Macroeconomics Unit Overview
|
|
|
- Dwain Williams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit Overview 3.1 Measuring national income * Circular flow of income * Methods of measurement - income, expenditure and output * Distinction between o gross and net o national and domestic o nominal and real o total and per capita 3.2 Introduction to development * Definitions of economic growth and economic development * Differences in the definitions of the two concepts * Gross Domestic Product (GDP) vs. Gross National Product (GNP) as measures of growth * Limitations of using GDP as a measure to compare welfare between countries * Allowance for differences in purchasing power when comparing welfare between countries * Alternative methods of measurement * Problems of measuring development 3.3 Macroeconomic models * Aggregate demand - components * Aggregate supply o short-run o long-run (Keynesian vs. neo-classical approach) o Full employment level of national income o Equilibrium level of national income o Inflationary gap o Deflationary gap o Diagram illustrating trade/business cycle 2
2 Unit Overview 3.4 Demand-side and supply-side policies * Shifts in the AD curve / demand-side policies o fiscal policy o interest rates as a tool of monetary policy * Shifts in the AS curve / supply-side policies * Strengths and weaknesses of these policies Higher level only: * Multiplier o calculation of multiplier * Accelerator * "Crowding out" 3.5 Unemployment and inflation Unemployment * Full employment and underemployment * Unemployment rate * Costs of unemployment * Types of unemployment o structural o frictional o seasonal o cyclical/demand-deficient o real wage * Measures to deal with unemployment Inflation * Definitions of inflation and deflation * Costs of inflation and deflation * Causes of inflation o cost push o demand pull o excess monetary growth Higher level only: * Methods of measuring inflation * Problems of the methods of measuring inflation * Phillips curve o short-run o long-run * Natural rate of unemployment (NRU) * Non-Accelerating Inflation Rate of Unemployment (NAIRU) 3.6 Distribution of income * Direct taxation * Indirect taxation * Progressive taxation * Proportional taxation * Regressive taxation * Transfer payments Higher level only: * Laffer curve * Lorenz curve and Gini coefficient 4
3 Micro concept >>>>>> Macro equivalent Market Demand Supply Price Quantity Decrease in demand Increase in demand Decrease in supply Increaese in supply Excise (indirect) tax Subsidy Micro vs. Macro Intro to : What is? Welker s Wikinomics Blog» - Trying to see the forest through the trees National Economy Aggregate Demand Aggregate Supply Price level National Output/Income (GDP) Recession and unemployment Inflation Supply shock, stagflation Economic growth Income (direct) tax Government spending 0
4 The circular flow of income - macro version Revisiting the circular flow: The macro circular flow model includes household saving and firm investment, government taxation and spending on G&S, and foreigners who buy exports and sell imports. Injections: Investment and purchase of exports Expenditures / revenue Product market Goods/Services Households Taxes Goods/services Government Taxes Goods/services Firms Factors of productin Resource market Income: W I R P Leakages: Savings and purchase of imports Leakages: The money that leaves the circular flow because it is not being spent on domestic G&S. Injections: Spending that enters the circular flow from external sources i.e. foreign investors and consumers. F
5 The Macroeconomic Objectives In Microeconomics, the objectives are: firms aim to maximize profits consumers aim to maximize utility efficient resource allocation in competitive markets the correction of market failure through government intervention These can be thought of the goals of microeconomics In, the objectives are: 1) 2) 3) 4) Full - employment: Does NOT mean every single person has a job. Means that most people who want to work are working. Some unemploymenet will exist in a healthy economy. Stable prices: This refers not to the prices of individual products, but to the price level in the economy as a whole. A rise in the overall price level is called inflation, a fall is called deflation. Economic growth: The most talked about macroeconomic goal, growth occurs when the total amount of goods and services an economy produces increases from year to year. Income distribution: A nation's income should be somewhat equally distributed between the upper and lower "classes" in society. Some tax systems are designed to achieve more equitable income distribution. G
6 Measuring national income Gross Domestic Product: GDP is the monetary measure of the total market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in one year. Can be thought of as: national income or national output or national expenditures GDP=W+R+I+P GDP=primary output + secondary output + tertiery output GDP=C+I+G+(X-M) Why is GDP important? >>It tells us something about the relative size of different countries' economies >>It is a monetary measure, so it tells us how much income a country earns in a year (assuming everything that is produced is sold). >>When we divide GDP by the populuation, we get GDP per capita, which tells us how many goods and services the average person consumes in a country. >>When real GDP grows more than the population, that tells us that people on average, have more stuff than they did before. >>If you believe that having more stuff makes people better off, then GDP per capita tells us how well off people in society are. IMPLICATIONS: GDP is the most important macroeconomic measurement! H
7 Measuring national income What's included and not included in GDP? GDP includes: GDP includes only final products and services GDP is the value of what has been produced within the borders of a nation over one year, not what was actually sold. GDP Excludes "nonproduction transactions": Purely financial transactions are excluded. >>Public transfer payments, like social security or cash welfare benefits. >>Private transfer payments, like student allowances or alimony payments. >>The sale of stocks and bonds represent a transfer of existing assets (However, the brokers fees are included for services rendered.) Secondhand sales: If I buy a used car in 2008, that sale does not count towards 2008's GDP, because the car was not made in 2008! The price of the car was originally included in the year's GDP when it was produced. I
8 Measuring national income Gross National Product: the total income that is earned by a country's factors of production regardless of where the assets are located. GNP = GDP + net property income from abroad The value of the cars made in a Honda factory in the US count towards Japan's GNP and America's GDP. Bank of America's operations in Japan count towards US GNP and Japan's GDP. Nominal GDP and real GDP: Nominal GDP measures the money value of a nation's output. To measure the REAL value of the nation's output, the value of money must be taken into account. Inflation erodes the value of money and therefore the nation's output. REAL GDP = Nominal GDP adjusted for inflation. J
9 Measuring national income How do we determine Real GDP? We will assume that we live in an economy that produces only one thing, Pizza.. 1. Find Nominal GDP for each year 2. Determine a price index for each year (using the price index formula), 3. Adjust the nominal GDP figures by dividing by the price index (in hundredths). What is a price index? A price index is a measure of the price of a specified collection of goods and services called a, market basket in a given year as compared to the price of an identical basket of goods and services in a reference year. Price index for a given year = Real GDP = Price of a "market basket" of goods in a specific year Price of same "basket" in the base year Nominal GDP Price index (in hundredths) X 100 K
10 Example: Measuring national income 2008: 10 $10/pizza. Nominal GDP = $ : 12 $12/pizza. Nominal GDP = $144 What is the REAL GDP in 2009? Price index= P pizza 2009 = $12 P pizza 2008 = $10 =1.2 x 100 = 120 Nominal GDP in 2009 = 12 x $12 = $144 Real GDP in 2009 = $ = $120 Conclusions: Because the price of pizza's increased by 20% (inflation rate was 20%), the nominal GDP growth of 44% was over-stated. After adjusting for inflation, the nations' growth rate is only 20% 2L
11 Measuring national income GDP: How is it measured? Two methods are used for measuring GDP Expenditures approach: Measures all the spending on final goods and services that has take place during a year. This includes: Personal Consumption (C): the purchase by households of all goods and services Including non-durables: bread, milk, toothpaste, t-shirts, socks, toys, etc... and durables: TVs, computers, cars, refrigerators, etc... and services: dentist visits, haircuts, taxi rides, accountants, lawyers, etc... Gross Private Domestic Investment- (Ig) All final purchases of machinery, equipment, and tools by businesses. All construction (including residential). Changes in business inventory. >>If total output exceeds current sales, inventories build up. >>If businesses are able to sell more than they currently produce, this entry will be a negative number. 22
12 Components of GDP, continued... Measuring national income Government Purchases (of consumption goods and capital goods) - (G) Includes spending by all levels of government (federal, state and local). Includes all direct purchases of resources (labor in particular). This entry excludes transfer payments since these outlays do not reflect current production. Net Exports- (Xn) All spending on goods produced in the U.S. must be included in GDP, whether the purchase is made here or abroad. Often goods purchased and measured in the U.S. are produced elsewhere (Imports). Therefore, net exports, (Xn) is the difference: (exports - imports) and can be either a positive or negative number depending on which is the larger amount. Summary: GDP = C + I + G + Xn (X-M) 24
13 Four broad Macroeconomic Goals: Unemployment 1) Full-employment (low unemployment) 2) Price level stability (low inflation) 3) Economic growth (increase in real GDP year on year) 4) Income distribution Measuring unemployment: The unemployment rate is the number of people who are unemployed (actively seeking employment but unable to find work) expressed as a percentage of the total labor force. Labor force: "the economically active population", usually between the ages of Part-time workers are counted as employed. Discouraged workers who want a job, but are not actively seeking one, are not counted as being in the labor force, so they are not part of unemployment statistic. This means that most country's unemployment data is skewed, i.e. it may underestimate the number of people who are truly unemployed. 20
14 Types of unemployment: Unemployment Frictional unemployment consists of those searching for jobs or waiting to take jobs soon; it is regarded as somewhat desirable, because it indicates that there is mobility as people change or seek jobs. Structural unemployment: due to changes in the structure of demand for labor; e.g., when certain skills become obsolete or geographic distribution of jobs changes; examples, Glass blowers were replaced by bottle-making machines., Oil-field workers were displaced when oil demand fell in 1980s, Airline mergers displaced many airline workers in 1980s.,Foreign competition has led to downsizing in U.S. industry and loss of jobs. Cyclical unemployment is caused by the recession phase of the business cycle, which is sometimes called deficient demand unemployment 2F
15 Unemployment Definition of Full Employment : Full employment does not mean zero unemployment. but is equal to the total of frictional and structural unemployment When the economy is at full-employment, the natural rate of unemployment or NRU prevails in the economy. With some unemployment, the economy still has room to grow in the short-run, as there are some workers available for firms to hire if they wish to expand output. The NRU is achieved when labor markets are in balance At this point the economy's potential output is being achieved. The natural rate of unemployment is not fixed, but depends on the demographic makeup of the labor force and the laws and customs of the nations. Historically, Western European nations have a higher NRU than the USand East Asian economies WHY? Better "social safety net" in Western Europe means that when workers are unemployed, they receive more government support and benefits. The incentive is not as strong in such economies to seek employment than in countries with few social safety nets. In the US, unemployment benefits expire after only 3 months of collecting them. The incentive, therefore, is to find work as quickly as possible in the US, whereas in France unemployment benefits can be collected for much longer. 2G
16 Unemployment Economic cost of unemployment: GDP gap and Okun s Law: GDP gap is the difference between potential and actual GDP. >>Economist Okun quantified relationship between unemployment and GDP as follows: For every 1 percent of unemployment above the natural rate, a 2 percent GDP gap occurs. This has become known as Okun s law. Unequal burdens of unemployment exist. Examples: >>Rates are lower for white-collar workers than blue-collar, >>teenagers have the highest rates, >>blacks have higher rates than whites, >>less educated workers, on average, have higher unemployment rates than workers with more education. Non-economic costs include loss of self-respect and social and political unrest. 2H
17 Inflation Measuring Inflation: Inflation is defined as a persistent increase in the average price level in the economy, usually measured through the calculation of a consumer price index (CPI) Rate of inflation This year s CPI - last year s CPI = X 100 Last year s CPI Example: Assume our economy produces only pizzas. Therefore, the "basket of goods" our CPI will use consists of one pizza. In a real economy the basket of goods would be made up of hundreds of consumer products from utilities to automobiles to petrol to shoes and electronics. 2008: P pizza = $ : P pizza = $12 Rate of inflation = X 100 = 20% 2I
18 Inflation Degrees of inflation: Not all inflation is bad. Some inflation is considered an indication of a healthily growing economy. However, high inflation is clearly undesirable as it erodes the value of people's incomes and the nation's output. Single digit inflation is called moderate inflation. Rapid inflation of double digits is called galloping inflation Extremely high inflation exceeding 50% per month, is called hyperinflation. Deflation: A persistent fall in the average level of prices in the economy. Deflation sounds like a good thing at first because it means the real values of people's incomes are rising. However, deflation leads to a disincentive for firms to increase production, meaning they will cut back output, lay off workers, leading to a recession and rising unemployment. the Rule of 70 : 70 / inflation rate = # years for the price level to double) Interpretation: In a country experiencing 5% inflation, the price level will double in only 14 years. If inflation reaches 10%, prices will double in only 7 years. 2J
19 Inflation Causes and theories of inflation: Demand-pull inflation: an excess of total spending beyond the economy s capacity to produce. When resources are already fully employed, firms cannot respond to increases in demand. Too much spending chasing too few goods. Cost-push or supply-side inflation: Prices rise because of rise in per-unit production costs (Unit cost = total input cost/units of output). >>Wage-push can occur as result of union strength. And Supply shocks may occur with unexpected increases in the price of raw materials. >>Cost push; experience has shown that rising prices and unemployment can exist together, it is called stagflation Complexities: It is difficult to distinguish between demand-pull and costpush causes of inflation, although cost-push will die out in a recession if spending does not also rise. 2K
20 Inflation The Output Effects of Inflation Cost-push inflation, where resource prices rise unexpectedly, could cause both output and employment to decline. Real income falls. Real income is nominal income /price index Mild inflation (<3%) has uncertain effects. It may be a healthy by-product of a prosperous economy, or it may have an undesirable impact on real income. Danger of creeping inflation turning into hyperinflation, which can cause speculation, reckless spending, and more inflation The Redistributive effects of inflation: Who is hurt? 1. Fixed-income groups will be hurt because their real income suffers. Their nominal income does not rise with prices. 2. Savers will be hurt by unanticipated inflation, because interest rate returns may not cover the cost of inflation. 3. Creditors: Unanticipated inflation hurts creditors. Who benefits? Debtors (borrowers) Interest payments may be less than the inflation rate Is there any cushioning for inflation built into the economy? If inflation is anticipated, the effects of inflation may be less severe, >>since wage and pension contracts may have inflation clauses built in >>interest rates will be high enough to cover the cost of inflation to savers Ex; Inflation premium is amount that interest rate is raised to cover effects of anticipated inflation. >> Real interest rate is defined as nominal rate minus inflation premium. 4L
21 Economic Growth Measuring economic growth: Economic growth is achieved when there is an increase in a nation's real income and output in a given year. GDP Growth rate = Real GDP in year 2 - Real GDP in year 1 Real GDP in year 1 Example: Switzerland's real GDP in 2008: $309 billion Switzerland's real GDP in 2007: $305 billion X b - 303b Switzerland's GDP growth rate =.019 X 100 = 1.9% 305b Per-capita economic growth: If population grows faster than GDP, then the average person may be worse off even with real economic growth. Example: If real GDP increases by 3% while population increases by 2%, then real GDP per capita has only increased by 1% 42
22 Measuring Economic Goals PPC analysis of Macroeconomic goals: The simple production possibilities curve can be used to illustrate three of the economic goals Switzerland Consumer goods A B Full-employment output: The economy is producing just inside its PPC, the NRU prevailes D C Economic growth: A point beyond the nation's PPC represents what could be attained through economic growth Inflationary gap: The economy is producing beyond fullemployment at less than NRU. Competition for workers puts upward pressure on prices. Deflationary gap: when the economy is producing below fullemployment. Low aggregate demand and high unemployment puts downward pressure on prices Capital goods Practice Measuring Macroeconomic Goals: NCEE activity 11 44
23 Income Distribution Measuring Income distribution: the Lorenz Curve. The Lorenz curve is a graphical representation of the income distribution of a country. Organizes a country's households into the richest 20% down to the poorest 20% Determines what percentage of national income is received by each group. Graphs the data with % of total income on the Y-axis, % of total population on the X- axis % of total income Lorenz Curve line of absolute equality % of total population Country 1st 20% 2nd 20% 3rd 20% 4th 20% 5th 20% Gini index Australia Brazil Croatia Hungary Sierra Leone
24 Income Distribution Practice with the Lorenz Curve: In the graphs below, illustrate the Lorenz curves for a country with relatively equal income distribution and one for a country with relatively unequal income distribution 100 Lorenz Curve relatively equal income distribution 100 Lorenz Curve relatively unequal income distribution % of total income line of absolute equality % of total income line of absolute equality % of total population % of total population 4F
25 Shortcomings of GDP: GDP is reasonable and useful in measuring how well or poorly the economy is performing but it has some shortcomings: certain important work is left out of accounting (homemakers, labor of carpenters who make own homes because GDP measures only the MARKET VALUE of output. GDP therefore is understated. Our accounting system does not take reflect that we work less hours than in past years (1900 avg was 53 hours) and that we have more leisure time Does not reflect improved product quality Does not include the underground economy Evaluating GDP GDP does not put a market value/cost on the environment. Higher GDP may be accompanied by negative externalities, which are NOT subtracted from GDP. GDP does not tell us if the best combo of G and S are produced, weighs G and S equally, a rifle and encyclopedias are assigned equal weight. Nor does it measure how GDP is distributed in among the population GDP does not measure the total well being, happiness, a reduction of crime or better relationships with society, with other countries, etc... 4G
26 Discussion Questions: Measuring Economic Goals 1) How can only half the people in a country be working, and the unemployment rate be only 5%? Explain. 2) How can you get paid 5% more this year than last year, but actually experience a fall in real wages? Explain. 3) When the economy is at full-employment, the unemployment rate is ZERO. True or false, explain. 4) Because policymakers understand so much about macroeconomics, modern economies will always experience economic growth. True or false, explain. 4H
27 the Business Cycle Four phases of the business cycle are identified over a several-year period: 1.A boom is when business activity reaches a temporary maximum with full employment and near-capacity output. 2.A recession is a decline in total output, income, employment, and trade lasting six months or more. 3.The trough is the bottom of the recession period. 4.Recovery is when output and employment are expanding toward fullemployment level. Level of real output Boom Recession the Business Cycle Boom Expansion Boom Trough Recession Expansion Trough Theories about causation: Time Major innovations may trigger new investment and/or consumption spending. Changes in productivity may be a related cause. Most agree that the level of aggregate spending is important, especially changes on capital goods and consumer durables. Cyclical fluctuations: Durable goods output is more unstable than non-durables and services because spending on latter usually can not be postponed. 4I
28 !""#$%&'(") *#$+,'$,(,&-$./(0-$#",+).1,+23,,245("
ECON 201. The Business Cycle. Business Cycle 4 phases 10/1/2009. Chapter 6 Business Cycles, Unemployment, & Inflation
 ECON 201 Chapter 6 Business Cycles, Unemployment, & Inflation The Business Cycle The U.S. has experienced economic instability associated with business cycles. Business Cycles alternating rises and declines
ECON 201 Chapter 6 Business Cycles, Unemployment, & Inflation The Business Cycle The U.S. has experienced economic instability associated with business cycles. Business Cycles alternating rises and declines
Chapter 7 Introduction to Economic Growth and Instability
 Chapter 7 Introduction to Economic Growth and Instability Chapter Overview This chapter previews economic growth, the business cycle, unemployment, and inflation. It sets the stage for the analytical presentation
Chapter 7 Introduction to Economic Growth and Instability Chapter Overview This chapter previews economic growth, the business cycle, unemployment, and inflation. It sets the stage for the analytical presentation
Figure Sarver
 I. Learning Objectives In this chapter students will learn: A. About the business cycle and its primary phases. B. How unemployment and inflation are measured. C. About the types of unemployment and inflation
I. Learning Objectives In this chapter students will learn: A. About the business cycle and its primary phases. B. How unemployment and inflation are measured. C. About the types of unemployment and inflation
Introduction to Economic Growth and Instability
 on C H A P T E R Introduction to Economic Growth and Instability 8-1 ECONOMIC GROWTH Economic Growth on 8-2 An increase in real GDP over some time period An increase in real GDP per capita over some time
on C H A P T E R Introduction to Economic Growth and Instability 8-1 ECONOMIC GROWTH Economic Growth on 8-2 An increase in real GDP over some time period An increase in real GDP per capita over some time
AP Macroeconomics - Mega Macro Review Sheet Answers
 AP Macroeconomics - Mega Macro Review Sheet Answers 1. The business cycle. 2. Aggregate supply curve (with breakdown of sections). 3. Expansionary ( easy ) monetary policy (Buy bonds, discount rate, reserve
AP Macroeconomics - Mega Macro Review Sheet Answers 1. The business cycle. 2. Aggregate supply curve (with breakdown of sections). 3. Expansionary ( easy ) monetary policy (Buy bonds, discount rate, reserve
AP Macroeconomics Graphical Overview
 AP Macroeconomics Graphical Overview 1. The business cycle. 2. Aggregate supply curve (with breakdown of sections). 3. Expansionary ( easy ) monetary policy (Buy bonds, discount rate, reserve requirement).
AP Macroeconomics Graphical Overview 1. The business cycle. 2. Aggregate supply curve (with breakdown of sections). 3. Expansionary ( easy ) monetary policy (Buy bonds, discount rate, reserve requirement).
Dunbar s Big Review Sheet AP Macroeconomics Exam Content Area [Hubbard Textbook pages] (percentage coverage on AP Macroeconomics Exam) I.
![Dunbar s Big Review Sheet AP Macroeconomics Exam Content Area [Hubbard Textbook pages] (percentage coverage on AP Macroeconomics Exam) I. Dunbar s Big Review Sheet AP Macroeconomics Exam Content Area [Hubbard Textbook pages] (percentage coverage on AP Macroeconomics Exam) I.](/thumbs/77/76534172.jpg) Dunbar s Big Review Sheet AP Macroeconomics Exam Content Area [Hubbard Textbook pages] (percentage coverage on AP Macroeconomics Exam) I. Basic Economic Concepts (8-12%) Three Fundamental Questions [8]:
Dunbar s Big Review Sheet AP Macroeconomics Exam Content Area [Hubbard Textbook pages] (percentage coverage on AP Macroeconomics Exam) I. Basic Economic Concepts (8-12%) Three Fundamental Questions [8]:
Chapter 6 GDP, Unemployment and Inflation
 Chapter 6 GDP, Unemployment and Inflation - Microeconomics: study of how households and firms make choices & how they interact in markets. - Macroeconomics: study of the economy as a whole, including topics
Chapter 6 GDP, Unemployment and Inflation - Microeconomics: study of how households and firms make choices & how they interact in markets. - Macroeconomics: study of the economy as a whole, including topics
Unit 3.3 Macroeconomic Models Unit Overview
 Unit 3.3 Unit Overview 3.3 Macroeconomic models Aggregate demand - components Aggregate supply >>short-run >>long-run (Keynesian versus neo-classical approach) Full employment level of national income
Unit 3.3 Unit Overview 3.3 Macroeconomic models Aggregate demand - components Aggregate supply >>short-run >>long-run (Keynesian versus neo-classical approach) Full employment level of national income
ECF2331 Final Revision
 Table of Contents Week 1 Introduction to Macroeconomics... 5 What Macroeconomics is about... 5 Macroeconomics 5 Issues addressed by macroeconomists 5 What Macroeconomists Do... 5 Macro Research 5 Develop
Table of Contents Week 1 Introduction to Macroeconomics... 5 What Macroeconomics is about... 5 Macroeconomics 5 Issues addressed by macroeconomists 5 What Macroeconomists Do... 5 Macro Research 5 Develop
Introduction to Economic Growth, Unemployment, and Inflation McGraw-Hill Ryerson Ltd. Macroeconomics, Chapter 6 1
 Introduction to Economic Growth, Unemployment, and Inflation 2005 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Ltd. Macroeconomics, Chapter 6 1 In this chapter you will learn 6.1 The definition and causes of economic growth 6.2
Introduction to Economic Growth, Unemployment, and Inflation 2005 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Ltd. Macroeconomics, Chapter 6 1 In this chapter you will learn 6.1 The definition and causes of economic growth 6.2
Unemployment Inflation
 See webnotes: 235 236 237 238 2.3 Big Ideas Unemployment Inflation Read the syllabus items to understand the IB focus for this economic theory! Growth Distribution Big Idea Big Idea Big Idea Big Idea Big
See webnotes: 235 236 237 238 2.3 Big Ideas Unemployment Inflation Read the syllabus items to understand the IB focus for this economic theory! Growth Distribution Big Idea Big Idea Big Idea Big Idea Big
MEASURING ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE PRODUCT MARKET
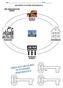 Name: Period THE CIRCULAR FLOW MODEL MEASURING ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE PRODUCT MARKET BUSINESSES HOUSEHOLDS RESOURCE MARKET 1. AKA: 2. 3. Additional Notes on Previous Page/Practice Workspace Quick Write Space
Name: Period THE CIRCULAR FLOW MODEL MEASURING ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE PRODUCT MARKET BUSINESSES HOUSEHOLDS RESOURCE MARKET 1. AKA: 2. 3. Additional Notes on Previous Page/Practice Workspace Quick Write Space
What is Macroeconomics?
 MACRO ECONOMICS 1 What is Macroeconomics? Macroeconomics is the study of the large economy as a whole. It is the study of the big picture. Instead of analyzing one consumer, we analyze everyone. Instead
MACRO ECONOMICS 1 What is Macroeconomics? Macroeconomics is the study of the large economy as a whole. It is the study of the big picture. Instead of analyzing one consumer, we analyze everyone. Instead
The Aggregate Expenditures Model. A continuing look at Macroeconomics
 The Aggregate Expenditures Model A continuing look at Macroeconomics The first macroeconomic model The Aggregate Expenditures Model What determines the demand for real domestic output (GDP) and how an
The Aggregate Expenditures Model A continuing look at Macroeconomics The first macroeconomic model The Aggregate Expenditures Model What determines the demand for real domestic output (GDP) and how an
IB Economics Unit 2: Macroeconomics. Class Assignments: Week #11
 IB Economics Unit 2: Class Assignments: Week #11 Monday November 9, 2015 Read & Discuss: 11.1 The Circular Flow Model of Income pages 234-237 Explain: The Circular Flow Diagram on page 236 (put in your
IB Economics Unit 2: Class Assignments: Week #11 Monday November 9, 2015 Read & Discuss: 11.1 The Circular Flow Model of Income pages 234-237 Explain: The Circular Flow Diagram on page 236 (put in your
Basic Concepts. MICROECONOMICS: deals with specific economic units and a detailed consideration of these individual units.
 Basic Concepts ECONOMICS: The study of how limited productive resources are efficiently allocated in a world of unlimited wants. SCARCITY: WANTS EXCEED RESOURCES We want more than we are capable of getting.
Basic Concepts ECONOMICS: The study of how limited productive resources are efficiently allocated in a world of unlimited wants. SCARCITY: WANTS EXCEED RESOURCES We want more than we are capable of getting.
APE Unit 3 UGRP: Intro to Macroeconomics
 /40 UGRP Score: /10 UEQ Score: Name Date Period Time: 2.5 Weeks APE Unit 3 UGRP: Intro to Macroeconomics /50 Total Score Anchor Text and Video: Please visit: https://www.federalreserve.gov/faqs/what-is-macroeconomics.htm
/40 UGRP Score: /10 UEQ Score: Name Date Period Time: 2.5 Weeks APE Unit 3 UGRP: Intro to Macroeconomics /50 Total Score Anchor Text and Video: Please visit: https://www.federalreserve.gov/faqs/what-is-macroeconomics.htm
A. unchanged decrease B. surplus decrease C. unchanged no change D. surplus increase E. unchanged increase A. A B. B C. C D. D E. E.
 AP Macroeconomics Test (Answers on last Page) 1. Which of the following correctly describes the components of Aggregate Demand? A. Consumption expenditures + Investment expenditures + Government expenditures
AP Macroeconomics Test (Answers on last Page) 1. Which of the following correctly describes the components of Aggregate Demand? A. Consumption expenditures + Investment expenditures + Government expenditures
AS Economics: ECON2 Economics: The National Economy 2009/10
 2 weeks 1 st Sep - 11 th Sep Term 1 Introduction to the objectives and instruments of government This is an introduction to 3.2.3, 3.2.1 macroeconomic policy the Unit and most of the content Candidates
2 weeks 1 st Sep - 11 th Sep Term 1 Introduction to the objectives and instruments of government This is an introduction to 3.2.3, 3.2.1 macroeconomic policy the Unit and most of the content Candidates
Unit 6 Measuring and Monitoring Economics (Ch 12 and 13)
 Unit 6 Measuring and Monitoring Economics (Ch 12 and 13) -Macroeconomics 0 & Microeconomics- Government tries to prevent free enterprise from having wild swings in economic behavior. Microeconomics - analyzes
Unit 6 Measuring and Monitoring Economics (Ch 12 and 13) -Macroeconomics 0 & Microeconomics- Government tries to prevent free enterprise from having wild swings in economic behavior. Microeconomics - analyzes
ECC Macroeconomics Summary Notes
 ECC1100 - Macroeconomics Summary Notes Contents General Definitions... 3 Australia s National and International Accounts... 4 Nominal and Real GDP... 4 Balance of Payment Accounts... 5 Other National Accounting
ECC1100 - Macroeconomics Summary Notes Contents General Definitions... 3 Australia s National and International Accounts... 4 Nominal and Real GDP... 4 Balance of Payment Accounts... 5 Other National Accounting
Principles of Macroeconomics December 17th, 2005 name: Final Exam (100 points)
 EC132.02 Serge Kasyanenko Principles of Macroeconomics December 17th, 2005 name: Final Exam (100 points) This is a closed-book exam - you may not use your notes and textbooks. Calculators are not allowed.
EC132.02 Serge Kasyanenko Principles of Macroeconomics December 17th, 2005 name: Final Exam (100 points) This is a closed-book exam - you may not use your notes and textbooks. Calculators are not allowed.
Revision Sheets. AS Economics National Economy in a Global Context. Revision Sheets
 2018 http://www.publicdomainpictures.net/pictures/150000/velka/uk-map.jpg AS Economics National Economy in a Global Context Macroeconomic Objectives Low unemployment Improve external performance Objectives
2018 http://www.publicdomainpictures.net/pictures/150000/velka/uk-map.jpg AS Economics National Economy in a Global Context Macroeconomic Objectives Low unemployment Improve external performance Objectives
Economics is the study of decision making
 TOPIC 1 - INTRODUCTION TO THE GLOBAL ECONOMY WHAT IS ECONOMICS Economics is the study of decision making Every time we take a decision, we are choosing between at least two possibilities How do you take
TOPIC 1 - INTRODUCTION TO THE GLOBAL ECONOMY WHAT IS ECONOMICS Economics is the study of decision making Every time we take a decision, we are choosing between at least two possibilities How do you take
Garden City High School Course: AP Macroeconomics
 Garden City High School Course: AP Macroeconomics Instructional Philosophy The Advanced Placement Macroeconomics curriculum is a full year program designed to provide both an overview of economics. Economics
Garden City High School Course: AP Macroeconomics Instructional Philosophy The Advanced Placement Macroeconomics curriculum is a full year program designed to provide both an overview of economics. Economics
1. What was the unemployment rate in December 2001?
 EC2105, Spring 2002 Weekly Quiz 1 (January 16, 2002) 1. What was the unemployment rate in December 2001? 2. When the Fed meets later this month and decides whether to lower interest rates, it is conducting:
EC2105, Spring 2002 Weekly Quiz 1 (January 16, 2002) 1. What was the unemployment rate in December 2001? 2. When the Fed meets later this month and decides whether to lower interest rates, it is conducting:
Unit Two, Day One (pages , )
 Unit Two, Day One (pages 860-889, 585-608) What is the difference between macro and micro? National Debt v. Deficit (NOT THE SAME THING) National Debt Deficit In the circular flow the seller receives exactly
Unit Two, Day One (pages 860-889, 585-608) What is the difference between macro and micro? National Debt v. Deficit (NOT THE SAME THING) National Debt Deficit In the circular flow the seller receives exactly
CURRICULUM COURSE OUTLINE
 CURRICULUM COURSE OUTLINE Course Name(s): Grade(s): 11-12 Department: Course Length: Pre-requisite: Macroeconomics Social Studies 1 Semester Microeconomics Textbook/Key Resource: McConnell and Brue. Macroeconomics
CURRICULUM COURSE OUTLINE Course Name(s): Grade(s): 11-12 Department: Course Length: Pre-requisite: Macroeconomics Social Studies 1 Semester Microeconomics Textbook/Key Resource: McConnell and Brue. Macroeconomics
Disclaimer: This resource package is for studying purposes only EDUCATION
 Disclaimer: This resource package is for studying purposes only EDUCATION Ch 26: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Aggregate Supply Purpose of aggregate supply: aggregate demand model is to explain
Disclaimer: This resource package is for studying purposes only EDUCATION Ch 26: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Aggregate Supply Purpose of aggregate supply: aggregate demand model is to explain
Answers and Explanations
 Answers and Explanations 1. The correct answer is (E). A change in the composition of output causes a movement along the production possibilities curve. A shift in the curve is caused by changes in technology,
Answers and Explanations 1. The correct answer is (E). A change in the composition of output causes a movement along the production possibilities curve. A shift in the curve is caused by changes in technology,
INDIAN HILL EXEMPTED VILLAGE SCHOOL DISTRICT Social Studies Curriculum - May 2009 AP Economics
 Course Description: This full-year college-level course begins with basic economic concepts and proceeds to examine both microeconomics and macroeconomics in greater detail. There are five units which
Course Description: This full-year college-level course begins with basic economic concepts and proceeds to examine both microeconomics and macroeconomics in greater detail. There are five units which
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Questions of this SAMPLE exam were randomly chosen and may NOT be representative of the difficulty or focus of the actual examination. The professor did NOT review these questions. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose
Questions of this SAMPLE exam were randomly chosen and may NOT be representative of the difficulty or focus of the actual examination. The professor did NOT review these questions. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose
Economic Growth, Business Cycles, Unemployment, and Inflation
 CHAPTER 24 Economic Growth, Business Cycles, Unemployment, and Inflation Remember that there is nothing stable in human affairs; therefore avoid undue elation in prosperity, or undue depression in adversity.
CHAPTER 24 Economic Growth, Business Cycles, Unemployment, and Inflation Remember that there is nothing stable in human affairs; therefore avoid undue elation in prosperity, or undue depression in adversity.
3. The phase of the business cycle in which real GDP is at a minimum is called: A. the peak. B. a recession. C. the trough. D. the underside.
 1. Most economists agree that the immediate determinant of the volume of output and employment is the: A. composition of consumer spending. B. ratio of public goods to private goods production. C. level
1. Most economists agree that the immediate determinant of the volume of output and employment is the: A. composition of consumer spending. B. ratio of public goods to private goods production. C. level
EXPENDITURE APPROACH: The expenditures on all final goods and services made by all sectors of the economy are added to calculate GDP. Expenditures are
 Chapter 1 MEASURING GDP AND PRICE LEVEL MEASURING EONOMIC ACTIVITY Macroeconomics studies the aggregate (or total) concept of economic activity. Its focus is on the aggregate output, the aggregate income,
Chapter 1 MEASURING GDP AND PRICE LEVEL MEASURING EONOMIC ACTIVITY Macroeconomics studies the aggregate (or total) concept of economic activity. Its focus is on the aggregate output, the aggregate income,
CIE Economics A-level
 CIE Economics A-level Topic 4: The Macroeconomy d) Employment and unemployment Notes Size and components of labour force The working age population is between the ages of 18 and 65 who are actively looking
CIE Economics A-level Topic 4: The Macroeconomy d) Employment and unemployment Notes Size and components of labour force The working age population is between the ages of 18 and 65 who are actively looking
AP Macroeconomics Syllabus Course Outline Required text: Economics: Principles, Problems, and Policies McConnel and Brue 15 th edition
 AP Macroeconomics Mrs. Cook 1 st Period Room 210 AP Macroeconomics Syllabus Course Outline Required text: Economics: Principles, Problems, and Policies McConnel and Brue 15 th edition Unit One: Basic Economic
AP Macroeconomics Mrs. Cook 1 st Period Room 210 AP Macroeconomics Syllabus Course Outline Required text: Economics: Principles, Problems, and Policies McConnel and Brue 15 th edition Unit One: Basic Economic
INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA UNIVERSITY FOUNDATION PROGRAMME ECO 183 : FOUNDATION ECONOMICS (MACROECONOMICS) RESIT EXAMINATION : AUGUST 2002 SESSION
 ECO 183 (R) / Page 1 of 9 INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA UNIVERSITY FOUNDATION PROGRAMME ECO 183 : FOUNDATION ECONOMICS (MACROECONOMICS) RESIT EXAMINATION : AUGUST 2002 SESSION Section A : Answer ALL questions.
ECO 183 (R) / Page 1 of 9 INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA UNIVERSITY FOUNDATION PROGRAMME ECO 183 : FOUNDATION ECONOMICS (MACROECONOMICS) RESIT EXAMINATION : AUGUST 2002 SESSION Section A : Answer ALL questions.
FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE
 AP MACROECONOMICS-2018 Name: FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Instructions: DUE: Day of FINAL EXAM => Friday 12/21 st (1 st & 2 nd Periods) Thursday 12/20 th (4 th period) Section 1: PRODUCTION POSSIBLITIES FRONTIER
AP MACROECONOMICS-2018 Name: FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Instructions: DUE: Day of FINAL EXAM => Friday 12/21 st (1 st & 2 nd Periods) Thursday 12/20 th (4 th period) Section 1: PRODUCTION POSSIBLITIES FRONTIER
Principles of Macroeconomics December 15th, 2005 name: Final Exam (100 points)
 EC132.01 Serge Kasyanenko Principles of Macroeconomics December 15th, 2005 name: Final Exam (100 points) This is a closed-book exam - you may not use your notes and textbooks. Calculators are not allowed.
EC132.01 Serge Kasyanenko Principles of Macroeconomics December 15th, 2005 name: Final Exam (100 points) This is a closed-book exam - you may not use your notes and textbooks. Calculators are not allowed.
Macroeconomics, Spring 2007, Final Exam, several versions, Early May
 Name: _ Days/Times Class Meets: Today s Date: Macroeconomics, Spring 2007, Final Exam, several versions, Early May Read these Instructions carefully! You must follow them exactly! I) On your Scantron card
Name: _ Days/Times Class Meets: Today s Date: Macroeconomics, Spring 2007, Final Exam, several versions, Early May Read these Instructions carefully! You must follow them exactly! I) On your Scantron card
MACROECONOMICS - CLUTCH CH UNEMPLOYMENT AND INFLATION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: LABOR FORCE AND UNEMPLOYMENT Tracking levels of employment within an economy gives meaningful data regarding the nation s productivity Labor Force the total number of workers,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: LABOR FORCE AND UNEMPLOYMENT Tracking levels of employment within an economy gives meaningful data regarding the nation s productivity Labor Force the total number of workers,
Midterm #2, version A, given Spring 2002 Note question #50 is from Chapter 11, which students are not responsible for on Exam 2 - Summer 02.
 Midterm #2, version A, given Spring 2002 Note question #50 is from Chapter 11, which students are not responsible for on Exam 2 - Summer 02. Answers (if you think you see an error, please contact me ASAP.
Midterm #2, version A, given Spring 2002 Note question #50 is from Chapter 11, which students are not responsible for on Exam 2 - Summer 02. Answers (if you think you see an error, please contact me ASAP.
2.1 Economic activity The level of overall economic activity
 2.1 Economic activity The level of overall economic activity Learning Outcomes Describe, using a diagram, the circular flow of income between households and firms in a closed economy with no government.
2.1 Economic activity The level of overall economic activity Learning Outcomes Describe, using a diagram, the circular flow of income between households and firms in a closed economy with no government.
2/14/2008. The circular flow of goods and incomes. firms and households. goods markets. Goods and services. real flows: goods and services
 The circular flow of income Chapter 22 Introduction to Macroeconomics Economics, 4 th edition Stiglitz & Walsh firms and households goods markets real flows: goods and services The Economic Problem Goods
The circular flow of income Chapter 22 Introduction to Macroeconomics Economics, 4 th edition Stiglitz & Walsh firms and households goods markets real flows: goods and services The Economic Problem Goods
Economics Unit 3 Summary
 SSEMA1 Illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. Economic activity derives from the sectors of the economy explored in the fundamentals and microeconomics units. Individuals, businesses,
SSEMA1 Illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. Economic activity derives from the sectors of the economy explored in the fundamentals and microeconomics units. Individuals, businesses,
Model Question Paper Economics - II (MSF1A4)
 Model Question Paper Economics - II (MSF1A4) Answer all 74 questions. Marks are indicated against each question. 1. Which of the following is true if the central bank of a country sells government securities
Model Question Paper Economics - II (MSF1A4) Answer all 74 questions. Marks are indicated against each question. 1. Which of the following is true if the central bank of a country sells government securities
HCCS 2011 REVIEW FOR TEST II Covering chapters from Case, Fair, Oster text. GDP and the Standard of Living
 HCCS 2011 REVIEW FOR TEST II Covering chapters 20 -- 24 from Case, Fair, Oster text GDP and the Standard of Living What is Gross Domestic Product and how is it measured? Expenditure Approach (C+I+G+NX)
HCCS 2011 REVIEW FOR TEST II Covering chapters 20 -- 24 from Case, Fair, Oster text GDP and the Standard of Living What is Gross Domestic Product and how is it measured? Expenditure Approach (C+I+G+NX)
Chapter 7 Unemployment, Inflation, and Long-Run Growth
 Chapter 7 Unemployment, Inflation, and Long-Run Growth 7.1 Unemployment 1 Multiple Choice 1) We can safely say that total output can increase if there is a(n) A) increase in the size of the labor force
Chapter 7 Unemployment, Inflation, and Long-Run Growth 7.1 Unemployment 1 Multiple Choice 1) We can safely say that total output can increase if there is a(n) A) increase in the size of the labor force
In recessions the aggregate demand of economies falls. John Maynard Keynes
 In recessions the aggregate demand of economies falls. John Maynard Keynes Disposable Income (YD) Autonomous Consumption + Consumption = $50 + 0.75YD Dependent Income- = Consumption Total Consumption A
In recessions the aggregate demand of economies falls. John Maynard Keynes Disposable Income (YD) Autonomous Consumption + Consumption = $50 + 0.75YD Dependent Income- = Consumption Total Consumption A
MACROECONOMICS. Section I Time 70 minutes 60 Questions
 MACROECONOMICS Section I Time 70 minutes 60 Questions Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or completions. Select the one that is best
MACROECONOMICS Section I Time 70 minutes 60 Questions Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or completions. Select the one that is best
Name: Days/Times Class Meets: Today s Date:
 Name: _ Days/Times Class Meets: Today s Date: Macroeconomics, Spring 2008 Exam 3, TTh classes, various versions Read these Instructions carefully! You must follow them exactly! I) On your Scantron card
Name: _ Days/Times Class Meets: Today s Date: Macroeconomics, Spring 2008 Exam 3, TTh classes, various versions Read these Instructions carefully! You must follow them exactly! I) On your Scantron card
Unit 3: Aggregate Demand and Supply and Fiscal Policy
 Unit 3: Aggregate Demand and Supply and Fiscal Policy 1 Aggregate Demand 2 What is Aggregate Demand? Aggregate means added all together. When we use aggregates we combine all prices and all quantities.
Unit 3: Aggregate Demand and Supply and Fiscal Policy 1 Aggregate Demand 2 What is Aggregate Demand? Aggregate means added all together. When we use aggregates we combine all prices and all quantities.
FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE
 AP MACROECONOMICS-2017 Name: FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Instructions: DUE: Day of FINAL EXAM => Friday 12/22 nd (1 st & 2 nd Periods) Thursday 12/21 st (4 th period) Section 1: PRODUCTION POSSIBLITIES FRONTIER
AP MACROECONOMICS-2017 Name: FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Instructions: DUE: Day of FINAL EXAM => Friday 12/22 nd (1 st & 2 nd Periods) Thursday 12/21 st (4 th period) Section 1: PRODUCTION POSSIBLITIES FRONTIER
AP Macroeconomics review. By: Maria Villasmil. Economis: The study of how people, firms, and government make decisions when faced with scarcity.
 AP Macroeconomics review By: Maria Villasmil Economis: The study of how people, firms, and government make decisions when faced with scarcity. Factors of Production: 1)Land: natural resources 2) Labor:
AP Macroeconomics review By: Maria Villasmil Economis: The study of how people, firms, and government make decisions when faced with scarcity. Factors of Production: 1)Land: natural resources 2) Labor:
Objectives of Macroeconomics ECO403
 Objectives of Macroeconomics ECO403 http//vustudents.ning.com Actual budget The amount spent by the Federal government (to purchase goods and services and for transfer payments) less the amount of tax
Objectives of Macroeconomics ECO403 http//vustudents.ning.com Actual budget The amount spent by the Federal government (to purchase goods and services and for transfer payments) less the amount of tax
EC and MIDTERM EXAM I. March 26, 2015
 EC102.03 and 102.05 Spring 2015 Instructions: MIDTERM EXAM I March 26, 2015 NAME: ID #: You have 80 minutes to complete the exam. There will be no extensions. The exam consists of 40 multiple choice questions.
EC102.03 and 102.05 Spring 2015 Instructions: MIDTERM EXAM I March 26, 2015 NAME: ID #: You have 80 minutes to complete the exam. There will be no extensions. The exam consists of 40 multiple choice questions.
OUTLINE October 18, Key concepts. Expenditure 10/16/ :53 PM. Focus: Total Expenditure
 OUTLINE October 18, 2017 Expenditure = C + I + G + (EX IM), continued 3 equations you must know Measuring Unemployment Measuring Inflation Key concepts When figuring out IF some activity is counted in
OUTLINE October 18, 2017 Expenditure = C + I + G + (EX IM), continued 3 equations you must know Measuring Unemployment Measuring Inflation Key concepts When figuring out IF some activity is counted in
2.2 Aggregate demand and aggregate supply
 The business cycle Short-term fluctuations and long-term trend Explain, using a business cycle diagram, that economies typically tend to go through a cyclical pattern characterized by the phases of the
The business cycle Short-term fluctuations and long-term trend Explain, using a business cycle diagram, that economies typically tend to go through a cyclical pattern characterized by the phases of the
Indicators of National Econmoy. Ing. Mansoor Maitah Ph.D. et Ph.D.
 Indicators of National Econmoy Ing. Mansoor Maitah Ph.D. et Ph.D. Circular Flows in the Market Economy Describes the flow of resources, products, income, and revenue among the four decision makers (Households;
Indicators of National Econmoy Ing. Mansoor Maitah Ph.D. et Ph.D. Circular Flows in the Market Economy Describes the flow of resources, products, income, and revenue among the four decision makers (Households;
1. The most basic premise of the aggregate expenditures model is that:
 1. The most basic premise of the aggregate expenditures model is that: A. The total output produced in the economy depends directly on the level of total spending B. The level of employment in the economy
1. The most basic premise of the aggregate expenditures model is that: A. The total output produced in the economy depends directly on the level of total spending B. The level of employment in the economy
GDP and The Measurement of Progress
 GDP and The Measurement of Progress What is GDP Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a year. GDP per capita GDP divided by population
GDP and The Measurement of Progress What is GDP Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a year. GDP per capita GDP divided by population
Unemployment and Inflation
 Unemployment and Inflation By A. V. Vedpuriswar October 15, 2016 Inflation This refers to the phenomenon by which the price level rises and money loses value. There are two kinds of inflation: Demand pull
Unemployment and Inflation By A. V. Vedpuriswar October 15, 2016 Inflation This refers to the phenomenon by which the price level rises and money loses value. There are two kinds of inflation: Demand pull
Macroeconomics Unit 1: Basic Economics Concepts
 Macroeconomics Unit 1: Basic Economics Concepts Key Terms- Define the following: 3 Economic Systems 1. Scarcity 1. Centrally Planned Economies Individuals, businesses, and governments have Economic system
Macroeconomics Unit 1: Basic Economics Concepts Key Terms- Define the following: 3 Economic Systems 1. Scarcity 1. Centrally Planned Economies Individuals, businesses, and governments have Economic system
MACROECONOMICS EXAM REVIEW CHAPTERS 5 THROUGH 10
 MACROECONOMICS EXAM REVIEW CHAPTERS 5 THROUGH 10 Key Terms and Concepts to Know CHAPTER 5 FUNDAMENTALS OF MACROECONOMICS I. The National Economy: Economy: the structure of economic life, or economic activity,
MACROECONOMICS EXAM REVIEW CHAPTERS 5 THROUGH 10 Key Terms and Concepts to Know CHAPTER 5 FUNDAMENTALS OF MACROECONOMICS I. The National Economy: Economy: the structure of economic life, or economic activity,
55. The Circular Flow of Income
 55. The Circular Flow of Income 1. Missing words For an economy to be in, injections must be to withdrawals. Injections into the circular flow are made up of investment, and, while withdrawals comprise
55. The Circular Flow of Income 1. Missing words For an economy to be in, injections must be to withdrawals. Injections into the circular flow are made up of investment, and, while withdrawals comprise
ECON 1102: MACROECONOMICS 1 Chapter 1: Measuring Macroeconomic Performance, Output and Prices
 ECON 1102: MACROECONOMICS 1 Chapter 1: Measuring Macroeconomic Performance, Output and Prices 1.1 Measuring Macroeconomic Performance 1. Rising Living Standards Economic growth is the tendency for output
ECON 1102: MACROECONOMICS 1 Chapter 1: Measuring Macroeconomic Performance, Output and Prices 1.1 Measuring Macroeconomic Performance 1. Rising Living Standards Economic growth is the tendency for output
IB Economics Macroeconomic Policies Student activity: 2.10 Low and Stable Rate of Inflation
 Student activity: 2.10 Low and Stable Rate of Inflation IB Economics: www.ibdeconomics.com 2.10 INFLATION: STUDENT LEARNING ACTIVITY Answer the questions that follow. 1. DEFINITIONS Define the following
Student activity: 2.10 Low and Stable Rate of Inflation IB Economics: www.ibdeconomics.com 2.10 INFLATION: STUDENT LEARNING ACTIVITY Answer the questions that follow. 1. DEFINITIONS Define the following
Economics 1012 A : Introduction to Macroeconomics FALL 2007 Dr. R. E. Mueller Second Midterm Examination October 19, 2007
 Economics 1012 A : Introduction to Macroeconomics FALL 2007 Dr. R. E. Mueller Second Midterm Examination October 19, 2007 ================================================================================
Economics 1012 A : Introduction to Macroeconomics FALL 2007 Dr. R. E. Mueller Second Midterm Examination October 19, 2007 ================================================================================
Final Term Papers. Fall 2009 (Session 03a) ECO401. (Group is not responsible for any solved content) Subscribe to VU SMS Alert Service
 Fall 2009 (Session 03a) ECO401 (Group is not responsible for any solved content) Subscribe to VU SMS Alert Service To Join Simply send following detail to bilal.zaheem@gmail.com Full Name Master Program
Fall 2009 (Session 03a) ECO401 (Group is not responsible for any solved content) Subscribe to VU SMS Alert Service To Join Simply send following detail to bilal.zaheem@gmail.com Full Name Master Program
Intro to macroeconomics. Rush October 2014
 Intro to macroeconomics Rush October 2014 Micro means small. Macro means big. We are moving from micro to macro What is microeconomics? Microeconomics is the study of SPECIFIC markets and the behavior
Intro to macroeconomics Rush October 2014 Micro means small. Macro means big. We are moving from micro to macro What is microeconomics? Microeconomics is the study of SPECIFIC markets and the behavior
Week 1. H1 Notes ECON10003
 Week 1 Some output produced by the government is free. Education is a classic example. This is still viewed as a service and valued at the cost of production which is primarily the salary of the workers
Week 1 Some output produced by the government is free. Education is a classic example. This is still viewed as a service and valued at the cost of production which is primarily the salary of the workers
22/03/2012. Inflation Cycles. The 1920s were years of unprecedented prosperity.
 The 1920s were years of unprecedented prosperity. Then, in October 1929, the stock market crashed. Overnight, stock prices fell by 30 percent. The Great Depression began and by 1933, real GDP had fallen
The 1920s were years of unprecedented prosperity. Then, in October 1929, the stock market crashed. Overnight, stock prices fell by 30 percent. The Great Depression began and by 1933, real GDP had fallen
Introduction to Economics. MACROECONOMICS Chapter 3 Business Cycles, Unemployment and Inflation
 Introduction to Economics MACROECONOMICS Chapter 3 Business Cycles, Unemployment and Inflation contents 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 Causes of Business Cycles Reasons for the Insufficiency of Aggregate Demand
Introduction to Economics MACROECONOMICS Chapter 3 Business Cycles, Unemployment and Inflation contents 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 Causes of Business Cycles Reasons for the Insufficiency of Aggregate Demand
MONITORING JOBS AND INFLATION
 21 MONITORING JOBS AND INFLATION After studying this chapter, you will be able to: Explain why unemployment is a problem and define the unemployment rate and other labour market indicators Explain why
21 MONITORING JOBS AND INFLATION After studying this chapter, you will be able to: Explain why unemployment is a problem and define the unemployment rate and other labour market indicators Explain why
Table 9-2. Base Year (2006) 2013 Product Quantity Price Price Milk 50 $2 $3 Bread 100 $3 $3.50
 1) The advice to "keep searching, there are plenty of jobs around here for which you are qualified," would be most appropriate for which of the following types of unemployment? A) frictional unemployment
1) The advice to "keep searching, there are plenty of jobs around here for which you are qualified," would be most appropriate for which of the following types of unemployment? A) frictional unemployment
Advanced Placement Macro Economics
 Advanced Placement Macro Economics Economics is a study of mankind in the ordinary business of life. Alfred Marshall Through the AP Macroeconomics course, students will have a better understanding of the
Advanced Placement Macro Economics Economics is a study of mankind in the ordinary business of life. Alfred Marshall Through the AP Macroeconomics course, students will have a better understanding of the
Chapter 5: Production, Income and Employment
 Chapter 5: Production, Income and Employment We will take our first look at production and employment, focusing on two key variables: Gross Domestic Product and Unemployment Rate The nation s Gross Domestic
Chapter 5: Production, Income and Employment We will take our first look at production and employment, focusing on two key variables: Gross Domestic Product and Unemployment Rate The nation s Gross Domestic
OCR Unit 2. Economics Revision. Judah Chandra
 1 OCR Unit 2 Economics Revision Economics Revision Judah Chandra 2 AD = C + I + G (X - M) KEY TERMS Economic growth - in the short run, an increase in real GDP, and in the long run, an increase in productive
1 OCR Unit 2 Economics Revision Economics Revision Judah Chandra 2 AD = C + I + G (X - M) KEY TERMS Economic growth - in the short run, an increase in real GDP, and in the long run, an increase in productive
Unit 3: Aggregate Demand and Supply and Fiscal Policy
 Unit 3: Aggregate Demand and Supply and Fiscal Policy 1 Demand and Supply Review 1. Define Demand and the Law of Demand. 2. Identify the three concepts that explain why demand is downward sloping. 3. Identify
Unit 3: Aggregate Demand and Supply and Fiscal Policy 1 Demand and Supply Review 1. Define Demand and the Law of Demand. 2. Identify the three concepts that explain why demand is downward sloping. 3. Identify
Measuring the Aggregate Economy
 CHAPTER 25 Measuring the Aggregate Economy The government is very keen on amassing statistics... They collect them, add them, raise them to the n th power, take the cube root and prepare wonderful diagrams.
CHAPTER 25 Measuring the Aggregate Economy The government is very keen on amassing statistics... They collect them, add them, raise them to the n th power, take the cube root and prepare wonderful diagrams.
Macroeconomics, 3e (Williamson) Chapter 2 Measurement
 Macroeconomics, 3e (Williamson) Chapter 2 Measurement 1) The principal printed source for reporting the US National Income and Product Accounts is called the A) Monthly Labor Review B) Survey of Current
Macroeconomics, 3e (Williamson) Chapter 2 Measurement 1) The principal printed source for reporting the US National Income and Product Accounts is called the A) Monthly Labor Review B) Survey of Current
download instant at
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The aggregate supply curve 1) A) shows what each producer is willing and able to produce
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The aggregate supply curve 1) A) shows what each producer is willing and able to produce
ABOUT THE EXAM. Multiple Choice Questions two thirds of total score: Free Response Questions one third of total score:
 ABOUT THE EXAM Multiple Choice Questions two thirds of total score: 60 questions, 70 minutes to complete 1 point each; no penalty for wrong answer Many of the questions are similar to the frqs; for questions
ABOUT THE EXAM Multiple Choice Questions two thirds of total score: 60 questions, 70 minutes to complete 1 point each; no penalty for wrong answer Many of the questions are similar to the frqs; for questions
AP Macroeconomics Formulas and Definitions: Key Formulas
 AP Macroeconomics Formulas and Definitions: Key Formulas 1. Rule of 70: Used to determine how many years it takes for a value to double, given a particular annual growth rate. For example, if you put $20,000
AP Macroeconomics Formulas and Definitions: Key Formulas 1. Rule of 70: Used to determine how many years it takes for a value to double, given a particular annual growth rate. For example, if you put $20,000
Unit 7 Measuring the Economy
 Unit 7 Measuring the Economy - Study Guide - Answer, Explain and define the following: 1) GNP 2) GDP 3) Dept. of Commerce 4) Intermediate goods 5) Disposable personal income 6) Contraction 7) Recession
Unit 7 Measuring the Economy - Study Guide - Answer, Explain and define the following: 1) GNP 2) GDP 3) Dept. of Commerce 4) Intermediate goods 5) Disposable personal income 6) Contraction 7) Recession
ECON 10020/20020 Principles of Macroeconomics Problem Set 2
 ECON 10020/20020 Principles of Macroeconomics Problem Set 2 Dennis C. Plott University of Notre Dame Department of Economics February 2, 2015 Email: dennis.plott@gmail.com 1 Name: 1. Due: Tuesday 10 th
ECON 10020/20020 Principles of Macroeconomics Problem Set 2 Dennis C. Plott University of Notre Dame Department of Economics February 2, 2015 Email: dennis.plott@gmail.com 1 Name: 1. Due: Tuesday 10 th
WJEC (Wales) Economics A-level
 WJEC (Wales) Economics A-level Macroeconomics Topic 2: Macroeconomic Objectives 2.3 Inflation and deflation Notes Inflation is the sustained rise in the general price level over time. This means that the
WJEC (Wales) Economics A-level Macroeconomics Topic 2: Macroeconomic Objectives 2.3 Inflation and deflation Notes Inflation is the sustained rise in the general price level over time. This means that the
Royal School of Administration. Macroeconomics
 Royal School of Administration Macroeconomics Chapter 9 By Group 6 1. Chum Chamreun 2. Sok Piseth 3. Kith Sothearith 4. Sreng Vichhay 5. Lay Piden 6. Chheang Damy IS-MP: A Short-Run Macroeconomic Model
Royal School of Administration Macroeconomics Chapter 9 By Group 6 1. Chum Chamreun 2. Sok Piseth 3. Kith Sothearith 4. Sreng Vichhay 5. Lay Piden 6. Chheang Damy IS-MP: A Short-Run Macroeconomic Model
Name: Econ 112 Test 2
 Name: Econ 112 Test 2 Spring 2005 Dr. Raymond ************************************************************************************************* Part One: Explain the following questions in a clear, very
Name: Econ 112 Test 2 Spring 2005 Dr. Raymond ************************************************************************************************* Part One: Explain the following questions in a clear, very
Macroeconomics, 12e (Gordon) Chapter 2 The Measurement of Income, Prices, and Unemployment
 Macroeconomics, 12e (Gordon) Chapter 2 The Measurement of Income, Prices, and Unemployment 2.1 Why We Care About Income 1) Job openings are plentiful when the A) actual real GDP is above the natural real
Macroeconomics, 12e (Gordon) Chapter 2 The Measurement of Income, Prices, and Unemployment 2.1 Why We Care About Income 1) Job openings are plentiful when the A) actual real GDP is above the natural real
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 These 101 questions have been randomly selected (for the chapters eligible for examination) by the computer from the test bank that accompanies your text. Your prof. has not seen these questions, so as
These 101 questions have been randomly selected (for the chapters eligible for examination) by the computer from the test bank that accompanies your text. Your prof. has not seen these questions, so as
Practice Test 1: Multiple Choice
 Practice Test 1: Multiple Choice 1. If aggregate planned expenditure exceeds real GDP A. actual inventories decrease below their target. B. firms are not maximizing their profits. C. planned consumption
Practice Test 1: Multiple Choice 1. If aggregate planned expenditure exceeds real GDP A. actual inventories decrease below their target. B. firms are not maximizing their profits. C. planned consumption
FINAL EXAM GROUP B. Instructions: EC and EC ID #: Spring May 26, 2015
 EC102.03 and EC 102.05 NAME: ID #: Spring 2015 FINAL EXAM GROUP B May 26, 2015 Instructions: You have 100 minutes to complete the exam. There will be no extensions. The exam consists of 50 multiple choice
EC102.03 and EC 102.05 NAME: ID #: Spring 2015 FINAL EXAM GROUP B May 26, 2015 Instructions: You have 100 minutes to complete the exam. There will be no extensions. The exam consists of 50 multiple choice
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE. -8- Unauthorized copying or reuse of any part of this page is illegal.
 30. Which of the following is most likely to be caused by an adverse supply shock? (A) Structural unemployment (B) Frictional unemployment (C) Demand-pull inflation (D) Cost-push inflation (E) Deflation
30. Which of the following is most likely to be caused by an adverse supply shock? (A) Structural unemployment (B) Frictional unemployment (C) Demand-pull inflation (D) Cost-push inflation (E) Deflation
Chapter 4: A First Look at Macroeconomics
 Chapter 4: A First Look at Macroeconomics Principles of Macroeconomics I. Economics as a Social Science A. Economics is the social science that studies the choices that individuals, businesses, governments,
Chapter 4: A First Look at Macroeconomics Principles of Macroeconomics I. Economics as a Social Science A. Economics is the social science that studies the choices that individuals, businesses, governments,
ECO403 Macroeconomics Solved Online Quiz For Midterm Exam Preparation Spring 2013
 ECO403 Macroeconomics Solved Online Quiz For Midterm Exam Preparation Spring 2013 Question # 1 of 15 ( Start time: 03:22:55 PM ) Total Marks: 1 If the U.S. real exchange rate increases, then U.S. ----------------
ECO403 Macroeconomics Solved Online Quiz For Midterm Exam Preparation Spring 2013 Question # 1 of 15 ( Start time: 03:22:55 PM ) Total Marks: 1 If the U.S. real exchange rate increases, then U.S. ----------------
Chapter 9: Unemployment and Inflation
 Chapter 9: Unemployment and Inflation Yulei Luo SEF of HKU January 28, 2013 Learning Objectives 1. Measuring the Unemployment Rate, the Labor Force Participation Rate, and the Employment Population Ratio.
Chapter 9: Unemployment and Inflation Yulei Luo SEF of HKU January 28, 2013 Learning Objectives 1. Measuring the Unemployment Rate, the Labor Force Participation Rate, and the Employment Population Ratio.
CHAPTER 2. A TOUR OF THE BOOK
 CHAPTER 2. A TOUR OF THE BOOK I. MOTIVATING QUESTIONS 1. How do economists define output, the unemployment rate, and the inflation rate, and why do economists care about these variables? Output and the
CHAPTER 2. A TOUR OF THE BOOK I. MOTIVATING QUESTIONS 1. How do economists define output, the unemployment rate, and the inflation rate, and why do economists care about these variables? Output and the
