RMB internationalization and China s economic transformation
|
|
|
- Bernadette Stewart
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RMB internationalization and China s economic transformation Jianguang Shen 1 Summary RMB internationalization involves two core steps: to achieve convertibility and status as a global reserve currency. Hence, convertibility is a fist step towards RMB s internationalisation, which requires four key changes, including capital account liberalization, circulation of RMB abroad, interest rate liberalization and a more flexible exchange rate mechanism. From a longer-term perspective, RMB internationalization will lead to four key transformations of the Chinese economy: from an export-oriented economy to an economy focused on domestic demand; from low-end manufacturing to moving upwards on the value-added chain and establishing a strong service sector; from being reliant on FDI to the go abroad strategy of Chinese enterprises; from policyoriented towards a more market-based financial market.. 1 Jianguang Shen, CF40 Invited researcher, Managing Director, Mizuho Securities Asia Limited.
2 Table of Contents 1.0 Two future trends impacts China s future The long and winding road towards global rebalancing Lewis Turning Point (LTP) leads to economic restructuring Implications of RMB internationalization RMB internationalization s influence on China economy s four key transformations Transformation 1: Export-led to domestic-demand-oriented economy Transformation 2: Manufacturing towards a strong service sector Transformation 3: From FDI to go abroad strategy Transformation 4: From policy-oriented towards market-based financial market Two potential risks of RMB internationalization Risk 1: Increasing difficulty of macro control Risk 2: Short-term capital movement impacts on RMB exchange rate Reference 24 2
3 % 1.0 New foreign and domestic developments accelerate RMB internationalization 1.1 The treacherous road towards global rebalancing Since the global financial crisis in 2008, the advanced economies have been shifting the debt burden from the private sector towards the public sector. As a result, US faces aggravating twin deficit like it once did in 1980s. Meanwhile, despite Federal Reserve s two rounds of quantitative easing in 2009 and 2010, the overall effect on US economic recovery was limited. Meanwhile, a sovereign debt crisis emerges in the Eurozone. Different from its American counterpart, Euro debt crisis also suffered from the difficult task of maintaining a monetary union without a fiscal union. Fig 1 US faces a twin deficit as it did once before during the 1980s 2% 1% 0% -1% -2% -3% -4% -5% -6% -7% 4% 2% 0% -2% -4% -6% -8% -10% -12% -14% Trade surplus as of GDP Budget surplus as of GDP Source: BEA, Mizuho Research The deteriorating global economic condition has brought about three major impacts on the Chinese economy: first, slowing foreign demand cut the overall Chinese export growth. Despite recent highs in China s overall export growth, export to US has dropped for several months, merely maintaining a single-digit growth. With wage increase and RMB appreciation against the US dollars, export firms competitiveness was compromised. Meanwhile, despite that the economic slowdown might lead to a fall in oil prices, alleviating the short-term inflationary pressure, the possibility of US proposing a further round of quantitative easing will still lead to surges in commodity prices in the medium term, further deteriorating the inflationary pressures. Moreover, China was the largest debt holder of US; US dollardenominated asset accounted for around 70% of China s 3.2 trillion worth of foreign exchange reserves, the depreciation of US dollar casts huge doubts on the asset security of China s foreign exchange reserves. 1.2 Lewis Turning Point (LTP) leads to economic restructuring Lewis Turning Point The market force to raise wages and reduce income gap The emergence of Lewis Turning Point reveals the market power to reduce the income gap. Current labour shortage indicates that the shift of excess labour from China s rural area has ended. Future wage increases, especially among manufacturing-based migrant workers, will serve as the major source to push income increases among low-income residents. Currently, 3
4 RMB a structural imbalance has already emerged, as wages of college graduate and rural workers are converging. Structural elements of wage increases became apparent. Fig 2 Migrant workers wages approaching the same level as college graduates Key Universities Non-key universities Professional Schools Migrant w orkers Source: CEIC, MOA, Mizuho Research Inadequate surplus rural labour force in China According to estimates of Mr. Cai Fang, Head of the Institute of Population and Labour Economics of Chinese Academy of Social Sciences (CASS), the surplus labour force in rural areas would decrease to only 5% at million. There is a serious shortage of surplus rural labour, especially those under 30 years old, while the amount of surplus labour over 30 years old accounts for 80%. Hence, the rural areas have no more young labour to provide. Fig 3 Labour shortage has been pronounced among under 30 years-olds Type Labour transferred Rural labour force million people % million people % Over All Source: CASS, Mizuho Research 1.3 Implications of RMB internationalization RMB internationalization s core implications are to achieve convertibility and status as global reserve currency. In order to reach RMB convertibility, capital account liberalization and RMB circulation offshore supported by RMB exchange rate reform and interest rate liberalization are the four pillars of further reforms. Meanwhile, as China s economic influence enhances, RMB will transition from a local currency towards a more global one. Along with more currency swap agreements signed between PBOC and other countries monetary authorities, as well as the increasing exposure of RMB as an investment currency, RMB may become one of the world s major reserve currencies in probably one decade. China s initial conditions for capital account opening are excellent: high growth rate and savings rate, surplus current account and huge foreign exchange reserves, sound fiscal condition and low non-performing loans in the banking system, strong long-term FDI inflows, minimum external indebtedness, and rapidly expanding domestic capital markets. International Monetary Funds (IMF) research shows that China is not lagging behind and has 4
5 progressed in many aspects in recent years, especially in portfolio investment. Now we believe the conditions are ripe for a breakthrough. RMB s offshore circulation and repatriation will inevitably lead to capital account liberalization. RMB s offshore circulation holds the key to the whole story: the RMB will first establish itself as a common currency for trade settlements, avoiding overreliance on US dollars and spread its influence worldwide. Meanwhile, Hong Kong s unique status as RMB offshore centre will provide adequate investment channels for offshore liquidity, including a return mechanism that will facilitate cross-border investment flows. China has also made significant progress on exchange rate flexibility and the abolishment of interest rate restrictions. In the 11 th five year plan (FYP), PBOC s regulatory framework on the currency market improved, and the tools for monetary policy enforcement became more effective. RMB internationalization will also facilitate faster currency reform, because the ultimate goal is to establish a market-based exchange rate. 5
6 Fig 4 RMB s roadmap towards a global currency Capital account liberalization ODI RMB settlement; Expansion of QDII, QFII and R-QFII; Open HK-linked ETF ODI surges; Further expansion of QDII, QFII and R-QFII; Shanghai Intl. Board ODI and overseas portfolio liberalized; Shanghai opens up as onshore centre Inward investment mostly liberalized; Foreign debt market partially opens Basic convertibility Capital account liberalized with some remaining restriction on short-term debt RMB to become a global reserve currency, around 10% of SDR basket Offshore RMB market HK RMB deposits to 700bn. Establishing a new offshore centre in London. More HK shares issued in RMB; London RMB deposits initiated Hong Kong with wide diversity of RMB products; A Euro-yuan market in London More offshore financial centers created, as Singapore, NYC, Taipei. Wider circulation of RMB abroad RMB exchange rate flexibility Appreciate against USD by 5-6% Further appreciation against USD by 5-6% Wider fluctuation in RMB exchange rate under a shifting band. RMB around CNY5-6 per dollar, more foreign participants in RMB forex market RMB to become free floating currency Interest rate liberalization Off-balance sheet lending and more structural wealth products Trials for deposit rate liberalization; SHIBOR market depth deepens PBOC to widen the scope in deposit and lending rate formation, and lending rate will be liberalized Deposit rate to become completely liberalized Source: Mizuho research
7 RMB internationalization 2.0 RMB internationalization facilitates China s four key transformations Recent literature [IMF (2011), Kenen (2009), Park and Shin (2009)] points out that the internationalization of emerging market countries currency will effectively curb the uneven distribution of currency risks among different economies and reduce the distortive effect of reserve currency countries monetary expansion on other economies. It will also help enhance the diversity of globally traded assets, improve capital allocation and risk sharing, reduce global imbalances and make domestic banks acquire competitive advantage over foreign banks. Moreover, previous IMF research showed that capital account liberalization could lead to better smoothing of consumption cycle and resource allocation efficiency. More available sources of foreign financing also stabilize domestic consumption when facing country-specific risks. In the meantime, however, it also imposes a higher requirement on curbing financial market risks and monetary policy adjustments. China pledges in its 12 th Five Year Plan to further enhance domestic demand, accelerate economic reforms and increase development efficiency. In order to achieve these goals, supply-side reforms, via four key transformations, are urgently required to clear the obstacles ahead for further development, including reforms on exchange rate mechanism to stimulate domestic demand, further development in service industry, enhancing ODI to achieve industry upgrade, as well as loosening up regulatory control on interest rates. Fig 5 RMB internationalization promotes Increase residents real income Currency reform stimulates import demand Further supplyside reform to enhance domestic demand Product market reform Investment and industry upgrade Development of financial industry and service trade ODI Go Abroad Strategy Loosen up regulatory control Interest rate liberalization Source: Mizuho research 2.1 Transformation 1: From export-led to a domestic-demandoriented economy Domestic consumption ratio still trails behind Despite the remarkable economic growth in China since the economic reform began in 1978, the share of consumption in overall GDP has been remarkably low. A quick comparison between the consumption ratio in China and other economies show that the phenomenon is unique. 7
8 % of GDP % Fig 6 China has a low consumption rate China's consumption rate Source: CEIC, Mizuho research The potential for China s consumption is immense, and the government s revision of the existing policies, including high tax burden, retained SOE dividend payment, and PBOCs restriction on interest rate, along with income increase following the emergence of Lewis Turning Point, will unleash the potential for higher income and consumption growth. It will have significant benefit to China s service sector and discretionary spending. Fig 7 China s consumption of GDP much lower than other BRIC countries Brazil China India Russia Source: WDI, Mizuho research Export-oriented pattern could not sustain During the 11th five-year plan, the surplus of China s balance of payments has widened further, as the current account surplus in terms of GDP exceeded 10% in 2007, and capital account surplus also rose rapidly. 8
9 YoY % % Fig 8 Current account surplus peaked in 2007 Current account as % of GDP 12 6th five 7th five 8th five 9th five 10th five 11th five Source: CEIC, Mizuho research But from a longer term perspective, export-led growth has become unsustainable under weak foreign demand. Facing recurrent debt crises of western countries, China cannot find the right cure to solve all problems. But as China s consistent economic growth increased its overall voice in global economic and political arena, proposing RMB internationalization would not only adjust China s position of passively accumulating US dollar-denominated assets, but also would facilitate active participation in international trade and regional investments. Meanwhile, China will adopt a more balanced foreign trade policy, in order to reduce overall foreign trade surplus while increasing exports. In five years, China is expected to import 8 trillion USD worth of products and the retail sales will reach 31 trillion RMB. With expectations of RMB appreciation, RMB internationalization would increase China s purchasing power of energy and raw materials, raising China s overall competitiveness Contribution of domestic demand to the economy will significantly increase Fig 9 Contribution of domestic demand a main factor in recent economic growth Mar-09 Jun-09 Sep-09 Dec-09 Mar-10 Jun-10 Sep-10 Dec-10 Mar-11 Jun-11 Domestic consumption Gross capital formation Net export Source: CEIC, Mizuho research China has long been a country with a high savings rate and a low consumption rate. The emergence of the LTP should boost incomes, and provide an opportunity for China to shift its economy from investment-led to consumption-led. In the next five years, we believe China s household consumption should increase rapidly, and that China is very likely to become the second largest country globally, in consumption terms. 9
10 % % Income growth generates power for economic growth and structural shifts From the experiences of Japan and Korea, the emergence of the LTP is a necessary step for development. Japan and Korea reached their own LTP at the end of the 1960s or 1970s. After the LTP, both economies faced labour shortages, wage hikes as well as rapid economic growth and radical structural adjustments. Wage increases generally lead to stronger consumption. From Japan s experience, residential consumption picked up and the share of consumption in GDP surged after the emergence of the LTP. Korea saw a similar scenario. Fig 10 Consumption rates in Japan and Korea Japan: consumption ratio Korea: consumption ratio Source: CEIC, Mizuho research RMB internationalization facilitates increase in domestic demand The lack of significant increase in China s domestic demand results from a variety of reasons: primarily, the lack of purchasing power is the root cause, as both rural and urban residents real income growth has been slow. Meanwhile, China s traditional consumption and saving pattern restricts China s internal consumption growth, also impeded by high precautious saving need. Moreover, China s domestic savers have limited channels of investing overseas. Together with strict capital control, domestic FAI level remains high. Earlier IMF research showed that capital account liberalization will more effectively smooth consumption over life cycle and achieve better resource allocation. Foreign financing also has a stabilizing effect towards residents consumption rate. RMB internationalization could facilitate policies in stimulating domestic demand from three main aspects: RMB internationalization will lead to cost saving within trade-related firms or firms that are dependent on foreign raw material imports. These firms profitability will increase and employees income level will be enhanced. RMB internationalization stretches domestic demand outwards, namely the increase in demand of foreign exports and overseas consumption. Meanwhile, price level of certain domestic products will be adjusted, as lots of them are significantly higher than their counterparts overseas, effectively increasing domestic residents purchasing power. Because of RMB internationalization, domestic residents will have more channels in investing overseas, thus having more ways of generating income apart from passively saving in banks or possessing limited investment channels. 10
11 2.2 Transformation 2: From manufacturing towards service sector Slow growth in service sector During the 11th five-year plan period, the service sector s contribution to GDP stopped rising, while heavy industry sectors as a share of GDP rose very rapidly. Since 1985 s 7 th FYP, promoting a strong service sector for production and welfare has been proposed. Yet service as of GDP ratio remain stagnant and even fall for some years. Meanwhile, China s service sector as of GDP s gap with other countries is increasing. For instance, in 2009, China s service sector is only 42.6% of GDP, while other developing and developed countries service sector weights are increasing, normally between 50% -80%. Fig 11 BRIC countries major sector contributions towards GDP 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% India Russia Brazil China Agriculture Industry Service Source: WDi, Mizuho research Domestic manufacturing stretching westward, great potential for service sector in the coastal region As of now, the wage increase in south-eastern costal region leads to significant cost increase in setting up factories. Many companies have decided to move their factories westward. This is helpful in balancing the economic development level of Eastern and Western China, also improving regional development pattern. China is still far from development phase of moving manufacturing base overseas as Japan and Korea did previously in 1980s and 1990s. Fig 12 Coastal region s service sector growth has huge growth potential (as of GDP) 60% 55% 50% 45% 40% 35% 30% Shanghai Shenzhen Tianjin Qingdao Source: CEIC, Mizuho research 11
12 % RMB internationalization facilitates export upgrade Despite the fact that China is a major world exporter, China is still far from being a product giant. As majority of Chinese exports focused on lower value-added products, most Chinese companies remain passive price takers on the international market. RMB internationalization will facilitate purchasing of high-end equipments, technology and intellectual property rights, a positive sign for exports moving up the value-added chain. Increasing proportion of service trade, RMB internationalization will help obtain full potential China s service trade achieved rapid growth in the past 30 years. Service trade contains both labour-intensive services, such as travel and transportation, as well as capital intensive ones, such as airlines, communication, architecture, finance and information services. China s overall service trade as of world proportion was still low, mainly due to two reasons: service as of GDP ratio was even lower than other three BRIC countries; capital control and low circulation of overseas RMB create obstacles for faster development of service trade. After RMB internationalization proceeds further, China s potential for service trade, including advantages of human resources and further expansion of service industry, will be fully exploited. Fig 13 RMB internationalization will help China service trade reach its full potential China service trade as of w orld Source: MOFCOM, Mizuho research RMB internationalization boosts development in financial services industry RMB internationalization s direct impact on China s service industry is to further develop financial services in China. Specifically, establishing Hong Kong as RMB offshore centre and ameliorating domestic capital markets will help boost growth in China s finance industry, while the increase in investment products becomes the key to sustainable growth Market infrastructure: interactions between onshore and offshore financial markets Before capital account liberalization, Hong Kong offshore RMB centre has become the touchstone for RMB internationalization. Because of a well-established financial service industry in Hong Kong, Hong Kong will act as a role model for later development in coastal areas. On July 19 th, 2010, the PBOC and HKMA refined the RMB settlement pact, enabling basic RMB convertibility in Hong Kong. Later on Aug 16 th, the opening up of domestic interbank bond market towards foreign institutional investors provided more channels for firms to allocate their RMB liquidity. As of August, Hong Kong s RMB deposits totalled more than 600 billion RMB, and is likely to reach 2 trillion in a couple of years. 12
13 On 17 August, Vice Premier Li Keqiang pledged in his official visit to Hong Kong, a series of new measures to reaffirm the city s status as the RMB s offshore hub. Some of the measures signal a breakthrough on capital account liberalisation and RMB s offshore circulations, and is a major step towards RMB convertibility. New measures include: Launching the mini-qfii scheme which would allow HK investors to invest in mainland securities with an initial quota size of CNY20bn Expanding an RMB trade settlement scheme nationwide Allowing Hong Kong enterprises to invest directly in the mainland using RMB Introducing an ETF linked to Hong Kong stocks in the mainland Broadening the RMB bond market in Hong Kong, including increasing issuance of offshore sovereign bond Successful interactions between onshore and offshore financial market is crucial towards the success of RMB internationalization. Without a repatriation channel, potential offshore liquidity will decrease investors willingness of holding RMB, leading to a lack of overall offshore demand. On the other hand, changes in ODI and patterns of trade finance will lead to overall outflow of onshore RMB, boosting overall overseas investment. 13
14 Fig 14 Interaction between RMB onshore and offshore market Offshore Onshore China s imports from RoW = about 8% of total world imports. RMB settlement of import = about 11% of total Chinese imports as of June Trade Settlement Hong Kong s RMB trade settlement = about roughly 75% of China s total China s export to RoW = about 9.6% of total world exports, RMB settlement of exports = merely 3% of total Chinese exports, as of June China s ODI = 5.2% of world s total outward FDI, RMB settlement about 5.4 billion RMB as of June 2011, only 1% of last year s volume. ODI FDI HK constitutes roughly 60% of total Chinese ODI; 40% of China s FDI inflow Investment flows to China = 8.5% of global FDI inflow. The pilot scheme for FDI inflow RMB settlement just began 23 June this year. QDII Scheme: USD72.6bn, 92 institutional investors Dim Sum Bonds: more than CNY138bn in total H-share linked ETFs Portfolio HK as RMB Dim Sum bond centre Singapore, London, NYC, etc. QFII Scheme: USD20.7bn, 116 institutional investors; RQFII Scheme: CNY20bn; Interbank bond market allows foreign investment Foreign aid and preferential loans to Africa and Latin America Foreign debt Foreign loans with domestic guarantees scheme Central banks of: HK, Korea, Singapore, Indonesia, Malaysia, Argentina, Iceland, Belarus, Mongolia, Nigeria, Russia and Thailand Currency swap agreements PBOC: Currency Swap agreements = about 5% of total foreign reserves Source: Mizuho research Diversified financial products strengthens RMB internationalization Following the promotion of more varied RMB-denominated financial products, China s finance industry would likely increase its product depth, which demands the government to devote more energy on building a stable institutional framework, attracting more financial experts, risk management as well as macro-planning. QFII & QDII As a prudent measure to avoid short-term capital volatility, the restriction on foreigners portfolio investment still existed. When inbound investment was finally allowed in 2003, it was achieved by the use of a pre-commitment vehicle, the Qualified Foreign Institutional Investor (QFII) scheme. As of now, a total of 116 foreign institutional investors have been approved under the QFII program, at an overall volume of 20.7 billion USD. The Qualified Domestic Institutional Investor (QDII) scheme was also introduced in 2006, allowing domestic financial institutions to invest in overseas markets. Similar to QFII investors, QDII participants are not affected by capital control. It is designed to be a 14
15 USDbn transitional arrangement which provides domestic investors the opportunity to access foreign markets via certain fund management institutions, insurance companies, securities companies and other assets management institutions. Starting from 2006, China s QDII has developed steadily, despite the 2008 global financial crisis which slowed down the overall QDII expansion. As of now, China permitted QDII of a total volume of CNY72.6bn. QDII provide more options for domestic residents. Fig 15 Approved QDII and QFII volumes are constantly expanding (April) QFII QDII RQFII Source: Mizuho research R-QFII and HK-linked ETF The long-awaited green light on the mini-qfii scheme, which has an initial quota at CNY20bn, facilitates the return of offshore RMB liquidity towards the mainland capital market. Also, the mini-qfii scheme will not use up the quota from the current QFII. The unveiling of an ETF linked to Hong Kong stocks in China will enable mainland China investors to access stocks listed in Hong Kong, such as the Hang Seng Index (HSI) constituents. Via this arrangement, Chinese investors can gain exposure to Hong Kong market directly, not via the mini-qdii scheme. Mainland Interbank Bond Market Opening up of the onshore interbank bond market is a rational choice for initiating return mechanism of offshore RMB liquidity based on several important reasons: First, interbank bond market consists of a variety of bond products, including government bonds, policy bank bonds, corporate bonds, etc. The trading volume within the interbank market was also huge. For instance, the interbank bond market contributed to 99.38% of non-financial enterprises bond issuance, with a total volume of CNY569.1bn. Second, the interbank bond market has a more attractive yield than the offshore RMB bond market, which mostly has an annual yield of 2-3%. Also, investment risks are relatively smaller in the interbank bond market, which currently has low level of speculation and volatility. On 16 August 2010, the PBOC published a notice which permits three types of offshore entities to invest RMB into China s domestic interbank bond market, including foreign central banks or monetary authorities, RMB clearing banks in Hong Kong and Macau, as well as participating banks for RMB cross-border trade settlement. The whole scheme is regulated by PBOC on a case-by-case basis, and funds will be channelled through currency swap agreements and cross-border trade or investments. Offshore RMB products A watershed year for RMB offshore bonds The year 2010 marked a watershed year for RMB offshore bonds, as international firms, supranational entity and domestic banking corporations all took advantage of the revised settlement agreement, which lifted restrictions on establishing RMB accounts and conducting RMB transfers in Hong Kong. As of now, RMB bonds issuance totaled 138 billion RMBand is likely to reach 500 billion RMB in 5 years. 15
16 1-Feb Feb-11 3-Mar Mar-11 2-Apr Apr-11 2-May May-11 1-Jun Jun-11 1-Jul Jul Jul Aug Aug Sep-11 NAV Fig 16 Entities that issue Dim Sum bonds have already achieved significant diversification ( ) 27% 35% Government + policy bank bonds Offshore FI bonds Multinational bonds China Corporate bonds Synthetic bonds 26% 8% 4% Source: Bloomberg, Mizuho research RMB-denominated shares and other products The Hong Kong Securities and Futures Commission (SFC), Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing Ltd (HKEx) and HKMA are testing Hong Kong s system preparedness for RMB listing and settlement, to boost their readiness to conduct listed RMB securities business. Apart from that, HKEx is considering to build up a liquidity pool to promote RMBdenominated investment. Apart from that, more offshore products, such as offshore RMB derivatives (RMBdenominated interest rate swap), as well as offshore RMB fund mostly situated in Hong Kong, Europe, Japan and Cayman Islands, will diversify offshore RMB products, enhancing its overall depth. Fig 17 Dim Sum Bond-linked funds have significantly increased at major financial centers (Initial NAV=10) Source: Bloomberg, Mizuho research Hong Kong-based Cayman-based Japan-based Europe-based 2.3 Transformation 3: From FDI to go abroad strategy An important part of the economic reform process in China has been the promotion of FDI inflows, and capital account convertibility has been achieved in this area. Since 1993, China has boosted the largest amount of FDI inflow among all developing countries, thanks to the favorable policies, such as tax incentives and the Guiding Directory on Industries Open to Foreign Investment. In fact, foreign enterprises have until recently enjoyed preferential treatment compared to domestic enterprises. 16
17 USD bn In comparison, Outward Direct Investment (ODI) did not flourish until the recent decade, when the government relaxed the restrictions on overseas investments and created government funds to support enterprises investing overseas. It is in line with the country s Go Global policy. The investments are primarily focused on the nearby economies, particularly in SE Asia, and developing economies. As China s economic growth expands, as does its appetite for natural resources. Much of the ODI quest abroad is related to acquisition of resources from resource abundant countries, and is usually spearheaded by State Owned Enterprises (SOEs). Fig 18 FDI & ODI in comparison FDI ODI Source: MOF, Mizuho research Recent China s ODI statistics revealed that China s overall FDI outflow as of world has reached 5.2%, higher than traditional FDI outflow giants as Japan and UK. Moreover, China s ODI stock reached billion USD, 17 th overall in the world. More importantly, China s overseas M&A volume expanded to 29.7 billion USD, increasing 5.5 billion yoy. As ODI volume increased further, Chinese government has already proposed RMB settlement of ODI. This will facilitate the go abroad strategy of Chinese enterprises and also provide opportunities to strengthen RMB internationalization. South Africa s Standard Bank Group recently revealed that eventually 40% of Sino-African trade will be denominated in RMB, namely 100 billion USD, 2010 s overall Sino-African trade volume. RMB internationalization will have a huge impact on China s overseas investment: First, RMB internationalization will promote more private enterprises going abroad. Despite various obstacles, RMB internationalization will clear away controls on capital movement and foreign exchange management. Meanwhile, RMB internationalization will increase Chinese enterprises competitiveness overseas, as pricing power and settlement procedures were mainly controlled by foreign enterprises and governments. Foreign currency control also imposed limits on Chinese enterprises M&A activities overseas, while RMB internationalization could solve this problem. Moreover, RMB internationalization will increase overall RMB ODI stock overseas. As of end 2010, China re-invest 34.9% of its current profits of ODI, RMB internationalization will further increase the re-investment ratio. 17
18 USDbn no.transactions Fig 19 M&A volume originated from Greater China Region rose rapidly since Volume Deals Source: Deloitte, Mizuho research ODI promotes industry upgrade Developed countries experience showed that ODI reflected the transition from lowproductivity, high volume growth towards an upgrade on the value-added chain and a more efficient growth. ODI pattern will also follow a transition from resource-seeking to companies grasping market share, and eventually seeking for more efficient business model and acquisition of strategic assets. Fig 20 ODI promotes industry upgrade Speeds up Industrialization ODI leads to industry upgrade Developed world NIEs Structural adjustment Expand advantaged industry Dynamic competitive advantage Emerging market Technology Accumulation/ R&D Source: Zhao and Jing (2011), Mizuho Research 2.4 Transformation 4: From policy-oriented towards market-based financial market The biggest current issue for China s financial market to interact globally was the lack of market-based mechanism, as policy measures were still the major power in adjusting local financial market. Among them interest rate liberalization and a more flexible exchange rate mechanism are the most crucial ones. We have already witnessed progresses in the past few years, but RMB internationalization will accelerate the reform progress, enhancing the market depth of the overall market Interest rate liberalization will progress A market-based interest rate formation mechanism has to go hand-in-hand with RMB s internationalization, because of four main reasons: First, a market based interest rate determination system that better facilitates the allocation of resources in the economy. Second, as China s money rates were not completely market-based, yield structure of financial products were not available for accurate pricing. The RMB internationalization required adequate channels with diversified products at a market-based pricing system. Third, a non-market based interest rate regime combined with a gradually opening capital account 18
19 might lead to increasing arbitrage opportunities and volatility in capital transactions. It will also affect policy decisions negatively, reversing the efforts made in previous reforms. Forth, it facilitates competition within the banking system, preparing domestic banks for potential risks of a gradually opening capital account Lack of interest rate liberalization leads to off-balance sheet risks In order to circumvent the regulated deposit interest rates amid tight supervision of the loandeposit ratio (LDR) and high pressure on funding, many banks increased their sales of financial products in 1H11, and subsequently started a price war on these products. Compared with a year ago, the number of short-term financial products (3-21 days) sold in September 2011 has increased by more than 120%, while the number of products sold with a one-year maturity has decreased. Banks have also been competing on yields offered. Although these financial products have catered to the capital needs for off-balance sheet, they nevertheless constitute a potential risk for the overall banking system. In addition, these financial products have diluted the effectiveness of monetary policy on the market. The growth of money supply (M2) and new loan were at 13% and CNY470bn respectively in August, both significantly below market expectation. The expansion of offbalance sheet financing products have compromised the effectiveness of the traditional policy tools. The financial products, and the off-balance sheet risk that ensued are both results of the overly low deposit interest rates regulated by the authority. Competition for deposits between banks, and it is a preview of what is to come when deposit rate becomes liberalized. To avoid the off-balance sheet risks from getting out of control, we believe the policymakers should move towards using interest rate as the primary policy tool, and move the assets back to the balance sheet. In the long run, we believe deposit rate liberalisation need to speed up to eradicate the problem at its roots Interest rate liberalization process Progress along the way Until now, China has already proactively progressed in interest rate liberalization. Zhang Xiaohui, head of the monetary policy department at the PBOC pointed out that since 1996, interest rate liberalization has been ongoing at China s economy. The PBOC has taken steps to relax its control on interest rates, and gradually set up the rate setting mechanism in the market. The priority of the liberalization process has been on the currency and bond market first, and followed by eliminating the control with the following principle: lending rate before deposit rate, foreign currency before RMB, long term deposit before near term ones, and large size account before small size ones. Against the general direction, PBOC has so far eliminated the control on 199 interest rate related products, accomplished the interest rate marketization in the currency and bond market, and removed the cap for lending and floor for deposit rate. The process strengthened the central bank s ability to monitor the market using interest rates, and set the ground for further reforms to come. We have compiled a short list of what China has already achieved towards interest rate liberalization. 19
20 Fig 21 Progress in China s Interest rate liberalization Category Foreign Currency interest rate Interest Rate Liberalization Moves Completely liberalized in 2003, covering 29 different currencies. Shanghai interbank offer rate Market determined SHIBOR rates in 2007 Corporate bonds/ Commercial Papers Market-based pricing with no restrictions (interest rate restrictions removed in 2009). Mortgage rate Loans/Deposits rate Source: PBOC, Mizuho research Expansion of mortgage rate s float width after Wenchuan Earthquake in 2008 ( not widely accepted by firms) Impose limits on only lower bound for loans and upper bound for deposit rates. From expansion of rate s float width towards removal of loan rate s upper bound and deposit rate s lower bound. So far, liberalization of commercial banks deposit and lending rates was basically stagnant. Banking risk is the main concern in the interest rate liberalization process ahead. A comprehensive reform of the banking system, including the imposition of hard-budget constraint, exit mechanism and deposit insurance system, as well as a better transformation mechanism from policy rates to commercial bank deposit and lending rates would have to be in place. The deposit rate will increase after the cap is abolished, and it will erode the interest rate spread, a main source of profit for commercial banks. It is therefore a significant challenge to the health of the banking system, and the major banks that are operational under the traditional mandate will be put under stress. A major hurdle for lifting capital controls in China has always been its fragile financial system, especially its troubled banking sector. The spread between the ceiling on deposit rates and the floor on lending rates, at roughly 3%, continues to over 80% of their profit. Scrapping a ceiling on deposit rates may promote more efficient pricing, allocation of capital and boost returns for savers, but it would have to be a gradual and orchestrated process, as it tests on the adoptability of the current banking system to open competition. However, the good news is that China s commercial banks have come a long way since the early 1990s, with significant improvement in their balance sheets and management structure. As late as 2002, BIS called China s banking system daunting, based on the scale of the non-performing loans problem. In 2002, the share of non-performing loans amounted to 23.6% of total loans outstanding. In the past decade, China has undertaken a sweeping reform program to restructure and rehabilitate its banking sector, with remarkable success. To begin to address this stock problem and to restore bank balance sheets, the Chinese government set up four stateowned asset management corporations (AMCs) in Their purpose was to buy bad debts of the four major state-owned commercial banks (the big four banks) and to dispose of them over 10 years. BIS stipulated that PBOC credit was the principal source of cash financing for the AMCs. Banks were also encouraged to using sizable amounts of provisioning funds to write off bad loans under the supervision of China Banking Regulatory Commission (CBRC), to prevent loans from deteriorating, and appearing on balance sheets. By 2010, China s NPL has fallen to a healthy 1.15%. We believe the government will likely continue with noticeable progress, and the cap for deposit rate may be one of the restrictions to be removed in five years. The reform will facilitate transition of monetary policy to relying more on "price-based mechanisms" rather than "quantitative mechanisms" such as lending quotas, a key to China s financial system reform. The price-based mechanism will likely be supplemented with more open market intervention in the future Currency rate regime towards more flexibility In order to achieve full convertibility, a more flexible RMB exchange rate mechanism is required to end the current slow-paced, one-way appreciation and a virtual peg with the US dollar. Since the beginning of 1994, China s exchange rate has been determined in the China Foreign Exchange Trading Centre (CFETC), an inter-bank foreign exchange market. The 20
21 actual exchange policy itself, however, is supported by an elaborate system of direct capital controls implemented through administrative measures. While encouraging foreign direct investment (FDI), foreign portfolio investment and short-term foreign borrowing was restricted. At the end of 1996, China reached an important milestone by permitting RMB convertibility under current accounts. But the Asian financial crisis crushed this hope and the central bank made currency stability its primary goal of exchange rate policy. China initially modified its exchange rate regime on 21 July 2005, abandoning the fixed dollar peg. The PBOC has also widened the RMB s daily trading band to 0.5% since 18 May However, the one-sided appreciation process was once halted since late 2008 because of the global financial crisis, when export firms in China had already suffered from decline in foreign demand and was afraid of more downward pressure caused by RMB appreciation. A de facto dollar peg was thus resumed. In June 2010, the PBOC decided to proceed further with the reform of the RMB exchange rate regime to enhance the RMB exchange rate flexibility. Other preparations for RMB s full convertibility are also on the way. The market infrastructure precursory to full convertibility is required, such as the trading and market maker system to improve the RMB mid-price formation process, and the development of various kinds of RMB related financial products, to provide hedging tools. In 2010, the size of RMB spot, forward, and swap markets were USD3.05tn, USD32.7bn, and USD1.27tn respectively. They were respectively around 4 times, 2 times and 25 times larger than the size in
22 Jan-06 May-06 Sep-06 Jan-07 May-07 Sep-07 Jan-08 May-08 Sep-08 Jan-09 May-09 Sep-09 Jan-10 May-10 Sep-10 Jan-11 May-11 % 3.0 Two risks of RMB internationalization 3.1 Risk 1: Increasing difficulty in macro control The greatest challenge that RMB internationalization will bring for the Chinese government is the increasing difficulty of macro control and curtailed effectiveness of policy measures. Specifically, due to increase of offshore RMB circulation, RMB cash and liquidity management will become harder to monitor, and PBoC s open market operations might be less effective than before. As RMB internationalization was not completed, we find the high interest rate gap between onshore and offshore staggering. The fact that couple of domestic enterprises could use low cost to raise debt in Hong Kong offshore markets (dim sum bonds) has already created pressures for effective macro control. Fig 22 Gap between Hong Kong and the mainland deposit rates widening China 1-yr deposit rate HK 1-yr deposit rate (HKD) Source: Mizuho research In order to prevent the foreign exchange reserves from further increases, China s foreign exchange control has shifted from restricting outflow to restricting inflow. However, SAFE has loosened up the policy of extending credit certificates for domestic enterprises seeking for foreign loans. The mechanism enabled domestic enterprises to deposit in domestic banks in exchange of a credit certificate for the company to seek overseas financing for its offshore subsidiary. HKMA s Norman Chan pointed out that 60% of the 444 billion HKD increase in loans towards Chinese non-financial clients are guaranteed by domestic banks. These clients normally transferred their funds borrowed back into Chinese domestic banks, in order to profit from the interest rate gap and the RMB appreciation. Meanwhile, PBOC will have a harder time choosing an appropriate monetary policy for the time being, as it not only needs to consider domestic inflation, but also has to look at increasing offshore RMB demand, which is likely to expand to around 5-10% of overall RMB liquidity in 5-10 years. 3.2 Risk 2: short-term capital flow and RMB exchange rate volatility RMB exchange rate regime will be based on market supply and demand after RMB internationalization is completed. Together with the parallel development in capital account liberalization and hence the increasing offshore RMB demand, RMB exchange rate will be unable to maintain at the current pace of gradual appreciation. 22
23 With increasing exposure to offshore RMB, volatility in the offshore markets is likely to lead to fluctuations in offshore RMB exchange rates, and this may subsequently have a knock-on effect on onshore exchange rates. Currently, however, we don t expect volatility in the offshore markets to significantly impact the performance of the onshore market, as offshore liquidity is relatively thin. Nevertheless, with increasing offshore RMB deposits and investment channels, such insulation will not last forever, and onshore rates will inevitably be influenced by offshore volatility. Fig 23 CNH-CNY rate differentiation not an unseen story /19 Difference of onshore and offshore rates reaches 1,700 bps /23 onshore and offshore rates differs by more than 1,200 bps Aug-10 Oct-10 Dec-10 Feb-11 Apr-11 Jun-11 Aug-11 USD-CNH USD-CNY Source: Bloomberg, Mizuho research 23
24 4.0 Reference 1 Annual Report on Exchange Arrangements and Exchange Restrictions International Monetary Fund, Aramaki, Kenji, Sequencing of Capital Account Liberalization - Japan s Experiences and Their Implications to China, Public Policy Review 2(1) (2006), China s capital account liberalization: international perspectives. BIS Papers No. 15, April. (2003) 4 Chung, Kyuil, "Mechanism to mitigate adverse effect of capital inflows: Korea's experience." High level workshop on "Strengthening the response to the global financial crisis in Asia-Pacific: the role of macroeconomic policies". UNESCAP. Phnom Penh, Cambodia June Fukao, Mitsuhiro Capital Account Liberalization: The Japanese Experience and 6 Implications for China, BIS Papers, No. 15 (2003): Fukao, Mitsuhiro The liberalization of Japanese exchange controls and structural changes in the balance of payments (1990) 8 Gil-Diaz, Francisco, "The origin of Mexico's 1994 financial crisis." Cato journal 17.3 (1998): Speech by André Icard, Deputy General Manager of the BIS, on the occasion of the joint BIS/SAFE seminar on 'Capital account liberalisation in China: international perspectives' in Beijing on September Iigima, Takao Financial Big Bang to Asia Bond Market, Keio University, KUMQRP Working Paper Series, DP (2005) 11 The IMF s approach to capital account liberalization: evaluation report. International Monetary Fund, "IMF develops framework to manage capital inflows." IMF survey magazine. 05 Apr IMF Strengthening the International Monetary System: Taking Stock and Looking Ahead. 23 Mar Kenen, Peter. Currency Internationalization: An Overview. BIS paper, 1 March Li, Xiaojia. "Six key questions on RMB internationalization." Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing Ltd. 29 Sep Lorenzo Cappiello and GIanluigi Ferrucci, The Sustainability of China s exchange rate policy and capital account liberalization, European Central Bank (2008) 17 Lu, Mai. "Is RMB exchange regime reform good for China?" CDRF research reference (2011): 18 Palley, Thomas, "Chilean unremunerated reserve requirement capital controls as a screening mechanism." Investigación Económica. LXIV.251 (2005):
RMB internationalization:
 RMB internationalization: Recent Development and headwinds Alicia Garcia-Herrero Chief Economist for Emerging Markets, BBVA Key points 1 Why is China pushing to internationalize the RMB? 2 Recent development
RMB internationalization: Recent Development and headwinds Alicia Garcia-Herrero Chief Economist for Emerging Markets, BBVA Key points 1 Why is China pushing to internationalize the RMB? 2 Recent development
Renminbi Internationalisation The Journey Begins
 Treasury Division Renminbi Monitor January 2013 Joanne Yim Chief Economist joanneyim@hangseng.com Renminbi Internationalisation The Journey Begins After decades of rapid growth, mainland China has become
Treasury Division Renminbi Monitor January 2013 Joanne Yim Chief Economist joanneyim@hangseng.com Renminbi Internationalisation The Journey Begins After decades of rapid growth, mainland China has become
Emergence of RMB as an International Currency
 Emergence of RMB as an International Currency Cindy Lo, Partner Allen & Overy, Beijing Office March 2013 1 Agenda An Overview: the Chinese Government s policy objectives and key regulatory developments
Emergence of RMB as an International Currency Cindy Lo, Partner Allen & Overy, Beijing Office March 2013 1 Agenda An Overview: the Chinese Government s policy objectives and key regulatory developments
The Development of the Offshore. Bonds. Peter J. Morgan, PhD Senior Consultant for Research Asian Development Bank Institute
 The Development of the Offshore Market of the Yuan-Denominated Bonds Peter J. Morgan, PhD Senior Consultant for Research Asian Development Bank Institute ADBI-OECD Roundtable on Capital Market Reform in
The Development of the Offshore Market of the Yuan-Denominated Bonds Peter J. Morgan, PhD Senior Consultant for Research Asian Development Bank Institute ADBI-OECD Roundtable on Capital Market Reform in
RMB Internationalization Status and Its Implications
 International Finance RMB Internationalization Status and Its Implications Hansoo Kim, Research Fellow* 1) China announced the RMB internationalization policy in 2009 and has carried forward many initiatives
International Finance RMB Internationalization Status and Its Implications Hansoo Kim, Research Fellow* 1) China announced the RMB internationalization policy in 2009 and has carried forward many initiatives
Second wind for offshore RMB market
 Citi OpenInvestor September 2012 7 Globalization Citi OpenInvestor presents: Second wind for offshore RMB market In just one year, the internationalization of the renminbi has seen a thriving market in
Citi OpenInvestor September 2012 7 Globalization Citi OpenInvestor presents: Second wind for offshore RMB market In just one year, the internationalization of the renminbi has seen a thriving market in
Increasing Competition among Markets for Offshore Renminbi Business
 Increasing Competition among Markets for Offshore Renminbi Business Eiichi Sekine Chief Representative, Beijing Representative Office Nomura Institute of Capital Markets Research Masanobu Iwatani Financial
Increasing Competition among Markets for Offshore Renminbi Business Eiichi Sekine Chief Representative, Beijing Representative Office Nomura Institute of Capital Markets Research Masanobu Iwatani Financial
The PBoC s progress report on renminbi internationalization
 Mizuho Securities Asia Ltd Economics Research 17 Jun 2015 The PBoC s progress report on renminbi internationalization Jianguang Shen jianguang.shen@hk.mizuho-sc.com +852 2685 2022 Michael Luk michael.luk@hk.mizuho-sc.com
Mizuho Securities Asia Ltd Economics Research 17 Jun 2015 The PBoC s progress report on renminbi internationalization Jianguang Shen jianguang.shen@hk.mizuho-sc.com +852 2685 2022 Michael Luk michael.luk@hk.mizuho-sc.com
China Financial Reforms: In need of further deregulation
 China Financial Reforms: In need of further deregulation Mingchun Sun 1 Summary Over the past decade, the Chinese government has implemented a series of financial reforms and transformed its financial
China Financial Reforms: In need of further deregulation Mingchun Sun 1 Summary Over the past decade, the Chinese government has implemented a series of financial reforms and transformed its financial
International Monetary System Reform and Asian Monetary and Financial Cooperation
 International Monetary System Reform and Asian Monetary and Financial Cooperation Dr. Zong Liang Deputy General Manager Strategic Development Department Bank of China New Delhi, March 20, 2012 0 Contents
International Monetary System Reform and Asian Monetary and Financial Cooperation Dr. Zong Liang Deputy General Manager Strategic Development Department Bank of China New Delhi, March 20, 2012 0 Contents
RMB Internationalization Policies & Trade Finance Services. Xi Jingjing April 2017
 RMB Internationalization Policies & Trade Finance Services Xi Jingjing April 2017 Contents China-Hungary Relationship Status quo and Future of RMB Internationalization BOC s Financial Services 2 China-Hungary
RMB Internationalization Policies & Trade Finance Services Xi Jingjing April 2017 Contents China-Hungary Relationship Status quo and Future of RMB Internationalization BOC s Financial Services 2 China-Hungary
The Impact of the Global Crisis on China and its Reaction (ARI)
 The Impact of the Global Crisis on China and its Reaction (ARI) Ming Zhang * Theme: The current global financial crisis is having a significant negative impact on the Chinese economy. Summary: The current
The Impact of the Global Crisis on China and its Reaction (ARI) Ming Zhang * Theme: The current global financial crisis is having a significant negative impact on the Chinese economy. Summary: The current
Internationalization of the RMB: Developments, Problems and Policies
 Internationalization of the RMB: Developments, Problems and Policies 23 October 2015 Zheng Liansheng Outline Introduction The development of RMB internationalization RMB Offshore markets The problems behind
Internationalization of the RMB: Developments, Problems and Policies 23 October 2015 Zheng Liansheng Outline Introduction The development of RMB internationalization RMB Offshore markets The problems behind
The Internationalisation of the Renminbi
 Tel: (852)3550-7070; Fax: (852)2104-6938 Email: lawrence@lawrencejlau.hk; WebPages: www.igef.cuhk.edu.hk/ljl *All opinions expressed herein are the author s own and do not necessarily reflect the views
Tel: (852)3550-7070; Fax: (852)2104-6938 Email: lawrence@lawrencejlau.hk; WebPages: www.igef.cuhk.edu.hk/ljl *All opinions expressed herein are the author s own and do not necessarily reflect the views
Management Discussion and Analysis
 Financial Review Economic and Financial Environment In the first half of 2015, the global economy experienced sluggish growth at various pace of recovery across different countries. Due to bad weather,
Financial Review Economic and Financial Environment In the first half of 2015, the global economy experienced sluggish growth at various pace of recovery across different countries. Due to bad weather,
Monetary Policy and Interest Rate Reform
 Thomas Shik Senior Economist thomasshik@hangseng.com Monetary Policy and Interest Rate Reform The benchmark lending rate set by the People s Bank of China (PBOC) has remained the key reference for banks
Thomas Shik Senior Economist thomasshik@hangseng.com Monetary Policy and Interest Rate Reform The benchmark lending rate set by the People s Bank of China (PBOC) has remained the key reference for banks
China: Beyond the headlines. Bill Maldonado HSBC Global Asset Management
 China: Beyond the headlines Bill Maldonado HSBC Global Asset Management Are you a China Bull or a Bear? Source: Various news publications 2 Bear myth #1: Hard landing? GDP: Growth is slowing, but it s
China: Beyond the headlines Bill Maldonado HSBC Global Asset Management Are you a China Bull or a Bear? Source: Various news publications 2 Bear myth #1: Hard landing? GDP: Growth is slowing, but it s
The Chinese Approach to Capital Account Liberalization: What Do We Learn from Renminbi Banking in Hong Kong?
 HKIMR First International Conference on the Chinese Economy The Chinese Approach to Capital Account Liberalization: What Do We Learn from Renminbi Banking in Hong Kong? Dong HE Hong Kong Monetary Authority
HKIMR First International Conference on the Chinese Economy The Chinese Approach to Capital Account Liberalization: What Do We Learn from Renminbi Banking in Hong Kong? Dong HE Hong Kong Monetary Authority
The Effect of Chinese Monetary Policy on Banking During the Global Financial Crisis
 27 The Effect of Chinese Monetary Policy on Banking During the Global Financial Crisis Prof. Dr. Tao Chen School of Banking and Finance University of International Business and Economic Beijing Table of
27 The Effect of Chinese Monetary Policy on Banking During the Global Financial Crisis Prof. Dr. Tao Chen School of Banking and Finance University of International Business and Economic Beijing Table of
ASF Hong Kong Market Report
 HONG KONG ECONOMY ASF 2016 - Hong Kong Market Report Background As everyone knows, Hong Kong has a very good geographic location, it is surround by sea and backup by a huge China market. HK has taken a
HONG KONG ECONOMY ASF 2016 - Hong Kong Market Report Background As everyone knows, Hong Kong has a very good geographic location, it is surround by sea and backup by a huge China market. HK has taken a
RIDING THE CHINA WAVE: HKEX S GROWTH STRATEGIES IN THE EXCHANGES ARENA
 A MEMBER OF THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG GROUP 香港大學機構成員 AMY YIP ROY ZHOU RIDING THE CHINA WAVE: HKEX S GROWTH STRATEGIES IN THE EXCHANGES ARENA Our vision at HKEx is to reshape the global market landscape
A MEMBER OF THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG GROUP 香港大學機構成員 AMY YIP ROY ZHOU RIDING THE CHINA WAVE: HKEX S GROWTH STRATEGIES IN THE EXCHANGES ARENA Our vision at HKEx is to reshape the global market landscape
The Impacts of RMB Cross-border Settlement on China's Economy 1
 Policy discussion No. 2016.002 Feb.4 2016 XU Qiyuan xuqiy@163.com The Impacts of RMB Cross-border Settlement on China's Economy 1 In Tokyo, I have frequently been asked about two renminbi (RMB) internationalization
Policy discussion No. 2016.002 Feb.4 2016 XU Qiyuan xuqiy@163.com The Impacts of RMB Cross-border Settlement on China's Economy 1 In Tokyo, I have frequently been asked about two renminbi (RMB) internationalization
2013 The year of the renminbi
 2013 The year of the renminbi Economic and regulatory conditions affecting the renminbi are unfolding quickly. This document reflects HSBC s views on how the development of the renminbi will unfold as
2013 The year of the renminbi Economic and regulatory conditions affecting the renminbi are unfolding quickly. This document reflects HSBC s views on how the development of the renminbi will unfold as
Leveraging China and RMB Internationalisation
 Leveraging China and RMB Internationalisation Goldman Sachs Luncheon Presentation Charles Li Chief Executive, HKEx 28 September 2010 4 0 0 3 0 0 2 0 0 1 0 0 0 First Phase: Primary Market Has Driven Growth
Leveraging China and RMB Internationalisation Goldman Sachs Luncheon Presentation Charles Li Chief Executive, HKEx 28 September 2010 4 0 0 3 0 0 2 0 0 1 0 0 0 First Phase: Primary Market Has Driven Growth
2015 Outlook: China s Economy and Bond Markets
 Special Comment 215 Outlook: China s Economy and Bond Markets January 215 Elle Hu +852-2868 317 elle_hu@ccxap.com Carter Liu +852-2868 377 carter_liu@ccxap.com Jolie Li +852-2868 319 jolie_li@ccxap.com
Special Comment 215 Outlook: China s Economy and Bond Markets January 215 Elle Hu +852-2868 317 elle_hu@ccxap.com Carter Liu +852-2868 377 carter_liu@ccxap.com Jolie Li +852-2868 319 jolie_li@ccxap.com
Unravel the complexities of RMB Internationalisation The Rising Role of RMB- A Corporate Perspective 24 May 2012 PUBLIC
 Unravel the complexities of RMB Internationalisation The Rising Role of RMB- A Corporate Perspective 24 May 2012 1. RMB Internationalisation Overview A Global Trade Currency A Global Investment Currency
Unravel the complexities of RMB Internationalisation The Rising Role of RMB- A Corporate Perspective 24 May 2012 1. RMB Internationalisation Overview A Global Trade Currency A Global Investment Currency
China Banking Regulatory Update November 2013
 China Banking Regulatory Update November 2013 Kreab Gavin Anderson is a leading communications consultancy with a global reach. We help our clients solve complicated and demanding communications issues
China Banking Regulatory Update November 2013 Kreab Gavin Anderson is a leading communications consultancy with a global reach. We help our clients solve complicated and demanding communications issues
Offshore RMB Market Update
 Offshore RMB Market Update Ricky Li Economics and Strategic Planning Department Bank of China (Hong Kong) Limited November 2014 Offshore RMB Market Update A. Offshore RMB Bond Market Update B. RMB Internationalization
Offshore RMB Market Update Ricky Li Economics and Strategic Planning Department Bank of China (Hong Kong) Limited November 2014 Offshore RMB Market Update A. Offshore RMB Bond Market Update B. RMB Internationalization
China s GDP slows out of double-digit growth
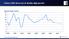 China s GDP slows out of double-digit growth Percent change, annual 16 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 198 1985 199 1995 2 25 21 215 Source: International Monetary Fund. China s growth forecasts slows among Asian countries
China s GDP slows out of double-digit growth Percent change, annual 16 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 198 1985 199 1995 2 25 21 215 Source: International Monetary Fund. China s growth forecasts slows among Asian countries
CHINA FOCUS II AIMING FOR THE SDR BASKET
 AIMING FOR THE SDR BASKET With its rising economic size and position as a top trading nation, China is aiming for the RMB to be included into the SDR basket of currencies at the 2015 IMF review, which
AIMING FOR THE SDR BASKET With its rising economic size and position as a top trading nation, China is aiming for the RMB to be included into the SDR basket of currencies at the 2015 IMF review, which
HKEX'S FIVE-YEAR CHINA MINISTRY OF FINANCE TREASURY BOND FUTURES THE WORLD'S FIRST RMB BOND DERIVATIVES ACCESSIBLE TO OFFSHORE INVESTORS
 April 2017 RESEARCH REPORT HKEX'S FIVE-YEAR CHINA MINISTRY OF FINANCE TREASURY BOND FUTURES THE WORLD'S FIRST RMB BOND DERIVATIVES ACCESSIBLE TO OFFSHORE INVESTORS CONTENTS Page Summary... 1 1. The openness
April 2017 RESEARCH REPORT HKEX'S FIVE-YEAR CHINA MINISTRY OF FINANCE TREASURY BOND FUTURES THE WORLD'S FIRST RMB BOND DERIVATIVES ACCESSIBLE TO OFFSHORE INVESTORS CONTENTS Page Summary... 1 1. The openness
Development of RMB Internationalization
 Development of RMB Internationalization RMB has become world s #6 payment currency, #3 trade finance currency (SWIFT), #8 FX currency (BIS) and the latest SDR basket currency. Trade Currency Investment
Development of RMB Internationalization RMB has become world s #6 payment currency, #3 trade finance currency (SWIFT), #8 FX currency (BIS) and the latest SDR basket currency. Trade Currency Investment
Key Insights. China Macro Pulse
 MACRO REPORT China Economy Update March 2015 Key Insights Monica Defend Head of Global Asset Allocation Research Qinwei Wang Economist Global Asset Allocation Research Economic Conditions: China s macro
MACRO REPORT China Economy Update March 2015 Key Insights Monica Defend Head of Global Asset Allocation Research Qinwei Wang Economist Global Asset Allocation Research Economic Conditions: China s macro
Notes on the monetary transmission mechanism in the Czech economy
 Notes on the monetary transmission mechanism in the Czech economy Luděk Niedermayer 1 This paper discusses several empirical aspects of the monetary transmission mechanism in the Czech economy. The introduction
Notes on the monetary transmission mechanism in the Czech economy Luděk Niedermayer 1 This paper discusses several empirical aspects of the monetary transmission mechanism in the Czech economy. The introduction
Capital account management in China. Yu Yongding CAFRAL Conference, New Delhi, Jan 12, 2014
 Capital account management in China Yu Yongding CAFRAL Conference, New Delhi, Jan 12, 2014 China now is more sympathetic with capital account liberalization, but why? since 2003, and especially since 2009
Capital account management in China Yu Yongding CAFRAL Conference, New Delhi, Jan 12, 2014 China now is more sympathetic with capital account liberalization, but why? since 2003, and especially since 2009
Emerging Markets Weekly Economic Briefing
 Emerging Markets Weekly Economic Briefing The risks of renewed capital flight from emerging markets Recent episodes of capital flight from emerging markets have highlighted the vulnerability of a number
Emerging Markets Weekly Economic Briefing The risks of renewed capital flight from emerging markets Recent episodes of capital flight from emerging markets have highlighted the vulnerability of a number
Asian Insights Third quarter 2016 Asia s commitment in policies and reforms
 Asian Insights Third quarter 2016 Asia s commitment in policies and reforms One of the commonalities between most Asian governments is the dedicated commitment they have in using policies and initiatives
Asian Insights Third quarter 2016 Asia s commitment in policies and reforms One of the commonalities between most Asian governments is the dedicated commitment they have in using policies and initiatives
Emerging Markets Debt: Outlook for the Asset Class
 Emerging Markets Debt: Outlook for the Asset Class By Steffen Reichold Emerging Markets Economist May 2, 211 Emerging market debt has been one of the best performing asset classes in recent years due to
Emerging Markets Debt: Outlook for the Asset Class By Steffen Reichold Emerging Markets Economist May 2, 211 Emerging market debt has been one of the best performing asset classes in recent years due to
Quarterly Economic Outlook: Quarter on 25 September 2018 Strong Economic Expansions amidst Uncertainty of Trade War
 Foregin Direct Investment (Billion USD) China U.S. Asia World Quarterly Economic Outlook: Quarter 3 2018 on 25 September 2018 Strong Economic Expansions amidst Uncertainty of Trade War Thai Economy: Thai
Foregin Direct Investment (Billion USD) China U.S. Asia World Quarterly Economic Outlook: Quarter 3 2018 on 25 September 2018 Strong Economic Expansions amidst Uncertainty of Trade War Thai Economy: Thai
Japan s Economy: Monthly Review
 Japan's Economy 18 July 214 (No. of pages: 8) Japanese report: 18 Jul 214 Japan s Economy: Monthly Review China s shadow banking problem requires continued monitoring Economic Intelligence Team Mitsumaru
Japan's Economy 18 July 214 (No. of pages: 8) Japanese report: 18 Jul 214 Japan s Economy: Monthly Review China s shadow banking problem requires continued monitoring Economic Intelligence Team Mitsumaru
an eye on east asia and pacific
 67887 East Asia and Pacific Economic Management and Poverty Reduction an eye on east asia and pacific 7 by Ardo Hansson and Louis Kuijs The Role of China for Regional Prosperity China s global and regional
67887 East Asia and Pacific Economic Management and Poverty Reduction an eye on east asia and pacific 7 by Ardo Hansson and Louis Kuijs The Role of China for Regional Prosperity China s global and regional
Indonesia Economic Outlook and Policy Challenges
 Indonesia Economic Outlook and Policy Challenges Daniel A. Citrin Asia and Pacific Department, IMF April 3, 28 Global Financial Stability Map: risks have risen; conditions have deteriorated October 27
Indonesia Economic Outlook and Policy Challenges Daniel A. Citrin Asia and Pacific Department, IMF April 3, 28 Global Financial Stability Map: risks have risen; conditions have deteriorated October 27
Recent Asia experiences with capital flows
 Recent Asia experiences with capital flows Rob Subbaraman, Chief Economist Asia Ex-Japan December 2007 Asia ex-japan's total balance of payments % of GDP 10 8 6 4 2 0-2 -4 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001
Recent Asia experiences with capital flows Rob Subbaraman, Chief Economist Asia Ex-Japan December 2007 Asia ex-japan's total balance of payments % of GDP 10 8 6 4 2 0-2 -4 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001
Global Investment Outlook for 2H 2016
 Global Investment Outlook for 2H 2016 Major central banks apart the Fed may stay in easing mode due to heightened economic and political risks. China s economy in 2H 2016 may continue to stabilize but
Global Investment Outlook for 2H 2016 Major central banks apart the Fed may stay in easing mode due to heightened economic and political risks. China s economy in 2H 2016 may continue to stabilize but
Efficacy of China s capital controls
 Efficacy of China s capital controls RIETI/BIS/BOC conference Globalisation of financial servceis in China: implications for capital flows, supervision and monetary policy Beijing, 19 March 2005 Guonan
Efficacy of China s capital controls RIETI/BIS/BOC conference Globalisation of financial servceis in China: implications for capital flows, supervision and monetary policy Beijing, 19 March 2005 Guonan
Chi on China. RMB Internationalisation (part 1 of 2): Short-term Tactics May have Changed SUMMARY. For professional investors 24 February
 For professional investors 24 February 2016 1 Chi on China RMB Internationalisation (part 1 of 2): Short-term Tactics May have Changed Change will not come if we wait for some other person or some other
For professional investors 24 February 2016 1 Chi on China RMB Internationalisation (part 1 of 2): Short-term Tactics May have Changed Change will not come if we wait for some other person or some other
Chi on China. RMB Internationalisation (part 1 of 2): Short-term Tactics May Have Changed SUMMARY. For professional investors 23 February
 For professional investors 23 February 2016 1 Chi on China RMB Internationalisation (part 1 of 2): Short-term Tactics May Have Changed Change will not come if we wait for some other person or some other
For professional investors 23 February 2016 1 Chi on China RMB Internationalisation (part 1 of 2): Short-term Tactics May Have Changed Change will not come if we wait for some other person or some other
Offshore Renminbi (CNH) Market: Opportunities Continue to Expand Silicon Valley Bank. January 13, 2012
 Offshore Renminbi (CNH) Market: Opportunities Continue to Expand Silicon Valley Bank January 13, 2012 1 Panelists Ed Sauve, Senior Advisor GFS, Silicon Valley Bank Mark Noble, Senior Foreign Exchange Trader,
Offshore Renminbi (CNH) Market: Opportunities Continue to Expand Silicon Valley Bank January 13, 2012 1 Panelists Ed Sauve, Senior Advisor GFS, Silicon Valley Bank Mark Noble, Senior Foreign Exchange Trader,
October 2012 Hong Kong Sustainable Development Research Institute Edmund Ho
 Featured Article: Role of Hong Kong as a RMB Offshore Center October 2012 Hong Kong Sustainable Development Research Institute Edmund Ho Introduction The economy of China developed rapidly after the open
Featured Article: Role of Hong Kong as a RMB Offshore Center October 2012 Hong Kong Sustainable Development Research Institute Edmund Ho Introduction The economy of China developed rapidly after the open
CLSA Investors Forum September Mrs Margaret Leung Vice-Chairman and Chief Executive Hang Seng Bank
 CLSA Investors Forum 2011 21 September 2011 Mrs Margaret Leung Vice-Chairman and Chief Executive Hang Seng Bank Good afternoon, ladies and gentlemen. I am delighted to have the opportunity to speak with
CLSA Investors Forum 2011 21 September 2011 Mrs Margaret Leung Vice-Chairman and Chief Executive Hang Seng Bank Good afternoon, ladies and gentlemen. I am delighted to have the opportunity to speak with
China s Growth Miracle: Past, Present, and Future
 China s Growth Miracle: Past, Present, and Future Li Yang 1 Over the past 35 years, China has achieved extraordinary economic performance thanks to the market-oriented reforms and opening-up. By the end
China s Growth Miracle: Past, Present, and Future Li Yang 1 Over the past 35 years, China has achieved extraordinary economic performance thanks to the market-oriented reforms and opening-up. By the end
China Economic Quarterly
 August 2016 Major economic indicators p1 /Policy updates p5 /Hot topic analysis p6 China Economic Quarterly www.pwccn.com/ceq Content I. Major economic indicators 1 II. Policy updates 5 III. Hot topic
August 2016 Major economic indicators p1 /Policy updates p5 /Hot topic analysis p6 China Economic Quarterly www.pwccn.com/ceq Content I. Major economic indicators 1 II. Policy updates 5 III. Hot topic
Summary. Chinese equities remained mired in a bear market, with the Shanghai composite losing nearly
 Summary Editor: Tristan Zhuo Senior Economist Phone: +852 2826 6193 Email: tristanzhuo@bochk.com In spite of fixed asset investment, industrial production, and exports all missing their targets, China
Summary Editor: Tristan Zhuo Senior Economist Phone: +852 2826 6193 Email: tristanzhuo@bochk.com In spite of fixed asset investment, industrial production, and exports all missing their targets, China
Transformation in China: New Opportunities and Challenges
 Transformation in China: New Opportunities and Challenges March 2008 The information contained herein does not constitute and shall not be construed to constitute investment, tax or legal advice by Deutsche
Transformation in China: New Opportunities and Challenges March 2008 The information contained herein does not constitute and shall not be construed to constitute investment, tax or legal advice by Deutsche
The Internationalisation of the Renminbi
 Tel: (852)3550-7070; Fax: (852)2104-6938 Email: lawrence@lawrencejlau.hk; WebPages: www.igef.cuhk.edu.hk/ljl *All opinions expressed herein are the author s own and do not necessarily reflect the views
Tel: (852)3550-7070; Fax: (852)2104-6938 Email: lawrence@lawrencejlau.hk; WebPages: www.igef.cuhk.edu.hk/ljl *All opinions expressed herein are the author s own and do not necessarily reflect the views
August 2017 The information contained in this publication is not intended as investment advice or recommendation. Non contractual document.
 Demystifying Chinese Bond Investing August 2017 The information contained in this publication is not intended as investment advice or recommendation. Non contractual document. Chinese bonds have been in
Demystifying Chinese Bond Investing August 2017 The information contained in this publication is not intended as investment advice or recommendation. Non contractual document. Chinese bonds have been in
Asia s strongest brand in banking, banking the world s strongest economies
 Credit Suisse Investor Conference Peter Wong, Chief Executive, HSBC Asia-Pacific Asia s strongest brand in banking, banking the world s strongest economies 21 March 2011 www.hsbc.com Forward-looking statements
Credit Suisse Investor Conference Peter Wong, Chief Executive, HSBC Asia-Pacific Asia s strongest brand in banking, banking the world s strongest economies 21 March 2011 www.hsbc.com Forward-looking statements
Lessons from GFC for Management and Liberalization of Capital Flows in Asia Mario B. Lamberte Director of Research
 Lessons from GFC for Management and Liberalization of Capital Flows in Asia Mario B. Lamberte Director of Research This draws largely on Chapter 1 of the forthcoming book, Managing Capital Flows: Search
Lessons from GFC for Management and Liberalization of Capital Flows in Asia Mario B. Lamberte Director of Research This draws largely on Chapter 1 of the forthcoming book, Managing Capital Flows: Search
Attila Tapaszti Zsanett Sütő: Push and pull! Developments in the renminbi exchange rate
 Attila Tapaszti Zsanett Sütő: Push and pull! Developments in the renminbi exchange rate The liberalisation of the Chinese capital and foreign exchange markets, the global enhancement of the role of the
Attila Tapaszti Zsanett Sütő: Push and pull! Developments in the renminbi exchange rate The liberalisation of the Chinese capital and foreign exchange markets, the global enhancement of the role of the
Chief Economist, BOC Cao Yuanzheng June 12, 2012 本材料仅供收件人参考未经中国银行允许, 不得以任何方式复印, 分发或传阅他人
 Chief Economist, BOC Cao Yuanzheng June 12, 2012 本材料仅供收件人参考未经中国银行允许, 不得以任何方式复印, 分发或传阅他人 Content Origination of RMB Internationalization RMB Cross-boarder Trade Settlement Hong Kong RMB Offshore Market
Chief Economist, BOC Cao Yuanzheng June 12, 2012 本材料仅供收件人参考未经中国银行允许, 不得以任何方式复印, 分发或传阅他人 Content Origination of RMB Internationalization RMB Cross-boarder Trade Settlement Hong Kong RMB Offshore Market
CHINA AND INDIA: SUSTAINING HIGH QUALITY GROWTH
 CHINA AND INDIA: SUSTAINING HIGH QUALITY GROWTH New Delhi March 19-20, 2012 Session V: Coping with Global Financial Instability Internationalizing the RMB: Pros and Cons Zhang Yuyan Presentation Internationalizing
CHINA AND INDIA: SUSTAINING HIGH QUALITY GROWTH New Delhi March 19-20, 2012 Session V: Coping with Global Financial Instability Internationalizing the RMB: Pros and Cons Zhang Yuyan Presentation Internationalizing
Reform of Global Reserve System and China s Choice 1
 Reform of Global Reserve System and China s Choice 1 Liqing Zhang Professor and Dean, School of Finance, Central University of Finance and Economics, Beijing Email: zhlq@cufe.edu.cn 1. Why the Regime should
Reform of Global Reserve System and China s Choice 1 Liqing Zhang Professor and Dean, School of Finance, Central University of Finance and Economics, Beijing Email: zhlq@cufe.edu.cn 1. Why the Regime should
ASF Hong Kong Market Report
 ASF 2013 - Hong Kong Market Report October 2013 HONG KONG ECONOMY Economic Performance The Hong Kong economy saw a modest growth in 2012, despite a difficult external global economic environment characterised
ASF 2013 - Hong Kong Market Report October 2013 HONG KONG ECONOMY Economic Performance The Hong Kong economy saw a modest growth in 2012, despite a difficult external global economic environment characterised
Economic Watch. As RMB internationalization advances, new headwinds call for policy steps. China
 China Hong Kong, July 17, 212 Economic Analysis Asia Chief Economist of Emerging Markets Alicia Garcia Herrero alicia.garcia-herrero@bbva.com.hk Chief Economist for Asia Stephen Schwartz Stephen.schwartz@bbva.com.hk
China Hong Kong, July 17, 212 Economic Analysis Asia Chief Economist of Emerging Markets Alicia Garcia Herrero alicia.garcia-herrero@bbva.com.hk Chief Economist for Asia Stephen Schwartz Stephen.schwartz@bbva.com.hk
A Century of History A Global Service
 A Century of History A Global Service Bank of China Limited 2012 Interim Results August 24, 2012 Forward-looking Statement Disclaimer This presentation and subsequent discussions may contain forward-looking
A Century of History A Global Service Bank of China Limited 2012 Interim Results August 24, 2012 Forward-looking Statement Disclaimer This presentation and subsequent discussions may contain forward-looking
Themes in bond investing
 For professional investors only Not for public distribution Themes in bond investing June Asia 2011 2009 outlook Introduction Asian markets enjoyed a Goldilocks economic scenario in 2010 that helped them
For professional investors only Not for public distribution Themes in bond investing June Asia 2011 2009 outlook Introduction Asian markets enjoyed a Goldilocks economic scenario in 2010 that helped them
Management Discussion and Analysis Financial Review
 % 8 6 4 2 0 Growth of Global and Chinese Economy (2013 to 2017) Growth rate of global economy Growth rate of Chinese economy 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 Source: International Monetary Fund (IMF), National
% 8 6 4 2 0 Growth of Global and Chinese Economy (2013 to 2017) Growth rate of global economy Growth rate of Chinese economy 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 Source: International Monetary Fund (IMF), National
Asian Insights What to watch closely in Asia in 2016
 Asian Insights What to watch closely in Asia in 2016 Q1 2016 The past year turned out to be a year where one of the oldest investment adages came true: Sell in May and go away, don t come back until St.
Asian Insights What to watch closely in Asia in 2016 Q1 2016 The past year turned out to be a year where one of the oldest investment adages came true: Sell in May and go away, don t come back until St.
26 Nov Executive Summary. Analyst Hillary Ho Li Ling
 Analyst Hillary Ho Li Ling +6565311517 hillaryho@phillip.com.sg Executive Summary United States: We maintain our stance that QE2 will not make a huge difference to economic conditions. Growth will continue
Analyst Hillary Ho Li Ling +6565311517 hillaryho@phillip.com.sg Executive Summary United States: We maintain our stance that QE2 will not make a huge difference to economic conditions. Growth will continue
Hong Kong s s Expanding Role as an Offshore RMB Centre
 Hong Kong s s Expanding Role as an Offshore RMB Centre Goldman Sachs Global Macro Conference Peter Pang Deputy Chief Executive Hong Kong Monetary Authority 22 February 211 Mainland s s Phenomenal Growth
Hong Kong s s Expanding Role as an Offshore RMB Centre Goldman Sachs Global Macro Conference Peter Pang Deputy Chief Executive Hong Kong Monetary Authority 22 February 211 Mainland s s Phenomenal Growth
Indonesia: Building on Resilience and Prospering Amid Global Economic Uncertainty
 Indonesia: Building on Resilience and Prospering Amid Global Economic Uncertainty 2016 Article IV Consultation Report on Indonesia John G. Nelmes IMF Senior Resident Representative for Indonesia Academic
Indonesia: Building on Resilience and Prospering Amid Global Economic Uncertainty 2016 Article IV Consultation Report on Indonesia John G. Nelmes IMF Senior Resident Representative for Indonesia Academic
* * * * * Executive Directors: (Vice Chairman and Chief Executive)
 BOC HONG KONG (HOLDINGS) LIMITED (the Company, BOCHK ) QUESTION AND ANSWER SESSION CONVENED IMMEDIATELY AFTER ANNUAL GENERAL MEETING HELD ON 6 JUNE 2016 * * * * * Present: Executive Directors: Mr. Yue
BOC HONG KONG (HOLDINGS) LIMITED (the Company, BOCHK ) QUESTION AND ANSWER SESSION CONVENED IMMEDIATELY AFTER ANNUAL GENERAL MEETING HELD ON 6 JUNE 2016 * * * * * Present: Executive Directors: Mr. Yue
Management Discussion and Analysis
 Financial Review Economic and Financial Environment In the first half of 2012, the global economic recovery slowed and uncertainty increased. The European sovereign debt crisis remained unresolved and
Financial Review Economic and Financial Environment In the first half of 2012, the global economic recovery slowed and uncertainty increased. The European sovereign debt crisis remained unresolved and
Global Economic Prospects: Navigating strong currents
 Global Economic Prospects: Navigating strong currents Andrew Burns World Bank January 18, 2011 http://www.worldbank.org/globaloutlook Main messages Most developing countries have passed with flying colors
Global Economic Prospects: Navigating strong currents Andrew Burns World Bank January 18, 2011 http://www.worldbank.org/globaloutlook Main messages Most developing countries have passed with flying colors
Paul Browne, Partner, London Yongmei Cai, Partner, Beijing Jay Lee, Partner, Hong Kong
 One Belt One Road and RMB internationalisation: a look at how recent PRC regulatory developments provide significant opportunities for market participants in the Financial Markets in the UK and Europe
One Belt One Road and RMB internationalisation: a look at how recent PRC regulatory developments provide significant opportunities for market participants in the Financial Markets in the UK and Europe
China Focus RMB Internationalization In Progress
 Quarterly Global Outlook 2Q211 RMB Internationalization In Progress 23 The RMB is internationalizing progressively as China opens up more avenues for the controlled outflow of its currency. The main factors
Quarterly Global Outlook 2Q211 RMB Internationalization In Progress 23 The RMB is internationalizing progressively as China opens up more avenues for the controlled outflow of its currency. The main factors
Presentation. The Boom in Capital Flows and Financial Vulnerability in Asia
 High-level Regional Policy Dialogue on "Asia-Pacific economies after the global financial crisis: Lessons learnt, challenges for building resilience, and issues for global reform" 6-8 September 2011, Manila,
High-level Regional Policy Dialogue on "Asia-Pacific economies after the global financial crisis: Lessons learnt, challenges for building resilience, and issues for global reform" 6-8 September 2011, Manila,
Summary. The RMB will be added to the IMF s SDR basket of currencies starting October 1 st, which will be
 Summary Editor: Tristan Zhuo Senior Economist Phone: +852 2826 6193 Email: tristanzhuo@bochk.com China s economic momentum strengthened somewhat in the month of August. Industrial production has largely
Summary Editor: Tristan Zhuo Senior Economist Phone: +852 2826 6193 Email: tristanzhuo@bochk.com China s economic momentum strengthened somewhat in the month of August. Industrial production has largely
Invesco Global Insights
 Invesco Global Insights May 2016 Countdown to MSCI China A-Share Inclusion Executive Summary Whether or not MSCI adds China A-shares to the MSCI Emerging Markets index as part of their next round of updates
Invesco Global Insights May 2016 Countdown to MSCI China A-Share Inclusion Executive Summary Whether or not MSCI adds China A-shares to the MSCI Emerging Markets index as part of their next round of updates
RMB Internationalization at Half-time: Retrospect and Prospect
 RMB Internationalization at Half-time: Retrospect and Prospect The Asian Financial Leaders Program Dr. Guan Tao Senior Fellow at China Finance 40 Forum Beijing, May 25, 2017 Main Contents 1 2 3 Historical
RMB Internationalization at Half-time: Retrospect and Prospect The Asian Financial Leaders Program Dr. Guan Tao Senior Fellow at China Finance 40 Forum Beijing, May 25, 2017 Main Contents 1 2 3 Historical
Globalization of Korea s Foreign Exchange System. Seoul Asian Financial Forum. June 4, Michael Hellbeck
 Globalization of Korea s Foreign Exchange System Seoul Asian Financial Forum June 4, 2012 Michael Hellbeck COO & Head of Regulatory Affairs Standard Chartered Bank Korea 2 Agenda Introduction to Standard
Globalization of Korea s Foreign Exchange System Seoul Asian Financial Forum June 4, 2012 Michael Hellbeck COO & Head of Regulatory Affairs Standard Chartered Bank Korea 2 Agenda Introduction to Standard
An Analysis of China's Money Supply and Its Changes in
 Financial Statistical Journal (2018) Original Research Article An Analysis of China's Money Supply and Its Changes in 2008-2010 Zhaoxin Wang,Tingting Tang,Xuebin Xia,Xiaohong Yan Business School, Shanxi
Financial Statistical Journal (2018) Original Research Article An Analysis of China's Money Supply and Its Changes in 2008-2010 Zhaoxin Wang,Tingting Tang,Xuebin Xia,Xiaohong Yan Business School, Shanxi
Understanding RQFII The Great Door Opener for China Access
 Markets and Securities Services Investor Services Understanding RQFII The Great Door Opener for China Access By: Stewart Aldcroft, Citi Investor Services Since China first started opening up its capital
Markets and Securities Services Investor Services Understanding RQFII The Great Door Opener for China Access By: Stewart Aldcroft, Citi Investor Services Since China first started opening up its capital
Indonesia: Changing patterns of financial intermediation and their implications for central bank policy
 Indonesia: Changing patterns of financial intermediation and their implications for central bank policy Perry Warjiyo 1 Abstract As a bank-based economy, global factors affect financial intermediation
Indonesia: Changing patterns of financial intermediation and their implications for central bank policy Perry Warjiyo 1 Abstract As a bank-based economy, global factors affect financial intermediation
Financial System Stabilized, but Exit, Reform, and Fiscal Challenges Lie Ahead
 January 21 Financial System Stabilized, but Exit, Reform, and Fiscal Challenges Lie Ahead Systemic risks have continued to subside as economic fundamentals have improved and substantial public support
January 21 Financial System Stabilized, but Exit, Reform, and Fiscal Challenges Lie Ahead Systemic risks have continued to subside as economic fundamentals have improved and substantial public support
The Outlook for Asian & Australian Economies
 The Outlook for Asian & Australian Economies Asian economies maintain stable growth led by domestic demand although growth pace slows down slightly AKI FUKUCHI, YOKO HAGIWARA ECONOMIC RESEARCH OFFICE TOKYO
The Outlook for Asian & Australian Economies Asian economies maintain stable growth led by domestic demand although growth pace slows down slightly AKI FUKUCHI, YOKO HAGIWARA ECONOMIC RESEARCH OFFICE TOKYO
ASIAN ECONOMIES. Economics, interest rates and currencies chart pack
 ASIAN ECONOMIES Economics, interest rates and currencies chart pack Amy Auster Senior Economist Melbourne 2 May 25 E-mail: austera@anz.com Internet: http://www.anz.com/go/economics 1 Major revisions to
ASIAN ECONOMIES Economics, interest rates and currencies chart pack Amy Auster Senior Economist Melbourne 2 May 25 E-mail: austera@anz.com Internet: http://www.anz.com/go/economics 1 Major revisions to
Outlook for the Chilean Economy
 Outlook for the Chilean Economy Jorge Marshall, Vice-President of the Board, Central Bank of Chile. Address to the Fifth Annual Latin American Banking Conference, Salomon Smith Barney, New York, March
Outlook for the Chilean Economy Jorge Marshall, Vice-President of the Board, Central Bank of Chile. Address to the Fifth Annual Latin American Banking Conference, Salomon Smith Barney, New York, March
The Future of Thai Fund Management Industry
 The Future of Thai Fund Management Industry Speech by Mr. Thirachai Phuvanat naranubala, Secretary-General of Securities and Exchange Commission On The Post / Lipper Thailand Fund Award for 2003 At Dusit
The Future of Thai Fund Management Industry Speech by Mr. Thirachai Phuvanat naranubala, Secretary-General of Securities and Exchange Commission On The Post / Lipper Thailand Fund Award for 2003 At Dusit
Research FTSE Russell China Bond Research Report
 Research FTSE Russell China Bond Research Report January 2018 ftserussell.com FTSE Russell China Bond Research Report Highlights China s debt markets declined on the back of selling pressure after the
Research FTSE Russell China Bond Research Report January 2018 ftserussell.com FTSE Russell China Bond Research Report Highlights China s debt markets declined on the back of selling pressure after the
Monetary Policy under Fed Normalization and Other Challenges
 Javier Guzmán Calafell, Deputy Governor, Banco de México* Santander Latin America Day London, June 28 th, 2018 */ The opinions and views expressed in this document are the sole responsibility of the author
Javier Guzmán Calafell, Deputy Governor, Banco de México* Santander Latin America Day London, June 28 th, 2018 */ The opinions and views expressed in this document are the sole responsibility of the author
THE HONGKONG AND SHANGHAI BANKING CORPORATION LIMITED 2012 CONSOLIDATED RESULTS HIGHLIGHTS. Pre-tax profit up 19% to HK$108,729m (HK$91,370m in 2011).
 News Release 4 March 2013 THE HONGKONG AND SHANGHAI BANKING CORPORATION LIMITED CONSOLIDATED RESULTS HIGHLIGHTS Pre-tax profit up 19% to HK$108,729m (HK$91,370m in ). tributable profit up 23% to HK$83,008m
News Release 4 March 2013 THE HONGKONG AND SHANGHAI BANKING CORPORATION LIMITED CONSOLIDATED RESULTS HIGHLIGHTS Pre-tax profit up 19% to HK$108,729m (HK$91,370m in ). tributable profit up 23% to HK$83,008m
PURSUING SHARED PROSPERITY IN AN ERA OF TURBULENCE AND HIGH COMMODITY PRICES
 2012 Key messages Asia-Pacific growth to slow in 2012 amidst global turbulence: Spillovers of the euro zone turmoil Global oil price hikes Excess liquidity and volatile capital flows Key long-term challenge:
2012 Key messages Asia-Pacific growth to slow in 2012 amidst global turbulence: Spillovers of the euro zone turmoil Global oil price hikes Excess liquidity and volatile capital flows Key long-term challenge:
B-GUIDE: Economic Outlook
 Aug-12 Apr-13 Dec-13 Aug-14 Apr-15 Dec-15 Aug-16 Apr-17 Jul-15 Nov-15 Mar-16 Jul-16 Nov-16 Mar-17 Jul-17 Quarterly Economic Outlook: Quarter 4 2017 4 January 2018 B-GUIDE: Economic Outlook The economy
Aug-12 Apr-13 Dec-13 Aug-14 Apr-15 Dec-15 Aug-16 Apr-17 Jul-15 Nov-15 Mar-16 Jul-16 Nov-16 Mar-17 Jul-17 Quarterly Economic Outlook: Quarter 4 2017 4 January 2018 B-GUIDE: Economic Outlook The economy
Greater China Week in Review Monday, 30 May, 2016
 Summary PBoC kept its RMB index in a tight range last week. Frankly speaking, the fact that we are able to forecast the daily USDCNY fixing more accurately shows that RMB has been more predictable than
Summary PBoC kept its RMB index in a tight range last week. Frankly speaking, the fact that we are able to forecast the daily USDCNY fixing more accurately shows that RMB has been more predictable than
The USD/CNY Adjustment Is It Complete?
 The USD/CNY Adjustment Is It Complete? Derek Halpenny European Head of Global Currency Research European Central Bank June 29 1 Substantial REER Appreciation 1 USD/CNY vs Renminbi REER 9 8 7 6 5 12 11
The USD/CNY Adjustment Is It Complete? Derek Halpenny European Head of Global Currency Research European Central Bank June 29 1 Substantial REER Appreciation 1 USD/CNY vs Renminbi REER 9 8 7 6 5 12 11
Letter from Hong Kong
 Letter from Hong Kong April 2015 The Hong Kong Capital Markets Welcome to our new publication. Our intention is to send out a high scope commentary, twice a year, focussing on a particular feature of the
Letter from Hong Kong April 2015 The Hong Kong Capital Markets Welcome to our new publication. Our intention is to send out a high scope commentary, twice a year, focussing on a particular feature of the
Greater China Week in Review Monday, 22 January, 2018
 01/2014 03/2014 05/2014 07/2014 09/2014 11/2014 01/2015 03/2015 05/2015 07/2015 09/2015 11/2015 01/2016 03/2016 05/2016 07/2016 09/2016 11/2016 01/2017 03/2017 05/2017 07/2017 09/2017 11/2017 % Highlights:
01/2014 03/2014 05/2014 07/2014 09/2014 11/2014 01/2015 03/2015 05/2015 07/2015 09/2015 11/2015 01/2016 03/2016 05/2016 07/2016 09/2016 11/2016 01/2017 03/2017 05/2017 07/2017 09/2017 11/2017 % Highlights:
Hong Kong: Will service exports shine again?
 Jackit Wong Senior Economist jackitwswong@hangseng.com Thomas Shik Acting Chief Economist thomasshik@hangseng.com Hong Kong: Will service exports shine again? Since the end of the global financial crisis,
Jackit Wong Senior Economist jackitwswong@hangseng.com Thomas Shik Acting Chief Economist thomasshik@hangseng.com Hong Kong: Will service exports shine again? Since the end of the global financial crisis,
Flash Notes. China: Aiming for the SDR Basket
 UOB Global Economics and Markets Research Company Reg No. 193500026Z Suan Teck Kin Thursday, 30 April 2015 Suan.TeckKin@UOBgroup.com Flash Notes China: Aiming for the SDR Basket With its rising economic
UOB Global Economics and Markets Research Company Reg No. 193500026Z Suan Teck Kin Thursday, 30 April 2015 Suan.TeckKin@UOBgroup.com Flash Notes China: Aiming for the SDR Basket With its rising economic
