APE Unit 3 UGRP: Intro to Macroeconomics
|
|
|
- Ira Cain
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 /40 UGRP Score: /10 UEQ Score: Name Date Period Time: 2.5 Weeks APE Unit 3 UGRP: Intro to Macroeconomics /50 Total Score Anchor Text and Video: Please visit: and answer the following questions: 1. What is the goal of macroeconomics? 2. What do macroeconomists study? Why? 3. How is the field of macroeconomics connected to government? UEQ: Answer this on a separate sheet of paper and staple it to the back of this packet. Answers must have a thesis, a piece of evidence and a conclusion Macro-what-economics! Explain all of the components to macroeconomics and how those components are used to create and measure the U.S. economy. Objectives: These are the key concepts that you must be able to answer after Unit 3. These are also your review topics for our online study guide. They are also the guided reading questions. Have at it TeamAP! Chapter 20 An Introduction to Macroeconomics 20.1 Explain why economists focus on GDP, inflation, and unemployment when assessing the health of an entire economy 20.2 Discuss why sustained increases in living standards are a historically recent phenomenon 20.3 Identify why saving and investment are key factors in promoting rising living standards 20.4 Describe why economists believe that shocks and sticky prices are responsible for short-run fluctuations in output and employment 20.5 Characterize the degree to which various prices in the economy are sticky 20.6 Explain why the greater flexibility of prices as time passes causes economists to utilize different macroeconomic models for different time horizons Chapter 21 Measuring Domestic Output and National Income 21.1 Explain how GDP is defined and measure 21.2 Describe how expenditures on goods/services can be summed to determine GDP 21.3 Explain how GDP can be determined by summing up all of the incomes that were derived from producing the economy s output of goods/services 21.4 Describe the relationships among GDP, net domestic product, national income, personal income, and disposable income 21.5 Discuss the nature and function of a GDP price index and describe the difference between nominal GDP and real GDP 21.6 List and explain some limitations of the GDP measure Chapter 22 Economic Growth 22.1 List two ways that economic growth is measured 22.2 Define modern economic growth and explain the institutional structures needed for an economy to experience it 22.3 Identify the general supply, demand, and efficiency forces that give rise to economic growth 22.4 Describe growth accounting and the specific factors accounting for economic growth in the United States 22.5 Explain how the average rate of U.S. productivity growth has fluctuated since Discuss differing perspectives as to whether growth is desirable and sustainable 1
2 Chapter 23 Business Cycles, Unemployment and Inflation 23.1 Describe the business cycle and its primary phases 23.2 Illustrate how unemployment is measured and explain the different types of unemployment 23.3 Explain how inflation is measured and distinguish between cost-push inflation and demand-pull inflation 23.4 Relate how unanticipated inflation can redistribute real income 23.5 Discuss how inflation may affect the economy s level of real output Vocabulary: Complete these on a 3x5 notecard. The front has the term, the back has the definition and a personal sentence with the term used in its proper context. Chapter 20: Business cycle, recession, Real GDP (GDPr), Nominal GDP (GDPn), unemployment, inflation, savings, investment, inflexible prices (sticky prices), flexible prices, demand shock, supply shock (12) Chapter 21: National income accounting, intermediate goods, final goods, multiple counting, expenditures approach, income approach, personal consumption expenditures (C), gross private domestic investment (I), government purchases (G), net exports (Xn) (10) Chapter 22: Labor productivity, labor-force participation rate, infrastructure, economies of scale (4) Chapter 23: Labor force, unemployment rate, discouraged workers, frictional unemployment, structural unemployment, cyclical unemployment, full-employment rate of unemployment, natural rate of unemployment (NRU), GDP gap, Okun s Law, consumer price index (CPI), deflation, demand-pull inflation, cost-push inflation, nominal income, real income, unanticipated inflation, anticipated inflation, cost-of-loving-adjustment (COLA), real interest rate, nominal interest rate, hyperinflation (23) Homework Assignments Chapter Assignment/Topic Due Date/Stamp 20 Read Chapter 20 An Introduction to Macroeconomics (pp ) and answer UGRP Q s Complete Chapter 20 VNC and quiz 21 Read Chapter 21 Measuring Domestic Output and National Income (pp ) and answer UGRP Q s Complete Chapter 21 VNC and quiz 22 Read Chapter 22 Economic Growth (pp ) and answer UGRP Q s Complete Chapter 22 VNC and quiz 23 Read Chapter 23 Business Cycles, Unemployment and Inflation (pp ) and answer UGRP Q s Complete Chapter 23 VNC and quiz Extra Unit 3 Practice: Jacob Clifford Macroecomics Videos Unit 2 Youtube, Economic Review Graphing App Unit 3 Test: 2
3 Chapter 20: An Introduction to Macroeconomics. Answer below or on a separate sheet of paper only if noted Explain why economists focus on GDP, inflation, and unemployment when assessing the health of an entire economy 1. Why do you think macroeconomists focus on just a few key statistics when trying to understand the health and trajectory of an economy? Would it be better to try to examine all possible data? Explain 20.2 Discuss why sustained increases in living standards are a historically recent phenomenon 1. Did economic output start growing faster than population from the beginning of the human inhabitation of the earth? When did modern economic growth begin? Have all of the world s nations experienced the same extent of modern economic growth? Explain Identify why saving and investment are key factors in promoting rising living standards 1. Why is there a trade-off between the amount of consumption that people can enjoy today and the amount of consumption that they can enjoy in the future? Why can t people enjoy more of both? 2. How does saving relate to investment ant thus to economic growth? 3. What role do banks and other financial institutions play in aiding the growth process? 20.4 Describe why economists believe that shocks and sticky prices are responsible for short-run fluctuations in output and employment 1. Why, in general, do shocks force people to make changes? Give two examples from your own experiences Characterize the degree to which various prices in the economy are sticky 1. Are all prices in the economy equally inflexible? Which ones show large amounts of short-run flexibility? Which ones show a great deal of inflexibility even over months and years? 20.6 Explain why the greater flexibility of prices as time passes causes economists to utilize different macroeconomic models for different time horizons 1. Do prices tend to become more or less flexible as time passes? a. If there is a trend, how does it affect macroeconomists choice of models? 3
4 Chapter 21: Measuring Domestic Output and National Income. Answer below or on a separate sheet of paper only if noted. Definition of Gross Domestic Product (GDP)- Measuring Growth Nominal GDP- GDP = C: Real GDP- I: G: GDP Deflator- X n: Three things not included in GDP: Explain how GDP is defined and measured 21.2 Describe how expenditures on goods/services can be summed to determine GDP 21.3 Explain how GDP can be determined by summing up all of the incomes that were derived from producing the economy s output of goods/services 21.4 Describe the relationships among GDP, net domestic product, national income, personal income, and disposable income 21.5 Discuss the nature and function of a GDP price index and describe the difference between nominal GDP and real GDP 21.6 List and explain some limitations of the GDP measure 4
5 Chapter 22: Economic Growth. Answer below or on a separate sheet of paper only if noted. Helped or Hurt by Unexpected Inflation Assume expected inflation is 2% but actual inflation turns out to be 5%. Who is helped and hurt by inflation? Helped Hurt Real interest rate= Nominal interest rate= Interest Rates and Inflation 1. If the nominal interest rate is 7% and expected inflation is 3%, what is the real interest rate? 2. If the real interest rate is -2% and the nominal interest rate was 3%, what was the inflation rate? 1. Causes of Inflation Quantity Theory of Money Quantity Theory of Money Equation: x = x 2. = = = = 3. Assume the amount of money is $5 and it is being used to buy 10 products with a price of $2 each. 1. How much is the velocity of money? 2. If the velocity and output stay the same, what will happen if the amount of money increases to $10? 22.1 List two ways that economic growth is measured 5
6 22.2 Define modern economic growth and explain the institutional structures needed for an economy to experience it 22.3 Identify the general supply, demand, and efficiency forces that give rise to economic growth 22.4 Describe growth accounting and the specific factors accounting for economic growth in the United States 22.5 Explain how the average rate of U.S. productivity growth has fluctuated since Discuss differing perspectives as to whether growth is desirable and sustainable Chapter 23: Business Cycles, Unemployment and Inflation. Answer below or on a separate sheet of paper only if noted. Measuring Unemployment* 1. Frictional Unemployment Full Employment Natural Rate of Unemployment (NRU) 2. Structural Unemployment Problems With Unemployment Rate Discouraged Job Seekers- 3. Cyclical Unemployment Underemployed (part-time) Workers- 6
7 Business Cycle Label peak, recession/contraction, trough, expansion Real GDP GDP Deflator Practice 1. The Nominal GDP is $100 billion and the Real GDP is $80 billion. Calculate the GDP deflator. 2. The Real GDP is $100 billion and the GDP deflator is 200. Calculate the Nominal GDP. Time 3. The Real GDP is $200 billion and the GDP deflator is 120. Calculate the Nominal GDP. Label: guns, butter, efficiency, underutilization, and growth 4. The Nominal GDP is $300 billion and the GDP deflator is 150. Calculate the Real GDP. 5. The Nominal GDP is $100 billion and the GDP deflator is 125. Calculate the Real GDP Describe the business cycle and its primary phases 23.2 Illustrate how unemployment is measured and explain the different types of unemployment 23.3 Explain how inflation is measured and distinguish between cost-push inflation and demand-pull inflation 7
8 23.4 Relate how unanticipated inflation can redistribute real income 23.5 Discuss how inflation may affect the economy s level of real output APE Unit 3 Concept Reviews Directions: With your partner, write a quick response to each question. We will review as a class. Concept Review #1 Macro and GDP 1. Define Macroeconomics Concept Review #4 Inflation and the CPI 1. Who is helped and hurt by inflation? 2. What are the 3 economic goals that all countries have 3. Identify the 3 key parts of the definition of GDP 4. How do we use GDP 5. Identify what is NOT included in GDP Concept Review #2 GDP and the Business Cycle 1. What is the GDP Deflator? 2. What are the components to the Business Cycle? 3. How is the Business Cycle connected to the PPF? 4. Explain the difference between Nominal and Real GDP. 5. Explain Real GDP per Capita. Concept Review #3 -Employment 1. Name the three types of unemployment. 2. Define Natural Rate of Unemployment. 2. In an economy, Real GDP (base year = 1996) is $100 billion and the Nominal GDP is $150 billion. Calculate the GDP deflator. 3. In an economy, Real GDP (base year = 1996) is $125 billion and the Nominal GDP is $150 billion. Calculate the GDP deflator. 4. In an economy, Real GDP for year 2002 (base year = 1996) is $200 billion and the GDP deflator 2002 (base year = 1996) is 120. Calculate the Nominal GDP for In an economy, Nominal GDP for year 2005 (base year = 1996) is $60 billion and the GDP deflator 2005 (base year = 1996) is 120. Calculate the Real GDP for What are some issues with the CPI? 3. What is the: Unemployment rate formula? Labor force participation rate formula? Name that Concept!
Introduction to Economic Growth and Instability
 on C H A P T E R Introduction to Economic Growth and Instability 8-1 ECONOMIC GROWTH Economic Growth on 8-2 An increase in real GDP over some time period An increase in real GDP per capita over some time
on C H A P T E R Introduction to Economic Growth and Instability 8-1 ECONOMIC GROWTH Economic Growth on 8-2 An increase in real GDP over some time period An increase in real GDP per capita over some time
Introduction to Economic Growth, Unemployment, and Inflation McGraw-Hill Ryerson Ltd. Macroeconomics, Chapter 6 1
 Introduction to Economic Growth, Unemployment, and Inflation 2005 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Ltd. Macroeconomics, Chapter 6 1 In this chapter you will learn 6.1 The definition and causes of economic growth 6.2
Introduction to Economic Growth, Unemployment, and Inflation 2005 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Ltd. Macroeconomics, Chapter 6 1 In this chapter you will learn 6.1 The definition and causes of economic growth 6.2
The diagram above illustrates the pattern of: A) Wage movements over time B) Price level movements C) Economic growth patterns D) Business cycles
 Problem Set Econ 2013: Chapter 9: Business Cycles, Unemployment, and Inflation Name ID: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) 1) The
Problem Set Econ 2013: Chapter 9: Business Cycles, Unemployment, and Inflation Name ID: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) 1) The
MEASURING ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE PRODUCT MARKET
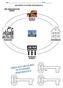 Name: Period THE CIRCULAR FLOW MODEL MEASURING ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE PRODUCT MARKET BUSINESSES HOUSEHOLDS RESOURCE MARKET 1. AKA: 2. 3. Additional Notes on Previous Page/Practice Workspace Quick Write Space
Name: Period THE CIRCULAR FLOW MODEL MEASURING ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE PRODUCT MARKET BUSINESSES HOUSEHOLDS RESOURCE MARKET 1. AKA: 2. 3. Additional Notes on Previous Page/Practice Workspace Quick Write Space
ECON 201. The Business Cycle. Business Cycle 4 phases 10/1/2009. Chapter 6 Business Cycles, Unemployment, & Inflation
 ECON 201 Chapter 6 Business Cycles, Unemployment, & Inflation The Business Cycle The U.S. has experienced economic instability associated with business cycles. Business Cycles alternating rises and declines
ECON 201 Chapter 6 Business Cycles, Unemployment, & Inflation The Business Cycle The U.S. has experienced economic instability associated with business cycles. Business Cycles alternating rises and declines
Figure Sarver
 I. Learning Objectives In this chapter students will learn: A. About the business cycle and its primary phases. B. How unemployment and inflation are measured. C. About the types of unemployment and inflation
I. Learning Objectives In this chapter students will learn: A. About the business cycle and its primary phases. B. How unemployment and inflation are measured. C. About the types of unemployment and inflation
Buchholz, Todd. New Ideas From Dead Economists. New York: Plame, 1999
 AP MACROECONOMICS COURSE SYLLABUS AP Macroeconomics is a one semester college level course. The AP Macroeconomics course is designed as an initial college level course in macroeconomics and as a foundation
AP MACROECONOMICS COURSE SYLLABUS AP Macroeconomics is a one semester college level course. The AP Macroeconomics course is designed as an initial college level course in macroeconomics and as a foundation
Unit 5 Notes. National Economic Performance
 Unit 5 Notes National Economic Performance Economic Indicators Economic Indicators are statistics that economists use to determine the health of a nation s economy. We are going to focus on three statistics
Unit 5 Notes National Economic Performance Economic Indicators Economic Indicators are statistics that economists use to determine the health of a nation s economy. We are going to focus on three statistics
AP Macroeconomics (APE) Course Syllabus
 Contact Information AP Macroeconomics (APE) Course Syllabus Teacher: Edmund Ned Maino Email: emaino@teh.k12.ca.us (I check email until 5pm, Monday-Friday) Phone: 661-822-2130 ext. 1701 (Please call between
Contact Information AP Macroeconomics (APE) Course Syllabus Teacher: Edmund Ned Maino Email: emaino@teh.k12.ca.us (I check email until 5pm, Monday-Friday) Phone: 661-822-2130 ext. 1701 (Please call between
Garden City High School Course: AP Macroeconomics
 Garden City High School Course: AP Macroeconomics Instructional Philosophy The Advanced Placement Macroeconomics curriculum is a full year program designed to provide both an overview of economics. Economics
Garden City High School Course: AP Macroeconomics Instructional Philosophy The Advanced Placement Macroeconomics curriculum is a full year program designed to provide both an overview of economics. Economics
2. In terms of dollar volume of exports and imports, the most important trading partner for the United States is:
 1. In the U.S. economy, all are generally accepted economic functions of government except: A) The provision of public goods B) The production and distribution of consumer goods C) Pursuing policies that
1. In the U.S. economy, all are generally accepted economic functions of government except: A) The provision of public goods B) The production and distribution of consumer goods C) Pursuing policies that
Dunbar s Big Review Sheet AP Macroeconomics Exam Content Area [Hubbard Textbook pages] (percentage coverage on AP Macroeconomics Exam) I.
![Dunbar s Big Review Sheet AP Macroeconomics Exam Content Area [Hubbard Textbook pages] (percentage coverage on AP Macroeconomics Exam) I. Dunbar s Big Review Sheet AP Macroeconomics Exam Content Area [Hubbard Textbook pages] (percentage coverage on AP Macroeconomics Exam) I.](/thumbs/77/76534172.jpg) Dunbar s Big Review Sheet AP Macroeconomics Exam Content Area [Hubbard Textbook pages] (percentage coverage on AP Macroeconomics Exam) I. Basic Economic Concepts (8-12%) Three Fundamental Questions [8]:
Dunbar s Big Review Sheet AP Macroeconomics Exam Content Area [Hubbard Textbook pages] (percentage coverage on AP Macroeconomics Exam) I. Basic Economic Concepts (8-12%) Three Fundamental Questions [8]:
Chapter 7 Introduction to Economic Growth and Instability
 Chapter 7 Introduction to Economic Growth and Instability Chapter Overview This chapter previews economic growth, the business cycle, unemployment, and inflation. It sets the stage for the analytical presentation
Chapter 7 Introduction to Economic Growth and Instability Chapter Overview This chapter previews economic growth, the business cycle, unemployment, and inflation. It sets the stage for the analytical presentation
Macroeconomics Unit 1: Basic Economics Concepts
 Macroeconomics Unit 1: Basic Economics Concepts Key Terms- Define the following: 3 Economic Systems 1. Scarcity 1. Centrally Planned Economies Individuals, businesses, and governments have Economic system
Macroeconomics Unit 1: Basic Economics Concepts Key Terms- Define the following: 3 Economic Systems 1. Scarcity 1. Centrally Planned Economies Individuals, businesses, and governments have Economic system
AP Macroeconomics Syllabus Course Outline Required text: Economics: Principles, Problems, and Policies McConnel and Brue 15 th edition
 AP Macroeconomics Mrs. Cook 1 st Period Room 210 AP Macroeconomics Syllabus Course Outline Required text: Economics: Principles, Problems, and Policies McConnel and Brue 15 th edition Unit One: Basic Economic
AP Macroeconomics Mrs. Cook 1 st Period Room 210 AP Macroeconomics Syllabus Course Outline Required text: Economics: Principles, Problems, and Policies McConnel and Brue 15 th edition Unit One: Basic Economic
ECO403 - Macroeconomics Faqs For Midterm Exam Preparation Spring 2013
 ECO403 - Macroeconomics Faqs For Midterm Exam Preparation Spring 2013 FAQs Question: 53-How the consumer can get the optimal level of satisfaction? Answer: A point where the indifference curve is tangent
ECO403 - Macroeconomics Faqs For Midterm Exam Preparation Spring 2013 FAQs Question: 53-How the consumer can get the optimal level of satisfaction? Answer: A point where the indifference curve is tangent
Mankiw Chapter 10. Introduction to Economic Fluctuations. Introduction to Economic Fluctuations CHAPTER 10
 Mankiw Chapter 10 0 IN THIS CHAPTER, WE WILL COVER: facts about the business cycle how the short run differs from the long run an introduction to aggregate demand an introduction to aggregate supply in
Mankiw Chapter 10 0 IN THIS CHAPTER, WE WILL COVER: facts about the business cycle how the short run differs from the long run an introduction to aggregate demand an introduction to aggregate supply in
FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE
 AP MACROECONOMICS-2018 Name: FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Instructions: DUE: Day of FINAL EXAM => Friday 12/21 st (1 st & 2 nd Periods) Thursday 12/20 th (4 th period) Section 1: PRODUCTION POSSIBLITIES FRONTIER
AP MACROECONOMICS-2018 Name: FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Instructions: DUE: Day of FINAL EXAM => Friday 12/21 st (1 st & 2 nd Periods) Thursday 12/20 th (4 th period) Section 1: PRODUCTION POSSIBLITIES FRONTIER
Economic Growth, Business Cycles, Unemployment, and Inflation
 CHAPTER 24 Economic Growth, Business Cycles, Unemployment, and Inflation Remember that there is nothing stable in human affairs; therefore avoid undue elation in prosperity, or undue depression in adversity.
CHAPTER 24 Economic Growth, Business Cycles, Unemployment, and Inflation Remember that there is nothing stable in human affairs; therefore avoid undue elation in prosperity, or undue depression in adversity.
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE. -8- Unauthorized copying or reuse of any part of this page is illegal.
 30. Which of the following is most likely to be caused by an adverse supply shock? (A) Structural unemployment (B) Frictional unemployment (C) Demand-pull inflation (D) Cost-push inflation (E) Deflation
30. Which of the following is most likely to be caused by an adverse supply shock? (A) Structural unemployment (B) Frictional unemployment (C) Demand-pull inflation (D) Cost-push inflation (E) Deflation
Chapter 4: A First Look at Macroeconomics
 Chapter 4: A First Look at Macroeconomics Principles of Macroeconomics I. Economics as a Social Science A. Economics is the social science that studies the choices that individuals, businesses, governments,
Chapter 4: A First Look at Macroeconomics Principles of Macroeconomics I. Economics as a Social Science A. Economics is the social science that studies the choices that individuals, businesses, governments,
Name Economics: Unit Three Study Guide Unit One Standards
 Name Economics: Unit Three Study Guide Unit One Standards Macroeconomic Concepts: SSEMA1 Illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. a. Identify and describe the macroeconomic goals of
Name Economics: Unit Three Study Guide Unit One Standards Macroeconomic Concepts: SSEMA1 Illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. a. Identify and describe the macroeconomic goals of
MONITORING JOBS AND INFLATION
 21 MONITORING JOBS AND INFLATION After studying this chapter, you will be able to: Explain why unemployment is a problem and define the unemployment rate and other labour market indicators Explain why
21 MONITORING JOBS AND INFLATION After studying this chapter, you will be able to: Explain why unemployment is a problem and define the unemployment rate and other labour market indicators Explain why
ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Chapter 10
 ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Chapter 10 Introduction to Economic Fluctuations Facts about the business cycle GDP growth averages 3 3.5 percent per year C (consumption) and I (Investment) fluctuate
ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Chapter 10 Introduction to Economic Fluctuations Facts about the business cycle GDP growth averages 3 3.5 percent per year C (consumption) and I (Investment) fluctuate
FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE
 AP MACROECONOMICS-2017 Name: FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Instructions: DUE: Day of FINAL EXAM => Friday 12/22 nd (1 st & 2 nd Periods) Thursday 12/21 st (4 th period) Section 1: PRODUCTION POSSIBLITIES FRONTIER
AP MACROECONOMICS-2017 Name: FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Instructions: DUE: Day of FINAL EXAM => Friday 12/22 nd (1 st & 2 nd Periods) Thursday 12/21 st (4 th period) Section 1: PRODUCTION POSSIBLITIES FRONTIER
A. Regular attendance is crucial to success in this class. Poor attendance will harm your participation grade. Grade categories are as follows:
 AP Macroeconomics JOHNSON Spring 11 AP Macroeconomics is a one-semester, college-level course. Each student is expected to take the AP Macroeconomics Exam that is administered in May. Successful achievement
AP Macroeconomics JOHNSON Spring 11 AP Macroeconomics is a one-semester, college-level course. Each student is expected to take the AP Macroeconomics Exam that is administered in May. Successful achievement
ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Solutions to the Final Exam
 ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Solutions to the Final Exam Multiple Choice Questions. (60 points; 2 pts each) #1. Which of the following is a stock variable? a) wealth b) consumption c) investment
ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Solutions to the Final Exam Multiple Choice Questions. (60 points; 2 pts each) #1. Which of the following is a stock variable? a) wealth b) consumption c) investment
Business Cycle Theory
 Business Cycle Theory Changes in Business Activity Economics, Unit: 06 Lesson: 01 Objectives 1.Describe phases of business cycle 2.Identify and explain the factors that cause business cycles 3.Analyze
Business Cycle Theory Changes in Business Activity Economics, Unit: 06 Lesson: 01 Objectives 1.Describe phases of business cycle 2.Identify and explain the factors that cause business cycles 3.Analyze
INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA UNIVERSITY FOUNDATION PROGRAMME ECO 183 : FOUNDATION ECONOMICS (MACROECONOMICS) RESIT EXAMINATION : AUGUST 2002 SESSION
 ECO 183 (R) / Page 1 of 9 INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA UNIVERSITY FOUNDATION PROGRAMME ECO 183 : FOUNDATION ECONOMICS (MACROECONOMICS) RESIT EXAMINATION : AUGUST 2002 SESSION Section A : Answer ALL questions.
ECO 183 (R) / Page 1 of 9 INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA UNIVERSITY FOUNDATION PROGRAMME ECO 183 : FOUNDATION ECONOMICS (MACROECONOMICS) RESIT EXAMINATION : AUGUST 2002 SESSION Section A : Answer ALL questions.
Measuring the Economy. Measur
 Measuring the Economy Measur Economic indicators Economic indicators are statistics that help economists judge the health of an economy. They provide information about important aspects of the economy.
Measuring the Economy Measur Economic indicators Economic indicators are statistics that help economists judge the health of an economy. They provide information about important aspects of the economy.
Principles of Macroeconomics Economics 202 Spring 2010
 Principles of Macroeconomics Economics 202 Spring 2010 Dr. Stuart Allen 334-3166 Office Hours: Before Class Department Office 462 Bryan E-mail: stuart_allen@uncg.edu PURPOSE This course uses market analysis
Principles of Macroeconomics Economics 202 Spring 2010 Dr. Stuart Allen 334-3166 Office Hours: Before Class Department Office 462 Bryan E-mail: stuart_allen@uncg.edu PURPOSE This course uses market analysis
Unit 2: Macro Measures REVIEW ACTIVITY Name That Concept Rules: 1. Cannot use the word(s) 2. Focus on the concept not word Ex: Price Maker
 1 Unit 2: Macro Measures 1 REVIEW ACTIVITY Name That Concept Rules: 1. Cannot use the word(s) 2. Focus on the concept not word Ex: Price Maker 2 NAME THAT CONCEPT 1.Macroeconomics 2.Inflation 3.Nominal
1 Unit 2: Macro Measures 1 REVIEW ACTIVITY Name That Concept Rules: 1. Cannot use the word(s) 2. Focus on the concept not word Ex: Price Maker 2 NAME THAT CONCEPT 1.Macroeconomics 2.Inflation 3.Nominal
EQ: How Do Changes in AD and SRAS Affect Real GDP, Unemployment, & Price Level?
 EQ: How Do Changes in and Affect So, what happens when changes? Increases in Consumption (C), Investment (I), Government Spending (G), & Net Exports (X) will: Increase Total Expenditures ( TE) Increase
EQ: How Do Changes in and Affect So, what happens when changes? Increases in Consumption (C), Investment (I), Government Spending (G), & Net Exports (X) will: Increase Total Expenditures ( TE) Increase
Chapter 9 Introduction to Economic Fluctuations
 Chapter 9 Introduction to Economic Fluctuations facts about the business cycle how the short run differs from the long run an introduction to aggregate demand an introduction to aggregate supply in the
Chapter 9 Introduction to Economic Fluctuations facts about the business cycle how the short run differs from the long run an introduction to aggregate demand an introduction to aggregate supply in the
An Introduction to Macroeconomics
 23 An Introduction to Macroeconomics McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.. AGENDA Thurs 1/21 QOD #6: National Income GDP, Growth & Stability Partner
23 An Introduction to Macroeconomics McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.. AGENDA Thurs 1/21 QOD #6: National Income GDP, Growth & Stability Partner
** Review ** For Test - 3
 ** Review ** For Test - 3 1. Gross domestic product or GDP is: A) the total dollar value intermediate goods and services produced in the economy in a given time period. B) the total dollar value of wages
** Review ** For Test - 3 1. Gross domestic product or GDP is: A) the total dollar value intermediate goods and services produced in the economy in a given time period. B) the total dollar value of wages
We use GDP to compare different economies or to track the same economy over time.
 Lecture Notes ECON 1A: Principles of Macroeconomics Chapter 5 - Introduction to Macroeconomics Introduction Macroeconomics looks at the big picture: Demand for: Average price of: Consumption by: Investment
Lecture Notes ECON 1A: Principles of Macroeconomics Chapter 5 - Introduction to Macroeconomics Introduction Macroeconomics looks at the big picture: Demand for: Average price of: Consumption by: Investment
3. The phase of the business cycle in which real GDP is at a minimum is called: A. the peak. B. a recession. C. the trough. D. the underside.
 1. Most economists agree that the immediate determinant of the volume of output and employment is the: A. composition of consumer spending. B. ratio of public goods to private goods production. C. level
1. Most economists agree that the immediate determinant of the volume of output and employment is the: A. composition of consumer spending. B. ratio of public goods to private goods production. C. level
OUTLINE October 18, Key concepts. Expenditure 10/16/ :53 PM. Focus: Total Expenditure
 OUTLINE October 18, 2017 Expenditure = C + I + G + (EX IM), continued 3 equations you must know Measuring Unemployment Measuring Inflation Key concepts When figuring out IF some activity is counted in
OUTLINE October 18, 2017 Expenditure = C + I + G + (EX IM), continued 3 equations you must know Measuring Unemployment Measuring Inflation Key concepts When figuring out IF some activity is counted in
OCR Unit 2. Economics Revision. Judah Chandra
 1 OCR Unit 2 Economics Revision Economics Revision Judah Chandra 2 AD = C + I + G (X - M) KEY TERMS Economic growth - in the short run, an increase in real GDP, and in the long run, an increase in productive
1 OCR Unit 2 Economics Revision Economics Revision Judah Chandra 2 AD = C + I + G (X - M) KEY TERMS Economic growth - in the short run, an increase in real GDP, and in the long run, an increase in productive
Chapter 6 GDP, Unemployment and Inflation
 Chapter 6 GDP, Unemployment and Inflation - Microeconomics: study of how households and firms make choices & how they interact in markets. - Macroeconomics: study of the economy as a whole, including topics
Chapter 6 GDP, Unemployment and Inflation - Microeconomics: study of how households and firms make choices & how they interact in markets. - Macroeconomics: study of the economy as a whole, including topics
ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Final Exam
 ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Final Exam Multiple Choice Questions. (60 points; 2 pts each) #1. Which of the following is a stock variable? a) wealth b) consumption c) investment d) income #2.
ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Final Exam Multiple Choice Questions. (60 points; 2 pts each) #1. Which of the following is a stock variable? a) wealth b) consumption c) investment d) income #2.
Disclaimer: This resource package is for studying purposes only EDUCATION
 Disclaimer: This resource package is for studying purposes only EDUCATION Ch 26: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Aggregate Supply Purpose of aggregate supply: aggregate demand model is to explain
Disclaimer: This resource package is for studying purposes only EDUCATION Ch 26: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Aggregate Supply Purpose of aggregate supply: aggregate demand model is to explain
Basic Concepts. MICROECONOMICS: deals with specific economic units and a detailed consideration of these individual units.
 Basic Concepts ECONOMICS: The study of how limited productive resources are efficiently allocated in a world of unlimited wants. SCARCITY: WANTS EXCEED RESOURCES We want more than we are capable of getting.
Basic Concepts ECONOMICS: The study of how limited productive resources are efficiently allocated in a world of unlimited wants. SCARCITY: WANTS EXCEED RESOURCES We want more than we are capable of getting.
What is Macroeconomics?
 MACRO ECONOMICS 1 What is Macroeconomics? Macroeconomics is the study of the large economy as a whole. It is the study of the big picture. Instead of analyzing one consumer, we analyze everyone. Instead
MACRO ECONOMICS 1 What is Macroeconomics? Macroeconomics is the study of the large economy as a whole. It is the study of the big picture. Instead of analyzing one consumer, we analyze everyone. Instead
ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Final Exam
 ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Final Exam Multiple Choice Questions. (60 points; 3 pts each) #1. An economy s equals its. a. consumption; income b. consumption; expenditure on goods and services
ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Final Exam Multiple Choice Questions. (60 points; 3 pts each) #1. An economy s equals its. a. consumption; income b. consumption; expenditure on goods and services
AP Macroeconomics review. By: Maria Villasmil. Economis: The study of how people, firms, and government make decisions when faced with scarcity.
 AP Macroeconomics review By: Maria Villasmil Economis: The study of how people, firms, and government make decisions when faced with scarcity. Factors of Production: 1)Land: natural resources 2) Labor:
AP Macroeconomics review By: Maria Villasmil Economis: The study of how people, firms, and government make decisions when faced with scarcity. Factors of Production: 1)Land: natural resources 2) Labor:
Introduction. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives. Chapter 7. Explain how the U.S. government calculates the official unemployment rate
 Chapter 7 The Macroeconomy:, Inflation, and Deflation Introduction Why is it that the responsibility for announcing the start of economic contractions and expansions does not rest with elected officials?
Chapter 7 The Macroeconomy:, Inflation, and Deflation Introduction Why is it that the responsibility for announcing the start of economic contractions and expansions does not rest with elected officials?
ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Final Exam
 ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Final Exam Multiple Choice Questions. (60 points; 3 pts each) #1. How does the distinction between flexible and sticky prices impact the study of macroeconomics? a.
ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Final Exam Multiple Choice Questions. (60 points; 3 pts each) #1. How does the distinction between flexible and sticky prices impact the study of macroeconomics? a.
Chapter 11 Macroeconomic Issues: Economic Growth and the Business Cycle
 Chapter 11 Macroeconomic Issues: Economic Growth and the Business Cycle Multiple Choice Questions Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The sources of
Chapter 11 Macroeconomic Issues: Economic Growth and the Business Cycle Multiple Choice Questions Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The sources of
MACROECONOMICS REVIEW FOR EXAM #1. 1. Real GDP is better than nominal GDP in making comparisons of GDP over time because:
 MACROECONOMICS REVIEW FOR EXAM #1 1. Real GDP is better than nominal GDP in making comparisons of GDP over time because: A. Nominal GDP can increase simply because of price increases over time. B. Real
MACROECONOMICS REVIEW FOR EXAM #1 1. Real GDP is better than nominal GDP in making comparisons of GDP over time because: A. Nominal GDP can increase simply because of price increases over time. B. Real
Economic Performance Indicators - Unemployment, CPI, GDP
 Supply and Demand law of demand income effect substitution effect change in quantity demanded vs. change in demand determinants of demand (TRIBE) normal vs. inferior goods supplied vs. change in supply
Supply and Demand law of demand income effect substitution effect change in quantity demanded vs. change in demand determinants of demand (TRIBE) normal vs. inferior goods supplied vs. change in supply
MACROECONOMICS. Section I Time 70 minutes 60 Questions
 MACROECONOMICS Section I Time 70 minutes 60 Questions Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or completions. Select the one that is best
MACROECONOMICS Section I Time 70 minutes 60 Questions Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or completions. Select the one that is best
Intro to macroeconomics. Rush October 2014
 Intro to macroeconomics Rush October 2014 Micro means small. Macro means big. We are moving from micro to macro What is microeconomics? Microeconomics is the study of SPECIFIC markets and the behavior
Intro to macroeconomics Rush October 2014 Micro means small. Macro means big. We are moving from micro to macro What is microeconomics? Microeconomics is the study of SPECIFIC markets and the behavior
2) The Great Recession occurred in: A) B) C) D)
 Problem Set Econ 2013: Chapter : An Introduction to Macroenonomics Name ID: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Short-run fluctuations
Problem Set Econ 2013: Chapter : An Introduction to Macroenonomics Name ID: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Short-run fluctuations
BUSI 101 Capital Markets and Real Estate
 BUSI 101 Capital Markets and Real Estate PURPOSE AND SCOPE The Capital Markets and Real Estate course (BUSI 101) is intended to acquaint the student with the basic principles of macroeconomics and to give
BUSI 101 Capital Markets and Real Estate PURPOSE AND SCOPE The Capital Markets and Real Estate course (BUSI 101) is intended to acquaint the student with the basic principles of macroeconomics and to give
Macroeconomics Unit Overview
 Unit Overview 3.1 Measuring national income * Circular flow of income * Methods of measurement - income, expenditure and output * Distinction between o gross and net o national and domestic o nominal and
Unit Overview 3.1 Measuring national income * Circular flow of income * Methods of measurement - income, expenditure and output * Distinction between o gross and net o national and domestic o nominal and
Chapter Outline. Chapter 6 Every Macroeconomic Word You Have Ever Heard: Gross Domestic Product, Inflation, Unemployment, Recession and Depression
 Chapter 6 Every Macroeconomic Word You Have Ever Heard: Gross Domestic Product, Inflation, Unemployment, Recession and Depression Chapter Outline Measuring the Economy Real Gross Domestic Product and Why
Chapter 6 Every Macroeconomic Word You Have Ever Heard: Gross Domestic Product, Inflation, Unemployment, Recession and Depression Chapter Outline Measuring the Economy Real Gross Domestic Product and Why
Murrieta Valley Unified School District High School Course Outline June 2013
 Murrieta Valley Unified School District High School Course Outline June 2013 Department: Course Title: Social Science Advanced Placement Macroeconomics Grade Level: 12 Course Number: 1705 Prerequisite:
Murrieta Valley Unified School District High School Course Outline June 2013 Department: Course Title: Social Science Advanced Placement Macroeconomics Grade Level: 12 Course Number: 1705 Prerequisite:
WJEC (Wales) Economics A-level
 WJEC (Wales) Economics A-level Macroeconomics Topic 2: Macroeconomic Objectives 2.3 Inflation and deflation Notes Inflation is the sustained rise in the general price level over time. This means that the
WJEC (Wales) Economics A-level Macroeconomics Topic 2: Macroeconomic Objectives 2.3 Inflation and deflation Notes Inflation is the sustained rise in the general price level over time. This means that the
Assessment Schedule 2014 Economics: Analyse inflation using economic concepts and models (91222)
 NCEA Level 2 Economics (91222) 2014 page 1 of 10 Assessment Schedule 2014 Economics: Analyse inflation using economic concepts and models (91222) Assessment criteria with Merit with Demonstrate understanding
NCEA Level 2 Economics (91222) 2014 page 1 of 10 Assessment Schedule 2014 Economics: Analyse inflation using economic concepts and models (91222) Assessment criteria with Merit with Demonstrate understanding
MACROECONOMICS - CLUTCH CH INTRODUCING ECONOMIC CONCEPTS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: INTRODUCING MACROECONOMIC CONCEPTS BUSINESS CYCLE Business Cycles describe the increases and decreases in economic activity that occur over periods of several years Employment
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: INTRODUCING MACROECONOMIC CONCEPTS BUSINESS CYCLE Business Cycles describe the increases and decreases in economic activity that occur over periods of several years Employment
Introduction to Economic Fluctuations
 CHAPTER 10 Introduction to Economic Fluctuations Modified for ECON 2204 by Bob Murphy 2016 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved IN THIS CHAPTER, OU WILL LEARN: facts about the business cycle how the short
CHAPTER 10 Introduction to Economic Fluctuations Modified for ECON 2204 by Bob Murphy 2016 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved IN THIS CHAPTER, OU WILL LEARN: facts about the business cycle how the short
Introduction to Economic Fluctuations. Instructor: Dmytro Hryshko
 Introduction to Economic Fluctuations Instructor: Dmytro Hryshko 1 / 32 Outline facts about the business cycle how the short run differs from the long run an introduction to aggregate demand an introduction
Introduction to Economic Fluctuations Instructor: Dmytro Hryshko 1 / 32 Outline facts about the business cycle how the short run differs from the long run an introduction to aggregate demand an introduction
Economic Ups and Downs: The PowerPoint
 : The PowerPoint Once you have finished reading and answering the questions in the attached Economic Ups and Downs worksheet, you should summarize the information in a PowerPoint presentation. Email the
: The PowerPoint Once you have finished reading and answering the questions in the attached Economic Ups and Downs worksheet, you should summarize the information in a PowerPoint presentation. Email the
LIMIT INFLATION Country and Time- Zimbabwe, 2008 Annual Inflation Rate- 79,600,000,000% Time for Prices to Double hours
 Inflation 1 Copyright LIMIT INFLATION Country and Time- Zimbabwe, 2008 Annual Inflation Rate- 79,600,000,000% Time for Prices to Double- 24.7 hours What is Inflation? Inflation is rising general level
Inflation 1 Copyright LIMIT INFLATION Country and Time- Zimbabwe, 2008 Annual Inflation Rate- 79,600,000,000% Time for Prices to Double- 24.7 hours What is Inflation? Inflation is rising general level
ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Solutions to the Final Exam
 ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Solutions to the Final Exam Multiple Choice Questions. (60 points; 3 pts each) #1. How does the distinction between flexible and sticky prices impact the study of
ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Solutions to the Final Exam Multiple Choice Questions. (60 points; 3 pts each) #1. How does the distinction between flexible and sticky prices impact the study of
ABOUT THE EXAM. Multiple Choice Questions two thirds of total score: Free Response Questions one third of total score:
 ABOUT THE EXAM Multiple Choice Questions two thirds of total score: 60 questions, 70 minutes to complete 1 point each; no penalty for wrong answer Many of the questions are similar to the frqs; for questions
ABOUT THE EXAM Multiple Choice Questions two thirds of total score: 60 questions, 70 minutes to complete 1 point each; no penalty for wrong answer Many of the questions are similar to the frqs; for questions
Advanced Placement Macro Economics
 Advanced Placement Macro Economics Economics is a study of mankind in the ordinary business of life. Alfred Marshall Through the AP Macroeconomics course, students will have a better understanding of the
Advanced Placement Macro Economics Economics is a study of mankind in the ordinary business of life. Alfred Marshall Through the AP Macroeconomics course, students will have a better understanding of the
Lecture 22. Aggregate demand and aggregate supply
 Lecture 22 Aggregate demand and aggregate supply By the end of this lecture, you should understand: three key facts about short-run economic fluctuations how the economy in the short run differs from the
Lecture 22 Aggregate demand and aggregate supply By the end of this lecture, you should understand: three key facts about short-run economic fluctuations how the economy in the short run differs from the
MONITORING JOBS AND INFLATION*
 Chapt er 5 MONITORING JOBS AND INFLATION* Key Concepts Employment and Unemployment Unemployment is a problem for both the unemployed worker and for society. Unemployed workers lose income and, if prolonged,
Chapt er 5 MONITORING JOBS AND INFLATION* Key Concepts Employment and Unemployment Unemployment is a problem for both the unemployed worker and for society. Unemployed workers lose income and, if prolonged,
Introduction. Learning Objectives. Chapter 17. Stabilization in an Integrated World Economy
 Chapter 17 Stabilization in an Integrated World Economy Introduction For more than 50 years, many economists have used an inverse relationship involving the unemployment rate and real GDP as a guide to
Chapter 17 Stabilization in an Integrated World Economy Introduction For more than 50 years, many economists have used an inverse relationship involving the unemployment rate and real GDP as a guide to
ECO403 Macroeconomics Solved Online Quiz For Midterm Exam Preparation Spring 2013
 ECO403 Macroeconomics Solved Online Quiz For Midterm Exam Preparation Spring 2013 Question # 1 of 15 ( Start time: 03:22:55 PM ) Total Marks: 1 If the U.S. real exchange rate increases, then U.S. ----------------
ECO403 Macroeconomics Solved Online Quiz For Midterm Exam Preparation Spring 2013 Question # 1 of 15 ( Start time: 03:22:55 PM ) Total Marks: 1 If the U.S. real exchange rate increases, then U.S. ----------------
ELIZABETHTOWN AREA HIGH SCHOOL SYLLABUS ADVANCED PLACEMENT MACROECONOMICS
 ELIZABETHTOWN AREA HIGH SCHOOL SYLLABUS ADVANCED PLACEMENT MACROECONOMICS Instructor: James J. Sostack Jr. Department: Social Studies Length of Course: Full Year (A/B Block format) Weight 1.20 Grade Level
ELIZABETHTOWN AREA HIGH SCHOOL SYLLABUS ADVANCED PLACEMENT MACROECONOMICS Instructor: James J. Sostack Jr. Department: Social Studies Length of Course: Full Year (A/B Block format) Weight 1.20 Grade Level
Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory / Macroeconomic Analysis (ECON 3560/5040) Midterm Exam (Answers)
 Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory / Macroeconomic Analysis (ECON 3560/5040) Midterm Exam (Answers) Part A (15 points) State whether you think each of the following questions is true (T), false (F), or
Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory / Macroeconomic Analysis (ECON 3560/5040) Midterm Exam (Answers) Part A (15 points) State whether you think each of the following questions is true (T), false (F), or
Economics 207: Introduction to Macroeconomics Final Exam Instructions:
 Economics 207: Introduction to Macroeconomics Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete the following exam. Be sure to write your anme and student id ON YOUR SCANTRON and BELOW. Failure
Economics 207: Introduction to Macroeconomics Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete the following exam. Be sure to write your anme and student id ON YOUR SCANTRON and BELOW. Failure
Economic Changes and Cycles
 7 more class periods! Textbook Return Thursday 5/18 Final Exam Thursday 5/18 100 MC 5 Free Response 15% of grade Extra credit opportunities will be handed out on Thursday. Economic Changes and Cycles Chapter
7 more class periods! Textbook Return Thursday 5/18 Final Exam Thursday 5/18 100 MC 5 Free Response 15% of grade Extra credit opportunities will be handed out on Thursday. Economic Changes and Cycles Chapter
Introduction to Economic Fluctuations
 Chapter 9 Introduction to Economic Fluctuations slide 0 In this chapter, you will learn facts about the business cycle how the short run differs from the long run an introduction to aggregate demand an
Chapter 9 Introduction to Economic Fluctuations slide 0 In this chapter, you will learn facts about the business cycle how the short run differs from the long run an introduction to aggregate demand an
Motivated Monday, November 5 (No school tomorrow!)
 Motivated Monday, November 5 (No school tomorrow!) Learning targets: I can research inflation and CPI and I can review GDP and unemployment. (Sub work from Friday) New USATP is up Unit 2 test Nov. 13 and
Motivated Monday, November 5 (No school tomorrow!) Learning targets: I can research inflation and CPI and I can review GDP and unemployment. (Sub work from Friday) New USATP is up Unit 2 test Nov. 13 and
Unit 6 Measuring the Economy
 Unit 6 Measuring the Economy - Study Guide - Answer, Explain and define the following: 1) GNP 2) GDP 3) Dept. of Commerce 4) Intermediate goods 5) Disposable personal income 6) Contraction 7) Recession
Unit 6 Measuring the Economy - Study Guide - Answer, Explain and define the following: 1) GNP 2) GDP 3) Dept. of Commerce 4) Intermediate goods 5) Disposable personal income 6) Contraction 7) Recession
The Goals of Stabilization Policy. The Goals of Stabilization Policy: Low Inflation and Low Unemployment. The Goals of Stabilization Policy
 : Low Inflation and Low Unemployment The Costs and Causes of Inflation While inflation is viewed as evil the degree of evilness is highly and hotly debated Basic cause of inflation is excessive growth
: Low Inflation and Low Unemployment The Costs and Causes of Inflation While inflation is viewed as evil the degree of evilness is highly and hotly debated Basic cause of inflation is excessive growth
SSEMA1 The student will illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. a. Explain that overall levels of income, employment, and prices
 SSEMA1 The student will illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. a. Explain that overall levels of income, employment, and prices are determined by the spending and production decisions
SSEMA1 The student will illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. a. Explain that overall levels of income, employment, and prices are determined by the spending and production decisions
ECON Drexel University Summer 2008 Assignment 2. Due date: July 29, 2008
 ECON 202-001 Drexel University Summer 2008 Assignment 2 Due date: July 29, 2008 Instructor: Yuan Yuan Name This homework has up to 10 points bonus. Question 1 (40 points, 2 points each): MULTIPLE CHOICE.
ECON 202-001 Drexel University Summer 2008 Assignment 2 Due date: July 29, 2008 Instructor: Yuan Yuan Name This homework has up to 10 points bonus. Question 1 (40 points, 2 points each): MULTIPLE CHOICE.
Shanghai Livingston American School Quarterly / Trimester Plan 3 AP Macro
 Shanghai Livingston American School Quarterly / Trimester Plan 3 AP Macro Concept / Topic To Teach: Unit 4 MODULE 22: SAVING, INVESTMENT, AND THE FINANCIAL Specific Objectives: ELD Standards SYSTEM Week
Shanghai Livingston American School Quarterly / Trimester Plan 3 AP Macro Concept / Topic To Teach: Unit 4 MODULE 22: SAVING, INVESTMENT, AND THE FINANCIAL Specific Objectives: ELD Standards SYSTEM Week
Practice Test Unit 4 DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST! Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST! Practice Test Unit 4 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Consider an economy that only produces two goods: DVDs
DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST! Practice Test Unit 4 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Consider an economy that only produces two goods: DVDs
AP Macroeconomics Fall Semester 2016
 AP Macroeconomics Fall Semester 2016 Ms. Huynh ( Win ), Room 126 Phone: (626) 441-5820 Ext 2126 Email: Thuynh@spusd.net Curricular Overview This semester long course will introduce students to the principles
AP Macroeconomics Fall Semester 2016 Ms. Huynh ( Win ), Room 126 Phone: (626) 441-5820 Ext 2126 Email: Thuynh@spusd.net Curricular Overview This semester long course will introduce students to the principles
2/14/2008. The circular flow of goods and incomes. firms and households. goods markets. Goods and services. real flows: goods and services
 The circular flow of income Chapter 22 Introduction to Macroeconomics Economics, 4 th edition Stiglitz & Walsh firms and households goods markets real flows: goods and services The Economic Problem Goods
The circular flow of income Chapter 22 Introduction to Macroeconomics Economics, 4 th edition Stiglitz & Walsh firms and households goods markets real flows: goods and services The Economic Problem Goods
Disputes In Macroeconomics
 No G G & T 3-5% Monetary Rule Expectations negate fiscal and monetary Policy. Adam Smith John M. Keynes Milton Friedman Classicals Keynesians Monetarists Robert Lucas Get the G off of our backs. Ronald
No G G & T 3-5% Monetary Rule Expectations negate fiscal and monetary Policy. Adam Smith John M. Keynes Milton Friedman Classicals Keynesians Monetarists Robert Lucas Get the G off of our backs. Ronald
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Questions of this SAMPLE exam were randomly chosen and may NOT be representative of the difficulty or focus of the actual examination. The professor did NOT review these questions. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose
Questions of this SAMPLE exam were randomly chosen and may NOT be representative of the difficulty or focus of the actual examination. The professor did NOT review these questions. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose
Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Chapter 19 Copyright 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. All rights reserved. Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to: Permissions Department,
Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Chapter 19 Copyright 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. All rights reserved. Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to: Permissions Department,
Macroeconomics, 7e (Blanchard) Chapter 2: A Tour of the Book. 2.1 Aggregate Output.
 Macroeconomics, 7e (Blanchard) Chapter 2: A Tour of the Book 2.1 Aggregate Output. 1) Fill in the blank for the following: GDP is the value of all produced in a given period. A) final and intermediate
Macroeconomics, 7e (Blanchard) Chapter 2: A Tour of the Book 2.1 Aggregate Output. 1) Fill in the blank for the following: GDP is the value of all produced in a given period. A) final and intermediate
Professor Christina Romer. LECTURE 15 MEASUREMENT AND BEHAVIOR OF REAL GDP March 8, 2018
 Economics 2 Spring 2018 Professor Christina Romer Professor David Romer LECTURE 15 MEASUREMENT AND BEHAVIOR OF REAL GDP March 8, 2018 I. MACROECONOMICS VERSUS MICROECONOMICS II. REAL GDP A. Definition
Economics 2 Spring 2018 Professor Christina Romer Professor David Romer LECTURE 15 MEASUREMENT AND BEHAVIOR OF REAL GDP March 8, 2018 I. MACROECONOMICS VERSUS MICROECONOMICS II. REAL GDP A. Definition
Economics Chapters Duke Unit III Measuring Economic Performance
 Economics Chapters 12-16 Duke Unit III Measuring Economic Performance Chapter 12 Section 1 (Pgs. 301-308) Gross Domestic Product (GDP)- 1. What is the difference between final goods and services as opposed
Economics Chapters 12-16 Duke Unit III Measuring Economic Performance Chapter 12 Section 1 (Pgs. 301-308) Gross Domestic Product (GDP)- 1. What is the difference between final goods and services as opposed
2.2 Aggregate demand and aggregate supply
 The business cycle Short-term fluctuations and long-term trend Explain, using a business cycle diagram, that economies typically tend to go through a cyclical pattern characterized by the phases of the
The business cycle Short-term fluctuations and long-term trend Explain, using a business cycle diagram, that economies typically tend to go through a cyclical pattern characterized by the phases of the
Chapter 9 Introduction to Economic Fluctuations
 art IV Business Cycle Theory: Short Run Chapter 9 Introduction to Economic Fluctuations Zhengyu Cai h.d. Institute of Development Southwestern University of Finance and Economics All rights reserved http://www.escience.cn/people/zhengyucai/index.html
art IV Business Cycle Theory: Short Run Chapter 9 Introduction to Economic Fluctuations Zhengyu Cai h.d. Institute of Development Southwestern University of Finance and Economics All rights reserved http://www.escience.cn/people/zhengyucai/index.html
ECNS Fall 2009 Practice Examination Opportunity
 ECNS 202 -- Fall 2009 Practice Examination Opportunity Mark the answer on the provided scantron sheet using a #2 lead pencil. Erase completely. I am not responsible for poorly marked or poorly erased asnwers.
ECNS 202 -- Fall 2009 Practice Examination Opportunity Mark the answer on the provided scantron sheet using a #2 lead pencil. Erase completely. I am not responsible for poorly marked or poorly erased asnwers.
Principles of Macroeconomics December 17th, 2005 name: Final Exam (100 points)
 EC132.02 Serge Kasyanenko Principles of Macroeconomics December 17th, 2005 name: Final Exam (100 points) This is a closed-book exam - you may not use your notes and textbooks. Calculators are not allowed.
EC132.02 Serge Kasyanenko Principles of Macroeconomics December 17th, 2005 name: Final Exam (100 points) This is a closed-book exam - you may not use your notes and textbooks. Calculators are not allowed.
Economics 1012 A : Introduction to Macroeconomics FALL 2007 Dr. R. E. Mueller Second Midterm Examination October 19, 2007
 Economics 1012 A : Introduction to Macroeconomics FALL 2007 Dr. R. E. Mueller Second Midterm Examination October 19, 2007 ================================================================================
Economics 1012 A : Introduction to Macroeconomics FALL 2007 Dr. R. E. Mueller Second Midterm Examination October 19, 2007 ================================================================================
Introduction to Macroeconomics. Introduction to Macroeconomics
 C H A P T E R 17 Introduction to Macroeconomics Prepared by: Fernando Quijano and Yvonn Quijano Introduction to Macroeconomics Microeconomics examines the behavior of individual decision-making units business
C H A P T E R 17 Introduction to Macroeconomics Prepared by: Fernando Quijano and Yvonn Quijano Introduction to Macroeconomics Microeconomics examines the behavior of individual decision-making units business
Econ 302 Fall Don t forget to download a copy of the Homework Cover Sheet. Mark the location where you handed in your work.
 Econ 302 Fall 2005 Don t forget to download a copy of the Homework Cover Sheet. Mark the location where you handed in your work. Homework #1; Chapter 1. This homework has three parts (A, B, C). Each part
Econ 302 Fall 2005 Don t forget to download a copy of the Homework Cover Sheet. Mark the location where you handed in your work. Homework #1; Chapter 1. This homework has three parts (A, B, C). Each part
