Where The Rupee Goes. Where The Rupee Come From 11% 27% 27% 27% 28% 35% Non-Debt Capital Receipts 32% Central Plan 20% Interest 22%
|
|
|
- Gervais Williams
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Finance Bill, 2012 Ek Samiksha 306, Akruti Arcade, J.P. Road, Opp. Wadia High School, Andheri (West), Mumbai Ph: / Fax : Website : ssjco@bom5.vsnl.net.in ssjco@ssjco.in (For Private circulation only)
2 11% 2% Where The Rupee Come From % 3% 27% Borrowing & Other Liabilities % Corporation Tax 27% Excise 28% Non-Tax Revenue 35% Non-Debt Capital Receipts 32% Where The Rupee Goes 7% % 6% 9% 7% 5% 22% 20% Central Plan Interest State's Share Of Taxes, Duties Other non-plan Expenditure 11% Defence 13% 11% 18% 21% Subsidies 17% State & UT plan Assistance 5% Non-plan aid to state & UT's 15%
3 19 th March 2012 Dear Madam/Sir, Finance Minister Shri Pranabda narrated in his budget speech The life of a Finance Minister is not easy. Various players, including policy makers, politicians, agriculturists and business houses, participate in the making of the economy. When everything goes well with the economy, we all share in the joy. However, when things go wrong, it is the Finance Minister who is called upon to administer the medicine. Economic policy, as in medical treatment, often requires us to do something, which, in the short run, may be painful, but is good for us in the long run. As Hamlet, the Prince of Denmark had said in Shakespeare s immortal words, I must be cruel only to be kind. Direct Taxes Code (DTC) Bill has missed the target launch date of April 2012 and, therefore, the Hon ble Minister has introduced many of its provisions in the present Finance Bill. Advance pricing agreement, General Anti Avoidance Rule (GAAR), tax slab changes and reduction in securities transaction tax are among the DTC provisions that are brought in ahead of the full legislation. We as tax professional and tax payer need to understand the provisions of Finance Bill because ultimately we have to take the medicines given by Hon ble Minister. We have, like all these years, made an attempt to appraise our esteemed clients of the important amendments as proposed by the Finance Bill especially in the arena of Income tax Act, An attempt is made to cover Service Tax also by broadly outlining major proposals thereof. This study note of ours titled The Finance Bill, 2012 Ek Samiksha is enclosed herewith. After you had an opportunity to go through the same, we may discuss this further at your convenience. Happy Reading! With regards, Yours truly, Team-S S Jhunjhunwala & Co. 3
4 C O N T E N T S Particulars Page Nos. Budget at a Glance 8 Tax Receipts 9 Excerpts from Experts 10 Income Tax Provisions: 1) Effective Dates 12 A. RATES OF INCOME TAX 2) Rates of Taxes 12 3) Surcharge and Education Cess 13 4) Rate of tax for Firms, Company 14 5) Rate of Tax Deduction at Source 15 B. WIDENING OF TAX BASE 6) Alternate Minimum Tax (AMT) on all persons other than 18 Companies [Sections 115JC to 115JF] 7) Daily tonnage income of shipping company [Section VG] 8) TDS Provisions C. MEASURES TO PREVENT GENERATION AND CIRCULATION OF UNACCOUNTED MONEY 9) Cash Credits [Section 68] 20 10) Rate of tax for Unexplained money, investments, 21 unexplained expenditure and amount borrowed or repaid on hundi [Section 115BBE] 11) Filing of return of income [Section 139] 22 12) Income escaping assessment [Sections 147 and 149 of the Income Tax Act, 1961 and Section 17 of the Wealth Tax Act] 22 13) Penalty where search has been initiated [Section 271AAB] 23 14) Income from Other Sources [Section 56] 24 15) Prosecution proceedings under the Income Tax Act 25 D. TAX INCENTIVES AND RELIEFS 16) Tax Incentives for funding of certain Infrastructure Sectors [Section 115A] 17) Lower rate of tax on dividends received from foreign companies [Section 115BBD] 18) Provisions relating to Venture Capital Fund (VCF) or Venture Capital Company (VCC) [Sections 115U and 10(23FB)] 19) Removal of the cascading effect of Dividend Distribution Tax (DDT) [Section 115-O] 20) Exemption in respect of income received by certain foreign companies [Section 10(48)] 21) Extending benefit of initial depreciation to the power sector [Section 32(1)(iia)]
5 22) Weighted deduction for scientific research and development 30 [Section 35(2AB)] 23) Weighted deduction for expenditure incurred on agricultural 30 extension project [Section 35CCC] 24) Weighted deduction for expenditure for skill development 31 [Section 35CCD] 25) Turnover or gross receipts for audit of accounts and 31 presumptive taxation [Sections 44AB and 44AD] 26) Exemption for Senior Citizens from payment of advance tax 33 [Section 207] 27) Relief from long-term capital gains tax on transfer of 33 residential property if invested in a manufacturing small or medium enterprise [Section 54GB] 28) Reduction in the rate of Securities Transaction Tax (STT) 34 29) Deduction in respect of capital expenditure on specified 34 business [Section 35AD] 30) Extension of sunset date for tax holiday for power sector 36 [Section 80 IA] 31) Reduction of the eligible age for senior citizens for certain 36 tax reliefs [Sections 80D, 80DDB and 197A] 32) Deduction for expenditure on preventive health check-up 36 [Section 80D] 33) Deduction in respect of interest on deposits in savings 36 accounts [Section 80TTA] E. RATIONALIZATION OF TAX DEDUCTION AT SOURCE (TDS) AND TAX COLLECTION AT SOURCE (TCS) PROVISIONS 34) Tax Deduction at Source (TDS) on transfer of certain 37 immovable properties (other than agricultural land) [Section 194LAA] 35) TDS on remuneration to a director [Section 194J] 38 36) Tax Collection at Source (TCS) on cash sale of bullion and 38 jewellery [Section 206C(1D)] 37) Tax Collection on sale of certain minerals [Section 206C(1)] 38 38) Deemed date of payment of tax by the resident payee 39 39) Disallowance of business expenditure on account of nondeduction 39 of tax on payment to resident payee [Section 40(a)(ia)] 40) Fee and penalty for delay in furnishing of TDS/TCS 40 Statement and penalty for incorrect information in TDS/TCS Statement [Sections 272A and 273B] 41) Intimation after processing of TDS statement [Sections and 246A] 42) Person responsible for paying in case of payment by 41 Central Government or Government of a State [Section 204] 43) Extension of time for passing an order under section 201 in certain cases [Section 201] 42 5
6 F. RATIONALIZATION OF INTERNATIONAL TAXATION PROVISIONS 44) Provisions relating to Cross Boarder Transactions [Section 42 2(14), 2(42), 9(1) and 195] 45) Taxation of Royalty Income [Section 9(1)(vi)] 46 46) Time limit for issue of Notice [Section 149] 47 47) Withholding tax on payment to non-resident [Section 195] 47 48) Validation Clause [Clause 113 of Finance Bill] 48 49) Taxation of non-resident entertainer, sports person, etc. [Section 115BBA] 48 50) Agreement with Foreign Countries and Specified 49 Association for Double Taxation relief (DTAA) [Section 90 and 90A] 51) Extension of time limit for completion of assessment or reassessment where information is sought under DTAA [Sections 153 and 153B] 50 G. RATIONALIZATION OF TRANSFER PRICING PROVISIONS 52) Advance Pricing Agreement [Sections 92CC and 92CD] 50 53) Examination by the Transfer Pricing Officer of International 52 Transaction [Section 92CA] 54) Transfer Pricing Regulations to apply to certain domestic 53 transactions [Sections 40A(2), 80A, 80IA, 92, 92BA, 92C, 92CA, 92D, 92E, 271, 271AA and 271G] 55) Determination of Arms Length Price (ALP) [Section 92C] 55 56) Definition of international transaction and intangible 56 property [Section 92B] 57) Other amendments to Transfer Pricing Regulations [Sections , 147, 271AA] 58) Amendments in respect to Dispute Resolution Penal (DRP) 58 [Sections 144C, 253, 254] H. GENERAL ANTI-AVOIDANCE RULE (GAAR) 59) General Anti Avoidance Rule [Sections 95 to 102] 59 I. OTHER AMENDMENTS 60) Extension of time for completion of assessments and reassessments [Sections 153 and 153B] 61) Assessment of charitable organization in case commercial receipts exceed the specified threshold [Sections 10(23C), 13 and 143] 62) Due date of furnishing audit report in case of international 63 transactions [Sections 44AB and 139] 63) Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT) [Section 115JB] 63 64) Liability to pay advance tax in case of non-deduction of tax 64 [Section 209] 65) Definition of Commissioner to include Director [Section 2 65 and Section 117(1)] 66) Cost of acquisition in case of certain transfers [Section 49]
7 67) Capital gains tax from sale of agricultural land by a Hindu 65 undivided family (HUF) [Section 54B] 68) Reference to a Valuation Officer [Section 55A] 66 69) Rate of tax for short term capital gain under [Section 111A] 66 70) Capital gains in cases of amalgamation and demerger 67 [Sections 47(vii) and 2(19AA)] 71) Fair Market Value to be full value of consideration in certain 67 cases [Section 50D] 72) Processing of return of income where scrutiny notice issued 67 [Section 143] 73) Notification of a class of search cases where compulsory 68 reopening of past six years not required 74) Charging of interest on recovery of refund granted earlier 68 [Section 234D] 75) Related person for the purpose of making an application 69 before Settlement Commission [Section 245C] 76) Fee for filing of applications before Authority for Advance 69 Rulings (AAR) [Section 245Q] 77) Authorization or requisition and subsequent assessment in 69 search cases [Section 292CC] 78) Prohibition of cash donations in excess of ten thousand 70 rupees [Sections 80G and 80GGA] 79) Eligibility conditions for exempt life insurance policies 71 [Section 10(10D)] 80) Eligibility condition for deduction in respect of life 71 insurance policies [Section 80C] 81) Wealth Tax Provisions 71 82) Other Proposals 72 Service Tax Provisions 75 Gup Shup o Income Tax 80 o Taxation of Cross Boarder Transactions 84 o Company Law 86 o Other Bullet Points 89 Food for Thought 93 In this note an attempt has been made to summaries various proposals of Finance Bill, Specific guidance may be obtained before acting on the proposals and provisions. It should be noted that the Finance Bill, 2012 will be discussed in the Parliament and is subject to any amendments that may be made pursuant to such discussion. 7
8 Budget at a Glance Actuals Budget Revised Budget Estimates Estimates Estimates 1 Revenue Receipts Tax Revenue (net to centre) Non-Tax Revenue Capital Receipts (5+6+7)$ Recoveries of Loans Other Receipts Borrowings and other liabilities * Total Receipts (1+4)$ Non-Plan Expenditure On Revenue Account of which Interest Payments On Capital Account Plan Expenditure On Revenue Account On Capital Account Total Expenditure (9+13) Revenue Expenditure (10+14) Of Which, Grants for creation of Capital Assets 19 Capital Expenditure (12+15) Revenue Deficit (17-1) Effective Revenue Deficit (20-18) Fiscal Deficit {16-(1+5+6)} Primary Deficit (22-11) Actuals for in this document are provisional. $ Excluding receipts under Market Stabilisation Scheme. * Includes draw down of Cash Balance. Notes: GDP for BE has been projected at ` crore assuming 14% growth over the 1 Advance Estimates of (` crore) released by CSO. 2 Individual items in this document may not sum up to the totals due to rounding off. 8
9 TAX RECIEPTS The Statement below summarizes, by broad categories, the estimates of tax revenue receipts over a period. The estimates include the effect of Budget proposals. Profile of central gross tax revenues ( in Crores) Actual Actual Budget DIRECT Income Corporation Wealth Tax & Others INDIRECT Excise Customs Service Other Taxes TOTAL DIRECT (%) Service Tax to total (%)
10 EXCERPTS FROM EXPERTS 1) Hon ble Prime Minister Shri Manmohan Singhji India s GDP growth is favorable when we look at what s happening in the rest of the world. We are still in the league of front- runners in growth the challenge is to get back to the path of 8% and 9% 2) Shri Pranab Mukharjee- Finance Minister Himself He opened the part of his speech on Friday that dealt with tax proposals by quoting from Shakespeare s Hamlet. I must be cruel only to be kind. If the hike in Service tax was cruel, the kindest cut came by way increased I-T Exemption limits that could save individual taxpayers up to Rs. 22, 600 annually. In reply to questions put before Mr Minister as to whether the tax amendments were aimed at taxing Vodafone, he replied that- It need not be interpreted in this way. What we are doing(is) we are making the intention of the legislature clear about the taxation on which there was a doubt(and) on the basis of which Supreme court has given its direction. We are making retrospective clarifications through the Finance Bill. 3) Shri Yashwant Sinha - Former finance minister Fails to lift the sentiment of the economy it is an accounting statement but not a policy enhancing document. It has just tinkered with schemes and programmes. 4) Shri Mukesh Ambani- Chairman Reliance Industries Ltd Finance Minister showed a resolve to address infirmities in governance and plug leakages in tax collection system. 5) Shri Sunil Mittal- Chairman & Group CEO Bharti Enterprises. Broadening the service tax net is a move in the right direction given the growing share of the sector in our GDP. 6) Shri Akhilesh Yadav- Chief Minister Uttar Pradesh Higher taxes will lead to a rise in inflation: Service tax has been raised to 12%, which will push up inflation since services accounts for 59% of the GDP. 10
11 7) Shri Uday Kotak- VC & MD of Kotak Mahindra Bank The FM could have done more to boost our sagging capital markets that are dependent on foreign investors. 8) Shri Adi Godrej- Chairman, Godrej Group The positives include the cap on subsidies to 2% of GDP and the provisions of passthrough of dividend distribution tax. The negatives include increase in excise duties and introducing a retrospective amendment t I-T Act. 9) Smt. Chanda Kocchar -CEO & MD, ICICI Bank The intent to contain subsidies at 2% of GDP next year and 1.75% of GDP within 3 years is laudable. Specific measures on infrastructure, including permitting external commercial borrowings and reducing withholding tax are positive steps. 10) Shri Harsh Mariwala, Chairman & Managing Director, Marico If you were expecting sweeping reforms in this budget, you would be disappointed.the budget comes across as realistic. The finance minister held out five lofty objectives boost demand, encourage private investment, remove supply bottlenecks, mitigate malnutrition and improve delivery system, governance and transparency. However, one doubts whether the budget has really done full justice to these intents. 11) Shri Deepak Parekh, Chairman, HDFC. Admittedly, the Budget has no big-bang reforms or a roadmap on increasing foreign direct investment. Understandably, the current political scenario does not allow the FM to rock the boat. Yet, there are sufficient positive measures taken. For instance, in the capital markets, the introduction of the Rajiv Gandhi Equity Savings Scheme is a small but important step in encouraging larger retail participation in the equity market. However, the focus of this year s Budget was definitely infrastructure, especially the benefits awarded to the powers sector. 11
12 FINANCE BILL, 2012 AN INTRODUCTION Finance Bill The proposal of government for levy of new taxes, modification of the existing tax structure or continuance of the existing tax structure beyond the period approved by Parliament are submitted to Parliament through this bill. It is the key document as far as taxes are concerned. INCOME TAX PROVISIONS In this chapter, we have dealt with the proposed amendments to Income Tax Act, 1961 by Finance Bill, 2012 (hereinafter referred to as Bill). We have made references from Notes on Clauses and Memorandum explaining the provisions of the Bill. In this study note, we have discussed the provisions as per broad head in the Memorandum explaining the provisions of the Bill. The related amendments are put under one topic head in these notes. 1. Effective Dates: The amendments in income tax provisions are proposed to be effective from 1 st April, 2013 relevant to the assessment year unless otherwise specified. The amendments proposed in procedural section are effective for the proceedings taken on or after the date as specified. The amendments made in substantive sections are effective from the first day of the assessment year from which it is proposed to be effective. A. RATES OF INCOME TAX 2. Rates of Taxes: There is a change in basic limit and slab rates. The revised table is as under: For very senior citizen - individuals who is of the age 80 years or more being resident in India: Existing Proposed Taxable income Rate of tax Taxable income Rate of tax Upto 5,00,000 NIL Upto 5,00,000 NIL 5,00,001 to 20% on amount 5,00,001 to 20% on amount 8,00,000 exceeding 5,00,000 10,00,000 exceeding 5,00,000 8,00,001 and Rs. 60,000/- + 30% 10,00,001 and Rs. 1,00,000/- + above on amount above 30% on amount exceeding 8,00,000 exceeding 10,00,000 12
13 For senior citizen - individuals who is of the age 60 years or more but less than 80 years being resident in India: Existing Proposed Taxable income Rate of tax Taxable income Rate of tax Upto 2,50,000 NIL Upto 2,50,000 NIL 2,50,001 to 10% on amount 2,50,001 to 10% on amount 5,00,000 exceeding 2,50,000 5,00,000 exceeding 2,50,000 5,00,001 to Rs. 25,000/- + 20% 5,00,001 to Rs. 25,000/- + 20% 8,00,000 on amount 10,00,000 on amount exceeding 5,00,000 exceeding 5,00,000 8,00,001 and Rs. 85,000/- + 30% 10,00,001 and Rs. 1,25,000/- + above on amount above 30% on amount exceeding 8,00,000 exceeding 10,00,000 Other individuals (including female assessees), HUF, AOP, BOI: Existing Proposed Taxable income Rate of tax Taxable income Rate of tax Upto 1,80,000 NIL Upto 2,00,000 NIL 1,80,001 to 10% on amount 2,00,001 to 10% on amount 5,00,000 exceeding 1,80,000 5,00,000 exceeding 2,00,000 5,00,001 to Rs. 32,000/- + 20% 5,00,001 to Rs. 30,000/- + 20% on 8,00,000 on amount 10,00,000 amount exceeding exceeding 5,00,000 5,00,000 8,00,001 and Rs. 92,000/- + 30% 10,00,001 and Rs. 1,30,000/- + 30% above on amount above on amount exceeding exceeding 8,00,000 10,00,000 Under the existing provisions, the basic exemption limit for female assessees is Rs. 1,90,000/-. 3. Surcharge and Education Cess: The surcharge on assessee s other than companies continues to be NIL. The education cess continues to be 3%. The surcharge on domestic company continues to be at 5% and on foreign company it continues to be at 2% for income above Rs. 100 lakhs. 13
14 4. Rate of tax for Firms, Company - domestic and Company - foreign continues to be same be as under: Income Surcharge Education Total tax cess % % % % Firm (including LLP) For income upto Rs. 100 Lacs 30 Nil For income exceeding Rs. 100 Lacs 30 Nil Domestic Company For income upto Rs. 100 Lacs 30 Nil For income exceeding Rs. 100 Lacs Company Foreign For income upto Rs. 100 Lacs 40 Nil For income exceeding Rs. 100 Lacs The existing surcharge of 5% in all cases including under sections 115JB, 115O, 115R, etc. continues to be same for AY The existing MAT of 18.5% continues to be same for AY Also, AMT is proposed to be levied on person other than a company, who has claimed deductions under chapter VIA or deductions claimed under section 10AA at the rate of 18.5%. The effective rates under the MAT and AMT for the A.Y would be as under: Particulars Basic Rate Surcharge Cess Effective Rate Domestic Company For income upto Rs. 100 Lacs 18.5% Nil 3% % For income exceeding Rs. 100 Lacs 18.5% 5% 3% % Company Foreign For income upto Rs. 100 Lacs 18.5% Nil 3% % For income exceeding Rs. 100 Lacs 18.5% 2% 3% % Person other than a company (Also refer para 6 of the notes) For income upto Rs. 100 Lacs 18.5% Nil 3% % For income exceeding Rs. 100 Lacs 18.5% Nil 3% % 14
15 No change is proposed in the rate u/s 115-O and 115R. The effective rates for the A.Y under sections 115O and 115R would be as under: Particular Section Basic Rate Surcharge Cess Effective Rate Dividend Distribution Tax: On Shares 115-O 15% 5% 3% 16.22% On Mutual Funds: 115-R Equity Oriented Nil Nil Nil Nil Money Market or Liquid Fund (i) Individual or HUF 25% 5% 3% 27.04% (ii) Others 30% 5% 3% 32.45% Others: (i) Individual or HUF 12.50% 5% 3% 13.52% (ii) Others 30% 5% 3% 32.45% 5. Rate of Tax Deduction at Source: 5.1) There is no change proposed (except as stated in para 5.6 to 5.8 below) in the rate at which tax is required to be deducted at source and the rates as applicable for financial year will continue to apply for financial year ) In case of payment to a company other than domestic company, the amount of tax so deducted shall be increased by a surcharge at the rate of two percent and education cess at the rate of 3% on the amount of tax deducted at source and surcharge. 5.3) In the case of a resident assessee including a domestic company no surcharge and education cess would be levied on the amount of tax deducted at source. 5.4) However, education cess of 3% would continue to apply on tax deducted at source in the case salary payments. 5.5) For discussion on TDS/TCS provisions, please refer Para 34 to 43 of this note. 15
16 5.6) The proposed changes in basic threshold limit for deduction of tax at source (TDS) and rate of TDS effective from 1 st July, 2012 are as under: Sr. No. Section Nature of Payment Existing threshold limit of payment / Rate of tax deduction (Rs.) Interest on debentures (both listed and unlisted) of a listed company E Payments to non-resident sportsmen (including an athlete) or an entertainer or sports association LA Compensation for compulsory acquisition of immovable property Proposed threshold limit of payment / Rate of tax deduction (Rs.) 2,500 5,000 10% 20% 1,00,000 2,00, ) A new rate of TDS is proposed in following cases with effect from 1 st July, Sr. No. Section Nature of Payment Existing rate of Deduction (%) J Any remuneration paid to a (1)(ba) director (other than salary) LAA Transfer of immoveable properties (other than agriculture land) LC Interest income payable to Non Resident by specified company as mentioned u/s 115A relating to infrastructure sector Proposed rate of deduction (%) Not Applicable 10 Not Applicable 1 Not Applicable 5 5.8) A new rate of TCS is proposed in following cases with effect from 1 st July, Sr. No. Section Nature of Payment Existing rate of Deduction (%) C(1) Minerals, being coal or lignite or iron ore C(1D) Receives any amount in cash as consideration for sale of bullion or jewellery, if such consideration exceeds Rs. 2,00,000/- Proposed rate of deduction (%) Not Applicable 1 Not Applicable 1 16
17 Table for personal taxation Taxable Income All Individuals other than resident senior citizen Pre- Post Savings Budget Budget in Tax Resident Female Assessee other than senior citizen Pre- Post Savings in Budget Budget Tax Resident Senior Citizen (Age 60 years or more but less than 80 years) Pre- Post Savings in Budget Budget Tax Very Senior Citizen (Resident) (Age above 80 years) Pre- Post Savings Budget Budget in Tax (Rs.) (Rs.) (Rs.) (Rs.) (Rs.) (Rs.) (Rs.) (Rs.) (Rs.) (Rs.) (Rs.) (Rs.) (Rs.) 1,80,000 NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL 1,90,000 1,030 NIL 1,030 NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL 2,00,000 2,060 NIL 2,060 1,030 NIL 1,030 NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL 2,50,000 7,210 5,150 2,060 6,180 5,150 1,030 NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL 5,00,000 32,960 30,900 2,060 31,930 30,900 1,030 25,750 25,750 NIL NIL NIL NIL 7,00,000 74,160 72,100 2,060 73,130 72,100 1,030 66,950 66,950 NIL 41,200 41,200 NIL 8,00,000 94,760 92,700 2,060 93,730 92,700 1,030 87,550 87,550 NIL 61,800 61,800 NIL 10,00,000 1,56,560 1,33,900 22,660 1,55,530 1,33,900 21,630 1,49,350 1,28,750 20,600 1,23,600 1,03,000 20,600 15,00,000 3,11,060 2,88,400 22,660 3,10,030 2,88,400 21,630 3,03,850 2,83,250 20,600 2,78,100 2,57,500 20,600 20,00,000 4,65,560 4,42,900 22,660 4,64,530 4,42,900 21,630 4,58,350 4,37,750 20,600 4,32,600 4,12,000 20,600 25,00,000 6,20,060 5,97,400 22,660 6,19,030 5,97,400 21,630 6,12,850 5,92,250 20,600 5,87,100 5,66,500 20,600 50,00,000 13,92,560 13,69,900 22,660 13,91,530 13,69,900 21,630 13,85,350 13,64,750 20,600 13,59,600 13,39,000 20,600 75,00,000 21,65,060 21,42,400 22,660 21,64,030 21,42,400 21,630 21,57,850 21,37,250 20,600 21,32,100 21,11,500 20,600 1,00,00,000 29,37,560 29,14,900 22,660 29,36,530 29,14,900 21,630 29,30,350 29,09,750 20,600 29,04,600 28,84,000 20,600 For the first time male tax payers are ahead in proposed saving in tax as compared to others. Enjoy This saving in direct tax will go in paying indirect taxes. Hope the tax payer is not out of pocket (Source: Economic Times dated 18 th March, 2012) 17
18 B. WIDENING OF TAX BASE 6. Alternate Minimum Tax (AMT) on all persons other than Companies [Sections 115JC to 115JF]: Existing Provision Section 115JC provide that where the regular income-tax payable for a previous year by any limited liability partnership is less than the alternate minimum tax payable for such previous year, the adjusted total income shall be deemed to be the total income of such limited liability partnership and it shall be liable to pay income-tax on such total income at the rate of eighteen and one-half per cent. Proposed Amendment It is proposed to substitute the section so as to provide that where the regular income-tax payable for a previous year by any person, other than a company (i.e., partnership, sole proprietorship, association of persons etc), is less than the alternate minimum tax payable for such previous year, the adjusted total income shall be deemed to be the total income of such person and it shall be liable to pay income-tax on such total income at the rate of eighteen and onehalf per cent. For the purpose of the above, (i) (ii) (iii) adjusted total income shall be the total income before giving effect to provisions of Chapter XII-BA as increased by the deductions claimed under any section (other than section 80P) included in Chapter VI-A under the heading C-Deductions in respect of certain incomes and deduction claimed under section 10AA; alternate minimum tax: shall be the amount of tax computed on adjusted total income at a rate of 18.5%; and regular income-tax shall be the income-tax payable for a previous year by a person other than a company on his total income in accordance with the provisions of the Act other than the provisions of Chapter XII-BA. The proposed new section shall not apply to an individual or a Hindu undivided family or an association of persons or a body of individuals, whether incorporated or not, or an artificial juridical person referred to in sub-clause (vii) of clause (31) of section 2, if the adjusted total income of such person does not exceed twenty lakh rupees. Thus previously only LLP were subject to AMT but now every assessee other than Company having adjusted total income of more than Rs. 20,00,000/- will be liable to pay AMT at 18.5%. 18
19 Credit for tax (tax credit) paid by a person on account of AMT under Chapter XII-BA shall be allowed to the extent of the excess of the AMT paid over the regular incometax. This tax credit shall be allowed to be carried forward up to the tenth assessment year immediately succeeding the assessment year for which such credit becomes allowable. It shall be allowed to be set off for an assessment year in which the regular income-tax exceeds the AMT to the extent of the excess of the regular income-tax over the AMT. This amendment will take effect from 1st April, 2013 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the assessment year and subsequent assessment years. Under Company MAT, calculation starts with Net Profit as per Profit and Loss Account while for AMT calculation starts with total income. If one compares the provisions of section 115JB (company MAT) and section 115JC (AMT), there are certain items for which treatment is different and there are certain items for which treatment is same under both the provisions. Some of the examples are listed hereinbelow: Sr. No. Particulars Treatment under Company MAT Treatment under AMT 1. Dividend received (section Company MAT not AMT not payable 10(34) ) payable 2. Long term capital gain on sale Company MAT payable AMT not payable of listed shares through Stock Exchanges (Section 10(38)) 3. Provision for doubtful debts Company MAT payable AMT payable 4. Disallowance u/s 40(a)(i) and Company MAT not AMT payable 40(a)(ia) for non payment of payable TDS 5. Disallowance u/s 43B certain Company MAT not AMT payable deduction on actual payment 6. Allowance of deduction when the TDS is paid in respect of amount earlier disallowed u/s 40(a)(i) and 40(a)(ia) 7. Allowance u/s 43B for items paid during the year which were disallowed earlier u/s 43B 19 payable Company MAT payable Company MAT payable 8. Depreciation Depreciation as per accounts is allowed as deduction in Company MAT There can be more of such items. AMT not payable AMT not payable depreciation as tax working u/s 32 is allowed as deduction in AMT
20 7. Daily tonnage income of shipping company [Section 115VG]: The Tonnage Tax Scheme introduced vide Finance Act 2005 provides for taxation of income of a shipping company on presumptive basis. Under this scheme, the operating profit of a shipping company is determined on the basis of tonnage capacity of its ships. It is proposed to amend section 115VG to revise the rate of daily tonnage income under this scheme as under: Qualifying ship having net tonnage Existing amount of daily tonnage income Proposed amount of daily tonnage income (1) (2) (3) Up to 1,000 Rs.46 for each 100 tons Rs.70 for each 100 tons exceeding 1,000 but not Rs.460 plus Rs.35 for each Rs.700 plus Rs.53 for more than 10, tons exceeding 1,000 each 100 tons exceeding exceeding 10,000 but not more than 25,000 exceeding 25,000 tons Rs.3,610 plus Rs.28 for each 100 tons exceeding 10,000 tons Rs.7,810 plus Rs.19 for each 100 tons exceeding 25,000 tons 1,000 tons Rs.5,470 plus Rs.42 for each 100 tons exceeding 10,000 tons Rs.11,770 plus Rs.29 for each 100 tons exceeding 25,000 tons This amendment will take effect from 1st April, 2013 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the assessment year and subsequent assessment years. 8. TDS provisions under this broad head are considered under para 34 to 43 of this Note. C. MEASURES TO PREVENT GENERATION AND CIRCULATION OF UNACCOUNTED MONEY 9. Cash Credits [Section 68]: Section 68 provides that where any sum is found credited in the books of an assessee maintained for any previous year, and the assessee offers no explanation about the nature and source thereof or the explanation offered by him is not satisfactory in the opinion of the Assessing Officer, then the sum so credited may be charged to incometax as the income of the assessee of that previous year. It is proposed to insert two new provisos to the aforesaid section. The first proviso seeks to provide that where the assessee is a company, (not being a company in which the public are substantially interested) and the sum so credited 20
21 consists of share application money, share capital, share premium or any such amount by whatever name called, any explanation offered by such assessee company shall be deemed to be not satisfactory, unless (a) (b) the person, being a resident in whose name such credit is recorded in the books of such company also offers an explanation about the nature and source of such sum so credited; and such explanation in the opinion of Assessing Officer aforesaid has been found to be satisfactory. The second proviso seeks to provide that nothing contained in the first proviso shall apply if the person, in whose name the sum referred to therein is recorded, is a venture capital fund or a venture capital company as referred to in clause (23FB) of section 10. The Memorandum explains the proposed provision as under: In the case of closely held companies, investments are made by known persons. Therefore, a higher onus is required to be placed on such companies besides the general onus to establish identity and credit worthiness of creditor and genuineness of transaction. This additional onus needs to be placed on such companies to also prove the source of money in the hands of such shareholder or persons making payment towards issue of shares before such sum is accepted as genuine credit. If the company fails to discharge the additional onus, the sum shall be treated as income of the company and added to its income. The amendment is proposed to take effect from 1 st April, 2013 and will, accordingly, apply to Assessment year and subsequent years. 10. Rate of tax for Unexplained money, investments, unexplained expenditure and amount borrowed or repaid on hundi [Section 115BBE]: A new section is proposed to be inserted. This will be applicable only to individuals and HUF. The proposed new section provides that the rate of tax in respect of following income would be 30%: Section Nature of Income 68 Cash credits 69 Unexplained investments 69A Unexplained money 69B Amount of investments not fully disclosed in books of accounts 69C Unexplained expenditure 69D Amount borrowed or repaid on hundi 21
22 It is further proposed to be provided that notwithstanding anything contained in the Act, no deduction in respect of any expenditure or allowance shall be allowed to the assessee under any provisions of this Act in computing the above income. These proposed amendments would take away the benefit of availing basic exemption limit and claiming deduction in taxing the unaccounted money in the case of individuals and HUFs. The amendment is proposed to take effect from 1 st April, 2013 and will, accordingly, apply to Assessment year and subsequent years. 11. Filing of return of income [Section 139]: It is proposed to provide that every resident person is mandatorily required to file the return of income even if his total income does not exceed maximum amount not chargeable to tax, if he has any asset located outside India or he is a signing authority in any account located outside India. It is not clarified as to if such person has no beneficial interest in the account whether he would still be covered under this proposed clause. In absence of any provision, it seems such person will be covered even if he is just a trustee or a director. The amendment is proposed to take effect retrospectively from 1 st April, 2012 and will, accordingly, apply to Assessment year and subsequent years. 12. Income escaping assessment [Sections 147 and 149 of the Income Tax Act, 1961 and Section 17 of the Wealth Tax Act]: The provision of section 147 enables the Assessing Officer to assess or re-assess income which has escaped assessment for any assessment year, after recording reasons for doing so. It is proposed to insert a proviso to provide that in case where any income in relation to any asset (including financial interest in any entity) located outside India, chargeable to tax, has escaped assessment for any assessment year; the limitation of four years will not apply. It is further proposed that following will also be deemed to be the cases where income chargeable to tax has escaped assessment: (ba) where the assessee has failed to furnish a report in respect of any international transaction which he was so required under section 92E; (d) where a person is found to have any asset (including financial interest in any entity) located outside India. The provisions of section 147 are procedural in nature. However, it is clarified by inserting a new Explanation 4 to the aforesaid section that the above amendments 22
23 shall also be applicable to the proceedings initiated under this section for any assessment year beginning on or before 1st April, These amendments are proposed to take effect from 1 st July, It is proposed to provide u/s 149 that time limit has been increased for issue of notice for reopening an assessment to 16 years where the income relation to any asset (including financial interest in any entity) located outside India, chargeable to tax, has escaped assessment. 13. Penalty where search has been initiated [Section 271AAB]: Existing Provision The existing provision contained in subsection (1) of the aforesaid section 271AAA provides that in a case where the search has been initiated under section 132 on or after the 1st day of June, 2007, the assessee shall be liable to pay by way of penalty, in addition to tax, if any, payable by him, a sum computed at the rate of ten per cent of the undisclosed income of the specified previous year. Proposed Amendment It is proposed to provide that the existing provisions of the section shall be applicable in respect of cases where a search has been initiated under section 132 on or after the 1st day of June, 2007 but before 1st day of July, For case where search has been initiated under section 132 on or after the 1st day of July, 2012, a new penalty section 271AAB is proposed to be inserted. The proposed new section 271AAB provides as under: Sr. No. Particulars Penalty i) If undisclosed income is admitted during the course of search ii) If undisclosed income is not admitted during the course of search but disclosed in the return of income filed after the search iii) In a case not covered under (i) and (ii) above 10% of undisclosed income 20% of undisclosed income 30% to 90% of undisclosed income It is also proposed to provide that no penalty under Section 271(1)(c) shall be imposed upon the assessee in respect of the undisclosed income referred to above. It is also proposed to provide that a reasonable opportunity of being heard will be granted to the assessee. 23
24 It is also proposed to define the expressions undisclosed income, specified previous year and specified date for the purposes of the said section. The term undisclosed income is defined to mean (i) any income of the specified previous year represented, either wholly or partly, by any money, bullion, jewellery or other valuable article or thing or any entry in the books of account or other documents or transactions found in the course of a search under section 132, which has (A) (B) not been recorded on or before the date of search in the books of account or other documents maintained in the normal course relating to such previous year; or otherwise not been disclosed to the Chief Commissioner or Commissioner before the date of search; or (ii) any income of the specified previous year represented, either wholly or partly, by any entry in respect of an expense recorded in the books of account or other documents maintained in the normal course relating to the specified previous year which is found to be false and would not have been found to be so had the search not been conducted. These amendments will take effect from 1st July, Income from Other Sources [Section 56]: (a) The existing provisions of clause (vii) of sub-section (2) of the aforesaid section 56, inter alia, provide that where any sum of money, immoveable property or any other property, the aggregate value of which exceeds fifty thousand rupees, is received without consideration, by an individual or a Hindu undivided family, in any previous year from any person on or after the 1st day of October, 2009, the whole of the aggregate value of such money shall be chargeable to income-tax under the head Income from other sources. The second proviso to the said clause provides that the provisions of this clause shall not apply to any sum of money or any property received from any relative. Existing Provision Relative is defined in relation to an individual only. Proposed Amendment It is proposed to substitute clause (e). The proposed clause (e) continues to define relative in relation to an individual. It also further provides that relative in case of HUF means any member thereof. 24
25 Thus, any amount and/or property received by HUF from any member thereof will not be subject to tax under this clause. However, the amendment does not cover a situation where an individual has received any amount and/or property from a HUF. The amendment is proposed to take effect retrospectively from 1 st October, In respect of company assessee, it is proposed to insert a new clause (viib) in Section 56. (b) A new sub-section (viib) is proposed to be inserted to provide that where a company, not being a company in which the public are substantially interested, receives, in any previous year, from any person being a resident, any consideration for issue of shares that exceeds the face value of such shares, the aggregate consideration received for such shares as exceeds the fair market value of the shares shall be chargeable to income-tax under the head Income from other sources. It is further proposed that the company receiving the consideration for issue of shares shall be provided an opportunity to substantiate its claim regarding the fair market value of the shares. However, the said new clause shall not apply where the consideration for issue of shares is received by a venture capital undertaking from a venture capital company or a venture capital fund. Explanation. For the purposes of this clause (a) (i) (ii) the fair market value of the shares shall be the value as may be determined in accordance with such method as may be prescribed; or as may be substantiated by the company to the satisfaction of the Assessing Officer, based on the value, on the date of issue of shares, of its assets, including intangible assets being goodwill, know-how, patents, copyrights, trademarks, licences, franchises or any other business or commercial rights of similar nature, whichever is higher; This amendment will take effect from 1st April, 2013 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the assessment year and subsequent assessment years. 15. Prosecution proceedings under the Income Tax Act: It is proposed to strengthen the prosecution mechanism (through new sections 280A, 280B, 280C and 280D) under the Income-tax Act by 25
26 (i) (ii) (iii) Providing for constitution of Special Courts for trial of offences. Application of summons trial for offences under the Act to expedite prosecution proceedings as the procedures in a summons trial are simpler and less time consuming. Providing for appointment of public prosecutors. It is proposed to provide under sections 276C, 276CC, 277, 277A and section 278 of the Act that in a case where the amount of tax, penalty or interest which would have been evaded by a person exceeds by twenty-five hundred thousand rupees (earlier it was one hundred thousand rupees), he shall be punishable with rigorous imprisonment for a term which shall not be less than six months but which may extend to seven years and with fine. It is also proposed to provide that in case the amount which would have been evaded by a person does not exceed twenty-five hundred thousand rupees (earlier it was - one hundred thousand rupees), he shall be punishable with rigorous imprisonment for a term which shall not be less than three months but which may extend to two years and with fine (earlier it was - three months but which may extend to three years and with fine). These amendments will take effect from the 1st day of July, D. TAX INCENTIVES AND RELIEFS 16. Tax Incentives for funding of certain Infrastructure Sectors [Section 115A]: It is proposed to amend Section 115A of the Income Tax Act to provide that any interest paid by a specified company to a non-resident in respect of borrowing made in foreign currency from sources outside India between 1st July, 2012 and 1st July, 2015, under an agreement, including rate of the interest payable, approved by the Central Government, shall be taxable at the rate of 5% (plus applicable surcharge and cess). The specified company shall be an Indian company engaged in the business of - (i) construction of dam, (ii) operation of Aircraft, (iii) manufacture or production of fertilizers, (iv) construction of port including inland port, (v) construction of road, toll road or bridge; (vi) generation, distribution of transmission of power (vii) construction of ships in a shipyard; or (viii) developing and building an affordable housing project as is presently referred to in section 35AD(8)(c)(vii). This amendment will take effect from 1st April, 2013 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the Assessment Year and subsequent assessment years. 26
27 Thus new section 194LC to provide that interest income paid by such specified company to a non resident shall be subjected to tax deduction at source at the rate of 5% (plus applicable surcharge and cess). This amendment will take effect from 1st July, Lower rate of tax on dividends received from foreign companies [Section 115BBD]: Existing Provision Section 115BBD of the Act provides for taxation of gross dividends received by an Indian company from a specified foreign company (in which it has shareholding of 26% or more) at the rate of 15% if such dividend is included in the total income for the Financial Year i.e. Assessment Year Proposed Amendment It is proposed to extend the applicability of this section in respect of income by way of foreign dividends received in Financial Year also, subject to the same conditions. Repatriation of dividends from foreign companies in which Indian Companies hold substantial shares at a lower rate of 15% has been extended upto 31 st March 2013.This would encourage companies to repatriate foreign funds back into the country. This amendment will take effect from 1st April, 2013 and shall apply to the Assessment year Provisions relating to Venture Capital Fund (VCF) or Venture Capital Company (VCC) [Sections 115U and 10(23FB)]: Provisions of Section 10(23FB) and Section 115U of the Act were intended to ensure a tax pass through status to Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) registered Venture Capital Fund (VCF) or Venture Capital Company (VCC). Section 10(23FB) granted exemption in respect of income of such VCF/VCC. The benefit was available if investment by such VCC/VCF was in unlisted shares of a domestic company, i.e. a Venture Capital Undertaking (VCU). Section 115U ensures that income, in the hand of the investor through VCF/VCC is taxed in like manner and to the same extent as if the investment was directly made by investor in the VCU. Further, TDS provisions are not applicable to any payment made by the VCF to its investor and payment by VCC to the investor is exempted from Dividend Distribution Tax (DDT). Section 10(23FB) further provides that income of a SEBI regulated VCF or VCC, derived from investment in a domestic company i.e. Venture Capital Undertaking (VCU), is exempt from taxation, provided the VCU is engaged in only nine specified businesses. The working of VCF, VCC or VCU are regulated by SEBI and RBI. In order to avoid multiplicity of conditions in different regulations for the same entities, the sectoral restriction on business of VCU is required to be removed from Income 27
28 Tax Act and such VCU is to be allowed to be governed by conditions imposed by SEBI and RBI. The provisions of section 115U currently allow an opportunity of indefinite deferral of taxation in the hands of investor. With a view to rationalize the above position and to align it with the true intent of a pass-through status, it is proposed to amend section 10(23FB) and section 115U to provide that.- i) The venture Capital undertaking shall have same meaning as provided in relevant SEBI regulations and there would be no sectoral restriction. ii) iii) Income accruing to VCF/ VCC shall be taxable in the hands of investor on accrual basis with no deferral. The exemption from applicability of TDS provisions on income credited or paid by VCF/ VCC to investors shall be withdrawn. These amendments will take effect from 1st April, 2013, and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the assessment year and subsequent years. 19. Removal of the cascading effect of Dividend Distribution Tax (DDT) [Section 115-O]: Existing Provision Sub-section (1A) of the aforesaid section 115-O provide that the amount of dividends referred to in sub-section (1) shall be reduced by the amount of dividend, if any, received by the domestic company during the financial year, if (a) such amount of dividend is received from its subsidiary; (b) the subsidiary has paid tax under this section on such dividend; and (c) the domestic company is not a subsidiary of any other company. Proposed Amendment To omit sub-clause (c), so as to remove the condition that such domestic company is not a subsidiary of any other company. Thus with a view to remove the cascading effect of DDT in multi-tier corporate structure, it is proposed to amend Section 115-O of the Act. The section provides that the same amount of dividend shall not be reduced more than once. This position is unchanged. Let us take an example, Company C is a subsidiary of a Company B and Company B is a subsidiary of a Company A. 28
29 Company C declares dividend of Rs. 100/- and pays DDT of Rs.16.22/- on the same. Company B also declares the dividend of Rs. 100/- out of dividend received from Company C. Under existing provisions Company B would not have got the set off of DDT paid by Company C because Company B is a subsidiary of Company A. However, as per proposed amendment now Company B will get setoff of DDT in respect of dividend received from Company C and Company B will not pay any DDT. Now if Company A also declares dividend of say Rs. 80/- from dividend received from Company B, than Company A will not get the set off of DDT second time and will have to pay DDT of Rs.12.97/-. This amendment will take with effect from 1st July, Exemption in respect of income received by certain foreign companies [Section 10(48)]: It is proposed to insert a new clause (48) in section 10 of the Income-tax Act to provide for exemption in respect of any income of a foreign company received in India in Indian currency on account of sale of crude oil to any person in India subject to the following conditions: (i) (ii) (iii) The receipt of money is under an agreement or an arrangement which is either entered into by the Central Government or approved by it. The foreign company, and the arrangement or agreement has been notified by the Central Government having regard to the national interest in this behalf. The receipt of the money is the only activity carried out by the foreign company in India. The Memorandum explains that the current provisions of the Act would render such payment taxable in India because payment is being received by these foreign companies in India in Indian currency. This would not be justified when such payment is based on national interest and particularly when no other activity is being carried out in India by these foreign companies except receipt of payment in Indian currency. These amendments will take effect retrospectively from 1st April, 2012 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the assessment year and subsequent years once such arrangement or agreement is notified. 21. Extending benefit of initial depreciation to the power sector [Section 32(1)(iia)]: Existing Provision Section 32(1)(iia) provides for allowance of initial depreciation (in Proposed Amendment It is proposed to amend this section to provide that an assessee engaged in the 29
30 addition to normal depreciation) at the rate of 20% of the actual cost on new machinery or plant (other than ships and aircraft) to the assessee engaged in the business of manufacture or production of any article or thing in the year of acquisition and installment. business of generation or generation and distribution of power shall also be allowed initial depreciation at the rate of 20% of actual cost of new machinery or plant (other than ships and aircraft) acquired and installed in a previous year. In the Memorandum it is explained that in order to encourage new investment by the assessees engaged in the business of generation or generation and distribution of power, shall also be allowed initial Depreciation. This amendment will take effect from 1st April, 2013 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the assessment year and subsequent assessment years. 22. Weighted deduction for scientific research and development [Section 35(2AB)]: Existing Provision Under Section 35(2AB) of the Act, a company is allowed weighted deduction at the rate of 200% of expenditure (not being in the nature of cost of any land or building) incurred on approved in-house research and development facilities. These provisions are not applicable in respect of any expenditure incurred by a company after 31 st March, Proposed Amendment It is proposed to extend the benefit of the weighted deduction for a further period of five years i.e. up to 31st March, It is stated in Memorandum that in order to incentivise the corporate sector to continue to spend on in-house research, it is proposed to amend this section. This amendment will take effect from 1st April, 2013 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the assessment year and subsequent assessment years up to assessment year Weighted deduction for expenditure incurred on agricultural extension project [Section 35CCC]: It is proposed to insert a new provision in the Act to allow weighted deduction of 150% of the expenditure incurred on agricultural extension project. 30
31 Since agricultural extension services play a critical role in enhancing the productivity in the agricultural sector, in order to incentivise the business entities to provide better and effective agriculture extensive services, it is proposed to insert this new provision. The agricultural extension project eligible for this weighted deduction shall be notified by the Board in accordance with the prescribed guidelines. This amendment will take effect from 1st April, 2013 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the assessment year and subsequent assessment years. 24. Weighted deduction for expenditure for skill development [Section 35CCD]: It is proposed to insert a new provision in the Income-tax Act to provide weighted deduction of 150% of expenses (not being expenditure in the nature of cost of any land or building) incurred on skill development project. The Department of Industrial Policy & Promotion (DIPP) has notified the National Manufacturing Policy (NMP) vide Press Note dated 4 th November, The notified NMP inter alia propose to provide following direct tax incentive for skill development in manufacturing sector: To encourage the private sector to set up their own institutions, the government will provide weighted standard deduction of 150% of the expenditure (other than land or building) incurred on Public Private Partnership (PPP) project for skill development in the ITIs in manufacturing sector in separate facilities in coordination with NSDC. Thus, in order to incentivise companies to invest on skill development projects in the manufacturing sector; it is proposed to insert this new provision in the Income-tax Act. The proposed amendment will take effect from 1 st April, 2013 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the assessment year and subsequent assessment years. 25. Turnover or gross receipts for audit of accounts and presumptive taxation [Sections 44AB and 44AD]: The prescribed limit for applicability of Tax Audit u/s 44AB is proposed to be modified as under: Existing Limit (Rs. in lakhs) Proposed Limit (Rs. in lakhs) Turnover Gross Receipt Section 44AD of the Act deals with special provision for computing profits and gains of business on presumptive basis. It is proposed to insert a new sub-section (6) to the 31
32 aforesaid section 44AD so as to provide that the provisions of this section, notwithstanding anything contained in the foregoing provisions, shall not apply to- (i) (ii) (iii) a person carrying on profession as referred to in sub-section (1) of section 44AA; a person earning income in the nature of commission or brokerage; or a person carrying on any agency business. This amendment will take effect retrospectively from 1st April, 2011 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the assessment year and subsequent assessment years. Existing Provision Clause (b) of the Explanation to the aforesaid section 44AD defines the term eligible business to mean any business except the business of plying, hiring or leasing goods carriages referred to in section 44AE and whose total turnover or gross receipts in the previous year does not exceed sixty lakh rupees for the purpose of computing profits and gains of business on presumptive basis. Proposed Amendment It is proposed to enhance the said limit from sixty lakhs rupees to one crore rupees under this clause as well Under Section 44AD The Income from Eligible business is estimated at 8% of the gross receipt or total turnover Let us take an example-taxpayer A is carrying on retail business with a turnover of Rs.90 Lakhs. The deemed income under section 44AD would of Rs 7.2 Lakhs (Rs. 90Lakh *8%) Assuming that A has no other income and he is not claiming any deduction under Chapter VI A, the tax payable under proposed new slab system would be Rs. 76,220/- including cess. If a taxpayer is carrying on business with turnover of Rs. 90 lakhs, Is tax cost of Rs. 76,220/- very high! If the Taxpayer deems it to be high, he has to get his books of accounts audited u/s 44AB. These amendments will take effect from 1st April, 2013 and will, accordingly, apply to the assessment year and subsequent assessment years. 32
33 26. Exemption for Senior Citizens from payment of advance tax [Section 207]: Existing Provision Every assessee is required to pay advance tax if the tax liability for the previous year exceeds ten thousand rupees. Proposed Amendment Resident senior citizen, not having any income chargeable under the head Profits and gains of business or profession, shall not be liable to pay advance tax and such senior citizen shall be allowed to discharge his tax liability (other than TDS) by payment of self assessment tax. This amendment will take effect from the 1st April, Accordingly, the aforesaid senior citizen would not be required to pay advance tax for the financial year and subsequent financial years. 27. Relief from long-term capital gains tax on transfer of residential property if invested in a manufacturing small or medium enterprise [Section 54GB]: It is proposed to insert a new section 54GB so as to provide rollover relief from long term capital gains tax to an individual or an HUF on sale of a residential property (house or plot of land) in case of re-investment of sale consideration in the equity of a new start-up SME company in the manufacturing sector which is utilized by the company for the purchase of new plant and machinery. The Government had announced National Manufacturing Policy (NMP) in 2011, one of the goals of which is to incentivise investment in the Small and Medium Enterprises (SME) in the manufacturing sector. This relief would be allowed subject to complying with the following - i) the amount of net consideration is used by the individual or HUF before the due date of furnishing of return of income under sub-section (1) of section 139, for subscription in equity shares in the SME company in which he holds more than 50% share capital or more than 50% voting rights. ii) iii) The amount of subscription as share capital is to be utilized by the SME company for the purchase of new plant and machinery within a period of one year from the date of subscription in the equity shares. If the amount of net consideration subscribed as equity shares in the SME company is not utilized by the SME company for the purchase of plant and machinery before the due date of filing of return by the individual or HUF, the unutilized amount shall be deposited under a deposit scheme to be prescribed in this behalf. 33
34 iv) Suitable safeguards so as to restrict the transfer of the shares of the company, and of the plant and machinery for a period of 5 years are proposed to be provided to prevent diversion of these funds. Further, capital gains would be subject to taxation in case any of the conditions are violated. v) The relief would be available in case of any transfer of residential property made on or before 31st March, The proposed amendments in the provisions of the Act shall be effective from 1st April, 2013 and would accordingly apply to assessment year and subsequent assessment years. 28. Reduction in the rate of Securities Transaction Tax (STT): Securities Transaction Tax (STT) on transactions in specified securities was introduced vide Finance (No.2) Act, It is proposed to reduce STT in Cash Delivery segment as under: Sr. No. Nature of taxable securities transaction Payable by Existing Rates % Proposed rates% (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) 1. Delivery based purchase of equity shares in a company/ units of an equity oriented fund entered into through a recognised stock exchange in India. Purchaser Delivery based sale of equity shares in a company / units of an equity oriented fund entered into through a recognised stock exchange in India. Seller The proposed amendments in the rates of Securities Transaction Tax (STT) will be effective from the 1st day of July, 2012 and will accordingly apply to any transaction made on or after that date. 29. Deduction in respect of capital expenditure on specified business [Section 35AD]: Under Section 35AD of the Income-tax Act, investment-linked tax incentive is provided by way of allowing 100% deduction in respect of the whole of any expenditure of capital nature (other than on land, goodwill and financial instrument) incurred wholly and exclusively, for the purposes of the specified business during the previous year in which such expenditure is incurred. The proposed amendments are as under- 34
35 Specified Business Existing Provision (Amount of Deduction in %) Proposed Amendment (Amount of Deduction in %) (i) setting up and operating a cold chain facility; (ii) setting up and operating a warehousing facility for storage of agricultural produce; (iii) laying and operating a cross-country natural gas or crude or petroleum oil pipeline network for distribution, including storage facilities being an integral part of such network (iv) building and operating, anywhere in India, a new hotel of two-star or above category as classified by the Central Government; (v) building and operating, anywhere in India, a new hospital with at least one hundred beds for patients; (vi) developing and building a housing project under a scheme for slum redevelopment or rehabilitation, (vii) developing and building a housing project under a scheme for affordable housing (ix) production of fertilizer in India (x) setting up and operating an inland container depot or a container freight station notified or approved under the Customs Act, 1962 (52 of 1962); NIL 100 (xi) bee-keeping and production of honey and beeswax; and (xii) setting up and operating a warehousing facility for storage of sugar. NIL 100 NIL 100 Above amendments will apply only to specified businesses commencing operations on or after 1 st April, 2012 and the amendments will take effect from 1st April, 2013 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the assessment year and subsequent assessment years. It is further proposed to insert new sub-section (1A) in section 35AD to provide that where the assessee builds a hotel of two-star or above category as classified by the Central Government and subsequently, while continuing to own the hotel, transfers the operation thereof to another person, the assessee shall be deemed to be carrying on the specified business of building and operating hotel and he will be eligible to claim deduction. This amendment will take effect retrospectively from 1st April, 2011 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the assessment year and subsequent assessment years. 35
36 30. Extension of sunset date for tax holiday for power sector [Section 80 IA]: The sunset date for claiming deduction for the undertaking engaged in business of generation and distribution of power, transmission and distribution of power by laying network of transmission and distribution lines, undertaking renovation or modernization of existing distribution lines is extended to 31 st March, 2013 from 30 th March, Reduction of the eligible age for senior citizens for certain tax reliefs [Sections 80D, 80DDB and 197A]: The Finance Act, 2011 amended the effective age of a senior citizen being an Indian resident from sixty-five years of age to sixty years for the purposes of application of various tax slabs and rates of tax under the Income Tax Act, 1961 for income earned during the financial year (assessment year ). Under certain other provisions of the Act, it has remained to be amended last year which is now proposed to be done. The amendments to section 80D and section 80DDB will take effective from 1st April, 2013 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the assessment year and subsequent assessment years. The amendment to section 197A will take effect from 1st July, Deduction for expenditure on preventive health check-up [Section 80D]: It is proposed to include any payment made by an assessee on account of preventive health check-up of self, spouse, dependant children or parents(s) during the previous year will be eligible for deduction within the overall limits but not exceeding in the aggregate Rs.5,000/-. That for the purpose of the deduction under section 80D, payment can be made (i) by any mode, including cash, in respect of any sum paid on account of preventive health check-up and (ii) for mediclaim it has to be other than cash. These amendments will take effect from 1st April, 2013 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the assessment year and subsequent assessment years. 33. Deduction in respect of interest on deposits in savings accounts [Section 80TTA]: Existing Provision Interest on deposit (not being time deposits) in a saving account is taxable in hands of all assessee. Proposed Amendment It is proposed to insert a new section 80TTA of the Act, to allow a deduction up to an extent of ten thousand rupees in aggregate. This will be allowed to an individual or a Hindu undivided family. 36
37 This amendment will take effect from 1st April, 2013 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the assessment year and subsequent assessment years. E. RATIONALIZATION OF TAX DEDUCTION AT SOURCE (TDS) AND TAX COLLECTION AT SOURCE (TCS) PROVISIONS 34. Tax Deduction at Source (TDS) on transfer of certain immovable properties (other than agricultural land) [Section 194LAA]: Under the existing provision of the Income Tax Act, 1961 (the Act), there is no specific provision to deduct TDS by the transferee, when an Immovable Property is transferred by a Resident except: (a) (b) in the case of compulsory acquisition of certain immovable properties and on transfer of immovable property by a non-resident, tax is required to be deducted at source by the transferee. It is proposed to provide that every transferee, at the time of making payment or crediting any sum by way of consideration for transfer of immovable property (other than agricultural land), shall deduct tax, at the rate of 1% of such sum, if the consideration paid or payable for the transfer of such property exceeds (a) (b) fifty lakh rupees in case such property is situated in a specified urban agglomeration; Or twenty lakh rupees in case such property is situated in any other area. It is further provided that: Where the consideration paid or payable for the transfer of such property is less than the value adopted or assessed or assessable by any authority of a State Government for the purposes of payment of stamp duty, the value so adopted or assessed or assessable shall be deemed as consideration paid or payable for the transfer of such immovable property. The TDS would have to be deducted on this amount. A registering officer appointed under the Indian Registration Act, 1908 (Registrar) shall not register the transfer of any immovable property where taxes are required to be deducted under this Provision unless the transferee furnishes proof of deduction and payment of TDS. A simple one page challan for payment of TDS would be prescribed containing details (including PAN) of transferor and transferee and also certain details of the property. 37
38 The transferee would not be required to obtain any Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number (TAN) or to furnish any TDS statement as this would be mostly a one time transaction. The transferor would get credit of TDS like any other pre-paid taxes on the basis of information furnished by the transferee in the challan of payment of TDS. This amendment will take effect from 1st October, TDS on remuneration to a director [Section 194J]: It is proposed to amend section 194J to provide that tax is required to be deducted on the remuneration paid to a director, which is not in the nature of salary, at the rate of 10% of such remuneration. This amendment will take effect from 1st July, Tax Collection at Source (TCS) on cash sale of bullion and jewellery [Section 206C(1D)]: Under the existing provisions of the Income-tax Act, tax is required to be collected at source by the seller at the specified rate on certain goods like alcoholic liquor, tendu leaves, scrap etc. at the time of sale. However, there is no specific provision to collect TCS on trading of bullion and jewellery. It is proposed to insert a new sub-section in section 206C to provide that the seller of bullion and jewellery shall collect tax at the rate of 1% of sale consideration from every buyer of bullion and jewellery if sale consideration exceeds two lakh rupees and the sale is in cash. Memorandum explains the rational as under: In order to reduce the quantum of cash transaction in bullion and jewellery sector and for curbing the flow of unaccounted money in the trading system of bullion and jewellery; This would be irrespective of the fact whether buyer is a manufacturer, trader or purchase is for personal use. This amendment will take effect from 1st July, Tax Collection on sale of certain minerals [Section 206C(1)]: It is proposed to provide that tax at the rate of 1% shall be collected by the seller from the buyer of Coal, Lignite and Iron ore. However, the seller shall also not collect tax on sale of the said minerals if 38
39 (a) (b) the same are purchased by the buyer for personal consumption. the buyer declares that these minerals are to be utilized for the purposes of manufacturing, processing or producing articles or things. This amendment will take effect from 1st July, Deemed date of payment of tax by the resident payee: It is proposed to amend section 201 to provide that the payer who fails to deduct the whole or any part of the tax on the payment made to a resident payee shall not be deemed to be an assessee in default in respect of such tax if such resident payee (i) has furnished his return of income under section 139; (ii) (iii) has taken into account such sum for computing income in such return of income; and has paid the tax due on the income declared by him in such return of income, and the payer furnishes a certificate to this effect from an accountant in such form as may be prescribed. The date of payment of taxes by the resident payee shall be deemed to be the date on which return has been furnished by the payer. It is also proposed to provide that the interest under section 201(1A)(i) shall be payable from the date on which such tax was deductible to the date of furnishing of return of income by such resident payee. Amendments on similar lines are also proposed to be made in the provisions of section 206C relating to TCS for clarifying the deemed date of discharge of tax liability by the buyer or licensee or lessee. These amendments will take effect from 1st July, Disallowance of business expenditure on account of non-deduction of tax on payment to resident payee [Section 40(a)(ia)]: It is proposed to amend section 40(a)(ia) to provide that where an assessee makes payment of the nature specified in the said section to a resident payee without deduction of tax and is not deemed to be an assessee in default under section 201(1) on account of payment of taxes by the payee, then, for the purpose of allowing deduction of such sum, it shall be deemed that the assessee has deducted and paid the tax on such sum on the date of furnishing of return of income by the resident payee. 39
40 These provisions are proposed to be applicable only in the case of resident payee. These amendments will take effect from 1st April, 2013 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the assessment year and subsequent assessment years. 40. Fee and penalty for delay in furnishing of TDS/TCS Statement and penalty for incorrect information in TDS/TCS Statement [Sections 272A and 273B]: As per the existing provisions of the Income-tax Act, a deductor is required to furnish a periodical TDS statement (quarterly) containing the details of deduction of tax made during the quarter by the prescribed due date. Under the existing provisions of section 272A, penalty of Rs.100 per day is levied for delay in furnishing of TDS statement, However, no specific penalty is specified for furnishing of incorrect information in the TDS statement. It is proposed (i) to provide for levy of fee of Rs.200 per day for late furnishing of TDS statement from the due date of furnishing of TDS statement to the date of furnishing of TDS statement. However, the total amount of fee shall not exceed the total amount of tax deductible during the period for which the TDS statement is delayed, and (ii) to provide that in addition to said fee, a penalty ranging from Rs.10,000 to Rs.1,00,000 shall also be levied for not furnishing TDS statement within the prescribed time. It is also proposed to provide that no penalty shall be levied for delay in furnishing of TDS statement if the TDS statement is furnished within one year of the prescribed due date after payment of tax deducted along with applicable interest and fee. It is proposed to provide that a penalty ranging from Rs.10,000 to Rs.1,00,000 shall be levied for furnishing incorrect information in the TDS statement. Consequential amendment is proposed in section 273B so that no penalty shall be levied if the deductor proves that there was a reasonable cause for the failure. Consequential amendment is also proposed in section 272A to provide that no penalty under this section shall be levied for late filing of TDS statement in respect of tax deducted on or after 1st July,
41 Amendments on the similar lines for levy of fee and penalty for delay in furnishing of TCS statement and furnishing of incorrect information in the TCS statement are also proposed to be made. These amendments will take effect from 1st July, 2012 and will, accordingly, apply to the TDS or TCS statement to be furnished in respect of tax deducted or collected on or after 1st July, Intimation after processing of TDS statement [Sections 154 and 246A]: Vide Finance (No.2) Act, 2009, section 200A was inserted in the Act to provide for processing of TDS statement. After processing of TDS statement, intimation is generated specifying the amount payable or refundable. The intimation generated after processing of TDS statement is not: (i) subject to rectification under section 154; (ii) appealable under section 246A; and (iii) deemed as notice of demand under section 156. It is proposed to provide that the intimation generated after processing of TDS statement shall be: (i) subject to rectification under section 154; (ii) appealable under section 246A; and (iii) deemed as notice of demand under section 156. These amendments will take effect from 1st July, Person responsible for paying in case of payment by Central Government or Government of a State [Section 204]: Existing Provision Under the existing provisions of section 204 of the Income-tax Act, a person responsible for paying has been defined to include employer, company or its principal officer or the payer. There is a lack of clarity in the case of payment made by Central Government or by a State Government as to who is the person responsible for paying the sum to the payee. Proposed Amendment It is proposed to provide that in the case of payment by Central Government or a State Government: The Drawing and Disbursing Officer or any other person (by whatever name called) responsible for making payment shall be the person responsible for paying within the meaning of section 204. This amendment will take effect from 1st July,
42 43. Extension of time for passing an order under section 201 in certain cases [Section 201]: Existing Provision A person can be deemed to be an assessee in default, by an order, in respect of non-deduction/short deduction of tax. Such order can be passed within a period of four years from end of financial year in a case where no statement as referred to in section 200 has been filed. Proposed Amendment It is proposed to amend provision of section 201, so as to extend the time limit from four years to six years. This amendment will take effect retrospectively from 1st April, F. RATIONALIZATION OF INTERNATIONAL TAXATION PROVISIONS 44. Provisions relating to Cross Boarder Transactions [Section 2(14), 2(42), 9(1) and 195]: Section 9 of the Income Tax provides cases of income, which are deemed to accrue or arise in India. This is a legal fiction created to tax income, which may or may not arise in India and would not have been taxable but for the deeming provision created by this section. Sub-section (1)(i) provides a set of circumstances in which income accruing or arising, directly or indirectly, is taxable in India. One of the limbs of clause (i) is income accruing or arising directly or indirectly through the transfer of a capital asset situate in India. Section 195 of the Income-tax Act requires any person to deduct tax at source before making payments to a non-resident if the income of such non-resident is chargeable to tax in India. Recently, the Hon ble Supreme Court in the celebrity case of Vodafone International Holdings B.V. v/s Union of India has held that the transfer of shares of a foreign company, a special purpose vehicle, which holds underlying assets in India, by a nonresident to another non-resident would not be liable to tax in India. This decision also underlines the doctrine that the situs of shares is where the company is incorporated, where its shares can be transferred and where the register of members is maintained, and not the place where the underlying economic interests of such shares lies. As per media reports, this case had a tax impact of about Rs. 11,000/- crores and it is stated that similar cases are pending at different levels, few of them are as under: Idea Cellular AT&T $ 150 mn deal pending in Bombay High Court GE-Genpact $ 500 mn deal pending in Delhi High Court Mitsul-Vedanta $ 981 mn deal in Sesa Goa pending in Goa High Court 42
43 Sabmiller-Fosters 2006 deal pending in Bombay HC Sanofi Aventis-Shantha Biotech $ 770 mn deal pending in Bombay High Court To over come the decision of Hon ble Supreme Court, a set of amendments have been proposed and that to with retrospective effect from 1st April, The proposed amendments are as under: i) Definition of Capital Asset [Section 2(14)]: For the purposes of the Income-tax Act, "capital asset" has been defined in section 2(14). The following new Explanation is proposed to be added to this section: Explanation. For the removal of doubts, it is hereby clarified that property includes and shall be deemed to have always included any rights in or in relation to an Indian company, including rights of management or control or any other rights whatsoever. The insertion of the explanation widens the definition of capital asset and clarifies that the term 'property' includes and shall be deemed to have always included any rights in or in relation to an Indian company, including rights of management or control or any rights whatsoever. This amendment is also directed to overrule observation in the case of Vodafone (supra), wherein it has been held that the capital asset transferred were the shares of a foreign company and transfer of controlling interest is not a capital asset in itself but is incidental to transfer of shares. After the amendment, transfer of shares (at any level) which result in transfer of controlling interest of an Indian Company could give rise to a taxable event in India. ii) Definition of Transfer [Section 2(47)]: The following new Explanation 2 is proposed to be added to this section: Explanation 2. For the removal of doubts, it is hereby clarified that transfer includes and hall be deemed to have always included disposing of or parting with an asset or any interest therein, or creating any interest in any asset in any manner whatsoever, directly or indirectly, absolutely or conditionally, voluntarily or involuntarily, by way of an agreement (whether entered into in India or outside India) or otherwise, notwithstanding that such transfer of rights has been characterized as being effected or dependent upon or flowing from the transfer of a share or shares of a company registered or incorporated outside India. 43
44 The amendment clarifies that 'transfer' in relation to capital assets includes disposing or parting of an asset or interest therein provided such transfer of rights is effected or dependent upon the transfer of a shares of a company (whether registered or incorporated outside India). Thus, 'transfer' would include indirect transfer of shares if rights in such shares are effected and dependent upon transfer of shares even of a foreign company. iii) Income deemed to accrue or arise in India [Section 9(1)(i)]: Two new Explanations 4 and 5 are proposed to be inserted. Existing Provision The existing provisions of clause (i) of sub-section (1) of the aforesaid section 9 provide that all income accruing or arising, whether directly or indirectly, through or from any business connection in India, or through or from any property in India, or through or from any asset or source of income in India, or through the transfer of a capital asset situate in India shall be deemed to accrue or arise in India. Proposed Amendment Explanation 4. For the removal of doubts, it is hereby clarified that the expression through shall mean and include and shall be deemed to have always meant and included by means of, in consequence of or by reason of. Explanation 5. For the removal of doubts, it is hereby clarified that an asset or a capital asset being any share or interest in a company or entity registered or incorporated outside India shall be deemed to be and shall always be deemed to have been situated in India, if the share or interest derives, directly or indirectly, its value substantially from the assets located in India. The Bill further proposes to clarify that the expression 'through' shall mean and include and shall be deemed to have always meant and included 'by means of', 'in consequence of" or 'by reason of. As a result of the amendment, the bill proposes to clarify that income deemed to accrue or arise in India by means of/ in consequence of/ by reason of a capital asset situated in India would also be taxable in India. Thus, the amendment seeks to side-step the observation of the SC in the case of Vodafone (supra) where the SC had ruled that income from capital gains accruing or arising outside India would be deemed to accrue or arise in India only when the capital asset is situated in India. Accordingly, the amendment seeks to widen the scope of income under Section 9 of the ITA and bring into tax net, the gains derived from transfer of share or interest if such share or interest derives either directly or indirectly its value substantially from assets located in India 44
45 iv) Withholding tax on payment to non-residents [Section 195]: The following explanation is proposed to be added as Explanation 2: Explanation 2. For the removal of doubts, it is hereby clarified that the obligation to comply with sub-section (1) and to make deduction thereunder applies and shall be deemed to have always applied and extends and shall be deemed to have always extended to all persons, resident or non-resident, whether or not the non-resident person has (i) a residence or place of business or business connection in India; or (ii) any other presence in any manner whatsoever in India. The amendment widens the withholding tax provisions of Section 195 of the ITA by applying it to all persons whether resident or non- resident. It is further clarified that such non- resident may or may not have a residence or place of business or business connection or any other presence in India. The memorandum explaining the provisions of Finance Bill (Memorandum) provides the rational of these amendments as under: The legislative intent of this clause is to widen the application as it covers incomes, which are accruing or arising directly or indirectly. The section codifies source rule of taxation wherein the state where the actual economic nexus of income is situated has a right to tax the income irrespective of the place of residence of the entity deriving the income. Where corporate structure is created to route funds, the actual gain or income arises only in consequence of the investment made in the activity to which such gains are attributable and not the mode through which such gains are realized. Internationally this principle is recognized by several countries, which provide that the source country has taxation right on the gains derived of offshore transactions where the value is attributable to the underlying assets. In nutshell, the impact of all these amendments is to nullify the effect of decision of Hon ble Supreme Court in the case of Vodafone. The point for consideration is as to what would be the impact of these amendments when the taxability is to be examined under the provisions of Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA). There are interesting views floating in media. The legal team of Vodafone Plc states that the Vodafone tax case having had the benefit of the final un-appealable verdict of the apex court is effectively entitled to be excluded from the ambit of any purported retrospective proposed legislation. Whereas the legal counsel of tax department are of the view that they are back to square one now. There is an order in place and case will automatically stands opened unless, of course, someone challenges the amendment. Who is right and who is not only time will say. Who has lost and who has earned? Yes! definitely the professionals have earned a lot in the matter. 45
46 45. Taxation of Royalty Income [Section 9(1)(vi)]: Section 9(1)(vi) provides that any income payable by way of royalty in respect of any right, property or information is deemed to be accruing or arising in India. The term royalty has been defined in Explanation 2 which means consideration received or receivable for transfer of all or any right in respect of certain rights, property or information. It is proposed to be clarified by insertion of new Explanation 4 that the transfer of all or any rights in respect of any right, property or information includes and has always included transfer of all or any right for use or right to use a computer software (including granting of a licence) irrespective of the medium through which such right is transferred. It is further proposed to be clarified that the royalty includes and has always included consideration in respect of any right, property or information, whether or not (a) (b) (c) the possession or control of such right, property or information is with the payer; such right, property or information is used directly by the payer; the location of such right, property or information is in India. Further an Explanation 6 is proposed to be inserted to clarify that the expression process includes and shall be deemed to have always included transmission by satellite (including up-linking, amplification, conversion for down-linking of any signal), cable, optic fibre or by any other similar technology, whether or not such process is secret. Thus, the question arises is whether considerations for use of computer software is a royalty or not. Also, whether the right, property or information has to be used directly by the payer or is to be located in India or controlled or possession of it has to be with the payer. The judicial decisions on the subject has held that use of copyrighted articles is not a royalty Tata Consultancy Services v/s State of AP (271 ITR 401 (SC); Velankani Mauritius Ltd. v/s DCIT (132 TTJ 124) (Bang.)(Trib.); ADIT v/s TII Team Telecom International (P) Ltd. (140 TTJ 649) (Mum.)(Trib.) The decisions against the tax payer on the subject are: CIT v. Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd. (203 Taxman 477) (Karn); Gracemac Corp. (42 SOT 550) (Del)(Trib.); 46
47 The Memorandum explains that considering the conflicting decisions of various courts in respect of taxability of royalty income and to restate the legislative intent, the amendments have been proposed. Thus, now any consideration received for use of computer software will be subject to tax u/s 9(1)(vi) of the Act. All the amendments are proposed retrospectively with effect from 1 st June, Here also, the point for consideration is as to what would be the impact of these amendments when the taxability is to be examined under the provisions of Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA). 46. Time limit for issue of Notice [Section 149]: The following amendments are proposed in respect of time limit for issue of Notice. Existing Provision The existing provisions of sub-section (3) of the aforesaid section 149 provide that if the person on whom a notice under section 148 is to be served is a person treated as the agent of a nonresident under section 163 and the assessment, reassessment or recomputation to be made in pursuance of the notice is to be made by him as the agent of such non-resident, the notice shall not be issued after the expiry of a period of two years from the end of the relevant assessment year. Proposed Amendment It is proposed to amend the aforesaid subsection to substitute the words two years with the words six years so as to provide that the notice shall not be issued after the expiry of a period of six years from the end of the relevant assessment year. The provisions of section 149 are procedural in nature. A new Explanation is proposed to be inserted to provide that the provisions of sub-sections (1) and (3) of this section as amended by the Finance Act 2012, shall also be applicable to the proceedings initiated under this section for any assessment year beginning on or before 1st April, These amendments will take effect from 1st day of July, Withholding tax on payment to non-resident [Section 195]: The following new sub-section (7) is proposed to be inserted: (7) Notwithstanding anything contained in sub-section (1) and sub-section (2), the Board may, by notification in the Official Gazette, specify a class of persons or cases, where the person responsible for paying to a non-resident, not being a company, or to a foreign company, any sum, whether or not chargeable under the provisions of this Act, shall make an application to the Assessing Officer to determine, by general or special order, the appropriate 47
48 proportion of sum chargeable, and upon such determination, tax shall be deducted under sub-section (1) on that proportion of the sum which is so chargeable. The amendment is proposed to be effective from 1 st July, Validation Clause [Clause 113 of Finance Bill]: Validation clause: It is proposed to provide for validation of demands raised under the Income-tax Act in certain cases in respect of income accruing or arising, through or from transfer of a capital asset situated in India, in consequence of the transfer of a share or shares of a company registered or incorporated outside India or in consequence of agreement or otherwise outside India. It is proposed to provide through this validation clause that any notice sent or purporting to have been sent, taxes levied, demanded, assessed, imposed or collected or recovered during any period prior to coming into force of the validating clause shall be deemed to have been validly made and such notice or levy of tax shall not be called in question on the ground that the tax was not chargeable or any ground including that it is a tax on capital gains arising out of transactions which have taken place outside India. The validating clause shall operate notwithstanding anything contained in any judgment, decree or order of any Court or Tribunal or any Authority. This validation shall take effect from coming into force of the Finance Act, Taxation of non-resident entertainer, sports person, etc. [Section 115BBA]: Existing Provision The provisions of section 115BBA provides for imposition of ten per cent tax where the total income of an assessee being a sportsman (including an athlete) who is not citizen of India and is a non-resident, includes any income received or receivable by way of participation in India in any game (other than a game the winnings wherefrom are taxable under section 115BB) or sport or advertisement or contribution of articles relating to any game or sport in India in newspapers, magazines or journals or being a non-resident sports association or institution includes any amount guaranteed to be paid or payable to such associations or institutions in relation to any games (other than a game the winnings wherefrom are taxable under section 115BB) or sport played in India, the income-tax payable by the assessee Proposed Amendment It is proposed to insert a new clause (c) in sub-section (1) so as to include any income received or receivable by an entertainer, who is not a citizen of India and is a non-resident, from his performance in India. It is also proposed to increase the rate of tax to 20% on gross receipt in respect of all the persons covered under this section, i.e. Non-citizen non-resident sports man; Non-resident sports association; and Non-citizen non-resident entertainer. 48
49 on such income shall be the aggregate of the amount of income tax calculated on income at the rate of ten per cent. The term entertainer is not defined under the Act. However, in the Memorandum it is stated that the section 115BBA is proposed to be amended to provide that income arising to a non-citizen, non-resident entertainer (such as theatre, radio or television artists and musicians) from performance in India shall be taxable at the rate of 20% of gross receipts. 50. Agreement with Foreign Countries and Specified Association for Double Taxation relief (DTAA) [Section 90 and 90A]: The existing provisions of section 90 of the Act confers power upon the Central Government to enter into agreement with the Government of any specified territory outside India in addition to entering into agreement with foreign countries. Three amendments have been proposed in this section. a) It is proposed to insert a new sub-section (2A) in the aforesaid section 90 so as to provide that the provisions of newly inserted Chapter X-A [i.e. provision relating to General Anti Avoidance Rule (GAAR)] shall apply even if such provisions are not beneficial to the assessee. b) It is further proposed to insert a new sub-section (4) in the aforesaid section so as to provide that an assessee, not being a resident, to whom an agreement referred to in sub-section (1) applies, shall not be entitled to claim any relief under such agreement unless a certificate, containing prescribed particulars, of his being a resident in any country outside India or specified territory outside India, as the case may be, is obtained by him from the Government of that country or specified territory. It is proposed to make submission of Tax Residency Certificate (TRC) containing prescribed particular as a necessary but not sufficient condition for availing benefit of DTAA. The above two amendments will take effect from 1st April, 2013 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to assessment year and subsequent assessment years. c) The existing sub-section (3) of the aforesaid section provides that any term used but not defined in this Act or in the agreement referred to in sub-section (1) shall, unless the context otherwise requires, and is not inconsistent with the provisions of this Act or the agreement, have the same meaning as assigned to it in the notification issued by the Central Government in the Official Gazette in this behalf. 49
50 It is proposed to insert an Explanation after Explanation 2 in the aforesaid section so as to provide that for the removal of doubts, it is hereby declared that where any term is used in any agreement entered into under sub-section (1) and not defined in the agreement or the Act, but is assigned a meaning to it in the notification issued under sub-section (3) and such notification issued thereunder being in force, then, the meaning assigned to such term shall be deemed to have effect from the date on which the said agreement came into force. This amendment will take effect retrospectively from 1st October, Section 90A of the Act similarly empowers the Central Government to adopt and implement an agreement between a specified association in India and any specified association in a specified territory outside India for granting relief from double taxation, etc. on the lines of Section 90 of the Act. Similar amendments have been proposed in section 90A of the Act. 51. Extension of time limit for completion of assessment or re-assessment where information is sought under DTAA [Sections 153 and 153B]: The time limit for completion of an assessment or reassessment has been provided in the provisions of section 153 and 153B of the Income-tax Act. These provisions were amended vide Finance Act, 2011 to exclude the time taken in obtaining information (form foreign tax authorities) from the time prescribed for completion of assessment or reassessment in the case of an assessee. This time period to be excluded would start from the date on which the process of getting information is initiated by making a reference by the competent authority in India to the foreign tax authorities and end with the date on which information is received by the Commissioner. Currently, this period of exclusion is limited to six months. It is proposed to extend the time limit to one year on the ground that foreign inquiries generally by nature take longer time for obtaining information. These amendments will take effect from the 1st day of July, G. RATIONALIZATION OF TRANSFER PRICING PROVISIONS 52. Advance Pricing Agreement [Sections 92CC and 92CD]: It is proposed to insert new sections 92CC and 92CD in the Act relating to Advance Pricing Agreement and effect to an Advance Pricing Agreement (APA). The proposed sections provide as under: a) It empowers Board, to enter into an advance pricing agreement with any person undertaking an international transaction. 50
51 b) Such APAs shall include determination of the arm s length price or specify the manner in which arm s length price shall be determined, in relation to an international transaction which the person undertake. c) The manner of determination of arm s length price in such cases shall be any method including those provided in sub section (1) of section 92C, with necessary adjustments or variations. d) The arm s length price of any international transaction, which is covered under such APA, shall be determined in accordance with the APA so entered and the provisions of section 92C or section 92CA which normally apply for determination of arm s length price would be modified to this extent and arm s length price shall be determined in accordance with APA. e) The APA shall be valid for such previous years as specified in the agreement which in no case shall exceed five consecutive previous years. f) The APA shall be binding only on the person and the Commissioner (including income-tax authorities subordinate to him) in respect of the transaction in relation to which the agreement has been entered into. The APA shall not be binding if there is any change in law or facts having bearing on such APA. g) The Board is empowered to declare, with the approval of Central Government, any such agreement to be void ab initio, if it finds that the agreement has been obtained by the person by fraud or misrepresentation of facts. Once an agreement is declared void ab-initio, all the provisions of the Act shall apply to the person as if such APA had never been entered into. h) For the purpose of computing any period of limitation under the Act, the period beginning with the date of such APA and ending on the date of order declaring the agreement void ab-initio shall be excluded. However if after the exclusion of the aforesaid period, the period of limitation referred to in any provision of the Act is less than sixty days, such remaining period shall be extended to sixty days. i) The Board is empowered to prescribe a Scheme providing for the manner, form, procedure and any other matter generally in respect of the Advance Pricing Agreement. j) Where an application is made by a person for entering into such an APA, proceedings shall be deemed to be pending in the case of the person for the purposes of the Act like for making enquiries under section 133(6) of the Act. k) The person entering in to such APA shall necessarily have to furnish a modified return within a period of three months from the end of the month in 51
52 which the said APA was entered in respect of the return of income already filed for a previous year to which the APA applies. The modified return has to reflect modification to the income only in respect of the issues arising from the APA and in accordance with it. l) Where the assessment or reassessment proceedings for an assessment year relevant to the previous year to which the agreement applies are pending on the date of filing of modified return, the Assessing Officer shall proceed to complete the assessment or reassessment proceedings in accordance with the agreement taking into consideration the modified return so filed and normal period of limitation of completion of proceedings shall be extended by one year. m) If the assessment or reassessment proceedings for an assessment year relevant to a previous year to which the agreement applies has been completed before the expiry of period allowed for furnishing of modified return, the Assessing Officer shall, in a case where modified return is filed, proceed to assess or reassess or recompute the total income of the relevant assessment year having regard to and in accordance with the APA and to such assessment, all the provisions relating to assessment shall apply as if the modified return is a return furnished under section 139 of the Act. The period of limitation for completion of such assessment or reassessment is one year from the end of the financial year in which the modified return is furnished. n) All the other provisions of this Act shall apply accordingly as if the modified return is a return furnished under section 139. These amendments will take effect from 1st July, Examination by the Transfer Pricing Officer of International Transaction [Section 92CA]: Provisions of section 92CA provides for reference to Transfer Pricing Officer for computation of Arms Length Price in relation to an international transaction. It is proposed to insert a new sub-section (2B) in the aforesaid section so as to provide that where in respect of an international transaction, the assessee has not furnished the report under section 92E and such transaction comes to the notice of the Transfer Pricing Officer in the course of proceeding before him, then he shall be empowered to take into account such transaction as if it is an international transaction referred to him by the Assessing Officer under sub-section (1) and all the provisions of Chapter X of the Income-tax Act shall apply accordingly. This amendment will take effect retrospectively from 1st June, It is also proposed to provide that no action will be taken in respect of proceedings which have been completed before the 1st day of July,
53 This amendment will take effect from 1st July, If the matter is pending in any appeal, whether the Assessing Officer will be empowered to apply this provision? The answer seems to be yes, because when appeal is pending it cannot be said that the proceedings are completed and the section says if the proceedings have been completed before 1 st July, 2012, then only Assessing Officer will not be able to apply provisions of sub-section (2B). 54. Transfer Pricing Regulations to apply to certain domestic transactions [Sections 40A(2), 80A, 80IA, 92, 92BA, 92C, 92CA, 92D, 92E, 271, 271AA and 271G]: Section 40A of the Act empowers the Assessing Officer to disallow unreasonable expenditure incurred between related parties. Further, under Chapter VI-A and section 10AA, the Assessing Officer is empowered to re-compute the income (based on fair market value) of the undertaking to which profit linked deduction is provided if there are transactions with the related parties or other undertakings of the same entity. However, no specific method to determine reasonableness of expenditure or fair market value to re-compute the income in such related transactions is provided under these sections. The Supreme Court in the case of CIT Vs. Glaxo SmithKline Asia (P) Ltd., in its order has, after examining the complications which arise in cases where fair market value is to be assigned to transactions between domestic related parties, suggested that Ministry of Finance should consider appropriate provisions in law to make transfer pricing regulations applicable to such related party domestic transactions. In the light of the decision of the Hon ble Supreme Court, the amendments have been proposed to bring in Transfer Pricing provisions to apply to certain domestic transactions. Section 40A of the Act, deals with expenses or payment not deductible in certain circumstances. Existing Provision The provisions of section 40A(2)(a) provides that where the assessee incurs any expenditure in respect of which payment has been or is to be made to any person referred to in clause (b) of the said section and the Assessing Officer is of the opinion that such expenditure is excessive or unreasonable having regard to fair market value of the goods, services or facilities for which the payment is made or the legitimate needs of the business or profession of Proposed Amendment It is proposed to amend the aforesaid clause so as to provide that no disallowance under this clause, on account of any expenditure being excessive or unreasonable having regard to the fair market value, shall be made in respect of a specified domestic transaction referred to in section 92BA, if such transaction is at arm s length price as defined in clause (ii) of section 92F. 53
54 the assessee or the benefit derived by or accruing to him therefrom, so much of expenditure as is so considered by him to be excessive or unreasonable shall not be allowed as deduction. Existing Provision The provisions of clause (b) of the aforesaid sub-section defines the persons referred to in clause (a). Subclause (iv) of the said clause defines the persons in a company, firm, association of persons or Hindu undivided family having a substantial interest in the business or profession of the assessee or any director, partner or member of such company, firm, association or family, relative of such director, partner or member. Proposed Amendment It is proposed to amend the aforesaid clause (b) so as to include therein any other company carrying on a business or profession in which the company referred to in the aforesaid sub-clause has substantial interest. It is proposed to amend the meaning of related person to include companies having the same holding company. The amendments have been proposed in Sections 80A and 80IA to provide that market value in relation to any goods or services sold, supplied or acquired, in case of a transaction being a domestic transaction referred to in section 92BA shall be the arm s length price as defined in clause (ii) of section 92F. Section 92 of the Act deals with computation of income from international transaction having regard to arms length price. It is proposed to amend the aforesaid section to insert a new sub-section (2A) so as to provide that any allowance for an expenditure or interest or allocation of any cost or expense or any income in relation to the specified domestic transaction shall be computed having regard to the arm s length price. It is further proposed to amend sub-sections (2) and (3) of the aforesaid section to substitute the expression international transaction or specified domestic transaction in place of international transaction so as to include therein the specified domestic transaction and apply the provisions of sub-sections (2) and (3) to specified domestic transactions. A new section 92BA is proposed to be inserted relating to meaning of specified domestic transactions: 54
55 For the purposes of this section and sections 92, 92C, 92D and 92E, specified domestic transaction in case of an assessee means any of the following transactions, not being an international transaction, namely: (i) any expenditure in respect of which payment has been made or is to be made to a person referred to in clause (b) of sub-section (2) of section 40A; (ii) any transaction referred to in section 80A; (iii) any transfer of goods or services referred to in sub-section (8) of section 80- IA; (iv) (v) (vi) any business transacted between the assessee and other person as referred to in sub-section (10) of section 80-IA; any transaction, referred to in any other section under Chapter VI-A or section 10AA, to which provisions of sub-section (8) or sub-section (10) of section 80-IA are applicable; or any other transaction as may be prescribed, and where the aggregate of such transactions entered into by the assessee in the previous year exceeds a sum of five crore rupees. Consequential amendments have been proposed in following sections to extend the provisions of these sections to specified domestic transactions: Sections Particulars 92C Computation of Arms Length Price 92CA Reference to Transfer Pricing Officer 92D Maintenance and keeping information and documents 92E Report from an accountant 271 Penalty for failure to furnish returns, comply with notices, concealment of income 271AA Penalty for failure to keep and maintain information and document in respect of international transaction 271G Penalty for failure to furnish information or document u/s 92D These amendments will take effect from 1st April, 2013 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to assessment year and subsequent assessment years. 55. Determination of Arms Length Price (ALP) [Section 92C]: a. The Finance Bill seeks to put a ceiling of 3% in respect of power of the Central Government to notify the tolerance range for determination of ALP. b. The amendment will take effect from 1 st April, 2013 and will accordingly, apply in relation to the A.Y and subsequent assessment years. 55
56 c. Further it is clarified by way of an Explanation that the second proviso to the section 92C(2) as amended with effect from 1 st October, 2009 which stated that the erstwhile tolerance range of 5% shall be applicable to any assessment or reassessment proceedings, if pending as on 1 st October, 2009 before an Assessing Officer. d. It is also clarified that the tolerance range does not tantamount to a standard deduction even as per the provisions as it stood before 1 st October, 2009 and the same shall be applicable retrospectively i.e. A.Y onwards. 56. Definition of international transaction and intangible property [Section 92B]: It is proposed to expand the definition of international transaction and intangible property by insertion of an explanation to section 92B. The proposed explanation is as under: (i) the expression international transaction shall include (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) the purchase, sale, transfer, lease or use of tangible property including building, transportation vehicle, machinery, equipment, tools, plant, furniture, commodity or any other article, product or thing; the purchase, sale, transfer, lease or use of intangible property, including the transfer of ownership or the provision of use of rights regarding land use, copyrights, patents, trademarks, licences, franchises, customer list, marketing channel, brand, commercial secret, know-how, industrial property right, exterior design or practical and new design or any other business or commercial rights of similar nature; capital financing, including any type of long-term or short-term borrowing, lending or guarantee, purchase or sale of marketable securities or any type of advance, payments or deferred payment or receivable or any other debt arising during the course of business; provision of services, including provision of market research, market development, marketing management, administration, technical service, repairs, design, consultation, agency, scientific research, legal or accounting service; a transaction of business restructuring or reorganization, entered into by an enterprise with an associated enterprise, irrespective of the fact that it has bearing on the profit, income, losses or assets of such enterprises at the time of the transaction or at any future date; 56
57 (ii) the expression intangible property shall include (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) (k) (l) marketing related intangible assets, such as, trademarks, trade names, brand names, logos; technology related intangible assets, such as, process patents, patent applications, technical documentation such as laboratory notebooks, technical know-how; artistic related intangible assets, such as, literary works and copyrights, musical compositions, copyrights, maps, engravings; data processing related intangible assets, such as, proprietary computer software, software copyrights, automated databases, and integrated circuit masks and masters; engineering related intangible assets, such as, industrial design, product patents, trade secrets, engineering drawing and schematics, blueprints, proprietary documentation; customer related intangible assets, such as, customer lists, customer contracts, customer relationship, open purchase orders; contract related intangible assets, such as, favourable supplier, contracts, licence agreements, franchise agreements, non-compete agreements; human capital related intangible assets, such as, trained and organized work force, employment agreements, union contracts; location related intangible assets, such as, leasehold interest, mineral exploitation rights, easements, air rights, water rights; goodwill related intangible assets, such as, institutional goodwill, professional practice goodwill, personal goodwill of professional, celebrity goodwill, general business going concern value; methods, programmes, systems, procedures, campaigns, surveys, studies, forecasts, estimates, customer lists, or technical data; any other similar item that derives its value from its intellectual content rather than its physical attributes. This amendment will take effect retrospectively from 1 st April, 2002 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the assessment year and subsequent assessment years. 57
58 57. Other amendments to Transfer Pricing Regulations [Sections 139, 147, 271AA]: a) The extended due date of 30 th November of the assessment year for filing the return of income is now proposed to be applicable the non-company assessees who are required to obtain and file transfer pricing report as per section 92E of the Act. The amendment is proposed to be effective from A.Y b) Section 147 of the Act provides for reopening of the cases if any income chargeable to tax has escaped assessment. Explanation to this section provides certain circumstances where it will be deemed that income has escaped assessment. It is proposed to provide that in all cases where it is found that an international transaction has not been reported either by non-filing of report or otherwise by not including such transaction in the report mentioned in section 92E then such non-reporting would be considered as a case of deemed escapement of income and such a case can be reopened under section 147 of the Act. This amendment will take effect from 1st July, c) The penalty u/s 271AA is proposed to be increased by substituting new section 271AA. It is proposed to provide levy of a penalty at the rate of 2% of the value of the international transaction, if the taxpayer.- (i) (ii) (iii) fails to maintain prescribed documents or information or; fails to report any international transaction which is required to be reported, or; maintains or furnishes any incorrect information or documents. This penalty would be in addition to penalties in section 271BA and 271G. This amendment will take effect from 1st July, Amendments in respect to Dispute Resolution Penal (DRP) [Sections 144C, 253, 254]: The institution of Dispute Resolution Penal was created by Finance Act 2009 with a view to bring about a speedy resolution of disputes in the case of international transactions particularly involving transfer pricing issues. a) A new explanation is proposed to be added after sub-section (8) of section 144C of the Act to provide 58
59 Explanation. For the removal of doubts, it is hereby declared that the power of the Dispute Resolution Panel to enhance the variation shall include and shall be deemed always to have included the power to consider any matter arising out of the assessment proceedings relating to the draft order, notwithstanding that such matter was raised or not by the eligible assessee. It is stated in the Memorandum that in a recent judgement, it was held that the power of DRP is restricted only to the issues raised in the draft assessment order and therefore it cannot enhance the variation proposed in the order as a result of any new issue which comes to the notice of the panel during the course of proceedings before it. This is not in accordance with the legislative intent. This amendment will be effective retrospectively from the 1st day of April, 2009 and will accordingly apply to assessment year and subsequent assessment years. b) Under the existing provisions, the Income Tax Department does not have a right to appeal against the direction given by the DRP. It is proposed to amend the provisions of section 253 and section 254 of the Income-tax Act to provide for filing of appeal by the Assessing Officer against an order passed in pursuance of directions of the DRP in respect of an objection filed on or after 1st July, These amendments will take effect from the 1st day of July, 2012 H. GENERAL ANTI-AVOIDANCE RULE (GAAR) 59. General Anti Avoidance Rule [Sections 95 to 102]: It is proposed to provide General Anti Avoidance Rule in the Act. These provisions were originally part of Direct Tax Code (DTC). Since DTC is post pone for some time these provisions are proposed to be brought in now by introducing a new Chapter X-A in the Act. The provisions are dealt with in proposed sections 95 to 102. A. The main feature of such a regime are: (i) (ii) An arrangement whose main purpose or one of the main purposes is to obtain a tax benefit and which also satisfies at least one of the four tests, can be declared as an impermissible avoidance arrangements. The four tests referred to in (i) are (a) The arrangement creates rights and obligations, which are not normally created between parties dealing at arm s length. 59
60 (b) (c) (d) It results in misuse or abuse of provisions of tax laws. It lacks commercial substance or is deemed to lack commercial substance. Is carried out in a manner, which is normally not employed for bonafide purpose. (iii) It shall be presumed that obtaining of tax benefit is the main purpose of an arrangement unless otherwise proved by the taxpayer. (iv) An arrangement will be deemed to lack commercial substance if (a) the substance or effect of the arrangement as a whole, is inconsistent with, or differs significantly from, the form of its individual steps or a part; or (b) it involves or includes (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (c) round trip financing; an accommodating party; elements that have effect of offsetting or cancelling each other; or a transaction which is conducted through one or more persons and disguises the value, location, source, ownership or control of fund which is subject matter of such transaction; or it involves the location of an asset or of a transaction or of the place of residence of any party which would not have been so located for any substantial commercial purpose other than obtaining tax benefit for a party. (v) (vi) It is also provided that certain circumstances like period of existence of arrangement, taxes arising from arrangement, exit route, shall not be taken into account while determining lack of commercial substance test for an arrangement. Once the arrangement is held to be an impermissible avoidance arrangement then the consequences of the arrangement in relation to tax or benefit under a tax treaty can be determined by keeping in view the circumstances of the case, however, some of the illustrative steps are:- (a) (b) (c) disregarding or combining any step of the arrangement; ignoring the arrangement for the purpose of taxation law; disregarding or combining any party to the arrangement; 60
61 (d) (e) reallocating expenses and income between the parties to the arrangement; relocating place of residence of a party, or location of a transaction or situs of an asset to a place other than provided in the arrangement; (f) considering or looking through the arrangement by disregarding any corporate structure; (g) re-characterizing equity into debt, capital into revenue etc. (vii) These provisions can be used in addition to or in conjunction with other anti avoidance provisions or provisions for determination of tax liability, which are provided in the taxation law. (viii) For effective application in cross border transaction and to prevent treaty abuse a limited treaty override is also provided. B. A detailed procedure for invoking GAAR provisions have been provided for. In addition to the above, it is provided that the Board shall prescribe a scheme for regulating the condition and manner of application of these provisions. These amendments will take effect from 1st April, 2013 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the assessment year and subsequent assessment years. I. OTHER AMENDMENTS 60. Extension of time for completion of assessments and reassessments [Sections 153 and 153B]: The existing provisions of section 153 and 153B provides the time limit for completion of assessment and reassessment of income by the Assessing Officer. The time limits are proposed to be revised as under: Proceedings under section Current time allowed Proposed Period 143(3) 21 months from the end of the A.Y. 24 months 143 (3) and 33 months from the end of the A.Y. 36 months 92CA months from the end of the F.Y. in which 12 months notice issued 148 and 92CA 21 months from the end of the F.Y. in which notice issued 24 months 61
62 250 or 254 or or 254 or 263, and 92CA 9 months from the end of the F.Y. in which order received 21 months from the end of the F.Y. in which order received 12 months 24 months Consequential amendments have been made in the provisions of section 17A of the Wealth-tax Act for increasing the time limit by three months for completion of assessment/reassessment proceedings. These amendments will take effect from 1st July, Assessment of charitable organization in case commercial receipts exceed the specified threshold [Sections 10(23C), 13 and 143]: Sections 11 and 12 of the Act exempt income of any charitable trust or institution, if such income is applied for charitable purposes in India and such institution is registered under section 12AA of the Act. Section 10(23C) of Income Tax Act also provides exemption in respect of approved charitable funds or institutions. Charitable purpose includes the advancement of any other object of general public utility. However, the advancement of any other object of general public utility is not a charitable purpose, if it involves the carrying on of any activity in the nature of trade, commerce or business, or any activity of rendering any service in relation to any trade, commerce or business, for a cess or fee or any other consideration, irrespective of the nature of use or application, or retention, of the income from such activity and receipts from such activities is rupees twenty five lakh or more in the previous year. This has a consequence of denial of benefit u/s 11 of the Act. It is proposed to amend section 10(23C), section 13 and section 143 of the Act to ensure that such organization does not get benefit of tax exemption in the year in which its receipts from commercial activities exceed the threshold whether or not the registration or approval granted or notification issued is cancelled, withdrawn or rescinded. Thus, a charitable trust or institution pursuing advancement of object of general public utility may be a charitable trust in one year and not a charitable trust in another year depending on the aggregate value of receipts from commercial activities. The temporary excess in one year may not be treated as altering the very nature of the trust or institution so as to lead to cancellation of registration or withdrawal of approval or rescinding of notification issued in respect of trust or institution. This amendment will take effect retrospectively from 1st April, 2009 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the A.Y and subsequent assessment years. 62
63 62. Due date of furnishing audit report in case of international transactions [Sections 44AB and 139]: It is proposed to provide u/s 44AB that the due date for furnishing the Tax Audit Report would be the date specified for furnishing the return of income u/s 139 of the Act. This amendment will take effect retrospectively from 1st April, 2012 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the assessment year and subsequent assessment years. 63. Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT) [Section 115JB]: Under the existing provisions of section 115JB of the Act, a company is liable to pay MAT of eighteen and one half percent of its book profit in case tax on its total income computed under the provisions of the Act is less than the MAT liability. Existing Provision Book profit for this purpose is computed by making certain adjustments to the profit disclosed in the profit and loss account prepared by the company in accordance with the Schedule VI of the Companies Act, As per section 115JB, every company is required to prepare its accounts as per Schedule VI of the Companies Act, However, as per the provisions of the Companies Act, 1956, certain companies, e.g. insurance, banking or electricity company, are allowed to prepare their profit and loss account in accordance with the provisions specified in their regulatory Acts. Existing Provision II. It is noted that in certain cases, the amount standing in the revaluation reserve is taken directly to general reserve on disposal of a revalued asset. Thus, the gains attributable to revaluation of the asset are not subject to MAT liability. III. New provision Proposed Amendment In order to align the provisions of Income-tax Act with the Companies Act, 1956, it is proposed to amend section 115JB to provide that the companies which are not required under section 211 of the Companies Act to prepare their profit and loss account in accordance with the Schedule VI of the Companies Act, 1956, profit and loss account prepared in accordance with the provisions of their regulatory Acts shall be taken as a basis for computing the book profit under section 115JB. Proposed Amendment It is proposed to amend section 115JB to provide that the book profit for the purpose of section 115JB shall be increased by the amount standing in the revaluation reserve relating to the revalued asset which has been retired or disposed, if the same is not credited to the profit and loss account. It is also proposed to omit the reference of Part III of the Schedule 63
64 VI of the Companies Act, 1956 from section 115JB in view of omission of Part III in the revised Schedule VI under the Companies Act, Earlier it was being done as under- a) When a Taxpayer is planning to sale any asset in the next years, then he would revalue it in the current year itself. For example, Co. A wants to sale some of listed shares held by it as investments in year 3. The book value is Rs. 100/- and the market value in year 1 is Rs. 500/- and is likely to be sold at Rs. 700/- in year 3. Co. A would revalue its shares investment at Rs. 500/- in year 1. The Investment in Shares account would be debited by Rs. 400/- and the profit on revaluation of Rs. 400/- would be credited to Revaluation Reserve Account. b) In the year of sale, the book profit on sale of shares would be Rs.200/- (Rs. 700/- less Rs 500/-). This Rs. 200/- will be credited to Profit and Loss account. The amount lying in the Revaluation Reserve Account of Rs. 400/- will be transferred to the General Reserve Account. No impact to Profit and Loss account. c) In tax computation, the long term capital gains would be exempt and MAT will be paid on Rs. 200/-, as against the actual profit of Rs. 600/-. It is proposed to remedy such leakage of tax revenue. These amendments will take effect from 1st April, 2013 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the assessment year and subsequent assessment years. 64. Liability to pay advance tax in case of non-deduction of tax [Section 209]: Existing Provision The amount of advance tax payable is computed by reducing the amount of income-tax which would be deductible or collectible during the financial year from income-tax on estimated income. Proposed Amendment It is proposed to amend the aforesaid section to provide that where a person has received any income without deduction or collection of tax, he shall be liable to pay advance tax in respect of such income. Under the existing provisions, in cases where the assessee receives or pays any amount (on which the tax was deductible or collectible) without deduction or collection of tax, it has been held by Courts that he is not liable to pay advance tax to the extent the tax is deductible or collectible from such amount. Consequently he was not liable to pay interest u/s 234B of the Act. In order to make an assessee liable for payment of advance tax in respect of income which has been received or paid without deduction or collection of tax, and 64
65 consequently in case of default to charge interest u/s 234B, the amendment has been proposed. This amendment will take effect from the 1st April, 2012 and would, accordingly, apply in relation to advance tax payable for the financial year and subsequent financial years. 65. Definition of Commissioner to include Director [Section 2 and Section 117(1)]: It is proposed to provide that the word Commissioner will include Director of Income-tax appointed under sub-section (1) of section 117. This amendment will take effect retrospectively from the 1st day of April, 1988 and will accordingly apply to assessment year and subsequent assessment years. 66. Cost of acquisition in case of certain transfers [Section 49]: Where transfer of an asset from one person to another is not regarded as a transfer under section 47, then, for the purpose of computation of capital gains, the cost of the asset in the hands of the successor under section 49 is taken as that of the predecessor. Existing Provision Certain transactions like transfer of assets by a sole proprietorship or a firm to a company on conversion are not regarded as transfer under the provisions of section 47(xiv) and section 47(xiii). While computing capital gains on subsequent sale of such assets by the company, there is no reference in the provisions of section 49 with regard to the cost to be taken for such assets. Proposed Amendment It is proposed to amend the provisions of section 49 of the Income-tax Act to provide that in case of conversion of sole proprietorship or firm into a company which is not regarded as a transfer, the cost of acquisition of asset in the hands of the company would be the same as that in the hand of the sole proprietary concern or the firm, as the case may be. This amendment will take effect retrospectively from 1st day of April, 1999 and will accordingly, apply to assessment year and subsequent assessment years. 67. Capital gains tax from sale of agricultural land by a Hindu undivided family (HUF) [Section 54B]: Existing Provision Capital gains on transfer of land which, in the two years preceding the year in which it has been sold, has been used for agricultural purposes by assessee or his parent, is exempt if the whole of capital gains has been reinvested in the Proposed Amendment It is now proposed that this benefit be also granted to a HUF. 65
66 purchase of agricultural land in the next two years. This amendment will take effect from 1st day of April, 2013 and will accordingly, apply to assessment year and subsequent assessment years. 68. Reference to a Valuation Officer [Section 55A]: Existing Provision Under the provisions of section 55A, where in the opinion of the Assessing Officer value of asset as claimed by the assessee is less than its market value; he may refer the valuation of a capital asset to a Valuation Officer. Proposed Amendment It is proposed to amend the provisions of section 55A of the Income-tax Act to enable the Assessing Officer to make a reference to the Valuation Officer where in his opinion the value declared by the assessee is at variance from the fair market value. Under section 55 in a case where the capital asset became the property of the assessee before 1st April, 1981, the assessee has the option of substituting the fair market value of the asset as on 1st April, 1981 as the cost of the asset. In such a case the adoption of a higher value for the cost of the asset as the fair market value as on 1st April, 1981, would lead to a lower amount of capital gains being offered for tax. In such a situation as per existing provisions, the assessing officer will not be able to make a reference to valuation officer because value claimed by the assessee is not less but more then its market value. Therefore post amendment, in case where the Assessing Officer is of the opinion that the value taken by the assessee as on is higher than the fair market value of the asset as on that date, the Assessing Officer would be enabled to make a reference to the Valuation Officer for determining the fair market value of the property. This amendment will take effect from 1st day of July, Rate of tax for short term capital gain under [Section 111A]: It is proposed to amend the provisions of proviso to section 111A of the Income-tax Act to provide reference of rate of tax at 15%. This amendment will take effect retrospectively from the 1st day of April, 2009 and will accordingly, apply to assessment year and subsequent assessment years. 66
67 70. Capital gains in cases of amalgamation and demerger [Sections 47(vii) and 2(19AA)]: In case of amalgamation, it is proposed to amend the provisions of section 47(vii) so as to exclude the requirement of issue of shares to the shareholder where such shareholder itself is the amalgamated company. In case of demerger, it is proposed to amend the provisions of section 2(19AA) so as to exclude the requirement of issue of shares where resulting company itself is a shareholder of the demerged company. The requirement of issuing shares would still have to be met by the resulting company in case of other shareholders of the demerged company. This amendment will take effect from 1st day of April, 2013 and will accordingly, apply to assessment year and subsequent assessment years. 71. Fair Market Value to be full value of consideration in certain cases [Section 50D]: Capital gains are calculated on transfer of a capital asset, as sale consideration minus cost of acquisition. In some recent rulings, it has been held that where the consideration in respect of transfer of an asset is not determinable under the existing provisions of the Incometax Act, then, as the machinery provision fails and therefore, the gains arising from the transfer of such assets is not taxable. It is proposed to insert a new section 50D in the Act to provide that fair market value of the asset shall be deemed to be the full value of consideration if actual consideration is not attributable or determinable. This amendment will take effect from 1st day of April, 2013 and will accordingly apply to assessment year and subsequent assessment years. 72. Processing of return of income where scrutiny notice issued [Section 143]: Existing Provision Under the existing provisions, every return of income is to be processed under sub-section (1) of section 143 and refund, if any; due is to be issued to the taxpayer. Some returns of income are also selected for scrutiny which may lead to raising a demand for taxes although refunds may have been issued earlier at the time of processing. Proposed Amendment It is proposed to amend the provisions of the Act to provide that processing of return will not be necessary in a case where notice under sub section (2) of section 143 has already been issued for scrutiny of the return. 67
68 The message is clear that if the case is selected for scrutiny, no refund be issued till finally assessed. This amendment will take effect from the 1st day of July, Notification of a class of search cases where compulsory reopening of past six years not required: Existing Provision Under the existing provisions of section 153A of the Income-tax Act, it is mandatory to issue a notice for filing of tax returns for 6 assessment years immediately proceeding the assessment year relevant to the previous year in which search is conducted under section 132 or requisition is made under section 132A. Proposed Amendment It is proposed to amend sections 153A and 153C to empower the Central Government to notify cases or class of cases in which the Assessing Officer shall not issue notice for initiation of proceedings for preceding 6 assessment years. However, action for completion of assessment proceedings for the assessment year relevant to the previous year in such class of cases in which search or requisition has been made would be taken. This would result in initiating assessment proceedings only for the assessment year relevant to the previous year in which search or requisition has been made. Consequential amendments are also proposed to be made to the provisions of section 296 of the Act. These amendments will take effect from the 1st day of July, Charging of interest on recovery of refund granted earlier [Section 234D]: Existing Provision Under the existing provisions of section 234D of the Income-tax Act (inserted with effect from , vide Finance Act, 2003), where any refund has been granted to the assessee under subsection (1) of section 143 and subsequently on regular assessment, no refund or lesser amount of refund is found due to the assessee, then, the assessee shall be liable to pay simple interest at the rate of one-half per cent Proposed Amendment It is proposed that the provisions of section 234D would be applicable to any proceeding which is completed on or after 1st June, 2003, irrespective of the assessment year to which it pertains. 68
69 on the excess amount so refunded for the period starting from the date of refund to the date of such regular assessment. An issue has arisen whether this section is applicable for the period prior to 1 st June, In a decision, it has been held that the provisions of section 234D inserted with effect from would be applicable from the assessment year only and accordingly no interest could be charged for earlier assessment years even though the regular assessments for such years were framed after 1st June, 2003 or refund was granted for those years after the said date. To overcome this decision the amendment has been proposed. This amendment will take effect retrospectively from the 1st day of June, Related person for the purpose of making an application before Settlement Commission [Section 245C]: It is proposed to provide that the substantial interest should exist as on the date of the search in place of at any time during the previous year as the proceedings before the Commission are filed for many previous years. It is accordingly proposed to amend the provisions of section 245C of the Income-tax Act so as to provide that a person shall be deemed to have a substantial interest in a business or profession if such person is a beneficial owner of not less than 20% of shares or of 20% share in profits on the date of search. This amendment will take effect from the 1st day of July, Fee for filing of applications before Authority for Advance Rulings (AAR) [Section 245Q]: It is proposed to increase filing fees of applications before Authority of Advance Rulings from Rs. 2,500/- to Rs. 10,000/- with effect from 1 st July, Authorization or requisition and subsequent assessment in search cases [Section 292CC]: Under the existing provisions of section 132 and section 132A, an authorization can be issued or a requisition can be made, as the case may be, where the Director General or the Director in consequence of information in his possession has reason to believe that any person is in possession of any money, bullion, jewellery or other valuable article or thing (hereafter referred to as undisclosed income or property), then, he may authorize any Additional Director or Deputy Director, etc. to enter and search any building, place, vehicle, etc. and seize any such books of accounts, other documents, undisclosed property, etc. 69
70 Where a search is initiated under section 132 or requisition is made under section 132A, assessment is to be completed under the provisions of section 153A or section 153C (and if search was prior to 31st May, 2003 under Chapter XIV-B of the Act) or section 143(3), etc. It is stated in the Memorandum that in a recent Court decision, it has been held that in search cases arising on the basis of warrant of authorization under section 132 of the Act, warrant of authorization must be issued individually and if it is not issued individually, assessment cannot be made in an individual capacity. It was also held that if the authorization was issued jointly, the assessment will have to be made collectively in the name of all the persons in the status of association of persons/body of individuals. It is also stated in the Memorandum that this decision is not in accordance with the legislative intent. It is accordingly proposed to insert a new section 292CC in the Income-tax Act to provide that (i) (ii) (iii) it shall not be necessary to issue an authorization under section 132 or make a requisition under section 132A separately in the name of each person; where an authorization under section 132 has been issued or a requisition under section 132A has been made mentioning therein the name of more than one person, the mention of such names of more than one person on such authorization or requisition shall not be deemed to construe that it was issued in the name of an association of persons or body of individuals consisting of such persons; notwithstanding that an authorization under section 132 has been issued or requisition under section 132A has been made mentioning therein the name of more than one person, the assessment or reassessment shall be made separately in the name of each of the persons mentioned in such authorization or requisition. These amendments will take effect retrospectively from the 1st day of April, 1976 and will accordingly, apply to assessment year and subsequent assessment years. 78. Prohibition of cash donations in excess of ten thousand rupees [Sections 80G and 80GGA]: It is proposed to amend sections 80G and 80GGA to provide that any payment exceeding a sum of ten thousand rupees shall only be allowed as a deduction if such sum is paid by any mode other than cash. These amendments will take effect from 1st April, 2013 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to assessment year and subsequent assessment years. 70
71 79. Eligibility conditions for exempt life insurance policies [Section 10(10D)]: It is proposed to provide that any sum received under a life insurance policy issued on or after 1 st April, 2012 shall be exempted only if the premium for the policy does not exceed 10% of the actual capital sum assured (reduced from 20%). For proposed newly inserted definition of actual capital sum assured please refer para below. This amendment will take effect from 1st April, 2013 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the assessment year and subsequent assessment years. 80. Eligibility condition for deduction in respect of life insurance policies [Section 80C]: It is proposed to provide that the deduction for life insurance premium as regards insurance policies issued on or after 1 st April, 2012 shall be available only if premium payable does not exceed 10% of actual capital sum assured (reduced from 20%). It is further proposed to insert the definition of actual capital sum assured so as to provide that the actual capital sum assured in relation to a life insurance policy shall be the minimum amount assured under the policy on happening of the insured event at any time during the term of the policy, not taking into account (i) (ii) the value of any premiums agreed to be returned, or any benefit by way of bonus or otherwise over and above the sum actually assured, which is to be or may be received under the policy by any person. These amendments will take effect from 1st April, 2013 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the assessment year and subsequent assessment years. 81. Wealth Tax Provisions: The proposed amendments to wealth tax provisions which are in line with proposed amendments to income tax provisions have been dealt with along with income tax provisions. 82. Wealth Tax Exemption of residential house allotted to employee etc. of a company [Section 2]: Existing Provision Section 2 of the Wealth-tax Act, the specified assets for the purpose of levy of wealth tax do not include a residential Proposed Amendment It is proposed to increase the existing threshold of gross salary from five lakh rupees to ten lakh rupees. 71
72 house allotted by a company to an employee or an officer or a whole time director if the gross annual salary of such employee or officer, etc. is less than five lakh rupees. This amendment will take effect from 1st April, 2013 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the assessment year and subsequent assessment years. 83. Exemption from Wealth Tax - Reserve Bank of India [Section 45 of Wealth Tax Act]: It is proposed to specifically provide that Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is not liable to pay wealth-tax. This amendment will take effect retrospectively from 1st April, 1957 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the assessment year and subsequent assessment years. 84. Other Proposals: The Hon ble Finance Minister has given other inputs/proposals in his Budget Speech as under: Tax Reforms 26. The Direct Taxes Code (DTC) Bill was introduced in Parliament in August It was our earnest desire to give effect to DTC from April 1, However, we received the Report of the Parliamentary Standing Committee on March 9, We will examine the report expeditiously and take steps for the enactment of DTC at the earliest. 28. The structure of GST Network (GSTN) has been approved by the Empowered Committee of State Finance Ministers. GSTN will be set up as a National Information Utility and will become operational by August The GSTN will implement common PAN-based registration, returns filing and payments processing for all States on a shared platform. The use of PAN as a common identifier in both direct and indirect taxes, will enhance transparency and check tax evasion. I solicit the support of all my colleagues cutting across party lines for an early passage of these landmark legislations. Financial Sector 35. To encourage flow of savings in financial instruments and improve the depth of domestic capital market, it is proposed to introduce a new scheme called Rajiv Gandhi Equity Savings Scheme. The scheme would allow for income tax deduction of 50 per cent to new retail investors, who invest up to ` 50,000 directly in equities 72
73 and whose annual income is below ` 10 lakh. The scheme will have a lock-in period of 3 years. The details will be announced in due course. Legislative Reforms 38. We have received the recommendations of the Standing Committee on Finance on The Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority Bill, 2011, The Banking Laws (Amendment) Bill, 2011 and The Insurance Laws (Amendment) Bill, The official amendments to these Bills will be moved in this session of the Parliament. 39. To take forward the process of financial sector legislative reforms, the Government proposes to move the following Bills in the Budget Session of the Parliament: The Micro Finance Institutions (Development and Regulation) Bill, 2012; The National Housing Bank (Amendment) Bill, 2012; The Small Industries Development Bank of India (Amendment) Bill, 2012; National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (Amendment) Bill, 2012; Regional Rural Banks (Amendment) Bill, 2012; Indian Stamp (Amendment) Bill, 2012; and Public Debt Management Agency of India Bill, Security 123. The scheme to create the National Population Register (NPR) is progressing well. It is likely to be completed within the next two years. The Government is also considering a proposal of issuing Resident Identity Cards bearing the Aadhaar numbers to all residents who are of age 18 years and above to help in the e- governance initiatives. Black Money 125. Last year I had outlined a five pronged strategy to tackle the malaise of generation and circulation of black money and its illegitimate transfer outside India. Government has taken a number of proactive steps to implement this strategy. As a result: 82 Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements (DTAA) and 17 Tax Information Exchange Agreements (TIEA) have been finalised and information regarding bank accounts and assets held by Indians abroad has started flowing in. In some cases prosecution will be initiated; 73
74 Dedicated exchange of information cell for speedy exchange of tax information with treaty countries is fully functional in CBDT; India became the 33 rd signatory of the Multilateral Convention on Mutual Administrative Assistance in Tax Matters; and Directorate of Income Tax Criminal Investigation has been established in CBDT I propose to lay on the table of the House a white paper on Black Money in the current session of Parliament. Unfortunately, now-a-days, through this key document Finance Bill a plethora of amendments (many of them applicable with retrospective effect) have been introduced to overrule judicial precedents in favour of tax payers. 74
75 SERVICE TAX Finance Minister At the end of June this year, this tax will attain adulthood by completing 18 years. It is therefore time to shift gears and accelerate ahead. RATE OF SERVICE TAX: 1. Rate of service tax has been increased from 10% to 12%. However there is no change in education cess and secondary and higher education cess. So effective rate of tax is increased from 10.3% to 12.36%. 2. Consequent to change in the rate of service tax, changes are also being made in specific and compounding rates of tax for the following: a) Service in relation to purchase and sale of foreign currency including money changing; b) Service of promotion, marketing, organizing or in any manner assisting in organizing lottery; c) Works contract service; d) Reversal of cenvat credit under rule 6(3)(i). 3. Life insurance service: Where the entire premium is not towards risk cover, the first year s premium shall be taxed at the rate of three per cent. while subsequent premia shall attract tax at the rate of 1.5 per cent. Availment of full cenvat credit is being allowed. 4. Transport of passengers embarking in India for domestic and international journey by air: The dual rate structure of maximum service tax of Rupees 150 and Rupees 750 in case of economy class travel is being replaced by an ad valorem rate of twelve per cent. with abatement of sixty per cent. subject to the condition that no credit on inputs and capital goods s taken; [The above changes will be applicable from ] INTRODUCTION OF NEGATIVE LIST APPROACH: A Negative List approach to taxation of services is being introduced vide new sections, namely, 65B, 66B, 66C, 66D, 66E and 66F proposed in Chapter V of the Finance Act, 1994 (please refer clause 143 of the Finance Bill, 2012). The services specified in the Negative List (section 66D) shall remain outside the tax net. All other services, except those specifically exempted by the exercise of powers under section 93(1) of the Finance Act, 1994, would thus be chargeable to service tax. Negative list approach to taxation of services shall come into effect from a date to be notified, after the Finance Bill, 2012 receives the 75
76 assent of the President. For operationalizing the Negative List approach, a number of changes have been proposed in Chapter V of the Finance Act, Detailed information regarding these changes is being made available as a Guidance Paper, which will be placed in the public domain. The consequential changes in Service Tax Rules, 1994, Service Tax (Determination of Value) Rules, 2006 and Cenvat Credit Rules, 2004 also form part of this Guidance Paper. Provisions relating to positive list approach, namely, sections 65, 65A, 66, and 66A currently appearing in Chapter V of the Finance Act, 1994, will cease to operate from a date to be notified later, as and when the negative list approach begins to operate. To support the negative list approach to taxation of services, draft Place of Provision of Services Rules, 2012 is being proposed. The draft Place of Provision of Services Rules contains principles on the basis of which taxing jurisdiction of a service can be determined. The Place of Provision of Services Rules, 2012 will be notified after (section 66C) the Finance Bill, 2012 receives the assent of the President. When the Place of Provision of Services Rules comes into effect, existing Export of Services Rules, 2005 and Taxation of Services (Provided from outside India and received in India) Rules, 2006 will be rescinded. The negative list of services is available on ( AMENDMENTS IN THE FINANCE ACT, 1994: Chapter V of the Finance Act, 1994 is being amended: 1. A new section 67A is being inserted to prescribe that the value of taxable service (particularly in the case of import and export of taxable services) and the rate of tax shall be determined in terms of Point of Taxation Rules, A new section 72A is being inserted to introduce provisions relating to special audit in the service tax law on the lines of section 14A and section 14AA of the Central Excise Act, Under this newly introduced section, special audit can be ordered under specified circumstances. Consequently, section 14AA is being omitted from section The one-year time limit for issuance of notice for specified category of offences prescribed under section 73(1) of the Finance Act, 1994, is being increased to eighteen months. A new sub-section (1A) is being inserted in section 73 of the Finance Act, 1994 to prescribe that follow-on notices issued on the same grounds need not repeat the grounds but only state the amount of service tax chargeable for the subsequent period. Statement of tax due for the subsequent period, served on the assessee with reference to the earlier demand notice, will be deemed as a notice under section 73(1) of the Finance Act,
77 4. Section 83 is being amended to make Settlement Commission provisions applicable to service tax in line with the similar provisions contained in sections 31, 32, 32A to 32P of the Central Excise Act, Section 83 is being amended to make the revision mechanism prescribed in section 35EE of the Central Excise Act, 1944, applicable to service tax, to the extent possible. 6. Section 85 and section 86 are being amended on the lines of section 35 and 35E of the Central Excise Act so as to harmonize the limitation for filing assessee appeal before Commissioner (Appeals) and revenue appeal before the Tribunal. 7. Section 94(2) is being amended to obtain powers (a) to provide for the manner of compounding and to specify the amount of compounding of offences along the lines of Central Excise (Compounding of Offences) Rules, 2005; (b) to provide for rules for settlement of cases, along the lines of central excise. [The above changes will come into effect from the date of enactment of the Finance Bill, 2012] NEW REVERSE CHARGE MECHANISM: 1. Section 68(2) of the Finance Act, 1994 is being amended to put the onus of payment of service tax on reverse charge basis partly on service provider and partly on service receiver. The scheme is proposed to be made applicable on three specific services i.e. hiring of means of transport; construction and man power supply. A notification will be issued after the Finance Bill, 2012 receives the assent of the President, in which the manner and extent of service tax payable by service provider and service receiver in the case of the three services will be specified. 2. Consequent to the above change, suitable amendment is also being made in the concept of person liable to pay provided in Rule 2(1)(d) of Service Tax Rules, RENTING OF IMMOVABLE PROPERTY SERVICE: Constitutional validity of the levy of service tax on renting of immovable property has been the subject matter of litigation leading to pronouncement of court judgments favorable to revenue, including those of Honorable Delhi High Court and Honorable Supreme Court. Taking an overall view, the Government has decided to waive the penalty for those taxpayers who pay the service tax due on the renting of immovable property service (as on ), in full along with interest. For this purpose, a new section 80A is being inserted in the Finance Act, This scheme of penalty waiver will be open only for a period of six months from the date of enactment of the Finance Bill, RETROSPECTIVE EXEMPTIONS: 1. Vide Notification No.24/2009-ST dated service tax on repair of roads is already exempted. Vide section 97 of the Finance Act, 1994, the exemption granted to repair of roads is being extended for the earlier period from to
78 2. Management, maintenance or repair service undertaken in relation to non-commercial Government buildings is being exempted from service tax vide section 98, with effect from till the new charging section, namely section 66B, comes into force. 3. In the last budget, sub-rule 6A was inserted under rule 6 of the Cenvat Credit Rules, 2004 to protect the service providers located in the Domestic Tariff Area from the reversal of Cenvat credit, when they supply taxable services under exemption, to the authorized operations of SEZ. The application of sub-rule 6A is being given retrospective effect from [clause 144 of the Finance Bill, 2012]. 4. Service provided by an association of dyeing units in relation to common effluent treatment plants was exempted from service tax vide Notification No.42/2011-ST dated The scope of the exemption is being expanded and the amended notification is being given retrospective effect from [clause 145 of the Finance Bill, 2012]. [The above retrospective exemptions will come into effect on the date of enactment of the Finance Bill, 2012] AMENDMENTS IN RULES: 1. Cenvat Credit Rules, 2004 is being amended: (a) Existing rule 5 to be replaced with a new rule to simplify the procedure for refund of unutilized credit on the account of exports; (b) Credit is being allowed on motor vehicles (except those of heading nos. 8702, 8703, 8704, 8711 and their chassis). The credit of tax paid on the supply of such vehicles on rent, insurance and repair shall also be allowed; (c) Credit of insurance and service station service is being allowed to (i) (ii) insurance companies in respect of motor vehicles insured and reinsured by them; and manufacturers in respect of motor vehicles manufactured by them. (d) (e) At present, credit on goods can be taken only after they are brought to the premises of the service provider. Rule 4(1) and 4(2) are being amended to allow a service provider to take credit of inputs or capital goods whenever the goods are delivered to him, subject to specified conditions. Rule 7 for input service distributors is being amended to provide that credit of service tax attributable to service used wholly in a unit shall be distributed only to that unit and that the credit of service tax attributable to service used in more than one unit shall be distributed prorata on the basis of the turnover of the concerned unit to the sum total of the turnover of all the units to which the service relates. 78
79 (f) Rule 9(1)(e) is being amended to allow availment of credit on the tax payment challan in case of payment of service tax by the service receiver on reverse charge basis. 2. Service Tax Rules, 1994 is being amended as follows: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) The time period provided in rule 4A for issuance of invoice is being increased to thirty days. For banks and financial institutions providing banking and other financial services, the period shall be forty five days; Rule 6(4A) is being amended to allow unlimited amount of permissible adjustments. At present, in the case of export and, individuals and firms rendering eight specified services, the point of taxation is the date of payment subject to certain conditions. This special dispensation is being shifted from the Point of Taxation Rules to the Service Tax Rules. In case of exporters, the period extended by the Reserve Bank of India on specific requests is also being included in the period for which the tax liability is allowed to be deferred. The option of deferred payment is being allowed for all service providers rather than for specific services. The facility will be available only to individuals and partnership firms (including limited liability partnership) upto a turnover of taxable services of Rupees Fifty lakhs subject to the condition that their turnover of taxable services in previous year was below Rupees Fifty lakhs. For computing the above limits, the turnover of the whole entity is required to be summed up and not any single registration. 3. Point of Taxation Rules, 2011 is being amended to (a) Change the definition of continuous supply of service to capture the entire dimension of the concept, namely, the recurrent nature of services and the obligation for payment periodically or from time-to-time; (b) Omit rule 6 in respect of continuous supply of service and merge it with rule 3. Rules 4 and 5, which deal with situations covering change in effective rate of tax and taxation of new services, shall now be applicable to continuous supply of services also; (c) (d) (e) Define the date of payment; To give an option to determine the point of taxation in respect of advances upto Rupees one thousand received in excess of the amount indicated in the invoice, on the basis of invoice or completion of service rather than payment; Incorporate a new residual rule to ascertain point of taxation in cases where the same cannot be ascertained by the rules prescribed. 79
80 GUP SHUP In this chapter, we have compiled some of the development in tax laws in last 12 months and also other points, which one may like to know about. It includes notes from journal published by BCAS. Part A: Direct Taxes 1. Revision of monetary limits for filing of appeals by the Department before Income Tax Appellate Tribunal, High Courts and Supreme Court - Measures for reducing litigation. - Instruction No. 3/2011 [F. NO. 279/MISC. 142/2007-ITJ], DATED Henceforth appeals shall not be filed by the tax department in cases where the tax effect does not exceed the monetary limits given hereunder: S. No. Appeals in Income-tax matters Monetary Limit (In Rs.) 1. Appeal before Appellate Tribunal 3,00, Appeal u/s 260A before High Court 10,00, Appeal before Supreme Court 25,00,000 It is clarified that an appeal should not be filed merely because the tax effect in a case exceeds the monetary limits prescribed above. Filing of appeal in such cases is to be decided on merits of the case. 2. United stock exchange of India notified as a recognised stock exchange. United stock exchange of India notified as a recognised stock exchange for the purpose of definition of speculative transaction u/s 43(5) Notification No. 12/2011, dated Changes in conditions to be fulfilled by a recognised stock exchange Income tax (First Amendment) Rules, 2011 dated The CBDT has amended Rule 6DDA wherein the recognised stock exchange shall ensure that the transactions entered in respect of cash and derivative markets once registered cannot be erased further, in case there are genuine errors and such transaction are modified, a monthly reports need to be filed with the tax department within 15 days from the end of each month in prescribed form 3BB. 4. Scrutiny norms for small taxpayers and senior citizens - Press Release dated In the aforementioned Press Note, during the financial year , the CBDT has decided not to subject to scrutiny small taxpayers being individuals and HUF s who have their Annual taxable income less than 10 lakhs before availing deduction under chapter VIA and senior citizens (age 60 and above), except when the tax officers have credible information. 80
81 5. CBDT Circular No. 3/2011, dated New procedure for issuance of Form 16A. For deductions made during the current financial year viz , by companies including banking companies, banks, financial institutions including co-operative societies engaged in banking business, the deductor shall issue TDS certificates generated from the central system of the TIN website which can be downloaded and authenticated using either the digital signature or manual one. For other deductors for the current fiscal this facility is optional viz. they can issue a manual TDS certificate else follow the above procedure. 6. Amendment in Rule 114B relating to furnishing of PAN for certain transactions Notification No. 27/2011 [F. No. 149/122/2010-SO (TPL)], dated The Rule is amended to provide that in addition to transactions prescribed in the Rule, every person shall quote his PAN in the following transactions:- (a) (b) (c) Payment in cash for travel to an authorized person as defined in clause (c) of section 2 of FEMA, Making an application to any banking company or to any other company or institution for issue of a debit card. Payment of an amount aggregating to Rs. 50,000 or more in a year as life insurance premium to an insurer. Payment to a dealer of an amount of Rs. 5 lakh or more at any one time or against a bill for an amount of Rs. 5 lakh or more for purchase of bullion or jewellery. 7. Requirement to file digitally signed tax returns in certain cases Notification No. 37/2011, dated The CBDT has notified that partnership firms filing return in ITR-5 or individuals and HUFs filing returns in ITR-4 and subjected tax audit u/s.44ab would require to digitally sign and submit their income tax returns for A.Y and onwards. 8. CBDT notifies new PAN Form and incorporates new condition Notification No. 56/2011, dated Income Tax department has issued new PAN application Form 49AA for individuals not being citizen of India, LLP registered outside India, Firm formed or registered outside India, Association of Persons (Trusts) formed outside India, Association of Persons (other than Trusts) or body of individuals or local authority or artificial judicial person formed or any other entity (by whatever name called) registered outside India. 81
82 9. Insertion of Rule 40BA and Form No. 29C Notification No. 60/2011 F. No. 133/70/2011-SO (TPL), dated CBDT has made following amendments vide Income Tax (Ninth Amendment) Rules, 2011 with effect from 1 st December, 2011: Rules 40BA inserted to provide for special provisions for payment of tax by Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) LLP shall furnish the report of an accountant as required by section 115JC for the purpose of computation of adjusted total income and minimum alternate tax in Form No. 29C. 10. New procedure of challan correction by banks (for physical challans). Under OLTAS (On Line Tax Accounting System), the physical challans of all Direct Tax payments received from the deductors / taxpayers are digitized on daily basis by the collecting banks and the data transmitted to TIN (Tax Information Network) through link cell. At present, the banks are permitted to correct data relating to three fields only i.e. amount, major head code and name. The other errors can be corrected only by the assessing officers. To remedy this situation, a new Challan Correction Mechanism for physical challans has been put in place. Under this mechanism, for income tax payments made on or after , the following fields can be got corrected through the concerned bank branch within the given time window for correction request by tax payer: S. No. Correction required in field name Period of Correction Request (from Challan Deposit Date) 1 TAN/ PAN 7 days 2 Assessment Year 7 days 3 Amount 7 days 4 Other fields (Major head, Minor head, Nature of payment) Within 3 months 11. Guidelines for Notification of Affordable Housing Project as Specified Business u/s 35AD. The CBDT Vide Notification No. 1/2012 [F. No. 142/24/2011-SO (TPL)] dated gives the Income tax (First Amendment) Rules, It inserts rule 11- OA and Form No. 3CN in Income Tax Rules, The rule 11-OA gives the guidelines for notification of affordable housing project as specified business under section 35AD of the Income tax Act. The Form No. 3CN is prescribed for application for notification for affordable housing project as a specified business u/s 35AD of Income tax Act. (Source: 82
83 12. Direct Tax Instruction No. 01/2012 [F.NO.225/34/2011-ITA.II], dated Instructions for processing returns for AY (reproduced). The issue of processing of returns for the Asst. Year and giving credit for TDS has been considered by the Board. In order to clear backlog of returns, the following decisions have been taken: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) In all returns (ITR-1 to ITR-6), where the difference between the TDS claim and matching TDS amount reported in AS-26 data does not exceed Rs. One lac, the TDS claim may be accepted without verification. Where there is zero TDS matching, TDS credit shall be allowed only after due verification. However, in case of returns of ITR-1 and ITR-2, credit may be allowed in full, even if there is zero matching, if the total TDS claimed is Rs. Five thousand or lower. Where there are TDS claims with invalid TAN, TDS credit for such claims are not to be allowed. In all other cases, TDS credit shall be allowed after due verification. 13. Salaried employees exempted from filing tax returns Notification No. 9/2012, dated Salaried employees having total taxable income of less than Rs. 5 lac have been exempted for filing the tax returns for A..Y , subject to the fulfillment of the following conditions: The only source of income is salary and income from savings bank interest does not exceed Rs. 10,000/-. The PAN of the employee is available with the employer and is mentioned in the Form 16 issued by the employer. The bank interest income is disclosed to the employer, and is included in employee s total income, and tax is duly deducted thereon and paid to the Government. Total tax liability of such person is discharged by way of TDS deducted by the employer which has been duly paid by the employer to the Government. The employee has received a certificate of tax deduction in Form 16 from his employer. The employee has no claim of refund. No specific notice is issued under the Act to the employees for filing a return of income. 83
84 14. Cost Inflation Index for the financial year has been notified as 785 Notification No. 35/2011, dated Part B: Taxation of Cross Border Transactions: 1. Finance Ministry probes overseas deals for tax evasion. The finance ministry has begun its maiden investigation into over 100 offshore financial structuring deals, undertaken by Indian business entities in foreign tax havens to allegedly evade the taxman s net. The multi-pronged probe has been undertaken by the international taxation wing of the Income Tax department and the foreign taxation unit in the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT). A number of investments and deals to the tune of hundreds of crores of rupees have already been executed in tax havens like the Mauritius, Isle of Man, Cyprus, British Virgin Islands and Bermuda, among others. The finance ministry is already working to finalise Tax Information Exchange Agreements (TIEAs) with countries like the UAE, Kuwait, Oman, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Jordan, Syria, China, Indonesia, Israel, Japan, Malaysia, Mangolia, South Korea and Vietnam. Furthermore, Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements (DTAA s) with more than 70 countries are being fine tuned. The Income Tax department is also looking into evasion of Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) by some companies while making payments to purchase overseas shares, but sources declined to name the entities involved. (Source: Business Standard, dated ) 2. Agreement for exchange of Information with respect to Taxes with Commonwealth of Bahamas Notification No. 25/2011 [F. No. 503/6/2009], dated The Tax Information Exchange Agreement (TIEA) with the Bahamas signed on 11 th February, 2011 has been notified to enter into force on 1 st March, All the provisions of this Agreement shall be given effect to, in India on or after 11 th February, Agreement for Exchange of Information with respect to Taxes with Isle of Man Notification No.26/2011 [F.No. 503/01/2009], dated The Tax Information Exchange Agreement (TIEA) with Isle of Man signed on 4 th February, 2011 has been notified to enter into force on 17 th March, All the provisions of this Agreement shall be given effect to, in India on or after 4 th February,
85 4. Double Tax Avoidance Agreement between India and Republic of Mozambique Notification No. 30, dated The Double Tax Avoidance Agreement signed between India and Republic of Mozambique on 30 th September, 2010 has been notified to enter into force on 28 th February, The treaty shall apply from 1 st April, 2012 for India. 5. Press Release Central Board of Direct Taxes No. 402/92/2006-MC (09 of 2011), dated The Double Tax Avoidance Agreement is signed between India and Ethiopia on 25 th May, Press release Central Board of Direct Taxes No. 402/92/2006-MC (10 of 2011), dated The Double Tax Avoidance Agreement is signed between India and Tanzania on 27 th May, Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement between India and Cayman Islands Notification No. 61/2011 [F.No.503/03/2009-FTD.I], dated 27/12/2011 It notifies the Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement entered into between Government of Republic of India and Government of Cayman Islands desiring to facilitate the exchange of information with respect to taxes. The Agreement was signed on 21st day of March, The information will include information that is foreseeable relevant to the determination, assessment and collection of taxes, the recovery and enforcement of tax claims or the investigation or prosecution of tax matters. 8. Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement Protocol between Republic of India and Swiss Confederation Notification No. 62/2011 [F.No.501/01/1973-FTD.I], dated 27/12/2011. It notifies agreement amending the DTAA between Republic of India and Swiss Confederation with respect to taxes on income with protocol signed at New Delhi at 2nd November, 1994 as amended by the supplementary protocol signed at New Delhi on 16th February, The protocol amending the agreement was signed at New Delhi on 3th day of August, The Central Government hereby directs that all the provisions of the said protocol shall be given effect to in the Union of India in respect of income arising in any fiscal year beginning on or after the 1st day of April, 2012 and with respect to the Article 26 of the agreement, the exchange of information provided for in the said protocol will be applicable for information that relates to any fiscal year beginning on or after the 1st day of April,
86 9. Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement between Government of Republic of India and Government of Georgia - Notification No. 4/2012 [F. No. 503/05/2006- FTD.I], dated 06/01/2012. The Central Governments notifies the double taxation avoidance agreement between the government of India and the Government of Georgia for the avoidance of double taxation and the prevention of fiscal evasion with respect to taxes on income and on capital. 10. Section 90A of The Income Tax Act, 1961 DTAA Adoption By Central Government Of Agreement with Taipei - Notification No. 48/2011 F.No. 500/02/2001-FTD-II], dated 02/09/2011 The Central Government has adopted the agreement between India-Taipei Association in Taipei and Taipei Economic and Cultural Center in New Delhi for the avoidance of double taxation and the prevention of fiscal evasion with respect to taxes on income and has notified that all the provisions of the said agreement shall be given effect to in the Union of India with effect from the 1st day of April, Annual Statement to be filed by liaison offices- Notification No. 5/2012, dated The Finance Act, 2011 has directed all liaison offices to submit an annual statement to the Tax Department in the prescribed form and manner. The CBDT has inserted a new rule 114DA vide Income-tax (2 nd Amendment) Rules, 2012 wherein a Form 49C has been prescribed for filing such annual statement within 60 days from the end of the financial year. This Form needs to be verified by a CA or a person authorized by the non-resident to sign such form. It needs to be furnished electronically, digitally signed and the related rules shall be formed by the DGIT (Systems). Part C - Company Law: 1. No Government Approval For Managerial Remuneration For Unlisted Companies With No Profits : The Ministry of Corporate Affairs ( MCA ) has issued Notification No. 70(E) dated in relation to managerial remuneration in unlisted companies having no profits/inadequate profits where previous approval of government is not necessary. 2. Companies Name Availability Rules The MCA has issued the Companies (Name Availability) Rules, 2011 superseding all previous Circulars and Instructions and has laid down the principles for deciding cases for availability of names. The rules also give an illustrative list of names considered to be undesirable within the meaning of section 20 of the Companies Act, 1956 has also been given in an Appendix. The details of minimum authorized capital requirement has also been furnished. 86
87 3. Director s Relatives (Office Or Place Of Profit) Amendment Rules, 2011: Rule 3 of the Director s Relative (Office or Place of Profit) Rules, 2003, the current limit of Rs.50,000 per month has been raised to Rs. 2,50,000/- per month for payment remuneration to relatives or partners of the directors of the company covered by section 314(1B) of the Companies Act, Year of Applicability For Disclosure Of Particulars Of Employees Salary In Board Report It is clarified that the said notification shall be applicable to all Director s Reports under section 217 of the Companies Act, 1956 approved by the Board of Directors on or after , irrespective of the accounting year of the annual account, being approved by the Board. 5. Sending Of Balance Sheet, Etc. By Electronic Mode The MCA has issued General Circular No. 18/2011 dtd under the green initiative in the corporate governance to clarify regarding sending copies of balance sheets and auditor s report, etc., to the members of the company as required under section 219 of the Companies Act, 1956 through electronic mode by allowing paperless compliances by companies. 6. The Companies (Cost Audit Report) Rules, 2011 Under section 233B(1) of the Act. The rules specify the manner and mode of appointment of a cost auditor, form of cost audit report, timeline for submission of the cost audit report, rights of cost auditor in relation to the production of the accounting records, penalty for contravention of the rules, etc. 7. Master Circular On Cost Accounting Records And Cost Audit The MCA has issued Master Circular No. 22/2011 dated giving consolidatedly all the circulars issued by the MCA from time-to-time with regard to various matters concerning cost accounting records and cost audit in the corporate sector. After reviewing all these circulars, and in supersession of all the earlier 15 circulars as listed in the Appendix to the above master circular, this Master Circular is issued. 8. Amendment To Schedule XIV Rates Of Depreciation The MCA has issued Notification No. F:2/6/2008/CL-V dtd amending Schedule XIV under the heading II PLANT AND MACHINERY, under item (ii) relating to special rates, in sub-item B.7, and replacing with the following entries: Names of assets Single Shift W.D.V. S.L.M. (1) (2) (3) 7. Mineral oil Concerns Field operations (above ground) Portable boilers, drilling tools, well-head tanks, etc. (NESD) 30 percent percent 7A. Rigs (NESD) 10 percent 3.34 percent 87
88 9. Amendment TO COMPANIES (ACCOUNTING STANDARDS) RULES, 2006 The Companies (Accounting Standards) Rules, 2006 in relation to Accounting Standard (AS) 11 "The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates" has been amended in Notification No.17/133/2008-CL.V dtd General Instruction For Preparation Of Statement of Accounts in Revised Schedule VI MCA vide Notification No 538, dated 30 th March, 2011, clarified that The revised schedule VI shall come into force for the Balance Sheet and Statement of Profit and Loss to be prepared for the financial year commencing on or after Hence all corporate are now required to prepare Balance Sheet and Statement of Profit and Loss in revised schedule VI format for the financial year Participation By Directors In Meetings Of Board / Committee Of Directors Through Electronic Mode: The Ministry of Corporate Affairs has vide General Circular No. 28/2011, dated 20 th May, 2011 has clarified that directors of a company may participate in a meeting/committee of directors through electronic mode i.e., video conference facility so long as other terms and conditions mentioned in the Circular are fulfilled. 12. Prosecution of Directors. The ministry of corporate affairs has issued a general Circular No. 2/13/2003/CL V regarding the prosecution of independent directors of listed companies, nominee directors of the central govt. or of the public financial institutions. The circular states that the Registrar of companies should take extra care in examining the cases where above directors are identified as officer in default. Such directors should not be held liable for any act of omission or commission by the company or by any officers of the company which constitute a breach or violation of any provision of the Companies Act, 1956, and which occurred without their knowledge and without their consent or connivance or where they have acted diligently in the board process. The board process includes meeting of any committee of the board and any information which the director was authorized to receive as a director of the Board as per the decision of the board. The Circular also specifies compliance to be verified by the Registrar of Companies before taking penal action against directors. Also the list of person who can be treated as officers in default has been listed for prosecutions u/s 209(v), 209(vi), 211 and 212 is given. 13. XBRL Filing Of Balance Sheet And Profit And Loss Account The Ministry of corporate Affairs by Circular No. 9/2011 dated 31 st March, 2011 has mandated certain companies to file their balance sheets and profit and loss account for 88
89 the year and onwards using XBRL taxonomy in the phase 1 following companies are covered : i) All companies listed in India and their subsidiaries, including overseas subsidiaries. ii) All companies having a paid up capital of Rs 5 crore and above or a turnover of Rs 100 crore and above. The financial statements required to be filed in XBRL format will be based on the taxonomy on XBRL developed for the existing Schedule VI and non- Converged accounting standards notified under the companies (Accounting standards) Rules, NBFCs not to be Partners In Partnership Firms RBI has noticed that some NBFCs have made large investments in capital to partnership, Firms.In view of the Risks involved in NBFCs associating themselves with partnership firms RBI has now decided to prohibit all NBFCs from contributing capital to any partnership firm or to be a partner in partnership firms. In cases of existing partnerships, NBFCs may seek early retirement. 15. Company s Bill 2011 is introduced in Parliament on 14 th December, 2011 Part D Other Bullet Points: 1. Public Provident Fund (Amendment) Scheme Notification G.S.R. 844(E) and Notification S.O. 2681(E) F.No. 1/9/2011-NS-II, dated 25/11/2011 The Central Government has w.e.f. 1st December, 2011 increased the annual PPF subscription amount from Rs.70,000/- to Rs. 1,00,000/-. Further, the subscriptions made to the fund on or after the 1st day of December, 2011 and balances at the credit of the subscriber shall bear interest at the rate of 8.6 percent, per annum. 2. Kisan Vikas Patras - Discontinuance of sale with effect from Notification F.No. 1/10/2011-NS-II, dated The CBDT notified for general information that the sale of Kisan Vikas Patras shall be discontinued with effect from the close of business on Wednesday, the 30th November, Post Office Savings Account Rules - interest with effect from Notification S.o. 2682(E) F.No. 1/10/2011-NS-II, dated In pursuance of rule 6 of the Post Office Savings Account Rules, 1981, the Central Government notified with effect from the 1st day of December, 2011, interest on the balance at credit of an account shall be allowed at the rate of four per cent, per annum. 89
90 4. Correction of mistakes made by the dealers - Miscellaneous refunds of excess payment of taxes - Trade Circular 17T of 2011, dated 25/11/2011 (MVAT). This Circular lays down the procedure for correction of mistakes made while making e-payment of taxes by dealers due to mention of wrong TIN or wrong Act or wrong period. It also lays down procedure for miscellaneous refunds due to double payment of taxes or excess payment of taxes. 5. Mandatory e-returns for employers registered under Profession Tax Act, 1975 Trade Circular IT of 2011 under Profession Tax, dated By this Circular, e-service of filing e-returns for registered employers (PTRC holders) has been introduced. By Notification issued on it was provided that from , every PTRC holder whose tax liability during the previous year was rupees twenty thousand or more shall mandatorily file electronic return. PTRC holders, eligible to file quarterly or annual returns, may get themselves enrolled and file e-returns voluntarily. Detailed procedures for enrolment for PTRC e-services and procedure for uploading PTRC e-returns are explained in the Circular. 6. Charitable Trusts under I.T. scanner. The Income-tax (I.T.) Department has launched a comprehensive exercise for tightening the administrative mechanism for charitable institutions. Scrutiny of cases where misuse of tax exemption has been noticed and modifications in reporting procedures to capture their activities, funding patterns and income are among measures taken for streamlining procedures. The Directorate of Exemption has already identified a substantial number of cases, which are being selected for scrutiny. A new income tax return form for public charitable trusts is also being prepared by the Directorate to facilitate comprehensive reporting of their income and expenditure. It would facilitate e-filing and help in selecting cases for investigation and would also provide details of foreign, anonymous and corpus donations, donation in kind and FCRA approvals. (Sources: Business Standard, dated ) 7. Majority wins: Bombay High Court paves way for redevelopment. Dissenting members who deliberately skipped housing society meetings have no right to object to a resolution favouring redevelopment passed by majority of the members, observed a cooperative Court recently. The Court upheld a resolution passed by majority of the members to redevelop a four-storey building in Khar (W). 90
91 The ruling is significant as it seals the fate of the dissenting few and holds that the resolution, if passed at a meeting held legally, will be binding on all members of a cooperative housing society. (Source: The Times of India, dated 28/01/2012) 8. Wrong move The point is to go after the tax evader, not squeeze taxpayers further. The Finance Ministry s move to subject high net worth taxpayers (HNIs) to intense year- round scrutiny is not correct. It should stop harassing those who duly file their income tax returns. The Government should drop the proposal to create a dedicated cell to monitor those who report earnings over Rs.1 crore per annum, spending more than Rs.10 crore a year or having assets in excess of Rs.100 crore. Instead of squeezing more from those who already file returns and pay taxes, the Department should go after those who remain outside the tax net. This is eminently feasible with rigorous analysis of annual information returns (AIR) that identify potential taxpayers by examining expenditure patterns. Today, the Department is behind the curve in mining information gathered through the tax information network (TIN). Audit trails break-up as the Permanent Account Number (PAN) is found missing in several large financial transactions gathered through TIN. This is untenable. Every transaction should be tagged by a PAN and the unique identifier should be made mandatory for all those who make high-value purchases. A fool-proof Pan and robust TIN, not a dedicated cell for HNIs, will enable the Department to identify tax evaders. Selective focus on HNIs is a bad idea that would only duplicate work for the Department that already has a system in place to scrutinize income tax returns, selecting cases through the computer-assisted scrutiny system (CASS) that also captures information provided by banks, credit card companies, mutual funds through the AIR. A 360-degree profile of every taxpayer can be easily created with creative and intelligent use of information technology. Last year, around 10,600 tax-filers reported annual incomes over Rs.1 crore. The number dropped to 1,257 for those with a yearly income of over Rs.5 crore. Hardly surprising, given that less than 3% of people file tax returns in India. The base of income tax should be widened to raise the level of tax collection to GDP. The best way to do that is to expand the coverage of AIR. Also, moderate income tax rates, simple and transparent tax laws will improve compliance and stop generation of black money. (Source: The Economic Times, dated ) 9. Curbing the lust for litigation The Supreme Court has abruptly replaced an internal mechanism to weed out wasteful government appeals with a think tank. In more than one-third of the litigations in India s courts, the government is a party. In criminal cases, it cannot be avoided. According to one estimate, the government is involved in 10 million cases. No wonder, the union Law minister and attorney general have described the government as a compulsive litigant. 91
92 Some Supreme Court judges also echoed this sentiment, in stronger terms. They criticized the government for resorting to prolonged litigation on `trivial issues, and pointed out that not only did this waste the judiciary s time but also caused the public exchequer a colossal loss. 10. I- T to make staff s work less taxing In a bid to reduce the burden on officials, the income- tax department is planning to outsource record management to private entities. The number of income tax payers in the country is about 35 million. It is expected to reach around 80 million by Considering that a substantial number of taxpayers file returns manually, managing records has become a major task for the department. The Department says it requires about 12,000 officials just for scrutiny cases. At present, around 4,000 officials are handling 7,00,000 scrutiny cases a year. (Source: Business standard, dated ) 92
93 FOOD FOR THOUGHT Why food is costlier! Twenty years ago, a Maruti 800, with an air-conditioner fitted, cost a little less than Rs. 2 lakh. Today it costs about Rs. 2.5 lakh. Twenty years ago, a branded 1.5 tonne window air-conditioner cost about Rs.30,000; today, you can get a split AC unit for that price. Then, Videocon was offering large refrigerators for more than Rs.30,000; you can get better units today for much less. TV prices have crashed too, and one can go on with this list. In a period when salaries in the corporate sector have gone up by about 15% annually, and inflation-adjusted per capita income has roughly trebled, consumer durables of virtually every hue have become infinitely more affordable. Why has that not happened with onions? In 1980, Indira Gandhi swept back to power on the back of an election campaign that talked of onions costing the then stratospheric sum of Rs.5 per kg. Now it is Rs.70. Home-grown apples (not the ones from Down Under) cost over Rs.100 in Delhi, and lentils of various sorts have also hit triple-digits. These price increases far outdo income increases, rapid though they have been for most people, and it is simply not enough to seek palliatives in short-term measures like raising interest rates. Nor is it enough to say that there has been demand growth for proteins because of higher incomes. There has been comparable demand growth for eggs, but they have not seen similar price inflation. Nor is it good enough to argue that there are global shortages in commodities both cyclical (as in sugar) and structural (lentils). The truth is that we face inflation in agricultural products, on a scale that we don t see in manufactured products, because agriculture has not been reformed, whereas industry has. There is talk of collusion in onion prices which raises the question of reforming trade. Everyone knows that the difference between farm gate and retail prices is unusually high in India, in part because of multiple intermediaries. But the country has not been able to benefit from supply chain efficiencies because organised retail has not been allowed to grow, and to link producer and consumer prices more closely by squeezing out middlemen. Politicians who for two decades have opposed reforms in both agriculture and trade will be loath to own up responsibility for today s food price inflation; they should know that the situation will get worse if reforms are not introduced even at this late stage. The prime minister should do for agriculture and domestic trade what he did for industry and export trade 20 years ago. (Source: Business Standard) 93
94
95 Anay : What is the aadhar of this years tax proposals Kush : Non-Discrimination Chikita : How? Why do you say so Vishi : The special rate of tax for female tax payers is done away with and now the male tax payers are promoted to be at par with them. Datar : All services are made liable to service tax Enjoy while you re here. This is one of the few places where you receive service without attracting service tax! Khushboo : Transfer Pricing Regulations (earlier applicable to international transactions only) are made applicable to domestic transactions as well Sonu : Non Residents are also made liable to pay tax on direct and indirect transfer of shares of Indian Companies Varsha : Ok Ok where is the discrimination still exist Tims : A tax payer is accountable for everything, any bonafide or even intentional mistake made results into heavy demand being slapped with interest and penalty, prosecution proceedings, harassment for recovery etc. etc. But a Taxman is Not Accountable for anything. All : If we want proper and fair tax administration then Taxman should be made Accountable for their actions.
T. P. Ostwal & Associates (Regd.) Key Budget Proposal Budget 2012 CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS
 IMPORTANT AMENDMENTS & MAJOR DIRECT TAX PROPOSALS IN FINANCE BILL, 2012 CORPORATE TAX No change in the head corporate tax. Extension of sunset date for tax holiday for power sector to 2013; Initial depreciation
IMPORTANT AMENDMENTS & MAJOR DIRECT TAX PROPOSALS IN FINANCE BILL, 2012 CORPORATE TAX No change in the head corporate tax. Extension of sunset date for tax holiday for power sector to 2013; Initial depreciation
Budget Upto Rs. 5,00,000. Rs. 2,00,001 to Rs. 5,00, per cent. Rs. 5,00,001 to Rs. 10,00, per cent.
 Budget 2012-13 Explanatory Memorandum & Finance Bill Ahmedabad, Bangalore, Bhubaneswar, Chandigarh, Chennai, Hyderabad, Kochi, Kolkata, Lucknow, Mumbai, New Delhi and Pune WALKING THE TIGHTROPE "For the
Budget 2012-13 Explanatory Memorandum & Finance Bill Ahmedabad, Bangalore, Bhubaneswar, Chandigarh, Chennai, Hyderabad, Kochi, Kolkata, Lucknow, Mumbai, New Delhi and Pune WALKING THE TIGHTROPE "For the
ADVANCED TAX LAWS AND PRACTICE UPDATES APPLICABLE FOR JUNE 2013 EXAMINATION FOR PROFESSIONAL PROGRAMME
 ADVANCED TAX LAWS AND PRACTICE UPDATES APPLICABLE FOR JUNE 2013 EXAMINATION FOR PROFESSIONAL PROGRAMME Disclaimer- This document has been prepared purely for academic purposes only and it does not necessarily
ADVANCED TAX LAWS AND PRACTICE UPDATES APPLICABLE FOR JUNE 2013 EXAMINATION FOR PROFESSIONAL PROGRAMME Disclaimer- This document has been prepared purely for academic purposes only and it does not necessarily
DIRECT TAX PROPOSALS OF UNION BUDGET 2012
 DIRECT TAX PROPOSALS OF UNION BUDGET 2012 WWW.ITRVAULT.IN ITR VAULT is your one stop solution to store, save, extract, send and print all your important documents. Searching for the required documents
DIRECT TAX PROPOSALS OF UNION BUDGET 2012 WWW.ITRVAULT.IN ITR VAULT is your one stop solution to store, save, extract, send and print all your important documents. Searching for the required documents
A BILL to give effect to the financial proposals of the Central Government for the financial year
 FINANCE BILL, 2012* Bill No. 11 of 2012 A BILL to give effect to the financial proposals of the Central Government for the financial year 2012-2013. BE it enacted by Parliament in the Sixty-third Year
FINANCE BILL, 2012* Bill No. 11 of 2012 A BILL to give effect to the financial proposals of the Central Government for the financial year 2012-2013. BE it enacted by Parliament in the Sixty-third Year
Supplementary Memorandum Explaining the Official Amendments Moved in the Finance Bill, 2012 AS REFLECTED IN THE FINANCE ACT, 2012.
 INCOME TAX CIRCULAR No. 3/2012, Dated 12 th June, 2012. Supplementary Memorandum Explaining the Official Amendments Moved in the Finance Bill, 2012 AS REFLECTED IN THE FINANCE ACT, 2012. FINANCE ACT, 2012
INCOME TAX CIRCULAR No. 3/2012, Dated 12 th June, 2012. Supplementary Memorandum Explaining the Official Amendments Moved in the Finance Bill, 2012 AS REFLECTED IN THE FINANCE ACT, 2012. FINANCE ACT, 2012
Supplementary Memorandum Explaining the Official Amendments Moved in the Finance Bill, 2012 As Reflected In The Finance Act, 2012
 Supplementary Memorandum Explaining the Official Amendments Moved in the Finance Bill, 2012 As Reflected In The Finance Act, 2012 Circular no. 3/2012, dated 12-6-2012 FINANCE ACT, 2012 - PROVISIONS RELATING
Supplementary Memorandum Explaining the Official Amendments Moved in the Finance Bill, 2012 As Reflected In The Finance Act, 2012 Circular no. 3/2012, dated 12-6-2012 FINANCE ACT, 2012 - PROVISIONS RELATING
BUDGET AT GLANCE (` In Crore )
 Sr. No. Particulars BUDGET AT GLANCE (` In Crore ) 2010 11 2011 12 2011 12 2012 13 Actuals @ Budget Estimates Revised Estimates Budget Estimates 1 Revenue Receipts [2+3] 788471 789892 766989 935685 2 Tax
Sr. No. Particulars BUDGET AT GLANCE (` In Crore ) 2010 11 2011 12 2011 12 2012 13 Actuals @ Budget Estimates Revised Estimates Budget Estimates 1 Revenue Receipts [2+3] 788471 789892 766989 935685 2 Tax
FINANCE BILL 2017-DIRECT TAX PROPOSALS AT GLANCE
 FINANCE BILL 2017-DIRECT TAX PROPOSALS AT GLANCE COMPILED BY: CA.ARUN GUPTA ca.arungupta77@gmail.com A. Rates of Taxes: 1. It is proposed to make the following changes in tax rates: In case of Resident
FINANCE BILL 2017-DIRECT TAX PROPOSALS AT GLANCE COMPILED BY: CA.ARUN GUPTA ca.arungupta77@gmail.com A. Rates of Taxes: 1. It is proposed to make the following changes in tax rates: In case of Resident
thousand rupees of the total income but without being liable to tax], only for the purpose of charging income-tax in respect of the total income; and
![thousand rupees of the total income but without being liable to tax], only for the purpose of charging income-tax in respect of the total income; and thousand rupees of the total income but without being liable to tax], only for the purpose of charging income-tax in respect of the total income; and](/thumbs/74/69854896.jpg) ACT FINANCE ACT *Finance Act, 2011 [8 OF 2011] An Act to give effect to the financial proposals of the Central Government for the financial year 2011-2012. BE it enacted by Parliament in the Sixty-second
ACT FINANCE ACT *Finance Act, 2011 [8 OF 2011] An Act to give effect to the financial proposals of the Central Government for the financial year 2011-2012. BE it enacted by Parliament in the Sixty-second
Salient features of Direct Tax Proposals of Union Budget 2011
 Salient features of Direct Tax Proposals of Union Budget 2011 RATES OF INCOME-TAX FOR THE ASSESSMENT YEAR 2012-13 o Tax slab rates have been changed for individuals and HUF, which is given by way of a
Salient features of Direct Tax Proposals of Union Budget 2011 RATES OF INCOME-TAX FOR THE ASSESSMENT YEAR 2012-13 o Tax slab rates have been changed for individuals and HUF, which is given by way of a
MINISTRY OF LAW AND JUSTICE (Legislative Department)
 MINISTRY OF LAW AND JUSTICE (Legislative Department) New Delhi, the 28th May, 2012/Jyaistha 7, 1934 (Saka) The following Act of Parliament received the assent of the President on the 28th May, 2012 and
MINISTRY OF LAW AND JUSTICE (Legislative Department) New Delhi, the 28th May, 2012/Jyaistha 7, 1934 (Saka) The following Act of Parliament received the assent of the President on the 28th May, 2012 and
EXPLANATORY NOTES TO THE PROVISIONS OF THE FINANCE ACT, 2013
 CIRCULAR NO.03/2014 F. No. 142/24/2013-TPL Government of India Ministry of Finance Department of Revenue (Central Board of Direct Taxes) ******* Dated, the 24 th January, 2013 EXPLANATORY NOTES TO THE
CIRCULAR NO.03/2014 F. No. 142/24/2013-TPL Government of India Ministry of Finance Department of Revenue (Central Board of Direct Taxes) ******* Dated, the 24 th January, 2013 EXPLANATORY NOTES TO THE
SALIENT FEATURES OF THE FINANCE BILL, [Relating to Direct Taxes]
![SALIENT FEATURES OF THE FINANCE BILL, [Relating to Direct Taxes] SALIENT FEATURES OF THE FINANCE BILL, [Relating to Direct Taxes]](/thumbs/77/76609678.jpg) SALIENT FEATURES OF THE FINANCE BILL, 2013 1 [Relating to Direct Taxes] Published in 351 ITR (Journ.) p.61 (Part-5) - By S.K. Tyagi The Finance Bill, 2013, or the Union Budget, 2013-14, was presented in
SALIENT FEATURES OF THE FINANCE BILL, 2013 1 [Relating to Direct Taxes] Published in 351 ITR (Journ.) p.61 (Part-5) - By S.K. Tyagi The Finance Bill, 2013, or the Union Budget, 2013-14, was presented in
THE FINANCE BILL, 2011
 Bill No. 8-F of 2011 THE FINANCE BILL, 2011 (AS PASSED BY THE HOUSES OF PARLIAMENT LOK SABHA ON 22ND MARCH, 2011 RAJYA SABHA ON 24TH MARCH, 2011) ASSENTED TO ON 8TH APRIL, 2011 ACT NO. 8 OF 2011 Bill No.
Bill No. 8-F of 2011 THE FINANCE BILL, 2011 (AS PASSED BY THE HOUSES OF PARLIAMENT LOK SABHA ON 22ND MARCH, 2011 RAJYA SABHA ON 24TH MARCH, 2011) ASSENTED TO ON 8TH APRIL, 2011 ACT NO. 8 OF 2011 Bill No.
budget tax law `012 growth income rates rupee abroad banks agriculture The Finance Bill world economy incometax import help policy review government
 large scale industry small scale family saving state infrastructurewages employment value added tax economy country benefit debt taxation growth system give Housing budget consumer food help rebate tax
large scale industry small scale family saving state infrastructurewages employment value added tax economy country benefit debt taxation growth system give Housing budget consumer food help rebate tax
FINANCE ACT, EXPLANATORY NOTES TO THE PROVISIONS OF THE FINANCE ACT, Explanatory notes to the provisions of the Finance Act, 2011
 FINANCE ACT, 2011 - EXPLANATORY NOTES TO THE PROVISIONS OF THE FINANCE ACT, 2011 CIRCULAR NO. 02/2012 [F. NO.142/01/2012-SO(TPL)], DATED 22-5-2012 Explanatory notes to the provisions of the Finance Act,
FINANCE ACT, 2011 - EXPLANATORY NOTES TO THE PROVISIONS OF THE FINANCE ACT, 2011 CIRCULAR NO. 02/2012 [F. NO.142/01/2012-SO(TPL)], DATED 22-5-2012 Explanatory notes to the provisions of the Finance Act,
Union Budget 2014 Analysis of Major Direct tax proposals
 RATES OF INCOME TAX Union Budget 2014 Analysis of Major Direct tax proposals Basic exemption limit has been increased from Rs 2 lacs to Rs 2.50 lacs for resident individuals or HUF. Income slabs Income
RATES OF INCOME TAX Union Budget 2014 Analysis of Major Direct tax proposals Basic exemption limit has been increased from Rs 2 lacs to Rs 2.50 lacs for resident individuals or HUF. Income slabs Income
Total turnover/ Gross receipts 30% 30% of FY > Rs 50 Cr No change in rate of Surcharge
 1. Income Tax Rates: Category of Income New rate of tax Old rate Taxpayer for FY 2017-18 of tax Individuals/ Upto Rs 2.5 L Nil Nil HUF/ BOI/ Rs 2.5 to 5 L 5% 10% AOP/ Rs 5 to 10 L 20% 20% Artificial Above
1. Income Tax Rates: Category of Income New rate of tax Old rate Taxpayer for FY 2017-18 of tax Individuals/ Upto Rs 2.5 L Nil Nil HUF/ BOI/ Rs 2.5 to 5 L 5% 10% AOP/ Rs 5 to 10 L 20% 20% Artificial Above
FB.COM/SUPERWHIZZ4U Income Tax Amendment for the Assessment
 FB.COM/SUPERWHIZZ4U Income Tax Amendment for the Assessment Year 2014-15 - SIPOY SATISH Highlights of Change in Direct Taxes in the Union Budget 2013 1. Rate of Income Tax for Individual a) Slab Rate Assessment
FB.COM/SUPERWHIZZ4U Income Tax Amendment for the Assessment Year 2014-15 - SIPOY SATISH Highlights of Change in Direct Taxes in the Union Budget 2013 1. Rate of Income Tax for Individual a) Slab Rate Assessment
THE FINANCE BILL, 2015
 BILL No. 26 OF THE FINANCE BILL, (AS INTRODUCED IN LOK SABHA) THE FINANCE BILL, ARRANGEMENT OF CLAUSES CHAPTER I PRELIMINARY CLAUSES 1. Short title and commencement. CHAPTER II RATES OF INCOME-TAX 2. Income-tax.
BILL No. 26 OF THE FINANCE BILL, (AS INTRODUCED IN LOK SABHA) THE FINANCE BILL, ARRANGEMENT OF CLAUSES CHAPTER I PRELIMINARY CLAUSES 1. Short title and commencement. CHAPTER II RATES OF INCOME-TAX 2. Income-tax.
FINANCE (NO.2) ACT, 2014 EXPLANATORY NOTES TO THE PROVISIONS OF SAID ACT AMENDMENTS AT A GLANCE
 FINANCE (NO.2) ACT, 2014 EXPLANATORY NOTES TO THE PROVISIONS OF SAID ACT Section/Schedule CIRCULAR NO.1/2015 [F.NO.142/13/2014 TPL], DATED 21 1 2015 AMENDMENTS AT A GLANCE Finance (No.2) Act, 2014 First
FINANCE (NO.2) ACT, 2014 EXPLANATORY NOTES TO THE PROVISIONS OF SAID ACT Section/Schedule CIRCULAR NO.1/2015 [F.NO.142/13/2014 TPL], DATED 21 1 2015 AMENDMENTS AT A GLANCE Finance (No.2) Act, 2014 First
EXPLANATORY NOTES TO THE PROVISIONS OF THE FINANCE(No.2) ACT, 2014
 CIRCULAR NO. 01/2015 F. No. 142/13/2014-TPL Government of India Ministry of Finance Department of Revenue (Central Board of Direct Taxes) ******* Dated, the 21st January, 2015 EXPLANATORY NOTES TO THE
CIRCULAR NO. 01/2015 F. No. 142/13/2014-TPL Government of India Ministry of Finance Department of Revenue (Central Board of Direct Taxes) ******* Dated, the 21st January, 2015 EXPLANATORY NOTES TO THE
DEDUCTION OF TAX AT SOURCE
 DEDUCTION OF TAX AT SOURCE SECTION 190 TO 206AA Section 190 Deduction at source and advance payment Section 191 Direct payment Section 192 Deduction of tax from salary income Section 193 Deduction of tax
DEDUCTION OF TAX AT SOURCE SECTION 190 TO 206AA Section 190 Deduction at source and advance payment Section 191 Direct payment Section 192 Deduction of tax from salary income Section 193 Deduction of tax
Web:
 PRESENTED ON 1st FEB 2017 HIGHLIGHTS 1 A Rates of Income-tax Rates of income-tax in respect of income liable to tax for the assessment year 2017-18. Rates for deduction of income-tax at source during the
PRESENTED ON 1st FEB 2017 HIGHLIGHTS 1 A Rates of Income-tax Rates of income-tax in respect of income liable to tax for the assessment year 2017-18. Rates for deduction of income-tax at source during the
Income Tax Budget Analysis
 --- 2014 --- Income Tax Budget Analysis (For Private Circulation Only) Surana Maloo & Co. Chartered Accountants 2 nd Floor, Aakash Ganga Complex, Parimal Under Bridge, Nr Suvidha Shopping Center, Paldi,
--- 2014 --- Income Tax Budget Analysis (For Private Circulation Only) Surana Maloo & Co. Chartered Accountants 2 nd Floor, Aakash Ganga Complex, Parimal Under Bridge, Nr Suvidha Shopping Center, Paldi,
INCOME TAX. BUDGET ANALYSIS All right Reserved with Bizsolindia Services Pvt. Ltd.
 INCOME TAX 2 (22) 1 st April 2018 2 (24) & 28, 49 1 st April 2019 2 (24) & 56 1 st April 2019 Definition of Dividend for the purpose of taxation on distribution Definition of Income and Income from Business
INCOME TAX 2 (22) 1 st April 2018 2 (24) & 28, 49 1 st April 2019 2 (24) & 56 1 st April 2019 Definition of Dividend for the purpose of taxation on distribution Definition of Income and Income from Business
Major direct tax proposals in Finance Bill, 2017
 Major direct tax proposals in Finance Bill, 2017 Member firm Individual, HUF, BOI, AOP, AJP Tax Rates There is no change in the basic exemption limit for individuals/hufs. It is proposed to reduce the
Major direct tax proposals in Finance Bill, 2017 Member firm Individual, HUF, BOI, AOP, AJP Tax Rates There is no change in the basic exemption limit for individuals/hufs. It is proposed to reduce the
Executive Summary of Finance Bill, 2014 Direct Taxes
 * The applicable date being denotes the amendment is applicable w.e.f. A.Y. 2015-16 CLAUSE NO. OF FINANCE BILL SECTION NEW LAW APPLICABLE w.e.f.* BRIEF OF AMENDMENT 2 Tax Slabs Changes for Individual,
* The applicable date being denotes the amendment is applicable w.e.f. A.Y. 2015-16 CLAUSE NO. OF FINANCE BILL SECTION NEW LAW APPLICABLE w.e.f.* BRIEF OF AMENDMENT 2 Tax Slabs Changes for Individual,
JAYESH SANGHRAJKA & CO. LLP CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS
 Income Tax Rates Applicable for Financial Year 2018-19 Status of Person Rate of Income Tax 1.Individual/HUF a. Income: Upto Rs. 2,50,000 Nil b. Income: Rs. 2,50,001 to Rs. 5,00,000 5% c. Income: Rs. 5,00,001
Income Tax Rates Applicable for Financial Year 2018-19 Status of Person Rate of Income Tax 1.Individual/HUF a. Income: Upto Rs. 2,50,000 Nil b. Income: Rs. 2,50,001 to Rs. 5,00,000 5% c. Income: Rs. 5,00,001
25 Penalties Introduction Penalties
 25 Penalties 25.1 Introduction The Income-tax Act, 1961 provides for the imposition of a penalty on an assessee who wilfully commits any offence under the provisions of the Act. Penalty is levied over
25 Penalties 25.1 Introduction The Income-tax Act, 1961 provides for the imposition of a penalty on an assessee who wilfully commits any offence under the provisions of the Act. Penalty is levied over
TAX RECKONER
 TAX RECKONER 2018-19 The rates are applicable for the Financial Year 2018-19 (AY 2019-20) and subject to enactment of the Finance Bill, 2018 Note: The tax rate card will be re-visited post enactment of
TAX RECKONER 2018-19 The rates are applicable for the Financial Year 2018-19 (AY 2019-20) and subject to enactment of the Finance Bill, 2018 Note: The tax rate card will be re-visited post enactment of
ALL GUJARAT FEDERATION OF TAX CONSULTANTS
 ALL GUJARAT FEDERATION OF TAX CONSULTANTS PRE-BUDGET MEMORANDUM FOR 2015-16 1. Section 2(22)(e) : Deemed Dividend As per the present provision, even if advance or loan is given to a share holder for one
ALL GUJARAT FEDERATION OF TAX CONSULTANTS PRE-BUDGET MEMORANDUM FOR 2015-16 1. Section 2(22)(e) : Deemed Dividend As per the present provision, even if advance or loan is given to a share holder for one
The Union Budget -An Analysis Analysis of important Amendments proposed in the Finance Bill, 2012 DIRECT TAXES
 Disclaimer :- Utmost care has been taken to compile this circular, however the firm shall not be responsible for any error or omission that may have cropped up during its compilation. The views expressed
Disclaimer :- Utmost care has been taken to compile this circular, however the firm shall not be responsible for any error or omission that may have cropped up during its compilation. The views expressed
Notes on clauses.
 52 Notes on clauses Clause 2, read with the First Schedule to the Bill, seeks to specify the rates at which income-tax is to be levied on income chargeable to tax for the assessment year 2009-2010 Further,
52 Notes on clauses Clause 2, read with the First Schedule to the Bill, seeks to specify the rates at which income-tax is to be levied on income chargeable to tax for the assessment year 2009-2010 Further,
Circular The Schedule of dates for filing income-tax returns is given below:
 Circular-2012 To, July 14, 2012 Dear Sir(s)/Madam, Sub: Income-tax, Wealth-tax, Service-tax and TDS returns for Assessment Year 2012-13 and payment of advance-tax for Assessment Year 2013-14 -------------------------------------------------------
Circular-2012 To, July 14, 2012 Dear Sir(s)/Madam, Sub: Income-tax, Wealth-tax, Service-tax and TDS returns for Assessment Year 2012-13 and payment of advance-tax for Assessment Year 2013-14 -------------------------------------------------------
S. S. Jhunjhunwala & Co. Chartered Accountants
 .. S. S. Jhunjhunwala & Co. Chartered Accountants 306, Akruti Arcade, J.P. Road, Opp. Wadia High School, Andheri (West), Mumbai-400 053. Ph: 2674 3351/2674 3352 Fax : 2673 4498 Email : ssjco@bom5.vsnl.net.in
.. S. S. Jhunjhunwala & Co. Chartered Accountants 306, Akruti Arcade, J.P. Road, Opp. Wadia High School, Andheri (West), Mumbai-400 053. Ph: 2674 3351/2674 3352 Fax : 2673 4498 Email : ssjco@bom5.vsnl.net.in
DIRECT TAXES AND INDIRECT TAXES UPDATES APPLICABLE FOR DECEMBER 2012 EXAMINATION FOR EXECUTIVE & PROFESSIONAL PROGRAMME
 DIRECT TAXES AND INDIRECT TAXES UPDATES APPLICABLE FOR DECEMBER 2012 EXAMINATION FOR EXECUTIVE & PROFESSIONAL PROGRAMME *Disclaimer- This document has been prepared purely for academics purposes only and
DIRECT TAXES AND INDIRECT TAXES UPDATES APPLICABLE FOR DECEMBER 2012 EXAMINATION FOR EXECUTIVE & PROFESSIONAL PROGRAMME *Disclaimer- This document has been prepared purely for academics purposes only and
INCOME-TAX AND BASED ON FINANCE ACT, FINANCE ACT, 2007 WITH NOTES 49 I.T. NOTES 69 I.T. NOTES 97 I.T. NOTES I.T. NOTES 139 I.T.
 EHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR VG.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA
EHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR VG.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA
Budget Presented For: Klaus Vogel Group Presented By: Mr. Kuntal Dave Date: March 8, 2013
 Budget 2013 Presented For: Klaus Vogel Group Presented By: Mr. Kuntal Dave Date: March 8, 2013 Index Direct Tax Proposals Implications of amendments proposed in the Finance Bill, 2013 2 Direct Tax Proposals
Budget 2013 Presented For: Klaus Vogel Group Presented By: Mr. Kuntal Dave Date: March 8, 2013 Index Direct Tax Proposals Implications of amendments proposed in the Finance Bill, 2013 2 Direct Tax Proposals
Finance Bill, 2015 Direct Tax Highlights
 Finance Bill, 2015 Direct Tax Highlights Bansi S. Mehta & Co. All the following amendment are made effective from Assessment Years 2016-17, unless specifically mentioned otherwise. I - Residential Status,
Finance Bill, 2015 Direct Tax Highlights Bansi S. Mehta & Co. All the following amendment are made effective from Assessment Years 2016-17, unless specifically mentioned otherwise. I - Residential Status,
VOLUNTARY DISCLOSURE SCHEME [CA P N SHAH]
![VOLUNTARY DISCLOSURE SCHEME [CA P N SHAH] VOLUNTARY DISCLOSURE SCHEME [CA P N SHAH]](/thumbs/72/67119637.jpg) VOLUNTARY DISCLOSURE SCHEME [CA P N SHAH] 1 BACK GROUND In his Budget Speech on 29 th February, 2016, the Finance Minister has listed 9 objectives for his tax proposals. One of the objectives relates to
VOLUNTARY DISCLOSURE SCHEME [CA P N SHAH] 1 BACK GROUND In his Budget Speech on 29 th February, 2016, the Finance Minister has listed 9 objectives for his tax proposals. One of the objectives relates to
Failure to furnish returns, comply with notices, concealment of income, etc.
 Failure to furnish returns, comply with notices, concealment of income, etc. 271. (1) If the Assessing Officer or the Commissioner (Appeals) or the [Principal Commissioner or] Commissioner in the course
Failure to furnish returns, comply with notices, concealment of income, etc. 271. (1) If the Assessing Officer or the Commissioner (Appeals) or the [Principal Commissioner or] Commissioner in the course
Key changes / amendments to take effect from June 1, 2016
 1. Equalisation Levy Section 10 Key changes / amendments to take effect from June 1, 2016 Under section 10, a new Clause 50 has been inserted that provides for exemption of income from specified services
1. Equalisation Levy Section 10 Key changes / amendments to take effect from June 1, 2016 Under section 10, a new Clause 50 has been inserted that provides for exemption of income from specified services
As proposed in The Finance Bill, 2017 introduced by Finance Minister of India on 1 st February, 2017.
 Budget 2017-18 Highlights for Non-Residents As proposed in The Finance Bill, 2017 introduced by Finance Minister of India on 1 st February, 2017. The Indian Budget has provisions affecting the taxability
Budget 2017-18 Highlights for Non-Residents As proposed in The Finance Bill, 2017 introduced by Finance Minister of India on 1 st February, 2017. The Indian Budget has provisions affecting the taxability
Income Tax Changes made in Income Tax Provisions in the Union Budget which would affect Salaried Class
 Income Tax 2013-14 Changes made in Income Tax Provisions in the Union Budget 2013-14 which would affect Salaried Class A. RATES OF INCOME-TAX I. Rates of income-tax in respect of income liable to tax for
Income Tax 2013-14 Changes made in Income Tax Provisions in the Union Budget 2013-14 which would affect Salaried Class A. RATES OF INCOME-TAX I. Rates of income-tax in respect of income liable to tax for
F O R E W O R D. We trust that this presentation would be useful. If you have any suggestions for improvement, please do write to us.
 F O R E W O R D The objective of this note is to inform our clients and staff of the important changes proposed in Direct Taxes and Indirect Taxes (Service Tax) by the Finance Bill, 2013 which was introduced
F O R E W O R D The objective of this note is to inform our clients and staff of the important changes proposed in Direct Taxes and Indirect Taxes (Service Tax) by the Finance Bill, 2013 which was introduced
CA Final Paper 7 Direct Tax Laws Ch13 Unit1 CA Sudhindra Kumar Jain
 CA Final Paper 7 Direct Tax Laws Ch13 Unit1 CA Sudhindra Kumar Jain 2 Definition Section 2(17) In Which Public Are Substantially Interested Section 2(18) Indian Company Section 2(26) Domestic Company Section
CA Final Paper 7 Direct Tax Laws Ch13 Unit1 CA Sudhindra Kumar Jain 2 Definition Section 2(17) In Which Public Are Substantially Interested Section 2(18) Indian Company Section 2(26) Domestic Company Section
Insight of Few Sections
 Insight of Few Sections Relevant for Handling Income Tax Assessments - C.A. Mehul Thakker SECTION 2(14) SECTION 2(14) CAPITAL ASSET [W.E.F A.Y.2014-15] Modification in parameters defining scope of land
Insight of Few Sections Relevant for Handling Income Tax Assessments - C.A. Mehul Thakker SECTION 2(14) SECTION 2(14) CAPITAL ASSET [W.E.F A.Y.2014-15] Modification in parameters defining scope of land
Amendment of Direct Tax Dhruv Coaching Classes Pvt. Ltd. CMA Akshay Sen Direct Tax
 1 Direct Tax (AMENDMENTS) Finance Act, 2017 For CMA Inter & Final (June-18 & Dec-18 Exam.) By CMA AKSHAY SEN Dhruv Coaching Classes Pvt. Ltd. A1-A2,opposite Saras Dairy,Janta Store, Jaipur E-mail-dhruvcoachingclasses@gmail.com
1 Direct Tax (AMENDMENTS) Finance Act, 2017 For CMA Inter & Final (June-18 & Dec-18 Exam.) By CMA AKSHAY SEN Dhruv Coaching Classes Pvt. Ltd. A1-A2,opposite Saras Dairy,Janta Store, Jaipur E-mail-dhruvcoachingclasses@gmail.com
BUDGET 2016 SONALEE GODBOLE
 1 BUDGET 2016 SONALEE GODBOLE Penalties 2 3 Section 270A Section 271 levying penalty for failure to furnish returns, comply with notices, concealment of income, etc. will be applicable upto A.Y. 2016-17.
1 BUDGET 2016 SONALEE GODBOLE Penalties 2 3 Section 270A Section 271 levying penalty for failure to furnish returns, comply with notices, concealment of income, etc. will be applicable upto A.Y. 2016-17.
UNION BUDGET
 UNION BUDGET 2017-18 Hon ble Prime Minister Narendra Modi has shown his determination to come heavily on tax evaders. He has also shown his commitment to eliminate high value cash transactions from the
UNION BUDGET 2017-18 Hon ble Prime Minister Narendra Modi has shown his determination to come heavily on tax evaders. He has also shown his commitment to eliminate high value cash transactions from the
ARTICLE. On Finance Bill (Budget) Proposals 2013 Income Tax Act, 1961 By CA. SATISH AGARWAL
 ARTICLE On Finance Bill (Budget) Proposals 0 Income Tax Act, 96 By CA. SATISH AGARWAL Mobile : +99808957 Phone : +95769 Office : 9/4, East Patel Nagar, (Near Jaypee Sidharthe Hotel) New Delhi - 0008 :
ARTICLE On Finance Bill (Budget) Proposals 0 Income Tax Act, 96 By CA. SATISH AGARWAL Mobile : +99808957 Phone : +95769 Office : 9/4, East Patel Nagar, (Near Jaypee Sidharthe Hotel) New Delhi - 0008 :
Finance (No. 2) Bill 2014
 Finance (No. 2) Bill 2014 Proposed Income Tax Amendments Mr. R.N. LAKHOTIA Leading Income Tax Consultant & Author The Finance Minister presented the Finance (No.2) Bill 2014 along with the Union Budget
Finance (No. 2) Bill 2014 Proposed Income Tax Amendments Mr. R.N. LAKHOTIA Leading Income Tax Consultant & Author The Finance Minister presented the Finance (No.2) Bill 2014 along with the Union Budget
Amendments in Direct Taxes (AY ) DT by CARanjeet Kunwar. CA Ranjeet Kunwar. GAAP BRIGHT; ; taxgururanjeetkunwar.
 CA Ranjeet Kunwar GAAP BRIGHT; 011-41404111; taxgururanjeetkunwar.com 1 Tax Rates on Normal Income for AY 2015-16 For RESIDENT SENIOR CITIZEN (who is 60 Years or more but less than 80 years at any time
CA Ranjeet Kunwar GAAP BRIGHT; 011-41404111; taxgururanjeetkunwar.com 1 Tax Rates on Normal Income for AY 2015-16 For RESIDENT SENIOR CITIZEN (who is 60 Years or more but less than 80 years at any time
FOREWORD. There is a dearth of job opportunities in India. In order to augment the job opportunities a national multi-skill
 FOREWORD The much anticipated Budget 2014 has been delivered amid an environment of price rise and huge expectations from the government. The people of India have decisively voted for a change. Slow decision
FOREWORD The much anticipated Budget 2014 has been delivered amid an environment of price rise and huge expectations from the government. The people of India have decisively voted for a change. Slow decision
Direct Tax. March Budget Highlights :
 Direct Tax An e-newsletter from Lakshmikumaran & Sridharan, New Delhi, India March 2015 / Issue 8 March 2015 Budget 2015 - Highlights : Test of tax residence by reference to POEM Source rules for foreign
Direct Tax An e-newsletter from Lakshmikumaran & Sridharan, New Delhi, India March 2015 / Issue 8 March 2015 Budget 2015 - Highlights : Test of tax residence by reference to POEM Source rules for foreign
CHANGES IN 3CD TAX AUDIT REPORT FOR THE A.Y
 CHANGES IN 3CD TAX AUDIT REPORT FOR THE A.Y. 2013-2014 AMENDMENTS IN FINANCE ACT, 2012 HAVING IMPACT ON TAX AUDIT REPORT Rule 12 From A.Y. 2013-14 inter-alia e-filing of Audit Reports u/s. 44AB (Tax Audit
CHANGES IN 3CD TAX AUDIT REPORT FOR THE A.Y. 2013-2014 AMENDMENTS IN FINANCE ACT, 2012 HAVING IMPACT ON TAX AUDIT REPORT Rule 12 From A.Y. 2013-14 inter-alia e-filing of Audit Reports u/s. 44AB (Tax Audit
RECENT AMENDMENTS COMPUTATION OF TAX HOW TO COMPUTE REGULAR TAX
 RECENT AMENDMENTS The amendments as applicable to AY 2014-15 are given below. These amendments have been incorporated at all relevant places in this book. For any clarification / suggestion, please feel
RECENT AMENDMENTS The amendments as applicable to AY 2014-15 are given below. These amendments have been incorporated at all relevant places in this book. For any clarification / suggestion, please feel
INDIA BUDGET STATEMENT 2012
 HEMANT ARORA & CO. Chartered Accountants INDIA BUDGET STATEMENT 2012 The Direct Tax proposals HEMANT ARORA & CO. Chartered Accountants Offices - Gurgaon 1118-1119, 11 th Floor, DLF Galleria Tower DLF Phase
HEMANT ARORA & CO. Chartered Accountants INDIA BUDGET STATEMENT 2012 The Direct Tax proposals HEMANT ARORA & CO. Chartered Accountants Offices - Gurgaon 1118-1119, 11 th Floor, DLF Galleria Tower DLF Phase
Brief Note on Provisions of Section 194A(3)(v) relating to Co-operative Banks
 Brief Note on Provisions of Section 194A(3)(v) relating to Co-operative Banks Section 194A of the Income-tax Act, 1961 ( the Act ) was introduced through the Finance Act, 1967 with effect from 1 st April,
Brief Note on Provisions of Section 194A(3)(v) relating to Co-operative Banks Section 194A of the Income-tax Act, 1961 ( the Act ) was introduced through the Finance Act, 1967 with effect from 1 st April,
SURENDER KR. SINGHAL & CO
 PROPOSED TAX RATES FOR FINANCIAL YEAR 2016-17 A. Y. 2017-18 Income Tax Rates for Individuals, HUF Individuals, Hindu Undivided Families (HUF) and Artificial Jurisdictional Person: Net Income Range Income
PROPOSED TAX RATES FOR FINANCIAL YEAR 2016-17 A. Y. 2017-18 Income Tax Rates for Individuals, HUF Individuals, Hindu Undivided Families (HUF) and Artificial Jurisdictional Person: Net Income Range Income
Budget Highlights
 Budget Highlights 2018-19 DIRECT TAX PROPOSALS Chartered Accountants 1 st Floor, Sapphire Business Centre, Above SBI Vadaj Branch, Usmanpura, Ashram Road, Ahmedabad-380013 Email: apcca@apcca.com Website:
Budget Highlights 2018-19 DIRECT TAX PROPOSALS Chartered Accountants 1 st Floor, Sapphire Business Centre, Above SBI Vadaj Branch, Usmanpura, Ashram Road, Ahmedabad-380013 Email: apcca@apcca.com Website:
13 ASSESSMENT OF VARIOUS ENTITIES
 13 ASSESSMENT OF VARIOUS ENTITIES AMENDMENTS BY THE FINANCE ACT, 2015 (a) Special Taxation Regime for Investment Funds [Sections 115UB & 10(23FB)] Related amendment in sections: 115U, 139 & 194LBB (i)
13 ASSESSMENT OF VARIOUS ENTITIES AMENDMENTS BY THE FINANCE ACT, 2015 (a) Special Taxation Regime for Investment Funds [Sections 115UB & 10(23FB)] Related amendment in sections: 115U, 139 & 194LBB (i)
Appeal, Set comm., DRP Etc Mock Test IGP-CS CA Vivek Gaba
 1. Taking full advantage of loopholes of law so as to attract least incidence of tax is known as a) Tax planning b) Tax evasion c) Tax avoidance d) Tax management 2. Which is the relevant Form No. for
1. Taking full advantage of loopholes of law so as to attract least incidence of tax is known as a) Tax planning b) Tax evasion c) Tax avoidance d) Tax management 2. Which is the relevant Form No. for
Elective Course in Commerce ECO-11 Elements of Income Tax APPENDIX 2014 Assessment Year
 Elective Course in Commerce ECO-11 Elements of Income Tax APPENDIX 2014 Assessment Year 2013-2014 School of Management Studies Indira Gandhi National Open University New Delhi 110068 Dear Student, As you
Elective Course in Commerce ECO-11 Elements of Income Tax APPENDIX 2014 Assessment Year 2013-2014 School of Management Studies Indira Gandhi National Open University New Delhi 110068 Dear Student, As you
Income Tax Reckoner AY:
 1. Rates of Income Tax Individuals having income > 5 Lacs* Individuals & Charitable Trust Senior Citizen (60 to 79) Very Senior citizen (80 and above) Rates Up to ` 2.00 Lacs Up to ` 2.50 Lacs Up to `
1. Rates of Income Tax Individuals having income > 5 Lacs* Individuals & Charitable Trust Senior Citizen (60 to 79) Very Senior citizen (80 and above) Rates Up to ` 2.00 Lacs Up to ` 2.50 Lacs Up to `
A DISCUSSION PAPER ON CHAPTER III DIRECT TAXES OF FINANCE BILL, 2017 FEBRUARY 2017.
 A DISCUSSION PAPER ON CHAPTER III DIRECT TAXES OF FINANCE BILL, 2017 FEBRUARY 2017. By CA. V. Vivek Rajan, B. Com, ACA Introduction- Thanking everyone for the response to our Discussion Paper of 2016 The
A DISCUSSION PAPER ON CHAPTER III DIRECT TAXES OF FINANCE BILL, 2017 FEBRUARY 2017. By CA. V. Vivek Rajan, B. Com, ACA Introduction- Thanking everyone for the response to our Discussion Paper of 2016 The
INCOME TAX. -COPY OF- CIRCULAR NO.19/2015 Dated 27 th November, 2015
 INCOME TAX -COPY OF- CIRCULAR NO.19/2015 Dated 27 th November, 2015 F.No.142/14/2015-TPL Government of India Ministry of Finance Department of Revenue (Central Board of Direct Taxes) New Delhi ** ** **
INCOME TAX -COPY OF- CIRCULAR NO.19/2015 Dated 27 th November, 2015 F.No.142/14/2015-TPL Government of India Ministry of Finance Department of Revenue (Central Board of Direct Taxes) New Delhi ** ** **
CHANGES IN INCOME TAX BY UNION BUDGET 2017
 CHANGES IN INCOME TAX BY UNION BUDGET 2017 CA SOHRABH JINDAL The Hon ble Finance Minister has announced the Union Budget 2017 on 1-2-2017. There are various changes in Law related to Income Tax. I have
CHANGES IN INCOME TAX BY UNION BUDGET 2017 CA SOHRABH JINDAL The Hon ble Finance Minister has announced the Union Budget 2017 on 1-2-2017. There are various changes in Law related to Income Tax. I have
Ledger Services Private Limited Union Budget 2018 Inside Finance Bill
 Key Policy Announcements in Budget 2018 Agriculture and Rural Economy Health, Education and Social Protection MSME & Employment Page 1 Page 2 Ledger Services Private Limited UNION BUDGET 2018 1. Direct
Key Policy Announcements in Budget 2018 Agriculture and Rural Economy Health, Education and Social Protection MSME & Employment Page 1 Page 2 Ledger Services Private Limited UNION BUDGET 2018 1. Direct
Salient features of the Finance Bill, 2015 [Relating to direct taxes]
![Salient features of the Finance Bill, 2015 [Relating to direct taxes] Salient features of the Finance Bill, 2015 [Relating to direct taxes]](/thumbs/88/116892728.jpg) 1 Salient features of the Finance Bill, 2015 [Relating to direct taxes] [Published in 373 ITR (Jour) 1 (Part-1)] By. S.K. Tyagi The Finance Bill, 2015 or the Union Budget, 2015-16, was presented in the
1 Salient features of the Finance Bill, 2015 [Relating to direct taxes] [Published in 373 ITR (Jour) 1 (Part-1)] By. S.K. Tyagi The Finance Bill, 2015 or the Union Budget, 2015-16, was presented in the
INTERMEDIATE (IPC) COURSE/ ACCOUNTING TECHNICIAN COURSE SUPPLEMENTARY STUDY PAPER TAXATION
 INTERMEDIATE (IPC) COURSE/ ACCOUNTING TECHNICIAN COURSE SUPPLEMENTARY STUDY PAPER - 2013 TAXATION [A discussion on the amendments made by the Finance Act, 2013 and significant Notifications & Circulars
INTERMEDIATE (IPC) COURSE/ ACCOUNTING TECHNICIAN COURSE SUPPLEMENTARY STUDY PAPER - 2013 TAXATION [A discussion on the amendments made by the Finance Act, 2013 and significant Notifications & Circulars
Analysis of Tax Proposals under Union. Budget B K Ramadhyani & Co. LLP Chartered Accountants
 Analysis of Tax Proposals under Union Budget 2016 B K Ramadhyani & Co. LLP Chartered Accountants TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Direct tax proposals a. Individuals and HUFs b. Partnership firms c. Corporates d.
Analysis of Tax Proposals under Union Budget 2016 B K Ramadhyani & Co. LLP Chartered Accountants TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Direct tax proposals a. Individuals and HUFs b. Partnership firms c. Corporates d.
6. PROFITS AND GAINS OF BUSINESS OR PROFESSION 2
 Ph: 98851 25025/26 www.mastermindsindia.com 6. PROFITS AND GAINS OF BUSINESS OR PROFESSION 2 SOLUTIONS TO ASSIGNMENT PROBLEMS Problem No. 1 Computing business income for A.Y.2015-16 is as follows Amount
Ph: 98851 25025/26 www.mastermindsindia.com 6. PROFITS AND GAINS OF BUSINESS OR PROFESSION 2 SOLUTIONS TO ASSIGNMENT PROBLEMS Problem No. 1 Computing business income for A.Y.2015-16 is as follows Amount
Income Tax Act DIVISION ONE 1 DIVISION TWO 2
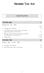 Income Tax Act SECTION DIVISION ONE 1 Income-tax Act, 1961 Arrangement of Sections I-3 Text of the Income-tax Act, 1961 as amended by the Finance (No. 2) Act, 2014 1.1 Appendix : Text of remaining provisions
Income Tax Act SECTION DIVISION ONE 1 Income-tax Act, 1961 Arrangement of Sections I-3 Text of the Income-tax Act, 1961 as amended by the Finance (No. 2) Act, 2014 1.1 Appendix : Text of remaining provisions
FINANCE BILL He has proposed to revise the tax slabs upwards as under:
 FINANCE BILL - 2010 The 2 nd budget of the 2 nd UPA Government for the year 2010 2011 was presented by the finance minister on 26 th February 2010. The finance minister has attempted to balance his direct
FINANCE BILL - 2010 The 2 nd budget of the 2 nd UPA Government for the year 2010 2011 was presented by the finance minister on 26 th February 2010. The finance minister has attempted to balance his direct
CHAPTER 1: BASIC CONCEPTS AND CALCULATION OF INCOME TAX
 CHAPTER 1: BASIC CONCEPTS AND CALCULATION OF INCOME TAX (1) TAX RATES FOR INDIVIDUAL, HUF, AOP, BOI AND AJP: The slabs rates for the AY 2018-2019 i.e. PY 2017-2018 are as follows: Total Income Range Basic
CHAPTER 1: BASIC CONCEPTS AND CALCULATION OF INCOME TAX (1) TAX RATES FOR INDIVIDUAL, HUF, AOP, BOI AND AJP: The slabs rates for the AY 2018-2019 i.e. PY 2017-2018 are as follows: Total Income Range Basic
Issues in Taxation of Income (Non-Corporate)
 Issues in Taxation of Income (Non-Corporate) By CA Mahavir Jain B.Com.; DISA; FCA Partner : JMT & Associates Email: jmtca301@gmail.com Issues in Taxation of Non-Corporate Income is a very vast subject.
Issues in Taxation of Income (Non-Corporate) By CA Mahavir Jain B.Com.; DISA; FCA Partner : JMT & Associates Email: jmtca301@gmail.com Issues in Taxation of Non-Corporate Income is a very vast subject.
THE BANKING LAWS (AMENDMENT) BILL, 2011
 1 As INTRODUCED IN LOK SABHA Bill No. 18 of 2011 5 10 THE BANKING LAWS (AMENDMENT) BILL, 2011 A BILL further to amend the Banking Regulation Act, 1949, the Banking Companies (Acquisition and Transfer of
1 As INTRODUCED IN LOK SABHA Bill No. 18 of 2011 5 10 THE BANKING LAWS (AMENDMENT) BILL, 2011 A BILL further to amend the Banking Regulation Act, 1949, the Banking Companies (Acquisition and Transfer of
Being good in business is the most fascinating kind of art. Making money is art and working is art and good business is the best art.
 Chartered Accountant Being good in business is the most fascinating kind of art. Making money is art and working is art and good business is the best art. -Team RSA 1 GUIDE TO BUDGET 2018 Direct Tax &
Chartered Accountant Being good in business is the most fascinating kind of art. Making money is art and working is art and good business is the best art. -Team RSA 1 GUIDE TO BUDGET 2018 Direct Tax &
FINANCE BILL, 2018 PROVISIONS RELATING TO DIRECT TAXES. Introduction
 FINANCE BILL, 2018 PROVISIONS RELATING TO DIRECT TAXES Introduction The provisions of Finance Bill, 2018 relating to direct taxes seek to amend the Income-tax Act, 1961 (hereafter referred to as 'the Act')
FINANCE BILL, 2018 PROVISIONS RELATING TO DIRECT TAXES Introduction The provisions of Finance Bill, 2018 relating to direct taxes seek to amend the Income-tax Act, 1961 (hereafter referred to as 'the Act')
BUDGET SIGNIFICANT PROPOSALS IN BRIEF GENERAL
 2018 BUDGET SIGNIFICANT PROPOSALS IN BRIEF GENERAL INDEX Sr. No. Particulars Page No. HIGHLIGHTS OF FINANCE BUDGET 2018 3-7 DIRECT TAX A Rates of Income Tax 8-10 B Widening and Deepening of Tax Base 11
2018 BUDGET SIGNIFICANT PROPOSALS IN BRIEF GENERAL INDEX Sr. No. Particulars Page No. HIGHLIGHTS OF FINANCE BUDGET 2018 3-7 DIRECT TAX A Rates of Income Tax 8-10 B Widening and Deepening of Tax Base 11
Introduction. Introduction. Introduction 8/2/2014
 Introduction Real estate transactions are one of the main source for generation and application of black money. The Government is regularly trying to plug loop holes in such transactions by inserting various
Introduction Real estate transactions are one of the main source for generation and application of black money. The Government is regularly trying to plug loop holes in such transactions by inserting various
W S & Co. Contact us FCA Shipra Walia Domestic & International Tax Advisor
 Contact us FCA Shipra Walia Domestic & International Tax Advisor www.wsco.in www.shiprawalia.in mail:info@wsco.in Individuals, HUF, AOP, BOI 1. No change in Tax Rate (a) For a resident senior citizen (who
Contact us FCA Shipra Walia Domestic & International Tax Advisor www.wsco.in www.shiprawalia.in mail:info@wsco.in Individuals, HUF, AOP, BOI 1. No change in Tax Rate (a) For a resident senior citizen (who
Interim Union Budget 2019 & Important changes for AY CA. PRAMOD JAIN B. COM (H), FCA, FCS, FCMA, LL.B, MIMA, DISA, IP
 Interim Union Budget 2019 & Important changes for AY 2019-20 CA. PRAMOD JAIN B. COM (H), FCA, FCS, FCMA, LL.B, MIMA, DISA, IP Shared at Nehru Place CPE Study Circle of NIRC of ICAI 7 th February 2019 INCOME
Interim Union Budget 2019 & Important changes for AY 2019-20 CA. PRAMOD JAIN B. COM (H), FCA, FCS, FCMA, LL.B, MIMA, DISA, IP Shared at Nehru Place CPE Study Circle of NIRC of ICAI 7 th February 2019 INCOME
SALIENT FEATURES OF THE FINANCE BILL, 2012 DIRECT TAXES VED JAIN
 SALIENT FEATURES OF THE FINANCE BILL, 2012 DIRECT TAXES VED JAIN ABOUT THE AUTHOR Mr. Ved Jain, Chairman, Committee on Direct Taxes of Assocham, is a Chartered Accountant. Mr Jain passed the Chartered
SALIENT FEATURES OF THE FINANCE BILL, 2012 DIRECT TAXES VED JAIN ABOUT THE AUTHOR Mr. Ved Jain, Chairman, Committee on Direct Taxes of Assocham, is a Chartered Accountant. Mr Jain passed the Chartered
EXPLANATORY NOTES THE PROVISIONS OF THE FINANCE ACT, 2018
 F. No. 370142/07/2018-TPL Government of India Ministry of Finance Department of Revenue (Central Board of Direct Taxes) CIRCULAR No.-Z/2018 **** Dated, the 26 th of December, 2018 EXPLANATORY NOTES TO
F. No. 370142/07/2018-TPL Government of India Ministry of Finance Department of Revenue (Central Board of Direct Taxes) CIRCULAR No.-Z/2018 **** Dated, the 26 th of December, 2018 EXPLANATORY NOTES TO
Income Tax Authorities
 20 Income Tax Authorities Question 1 Rajesh regularly files his return of income electronically. While he was trying to upload his return of income for assessment year 2014-15 on 31 st July, 2014, last
20 Income Tax Authorities Question 1 Rajesh regularly files his return of income electronically. While he was trying to upload his return of income for assessment year 2014-15 on 31 st July, 2014, last
FINAL CA May 2018 DIRECT TAXATION
 FINAL CA May 2018 DIRECT TAXATION Test Code F 90 Branch: MULTIPLE Date: (50 Marks) compulsory. Note: All questions are Question 1 (10 marks) Computation of Book Profit for levy of MAT under section 115JB
FINAL CA May 2018 DIRECT TAXATION Test Code F 90 Branch: MULTIPLE Date: (50 Marks) compulsory. Note: All questions are Question 1 (10 marks) Computation of Book Profit for levy of MAT under section 115JB
RESTRICTION ON CASH TRANSACTIONS UNDER INCOME TAX ACT
 RESTRICTION ON CASH TRANSACTIONS UNDER INCOME TAX ACT CMA NIRANJAN SWAIN Senior General Manager (Finance), Odisha Power Generation Corporation Ltd Slowly and gradually, the Indian economy is getting digitized
RESTRICTION ON CASH TRANSACTIONS UNDER INCOME TAX ACT CMA NIRANJAN SWAIN Senior General Manager (Finance), Odisha Power Generation Corporation Ltd Slowly and gradually, the Indian economy is getting digitized
SUPPLEMENT FOR TAX LAWS AND PRACTICE
 EXECUTIVE PROGRAMME SUPPLEMENT FOR TAX LAWS AND PRACTICE (Relevant for students appearing in June, 2016 examination) MODULE 1- PAPER 4 Disclaimer- This document has been prepared purely for academic purposes
EXECUTIVE PROGRAMME SUPPLEMENT FOR TAX LAWS AND PRACTICE (Relevant for students appearing in June, 2016 examination) MODULE 1- PAPER 4 Disclaimer- This document has been prepared purely for academic purposes
NOTES ON BUDGET 2013
 NOTES ON BUDGET 2013 MAJOR AMENDMENTS PROPOSED IN FINANCE BILL 2013 & CHANGES IN SERVICE TAX PROVISIONS Prepared by BY Chartered Accountants 3 rd & 4 th Floor, Vaastu Darshan Bldg., B Wing, Azaad Road,
NOTES ON BUDGET 2013 MAJOR AMENDMENTS PROPOSED IN FINANCE BILL 2013 & CHANGES IN SERVICE TAX PROVISIONS Prepared by BY Chartered Accountants 3 rd & 4 th Floor, Vaastu Darshan Bldg., B Wing, Azaad Road,
SUNIL CHOPRA & CO. Chartered Accountants
 2016-2017 SUNIL CHOPRA & CO. Chartered Accountants 3, 1 st Floor, Mandar, 193, Turner Road, Bandra (W), Mumbai 400050 Tel: 26515394 / 95, Fax: 26515438 Email: sccoca@gmail.com UNION BUDGET 2016-17 Our
2016-2017 SUNIL CHOPRA & CO. Chartered Accountants 3, 1 st Floor, Mandar, 193, Turner Road, Bandra (W), Mumbai 400050 Tel: 26515394 / 95, Fax: 26515438 Email: sccoca@gmail.com UNION BUDGET 2016-17 Our
Assessment of Various Entities (Revision)
 CA Final Direct Tax 1 Assessment of Various Entities (Revision) Assessment of Companies: Tax on income from life insurance business: (Section 115B) - Profits and gains derived from the business of life
CA Final Direct Tax 1 Assessment of Various Entities (Revision) Assessment of Companies: Tax on income from life insurance business: (Section 115B) - Profits and gains derived from the business of life
CIRCULAR NO 5/2010, Dated: June 3, 2010 EXPLANATORY NOTES TO THE PROVISIONS OF THE FINANCE (NO.2) ACT, 2009 AMENDMENTS AT A GLANCE
 CIRCULAR NO 5/2010, Dated: June 3, 2010 EXPLANATORY NOTES TO THE PROVISIONS OF THE FINANCE (NO.2) ACT, 2009 AMENDMENTS AT A GLANCE Section /Schedule Particulars/paragraph number Finance Act First Schedule
CIRCULAR NO 5/2010, Dated: June 3, 2010 EXPLANATORY NOTES TO THE PROVISIONS OF THE FINANCE (NO.2) ACT, 2009 AMENDMENTS AT A GLANCE Section /Schedule Particulars/paragraph number Finance Act First Schedule
VGGLOBAL HIGHLIGHTS OF THE FINANCE BILL VGGlobal
 VGGLOBAL HIGHLIGHTS OF THE FINANCE BILL 2014 VGGlobal 2014. www.vgglobal.co.in From the Desk of: CA Ved Parkash Gupta Managing Partner Email: vedgupta@vgglobal.co.in Dear All, One word that comes to mind
VGGLOBAL HIGHLIGHTS OF THE FINANCE BILL 2014 VGGlobal 2014. www.vgglobal.co.in From the Desk of: CA Ved Parkash Gupta Managing Partner Email: vedgupta@vgglobal.co.in Dear All, One word that comes to mind
As proposed in The Finance Bill, 2016 introduced by Finance Minister of India on 29th February, 2016.
 1 Budget 2016-2017 Highlights for Non-Residents As proposed in The Finance Bill, 2016 introduced by Finance Minister of India on 29th February, 2016. The Indian Budget presented by the Finance Minister
1 Budget 2016-2017 Highlights for Non-Residents As proposed in The Finance Bill, 2016 introduced by Finance Minister of India on 29th February, 2016. The Indian Budget presented by the Finance Minister
Section - 271, Income-tax Act,
 1 of 7 29-Feb-16 2:37 PM Section - 271, Income-tax Act, 1961-2015 35 [Failure to furnish returns, comply with notices, concealment of income, etc. 36 271. 36a (1) If the 37 [Assessing] Officer or the 38
1 of 7 29-Feb-16 2:37 PM Section - 271, Income-tax Act, 1961-2015 35 [Failure to furnish returns, comply with notices, concealment of income, etc. 36 271. 36a (1) If the 37 [Assessing] Officer or the 38
MINISTRY OF LAW AND JUSTICE
 ÀA À ÃAiÀÄ ªÀåªÀºÁgÀUÀ¼ÀÄ ªÀÄvÀÄÛ ±Á À À gàzà É ÀaªÁ AiÀÄ C ü ÀÆZÀ É (PÀ ÁðlPÀ gádå ÀvÀæ ÁAPÀ: r ÉA gï 20, 2012 sáuà-4 ÀÄl ÀASÉå:301-401) ÀASÉå: ÀAªÀå±ÁE 25 PÉñÁ Àæ 2012, ÉAUÀ¼ÀÆgÀÄ, ÁAPÀ: 31 Éà dä ÉÊ,
ÀA À ÃAiÀÄ ªÀåªÀºÁgÀUÀ¼ÀÄ ªÀÄvÀÄÛ ±Á À À gàzà É ÀaªÁ AiÀÄ C ü ÀÆZÀ É (PÀ ÁðlPÀ gádå ÀvÀæ ÁAPÀ: r ÉA gï 20, 2012 sáuà-4 ÀÄl ÀASÉå:301-401) ÀASÉå: ÀAªÀå±ÁE 25 PÉñÁ Àæ 2012, ÉAUÀ¼ÀÆgÀÄ, ÁAPÀ: 31 Éà dä ÉÊ,
