PROFIT MAXIMIZATION AND STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT FOR CONSTRUCTION PROJECTS
|
|
|
- Loraine McCoy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Slide 1 PROFIT MAXIMIZATION AND STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT FOR CONSTRUCTION PROJECTS Hakob Avetisyan Ph.D. Miroslaw Skibniewski Ph.D Project Management Symposium
2 Slide 2 Overview Resource Allocation Business as Usual Strategic and Business Attitude Modelling for Success Mathematical Formulation of the Tool Case Study and Results Questions?
3 Slide 3 Resource Allocation Business as Usual WHAT IS IT AND WHY IS IT NO LONGER ACCEPTABLE?
4 Slide 4 Resource Allocation Business as Usual Traditionally projects are scheduled with an assumption that resources are limitless and available The main reason was the complexity of analysis and the trouble associated with losing the critical path
5 Slide 5 Strategic and Business Attitude HOW TO MAKE IT BETTER?
6 Slide 6 Competition Competition acts as a driving force in the industry and companies try to become more cost effective and profitable Competition also makes the margin of potential profit smaller and smaller.
7 Slide 7 Managing and Competing for Projects When companies have more than one project resource allocation may become more challenging. When combined with the requirements from stakeholders and financial limitations the decisionmaking becomes more challenging.
8 Slide 8 Schematic Representation CPM and Resource Allocation for Site 1 Strategic and Business Management CPM and Resource Allocation for Site 2 Exchange of information among construction sites CPM and Resource Allocation for Site k
9 Slide 9 Modelling for Success WHAT IS IMPORTANT AND HOW TO DO IT?
10 Slide 10 Mathematical Formulation of the Tool With Management Science applications along with carefully designed constraints informed decision-making becomes easier The key of success is to identify the limitations that actually make a difference in decision-making and formulate those as constraints
11 Slide 11 Mathematical Model First lets discuss unlimited resource availability case Next the limited availability will be discussed
12 Slide 12 Notation I = set of origin where activity starts J = set of destination where activity finishes, J* is the last element in the set TD = total duration right hand sight value where necessary RR kk = construction resource types right hand sight value where necessary (e.g. material, labor, budget, time, stakeholder needs, sustainability, etc.) k K RR iiiiii = usage of resource type k for activity ij i I, j J, k K CCCC iiii = cost of crashing activity ij i I, j J LL iiii = right hand side value as limitation on crashing activity ij i I, j J LLLL iiii = estimate of the activity s crashing duration under the most favorable conditions LLbb iiii = estimate of the activity s crashing duration under the least favorable conditions LLmm iiii = most likely value for the activity s crashing duration tttt iiii = estimate of the activity s duration under the most favorable conditions ttbb iiii = estimate of the activity s duration under the least favorable conditions ttmm iiii = most likely value for the activity s duration
13 Slide 13 Notation Decision variables xx ii aaaaaa xx jj = start and finish times of activity ij, i I, j J CCCC iiii = crashing duration of activity ij, i I, j J where applied Z = objective function value
14 Slide 14 Mathematical Model Objective function: min ZZ = xx JJ xx 1 (1) Subject to: xx jj xx ii + tt iiii i I, j J (2) xx ii aaaaaa xx jj UUUUUU i I, j J (3)
15 Slide 15 Mathematical Model - limits Objective function: min ZZ = 0 JJ CCCC iiii CCCC iiii (4) Subject to: CCCC iiii LL iiii i I, j J (5) xx jj xx ii + tt iiii CCCC iiii i I, j J (6) xx JJ xx 1 TTTT i I, j J (7) CCCC iiii 0 i I, j J (8) xx ii aaaaaa xx jj UUUUUU i I, j J (9)
16 Slide 16 Mathematical Model - combined Objective function: min ZZ = xx JJ + 0 JJ CCCC iiii CCCC iiii xx 1 (10) Subject to: CCCC iiii (LLLL iiii+4llll iiii +LLLL iiii ) 6 xx jj xx ii + (tttt iiii+4tttt iiii +tttt iiii ) 6 i I, j J (11) CCCC iiii i I, j J (12) xx JJ xx 1 TTTT i I, j J (13) CCCC iiii 0 i I, j J (14) xx ii aaaaaa xx jj UUUUUU i I, j J (15)
17 Slide 17 Mathematical Model - SMCP Objective function of SMCP: min ZZ = xx JJ + JJ 0 CCCC iiii CCCC iiii + JJ 0 xx 1 (16) Subject to: CCCC iiii (LLLL iiii+4llll iiii +LLLL iiii ) 6 i I, j J (17) xx jj xx ii + (tttt iiii+4tttt iiii +tttt iiii ) CCCC iiii i I, j J (18) 6 xx JJ xx 1 TTTT i I, j J (19) RR iiiiii RR kk i I, j J (20 ) CCCC iiii 0 i I, j J (21) TPD = xx JJ xx 1 (22) TTTTTTTT = JJ 0 CCCC iiii CCCC iiii xx ii aaaaaa xx jj UUUUUU i I, j J (24) (23)
18 Slide 18 Case Study and Results Activity Predecessors Duration in Days A None 6 B None 9 C A and B 8 D A and B 7 E D 10 F C and E 12 Activity Crashing Cost Per Day ($) A 10 5 B 20 5 C 3 5 D 30 5 E 40 5 F 50 5 Limit on Crashing Duration (Days)
19 Slide 19 Case Study and Results Activity Predec Duration in Days essors ta tb tm A None B None C A and B D A and B E D F C and E LP OPTIMUM FOUND AT STEP 11 OBJECTIVE FUNCTION VALUE IS 415 VARIABLE VALUE REDUCED COST VARIABLE VALUE REDUCED COST X F 0 10 X1 0 0 X3 4 0 A 2 0 X2 4 0 B 5 0 X C 0 3 X4 6 0 D 5 0 TPD 25 0 E 3 0 TPCC 390 0
20 Slide 20 Case Study and Results Objective function value of SMCP as discussed above is not intuitive Values for Total Project Duration (TPD) and Total Project Crashing Cost (TPCC) (shaded cells) are reported as 25 days consistent with the constraint for duration limitation $390 as crashing cost
21 Slide 21 Case Study and Results SLACK OR DUAL SLACK OR DUAL ROW SURPLUS PRICES ROW SURPLUS PRICES 2) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) )
22 Slide 22 Contact: QUESTIONS?
Profit Maximization and Strategic Management for Construction Projects
 Profit Maximization and Strategic Management for Construction Projects Hakob Avetisyan, Ph.D. 1 and Miroslaw Skibniewski, Ph.D. 2 1 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, E-209, 800 N. State
Profit Maximization and Strategic Management for Construction Projects Hakob Avetisyan, Ph.D. 1 and Miroslaw Skibniewski, Ph.D. 2 1 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, E-209, 800 N. State
Homework solutions, Chapter 8
 Homework solutions, Chapter 8 NOTE: We might think of 8.1 as being a section devoted to setting up the networks and 8.2 as solving them, but only 8.2 has a homework section. Section 8.2 2. Use Dijkstra
Homework solutions, Chapter 8 NOTE: We might think of 8.1 as being a section devoted to setting up the networks and 8.2 as solving them, but only 8.2 has a homework section. Section 8.2 2. Use Dijkstra
Project Planning. Jesper Larsen. Department of Management Engineering Technical University of Denmark
 Project Planning jesla@man.dtu.dk Department of Management Engineering Technical University of Denmark 1 Project Management Project Management is a set of techniques that helps management manage large-scale
Project Planning jesla@man.dtu.dk Department of Management Engineering Technical University of Denmark 1 Project Management Project Management is a set of techniques that helps management manage large-scale
56:171 Operations Research Midterm Exam Solutions October 22, 1993
 56:171 O.R. Midterm Exam Solutions page 1 56:171 Operations Research Midterm Exam Solutions October 22, 1993 (A.) /: Indicate by "+" ="true" or "o" ="false" : 1. A "dummy" activity in CPM has duration
56:171 O.R. Midterm Exam Solutions page 1 56:171 Operations Research Midterm Exam Solutions October 22, 1993 (A.) /: Indicate by "+" ="true" or "o" ="false" : 1. A "dummy" activity in CPM has duration
A Linear Programming Approach for Optimum Project Scheduling Taking Into Account Overhead Expenses and Tardiness Penalty Function
 A Linear Programming Approach for Optimum Project Scheduling Taking Into Account Overhead Expenses and Tardiness Penalty Function Mohammed Woyeso Geda, Industrial Engineering Department Ethiopian Institute
A Linear Programming Approach for Optimum Project Scheduling Taking Into Account Overhead Expenses and Tardiness Penalty Function Mohammed Woyeso Geda, Industrial Engineering Department Ethiopian Institute
 Subject O Basic of Operation Research (D-01) Date O 20/04/2011 Time O 11.00 to 02.00 Q.1 Define Operation Research and state its relation with decision making. (14) What are the opportunities and short
Subject O Basic of Operation Research (D-01) Date O 20/04/2011 Time O 11.00 to 02.00 Q.1 Define Operation Research and state its relation with decision making. (14) What are the opportunities and short
56:171 Operations Research Midterm Exam Solutions Fall 1994
 56:171 Operations Research Midterm Exam Solutions Fall 1994 Possible Score A. True/False & Multiple Choice 30 B. Sensitivity analysis (LINDO) 20 C.1. Transportation 15 C.2. Decision Tree 15 C.3. Simplex
56:171 Operations Research Midterm Exam Solutions Fall 1994 Possible Score A. True/False & Multiple Choice 30 B. Sensitivity analysis (LINDO) 20 C.1. Transportation 15 C.2. Decision Tree 15 C.3. Simplex
Financial Market Models. Lecture 1. One-period model of financial markets & hedging problems. Imperial College Business School
 Financial Market Models Lecture One-period model of financial markets & hedging problems One-period model of financial markets a 4 2a 3 3a 3 a 3 -a 4 2 Aims of section Introduce one-period model with finite
Financial Market Models Lecture One-period model of financial markets & hedging problems One-period model of financial markets a 4 2a 3 3a 3 a 3 -a 4 2 Aims of section Introduce one-period model with finite
56:171 Operations Research Midterm Exam Solutions October 19, 1994
 56:171 Operations Research Midterm Exam Solutions October 19, 1994 Possible Score A. True/False & Multiple Choice 30 B. Sensitivity analysis (LINDO) 20 C.1. Transportation 15 C.2. Decision Tree 15 C.3.
56:171 Operations Research Midterm Exam Solutions October 19, 1994 Possible Score A. True/False & Multiple Choice 30 B. Sensitivity analysis (LINDO) 20 C.1. Transportation 15 C.2. Decision Tree 15 C.3.
Game Theory Tutorial 3 Answers
 Game Theory Tutorial 3 Answers Exercise 1 (Duality Theory) Find the dual problem of the following L.P. problem: max x 0 = 3x 1 + 2x 2 s.t. 5x 1 + 2x 2 10 4x 1 + 6x 2 24 x 1 + x 2 1 (1) x 1 + 3x 2 = 9 x
Game Theory Tutorial 3 Answers Exercise 1 (Duality Theory) Find the dual problem of the following L.P. problem: max x 0 = 3x 1 + 2x 2 s.t. 5x 1 + 2x 2 10 4x 1 + 6x 2 24 x 1 + x 2 1 (1) x 1 + 3x 2 = 9 x
WRITTEN PRELIMINARY Ph.D. EXAMINATION. Department of Applied Economics. January 28, Consumer Behavior and Household Economics.
 WRITTEN PRELIMINARY Ph.D. EXAMINATION Department of Applied Economics January 28, 2016 Consumer Behavior and Household Economics Instructions Identify yourself by your code letter, not your name, on each
WRITTEN PRELIMINARY Ph.D. EXAMINATION Department of Applied Economics January 28, 2016 Consumer Behavior and Household Economics Instructions Identify yourself by your code letter, not your name, on each
Optimizing the service of the Orange Line
 Optimizing the service of the Orange Line Overview Increased crime rate in and around campus Shuttle-UM Orange Line 12:00am 3:00am late night shift A student standing or walking on and around campus during
Optimizing the service of the Orange Line Overview Increased crime rate in and around campus Shuttle-UM Orange Line 12:00am 3:00am late night shift A student standing or walking on and around campus during
A STUDY OF THE BASIC CONCEPT OF CRASHING CPM NETWORK USING DERIVATIVE MARGINAL COST IN LINEAR PROGRAMMING
 ISSN : 98-X STUDY OF THE BSI ONEPT OF RSHING PM NETWORK USING DERIVTIVE MRGINL OST IN LINER PROGRMMING Ismail H. srul tma Jaya atholic University, Jakarta, Indonesia ismael.aaron@gmail.com BSTRT For crashing
ISSN : 98-X STUDY OF THE BSI ONEPT OF RSHING PM NETWORK USING DERIVTIVE MRGINL OST IN LINER PROGRMMING Ismail H. srul tma Jaya atholic University, Jakarta, Indonesia ismael.aaron@gmail.com BSTRT For crashing
LP OPTIMUM FOUND AT STEP 2 OBJECTIVE FUNCTION VALUE
 The Wilson Problem: Graph is at the end. LP OPTIMUM FOUND AT STEP 2 1) 5520.000 X1 360.000000 0.000000 X2 300.000000 0.000000 2) 0.000000 1.000000 3) 0.000000 2.000000 4) 140.000000 0.000000 5) 200.000000
The Wilson Problem: Graph is at the end. LP OPTIMUM FOUND AT STEP 2 1) 5520.000 X1 360.000000 0.000000 X2 300.000000 0.000000 2) 0.000000 1.000000 3) 0.000000 2.000000 4) 140.000000 0.000000 5) 200.000000
Operations Research I: Deterministic Models
 AMS 341 (Spring, 2010) Estie Arkin Operations Research I: Deterministic Models Exam 1: Thursday, March 11, 2010 READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. Do not start the exam until told to do so. Make certain
AMS 341 (Spring, 2010) Estie Arkin Operations Research I: Deterministic Models Exam 1: Thursday, March 11, 2010 READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. Do not start the exam until told to do so. Make certain
Logistics. Lecture notes. Maria Grazia Scutellà. Dipartimento di Informatica Università di Pisa. September 2015
 Logistics Lecture notes Maria Grazia Scutellà Dipartimento di Informatica Università di Pisa September 2015 These notes are related to the course of Logistics held by the author at the University of Pisa.
Logistics Lecture notes Maria Grazia Scutellà Dipartimento di Informatica Università di Pisa September 2015 These notes are related to the course of Logistics held by the author at the University of Pisa.
Advanced Operations Research Prof. G. Srinivasan Dept of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Advanced Operations Research Prof. G. Srinivasan Dept of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 23 Minimum Cost Flow Problem In this lecture, we will discuss the minimum cost
Advanced Operations Research Prof. G. Srinivasan Dept of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 23 Minimum Cost Flow Problem In this lecture, we will discuss the minimum cost
CHAPTER 6 CRASHING STOCHASTIC PERT NETWORKS WITH RESOURCE CONSTRAINED PROJECT SCHEDULING PROBLEM
 CHAPTER 6 CRASHING STOCHASTIC PERT NETWORKS WITH RESOURCE CONSTRAINED PROJECT SCHEDULING PROBLEM 6.1 Introduction Project Management is the process of planning, controlling and monitoring the activities
CHAPTER 6 CRASHING STOCHASTIC PERT NETWORKS WITH RESOURCE CONSTRAINED PROJECT SCHEDULING PROBLEM 6.1 Introduction Project Management is the process of planning, controlling and monitoring the activities
Handout 4: Deterministic Systems and the Shortest Path Problem
 SEEM 3470: Dynamic Optimization and Applications 2013 14 Second Term Handout 4: Deterministic Systems and the Shortest Path Problem Instructor: Shiqian Ma January 27, 2014 Suggested Reading: Bertsekas
SEEM 3470: Dynamic Optimization and Applications 2013 14 Second Term Handout 4: Deterministic Systems and the Shortest Path Problem Instructor: Shiqian Ma January 27, 2014 Suggested Reading: Bertsekas
Sensitivity Analysis LINDO INPUT & RESULTS. Maximize 7X1 + 10X2. Subject to X1 < 500 X2 < 500 X1 + 2X2 < 960 5X1 + 6X2 < 3600 END
 Sensitivity Analysis Sensitivity Analysis is used to see how the optimal solution is affected by the objective function coefficients and to see how the optimal value is affected by the right- hand side
Sensitivity Analysis Sensitivity Analysis is used to see how the optimal solution is affected by the objective function coefficients and to see how the optimal value is affected by the right- hand side
Advanced Operations Research Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Advanced Operations Research Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 21 Successive Shortest Path Problem In this lecture, we continue our discussion
Advanced Operations Research Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 21 Successive Shortest Path Problem In this lecture, we continue our discussion
INTRODUCTION PROJECT MANAGEMENT
 CHAPTER 7. 1 RESOURCE INTRODUCTION ALLOCATION TO PROJECT MANAGEMENT Prepared by: Dr. Maria Elisa Linda T. Cruz Prepared by: Dr. Maria Elisa Linda T. Cruz 1 Chapter 7. Resource Allocation 7.1 Critical Path
CHAPTER 7. 1 RESOURCE INTRODUCTION ALLOCATION TO PROJECT MANAGEMENT Prepared by: Dr. Maria Elisa Linda T. Cruz Prepared by: Dr. Maria Elisa Linda T. Cruz 1 Chapter 7. Resource Allocation 7.1 Critical Path
Matt Morgan Assistant Superintendent of Support Services. Severin Castro Director of Purchasing. June 6, Date: Re:
 To: From: Date: Re: Matt Morgan Assistant Superintendent of Support Services Severin Castro Director of Purchasing June 6, 2018 Fencing and Wire Mesh Partitions Annual Contract #18-06-5175R-RFP The following
To: From: Date: Re: Matt Morgan Assistant Superintendent of Support Services Severin Castro Director of Purchasing June 6, 2018 Fencing and Wire Mesh Partitions Annual Contract #18-06-5175R-RFP The following
Continuing Education Course #287 Engineering Methods in Microsoft Excel Part 2: Applied Optimization
 1 of 6 Continuing Education Course #287 Engineering Methods in Microsoft Excel Part 2: Applied Optimization 1. Which of the following is NOT an element of an optimization formulation? a. Objective function
1 of 6 Continuing Education Course #287 Engineering Methods in Microsoft Excel Part 2: Applied Optimization 1. Which of the following is NOT an element of an optimization formulation? a. Objective function
CHAPTER 13: A PROFIT MAXIMIZING HARVEST SCHEDULING MODEL
 CHAPTER 1: A PROFIT MAXIMIZING HARVEST SCHEDULING MODEL The previous chapter introduced harvest scheduling with a model that minimized the cost of meeting certain harvest targets. These harvest targets
CHAPTER 1: A PROFIT MAXIMIZING HARVEST SCHEDULING MODEL The previous chapter introduced harvest scheduling with a model that minimized the cost of meeting certain harvest targets. These harvest targets
CHAPTER 9: PROJECT MANAGEMENT
 CHAPTER 9: PROJECT MANAGEMENT The aim is to coordinate and plan a single job consisting lots of tasks between which precedence relationships exist Project planning Most popular planning tools are utilized
CHAPTER 9: PROJECT MANAGEMENT The aim is to coordinate and plan a single job consisting lots of tasks between which precedence relationships exist Project planning Most popular planning tools are utilized
The Neo-Ricardian Trade Theory and the New Theory of International Values
 The Neo-Ricardian Trade Theory and the New Theory of International Values Akira Takamasu Kansai University Abstract Ricardo s (1817) theory of comparative advantage is the first rigorous theory that demonstrates
The Neo-Ricardian Trade Theory and the New Theory of International Values Akira Takamasu Kansai University Abstract Ricardo s (1817) theory of comparative advantage is the first rigorous theory that demonstrates
Operations Research I: Deterministic Models
 AMS 341 (Spring, 2009) Estie Arkin Operations Research I: Deterministic Models Exam 1: Thursday, March 12, 2009 READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. Do not start the exam until told to do so. Make certain
AMS 341 (Spring, 2009) Estie Arkin Operations Research I: Deterministic Models Exam 1: Thursday, March 12, 2009 READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. Do not start the exam until told to do so. Make certain
Introduction to Operations Research
 Introduction to Operations Research Unit 1: Linear Programming Terminology and formulations LP through an example Terminology Additional Example 1 Additional example 2 A shop can make two types of sweets
Introduction to Operations Research Unit 1: Linear Programming Terminology and formulations LP through an example Terminology Additional Example 1 Additional example 2 A shop can make two types of sweets
TUFTS UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL AND ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING ES 152 ENGINEERING SYSTEMS Spring Lesson 16 Introduction to Game Theory
 TUFTS UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL AND ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING ES 52 ENGINEERING SYSTEMS Spring 20 Introduction: Lesson 6 Introduction to Game Theory We will look at the basic ideas of game theory.
TUFTS UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL AND ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING ES 52 ENGINEERING SYSTEMS Spring 20 Introduction: Lesson 6 Introduction to Game Theory We will look at the basic ideas of game theory.
56:171 Operations Research Midterm Examination Solutions PART ONE
 56:171 Operations Research Midterm Examination Solutions Fall 1997 Answer both questions of Part One, and 4 (out of 5) problems from Part Two. Possible Part One: 1. True/False 15 2. Sensitivity analysis
56:171 Operations Research Midterm Examination Solutions Fall 1997 Answer both questions of Part One, and 4 (out of 5) problems from Part Two. Possible Part One: 1. True/False 15 2. Sensitivity analysis
Problem 1 Food Manufacturing. The final product sells for $150 per ton.
 Problem 1 Food Manufacturing A food is manufactured by refining raw oils and blending them together. The raw oils come in two categories, and can be bought for the following prices per ton: vegetable oils
Problem 1 Food Manufacturing A food is manufactured by refining raw oils and blending them together. The raw oils come in two categories, and can be bought for the following prices per ton: vegetable oils
56:171 Operations Research Midterm Examination October 25, 1991 PART ONE
 56:171 O.R. Midterm Exam - 1 - Name or Initials 56:171 Operations Research Midterm Examination October 25, 1991 Write your name on the first page, and initial the other pages. Answer both questions of
56:171 O.R. Midterm Exam - 1 - Name or Initials 56:171 Operations Research Midterm Examination October 25, 1991 Write your name on the first page, and initial the other pages. Answer both questions of
Non-negativity: negativity:
 Chapter 3 Linear Programming Applications The process of problem formulation Marketing and media applications Financial Applications Transportation Problem The process of problem formulation 1. Provide
Chapter 3 Linear Programming Applications The process of problem formulation Marketing and media applications Financial Applications Transportation Problem The process of problem formulation 1. Provide
32 Chapter 3 Analyzing Solutions. The solution is:
 3 Analyzing Solutions 3.1 Economic Analysis of Solution Reports A substantial amount of interesting economic information can be gleaned from the solution report of a model. In addition, optional reports,
3 Analyzing Solutions 3.1 Economic Analysis of Solution Reports A substantial amount of interesting economic information can be gleaned from the solution report of a model. In addition, optional reports,
Volatility and Growth: Credit Constraints and the Composition of Investment
 Volatility and Growth: Credit Constraints and the Composition of Investment Journal of Monetary Economics 57 (2010), p.246-265. Philippe Aghion Harvard and NBER George-Marios Angeletos MIT and NBER Abhijit
Volatility and Growth: Credit Constraints and the Composition of Investment Journal of Monetary Economics 57 (2010), p.246-265. Philippe Aghion Harvard and NBER George-Marios Angeletos MIT and NBER Abhijit
EconS 424 Strategy and Game Theory. Homework #5 Answer Key
 EconS 44 Strategy and Game Theory Homework #5 Answer Key Exercise #1 Collusion among N doctors Consider an infinitely repeated game, in which there are nn 3 doctors, who have created a partnership. In
EconS 44 Strategy and Game Theory Homework #5 Answer Key Exercise #1 Collusion among N doctors Consider an infinitely repeated game, in which there are nn 3 doctors, who have created a partnership. In
Integrated Resource Planning. Technical Meeting April 26, 2018
 Integrated Resource Planning Technical Meeting April 26, 2018 Meeting Logistics Local Participants: World Trade Center facility Wireless internet access Network: Password: Sign-in sheets Virtual Participants:
Integrated Resource Planning Technical Meeting April 26, 2018 Meeting Logistics Local Participants: World Trade Center facility Wireless internet access Network: Password: Sign-in sheets Virtual Participants:
Master of Business Administration - General. Cohort: MBAG/14/PT Mar. Examinations for Semester II / 2014 Semester I
 Master of Business Administration - General Cohort: MBAG/14/PT Mar Examinations for 2013 2014 Semester II / 2014 Semester I MODULE: OPERATIONS RESEARCH MODULE CODE: MGMT5214 DURATION: 3 HOURS Instructions
Master of Business Administration - General Cohort: MBAG/14/PT Mar Examinations for 2013 2014 Semester II / 2014 Semester I MODULE: OPERATIONS RESEARCH MODULE CODE: MGMT5214 DURATION: 3 HOURS Instructions
An Application of Mathematical Model to Time-cost Trade off Problem (Case Study)
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(7): 208-214, 2011 ISSN 1991-8178 An Application of Mathematical Model to Time-cost Trade off Problem (ase Study) 1 Amin Zeinalzadeh 1 Tabriz Branch,
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(7): 208-214, 2011 ISSN 1991-8178 An Application of Mathematical Model to Time-cost Trade off Problem (ase Study) 1 Amin Zeinalzadeh 1 Tabriz Branch,
SCHEDULE CREATION AND ANALYSIS. 1 Powered by POeT Solvers Limited
 SCHEDULE CREATION AND ANALYSIS 1 www.pmtutor.org Powered by POeT Solvers Limited While building the project schedule, we need to consider all risk factors, assumptions and constraints imposed on the project
SCHEDULE CREATION AND ANALYSIS 1 www.pmtutor.org Powered by POeT Solvers Limited While building the project schedule, we need to consider all risk factors, assumptions and constraints imposed on the project
Backpropagation. Deep Learning Theory and Applications. Kevin Moon Guy Wolf
 Deep Learning Theory and Applications Backpropagation Kevin Moon (kevin.moon@yale.edu) Guy Wolf (guy.wolf@yale.edu) CPSC/AMTH 663 Calculating the gradients We showed how neural networks can learn weights
Deep Learning Theory and Applications Backpropagation Kevin Moon (kevin.moon@yale.edu) Guy Wolf (guy.wolf@yale.edu) CPSC/AMTH 663 Calculating the gradients We showed how neural networks can learn weights
What is spatial transferability?
 Improving the spatial transferability of travel demand forecasting models: An empirical assessment of the impact of incorporatingattitudeson model transferability 1 Divyakant Tahlyan, Parvathy Vinod Sheela,
Improving the spatial transferability of travel demand forecasting models: An empirical assessment of the impact of incorporatingattitudeson model transferability 1 Divyakant Tahlyan, Parvathy Vinod Sheela,
Of Rocket Science, Finance, and Nuclear Data: REWIND (Ranking Experiments by Weighting for Improved Nuclear Data)
 Of Rocket Science, Finance, and Nuclear Data: REWIND (Ranking Experiments by Weighting for Improved Nuclear Data) G. Palmiotti Idaho National Laboratory May 20, 2015 December 2012 SG39, Paris, France Introduction
Of Rocket Science, Finance, and Nuclear Data: REWIND (Ranking Experiments by Weighting for Improved Nuclear Data) G. Palmiotti Idaho National Laboratory May 20, 2015 December 2012 SG39, Paris, France Introduction
Optimization Prof. A. Goswami Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur. Lecture - 18 PERT
 Optimization Prof. A. Goswami Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 18 PERT (Refer Slide Time: 00:56) In the last class we completed the C P M critical path analysis
Optimization Prof. A. Goswami Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 18 PERT (Refer Slide Time: 00:56) In the last class we completed the C P M critical path analysis
UNIT-II Project Organization and Scheduling Project Element
 UNIT-II Project Organization and Scheduling Project Element Five Key Elements are Unique. Projects are unique, one-of-a-kind, never been done before. Start and Stop Date. Projects must have a definite
UNIT-II Project Organization and Scheduling Project Element Five Key Elements are Unique. Projects are unique, one-of-a-kind, never been done before. Start and Stop Date. Projects must have a definite
A convenient analytical and visual technique of PERT and CPM prove extremely valuable in assisting the managers in managing the projects.
 Introduction Any project involves planning, scheduling and controlling a number of interrelated activities with use of limited resources, namely, men, machines, materials, money and time. The projects
Introduction Any project involves planning, scheduling and controlling a number of interrelated activities with use of limited resources, namely, men, machines, materials, money and time. The projects
4. Introduction to Prescriptive Analytics. BIA 674 Supply Chain Analytics
 4. Introduction to Prescriptive Analytics BIA 674 Supply Chain Analytics Why is Decision Making difficult? The biggest sources of difficulty for decision making: Uncertainty Complexity of Environment or
4. Introduction to Prescriptive Analytics BIA 674 Supply Chain Analytics Why is Decision Making difficult? The biggest sources of difficulty for decision making: Uncertainty Complexity of Environment or
DISCLAIMER. The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India
 DISCLAIMER The Suggested Answers hosted in the website do not constitute the basis for evaluation of the students answers in the examination. The answers are prepared by the Faculty of the Board of Studies
DISCLAIMER The Suggested Answers hosted in the website do not constitute the basis for evaluation of the students answers in the examination. The answers are prepared by the Faculty of the Board of Studies
Allocate and Level Project Resources
 Allocate and Level Project Resources Resource Allocation: Defined Resource Allocation is the scheduling of activities and the resources required by those activities while taking into consideration both
Allocate and Level Project Resources Resource Allocation: Defined Resource Allocation is the scheduling of activities and the resources required by those activities while taking into consideration both
Project Management Techniques (PMT)
 Project Management Techniques (PMT) Critical Path Method (CPM) and Project Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) are 2 main basic techniques used in project management. Example: Construction of a house.
Project Management Techniques (PMT) Critical Path Method (CPM) and Project Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) are 2 main basic techniques used in project management. Example: Construction of a house.
Optimization Methods in Management Science
 Problem Set Rules: Optimization Methods in Management Science MIT 15.053, Spring 2013 Problem Set 6, Due: Thursday April 11th, 2013 1. Each student should hand in an individual problem set. 2. Discussing
Problem Set Rules: Optimization Methods in Management Science MIT 15.053, Spring 2013 Problem Set 6, Due: Thursday April 11th, 2013 1. Each student should hand in an individual problem set. 2. Discussing
Project Planning. Identifying the Work to Be Done. Gantt Chart. A Gantt Chart. Given: Activity Sequencing Network Diagrams
 Project Planning Identifying the Work to Be Done Activity Sequencing Network Diagrams Given: Statement of work written description of goals work & time frame of project Work Breakdown Structure Be able
Project Planning Identifying the Work to Be Done Activity Sequencing Network Diagrams Given: Statement of work written description of goals work & time frame of project Work Breakdown Structure Be able
Linear Programming: Sensitivity Analysis and Interpretation of Solution
 8 Linear Programming: Sensitivity Analysis and Interpretation of Solution MULTIPLE CHOICE. To solve a linear programming problem with thousands of variables and constraints a personal computer can be use
8 Linear Programming: Sensitivity Analysis and Interpretation of Solution MULTIPLE CHOICE. To solve a linear programming problem with thousands of variables and constraints a personal computer can be use
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF TIME-COST OPTIMIZATION
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 8, Issue 4, April 2017, pp. 659 663, Article ID: IJCIET_08_04_076 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=8&itype=4
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 8, Issue 4, April 2017, pp. 659 663, Article ID: IJCIET_08_04_076 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=8&itype=4
Tests for the Matched-Pair Difference of Two Event Rates in a Cluster- Randomized Design
 Chapter 487 Tests for the Matched-Pair Difference of Two Event Rates in a Cluster- Randomized Design Introduction Cluster-randomized designs are those in which whole clusters of subjects (classes, hospitals,
Chapter 487 Tests for the Matched-Pair Difference of Two Event Rates in a Cluster- Randomized Design Introduction Cluster-randomized designs are those in which whole clusters of subjects (classes, hospitals,
Advanced Microeconomic Theory. Chapter 3: Demand Theory Applications
 Advanced Microeconomic Theory Chapter 3: Demand Theory Applications Outline Welfare evaluation Compensating variation Equivalent variation Quasilinear preferences Slutsky equation revisited Income and
Advanced Microeconomic Theory Chapter 3: Demand Theory Applications Outline Welfare evaluation Compensating variation Equivalent variation Quasilinear preferences Slutsky equation revisited Income and
Assignment 2 Answers Introduction to Management Science 2003
 Assignment Answers Introduction to Management Science 00. a. Top management will need to know how much to produce in each quarter. Thus, the decisions are the production levels in quarters,,, and. The
Assignment Answers Introduction to Management Science 00. a. Top management will need to know how much to produce in each quarter. Thus, the decisions are the production levels in quarters,,, and. The
February 24, 2005
 15.053 February 24, 2005 Sensitivity Analysis and shadow prices Suggestion: Please try to complete at least 2/3 of the homework set by next Thursday 1 Goals of today s lecture on Sensitivity Analysis Changes
15.053 February 24, 2005 Sensitivity Analysis and shadow prices Suggestion: Please try to complete at least 2/3 of the homework set by next Thursday 1 Goals of today s lecture on Sensitivity Analysis Changes
Examinations for Semester II. / 2011 Semester I
 PROGRAMME MBA-Human Resources & knowledge Management MBA- Project Management Master of Business Administration General MBA-Marketing Management COHORT MBAHR/11/PT MBAPM/11/PT MBAG/11/PT MBAMM/11/PT Examinations
PROGRAMME MBA-Human Resources & knowledge Management MBA- Project Management Master of Business Administration General MBA-Marketing Management COHORT MBAHR/11/PT MBAPM/11/PT MBAG/11/PT MBAMM/11/PT Examinations
11/1/2018. Overview PERT / CPM. Network representation. Network representation. Project Scheduling. What is a path?
 PERT / CPM BSD Dave Novak Fall Overview Introduce Discuss what a critical path is Discuss critical path algorithm Example Source: nderson et al., 1 Quantitative Methods for Business 1 th edition some slides
PERT / CPM BSD Dave Novak Fall Overview Introduce Discuss what a critical path is Discuss critical path algorithm Example Source: nderson et al., 1 Quantitative Methods for Business 1 th edition some slides
INSE 6230: Assignment 1 - Winter (0% of final grade) 1. The table below provides information about a short IT project.
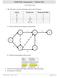 INSE 6230: Assignment - Winter 208 (0% of final grade). The table below provides information about a short IT project. Activity Predecessors Duration (Months) A - 2 B - 3 C A 4 D A, B 2 E D 2 F B, C, E
INSE 6230: Assignment - Winter 208 (0% of final grade). The table below provides information about a short IT project. Activity Predecessors Duration (Months) A - 2 B - 3 C A 4 D A, B 2 E D 2 F B, C, E
6. Pricing deterministic payoffs
 Some of the content of these slides is based on material from the book Introduction to the Economics and Mathematics of Financial Markets by Jaksa Cvitanic and Fernando Zapatero. Pricing Options with Mathematical
Some of the content of these slides is based on material from the book Introduction to the Economics and Mathematics of Financial Markets by Jaksa Cvitanic and Fernando Zapatero. Pricing Options with Mathematical
56:171 Operations Research Midterm Examination Solutions PART ONE
 56:171 Operations Research Midterm Examination Solutions Fall 1997 Write your name on the first page, and initial the other pages. Answer both questions of Part One, and 4 (out of 5) problems from Part
56:171 Operations Research Midterm Examination Solutions Fall 1997 Write your name on the first page, and initial the other pages. Answer both questions of Part One, and 4 (out of 5) problems from Part
Probabilistic Completion Time in Project Scheduling Min Khee Chin 1, Sie Long Kek 2, Sy Yi Sim 3, Ta Wee Seow 4
 Probabilistic Completion Time in Project Scheduling Min Khee Chin 1, Sie Long Kek 2, Sy Yi Sim 3, Ta Wee Seow 4 1 Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia 2 Center
Probabilistic Completion Time in Project Scheduling Min Khee Chin 1, Sie Long Kek 2, Sy Yi Sim 3, Ta Wee Seow 4 1 Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia 2 Center
Elastic demand solution methods
 solution methods CE 392C October 6, 2016 REVIEW We ve added another consistency relationship: Route choices No vehicle left behind Link performance functions Shortest path OD matrix Travel times Demand
solution methods CE 392C October 6, 2016 REVIEW We ve added another consistency relationship: Route choices No vehicle left behind Link performance functions Shortest path OD matrix Travel times Demand
Homework #3 Supply Chain Models: Manufacturing & Warehousing (ISyE 3104) - Fall 2001 Due September 20, 2001
 Homework #3 Supply Chain Models: Manufacturing & Warehousing (ISyE 3104) - Fall 2001 Due September 20, 2001 Show all your steps to get full credit. (Total 45 points) Reading assignment: Read Supplement
Homework #3 Supply Chain Models: Manufacturing & Warehousing (ISyE 3104) - Fall 2001 Due September 20, 2001 Show all your steps to get full credit. (Total 45 points) Reading assignment: Read Supplement
Do all of Part One (1 pt. each), one from Part Two (15 pts.), and four from Part Three (15 pts. each) <><><><><> PART ONE <><><><><>
 56:171 Operations Research Final Exam - December 13, 1989 Instructor: D.L. Bricker Do all of Part One (1 pt. each), one from Part Two (15 pts.), and four from
56:171 Operations Research Final Exam - December 13, 1989 Instructor: D.L. Bricker Do all of Part One (1 pt. each), one from Part Two (15 pts.), and four from
Week 6: Sensitive Analysis
 Week 6: Sensitive Analysis 1 1. Sensitive Analysis Sensitivity Analysis is a systematic study of how, well, sensitive, the solutions of the LP are to small changes in the data. The basic idea is to be
Week 6: Sensitive Analysis 1 1. Sensitive Analysis Sensitivity Analysis is a systematic study of how, well, sensitive, the solutions of the LP are to small changes in the data. The basic idea is to be
Ph.D. MICROECONOMICS CORE EXAM August 2018
 Ph.D. MICROECONOMICS CORE EXAM August 2018 This exam is designed to test your broad knowledge of microeconomics. There are three sections: one required and two choice sections. You must complete both problems
Ph.D. MICROECONOMICS CORE EXAM August 2018 This exam is designed to test your broad knowledge of microeconomics. There are three sections: one required and two choice sections. You must complete both problems
10.1 DEFINITIONS... 1
 10.1 DEFINITIONS.... 1 10.2 INTRODUCTION... 6 10.3 CHART OF INCOME SOURCES.... 8 A. ACE... 9 B. ADOPTION ASSISTANCE... 9 C. ADULT FAMILY CARE PROVIDER INCOME... 9 D. ADVANCE PAY... 9 E. AGENT ORANGE PAYMENT
10.1 DEFINITIONS.... 1 10.2 INTRODUCTION... 6 10.3 CHART OF INCOME SOURCES.... 8 A. ACE... 9 B. ADOPTION ASSISTANCE... 9 C. ADULT FAMILY CARE PROVIDER INCOME... 9 D. ADVANCE PAY... 9 E. AGENT ORANGE PAYMENT
NODIA AND COMPANY. GATE SOLVED PAPER Mechanical Engineering Industrial Engineering. Copyright By NODIA & COMPANY
 No part of this publication may be reproduced or distributed in any form or any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, or otherwise without the prior permission of the author. GATE SOLVED PAPER Mechanical
No part of this publication may be reproduced or distributed in any form or any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, or otherwise without the prior permission of the author. GATE SOLVED PAPER Mechanical
International Project Management. prof.dr MILOŠ D. MILOVANČEVIĆ
 International Project Management prof.dr MILOŠ D. MILOVANČEVIĆ Project time management Project cost management Time in project management process Time is a valuable resource. It is also the scarcest. Time
International Project Management prof.dr MILOŠ D. MILOVANČEVIĆ Project time management Project cost management Time in project management process Time is a valuable resource. It is also the scarcest. Time
POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA
 POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF MANAGEMENT PROJECT MANAGEMENT BACHELOR OF BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION 07BBMA SUBJECT CODE: PRM422S DATE: DURATION: MARKS: EXAMINERS: MODERATOR:
POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF MANAGEMENT PROJECT MANAGEMENT BACHELOR OF BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION 07BBMA SUBJECT CODE: PRM422S DATE: DURATION: MARKS: EXAMINERS: MODERATOR:
Tests for the Difference Between Two Poisson Rates in a Cluster-Randomized Design
 Chapter 439 Tests for the Difference Between Two Poisson Rates in a Cluster-Randomized Design Introduction Cluster-randomized designs are those in which whole clusters of subjects (classes, hospitals,
Chapter 439 Tests for the Difference Between Two Poisson Rates in a Cluster-Randomized Design Introduction Cluster-randomized designs are those in which whole clusters of subjects (classes, hospitals,
car, in years 0 (new car)
 Chapter 2.4: Applications of Linear Equations In this section, we discuss applications of linear equations how we can use linear equations to model situations in our lives. We already saw some examples
Chapter 2.4: Applications of Linear Equations In this section, we discuss applications of linear equations how we can use linear equations to model situations in our lives. We already saw some examples
Economics 230a, Fall 2017 Lecture Note 6: Basic Tax Incidence
 Economics 230a, Fall 2017 Lecture Note 6: Basic Tax Incidence Tax incidence refers to where the burden of taxation actually falls, as distinguished from who has the legal liability to pay taxes. As with
Economics 230a, Fall 2017 Lecture Note 6: Basic Tax Incidence Tax incidence refers to where the burden of taxation actually falls, as distinguished from who has the legal liability to pay taxes. As with
A Formal Study of Distributed Resource Allocation Strategies in Multi-Agent Systems
 A Formal Study of Distributed Resource Allocation Strategies in Multi-Agent Systems Jiaying Shen, Micah Adler, Victor Lesser Department of Computer Science University of Massachusetts Amherst, MA 13 Abstract
A Formal Study of Distributed Resource Allocation Strategies in Multi-Agent Systems Jiaying Shen, Micah Adler, Victor Lesser Department of Computer Science University of Massachusetts Amherst, MA 13 Abstract
Optimization Models in Financial Mathematics
 Optimization Models in Financial Mathematics John R. Birge Northwestern University www.iems.northwestern.edu/~jrbirge Illinois Section MAA, April 3, 2004 1 Introduction Trends in financial mathematics
Optimization Models in Financial Mathematics John R. Birge Northwestern University www.iems.northwestern.edu/~jrbirge Illinois Section MAA, April 3, 2004 1 Introduction Trends in financial mathematics
MS-E2114 Investment Science Lecture 4: Applied interest rate analysis
 MS-E2114 Investment Science Lecture 4: Applied interest rate analysis A. Salo, T. Seeve Systems Analysis Laboratory Department of System Analysis and Mathematics Aalto University, School of Science Overview
MS-E2114 Investment Science Lecture 4: Applied interest rate analysis A. Salo, T. Seeve Systems Analysis Laboratory Department of System Analysis and Mathematics Aalto University, School of Science Overview
COS 511: Theoretical Machine Learning. Lecturer: Rob Schapire Lecture #24 Scribe: Jordan Ash May 1, 2014
 COS 5: heoretical Machine Learning Lecturer: Rob Schapire Lecture #24 Scribe: Jordan Ash May, 204 Review of Game heory: Let M be a matrix with all elements in [0, ]. Mindy (called the row player) chooses
COS 5: heoretical Machine Learning Lecturer: Rob Schapire Lecture #24 Scribe: Jordan Ash May, 204 Review of Game heory: Let M be a matrix with all elements in [0, ]. Mindy (called the row player) chooses
Duality & The Dual Simplex Method & Sensitivity Analysis for Linear Programming. Metodos Cuantitativos M. En C. Eduardo Bustos Farias 1
 Dualit & The Dual Simple Method & Sensitivit Analsis for Linear Programming Metodos Cuantitativos M. En C. Eduardo Bustos Farias Dualit EverLP problem has a twin problem associated with it. One problem
Dualit & The Dual Simple Method & Sensitivit Analsis for Linear Programming Metodos Cuantitativos M. En C. Eduardo Bustos Farias Dualit EverLP problem has a twin problem associated with it. One problem
Chapter 4 Money and Inflation
 Chapter 4 Money and Inflation Zhengyu Cai Ph.D. Institute of Development Southwestern University of Finance and Economics All rights reserved http://www.escience.cn/people/zhengyucai/index.html Refresh
Chapter 4 Money and Inflation Zhengyu Cai Ph.D. Institute of Development Southwestern University of Finance and Economics All rights reserved http://www.escience.cn/people/zhengyucai/index.html Refresh
CSCI 1951-G Optimization Methods in Finance Part 00: Course Logistics Introduction to Finance Optimization Problems
 CSCI 1951-G Optimization Methods in Finance Part 00: Course Logistics Introduction to Finance Optimization Problems January 26, 2018 1 / 24 Basic information All information is available in the syllabus
CSCI 1951-G Optimization Methods in Finance Part 00: Course Logistics Introduction to Finance Optimization Problems January 26, 2018 1 / 24 Basic information All information is available in the syllabus
8. Model independent pricing relations: forwards, futures and swaps
 Pricing Options with Mathematical Models 8. Model independent pricing relations: forwards, futures and swaps Some of the content of these slides is based on material from the book Introduction to the Economics
Pricing Options with Mathematical Models 8. Model independent pricing relations: forwards, futures and swaps Some of the content of these slides is based on material from the book Introduction to the Economics
Algorithmic Game Theory (a primer) Depth Qualifying Exam for Ashish Rastogi (Ph.D. candidate)
 Algorithmic Game Theory (a primer) Depth Qualifying Exam for Ashish Rastogi (Ph.D. candidate) 1 Game Theory Theory of strategic behavior among rational players. Typical game has several players. Each player
Algorithmic Game Theory (a primer) Depth Qualifying Exam for Ashish Rastogi (Ph.D. candidate) 1 Game Theory Theory of strategic behavior among rational players. Typical game has several players. Each player
Chapter 21. Dynamic Programming CONTENTS 21.1 A SHORTEST-ROUTE PROBLEM 21.2 DYNAMIC PROGRAMMING NOTATION
 Chapter 21 Dynamic Programming CONTENTS 21.1 A SHORTEST-ROUTE PROBLEM 21.2 DYNAMIC PROGRAMMING NOTATION 21.3 THE KNAPSACK PROBLEM 21.4 A PRODUCTION AND INVENTORY CONTROL PROBLEM 23_ch21_ptg01_Web.indd
Chapter 21 Dynamic Programming CONTENTS 21.1 A SHORTEST-ROUTE PROBLEM 21.2 DYNAMIC PROGRAMMING NOTATION 21.3 THE KNAPSACK PROBLEM 21.4 A PRODUCTION AND INVENTORY CONTROL PROBLEM 23_ch21_ptg01_Web.indd
SCHOOL OF BUSINESS, ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT. BF360 Operations Research
 SCHOOL OF BUSINESS, ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT BF360 Operations Research Unit 3 Moses Mwale e-mail: moses.mwale@ictar.ac.zm BF360 Operations Research Contents Unit 3: Sensitivity and Duality 3 3.1 Sensitivity
SCHOOL OF BUSINESS, ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT BF360 Operations Research Unit 3 Moses Mwale e-mail: moses.mwale@ictar.ac.zm BF360 Operations Research Contents Unit 3: Sensitivity and Duality 3 3.1 Sensitivity
Application of Earned Value Management (EVM) for Effective Project Control
 Application of Earned Value Management (EVM) for Effective Project Control Course No: B02-012 Credit: 2 PDH Boris Shvartsberg, Ph.D., P.E., P.M.P. Continuing Education and Development, Inc. 9 Greyridge
Application of Earned Value Management (EVM) for Effective Project Control Course No: B02-012 Credit: 2 PDH Boris Shvartsberg, Ph.D., P.E., P.M.P. Continuing Education and Development, Inc. 9 Greyridge
Expediting a Project, an Optimized Strategy Approach to Milestones Delay Management (MDM)
 Expediting a Project, an Optimized Strategy Approach to Milestones Delay Management (MDM) Homayoun Khamooshi Fax 202-994-2736 Tel 202-994-4862 E_Mail: hkh@gwu.edu Department of Management Science School
Expediting a Project, an Optimized Strategy Approach to Milestones Delay Management (MDM) Homayoun Khamooshi Fax 202-994-2736 Tel 202-994-4862 E_Mail: hkh@gwu.edu Department of Management Science School
56:171 Operations Research Midterm Examination October 28, 1997 PART ONE
 56:171 Operations Research Midterm Examination October 28, 1997 Write your name on the first page, and initial the other pages. Answer both questions of Part One, and 4 (out of 5) problems from Part Two.
56:171 Operations Research Midterm Examination October 28, 1997 Write your name on the first page, and initial the other pages. Answer both questions of Part One, and 4 (out of 5) problems from Part Two.
Activity Predecessors Durations (days) a - 3 b a 4 c a 5 d a 4 e b 2 f d 9 g c, e 6 h f, g 2
 CHAPTER 11 INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING YEAR 2012 ONE MARK MCQ 11.1 Which one of the following is NOT a decision taken during the aggregate production planning stage? (A) Scheduling of machines (B) Amount of
CHAPTER 11 INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING YEAR 2012 ONE MARK MCQ 11.1 Which one of the following is NOT a decision taken during the aggregate production planning stage? (A) Scheduling of machines (B) Amount of
SCM 301 (Solo) Exam 1 Practice Exam Solutions
 1. D $118,000 www.liontutors.com SCM 301 (Solo) Exam 1 Practice Exam Solutions The first thing we need to do here is use the information given in the table to create a network diagram. Once we have a network
1. D $118,000 www.liontutors.com SCM 301 (Solo) Exam 1 Practice Exam Solutions The first thing we need to do here is use the information given in the table to create a network diagram. Once we have a network
PAPER 5: ADVANCED MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING QUESTIONS
 Total Quality Management PAPER 5: ADVANCED MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING QUESTIONS 1. KNM Road Carriers is a transporting company that transports goods from one place to another. It measures quality of service
Total Quality Management PAPER 5: ADVANCED MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING QUESTIONS 1. KNM Road Carriers is a transporting company that transports goods from one place to another. It measures quality of service
The Process of Modeling
 Session #3 Page 1 The Process of Modeling Plan Visualize where you want to finish Do some calculations by hand Sketch out a spreadsheet Build Start with a small-scale model Expand the model to full scale
Session #3 Page 1 The Process of Modeling Plan Visualize where you want to finish Do some calculations by hand Sketch out a spreadsheet Build Start with a small-scale model Expand the model to full scale
Optimization Methods in Management Science
 Optimization Methods in Management Science MIT 15.053, Spring 013 Problem Set (Second Group of Students) Students with first letter of surnames I Z Due: February 1, 013 Problem Set Rules: 1. Each student
Optimization Methods in Management Science MIT 15.053, Spring 013 Problem Set (Second Group of Students) Students with first letter of surnames I Z Due: February 1, 013 Problem Set Rules: 1. Each student
{List Sales (1 Trade Discount) Total Cost} (1 Tax Rate) = 0.06K
 FINAL CA MAY 2018 ADVANCED MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING Test Code F84 Branch: Date : 04.03.2018 (50 Marks) Note: All questions are compulsory. Question 1(4 Marks) (c) Selling Price to Yield 20% Return on Investment
FINAL CA MAY 2018 ADVANCED MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING Test Code F84 Branch: Date : 04.03.2018 (50 Marks) Note: All questions are compulsory. Question 1(4 Marks) (c) Selling Price to Yield 20% Return on Investment
Alg2A Factoring and Equations Review Packet
 1 Factoring using GCF: Take the greatest common factor (GCF) for the numerical coefficient. When choosing the GCF for the variables, if all the terms have a common variable, take the one with the lowest
1 Factoring using GCF: Take the greatest common factor (GCF) for the numerical coefficient. When choosing the GCF for the variables, if all the terms have a common variable, take the one with the lowest
Alg2A Factoring and Equations Review Packet
 1 Multiplying binomials: We have a special way of remembering how to multiply binomials called FOIL: F: first x x = x 2 (x + 7)(x + 5) O: outer x 5 = 5x I: inner 7 x = 7x x 2 + 5x +7x + 35 (then simplify)
1 Multiplying binomials: We have a special way of remembering how to multiply binomials called FOIL: F: first x x = x 2 (x + 7)(x + 5) O: outer x 5 = 5x I: inner 7 x = 7x x 2 + 5x +7x + 35 (then simplify)
Project Management Professional (PMP) Exam Prep Course 06 - Project Time Management
 Project Management Professional (PMP) Exam Prep Course 06 - Project Time Management Slide 1 Looking Glass Development, LLC (303) 663-5402 / (888) 338-7447 4610 S. Ulster St. #150 Denver, CO 80237 information@lookingglassdev.com
Project Management Professional (PMP) Exam Prep Course 06 - Project Time Management Slide 1 Looking Glass Development, LLC (303) 663-5402 / (888) 338-7447 4610 S. Ulster St. #150 Denver, CO 80237 information@lookingglassdev.com
