Financial mathematics 111 Chapter two: Compound Interest
|
|
|
- Thomasina Dorsey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Financial mathematics 111 Chapter two: Compound Interest Bank اسم الطالب:... رقم الطالب:... الصف:... المدرسة:... الرقم التسلسلي
2 Compound interest:.. KEY TERM INTRODUCED: Compound amount:.. Unit four and five: calculate compound amount and compound interest. Example: A person invested BD 1000 in a bank for 3 years at 7% annually. Find the simple interest and compound amount at the end of each year.-- No of year Simple Interest SI = P x i x T Compound Interest CI = P x i x T 1 SI = % 1 = BD 70 2 SI = % 1 = BD 70 CI = % 1 = BD 70 CA = = BD 1070 CI = % 1 = BD 75 CA = = BD SI = % 1 = BD 70 CI = % 1 = BD 80 CA = = BD 1225 Notices Total SI =.. A=. Total CI =.. A=.. P =. I =. N (T)=... CA =. CI=.. CA = P x (1 + i ) N CI = P x (1 + i ) N - 1. Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 2 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
3 Exercise 2-1: Find the value of the following (by using calculator and the interest table):- Calculator interest table a -(1.06) 12 = b-(1.05) 60 = c -(1.005) 125 = Exercise 2-2: Rabab deposited BD4,200 for 14 years at 5.6% annually. Find the compound interest at the end of the period?..... Exercise 2-3: A trader wants to borrow 20,000 and pays it after 3 years, he has two choices: Borrowing on a simple interest at 5¾% annually Borrowing on a compound interest at 4% annually Which choice he should choose (by knowing the interest)? Why?..... He should choose interest, because it interest. Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 3 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
4 Exercise 2-4: Find the compound amount of BD1 at 12% annually for 8 years without using tables?. Exercise 2-5: Find the compound amount and compound interest for BD1 at 4.5% annually for 74 years by using interest tables?. Exercise 2-6: A person deposited $6000 for 4 years at 5.5% annually. Find the compound amount and the compound interest at the end of the period?. Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 4 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
5 Unit six: Annual and partial interest rate:.. Note: Must achieve compatibility between the arithmetic interest rate and the number of times the ramp. ملاحظة: یجب تحقیق التطابق الحسابي بین معدل الفاي دة وعدد مرات التعلیة. One year = month. Example: Suppose 12% annually for 5 years compounding for the following Type of compounding: 1-Monthly: (Twelfth times a year / every month) n =.. i =.. ( ) 2-Semi-annually: (Two times a year / every 6 months) Annually: n = 5 i = 12% ( ) 5 One time a year n =.. i =.. ( ) 3- Thirdly: (Three times a year / every 4 months) n =.. i =.. ( ) 4-Quarterly: (Four times a year / Every 3 months) n =.. i =.. ( ) Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 5 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
6 Exercise 2-7 Suppose 24% annually for 10 years compounding for the following Type of compounding: 1-Monthly: (Twelfth times a year / every month) n =.. i =.. ( ) 2-Semi-annually: (Two times a year / every 6 months) Annually: n = 10 i = 24% (1. 24 ) 10 One time a year n =.. i =.. ( ) 3- Thirdly: (Three times a year / every 4 months) n =.. i =.. ( ) 4-Quarterly: (Four times a year / Every 3 months) n =.. i =.. ( ) Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 6 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
7 Exercise 2-8: Shahd invested BD1000 in a bank at 6% annually for 4 years find the compound amount if the interest is: 1- Compounded annually 2- Compounded semi-annually. 3-Compounded thirdly 4-Compounded quarterly.. 5-Compounded monthly... Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 7 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
8 Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 8 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
9 Exercise 2-9: A woman deposited BD5,000 in a bank that pays 7.8% annually compounded quarterly on saving accounts for 4years and 6 months. Find the compound amount.. Exercise 2-10: Ali deposited BD3000 at 4% every 4 months find the compound amount at the end of 8 years and 8 months?. Exercise 2-11: Mariam deposited BD2550 in a bank at an effective rate of 6%annually. If the interest compounded semi-annually Calculate her fund at the end of 8 years, then find the compound interest?.. Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 9 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
10 Exercise 2-12: Faisal wants to borrow KD7200 from a bank to buy a new car if you know the interest rate is 6% annually compounded monthly. Find how much he paid to the bank at the end of 10 years?. Exercise 2-13: Sakeena Ahmed deposited BD2600 in a bank at 12% annually compounded quarterly- Find her fund at the end of 5 years and 9 months? And find the compound interest?. Exercise 2-14: A person deposited BD8750 at 3% each quarter find the amount and the interest at the end of 6 years?. Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 10 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
11 Exercise 2-15: A person deposited BD3500 at 4% every 6 months. Find the amount at the end of 8 years and 6 months?. Exercise 2-16: Laila borrowed $6400 from a bank at 5% every 4 months. Find the amount she paid at the end of three years and 8 months? And calculate the interest?. Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 11 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
12 Changeable interest rate: Exercise 2-17: Hashim invested BD5,000 for 6 years at 4% annually for the first two years, 6% annually for the following 3 years and 7% annually for the last year find the compound interest at the end of the period? Calculate the interest? Interest rate: 4% 6% 7% Years: years 3years 1year. Exercise 2-18: Find the compound interest for BD10,000 invested for 4 years, if you know that the rate is changing as follows : 3% for the first year, 2.5% for the second year, 2% for the third year and 1% for the fourth year?.. Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 12 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
13 Exercise 2-19: What is the compound amount for BD2,000 invested at 6% for 3 years and 4.8% for 5 more years?... Exercise 2-20: Find the total amount that saad will get if he saves BD2,000 in a bank for 10 years at changing rate, as following: at 5% annually for the first 5 years, 4.6% annually for the sixth year and 5.25 % annually for the rest years?. Exercise 2-21: Find the compound amount for BD2,000 invested for 7 years at 4.5% for the first 3 years and 5¾% for the rest years?. Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 13 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
14 ..... Changeable principal:... P=1,000 CA=1,500 P CA Exercise 2-22: Fayez invested BD3500 at 7% annually after 3 years he withdrew from his account BD1000 and invested the rest at 8% annually - find the compound amount and the interest at the end of 10 years?.. Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 14 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
15 Exercise 2-23: Noora invested BD4000 at Al- Ahli bank at interest rate of 9% annually and after 3 years she deposited BD3000 to her account at 4% every 4 months find the compound amount and the compound interest at the end of 8 years from the first deposit?. Exercise 2-24: A person deposited BD7,000 at 6% annually, after two years he withdrew BD2,618 from his account and invested the rest at 7.5% annually. Find: a- His fund after withdrawal b- The compound amount for the remaining sum at the end of four years.. Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 15 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
16 Exercise 2-25: Dawood deposited BD3,000 at a compound interest of 8% annually, after 3 years he added BD to his account and the rate of interest increased to 10% annually. Find the amount at the end of 8 years from the first deposit.. Exercise 2-26: A trader borrowed BD20,000 on 1 st January 2000 from BBK and BD15,000 on 1 st January 2001 and finally BD30,000 on 1 st January He promised to pay the debt on 31/12/ If the bank gives compound interest rate of 12% annually find the amount that should be paid on 31/12/ Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 16 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
17 Finding the principal: First: Finding the Principal by knowing amount: CA = P x (1 + i ) N Exercise 2-27: Hassan deposited an amount of money in a bank at 5% annually. If the compound amount at the end of 12 years is BD8, Calculate the principal? Exercise 2-28: Find the principal if the compound amount after 5 years is BD and the compound interest rate is 8% annually, then find the interest? Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 17 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
18 Exercise 2-29: Find the principal if the compound amount at the end of 7 years is BD6,450 and the compound interest rate is 4.5% annually for the first three years and 5% annually for the rest years? Exercise 2-30: How much must be deposited for an investment paying 8% annually compounded quarterly to give an amount of BD2, in 5 years? Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 18 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
19 Exercise 2-31: A man deposited money in NBB at 3%annually, after 5 years he withdrew BD from his account and invested the rest for 5 years at 2% every 6 months if the amount at the end of the period is BD3657 find the principal? Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 19 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
20 Second: Finding the Principal by knowing the interest:. CI = P x (1 + i ) N Exercise 2-32: A person deposited an amount of money in a bank at 3% annually. If the compound interest at the end of 10 years was BD find: a) The deposited amount? b) The compound amount at the end of the period Exercise 2-33: Find the principal that generates an interest of BD700 at 2% annually for 5 years? Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 20 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
21 Exercise 2-34: Taha calculated the compound interest he will get if he deposits his money in a bank at 3% annually for 20 years and it was BD , find the principal? Exercise 2-35: A principal invested for 3 years and a half at 5.75% every 3 months which gives an interest of BD Find the compound amount? Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 21 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
22 Finding the Time/periods:.. CA = P x (1 + i ) N... Exercise 2-36: A principal of BD invested at 8% annually, how long would it take to make the amount to BD ? A. By using calculator B. By using interest table No 1: page Searching for under 8%. Press log.. log. N 8% 8.25% 8.5% 8.75% We find n = 23 years. Exercise 2-37: How long will it take for BD1600 at 4% every semi-annual to make the amount to BD ? Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 22 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
23 Exercise 2-38: A loan of BD2,000 amounted to BD Find interest rate was 5% annually? the borrowing period if the Exercise 2-39: Nawal borrowed BD5,000 from a bank at 6% annually Find the borrowing period if the compound interest was BD8954? Exercise 2-40: How long will it take BD2,000 at 2.5% compounded every semi-annually to give an interest of BD ? Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 23 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
24 Exercise 2-41: How long will it take an investment of BD4,000 to amount of BD 5, at 7% annually? Exercise 2-42: How long will it take the money to double itself at 4% annually? Exercise 2-43: How long will it take the money to triple itself at 6.5% annually? Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 24 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
25 Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 25 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
26 Finding the interest rate:. CA = P x (1 + i ) N.. Exercise 2-44: Mahmood deposited BD3000 in the bank, if the amount at the end of 6 years was BD Find the interest rate? A. By using calculator B. By using interest table No 1: page Press x = Searching for opposite to n=6 b) By using interest table No 1 Searching for opposite to n = 6. N 8.75% 8.5% 9% 9.25% We Find the i = 9% Exercise 2-45: Saad deposited BD1400 in a bank that gives compound interest of BD at the end of 10 years - Find the rate of interest? Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 26 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
27 Exercise 2-46: Tahera borrowed 4,500 from a bank that gives compound interest of 1,916 at the end of 3 years. Find the quarterly interest rate and the annual rate of interest? Exercise 2-47: If BD 6,600 amounts to BD10, in 10 years. Find the rate of interest? Exercise 2-48: Jawad borrowed BD8,000 for 4 years. If the compound interest was BD2, find the semi-annually interest rate, and the annually interest rate? Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 27 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
28 Exercise 2-49: Find the rate of interest for amounts to 10,000 after 13 years? Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 28 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
29 General Exercise 1. Find the compound amount & interest of BD 2500 at the end of 20 years at 5.25% annually. 2. Find the compound interest and compound amount for BD 1500 invested at 6.25% annually for 25 years. 3. Find the compound amount for BD8, 750 invested for 10 years, if you know that the rate is changing as follows: 5% for the first 5 years, 5.25% for the sixth year, 5.5% for the rest years? 4. Ahmed invested BD 7,400 at 6.5% annually; find the compound amount after 85 years? 5. Moayyed deposited BD1400 at 6% annually, find the compound amount at the end of 10 years and 8 months if you know that interest is compounded quarterly. 6. Shahd invested BD 6000 at 10% annually compounded semi- annually find the compound amount at the end of 4 years and 5 months? 7. Malak invested BD 3150 at 2¼% every semi annual, find the compound amount at the end of 4 years and 7 months? 8. Omar borrowed BD 6,000 from BBK for 5 years at 4% annually compounded semi - annually. Two years from the borrowing date he borrowed BD 2, at 2% annually compounded quarterly. 9. How much would he pay after 7 years from first borrowed date? 10. Fawaz wants to buy a new house at Sanad, he has two choices either to pay BD65,000 cash today or to pay BD73,500 after 3 years. If you know that, the compound interest rate at market is 7% annually. Which choice is better for him if he wants to make a decision? Why? 11. Jassim deposited money in B.B.K for investment at 5%annually, after 5 years he added BD to his account at a new interest rate of 5.5% annually. After another 3 years, his account was BD Find the first sum deposited? Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 29 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
30 TABLE No.1 Equation : CA = P ( 1 + i ) N CA for one monetary unit N 0.5% 0.75% 1% 1.25% 1.5% 1.75% 2% 2.25% 2.5% Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 30 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
31 TABLE No.1 Equation : CA = P ( 1 + i ) N CA for one monetary unit N 2.75% 3% 3.25% 3.5% 3.75% 4% 4.25% 4.5% 4.75% Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 31 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
32 TABLE No.1 Equation : CA = P ( 1 + i ) N CA for one monetary unit N 5% 5.25% 5.5% 5.75% 6% 6.25% 6.5% 6.75% 7% Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 32 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
33 TABLE No.1 Equation : CA = P ( 1 + i ) N CA for one monetary unit N 7.25% 7.5% 7.75% 8% 8.25% 8.5% 8.75% 9% 9.25% Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 33 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
34 TABLE No.1 Equation : CA = P ( 1 + i ) N CA for one monetary unit N 9.5% 9.75% 10% 10.25% 10.5% 10.75% 11% 11.25% 11.5% Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 34 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
35 Uploaded by: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) 35 Prepared by T: A. JALIL ALAIWI
Financial mathematics 111 Chapter three: Discount & Present Value
 Financial mathematics 111 Chapter three: Discount & Present Value Bank اسم الطالب:... رقم الطالب:... الصف:... المدرسة:... الرقم التسلسلي القیمة المستقبلیة value: Future القیمة الحالیة value: Present تاریخ
Financial mathematics 111 Chapter three: Discount & Present Value Bank اسم الطالب:... رقم الطالب:... الصف:... المدرسة:... الرقم التسلسلي القیمة المستقبلیة value: Future القیمة الحالیة value: Present تاریخ
Financial mathematics 111 Chapter four: Annuities
 Financial mathematics 111 Chapter four: Annuities Bank اسم الطالب:... رقم الطالب:... الصف:... المدرسة:... الرقم التسلسلي Chapter Four: Annuities:. KEY TERM INTRODUCED: متساویة.. Equal دفعات. Annuity مدة
Financial mathematics 111 Chapter four: Annuities Bank اسم الطالب:... رقم الطالب:... الصف:... المدرسة:... الرقم التسلسلي Chapter Four: Annuities:. KEY TERM INTRODUCED: متساویة.. Equal دفعات. Annuity مدة
Unit five: Adjusting the accounts Accruals and Prepayments
 Unit five: Adjusting the accounts Accruals and Prepayments اسم الطالب:... رقم الطالب:... الصف:... المدرسة:... الرقم التسلسلي Uploaded By: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) Prepare by T. Abdul Jalil Alaiwi Uploaded
Unit five: Adjusting the accounts Accruals and Prepayments اسم الطالب:... رقم الطالب:... الصف:... المدرسة:... الرقم التسلسلي Uploaded By: Ayman Ayyad (Danger3) Prepare by T. Abdul Jalil Alaiwi Uploaded
Unit three: Property, Plant and Equipment Depreciation
 Unit three: Property, Plant and Equipment اسم الطالب:... رقم الطالب:... الصف:... المدرسة:... الرقم التسلسلي * Years Line and Going Concept: 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 Jan. Feb. Mar. Apr. May. Jun. Jul. Aug.
Unit three: Property, Plant and Equipment اسم الطالب:... رقم الطالب:... الصف:... المدرسة:... الرقم التسلسلي * Years Line and Going Concept: 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 Jan. Feb. Mar. Apr. May. Jun. Jul. Aug.
Financial Mathematics
 Financial Mathematics Introduction Interest can be defined in two ways. 1. Interest is money earned when money is invested. Eg. You deposited RM 1000 in a bank for a year and you find that at the end of
Financial Mathematics Introduction Interest can be defined in two ways. 1. Interest is money earned when money is invested. Eg. You deposited RM 1000 in a bank for a year and you find that at the end of
QUESTION BANK SIMPLE INTEREST
 Chapter 5 Financial Mathematics I References r = rate of interest (annual usually) R = Regular period equal amount Also called equivalent annual cost P = Present value (or Principal) SI = Simple Interest
Chapter 5 Financial Mathematics I References r = rate of interest (annual usually) R = Regular period equal amount Also called equivalent annual cost P = Present value (or Principal) SI = Simple Interest
Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 4 Mathematics of Finance Section 4.1 Simple Interest and Discount A fee that is charged by a lender to a borrower for the right to use the borrowed funds. The funds can be used to purchase a house,
Chapter 4 Mathematics of Finance Section 4.1 Simple Interest and Discount A fee that is charged by a lender to a borrower for the right to use the borrowed funds. The funds can be used to purchase a house,
Year 10 General Maths Unit 2
 Year 10 General Mathematics Unit 2 - Financial Arithmetic II Topic 2 Linear Growth and Decay In this area of study students cover mental, by- hand and technology assisted computation with rational numbers,
Year 10 General Mathematics Unit 2 - Financial Arithmetic II Topic 2 Linear Growth and Decay In this area of study students cover mental, by- hand and technology assisted computation with rational numbers,
Your gateway to the world of accounting 1
 Your gateway to the world of accounting 1 Accounting 212 Explain all the lessons of Accounting 212 for the third grade of secondary Ayman Ayyad Students-BH.com 2012 1 Index No. Lesson Title Page 1 Index
Your gateway to the world of accounting 1 Accounting 212 Explain all the lessons of Accounting 212 for the third grade of secondary Ayman Ayyad Students-BH.com 2012 1 Index No. Lesson Title Page 1 Index
Financial Mathematics II. ANNUITY (Series of payments or receipts) Definition ( ) m = parts of the year
 Chapter 6 Financial Mathematics II References r = rate of interest (annual usually) R = Regular period equal amount Also called equivalent annual cost P = Present value (or Principal) SI = Simple Interest
Chapter 6 Financial Mathematics II References r = rate of interest (annual usually) R = Regular period equal amount Also called equivalent annual cost P = Present value (or Principal) SI = Simple Interest
Model Paper Principals of Accounting Objective
 Model Paper Principals of Accounting Objective Intermediate Part I (11 th Class) Examination Session 2012-2013 and onward Total marks: 15 Paper Code Time Allowed: 20 minutes Note:- You have four choices
Model Paper Principals of Accounting Objective Intermediate Part I (11 th Class) Examination Session 2012-2013 and onward Total marks: 15 Paper Code Time Allowed: 20 minutes Note:- You have four choices
MTH302-Business Mathematics and Statistics. Solved Subjective Questions Midterm Examination. From Past Examination also Including New
 MTH302-Business Mathematics and Statistics Solved Subjective s Midterm Examination From Past Examination also Including New Composed by Sparkle Fairy A man borrows $39000 for 1and half year at a rate of
MTH302-Business Mathematics and Statistics Solved Subjective s Midterm Examination From Past Examination also Including New Composed by Sparkle Fairy A man borrows $39000 for 1and half year at a rate of
The Monthly Payment. ( ) ( ) n. P r M = r 12. k r. 12C, which must be rounded up to the next integer.
 MATH 116 Amortization One of the most useful arithmetic formulas in mathematics is the monthly payment for an amortized loan. Here are some standard questions that apply whenever you borrow money to buy
MATH 116 Amortization One of the most useful arithmetic formulas in mathematics is the monthly payment for an amortized loan. Here are some standard questions that apply whenever you borrow money to buy
Unit seven: The control of cash (Bank Reconciliation Statement)
 Unit seven: The control of cash (Bank Reconciliation Statement) اسم الطالب:... رقم الطالب:... الصف:... المدرسة:... الرقم التسلسلي Chapter Six: The Control of Cash. (Bank Reconciliation Statement). Bank
Unit seven: The control of cash (Bank Reconciliation Statement) اسم الطالب:... رقم الطالب:... الصف:... المدرسة:... الرقم التسلسلي Chapter Six: The Control of Cash. (Bank Reconciliation Statement). Bank
Compound Interest. Principal # Rate # Time 100
 7 introduction In Class VII, you have already learnt about simple interest. In this chapter, we shall review simple interest and shall also learn about compound interest, difference between simple and
7 introduction In Class VII, you have already learnt about simple interest. In this chapter, we shall review simple interest and shall also learn about compound interest, difference between simple and
Introduction to Earning Interest: APR, APY and Compound Interest
 Principal and Interest Example 1 Michael is saving money to buy a car. He takes $8,000 to the bank and opens an annual CD upon which the bank agrees to pay him 2% interest. Principal = 8000 Term = 1 year
Principal and Interest Example 1 Michael is saving money to buy a car. He takes $8,000 to the bank and opens an annual CD upon which the bank agrees to pay him 2% interest. Principal = 8000 Term = 1 year
The most important and simple rule to financial success.
 *The Rule of 72 The most important and simple rule to financial success. Take Charge Today March 2014 Rule of 72 Slide 1 How are Albert Einstein and the Rule of 72 related? *Albert Einstein Take Charge
*The Rule of 72 The most important and simple rule to financial success. Take Charge Today March 2014 Rule of 72 Slide 1 How are Albert Einstein and the Rule of 72 related? *Albert Einstein Take Charge
CHAPTER 2. Financial Mathematics
 CHAPTER 2 Financial Mathematics LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this chapter, you should be able to explain the concept of simple interest; use the simple interest formula to calculate interest, interest
CHAPTER 2 Financial Mathematics LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this chapter, you should be able to explain the concept of simple interest; use the simple interest formula to calculate interest, interest
Time value of money-concepts and Calculations Prof. Bikash Mohanty Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee
 Time value of money-concepts and Calculations Prof. Bikash Mohanty Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Lecture 04 Compounding Techniques- 1&2 Welcome to the lecture
Time value of money-concepts and Calculations Prof. Bikash Mohanty Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Lecture 04 Compounding Techniques- 1&2 Welcome to the lecture
9.1 Financial Mathematics: Borrowing Money
 Math 3201 9.1 Financial Mathematics: Borrowing Money Simple vs. Compound Interest Simple Interest: the amount of interest that you pay on a loan is calculated ONLY based on the amount of money that you
Math 3201 9.1 Financial Mathematics: Borrowing Money Simple vs. Compound Interest Simple Interest: the amount of interest that you pay on a loan is calculated ONLY based on the amount of money that you
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Math 131-03 Practice Questions for Exam# 2 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 1) What is the effective rate that corresponds to a nominal
Math 131-03 Practice Questions for Exam# 2 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 1) What is the effective rate that corresponds to a nominal
Interest: The money earned from an investment you have or the cost of borrowing money from a lender.
 8.1 Simple Interest Interest: The money earned from an investment you have or the cost of borrowing money from a lender. Simple Interest: "I" Interest earned or paid that is calculated based only on the
8.1 Simple Interest Interest: The money earned from an investment you have or the cost of borrowing money from a lender. Simple Interest: "I" Interest earned or paid that is calculated based only on the
Mathematics for Economists
 Department of Economics Mathematics for Economists Chapter 4 Mathematics of Finance Econ 506 Dr. Mohammad Zainal 4 Mathematics of Finance Compound Interest Annuities Amortization and Sinking Funds Arithmetic
Department of Economics Mathematics for Economists Chapter 4 Mathematics of Finance Econ 506 Dr. Mohammad Zainal 4 Mathematics of Finance Compound Interest Annuities Amortization and Sinking Funds Arithmetic
Finance 197. Simple One-time Interest
 Finance 197 Finance We have to work with money every day. While balancing your checkbook or calculating your monthly expenditures on espresso requires only arithmetic, when we start saving, planning for
Finance 197 Finance We have to work with money every day. While balancing your checkbook or calculating your monthly expenditures on espresso requires only arithmetic, when we start saving, planning for
Lesson 39 Appendix I Section 5.6 (part 1)
 Lesson 39 Appendix I Section 5.6 (part 1) Any of you who are familiar with financial plans or retirement investments know about annuities. An annuity is a plan involving payments made at regular intervals.
Lesson 39 Appendix I Section 5.6 (part 1) Any of you who are familiar with financial plans or retirement investments know about annuities. An annuity is a plan involving payments made at regular intervals.
Chapter 3 Mathematics of Finance
 Chapter 3 Mathematics of Finance Section 2 Compound and Continuous Interest Learning Objectives for Section 3.2 Compound and Continuous Compound Interest The student will be able to compute compound and
Chapter 3 Mathematics of Finance Section 2 Compound and Continuous Interest Learning Objectives for Section 3.2 Compound and Continuous Compound Interest The student will be able to compute compound and
LESSON 2 INTEREST FORMULAS AND THEIR APPLICATIONS. Overview of Interest Formulas and Their Applications. Symbols Used in Engineering Economy
 Lesson Two: Interest Formulas and Their Applications from Understanding Engineering Economy: A Practical Approach LESSON 2 INTEREST FORMULAS AND THEIR APPLICATIONS Overview of Interest Formulas and Their
Lesson Two: Interest Formulas and Their Applications from Understanding Engineering Economy: A Practical Approach LESSON 2 INTEREST FORMULAS AND THEIR APPLICATIONS Overview of Interest Formulas and Their
Compound Interest COMPOUND INTEREST INTRODUCTION
 Compound Interest INTRODUCTION The second method of calculating interest is the compound interest method where the interest earned by an invested amc;mnt of money (principal) is reinvested so that it too
Compound Interest INTRODUCTION The second method of calculating interest is the compound interest method where the interest earned by an invested amc;mnt of money (principal) is reinvested so that it too
SAMPLE. Financial arithmetic
 C H A P T E R 6 Financial arithmetic How do we determine the new price when discounts or increases are applied? How do we determine the percentage discount or increase applied, given the old and new prices?
C H A P T E R 6 Financial arithmetic How do we determine the new price when discounts or increases are applied? How do we determine the percentage discount or increase applied, given the old and new prices?
n = Compounding periods( ( how often the interest is added to the principle) I = =
 Abe Mirza Finance r F = P( + ) nt n F = Future Value P = Present Value t = time in years r =rate n = Compounding periods( ( how often the interest is added to the principle) Ex. If $4000.00 is invested
Abe Mirza Finance r F = P( + ) nt n F = Future Value P = Present Value t = time in years r =rate n = Compounding periods( ( how often the interest is added to the principle) Ex. If $4000.00 is invested
4. The compound interest on Rs. 30,000 at 7% per annum is Rs The period (in years) is: A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 3.5
 1. What is the difference between the compound interests on Rs. 5000 for 1 1 2 years at 4% per annum compounded yearly and half-yearly? A. Rs. 2.04 B. Rs. 4.80 C. Rs. 3.06 D. Rs. 8.30 2. A bank offers
1. What is the difference between the compound interests on Rs. 5000 for 1 1 2 years at 4% per annum compounded yearly and half-yearly? A. Rs. 2.04 B. Rs. 4.80 C. Rs. 3.06 D. Rs. 8.30 2. A bank offers
Lesson Exponential Models & Logarithms
 SACWAY STUDENT HANDOUT SACWAY BRAINSTORMING ALGEBRA & STATISTICS STUDENT NAME DATE INTRODUCTION Compound Interest When you invest money in a fixed- rate interest earning account, you receive interest at
SACWAY STUDENT HANDOUT SACWAY BRAINSTORMING ALGEBRA & STATISTICS STUDENT NAME DATE INTRODUCTION Compound Interest When you invest money in a fixed- rate interest earning account, you receive interest at
Principal Rate Time 100
 Commercial mathematics 1 Compound Interest 2 Introduction In the previous classes, you have learnt about simple interest and other related terms. You have also solved many problems on simple interest.
Commercial mathematics 1 Compound Interest 2 Introduction In the previous classes, you have learnt about simple interest and other related terms. You have also solved many problems on simple interest.
MTH302- Business Mathematics
 MIDTERM EXAMINATION MTH302- Business Mathematics Question No: 1 ( Marks: 1 ) - Please choose one Store A marked down a $ 50 perfume to $ 40 with markdown of $10 The % Markdown is 10% 20% 30% 40% Question
MIDTERM EXAMINATION MTH302- Business Mathematics Question No: 1 ( Marks: 1 ) - Please choose one Store A marked down a $ 50 perfume to $ 40 with markdown of $10 The % Markdown is 10% 20% 30% 40% Question
HSC Mathematics DUX. Sequences and Series Term 1 Week 4. Name. Class day and time. Teacher name...
 DUX Phone: (02) 8007 6824 Email: info@dc.edu.au Web: dc.edu.au 2018 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE COURSE MATERIALS HSC Mathematics Sequences and Series Term 1 Week 4 Name. Class day and time Teacher name...
DUX Phone: (02) 8007 6824 Email: info@dc.edu.au Web: dc.edu.au 2018 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE COURSE MATERIALS HSC Mathematics Sequences and Series Term 1 Week 4 Name. Class day and time Teacher name...
7-4. Compound Interest. Vocabulary. Interest Compounded Annually. Lesson. Mental Math
 Lesson 7-4 Compound Interest BIG IDEA If money grows at a constant interest rate r in a single time period, then after n time periods the value of the original investment has been multiplied by (1 + r)
Lesson 7-4 Compound Interest BIG IDEA If money grows at a constant interest rate r in a single time period, then after n time periods the value of the original investment has been multiplied by (1 + r)
Using the Finance Menu of the TI-83/84/Plus calculators
 Using the Finance Menu of the TI-83/84/Plus calculators To get to the FINANCE menu On the TI-83 press 2 nd x -1 On the TI-83, TI-83 Plus, TI-84, or TI-84 Plus press APPS and then select 1:FINANCE The FINANCE
Using the Finance Menu of the TI-83/84/Plus calculators To get to the FINANCE menu On the TI-83 press 2 nd x -1 On the TI-83, TI-83 Plus, TI-84, or TI-84 Plus press APPS and then select 1:FINANCE The FINANCE
Compound Interest Revisited - Homework
 Advanced Algebra Chapter 5C LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS Name Period Date Compound Interest Revisited - Homework SET UP AN EQUATION OR AN EXPRESSION FOR EACH PROBLEM. SHOW ALL THE NECESSARY WORK TO SOLVE YOUR
Advanced Algebra Chapter 5C LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS Name Period Date Compound Interest Revisited - Homework SET UP AN EQUATION OR AN EXPRESSION FOR EACH PROBLEM. SHOW ALL THE NECESSARY WORK TO SOLVE YOUR
CHAPTER 4 SIMPLE AND COMPOUND INTEREST INCLUDING ANNUITY APPLICATIONS. Copyright -The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India
 CHAPTER 4 SIMPLE AND COMPOUND INTEREST INCLUDING ANNUITY APPLICATIONS SIMPLE AND COMPOUND INTEREST INCLUDING ANNUITY- APPLICATIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter students will be able
CHAPTER 4 SIMPLE AND COMPOUND INTEREST INCLUDING ANNUITY APPLICATIONS SIMPLE AND COMPOUND INTEREST INCLUDING ANNUITY- APPLICATIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter students will be able
2. Do you have family members or friends who are currently retired? If so, how are they spending their retirement days?
 Bellwork 4-25-16 A whole generation of American will retire in poverty instead of prosperity, because they simply are not preparing for retirement now. Scott Cook, American Businessman 1. How can you save
Bellwork 4-25-16 A whole generation of American will retire in poverty instead of prosperity, because they simply are not preparing for retirement now. Scott Cook, American Businessman 1. How can you save
Math 346. First Midterm. Tuesday, September 16, Investments Time (in years)
 Math 34. First Midterm. Tuesday, September 1, 2008. Name:... Show all your work. No credit for lucky answers. 1. On October 1, 200, Emily invested $5,500 in a bank account which pays simple interest. On
Math 34. First Midterm. Tuesday, September 1, 2008. Name:... Show all your work. No credit for lucky answers. 1. On October 1, 200, Emily invested $5,500 in a bank account which pays simple interest. On
Practice Test Questions. Exam FM: Financial Mathematics Society of Actuaries. Created By: Digital Actuarial Resources
 Practice Test Questions Exam FM: Financial Mathematics Society of Actuaries Created By: (Sample Only Purchase the Full Version) Introduction: This guide from (DAR) contains sample test problems for Exam
Practice Test Questions Exam FM: Financial Mathematics Society of Actuaries Created By: (Sample Only Purchase the Full Version) Introduction: This guide from (DAR) contains sample test problems for Exam
Honors Pre-Calculus 3.5 D1 Worksheet Name Exponential Growth and Decay
 Honors Pre-Calculus 3.5 D1 Worksheet Name Exponential Growth and Decay Exponential Growth: Exponential Decay: Compound Interest: Compound Interest Continuously: 1. The value in dollars of a car years from
Honors Pre-Calculus 3.5 D1 Worksheet Name Exponential Growth and Decay Exponential Growth: Exponential Decay: Compound Interest: Compound Interest Continuously: 1. The value in dollars of a car years from
Lesson 1: How Your Money Changes Appreciation & Depreciation
 : How Your Money Changes Appreciation & Depreciation Learning Target I can solve Appreciation and Depreciation word problems I can calculate simple and compound interests In your own words write answer
: How Your Money Changes Appreciation & Depreciation Learning Target I can solve Appreciation and Depreciation word problems I can calculate simple and compound interests In your own words write answer
SIMPLE AND COMPOUND INTEREST
 INTRODUCTION Interest is called as the cost of boowing money, and depending on how it is calculated, can be classified as simple interest or compound interest. IMPORTANT FACTS AND FORMULAE 1. Principal:
INTRODUCTION Interest is called as the cost of boowing money, and depending on how it is calculated, can be classified as simple interest or compound interest. IMPORTANT FACTS AND FORMULAE 1. Principal:
Compound Interest Questions Quiz for Bank Clerk Mains and PO Pre Exams.
 Compound Interest Questions Quiz for Bank Clerk Mains and PO Pre Exams. Compound Interest Quiz 9 Directions: Kindly study the following Questions carefully and choose the right answer: 1. Pankaj borrowed
Compound Interest Questions Quiz for Bank Clerk Mains and PO Pre Exams. Compound Interest Quiz 9 Directions: Kindly study the following Questions carefully and choose the right answer: 1. Pankaj borrowed
Interest Compounded Annually. Table 3.27 Interest Computed Annually
 33 CHAPTER 3 Exponential, Logistic, and Logarithmic Functions 3.6 Mathematics of Finance What you ll learn about Interest Compounded Annually Interest Compounded k Times per Year Interest Compounded Continuously
33 CHAPTER 3 Exponential, Logistic, and Logarithmic Functions 3.6 Mathematics of Finance What you ll learn about Interest Compounded Annually Interest Compounded k Times per Year Interest Compounded Continuously
SHORT METHOD for Difference between C. I & S. I for 3 years C. I
 SIMPLE INTEREST S. I = PTR S. I = Simple interest P = principal T = time in years R = rate of interest A = P + S. I A = total amount COMPOUND INTEREST C. I = P (1 + R )T P C.I = Compound interest P = principal
SIMPLE INTEREST S. I = PTR S. I = Simple interest P = principal T = time in years R = rate of interest A = P + S. I A = total amount COMPOUND INTEREST C. I = P (1 + R )T P C.I = Compound interest P = principal
In a growing midwestern town, the number of eating establishments at the end of each of the last five years are as follows:
 Name: Date: In a growing midwestern town, the number of eating establishments at the end of each of the last five years are as follows: Year 1 = 273; Year 2 = 279; Year 3 = 302; Year 4 = 320; Year 5 =
Name: Date: In a growing midwestern town, the number of eating establishments at the end of each of the last five years are as follows: Year 1 = 273; Year 2 = 279; Year 3 = 302; Year 4 = 320; Year 5 =
Introduction to Investing
 Introduction to Investing "Take Charge of Your Finances" Advanced Level Saving and Investing Once an appropriate amount of liquid assets are reached Remember: The purpose of savings is to develop financial
Introduction to Investing "Take Charge of Your Finances" Advanced Level Saving and Investing Once an appropriate amount of liquid assets are reached Remember: The purpose of savings is to develop financial
SAVINGS. Maximizing your Return
 SAVINGS Maximizing your Return Savings Setting aside money for future use Discretionary income (aka disposable income): the amount of money left over after all obligations have been met Gross Pay Taxes
SAVINGS Maximizing your Return Savings Setting aside money for future use Discretionary income (aka disposable income): the amount of money left over after all obligations have been met Gross Pay Taxes
Math 134 Tutorial 7, 2011: Financial Maths
 Math 134 Tutorial 7, 2011: Financial Maths For each question, identify which of the formulae a to g applies. what you are asked to find, and what information you have been given. Final answers can be worked
Math 134 Tutorial 7, 2011: Financial Maths For each question, identify which of the formulae a to g applies. what you are asked to find, and what information you have been given. Final answers can be worked
Compound Interest: 10 Important Shortcuts & Tricks explained with Examples
 Compound Interest: 10 Important Shortcuts & Tricks explained with Examples Majority of business operations and goes by the name of Compound Interest. The basic concept operating behind compound interest
Compound Interest: 10 Important Shortcuts & Tricks explained with Examples Majority of business operations and goes by the name of Compound Interest. The basic concept operating behind compound interest
practice: simple & compound interest/depreciation
 practice: simple & compound interest/depreciation [145 marks] Jackson invested 12 000 Australian dollars (AUD) in a bank that offered simple interest at an annual interest rate of r %. The value of Jackson
practice: simple & compound interest/depreciation [145 marks] Jackson invested 12 000 Australian dollars (AUD) in a bank that offered simple interest at an annual interest rate of r %. The value of Jackson
1.1. Simple Interest. INVESTIGATE the Math
 1.1 Simple Interest YOU WILL NEED calculator graph paper straightedge EXPLORE An amount of money was invested. Interpret the graph below to determine a) how much money was invested, b) the value of the
1.1 Simple Interest YOU WILL NEED calculator graph paper straightedge EXPLORE An amount of money was invested. Interpret the graph below to determine a) how much money was invested, b) the value of the
Compounding More than Once a Year
 Compounding More than Once a Year by CHED on December 22, 2017 lesson duration of 5 minutes under General Mathematics generated on December 22, 2017 at 04:18 pm Tags: Simple and Compound Interest Generated:
Compounding More than Once a Year by CHED on December 22, 2017 lesson duration of 5 minutes under General Mathematics generated on December 22, 2017 at 04:18 pm Tags: Simple and Compound Interest Generated:
Sequences and Series
 Edexcel GCE Core Mathematics C2 Advanced Subsidiary Sequences and Series Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae (Pink or Green) Items included with question papers Nil Advice to Candidates
Edexcel GCE Core Mathematics C2 Advanced Subsidiary Sequences and Series Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae (Pink or Green) Items included with question papers Nil Advice to Candidates
Chapter 5 Finance. i 1 + and total compound interest CI = A P n
 Mat 2 College Mathematics Nov, 08 Chapter 5 Finance The formulas we are using: Simple Interest: Total simple interest on principal P is I = Pr t and Amount A = P + Pr t = P( + rt) Compound Interest: Amount
Mat 2 College Mathematics Nov, 08 Chapter 5 Finance The formulas we are using: Simple Interest: Total simple interest on principal P is I = Pr t and Amount A = P + Pr t = P( + rt) Compound Interest: Amount
richard/math101
 1. Personal Finance Lecture Notes Continued Professor Richard Blecksmith richard@math.niu.edu Dept. of Mathematical Sciences Northern Illinois University http://math.niu.edu/ richard/math101 2. Investment
1. Personal Finance Lecture Notes Continued Professor Richard Blecksmith richard@math.niu.edu Dept. of Mathematical Sciences Northern Illinois University http://math.niu.edu/ richard/math101 2. Investment
Financial institutions pay interest when you deposit your money into one of their accounts.
 KEY CONCEPTS Financial institutions pay interest when you deposit your money into one of their accounts. Often, financial institutions charge fees or service charges for providing you with certain services
KEY CONCEPTS Financial institutions pay interest when you deposit your money into one of their accounts. Often, financial institutions charge fees or service charges for providing you with certain services
The second and fourth terms of a geometric series are 7.2 and respectively.
 Geometric Series The second and fourth terms of a geometric series are 7.2 and 5.832 respectively. The common ratio of the series is positive. For this series, find (a) the common ratio, (c) the sum of
Geometric Series The second and fourth terms of a geometric series are 7.2 and 5.832 respectively. The common ratio of the series is positive. For this series, find (a) the common ratio, (c) the sum of
JAGANNATH INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT SCIENCES BUSINESS MATHEMATICS II BBA- 2 ND SEMESTER (Code -205)
 JAGANNATH INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT SCIENCES BUSINESS MATHEMATICS II BBA- 2 ND SEMESTER (Code -205) UNIT-1 SCOPE AND IMPORTANCE OF BUSINESS MATHS : Mathematics is an important subject and knowledge of it
JAGANNATH INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT SCIENCES BUSINESS MATHEMATICS II BBA- 2 ND SEMESTER (Code -205) UNIT-1 SCOPE AND IMPORTANCE OF BUSINESS MATHS : Mathematics is an important subject and knowledge of it
Annuities and Income Streams
 Annuities and Income Streams MATH 151 Calculus for Management J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 212 Objectives After completing this lesson we will be able to: determine the value of
Annuities and Income Streams MATH 151 Calculus for Management J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 212 Objectives After completing this lesson we will be able to: determine the value of
REVIEW OF KEY CONCEPTS
 REVIEW OF KEY CONCEPTS 7.2 Compound Interest Refer to the Key Concepts on page 507. 1. Find the amount of each investment. a) $400 at 6% per annum, compounded monthly, for 5 years b) $1500 at 4.25% per
REVIEW OF KEY CONCEPTS 7.2 Compound Interest Refer to the Key Concepts on page 507. 1. Find the amount of each investment. a) $400 at 6% per annum, compounded monthly, for 5 years b) $1500 at 4.25% per
Section 3.4: EXPLORE COMPOUND INTEREST. Understand the concept of getting interest on your interest. Compute compound interest using a table.
 Section 3.4: EXPLORE COMPOUND INTEREST OBJECTIVES Understand the concept of getting interest on your interest. Compute compound interest using a table. Key Terms compound interest annual compounding semiannual
Section 3.4: EXPLORE COMPOUND INTEREST OBJECTIVES Understand the concept of getting interest on your interest. Compute compound interest using a table. Key Terms compound interest annual compounding semiannual
Chapter Organization. The future value (FV) is the cash value of. an investment at some time in the future.
 Chapter 5 The Time Value of Money Chapter Organization 5.2. Present Value and Discounting The future value (FV) is the cash value of an investment at some time in the future Suppose you invest 100 in a
Chapter 5 The Time Value of Money Chapter Organization 5.2. Present Value and Discounting The future value (FV) is the cash value of an investment at some time in the future Suppose you invest 100 in a
1. If x² - y² = 55, and x - y = 11, then y = 2. If the slope of a line is ½ and the y- intercept is 3, what is the x-intercept of the same line?
 1/20/2016 SAT Warm-Up 1. If x² - y² = 55, and x - y = 11, then y = 2. If the slope of a line is ½ and the y- intercept is 3, what is the x-intercept of the same line? Simple Interest = Pin where P = principal
1/20/2016 SAT Warm-Up 1. If x² - y² = 55, and x - y = 11, then y = 2. If the slope of a line is ½ and the y- intercept is 3, what is the x-intercept of the same line? Simple Interest = Pin where P = principal
Year 10 Mathematics Semester 2 Financial Maths Chapter 15
 Year 10 Mathematics Semester 2 Financial Maths Chapter 15 Why learn this? Everyone requires food, housing, clothing and transport, and a fulfilling social life. Money allows us to purchase the things we
Year 10 Mathematics Semester 2 Financial Maths Chapter 15 Why learn this? Everyone requires food, housing, clothing and transport, and a fulfilling social life. Money allows us to purchase the things we
Measuring Interest Rates
 Measuring Interest Rates Economics 301: Money and Banking 1 1.1 Goals Goals and Learning Outcomes Goals: Learn to compute present values, rates of return, rates of return. Learning Outcomes: LO3: Predict
Measuring Interest Rates Economics 301: Money and Banking 1 1.1 Goals Goals and Learning Outcomes Goals: Learn to compute present values, rates of return, rates of return. Learning Outcomes: LO3: Predict
Chapter 21: Savings Models Lesson Plan
 Lesson Plan For All Practical Purposes Arithmetic Growth and Simple Interest Geometric Growth and Compound Interest Mathematical Literacy in Today s World, 8th ed. A Limit to Compounding A Model for Saving
Lesson Plan For All Practical Purposes Arithmetic Growth and Simple Interest Geometric Growth and Compound Interest Mathematical Literacy in Today s World, 8th ed. A Limit to Compounding A Model for Saving
Chapter 10: The Mathematics of Money
 Chapter 10: The Mathematics of Money Percent Increases and Decreases If a shirt is marked down 20% and it now costs $32, how much was it originally? Simple Interest If you invest a principle of $5000 and
Chapter 10: The Mathematics of Money Percent Increases and Decreases If a shirt is marked down 20% and it now costs $32, how much was it originally? Simple Interest If you invest a principle of $5000 and
Valuing Stock Options: The Black-Scholes-Merton Model. Chapter 13
 Valuing Stock Options: The Black-Scholes-Merton Model Chapter 13 1 The Black-Scholes-Merton Random Walk Assumption l Consider a stock whose price is S l In a short period of time of length t the return
Valuing Stock Options: The Black-Scholes-Merton Model Chapter 13 1 The Black-Scholes-Merton Random Walk Assumption l Consider a stock whose price is S l In a short period of time of length t the return
Investigate. Name Per Algebra IB Unit 9 - Exponential Growth Investigation. Ratio of Values of Consecutive Decades. Decades Since
 Name Per Algebra IB Unit 9 - Exponential Growth Investigation Investigate Real life situation 1) The National Association Realtors estimates that, on average, the price of a house doubles every ten years
Name Per Algebra IB Unit 9 - Exponential Growth Investigation Investigate Real life situation 1) The National Association Realtors estimates that, on average, the price of a house doubles every ten years
7.5 exponential growth and decay 2016 ink.notebook. February 13, Page 69. Page Exponential Growth and Decay. Standards.
 7.5 exponential growth and decay 2016 ink.notebook Page 69 Page 70 7.5 Exponential Growth and Decay Lesson Objectives Standards Lesson Notes Page 71 7.5 Exponential Growth and Decay Press the tabs to view
7.5 exponential growth and decay 2016 ink.notebook Page 69 Page 70 7.5 Exponential Growth and Decay Lesson Objectives Standards Lesson Notes Page 71 7.5 Exponential Growth and Decay Press the tabs to view
Mathematics of Finance
 CHAPTER 55 Mathematics of Finance PAMELA P. DRAKE, PhD, CFA J. Gray Ferguson Professor of Finance and Department Head of Finance and Business Law, James Madison University FRANK J. FABOZZI, PhD, CFA, CPA
CHAPTER 55 Mathematics of Finance PAMELA P. DRAKE, PhD, CFA J. Gray Ferguson Professor of Finance and Department Head of Finance and Business Law, James Madison University FRANK J. FABOZZI, PhD, CFA, CPA
Chapter 2. Time Value of Money (TVOM) Principles of Engineering Economic Analysis, 5th edition
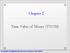 Chapter 2 Time Value of Money (TVOM) Cash Flow Diagrams $5,000 $5,000 $5,000 ( + ) 0 1 2 3 4 5 ( - ) Time $2,000 $3,000 $4,000 Example 2.1: Cash Flow Profiles for Two Investment Alternatives (EOY) CF(A)
Chapter 2 Time Value of Money (TVOM) Cash Flow Diagrams $5,000 $5,000 $5,000 ( + ) 0 1 2 3 4 5 ( - ) Time $2,000 $3,000 $4,000 Example 2.1: Cash Flow Profiles for Two Investment Alternatives (EOY) CF(A)
A nd Edition, (Updated: July 25, 2011)
 A-201 2 nd Edition, 2008 (Updated: July 25, 2011) A201 - T1-2 28 Taxation Concepts pertaining to Insurance of Persons The actual amount of assessable dividends 6 is grossed-up by 45% to arrive at a taxable
A-201 2 nd Edition, 2008 (Updated: July 25, 2011) A201 - T1-2 28 Taxation Concepts pertaining to Insurance of Persons The actual amount of assessable dividends 6 is grossed-up by 45% to arrive at a taxable
Casio 9750G PLUS Calculator
 Casio 9750G PLUS Calculator Keystrokes for the Casio 9750G PLUS are shown for a few topics in which keystrokes are unique. Start by reading the Quik Start section. Then, before beginning a specific unit
Casio 9750G PLUS Calculator Keystrokes for the Casio 9750G PLUS are shown for a few topics in which keystrokes are unique. Start by reading the Quik Start section. Then, before beginning a specific unit
MATH/STAT 2600, Theory of Interest FALL 2014 Toby Kenney
 MATH/STAT 2600, Theory of Interest FALL 2014 Toby Kenney In Class Examples () September 11, 2014 1 / 75 Compound Interest Question 1 (a) Calculate the accumulated value on maturity of $5,000 invested for
MATH/STAT 2600, Theory of Interest FALL 2014 Toby Kenney In Class Examples () September 11, 2014 1 / 75 Compound Interest Question 1 (a) Calculate the accumulated value on maturity of $5,000 invested for
Math 147 Section 6.4. Application Example
 Math 147 Section 6.4 Present Value of Annuities 1 Application Example Suppose an individual makes an initial investment of $1500 in an account that earns 8.4%, compounded monthly, and makes additional
Math 147 Section 6.4 Present Value of Annuities 1 Application Example Suppose an individual makes an initial investment of $1500 in an account that earns 8.4%, compounded monthly, and makes additional
PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION 2018 MATHEMATICS GRADE 12 PAPER 1. Time: 3 hours Total: 150 PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY
 PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION 2018 MATHEMATICS GRADE 12 PAPER 1 Time: 3 hours Total: 150 Examiner: P R Mhuka Moderators: J Scalla E Zachariou PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY 1. This question
PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION 2018 MATHEMATICS GRADE 12 PAPER 1 Time: 3 hours Total: 150 Examiner: P R Mhuka Moderators: J Scalla E Zachariou PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY 1. This question
DEBITS AND CREDITS: ANALYZING AND RECORDING BUSINESS TRANSACTIONS
 DEBITS AND CREDITS: ANALYZING AND RECORDING BUSINESS TRANSACTIONS 2-1 Chapter 2 Learning Objectives 1. Setting up and organizing a chart of accounts. 2. Recording transactions in T accounts according to
DEBITS AND CREDITS: ANALYZING AND RECORDING BUSINESS TRANSACTIONS 2-1 Chapter 2 Learning Objectives 1. Setting up and organizing a chart of accounts. 2. Recording transactions in T accounts according to
Simple Interest: Interest earned on the original investment amount only
 c Kathryn Bollinger, November 30, 2005 1 Chapter 5 - Finance 5.1 - Compound Interest Simple Interest: Interest earned on the original investment amount only = I = Prt I = the interest earned, P = the amount
c Kathryn Bollinger, November 30, 2005 1 Chapter 5 - Finance 5.1 - Compound Interest Simple Interest: Interest earned on the original investment amount only = I = Prt I = the interest earned, P = the amount
Compound Interest. Contents. 1 Mathematics of Finance. 2 Compound Interest
 Compound Interest Contents 1 Mathematics of Finance 1 2 Compound Interest 1 3 Compound Interest Computations 3 4 The Effective Rate 5 5 Document License CC BY-ND 4.0) 7 5.1 License Links.....................................
Compound Interest Contents 1 Mathematics of Finance 1 2 Compound Interest 1 3 Compound Interest Computations 3 4 The Effective Rate 5 5 Document License CC BY-ND 4.0) 7 5.1 License Links.....................................
1. Assume that monthly payments begin in one month. What will each payment be? A) $ B) $1, C) $1, D) $1, E) $1,722.
 Name: Date: You and your spouse have found your dream home. The selling price is $220,000; you will put $50,000 down and obtain a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage at 7.5% APR for the balance. 1. Assume that
Name: Date: You and your spouse have found your dream home. The selling price is $220,000; you will put $50,000 down and obtain a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage at 7.5% APR for the balance. 1. Assume that
Lesson 8: Modeling a Context from a Verbal Description
 Classwork Example Christine has $ to deposit in a savings account and she is trying to decide between two banks. Bank A offers % annual interest compounded quarterly. Rather than compounding interest for
Classwork Example Christine has $ to deposit in a savings account and she is trying to decide between two banks. Bank A offers % annual interest compounded quarterly. Rather than compounding interest for
Date Transaction Deposits Withdrawals Balance 3 August 2009 Salary $ $
 CHAPTER REVIEW MULTIPLE CHOICE 1 Anthony earned $1016 in simple interest when he invested $19 800 for 9 months. The rate of simple interest was: A 5.13% B 6.14% C 6.84% D 7.62% E 8.21% 2 With an interest
CHAPTER REVIEW MULTIPLE CHOICE 1 Anthony earned $1016 in simple interest when he invested $19 800 for 9 months. The rate of simple interest was: A 5.13% B 6.14% C 6.84% D 7.62% E 8.21% 2 With an interest
Paper Reference(s) 7011/01 London Examinations GCE. Friday 15 May 2009 Afternoon. Source booklet for use with Questions 1 to 6.
 Paper Reference(s) 7011/01 London Examinations GCE Accounting Ordinary Level Friday 15 May 2009 Afternoon Source booklet for use with Questions 1 to 6. Do not return the insert with the question paper.
Paper Reference(s) 7011/01 London Examinations GCE Accounting Ordinary Level Friday 15 May 2009 Afternoon Source booklet for use with Questions 1 to 6. Do not return the insert with the question paper.
MATH COLLEGE ALGEBRA/BUSN - PRACTICE EXAM #3 - FALL DR. DAVID BRIDGE
 MATH 15 - COLLEGE ALGEBRA/BUSN - PRACTICE EXAM # - FALL 2007 - DR. DAVID BRIDGE MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the simple interest.
MATH 15 - COLLEGE ALGEBRA/BUSN - PRACTICE EXAM # - FALL 2007 - DR. DAVID BRIDGE MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the simple interest.
Manual for SOA Exam FM/CAS Exam 2.
 Manual for SOA Exam FM/CAS Exam 2. Chapter 2. Cashflows. c 2009. Miguel A. Arcones. All rights reserved. Extract from: Arcones Manual for the SOA Exam FM/CAS Exam 2, Financial Mathematics. Fall 2009 Edition,
Manual for SOA Exam FM/CAS Exam 2. Chapter 2. Cashflows. c 2009. Miguel A. Arcones. All rights reserved. Extract from: Arcones Manual for the SOA Exam FM/CAS Exam 2, Financial Mathematics. Fall 2009 Edition,
Determine the amount that Danny will actually have at the end of 10 years.
 Chapter 2, Section 2 1. JT invests 3000 in an account earning interest at an annual effective rate of 6%. How much will JT have at the end of three and one half years? 2. Elsa invests 3000 in an account
Chapter 2, Section 2 1. JT invests 3000 in an account earning interest at an annual effective rate of 6%. How much will JT have at the end of three and one half years? 2. Elsa invests 3000 in an account
Foundations of Math 12 FIRST ASSIGNMENT Unit 1 On-Line Course
 Welcome to Navigate Powered by NIDES Foundations of Mathematics 12. Please note that the First Assignment is a requirement to be registered in the course. Legal last name: First name: Other last name:
Welcome to Navigate Powered by NIDES Foundations of Mathematics 12. Please note that the First Assignment is a requirement to be registered in the course. Legal last name: First name: Other last name:
3. Using an annual effective rate of 6%, calculate the present value of an annuity that pays 100 at the end of each month for 20 years.
 1. Calculate the present value of an annuity immediate that pays 1000 at the end of each year for 20 years. The interest rate is an annual effective interest rate of 8%. 2. Using a nominal rate of 6% compounded
1. Calculate the present value of an annuity immediate that pays 1000 at the end of each year for 20 years. The interest rate is an annual effective interest rate of 8%. 2. Using a nominal rate of 6% compounded
22. Construct a bond amortization table for a $1000 two-year bond with 7% coupons paid semi-annually bought to yield 8% semi-annually.
 Chapter 6 Exercises 22. Construct a bond amortization table for a $1000 two-year bond with 7% coupons paid semi-annually bought to yield 8% semi-annually. 23. Construct a bond amortization table for a
Chapter 6 Exercises 22. Construct a bond amortization table for a $1000 two-year bond with 7% coupons paid semi-annually bought to yield 8% semi-annually. 23. Construct a bond amortization table for a
(A) 20:13 (B) 13:20 (C) 4:5 (D) (A) 25:50(B) (C) 50% (D) 25% Comparing Quantities. Comparing Quantities
 Comparing Quantities 1.When 5% sale tax is added on the purchase of a bedsheet of Rs. 300, find the buying price or the cost price of the bedsheet. 2.A man bought 200 bulls for Rs. 10 each and sold
Comparing Quantities 1.When 5% sale tax is added on the purchase of a bedsheet of Rs. 300, find the buying price or the cost price of the bedsheet. 2.A man bought 200 bulls for Rs. 10 each and sold
Exponential Growth & Decay
 Name: Date: Eponential Growth & Decay Warm-Up: Evaluate the following eponential functions over the given domain. Graph the function over the given domain on the coordinate plane below. Determine the average
Name: Date: Eponential Growth & Decay Warm-Up: Evaluate the following eponential functions over the given domain. Graph the function over the given domain on the coordinate plane below. Determine the average
3.1 Simple Interest. Definition: I = Prt I = interest earned P = principal ( amount invested) r = interest rate (as a decimal) t = time
 3.1 Simple Interest Definition: I = Prt I = interest earned P = principal ( amount invested) r = interest rate (as a decimal) t = time An example: Find the interest on a boat loan of $5,000 at 16% for
3.1 Simple Interest Definition: I = Prt I = interest earned P = principal ( amount invested) r = interest rate (as a decimal) t = time An example: Find the interest on a boat loan of $5,000 at 16% for
Economics 135. Bond Pricing and Interest Rates. Professor Kevin D. Salyer. UC Davis. Fall 2009
 Economics 135 Bond Pricing and Interest Rates Professor Kevin D. Salyer UC Davis Fall 2009 Professor Kevin D. Salyer (UC Davis) Money and Banking Fall 2009 1 / 12 Bond Pricing Formulas - Interest Rates
Economics 135 Bond Pricing and Interest Rates Professor Kevin D. Salyer UC Davis Fall 2009 Professor Kevin D. Salyer (UC Davis) Money and Banking Fall 2009 1 / 12 Bond Pricing Formulas - Interest Rates
Mathematics of Financial Derivatives
 Mathematics of Financial Derivatives Lecture 9 Solesne Bourguin bourguin@math.bu.edu Boston University Department of Mathematics and Statistics Table of contents 1. Zero-coupon rates and bond pricing 2.
Mathematics of Financial Derivatives Lecture 9 Solesne Bourguin bourguin@math.bu.edu Boston University Department of Mathematics and Statistics Table of contents 1. Zero-coupon rates and bond pricing 2.
Mathematics of Financial Derivatives. Zero-coupon rates and bond pricing. Lecture 9. Zero-coupons. Notes. Notes
 Mathematics of Financial Derivatives Lecture 9 Solesne Bourguin bourguin@math.bu.edu Boston University Department of Mathematics and Statistics Zero-coupon rates and bond pricing Zero-coupons Definition:
Mathematics of Financial Derivatives Lecture 9 Solesne Bourguin bourguin@math.bu.edu Boston University Department of Mathematics and Statistics Zero-coupon rates and bond pricing Zero-coupons Definition:
