Earnings for Estimating Alternative Dividend Payment Behavioral Model: Theory, Methods and Applications
 Curren vs. ermanen Earnings for Esimaing Alernaive Dividend aymen Behavioral Model: Theory, Mehods and Applicaions Cheng Few Lee Rugers Universiy, USA lee@business.rugers.edu Hong-Yi Chen Naional Cenral
Curren vs. ermanen Earnings for Esimaing Alernaive Dividend aymen Behavioral Model: Theory, Mehods and Applicaions Cheng Few Lee Rugers Universiy, USA lee@business.rugers.edu Hong-Yi Chen Naional Cenral
The Relationship between Money Demand and Interest Rates: An Empirical Investigation in Sri Lanka
 The Relaionship beween Money Demand and Ineres Raes: An Empirical Invesigaion in Sri Lanka R. C. P. Padmasiri 1 and O. G. Dayarana Banda 2 1 Economic Research Uni, Deparmen of Expor Agriculure 2 Deparmen
The Relaionship beween Money Demand and Ineres Raes: An Empirical Invesigaion in Sri Lanka R. C. P. Padmasiri 1 and O. G. Dayarana Banda 2 1 Economic Research Uni, Deparmen of Expor Agriculure 2 Deparmen
EQUILIBRIUM ASSET PRICING MODELS
 EQUILIBRIUM ASSET PRICING MODELS 2 Asse pricing derived rom heory o consumpion and invesmen behavior 2 Pricing equaions oen ake he orm o PV models: 4 Asse value equals expeced sum o discouned uure CFs
EQUILIBRIUM ASSET PRICING MODELS 2 Asse pricing derived rom heory o consumpion and invesmen behavior 2 Pricing equaions oen ake he orm o PV models: 4 Asse value equals expeced sum o discouned uure CFs
1 Purpose of the paper
 Moneary Economics 2 F.C. Bagliano - Sepember 2017 Noes on: F.X. Diebold and C. Li, Forecasing he erm srucure of governmen bond yields, Journal of Economerics, 2006 1 Purpose of he paper The paper presens
Moneary Economics 2 F.C. Bagliano - Sepember 2017 Noes on: F.X. Diebold and C. Li, Forecasing he erm srucure of governmen bond yields, Journal of Economerics, 2006 1 Purpose of he paper The paper presens
Consumption Patterns over Pay Periods. Clare Kelly 1 Departments of Economics, University College Dublin and Keele University,
 Consumpion Paerns over Pay Periods Clare Kelly Deparmens of Economics, Universiy College Dublin and Keele Universiy, and Gauhier Lano Deparmen of Economics, Keele Universiy. January 00 VERY PRELIMINARY
Consumpion Paerns over Pay Periods Clare Kelly Deparmens of Economics, Universiy College Dublin and Keele Universiy, and Gauhier Lano Deparmen of Economics, Keele Universiy. January 00 VERY PRELIMINARY
Balance of Payments. Second quarter 2012
 Balance of Paymens Second quarer 2012 Balance of Paymens Second quarer 2012 Saisics Sweden 2012 Balance of Paymens. Second quarer 2012 Saisics Sweden 2012 Producer Saisics Sweden, Balance of Paymens and
Balance of Paymens Second quarer 2012 Balance of Paymens Second quarer 2012 Saisics Sweden 2012 Balance of Paymens. Second quarer 2012 Saisics Sweden 2012 Producer Saisics Sweden, Balance of Paymens and
I. Labour Supply. B. Intertemporal/Life-cycle Behaviour. Plan 1. Recent Trends: Age-LFP Profiles. 2. Life-Cycle/Intertemporal Labour Supply Model
 Forin Econ 560 Lecure 1B I. Labour Supply B. Ineremporal/Life-cycle Behaviour Plan 1. Recen Trends: Age-LFP Profiles 2. Life-Cycle/Ineremporal Labour Supply Model 3. Esimaing he life-cycle model Forin
Forin Econ 560 Lecure 1B I. Labour Supply B. Ineremporal/Life-cycle Behaviour Plan 1. Recen Trends: Age-LFP Profiles 2. Life-Cycle/Ineremporal Labour Supply Model 3. Esimaing he life-cycle model Forin
Fundamental Basic. Fundamentals. Fundamental PV Principle. Time Value of Money. Fundamental. Chapter 2. How to Calculate Present Values
 McGraw-Hill/Irwin Chaper 2 How o Calculae Presen Values Principles of Corporae Finance Tenh Ediion Slides by Mahew Will And Bo Sjö 22 Copyrigh 2 by he McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All righs reserved. Fundamenal
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Chaper 2 How o Calculae Presen Values Principles of Corporae Finance Tenh Ediion Slides by Mahew Will And Bo Sjö 22 Copyrigh 2 by he McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All righs reserved. Fundamenal
Whelan, Karl; Palumbo, Michael; Rudd, Jeremy. Central Bank of Ireland Research Technical Paper; 4/RT/02.
 Provided by he auhor(s) and Universiy College Dublin Library in accordance wih publisher policies. Please cie he published version when available. Tile On he relaionships beween real consumpion, income,
Provided by he auhor(s) and Universiy College Dublin Library in accordance wih publisher policies. Please cie he published version when available. Tile On he relaionships beween real consumpion, income,
CHAPTER 3 How to Calculate Present Values. Answers to Practice Questions
 CHAPTER 3 How o Calculae Presen Values Answers o Pracice Quesions. a. PV $00/.0 0 $90.53 b. PV $00/.3 0 $9.46 c. PV $00/.5 5 $ 3.5 d. PV $00/. + $00/. + $00/. 3 $40.8. a. DF + r 0.905 r 0.050 0.50% b.
CHAPTER 3 How o Calculae Presen Values Answers o Pracice Quesions. a. PV $00/.0 0 $90.53 b. PV $00/.3 0 $9.46 c. PV $00/.5 5 $ 3.5 d. PV $00/. + $00/. + $00/. 3 $40.8. a. DF + r 0.905 r 0.050 0.50% b.
This specification describes the models that are used to forecast
 PCE and CPI Inflaion Differenials: Convering Inflaion Forecass Model Specificaion By Craig S. Hakkio This specificaion describes he models ha are used o forecas he inflaion differenial. The 14 forecass
PCE and CPI Inflaion Differenials: Convering Inflaion Forecass Model Specificaion By Craig S. Hakkio This specificaion describes he models ha are used o forecas he inflaion differenial. The 14 forecass
Chapter 12 Fiscal Policy, page 1 of 8
 Chaper 12 Fiscal olicy, page 1 of 8 fiscal policy and invesmen: fiscal policy refers o governmen policy regarding revenue and expendiures fiscal policy is under he capial resources secion of he ex because
Chaper 12 Fiscal olicy, page 1 of 8 fiscal policy and invesmen: fiscal policy refers o governmen policy regarding revenue and expendiures fiscal policy is under he capial resources secion of he ex because
Advanced Forecasting Techniques and Models: Time-Series Forecasts
 Advanced Forecasing Techniques and Models: Time-Series Forecass Shor Examples Series using Risk Simulaor For more informaion please visi: www.realopionsvaluaion.com or conac us a: admin@realopionsvaluaion.com
Advanced Forecasing Techniques and Models: Time-Series Forecass Shor Examples Series using Risk Simulaor For more informaion please visi: www.realopionsvaluaion.com or conac us a: admin@realopionsvaluaion.com
Advanced and Contemporary Topics in Macroeconomics I. Consumption/Saving
 Advanced and onemporary opics in Macroeconomics I Alemayehu Geda Email: ag56@gmail.com Web Page: www.alemayehu.com lass Lecure Noe 6 onsumpion/saving Based on David Romer (0) Addis Ababa Universiy Deparemen
Advanced and onemporary opics in Macroeconomics I Alemayehu Geda Email: ag56@gmail.com Web Page: www.alemayehu.com lass Lecure Noe 6 onsumpion/saving Based on David Romer (0) Addis Ababa Universiy Deparemen
Problem 1 / 25 Problem 2 / 25 Problem 3 / 30 Problem 4 / 20 TOTAL / 100
 Deparmen of Economics Universiy of Maryland Economics 325 Inermediae Macroeconomic Analysis Final Exam Suggesed Soluions Professor Sanjay Chugh Spring 2009 NAME: TA S NAME: The Exam has a oal of four (4)
Deparmen of Economics Universiy of Maryland Economics 325 Inermediae Macroeconomic Analysis Final Exam Suggesed Soluions Professor Sanjay Chugh Spring 2009 NAME: TA S NAME: The Exam has a oal of four (4)
2. Quantity and price measures in macroeconomic statistics 2.1. Long-run deflation? As typical price indexes, Figure 2-1 depicts the GDP deflator,
 1 2. Quaniy and price measures in macroeconomic saisics 2.1. Long-run deflaion? As ypical price indexes, Figure 2-1 depics he GD deflaor, he Consumer rice ndex (C), and he Corporae Goods rice ndex (CG)
1 2. Quaniy and price measures in macroeconomic saisics 2.1. Long-run deflaion? As ypical price indexes, Figure 2-1 depics he GD deflaor, he Consumer rice ndex (C), and he Corporae Goods rice ndex (CG)
Financial Econometrics Jeffrey R. Russell Midterm Winter 2011
 Name Financial Economerics Jeffrey R. Russell Miderm Winer 2011 You have 2 hours o complee he exam. Use can use a calculaor. Try o fi all your work in he space provided. If you find you need more space
Name Financial Economerics Jeffrey R. Russell Miderm Winer 2011 You have 2 hours o complee he exam. Use can use a calculaor. Try o fi all your work in he space provided. If you find you need more space
Lecture 23: Forward Market Bias & the Carry Trade
 Lecure 23: Forward Marke Bias & he Carry Trade Moivaions: Efficien markes hypohesis Does raional expecaions hold? Does he forward rae reveal all public informaion? Does Uncovered Ineres Pariy hold? Or
Lecure 23: Forward Marke Bias & he Carry Trade Moivaions: Efficien markes hypohesis Does raional expecaions hold? Does he forward rae reveal all public informaion? Does Uncovered Ineres Pariy hold? Or
On Phase Shifts in a New Keynesian Model Economy. Joseph H. Haslag. Department of Economics. University of Missouri-Columbia. and.
 On Phase Shifs in a New Keynesian Model Economy Joseph H. Haslag Deparmen of Economics Universiy of Missouri-Columbia and Xue Li Insiue of Chinese Financial Sudies & Collaboraive Innovaion Cener of Financial
On Phase Shifs in a New Keynesian Model Economy Joseph H. Haslag Deparmen of Economics Universiy of Missouri-Columbia and Xue Li Insiue of Chinese Financial Sudies & Collaboraive Innovaion Cener of Financial
SIMPLE DSGE MODELS OF MONEY DEMAND: PART I OCTOBER 14, 2014
 SIMPLE DSGE MODELS OF MONEY DEMAND: PART I OCTOBER 4, 204 Inroducion BASIC ISSUES Money/moneary policy issues an enduring fascinaion in macroeconomics How can/should cenral bank conrol he economy? Should
SIMPLE DSGE MODELS OF MONEY DEMAND: PART I OCTOBER 4, 204 Inroducion BASIC ISSUES Money/moneary policy issues an enduring fascinaion in macroeconomics How can/should cenral bank conrol he economy? Should
Erratic Price, Smooth Dividend. Variance Bounds. Present Value. Ex Post Rational Price. Standard and Poor s Composite Stock-Price Index
 Erraic Price, Smooh Dividend Shiller [1] argues ha he sock marke is inefficien: sock prices flucuae oo much. According o economic heory, he sock price should equal he presen value of expeced dividends.
Erraic Price, Smooh Dividend Shiller [1] argues ha he sock marke is inefficien: sock prices flucuae oo much. According o economic heory, he sock price should equal he presen value of expeced dividends.
Chapter 10: The Determinants of Dividend Policy
 Chaper 10: The Deerminans of Dividend Policy 1. True True False 2. This means ha firms generally prefer no o change dividends, paricularly downwards. One explanaion for his is he clienele hypohesis. Tha
Chaper 10: The Deerminans of Dividend Policy 1. True True False 2. This means ha firms generally prefer no o change dividends, paricularly downwards. One explanaion for his is he clienele hypohesis. Tha
Bond Prices and Interest Rates
 Winer erm 1999 Bond rice Handou age 1 of 4 Bond rices and Ineres Raes A bond is an IOU. ha is, a bond is a promise o pay, in he fuure, fixed amouns ha are saed on he bond. he ineres rae ha a bond acually
Winer erm 1999 Bond rice Handou age 1 of 4 Bond rices and Ineres Raes A bond is an IOU. ha is, a bond is a promise o pay, in he fuure, fixed amouns ha are saed on he bond. he ineres rae ha a bond acually
Review of Ricardian Equivalence: Theoretical and Empirical Studies
 Economics 413 Insrucor : P. Mueser Fall 2003 Lieraure Synhesis By Wansup Kim 12. 5. 2003 Review of Ricardian Equivalence: Theoreical and Empirical Sudies Acknowledgemen: I would like o hank Dr. Ni and
Economics 413 Insrucor : P. Mueser Fall 2003 Lieraure Synhesis By Wansup Kim 12. 5. 2003 Review of Ricardian Equivalence: Theoreical and Empirical Sudies Acknowledgemen: I would like o hank Dr. Ni and
The Death of the Phillips Curve?
 The Deah of he Phillips Curve? Anhony Murphy Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas Research Deparmen Working Paper 1801 hps://doi.org/10.19/wp1801 The Deah of he Phillips Curve? 1 Anhony Murphy, Federal Reserve
The Deah of he Phillips Curve? Anhony Murphy Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas Research Deparmen Working Paper 1801 hps://doi.org/10.19/wp1801 The Deah of he Phillips Curve? 1 Anhony Murphy, Federal Reserve
On the Impact of Inflation and Exchange Rate on Conditional Stock Market Volatility: A Re-Assessment
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive On he Impac of Inflaion and Exchange Rae on Condiional Sock Marke Volailiy: A Re-Assessmen OlaOluwa S Yaya and Olanrewaju I Shiu Deparmen of Saisics, Universiy of Ibadan,
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive On he Impac of Inflaion and Exchange Rae on Condiional Sock Marke Volailiy: A Re-Assessmen OlaOluwa S Yaya and Olanrewaju I Shiu Deparmen of Saisics, Universiy of Ibadan,
Aging and Capital Flows in Japan and Korea. April Robert Dekle Department of Economics USC Los Angeles, CA 90089
 Aging and Capial Flows in Japan and Korea April 2001 Rober Dekle Deparmen of Economics USC Los Angeles, CA 90089 Prepared for he Asian Developmen Bank Insiue Conference: Aging and Capial Flows. I hank
Aging and Capial Flows in Japan and Korea April 2001 Rober Dekle Deparmen of Economics USC Los Angeles, CA 90089 Prepared for he Asian Developmen Bank Insiue Conference: Aging and Capial Flows. I hank
Research Division Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis Working Paper Series
 Research Division Federal Reserve Bank of S. Louis Working Paper Series Can Rising Housing Prices Explain China s High Household Saving Rae? Xin Wang and Yi Wen Working Paper 2-48A hp://research.slouisfed.org/wp/2/2-48.pdf
Research Division Federal Reserve Bank of S. Louis Working Paper Series Can Rising Housing Prices Explain China s High Household Saving Rae? Xin Wang and Yi Wen Working Paper 2-48A hp://research.slouisfed.org/wp/2/2-48.pdf
The Simple Analytics of Price Determination
 Econ. 511b Spring 1997 C. Sims The Simple Analyics of rice Deerminaion The logic of price deerminaion hrough fiscal policy may be bes appreciaed in an exremely lean model. We include no sochasic elemens,
Econ. 511b Spring 1997 C. Sims The Simple Analyics of rice Deerminaion The logic of price deerminaion hrough fiscal policy may be bes appreciaed in an exremely lean model. We include no sochasic elemens,
The Transitory VAT Cut in the UK: A Dynamic General Equilibrium Analysis. Gonzalo Fernández-de-Córdoba and José L Torres 1
 Economic Issues, Vol. 16, Par 1, 2011 The Transiory VAT Cu in he UK: A Dynamic General Equilibrium Analysis Gonzalo Fernández-de-Córdoba and José L Torres 1 ABSTRACT This paper sudies he macroeconomic
Economic Issues, Vol. 16, Par 1, 2011 The Transiory VAT Cu in he UK: A Dynamic General Equilibrium Analysis Gonzalo Fernández-de-Córdoba and José L Torres 1 ABSTRACT This paper sudies he macroeconomic
Technological progress breakthrough inventions. Dr hab. Joanna Siwińska-Gorzelak
 Technological progress breakhrough invenions Dr hab. Joanna Siwińska-Gorzelak Inroducion Afer The Economis : Solow has shown, ha accumulaion of capial alone canno yield lasing progress. Wha can? Anyhing
Technological progress breakhrough invenions Dr hab. Joanna Siwińska-Gorzelak Inroducion Afer The Economis : Solow has shown, ha accumulaion of capial alone canno yield lasing progress. Wha can? Anyhing
The Concept of Generational Accounts (GA) in Comparison with National Transfer Accounts (NTA)
 The Concep of Generaional Accouns (GA) in Comparison wih Naional Transfer Accouns (NTA) The GA is defined as he presen value of ne ax paymen (=ax paid minus benefi received from he governmen) for he remaining
The Concep of Generaional Accouns (GA) in Comparison wih Naional Transfer Accouns (NTA) The GA is defined as he presen value of ne ax paymen (=ax paid minus benefi received from he governmen) for he remaining
National saving and Fiscal Policy in South Africa: an Empirical Analysis. by Lumengo Bonga-Bonga University of Johannesburg
 Naional saving and Fiscal Policy in Souh Africa: an Empirical Analysis by Lumengo Bonga-Bonga Universiy of Johannesburg Inroducion A paricularly imporan issue in Souh Africa is he exen o which fiscal policy
Naional saving and Fiscal Policy in Souh Africa: an Empirical Analysis by Lumengo Bonga-Bonga Universiy of Johannesburg Inroducion A paricularly imporan issue in Souh Africa is he exen o which fiscal policy
Macroeconomics. Typical macro questions (I) Typical macro questions (II) Methodology of macroeconomics. Tasks carried out by macroeconomists
 Macroeconomics Macroeconomics is he area of economics ha sudies he overall economic aciviy in a counry or region by means of indicaors of ha aciviy. There is no essenial divide beween micro and macroeconomics,
Macroeconomics Macroeconomics is he area of economics ha sudies he overall economic aciviy in a counry or region by means of indicaors of ha aciviy. There is no essenial divide beween micro and macroeconomics,
Japan's High Saving Rate in the 1960s through the 1980s
 Japan's High Saving Rae in he 960s hrough he 980s ABSTRACT An endogenous growh model wih boh he beques moive and he precauionary moive for saving is calibraed o he Japanese and he U.S. economy in order
Japan's High Saving Rae in he 960s hrough he 980s ABSTRACT An endogenous growh model wih boh he beques moive and he precauionary moive for saving is calibraed o he Japanese and he U.S. economy in order
Working Paper Series. Costs of Inflation in Japan: Tax and Resource Allocation
 Working Paper Series Coss of Inflaion in Japan: Tax and Resource Allocaion Kozo Ueda Working Paper 0-0 Research and Saisics Deparmen Bank of Japan C.P.O BOX 03 TOKYO 00-8630 JAPAN e-mail:kouzou.ueda@boj.or.jp
Working Paper Series Coss of Inflaion in Japan: Tax and Resource Allocaion Kozo Ueda Working Paper 0-0 Research and Saisics Deparmen Bank of Japan C.P.O BOX 03 TOKYO 00-8630 JAPAN e-mail:kouzou.ueda@boj.or.jp
Myopia, Liquidity Constraints, and Aggregate Consumption: The Case of Greece
 Volume 7, Number, June 00 Myopia, Liquidiy Consrains, and Aggregae Consumpion: The Case of Greece Konsaninos Drakos In his paper we invesigae he behaviour of aggregae consumpion in Greece. In paricular,
Volume 7, Number, June 00 Myopia, Liquidiy Consrains, and Aggregae Consumpion: The Case of Greece Konsaninos Drakos In his paper we invesigae he behaviour of aggregae consumpion in Greece. In paricular,
Forecasting and Monetary Policy Analysis in Emerging Economies: The case of India (preliminary)
 Forecasing and Moneary Policy Analysis in Emerging Economies: The case of India (preliminary) Rudrani Bhaacharya, Pranav Gupa, Ila Panaik, Rafael Porillo New Delhi 19 h November This presenaion should
Forecasing and Moneary Policy Analysis in Emerging Economies: The case of India (preliminary) Rudrani Bhaacharya, Pranav Gupa, Ila Panaik, Rafael Porillo New Delhi 19 h November This presenaion should
