The Endogenous Mechanism of China s Money Supply: Evidence From Central Bank s Balance Sheet
|
|
|
- Richard Griffin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Endogenous Mechanism of China s Money Supply: Evidence From Central Bank s Balance Sheet ZHIGUO LI XIAORONG ZHANG SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT, FUDAN UNIVERSITY 220 Handan Rd, Shanghai, China, December, 2008 Abstract This paper investigates China s money supply mechanism and its micro foundation by analyzing the central bank s balance sheet adjustment. As People s Bank of China (PBC) takes different approaches in managing different items of its assets and liabilities, it affects not only the base money but also the firms and households cash holdings and the commercial banks reserve requirements, which changes the money multiplier consequently. This paper proposes the micro mechanism of money supply by minimizing the firms and households and commercial banks utility loss function in holding cash and reserve. Empirical results from unit root tests, co-integration analysis and ECM models show that both increasing foreign assets and central bank notes issuing have affected the money multiplier and thus money supply more significantly than the interest rate does. This suggests that in order to mitigate the pressure of excess liquidity, PBC should rely more on the price tool, i.e., the interest rate, than the quantitative adjustment on its balance sheet. Key Words: Money Supply; Central Bank; Asset and Liability Structure JEL Codes: E52 Zhiguo Li is an Associate Professor in the Department of Industrial Economics, Fudan Management School. Xiaorong Zhang (connecting author) is an Assistant Professor in the Department of Finance, Fudan Management School and visiting scholar (2008~2009) in the Division of Finance and Economics, Columbia Business School. Contacting: xrzhang@fudan.edu.cn, xz2195@columbia.edu. The views expressed in this working paper are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of the Fudan Management School.
2 1. INTRODUCTION A salient phenomenon during China's economic transition is that the Marshall K, i.e. the ratio of M2 to GDP, keeps rising continuously. The ratio was only 0.24 at the end of 1978, but reached 1.62 at the end of This corresponds to the fast growing in money supply, the annual growth of which was significantly higher than the sum of GDP growth rate and inflation rate by 6.8 percentage points in 1980s, 9.2 percentage points in 1990s and 4.6 percentage points in 2000~2007 on average (see Table 1). The excess and unexplained part was termed as the missing money, also known as excess liquidity, extra money or over-high Marshall s K in China (Lu, 2007; Wang, 2007; Li, 2007a). TABLE 1 MONEY SUPPLY GROWTH, OUTPUT GROWTH, INFLATION AND THE MISSING MONEY Money Supply Output Inflation the Missing Money Growth Growth 1980~ % 9.7% 7.7% 6.8 percentage points 1990~ % 10.0% 7.8% 9.2 percentage points % 10.0% 1.7% 4.6 percentage points SOURCES: China Statistical Yearbook, China Financial Yearbook A direct explanation for the too high growth in money supply is that the People s Bank of China (hereinafter PBC), the central bank in China, bears multi-tasks RMB exchange rate stability, price stability and economic growth in making monetary policies, thus ends up with a special formation process of money supply. However, a simple decomposition shows the persistent excessive money supply comes not only from the growing of base money but the rising of money multiplier as well. The base money grew from 1.36 trillion Yuan at the first quarter of 1994 to trillion Yuan at the end of 2007, where as the multiplier rose from 2.72 to 3.97 during the same period and reached the peak of 5.12 in the second quarter in Therefore, it is not surprising for researchers to raise the following questions: why both base money and the money multiplier experienced continuous rising? Does the co-existence of the two imply any endogenesis of the money supply? What is the money supply mechanism accounting for the persistent excessive monetary growth and the endogenesis? Theories of endogenous money supply state that money demand is determinative and money supply is determined. It emphasizes that opportunism of financial institutions, firms and households will lead to the uncontrollability of money supply, but admits central bank s ambition in controlling it as well. Burner and Meltzer (1964) first propose that with a given monetary policy, interest maximization in financial institutions, firms and households will affect money supply significantly. Spindt (1984) further explains that central bank s adjustments in assets alter those of the firms and banks, which affect money the multiplier and money supply as a consequnece. Shanmugam, Nai and Li(2003) give a view of endogenous money supply based on post-keynesian Economics that firms and households liquidity preference determines their cash holdings while commercial banks safety preference determine the reserve requirement. Empirical evidence from more than 100 countries by Stella and Lönnberg (2008) shows central banks are usually constrained by their assets and liabilities and partially lose independence in making monetary policies. Wang and Xu (2001) discuss how economic behaviors in the private sector influence the 1
3 money supply in China, and confirm the endogenesis of the latter. Based on an analysis of PBC s balance sheet, Huang and Gu (2006) conclude that since the central bank lacks an effective tool of control, the base money is strongly endogenetic. However, high growing of money in China comes from both supply and demand. As to the formation of money supply, the central bank s initiative in intervening the money supply affects the financial system and public behavior, which, in return, not only changes the base money and money multiplier but also affect the former s decision. To put it more straightforward, adjustment of the central bank s asset and liability will reshape the asset portfolio of financial institutions and firms and households, and then the base money and money multiplier. As a conclusion, by analyzing the central bank s balance sheet, we can have a better understand of the whole process. Taking this as the new perspective, this paper aims to analyzing China s money supply mechanism and its underlying micro foundation. It is organized as the following. Part 2 presents some facts of PBC asset and liability adjustments in the past years, based on which part 3 gives a model to describe the money supply mechanism and the micro foundation, part 4 tests the model by empirical works, and part 5 concludes. 2. MONEY SUPPLY AND CENTRAL BANK S BALANCE SHEET TABLE 2 BALANCE SHEET OF PBC Items 100 million yuan 2000 Year End 2007 Year End % 100 million yuan Total Assets Net Foreign Assets (FS) Claims on Government (LG) Claims on Depository institutions (LB) Claims on other financial institutions (LNMF) Claims on non-financial institutions Other Assets Total Liabilities Reserve Money (NB) Currency issue (CU) Deposits of financial institutions (RE) Deposits of non-financial institutions Deposits of government (DG) Bond issue (DB) Own capital Other liabilities % SOURCES: Conditioned to the multi-tasks in making monetary policies, PBC has to adjust its assets and liabilities frequently, and base money in the liabilities changes consequently. In fact, PBC has various ways of issuing and withdrawing base money, such as borrowing from or lending to Ministry of Finance, reloaning to or rediscounting from commercial banks, and buying or selling foreign currencies or securities in the financial market. As a snapshot of assets and liabilities, the 2
4 balance sheet and its changes reflect the process and characteristics of PBC s monetary policy operating. Table 2 compares PBC s 2000 year end and 2007 year end balance sheet. PBC s assets are composed of net foreign assets, claims on government, claims on depository institutions (also known as reloans to commercial banks), claims on other financial institutions and others. As shown in Table 2, the biggest increase comes from net foreign assets, the percentage of which grew from 40% at the end of 2000 to 75% at the end of Claims on depository institutions take the largest decline, with its percentage decreased from 35% to 5%. The second largest decline comes from claims on other financial institutions, and the percentage decreased from 22% to 7.7%. PBC s liabilities include reserve money (mainly currency issue and deposits of financial institutions), deposits of government and bond issue. The percentage of reserve money experienced the largest decrease, from more than 90% at the end of 2000 to 60% at the end of It comes mainly from the decrease of currency issue (from 40% to less than 20%) and deposits of non-financial institutions (from 11.63% to almost 0), whereas the share of reserve remains around 40%. Bond issue (also known as central bank bills ) was initiated in 2001, and by almost doubling every year since 2002, it accounted for more than 20% of the total liabilities at the end of Even though major changes in PBC s assets are the drastic increasing in net foreign assets and decreasing in reloans to commercial banks, the sum of the two maintains at about 70% of the total. Major changes in liabilities come from the declining of reserve currency and the increasing bond issues, but the sum still accounts for more than 80% of the total liabilities. Changes in any items in the balance sheet will lead to the change of base money. By ignoring claims on non-financial institution in the assets and own capital in the liabilities (both are very tiny compared with others), we have the following approximate equation FS + LB + LNMF + LG MB + DG + DB (1) The reserve money or base money (MB) then can be approximately given as: MB FS + LB + LNMF + ( LG DG) DB (2) From which we see that base money is determined collectively by PBC s net foreign assets (FS), claims on depository institutions (LB), claims on the other financial institutions (LNMF), net debt to government (LG - DG) and the bonds issuing (DB). Through commercial banks deposits and public circulation, there comes broad money M2. We can write M2 = μ MB, where μ is the money multiplier. By decomposing M2 into cash in circulation (CU) and bank deposits (DD) and further decomposing base money (MB) into CU and reserves (RE), the money multiplier can be expressed as: M 2 CU + DD ( CU / DD) + 1 cd + 1 µ = = = = MB CU + RE ( CU / DD) + ( RE / DD) cd + re (3) where cd denotes the public s cash holdings ratio and re the commercial banks reserve ratio. Equation (3) tells that both cash holdings ratio and reserve ratio have negative effects on the money multiplier. In other words, increase in either the cash demand by non-financial firms and households or the commercial banks reserve requirements results in a decline of the multiplier. Li (2007b) already finds that the persistent rising of money multiplier in China corresponds to the 3
5 persistent dropping of the cash holdings ratio, and as the government raised required reserve ratio since 1999, changes in money multiplier has a clear negative correlation with the change of the total reserve ratio. The magnitude of the effects on the multiplier, however, depends on shares of cash holdings and reserve in the base money. In addition, as the multiplier goes up, the effect from changes in cash holdings declines. Now we give the basic story that how the money multiplier will be influenced by PBC s monetary policy via balance sheet adjustment. Changes in PBC s assets and liabilities alter not only the cash holdings for firms and households but also the reserve requirements for commercial banks, and the money multiplier changes in the ultimate. Figure 1 gives the changes of broad money multiplier and PBC s major asset and liability structure from the 1 st quarter in 1993 to the 4 th quarter in Corresponding to the long-term increasing of the broad money multiplier, percentage of net foreign assets keeps growing, percentage of reloans to commercial banks keeps declining, and percentage of bond issuing increases drastically. The process is also confirmed by the fact that as PBC shifts its monetary policy from reloans and rediscounts to open market operations, there is corresponding changes not only in base money but also in money multiplier Broad Monetary Multiplier Ratio of Net Foreign Assests 1.0 Ratio of Claims on Depository Institutions 0.5 Ration of Bond Issues Q1 1994Q2 1995Q3 1996Q4 1998Q1 1999Q2 2000Q3 2001Q4 2003Q1 2004Q2 2005Q3 2006Q4 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% FIG 1 China s Money Multiplier and PBC s Asset and Liability Structure NOTES: money multiplier on LHS axis and others on RHS axis SOURCES: Quarterly Book of People s Bank of China and What is the mechanism that central bank s balance sheet adjustment alters the cash holding of firm and households and the reserve requirement of commercial bank? A direct guess is that it changes their liquidity preference and opportunity cost of cash holdings. Based on this assumption, we construct a model to provide the underlying micro foundation. 3. MONEY SUPPLY FORMATION AND THE MICRO FUNDATION 3.1 Endogeny of Money Supply Money supply is the product of base money and money multiplier, and base money (MB) is composed of currency issue (CU) and reserves from commercial banks (RE). As the former is similar to cash in circulation (M0), we take an approximation that MB M0 + RE. The reserve can also composed of required part (RD) and excess part (RO), or RE = RD + RO. With equation (2), which tells how the base money was determined by other items in the central bank s balance sheet, the money supply can be given as: 4
6 M 2= µ MB = µ ( CU + RE) = µ [ FS + LB + LNMF + ( LG DG) DB] (4) where μ is the money multiplier. During the economic transition, PBC gradually shifts from the direct quantity control on money supply to a middle target. By adjusting its assets and liabilities through open market operations, PBC alters the monetary supply and indirectly achieves the monetary policy target. Open market operations include buying foreign exchanges (which increases PBC s total assets) and bonds issuing (which increases PBC s total liabilities). In fact, the former is a passive response to the consistent surplus in both current accounts and capital and financial accounts, while the latter is an active conduct in absorbing excess liquidity resulted from the money issuing through buying foreign exchanges, which is known as funds outstanding for foreign exchanges. According to the process of balance sheet adjustment, we can distinguish three types of PBC s asset and liability management: internal, external and special operations (Li, 2007c). In PBC s conventional conducts, net foreign assets adjustment is classified as external, and reloans to commercial banks, claims to non-financial institutions and claims on government are all internal. However, when the government realized conventional operations could not deal with the conflicts within the multi-tasks framework, it introduced special operation of bonds issuing in 2001, which is a new tool in liability management that aims to curb the rapid growing not only in base money but also money supply. In order to see each type of operations separate influence on money supply, we decompose equation (4) as the following: M 3 2 = µ 1 FS + µ 2[ LB + LNMF + ( LG DG)] µ DB (5) Where μ 1, μ 2 and μ 3 denote M2 s reaction factors to each type of operations. Specifically, by assuming the factors maintaining constant in the short run, we can write the money supply change as ' ' ' ( M 2) = µ 1 ( FS) + µ 2 [ LB + LNMF + ( LG DG)] µ 3 ( DB) (6) Finally we come to the money supply endogeny. Confronted with any external money shock, PBC responses by not only adjusting the base interest rate and required reserve ratio directly, but also adjusting its assets and liabilities through open market operations. It then changes the reserve requirement of commercial banks and the cash preference of firms and households, and the money supply ultimately. 3.2 The Model for Money Multiplier Based on Baghestani and Mott(1997) and Handa(2000), we construct a model to describe China s money supply mechanism and its micro foundation during the transition period. We will start with the cash preference of firms and households and reserve requirement of commercial banks in the context of PBC s balance sheet adjustment. During China's economic transition, as the government provides full support to the financial system, it implicitly protects the commercial banks from going bankruptcy and guarantees the safety of deposit for firms and households. As a consequence, the latter only trades off between the opportunity cost of liquidity and return on investment in deciding how much cash to hold. For 5
7 example, when deposit rate goes up, they reduce cash holdings and turn to more bank deposits, and when the rate goes down, they tend to hold more cash for better liquidity. The optimal problem for firms and households, therefore, is to minimize the utility loss from holding cash, which can be given as: Min k { L αu[( 1 δ )(1 k)] + (1 α) U ( ik) } = (7) Where k is the cash holdings ratio, i is the average deposit rate, α (0 < α <1) the relative preference for liquidity (α for cash as 1), and 1-α the relative aversion to opportunity cost of holding cash. δ (0 < δ <1) measures the liquidity for bank deposits, which relies on innovation and efficiency of the financial markets. Consequently, U[(1-δ)(1-k)] is the utility loss in liquidity by holding deposits, and U(ik) is the utility loss in profitability by holding cash. The optimizing target is that with a given quantity of money, firms and households will choose the best amount of cash C and deposit D, i.e. the optimal ratio k (k= C/D), to minimize their utility loss of holding cash. By assume CRRA (constant relative risk aversion) in the utility function, i.e. 1 σ x 1 U ( x) =, U '( x) = x 1 σ we get the first order condition for equation (7) as σ α( 1 δ )[(1 k )(1 δ )] σ + (1 α) i( ik) = 0 (8) and have the partial relationship of α, δ and i with k as: + σ k = k( α, δ, i) (9) Commercial banks, on the other hand, choose the best cash holdings for its day-to-day business based on safety and profitability. As reserves earn a lower interest than loans, the more reserves commercial banks have, the less profitable they are. However, reserves have no chance to turn into bad debt and can also prevent potential bank runs, and they improve commercial banks safety. Consequently the optimal problem for commercial banks is to minimize the utility loss from holding reserves, which can be given as: Min re { T = U[( i i )( re rd)] + (1 β ) U[ φ(1 re)] } β (10) e Where re is the reserve ratio, β (0 < β < 1) and 1 - β are banks relative preference for profitability and safety respectively, rd the required reserve ratio, 1 - re the loans and other assets share in the banks total assets, i and i e reserve deposit rates and interest rates (thus i-i e the opportunity cost of reserve). φ measures the riskiness of loans and other assets. Consequently, (i-i e )(re-rd) is the utility loss in profitability by holding the excess reserve, and φ(1-re) is the utility loss in safety by holding risky assets such as loans. Still assuming CRRA for banks, we get first order condition for equation (10) as: σ σ β ( i ie )[( i ie)( re rd)] (1 β) φ[ φ(1 re)] = 0 (11) and the partial relationships of β, i-i e and φ on re as: φ + e + re = re( β, i i,, rd) (12) 6
8 Plugging (9) and (12) into (3), we get the relationship of money multiplier with all the parameters as µ = µ ( α, β, δ, φ, i, i i, rd) (13) e Now let s look at how PBC s balance sheet adjustment affects the parameters. When PBC buys foreign exchange in the market and issues money (ascending FS/AS), liquidity in the currency market goes up, which leads to a decline of liquidity preference of firms and households (declining α) and a decline of safety preference of commercial banks (ascending β), and an ascending µ consequently. When PBC reduces the percentage of claims on depository institutions (LB/AS), it imposes a credit contraction on commercial banks and changes the market expectation on liquidity, which indicates firms and households have higher preference for liquidity and banks are more conserved to risky assets such as bank loan. Then δ goes up and φ goes down and a higher µ results. When PBC issues more bonds to withdraw money (higher DT/AS) and commercial banks buy them at the requirement of the former, they are less riskier in assets and reduces the preference for safety accordingly, which indicate a lower φ, a higher β and a higher µ. Based on the above discussion, we replace parameter α, β and φ with the asset-liability structure in PBC s balance sheet, and rewrite (13) as: = FS LB DT µ µ,,, i, i ie, rd (14) AS AS AS 4. EMPIRICAL ANALYSIS Since late 1990s, surplus in both the current account and capital and financial account has confronted PBC with high pressure in making monetary policies. When it passively buys foreign exchange in the market, foreign reserve accumulates rapidly and funds outstanding for foreign exchange goes to the base money. In 2001, PBC started to issue bonds, the purpose of which is to adjust the base money and absorb excess liquidity. Compared with traditional open market operations such as repos and spot bond selling that are constrained to the total amount of securities held by PBC, such an innovation has no amount limit and can reduce base money and credit lines for commercial banks by adjusting the PBC s liabilities composition and keeping the total assets unchanged. In other words, PBC s balance sheet adjustment actually comes from the fact that it gradually shifts from reloans and rediscount to open market operations such as buying foreign exchanges and bonds issuing. Table 2 also gives the key items in the balance sheet in quantity. Total asset of PBC rose from 3.9 trillion yuan in the end of 2000 to trillion yuan in the end of 2007, where as net foreign assets grew from 1.52 trillion yuan to trillion yuan, reloan to commercial banks decreased from 1.35 trillion yuan to 0.78 trillion yuan, and the bonds issue rose sharply from zero to 3.45 trillion yuan. However, base money increased from 3.65 trillion yuan to trillion yuan and broad money supply rose from trillion yuan to trillion yuan during the same period, and it strongly indicates that effects from reloan reduction and bonds issuing didn t counter the effect from the fast increasing in net foreign assets. In this section, we test the model with quarterly data from 1993 to All the data are from China Statistical Yearbook, China Financial Yearbook and 7
9 4.1 Balance Sheet Adjustment, Base Money and Money Supply We first take the unit root test on all relevant variables to see if they are I (1) process. Since broad money, base money, money multiplier, net foreign assets and re-loans are seasonal and may lead to pseudo correlation, we make X11 seasonal adjustment for them. Particularly, as PBC didn t issue any bond before 2001 and the issuing almost doubled every year after 2002, percentage of bonds issuing in assets (DB/AS) is definitely not I(1). Table 3 gives the results of ADF and PP test. All level variables can t reject the unit root null hypothesis at the 5% significant level, and all differenced variables reject the null hypothesis at the 1% significant level. The only exception is differenced base money, for which the ADF test doesn t reject the null but PP tests rejects the null at the 1% significant level. Therefore we can take all variables as I(1). TABLE 3 UNIT ROOT TEST Level Data Differenced Data Variables ADF Test PP Test ADF Test PP Test Broad Money M2 5.3(1.00) 5.2(1.00) -4.6(0.00) *** -4.7(0.00) *** Base money MB 4.4(1.00) 4.1(1.00) -2.6(0.27) -5.6(0.00) *** Money multiplier M2/MB -0.9(0.77) -1.0(0.75) -7.4(0.00) *** -7.5(0.00) *** Ratio of Net Foreign Assets FS/AS -0.5(0.88) -0.6(0.87) -6.8(0.00) *** -6.8(0.00) *** Ratio of Claims on Depositary Institutions LB/AS -1.4(0.58) -0.6(0.85) -7.7(0.00) *** -9.0(0.00) *** 1-year Depositary Interest Rate R1-1.3(0.62) -1.0(0.76) -4.6(0.00) *** -4.4(0.00) *** 1-year Depositary Interest Rate less Reserve Interest Rate R1-RR -2.2(0.22) -1.9(0.33) -6.4(0.00) *** -3.6(0.00) *** Required Reserve Ratio RD -1.3(0.64) -1.2(0.69) -3.8(0.00) *** -3.9(0.00) *** NOTES: ***(**,*) indicates significance at the level of 1% (5%,10%). We also analyze how PBC s asset and liability structure affects the money supply by changing base money and money multiplier. Results are given in Table 4 and Table 5. From the perspective of long-run equilibrium, PBC s various assets and liabilities basically have similar size of effects on base money, but the effects on money supply differ largely. Before PBC s bonds issuing in 2001, the coefficient of net foreign assets on money supply is 6.61, significantly higher than that of the commercial bank loans (model 4). After 2002, however, the influence from external assets weakened, while the influence from internal assets such as reloans to commercial banks experience largely increased (Model 5). From the perspective of short-term fluctuations, PBC s various assets and liabilities have very different effects on both base money and money supply. Reaction coefficients of incremental base money to incremental net foreign assets, incremental internal assets and incremental bonds issuing are 0.51, 0.22 and respectively. This indicates that by decreasing internal assets and increasing bonds issuing, PBC has partially reduced the base money resulted from increasing external assets (Model 2'). However, reaction coefficients of incremental money supply to incremental net foreign assets, incremental internal assets and incremental bonds issuing are 1.14, and 0.35 respectively, which discloses the fact that all the operations have increased money supply (Model 5'). 8
10 TABLE 4 LONG-TREM EQUILIBRIUMS OF BASE MONEY AND MONEY SUPPLY MB M2 Model 1 93Q2-03Q4 Constant (3.9) FS 1.10 (37.1 *** ) LB+LNMF+(LG-DG) 0.80 (11.8 *** ) DB Model (0.5) 0.96 (17.2 *** ) 1.11 (8.2 *** ) (-6.6 *** ) FS-DB Model (0.5) 1.09 (8.7 *** ) Model 4 93Q2-03Q (0.2 *** ) 6.61 (20.8 *** ) 1.33 (1.8 ** ) 0.99 (48.1 *** ) Model (-2.9 *** ) 3.86 (8.5 *** ) 7.10 (6.4 *** ) (-1.8 ** ) Model (-2.5 *** ) 6.03 (5.6 *** ) 4.94 (28.0 *** ) adj.r S.E DW NOTES: ***(**,*) indicates significance at the level of 1% (5%,10%). TABLE 5 SHORT-TERM FLUCTUATIONS OF BASE MONEY AND MONEY SUPPLY MB M2 Model 1 93Q2-03Q4 Constant (2.3 *** ) 0.57 FS (2.8 *** ) [LB+LNMF+(LG-DG)] 0.61 (4.4 *** ) DB Model (2.9 *** ) 0.51 (9.3 *** ) 0.22 (1.8 ** ) (-3.1 *** ) (FS-DB) Model (4.5 *** ) 0.18 (1.4) Model 4 93Q2-03Q (8.2 *** ) 2.40 (2.3 *** ) (-1.5) 0.45 (8.0 *** ) Model (12.6 *** ) 1.14 (12.4 *** ) (-0.7) 0.35 (2.6 *** ) Model (10.6 *** ) (-0.9) 0.80 (5.2 *** ) adj.r S.E DW NOTES: ***(**,*) indicates significance at the level of 1% (5%,10%). Based on the above discussion, we find that PBC s asset and liability adjustments have similar effects on base money in the long run, but conflict with each other to some extent in the short run. The effects on money supply are more complicated. Even though liability management in recent years partially mitigated the effects from asset management, the deceasing of reloans and expanding of bonds issuing in the latter couldn t sufficiently absorb the funds outstanding for buying foreign exchanges, and resulted in a fast and uncontrolled growing of money supply. 9
11 4.2 Balance Sheet Adjustment and Money Multiplier By looking at the effect on the money multiplier, we now explain why PBC s balance sheet adjustment has different effects on base money and money supply. Li (2007b) shows with a Johansen co-integration test that during the transition of China s economy, PBC s balance sheet structure tends to push money supply to equilibrium in the long run but destabilize it in the short run. In this paper, we take a two-step approach of test instead. We test the money multiplier s long-run equilibrium with OLS and get error correction terms, which then will be used in an error correction model to identify the short-term fluctuation. Due to the special data generation process of central bank bills, we will analyze the effects on money multiplier both with and without PBC s bonds issuing. The results are given in Table 6 and Table 7. TABLE 6 LONG-TREM EQUILIBRIUM OF MONEY MULTIPLIER M2/MB: no bond issue M2/MB:with bond issue Constant 3.29 (18.5 *** ) 4.61 FS/AS (9.3 *** ) Model 7 Model 8 Model 9 Model 10 Model 11 Model (19.5 *** ) 4.20 (11.7 *** ) LB/AS 5.70 (43.0 *** ) 5.63 (54.7 *** ) (-14.2 *** ) (-17.4 *** ) DB/AS R1 R1-RR RD(-1) 13.4 (2.9 *** ) (-1.2) (-6.2 *** ) 8.98 (3.2 *** ) (-7.7 *** ) 6.42 (2.4 ** ) (-0.8) (-5.6 *** ) 4.83 (2.7 *** ) 4.53 (18.6 *** ) 1.10 (1.8 * ) 3.36 (5.8 *** ) 0.91 (0.3) 5.38 (40.2 *** ) (-4.6 *** ) 1.77 (3.0 *** ) 2.54 (1.4) (-6.4 *** ) (-7.1 *** ) (-7.5 *** ) adj.r S.E DW NOTES: ***(**,*) indicates significance at the level of 1% (5%,10%). From the perspective of long-run equilibrium, PBC s asst and liability structure has a significant effect on the money multiplier, which is consistent with our model in the third section. In order to avoid collinearity between percentages of net foreign assets and reloan to commercial banks, we use different models. In addition, as opportunity cost of holding cash (difference between deposit rate R1 and reserve interest rate RR) has negative effect on the money multiplier, which is not consistent with theoretical analysis, we take it out (Model 7 and Model 9). Without considering PBC s bonds issuing, coefficients of percentages of net foreign assets and reloans to commercial banks on money multiplier are 4.2 (Model 8) and (Model 10) respectively, which indicate that both the increasing of net foreign assets and decreasing of reloans have led to a higher money multiplier. When bonds issuing is considered, however, both effects have been weakened, but the weakening is offset by the effect of bonds issuing on the money multiplier (Model 11 and Model 12). From the perspective of short-term fluctuations, effects of PBC s asset and liability 10
12 adjustment on the money multiplier differ largely. When bonds issuing is not considered, coefficient of the percentages of net foreign assets is 2.95, which is significant at level of 1% (Model 8 ); coefficient of reloans to commercial banks is -1.85, and is significant at level of 5% (Model 10 ). As effect of interest rate change is not significant, the effect of net foreign assets outperformed that of reloans to commercial banks. When bonds issuing is considered, both effects have been mitigated, and effect of interest rate change is only significant at level of 10%. Furthermore, the effect of bonds issuing is larger than those of net foreign assets (model 11') and reloans to commercial banks (model 12') in terms of both magnitude and significance. The coefficient of error correction item shows that if the money multiplier deviates from its long-term equilibrium, the reversion can be completed in 3 or 4 quarters. TABLE 7 THE ECM MODEL OF MONEY MULTIPLIER (M2/MB) : no bond issue (M2/MB) : with bond issue Constant (-0.4) (FS/AS) Model 8 Model 10 Model 11 Model (3.3 *** ) (LB/AS) (-0.0) (-2.1 ** ) (DB/AS) (R1) (RD(-1)) (-0.6) (-2.7 *** ) ECM(-1) (-3.1 *** ) (-1.6) (-1.8 * ) (-4.0 *** ) (-0.9) 2.04 (2.5 ** ) 2.85 (3.6 *** ) (-1.8 * ) (-2.2 ** ) (-3.9 *** ) (-0.5) (-1.7 * ) 3.03 (3.7 *** ) (-1.8 * ) (-1.3) (-3.5 *** ) adj.r S.E DW NOTES: ***(**,*) indicates significance at the level of 1% (5%,10%). In conclusion, PBC s balance sheet adjustment has well explained the money multiplier s long-run equilibrium and short-run fluctuations, which are specific in China s the economic transition. Adjustments in various assets and liabilities have different effects on money supply, and it is accounted mainly by their different effects on money multiplier. Particularly, percentage change in the net foreign assets has a stronger influence on the multiplier than the percentage change in reloans does, and external asset management is more efficient than internal asset management in affecting the multiplier. As bonds issuing has a more significant positive effect than the increasing of net foreign assets or reduction of reloans, this special liability management actually fails in curbing the rapid growing of money supply. 5. CONCLUSION Monetary economics theory states that interest rate is the key factor in determining money 11
13 supply. Interest rate difference among monetary assets affects not only firms and households configuration between bank deposits and cash holdings, but also the commercial banks reserve requirement and asset portfolios (Baghestani and Mott, 1997). However, when we investigate how PBC s balance sheet adjustment affects China s base money and money supply in this paper, we get different conclusions. We explain the formation and the micro foundation of money supply by modeling firms and households preference of holding cash and commercial banks preference of reserve requirement. The empirical results show that adjustments in PBC s various assets and liabilities have different effects on money multiplier, and then on money supply as the consequence. The adjustments contribute to the multiplier s long-run equilibrium and short-run fluctuations, which are unique in China s transition economy. Specifically, increasing in net foreign assets, decreasing reloans to commercial banks and drastic growing in bonds issuing are the most significant factors in influencing China s base money, money multiplier and money supply. The effect from interest rate is not significant, and interest rate difference among monetary assets gives an explanation contrary to monetary economic theories. During the past 30 years, China has made a miracle of growth in its economic transition. However, quite different from Europe and North America where the financial systems are driven by private sectors, China keeps the financial system stated-owned and administrated by the government. Lagged reform in the financial sector leads to low efficiency and over intervention from the government, and results in non-performing loans in commercial banks (Boyreau-Debray and Wei, 2005; Xie and Zhang, 2007). On the other hand, however, the loose monetary policy and implicit guarantee of preventing banks from being insolvency attract huge deposit in banks from both firms and households, thus exempts China from the capital bottleneck that most developing countries experienced during economic transition (Zhang, 2006; China's economic growth and macroeconomic stability Group, 2007). The phenomenon confuses most western scholars and is termed China's financial mystery (McKinnon, 2008). Nevertheless, the central bank in China has taken over much pressure. Although PBC tries to control money supply by special operations in managing its assets and liabilities, the balance sheet adjustment has influenced both the cash preference of firms and households and the reserve requirement of commercial banks, and led to the instability in money multiplier and the money supply. We suggest PBC shift its operation from quantity adjusting of assets and liabilities to price adjustment of interest rate. The ultimate and long-run task should be the reform of financial sectors, such as improving its efficiency, reducing over intervention and restructuring the market. LITERATURE SITED Baghestani, H., and T. Mott, 1997, A Cointegration Analysis of the U.S. Money Supply Process. Journal of Macroeconomics, 19: Boyreau-Debray G. and S. Wei, 2005, Can China Grow Faster? A Diagnosis on the Fragmentation of the Domestic Capital Market, World Bank Report, No CHA Brunner, Karl, and A. E. Meltzer. 1964, Some Further Investigations of Demand and Supply Functions for Money, Journal of Finance, 19, Chinese Economic Growth and Macro Stability Research Group, 2007, Financial Development and Economic Growth: From Mobilized Expansion to Market Allocation, Economic Research (in Chinese), 4, Handa, J., Monetary Economics, 1 st Edition, Routledge,
14 Huang, Yanfen, and Yan Gu, 2006, An Analysis on the Sources of China s Base Money and the Central Bank s Intervention Ability, Management World (in Chinese), 6, Li, Zhiguo, 2007a, Money Demand Elasticity, Effective Money Supply and Disequilibrium Model: An Explanation on China s Monetary Puzzle and Long-term Excess Liquidity, Economic Theory and Economic Management (in Chinese), 11, Li, Zhiguo, 2007b, Relations on Base Money, Money multiplier and the Central Bank s Balance Sheet, Research on Quantitative Economics and Technical Economics (in Chinese) 11, Li, Zhiguo, 2007c, Excess Liquidity Based on Money Supply Determinations, Shanghai Management Science (in Chinese), 2, 1-6. Lu, Lei, 2007, On the Excess Liquidity in China s Banking System, Financial Research (in Chinese), 1, 1-11\ McKinnon R., and G. Schnabl, 2008, China s Financial Conundrum and Global Imbalances, BIS Annual Conference, Luzern Shanmugam, B. M. Nair, and O.W. Li, 2003, The Endogenous Money Hypothesis: Empirical Evidence from Malaysia ( ), Journal of Post Keynesian Economics, 25, Spindt, A. Paul, 1984, Modelling the Monetary Multiplier and the Controllability of the Divisia Monetary Quantity Aggregates, Review of Economics and Statistics, 66, Stella, P. and Å. Lönnberg, 2008, Issues in Central Bank Finance and Independence, IMF Working Paper, No. 08/37. Wan, Jieqiu, and Tao Xu, 2001, Endogenity of Money Supply and Efficiency of Monetary Policy: On China s Effectiveness of Monetary Policy, Economic Research (in Chinese), 3, Wang, Yang, 2007, A survey on China s M2/GDP, Management World (In Chinese), 1, Xie, Ping, Huaiqing Zhang, 2007, Financial Structure, Bad Loans and Chinese M2/GDP, Economic Research (In Chinese), 2, Zhang, Jie, 2006, The Chinese Puzzle of High Currency Degree, Economic Research (in Chinese), 6,
Human - currency exchange rate prediction based on AR model
 Volume 04 - Issue 07 July 2018 PP. 84-88 Human - currency exchange rate prediction based on AR model Jin-yuanWang 1, Ping Xiao 2* 1 (School of Hunan University of Humanities, Science and Technology, Hunan
Volume 04 - Issue 07 July 2018 PP. 84-88 Human - currency exchange rate prediction based on AR model Jin-yuanWang 1, Ping Xiao 2* 1 (School of Hunan University of Humanities, Science and Technology, Hunan
Analysis Factors of Affecting China's Stock Index Futures Market
 Volume 04 - Issue 07 July 2018 PP. 89-94 Analysis Factors of Affecting China's Stock Index Futures Market Peng Luo 1, Ping Xiao 2* 1 School of Hunan University of Humanities,Science and Technology, Hunan417000,
Volume 04 - Issue 07 July 2018 PP. 89-94 Analysis Factors of Affecting China's Stock Index Futures Market Peng Luo 1, Ping Xiao 2* 1 School of Hunan University of Humanities,Science and Technology, Hunan417000,
A Study on the Relationship between Monetary Policy Variables and Stock Market
 International Journal of Business and Management; Vol. 13, No. 1; 2018 ISSN 1833-3850 E-ISSN 1833-8119 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education A Study on the Relationship between Monetary
International Journal of Business and Management; Vol. 13, No. 1; 2018 ISSN 1833-3850 E-ISSN 1833-8119 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education A Study on the Relationship between Monetary
Zhenyu Wu 1 & Maoguo Wu 1
 International Journal of Economics and Finance; Vol. 10, No. 5; 2018 ISSN 1916-971X E-ISSN 1916-9728 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education The Impact of Financial Liquidity on the Exchange
International Journal of Economics and Finance; Vol. 10, No. 5; 2018 ISSN 1916-971X E-ISSN 1916-9728 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education The Impact of Financial Liquidity on the Exchange
The cointegration relationship between insurance investment and China's macroeconomic variables An empirical research based on time series analysis
 The cointegration relationship between insurance investment and China's macroeconomic variables An empirical research based on time series analysis Xiaochuan Tong 1 Binrong Wang 2 Shanghai University of
The cointegration relationship between insurance investment and China's macroeconomic variables An empirical research based on time series analysis Xiaochuan Tong 1 Binrong Wang 2 Shanghai University of
The Demand for Money in China: Evidence from Half a Century
 International Journal of Business and Social Science Vol. 5, No. 1; September 214 The Demand for Money in China: Evidence from Half a Century Dr. Liaoliao Li Associate Professor Department of Business
International Journal of Business and Social Science Vol. 5, No. 1; September 214 The Demand for Money in China: Evidence from Half a Century Dr. Liaoliao Li Associate Professor Department of Business
The Empirical Study on the Relationship between Chinese Residents saving rate and Economic Growth
 2017 4th International Conference on Business, Economics and Management (BUSEM 2017) The Empirical Study on the Relationship between Chinese Residents saving rate and Economic Growth Zhaoyi Xu1, a, Delong
2017 4th International Conference on Business, Economics and Management (BUSEM 2017) The Empirical Study on the Relationship between Chinese Residents saving rate and Economic Growth Zhaoyi Xu1, a, Delong
An Empirical Study on the Relationship between Money Supply, Economic Growth and Inflation
 An Empirical Study on the Relationship between Money Supply, Economic Growth and Inflation ZENG Li 1, SUN Hong-guo 1 * 1 (Department of Mathematics and Finance Hunan University of Humanities Science and
An Empirical Study on the Relationship between Money Supply, Economic Growth and Inflation ZENG Li 1, SUN Hong-guo 1 * 1 (Department of Mathematics and Finance Hunan University of Humanities Science and
The influence factors of short-term international capital flows in China Based on state space model Dong YANG1,a,*, Dan WANG1,b
 3rd International Conference on Science and Social Research (ICSSR 2014) The influence factors of short-term international capital flows in China Based on state space model Dong YANG1,a,*, Dan WANG1,b
3rd International Conference on Science and Social Research (ICSSR 2014) The influence factors of short-term international capital flows in China Based on state space model Dong YANG1,a,*, Dan WANG1,b
A comparative analysis on the factors promoting China s economic growth based on demand
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 5 (2011) 1388 1393 IACEED2010 A comparative analysis on the factors promoting China s economic growth based on demand Tang Anbao, Zhao Danhua School
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 5 (2011) 1388 1393 IACEED2010 A comparative analysis on the factors promoting China s economic growth based on demand Tang Anbao, Zhao Danhua School
Research on the Influence Factors of Chinese Local Government Debt Scale. Kun Li1, a
 nd International Conference on Economics, Management Engineering and Education Technology (ICEMEET 016) Research on the Influence Factors of Chinese Local Government Debt Scale Kun Li1, a 1 School of International
nd International Conference on Economics, Management Engineering and Education Technology (ICEMEET 016) Research on the Influence Factors of Chinese Local Government Debt Scale Kun Li1, a 1 School of International
Ndari Surjaningsih 1 Moh. Nuryazidi 2 Laura G. Gabriella 3
 RSEP International Conferences on Social Issues and Economic Studies ISBN: 978-65-37-788-6 5th RSEP Social Sciences Conference, 7-1 November, 217, Barcelona 1 2 3 ABSTRACT In order to finance its fiscal
RSEP International Conferences on Social Issues and Economic Studies ISBN: 978-65-37-788-6 5th RSEP Social Sciences Conference, 7-1 November, 217, Barcelona 1 2 3 ABSTRACT In order to finance its fiscal
The Effectiveness of Non-traditional Monetary Policy and the Inflation Target Policy : The Case of Japan in Comparison with the US
 Economics & Management Series EMS-2013-11 The Effectiveness of Non-traditional Monetary Policy and the Inflation Target Policy : The Case of Japan in Comparison with the US Osamu Nakamura International
Economics & Management Series EMS-2013-11 The Effectiveness of Non-traditional Monetary Policy and the Inflation Target Policy : The Case of Japan in Comparison with the US Osamu Nakamura International
Corresponding author: Gregory C Chow,
 Co-movements of Shanghai and New York stock prices by time-varying regressions Gregory C Chow a, Changjiang Liu b, Linlin Niu b,c a Department of Economics, Fisher Hall Princeton University, Princeton,
Co-movements of Shanghai and New York stock prices by time-varying regressions Gregory C Chow a, Changjiang Liu b, Linlin Niu b,c a Department of Economics, Fisher Hall Princeton University, Princeton,
Research on the Relationship between Sino-EU Trade and Economic Growth
 Research on the Relationship between Sino-EU Trade and Economic Growth Yaqing Liu 1* 1 School of Economics and Management, North China University of Technology, China Abstract. The dependence on foreign
Research on the Relationship between Sino-EU Trade and Economic Growth Yaqing Liu 1* 1 School of Economics and Management, North China University of Technology, China Abstract. The dependence on foreign
Forecasting Volatility in the Chinese Stock Market under Model Uncertainty 1
 Forecasting Volatility in the Chinese Stock Market under Model Uncertainty 1 Yong Li 1, Wei-Ping Huang, Jie Zhang 3 (1,. Sun Yat-Sen University Business, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 51075,China)
Forecasting Volatility in the Chinese Stock Market under Model Uncertainty 1 Yong Li 1, Wei-Ping Huang, Jie Zhang 3 (1,. Sun Yat-Sen University Business, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 51075,China)
Quantitative analysis of financial development s impact on economic growth
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 204, 6(4):86-9 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Quantitative analysis of financial development s impact
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 204, 6(4):86-9 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Quantitative analysis of financial development s impact
Application of Structural Breakpoint Test to the Correlation Analysis between Crude Oil Price and U.S. Weekly Leading Index
 Open Journal of Business and Management, 2016, 4, 322-328 Published Online April 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojbm http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojbm.2016.42034 Application of Structural Breakpoint
Open Journal of Business and Management, 2016, 4, 322-328 Published Online April 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojbm http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojbm.2016.42034 Application of Structural Breakpoint
Effects of Exchange Rate Change on Domestic Price Level: an Empirical Analysis
 Effects of Exchange Rate Change on Domestic Price Level: an Empirical Analysis PengkunZang ;Weijuan Shi Department of Mathematics, Hunan university of Humanities, Science, and Technology, Loudi,Hunan,
Effects of Exchange Rate Change on Domestic Price Level: an Empirical Analysis PengkunZang ;Weijuan Shi Department of Mathematics, Hunan university of Humanities, Science, and Technology, Loudi,Hunan,
An Empirical Analysis of Effect on Copper Futures Yield. Based on GARCH
 An Empirical Analysis of Effect on Copper Futures Yield Based on GARCH Feng Li 1, Ping Xiao 2 * 1 (School of Hunan University of Humanities, Science and Technology, Hunan 417000, China) 2 (School of Hunan
An Empirical Analysis of Effect on Copper Futures Yield Based on GARCH Feng Li 1, Ping Xiao 2 * 1 (School of Hunan University of Humanities, Science and Technology, Hunan 417000, China) 2 (School of Hunan
Can Financial Frictions Explain China s Current Account Puzzle: A Firm Level Analysis (Preliminary)
 Can Financial Frictions Explain China s Current Account Puzzle: A Firm Level Analysis (Preliminary) Yan Bai University of Rochester NBER Dan Lu University of Rochester Xu Tian University of Rochester February
Can Financial Frictions Explain China s Current Account Puzzle: A Firm Level Analysis (Preliminary) Yan Bai University of Rochester NBER Dan Lu University of Rochester Xu Tian University of Rochester February
The Effect of Chinese Monetary Policy on Banking During the Global Financial Crisis
 27 The Effect of Chinese Monetary Policy on Banking During the Global Financial Crisis Prof. Dr. Tao Chen School of Banking and Finance University of International Business and Economic Beijing Table of
27 The Effect of Chinese Monetary Policy on Banking During the Global Financial Crisis Prof. Dr. Tao Chen School of Banking and Finance University of International Business and Economic Beijing Table of
The Relationship between Foreign Direct Investment and Economic Development An Empirical Analysis of Shanghai 's Data Based on
 The Relationship between Foreign Direct Investment and Economic Development An Empirical Analysis of Shanghai 's Data Based on 2004-2015 Jiaqi Wang School of Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China
The Relationship between Foreign Direct Investment and Economic Development An Empirical Analysis of Shanghai 's Data Based on 2004-2015 Jiaqi Wang School of Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China
Empirical Study on Short-Term Prediction of Shanghai Composite Index Based on ARMA Model
 Empirical Study on Short-Term Prediction of Shanghai Composite Index Based on ARMA Model Cai-xia Xiang 1, Ping Xiao 2* 1 (School of Hunan University of Humanities, Science and Technology, Hunan417000,
Empirical Study on Short-Term Prediction of Shanghai Composite Index Based on ARMA Model Cai-xia Xiang 1, Ping Xiao 2* 1 (School of Hunan University of Humanities, Science and Technology, Hunan417000,
Interest rate uncertainty, Investment and their relationship on different industries; Evidence from Jiangsu, China
 Li Suyuan, Wu han, Adnan Khurshid, Journal of International Studies, Vol. 8, No 2, 2015, pp. 74-82. DOI: 10.14254/2071-8330.2015/8-2/7 Journal of International Studies Foundation of International Studies,
Li Suyuan, Wu han, Adnan Khurshid, Journal of International Studies, Vol. 8, No 2, 2015, pp. 74-82. DOI: 10.14254/2071-8330.2015/8-2/7 Journal of International Studies Foundation of International Studies,
3rd International Conference on Education, Management and Computing Technology (ICEMCT 2016)
 3rd International Conference on Education, Management and Computing Technology (ICEMCT 2016) The Dynamic Relationship between Onshore and Offshore Market Exchange Rate in the Process of RMB Internationalization
3rd International Conference on Education, Management and Computing Technology (ICEMCT 2016) The Dynamic Relationship between Onshore and Offshore Market Exchange Rate in the Process of RMB Internationalization
A Study on Asymmetric Preference in Foreign Exchange Market Intervention in Emerging Asia Yanzhen Wang 1,a, Xiumin Li 1, Yutan Li 1, Mingming Liu 1
 A Study on Asymmetric Preference in Foreign Exchange Market Intervention in Emerging Asia Yanzhen Wang 1,a, Xiumin Li 1, Yutan Li 1, Mingming Liu 1 1 School of Economics, Northeast Normal University, Changchun,
A Study on Asymmetric Preference in Foreign Exchange Market Intervention in Emerging Asia Yanzhen Wang 1,a, Xiumin Li 1, Yutan Li 1, Mingming Liu 1 1 School of Economics, Northeast Normal University, Changchun,
An Empirical Analysis on the Management Strategy of the Growth in Dividend Payout Signal Transmission Based on Event Study Methodology
 International Business and Management Vol. 7, No. 2, 2013, pp. 6-10 DOI:10.3968/j.ibm.1923842820130702.1100 ISSN 1923-841X [Print] ISSN 1923-8428 [Online] www.cscanada.net www.cscanada.org An Empirical
International Business and Management Vol. 7, No. 2, 2013, pp. 6-10 DOI:10.3968/j.ibm.1923842820130702.1100 ISSN 1923-841X [Print] ISSN 1923-8428 [Online] www.cscanada.net www.cscanada.org An Empirical
Research on the Forecast and Development of China s Public Fiscal Revenue Based on ARIMA Model
 Theoretical Economics Letters, 2015, 5, 482-493 Published Online August 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/tel http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/tel.2015.54057 Research on the Forecast and Development
Theoretical Economics Letters, 2015, 5, 482-493 Published Online August 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/tel http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/tel.2015.54057 Research on the Forecast and Development
An Empirical Study about Catering Theory of Dividends: The Proof from Chinese Stock Market
 Journal of Industrial Engineering and Management JIEM, 2014 7(2): 506-517 Online ISSN: 2013-0953 Print ISSN: 2013-8423 http://dx.doi.org/10.3926/jiem.1013 An Empirical Study about Catering Theory of Dividends:
Journal of Industrial Engineering and Management JIEM, 2014 7(2): 506-517 Online ISSN: 2013-0953 Print ISSN: 2013-8423 http://dx.doi.org/10.3926/jiem.1013 An Empirical Study about Catering Theory of Dividends:
China s Growth Miracle: Past, Present, and Future
 China s Growth Miracle: Past, Present, and Future Li Yang 1 Over the past 35 years, China has achieved extraordinary economic performance thanks to the market-oriented reforms and opening-up. By the end
China s Growth Miracle: Past, Present, and Future Li Yang 1 Over the past 35 years, China has achieved extraordinary economic performance thanks to the market-oriented reforms and opening-up. By the end
Commodity price movements and monetary policy in Asia
 Commodity price movements and monetary policy in Asia Changyong Rhee 1 and Hangyong Lee 2 Abstract Emerging Asian economies typically have high shares of food in their consumption baskets, relatively low
Commodity price movements and monetary policy in Asia Changyong Rhee 1 and Hangyong Lee 2 Abstract Emerging Asian economies typically have high shares of food in their consumption baskets, relatively low
A Test of Two Open-Economy Theories: The Case of Oil Price Rise and Italy
 International Review of Business Research Papers Vol. 9. No.1. January 2013 Issue. Pp. 105 115 A Test of Two Open-Economy Theories: The Case of Oil Price Rise and Italy Kavous Ardalan 1 Two major open-economy
International Review of Business Research Papers Vol. 9. No.1. January 2013 Issue. Pp. 105 115 A Test of Two Open-Economy Theories: The Case of Oil Price Rise and Italy Kavous Ardalan 1 Two major open-economy
Ricardo-Barro Equivalence Theorem and the Positive Fiscal Policy in China Xiao-huan LIU 1,a,*, Su-yu LV 2,b
 2016 3 rd International Conference on Economics and Management (ICEM 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-368-7 Ricardo-Barro Equivalence Theorem and the Positive Fiscal Policy in China Xiao-huan LIU 1,a,*, Su-yu LV
2016 3 rd International Conference on Economics and Management (ICEM 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-368-7 Ricardo-Barro Equivalence Theorem and the Positive Fiscal Policy in China Xiao-huan LIU 1,a,*, Su-yu LV
Does External Debt Increase Net Private Wealth? The Relative Impact of Domestic versus External Debt on the US Demand for Money
 Journal of Applied Finance & Banking, vol. 3, no. 5, 2013, 85-91 ISSN: 1792-6580 (print version), 1792-6599 (online) Scienpress Ltd, 2013 Does External Debt Increase Net Private Wealth? The Relative Impact
Journal of Applied Finance & Banking, vol. 3, no. 5, 2013, 85-91 ISSN: 1792-6580 (print version), 1792-6599 (online) Scienpress Ltd, 2013 Does External Debt Increase Net Private Wealth? The Relative Impact
An Empirical Analysis of the Impact of Disposable Income of Urban Residents on Consumption Expenditure in Beijing. Jia-Nan BAO
 2017 International Conference on Economics and Management Engineering (ICEME 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-451-6 An Empirical Analysis of the Impact of Disposable Income of Urban Residents on Consumption Expenditure
2017 International Conference on Economics and Management Engineering (ICEME 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-451-6 An Empirical Analysis of the Impact of Disposable Income of Urban Residents on Consumption Expenditure
The Empirical Research on the Relationship between Fixed Assets Investment and Economic Growth
 The Empirical Research on the Relationship between Fixed Assets Investment and Economic Growth A Case in Shaanxi Province of China Yuanliang Song *1, Yiyue Jiang 1, Guangyang Song, Pu Wang 1 Institute
The Empirical Research on the Relationship between Fixed Assets Investment and Economic Growth A Case in Shaanxi Province of China Yuanliang Song *1, Yiyue Jiang 1, Guangyang Song, Pu Wang 1 Institute
Chapter 9 Dynamic Models of Investment
 George Alogoskoufis, Dynamic Macroeconomic Theory, 2015 Chapter 9 Dynamic Models of Investment In this chapter we present the main neoclassical model of investment, under convex adjustment costs. This
George Alogoskoufis, Dynamic Macroeconomic Theory, 2015 Chapter 9 Dynamic Models of Investment In this chapter we present the main neoclassical model of investment, under convex adjustment costs. This
Notes VI - Models of Economic Fluctuations
 Notes VI - Models of Economic Fluctuations Julio Garín Intermediate Macroeconomics Fall 2017 Intermediate Macroeconomics Notes VI - Models of Economic Fluctuations Fall 2017 1 / 33 Business Cycles We can
Notes VI - Models of Economic Fluctuations Julio Garín Intermediate Macroeconomics Fall 2017 Intermediate Macroeconomics Notes VI - Models of Economic Fluctuations Fall 2017 1 / 33 Business Cycles We can
Reforming the Transmission Mechanism of Monetary Policy in China
 Reforming the Transmission Mechanism of Monetary Policy in China By Wang Yu*, Ma Ming* China's reform on the transmission mechanism of monetary policy has advanced dramatically, especially since 1998,
Reforming the Transmission Mechanism of Monetary Policy in China By Wang Yu*, Ma Ming* China's reform on the transmission mechanism of monetary policy has advanced dramatically, especially since 1998,
Demand and Supply for Residential Housing in Urban China. Gregory C Chow Princeton University. Linlin Niu WISE, Xiamen University.
 Demand and Supply for Residential Housing in Urban China Gregory C Chow Princeton University Linlin Niu WISE, Xiamen University. August 2009 1. Introduction Ever since residential housing in urban China
Demand and Supply for Residential Housing in Urban China Gregory C Chow Princeton University Linlin Niu WISE, Xiamen University. August 2009 1. Introduction Ever since residential housing in urban China
Macroeconomics 2. Lecture 5 - Money February. Sciences Po
 Macroeconomics 2 Lecture 5 - Money Zsófia L. Bárány Sciences Po 2014 February A brief history of money in macro 1. 1. Hume: money has a wealth effect more money increase in aggregate demand Y 2. Friedman
Macroeconomics 2 Lecture 5 - Money Zsófia L. Bárány Sciences Po 2014 February A brief history of money in macro 1. 1. Hume: money has a wealth effect more money increase in aggregate demand Y 2. Friedman
Money Market Uncertainty and Retail Interest Rate Fluctuations: A Cross-Country Comparison
 DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS JOHANNES KEPLER UNIVERSITY LINZ Money Market Uncertainty and Retail Interest Rate Fluctuations: A Cross-Country Comparison by Burkhard Raunig and Johann Scharler* Working Paper
DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS JOHANNES KEPLER UNIVERSITY LINZ Money Market Uncertainty and Retail Interest Rate Fluctuations: A Cross-Country Comparison by Burkhard Raunig and Johann Scharler* Working Paper
A Test of Two Open-Economy Theories: Oil Price Rise and Italy
 A Test of Two Open-Economy Theories: Oil Price Rise and Italy Kavous Ardalan Marist College The goal of the study is to empirically discriminate between two open-economy theories. The Keynesian theory
A Test of Two Open-Economy Theories: Oil Price Rise and Italy Kavous Ardalan Marist College The goal of the study is to empirically discriminate between two open-economy theories. The Keynesian theory
Return to Capital in a Real Business Cycle Model
 Return to Capital in a Real Business Cycle Model Paul Gomme, B. Ravikumar, and Peter Rupert Can the neoclassical growth model generate fluctuations in the return to capital similar to those observed in
Return to Capital in a Real Business Cycle Model Paul Gomme, B. Ravikumar, and Peter Rupert Can the neoclassical growth model generate fluctuations in the return to capital similar to those observed in
Theory. 2.1 One Country Background
 2 Theory 2.1 One Country 2.1.1 Background The theory that has guided the specification of the US model was first presented in Fair (1974) and then in Chapter 3 in Fair (1984). This work stresses three
2 Theory 2.1 One Country 2.1.1 Background The theory that has guided the specification of the US model was first presented in Fair (1974) and then in Chapter 3 in Fair (1984). This work stresses three
Chapter 8 A Short Run Keynesian Model of Interdependent Economies
 George Alogoskoufis, International Macroeconomics, 2016 Chapter 8 A Short Run Keynesian Model of Interdependent Economies Our analysis up to now was related to small open economies, which took developments
George Alogoskoufis, International Macroeconomics, 2016 Chapter 8 A Short Run Keynesian Model of Interdependent Economies Our analysis up to now was related to small open economies, which took developments
Stock Prices, Foreign Exchange Reserves, and Interest Rates in Emerging and Developing Economies in Asia
 International Journal of Business and Social Science Vol. 7, No. 9; September 2016 Stock Prices, Foreign Exchange Reserves, and Interest Rates in Emerging and Developing Economies in Asia Yutaka Kurihara
International Journal of Business and Social Science Vol. 7, No. 9; September 2016 Stock Prices, Foreign Exchange Reserves, and Interest Rates in Emerging and Developing Economies in Asia Yutaka Kurihara
An Empirical Study on the Determinants of Dollarization in Cambodia *
 An Empirical Study on the Determinants of Dollarization in Cambodia * Socheat CHIM Graduate School of Economics, Osaka University 1-7 Machikaneyama, Toyonaka, Osaka, 560-0043, Japan E-mail: chimsocheat3@yahoo.com
An Empirical Study on the Determinants of Dollarization in Cambodia * Socheat CHIM Graduate School of Economics, Osaka University 1-7 Machikaneyama, Toyonaka, Osaka, 560-0043, Japan E-mail: chimsocheat3@yahoo.com
The Research of the Correlation between Stock Market and Macroeconomy Based on Comparison of Chinese and American Stock Markets
 Economic Management Journal December 2018, Volume 7 Issue 2, PP. 203-212 The Research of the Correlation between Stock Market and Macroeconomy Based on Comparison of Chinese and American Stock Markets
Economic Management Journal December 2018, Volume 7 Issue 2, PP. 203-212 The Research of the Correlation between Stock Market and Macroeconomy Based on Comparison of Chinese and American Stock Markets
International Journal of Business and Economic Development Vol. 4 Number 1 March 2016
 A sluggish U.S. economy is no surprise: Declining the rate of growth of profits and other indicators in the last three quarters of 2015 predicted a slowdown in the US economy in the coming months Bob Namvar
A sluggish U.S. economy is no surprise: Declining the rate of growth of profits and other indicators in the last three quarters of 2015 predicted a slowdown in the US economy in the coming months Bob Namvar
Peer to Peer Lending Supervision Analysis base on Evolutionary Game Theory
 IJISET - International Journal of Innovative Science, Engineering & Technology, Vol. 3 Issue, January 26. Peer to Peer Lending Supervision Analysis base on Evolutionary Game Theory Lei Liu Department of
IJISET - International Journal of Innovative Science, Engineering & Technology, Vol. 3 Issue, January 26. Peer to Peer Lending Supervision Analysis base on Evolutionary Game Theory Lei Liu Department of
Long-run Stability of Demand for Money in China with Consideration of Bilateral Currency Substitution
 Long-run Stability of Demand for Money in China with Consideration of Bilateral Currency Substitution Yongqing Wang The Department of Business and Economics The University of Wisconsin-Sheboygan Sheboygan,
Long-run Stability of Demand for Money in China with Consideration of Bilateral Currency Substitution Yongqing Wang The Department of Business and Economics The University of Wisconsin-Sheboygan Sheboygan,
Principles of Banking (III): Macroeconomics of Banking (1) Introduction
 Principles of Banking (III): Macroeconomics of Banking (1) Jin Cao (Norges Bank Research, Oslo & CESifo, München) Outline 1 2 Disclaimer (If they care about what I say,) the views expressed in this manuscript
Principles of Banking (III): Macroeconomics of Banking (1) Jin Cao (Norges Bank Research, Oslo & CESifo, München) Outline 1 2 Disclaimer (If they care about what I say,) the views expressed in this manuscript
The Nightmare of the Leader: The Impact of Deregulation on an Oligopoly Insurance Market
 The Nightmare of the Leader: The Impact of Deregulation on an Oligopoly Insurance Market Jennifer L. Wang, * Larry Y. Tzeng, and En-Lin Wang Abstract: This paper explores the impact of deregulation of
The Nightmare of the Leader: The Impact of Deregulation on an Oligopoly Insurance Market Jennifer L. Wang, * Larry Y. Tzeng, and En-Lin Wang Abstract: This paper explores the impact of deregulation of
The Structure of China's Foreign Trade Imbalances and Coping Strategies
 International Journal of Humanities and Social Science Volume 7 Number 5 May 2017 The Structure of China's Foreign Trade Imbalances and Coping Strategies Jin Qian Full-time Ph.D. Student Department of
International Journal of Humanities and Social Science Volume 7 Number 5 May 2017 The Structure of China's Foreign Trade Imbalances and Coping Strategies Jin Qian Full-time Ph.D. Student Department of
Demand for Money in China with Currency Substitution: Evidence from the Recent Data
 Modern Economy, 2017, 8, 484-493 http://www.scirp.org/journal/me ISSN Online: 2152-7261 ISSN Print: 2152-7245 Demand for Money in China with Currency Substitution: Evidence from the Recent Data Yongqing
Modern Economy, 2017, 8, 484-493 http://www.scirp.org/journal/me ISSN Online: 2152-7261 ISSN Print: 2152-7245 Demand for Money in China with Currency Substitution: Evidence from the Recent Data Yongqing
A formal look at the negative interbank rate
 e Theoretical Applied Economics Volume XXIV (2017), No. 1(610), Spring, pp. 261-266 A formal look at the negative interbank rate Gerasimos T. SOLDATOS American University of Athens, Greece soldgera@yahoo.com
e Theoretical Applied Economics Volume XXIV (2017), No. 1(610), Spring, pp. 261-266 A formal look at the negative interbank rate Gerasimos T. SOLDATOS American University of Athens, Greece soldgera@yahoo.com
Liquidity Excess and Futures Copper Price
 International Journal of Finance and Banking Research 016; (6): 04-08 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijfbr doi: 10.11648/j.ijfbr.016006.13 ISSN: 47-6X (Print); ISSN: 47-78 (Online) Liquidity Excess
International Journal of Finance and Banking Research 016; (6): 04-08 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijfbr doi: 10.11648/j.ijfbr.016006.13 ISSN: 47-6X (Print); ISSN: 47-78 (Online) Liquidity Excess
EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION AND FIRM PERFORMANCE: BIG CARROT, SMALL STICK
 EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION AND FIRM PERFORMANCE: BIG CARROT, SMALL STICK Scott J. Wallsten * Stanford Institute for Economic Policy Research 579 Serra Mall at Galvez St. Stanford, CA 94305 650-724-4371 wallsten@stanford.edu
EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION AND FIRM PERFORMANCE: BIG CARROT, SMALL STICK Scott J. Wallsten * Stanford Institute for Economic Policy Research 579 Serra Mall at Galvez St. Stanford, CA 94305 650-724-4371 wallsten@stanford.edu
Comparative analysis of the BRICS Trade
 Comparative analysis of the BRICS Trade Su Ang March 27, 2016 Abstract This article analyzes how economic growth, economic population, budget deficit, disposable income per capita and currency affect the
Comparative analysis of the BRICS Trade Su Ang March 27, 2016 Abstract This article analyzes how economic growth, economic population, budget deficit, disposable income per capita and currency affect the
Research on the Selection of Discount Rate in Value-for-money Evaluation
 2018 International Conference on Computer, Civil Engineering and Management Science (ICCEMS 2018) Research on the Selection of Discount Rate in Value-for-money Evaluation Based on the Data Analysis of
2018 International Conference on Computer, Civil Engineering and Management Science (ICCEMS 2018) Research on the Selection of Discount Rate in Value-for-money Evaluation Based on the Data Analysis of
WHAT IT TAKES TO SOLVE THE U.S. GOVERNMENT DEFICIT PROBLEM
 WHAT IT TAKES TO SOLVE THE U.S. GOVERNMENT DEFICIT PROBLEM RAY C. FAIR This paper uses a structural multi-country macroeconometric model to estimate the size of the decrease in transfer payments (or tax
WHAT IT TAKES TO SOLVE THE U.S. GOVERNMENT DEFICIT PROBLEM RAY C. FAIR This paper uses a structural multi-country macroeconometric model to estimate the size of the decrease in transfer payments (or tax
The Effects of Public Debt on Economic Growth and Gross Investment in India: An Empirical Evidence
 Volume 8, Issue 1, July 2015 The Effects of Public Debt on Economic Growth and Gross Investment in India: An Empirical Evidence Amanpreet Kaur Research Scholar, Punjab School of Economics, GNDU, Amritsar,
Volume 8, Issue 1, July 2015 The Effects of Public Debt on Economic Growth and Gross Investment in India: An Empirical Evidence Amanpreet Kaur Research Scholar, Punjab School of Economics, GNDU, Amritsar,
INVESTOR SENTIMENT, MANAGERIAL OVERCONFIDENCE, AND CORPORATE INVESTMENT BEHAVIOR
 INVESTOR SENTIMENT, MANAGERIAL OVERCONFIDENCE, AND CORPORATE INVESTMENT BEHAVIOR You Haixia Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, China ABSTRACT In this paper, the nonferrous metals industry
INVESTOR SENTIMENT, MANAGERIAL OVERCONFIDENCE, AND CORPORATE INVESTMENT BEHAVIOR You Haixia Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, China ABSTRACT In this paper, the nonferrous metals industry
Study of Relationship Between USD/INR Exchange Rate and BSE Sensex from
 DOI : 10.18843/ijms/v5i3(1)/13 DOIURL :http://dx.doi.org/10.18843/ijms/v5i3(1)/13 Study of Relationship Between USD/INR Exchange Rate and BSE Sensex from 2008-2017 Hardeepika Singh Ahluwalia, Assistant
DOI : 10.18843/ijms/v5i3(1)/13 DOIURL :http://dx.doi.org/10.18843/ijms/v5i3(1)/13 Study of Relationship Between USD/INR Exchange Rate and BSE Sensex from 2008-2017 Hardeepika Singh Ahluwalia, Assistant
IMPLICATION OF TAYLOR RULE ON CHINA'S MONETARY POLICY AND INTEREAT RATE LIBERALISATION. BY YIP YAN TING Student No
 IMPLICATION OF TAYLOR RULE ON CHINA'S MONETARY POLICY AND INTEREAT RATE LIBERALISATION BY YIP YAN TING Student No. 12209082 A PROJECT SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE
IMPLICATION OF TAYLOR RULE ON CHINA'S MONETARY POLICY AND INTEREAT RATE LIBERALISATION BY YIP YAN TING Student No. 12209082 A PROJECT SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE
Feedback Effect and Capital Structure
 Feedback Effect and Capital Structure Minh Vo Metropolitan State University Abstract This paper develops a model of financing with informational feedback effect that jointly determines a firm s capital
Feedback Effect and Capital Structure Minh Vo Metropolitan State University Abstract This paper develops a model of financing with informational feedback effect that jointly determines a firm s capital
Redistribution Effects of Electricity Pricing in Korea
 Redistribution Effects of Electricity Pricing in Korea Jung S. You and Soyoung Lim Rice University, Houston, TX, U.S.A. E-mail: jsyou10@gmail.com Revised: January 31, 2013 Abstract Domestic electricity
Redistribution Effects of Electricity Pricing in Korea Jung S. You and Soyoung Lim Rice University, Houston, TX, U.S.A. E-mail: jsyou10@gmail.com Revised: January 31, 2013 Abstract Domestic electricity
Research of the Relationship between Defense Expenditure and Economic Operation Based on Unconstrained VAR Model
 International Conference on Economics, Social Science, Arts, Education and Management Engineering (ESSAEME 2015) Research of the Relationship between Defense Expenditure and Economic Operation Based on
International Conference on Economics, Social Science, Arts, Education and Management Engineering (ESSAEME 2015) Research of the Relationship between Defense Expenditure and Economic Operation Based on
The Demand and Supply of Safe Assets (Premilinary)
 The Demand and Supply of Safe Assets (Premilinary) Yunfan Gu August 28, 2017 Abstract It is documented that over the past 60 years, the safe assets as a percentage share of total assets in the U.S. has
The Demand and Supply of Safe Assets (Premilinary) Yunfan Gu August 28, 2017 Abstract It is documented that over the past 60 years, the safe assets as a percentage share of total assets in the U.S. has
Macroeconomics: Policy, 31E23000, Spring 2018
 Macroeconomics: Policy, 31E23000, Spring 2018 Lecture 8: Safe Asset, Government Debt Pertti University School of Business March 19, 2018 Today Safe Asset, basics Government debt, sustainability, fiscal
Macroeconomics: Policy, 31E23000, Spring 2018 Lecture 8: Safe Asset, Government Debt Pertti University School of Business March 19, 2018 Today Safe Asset, basics Government debt, sustainability, fiscal
An Empirical Research on Chinese Stock Market Volatility Based. on Garch
 Volume 04 - Issue 07 July 2018 PP. 15-23 An Empirical Research on Chinese Stock Market Volatility Based on Garch Ya Qian Zhu 1, Wen huili* 1 (Department of Mathematics and Finance, Hunan University of
Volume 04 - Issue 07 July 2018 PP. 15-23 An Empirical Research on Chinese Stock Market Volatility Based on Garch Ya Qian Zhu 1, Wen huili* 1 (Department of Mathematics and Finance, Hunan University of
REACTION OF THE INTEREST RATES IN POLAND TO THE INTEREST RATES CHANGES IN THE USA AND EURO ZONE 1
 QUANTITATIVE METHODS IN ECONOMICS Vol. XII, No. 1, 2011, pp. 125 133 REACTION OF THE INTEREST RATES IN POLAND TO THE INTEREST RATES CHANGES IN THE USA AND EURO ZONE 1 Grzegorz Przekota Faculty of Production
QUANTITATIVE METHODS IN ECONOMICS Vol. XII, No. 1, 2011, pp. 125 133 REACTION OF THE INTEREST RATES IN POLAND TO THE INTEREST RATES CHANGES IN THE USA AND EURO ZONE 1 Grzegorz Przekota Faculty of Production
Investment and Taxation in Germany - Evidence from Firm-Level Panel Data Discussion
 Investment and Taxation in Germany - Evidence from Firm-Level Panel Data Discussion Bronwyn H. Hall Nuffield College, Oxford University; University of California at Berkeley; and the National Bureau of
Investment and Taxation in Germany - Evidence from Firm-Level Panel Data Discussion Bronwyn H. Hall Nuffield College, Oxford University; University of California at Berkeley; and the National Bureau of
Cross- Country Effects of Inflation on National Savings
 Cross- Country Effects of Inflation on National Savings Qun Cheng Xiaoyang Li Instructor: Professor Shatakshee Dhongde December 5, 2014 Abstract Inflation is considered to be one of the most crucial factors
Cross- Country Effects of Inflation on National Savings Qun Cheng Xiaoyang Li Instructor: Professor Shatakshee Dhongde December 5, 2014 Abstract Inflation is considered to be one of the most crucial factors
The Empirical Study on Factors Influencing Investment Efficiency of Insurance Funds Based on Panel Data Model Fei-yue CHEN
 2017 2nd International Conference on Computational Modeling, Simulation and Applied Mathematics (CMSAM 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-499-8 The Empirical Study on Factors Influencing Investment Efficiency of
2017 2nd International Conference on Computational Modeling, Simulation and Applied Mathematics (CMSAM 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-499-8 The Empirical Study on Factors Influencing Investment Efficiency of
Influence of Interest Rates Fluctuations on the Stability of SSE Index
 Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Innovation & Management 1211 Influence of Interest Rates Fluctuations on the Stability of SSE Index Liu Xiangbin 1, Wang Zhuo 2 1 School of Finance,Harbin
Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Innovation & Management 1211 Influence of Interest Rates Fluctuations on the Stability of SSE Index Liu Xiangbin 1, Wang Zhuo 2 1 School of Finance,Harbin
Threshold cointegration and nonlinear adjustment between stock prices and dividends
 Applied Economics Letters, 2010, 17, 405 410 Threshold cointegration and nonlinear adjustment between stock prices and dividends Vicente Esteve a, * and Marı a A. Prats b a Departmento de Economia Aplicada
Applied Economics Letters, 2010, 17, 405 410 Threshold cointegration and nonlinear adjustment between stock prices and dividends Vicente Esteve a, * and Marı a A. Prats b a Departmento de Economia Aplicada
Empirical Analysis of GARCH Effect of Shanghai Copper Futures
 Volume 04 - Issue 06 June 2018 PP. 39-45 Empirical Analysis of GARCH Effect of Shanghai Copper 1902 Futures Wei Wu, Fang Chen* Department of Mathematics and Finance Hunan University of Humanities Science
Volume 04 - Issue 06 June 2018 PP. 39-45 Empirical Analysis of GARCH Effect of Shanghai Copper 1902 Futures Wei Wu, Fang Chen* Department of Mathematics and Finance Hunan University of Humanities Science
THE IMPACT OF IMPORT ON INFLATION IN NAMIBIA
 European Journal of Business, Economics and Accountancy Vol. 5, No. 2, 207 ISSN 2056-608 THE IMPACT OF IMPORT ON INFLATION IN NAMIBIA Mika Munepapa Namibia University of Science and Technology NAMIBIA
European Journal of Business, Economics and Accountancy Vol. 5, No. 2, 207 ISSN 2056-608 THE IMPACT OF IMPORT ON INFLATION IN NAMIBIA Mika Munepapa Namibia University of Science and Technology NAMIBIA
Discussion. Benoît Carmichael
 Discussion Benoît Carmichael The two studies presented in the first session of the conference take quite different approaches to the question of price indexes. On the one hand, Coulombe s study develops
Discussion Benoît Carmichael The two studies presented in the first session of the conference take quite different approaches to the question of price indexes. On the one hand, Coulombe s study develops
Research on the Influencing Factors of Dollar Exchange Rate Fluctuation after Financial Crisis
 2017 4th International Conference on Business, Economics and Management (BUSEM 2017) Research on the Influencing Factors of Dollar Exchange Rate Fluctuation after Financial Crisis Ruoxi Gong Majoring in
2017 4th International Conference on Business, Economics and Management (BUSEM 2017) Research on the Influencing Factors of Dollar Exchange Rate Fluctuation after Financial Crisis Ruoxi Gong Majoring in
Assessment on Credit Risk of Real Estate Based on Logistic Regression Model
 Assessment on Credit Risk of Real Estate Based on Logistic Regression Model Li Hongli 1, a, Song Liwei 2,b 1 Chongqing Engineering Polytechnic College, Chongqing400037, China 2 Division of Planning and
Assessment on Credit Risk of Real Estate Based on Logistic Regression Model Li Hongli 1, a, Song Liwei 2,b 1 Chongqing Engineering Polytechnic College, Chongqing400037, China 2 Division of Planning and
Research on Capital Cost Analysis of State Owned Enterprises in China
 Research on Capital Cost Analysis of State Owned Enterprises in China Pei Wang 1, a Department of Economics, China University Of Geosciences Great Wall College, Baoding, China a 724388082@qq.com Keywords:
Research on Capital Cost Analysis of State Owned Enterprises in China Pei Wang 1, a Department of Economics, China University Of Geosciences Great Wall College, Baoding, China a 724388082@qq.com Keywords:
Chapter 11 CAPITAL FLOWS AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS FOR CENTRAL BANK POLICIES IN TAIWAN. by Hsiao Yuan Yu 1
 Chapter 11 CAPITAL FLOWS AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS FOR CENTRAL BANK POLICIES IN TAIWAN by Hsiao Yuan Yu 1 1. Introduction Capital flows have significant repercussions for developing countries. In the past
Chapter 11 CAPITAL FLOWS AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS FOR CENTRAL BANK POLICIES IN TAIWAN by Hsiao Yuan Yu 1 1. Introduction Capital flows have significant repercussions for developing countries. In the past
R&D Portfolio Allocation & Capital Financing
 R&D Portfolio Allocation & Capital Financing Pin-Hua Lin, Assistant researcher, Science & Technology Policy Research and Information Center, National Applied Research Laboratories, Taiwan; Graduate Institution
R&D Portfolio Allocation & Capital Financing Pin-Hua Lin, Assistant researcher, Science & Technology Policy Research and Information Center, National Applied Research Laboratories, Taiwan; Graduate Institution
Foreign Direct Investment and Economic Growth in Some MENA Countries: Theory and Evidence
 Loyola University Chicago Loyola ecommons Topics in Middle Eastern and orth African Economies Quinlan School of Business 1999 Foreign Direct Investment and Economic Growth in Some MEA Countries: Theory
Loyola University Chicago Loyola ecommons Topics in Middle Eastern and orth African Economies Quinlan School of Business 1999 Foreign Direct Investment and Economic Growth in Some MEA Countries: Theory
*Corresponding author. Key Words: Exchange Rate Fluctuations, Export Trade, Electronic Communications Manufacturing Industry.
 2017 International Conference on Economics and Management Engineering (ICEME 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-451-6 An Empirical Study on the Impact of RMB Exchange Rate Fluctuation on Export Trade-Take China s
2017 International Conference on Economics and Management Engineering (ICEME 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-451-6 An Empirical Study on the Impact of RMB Exchange Rate Fluctuation on Export Trade-Take China s
The Analysis of ICBC Stock Based on ARMA-GARCH Model
 Volume 04 - Issue 08 August 2018 PP. 11-16 The Analysis of ICBC Stock Based on ARMA-GARCH Model Si-qin LIU 1 Hong-guo SUN 1* 1 (Department of Mathematics and Finance Hunan University of Humanities Science
Volume 04 - Issue 08 August 2018 PP. 11-16 The Analysis of ICBC Stock Based on ARMA-GARCH Model Si-qin LIU 1 Hong-guo SUN 1* 1 (Department of Mathematics and Finance Hunan University of Humanities Science
Testing the Stability of Demand for Money in Tonga
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Testing the Stability of Demand for Money in Tonga Saten Kumar and Billy Manoka University of the South Pacific, University of Papua New Guinea 12. June 2008 Online at
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Testing the Stability of Demand for Money in Tonga Saten Kumar and Billy Manoka University of the South Pacific, University of Papua New Guinea 12. June 2008 Online at
Online Appendix (Not intended for Publication): Federal Reserve Credibility and the Term Structure of Interest Rates
 Online Appendix Not intended for Publication): Federal Reserve Credibility and the Term Structure of Interest Rates Aeimit Lakdawala Michigan State University Shu Wu University of Kansas August 2017 1
Online Appendix Not intended for Publication): Federal Reserve Credibility and the Term Structure of Interest Rates Aeimit Lakdawala Michigan State University Shu Wu University of Kansas August 2017 1
The Great Housing Boom of China
 The Great Housing Boom of China Department of Economics HKUST October 18, 2018 1 1 Chen, K., & Wen, Y. (2017). The great housing boom of China. American Economic Journal: Macroeconomics, 9(2), 73-114.
The Great Housing Boom of China Department of Economics HKUST October 18, 2018 1 1 Chen, K., & Wen, Y. (2017). The great housing boom of China. American Economic Journal: Macroeconomics, 9(2), 73-114.
TOPICS IN MACROECONOMICS: MODELLING INFORMATION, LEARNING AND EXPECTATIONS LECTURE NOTES. Lucas Island Model
 TOPICS IN MACROECONOMICS: MODELLING INFORMATION, LEARNING AND EXPECTATIONS LECTURE NOTES KRISTOFFER P. NIMARK Lucas Island Model The Lucas Island model appeared in a series of papers in the early 970s
TOPICS IN MACROECONOMICS: MODELLING INFORMATION, LEARNING AND EXPECTATIONS LECTURE NOTES KRISTOFFER P. NIMARK Lucas Island Model The Lucas Island model appeared in a series of papers in the early 970s
Chapter 2 China s National Balance Sheet: Preparation and Analysis
 Chapter 2 China s National Balance Sheet: Preparation and Analysis 2.1 Basic Framework A national balance sheet aims to study a country s overall economic stocks. According to the System of National Accounts
Chapter 2 China s National Balance Sheet: Preparation and Analysis 2.1 Basic Framework A national balance sheet aims to study a country s overall economic stocks. According to the System of National Accounts
LECTURE 8 Monetary Policy at the Zero Lower Bound: Quantitative Easing. October 10, 2018
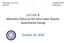 Economics 210c/236a Fall 2018 Christina Romer David Romer LECTURE 8 Monetary Policy at the Zero Lower Bound: Quantitative Easing October 10, 2018 Announcements Paper proposals due on Friday (October 12).
Economics 210c/236a Fall 2018 Christina Romer David Romer LECTURE 8 Monetary Policy at the Zero Lower Bound: Quantitative Easing October 10, 2018 Announcements Paper proposals due on Friday (October 12).
8th International Conference on the Chinese Economy CERDI-IDREC, University of Auvergne, France Clermont-Ferrand, October, 2011
 1 8th International Conference on the Chinese Economy CERDI-IDREC, University of Auvergne, France Clermont-Ferrand, 20-21 October, 2011 Global Imbalances and Exchange Regimes with a Four-Country Stock-Flow
1 8th International Conference on the Chinese Economy CERDI-IDREC, University of Auvergne, France Clermont-Ferrand, 20-21 October, 2011 Global Imbalances and Exchange Regimes with a Four-Country Stock-Flow
Present situation, forecasting and the analysis of fixed assets investment in Zhejiang province
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(6):2049-2055 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Present situation, forecasting and the analysis
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(6):2049-2055 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Present situation, forecasting and the analysis
INTER-ORGANIZATIONAL COOPERATIVE INNOVATION OF PROJECT-BASED SUPPLY CHAINS UNDER CONSIDERATION OF MONITORING SIGNALS
 ISSN 176-459 Int j simul model 14 (015) 3, 539-550 Original scientific paper INTER-ORGANIZATIONAL COOPERATIVE INNOVATION OF PROJECT-BASED SUPPLY CHAINS UNDER CONSIDERATION OF MONITORING SIGNALS Wu, G.-D.
ISSN 176-459 Int j simul model 14 (015) 3, 539-550 Original scientific paper INTER-ORGANIZATIONAL COOPERATIVE INNOVATION OF PROJECT-BASED SUPPLY CHAINS UNDER CONSIDERATION OF MONITORING SIGNALS Wu, G.-D.
A stable demand for money despite financial crisis: The case of Venezuela
 A stable demand for money despite financial crisis: The case of Venezuela Hilde C. Bjørnland* August 2004 Forthcoming in Applied Economics Abstract: This paper investigates the demand for broad money in
A stable demand for money despite financial crisis: The case of Venezuela Hilde C. Bjørnland* August 2004 Forthcoming in Applied Economics Abstract: This paper investigates the demand for broad money in
