LAB NOTES: EXAMPLES OF PRELIS RUNS
|
|
|
- Alicia Waters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LAB NOTES: EXAMPLES OF PRELIS RUNS PRELIS 2 is a data preprocessor for processing data in preparation for estimating a structural equation model in LISREL 8 or 9. For information on reading data into PRELIS, see Lab Notes: Inputting Data into PRELIS available on the course webpage. In this note, I will give some common examples of PRELIS runs. PRELIS provides two important tasks: (1) It provides a useful descriptive data diagnostics in preparation for an SEM model, including histograms and bivariate tables for ordinal and categorical indicators, tests of univariate and multivariate normality (including univariate tests of skewness and kurtosis), descriptives on patterns of missing values, and provides imputation methods for missing values. (2) it computes and saves moment matrices (covariance and correlation matrices) as well as asymptotic covariance or variance matrices (for ordinal and non-normal data) for input into LISREL to obtain estimates of SEM under correct scale (continuous, ordered, dichotomous) and distribution (normal vs. non-normal) assumptions. LECTURE 5 presents a description of PRELIS and LISREL commands (as well as a brief overview of SIMPLIS commands). Here are a couple of illustrations of major PRELIS runs, with a couple of examples of resulting LISREL runs. Annotations are in bold font. At the end of this memo are annotated output from the two PRELIS outputs. Example 1: Estimating a covariance matrix under the assumption of interval scales and multivariate normality. (PRELIS Commend file preexch1.pr2. )!PRELIS Exchange Assume Interval: exch1 All comments are preceded by! This is the title DA NI=4 There are four input variables; I didn t specify an N, LA Labels to follow so PRELIS will determine that for me. Here are the four labels! How often have you watched your neighbor's property when they were out of town? These details! How often have you borrowed tools or small food items from your neighbors? (comments)! How often have you helped a neighbor with a problem? are for me (to jog my RA FI=h:\529data\lisrel ob.dat memory). CO 1-4 The raw data are in a file called lisrel ob.dat OU MA=CM CM=h:\529data\lisrel-ob.CM All four variables are treated as continuous. I m asking to compute a covariance matrix of the four observed variables and save them in a file called lisrel-ob.cm, which can be read into LISREL Example 2: Treating all four indicators as ordinal variables and computing a 4 x 4 polychoric correlation matrix (with 10 elements) and a 10 x 10 asymptotic covariance matrix (with 55 elements) for those 10 polychoric correlations. (PRELIS Commend file preexch2.pr2. )!PRELIS Exchange Assume Ordinal: exch2 DA NI=4 LA! How often have you watched your neighbor's property when they were out of town?! How often have you borrowed tools or small food items from your neighbors?! How often have you helped a neighbor with a problem?
2 RA FI=h:\529data\lisrel ob.dat OR 1-4 OU MA=PM PM=h:\529data\lisrel-ob.PM SA=h:\529data\ACOV.PM1 All four variables are treated as ordinal. I m asking to compute a polychoric correlation matrix of the four observed variables and save them in a file called lisrel-ob.pm, which can be read into LISREL. I m also asking to compute the asymptotic covariance matrix of the polychoric correlations and saave it in a file called lisrel ob.dat. Example 3: LISREL run that reads in the covariance matrix saved above (I moved it to a different directory on my c: drive) and estimates a one factor confirmatory factor model using ML. This model assumes observable variables are continuous and distributed multivariate normal. (LISREL command file ML_CFA.LS8. )!LISREL Exchange CFA 1 err-corr ML_CFA1A DA NI=4 NO=4670 MA=CM I am analyzing a covariance matrix CM FI=c:\529\lisrel-ob.CM I am reading in the covariance matrix from above. LA *! How often have you watched your neighbor's property when they were out of town?! How often have you borrowed tools or small food items from your neighbors?! How often have you helped a neighbor with a problem? SE MO NY=4 NE=1 LY=FU, FI PS=SY, FR TE=SY, FI VA 1.0 LY 1 1 FR LY 2 1 LY 3 1 LY 4 1 FR TE 1 1 TE 2 2 TE 3 3 TE 4 4 TE 2 4 PATH DIAGRAM OU ME=ML SE TV SC RS MI I m asking for maximum likelihood estimation Example 4: LISREL run that reads in the polychoric correlation matrix and asymptotic covariance matrix saved above (I moved it to a different directory on my c: drive) and estimates a one factor confirmatory factor model using WLS. This model assumes observable variables are each measured on ordinal scales and uses WLS to obtain consistent and asymptotically efficient estimates without the assumption of multivariate normality of observed variables. (LISREL command file ML_CFA.LS8. )!LISREL Exchange CFA 1 err-corr ML_CFA1A DA NI=4 NO=4670 MA=PM I m analyzing a polychoric correlation matrix. PM=c:\529\lisrel-ob.PM I m reading in the polychoric matrix from above. AC=c:\529\ACOV.PM1 I m reading in the asymptotic covariance matrix from above. LA
3 *! How often have you watched your neighbor's property when they were out of town?! How often have you borrowed tools or small food items from your neighbors?! How often have you helped a neighbor with a problem? SE MO NY=4 NE=1 LY=FU, FI PS=SY, FR TE=SY, FI VA 1.0 LY 1 1 FR LY 2 1 LY 3 1 LY 4 1 FR TE 1 1 TE 2 2 TE 3 3 TE 4 4 TE 2 4 PATH DIAGRAM OU ME=WL SE TV SC RS MI I m choosing weighted least squares (WL) as an estimator, which requires that I have read the moment matrix and the asymptotic covariance matrix.
4 DATE: 05/09/2012 TIME: 23:23 P R E L I S 2.80 BY Karl G. Jöreskog & Dag Sörbom This program is published exclusively by Scientific Software International, Inc N. Lincoln Avenue, Suite 100 Lincolnwood, IL 60712, U.S.A. Phone: (800) , (847) , Fax: (847) Copyright by Scientific Software International, Inc., Use of this program is subject to the terms specified in the Universal Copyright Convention. Website: The following lines were read from file H:\529 examples\preexch1.ls8:!prelis Exchange Assume Interval: exch1 DA NI=4 I am inputting four observed variables LA I m giving labels to the variables in free format (the default)! How often have you watched your neighbor's property when they were out of town? Here I m writing out the entire survey question, so I have it in the! How often have you borrowed tools or small food items from your neighbors? output. Note the exclamation point means this is a comment line,! How often have you helped a neighbor with a problem? not a LISREL command. RA FI=h:\529data\lisrel ob.dat Here, I m reading the raw data file RA(w) with FI(lename) = lisrel ob.dat in folder h:\529data\ CO 1-4 I am treating all four variables as continuous variables This will give me skewness and kurtosis measures. OU MA=CM CM=h:\529data\lisrel-ob.CM This is the OU(put) line, in which I am specifying that I want to compute a covariance matrix (MA=CM) and save it with filename lisrel-ob.cm in the folder h:\529data\. Total Sample Size = 4670 PRELIS gives me the sample size. Univariate Summary Statistics for Continuous Variables Variable Mean St. Dev. T-Value Skewness Kurtosis Minimum Freq. Maximum Freq watched borrow help asked T-value gives the t-statistic for testing whether the mean is zero. Skewness is a sample estimate of the standardized population third moment about the mean ( For normallydistributed skewness is zero. If it is positive, the distribution is skewed to the left; if it is negative, the distribution is skewed to the right. Kurtosis is a sample estimate of the standardized population fourth moment about the mean minus three. For normally distributed variables, kurtosis is equal to three. If it is greater than 3, it has positive kurtosis, resulting in thinner tails than normal; if it is less than 3, it has negative kurtosis, resulting in fatter tails than normal. The measure of kurtosis here is standardized and then subtracts 3. Therefore, a normally distributed variable will have kurtosis of zero; positive values means positive kurtosis (thin tails); negative values means negative kurtosis (fat tails).
5 Test of Univariate Normality for Continuous Variables This gives significance tests for whether skewness and kurtosis depart from zero (normality). Skewness Kurtosis Skewness and Kurtosis Variable Z-Score P-Value Z-Score P-Value Chi-Square P-Value watched borrow help asked Relative Multivariate Kurtosis = This is Mardia s measure of multivariate kurtosis (see lecture notes p. 201). Test of Multivariate Normality for Continuous Variables This gives significance tests for Mardia s measure of multivariate skewness and kurtosis (see lecture notes p. 201). Skewness Kurtosis Skewness and Kurtosis Value Z-Score P-Value Value Z-Score P-Value Chi-Square P-Value Histograms for Continuous Variables watched Frequency Percentage Lower Class Limit borrow Frequency Percentage Lower Class Limit help
6 Frequency Percentage Lower Class Limit asked Frequency Percentage Lower Class Limit Covariance Matrix This is the covariance matrix of observed variables, assuming interval scales. watched borrow help asked Means Standard Deviations
7 DATE: 05/17/2012 TIME: 16:47 P R E L I S 2.80 BY Karl G. Jöreskog & Dag Sörbom This program is published exclusively by Scientific Software International, Inc N. Lincoln Avenue, Suite 100 Lincolnwood, IL 60712, U.S.A. Phone: (800) , (847) , Fax: (847) Copyright by Scientific Software International, Inc., Use of this program is subject to the terms specified in the Universal Copyright Convention. Website: The following lines were read from file H:\529 examples\preexch2.ls8:!prelis Exchange Assume Ordinal: exch2 DA NI=4 LA! How often have you watched your neighbor's property when they were out of town?! How often have you borrowed tools or small food items from your neighbors?! How often have you helped a neighbor with a problem? RA FI=h:\529data\lisrel ob.dat Reading in Raw data OR 1-4 OU MA=PM PM=h:\529data\lisrel-ob.PM SA=h:\529data\ACOV.PM1 PM Saves the matrix of polychoric correlations in file lisrel-ob.pm in folder h:\529data\ and the asymptotic covariance matrix of the polychoric correlations in file ACOV.PM in the same file. Total Sample Size = 4670 Univariate Marginal Parameters Variable Mean St. Dev. Thresholds watched These are thresholds for the three-category ordinal variables borrow help asked Univariate Distributions for Ordinal Variables Histograms for the ordinal variables watched Frequency Percentage Bar Chart borrow Frequency Percentage Bar Chart help Frequency Percentage Bar Chart asked Frequency Percentage Bar Chart There are 75 distinct response patterns, see FREQ-file. The 20 most common patterns are : Patterns in the data
8 Correlations and Test Statistics (PE=Pearson Product Moment, PC=Polychoric, PS=Polyserial) Test of Model Test of Close Fit Variable vs. Variable Correlation Chi-Squ. D.F. P-Value RMSEA P-Value borrow vs. watched (PC) help vs. watched (PC) help vs. borrow (PC) asked vs. watched (PC) asked vs. borrow (PC) asked vs. help (PC) This is a test of bivariate normality between the two latent variables; in each case we reject the null of bivariate normality; in each case we reject he hypothesis of normality; RMSEA <.05 suggests a reasonable fit in a large sample Percentage of Tests Exceeding 0.5% Significance Level: 0.0% Percentage of Tests Exceeding 1.0% Significance Level: 0.0% Percentage of Tests Exceeding 5.0% Significance Level: 0.0% Correlation Matrix watched borrow help asked Means Standard Deviations The Problem used 5184 Bytes (= 0.0% of available workspace)
Subject CS1 Actuarial Statistics 1 Core Principles. Syllabus. for the 2019 exams. 1 June 2018
 ` Subject CS1 Actuarial Statistics 1 Core Principles Syllabus for the 2019 exams 1 June 2018 Copyright in this Core Reading is the property of the Institute and Faculty of Actuaries who are the sole distributors.
` Subject CS1 Actuarial Statistics 1 Core Principles Syllabus for the 2019 exams 1 June 2018 Copyright in this Core Reading is the property of the Institute and Faculty of Actuaries who are the sole distributors.
Robust Estimation Methods in Confirmatory Factor Analysis of Likert Scales: A Simulation Study
 International Review of Social Sciences and Humanities Vol. 11, No. 2 (2016), pp. 80-96 www.irssh.com ISSN 2248-9010 (Online), ISSN 2250-0715 (Print) Robust Estimation Methods in Confirmatory Factor Analysis
International Review of Social Sciences and Humanities Vol. 11, No. 2 (2016), pp. 80-96 www.irssh.com ISSN 2248-9010 (Online), ISSN 2250-0715 (Print) Robust Estimation Methods in Confirmatory Factor Analysis
CHAPTER 12 EXAMPLES: MONTE CARLO SIMULATION STUDIES
 Examples: Monte Carlo Simulation Studies CHAPTER 12 EXAMPLES: MONTE CARLO SIMULATION STUDIES Monte Carlo simulation studies are often used for methodological investigations of the performance of statistical
Examples: Monte Carlo Simulation Studies CHAPTER 12 EXAMPLES: MONTE CARLO SIMULATION STUDIES Monte Carlo simulation studies are often used for methodological investigations of the performance of statistical
General structural model Part 2: Nonnormality. Psychology 588: Covariance structure and factor models
 General structural model Part 2: Nonnormality Psychology 588: Covariance structure and factor models Conditions for efficient ML & GLS 2 F ML is derived with an assumption that all DVs are multivariate
General structural model Part 2: Nonnormality Psychology 588: Covariance structure and factor models Conditions for efficient ML & GLS 2 F ML is derived with an assumption that all DVs are multivariate
Chapter 6 Simple Correlation and
 Contents Chapter 1 Introduction to Statistics Meaning of Statistics... 1 Definition of Statistics... 2 Importance and Scope of Statistics... 2 Application of Statistics... 3 Characteristics of Statistics...
Contents Chapter 1 Introduction to Statistics Meaning of Statistics... 1 Definition of Statistics... 2 Importance and Scope of Statistics... 2 Application of Statistics... 3 Characteristics of Statistics...
Lecture 6: Non Normal Distributions
 Lecture 6: Non Normal Distributions and their Uses in GARCH Modelling Prof. Massimo Guidolin 20192 Financial Econometrics Spring 2015 Overview Non-normalities in (standardized) residuals from asset return
Lecture 6: Non Normal Distributions and their Uses in GARCH Modelling Prof. Massimo Guidolin 20192 Financial Econometrics Spring 2015 Overview Non-normalities in (standardized) residuals from asset return
Hypothesis Tests: One Sample Mean Cal State Northridge Ψ320 Andrew Ainsworth PhD
 Hypothesis Tests: One Sample Mean Cal State Northridge Ψ320 Andrew Ainsworth PhD MAJOR POINTS Sampling distribution of the mean revisited Testing hypotheses: sigma known An example Testing hypotheses:
Hypothesis Tests: One Sample Mean Cal State Northridge Ψ320 Andrew Ainsworth PhD MAJOR POINTS Sampling distribution of the mean revisited Testing hypotheses: sigma known An example Testing hypotheses:
Valid Missing Total. N Percent N Percent N Percent , ,0% 0,0% 2 100,0% 1, ,0% 0,0% 2 100,0% 2, ,0% 0,0% 5 100,0%
 dimension1 GET FILE= validacaonestscoremédico.sav' (só com os 59 doentes) /COMPRESSED. SORT CASES BY UMcpEVA (D). EXAMINE VARIABLES=UMcpEVA BY NoRespostasSignif /PLOT BOXPLOT HISTOGRAM NPPLOT /COMPARE
dimension1 GET FILE= validacaonestscoremédico.sav' (só com os 59 doentes) /COMPRESSED. SORT CASES BY UMcpEVA (D). EXAMINE VARIABLES=UMcpEVA BY NoRespostasSignif /PLOT BOXPLOT HISTOGRAM NPPLOT /COMPARE
Lecture Week 4 Inspecting Data: Distributions
 Lecture Week 4 Inspecting Data: Distributions Introduction to Research Methods & Statistics 2013 2014 Hemmo Smit So next week No lecture & workgroups But Practice Test on-line (BB) Enter data for your
Lecture Week 4 Inspecting Data: Distributions Introduction to Research Methods & Statistics 2013 2014 Hemmo Smit So next week No lecture & workgroups But Practice Test on-line (BB) Enter data for your
YOUNGKYOUNG MIN UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA
 ROBUSTNESS IN CONFIRMATORY FACTOR ANALYSIS: THE EFFECT OF SAMPLE SIZE, DEGREE OF NON-NORMALITY, MODEL, AND ESTIMATION METHOD ON ACCURACY OF ESTIMATION FOR STANDARD ERRORS By YOUNGKYOUNG MIN A DISSERTATION
ROBUSTNESS IN CONFIRMATORY FACTOR ANALYSIS: THE EFFECT OF SAMPLE SIZE, DEGREE OF NON-NORMALITY, MODEL, AND ESTIMATION METHOD ON ACCURACY OF ESTIMATION FOR STANDARD ERRORS By YOUNGKYOUNG MIN A DISSERTATION
FV N = PV (1+ r) N. FV N = PVe rs * N 2011 ELAN GUIDES 3. The Future Value of a Single Cash Flow. The Present Value of a Single Cash Flow
 QUANTITATIVE METHODS The Future Value of a Single Cash Flow FV N = PV (1+ r) N The Present Value of a Single Cash Flow PV = FV (1+ r) N PV Annuity Due = PVOrdinary Annuity (1 + r) FV Annuity Due = FVOrdinary
QUANTITATIVE METHODS The Future Value of a Single Cash Flow FV N = PV (1+ r) N The Present Value of a Single Cash Flow PV = FV (1+ r) N PV Annuity Due = PVOrdinary Annuity (1 + r) FV Annuity Due = FVOrdinary
GGraph. Males Only. Premium. Experience. GGraph. Gender. 1 0: R 2 Linear = : R 2 Linear = Page 1
 GGraph 9 Gender : R Linear =.43 : R Linear =.769 8 7 6 5 4 3 5 5 Males Only GGraph Page R Linear =.43 R Loess 9 8 7 6 5 4 5 5 Explore Case Processing Summary Cases Valid Missing Total N Percent N Percent
GGraph 9 Gender : R Linear =.43 : R Linear =.769 8 7 6 5 4 3 5 5 Males Only GGraph Page R Linear =.43 R Loess 9 8 7 6 5 4 5 5 Explore Case Processing Summary Cases Valid Missing Total N Percent N Percent
XLSTAT TIP SHEET FOR BUSINESS STATISTICS CENGAGE LEARNING
 XLSTAT TIP SHEET FOR BUSINESS STATISTICS CENGAGE LEARNING INTRODUCTION XLSTAT makes accessible to anyone a powerful, complete and user-friendly data analysis and statistical solution. Accessibility to
XLSTAT TIP SHEET FOR BUSINESS STATISTICS CENGAGE LEARNING INTRODUCTION XLSTAT makes accessible to anyone a powerful, complete and user-friendly data analysis and statistical solution. Accessibility to
Statistics & Statistical Tests: Assumptions & Conclusions
 Degrees of Freedom Statistics & Statistical Tests: Assumptions & Conclusions Kinds of degrees of freedom Kinds of Distributions Kinds of Statistics & assumptions required to perform each Normal Distributions
Degrees of Freedom Statistics & Statistical Tests: Assumptions & Conclusions Kinds of degrees of freedom Kinds of Distributions Kinds of Statistics & assumptions required to perform each Normal Distributions
Summary of Statistical Analysis Tools EDAD 5630
 Summary of Statistical Analysis Tools EDAD 5630 Test Name Program Used Purpose Steps Main Uses/Applications in Schools Principal Component Analysis SPSS Measure Underlying Constructs Reliability SPSS Measure
Summary of Statistical Analysis Tools EDAD 5630 Test Name Program Used Purpose Steps Main Uses/Applications in Schools Principal Component Analysis SPSS Measure Underlying Constructs Reliability SPSS Measure
Chapter 6 Part 3 October 21, Bootstrapping
 Chapter 6 Part 3 October 21, 2008 Bootstrapping From the internet: The bootstrap involves repeated re-estimation of a parameter using random samples with replacement from the original data. Because the
Chapter 6 Part 3 October 21, 2008 Bootstrapping From the internet: The bootstrap involves repeated re-estimation of a parameter using random samples with replacement from the original data. Because the
Statistical Models of Stocks and Bonds. Zachary D Easterling: Department of Economics. The University of Akron
 Statistical Models of Stocks and Bonds Zachary D Easterling: Department of Economics The University of Akron Abstract One of the key ideas in monetary economics is that the prices of investments tend to
Statistical Models of Stocks and Bonds Zachary D Easterling: Department of Economics The University of Akron Abstract One of the key ideas in monetary economics is that the prices of investments tend to
ANALYSIS USING STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELING (SEM)
 CHAPTER V ANALYSIS USING STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELING (SEM) 5.1 Nature of SEM The model grows out of and serves purposes similar to multiple regression, but in a more powerful way which takes into account
CHAPTER V ANALYSIS USING STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELING (SEM) 5.1 Nature of SEM The model grows out of and serves purposes similar to multiple regression, but in a more powerful way which takes into account
Question scores. Question 1a 1b 1c 1d 1e 2a 2b 2c 2d 2e 2f 3a 3b 3c 3d M ult:choice Points
 Economics 02: Analysis of Economic Data Cameron Winter 204 January 30 Department of Economics, U.C.-Davis First Midterm Exam (Version A) Compulsory. Closed book. Total of 30 points and worth 22.5% of course
Economics 02: Analysis of Economic Data Cameron Winter 204 January 30 Department of Economics, U.C.-Davis First Midterm Exam (Version A) Compulsory. Closed book. Total of 30 points and worth 22.5% of course
SPSS I: Menu Basics Practice Exercises Target Software & Version: SPSS V Last Updated on January 17, 2007 Created by Jennifer Ortman
 SPSS I: Menu Basics Practice Exercises Target Software & Version: SPSS V. 14.02 Last Updated on January 17, 2007 Created by Jennifer Ortman PRACTICE EXERCISES Exercise A Obtain descriptive statistics (mean,
SPSS I: Menu Basics Practice Exercises Target Software & Version: SPSS V. 14.02 Last Updated on January 17, 2007 Created by Jennifer Ortman PRACTICE EXERCISES Exercise A Obtain descriptive statistics (mean,
1. Distinguish three missing data mechanisms:
 1 DATA SCREENING I. Preliminary inspection of the raw data make sure that there are no obvious coding errors (e.g., all values for the observed variables are in the admissible range) and that all variables
1 DATA SCREENING I. Preliminary inspection of the raw data make sure that there are no obvious coding errors (e.g., all values for the observed variables are in the admissible range) and that all variables
Key Objectives. Module 2: The Logic of Statistical Inference. Z-scores. SGSB Workshop: Using Statistical Data to Make Decisions
 SGSB Workshop: Using Statistical Data to Make Decisions Module 2: The Logic of Statistical Inference Dr. Tom Ilvento January 2006 Dr. Mugdim Pašić Key Objectives Understand the logic of statistical inference
SGSB Workshop: Using Statistical Data to Make Decisions Module 2: The Logic of Statistical Inference Dr. Tom Ilvento January 2006 Dr. Mugdim Pašić Key Objectives Understand the logic of statistical inference
Descriptive Analysis
 Descriptive Analysis HERTANTO WAHYU SUBAGIO Univariate Analysis Univariate analysis involves the examination across cases of one variable at a time. There are three major characteristics of a single variable
Descriptive Analysis HERTANTO WAHYU SUBAGIO Univariate Analysis Univariate analysis involves the examination across cases of one variable at a time. There are three major characteristics of a single variable
Equivalence Tests for Two Correlated Proportions
 Chapter 165 Equivalence Tests for Two Correlated Proportions Introduction The two procedures described in this chapter compute power and sample size for testing equivalence using differences or ratios
Chapter 165 Equivalence Tests for Two Correlated Proportions Introduction The two procedures described in this chapter compute power and sample size for testing equivalence using differences or ratios
Establishing a framework for statistical analysis via the Generalized Linear Model
 PSY349: Lecture 1: INTRO & CORRELATION Establishing a framework for statistical analysis via the Generalized Linear Model GLM provides a unified framework that incorporates a number of statistical methods
PSY349: Lecture 1: INTRO & CORRELATION Establishing a framework for statistical analysis via the Generalized Linear Model GLM provides a unified framework that incorporates a number of statistical methods
Problem max points points scored Total 120. Do all 6 problems.
 Solutions to (modified) practice exam 4 Statistics 224 Practice exam 4 FINAL Your Name Friday 12/21/07 Professor Michael Iltis (Lecture 2) Discussion section (circle yours) : section: 321 (3:30 pm M) 322
Solutions to (modified) practice exam 4 Statistics 224 Practice exam 4 FINAL Your Name Friday 12/21/07 Professor Michael Iltis (Lecture 2) Discussion section (circle yours) : section: 321 (3:30 pm M) 322
SPSS Reliability Example
 Psy 495 Psychological Measurement, Spring 2017 1 SPSS Reliability Example Menus To obtain descriptive statistics, such as mean, variance, skew, and kurtosis. Analyze Descriptive Statistics Descriptives
Psy 495 Psychological Measurement, Spring 2017 1 SPSS Reliability Example Menus To obtain descriptive statistics, such as mean, variance, skew, and kurtosis. Analyze Descriptive Statistics Descriptives
Contents. An Overview of Statistical Applications CHAPTER 1. Contents (ix) Preface... (vii)
 Contents (ix) Contents Preface... (vii) CHAPTER 1 An Overview of Statistical Applications 1.1 Introduction... 1 1. Probability Functions and Statistics... 1..1 Discrete versus Continuous Functions... 1..
Contents (ix) Contents Preface... (vii) CHAPTER 1 An Overview of Statistical Applications 1.1 Introduction... 1 1. Probability Functions and Statistics... 1..1 Discrete versus Continuous Functions... 1..
CHAPTER 6 DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION
 208 CHAPTER 6 DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION Sr. No. Content Page No. 6.1 Introduction 212 6.2 Reliability and Normality of Data 212 6.3 Descriptive Analysis 213 6.4 Cross Tabulation 218 6.5 Chi Square
208 CHAPTER 6 DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION Sr. No. Content Page No. 6.1 Introduction 212 6.2 Reliability and Normality of Data 212 6.3 Descriptive Analysis 213 6.4 Cross Tabulation 218 6.5 Chi Square
Small Sample Performance of Instrumental Variables Probit Estimators: A Monte Carlo Investigation
 Small Sample Performance of Instrumental Variables Probit : A Monte Carlo Investigation July 31, 2008 LIML Newey Small Sample Performance? Goals Equations Regressors and Errors Parameters Reduced Form
Small Sample Performance of Instrumental Variables Probit : A Monte Carlo Investigation July 31, 2008 LIML Newey Small Sample Performance? Goals Equations Regressors and Errors Parameters Reduced Form
Handout seminar 6, ECON4150
 Handout seminar 6, ECON4150 Herman Kruse March 17, 2013 Introduction - list of commands This week, we need a couple of new commands in order to solve all the problems. hist var1 if var2, options - creates
Handout seminar 6, ECON4150 Herman Kruse March 17, 2013 Introduction - list of commands This week, we need a couple of new commands in order to solve all the problems. hist var1 if var2, options - creates
34.S-[F] SU-02 June All Syllabus Science Faculty B.Sc. I Yr. Stat. [Opt.] [Sem.I & II] - 1 -
![34.S-[F] SU-02 June All Syllabus Science Faculty B.Sc. I Yr. Stat. [Opt.] [Sem.I & II] - 1 - 34.S-[F] SU-02 June All Syllabus Science Faculty B.Sc. I Yr. Stat. [Opt.] [Sem.I & II] - 1 -](/thumbs/87/96342487.jpg) [Sem.I & II] - 1 - [Sem.I & II] - 2 - [Sem.I & II] - 3 - Syllabus of B.Sc. First Year Statistics [Optional ] Sem. I & II effect for the academic year 2014 2015 [Sem.I & II] - 4 - SYLLABUS OF F.Y.B.Sc.
[Sem.I & II] - 1 - [Sem.I & II] - 2 - [Sem.I & II] - 3 - Syllabus of B.Sc. First Year Statistics [Optional ] Sem. I & II effect for the academic year 2014 2015 [Sem.I & II] - 4 - SYLLABUS OF F.Y.B.Sc.
Florida State University Libraries
 Florida State University Libraries Electronic Theses, Treatises and Dissertations The Graduate School 0 Effect-Size Index for Evaluation of Model- Data Fit in Structural Equation Modeling Mengyao Cui Follow
Florida State University Libraries Electronic Theses, Treatises and Dissertations The Graduate School 0 Effect-Size Index for Evaluation of Model- Data Fit in Structural Equation Modeling Mengyao Cui Follow
Rationale. Learning about return and risk from the historical record and beta estimation. T Bills and Inflation
 Learning about return and risk from the historical record and beta estimation Reference: Investments, Bodie, Kane, and Marcus, and Investment Analysis and Behavior, Nofsinger and Hirschey Nattawut Jenwittayaroje,
Learning about return and risk from the historical record and beta estimation Reference: Investments, Bodie, Kane, and Marcus, and Investment Analysis and Behavior, Nofsinger and Hirschey Nattawut Jenwittayaroje,
Effects of skewness and kurtosis on normal-theory based maximum likelihood test statistic in multilevel structural equation modeling
 Behav Res (2011) 43:1066 1074 DOI 10.3758/s13428-011-0115-7 Effects of skewness and kurtosis on normal-theory based maximum likelihood test statistic in multilevel structural equation modeling Ehri Ryu
Behav Res (2011) 43:1066 1074 DOI 10.3758/s13428-011-0115-7 Effects of skewness and kurtosis on normal-theory based maximum likelihood test statistic in multilevel structural equation modeling Ehri Ryu
Monetary Economics Measuring Asset Returns. Gerald P. Dwyer Fall 2015
 Monetary Economics Measuring Asset Returns Gerald P. Dwyer Fall 2015 WSJ Readings Readings this lecture, Cuthbertson Ch. 9 Readings next lecture, Cuthbertson, Chs. 10 13 Measuring Asset Returns Outline
Monetary Economics Measuring Asset Returns Gerald P. Dwyer Fall 2015 WSJ Readings Readings this lecture, Cuthbertson Ch. 9 Readings next lecture, Cuthbertson, Chs. 10 13 Measuring Asset Returns Outline
32.S [F] SU 02 June All Syllabus Science Faculty B.A. I Yr. Stat. [Opt.] [Sem.I & II] 1
![32.S [F] SU 02 June All Syllabus Science Faculty B.A. I Yr. Stat. [Opt.] [Sem.I & II] 1 32.S [F] SU 02 June All Syllabus Science Faculty B.A. I Yr. Stat. [Opt.] [Sem.I & II] 1](/thumbs/87/96342483.jpg) 32.S [F] SU 02 June 2014 2015 All Syllabus Science Faculty B.A. I Yr. Stat. [Opt.] [Sem.I & II] 1 32.S [F] SU 02 June 2014 2015 All Syllabus Science Faculty B.A. I Yr. Stat. [Opt.] [Sem.I & II] 2 32.S
32.S [F] SU 02 June 2014 2015 All Syllabus Science Faculty B.A. I Yr. Stat. [Opt.] [Sem.I & II] 1 32.S [F] SU 02 June 2014 2015 All Syllabus Science Faculty B.A. I Yr. Stat. [Opt.] [Sem.I & II] 2 32.S
Financial Econometrics
 Financial Econometrics Introduction to Financial Econometrics Gerald P. Dwyer Trinity College, Dublin January 2016 Outline 1 Set Notation Notation for returns 2 Summary statistics for distribution of data
Financial Econometrics Introduction to Financial Econometrics Gerald P. Dwyer Trinity College, Dublin January 2016 Outline 1 Set Notation Notation for returns 2 Summary statistics for distribution of data
Overview/Outline. Moving beyond raw data. PSY 464 Advanced Experimental Design. Describing and Exploring Data The Normal Distribution
 PSY 464 Advanced Experimental Design Describing and Exploring Data The Normal Distribution 1 Overview/Outline Questions-problems? Exploring/Describing data Organizing/summarizing data Graphical presentations
PSY 464 Advanced Experimental Design Describing and Exploring Data The Normal Distribution 1 Overview/Outline Questions-problems? Exploring/Describing data Organizing/summarizing data Graphical presentations
Data Distributions and Normality
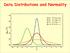 Data Distributions and Normality Definition (Non)Parametric Parametric statistics assume that data come from a normal distribution, and make inferences about parameters of that distribution. These statistical
Data Distributions and Normality Definition (Non)Parametric Parametric statistics assume that data come from a normal distribution, and make inferences about parameters of that distribution. These statistical
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novapdf printer (http://www.novapdf.com)
 Monday October 3 10:11:57 2011 Page 1 (R) / / / / / / / / / / / / Statistics/Data Analysis Education Box and save these files in a local folder. name:
Monday October 3 10:11:57 2011 Page 1 (R) / / / / / / / / / / / / Statistics/Data Analysis Education Box and save these files in a local folder. name:
Introduction to Descriptive Statistics
 Introduction to Descriptive Statistics 17.871 Types of Variables ~Nominal (Quantitative) Nominal (Qualitative) categorical Ordinal Interval or ratio Describing data Moment Non-mean based measure Center
Introduction to Descriptive Statistics 17.871 Types of Variables ~Nominal (Quantitative) Nominal (Qualitative) categorical Ordinal Interval or ratio Describing data Moment Non-mean based measure Center
Rationale Reference Nattawut Jenwittayaroje, Ph.D., CFA Expected Return and Standard Deviation Example: Ending Price =
 Rationale Lecture 4: Learning about return and risk from the historical record Reference: Investments, Bodie, Kane, and Marcus, and Investment Analysis and Behavior, Nofsinger and Hirschey Nattawut Jenwittayaroje,
Rationale Lecture 4: Learning about return and risk from the historical record Reference: Investments, Bodie, Kane, and Marcus, and Investment Analysis and Behavior, Nofsinger and Hirschey Nattawut Jenwittayaroje,
Data screening, transformations: MRC05
 Dale Berger Data screening, transformations: MRC05 This is a demonstration of data screening and transformations for a regression analysis. Our interest is in predicting current salary from education level
Dale Berger Data screening, transformations: MRC05 This is a demonstration of data screening and transformations for a regression analysis. Our interest is in predicting current salary from education level
Contents Part I Descriptive Statistics 1 Introduction and Framework Population, Sample, and Observations Variables Quali
 Part I Descriptive Statistics 1 Introduction and Framework... 3 1.1 Population, Sample, and Observations... 3 1.2 Variables.... 4 1.2.1 Qualitative and Quantitative Variables.... 5 1.2.2 Discrete and Continuous
Part I Descriptive Statistics 1 Introduction and Framework... 3 1.1 Population, Sample, and Observations... 3 1.2 Variables.... 4 1.2.1 Qualitative and Quantitative Variables.... 5 1.2.2 Discrete and Continuous
Diploma Part 2. Quantitative Methods. Examiner s Suggested Answers
 Diploma Part 2 Quantitative Methods Examiner s Suggested Answers Question 1 (a) The binomial distribution may be used in an experiment in which there are only two defined outcomes in any particular trial
Diploma Part 2 Quantitative Methods Examiner s Suggested Answers Question 1 (a) The binomial distribution may be used in an experiment in which there are only two defined outcomes in any particular trial
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF HUMANITIES AND CULTURAL STUDIES ISSN
 Investigating the Factors Impacting on the Implementation of the Operating Budget Regarding Activity-Based Costing in the Ministry of Economic Affairs and Finance Saeid Azimi Financial Management, Institution
Investigating the Factors Impacting on the Implementation of the Operating Budget Regarding Activity-Based Costing in the Ministry of Economic Affairs and Finance Saeid Azimi Financial Management, Institution
Business Statistics 41000: Probability 3
 Business Statistics 41000: Probability 3 Drew D. Creal University of Chicago, Booth School of Business February 7 and 8, 2014 1 Class information Drew D. Creal Email: dcreal@chicagobooth.edu Office: 404
Business Statistics 41000: Probability 3 Drew D. Creal University of Chicago, Booth School of Business February 7 and 8, 2014 1 Class information Drew D. Creal Email: dcreal@chicagobooth.edu Office: 404
Table of Contents. New to the Second Edition... Chapter 1: Introduction : Social Research...
 iii Table of Contents Preface... xiii Purpose... xiii Outline of Chapters... xiv New to the Second Edition... xvii Acknowledgements... xviii Chapter 1: Introduction... 1 1.1: Social Research... 1 Introduction...
iii Table of Contents Preface... xiii Purpose... xiii Outline of Chapters... xiv New to the Second Edition... xvii Acknowledgements... xviii Chapter 1: Introduction... 1 1.1: Social Research... 1 Introduction...
MEMORANDUM. TO: Me FROM: Me RE: Memo containing output for SPSS practice exam #2
 MEMORADUM DATE: ovember 5, 2024 TO: Me FROM: Me RE: Memo containing output for SPSS practice exam #2 Task 3a. Below is bar graph of the number of cases for the variable beltfrnt. 40 30 20 10 0 o Seat Belt
MEMORADUM DATE: ovember 5, 2024 TO: Me FROM: Me RE: Memo containing output for SPSS practice exam #2 Task 3a. Below is bar graph of the number of cases for the variable beltfrnt. 40 30 20 10 0 o Seat Belt
Analysis of Messy Data (Outliers etc.)
 Analysis of Messy Data (Outliers etc.) Saif Shahin The University of Texas at Austin Entry for International Encyclopedia of Communication Research Methods Saif Shahin School of Journalism The University
Analysis of Messy Data (Outliers etc.) Saif Shahin The University of Texas at Austin Entry for International Encyclopedia of Communication Research Methods Saif Shahin School of Journalism The University
Non-normality of Data in Structural Equation Models
 Research Report UCD-ITS-RR-08-47 Non-normality of Data in Structural Equation Models January 2008 Shengyi Gao Patricia Mokhtarian Robert Johnston Institute of Transportation Studies University of California,
Research Report UCD-ITS-RR-08-47 Non-normality of Data in Structural Equation Models January 2008 Shengyi Gao Patricia Mokhtarian Robert Johnston Institute of Transportation Studies University of California,
Maximum Likelihood Estimation Richard Williams, University of Notre Dame, https://www3.nd.edu/~rwilliam/ Last revised January 10, 2017
 Maximum Likelihood Estimation Richard Williams, University of otre Dame, https://www3.nd.edu/~rwilliam/ Last revised January 0, 207 [This handout draws very heavily from Regression Models for Categorical
Maximum Likelihood Estimation Richard Williams, University of otre Dame, https://www3.nd.edu/~rwilliam/ Last revised January 0, 207 [This handout draws very heavily from Regression Models for Categorical
Lecture 9: Markov and Regime
 Lecture 9: Markov and Regime Switching Models Prof. Massimo Guidolin 20192 Financial Econometrics Spring 2017 Overview Motivation Deterministic vs. Endogeneous, Stochastic Switching Dummy Regressiom Switching
Lecture 9: Markov and Regime Switching Models Prof. Massimo Guidolin 20192 Financial Econometrics Spring 2017 Overview Motivation Deterministic vs. Endogeneous, Stochastic Switching Dummy Regressiom Switching
KARACHI UNIVERSITY BUSINESS SCHOOL UNIVERSITY OF KARACHI BS (BBA) VI
 88 P a g e B S ( B B A ) S y l l a b u s KARACHI UNIVERSITY BUSINESS SCHOOL UNIVERSITY OF KARACHI BS (BBA) VI Course Title : STATISTICS Course Number : BA(BS) 532 Credit Hours : 03 Course 1. Statistical
88 P a g e B S ( B B A ) S y l l a b u s KARACHI UNIVERSITY BUSINESS SCHOOL UNIVERSITY OF KARACHI BS (BBA) VI Course Title : STATISTICS Course Number : BA(BS) 532 Credit Hours : 03 Course 1. Statistical
The University of Chicago, Booth School of Business Business 41202, Spring Quarter 2009, Mr. Ruey S. Tsay. Solutions to Final Exam
 The University of Chicago, Booth School of Business Business 41202, Spring Quarter 2009, Mr. Ruey S. Tsay Solutions to Final Exam Problem A: (42 pts) Answer briefly the following questions. 1. Questions
The University of Chicago, Booth School of Business Business 41202, Spring Quarter 2009, Mr. Ruey S. Tsay Solutions to Final Exam Problem A: (42 pts) Answer briefly the following questions. 1. Questions
Descriptive Statistics
 Petra Petrovics Descriptive Statistics 2 nd seminar DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Definition: Descriptive statistics is concerned only with collecting and describing data Methods: - statistical tables and graphs
Petra Petrovics Descriptive Statistics 2 nd seminar DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Definition: Descriptive statistics is concerned only with collecting and describing data Methods: - statistical tables and graphs
Analysis of the Influence of the Annualized Rate of Rentability on the Unit Value of the Net Assets of the Private Administered Pension Fund NN
 Year XVIII No. 20/2018 175 Analysis of the Influence of the Annualized Rate of Rentability on the Unit Value of the Net Assets of the Private Administered Pension Fund NN Constantin DURAC 1 1 University
Year XVIII No. 20/2018 175 Analysis of the Influence of the Annualized Rate of Rentability on the Unit Value of the Net Assets of the Private Administered Pension Fund NN Constantin DURAC 1 1 University
Manager Comparison Report June 28, Report Created on: July 25, 2013
 Manager Comparison Report June 28, 213 Report Created on: July 25, 213 Page 1 of 14 Performance Evaluation Manager Performance Growth of $1 Cumulative Performance & Monthly s 3748 3578 348 3238 368 2898
Manager Comparison Report June 28, 213 Report Created on: July 25, 213 Page 1 of 14 Performance Evaluation Manager Performance Growth of $1 Cumulative Performance & Monthly s 3748 3578 348 3238 368 2898
Ho Ho Quantitative Portfolio Manager, CalPERS
 Portfolio Construction and Risk Management under Non-Normality Fiduciary Investors Symposium, Beijing - China October 23 rd 26 th, 2011 Ho Ho Quantitative Portfolio Manager, CalPERS The views expressed
Portfolio Construction and Risk Management under Non-Normality Fiduciary Investors Symposium, Beijing - China October 23 rd 26 th, 2011 Ho Ho Quantitative Portfolio Manager, CalPERS The views expressed
Basic Procedure for Histograms
 Basic Procedure for Histograms 1. Compute the range of observations (min. & max. value) 2. Choose an initial # of classes (most likely based on the range of values, try and find a number of classes that
Basic Procedure for Histograms 1. Compute the range of observations (min. & max. value) 2. Choose an initial # of classes (most likely based on the range of values, try and find a number of classes that
CFA Level I - LOS Changes
 CFA Level I - LOS Changes 2017-2018 Topic LOS Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) LOS Level I - 2018 (529 LOS) Compared Ethics 1.1.a explain ethics 1.1.a explain ethics Ethics 1.1.b describe the role of a code of
CFA Level I - LOS Changes 2017-2018 Topic LOS Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) LOS Level I - 2018 (529 LOS) Compared Ethics 1.1.a explain ethics 1.1.a explain ethics Ethics 1.1.b describe the role of a code of
CFA Level I - LOS Changes
 CFA Level I - LOS Changes 2018-2019 Topic LOS Level I - 2018 (529 LOS) LOS Level I - 2019 (525 LOS) Compared Ethics 1.1.a explain ethics 1.1.a explain ethics Ethics Ethics 1.1.b 1.1.c describe the role
CFA Level I - LOS Changes 2018-2019 Topic LOS Level I - 2018 (529 LOS) LOS Level I - 2019 (525 LOS) Compared Ethics 1.1.a explain ethics 1.1.a explain ethics Ethics Ethics 1.1.b 1.1.c describe the role
Booth School of Business, University of Chicago Business 41202, Spring Quarter 2016, Mr. Ruey S. Tsay. Solutions to Midterm
 Booth School of Business, University of Chicago Business 41202, Spring Quarter 2016, Mr. Ruey S. Tsay Solutions to Midterm Problem A: (30 pts) Answer briefly the following questions. Each question has
Booth School of Business, University of Chicago Business 41202, Spring Quarter 2016, Mr. Ruey S. Tsay Solutions to Midterm Problem A: (30 pts) Answer briefly the following questions. Each question has
Economics 483. Midterm Exam. 1. Consider the following monthly data for Microsoft stock over the period December 1995 through December 1996:
 University of Washington Summer Department of Economics Eric Zivot Economics 3 Midterm Exam This is a closed book and closed note exam. However, you are allowed one page of handwritten notes. Answer all
University of Washington Summer Department of Economics Eric Zivot Economics 3 Midterm Exam This is a closed book and closed note exam. However, you are allowed one page of handwritten notes. Answer all
Financial Econometrics Notes. Kevin Sheppard University of Oxford
 Financial Econometrics Notes Kevin Sheppard University of Oxford Monday 15 th January, 2018 2 This version: 22:52, Monday 15 th January, 2018 2018 Kevin Sheppard ii Contents 1 Probability, Random Variables
Financial Econometrics Notes Kevin Sheppard University of Oxford Monday 15 th January, 2018 2 This version: 22:52, Monday 15 th January, 2018 2018 Kevin Sheppard ii Contents 1 Probability, Random Variables
Models of Patterns. Lecture 3, SMMD 2005 Bob Stine
 Models of Patterns Lecture 3, SMMD 2005 Bob Stine Review Speculative investing and portfolios Risk and variance Volatility adjusted return Volatility drag Dependence Covariance Review Example Stock and
Models of Patterns Lecture 3, SMMD 2005 Bob Stine Review Speculative investing and portfolios Risk and variance Volatility adjusted return Volatility drag Dependence Covariance Review Example Stock and
Exploring Data and Graphics
 Exploring Data and Graphics Rick White Department of Statistics, UBC Graduate Pathways to Success Graduate & Postdoctoral Studies November 13, 2013 Outline Summarizing Data Types of Data Visualizing Data
Exploring Data and Graphics Rick White Department of Statistics, UBC Graduate Pathways to Success Graduate & Postdoctoral Studies November 13, 2013 Outline Summarizing Data Types of Data Visualizing Data
Lecture 8: Markov and Regime
 Lecture 8: Markov and Regime Switching Models Prof. Massimo Guidolin 20192 Financial Econometrics Spring 2016 Overview Motivation Deterministic vs. Endogeneous, Stochastic Switching Dummy Regressiom Switching
Lecture 8: Markov and Regime Switching Models Prof. Massimo Guidolin 20192 Financial Econometrics Spring 2016 Overview Motivation Deterministic vs. Endogeneous, Stochastic Switching Dummy Regressiom Switching
Quantitative Methods for Economics, Finance and Management (A86050 F86050)
 Quantitative Methods for Economics, Finance and Management (A86050 F86050) Matteo Manera matteo.manera@unimib.it Marzio Galeotti marzio.galeotti@unimi.it 1 This material is taken and adapted from Guy Judge
Quantitative Methods for Economics, Finance and Management (A86050 F86050) Matteo Manera matteo.manera@unimib.it Marzio Galeotti marzio.galeotti@unimi.it 1 This material is taken and adapted from Guy Judge
St. Xavier s College Autonomous Mumbai STATISTICS. F.Y.B.Sc. Syllabus For 1 st Semester Courses in Statistics (June 2015 onwards)
 St. Xavier s College Autonomous Mumbai STATISTICS F.Y.B.Sc Syllabus For 1 st Semester Courses in Statistics (June 2015 onwards) Contents: Theory Syllabus for Courses: S.STA.1.01 Descriptive Statistics
St. Xavier s College Autonomous Mumbai STATISTICS F.Y.B.Sc Syllabus For 1 st Semester Courses in Statistics (June 2015 onwards) Contents: Theory Syllabus for Courses: S.STA.1.01 Descriptive Statistics
ENGM 720 Statistical Process Control 4/27/2016. REVIEW SHEET FOR FINAL Topics
 REVIEW SHEET FOR FINAL Topics Introduction to Statistical Quality Control 1. Definition of Quality (p. 6) 2. Cost of Quality 3. Review of Elementary Statistics** a. Stem & Leaf Plot b. Histograms c. Box
REVIEW SHEET FOR FINAL Topics Introduction to Statistical Quality Control 1. Definition of Quality (p. 6) 2. Cost of Quality 3. Review of Elementary Statistics** a. Stem & Leaf Plot b. Histograms c. Box
ARCH Models and Financial Applications
 Christian Gourieroux ARCH Models and Financial Applications With 26 Figures Springer Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 The Development of ARCH Models 1 1.2 Book Content 4 2 Linear and Nonlinear Processes 5
Christian Gourieroux ARCH Models and Financial Applications With 26 Figures Springer Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 The Development of ARCH Models 1 1.2 Book Content 4 2 Linear and Nonlinear Processes 5
Final Exam - section 1. Thursday, December hours, 30 minutes
 Econometrics, ECON312 San Francisco State University Michael Bar Fall 2013 Final Exam - section 1 Thursday, December 19 1 hours, 30 minutes Name: Instructions 1. This is closed book, closed notes exam.
Econometrics, ECON312 San Francisco State University Michael Bar Fall 2013 Final Exam - section 1 Thursday, December 19 1 hours, 30 minutes Name: Instructions 1. This is closed book, closed notes exam.
Two-term Edgeworth expansions of the distributions of fit indexes under fixed alternatives in covariance structure models
 Economic Review (Otaru University of Commerce), Vo.59, No.4, 4-48, March, 009 Two-term Edgeworth expansions of the distributions of fit indexes under fixed alternatives in covariance structure models Haruhiko
Economic Review (Otaru University of Commerce), Vo.59, No.4, 4-48, March, 009 Two-term Edgeworth expansions of the distributions of fit indexes under fixed alternatives in covariance structure models Haruhiko
Amath 546/Econ 589 Univariate GARCH Models: Advanced Topics
 Amath 546/Econ 589 Univariate GARCH Models: Advanced Topics Eric Zivot April 29, 2013 Lecture Outline The Leverage Effect Asymmetric GARCH Models Forecasts from Asymmetric GARCH Models GARCH Models with
Amath 546/Econ 589 Univariate GARCH Models: Advanced Topics Eric Zivot April 29, 2013 Lecture Outline The Leverage Effect Asymmetric GARCH Models Forecasts from Asymmetric GARCH Models GARCH Models with
Maximum Likelihood Estimation Richard Williams, University of Notre Dame, https://www3.nd.edu/~rwilliam/ Last revised January 13, 2018
 Maximum Likelihood Estimation Richard Williams, University of otre Dame, https://www3.nd.edu/~rwilliam/ Last revised January 3, 208 [This handout draws very heavily from Regression Models for Categorical
Maximum Likelihood Estimation Richard Williams, University of otre Dame, https://www3.nd.edu/~rwilliam/ Last revised January 3, 208 [This handout draws very heavily from Regression Models for Categorical
Financial Econometrics (FinMetrics04) Time-series Statistics Concepts Exploratory Data Analysis Testing for Normality Empirical VaR
 Financial Econometrics (FinMetrics04) Time-series Statistics Concepts Exploratory Data Analysis Testing for Normality Empirical VaR Nelson Mark University of Notre Dame Fall 2017 September 11, 2017 Introduction
Financial Econometrics (FinMetrics04) Time-series Statistics Concepts Exploratory Data Analysis Testing for Normality Empirical VaR Nelson Mark University of Notre Dame Fall 2017 September 11, 2017 Introduction
Lecture Slides. Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition. by Mario F. Triola. and the Triola Statistics Series. Section 7.4-1
 Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition and the Triola Statistics Series by Mario F. Triola Section 7.4-1 Chapter 7 Estimates and Sample Sizes 7-1 Review and Preview 7- Estimating a Population
Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition and the Triola Statistics Series by Mario F. Triola Section 7.4-1 Chapter 7 Estimates and Sample Sizes 7-1 Review and Preview 7- Estimating a Population
GETTING STARTED. To OPEN MINITAB: Click Start>Programs>Minitab14>Minitab14 or Click Minitab 14 on your Desktop
 Minitab 14 1 GETTING STARTED To OPEN MINITAB: Click Start>Programs>Minitab14>Minitab14 or Click Minitab 14 on your Desktop The Minitab session will come up like this 2 To SAVE FILE 1. Click File>Save Project
Minitab 14 1 GETTING STARTED To OPEN MINITAB: Click Start>Programs>Minitab14>Minitab14 or Click Minitab 14 on your Desktop The Minitab session will come up like this 2 To SAVE FILE 1. Click File>Save Project
1/2 2. Mean & variance. Mean & standard deviation
 Question # 1 of 10 ( Start time: 09:46:03 PM ) Total Marks: 1 The probability distribution of X is given below. x: 0 1 2 3 4 p(x): 0.73? 0.06 0.04 0.01 What is the value of missing probability? 0.54 0.16
Question # 1 of 10 ( Start time: 09:46:03 PM ) Total Marks: 1 The probability distribution of X is given below. x: 0 1 2 3 4 p(x): 0.73? 0.06 0.04 0.01 What is the value of missing probability? 0.54 0.16
Getting to know data. Play with data get to know it. Image source: Descriptives & Graphing
 Descriptives & Graphing Getting to know data (how to approach data) Lecture 3 Image source: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file:3d_bar_graph_meeting.jpg Survey Research & Design in Psychology James
Descriptives & Graphing Getting to know data (how to approach data) Lecture 3 Image source: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file:3d_bar_graph_meeting.jpg Survey Research & Design in Psychology James
2018 CFA Exam Prep. IFT High-Yield Notes. Quantitative Methods (Sample) Level I. Table of Contents
 2018 CFA Exam Prep IFT High-Yield Notes Quantitative Methods (Sample) Level I This document should be read in conjunction with the corresponding readings in the 2018 Level I CFA Program curriculum. Some
2018 CFA Exam Prep IFT High-Yield Notes Quantitative Methods (Sample) Level I This document should be read in conjunction with the corresponding readings in the 2018 Level I CFA Program curriculum. Some
Stat 328, Summer 2005
 Stat 328, Summer 2005 Exam #2, 6/18/05 Name (print) UnivID I have neither given nor received any unauthorized aid in completing this exam. Signed Answer each question completely showing your work where
Stat 328, Summer 2005 Exam #2, 6/18/05 Name (print) UnivID I have neither given nor received any unauthorized aid in completing this exam. Signed Answer each question completely showing your work where
CHAPTER II LITERATURE STUDY
 CHAPTER II LITERATURE STUDY 2.1. Risk Management Monetary crisis that strike Indonesia during 1998 and 1999 has caused bad impact to numerous government s and commercial s bank. Most of those banks eventually
CHAPTER II LITERATURE STUDY 2.1. Risk Management Monetary crisis that strike Indonesia during 1998 and 1999 has caused bad impact to numerous government s and commercial s bank. Most of those banks eventually
Measures of Dispersion (Range, standard deviation, standard error) Introduction
 Measures of Dispersion (Range, standard deviation, standard error) Introduction We have already learnt that frequency distribution table gives a rough idea of the distribution of the variables in a sample
Measures of Dispersion (Range, standard deviation, standard error) Introduction We have already learnt that frequency distribution table gives a rough idea of the distribution of the variables in a sample
Washington University Fall Economics 487. Project Proposal due Monday 10/22 Final Project due Monday 12/3
 Washington University Fall 2001 Department of Economics James Morley Economics 487 Project Proposal due Monday 10/22 Final Project due Monday 12/3 For this project, you will analyze the behaviour of 10
Washington University Fall 2001 Department of Economics James Morley Economics 487 Project Proposal due Monday 10/22 Final Project due Monday 12/3 For this project, you will analyze the behaviour of 10
Lecture 1: Empirical Properties of Returns
 Lecture 1: Empirical Properties of Returns Econ 589 Eric Zivot Spring 2011 Updated: March 29, 2011 Daily CC Returns on MSFT -0.3 r(t) -0.2-0.1 0.1 1986 1987 1988 1989 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996
Lecture 1: Empirical Properties of Returns Econ 589 Eric Zivot Spring 2011 Updated: March 29, 2011 Daily CC Returns on MSFT -0.3 r(t) -0.2-0.1 0.1 1986 1987 1988 1989 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996
One Sample T-Test With Howell Data, IQ of Students in Vermont
 One Sample T-Test With Howell Data, IQ of Students in Vermont data howell; infile 'C:\Users\Vati\Documents\StatData\howell.dat'; input addsc sex repeat iq engl engg gpa socprob dropout; IQ_diff = iq -
One Sample T-Test With Howell Data, IQ of Students in Vermont data howell; infile 'C:\Users\Vati\Documents\StatData\howell.dat'; input addsc sex repeat iq engl engg gpa socprob dropout; IQ_diff = iq -
Lecture Data Science
 Web Science & Technologies University of Koblenz Landau, Germany Lecture Data Science Statistics Foundations JProf. Dr. Claudia Wagner Learning Goals How to describe sample data? What is mode/median/mean?
Web Science & Technologies University of Koblenz Landau, Germany Lecture Data Science Statistics Foundations JProf. Dr. Claudia Wagner Learning Goals How to describe sample data? What is mode/median/mean?
Question 1a 1b 1c 1d 1e 1f 2a 2b 2c 2d 3a 3b 3c 3d M ult:choice Points
 Economics 102: Analysis of Economic Data Cameron Spring 2015 April 23 Department of Economics, U.C.-Davis First Midterm Exam (Version A) Compulsory. Closed book. Total of 30 points and worth 22.5% of course
Economics 102: Analysis of Economic Data Cameron Spring 2015 April 23 Department of Economics, U.C.-Davis First Midterm Exam (Version A) Compulsory. Closed book. Total of 30 points and worth 22.5% of course
CHAPTER 5. Introduction to Risk, Return, and the Historical Record INVESTMENTS BODIE, KANE, MARCUS. McGraw-Hill/Irwin
 CHAPTER 5 Introduction to Risk, Return, and the Historical Record McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 5-2 Interest Rate Determinants Supply Households
CHAPTER 5 Introduction to Risk, Return, and the Historical Record McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 5-2 Interest Rate Determinants Supply Households
St. Xavier s College Autonomous Mumbai F.Y.B.A. Syllabus For 1 st Semester Course in Statistics (June 2017 onwards)
 St. Xavier s College Autonomous Mumbai Syllabus For 1 st Semester Course in Statistics (June 2017 onwards) Contents: Theory Syllabus for Courses: A.STA.1.01 Descriptive Statistics (A). Practical Course
St. Xavier s College Autonomous Mumbai Syllabus For 1 st Semester Course in Statistics (June 2017 onwards) Contents: Theory Syllabus for Courses: A.STA.1.01 Descriptive Statistics (A). Practical Course
Tests for One Variance
 Chapter 65 Introduction Occasionally, researchers are interested in the estimation of the variance (or standard deviation) rather than the mean. This module calculates the sample size and performs power
Chapter 65 Introduction Occasionally, researchers are interested in the estimation of the variance (or standard deviation) rather than the mean. This module calculates the sample size and performs power
ROM Simulation with Exact Means, Covariances, and Multivariate Skewness
 ROM Simulation with Exact Means, Covariances, and Multivariate Skewness Michael Hanke 1 Spiridon Penev 2 Wolfgang Schief 2 Alex Weissensteiner 3 1 Institute for Finance, University of Liechtenstein 2 School
ROM Simulation with Exact Means, Covariances, and Multivariate Skewness Michael Hanke 1 Spiridon Penev 2 Wolfgang Schief 2 Alex Weissensteiner 3 1 Institute for Finance, University of Liechtenstein 2 School
On the Distribution and Its Properties of the Sum of a Normal and a Doubly Truncated Normal
 The Korean Communications in Statistics Vol. 13 No. 2, 2006, pp. 255-266 On the Distribution and Its Properties of the Sum of a Normal and a Doubly Truncated Normal Hea-Jung Kim 1) Abstract This paper
The Korean Communications in Statistics Vol. 13 No. 2, 2006, pp. 255-266 On the Distribution and Its Properties of the Sum of a Normal and a Doubly Truncated Normal Hea-Jung Kim 1) Abstract This paper
Point-Biserial and Biserial Correlations
 Chapter 302 Point-Biserial and Biserial Correlations Introduction This procedure calculates estimates, confidence intervals, and hypothesis tests for both the point-biserial and the biserial correlations.
Chapter 302 Point-Biserial and Biserial Correlations Introduction This procedure calculates estimates, confidence intervals, and hypothesis tests for both the point-biserial and the biserial correlations.
Econ 533 Problem Set #2 Answer Sheets
 Econ 533 Problem Set #2 Answer Sheets Using the data set hybrid.xls from the last homework set and TSP, estimate both a probit and a logit model of the decision to purchase a hybrid vehicle as a function
Econ 533 Problem Set #2 Answer Sheets Using the data set hybrid.xls from the last homework set and TSP, estimate both a probit and a logit model of the decision to purchase a hybrid vehicle as a function
Risk and Dependence. Lecture 3, SMMD 2005 Bob Stine
 Risk and Dependence Lecture 3, SMMD 2005 Bob Stine Review Key points from prior class Hypothesis tests Actions, decisions, and costs Standard error and t-ratio Role of assumptions, models One-sample, two-sample
Risk and Dependence Lecture 3, SMMD 2005 Bob Stine Review Key points from prior class Hypothesis tests Actions, decisions, and costs Standard error and t-ratio Role of assumptions, models One-sample, two-sample
THE USE OF THE LOGNORMAL DISTRIBUTION IN ANALYZING INCOMES
 International Days of tatistics and Economics Prague eptember -3 011 THE UE OF THE LOGNORMAL DITRIBUTION IN ANALYZING INCOME Jakub Nedvěd Abstract Object of this paper is to examine the possibility of
International Days of tatistics and Economics Prague eptember -3 011 THE UE OF THE LOGNORMAL DITRIBUTION IN ANALYZING INCOME Jakub Nedvěd Abstract Object of this paper is to examine the possibility of
