Improving the regulatory framework of floodplain management and development in the United Kingdom
|
|
|
- Victoria Wiggins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Improving the regulatory framework of floodplain management and development in the United Kingdom Alam, B and Pathirage, C Title Authors Type URL Published Date 2017 Improving the regulatory framework of floodplain management and development in the United Kingdom Alam, B and Pathirage, C Conference or Workshop Item This version is available at: USIR is a digital collection of the research output of the University of Salford. Where copyright permits, full text material held in the repository is made freely available online and can be read, downloaded and copied for non commercial private study or research purposes. Please check the manuscript for any further copyright restrictions. For more information, including our policy and submission procedure, please contact the Repository Team at: usir@salford.ac.uk.
2 ID 010 IMPROVING THE REGULATORY FRAMEWORK OF FLOODPLAIN MANAGEMENT AND DEVELOPMENT IN THE UNITED KINGDOM B.Alam 1 and C.Pathirage 2 1 School of the Built Environment, University of Salford, 43 Crescent, M5 4WT, United Kingdom 2 School of the Built Environment, University of Salford, 43 Crescent, M5 4WT, United Kingdom B.Alam@edu.salford.ac.uk Abstract: Flooding is a natural disaster that most commonly impacts the United Kingdom. The frequency of flooding makes it an important focus for a researcher. The scope of flooding is wide-ranging as it can affect people, society and the economy. A particular location vulnerable are the floodplains as these are naturally prone to flooding. Such developments suffer from varying degrees of risk during times of flooding. In the United Kingdom, floodplain developments have risen leading to added risk to occupants. Property owners are thus exposed to risk with flood regulation coming into effect through planning, defences, insurance and taking precautionary measures. A deep understanding of flood response and management will be needed for this research. For this project, each stage of the regulatory process involving flooding and floodplains in the United Kingdom will be examined to provide an overview of current flood management practice. Current findings show that there are regulatory gaps with regards to flood resilience in relation to aspects such as flood insurance and though a unified strategy exists there is a disconnect with flood response. An extensive literature review will be used to showcase the challenges and barriers to flood response on the floodplains. This is with the aim of better improving the existing regulatory framework of floodplain management in the United Kingdom. Keywords: Disaster Management, Flooding, Floodplain, Floodplain Development 1. INTRODUCTION Flooding is a natural disaster that is ranked as the most common the affect the world. It is held as the worst threat to the UK with the danger posed by it set to increase in the future (Defra, 2015). Their frequency makes it an important focus for research. Guha-Sapir et al. (2010) noted floods being the most common natural disaster worldwide. Thus, their effect is wide ranging and communities are more likely to be affected by it. Floodplains are particularly vulnerable as they are ecologically connected to a body of water making them naturally prone to flooding. In England, rivers and coastal floodplains have been populated for centuries with floodplains making 12% of the country and 8% of those having property developments (CCC, 2012). Flooding also impacts infrastructure such as energy, water and communications (EA, 2009). Thus, damages to affected regions can be extensive with floodplains being particularly vulnerable. The Environment Agency (2015) states that floodplains, would naturally be affected by flooding if a river rises above its banks, or high tides and stormy seas cause flooding in coastal areas. In 2009, an estimated 2.4 million properties were already situated in a floodplain (NAO, 2014). The damage can include disruption in the community, damage to structures and the loss of human lives. For methodology, an exploratory based research has been used to highlight improvements to the existing framework with qualitative methods being utilised through the use of an extensive literature review. 754
3 2. FLOODING Flooding is a natural hazard that can come from a variety of sources including river or ground water. The United Nations stated, flooding can arise from overflowing river, heavy rainfall over the short period or an unusual inflow of sea water onto land, such as storm surge, tidal flooding, seismic events (tsunami) or large landslide (Proverbs and Mambretti, 2012; pg. 156). Floods impact human life with them being a growing risk to populations, particularly those in floodplain areas. It has the greatest potential for damage among the natural disasters and affects large numbers of people (UN, 2004). The dangers posed by it are widespread with it capable of devastating entire communities. Fleming (2002; pg. 15) stated, "floods are a natural occurrence and the risk they pose is wide ranging. However, for society, the main focus is the risk to people and property." Thus, floodwaters can destroy both residential and commercial properties. It also affects; transportation, communication, agricultural developments and damages the environment. In addition, the after effects can lead to health risks from pollution and water-borne diseases (Marriott et al, 1999). The frequency of flooding makes it the most common of the natural disasters with is effects illustrated in Figure 25. Figure 25: Reported Flood Phenomena (number of floods per 10,000 km), per country (since 1980) (Source: EEA, 2015) A Climate Change Committee (2012) report noted that flood damage is expected to increase across the UK in the future. Flood damage amounts to 1.1 billion per year in costs in England (Bennett and Hartwell-Naguib, 2014). In 2000, 10,000 properties in England and Wales suffered from flooding and weather-related insurance claims totally to around 1 billion (POST, 2001). There are an estimated 5.8 million (nearly 20%) of properties that suffer from the risk of flooding in the UK (Defra, 2013). As such, the effects of flooding are wide-ranging in the UK. Research has indicated that the effects of flooding may be more extreme than previously estimated when taking into account the potential increases in rainfall 755
4 volume and intensity and risk of extreme sea level rise (Evans et al., 2008). Thus, the danger posed by flood risk is only set to increase in the future. 2.1 Floodplains An area prone to flooding are regions known as floodplains. These are, the land next to, or hydraulically or ecologically connected to, the flowing river (Freitag, 2009; pg. 44). These areas are naturally prone to flooding and therefore suffer from a higher degree of flood risk. However, Freitag (2009) noted human developments on floodplains can bring about a quick and deadly response from the river. Such areas are subject to urban development but suffer from extreme floods making them contested regions. Annually, extreme floods create enormous and mounting damage on floodplains (Hartmann, 2011). The IPCC (2007) noted human development on floodplains and inadequate flood response plans have led to greater potential for damage caused by flooding. Despite the dangers, there have been developments in floodplain areas (Hartmann, 2011). This is due to factors such as growing population pressures and the land being viable for development. Floodplains are among the most densely populated areas in the world with these being particularly well suited for development (Kron, 2005). However, environmental changes alongside wider societal changes can potentially alter the likelihood of human exposure to hazards and the susceptibility of people to their impacts (Few, 2007). In England and Wales, there were approximately 1.85 million homes, 185,000 commercial properties, around 5 million people and half of agricultural land suffering flood risk (Few, 2013). In 2009, the Environment Agency (EA) noted that 2.4 million properties were situated on the floodplains in the UK (EA, 2009). A CCC (2012) report stated that floodplain development grew faster in England over the past ten years. Many developments were deemed protected but one-in-five suffered from significant flood risk. It is for this reason a framework is necessary to better manage new developments in floodplain regions and prevent inappropriate constructions. These developments expose inhabitants to the danger of flood risk as floodplains are more vulnerable to hazards. During floods, such areas can experience disruption in the community, damage to property and possible loss of life. However, due to their nature, floodplains serve as sites that are subject to development. 2.2 Floodplain Developments Floodplain developments hold many advantages but unrestrained development is noted for being costly and dangerous (Owen, 1981). Marriott (1999) noted that many of the worlds densely populated areas resided on floodplains. Such sites face an ever-present danger as they are prone to flooding. In 2004, a consultation with the Association of British Insurers (ABI) stated a need for stronger and more transparent planning systems to curtail developments on floodplains (ABI, 2004). It recommended the EA be made a statutory consultee on all planning applications in flood areas. However, there have been a number of developments on floodplains. The CCC (2012) noted floodplain development had grown at a fast rate compared to the past ten years. Whilst 80% of floodplain development were in well-protected locations, one-in-five properties built in such areas suffered from significant flood risk (CCC, 2012). On the approval process, the report stated that it was not sufficiently transparent or accountable. Furthermore, the EA stated that they only knew the outcome of 65% of planning applications that they objected. 756
5 The CCC (2012) report also were concerned on whether local authorities considered alternative developments before agreeing to construction on floodplains and whether longterm effects of climate change with regards to flooding had been considered. In 2013, local councils allowed 87 planning developments that saw 560 homes built in areas of high flood risk in England and Wales (RIBA, 2014). In 2009, an estimated 2.4 million properties were already situated in a floodplain (EA, 2009). Floodplain development had grown at a fast rate compared to the past ten years with one-in-five properties built in such areas that suffered from a significant flood risk (CCC, 2012). The number of homes stated to be built in flood risk had risen by a third in 2013 as compared to the previous year (RIBA, 2014). Despite the risks, such developments are only increasing and exposing their occupants to danger from flooding. The CCC (2014) noted that continued floodplain development leads to an increasing reliance on the use of flood defences. As such, the regulation of floodplain developments can reduce the burden placed on flood defences through the use of an effective flood risk management system that seeks to avoid inappropriate construction in these areas. 3. REGULATORY FRAMEWORK Parliament, regulatory authorities and courts have recognised the dangers of flooding and have attempted to address this through regulatory frameworks. To combat these risks, efforts are made in order to mitigate their impact. Such mitigation takes the form of disaster management that seeks to either avoid or reduce the potential losses from the hazard. To mitigate their impact, disaster management aims to either avoid, adapt or control the hazards effect. Wisner (2003) stated that disasters are a, "complex mix of natural hazards and human action". The UNISDR noted that disaster risk is composed of multiple factors that include the occurrence of an extreme hazard event caused by natural forces/natural forces alongside human interference and that this affects something or someone (Holt, 2012). The approach adopted by the courts established in the case of Arscott v. The Coal Authority (2004) referred to flooding as a common enemy that needs to be prevented. This involves taking steps to reduces likelihood of flooding and mitigate its impact. The strategic overview and management of flooding lay with set regulatory bodies such as the EA (Defra, 2014). Legislation such as the Flood and Water Management Act (2010) provides the framework for flood management. Ultimately, flooding cannot be avoided though the general approach is to manage the risk (Schanze, Zeman and Marsalek, 2006). In the UK, the EA operates as the statutory consultee on all new developments within floodplains (RIBA, 2009). It offers guidance and operates as part of the regulatory framework in managing the risks in floodplain developments. It is a requirement that Local Authorities consult with the EA during planning applications when a proposed development can suffer from a risk of flooding. Despite these measures, the UK has experienced flooding on numerous occasions as detailed in the following section. 3.1 Flood Regulations Flood risk is the combination of probability/hazard and consequence/impact (Sene, 2008). Thus, flood risk management operates by mitigating the extent of the flood damage. To combat flooding, regulatory systems are used to create a system to implement and manage flood defences. As a result, through management and organization it seeks to better respond 757
6 and cope with hazards/disasters. The tools created as part of this framework include; flood risk assessments, hazard maps, management plans, improved strategic coordination and public participation. This creates an element of flood defence with the goal of protecting human lives and property from flooding events. Developments in the international landscape have also led to incorporation of such frameworks into the UK as highlighted in Figure 26. Through law, a system is introduced through which guidance and enforcement is produced to implement such a framework with the aim of mitigating the impact of flooding hazards. Figure 26: Flood Legislation in the United Kingdom (Source: Devon County Council, 2015) Within the UK, the EA operates as a regulatory body who provides guidance on measures needed to protect homes from floods. Effective flood risk management offers an important role for the UK in the defence against hazards and protects communities, businesses and infrastructure (NAO, 2014). Legislation is the basis through which regulatory bodies can enforce/implement means to combat flooding. Under the Climate Change Act (2008), there is a general duty to adapt and mitigate the dangers from climate change with Local Authorities taking part in active strategies to achieve this goal. As climate change can increase flood, these strategies seek to promote a policy of adaptation. As a result, the regulatory framework operates with the goal of empowering flood management by providing guidance, policy and regulations. 3.2 Regulatory Bodies In the UK, flood management involves a complex framework of institutions that are responsible for its administration, finance and service (Brown and Damery, 2002). Defra and the EA take the leading role in developing strategies to mitigate the effects of flooding. The EA operates as the primary authority and has a supervisory duty on matters of flood defence (Brown and Damery, 2002). Legislation such as the Environment Act (1995) confer investigatory powers to the EA in the commission of its duties. The Flood Risk Regulations (2009) placed duties on the EA and local authorities to prepare flood risk assessments, flood risk maps and flood risk management plans (Defra, 2009). Though operating in the role of flood defence, legislation also imparts on it a duty as a flood risk management authority. 758
7 Cooley (2006) stated that, land-use management is among the most effective mitigation measure available. Thus, proper control over its management is deemed as the best approach in managing flood risk. The Environment Agency (2009) noted that developing in such areas means being exposed to flood risk. It is for this reason that their guidance is to avoid developing in such areas as this eliminates the risk. 4. DISCUSSION Flood risk management was identified as a national priority area of development (HM Government, 2012). Floodplains suffer from added risk of flooding that can be mitigated by implementing regulations to reduced its impact and manging the flood risk. According to Hall et al. (2003), flood risk management uses a strategy that seeks to review prior decisions made with the aim to reduce, control, accept, or redistribute risks of flooding". Thus, it distinguishes itself from flood defence as it seeks to mitigate the impact rather than avoid it entirely. Flood risk management has been noted as moving towards a continuous holistic approach that emphasized the need to analyse, assess and mitigate risk on a catchment scale (Sayers et al., 2013). Despite such features, there have been significant cases of damage to properties as a result of flooding. The EA stated that one-in-six properties among 5.2 million such residences in England experience a risk of flooding (Abbey and Richards, 2016). In both residential and non-residential properties, expected annual damages are estimated to be more than 1 billion that are at risk from flooding (Bennett and Hartwell-Naguib, 2014). Similarly, flooding has led to 2.4 million properties at risk from river/sea, 3 million suffer from risk of flooding from surface water and 1 million are exposed to flood risk from both (Law Society, 2016). In 2007, the summer floods resulted in heavy downpours that caused 55,000 properties to be flooded (Defra, 2009; Jha et al., 2012). Similarly, the Bonfield Report has shown that sustained rain in 2016 led to extensive damage across the country with 17,000 properties being flooded and costs expected to amount to 1.3 billion (Defra, 2016). Reports indicated further research could bring about better management in order to reduce flood events (Efrac, 2008). There exists a need from policy and law to regulate and mitigate flooding due to it being an ever-present danger. The UK Climate Projections (2009) noted floods being among the extreme events to affect the country, with greater frequency in the future (Defra, 2009). A Climate Change Risk Assessment (2012) indicated the UK being already vulnerable to extreme weather changes from flooding and heatwaves. This highlights the key goal of avoiding developments should they be made in areas designated as being inappropriate due to flooding. However, it highlights that developments could be made if safety measures, such as adaptations, were made in case of flooding. An Environmental Audit report highlighted, planning system also has a flood defence role to play by minimising development on floodplains and maximising the use of 'sustainable drainage' techniques (House of Commons, 2015). This system attempts to steer such developments away from areas of risk. It was noted that crucial changes in flood risk management came in two aspects; a shift from reliance on physical power to social power and that no single organisation has the power to affect change (Pender, 2011). Thus, a holistic approach combines the various organisations power for the use of effective floodplain management that can only occur through regulatory influence. Insurers have sought better control of floodplain development and increase spending on flood defences (Crichton, 2012). This shows that better regulations and guidelines are needed to 759
8 control flood risk management including those in the floodplain areas. Crichton (2012) noted floodplain developments have become easier through a succession of planning policies and due to reduced flood defence spending. As such, rules come into effect as they create the boundaries on the use of power. According to Pender (2011), legal frameworks are the archetypal system of formal rules, whilst governments are the archetypal setters of formal rules. A research gap identified from literature shows a lack of a coordinated strategy towards managing flood risk. Pender (2011) noted holistic approaches to managing flood risk is needed to better cope with impacts of flooding and climate change. The OST Future Flooding project sought to develop a holistic thinking approach to flood risk (Pender, 2011). Similarly, Surminski and Eldridge (2015) noted that there does not exist a long-term strategy to managing flood risk with flood insurance affordability being a short-term perspective. In conclusion, they said insurance was simply, tool amongst the many that are required for a holistic strategy on flood risk management (pg. 12). Insurance operates by covering unexpected losses but it does not prevent the risk of flooding from returning. Thus, they noted that risk reduction operates as an important element in combating flooding with the use of effective planning policy along with flood risk management playing an even more important role. 5. CONCLUSION Whilst floodplain management has faced increased improvements over the years, research has indicated that the danger posed by flooding is set to increase in the future. Floodplain development has increased according to research and literature has shown that goal of a holistic approach towards floodplain management is in need of further improvements. Aspects such as insurance and flood adaptations operate independently from that of Flood resilience. Thus, this misses the goal of improving flood resilience, response and management. Such a gap can be better resolved through the use of regulation, legislation and policy to address this missing link. By linking policy and regulations flood resilience with a long-term strategy this could see a more holistic approach to being adopted with regards to floodplain management in the UK. 6. REFERENCES Abbey, R. and Richards, M. (2016) A Practical Approach to Conveyancing. OUP Oxford; 18th Edition. Association of British Insurers (2004) Taking it on: developing UK sustainable development strategy together. Retrieved from: Bennett, O. and Hartwell-Naguib, S. (2014) Flood defence spending in England. House of Commons Library. Retrieved from: Brown, J.D. and Damery, S.L. (2002) Managing flood risk in the UK: towards an integration of social and technical perspectives. Transactions of the Institute of British Geographers, Vol.27 (4), pp Climate Change Committee (2012) Climate change is the UK preparing for flooding and water scarcity? Adaptation Sub-Committee Progress Report Retrieved from: Cooley, H. and Gleick, P.H. (2006) The world's water, : the biennial report on freshwater resources. Washington, DC : Island Press. Crichton, D. (2012) Floodplain Speaking 3rd Edition. The Chartered Insurance Institute: London Defra (2009) Adapting to Climate Change: UK Climate Projections. Retrieved From: 760
9 Defra (2013) Securing the future availability and affordability of home insurance in areas of flood risk. Retrieved from: e%20of%20flood%20insurance%20%20consultation%20document.pdf Defra (2014) The National Flood Emergency Framework for England. Retrieved From: pdf Defra (2016) The Property Flood Resilience Action Plan. Retrieved From: Environment, Food and Rural Affairs Committee (2008) Flooding: Fifth Report of Session Volume I. House of Commons. Retrieved from: Evans, E.P., Simm, J.D., and Thorne, C.R. (2008) An Update of the Foresight Future Flooding 2004 Qualitative Risk Analysis. Cabinet Office, London. Few, R. (2007) Health and climate change hazards: Framing social research on vulnerability, response and adaptation. Global Environment Change, 17, Fleming, G. (2002) Flood risk management: learning to live with rivers. London: Thomas Telford. Freitag, B (2009) Floodplain management : a new approach for a new era. Washington, DC : Island Press. Guha-Sapir, D. (2010) Health impacts of floods in Europe: Data gaps and information needs from a spatial perspective. CRED: European Commission's Sixth Framework Programme - MICRODIS. Hall, J.W., Meadowcroft, I.C., Sayers, P.B., and Bramley, M.E. (2003) Integrated flood risk management in England and Wales. Natural Hazards Review, Volume 4(3), pp Hartmann, T. (2011) Contesting land policies for space for rivers rational, viable, and clumsy floodplain management. Journal of Flood Risk Management, September 2011, Vol.4(3), pp Holt, W.G. (2012) Urban Areas and Global Climate Change. Research in Urban Sociology. Bingley, U.K. : Emerald Book Serials and Monographs. House of Commons (2015) Environmental Audit, Tenth Report. Retrieved From: Kron, W. (2005) Flood Risk = Hazard Values Vulnerability. Water International Law Society (2016) Flood Risk. Law Society. Retrieved from: Marriott, S., Alexander, J., and Hey, R. (1999) Floodplains: Interdisciplinary Approaches. Geological Society; First Edition. National Audit Office (2014) Strategic flood risk management. Retrieved from: Owen, J.H. (1981) Floodplain management handbook. Water Resources Council (U.S.) ; Flood Loss Reduction Associates. Washington, D.C. Pender, G. (2011) Flood risk science and management. Oxford : Wiley-Blackwell. POST (2001) Managing Floods. Parliamentary Office of Science and Technology. Retrieved from: Proverbs, D.G. and Mambretti, S. (2012) Flood Recovery, Innovation and Response. WIT Press. RIBA (2014) Building a Better Britain: A vision for the next Government. Retrieved from: inchapter6flooding.pdf Sayers, P. Li, Y. Galloway, G. Penning-Rowsell, E. Shen, F. Wen, K. Chen, Y. and Le Quesne, T. (2013) Flood Risk Management: A strategic approach. Paris, UNESCO, WWF, ADB, GIWP. Schanze, J. Zeman, E. and Marsalek, J. (2006) Flood Risk Management hazards, vulnerability and mitigation measure. NATO Science Series, IV Earth and Environmental Sciences Vol. 67, Springer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands. Sene, K. (2008) Flood Warning, Forecasting and Emergency Response. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. Surminski, S. and Eldridge, J. (2015) Flood insurance in England an assessment of the current and newly proposed insurance scheme in the context of rising flood risk. Journal of Flood Risk Management. ISSN X. Wisner, B., Blaikie, P. and Cannon, T. and Davis, I. (2003) At Risk: Natural Hazards, People's Vulnerability and Disasters. Routledge Ltd; 2nd Edition. 761
SME Resilience to Extreme Weather Events: Important initiatives for informing policy making in the area
 SME Resilience to Extreme Weather Events: Important initiatives for informing policy making in the area Bingunath Ingirige School of the Built Environment, the University of Salford, UK (Email: m.j.b.ingirige@salford.ac.uk)
SME Resilience to Extreme Weather Events: Important initiatives for informing policy making in the area Bingunath Ingirige School of the Built Environment, the University of Salford, UK (Email: m.j.b.ingirige@salford.ac.uk)
A GUIDE TO BEST PRACTICE IN FLOOD RISK MANAGEMENT IN AUSTRALIA
 A GUIDE TO BEST PRACTICE IN FLOOD RISK MANAGEMENT IN AUSTRALIA McLuckie D. For the National Flood Risk Advisory Group duncan.mcluckie@environment.nsw.gov.au Introduction Flooding is a natural phenomenon
A GUIDE TO BEST PRACTICE IN FLOOD RISK MANAGEMENT IN AUSTRALIA McLuckie D. For the National Flood Risk Advisory Group duncan.mcluckie@environment.nsw.gov.au Introduction Flooding is a natural phenomenon
Assessing future flood risk and opportunities for adaptation at UK scale
 Assessing future flood risk and opportunities for adaptation at UK scale Paul Sayers Sayers and Partners (SPL), Associate Advisor WWF and Research Fellow, University of Oxford. Co-authors Matt Horritt,
Assessing future flood risk and opportunities for adaptation at UK scale Paul Sayers Sayers and Partners (SPL), Associate Advisor WWF and Research Fellow, University of Oxford. Co-authors Matt Horritt,
EFRA Select Committee Enquiry on Climate Change Submission from the Association of British Insurers (ABI), October 2004
 EFRA Select Committee Enquiry on Climate Change Submission from the Association of British Insurers (ABI), October 2004 Climate change will have a direct impact on the property insurance market, because
EFRA Select Committee Enquiry on Climate Change Submission from the Association of British Insurers (ABI), October 2004 Climate change will have a direct impact on the property insurance market, because
Solway Local Plan District 1 Flood risk management in Scotland 1.1 What is a Flood Risk Management Strategy? Flood Risk Management Strategies have bee
 Flood Risk Management Strategy Solway Local Plan District Section 1: Flood Risk Management in Scotland 1.1 What is a Flood Risk Management Strategy?... 1 1.2 How to read this Strategy... 1 1.3 Managing
Flood Risk Management Strategy Solway Local Plan District Section 1: Flood Risk Management in Scotland 1.1 What is a Flood Risk Management Strategy?... 1 1.2 How to read this Strategy... 1 1.3 Managing
FLOOD HAZARD AND RISK MANAGEMENT UTILIZING HYDRAULIC MODELING AND GIS TECHNOLOGIES IN URBAN ENVIRONMENT
 Proceedings of the 14 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 3-5 September 2015 FLOOD HAZARD AND RISK MANAGEMENT UTILIZING HYDRAULIC MODELING AND GIS TECHNOLOGIES
Proceedings of the 14 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 3-5 September 2015 FLOOD HAZARD AND RISK MANAGEMENT UTILIZING HYDRAULIC MODELING AND GIS TECHNOLOGIES
Evidence for Environmental Audit Committee Enquiry on Sustainable Housing Submission by Association of British Insurers, May 2004
 Evidence for Environmental Audit Committee Enquiry on Sustainable Housing Submission by Association of British Insurers, May 2004 The Government s plans to tackle the country s profound housing shortage
Evidence for Environmental Audit Committee Enquiry on Sustainable Housing Submission by Association of British Insurers, May 2004 The Government s plans to tackle the country s profound housing shortage
Strategic flood risk management
 Report by the Comptroller and Auditor General Department for Environment, Food & Rural Affairs and Environment Agency Strategic flood risk management HC 780 SESSION 2014-15 5 NOVEMBER 2014 4 Key facts
Report by the Comptroller and Auditor General Department for Environment, Food & Rural Affairs and Environment Agency Strategic flood risk management HC 780 SESSION 2014-15 5 NOVEMBER 2014 4 Key facts
RIVER LUGG INTERNAL DRAINAGE BOARD. Statement on Water Level and Flood Risk Management
 RIVER LUGG INTERNAL DRAINAGE BOARD Statement on Water Level and Flood Risk Management 1. Introduction Purpose 1.1. This policy statement has been prepared by the River Lugg Internal Drainage Board (the
RIVER LUGG INTERNAL DRAINAGE BOARD Statement on Water Level and Flood Risk Management 1. Introduction Purpose 1.1. This policy statement has been prepared by the River Lugg Internal Drainage Board (the
Introduction. Purpose
 Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Purpose... 1 Related Projects and Programs 3 Vision... 3 Legislation and Policy Framework... 3 Target Audience... 4 Guiding Principles... 5 Governance... 6 Roles and
Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Purpose... 1 Related Projects and Programs 3 Vision... 3 Legislation and Policy Framework... 3 Target Audience... 4 Guiding Principles... 5 Governance... 6 Roles and
Climate risk management plan. Towards a resilient business
 Type your organisation name here Climate risk management plan Towards a resilient business 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 Click the numbers to select your cover images 1 2 3 4 5 Document control sheet Document
Type your organisation name here Climate risk management plan Towards a resilient business 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 Click the numbers to select your cover images 1 2 3 4 5 Document control sheet Document
Kirkwall (Potentially Vulnerable Area 03/05) Local Plan District Local authority Main catchment Orkney Orkney Islands Council Orkney coastal Backgroun
 Kirkwall (Potentially Vulnerable Area 03/05) Local Plan District Orkney Local authority Orkney Islands Council Main catchment Orkney coastal Summary of flooding impacts 490 residential properties 460 non-residential
Kirkwall (Potentially Vulnerable Area 03/05) Local Plan District Orkney Local authority Orkney Islands Council Main catchment Orkney coastal Summary of flooding impacts 490 residential properties 460 non-residential
Reservoir safety risk assessment a new guide
 Reservoir safety risk assessment a new guide Mark Morris 1,2, Mike Wallis 1, Alan Brown 3, David Bowles 4, John Gosden 3, Dr Andy Hughes 5, Alex Topple 1, Paul Sayers 6 and Keith Gardiner 7 1 HR Wallingford
Reservoir safety risk assessment a new guide Mark Morris 1,2, Mike Wallis 1, Alan Brown 3, David Bowles 4, John Gosden 3, Dr Andy Hughes 5, Alex Topple 1, Paul Sayers 6 and Keith Gardiner 7 1 HR Wallingford
Flood Risk Management Strategy. Shetland
 Flood Risk Management Strategy Shetland Publication date: 14 December 2015 Terms and conditions Ownership: All intellectual property rights for Flood Risk Management Strategies are owned by SEPA or its
Flood Risk Management Strategy Shetland Publication date: 14 December 2015 Terms and conditions Ownership: All intellectual property rights for Flood Risk Management Strategies are owned by SEPA or its
Flood Risk Management Planning in Scotland: Arrangements for February 2012
 Flood Risk Management Planning in Scotland: Arrangements for 2012 2016 February 2012 Flood Risk Management (Scotland) Act 2009 1 Contents Forewords 1. Introduction to this document... 5 2. Sustainable
Flood Risk Management Planning in Scotland: Arrangements for 2012 2016 February 2012 Flood Risk Management (Scotland) Act 2009 1 Contents Forewords 1. Introduction to this document... 5 2. Sustainable
LOCAL FLOOD RISK STRATEGY EMYR WILLIAMS PEMBROKESHIRE COUNTY COUNCIL
 LOCAL FLOOD RISK STRATEGY EMYR WILLIAMS PEMBROKESHIRE COUNTY COUNCIL Flood Risk Management We can only manage flood risk. It is not possible to prevent all flooding even if we had the money. There will
LOCAL FLOOD RISK STRATEGY EMYR WILLIAMS PEMBROKESHIRE COUNTY COUNCIL Flood Risk Management We can only manage flood risk. It is not possible to prevent all flooding even if we had the money. There will
Homecheck Flood. Click here. Overall Flood Risk. Insurability. Flood Defences. Individual Flood Risks.
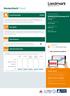 Homecheck Flood Overall Flood Risk PASSED The property is considered to be at minimal or no risk of flooding. However, you should ask the seller if the property has flooded in the past. The home buyer
Homecheck Flood Overall Flood Risk PASSED The property is considered to be at minimal or no risk of flooding. However, you should ask the seller if the property has flooded in the past. The home buyer
Assessing future flood risk across the UK
 Climate Change Risk Assessment: 2017 Assessing future flood risk across the UK (England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland) Presentation to the FoRUM Workshop Paul Sayers and Matt Horritt 17 March 2015
Climate Change Risk Assessment: 2017 Assessing future flood risk across the UK (England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland) Presentation to the FoRUM Workshop Paul Sayers and Matt Horritt 17 March 2015
Mapping flood risk its role in improving flood resilience in England
 Mapping flood risk its role in improving flood resilience in England Catherine Wright Director of Digital and Skills Flood and Coastal Risk Management Environment Agency 6 October 2017 The Environment
Mapping flood risk its role in improving flood resilience in England Catherine Wright Director of Digital and Skills Flood and Coastal Risk Management Environment Agency 6 October 2017 The Environment
Bates, P. D. (2016). Flooding: what is normal? Science in Parliament, 73(1),
 Bates, P. D. (2016). Flooding: what is normal? Science in Parliament, 73(1), 25-26. Peer reviewed version License (if available): Unspecified Link to publication record in Explore Bristol Research PDF-document
Bates, P. D. (2016). Flooding: what is normal? Science in Parliament, 73(1), 25-26. Peer reviewed version License (if available): Unspecified Link to publication record in Explore Bristol Research PDF-document
Consider the risks to your own business as well as to your operations
 Hayley Bowman Flood and Coastal Risk Management Mapping, Modelling and Data 07919 544 551 Hayley.bowman@environment-agency.gov.uk DataInfo@environment-agency.gov.uk EA covers England only. Wales covered
Hayley Bowman Flood and Coastal Risk Management Mapping, Modelling and Data 07919 544 551 Hayley.bowman@environment-agency.gov.uk DataInfo@environment-agency.gov.uk EA covers England only. Wales covered
Need for a Closer Look
 Need for a Closer Look - Natural Catastrophes in India Anup Jindal emphasizes that if a realistic assessment of the catastrophe risks is to be made, one should also take into account the future projections;
Need for a Closer Look - Natural Catastrophes in India Anup Jindal emphasizes that if a realistic assessment of the catastrophe risks is to be made, one should also take into account the future projections;
The AIR Inland Flood Model for Great Britian
 The AIR Inland Flood Model for Great Britian The year 212 was the UK s second wettest since recordkeeping began only 6.6 mm shy of the record set in 2. In 27, the UK experienced its wettest summer, which
The AIR Inland Flood Model for Great Britian The year 212 was the UK s second wettest since recordkeeping began only 6.6 mm shy of the record set in 2. In 27, the UK experienced its wettest summer, which
THE RIVER STOUR (KENT) INTERNAL DRAINAGE BOARD. Policy Statement on Water Level and Flood Risk Management
 THE RIVER STOUR (KENT) INTERNAL DRAINAGE BOARD Policy Statement on Water Level and Flood Risk Management 1. Introduction Purpose 1.1. This policy statement has been prepared by the River Stour (Kent) Internal
THE RIVER STOUR (KENT) INTERNAL DRAINAGE BOARD Policy Statement on Water Level and Flood Risk Management 1. Introduction Purpose 1.1. This policy statement has been prepared by the River Stour (Kent) Internal
River Lugg Internal Drainage Board. Policy Statement on Flood Protection and Water Level Management
 River Lugg Internal Drainage Board Policy Statement on Flood Protection and Water Level Management 1 INTRODUCTION Purpose 1.1 This policy statement has been prepared by the River Lugg Internal Drainage
River Lugg Internal Drainage Board Policy Statement on Flood Protection and Water Level Management 1 INTRODUCTION Purpose 1.1 This policy statement has been prepared by the River Lugg Internal Drainage
Volusia County Floodplain Management Plan 2012
 Volusia County Floodplain Management Plan 2012 Introduction The National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) provides federally supported flood insurance in communities that regulate development in floodplains.
Volusia County Floodplain Management Plan 2012 Introduction The National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) provides federally supported flood insurance in communities that regulate development in floodplains.
Republic of Mauritius. Official Statement for 2017 Global Platform. For Disaster Risk Reduction
 Republic of Mauritius Official Statement for 2017 Global Platform For Disaster Risk Reduction Your Excellency the Prime Minister of the United Mexican States Your Excellency the Secretary General of the
Republic of Mauritius Official Statement for 2017 Global Platform For Disaster Risk Reduction Your Excellency the Prime Minister of the United Mexican States Your Excellency the Secretary General of the
Understanding the risks, empowering communities, building resilience: the national flood and coastal erosion risk management strategy for England
 14669 NFS Cor Slip / Sig: 1 / Plate A Understanding the risks, empowering communities, building resilience: the national flood and coastal erosion risk management strategy for England Session: 2010-2012
14669 NFS Cor Slip / Sig: 1 / Plate A Understanding the risks, empowering communities, building resilience: the national flood and coastal erosion risk management strategy for England Session: 2010-2012
Indicators and trends
 Indicators and trends Monitoring climate change adaptation Indicator name Version BT8 Railway network at risk of flooding 31/03/16 Indicator type: Risk/opportunity Impact Action X SCCAP Theme SCCAP Objective
Indicators and trends Monitoring climate change adaptation Indicator name Version BT8 Railway network at risk of flooding 31/03/16 Indicator type: Risk/opportunity Impact Action X SCCAP Theme SCCAP Objective
2. Hazards and risks. 2 HAZARDS AND RISKS p1
 2. Hazards and risks Summary The National CDEM Plan 2015 identifies core functions for national management of the consequences of emergencies. It may also address the management of consequences of other
2. Hazards and risks Summary The National CDEM Plan 2015 identifies core functions for national management of the consequences of emergencies. It may also address the management of consequences of other
HRPP 358. Adapting flood risk management for an uncertain future: Flood management planning on the thames estuary. D. Ramsbottom & T.
 HRPP 358 Adapting flood risk management for an uncertain future: Flood management planning on the thames estuary D. Ramsbottom & T. Reeder Reproduced from a paper presented at: The 43rd Defra Flood and
HRPP 358 Adapting flood risk management for an uncertain future: Flood management planning on the thames estuary D. Ramsbottom & T. Reeder Reproduced from a paper presented at: The 43rd Defra Flood and
Glasgow City centre (Potentially Vulnerable Area 11/16) Local Plan District Local authority Main catchment Clyde and Loch Lomond Glasgow City Council
 Glasgow City centre (Potentially Vulnerable Area 11/16) Local Plan District Clyde and Loch Lomond Local authority Glasgow City Council Main catchment River Clyde Summary of flooding impacts At risk of
Glasgow City centre (Potentially Vulnerable Area 11/16) Local Plan District Clyde and Loch Lomond Local authority Glasgow City Council Main catchment River Clyde Summary of flooding impacts At risk of
Disaster resilient communities: Canada s insurers promote adaptation to the growing threat of high impact weather
 Disaster resilient communities: Canada s insurers promote adaptation to the growing threat of high impact weather by Paul Kovacs Executive Director, Institute for Catastrophic Loss Reduction Adjunct Research
Disaster resilient communities: Canada s insurers promote adaptation to the growing threat of high impact weather by Paul Kovacs Executive Director, Institute for Catastrophic Loss Reduction Adjunct Research
Integrated assessment of urban flood risk, coping capacity and vulnerability
 IAPS 00 Integrated assessment of urban flood risk, coping capacity and vulnerability Sebastian Scheuer Dagmar Haase Volker Meyer Humboldt Universität zu Berlin, Institute for Geography, Department of Landscape
IAPS 00 Integrated assessment of urban flood risk, coping capacity and vulnerability Sebastian Scheuer Dagmar Haase Volker Meyer Humboldt Universität zu Berlin, Institute for Geography, Department of Landscape
FLOODING INFORMATION SHEET YOUR QUESTIONS ANSWERED
 The information in this document has been written in partnership by the Association of British Insurers and the Environment Agency 1. Flood risk and insurance Q1. How can I find out the flood risk affecting
The information in this document has been written in partnership by the Association of British Insurers and the Environment Agency 1. Flood risk and insurance Q1. How can I find out the flood risk affecting
Shropshire Local Flood Risk Management Strategy. Summary for Consultation. July 2014
 Shropshire Local Flood Risk Management Strategy Summary for Consultation July 2014 SHROPSHIRE LOCAL FLOOD RISK MANAGEMENT STRATEGY 1 Introduction This Strategy is about managing flooding in Shropshire.
Shropshire Local Flood Risk Management Strategy Summary for Consultation July 2014 SHROPSHIRE LOCAL FLOOD RISK MANAGEMENT STRATEGY 1 Introduction This Strategy is about managing flooding in Shropshire.
Sendai Cooperation Initiative for Disaster Risk Reduction
 Sendai Cooperation Initiative for Disaster Risk Reduction March 14, 2015 Disasters are a threat to which human being has long been exposed. A disaster deprives people of their lives instantly and afflicts
Sendai Cooperation Initiative for Disaster Risk Reduction March 14, 2015 Disasters are a threat to which human being has long been exposed. A disaster deprives people of their lives instantly and afflicts
FLOOD SOLUTIONS Residence
 FLOOD SOLUTIONS Residence Report prepared on 22 Knighton Road, Liverpool, L4 9RD Report reference AEL028FLR022381 National grid reference 337815, 394462 Report prepared for Specimen Client Client reference
FLOOD SOLUTIONS Residence Report prepared on 22 Knighton Road, Liverpool, L4 9RD Report reference AEL028FLR022381 National grid reference 337815, 394462 Report prepared for Specimen Client Client reference
Garfield County NHMP:
 Garfield County NHMP: Introduction and Summary Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment DRAFT AUG2010 Risk assessments provide information about the geographic areas where the hazards may occur, the value
Garfield County NHMP: Introduction and Summary Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment DRAFT AUG2010 Risk assessments provide information about the geographic areas where the hazards may occur, the value
DRAFT Revised Guide to the National CDEM Plan 2015 July 2015
 2. Hazards and risks Summary The National CDEM Plan 2015 identifies core functions for national management of the consequences of emergencies. It may also address the management of consequences of other
2. Hazards and risks Summary The National CDEM Plan 2015 identifies core functions for national management of the consequences of emergencies. It may also address the management of consequences of other
The approach to managing natural hazards in this Plan is to: set out a clear regional framework for natural hazard management
 10 Natural Hazards 10.1 Scope and Background This chapter establishes an overall framework for natural hazard management under the Resource Management Act 1991 (RMA). It also sets out the division of responsibilities
10 Natural Hazards 10.1 Scope and Background This chapter establishes an overall framework for natural hazard management under the Resource Management Act 1991 (RMA). It also sets out the division of responsibilities
Flood Risk Management in England
 REPORT BY THE COMPTROLLER AND AUDITOR GENERAL HC 1521 SESSION 2010 2012 28 OCTOBER 2011 Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs and Environment Agency Flood Risk Management in England Flood
REPORT BY THE COMPTROLLER AND AUDITOR GENERAL HC 1521 SESSION 2010 2012 28 OCTOBER 2011 Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs and Environment Agency Flood Risk Management in England Flood
How insurance can support climate resilience
 Accepted manuscript - 1 Embargoed till 24 March at 9am GMT (10:00 CET) How insurance can support climate resilience Swenja Surminski (Grantham Research Institute on Climate Change and the Environment at
Accepted manuscript - 1 Embargoed till 24 March at 9am GMT (10:00 CET) How insurance can support climate resilience Swenja Surminski (Grantham Research Institute on Climate Change and the Environment at
Review of preliminary flood risk assessments (Flood Risk Regulations 2009): guidance for lead local flood authorities in England
 Review of preliminary flood risk assessments (Flood Risk Regulations 2009): guidance for lead local flood authorities in England 25 January 2017 We are the Environment Agency. We protect and improve the
Review of preliminary flood risk assessments (Flood Risk Regulations 2009): guidance for lead local flood authorities in England 25 January 2017 We are the Environment Agency. We protect and improve the
17. Reduction. 17 REDUCTION p1
 17. Reduction Summary Reduction involves identifying and analysing risks to life and property from hazards, taking steps to eliminate those risks if practicable, and, if not, reducing the magnitude of
17. Reduction Summary Reduction involves identifying and analysing risks to life and property from hazards, taking steps to eliminate those risks if practicable, and, if not, reducing the magnitude of
Aquidneck Island Resilience Strategy Issue Paper 4. Issue: RESIDENTIAL FLOODING
 Aquidneck Island Resilience Strategy Issue Paper 4 Issue: RESIDENTIAL FLOODING Description of Concern: While much of Aquidneck Island s geography lies outside the reach of coastal flooding, some of the
Aquidneck Island Resilience Strategy Issue Paper 4 Issue: RESIDENTIAL FLOODING Description of Concern: While much of Aquidneck Island s geography lies outside the reach of coastal flooding, some of the
Alyth (Potentially Vulnerable Area 08/04) Local Plan District Local authority Main catchment Tay Perth and Kinross Council Alyth Burn (River Tay) Back
 Alyth (Potentially Vulnerable Area 08/04) Local Plan District Tay Local authority Perth and Kinross Council Main catchment Alyth Burn (River Tay) Summary of flooding impacts 50 residential properties 20
Alyth (Potentially Vulnerable Area 08/04) Local Plan District Tay Local authority Perth and Kinross Council Main catchment Alyth Burn (River Tay) Summary of flooding impacts 50 residential properties 20
Nairn Central (Potentially Vulnerable Area 01/18) Local authority Main catchment The Highland Council Moray coastal Background This Potentially Vulner
 Nairn Central (Potentially Vulnerable Area 01/18) Local authority The Highland Council Main catchment Moray coastal Summary of flooding impacts At risk of flooding 350 residential 30 non-residential 340,000
Nairn Central (Potentially Vulnerable Area 01/18) Local authority The Highland Council Main catchment Moray coastal Summary of flooding impacts At risk of flooding 350 residential 30 non-residential 340,000
Towards a Post-2015 Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction
 Towards a Post-2015 Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction Introduction 1. The Hyogo Framework for Action 2005-2015 (HFA) Building the Resilience of Nations and Communities to Disasters, is the inspiration
Towards a Post-2015 Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction Introduction 1. The Hyogo Framework for Action 2005-2015 (HFA) Building the Resilience of Nations and Communities to Disasters, is the inspiration
Development and Flood Risk - the Environment Agency s approach to PPS25. scrutinised before planning decisions are made
 Development and Flood Risk - the Environment Agency s approach to PPS25 Steve Cook Flood Risk Policy Advisor Stephen.cook@environment-agency.gov.uk Our role in PPS25 h Providing advice and information
Development and Flood Risk - the Environment Agency s approach to PPS25 Steve Cook Flood Risk Policy Advisor Stephen.cook@environment-agency.gov.uk Our role in PPS25 h Providing advice and information
DRAFT STRATEGIC ENVIRONMENTAL ASSESSMENT SCREENING REPORT. Climate Change Sectoral Adaptation Plan for Flood Risk Management ( )
 Office of Public Works DRAFT STRATEGIC ENVIRONMENTAL ASSESSMENT SCREENING REPORT Climate Change Sectoral Adaptation Plan for Flood Risk Management (2014-2019) Determination of the need for strategic environmental
Office of Public Works DRAFT STRATEGIC ENVIRONMENTAL ASSESSMENT SCREENING REPORT Climate Change Sectoral Adaptation Plan for Flood Risk Management (2014-2019) Determination of the need for strategic environmental
COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES
 EN EN EN COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, 23.2.2009 COM(2009) 82 final COMMUNICATION FROM THE COMMISSION TO THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT, THE COUNCIL, THE EUROPEAN ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COMMITTEE
EN EN EN COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, 23.2.2009 COM(2009) 82 final COMMUNICATION FROM THE COMMISSION TO THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT, THE COUNCIL, THE EUROPEAN ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COMMITTEE
P art B 4 NATURAL HAZARDS. Natural Hazards ISSUE 1. River Flooding
 4 NATURAL HAZARDS ISSUE 1 River Flooding A large part of the plains within the Timaru District is subject to some degree of flooding risk. At least part of all of the main settlements in the District and
4 NATURAL HAZARDS ISSUE 1 River Flooding A large part of the plains within the Timaru District is subject to some degree of flooding risk. At least part of all of the main settlements in the District and
Response to EIOPA call for evidence for an opinion on sustainability within Solvency II. Ecofin department
 Position Paper Response to EIOPA call for evidence for an opinion on sustainability within Solvency II Our reference: Referring to: ECO-LTI-19-050 Call for evidence for an opinion on sustainability within
Position Paper Response to EIOPA call for evidence for an opinion on sustainability within Solvency II Our reference: Referring to: ECO-LTI-19-050 Call for evidence for an opinion on sustainability within
Government Decree on Flood Risk Management 659/2010
 Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry, Finland NB: Unofficial translation; legally binding texts are those in Finnish and Swedish. Government Decree on Flood Risk Management 659/2010 Section 1 Preliminary
Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry, Finland NB: Unofficial translation; legally binding texts are those in Finnish and Swedish. Government Decree on Flood Risk Management 659/2010 Section 1 Preliminary
Protocol for the maintenance of flood and coastal risk management assets (England only) Version 4, 27/01/2014 UNCLASSIFIED
 Protocol for the maintenance of flood and coastal risk management assets (England only) Version 4, 27/01/2014 UNCLASSIFIED We are the Environment Agency. We protect and improve the environment and make
Protocol for the maintenance of flood and coastal risk management assets (England only) Version 4, 27/01/2014 UNCLASSIFIED We are the Environment Agency. We protect and improve the environment and make
ADB s Experiences in Disaster Management. Neil Britton Senior Disaster Risk Management Specialist Asian Development Bank 25 November 2007
 ADB s Experiences in Disaster Management Neil Britton Senior Disaster Risk Management Specialist Asian Development Bank 25 November 2007 Presentation Format Asia s changing hazardscape and vulnerability
ADB s Experiences in Disaster Management Neil Britton Senior Disaster Risk Management Specialist Asian Development Bank 25 November 2007 Presentation Format Asia s changing hazardscape and vulnerability
Clyde south - Port Glasgow to Inchinnan (Potentially Vulnerable Area 11/09) Local Plan District Clyde and Loch Lomond Local authority Inverclyde Counc
 Clyde south - Port Glasgow to Inchinnan (Potentially Vulnerable Area 11/09) Local Plan District Clyde and Loch Lomond Local authority Inverclyde Council, Renfrewshire Council Main catchment Firth of Clyde
Clyde south - Port Glasgow to Inchinnan (Potentially Vulnerable Area 11/09) Local Plan District Clyde and Loch Lomond Local authority Inverclyde Council, Renfrewshire Council Main catchment Firth of Clyde
Strategic Flood Risk Assessment
 Strategic Flood Risk Assessment Ireland West Airport Knock Local Area Plan 2012 2018 Prepared by Forward Planning Section Mayo County Council 0 1 Table of Contents Section 1: Overview of the Guidelines...
Strategic Flood Risk Assessment Ireland West Airport Knock Local Area Plan 2012 2018 Prepared by Forward Planning Section Mayo County Council 0 1 Table of Contents Section 1: Overview of the Guidelines...
Strategic Flood Risk Assessment
 Strategic Flood Risk Assessment Draft Claremorris Local Area Plan 2012 2018 Prepared by Forward Planning Section Mayo County Council 1 Table of Contents Section 1: Overview of the Guidelines... 4 1.1 Introduction...
Strategic Flood Risk Assessment Draft Claremorris Local Area Plan 2012 2018 Prepared by Forward Planning Section Mayo County Council 1 Table of Contents Section 1: Overview of the Guidelines... 4 1.1 Introduction...
What can be done to minimise future economic and social harm caused by flooding and improve resilience. Flood Warning and Informing
 What can be done to minimise future economic and social harm caused by flooding and improve resilience Flood Warning and Informing Marc Becker SEPA Flood Risk Manager (Hydrology) 16 th September 2016 The
What can be done to minimise future economic and social harm caused by flooding and improve resilience Flood Warning and Informing Marc Becker SEPA Flood Risk Manager (Hydrology) 16 th September 2016 The
2018 Long Term Plan Financial forecasting assumptions
 2018 Long Term Plan Financial forecasting assumptions Forecasting assumption Risk Likelihood of occurrence Projected price change factors Forecast financial information That actual price changes vary Medium
2018 Long Term Plan Financial forecasting assumptions Forecasting assumption Risk Likelihood of occurrence Projected price change factors Forecast financial information That actual price changes vary Medium
Mitigation Works. 0 With its devastating combination of water, mud, and sewage, the damages caused by flooding are particularly wrenching.
 0 Nationwide, structures built to NFIP standards are estimated to suffer 80% less damage than other structures, and save more than $ 1 Billion in flood damages annually. 0 With its devastating combination
0 Nationwide, structures built to NFIP standards are estimated to suffer 80% less damage than other structures, and save more than $ 1 Billion in flood damages annually. 0 With its devastating combination
Resilience to Flooding of Grid and Primary Substations
 PRODUCED BY THE OPERATIONS DIRECTORATE OF ENERGY NETWORKS ASSOCIATION Engineering Technical Report 138 Resilience to Flooding of Grid and Primary Substations www.energynetworks.org PUBLISHING AND COPYRIGHT
PRODUCED BY THE OPERATIONS DIRECTORATE OF ENERGY NETWORKS ASSOCIATION Engineering Technical Report 138 Resilience to Flooding of Grid and Primary Substations www.energynetworks.org PUBLISHING AND COPYRIGHT
IRISH FLOOD PREVENTION PROGRAMME Example of integrating climate change adaptation into projects
 IRISH FLOOD PREVENTION PROGRAMME Example of integrating climate change adaptation into projects JASPERS Networking Platform Event Climate Change Adaptation: Vulnerability and Risk Assessment and the Resilience
IRISH FLOOD PREVENTION PROGRAMME Example of integrating climate change adaptation into projects JASPERS Networking Platform Event Climate Change Adaptation: Vulnerability and Risk Assessment and the Resilience
Suggested elements for the post-2015 framework for disaster risk reduction
 United Nations General Assembly Distr.: General 16 June 2014 A/CONF.224/PC(I)/6 Original: English Third United Nations World Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction Preparatory Committee First session Geneva,
United Nations General Assembly Distr.: General 16 June 2014 A/CONF.224/PC(I)/6 Original: English Third United Nations World Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction Preparatory Committee First session Geneva,
Local Government Group. Preliminary Framework to assist the development of the Local Strategy for Flood Risk Management.
 Preliminary Framework to assist the development of the Local Strategy for Flood Risk Management A Living Document February 2011 Preliminary Framework for Local Flood Risk Management Strategy Page 1 Table
Preliminary Framework to assist the development of the Local Strategy for Flood Risk Management A Living Document February 2011 Preliminary Framework for Local Flood Risk Management Strategy Page 1 Table
WHAT DOES CLIMATE CHANGE MEAN FOR YOUR LOCAL AREA?
 WHAT DOES CLIMATE CHANGE MEAN FOR YOUR LOCAL AREA? THE FEDERAL ELECTORATE OF FLINDERS The Climate Council is an independent, crowd-funded organisation providing quality information on climate change to
WHAT DOES CLIMATE CHANGE MEAN FOR YOUR LOCAL AREA? THE FEDERAL ELECTORATE OF FLINDERS The Climate Council is an independent, crowd-funded organisation providing quality information on climate change to
WEATHER EXTREMES, CLIMATE CHANGE,
 WEATHER EXTREMES, CLIMATE CHANGE, DURBAN 2011 ELECTRONIC PRESS FOLDER Status: 25.11.2011 Contents 1. Current meteorological knowledge 2. Extreme weather events 3. Political action required 4. Insurance
WEATHER EXTREMES, CLIMATE CHANGE, DURBAN 2011 ELECTRONIC PRESS FOLDER Status: 25.11.2011 Contents 1. Current meteorological knowledge 2. Extreme weather events 3. Political action required 4. Insurance
FROM FLOOD RISK MANAGEMENT TO QUANTITATIVE FLOOD DISASTER RESILIENCE: A PARADIGM SHIFT
 FROM FLOOD RISK MANAGEMENT TO QUANTITATIVE FLOOD DISASTER RESILIENCE: A PARADIGM SHIFT S. P. Simonovic 1 1. Professor, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Director of Engineering Works:
FROM FLOOD RISK MANAGEMENT TO QUANTITATIVE FLOOD DISASTER RESILIENCE: A PARADIGM SHIFT S. P. Simonovic 1 1. Professor, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Director of Engineering Works:
EDO Qld s submission on proposed changes to Coastal Management Districts
 30 Hardgrave Rd WEST END, QLD 4101 tel +61 7 3211 4466 fax +61 7 3211 4655 edoqld@edo.org.au www.edoqld.org.au 27 October 2014 Director, Environment Planning Department of Environment and Heritage Protection
30 Hardgrave Rd WEST END, QLD 4101 tel +61 7 3211 4466 fax +61 7 3211 4655 edoqld@edo.org.au www.edoqld.org.au 27 October 2014 Director, Environment Planning Department of Environment and Heritage Protection
Implementation processes for the Flood Risk Management (Scotland) Act 2009
 Implementation processes for the Flood Risk Management (Scotland) Act 2009 Final Report 30/05/2012 Page 0 Published by The James Hutton Institute on behalf of CREW Scotland s Centre of Expertise for Waters
Implementation processes for the Flood Risk Management (Scotland) Act 2009 Final Report 30/05/2012 Page 0 Published by The James Hutton Institute on behalf of CREW Scotland s Centre of Expertise for Waters
Planning and Flood Risk
 Planning and Flood Risk Patricia Calleary BE MEngSc MSc CEng MIEI After the Beast from the East Patricia Calleary Flood Risk and Planning Flooding in Ireland» Floods are a natural and inevitable part of
Planning and Flood Risk Patricia Calleary BE MEngSc MSc CEng MIEI After the Beast from the East Patricia Calleary Flood Risk and Planning Flooding in Ireland» Floods are a natural and inevitable part of
Kyrgyz Republic. Measuring Seismic Risk {P149630} Public Disclosure Authorized. Report No: AUS Public Disclosure Authorized.
 Public Disclosure Authorized Report No: AUS0000061 Kyrgyz Republic Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Measuring Seismic Risk {P149630} {December, 2017} URS Public Disclosure Authorized
Public Disclosure Authorized Report No: AUS0000061 Kyrgyz Republic Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Measuring Seismic Risk {P149630} {December, 2017} URS Public Disclosure Authorized
Natural Hazards Risks in Kentucky. KAMM Regional Training
 Natural Hazards Risks in Kentucky KAMM Regional Training Floodplain 101 Kentucky has approximately 92,000 linear miles of streams and rivers Approximately 31,000 linear miles have mapped flood hazards
Natural Hazards Risks in Kentucky KAMM Regional Training Floodplain 101 Kentucky has approximately 92,000 linear miles of streams and rivers Approximately 31,000 linear miles have mapped flood hazards
Lowestoft Flood Risk Management Project
 Volume 1, Issue 1 Winter 2017 Lowestoft Flood Risk Management Project I N S I D E T H I S I S S U E : Welcome 1 Background to the project 2 What are we considering 2 and how has the project progressed?
Volume 1, Issue 1 Winter 2017 Lowestoft Flood Risk Management Project I N S I D E T H I S I S S U E : Welcome 1 Background to the project 2 What are we considering 2 and how has the project progressed?
Heavy Weather. Tracking the fingerprints of climate change, two years after the Paris summit
 Heavy Weather Tracking the fingerprints of climate change, two years after the Paris summit December 2017 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Since the United Nations climate summit in Paris two years ago, scientists have
Heavy Weather Tracking the fingerprints of climate change, two years after the Paris summit December 2017 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Since the United Nations climate summit in Paris two years ago, scientists have
Canada s exposure to flood risk. Who is affected, where are they located, and what is at stake
 Canada s exposure to flood risk Who is affected, where are they located, and what is at stake Why a flood model for Canada? Catastrophic losses Insurance industry Federal government Average industry CAT
Canada s exposure to flood risk Who is affected, where are they located, and what is at stake Why a flood model for Canada? Catastrophic losses Insurance industry Federal government Average industry CAT
The 2004 Gilbert F. White National Flood Policy Forum September 21-22, 2004 FLOOD STANDARDS IN FOREIGN COUNTRIES
 The 2004 Gilbert F. White National Flood Policy Forum September 21-22, 2004 FLOOD STANDARDS IN FOREIGN COUNTRIES Firas Makarem, Dewberry, International Committee Chair, Association of State Floodplain
The 2004 Gilbert F. White National Flood Policy Forum September 21-22, 2004 FLOOD STANDARDS IN FOREIGN COUNTRIES Firas Makarem, Dewberry, International Committee Chair, Association of State Floodplain
Integrating intangible values in economic analyses of flood mitigation: a case study of the Brown Hill and Keswick creeks catchment in Adelaide
 ABSTRACT This study undertakes an economic analysis of flood mitigation options for a high flood-risk catchment in Adelaide. To date, economic analyses have focused primarily on estimating the tangible
ABSTRACT This study undertakes an economic analysis of flood mitigation options for a high flood-risk catchment in Adelaide. To date, economic analyses have focused primarily on estimating the tangible
Fort William (Potentially Vulnerable Area 01/25) Local authority Main catchment The Highland Council Appin coastal Background This Potentially Vulnera
 Fort William (Potentially Vulnerable Area 01/25) Local authority The Highland Council Main catchment Appin coastal Summary of flooding impacts 100 residential properties 80 non-residential properties 520,000
Fort William (Potentially Vulnerable Area 01/25) Local authority The Highland Council Main catchment Appin coastal Summary of flooding impacts 100 residential properties 80 non-residential properties 520,000
Turriff (Potentially Vulnerable Area 06/07) Local Plan District Local authority Main catchment North East Aberdeenshire Council River Deveron Backgrou
 Turriff (Potentially Vulnerable Area 06/07) Local Plan District North East Local authority Aberdeenshire Council Main catchment River Deveron Summary of flooding impacts At risk of flooding
Turriff (Potentially Vulnerable Area 06/07) Local Plan District North East Local authority Aberdeenshire Council Main catchment River Deveron Summary of flooding impacts At risk of flooding
Impacts of severe flood events in Central Viet Nam: Toward integrated flood risk management
 Impacts of severe flood events in Central Viet Nam: Toward integrated flood risk management Bui Duc Tinh, Tran Huu Tuan, Phong Tran College of Economics, Hue University Viet Nam 1. Research problem 2.
Impacts of severe flood events in Central Viet Nam: Toward integrated flood risk management Bui Duc Tinh, Tran Huu Tuan, Phong Tran College of Economics, Hue University Viet Nam 1. Research problem 2.
Frequently Asked Questions
 Frequently Asked Questions The West of Wales Shoreline Management Plan (SMP) provides a high level strategy for managing flood and erosion risk for the coastline and is a non statutory policy document
Frequently Asked Questions The West of Wales Shoreline Management Plan (SMP) provides a high level strategy for managing flood and erosion risk for the coastline and is a non statutory policy document
Strategic Flood Risk Management
 Strategic Management Duncan McLuckie (NSW Department of Infrastructure and Natural Resources) Introduction This paper discusses what is meant by strategic flood risk management, who is responsible in New
Strategic Management Duncan McLuckie (NSW Department of Infrastructure and Natural Resources) Introduction This paper discusses what is meant by strategic flood risk management, who is responsible in New
Climate Change Adaptation A Study in Risk Management. T.D. Hall AAC Conference, Halifax Session 8 September 2015
 Climate Change Adaptation A Study in Risk Management T.D. Hall AAC Conference, Halifax Session 8 September 2015 Themes Climate change as a risk Potential impacts and implications Risk Management considerations
Climate Change Adaptation A Study in Risk Management T.D. Hall AAC Conference, Halifax Session 8 September 2015 Themes Climate change as a risk Potential impacts and implications Risk Management considerations
Environment Agency pre-application advice incorporating Local Flood Risk Standing Advice from East Lindsey District Council
 Environment Agency pre-application advice incorporating Local Flood Risk Standing Advice from East Lindsey District Council Version 1 UNCLASSIFIED We are the Environment Agency. We protect and improve
Environment Agency pre-application advice incorporating Local Flood Risk Standing Advice from East Lindsey District Council Version 1 UNCLASSIFIED We are the Environment Agency. We protect and improve
Delineating hazardous flood conditions to people and property
 Delineating hazardous flood conditions to people and property G Smith 1, D McLuckie 2 1 UNSW Water Research Laboratory 2 NSW Office of Environment and Heritage, NSW Abstract Floods create hazardous conditions
Delineating hazardous flood conditions to people and property G Smith 1, D McLuckie 2 1 UNSW Water Research Laboratory 2 NSW Office of Environment and Heritage, NSW Abstract Floods create hazardous conditions
Flood Management Strategy Port Phillip and Westernport
 Flood Management Strategy Port Phillip and Westernport This strategy reflects the work and expertise of floodplain managers across the region. Melbourne Water prepared this strategy with governance and
Flood Management Strategy Port Phillip and Westernport This strategy reflects the work and expertise of floodplain managers across the region. Melbourne Water prepared this strategy with governance and
Flood Risk Assessment Insuring An Emerging CAT
 Flood Risk Assessment Insuring An Emerging CAT Vijay Manghnani Analytics and Exposure Officer Chartis Insurance Antitrust Notice The Casualty Actuarial Society is committed to adhering strictly to the
Flood Risk Assessment Insuring An Emerging CAT Vijay Manghnani Analytics and Exposure Officer Chartis Insurance Antitrust Notice The Casualty Actuarial Society is committed to adhering strictly to the
The AIR Coastal Flood Model for Great Britain
 The AIR Coastal Flood Model for Great Britain The North Sea Flood of 1953 inundated more than 100,000 hectares in eastern England. More than 24,000 properties were damaged, and 307 people lost their lives.
The AIR Coastal Flood Model for Great Britain The North Sea Flood of 1953 inundated more than 100,000 hectares in eastern England. More than 24,000 properties were damaged, and 307 people lost their lives.
COASTAL HAZARD MITIGATION TOOLS AND TECHNIQUES
 COASTAL HAZARD MITIGATION TOOLS AND TECHNIQUES Beach Nourishment Responsible Agency/Party: Mitigation for: Management Effort: Federal and/or State sponsored projects Long- and short-term erosion Flood
COASTAL HAZARD MITIGATION TOOLS AND TECHNIQUES Beach Nourishment Responsible Agency/Party: Mitigation for: Management Effort: Federal and/or State sponsored projects Long- and short-term erosion Flood
WHAT DOES CLIMATE CHANGE MEAN FOR YOUR LOCAL AREA?
 WHAT DOES CLIMATE CHANGE MEAN FOR YOUR LOCAL AREA? THE FEDERAL ELECTORATE OF GRAYNDLER The Climate Council is an independent, crowd-funded organisation providing quality information on climate change to
WHAT DOES CLIMATE CHANGE MEAN FOR YOUR LOCAL AREA? THE FEDERAL ELECTORATE OF GRAYNDLER The Climate Council is an independent, crowd-funded organisation providing quality information on climate change to
Justification for Floodplain Regulatory Standards in Illinois
 Justification for Floodplain Regulatory Standards in Illinois Office of Water Resources Issue Paper April, 2015 Proactive Illinois floodplain and floodway regulatory standards have prevented billions of
Justification for Floodplain Regulatory Standards in Illinois Office of Water Resources Issue Paper April, 2015 Proactive Illinois floodplain and floodway regulatory standards have prevented billions of
Decision-makers Barriers to Climate and Extreme Weather Adaptation for Seaports
 Decision-makers Barriers to Climate and Extreme Weather Adaptation for Seaports ELIZABETH L MCLEAN, PHD AUSTIN BECKER, PHD DUNCAN MCINTOSH, PHD DEPARTMENT OF MARINE AFFAIRS UNIVERSITY OF RHODE ISLAND Chris
Decision-makers Barriers to Climate and Extreme Weather Adaptation for Seaports ELIZABETH L MCLEAN, PHD AUSTIN BECKER, PHD DUNCAN MCINTOSH, PHD DEPARTMENT OF MARINE AFFAIRS UNIVERSITY OF RHODE ISLAND Chris
Derry City & Strabane District Council 17th July 2015, 3pm.
 Derry City & Strabane District Council 17th July 2015, 3pm Malcolm Calvert, (Principal Engineer, Mapping & Modelling Unit) Sean O Neill, (Regional Engineer - Western) Flood Hazard & Risk Mapping www.riversagencyni.gov.uk
Derry City & Strabane District Council 17th July 2015, 3pm Malcolm Calvert, (Principal Engineer, Mapping & Modelling Unit) Sean O Neill, (Regional Engineer - Western) Flood Hazard & Risk Mapping www.riversagencyni.gov.uk
Strategic Flood Risk Assessment for SDCC Development Plan
 Strategic Flood Risk Assessment for SDCC Development Plan Detailed Report on Flood Risk in the Baldonnell Area 8 th May 2015 rpsgroup.com/ireland Strategic Flood Risk Assessment for SDCC Development Plan
Strategic Flood Risk Assessment for SDCC Development Plan Detailed Report on Flood Risk in the Baldonnell Area 8 th May 2015 rpsgroup.com/ireland Strategic Flood Risk Assessment for SDCC Development Plan
Delaware River Basin Commission s Role in Flood Loss Reduction Efforts
 Delaware River Basin Commission s Role in Flood Loss Reduction Efforts There is a strong need to reduce flood vulnerability and damages in the Delaware River Basin. This paper presents the ongoing role
Delaware River Basin Commission s Role in Flood Loss Reduction Efforts There is a strong need to reduce flood vulnerability and damages in the Delaware River Basin. This paper presents the ongoing role
Riverine Flooding - Cedar Rapids, Iowa 2008
 Katrina 2005 Riverine Flooding - Cedar Rapids, Iowa 2008 Riverine and Pluvial Flooding Nashville 2010 Mississippi and Missouri Rivers 2011 INFRASTRUCTURE ECONOMY 21 st Century 20 th Century "Toto, I've
Katrina 2005 Riverine Flooding - Cedar Rapids, Iowa 2008 Riverine and Pluvial Flooding Nashville 2010 Mississippi and Missouri Rivers 2011 INFRASTRUCTURE ECONOMY 21 st Century 20 th Century "Toto, I've
THE CLIMATE RISK INSURANCE INITIATIVE
 THE CLIMATE RISK INSURANCE INITIATIVE InsuResilience at a glance The InsuResilience Climate Risk Insurance Initiative was adopted by the G7 partner countries Germany, France, Italy, Japan, Canada, the
THE CLIMATE RISK INSURANCE INITIATIVE InsuResilience at a glance The InsuResilience Climate Risk Insurance Initiative was adopted by the G7 partner countries Germany, France, Italy, Japan, Canada, the
